Patents
Literature
194 results about "Slot-waveguide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
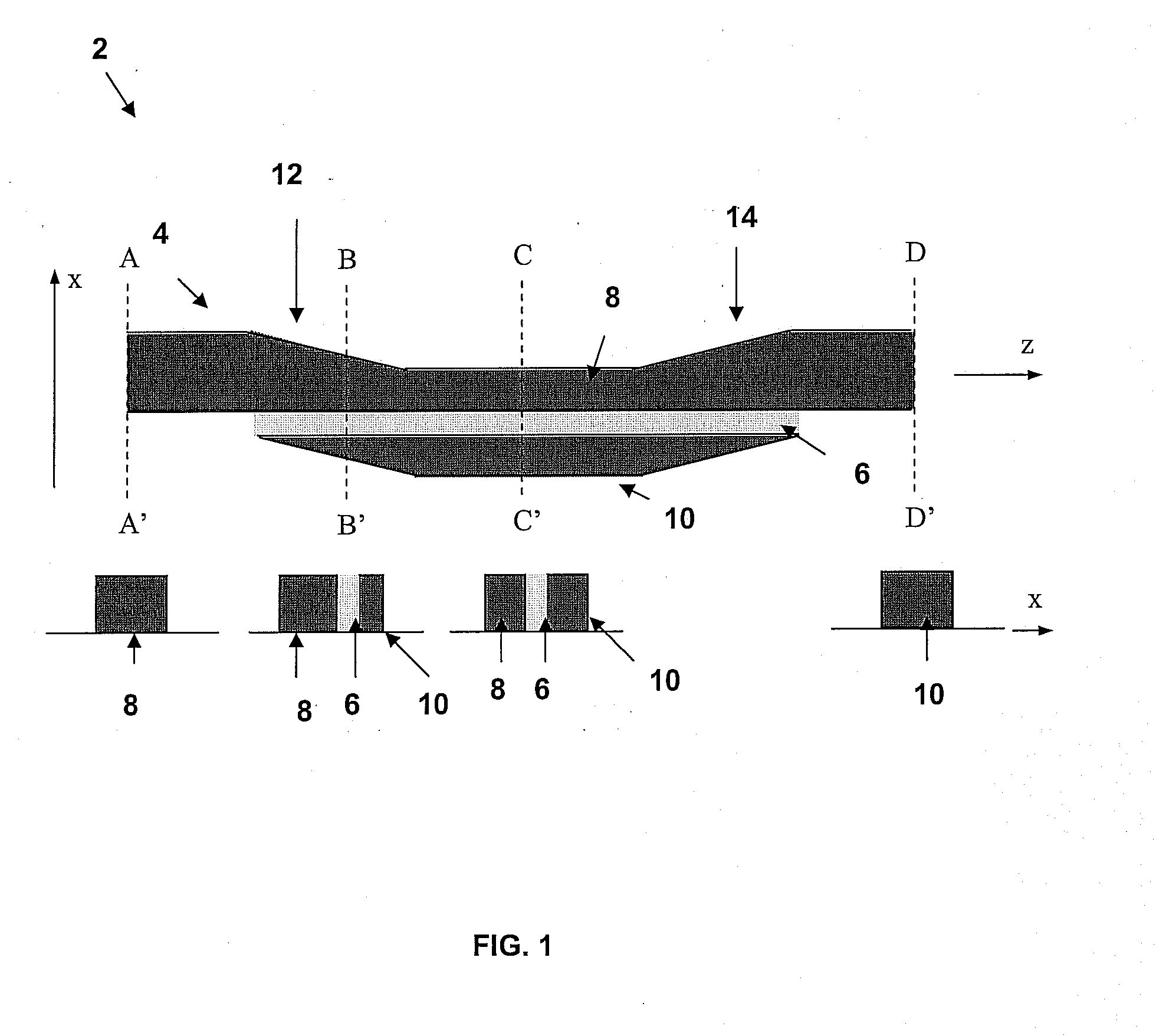
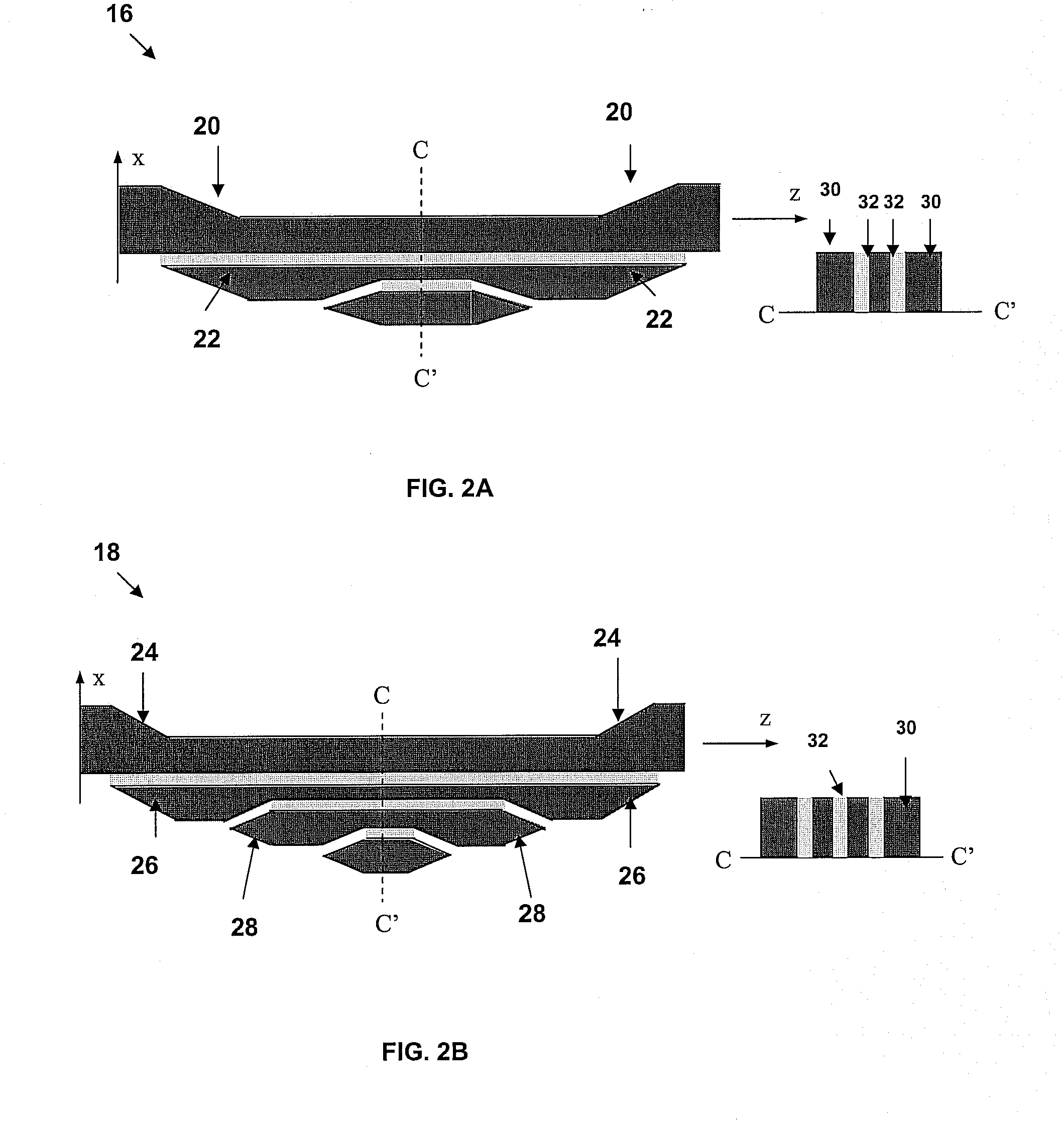
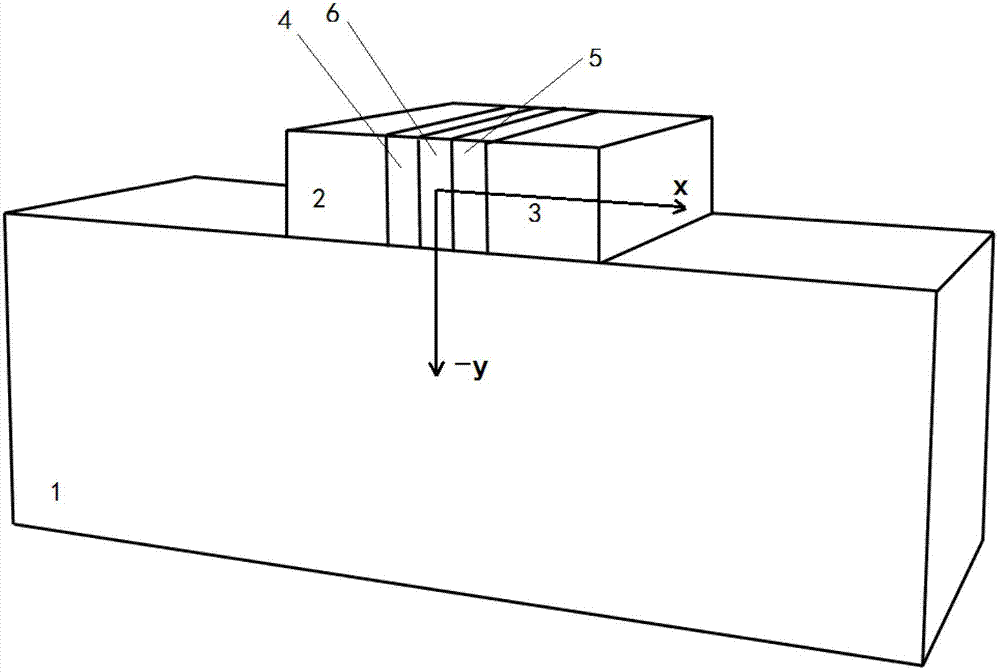
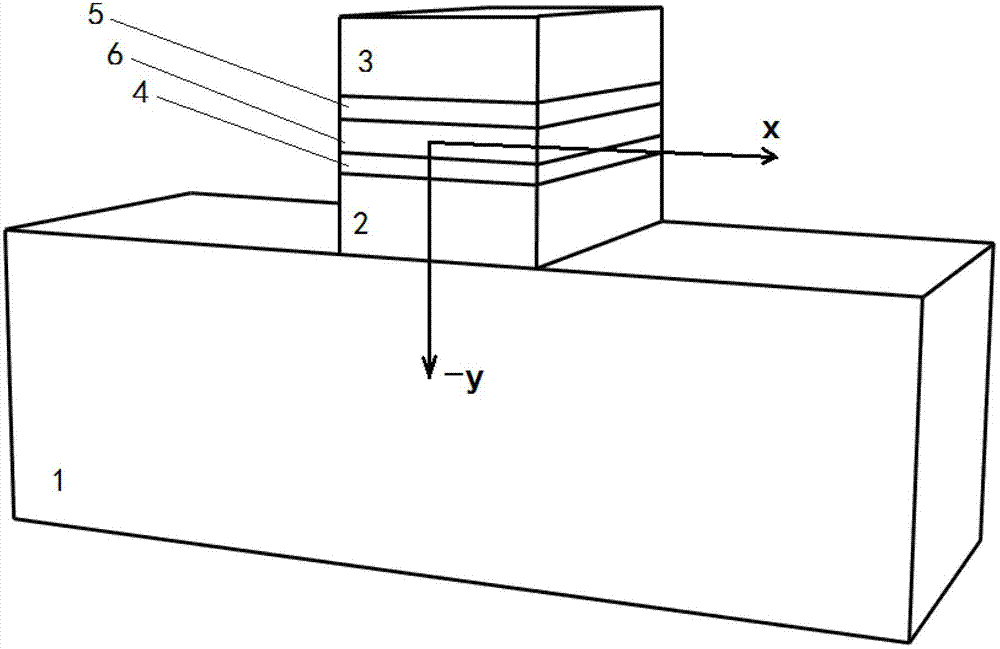
A slot-waveguide is an optical waveguide that guides strongly confined light in a subwavelength-scale low refractive index region by total internal reflection. A slot-waveguide consists of two strips or slabs of high-refractive-index (nH) materials separated by a subwavelength-scale low-refractive-index (nS) slot region and surrounded by low-refractive-index (nC) cladding materials.
