Patents
Literature
73results about How to "Coupling loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
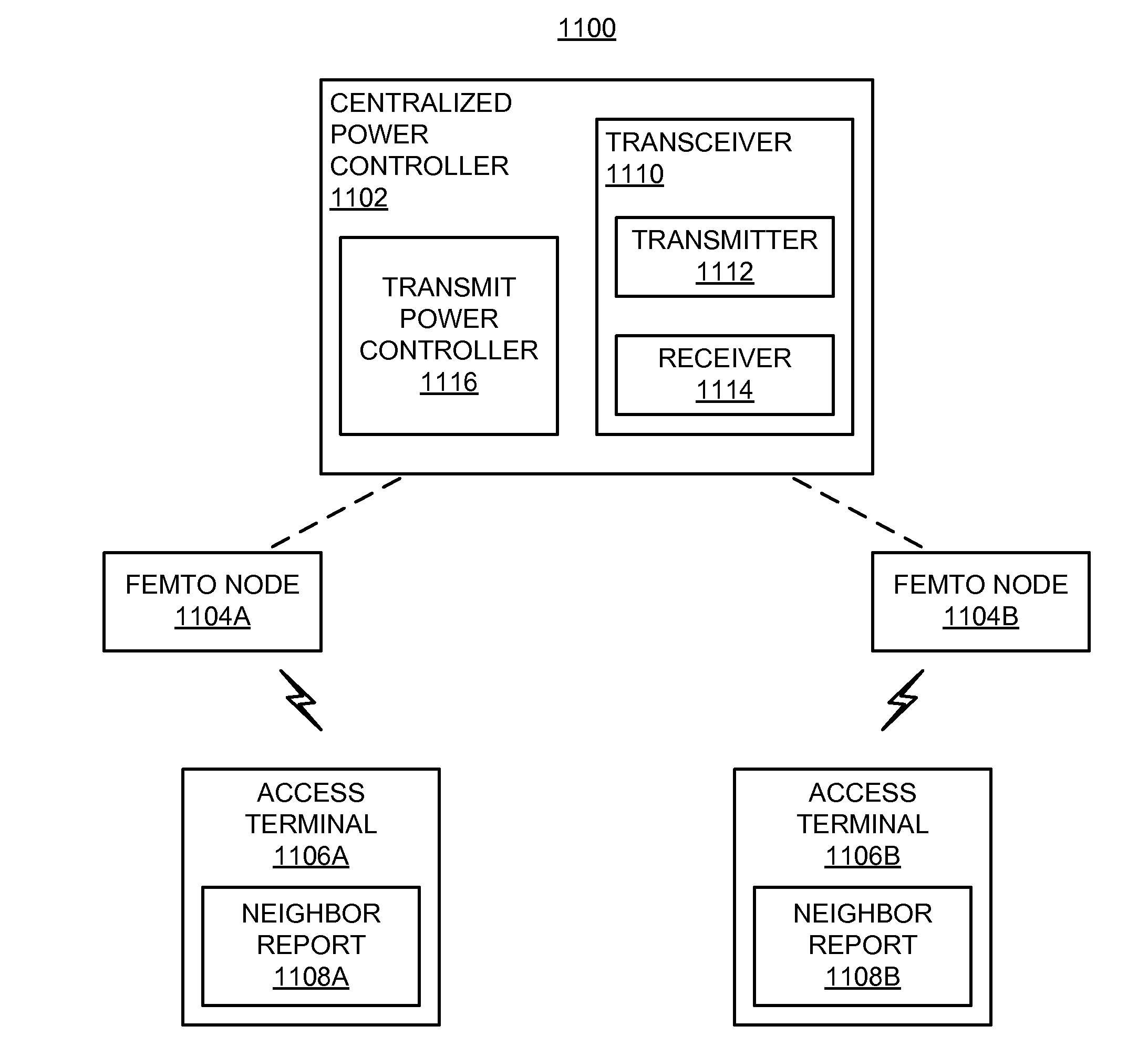
Adaptation of transmit power based on maximum received signal strength
ActiveUS20090042594A1Improve network performanceReduce transmit powerPower managementRadio transmission for post communicationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Femto-
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
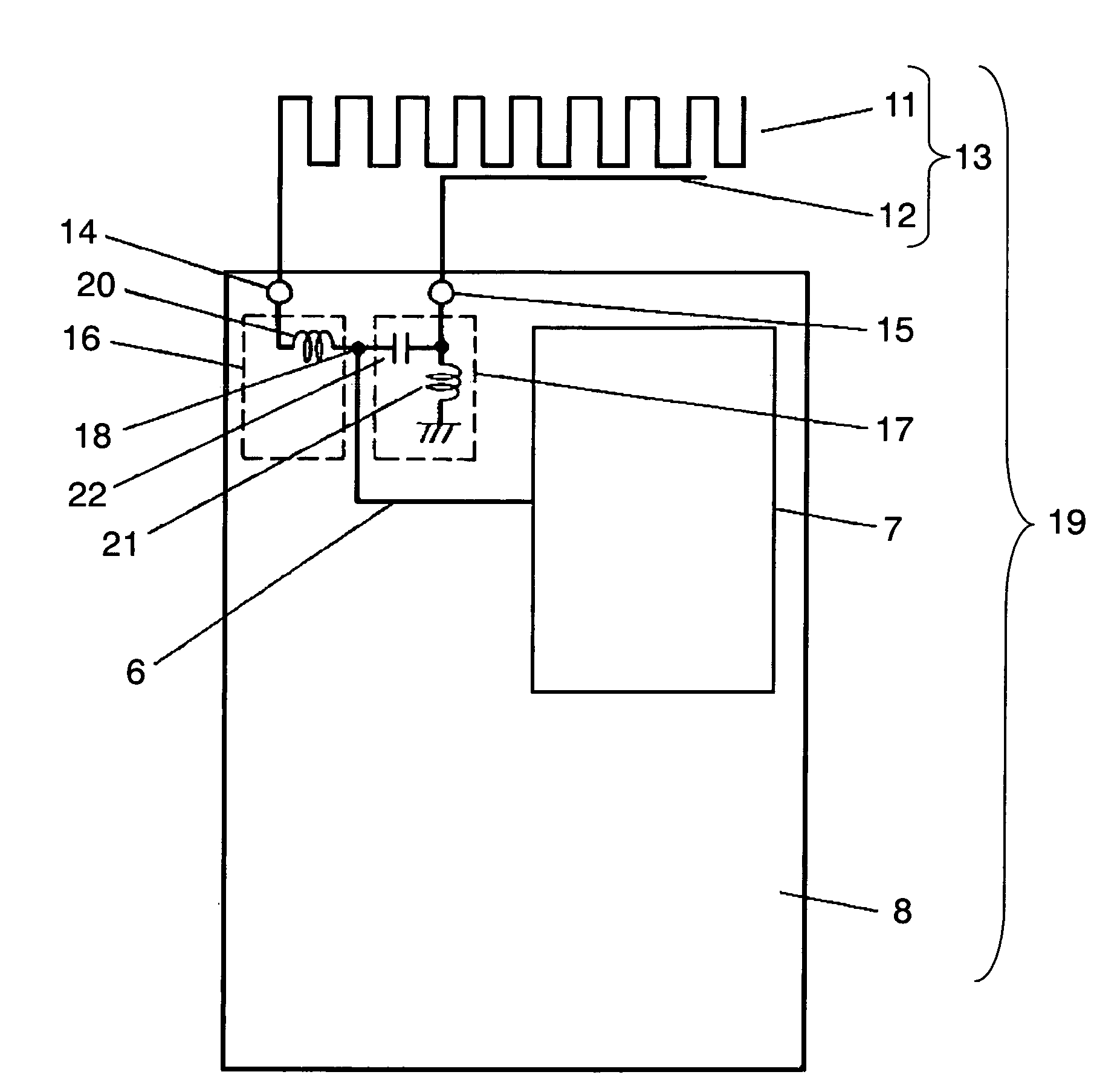
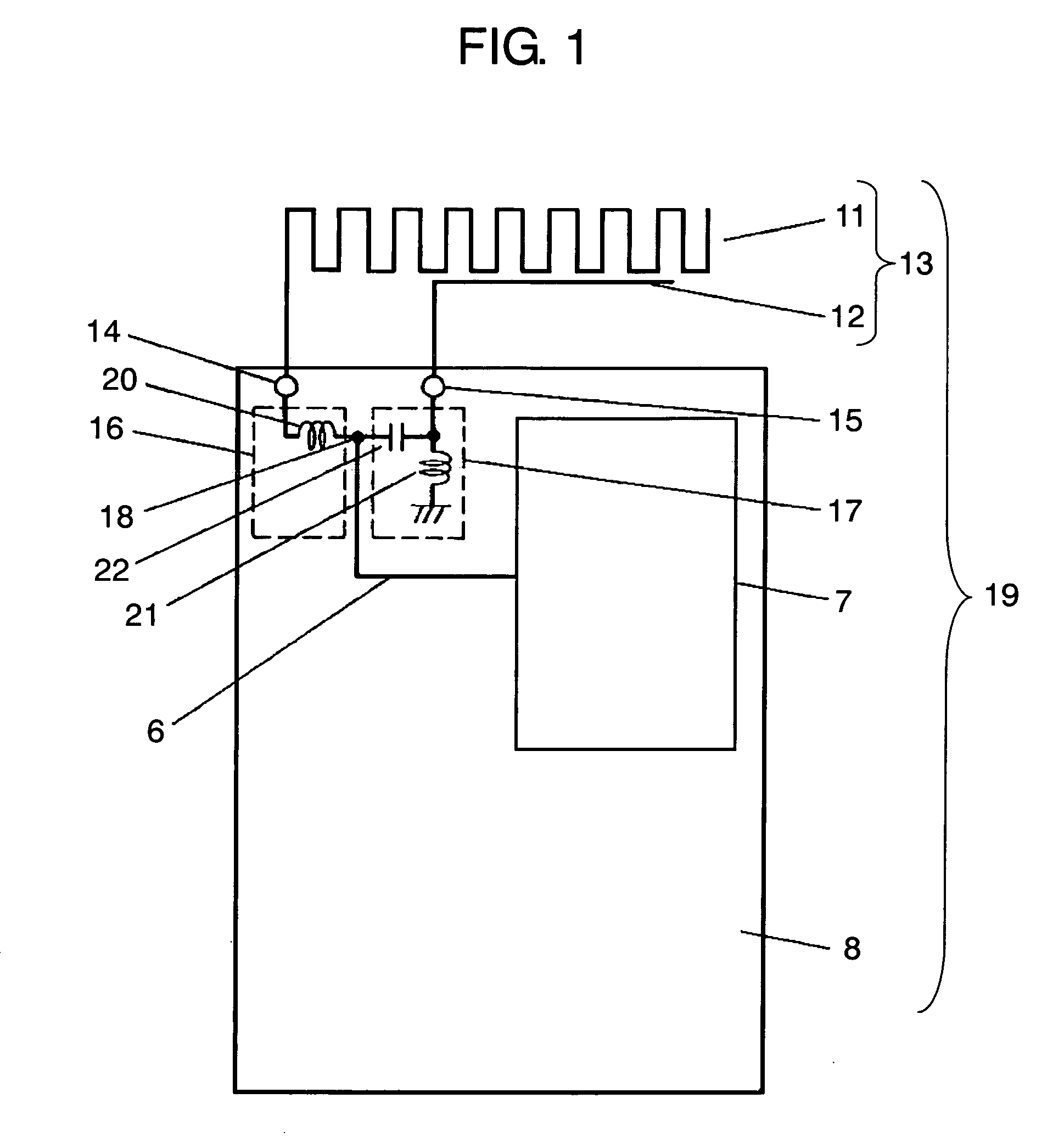
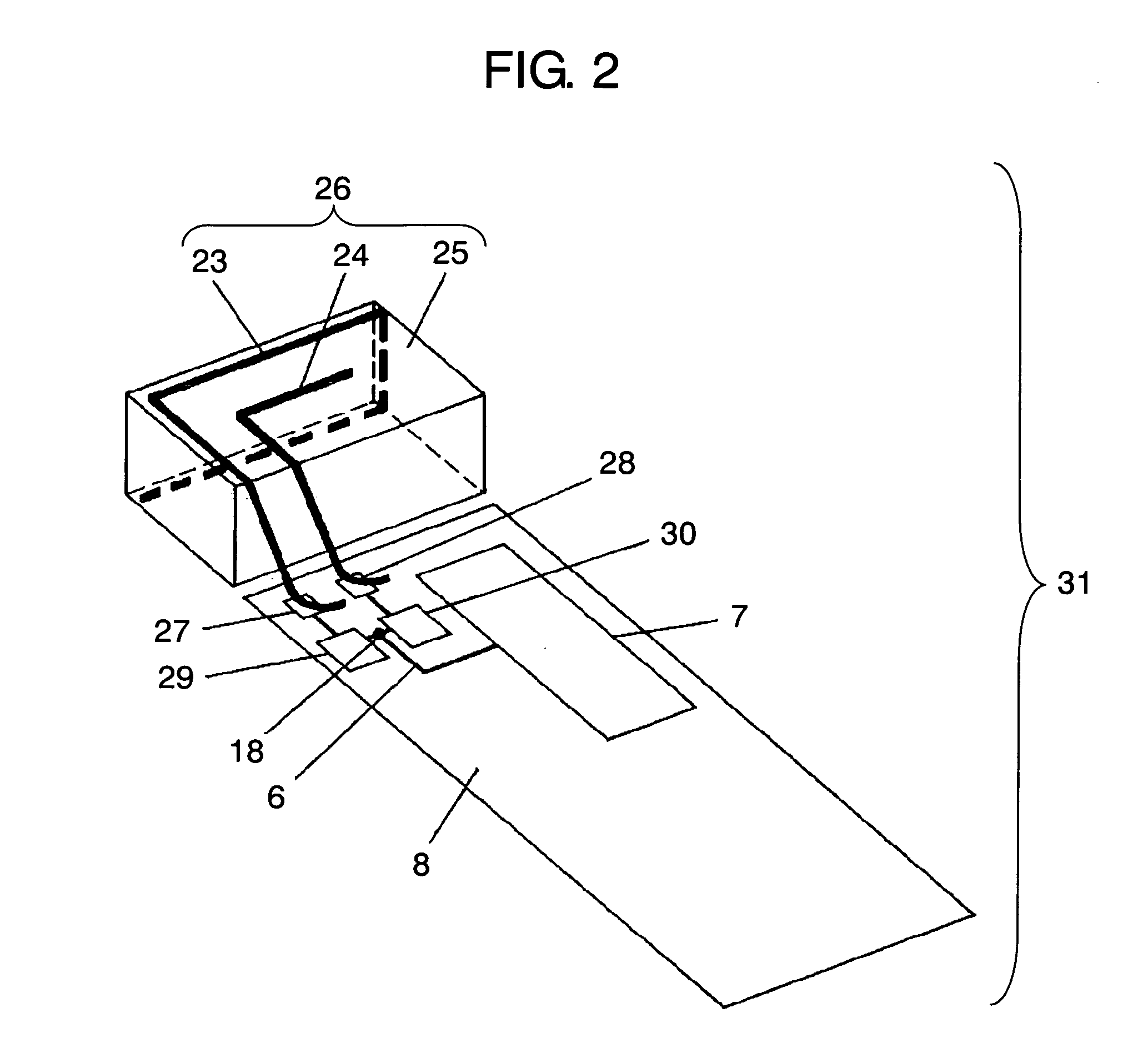
Wireless device having antenna
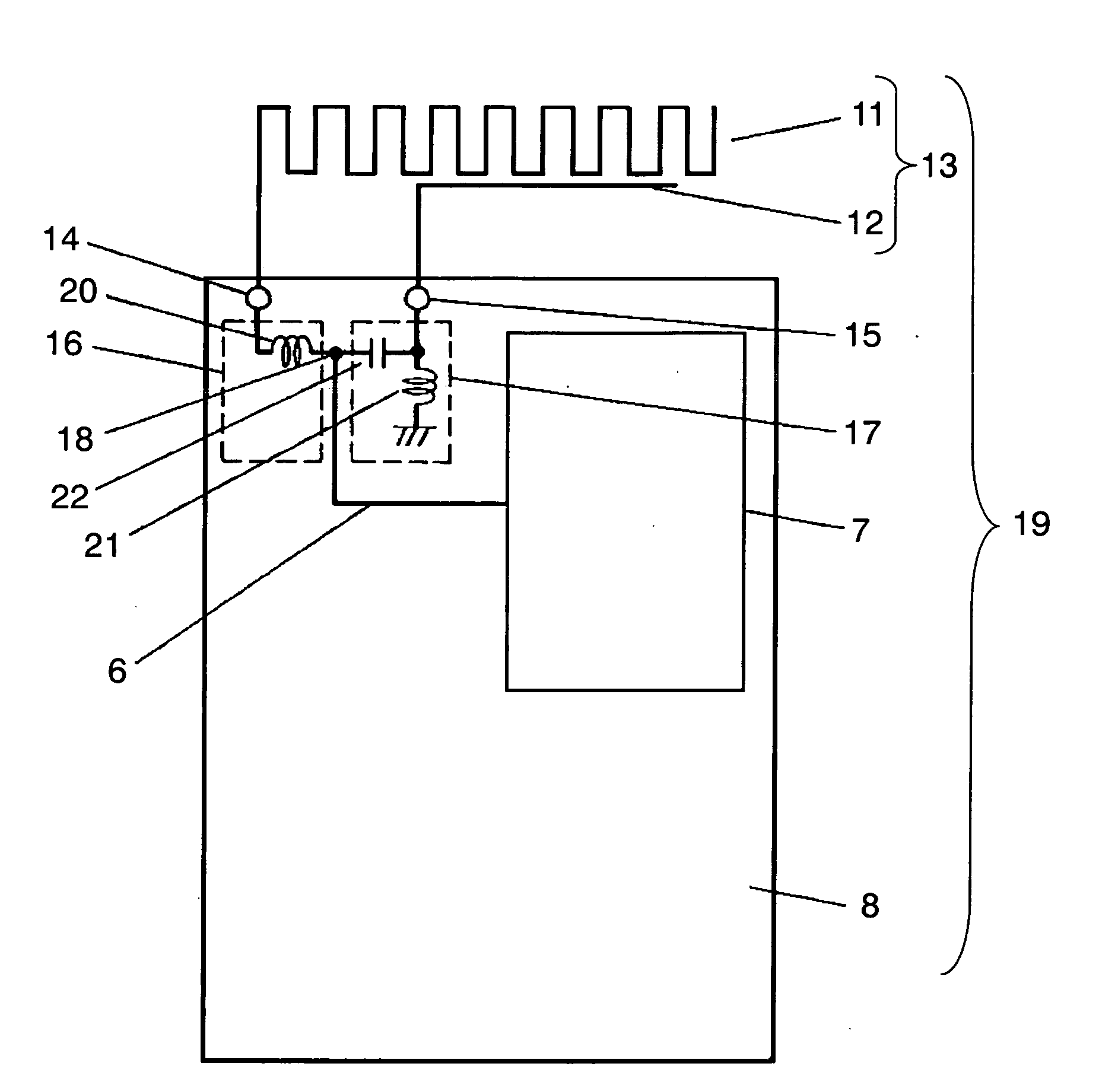
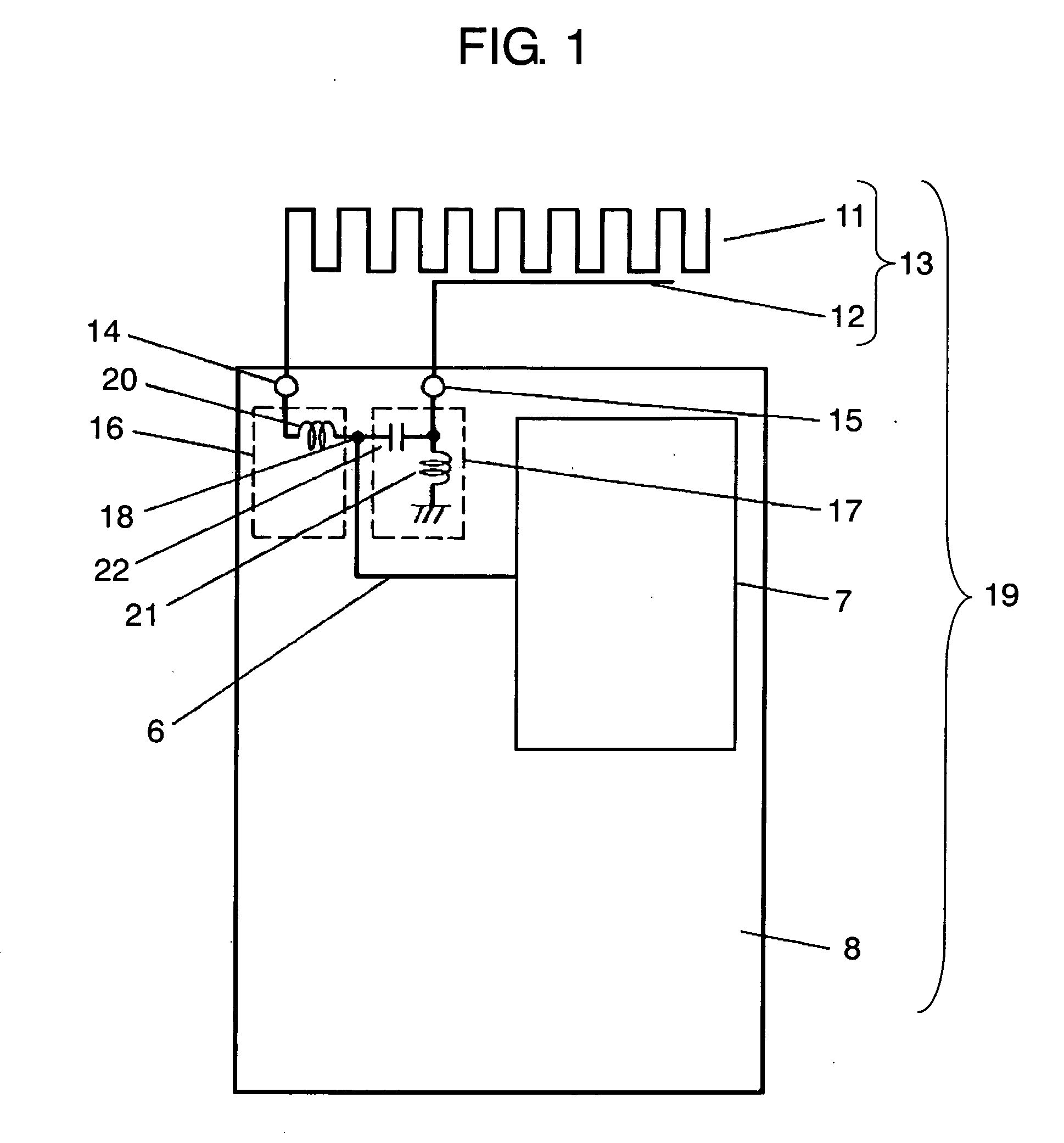
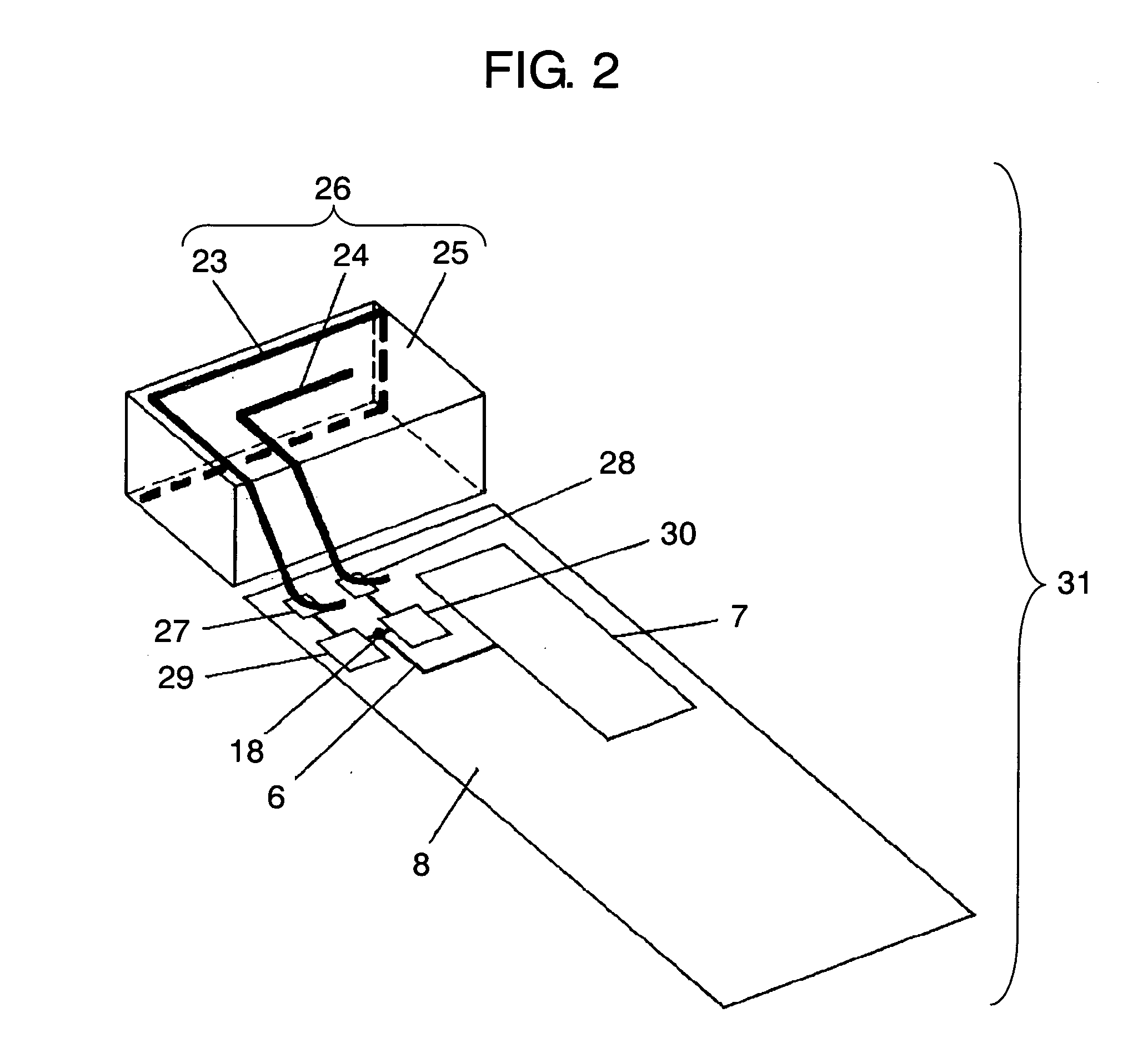
InactiveUS7084831B2Reduce couplingCoupling lossSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsGround planeAntenna element
A wireless device includes a first antenna element resonating with a first frequency, a first feeding point coupled to the first antenna element and disposed on a ground plane in the wireless device, and a first matching circuit of which its first end is coupled to the first feeding point. The wireless device also includes a second antenna element resonating a second frequency higher than the first frequency, a second feeding point coupled to the second antenna element and disposed on the ground plane, a second matching circuit of which one end is coupled to the second feeding point, and a radio circuit coupled via a transmission line to a common connection point shared by respective second ends of the first and second matching circuits.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
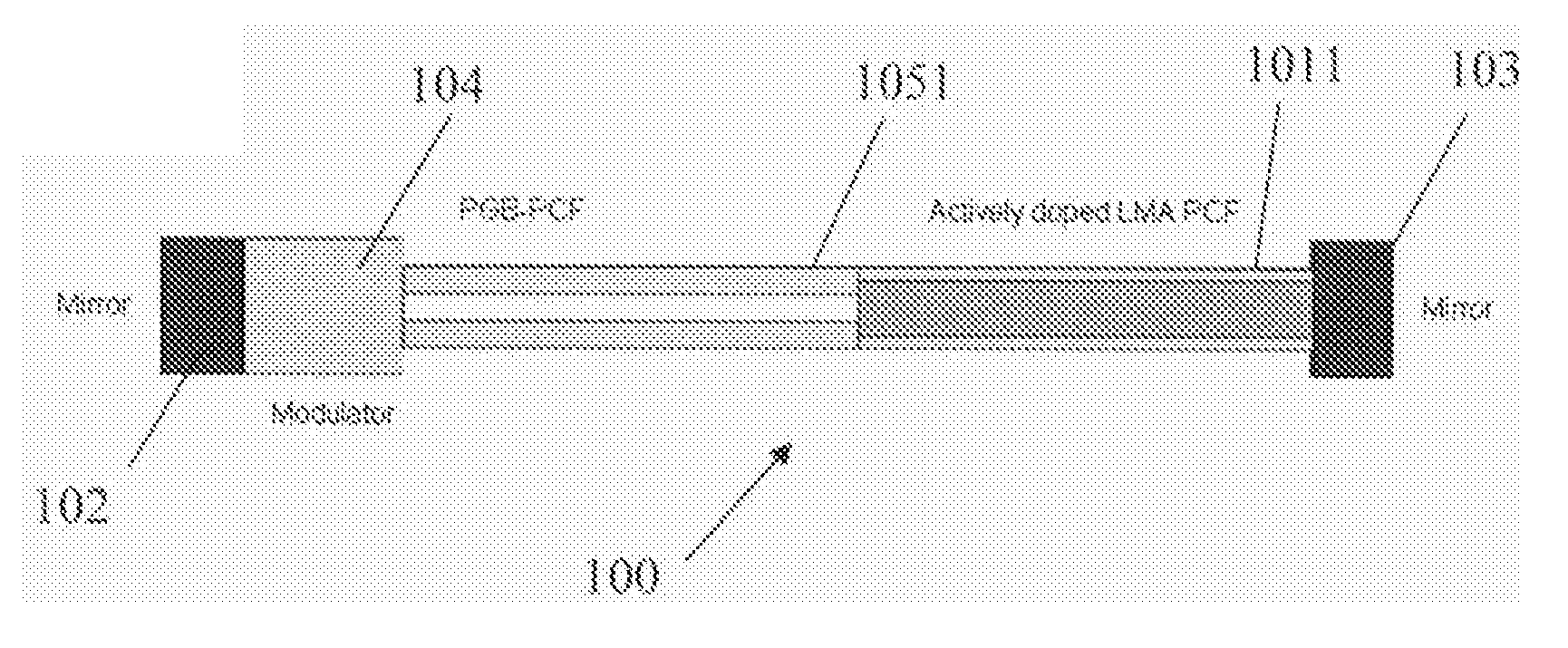
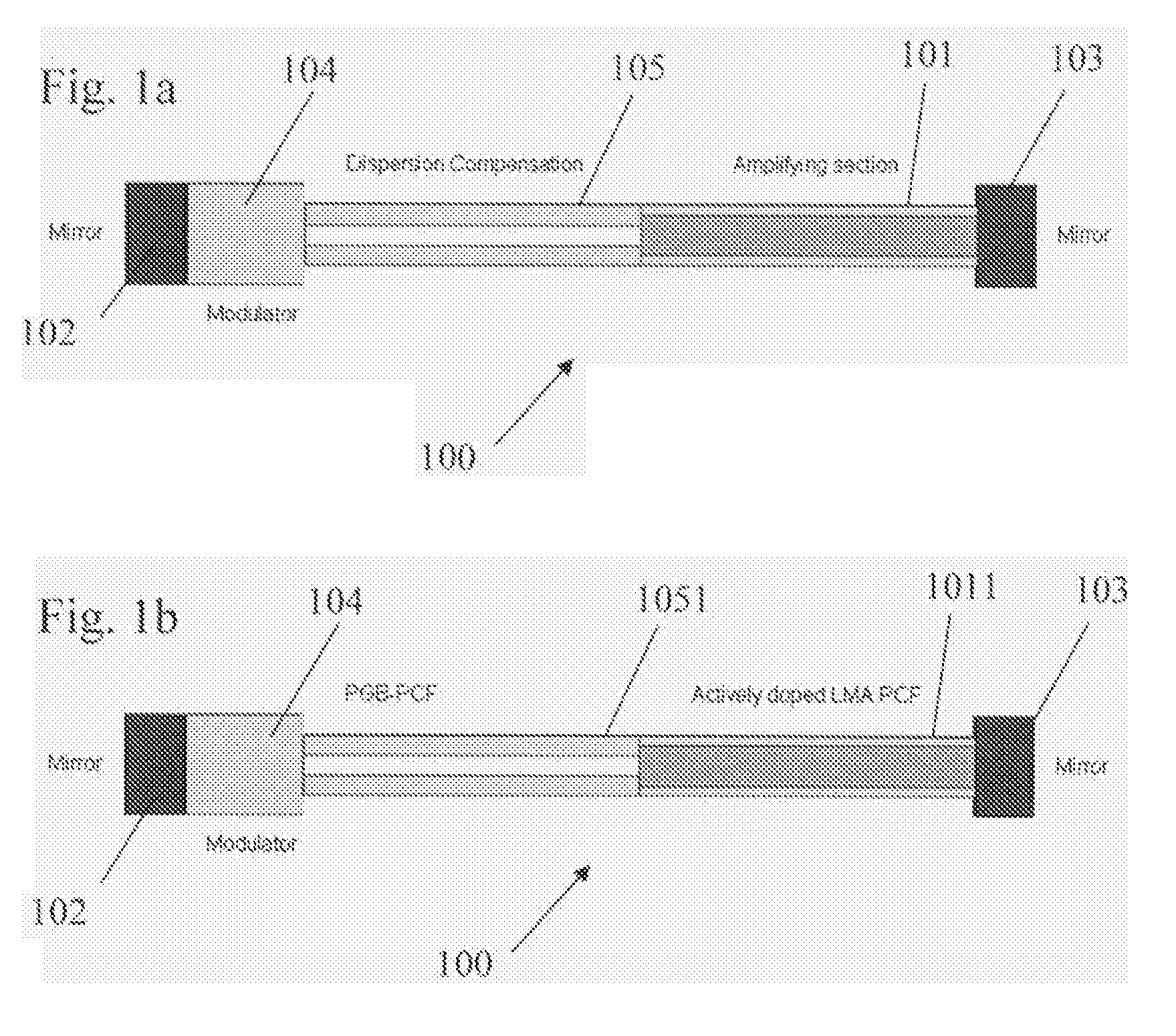
An Optical System For Providing Short Laser-Pulses
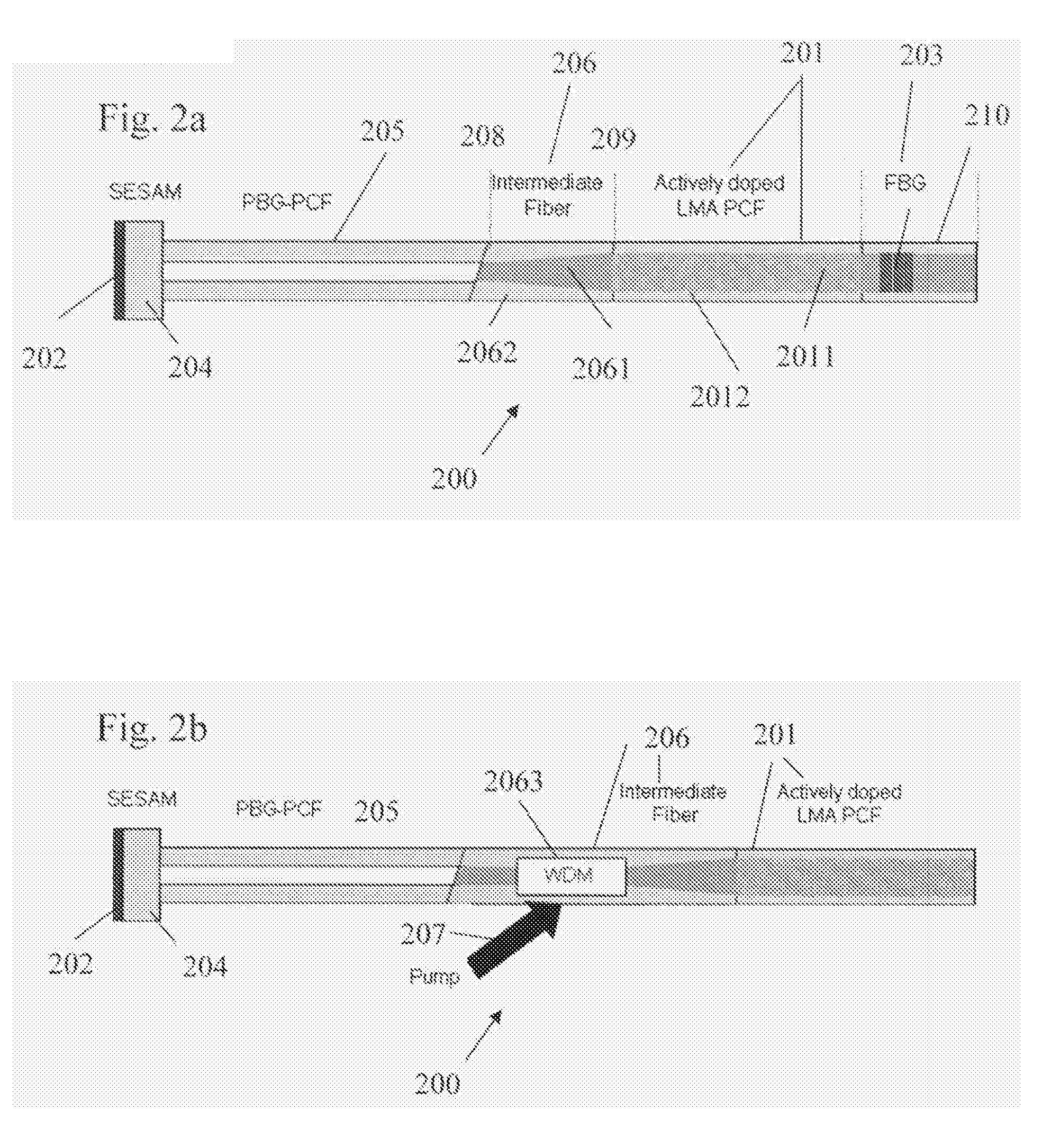
InactiveUS20060209908A1High core diameterIncrease valueCladded optical fibreLaser using scattering effectsCost effectivenessPhotonic bandgap
The present invention deals with optical systems for providing short laser pulses. An object of the invention is to provide an optical system providing compact and cost-effective short laser-pulses using fibers with anomalous dispersion and high non-linear thresholds. The object is achieved by a short pulse optical system for generating or processing short laser-pulses, said optical system comprises an optical fiber in the form of a photonic crystal fiber arranged to provide guidance of light in the core region due to the photonic bandgap effect (PBG), where light propagates in a hollow or solid core surrounded by a Silica cladding comprising a substantially periodic distribution of micro-structural elements, and where the refractive index of the core is lower than the effective refractive index of the cladding. The invention may be useful in applications such as laser-based micromachining, thin-film formation, laser cleaning, in medicine and biology.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
