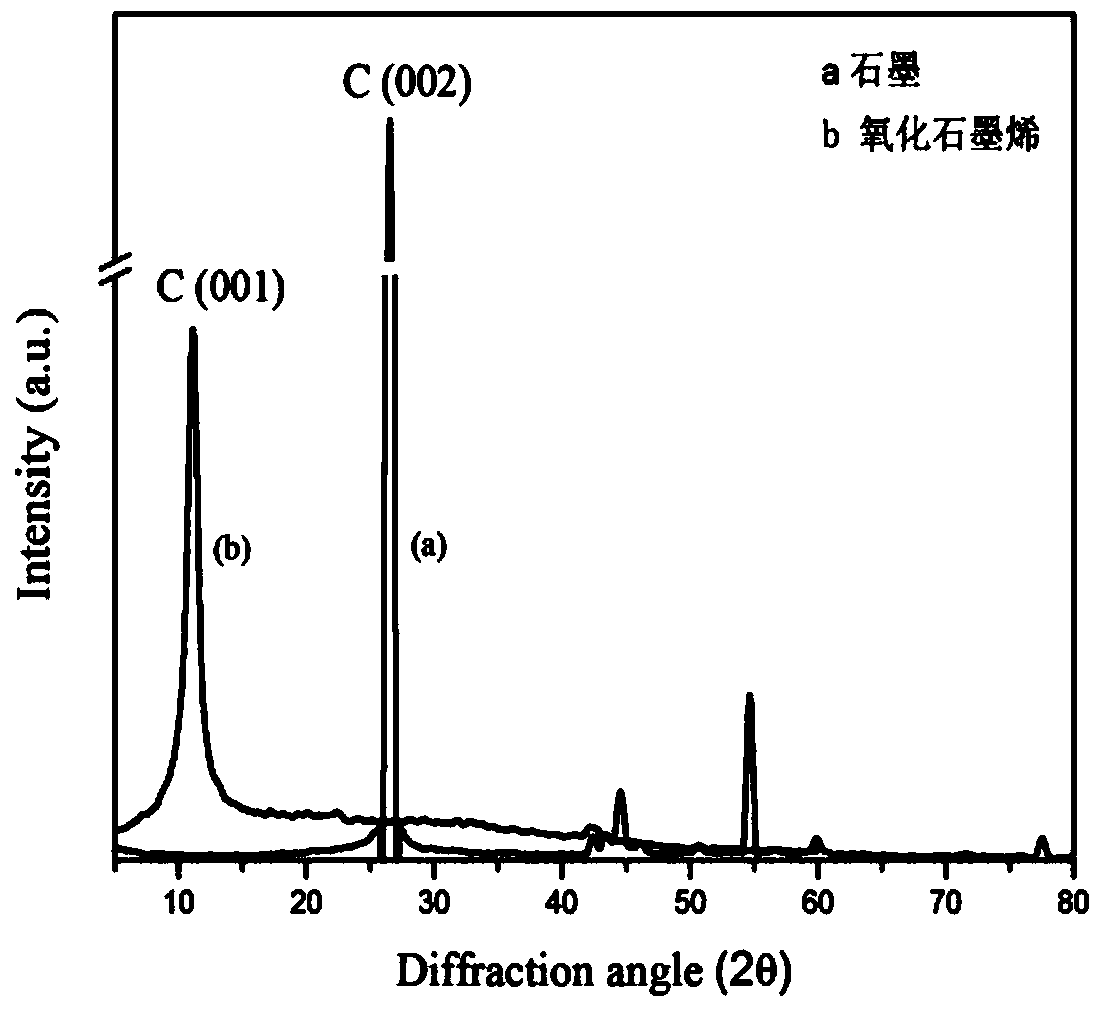
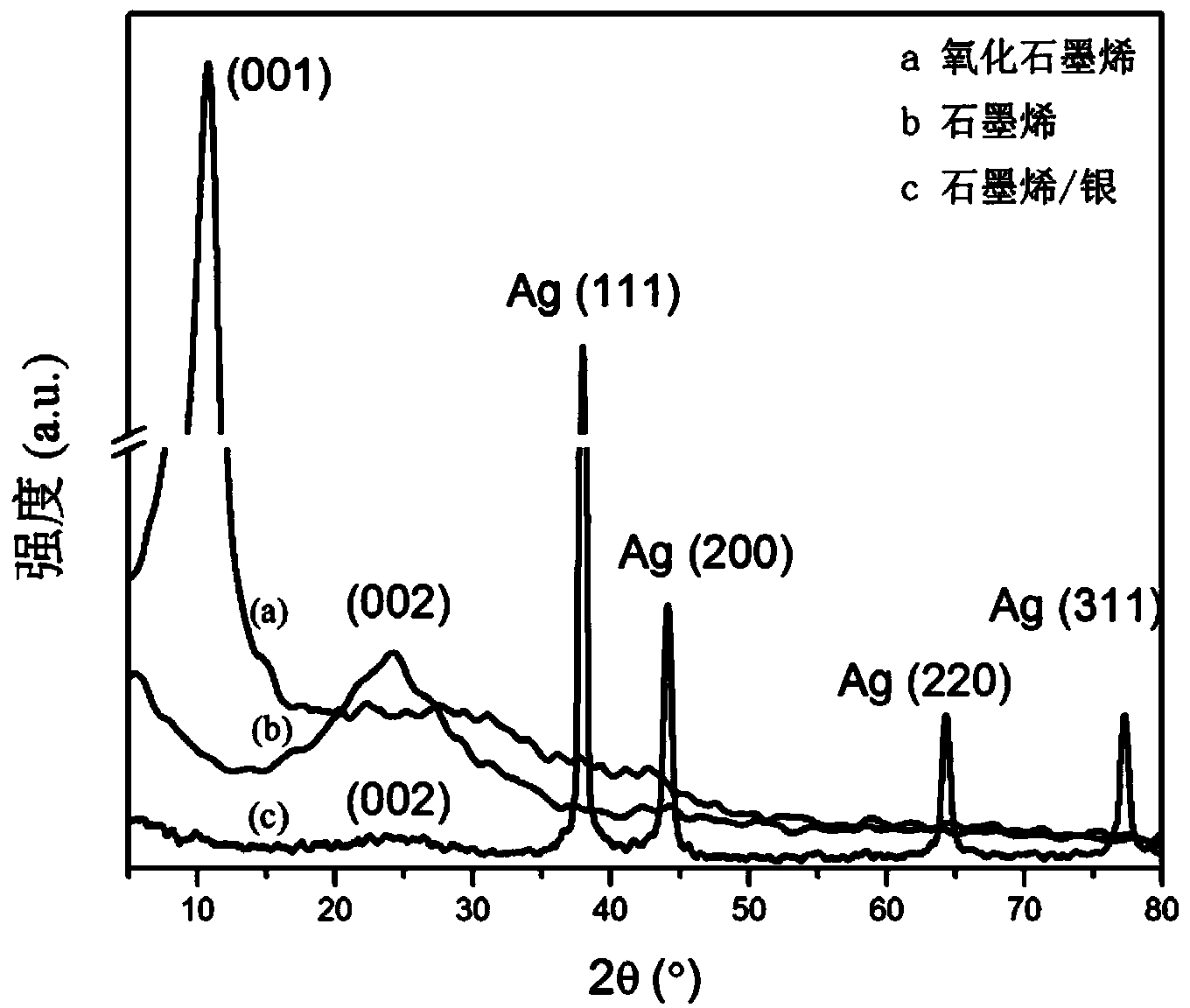
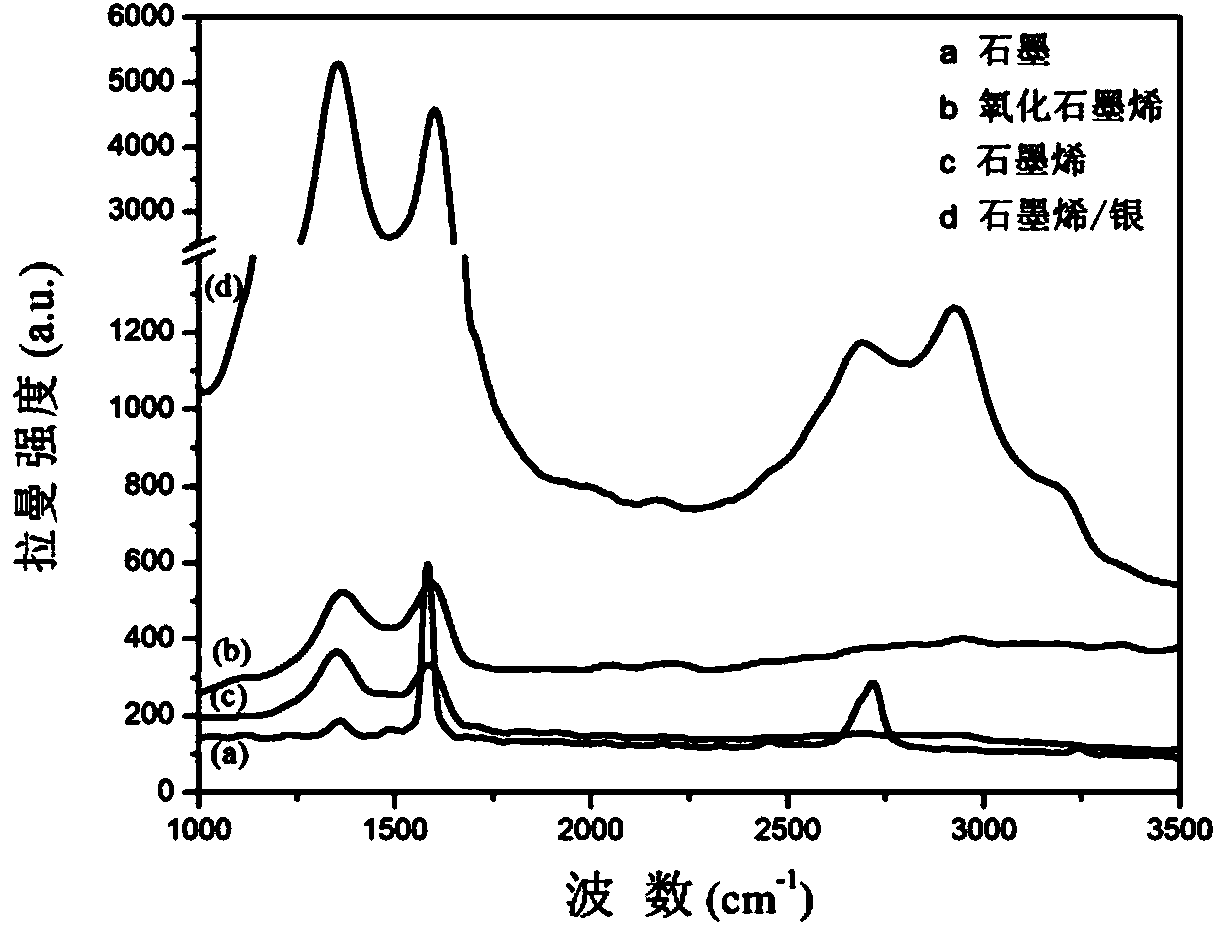
Patents
Literature
180 results about "Printed electronics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Printed electronics is a set of printing methods used to create electrical devices on various substrates. Printing typically uses common printing equipment suitable for defining patterns on material, such as screen printing, flexography, gravure, offset lithography, and inkjet. By electronic industry standards, these are low cost processes. Electrically functional electronic or optical inks are deposited on the substrate, creating active or passive devices, such as thin film transistors; capacitors; coils; resistors. Printed electronics is expected to facilitate widespread, very low-cost, low-performance electronics for applications such as flexible displays, smart labels, decorative and animated posters, and active clothing that do not require high performance.
Printable compositions having anisometric nanostructures for use in printed electronics
Compositions and methods for production of conductive paths can include a printable composition including a liquid carrier and a plurality of nanostructures. The plurality of nanostructures can have an aspect ratio of at least about 5:1 within the liquid carrier. Examples of nanostructures include nanobelts, nanoplates, nanodiscs, nanowires, nanorods, and mixtures of these materials. These printable compositions can be used to form a conductive path on a substrate. The printable composition can be applied to a substrate using any number of conventional printing techniques. Following application of the printable composition, at least a portion of the liquid carrier can be removed such that the nanostructures can be in sufficient contact to provide a conductive path. The nanostructures arranged in a conductive path can be sintered or used as a conductive material without sintering.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Printable compositions having anisometric nanostructures for use in printed electronics
Compositions and methods for production of conductive paths can include a printable composition including a liquid carrier and a plurality of nanostructures. The plurality of nanostructures can have an aspect ratio of at least about 5:1 within the liquid carrier. Examples of nanostructures include nanobelts, nanoplates, nanodiscs, nanowires, nanorods, and mixtures of these materials. These printable compositions can be used to form a conductive path on a substrate. The printable composition can be applied to a substrate using any number of conventional printing techniques. Following application of the printable composition, at least a portion of the liquid carrier can be removed such that the nanostructures can be in sufficient contact to provide a conductive path. The nanostructures arranged in a conductive path can be sintered or used as a conductive material without sintering.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Printed electronics
Printed electronic device comprising a substrate onto at least one surface of which has been applied a layer of an electrically conductive ink comprising functionalized graphene sheets and at least one binder. A method of preparing printed electronic devices is further disclosed.
Owner:VORBECK MATERIALS CORP +1
Preparation method for high-conductivity graphene and silver nanoparticle composite materials
ActiveCN103639421AEnhanced surface contactGuaranteed electrical conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyFreeze-dryingHydrazine compound
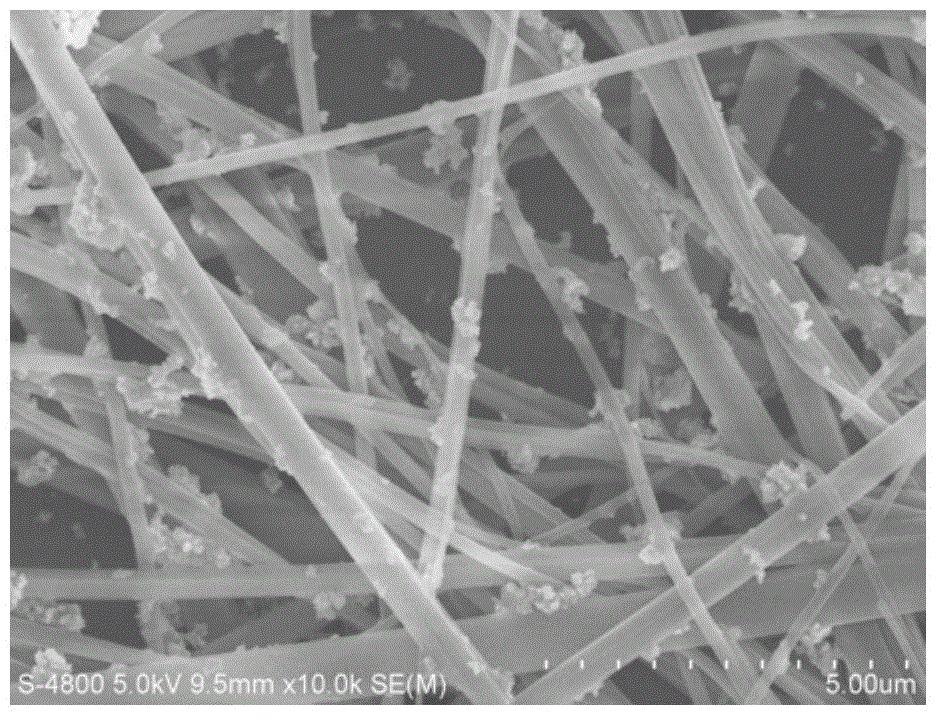
The invention relates to a preparation method for high-conductivity graphene and silver nanoparticle composite materials. The method comprises the steps that graphene oxide is prepared at first; a graphene oxide water solution is prepared; silver nitrate is added into the obtained graphene oxide water solution, the temperature is risen to be 90+ / -10 DEG C, sodium citrate is added in the solution, and stirring and reaction are conducted; ammonium hydroxide and hydrazine hydrate are added into the obtained solution, and stirring and reaction are conducted at the temperature of 90+ / -10 DEG C; deionized water and ethyl alcohol are adopted to clean the reaction product, vacuum freeze drying is conducted on the cleaned reaction product, and then the conductive graphene and silver nanoparticle composite materials are obtained. The conductivity of the composite materials is 3.71-18.32S / cm, the graphene and silver nanoparticle composite materials prepared based on the method can greatly improve the conductivity of graphene, and can be further applied in the field of printed electronics.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF GRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
Printed electronics
Printed electronic device comprising a substrate onto at least one surface of which has been applied a layer of an electrically conductive ink comprising functionalized graphene sheets and at least one binder. A method of preparing printed electronic devices is further disclosed.