Waveguide
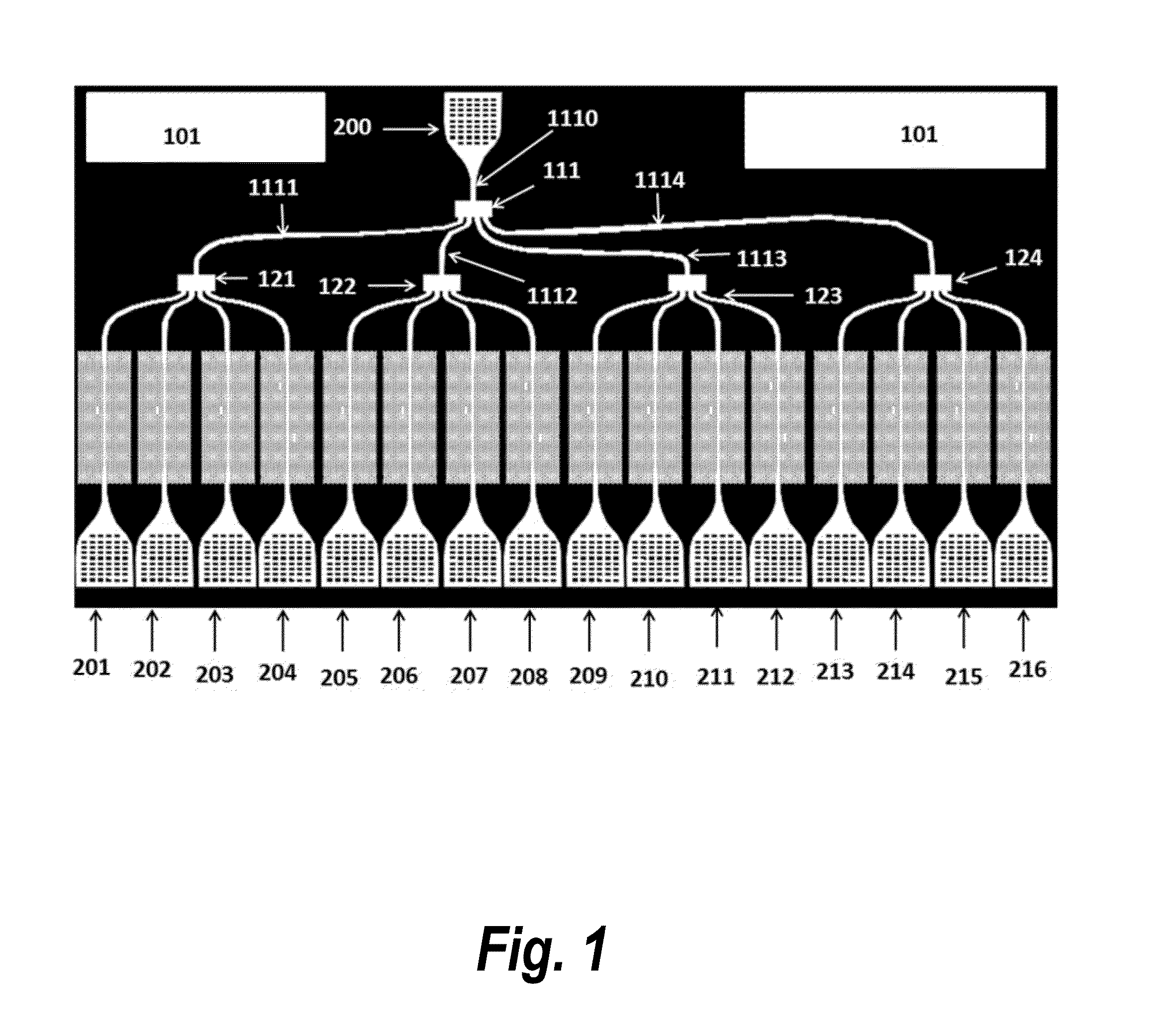
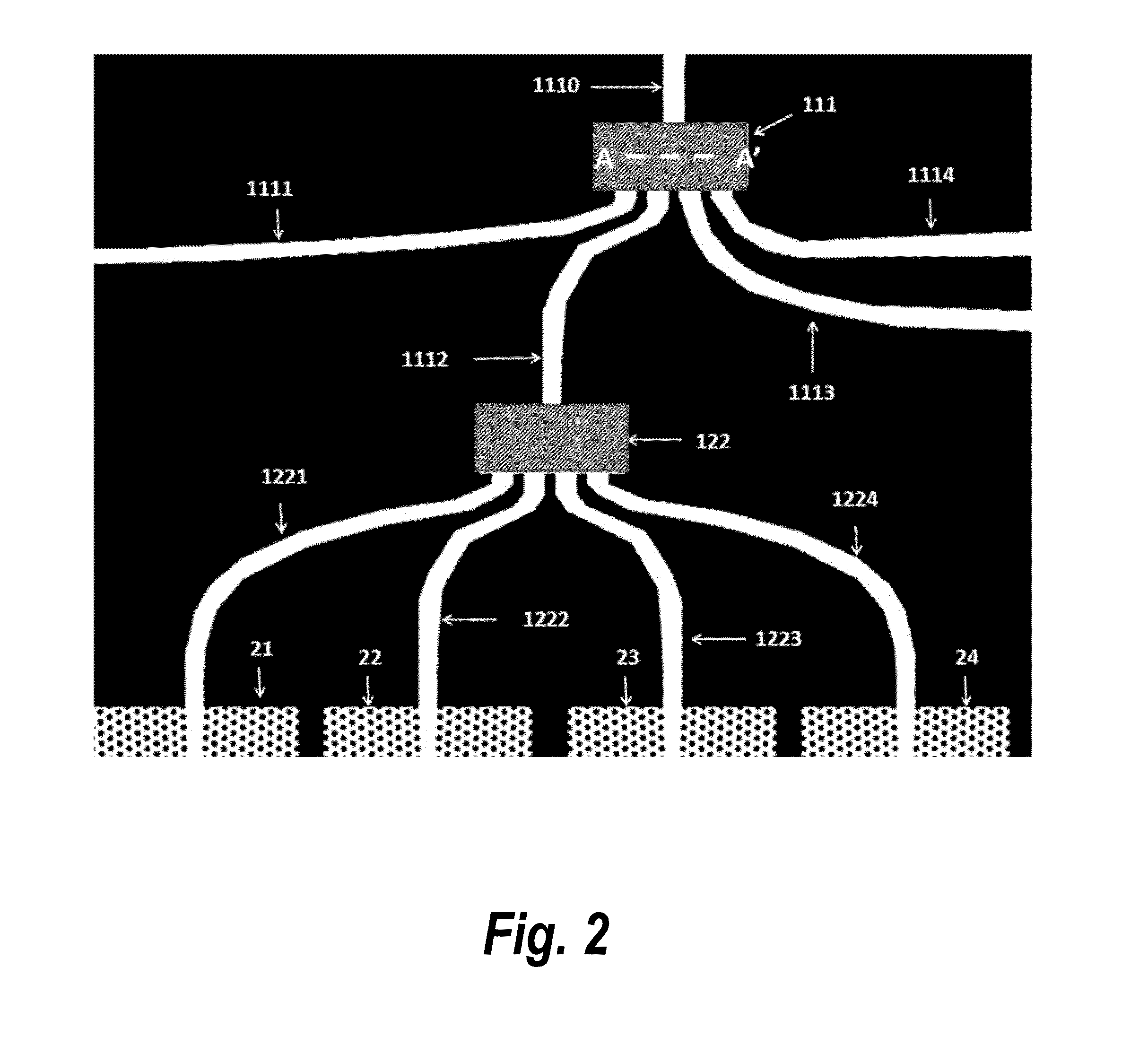
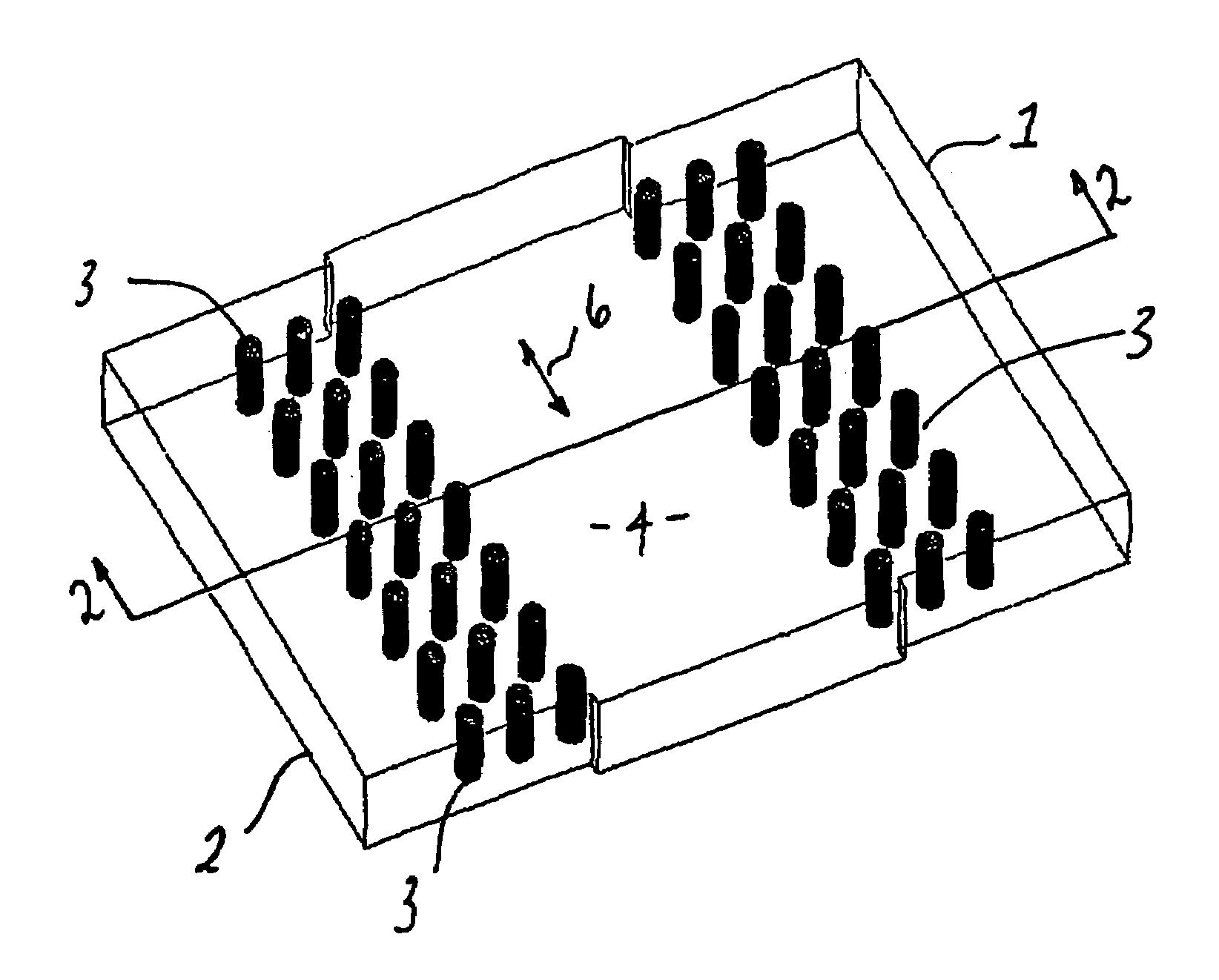
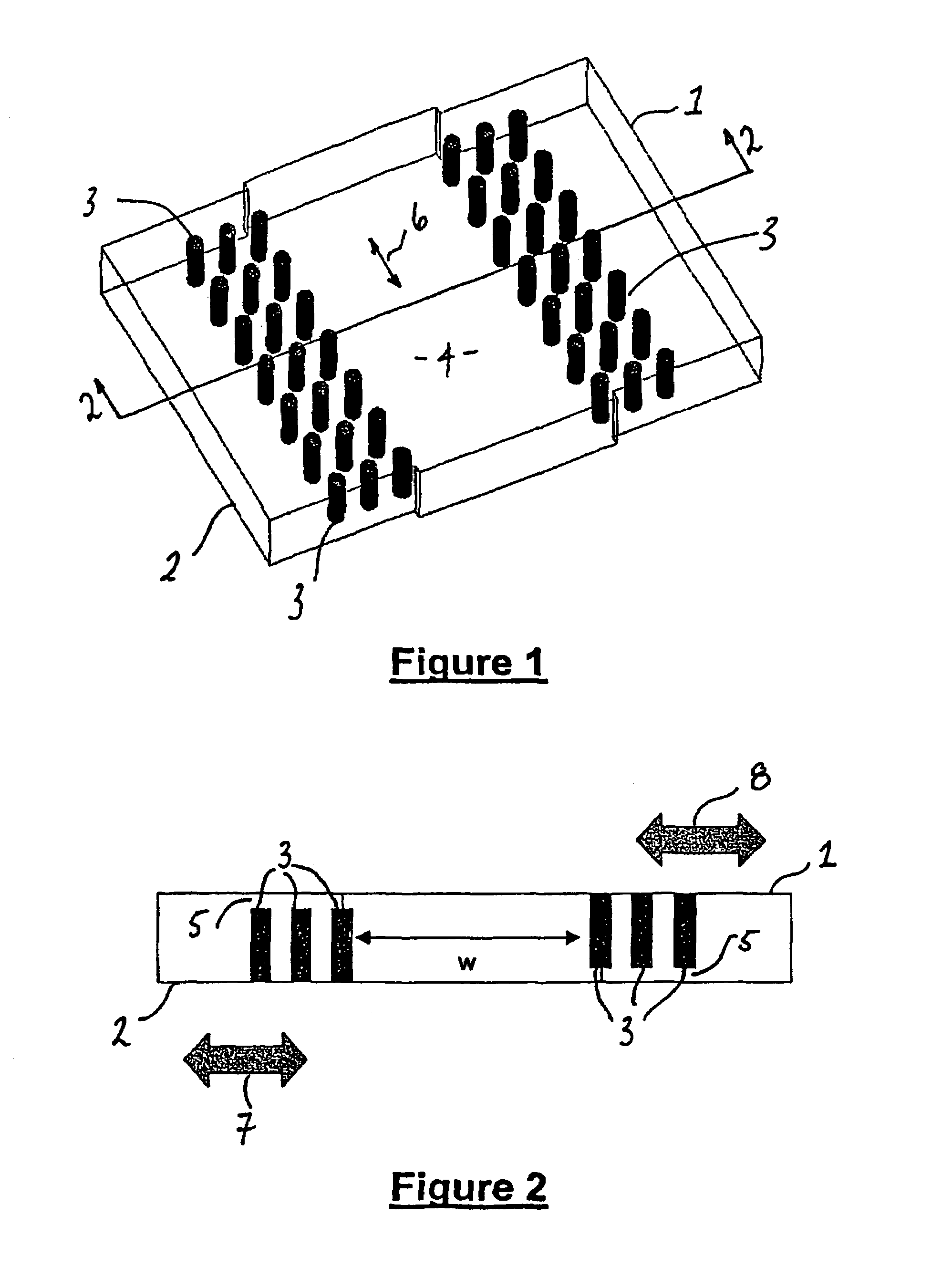
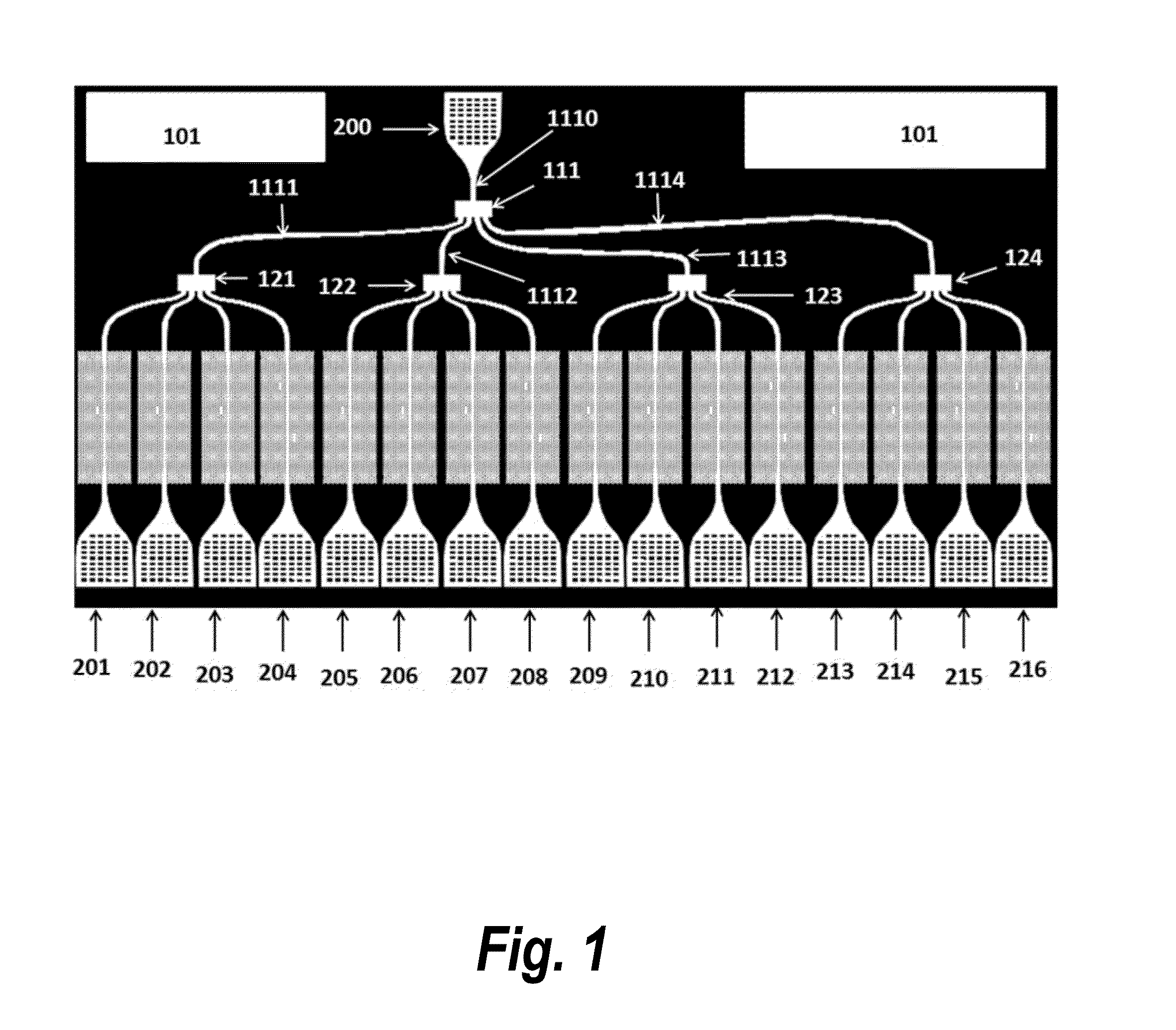
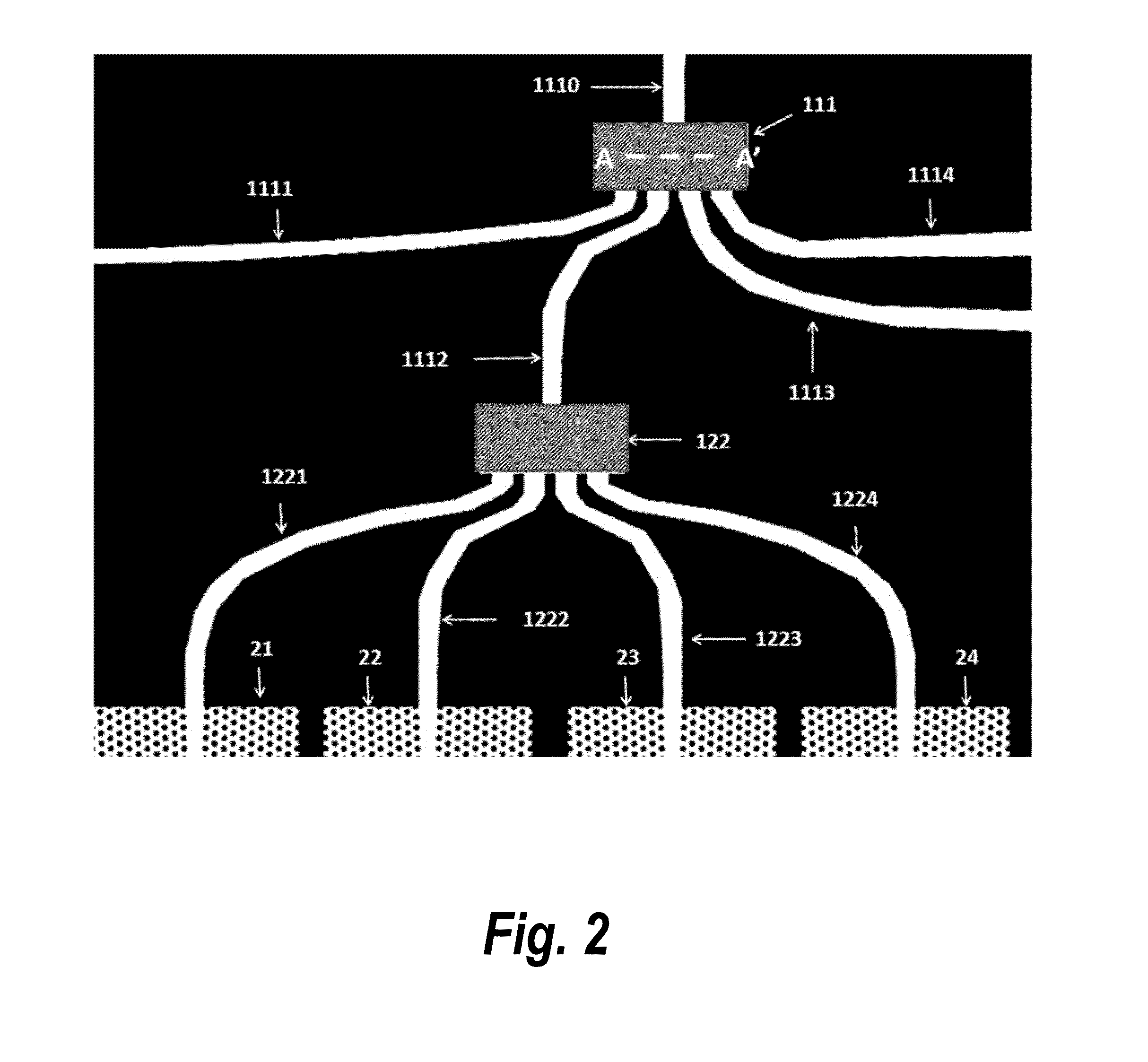
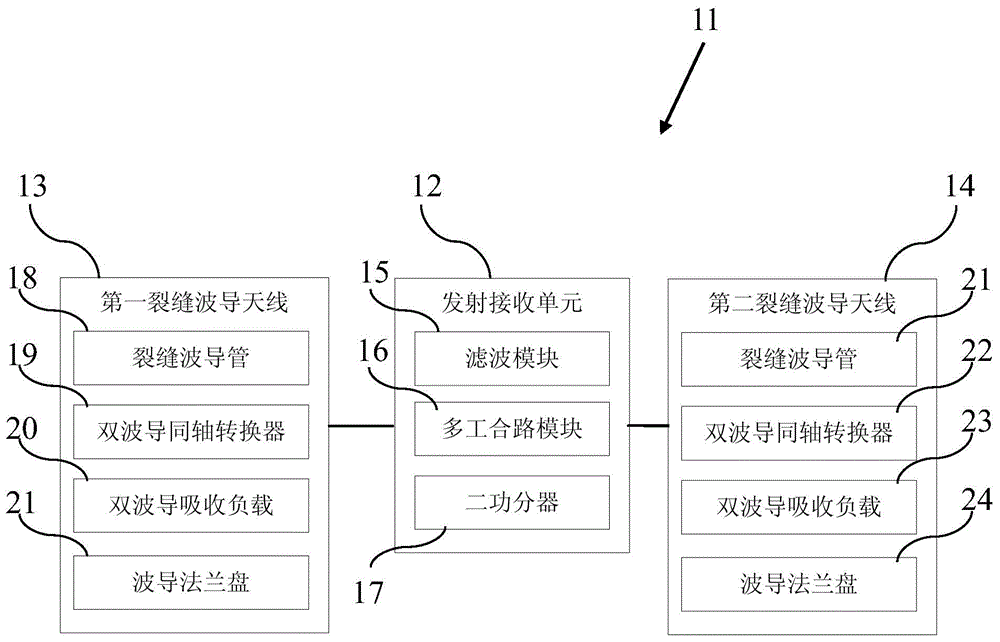
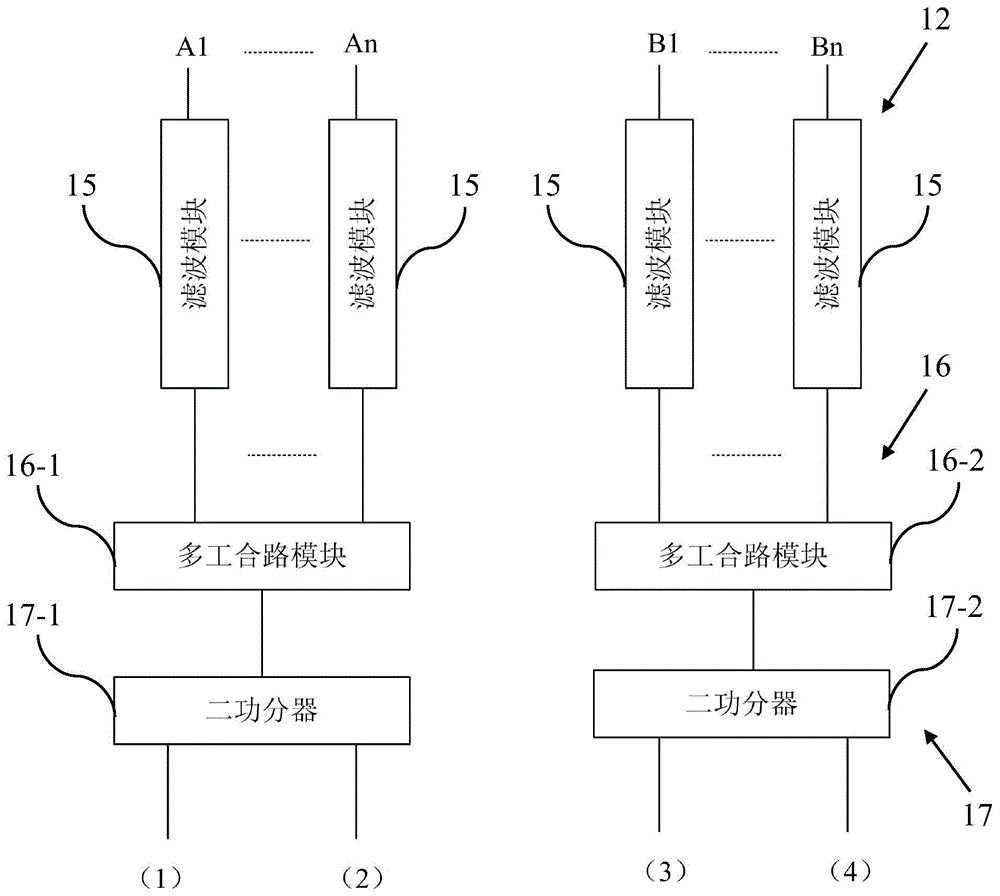
InactiveUS20050128028A1Minimize impactAvoid energy leakageLinear waveguide fed arraysDelay linesSlot-waveguideSlotted waveguide
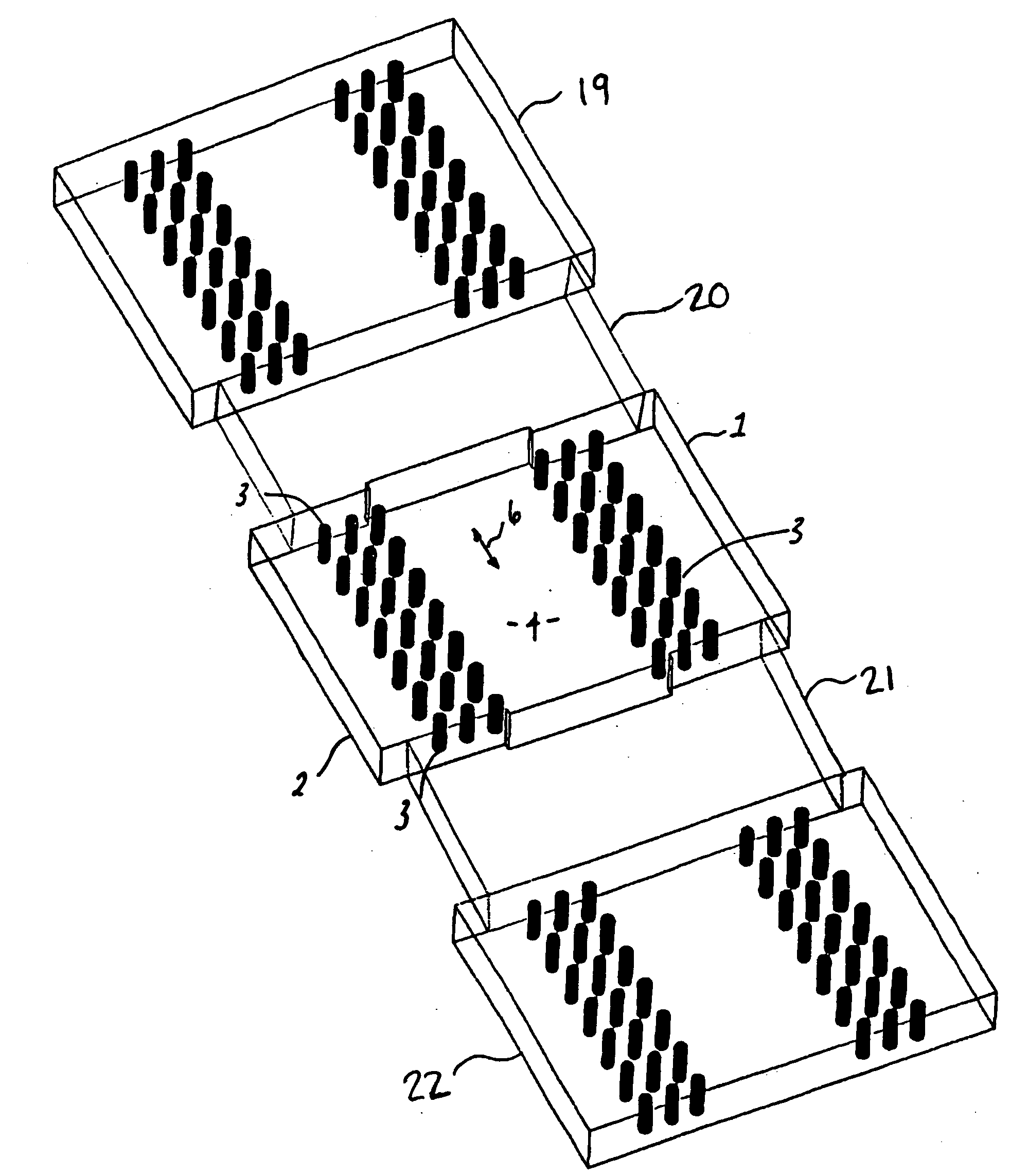
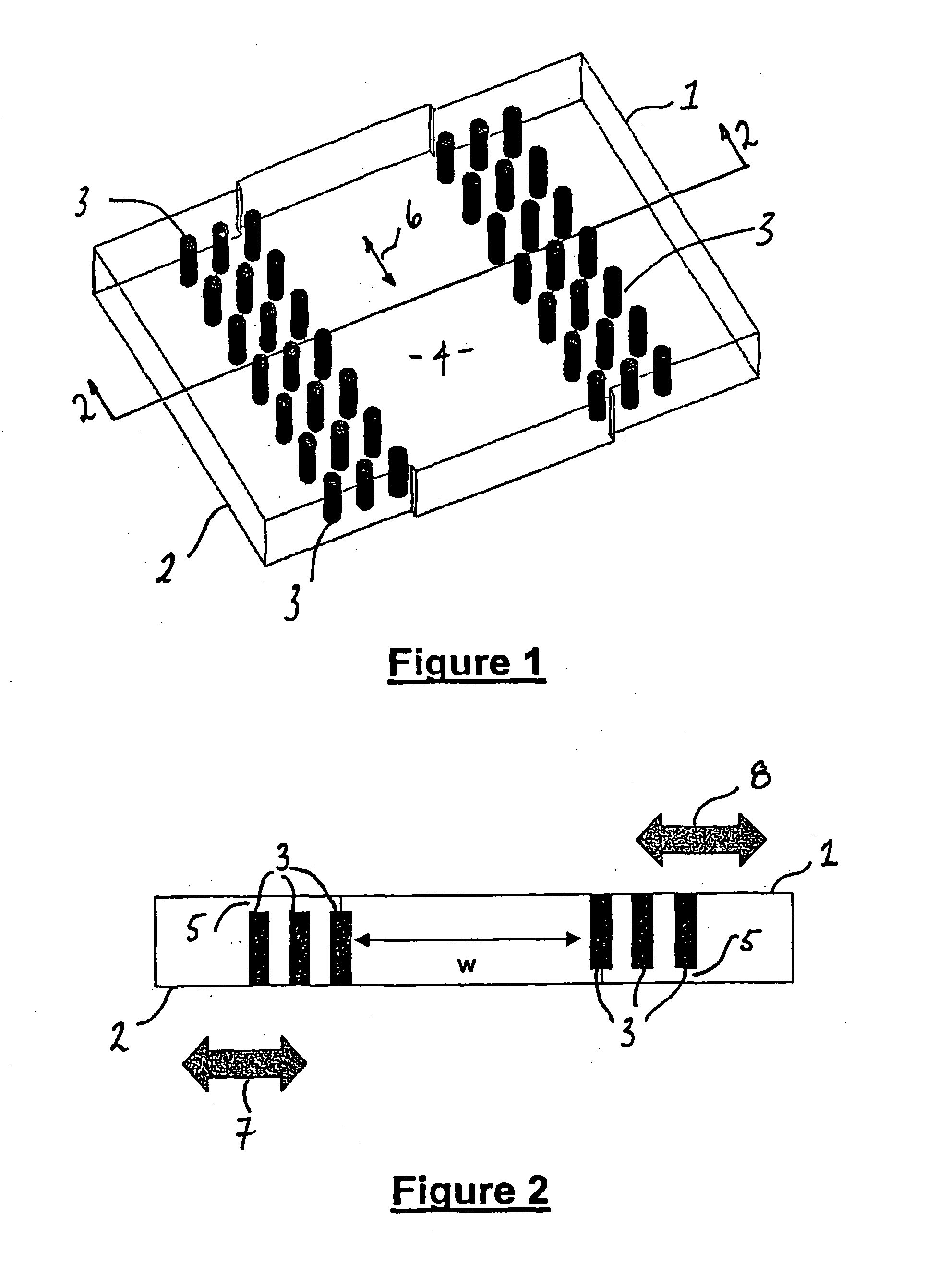
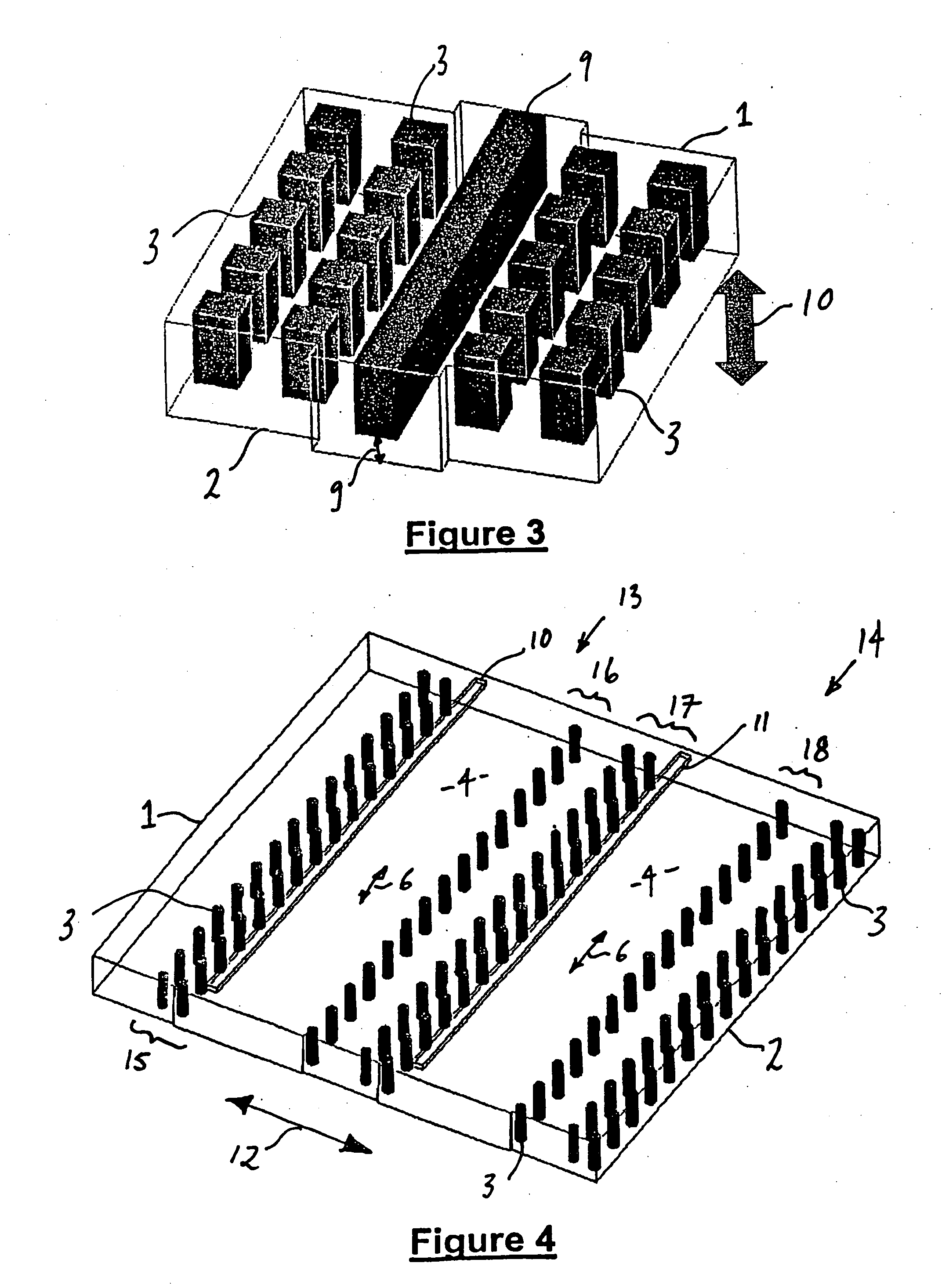
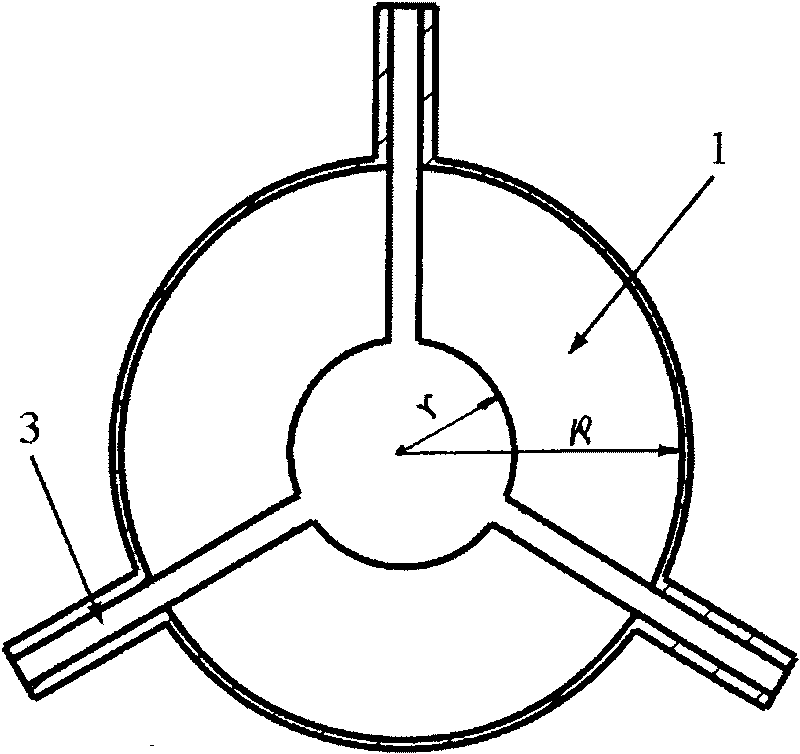
A waveguide structure including two parallels electrically conducting ground planes (1,2), each of which includes at least one row of spaced apart electrically conducting posts (3). The rows of posts are arranged substantially parallel to one another and the space bounded by the plates and posts defines a guided wave region (4) along which electromagnetic radiation may propagate. The posts are connected to only one of the planes so that there is no physical connection between the two ground planes (1,2). Actuating means may be connected to one or both of the ground planes to cause relative movement there between to thereby alter the electrical response of the waveguide. The direction of the relative movement may such that the distance between the rows of posts (3) is changed and / or the distance between the ground planes (1,2) is changed. Various device may utilize the described waveguide construction, including reconfigurable waveguide filters and antenna structures e.g. slotted waveguide arrays.
Owner:ERA PATENTS
Packaged chip for multiplexing photonic crystal waveguide and photonic crystal slot waveguide devices for chip-integrated label-free detection and absorption spectroscopy with high throughput, sensitivity, and specificity