Optical device integrated head
InactiveUS20080316872A1Reduce light lossReduce power consumptionCombination recordingRecord information storageWaveguideLaser
An optical device integrated head having high light utilizing efficiency by decreasing the propagation loss caused from an optical source to a recording medium, conducting by mounting according to compact active alignment method for efficiently guiding a light generated from a laser device to the top end of a head, in which a light source device mounted on a submount has a mirror portion having an inclinated surface to at least a portion of one edge thereof for reflecting an output light from the optical source device at the inclinated surface, a structural member including a lens structure for further allowing a light to pass through the submount, and an optical waveguide disposed passing through a slider for mounting the submount, and the optical source and the slider are positioned by using active alignment of light in a chip-on carrier structure having the optical source device mounted on the submount.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
User input arrangement and related method of manufacture
InactiveUS20120038593A1Rapid industrial scale manufacturingEasy to replaceTube/lamp screens manufactureLight effect designsTotal internal reflectionUser input
Arrangement (202) for a user input device, such as a touchscreen or a touchpad, comprising a substrate (206), such as an optically substantially transparent flex film or a multilayer film, said substrate comprising support electronics (212) for providing power, control and / or communications connection to further electronic components (210), a number of emitters and detectors (210) arranged to said substrate into contact with the support electronics, for emitting and detecting light, respectively, and a lightguide (208) provided, such as laminated, onto the substrate such that said emitters and detectors are optically coupled to the lightguide material, the properties of the lightguide including the refractive index of the lightguide material being selected and the emitters and detectors being configured so as to enable, when in use, total internal reflection (TIR) -type propagation of light within the lightguide between the emitters and detectors, and recognition of a touch on the basis of a drop in the TIR performance as determined from the detected light. A related method of manufacture is presented.