Owner:VORBECK MATERIALS CORP +1
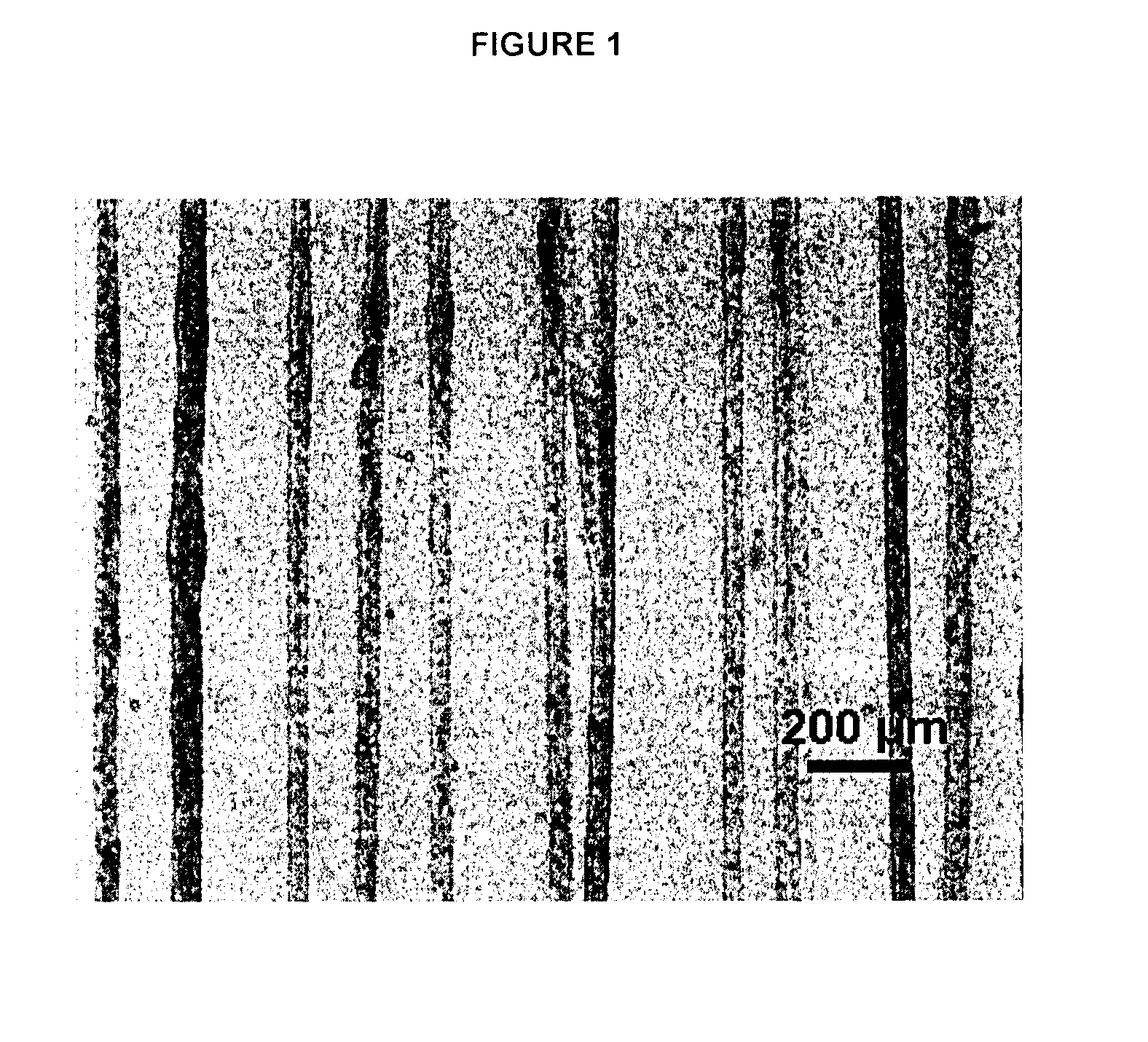
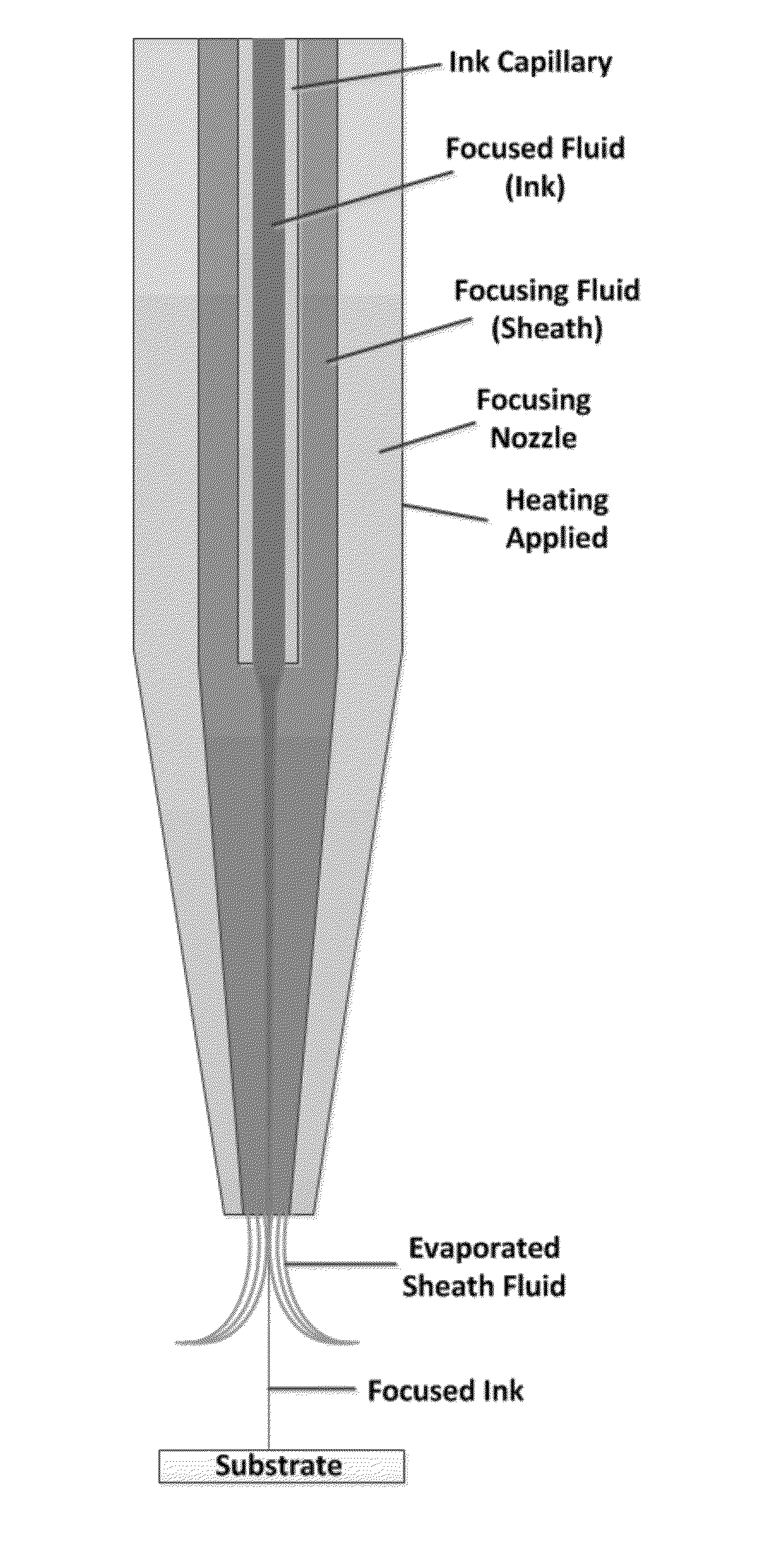
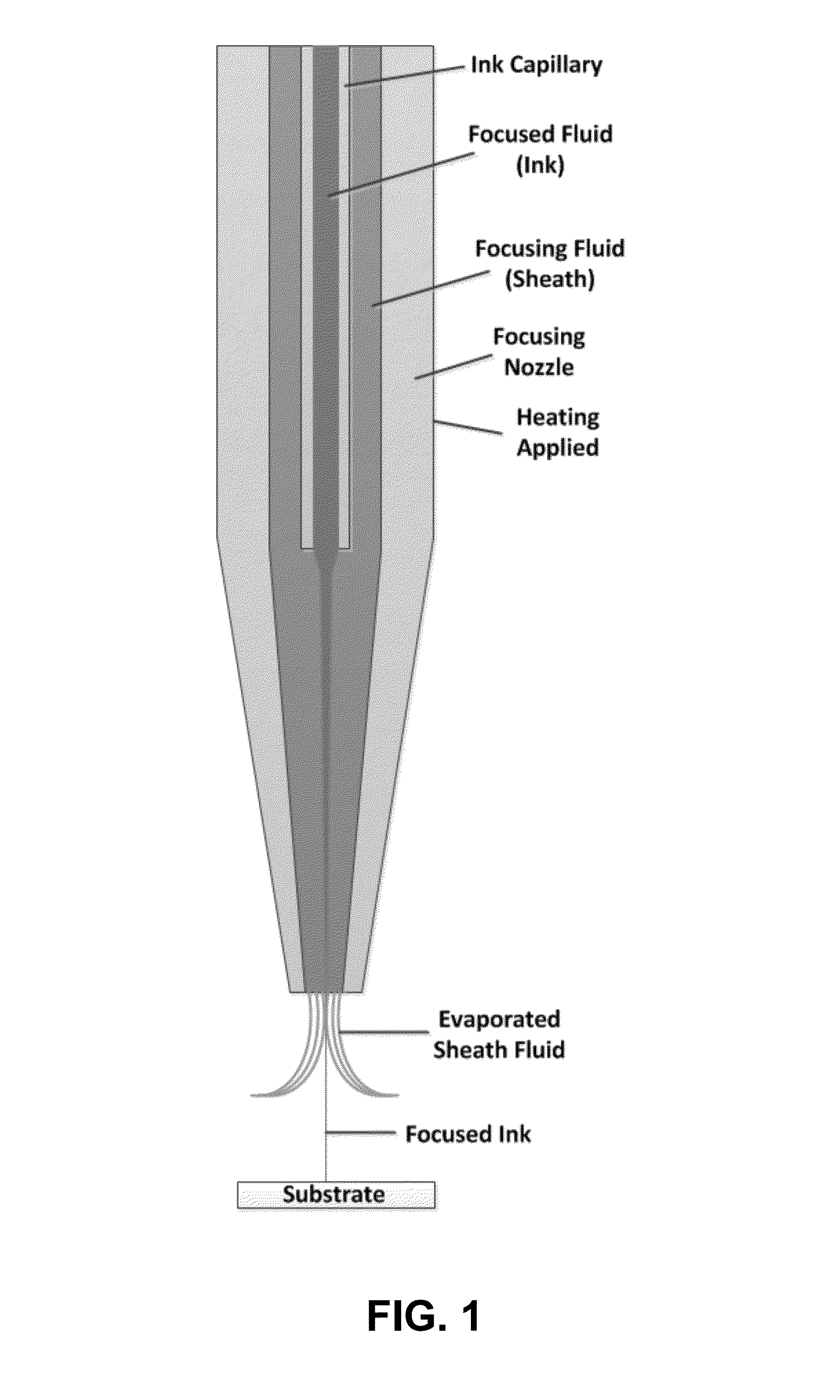
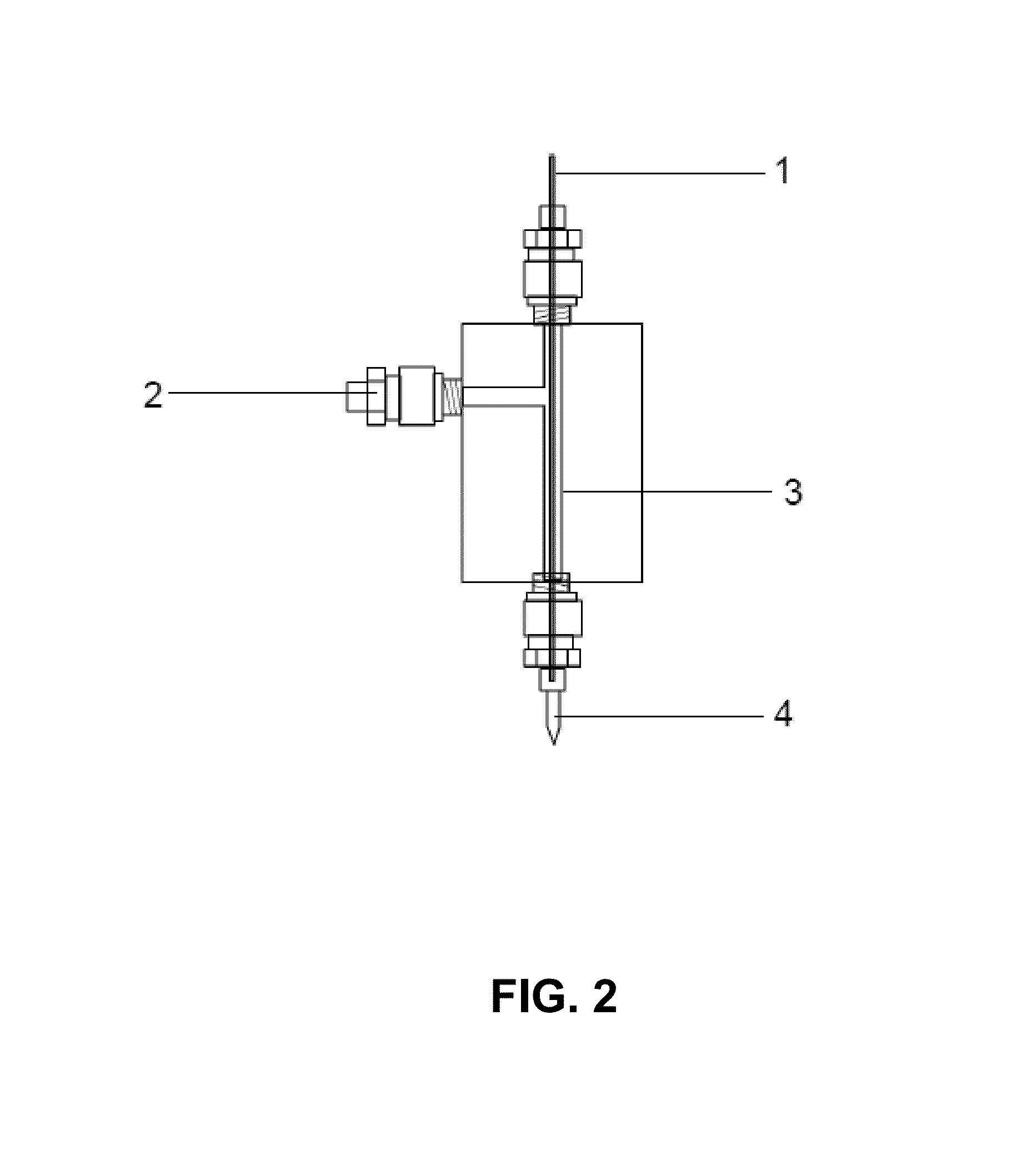
Two-Fluid Hydrodynamic Printing
ActiveUS20160129634A1Manufacturing platforms/substratesFilament/thread formingEngineeringPrinted electronics
Hydrodynamic focusing of two fluid steams provides a novel micro printing technology for printed electronics and other high performance applications.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
RFID antenna-battery assembly and the method to make the same
ActiveUS20090038746A1Decorative surface effectsPrinted electric component incorporationEngineeringElectronic assemblies
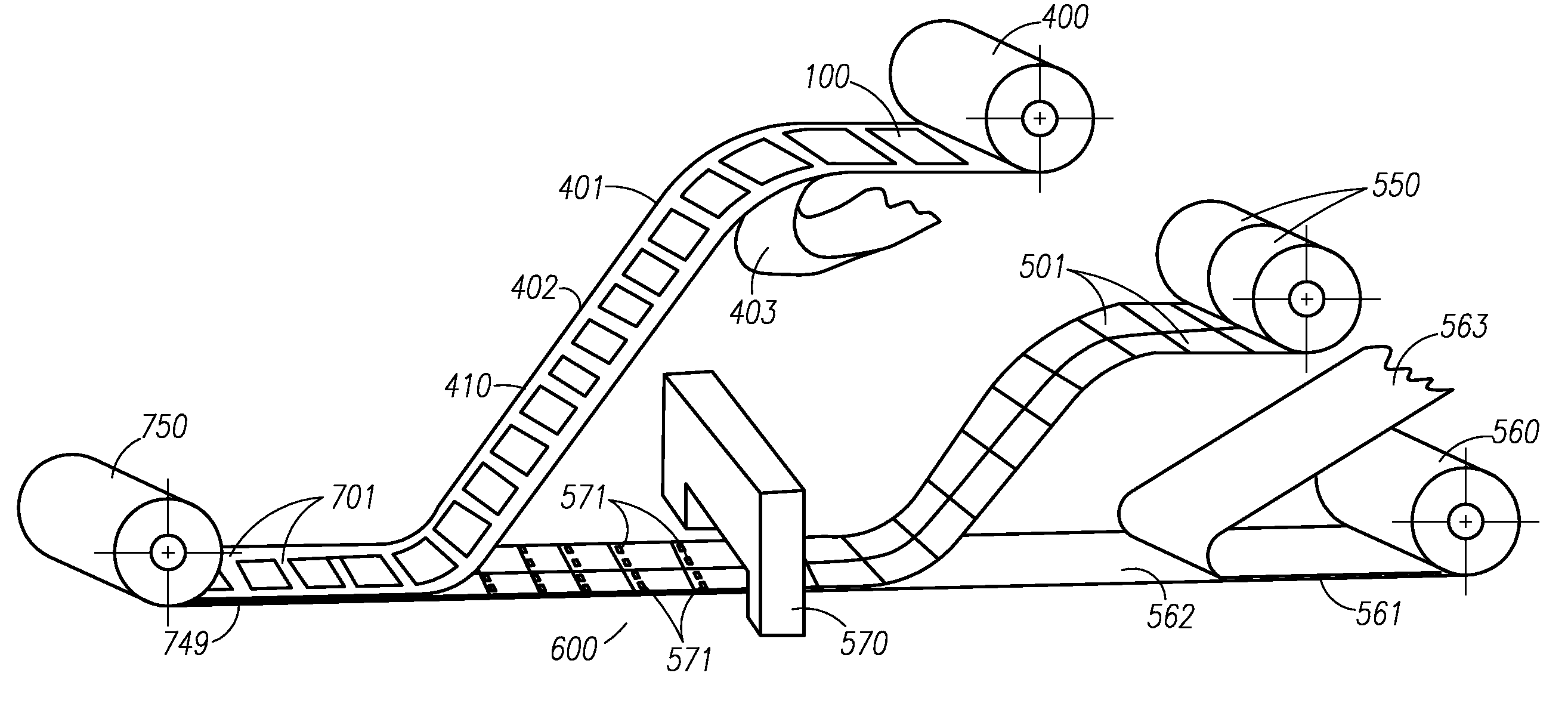
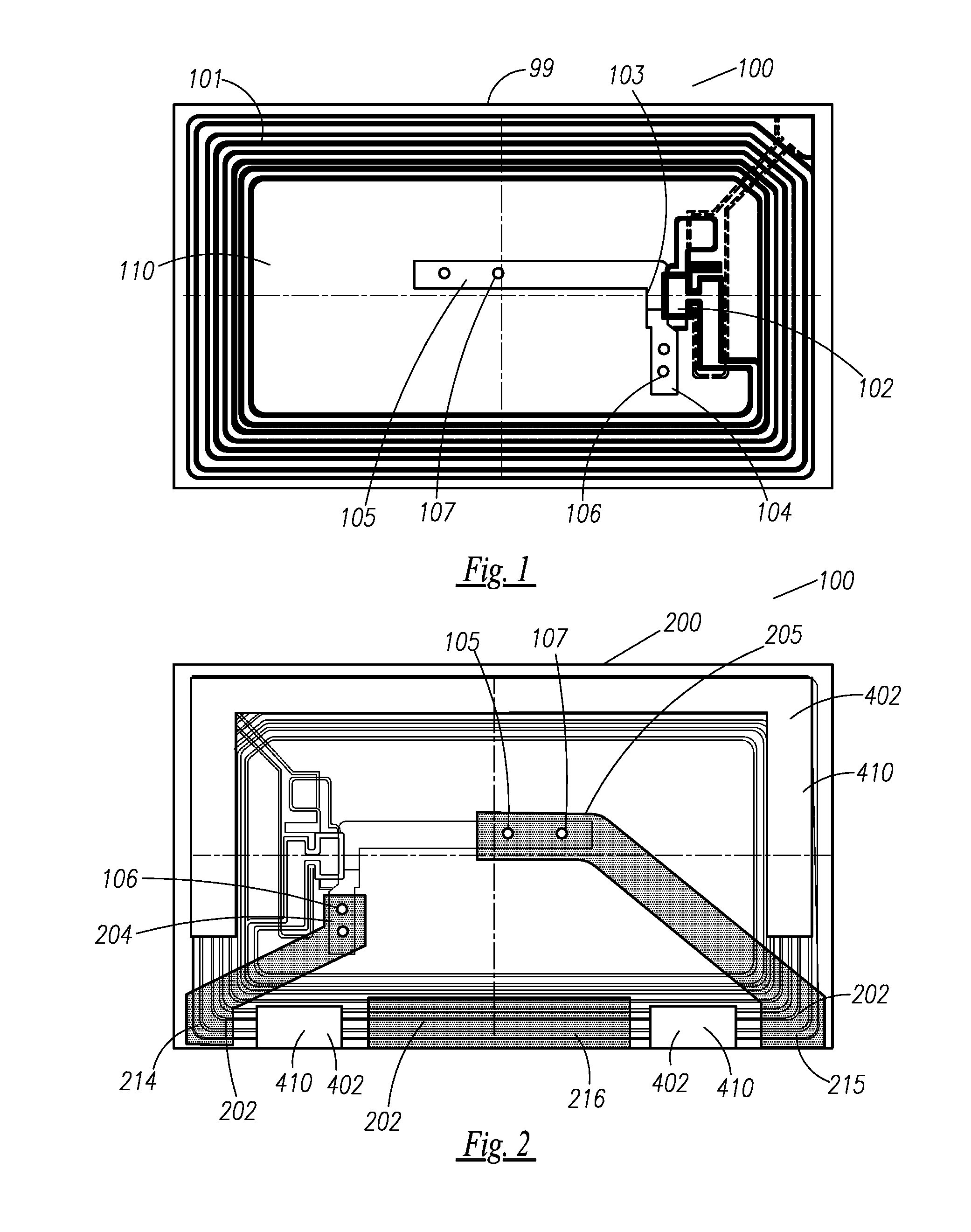
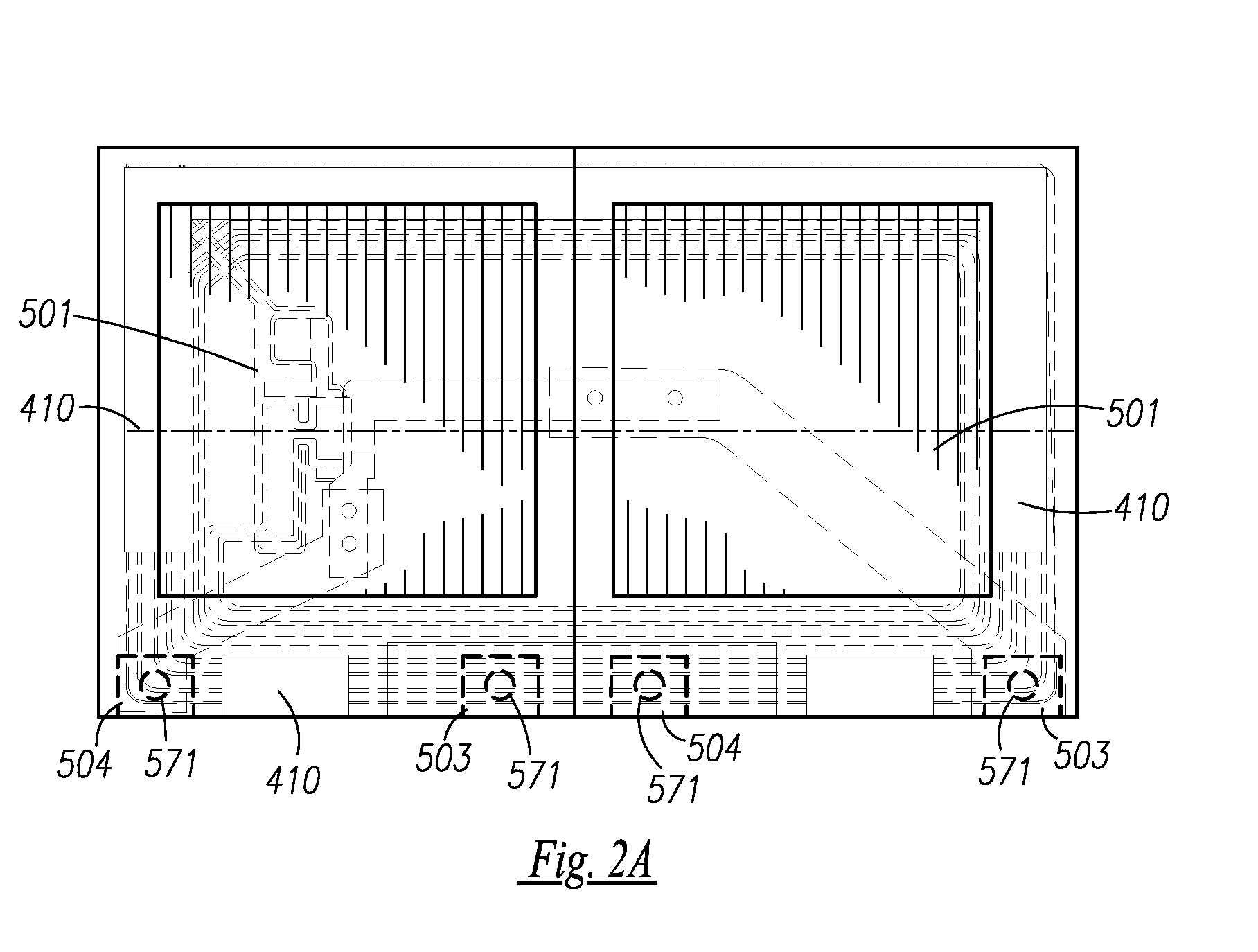
Printed electronics are increasingly becoming an important industry, thus innovations to integrate the various components and processes would be very useful to expand this industry. Disclosed are innovational concepts that would be very useful to accelerate this industry. Webs of printed electronics, antennas, power sources (cells / batteries), and assembly substrates can be merged together to form a completed electronic assembly that could be, for example, in label form or in a stand alone electronic device.
Owner:BLUE SPARK INNOVATIONS LLC
Functional composites, functional inks and applications thereof
Functional composite materials comprise elemental inorganic particles within an organic matrix. The elemental inorganic materials generally comprise elemental metal, elemental metalloid, alloys thereof, or mixtures thereof. In alternative or additional embodiments, the inorganic particles can comprise a metal oxide, a metalloid oxide, a combination thereof or a mixture thereof. The inorganic particles can have an average primary particle size of no more than abut 250 nm and a secondary particle size in a dispersion when blended with the organic matrix of no more than about 2 microns. The particles can be substantially unagglomerated