ActiveUS20130005606A1Most efficientPrecise positioningRadiation pyrometryColor measuring devicesSlot-waveguidePhotonic crystal
Systems and methods for chip-integrated label-free detection and absorption spectroscopy with high throughput, sensitivity, and specificity are disclosed. The invention comprises packaged chips for multiplexing photonic crystal waveguide and photonic crystal slot waveguide devices. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:OMEGA OPTICS
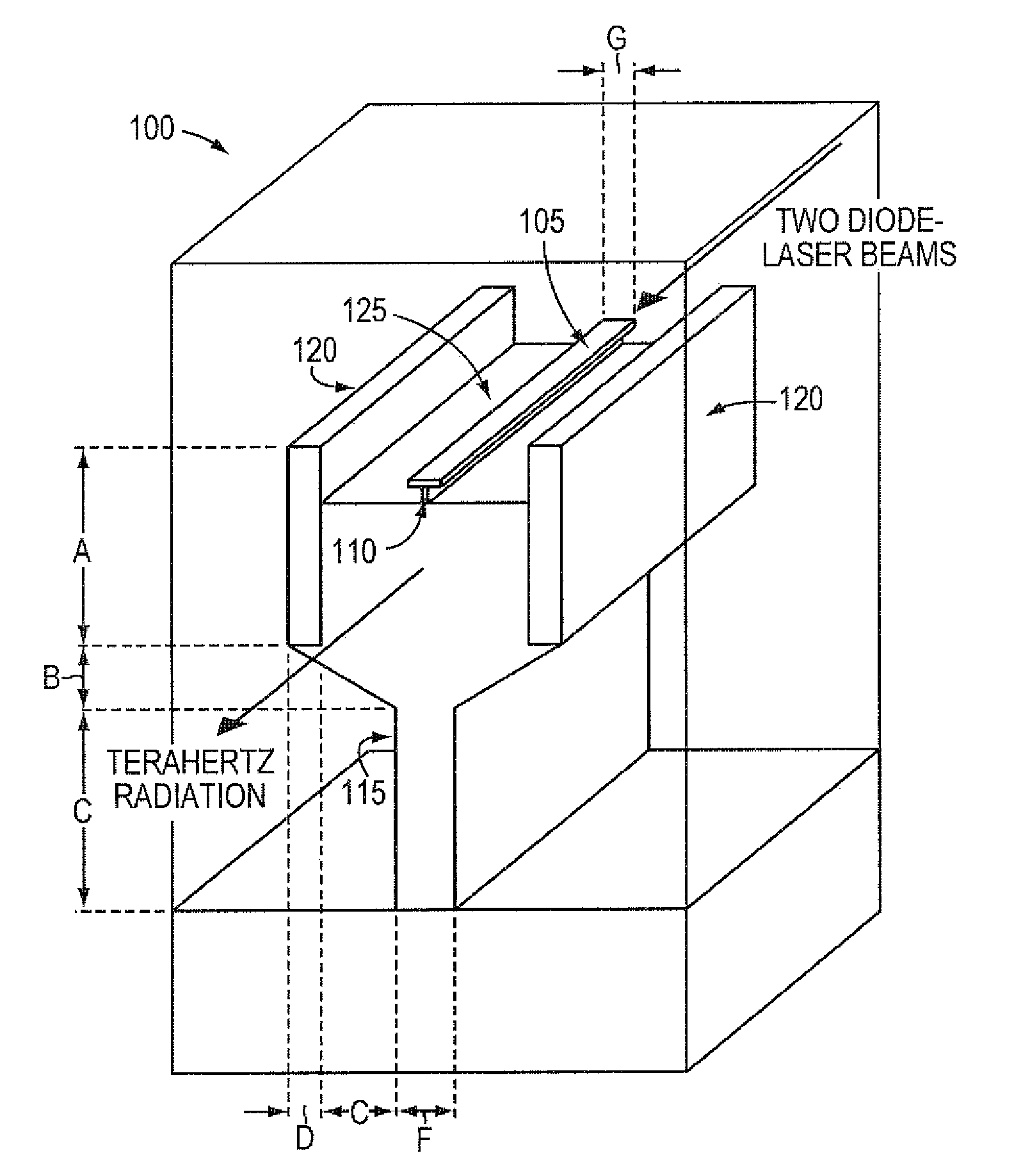
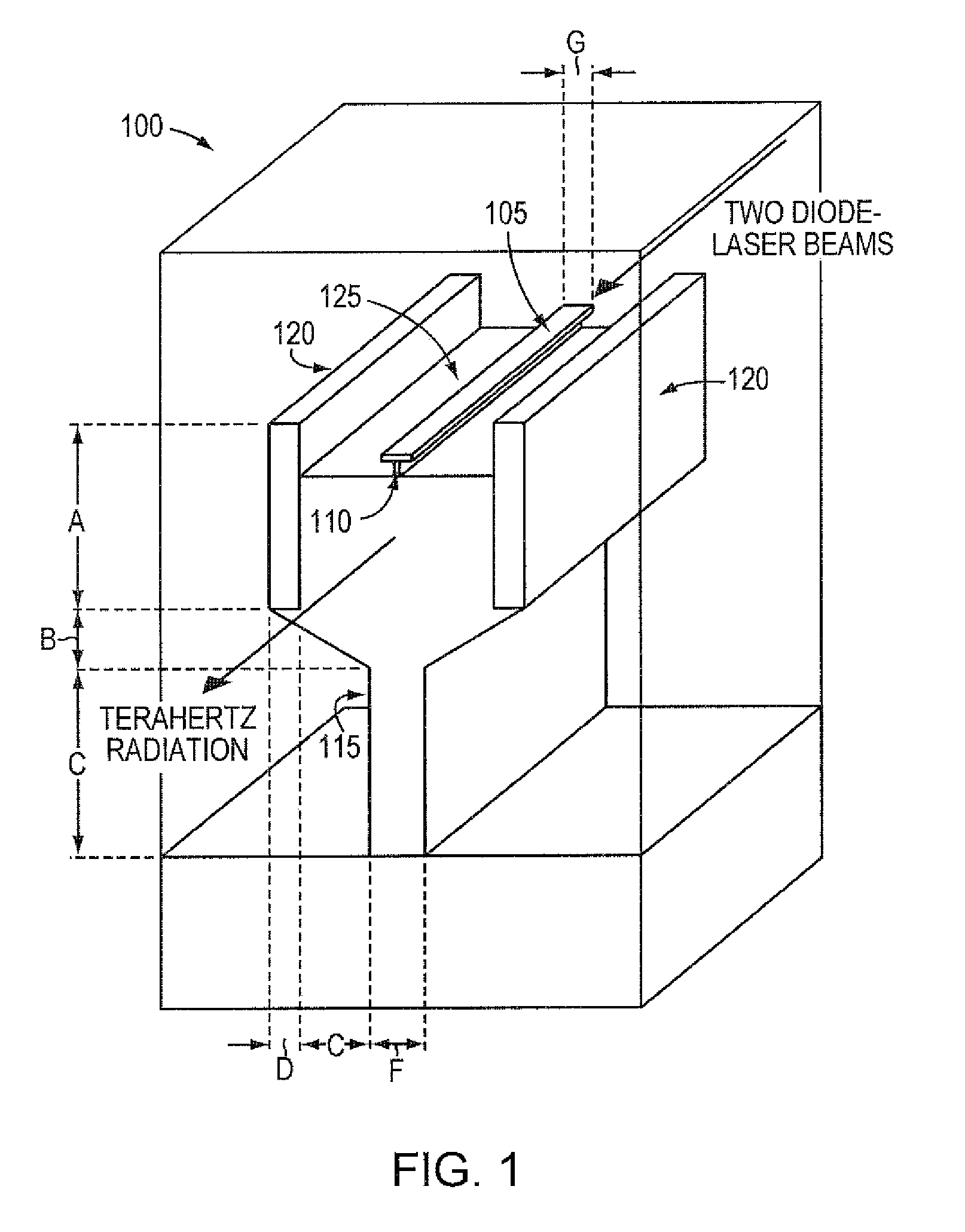
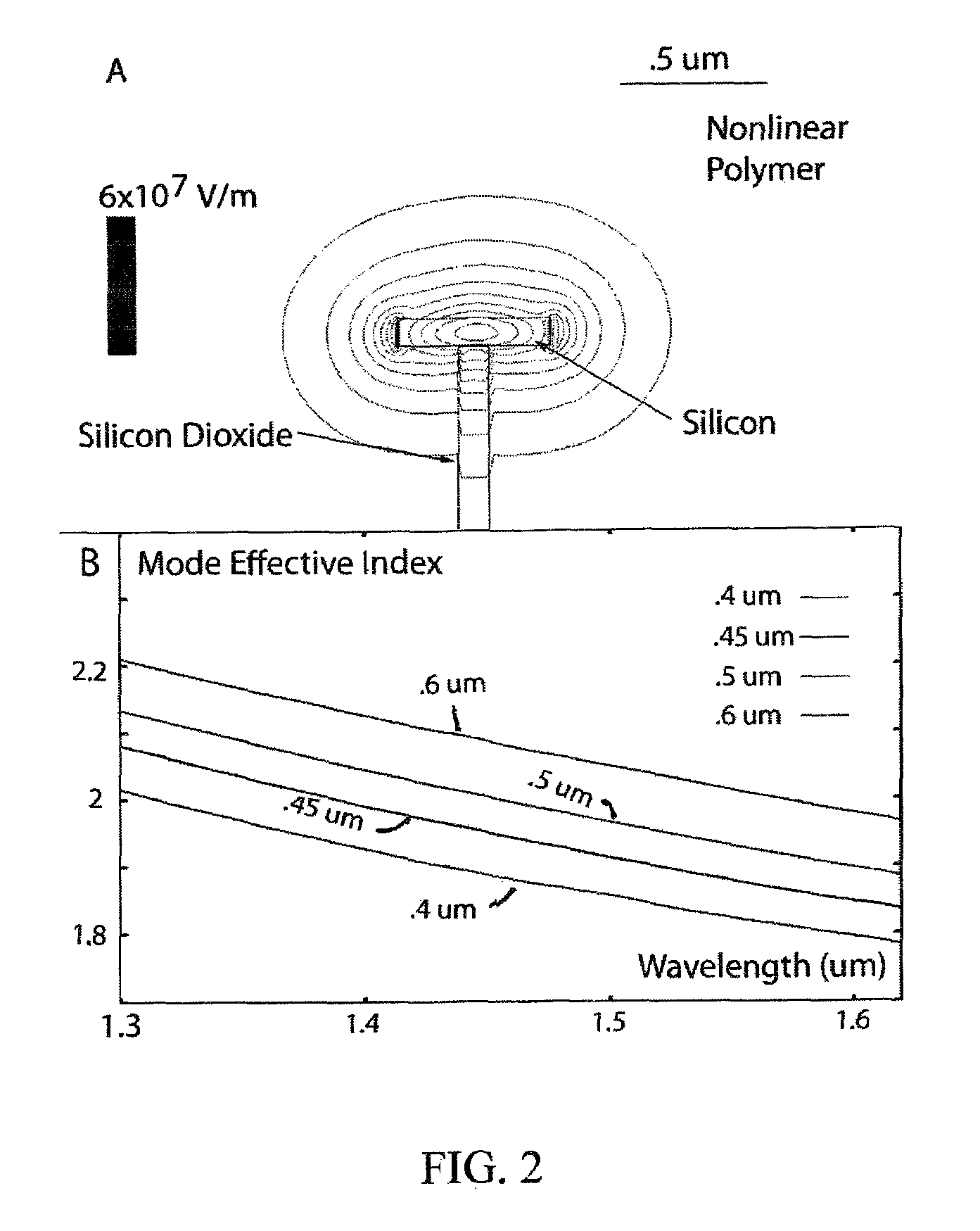
Low loss terahertz waveguides, and terahertz generation with nonlinear optical systems
InactiveUS7480434B2Solid masersOptical waveguide light guideTerahertz radiationNear infrared radiation
A silicon based source for radiation in the 0.5-14 Terahertz regime. This new class of devices will permit continuously tunable, milli-Watt scale, continuous-wave, room temperature operation, a substantial advance over currently available technologies. The Silicon Terahertz Generator (STG) employs a silicon waveguide for near infrared radiation, situated within a metal waveguide for Terahertz radiation. A nonlinear polymer cladding permits two near-infrared lasers to mix, and through difference frequency generation produces Terahertz output. The small dimensions of the design greatly increase the optical fields, enhancing the nonlinear effect. The design can also be used to detect Terahertz radiation.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
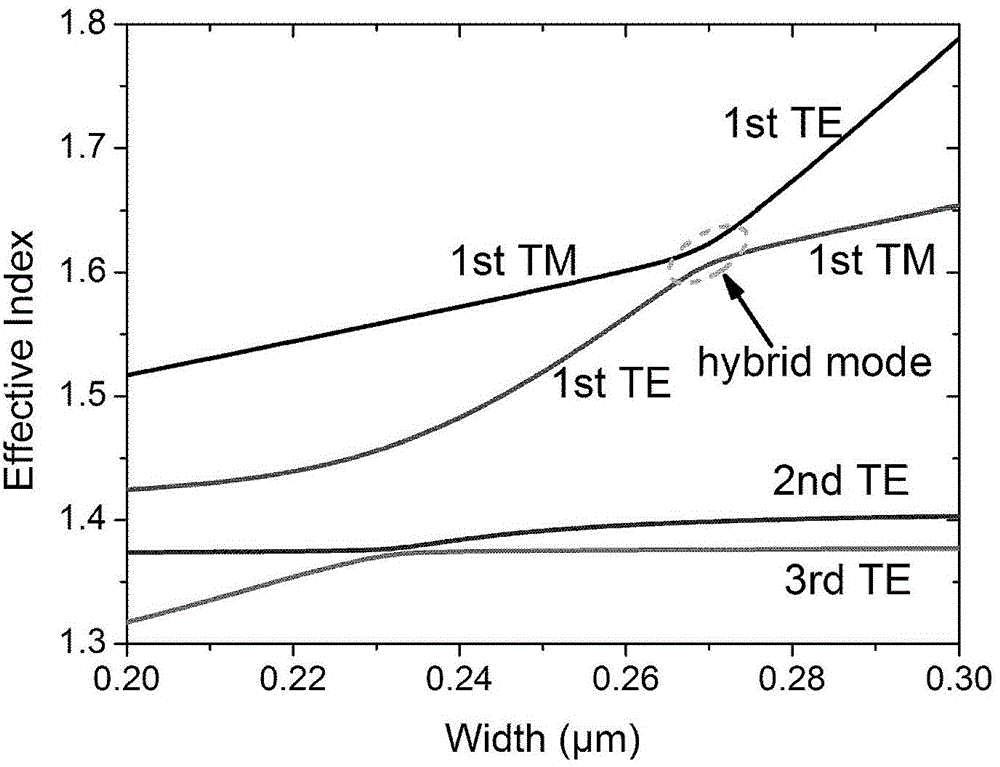
Polarization rotator based on asymmetric vertical slot waveguide
InactiveCN103336330ABreak symmetryEliminates the problem of precise alignmentOptical light guidesSlot-waveguideNon symmetric