Owner:TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT
Multiple-frequency ultrasonic test probe, inspection system, and inspection method
ActiveUS20070227250A1Improve efficiencyIncrease speedAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationCatheterMultiple frequency
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Ultrasonic array probe apparatus, system, and method for traveling over holes and off edges of a structure
ActiveUS20070006657A1Defect is detectedImprove efficiencyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesThermometers using physical/chemical changesControl systemEngineering
Improved apparatus, systems, and methods for inspecting a structure are provided that use a probe with sled appendages and an axial braking system. The probe uses pulse echo ultrasonic signals to inspect the structure. The sled appendages permit the probe to contact and ride along the surface of the structure and are rotatably connected and curved away from the surface of the structure to compensate for contoured surfaces and inspection around holes and edges. The axial braking system, in coordination with a motion control system moving the probe, fixes the positions of the sled appendages just before the probe travels over a hole or off an edge of the structure to prevent the probe from falling through the hole or off an edge and to permit the probe to return to the surface of the structure to continue inspection of the structure.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Wireless device having antenna
InactiveUS20050190107A1Reduce couplingCoupling lossSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsGround planeAntenna element
A wireless device includes a first antenna element resonating with a first frequency, a first feeding point coupled to the first antenna element and disposed on a ground plane in the wireless device, a first matching circuit of which first end is coupled to the first feeding point, a second antenna element resonating a second frequency higher than the first frequency, a second feeding point coupled to the second antenna element and disposed on the ground plane, a second matching circuit of which one end is coupled to the second feeding point, and a radio circuit coupled via a transmission line to a common connection point shared by respective second ends of the first and second matching circuits.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
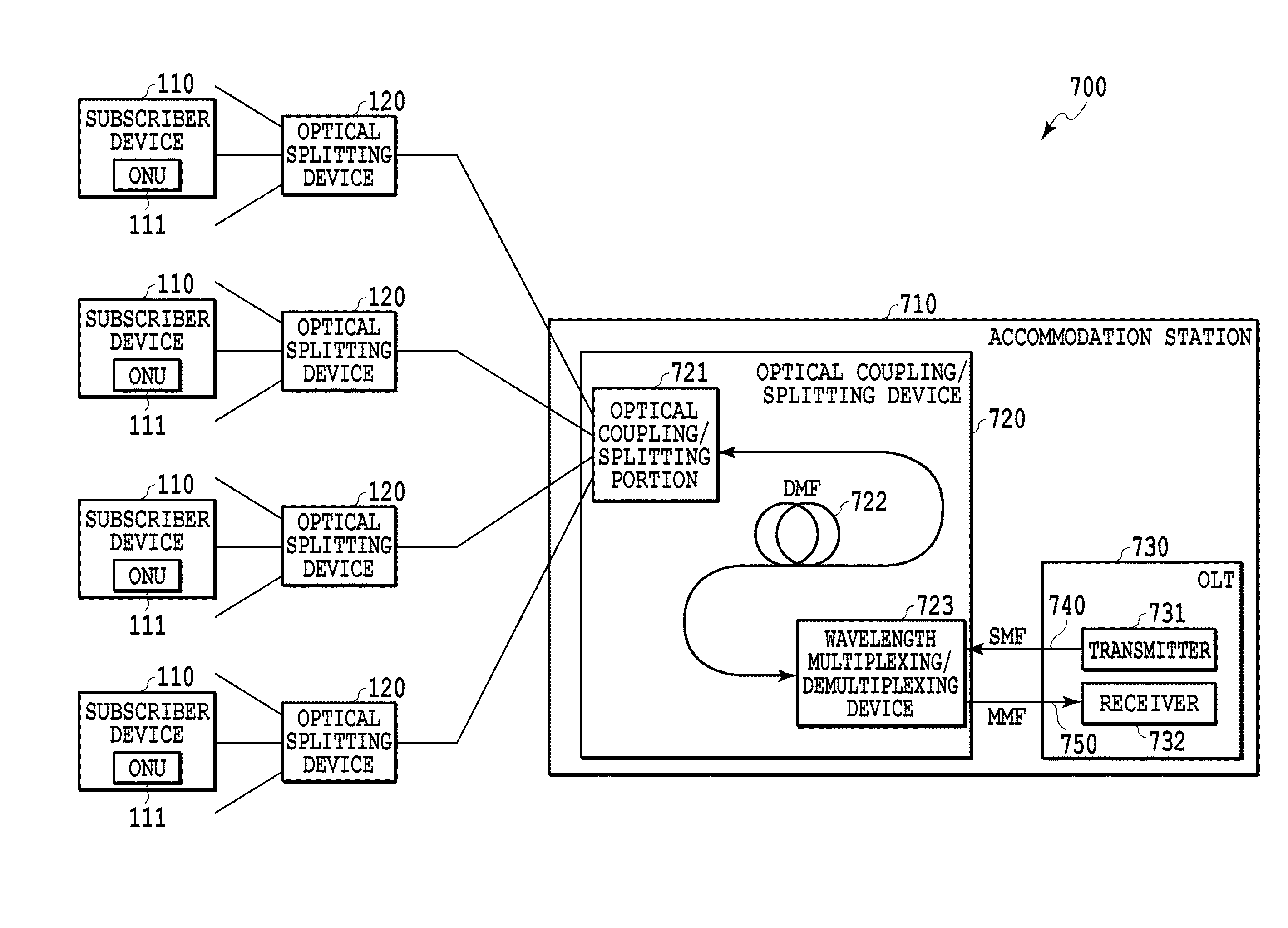
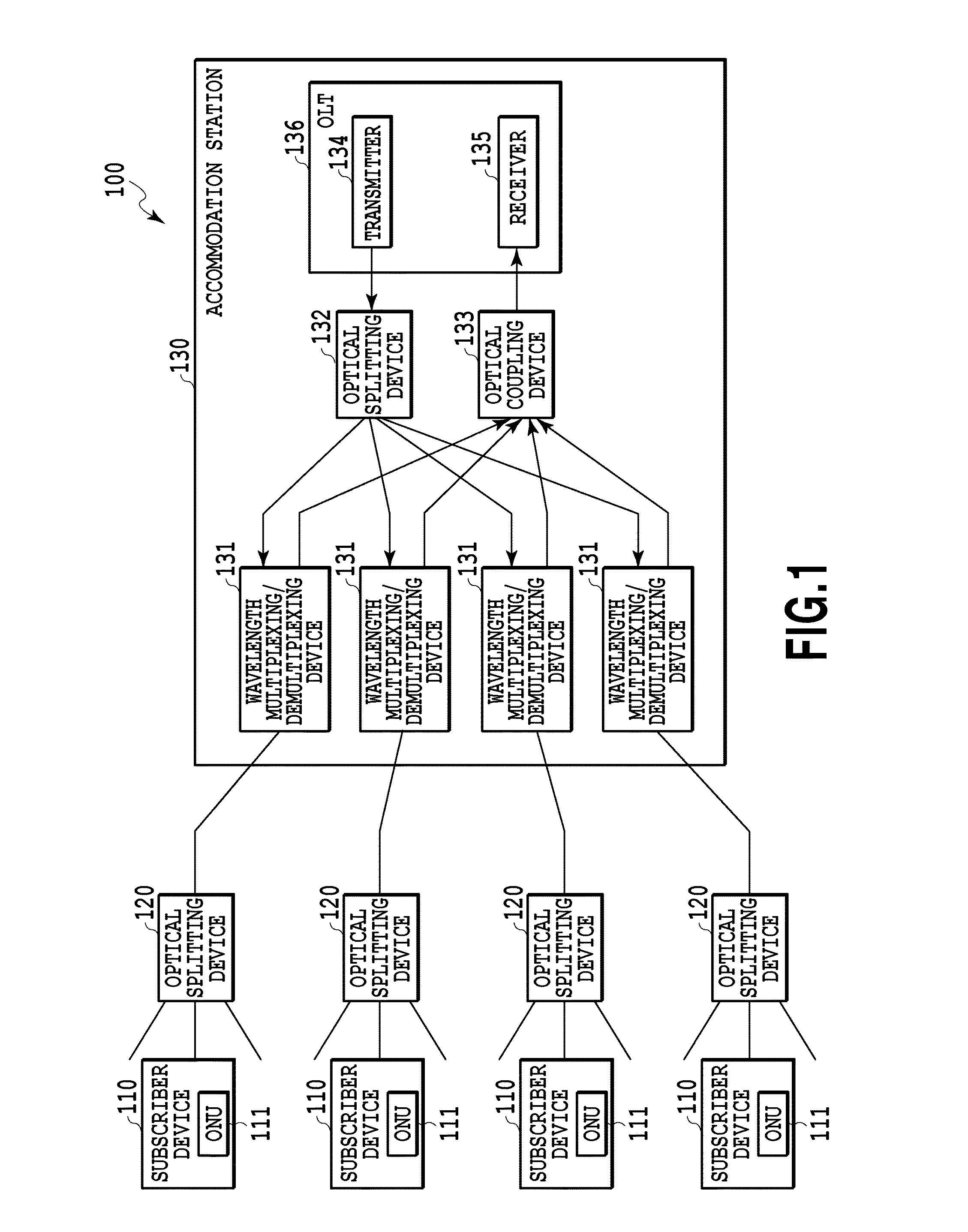
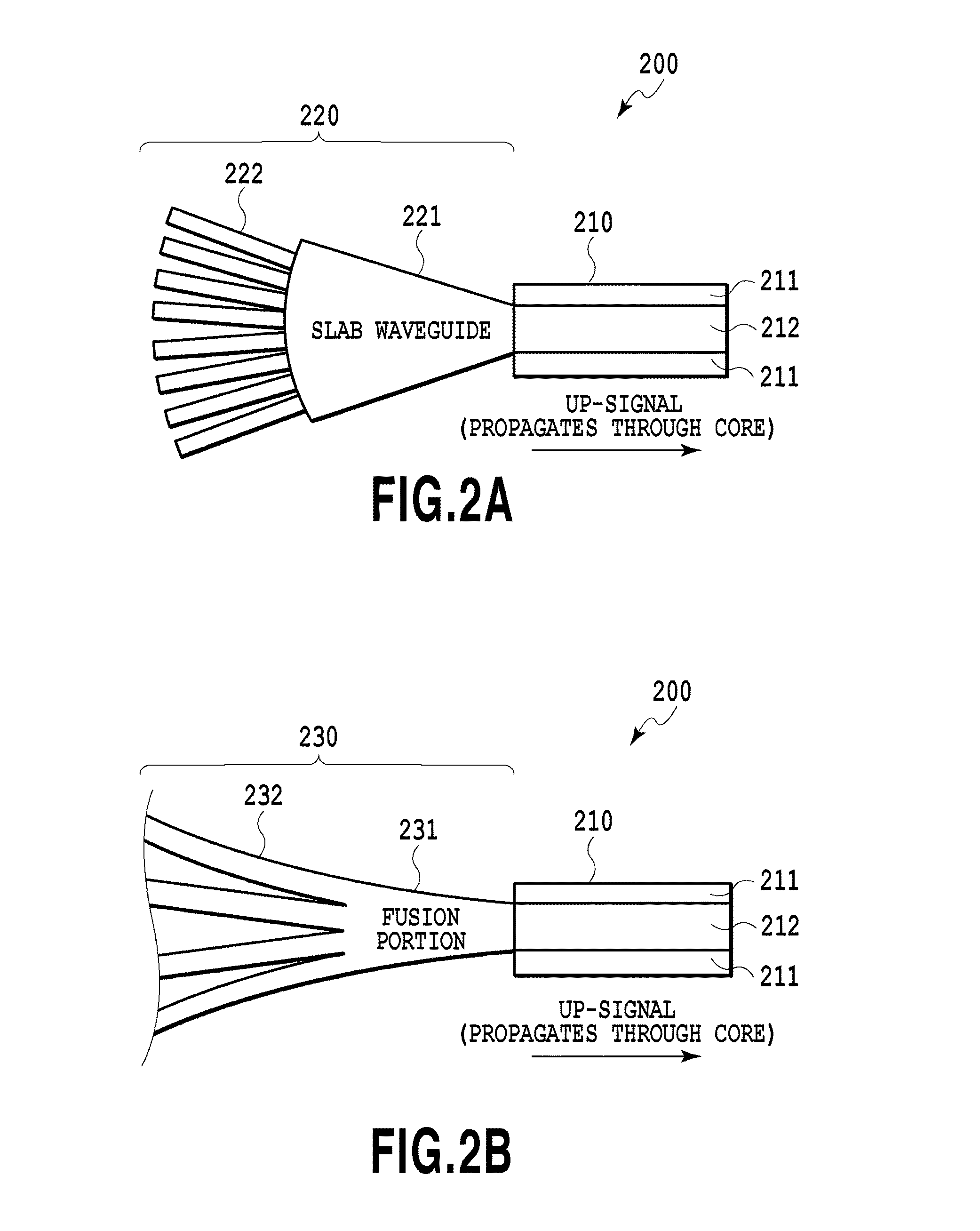
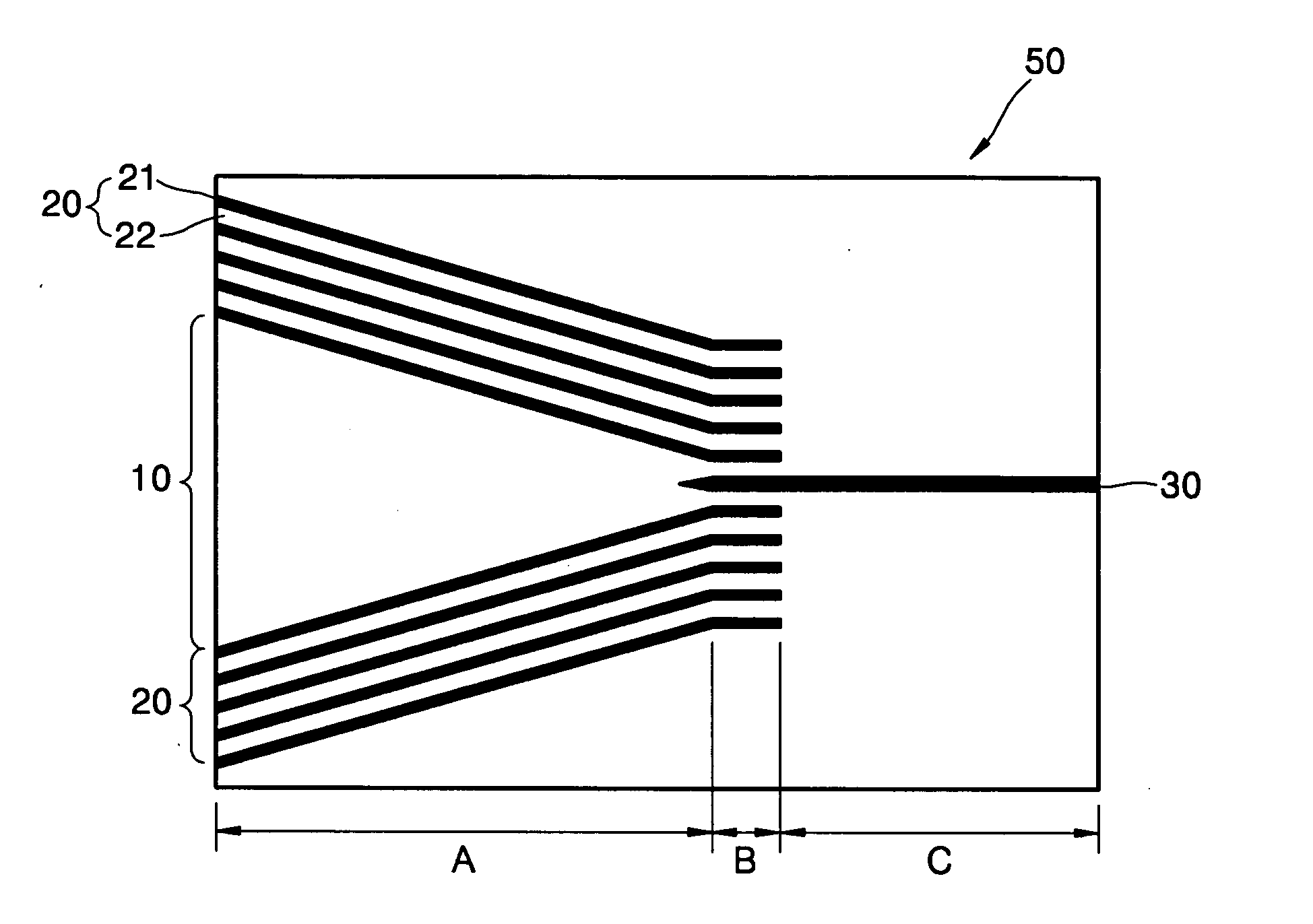
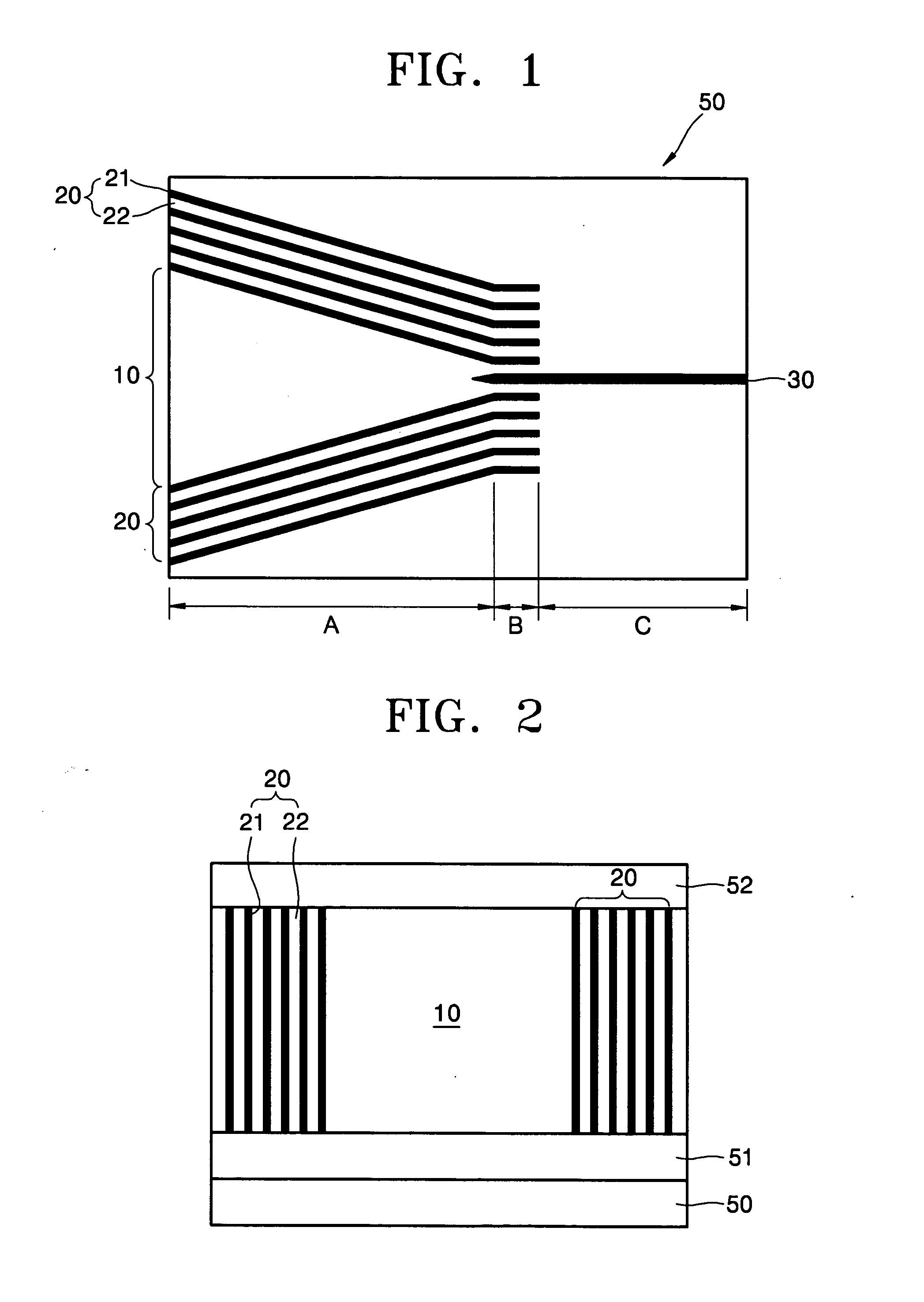
Light merging/branching device, bidirectional light propagation device, and light transmission/reception system
ActiveUS20140186040A1Reduce couplingIncreasing budgetCoupling light guidesOptical multiplexOptical propagationCoupling loss
The present invention relates to an optical coupling / splitting device that realizes the splitting of a down-signal and the coupling of up-signals by the same optical device, and reduces coupling losses of the up-signal. An optical coupling / splitting device in the present invention comprises an optical coupling / splitting means for coupling a plurality of up-signals in a multi-mode for output and splitting a down-signal in a single mode for output, and a two-way optical propagation means for propagating the up-signal that is output from the optical coupling / splitting means in a multi-mode for output and propagate the down-signal in a single mode to be output to the optical coupling / splitting means.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
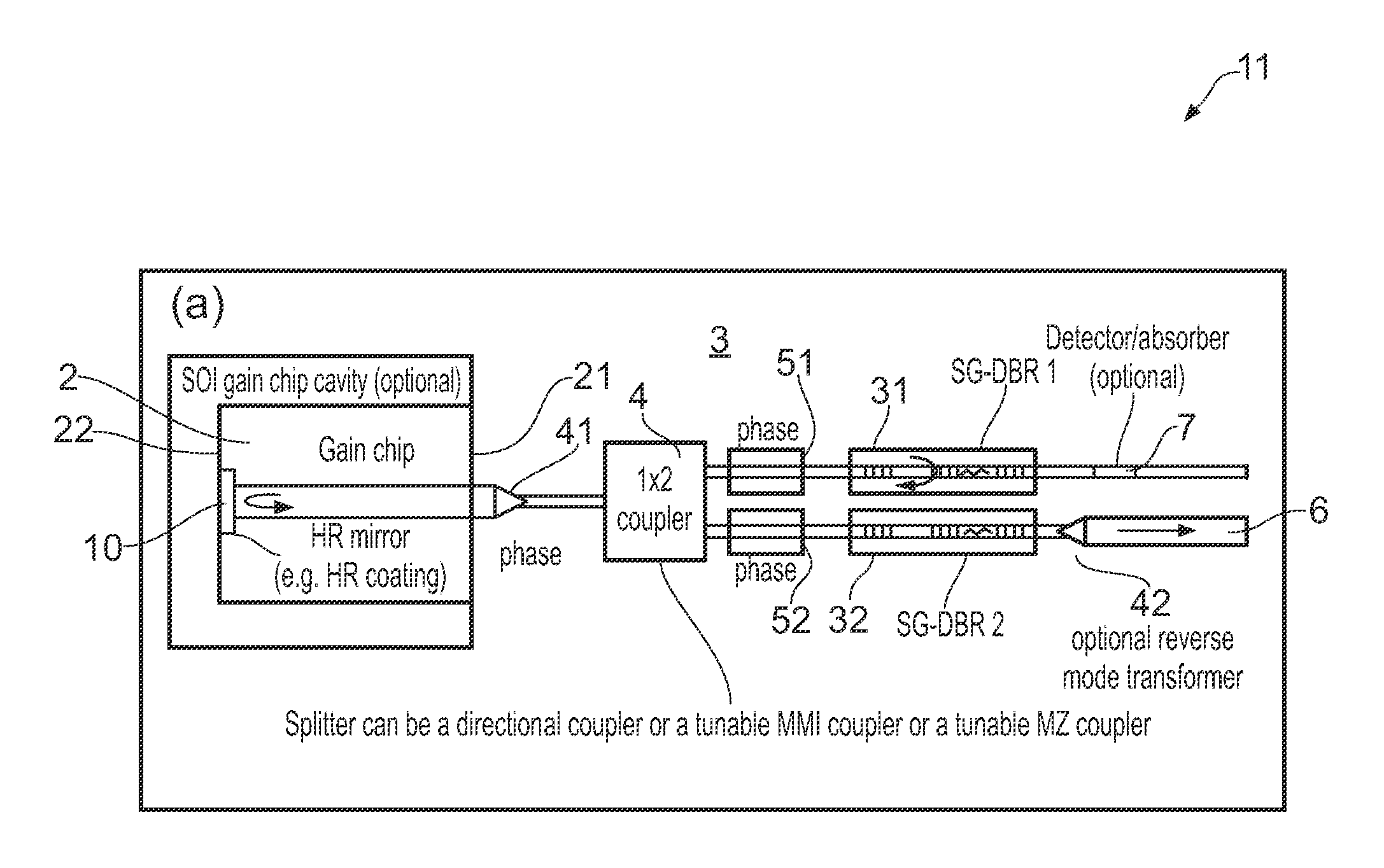
Tunable soi laser
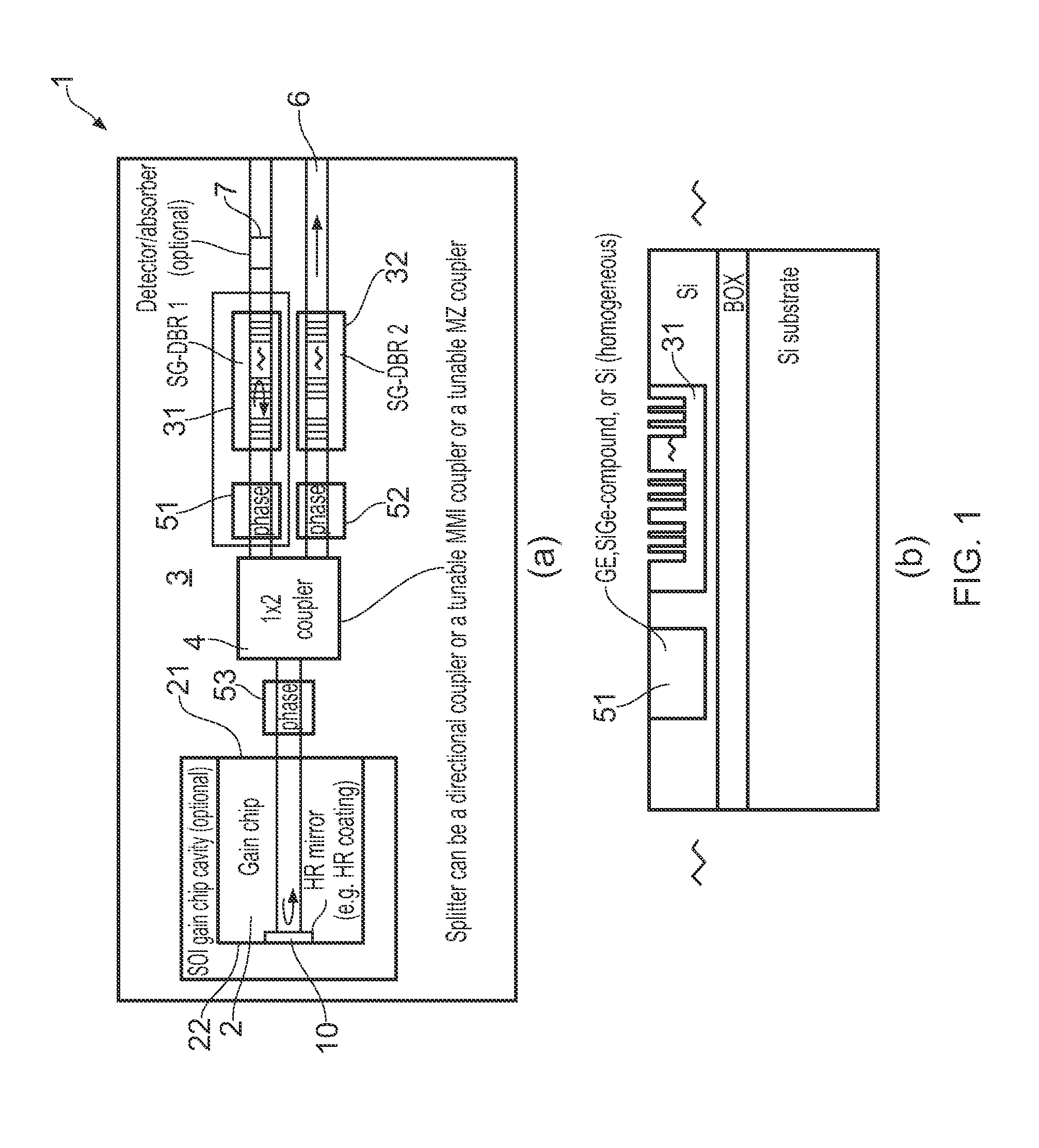
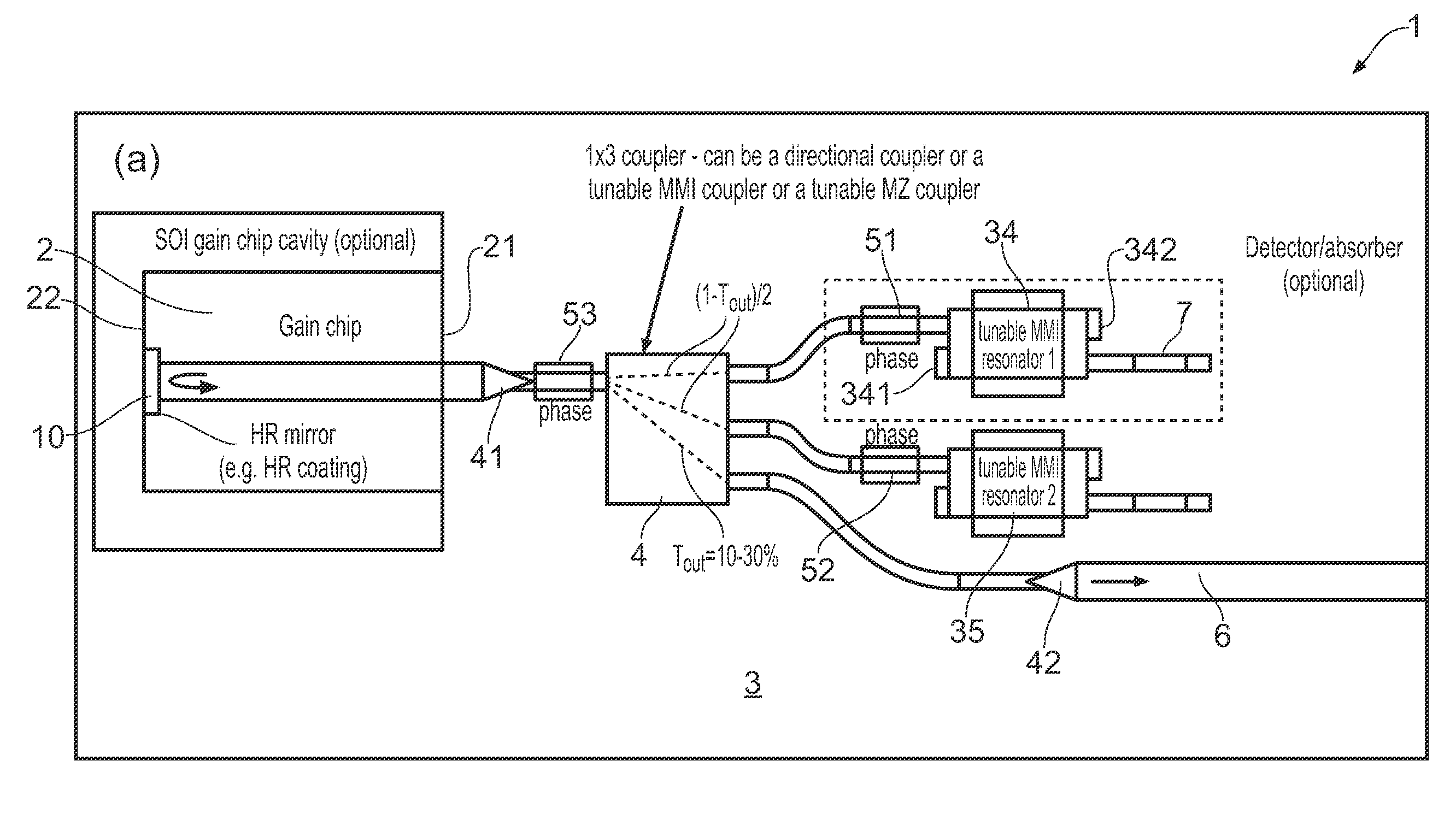
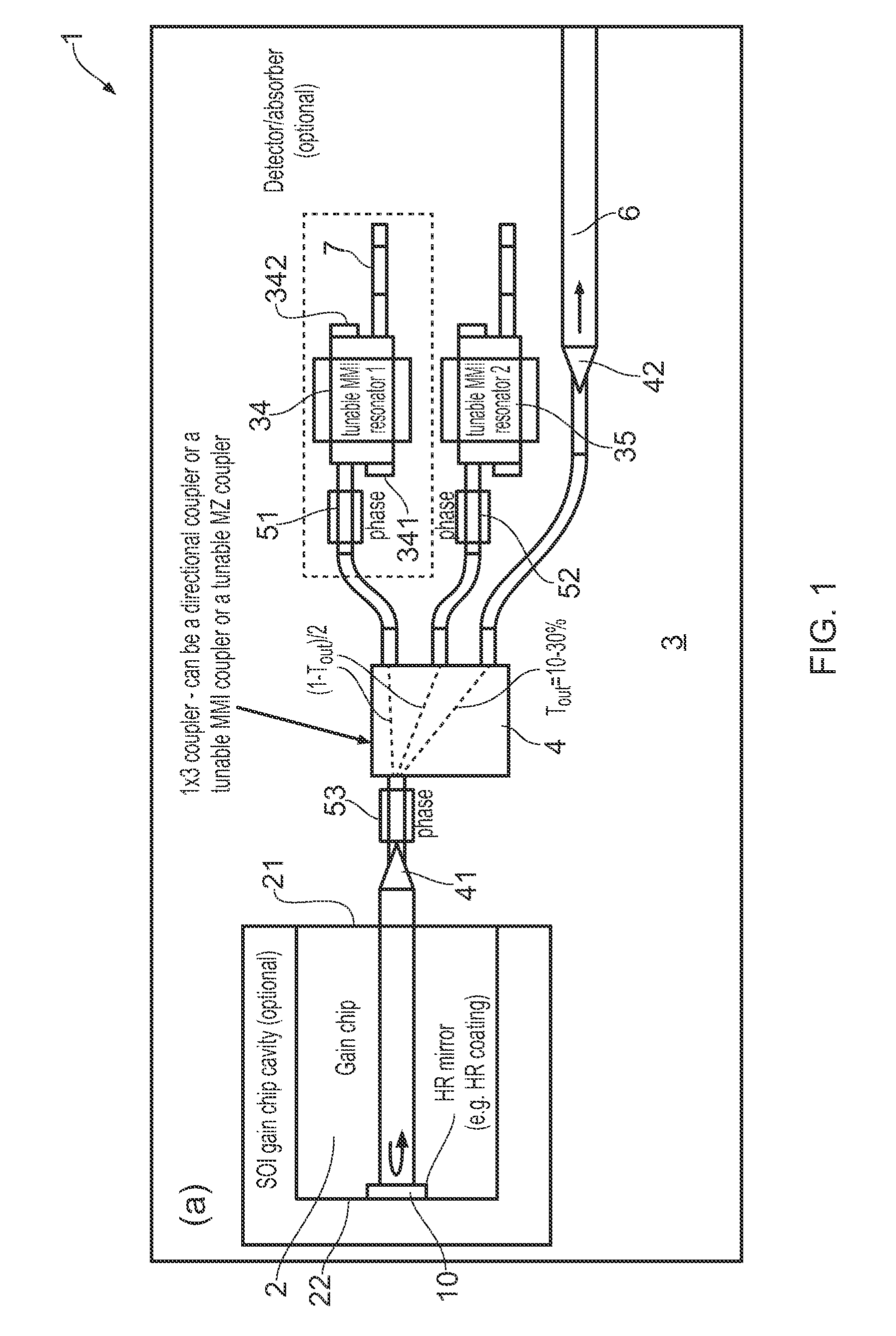