within the composite. The organic binder can be a functional polymer such as a semiconducting polymer. The inorganic particles can be surface modified, such as with a moiety having an aromatic functional group for desirable interactions with a semiconducting polymer. Appropriate solution based methods can be used for forming the composite from dispersions of the particles. The composites can be processed into products, such as printed electronics devices.
Owner:NANOGRAM
Metal precursor and metal precursor ink using the same
ActiveUS20150336878A1High metal contentInduce intramolecularOrganic compound preparationCopper organic compoundsSolubilityMetallurgy
Provided are a metal precursor containing an oxime group, which is represented by general formula 1, and a metal precursor ink containing same. The metal precursor ink according to the present invention enhance metal content, induce intramolecular and / or intermolecular complexation, thereby enabling low temperature sintering with excellent solubility and stability. The metal precursor ink according to the present invention can be used to form a metal wire with a desired shape. Therefore, the metal precursor ink can find applications in the field of printed electronics, particularly various electrodes, such as mesh type transparent electrodes.
Owner:PESOLVE
Multifunctional manufacturing platform and method of using the same
InactiveUS20130180450A1Easy to copyAdditive manufacturing apparatusLiquid surface applicatorsMachiningPrinted electronics
A single, flexible, robust and low rate capable manufacturing platform that may be associated with caseless munitions firing circuits, nano and microelectromechanical (“NEMS” and “MEMS”) devices, and / or fractal antennas is described. The platform may be designed for extensive research and development in printed electronics, 3D thermo-plastics and low melt metal casting, light machining, and other processing operations necessary for the integrated fabrication of various components, such as caseless munitions components. The platform may be used in a remote location.