The invention discloses a polarization rotator based on an asymmetric vertical slot waveguide, which comprises an incident end waveguide used for leading in external incident light, a mode conversion waveguide used for converting TE / TM (Transverse Electric / Transverse Magnetic) mode incident light into TM / TE (Transverse Magnetic / Transverse Electric) mode emergent light, and an emergent end waveguide used for leading out a TM / TE mode, wherein the incident end waveguide, the mode conversion waveguide and the emergent end waveguide are asymmetric slot waveguides. With the adoption of the structure, the symmetry of a material is broken longitudinally, and the symmetry of a geometrical dimension is broken transversely, so that intrinsic modes of specific waveguides are mixed modes; the two intrinsic mixed modes can be converted mutually; and mutual conversion between a TE mode and a TM mode can be achieved finally. The polarization rotator can convert a TE / TM mode into the TM / TE mode by once etching, so that the manufacturing difficulty of a device is reduced greatly.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Packaged Chip For Multiplexing Photonic Crystal Microcavity Coupled Waveguide And Photonic Crystal Slot Waveguide Devices For Chip-Integrated Label-Free Detection And Absorption Spectroscopy With High Throughput, Sensitivity, Specificity, And Wide Dynamic Range
ActiveUS20140140655A1Specificity of bindingHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansNanoopticsMicrofluidic channelWaveguide
Systems and methods for chip-integrated label-free detection and absorption spectroscopy with high throughput, sensitivity, and specificity are disclosed. The invention comprises packaged chips for multiplexing photonic crystal microcavity waveguide and photonic crystal slot waveguide devices. The packaged chips comprise crossing waveguides to prevent leakage of fluids from the microfluidic channels from the trenches or voids around the light guiding waveguides. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:OMEGA OPTICS
High-nonlinearity micro-ring waveguide optical device