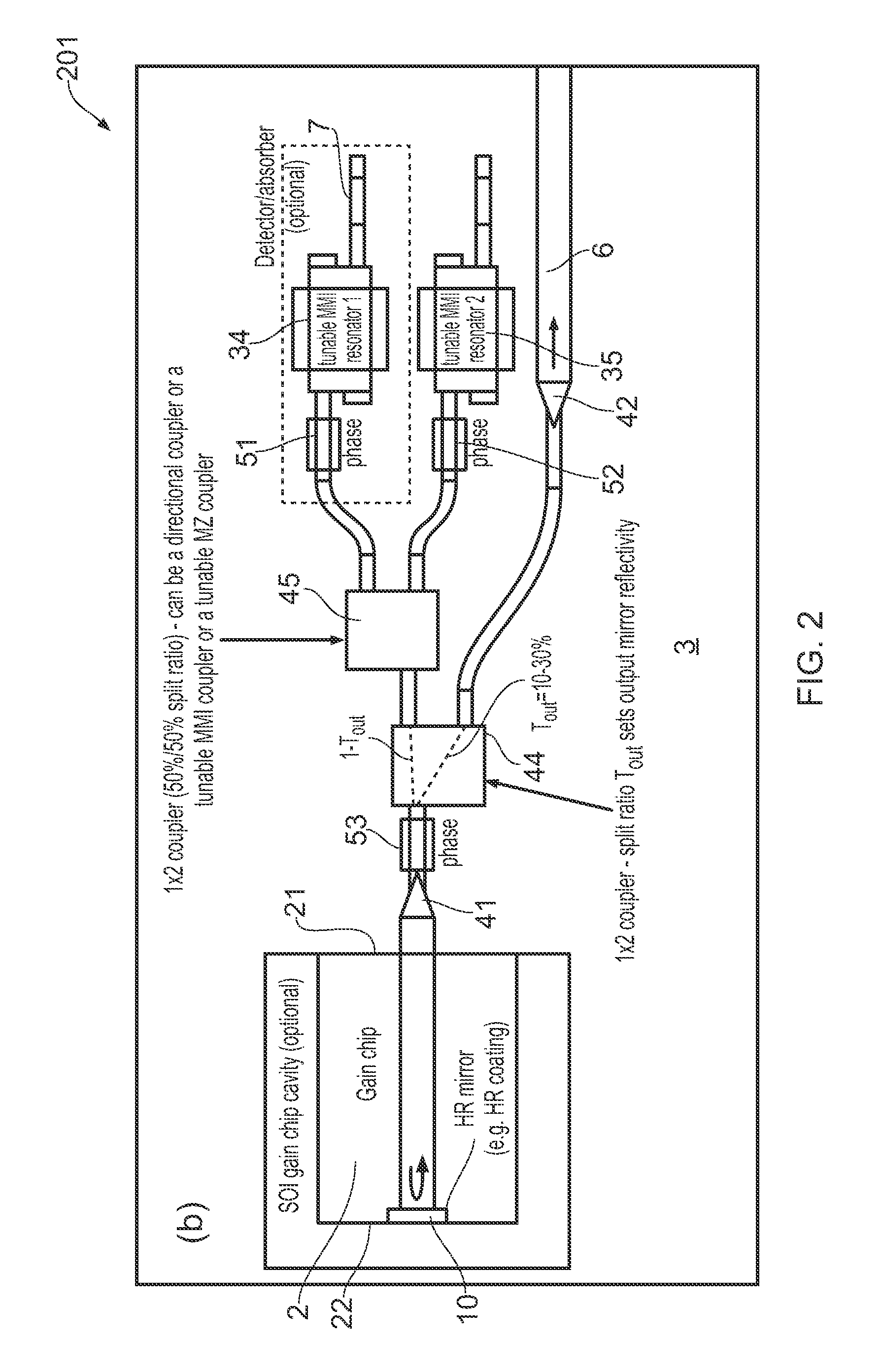
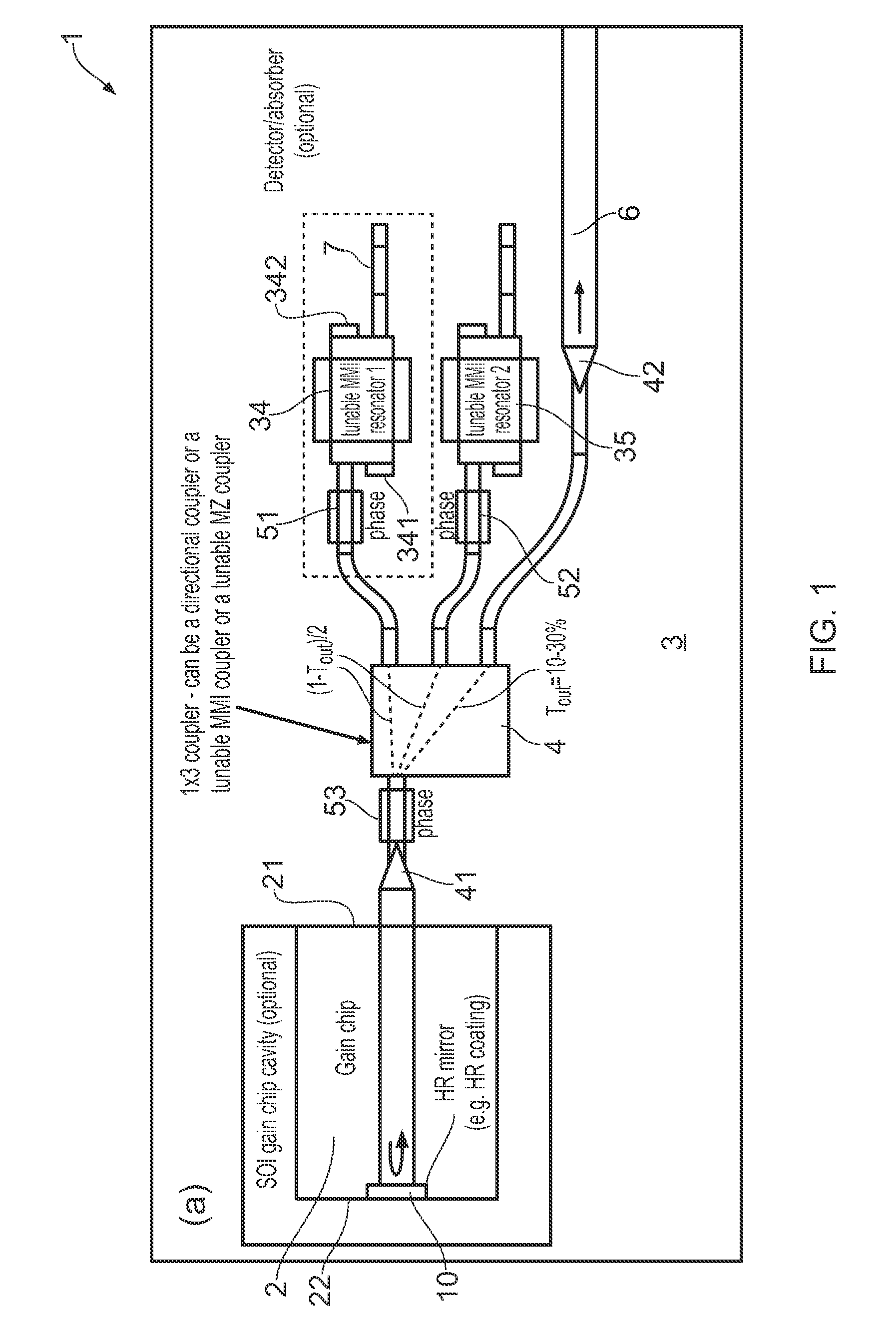
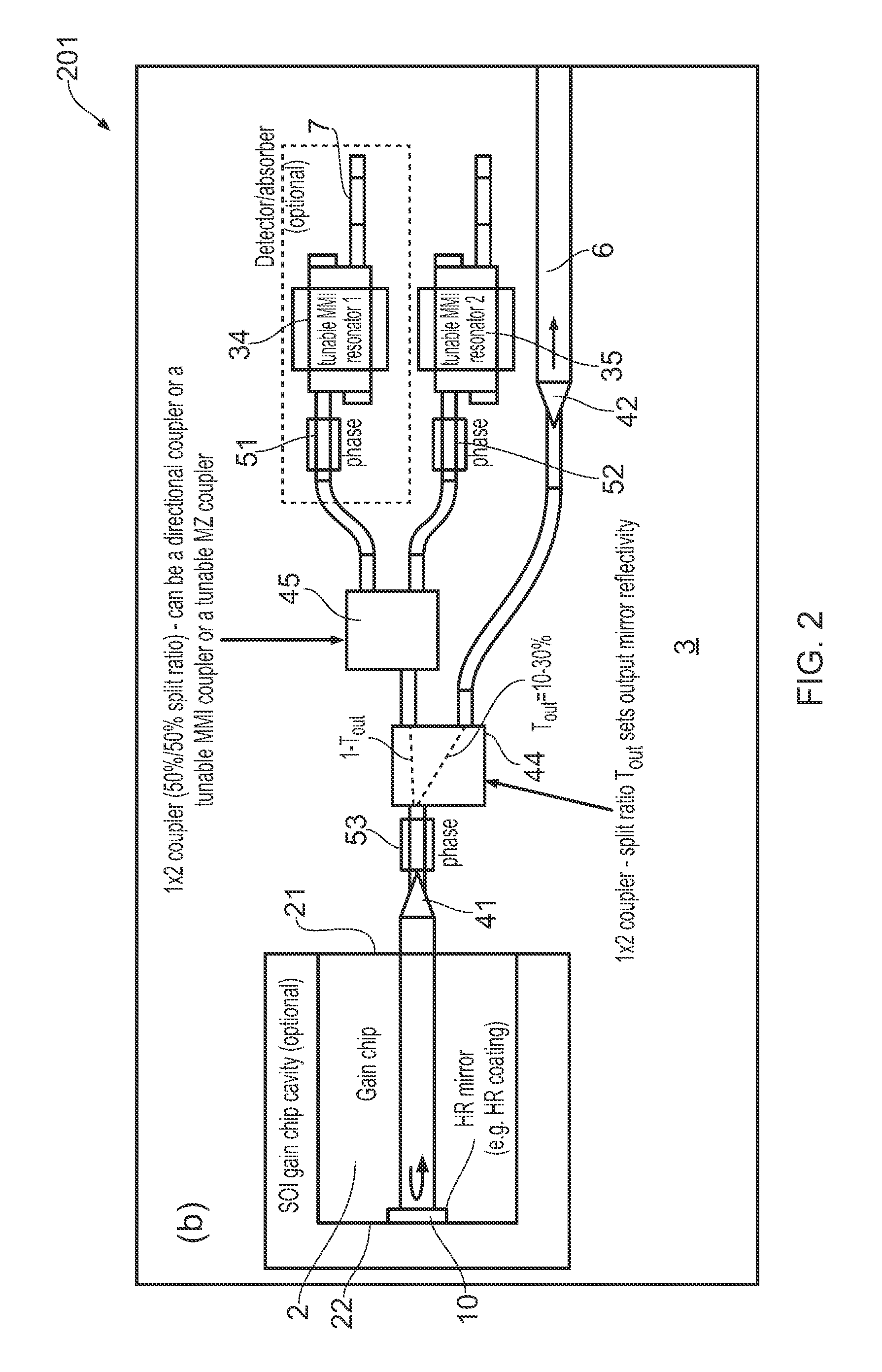
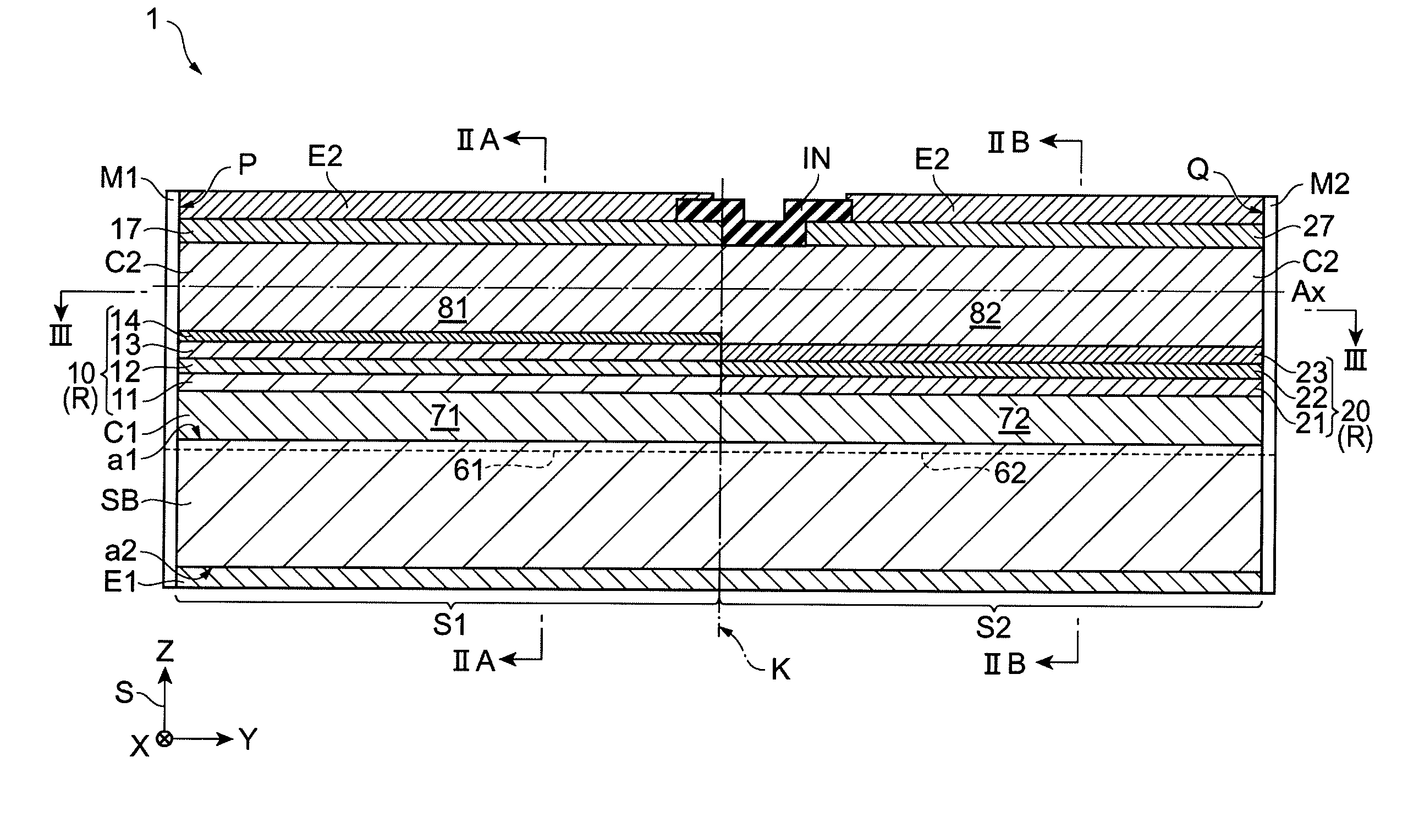
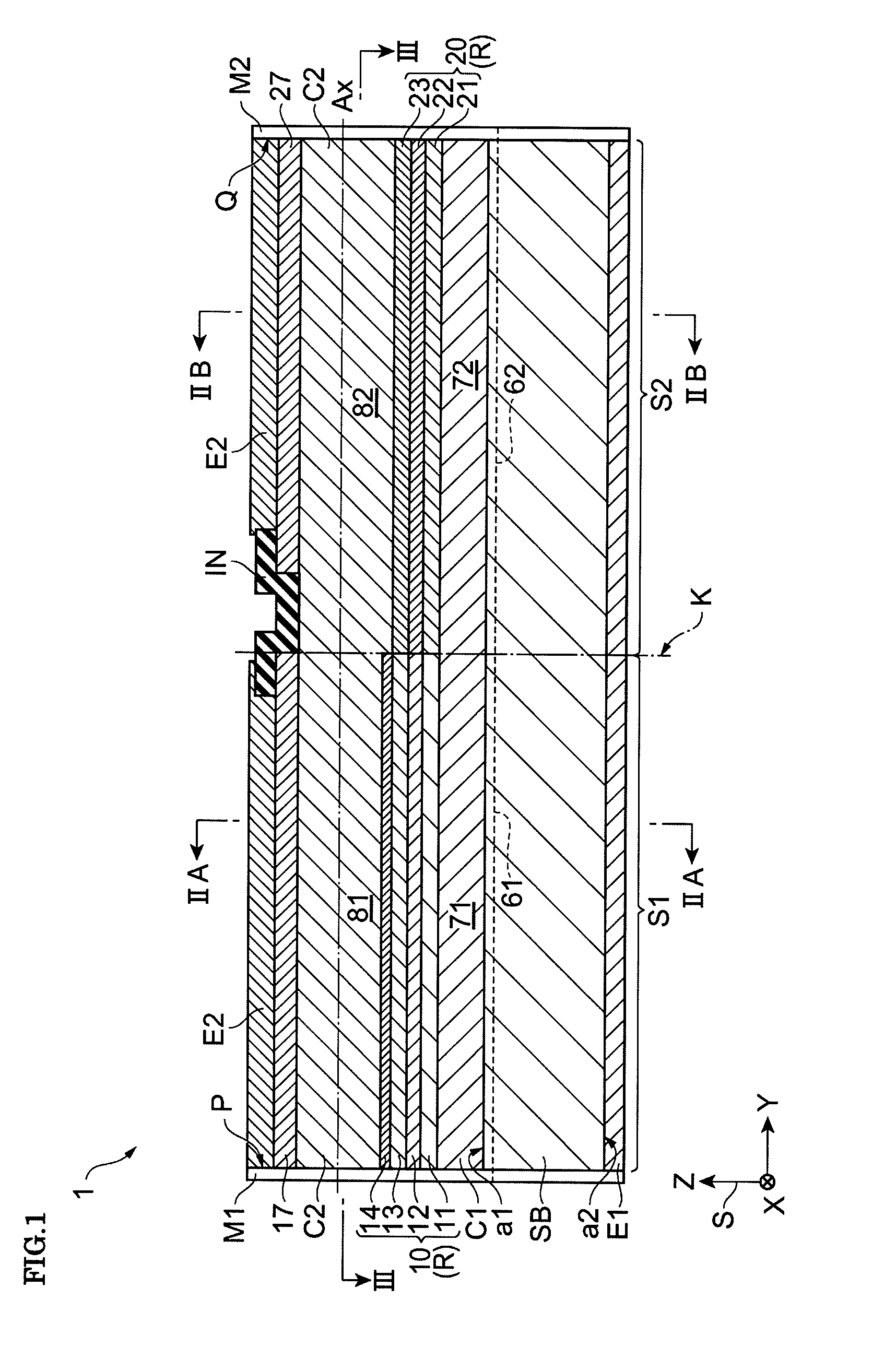
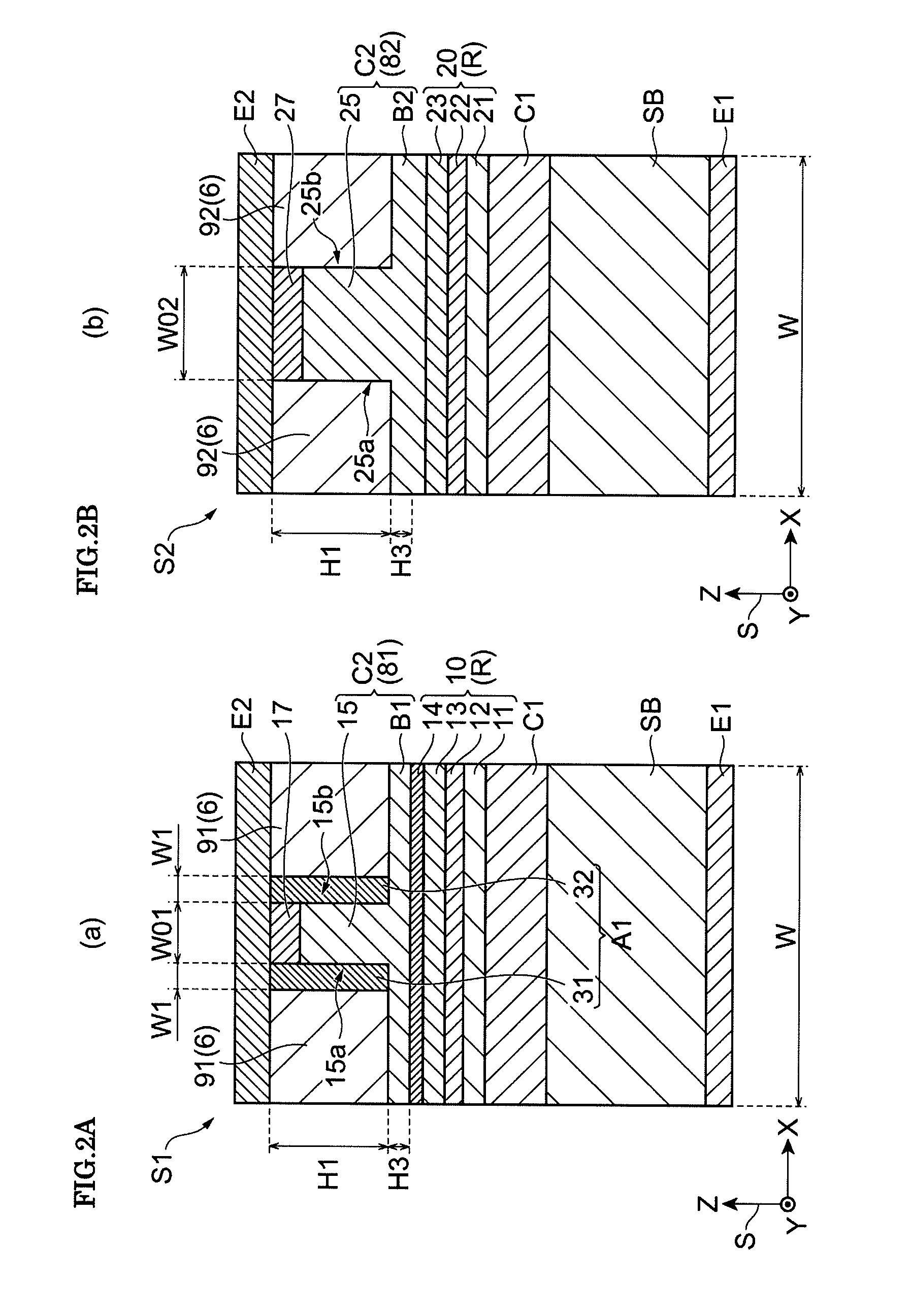
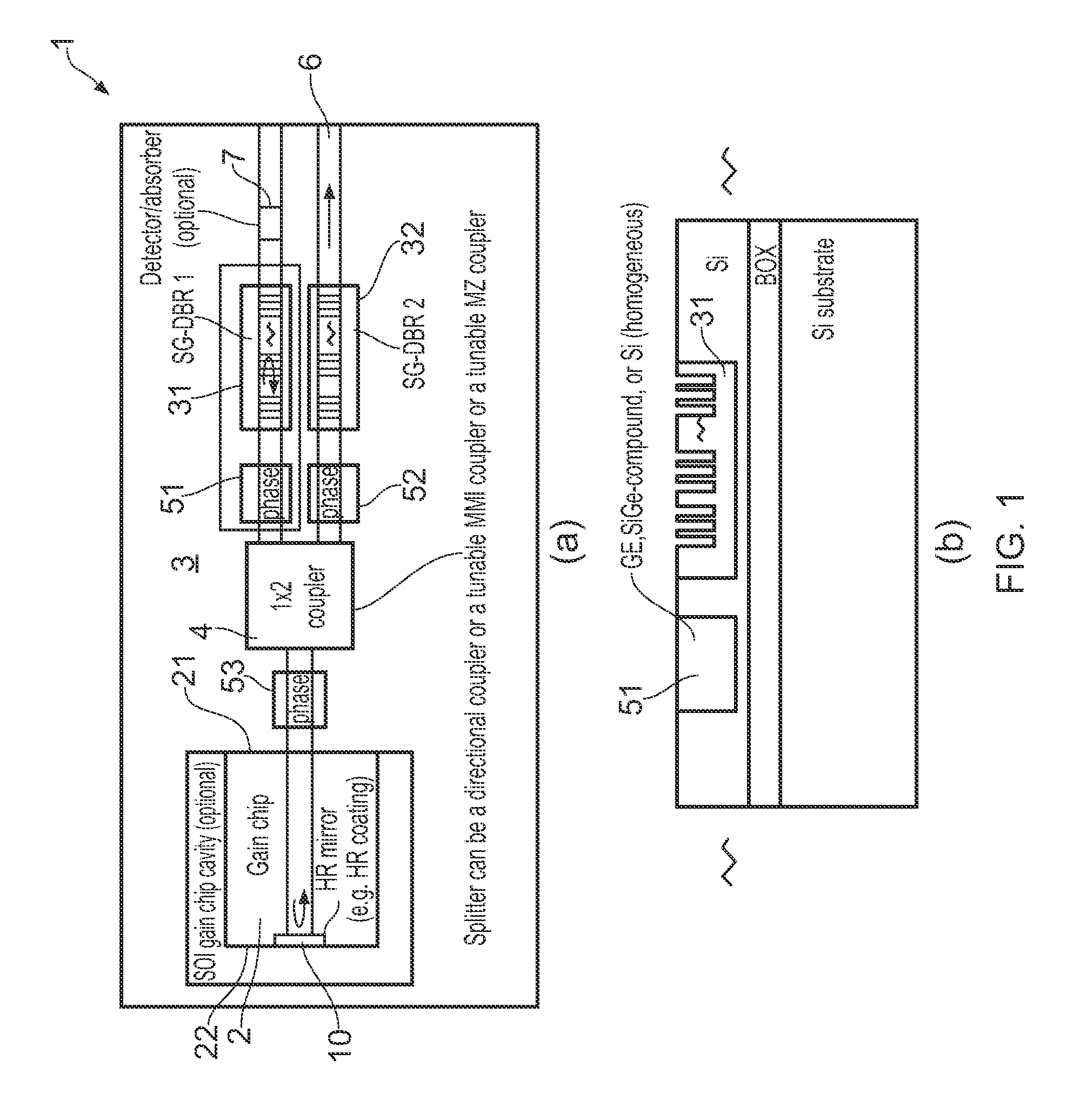
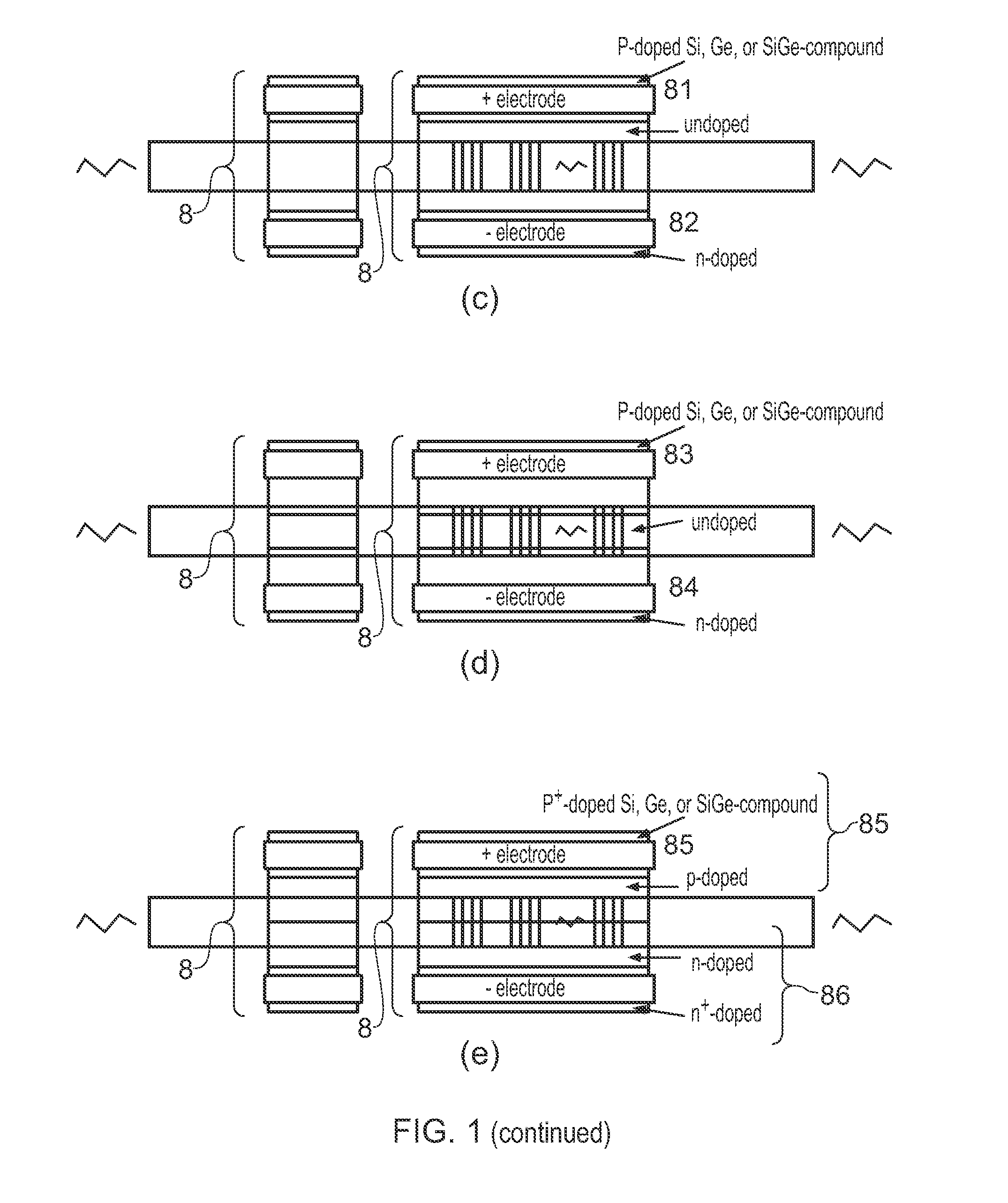
ActiveUS20150207296A1Improve power efficiencyCoupling lossLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionReflectance spectroscopyDistributed Bragg reflector laser
A wavelength tunable silicon-on-insulator (SOI) laser comprising: a laser cavity including: a semiconductor gain medium having a front end and a back end; and a phase-tunable waveguide platform coupled to the front end of the semiconductor gain medium; wherein the phase-tunable waveguide platform includes a first Distributed Bragg Reflector (DBR) and a second Distributed Bragg Reflector (DBR); at least one of the Distributed Bragg Reflectors having a comb reflectance spectrum; and wherein a mirror of the laser cavity is located at the back end of the semiconductor gain medium.
Owner:ROCKLEY PHOTONICS LTD +1
Photonics module and method of manufacturing
InactiveUS20120099816A1Increase optical powerMinimal optical coupling lossCircuit optical detailsPrinted circuit aspectsComputer modulePhotonics
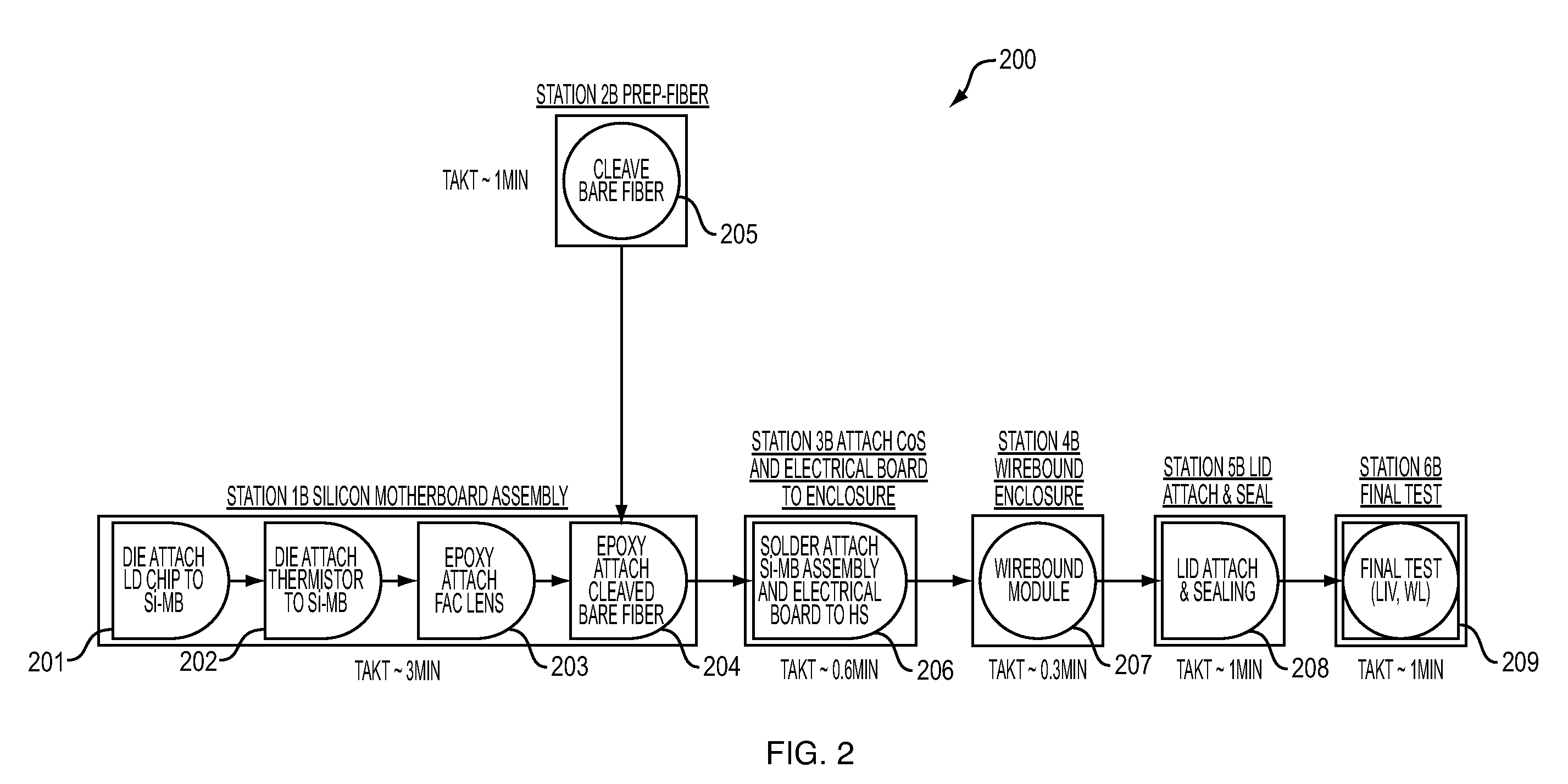
An improved photonics module includes a Silicon motherboard having a plurality of v-grooves that collimate and optically align a laser diode emission is held within an enclosure that includes two or more positioning portions that locate and guide the Silicon motherboard in the desired position within the enclosure. The enclosure acts as a heat sink that provides stability and aids in wicking Silicon motherboard mounting material such damage to the Silicon motherboard by the mounting material is avoided. Methods of making the improved photonics module are also disclosed.