Owner:HAMILTON RAY +1
Silver-organic conductive ink for printed electronics
The invention relates to a silver-organic conductive ink for printed electronics. The ink is a solution which is formed by dissolving a silver-organic compound in a specific solvent and can be subjected to ink jetting, gravure, silk screening to form conductive patterns. The silver-organic conductive ink comprises 10-60 wt.% of a saturated carboxylic acid silver compound, 5-50 wt.% of an amido compound, 10-85 wt.% of a solvent and 0-10 wt.% of a thickening agent, the saturated carboxylic acid silver compound comprises a linear chain, a branched chain and a hydroxyl, amido and sulfydryl substituted carboxylic acid silver compound, the amido compound is complex with carboxylic acid silver so as to improve dissolubility of the carboxylic acid silver, the amido compound is primary amine and secondary amine, the amido amount is two times of molar weight of silver ions, the solvent is not reacted with the carboxylic acid silver or amine, and the thickening agent is used for adjusting viscosity. The silver-organic conductive ink can be applied to preparation of conductive lines by means of methods of printed electronics and is capable of simplifying existing line preparation processes.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
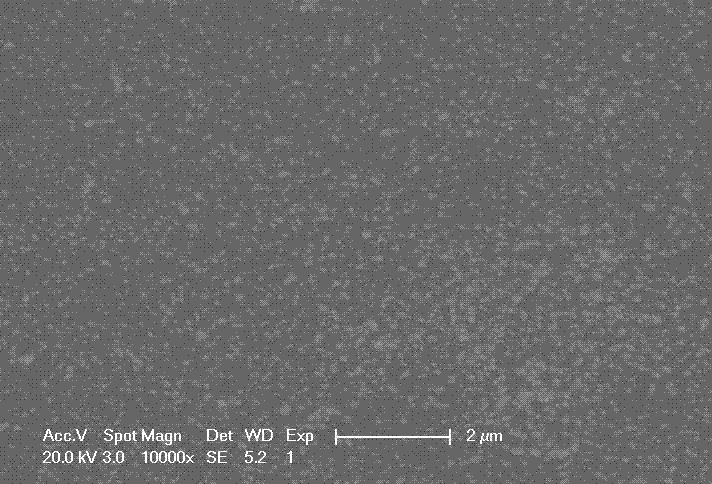
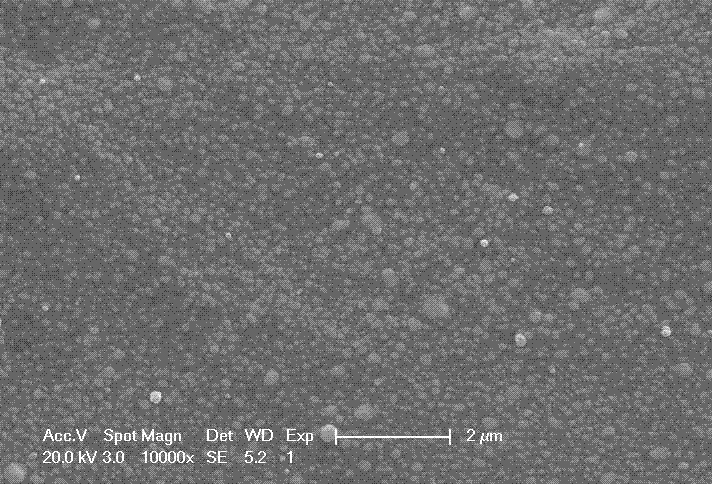
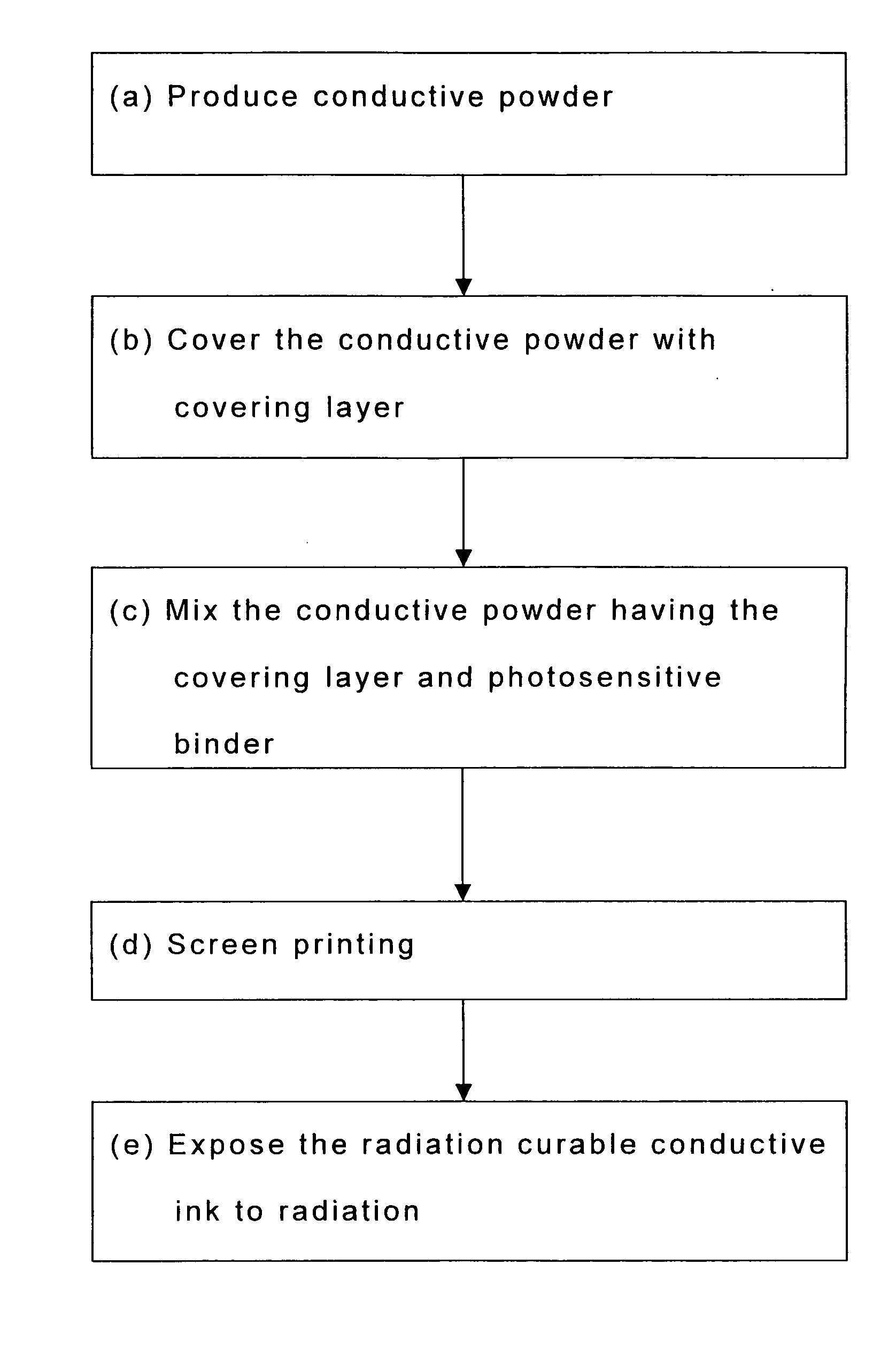
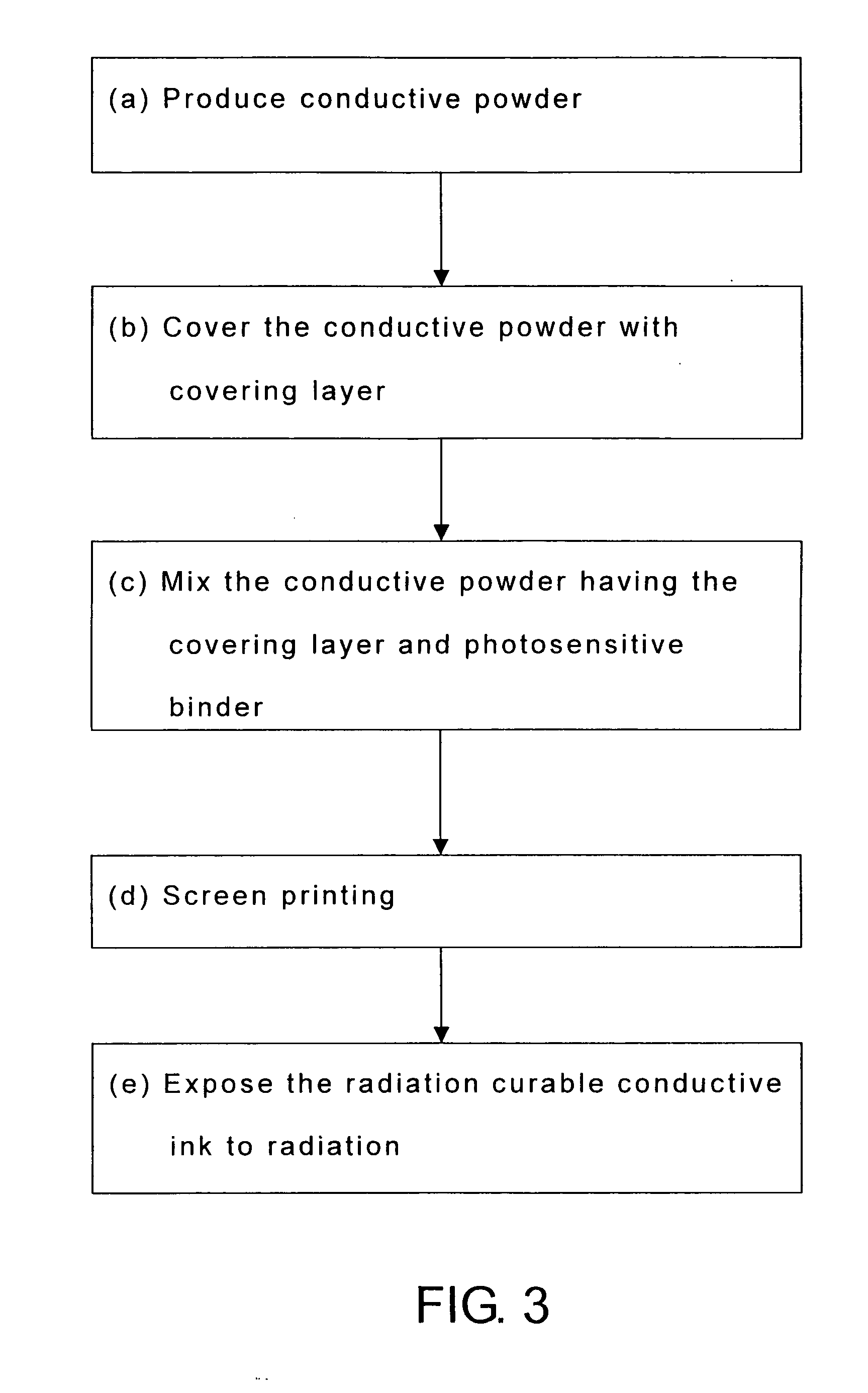
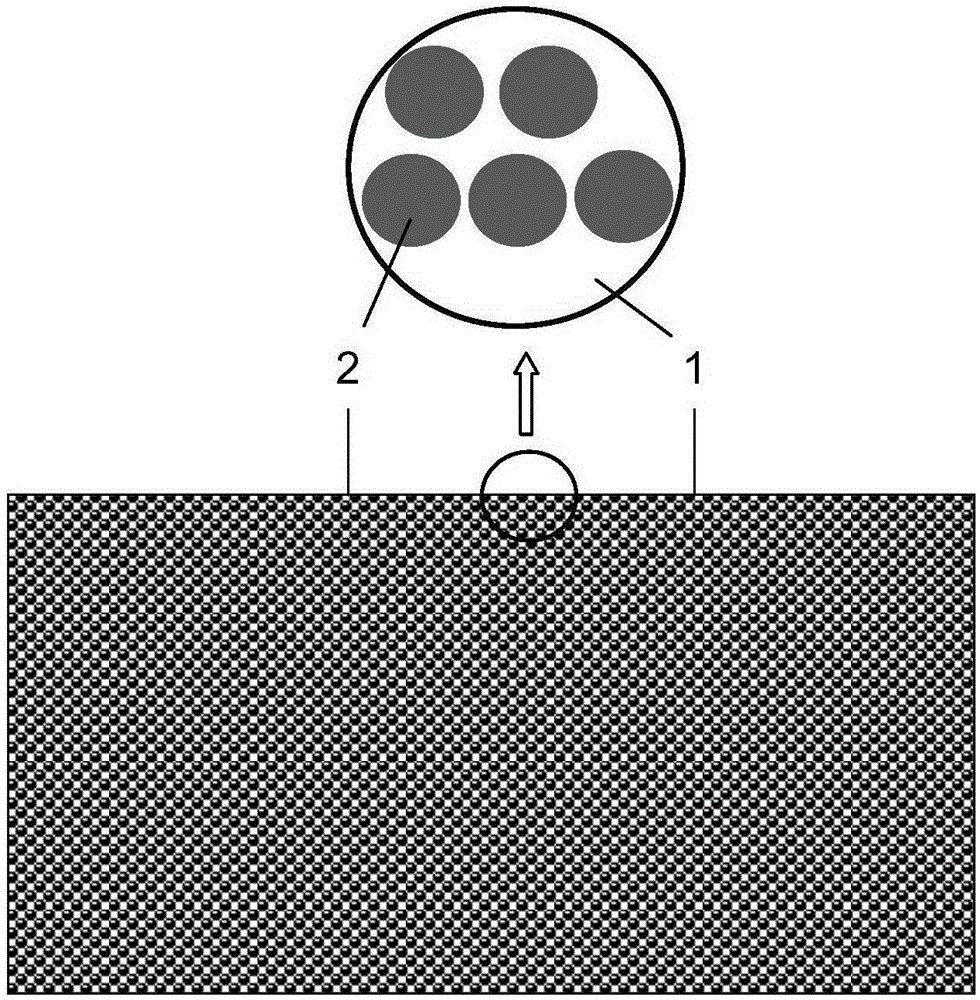
Radiation curable conductive ink and manufacturing method for using the same
The present invention provides a radiation curable conductive ink and a manufacturing method for conductive substrate using the conductive ink, wherein components of the radiation curable conductive ink contain at least conductive powder having a covering layer and a photosensitive binder. The radiation curable conductive ink is printed on surface of a substrate using a screen printing method, and a chemical crosslinking reaction is achieved by irradiating the conductive ink with ultraviolet ray, visible light or electron beam, thereby forming a conductive substrate. The conductive substrate is particularly applicable for use in laminate type electronic devices, including radio frequency identification (RFID) antenna, printed-circuit boards, smart cards (non-contact chip cards) components, smart labels, printed electronics, anti-electromagnetic interference (EMI) and anti-electrostatic materials.