InactiveCN103576413AEnhance nonlinear effectsLower the thresholdNon-linear opticsRidge waveguidesLogic gate
The invention relates to a micro-ring waveguide optical device capable of realizing all-optical signal processing by utilizing a high-nonlinearity effect, and aims to overcome the defect that nonlinear coefficients are insufficient when a conventional micro ring performs all-optical signal processing. The provided micro-ring waveguide optical device comprises a straight waveguide and a parallel growth micro ring on a substrate, wherein the micro ring is an annular resonant cavity; the ridge waveguide part of the micro ring adopts a parallel slot structure instead of a single ridge waveguide structure; and the straight waveguide is coupled with the micro ring. According to the micro-ring waveguide optical device, one parallel slot micro-ring waveguide structure is innovated; and when light is coupled into the parallel slot micro-ring waveguide structure, the slot waveguide structure can well limit a light field, the light intensity of resonance light is enhanced greatly due to the resonance effect of the micro ring, accordingly, various nonlinear effects of the micro ring are enhanced, the threshold value is reduced, the efficiency is improved, and the device can be applied to the all-optical signal processing fields such as optical frequency comb, wavelength conversion, logic gate, format conversion and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Light emitting slot-waveguide device
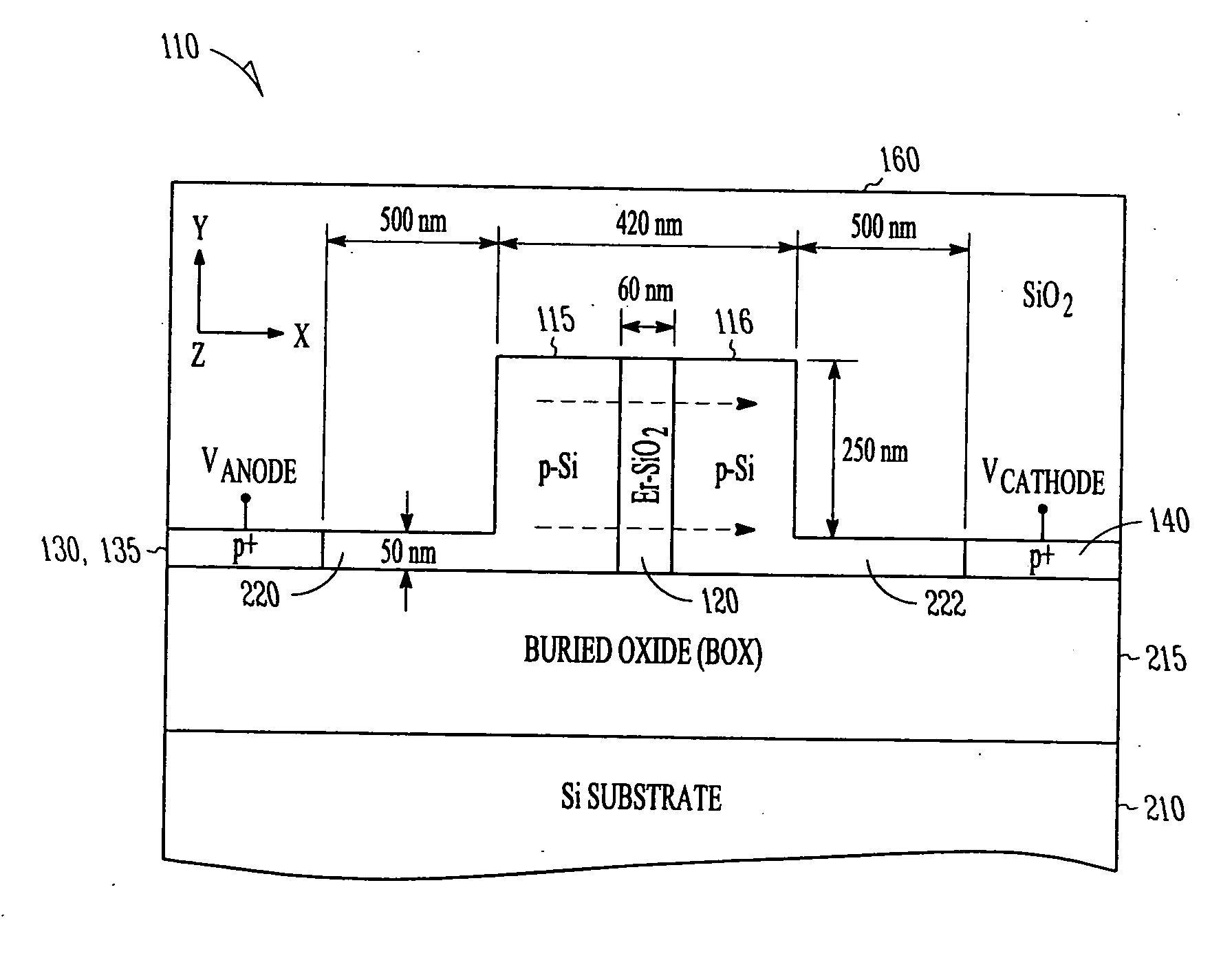
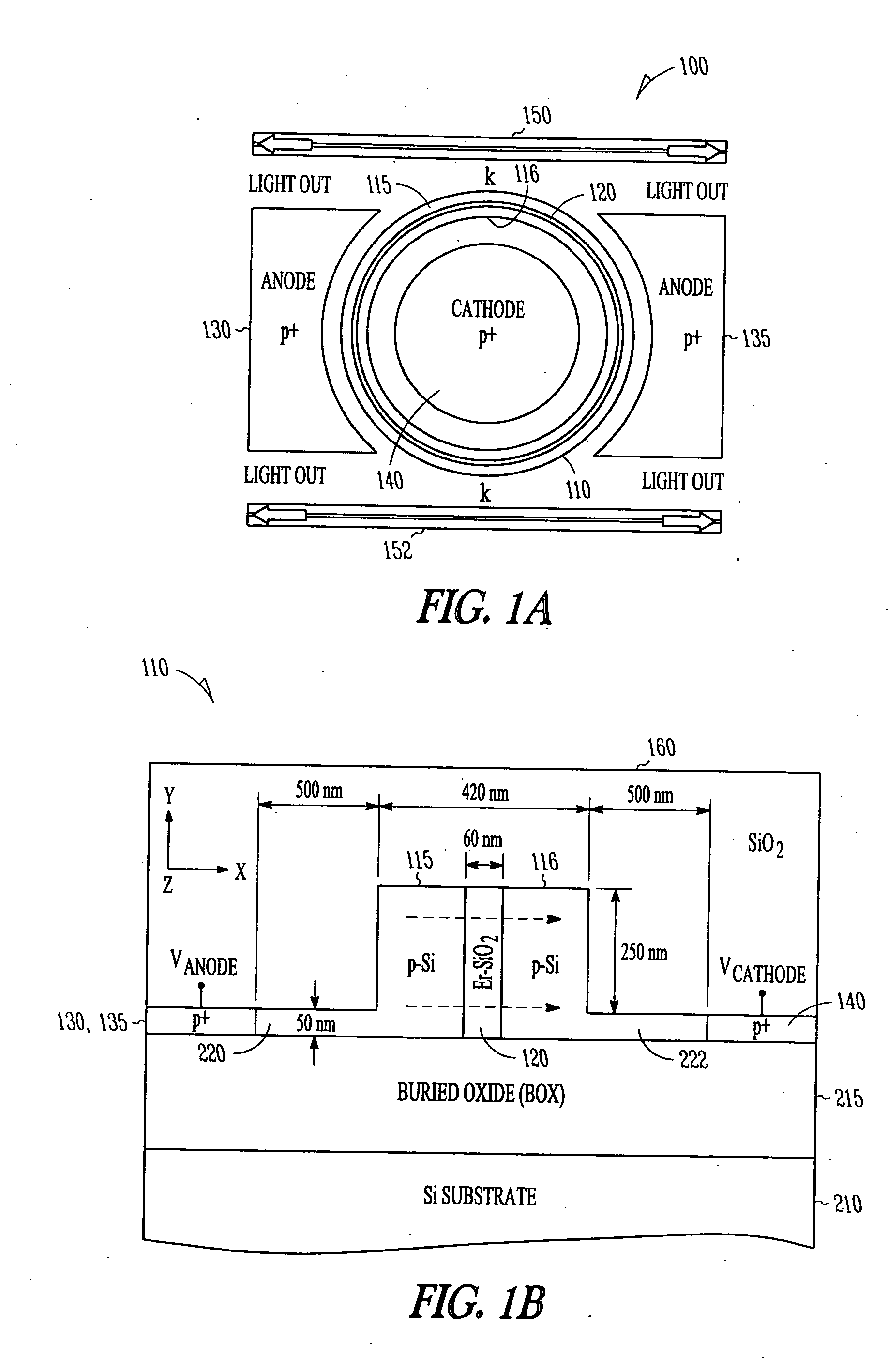
An electroluminescent material slot waveguide generates light in response to current injection. In one embodiment, the waveguide is formed as part of an optical resonator, such as ring resonator waveguide or distributed Bragg reflector with an anode and cathode for electrical stimulation. A compact, electrically-driven resonant cavity light emitting devices (RCLED) for Si microphotonics may be formed. Several different rare-earth ions, such as erbium, terbium and ytterbium, can be used to dope SiO2 in order to emit light at different wavelengths.