Owner:PALOMAR MEDICAL TECH
Optical fiber coupling part and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS7603008B2Easy alignmentEasy to manufactureGlass making apparatusCoupling light guidesCoupling lossOptical property
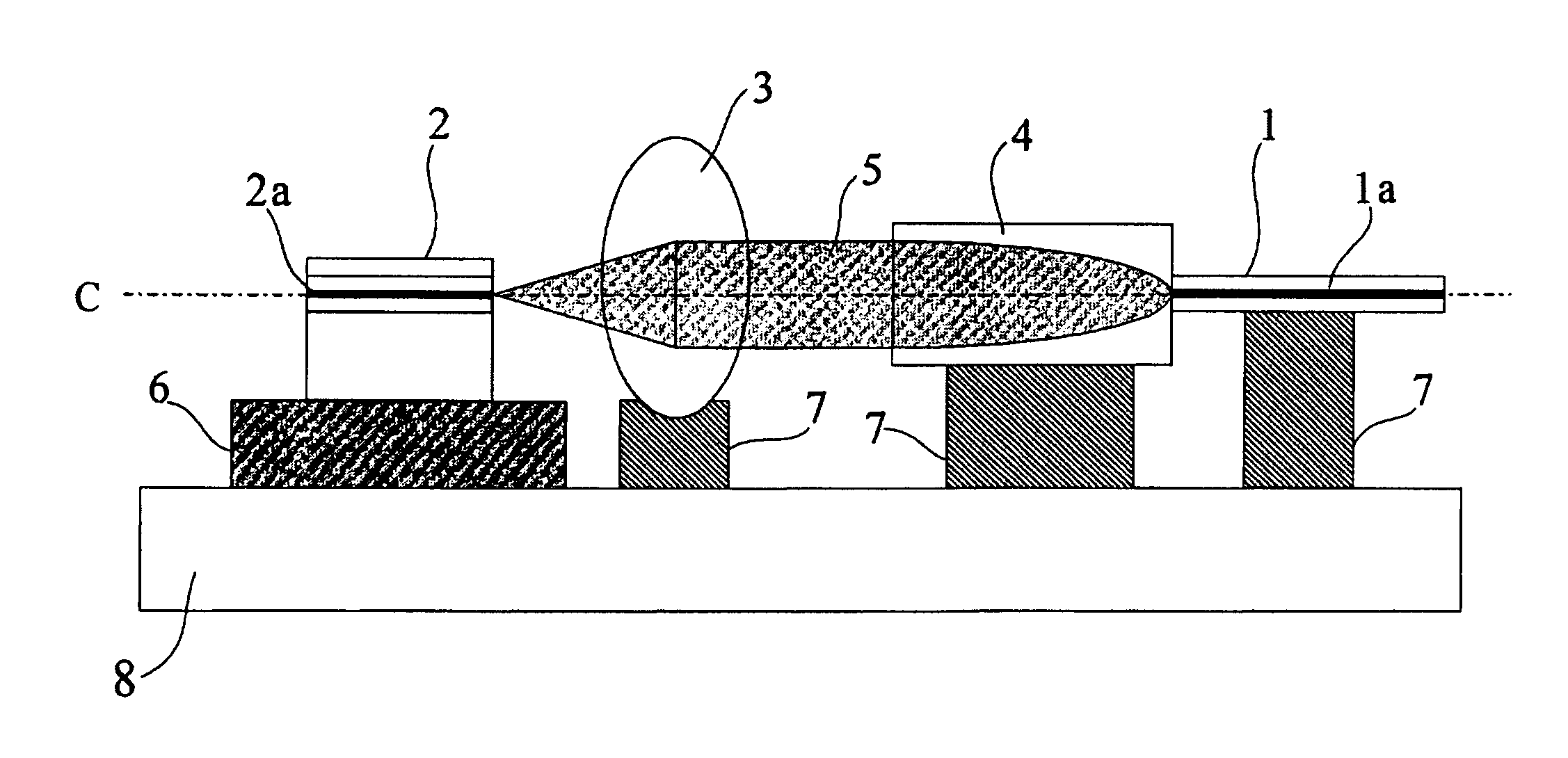
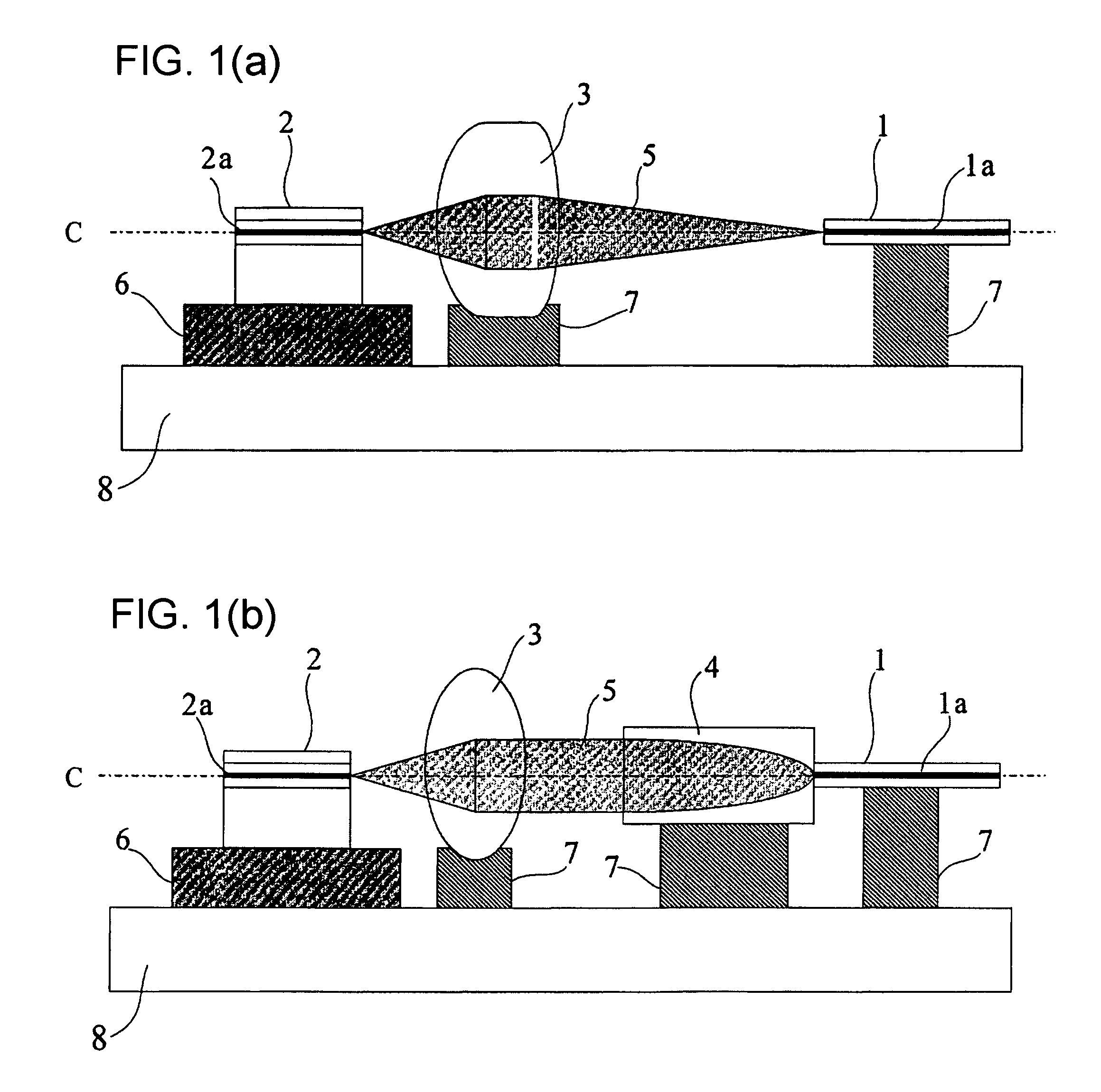
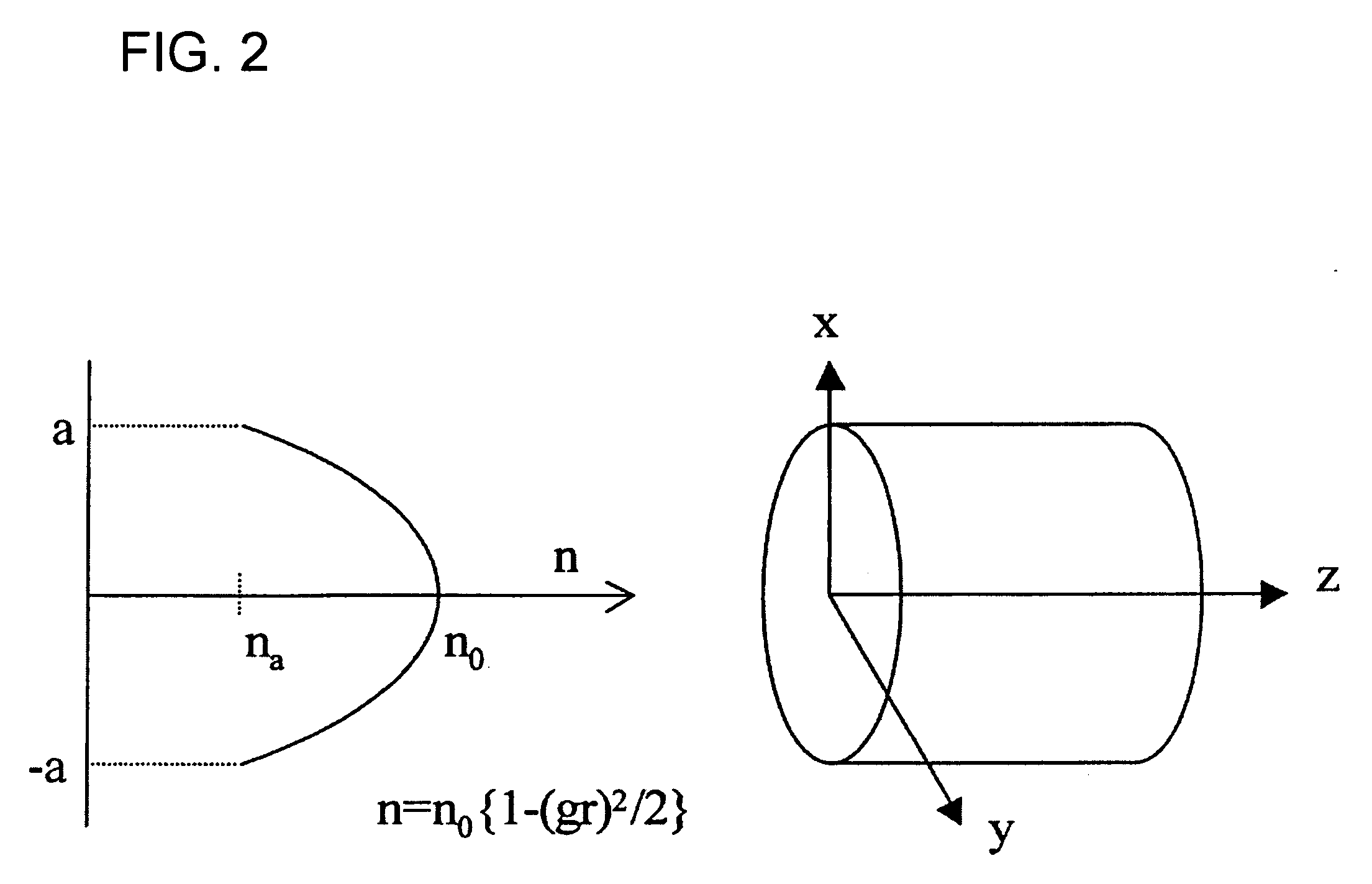
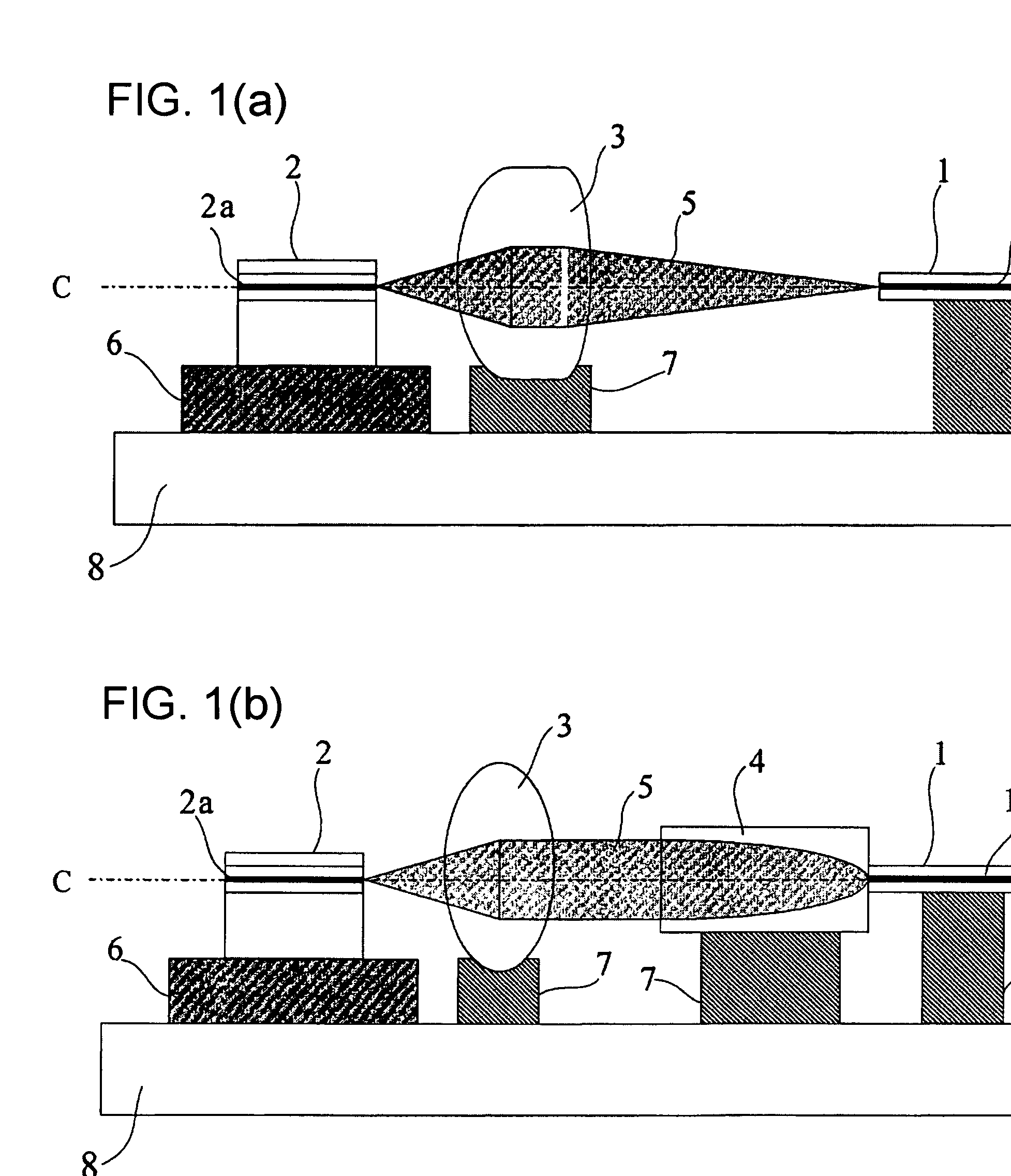
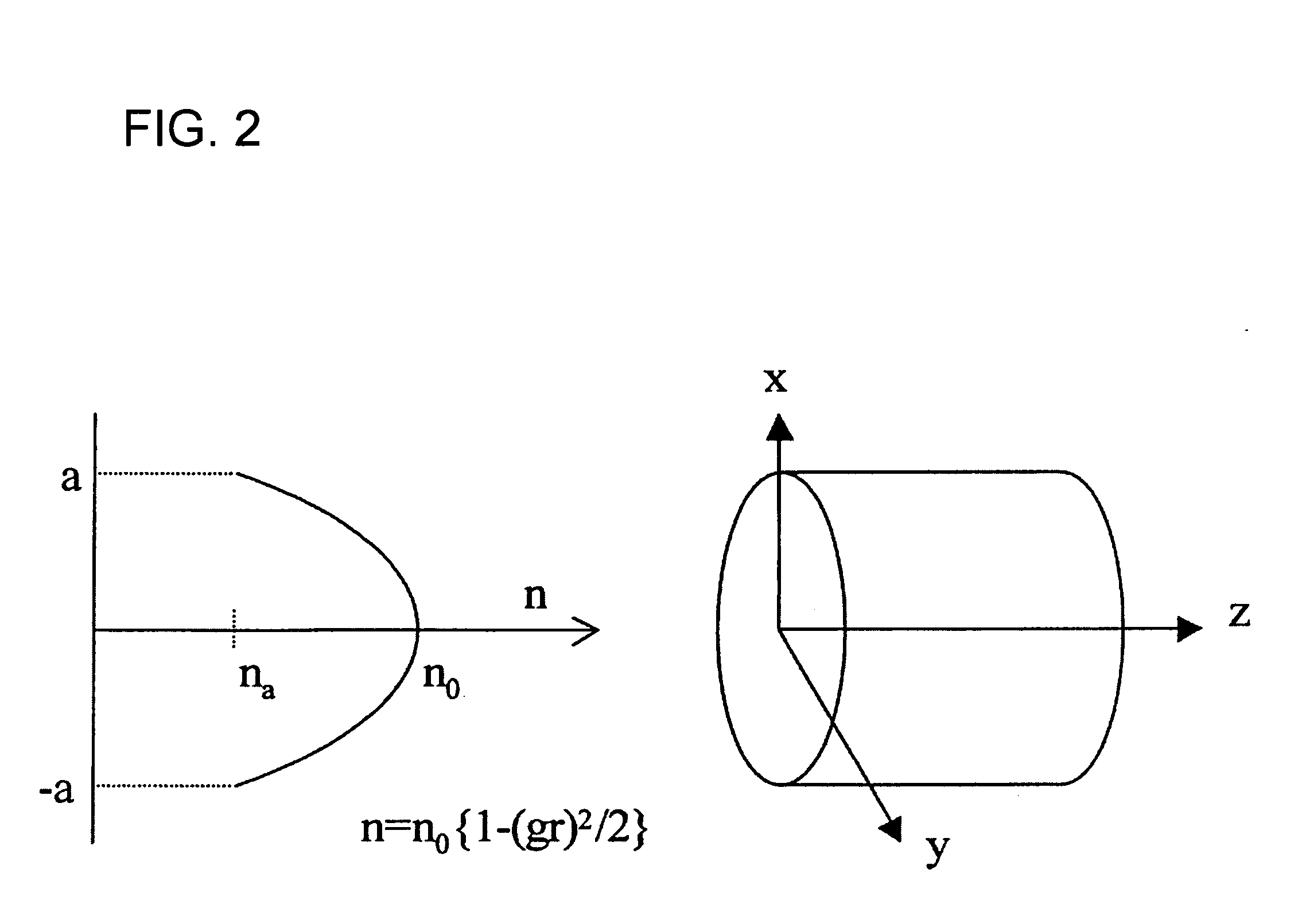
An optical fiber coupling part that reduces the difficulty in adjusting cores, minimizes coupling loss, and prevents optical characteristics from deteriorating. An optical fiber is fused to one end of a GRIN lens which includes a quartz glass containing one or more refractive index regulating substances selected from Sb2O3, Ta2O5, TiO2 or ZrO2. Optical characteristics are not deteriorated because an adhesive is not used, and self-alignment effects facilitate adjustment of the cores of the GRIN lens and the optical fiber. Furthemore, coupling loss can be minimized by setting a refractive index distribution constant g of the GRIN lens within an appropriate range.
Owner:TOYO SEIKAN GRP HLDG LTD
Arrangements for reducing wavelength sensitivity in prism-coupled SOI-based optical systems
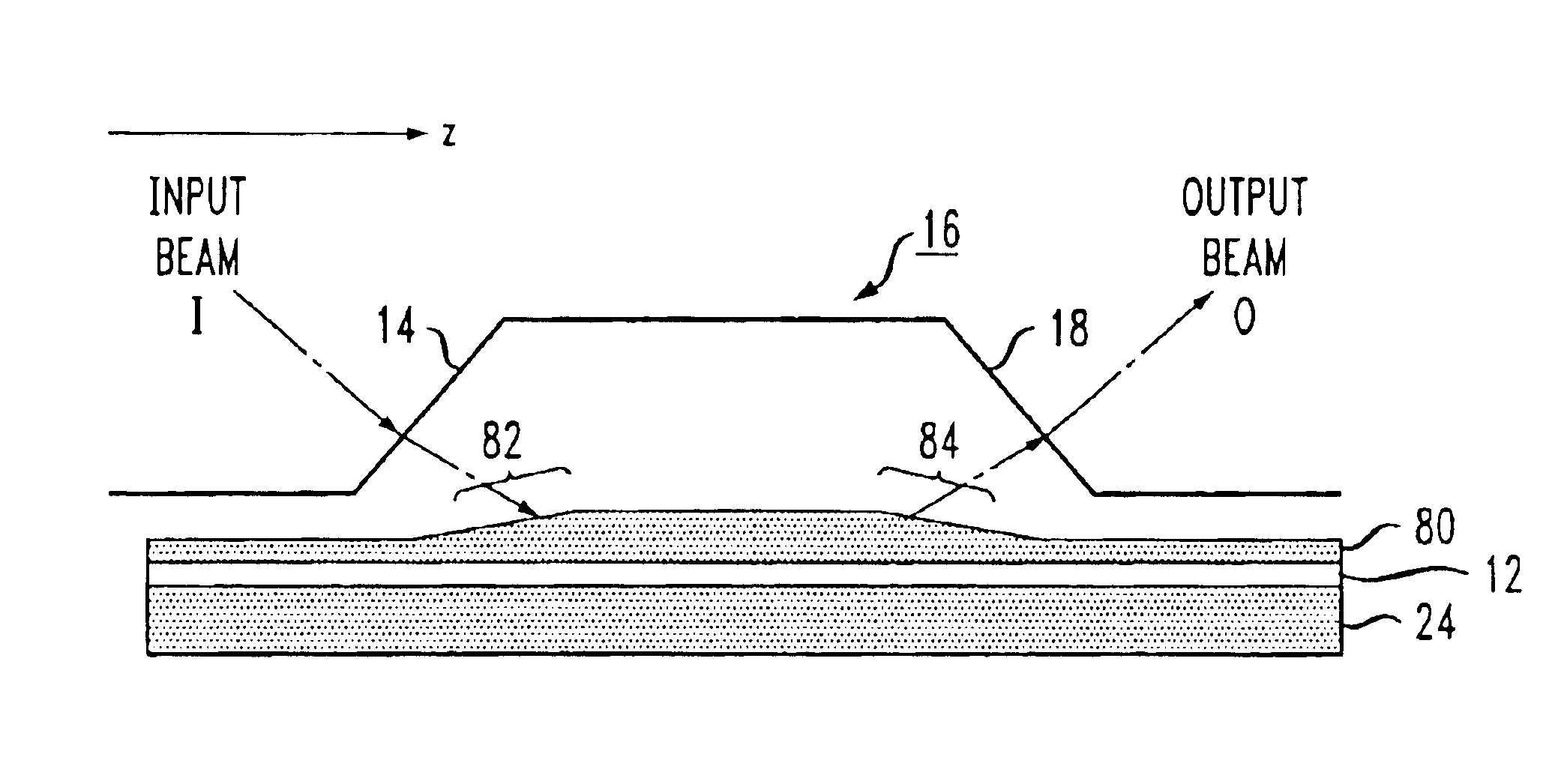
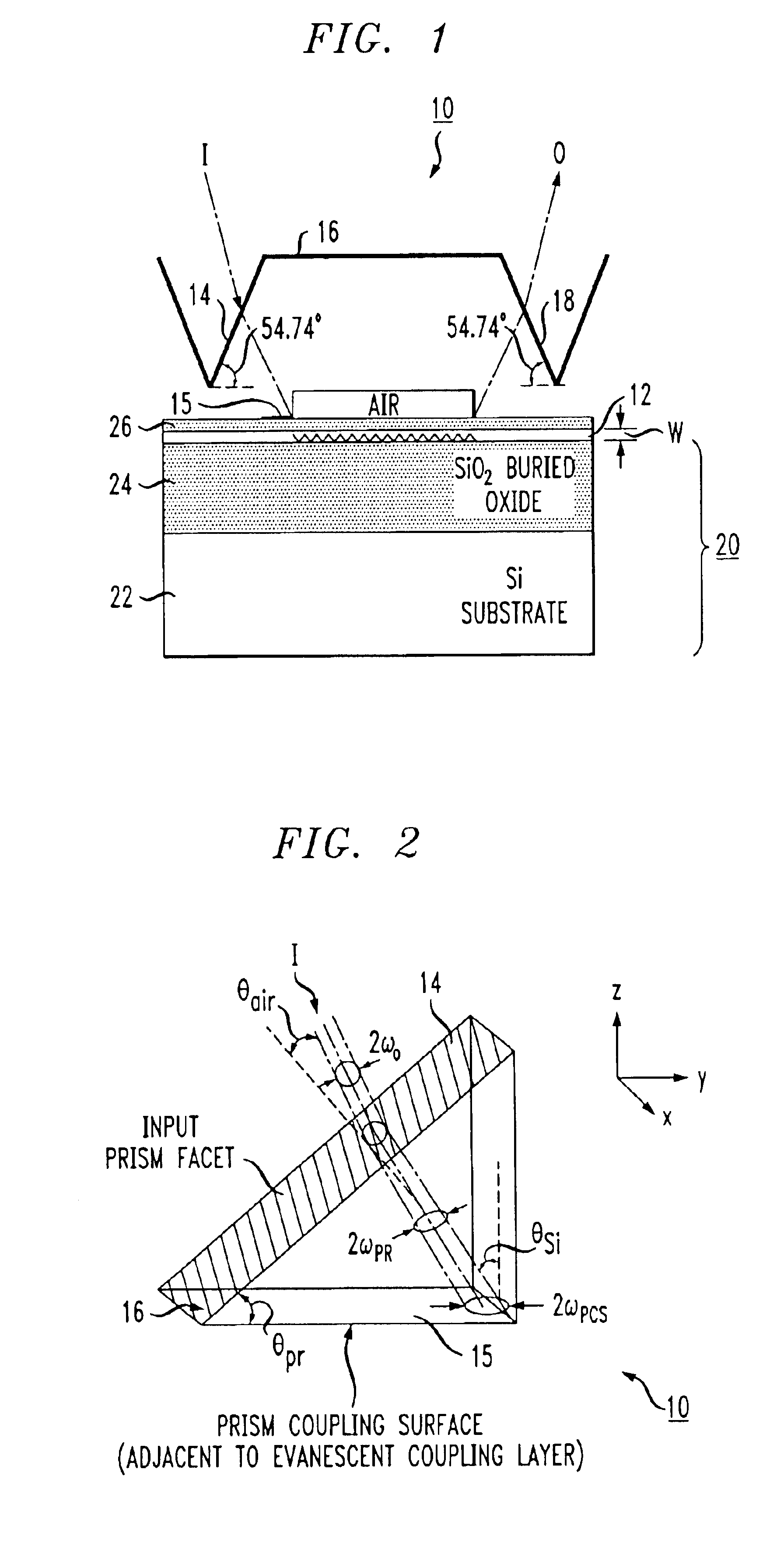
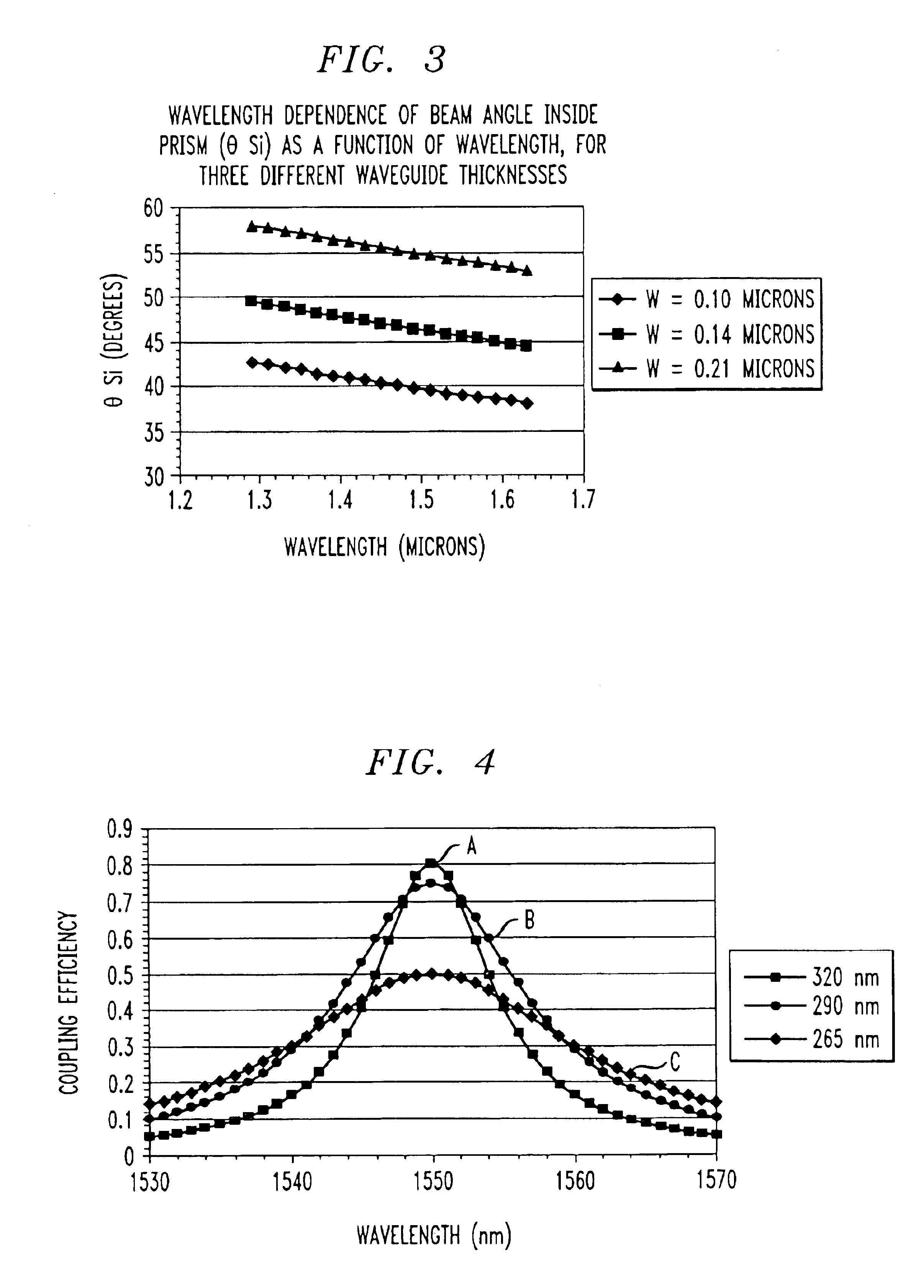
ActiveUS6917730B2Coupling efficiency is maximizedReduce thicknessCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideSurface layerPrism
An optical coupling system for use with multiple wavelength optical signals provides improved coupling efficiency between a free-space optical beam and a relatively thin, surface layer of an SOI structure (“SOI layer”), allowing for sufficient coupling efficiency (greater than 50%) over a predetermined wavelength range. An evanescent coupling layer, disposed between a coupling prism and an SOI layer, is particularly configured to improve the coupling efficiency. In one embodiment, the thickness of the evanescent layer is reduced below an optimum value for a single wavelength, the reduced thickness improving coupling efficiency over a predetermined wavelength range around a defined center wavelength. Alternatively, a tapered thickness evanescent coupling layer may be used to improve coupling efficiency (or a combination of reduced thickness and tapered configuration). Optical beam steering can be combined with a modified evanescent coupling layer to control the input beam launch angle and further improve coupling efficiency.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Arrangement for a touchscreen and related method of manufacture
ActiveUS20110199340A1Mitigate such drawbackRapid industrial scale manufacturingPrinted circuit assemblingOptical light guidesTotal internal reflectionRefractive index
Arrangement for use with a touchscreen, includes a substrate, such as an optically substantially transparent film or a film defining a through hole, the substrate including support electronics, such as printed electronics including a number of printed conductors, for providing power, control and / or communications connection to further electronic components, a number of emitters and detectors arranged on the substrate into contact with the support electronics, for emitting and detecting light, respectively, and a lightguide arranged onto the substrate such that the emitters and detectors, and optionally at least part of the support electronics, are substantially immersed in the lightguide material, the properties of the lightguide including the refractive index of the lightguide material being selected and the emitters and detectors being configured so as to enable, when in use, total internal reflection (TIR)-type propagation of light within the lightguide between the emitters and detectors and recognition of a touch on the basis of a drop in the TIR performance as determined from the detected light. A related method of manufacture is presented.