Owner:YANG YUNG SHU
Colored liquid metal and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN105220013AGood coloring effectImprove conductivityAdditive manufacturing apparatusLiquid metalElectron
The invention provides colored liquid metal and a manufacturing method thereof. A colored liquid metal raw material comprises a liquid metal body, pigment and / or nanometer conductive particles. The colored liquid metal can be presented in various specific colors while achieving electrical conduction. Firstly, the colored liquid metal has good electrical conductivity of liquid metal and rich colors of the pigment, an approach to color printed electronics can be opened up, and the aesthetic property and experience of the printed electronics can be remarkably promoted; meanwhile, the oxidation resistance and rust-proof property of traditional liquid metal are improved.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
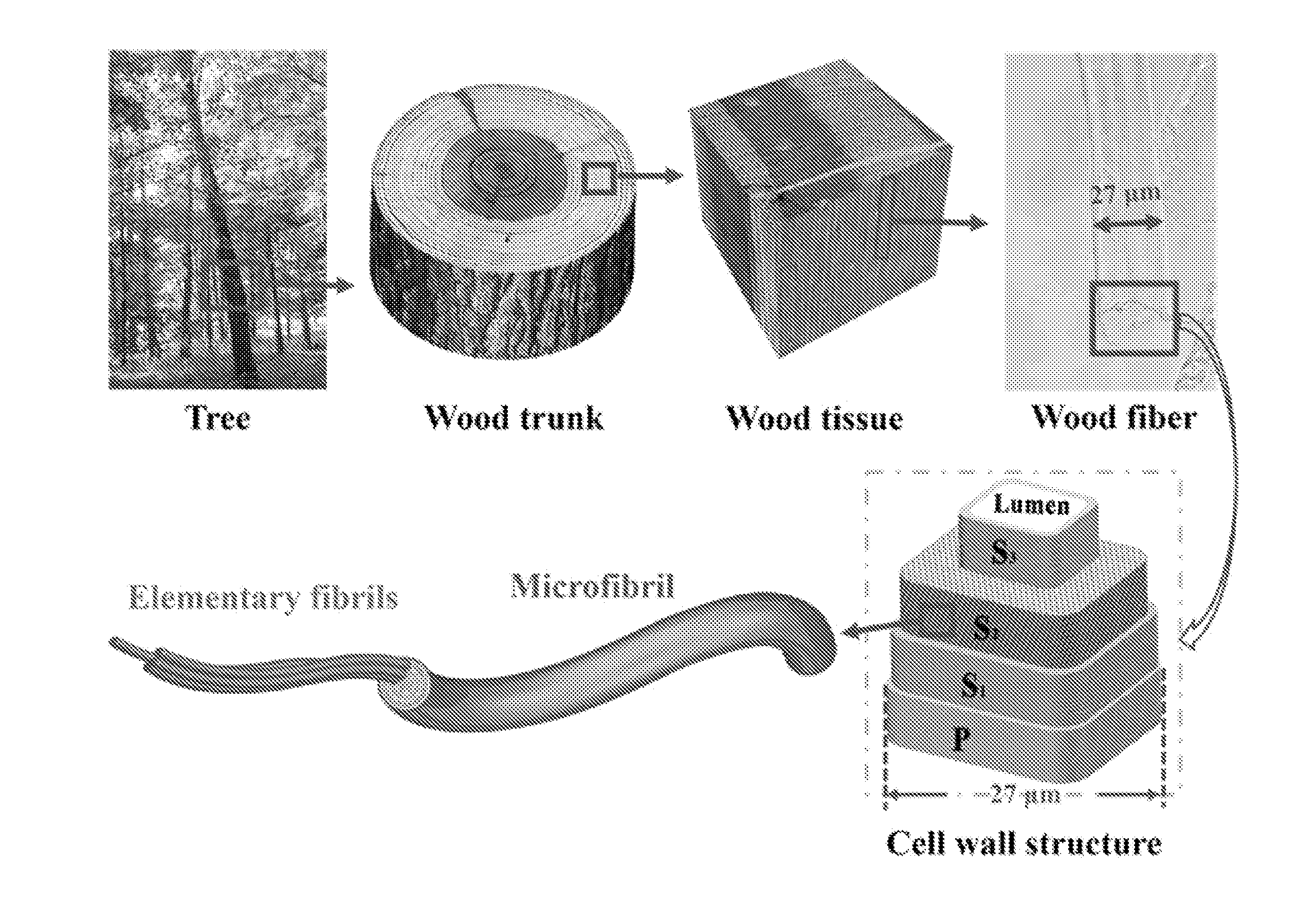
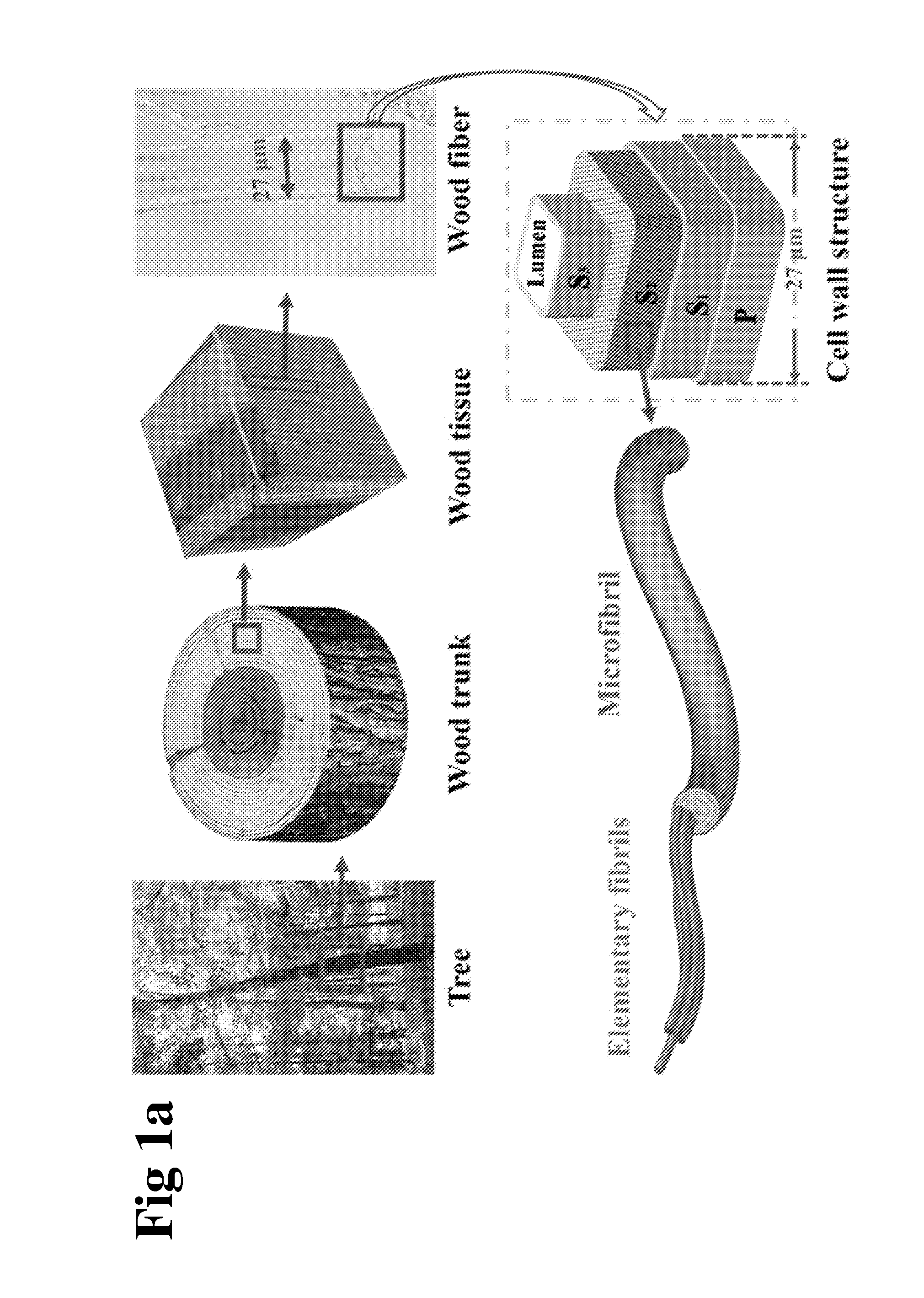
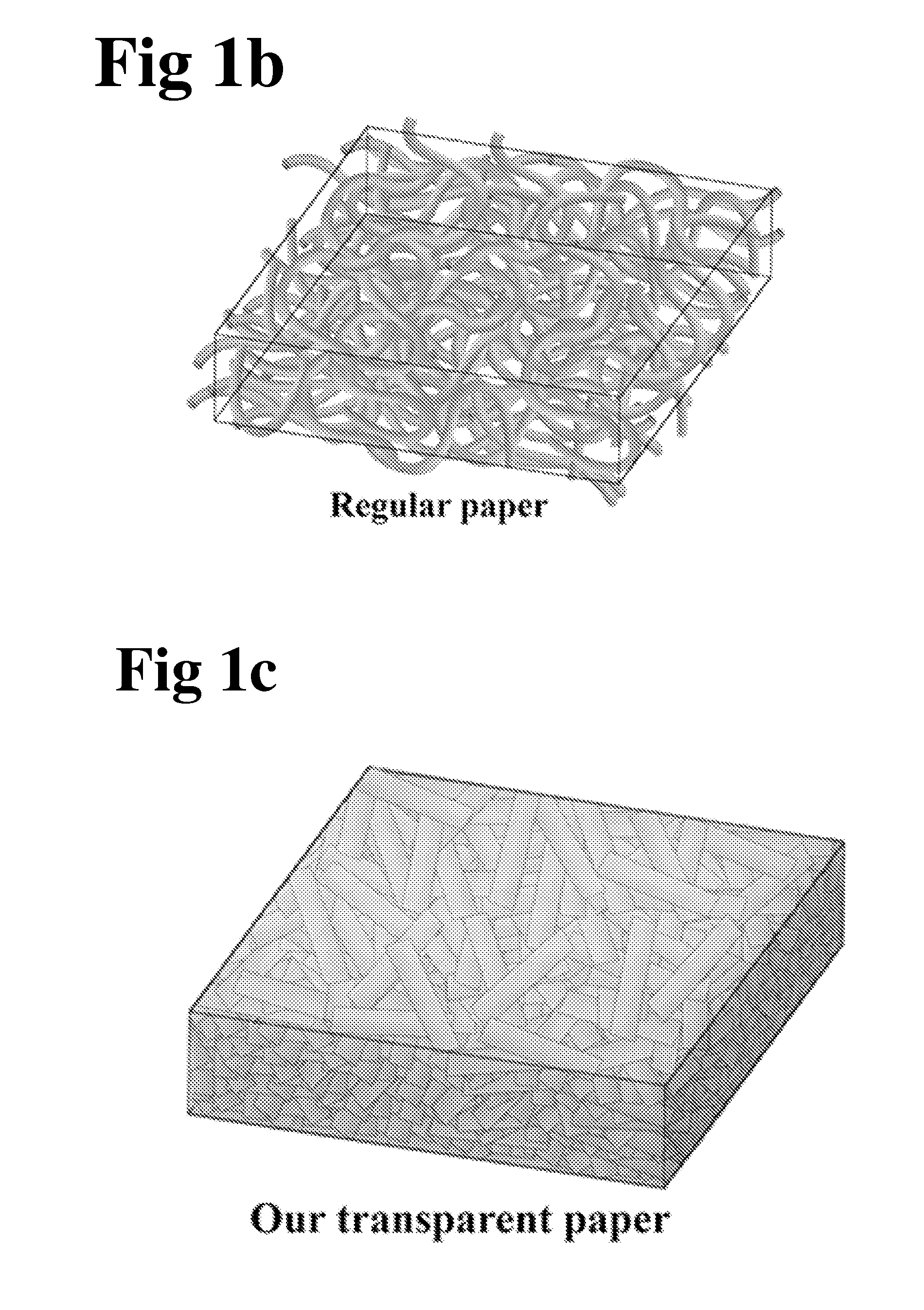
Scalable, highly transparent paper with microsized fiber
InactiveUS20160010279A1Ultra-high optical transparencyLow costNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperCelluloseFiber
Solar cell substrates require high optical transparency, but also prefer high optical haze to increase the light scattering and consequently the absorption in the active materials. Unfortunately there is a tradeoff between these optical properties, which is exemplified by common transparent paper substrates exhibiting a transparency of about 90% yet a low optical haze (<20%). In this work we introduce a novel transparent paper made of wood fibers that display both ultra-high optical transparency (˜96%) and ultra-high haze (˜60%), thus delivering an optimal substrate design for solar cell devices. Compared to previously demonstrated nanopaper composed of wood-based cellulose nanofibers, our novel transparent paper has better dual performance in transmittance and haze, but also is fabricated at a much lower cost. This high-performance, low-cost transparent paper is a potentially revolutionary material that may influence a new generation of environmentally friendly printed electronics.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
High-Resolution Patterning of Graphene by Screen and Gravure Printing for Highly Flexible Printed Electronics
ActiveUS20150307730A1Efficient and economical approachWithout compromising electrical characteristicLayered productsPhotomechanical apparatusScreen printingEngineering
Graphene ink compositions as can be utilized with gravure and screen printing processes, to provide flexible electronic components with high-resolution printed graphene circuitry.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA +1
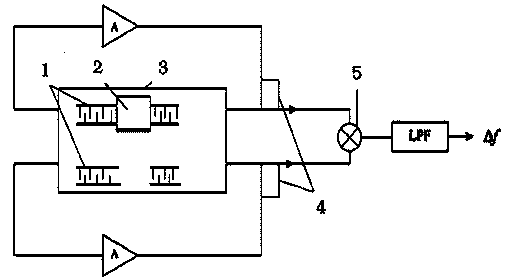
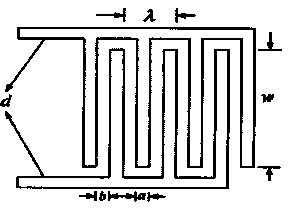
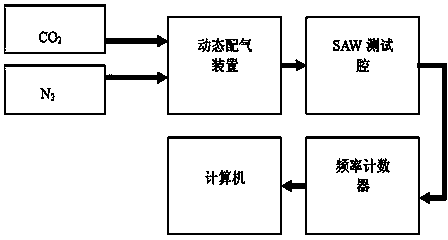
Manufacturing method of all-printed electronic carbon dioxide thin-film SAW (Surface Acoustic Wave) sensor
InactiveCN103994939ASimple processLow costWeighing by absorbing componentThin film sensorMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a manufacturing method of an all-printed electronic carbon dioxide thin-film SAW (Surface Acoustic Wave) sensor. The manufacturing method disclosed by the invention specifically comprises the following steps: selecting a piezoelectric substrate; designing and printing an electrode; preparing and printing a sensitive material; and designing and printing a driving circuit. Compared with the traditional microelectronic process, the carbon dioxide thin-film SAW sensor prepared based on printed electronics has the obvious advantages of being low in cost, simple and rapid in manufacturing process, environmentally friendly and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Assay test device, kit and method of using
InactiveUS20160231251A1Easy to useReduce manufacturing costMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrical batteryTest fixture
The present invention relates to assay test devices, and methods and kits for use to monitor, sense, read and display results by using devices with printed electronics, such as batteries, reading devices, and other circuitry and / or using colorimetric means for testing by using a sensitive indicator pH dye, or both.