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Mode transformers for low index high confinement waveguides
The mode transforming structure includes a first waveguide structure. A slot waveguide region is coupled to the first waveguide structure. The slot waveguide region includes one or more complementary tapered pairs so near lossless transforming between the first waveguide structure and the slot waveguide region occurs so as to allow optical modes to be transferred between the first waveguide and the slot waveguide region.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
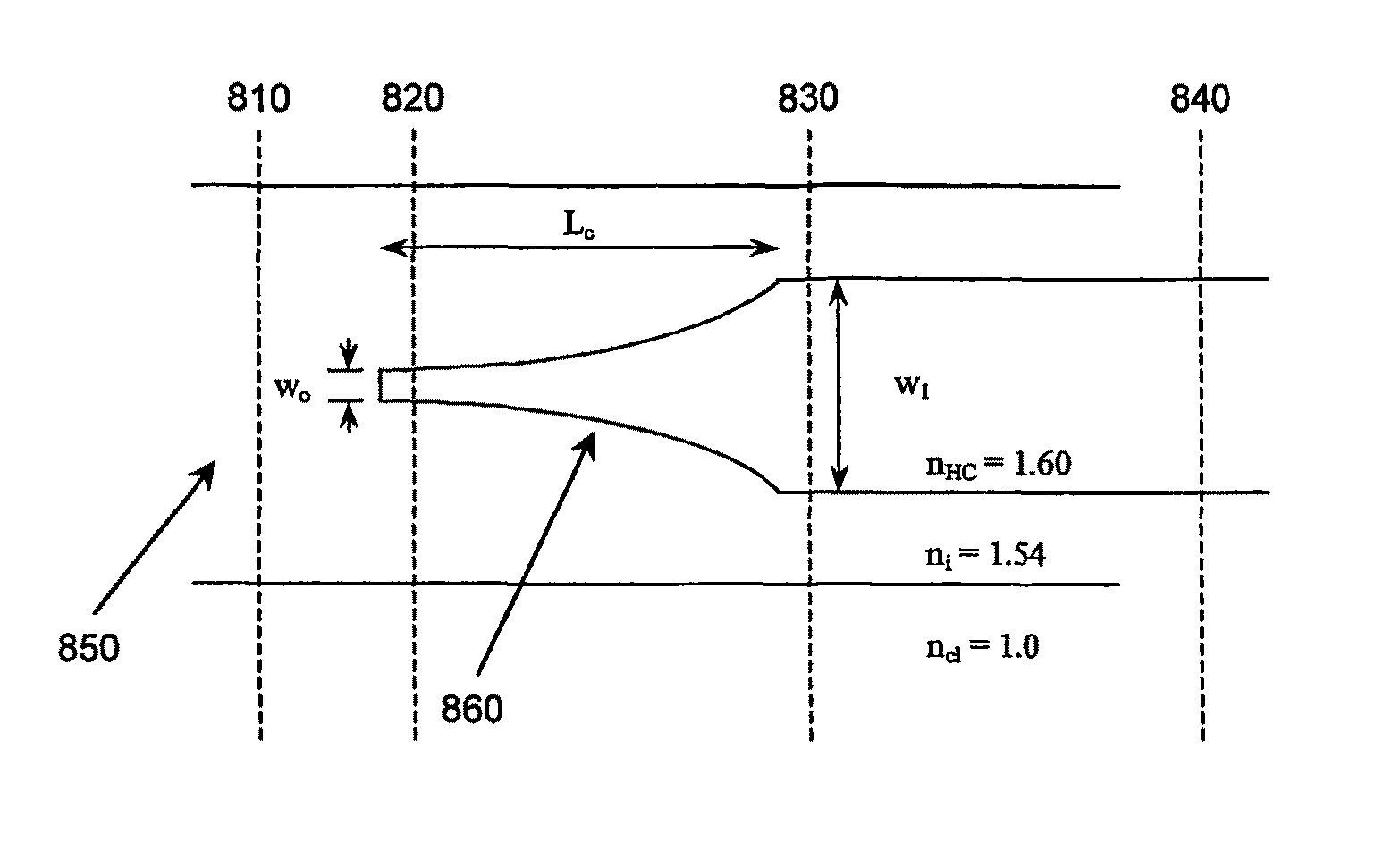
High efficiency optical mode transformer for matching a single mode fiber to a high index contrast planar waveguide
The present invention includes a device and a method for fabricating a device that is an optical power mode transformer that accepts light in a mode transformation direction where the transformer is attached to or embedded in a semiconductor microchip and includes a first single or multimode optical input (SM) waveguide including a first core surrounded by a cladding, and, a second high contrast index grade (HC) waveguide including a second core having a tapered region and surrounded by said cladding, a portion of the tapered region of the core being embedded within the first optical input waveguide region with an embedded length sufficient for efficient light transfer from the first input waveguide to the said second waveguide wherein the embedded portion of the tapered region is fully surrounded by the first input waveguide along an axial and radial cross-section of the second waveguide in the mode transformation direction. In this manner, it is possible that the long (SM) waveguide eventually actually acts as a cladding for the (HC) waveguide.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