Owner:TACTOTEK
Tunable soi laser
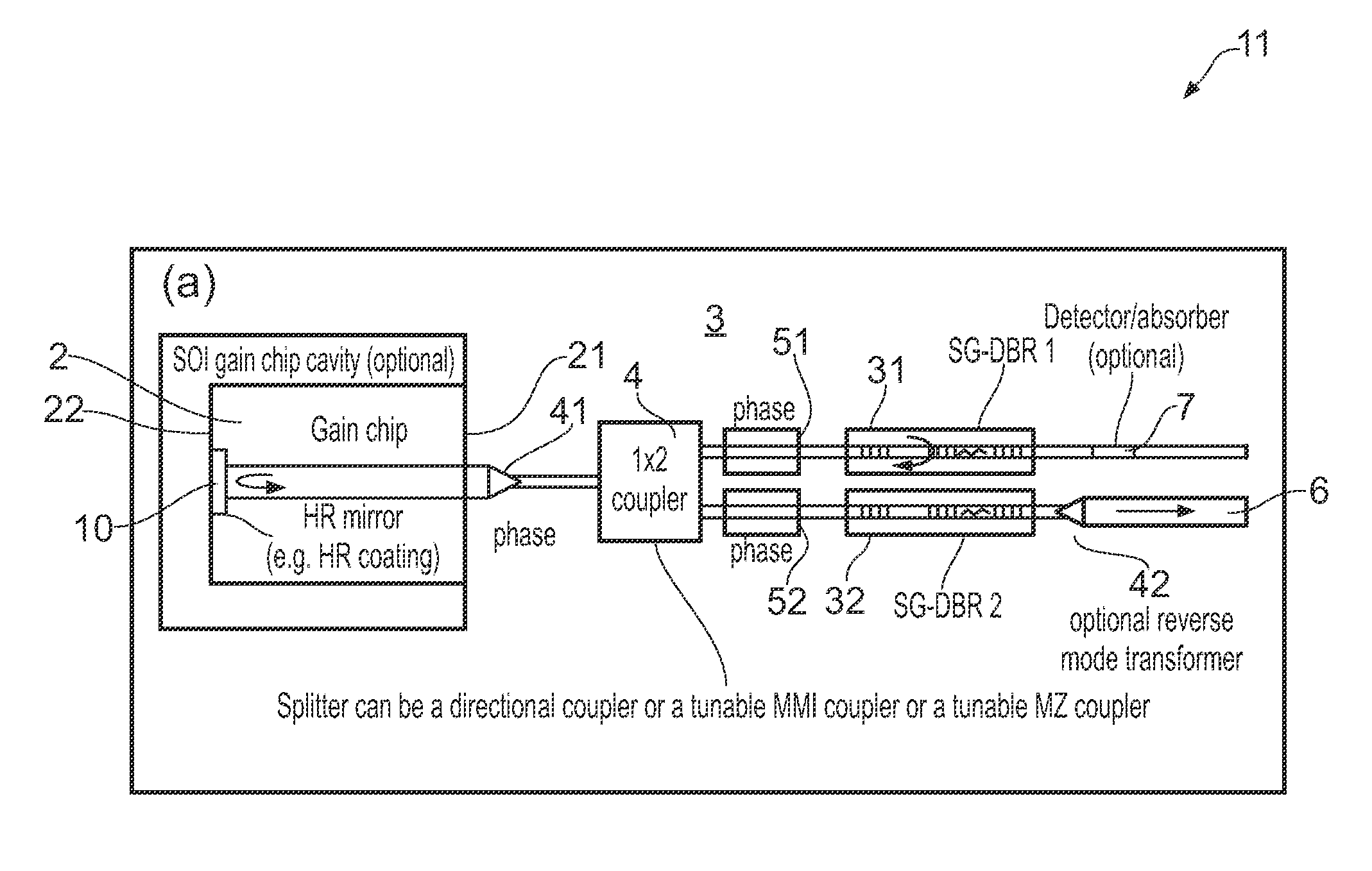
ActiveUS20150207291A1Strong index changeMinimal absorption increaseLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser structural detailsLength waveFront and back ends
A wavelength tunable silicon-on-insulator (SOI) laser comprising: a laser cavity including: a semiconductor gain medium having a front end and a back end, wherein a mirror of the laser cavity is located at the back end of the semiconductor gain medium; and a phase-tunable waveguide platform coupled to the front end of the semiconductor gain medium, the phase-tunable waveguide platform comprising: a first resonator and a second resonator; at least one resonator being a phase-tunable resonator; wherein the first resonator is any one of: an MMI device including a pair of reflective surfaces defining a resonator cavity therebetween such that the device is configured to act as a Fabry-Perot filter; a ring resonator; or a waveguide Fabry-Perot filter; and wherein the second resonator is any one of: an MMI device including a pair of reflective surfaces defining a resonator cavity therebetween such that the device is configured to act as a Fabry-Perot filter; a ring resonator; or a waveguide Fabry-Perot filter.
Owner:ROCKLEY PHOTONICS LTD
Multi-Finger Capacitor
InactiveUS20080128857A1Low AC coupling lossReduce layout areaSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesParasitic capacitanceEngineering
A multi-finger capacitor structure includes a capacitor input node having a first set of conductive fingers, a capacitor output node having a second set of conductive fingers interleaved with the first set of conductive fingers, and a conductive plate and / or pattern connected to the capacitor input node, and located between a substrate and the first and second sets of interleaved conductive fingers. The conductive plate / pattern renders the parasitic capacitance of the capacitor output node negligible, thereby imparting desirable operating characteristics to the capacitor structure. The capacitor input node may also include Faraday electric walls that laterally surround the capacitor output node, thereby limiting electrical energy leakage.
Owner:INTEGRATED DEVICE TECH INC
Lithium niobate coated optical fiber apparatus and method
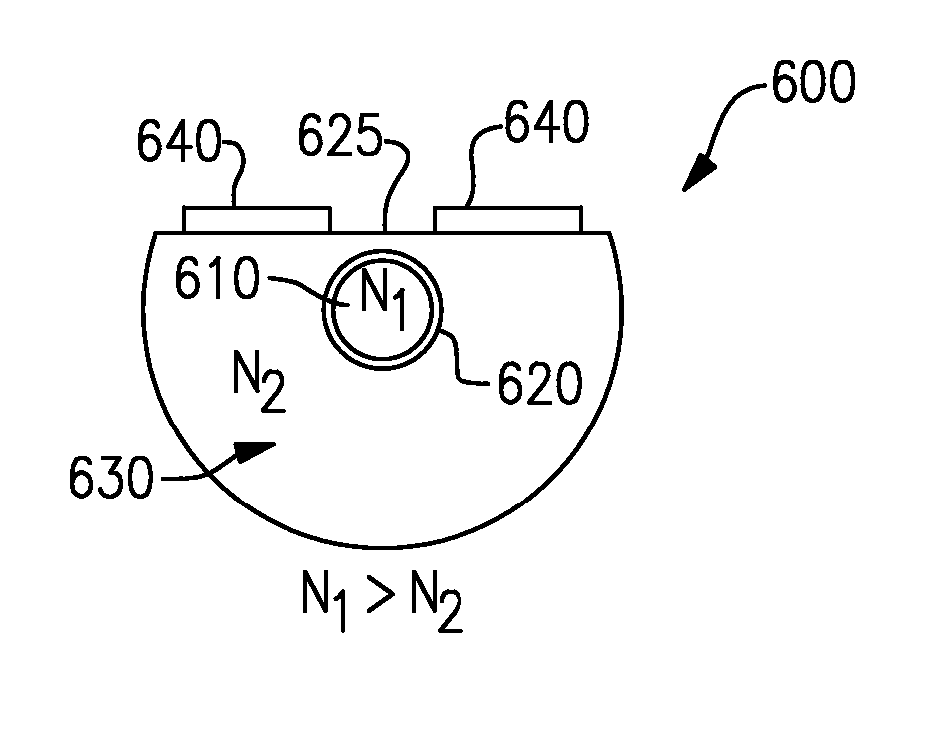
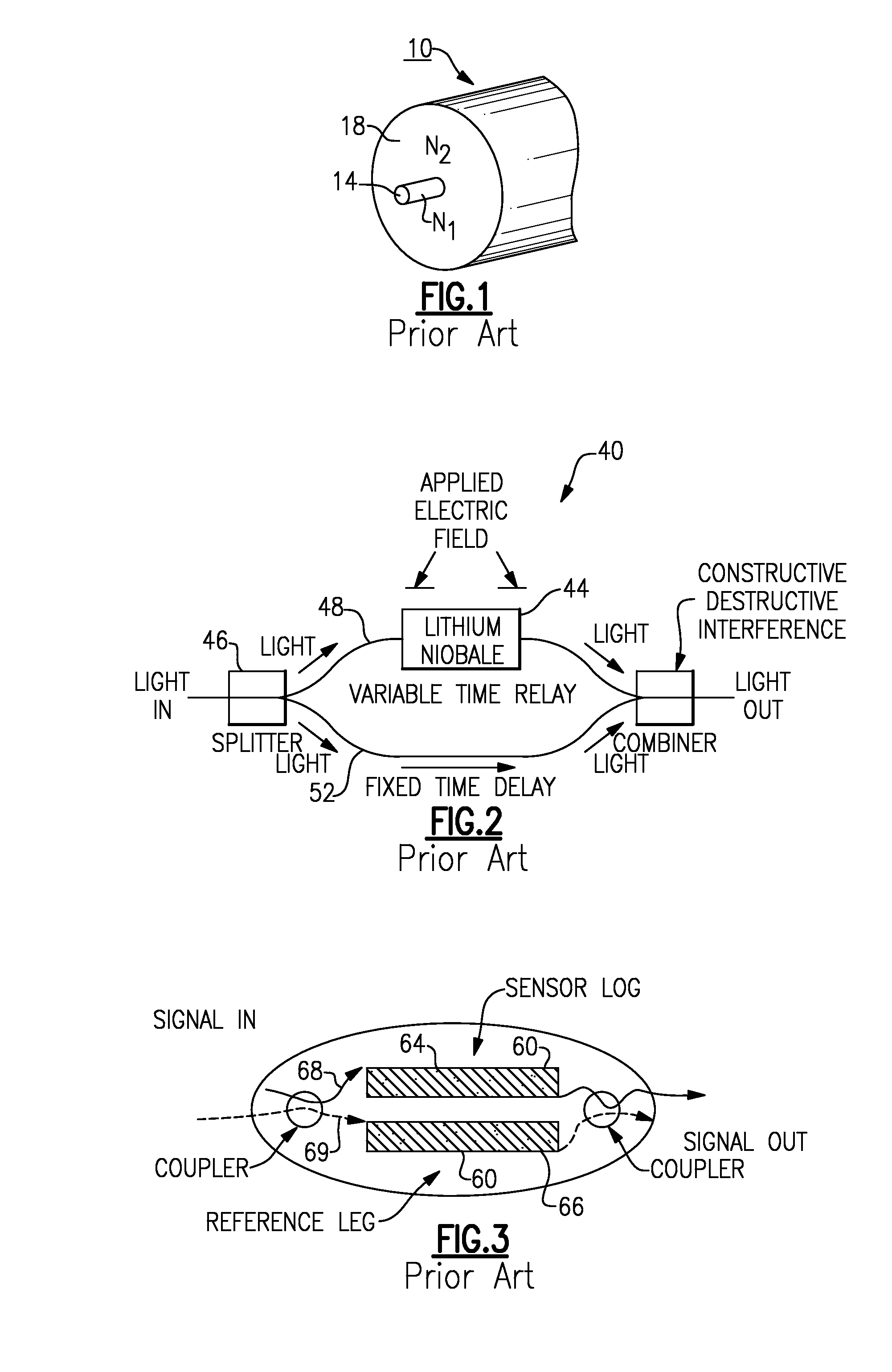
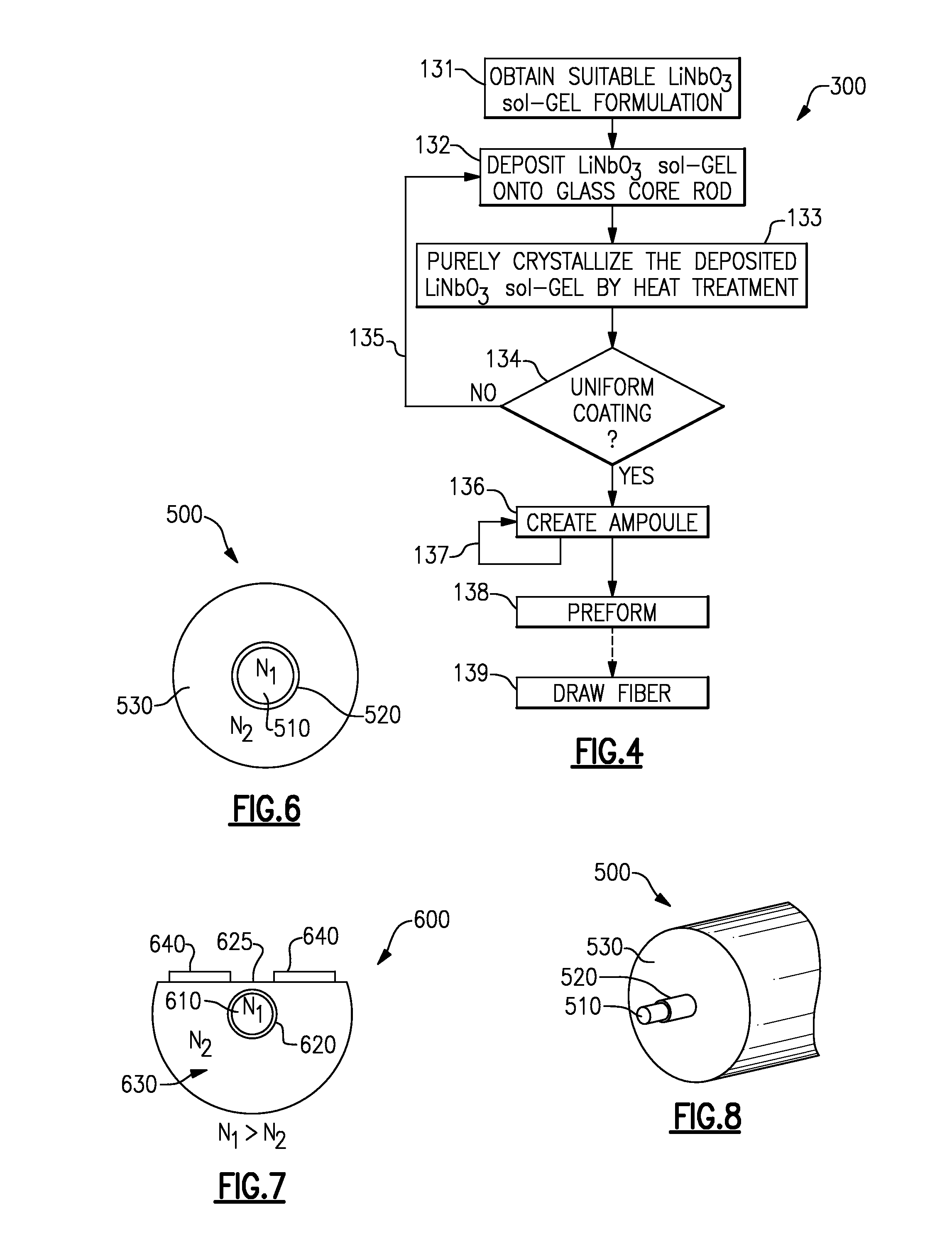
InactiveUS20070237476A1Coupling lossReduce distractionsCladded optical fibreForce measurementFiber optic sensorRefractive index
An optical fiber sensor having a central core, a cladding layer disposed about the central core, and a thin film of lithium niobate positioned between the core and the cladding layer. Each of the cladding layer and the central core are made from glass materials having different indices of refraction. The refractive index of the lithium niobate film changes when stress is applied to the optical fiber sensor. Accordingly, stress may be detected and measured by detecting and measuring the modulation of light passing through the optical fiber sensor while the stress is occurring.
Owner:FANASYS
Optical Fiber Coupling Part and Manufacturing Method Thereof
ActiveUS20080131052A1Facilitate alignmentFacilitate manufacturingGlass making apparatusCoupling light guidesRefractive index profileAdhesive
An optical fiber coupling part that reduces the difficulty in adjusting cores, minimizes coupling loss, and prevents optical characteristics from deteriorating. An optical fiber is fused to one end of a GRIN lens which includes a quartz glass containing one or more refractive index regulating substances selected from Sb2O3, Ta2O5, TiO2 or ZrO2. Optical characteristics are not deteriorated because an adhesive is not used, and self-alignment effects facilitate adjustment of the cores of the GRIN lens and the optical fiber. Furthermore, coupling loss can be minimized by setting a refractive index distribution constant g of the GRIN lens within an appropriate range.
Owner:TOYO SEIKAN GRP HLDG LTD
High speed swept frequency spectroscopic system
A high scan rate spectroscopic system converts a narrow-band laser pulse into a multispectral pulse, using, for example, a nonlinear fiber. The multispectral pulse is then converted to a swept frequency pulse through a second fiber impressing a frequency-dependent delay in the light beam which is then applied to the object to be tested.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
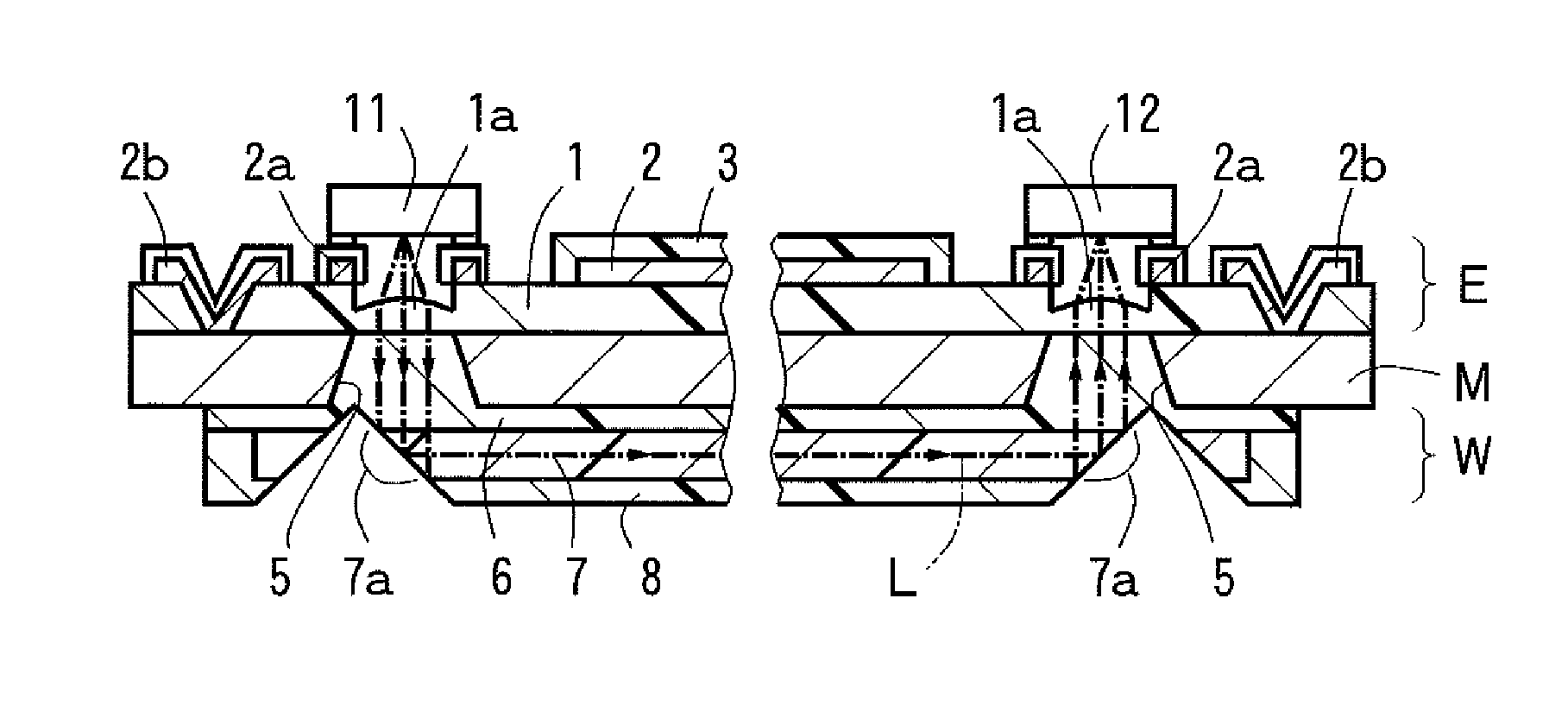
Optical fiber with reduced cladding-mode loss
InactiveUS20020126971A1Attenuating power propagatingReduce couplingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesCoupling lossFiber
The invention is directed toward an optical fiber that reduces the cladding mode coupling loss (CMCL) therein. The fiber includes a core, a cladding concentrically surrounding the core, and at least one lossy region concentrically surrounding the core. The lossy region is disposed within the cladding and is slightly displaced radially from the core.