Owner:CREDO BIOMEDICAL PTE
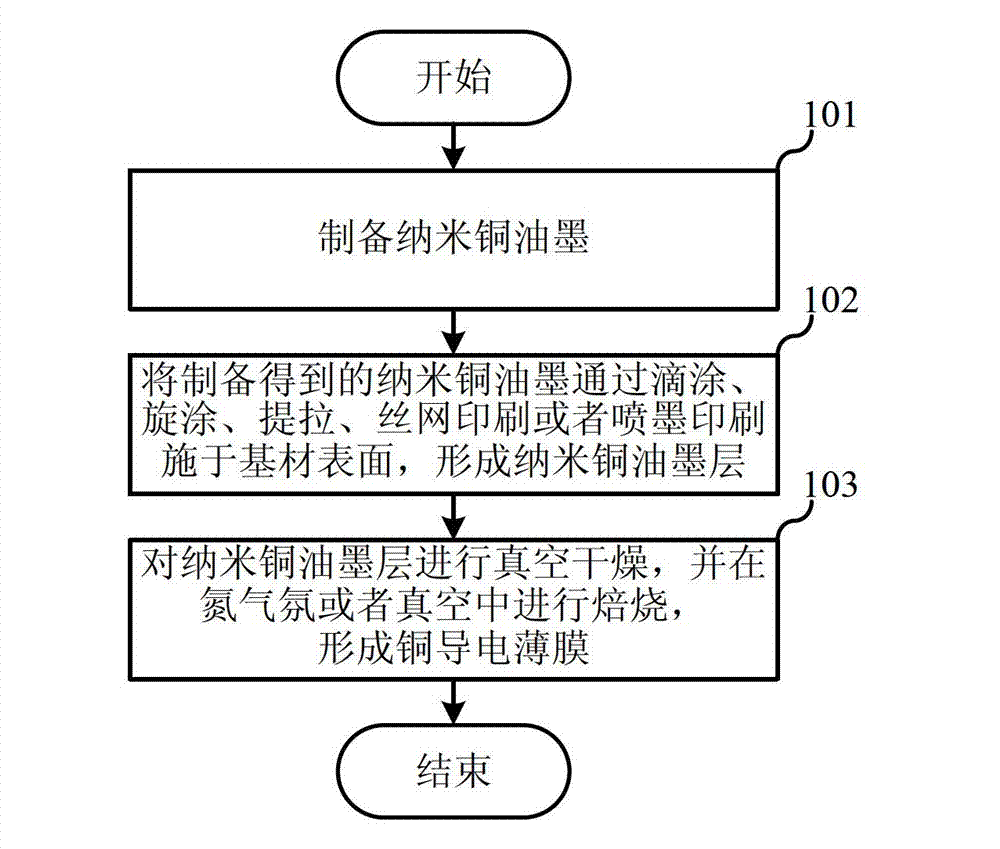
Preparation method for nano-copper ink applied to printed electronics
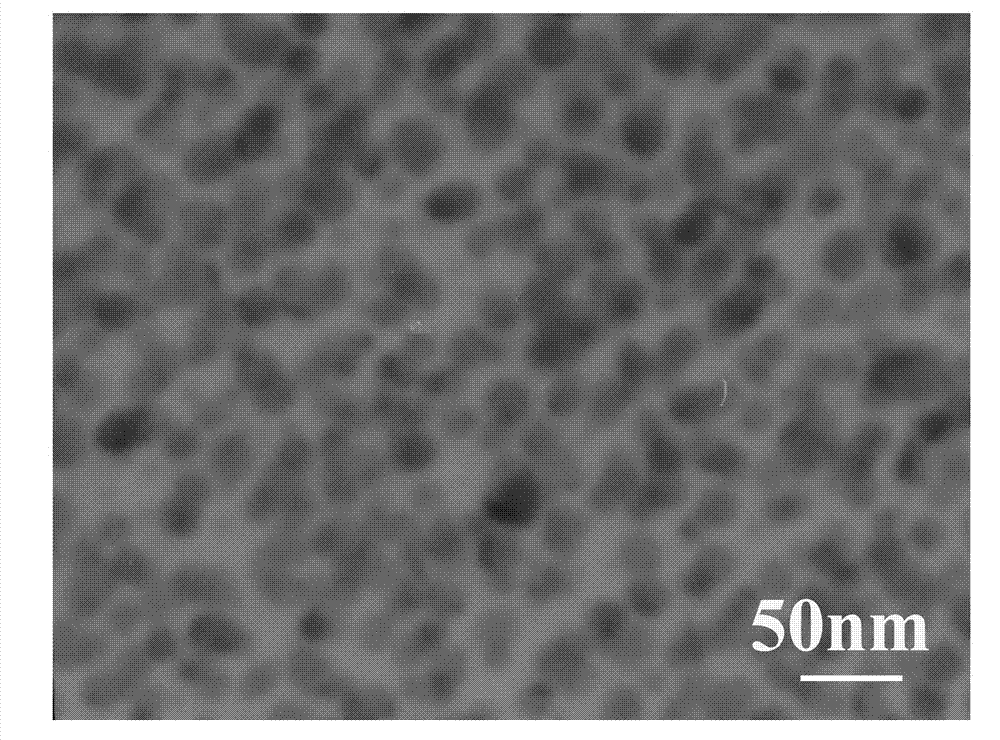
ActiveCN102558954ASimple processShort reaction timeInksConductive pattern formationNano copperSolvent
The invention belongs to the technical field of printed electronics and particularly discloses a preparation method for nano-copper ink applied to printed electronics. In the preparation method for the nano-copper ink applied to the printed electronics, under the action of ammoniand a reducing agent, the stable nano-copper ink applied to the printed electronics is obtained by dissolving an organic copper salt and an organic protective agent into a solvent. The preparation method is simple in process, free of heating and low in cost; water is taken as the solvent, so that the preparation method is more environment-friendly; the particle size of the prepared nano copper is less than 30nm; and the prepared nano copper is easily sintered into a film, is good in conductivity and has a wide application prospect in the field of printed electronic circuits.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method and products related to deposited particles
InactiveUS20120275119A1Low cost manufacturingGood electrical contactPorous dielectricsMaterial nanotechnologyParticulatesElectronic structure
The invention concerns a method of removing encapsulating material from encapsulated particles deposited onto a substrate. According to the method, a substrate is used which is capable of facilitating said removal of encapsulating material. The particles may be nanoparticles. In particular, the substrate-facilitated removal may result in sintering of the particles. The invention provides a novel way of functionalizing electronic structures using particulate matter and for conveniently producing e.g. printed electronics devices.
Owner:TEKNOLOGIAN TUTKIMUSKESKUS VTT
Precision overprinting method of printed electronics rotary printing where location can be adjusted in real time
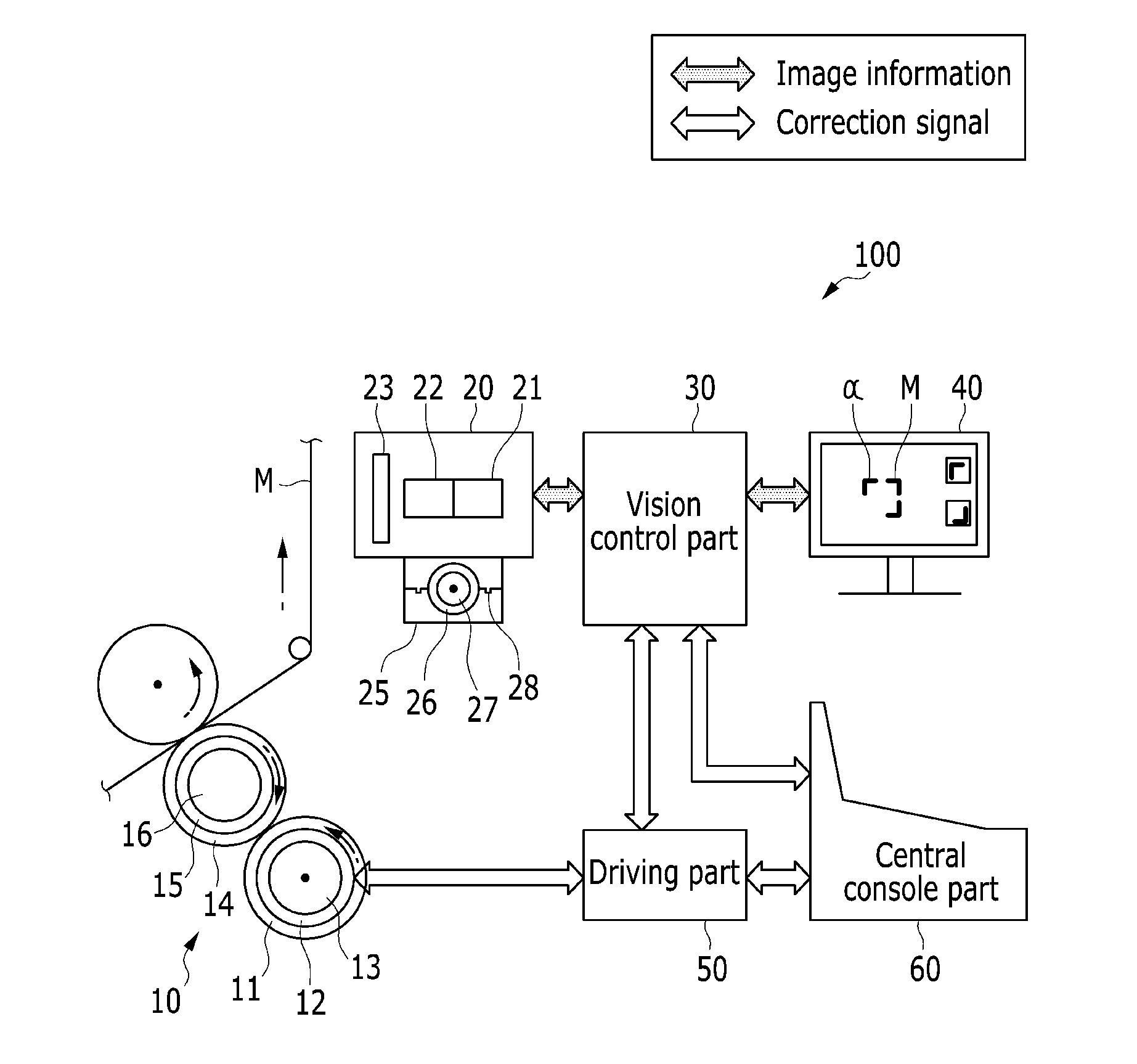
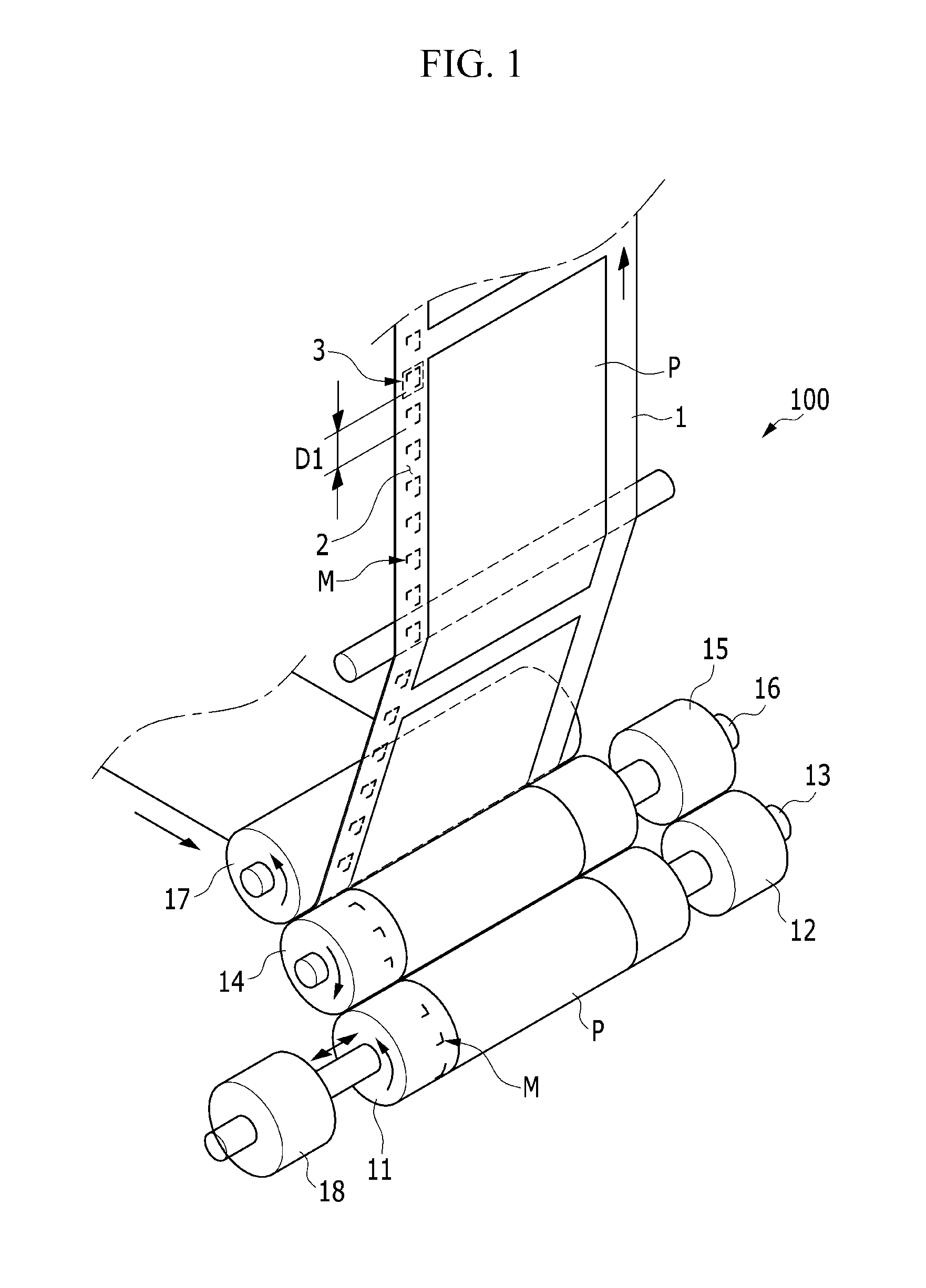
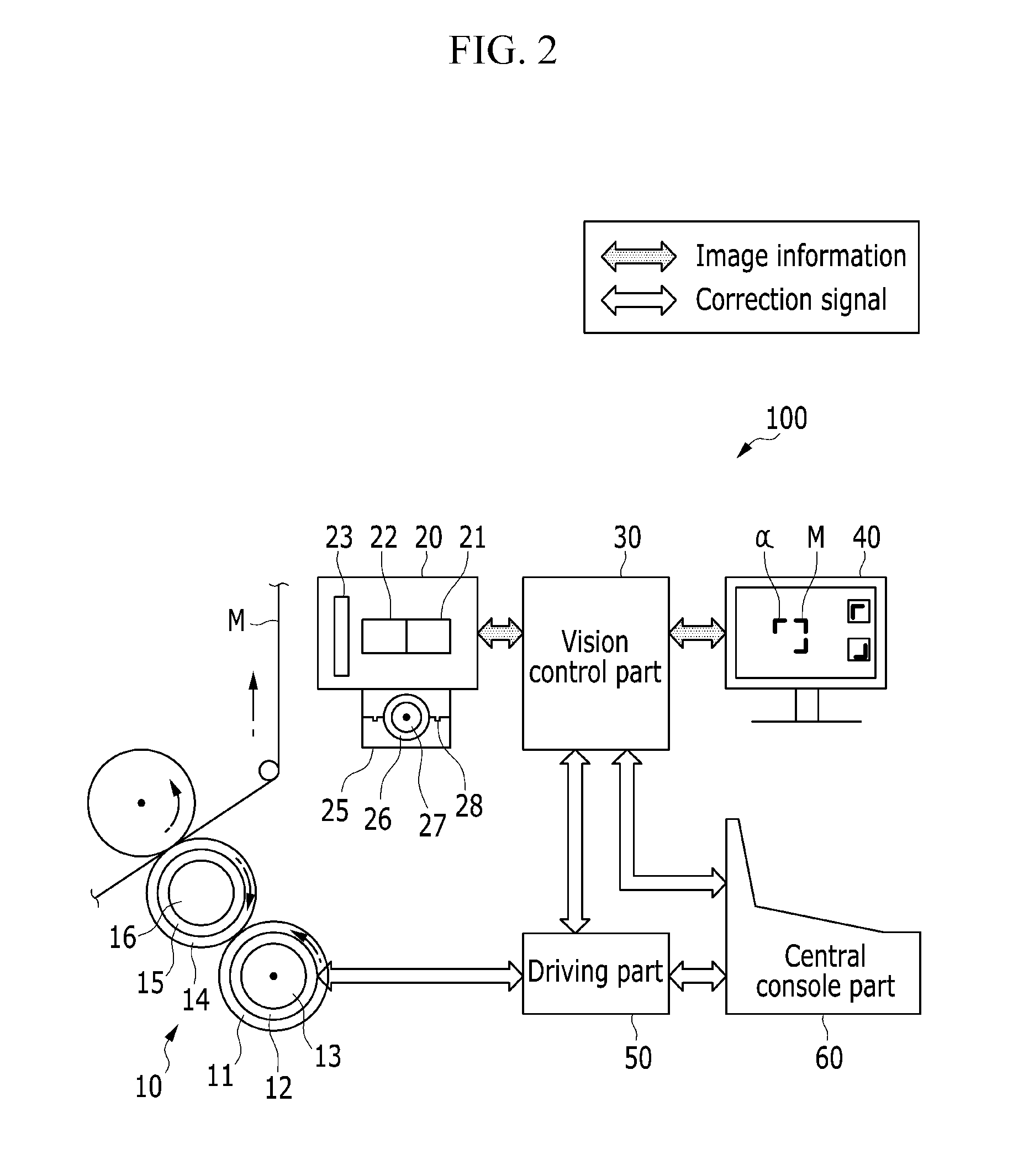
ActiveUS20140083316A1Precise processEasy to identifyPlaten pressesRotary intaglio printing pressMicrometerDisplay device
The present invention relates to a precision overprinting method of printed electronics rotary printing where a location can be adjusted in real time. More particularly, minute precise printing electronic patterns of a micrometer level which are multilayered by a plurality of gravure offset printing units are accurately overprinted, and a fine deviation in a rotation direction and an axial direction of a plate cylinder is quickly solved. The present invention also relates to a precision overprinting method of printed electronics rotary printing where a location can be adjusted in real time, capable of verifying a printing quality by displaying register marks printed in printing units and alignment state on a display device.