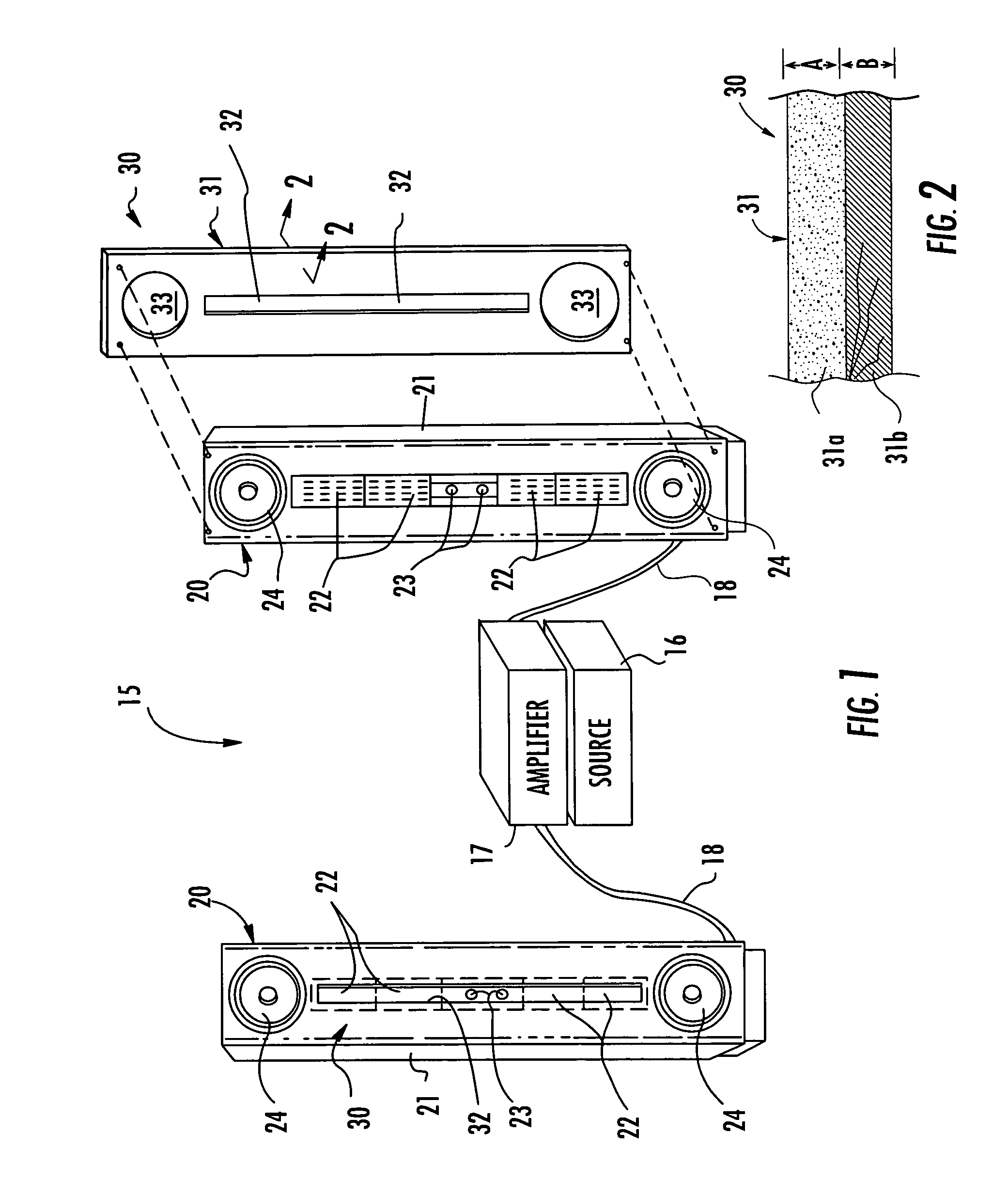
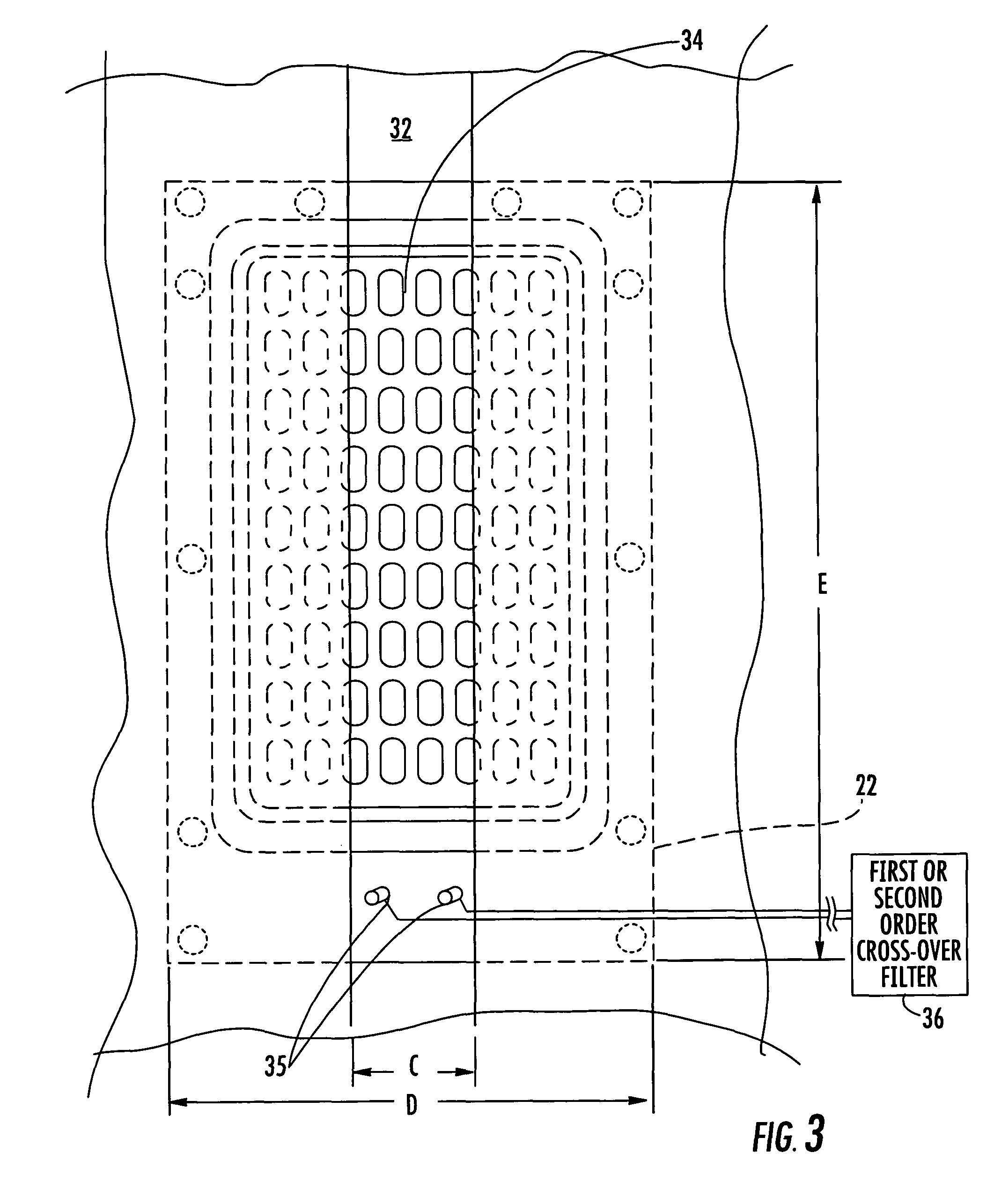
Loudspeaker including slotted waveguide for enhanced directivity and associated methods
InactiveUS7835537B2Improve directivityFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsSlot-waveguideSlotted waveguide
A loudspeaker may include a baffle, a planar diaphragm transducer carried by the baffle and having a front surface for radiating acoustic energy therefrom, and a slotted waveguide adjacent the front surface of the planar diaphragm transducer. The planar diaphragm transducer may be operable to a desired high frequency, and the slotted opening may have a width not substantially greater than a wavelength corresponding to the desired high frequency. For example, for a desired high frequency of about 20 KHz, the slotted opening may have a width not greater than about two-thirds of an inch. Accordingly, the loudspeaker including the slotted waveguide may provide nearly constant horizontal directivity over a large angle. In another embodiment, the loudspeaker may include a conical diaphragm transducer with a slotted waveguide adjacent its front surface.
Owner:CHENEY BRIAN E
Waveguide and slotted antenna array with moveable rows of spaced posts
InactiveUS7142165B2Minimize impactAvoid energy leakageLinear waveguide fed arraysDelay linesSlot-waveguideSlotted waveguide
A waveguide structure including two parallels electrically conducting ground planes (1,2), each of which includes at least one row of spaced apart electrically conducting posts (3). The rows of posts are arranged substantially parallel to one another and the space bounded by the plates and posts defines a guided wave region (4) along which electromagnetic radiation may propagate. The posts are connected to only one