Owner:VERRILLON
Twin waveguide based design for photonic integrated circuits
InactiveUS20050094924A1Reduce negative impactNegligible coupling lossLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionCoupling lossGrating
An asymmetric twin waveguide (ATG) structure is disclosed that significantly reduces the negative effects of inter-modal interference in symmetric twin-waveguide structures and which can be effectively used to implement a variety of optical devices. The ATG structure of the invention can be monolithically fabricated on a single epitaxial structure without the necessity of epitaxial re-growth. To achieve the ATG structure of the invention, the effective index of the passive waveguide in the ATG is varied from that of a symmetric twin waveguide such that one mode of the even and odd modes of propagation is primarily confined to the passive waveguide and the other to the active waveguide. The different effective indices of the two coupled waveguides result in the even and odd modes becoming highly asymmetric. As a result, the mode with the larger confinement factor in the active waveguide experiences higher gain and becomes dominant. In a further embodiment, the active waveguide is tapered to reduce coupling losses of the optical energy between the passive waveguide and the active waveguide. In a further embodiment, a grating region is incorporated atop the passive waveguide to select certain frequencies for transmission of light through the passive waveguide.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Tunable SOI laser
ActiveUS9270078B2Improve power efficiencyCoupling lossLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser structural detailsOptoelectronicsWavelength
A wavelength tunable silicon-on-insulator (SOI) laser comprising: a laser cavity including: a semiconductor gain medium having a front end and a back end, wherein a mirror of the laser cavity is located at the back end of the semiconductor gain medium; and a phase-tunable waveguide platform coupled to the front end of the semiconductor gain medium, the phase-tunable waveguide platform comprising: a first resonator and a second resonator; at least one resonator being a phase-tunable resonator; wherein the first resonator is any one of: an MMI device including a pair of reflective surfaces defining a resonator cavity therebetween such that the device is configured to act as a Fabry-Perot filter; a ring resonator; or a waveguide Fabry-Perot filter; and wherein the second resonator is any one of: an MMI device including a pair of reflective surfaces defining a resonator cavity therebetween such that the device is configured to act as a Fabry-Perot filter; a ring resonator; or a waveguide Fabry-Perot filter.
Owner:ROCKLEY PHOTONICS LTD
Optical interconnection module and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7248768B2Avoid lightCoupling lossSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputer moduleEngineering
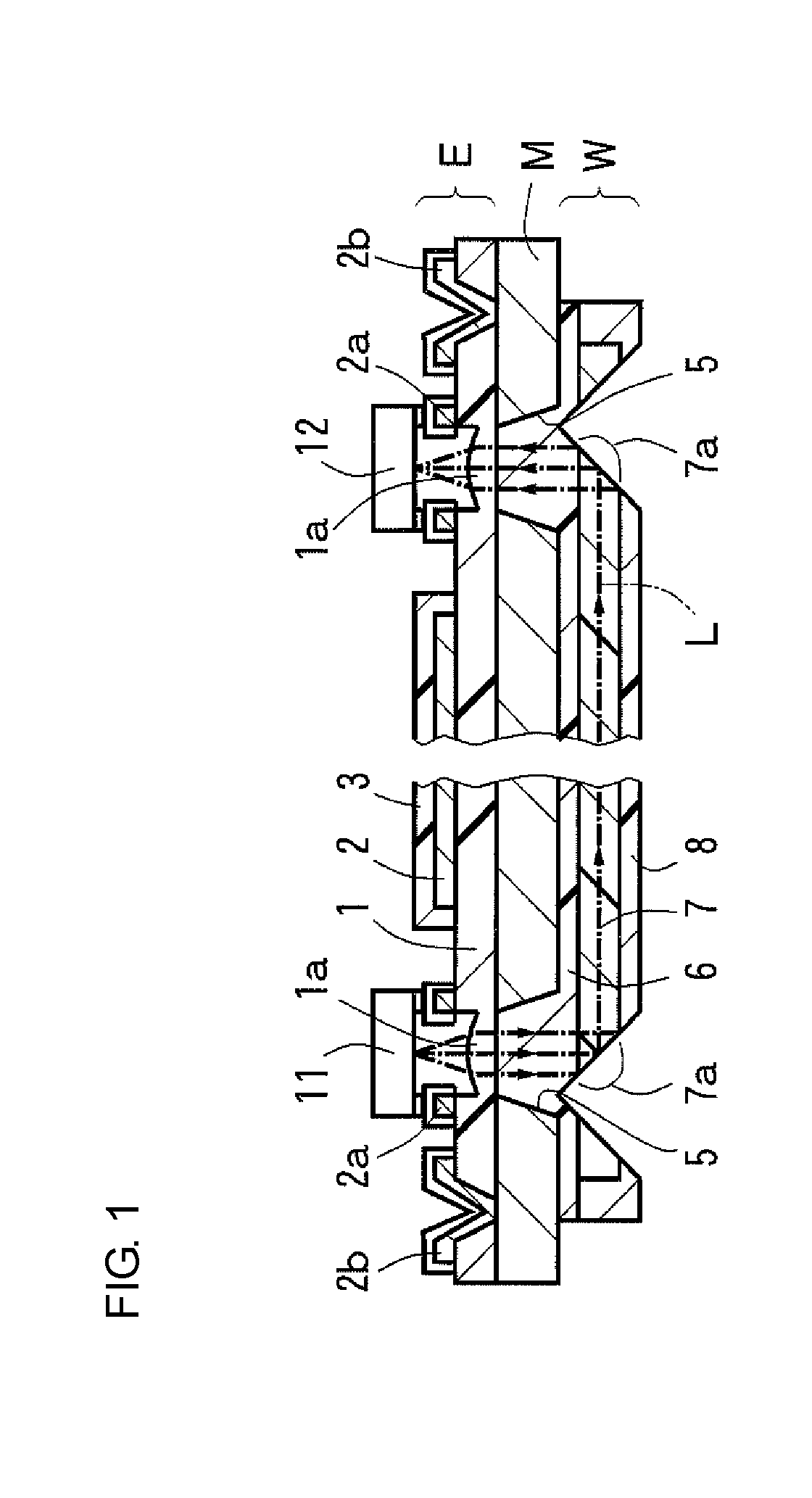
The present invention relates generally to an optical interconnection module for vertical optical coupling and a method of manufacturing the optical interconnection module. The optical interconnection module includes an optical waveguide. The optical waveguide includes substrate on which electrode pads and a predetermined circuit pattern are formed; a light source unit provided on the substrate and configured to generate an optical signal and emit the signal to an outside; an optical detection unit for receiving the optical signal from the light source unit and converting the optical signal into an electric signal; drive units provided on the substrate and configured to drive the light source unit and the light detection unit in response to electric signals supplied through the electrode pads; and a cladding layer, a core layer layered on the cladding layer, and an elliptical reflecting mirror surface placed on an end of the core layer facing the light source unit.
Owner:DOOSAN CORP
Illumination system and projection apparatus
ActiveUS20150077714A1Good luminescent spectrumImprove reliabilityProjectorsColor television detailsLighting systemWavelength conversion
An illumination system including at least one laser source, at least one anisotropic light expanding element and a wavelength conversion element is provided. The at least one laser source emits a laser beam. The at least one anisotropic light expanding element is disposed on the transmission path of the laser beam and causes the laser beam to expand along a light expanding direction. The light expanding direction is substantially parallel to the slow axis of the laser beam. The wavelength conversion element is disposed on the transmission path of the laser beam. A projection apparatus is also provided.
Owner:CORETRONIC
Mode converter device using omnidirectional reflectors
InactiveUS20050135739A1Minimum loss couplingHigh index contrastNanoopticsCoupling light guidesManufacturing technologyRefractive index
Provided is a mode converter for use in optical communication. The mode converter includes a first waveguide, a second waveguide optically coupled into the first waveguide, and omnidirectional reflectors that are disposed on either side of the first waveguide and have forward reflectivity with respect to a mode propagating in the first waveguide. The mode converter provides minimum loss coupling between either optical fiber or low index difference waveguide and a high index contrast waveguide. Furthermore, the mode converter achieves high, bi-directional optical coupling over a wide wavelength range with a simple manufacturing process.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Opto-electric hybrid board
ActiveUS20130259430A1Reduce light lossCoupling lossCircuit optical detailsPrinted circuit aspectsElectricityLight beam
An opto-electric hybrid board includes: an electric circuit board including an insulative layer having front and back surfaces, and electrical interconnect lines formed on the front surface of the insulative layer; an optical element mounted on a surface of the electric circuit board with the electrical interconnect lines formed thereon; and an optical waveguide including a core and formed on the back surface of the insulative layer of the electric circuit board. The core includes at its end portion a reflecting surface capable of reflecting alight beam to propagate the light beam between the core and the optical element. The insulative layer is made of a light-transmissive material. A portion of the insulative layer corresponding to an optical path between the reflecting surface of the core and the optical element is in the form of a lens portion.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
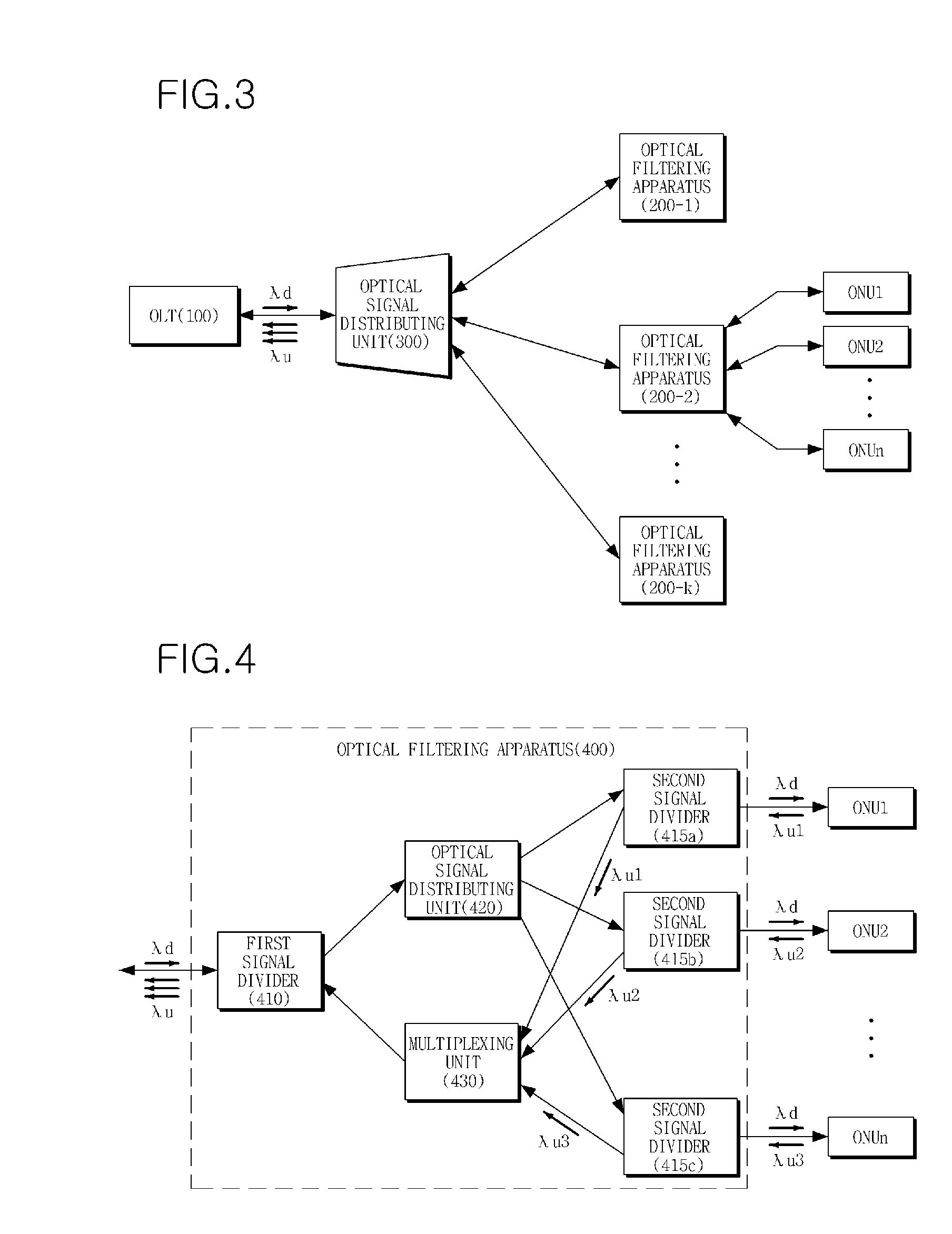
Optical filtering apparatus and optical communication system
InactiveUS20090148165A1Improve efficiencyLight loss is minimizedMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberOptical line termination
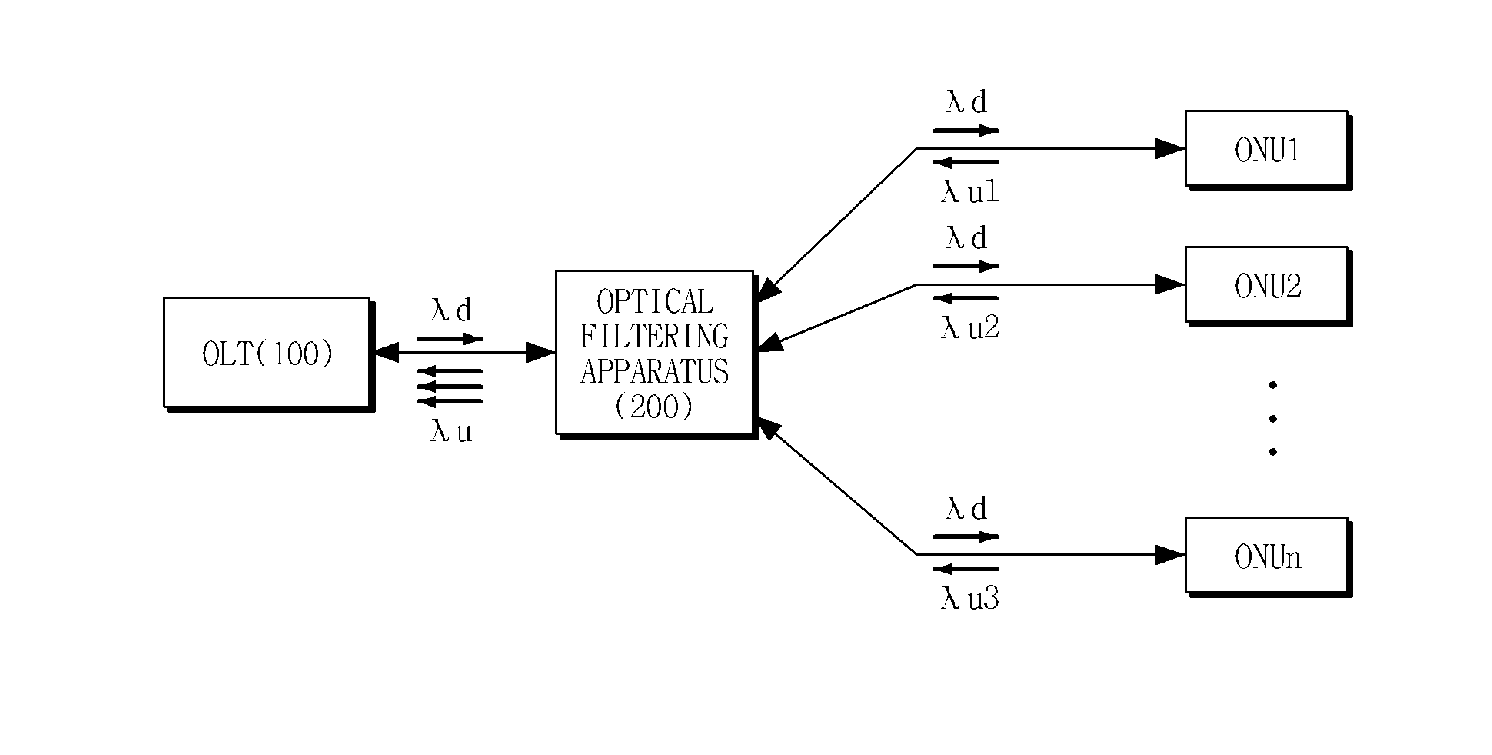
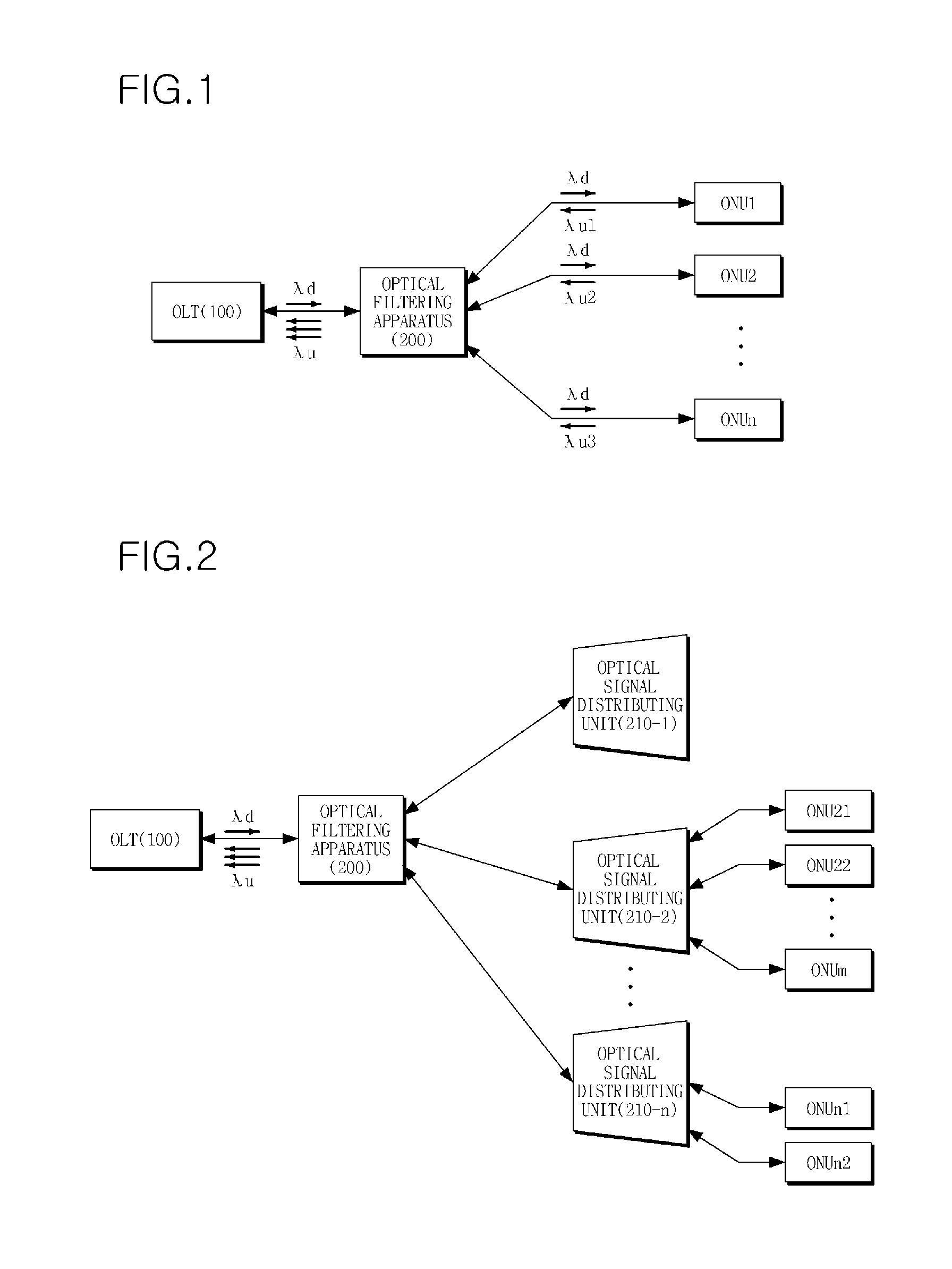
Provided is an optical filtering apparatus which is applied to a Time Division Multiplexing Passive Optical Network (TDM-PON) based on a wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) method. The optical filtering apparatus includes: an optical signal distributing unit dividing an optical signal received from an optical line terminal into at least one optical signal with uniform output intensity, and distributing the at least one optical signal into at least one optical network unit; and a multiplexing unit combining a plurality of optical signals having different wavelengths received from the at least one optical network unit using a wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) method, and outputting the combined optical signal to the optical line terminal. Therefore, by using the optical filtering apparatus, it is possible to connect a large number of subscribers to an Optical Line Terminal (OLT) on a network such as Fiber To The Home (FTTH), thereby increasing efficiency in costs.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Integrated semiconductor optical device
InactiveUS8472760B2Scattering or reflectionCoupling loss of guided light can be suppressedLight demodulationOptical waveguide light guideButt jointRefractive index
An integrated semiconductor optical device includes first and second semiconductor optical devices. The first semiconductor optical device includes a first core layer, a first upper cladding layer including a first ridge portion, a first buried layer surrounding the first ridge portion, and a first adjusting layer provided between the first buried layer and the first ridge portion. The second semiconductor optical device includes a second core layer, a second upper cladding layer including a second ridge portion. The first semiconductor optical device and the second semiconductor optical device are arranged next to each other in a predetermined axis direction. The first core layer is joined to the second core layer by a butt joint method at a joint boundary between the first and second semiconductor optical devices. The first adjusting layer has a refractive index lower than a refractive index of the first core layer and higher than a refractive index of the first buried layer. The first adjusting layer extends in the predetermined axis direction. The first adjusting layer has a constant width from one end facet to the joint boundary.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Integrated semiconductor optical device
InactiveUS20110091147A1Scattering or reflectionCoupling loss of guided light can be suppressedLaser optical resonator constructionNanoopticsButt jointRefractive index
An integrated semiconductor optical device includes first and second semiconductor optical devices. The first semiconductor optical device includes a first core layer, a first upper cladding layer including a first ridge portion, a first buried layer surrounding the first ridge portion, and a first adjusting layer provided between the first buried layer and the first ridge portion. The second semiconductor optical device includes a second core layer, a second upper cladding layer including a second ridge portion. The first semiconductor optical device and the second semiconductor optical device are arranged next to each other in a predetermined axis direction. The first core layer is joined to the second core layer by a butt joint method at a joint boundary between the first and second semiconductor optical devices. The first adjusting layer has a refractive index lower than a refractive index of the first core layer and higher than a refractive index of the first buried layer. The first adjusting layer extends in the predetermined axis direction. The first adjusting layer has a constant width from one end facet to the joint boundary.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Tunable SOI laser
ActiveUS9240673B2Improve power efficiencyCoupling lossLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionReflectance spectroscopyDistributed Bragg reflector laser
A wavelength tunable silicon-on-insulator (SOI) laser comprising: a laser cavity including: a semiconductor gain medium having a front end and a back end; and a phase-tunable waveguide platform coupled to the front end of the semiconductor gain medium; wherein the phase-tunable waveguide platform includes a first Distributed Bragg Reflector (DBR) and a second Distributed Bragg Reflector (DBR); at least one of the Distributed Bragg Reflectors having a comb reflectance spectrum; and wherein a mirror of the laser cavity is located at the back end of the semiconductor gain medium.
Owner:ROCKLEY PHOTONICS LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com