Owner:KOREA INST OF MACHINERY & MATERIALS
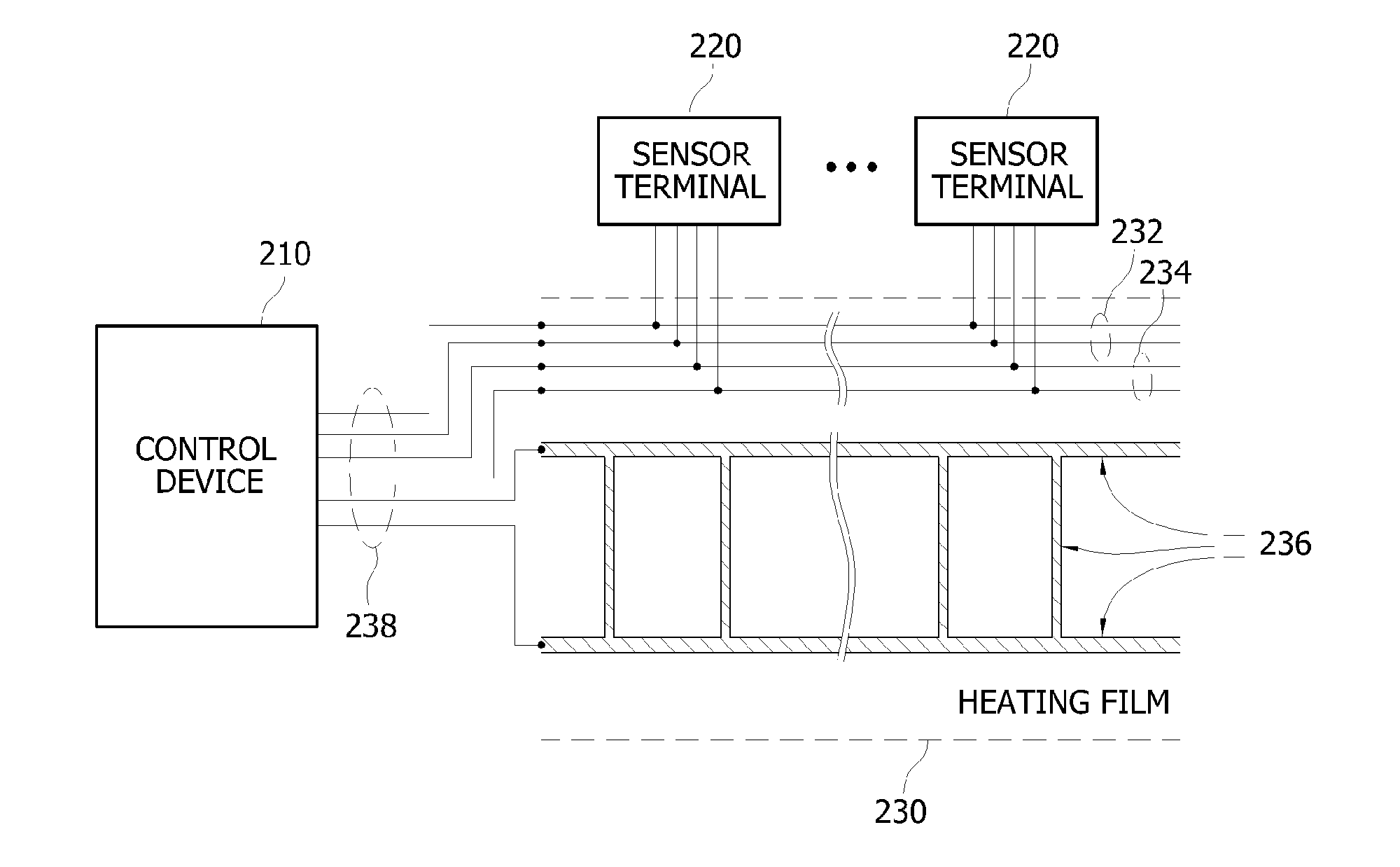
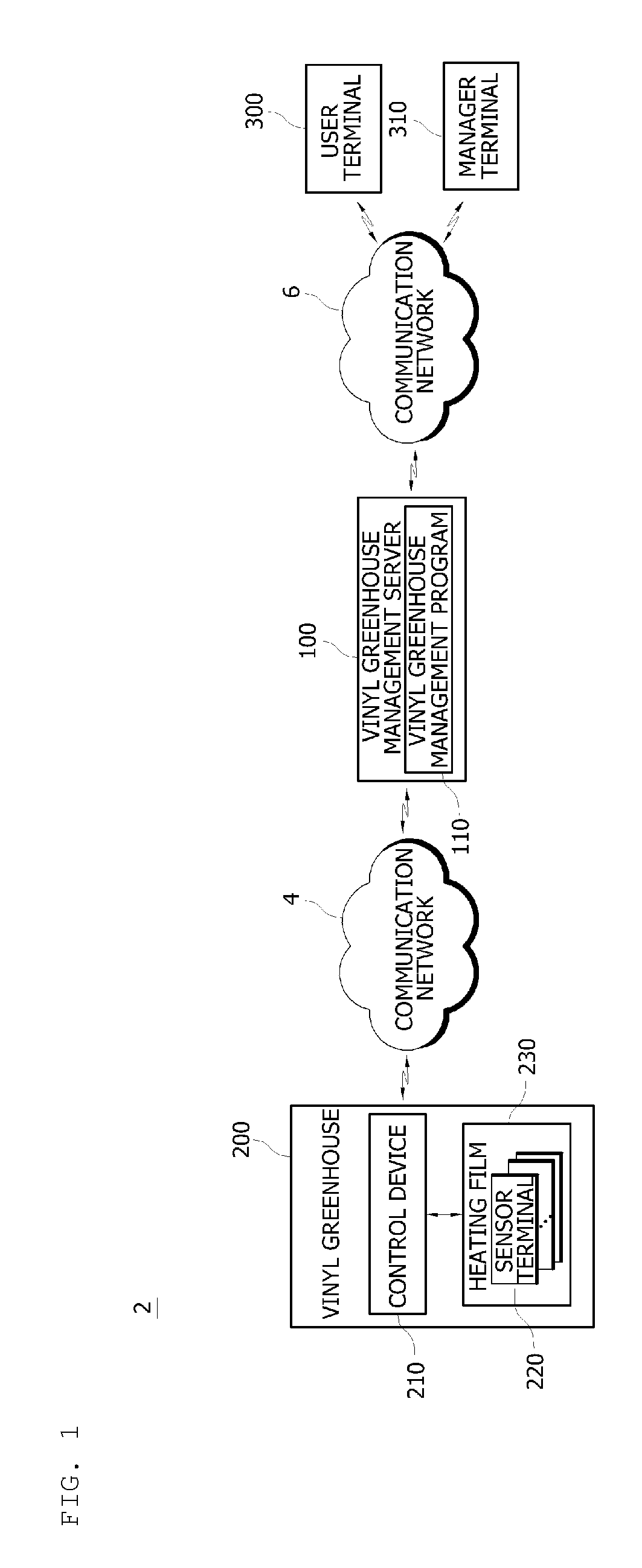
Management system for vinyl greenhouse and method for processing thereof
InactiveUS20160349769A1Guaranteed automatic operationLow costTemperature control without auxillary powerTemperature control using digital meansElectricityRemote control
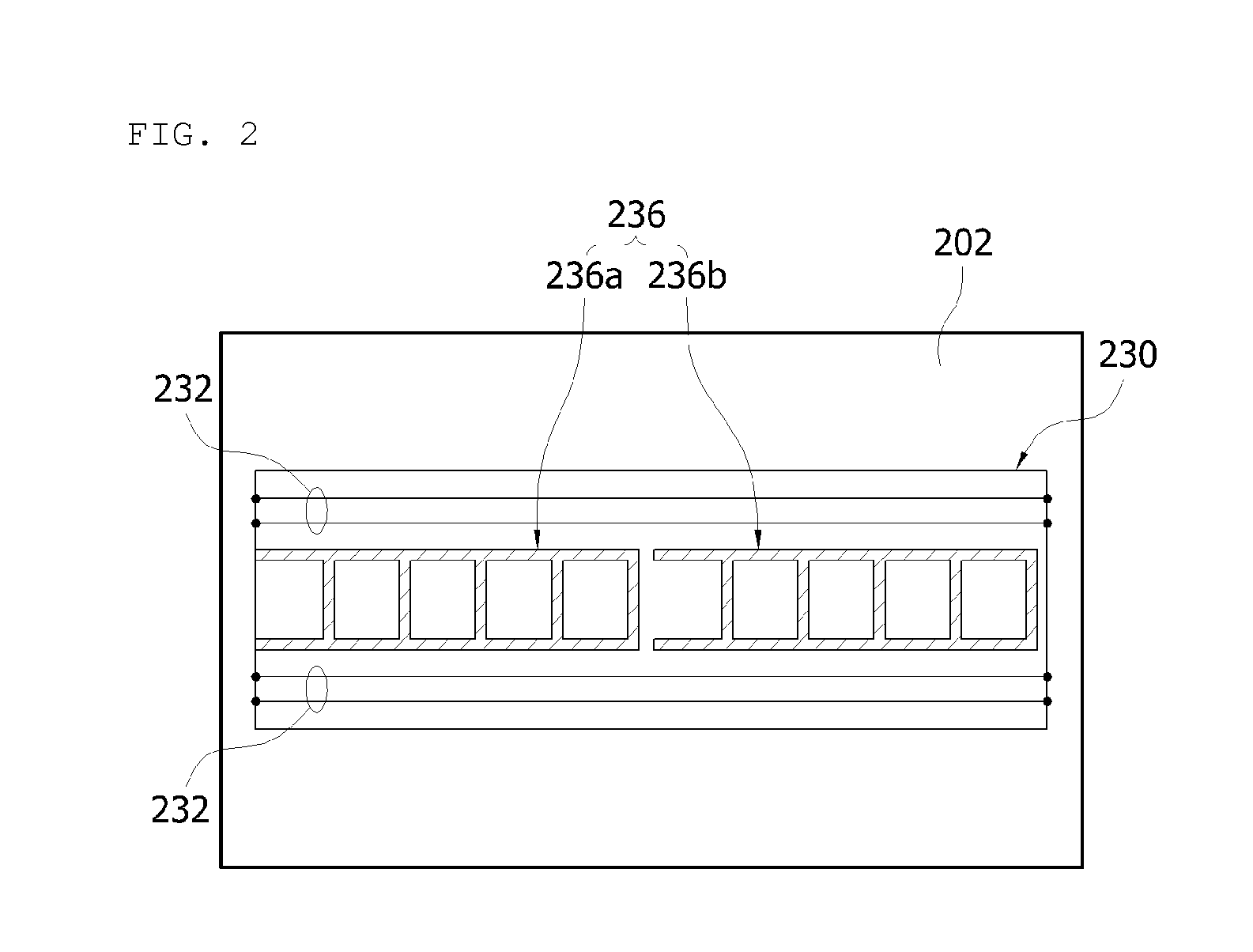
The present invention relates to a vinyl greenhouse management system and a processing method thereof. The vinyl greenhouse management system of the present invention includes a plurality of sensor terminals provided at a vinyl greenhouse, a control device configured to receive various sensed information about an environmental condition of the vinyl greenhouse from the sensor terminals so as to control a status of the vinyl greenhouse, a vinyl greenhouse management server connected with the control device and configured to collect the sensed information, and a user terminal and a manager terminal configured to monitor or remote control the status of the vinyl greenhouse as being linked with the vinyl greenhouse management server. The vinyl greenhouse includes a heating film on a partial surface of a structure. In the heating film, a plurality of heating patterns and a plurality of circuit patterns are formed of conductive ink on a surface of a polymer film by using the printed electronics. The sensor terminals are electrically connected with the control device through the circuit patterns so as to transfer the sensed information. In response to the sensed information of the vinyl greenhouse, power supply from the control device to the heating patterns may be performed or stopped. According to the present invention, the heating film can be mass-produced at a low cost, and a status of the vinyl greenhouse can be monitored and remotely controlled in real time.
Owner:ARAM SOLUTION
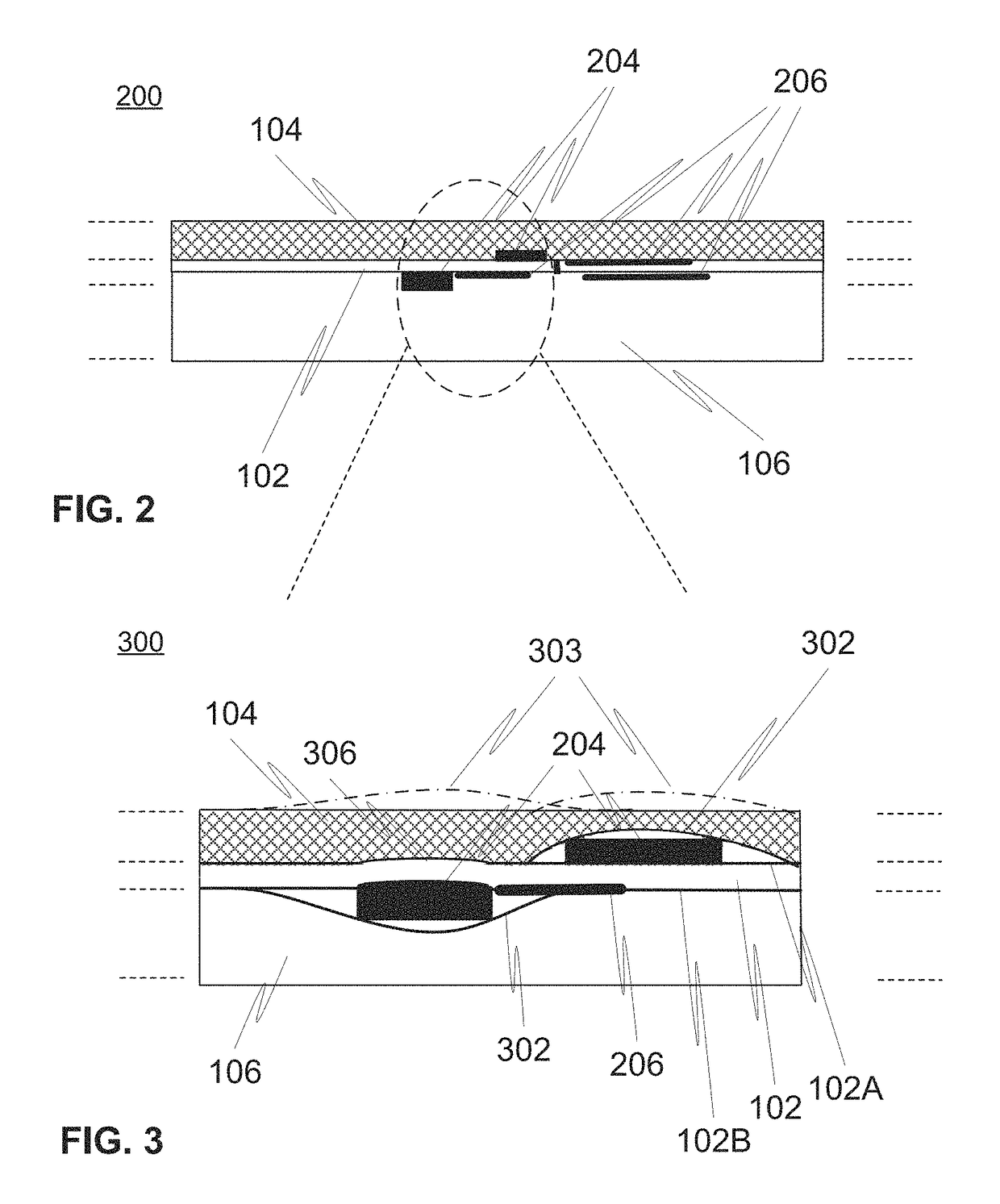
Multilayer structure for accommodating electronics and related method of manufacture
ActiveUS9724869B2High yieldAvoid smooth surface3D rigid printed circuitsTransparent dielectricsSurface mountingEngineering
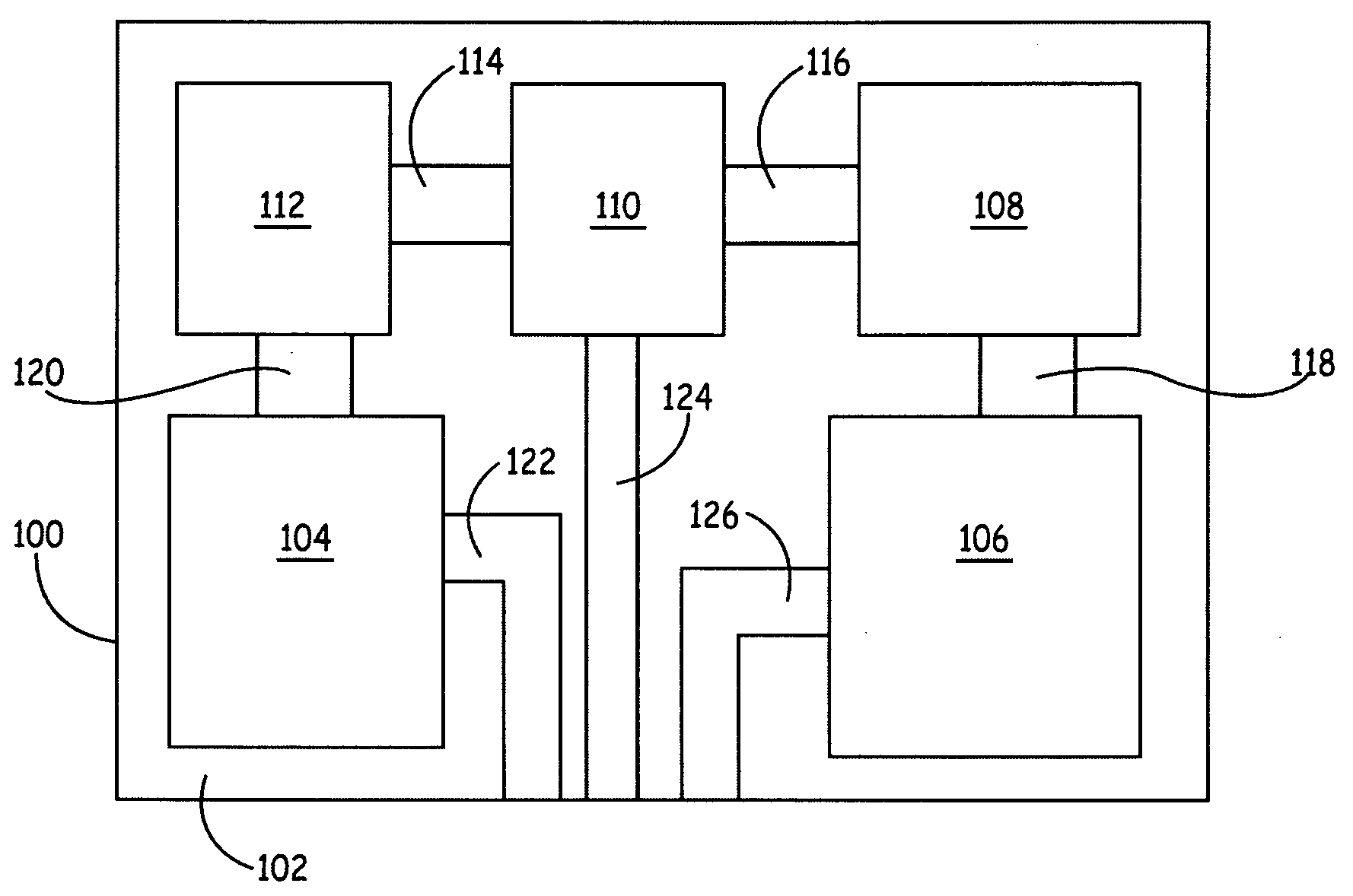
Multilayer structure (200) for electronic devices, including a flexible substrate film (102) for accommodating electronics, a number of electrical elements (204, 206) provided to the flexible substrate film, preferably by element of printed electronics and / or surface mounting, a protective layer (104) laminated onto at least first surface of the substrate film, the protective layer being configured to mask perceivable physical deviation of the substrate, such as uneven surface profile or coloring, substantially at the location of the number of elements, from outside perception, optionally visual perception and / or tactile inspection taking place via the protective layer, and plastic layer (106) molded over at least second surface of the substrate film opposite to the first surface. A corresponding method of manufacture is presented.
Owner:TACTOTEK
Hybrid membrane production method
InactiveCN104701455AGuaranteed flexibilityEasy to operateMaterial nanotechnologySolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsEvaporation
The invention relates to a semiconductor material production technology, in particular to a hybrid membrane production method. The hybrid membrane production method includes the following steps: dissolving an organic semiconductor material in a first solvent to form a first mixture with concentration of 0.01-20mg / mL; dispersing an inorganic nano material into a second solvent to form a second mixture with concentration of 0.01-10mg / mL; transferring the first mixture onto an inert substrate for standing, and forming an organic semiconductor nanocrystalline after evaporation of the first solvent; transferring the second mixture onto the surface of the organic semiconductor nanocrystalline, performing annealing treatment and obtaining a hybrid membrane made of organic-inorganic materials after evaporation of the second solvent. The production method is simple to operate without rigid environments of high temperature and high vacuum, compatible with printed electronics processing methods such as ink-jet printing and aerosol jet printing, short in production cycle, low in cost and suitable for large-area mass production.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
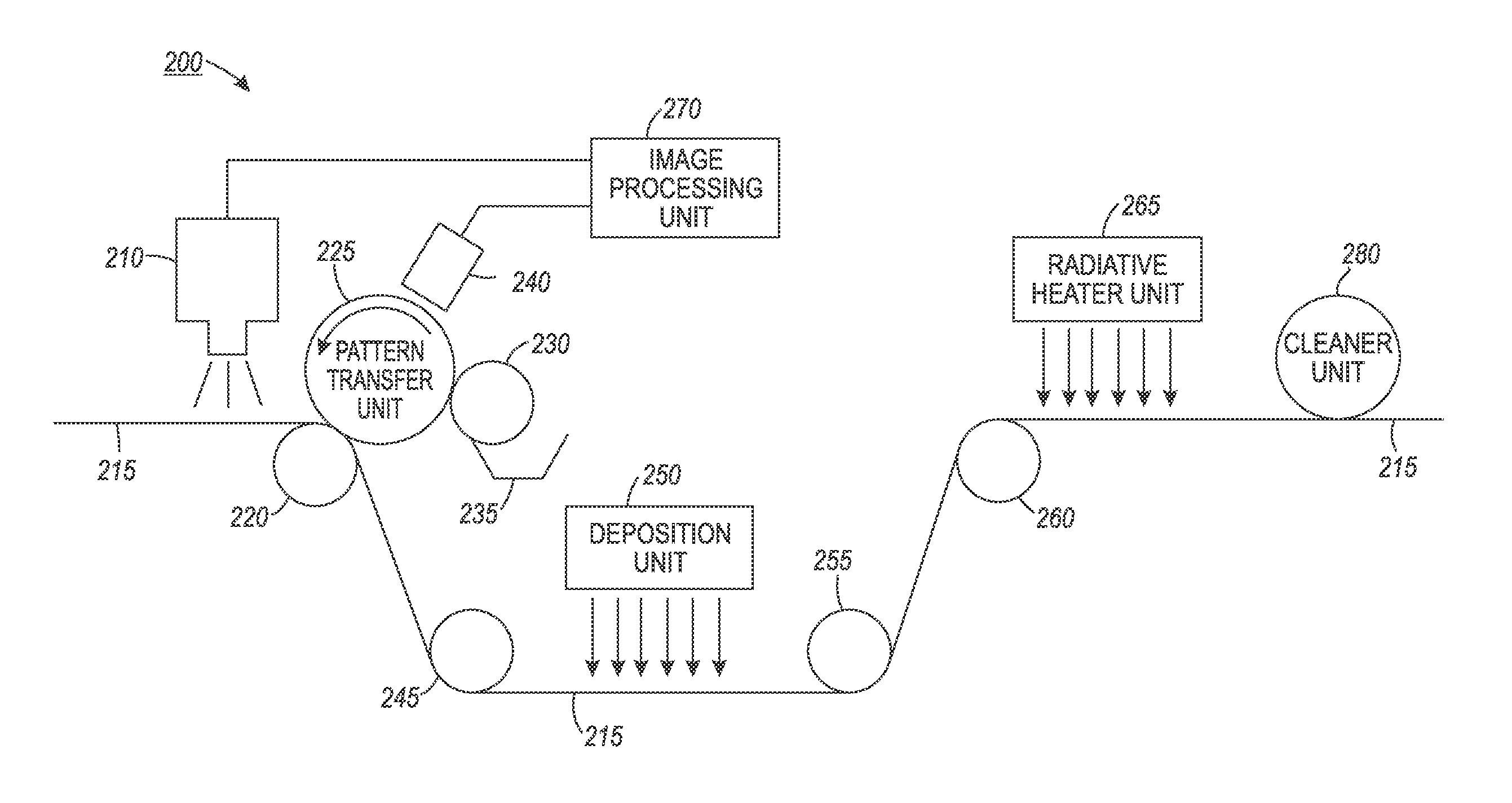
Systems and methods for implementing digital vapor phase patterning using variable data digital lithographic printing techniques
InactiveUS20150376768A1Increase freedomEasy to implementRadiation applicationsVacuum evaporation coatingGas phaseImage formation
A system and method are provided for implementing a unique scheme by which to execute digital vapor phase patterning on metals, semiconductor substrates and other surfaces using a proposed variable data digital lithographic image forming architecture or technique. For certain substrate printing and manufacturing applications, including some printed electronics applications, the disclosed schemes implement techniques to digitally pattern metal layers with bulk material properties in a manner that is aligned with underlying layers on the fly. The disclosed digital printing process may pattern a release oil on a substrate in support of a metal deposition process. Changeable patterning is implemented with an ability to modify the alignment of the patterns on-the-fly. The release layer on a drum is laser patterned in order that the patterned release layer is transferred to the substrate, or the patterning of the release layer is accomplished directly on the substrate.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
Assay test device, kit and method of using
InactiveCN105899947AImprove flexibilityAvoid damageMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorComponent separationAssayElectrical battery
The present invention relates to assay test devices, and methods and kits for use to monitor, sense, read and display results by using devices with printed electronics, such as batteries, reading devices, and other circuitry and / or using colorimetric means for testing by using a sensitive indicator pH dye, or both.
Owner:CREDO BIOMEDICAL PTE
A preparation method of silver wire for printed electronics with uniform conductivity
ActiveCN102300415ALower requirementEasy to implementInksConductive pattern formationMicroelectronic circuitsPrinting ink
The invention discloses a method for preparing a uniformly-conductive silver wire used for printed electronics. The method comprises the following specific steps of: spraying conductive printing ink on a printing substrate; and preparing the uniformly-conductive silver wire used for the printed electronics by a heating ablation method. The method has the good characteristics of convenience, rapidness, simple process, low ablation temperature and low electric conductivity, and can meet the requirement on production of modern microelectronic circuits.
Owner:SHANGHAI LANGYI FUNCTIONAL MATERIALS
Secured electronics device
InactiveUS20170024585A1Reduce the possibilityTelevision system detailsUser identity/authority verificationLithographic artistComputer module
An electronics device comprising one or more modules that implement a security-related operation in an obfuscated manner to thereby provide the security-related operation with resistance against a hardware attack, wherein the electronics device is either (a) a printed electronics device or (b) a device created using e-beam lithography.
Owner:IRDETO ACCESS
Method for assembling thermo-electric device through printed electronics manufacturing technology
InactiveCN102903840AHave diversitySimple methodThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentScreen printingManufacturing technology
The invention discloses a method for assembling a thermo-electric device through a printed electronics manufacturing technology. The method comprises the steps as follows: directly preparing a thermo-electric size on a bottom electrode in a silk screen printing way; adding the prepared thermo-electric size into a marking press; marking and sintering a substrate to obtain films; drying; then printing or welding a layer of top electrode on the substrate; leading wires from the bottom electrode and the top electrode, so as to assemble to form a thermocouple; and connecting a plurality of thermocouples in series so as to form a thermo-electric device with a large area. By adopting the method, the thermo-electric device can be assembled on a rigid foundation; the thermo-electric device also can be assembled on a flexible base plate such as an aluminum sheet, so that options are diversified; the method is simple, convenient to implement, and low in cost; and compared with conventional preparation technology for thermo-electric devices, the method is high in production efficiency, and particularly suitable for mass production.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method for preparing printed electronic resistance welding material based on household piezoelectric inkjet printing technology
InactiveCN103568612ASimplified coating processLow priceDuplicating/marking methodsEngineeringElectric resistance welding
The invention belongs to the field of printed electronics, and particularly discloses a method for preparing a printed electronic resistance welding material based on a household piezoelectric inkjet printing technology. A low-viscosity resistance welding ink formula is fabricated by adopting an improved household piezoelectric inkjet printer; the total time from beginning of inkjet to curing molding does not exceed 5 minutes; meanwhile, the method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of being simple to operate, economic in material, high in reliability and the like, and is applicable to preparation of a hard plate and a flexible plate of a printed circuit board (PCB), a resistance welding coating of a rigid-flexible board.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Preparation method of nano-copper printing ink and copper conductive film
InactiveCN102924996APrevent oxidationEasy to oxidizeConductive materialInksCooking & bakingBoiling point
The invention relates to technical field of printed electronics, and discloses a preparation method of nano-copper printing ink and a copper conductive film. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: dispersing nano-copper into ethanol containing short-chain hydroxyl carboxylic acid, ethylene glycol or a mixed solution of ethanol and ethylene glycol, coating onto the surface of a substrate; and baking at a low temperature to form a copper conductive film. In the dispersing process of nano-copper, the short-chain hydroxyl carboxylic acid can react with oxidized nano-copper to generate an organic copper salt, and the organic copper salt and residual hydroxyl carboxylic acid are coated on the surface of nano-copper for preventing the nano-copper from being further oxidized; and in a baking process, the generated organic copper salt can be reduced into copper, the hydroxyl carboxylic acid is used for preventing nano-copper from being oxidized, and residual short-chain hydroxyl carboxylic acid has relatively-low boiling point and low decomposing temperature and is very easy to remove in the baking process, so that the problem of easiness in oxidizing of nano-copper in treatment processes such as dispersing, printing, baking and the like is solved effectively.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com