of the planes so that there is no physical connection between the two ground planes (1,2). Actuating means may be connected to one or both of the ground planes to cause relative movement there between to thereby alter the electrical response of the waveguide. The direction of the relative movement may such that the distance between the rows of posts (3) is changed and / or the distance between the ground planes (1,2) is changed. Various device may utilize the described waveguide construction, including reconfigurable waveguide filters and antenna structures e.g. slotted waveguide arrays.
Owner:ERA PATENTS
Waveguide crescent slot array for low-loss, low-profile dual-polarization antenna
A low-loss, low-profile dual-polarization slotted waveguide antenna includes one or more waveguides having a characteristic wavelength. Radiation apertures comprised of a waveguide slot pairs are formed in each or the waveguides of the antenna. Each waveguide slot pair includes a first waveguide slot and a second waveguide slot which are configured for inducing a circularly polarized (CP) radiated field in the waveguide. The waveguide slots of each waveguide slot pair may be generally crescent-shaped and spaced a distance of at least approximately one-fourth of the characteristic wavelength from each other. The waveguide slots may further be positioned for allowing the antenna to receive and / or radiate both left-hand and right-hand circularly polarized fields (LHCP and RHCP) and for providing control of the sense of a circularly polarized (CP) field radiated by the antenna by changing the direction of incidence of an electromagnetic source wave propagated in the waveguide.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Flat scanning antenna for a terestrial mobile application, vehicle having such an antenna, and satellite telecommunication system comprising such a vehicle
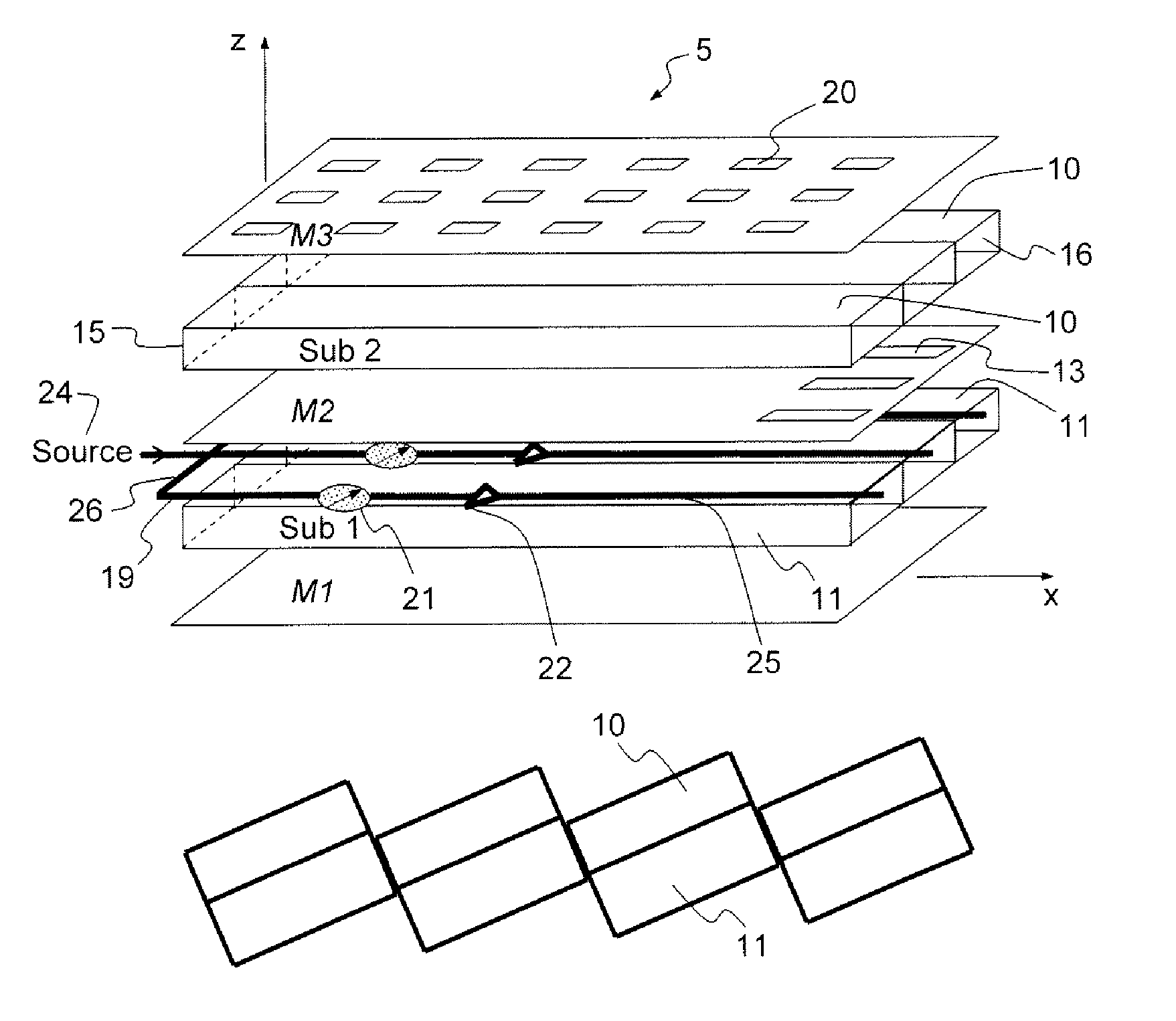
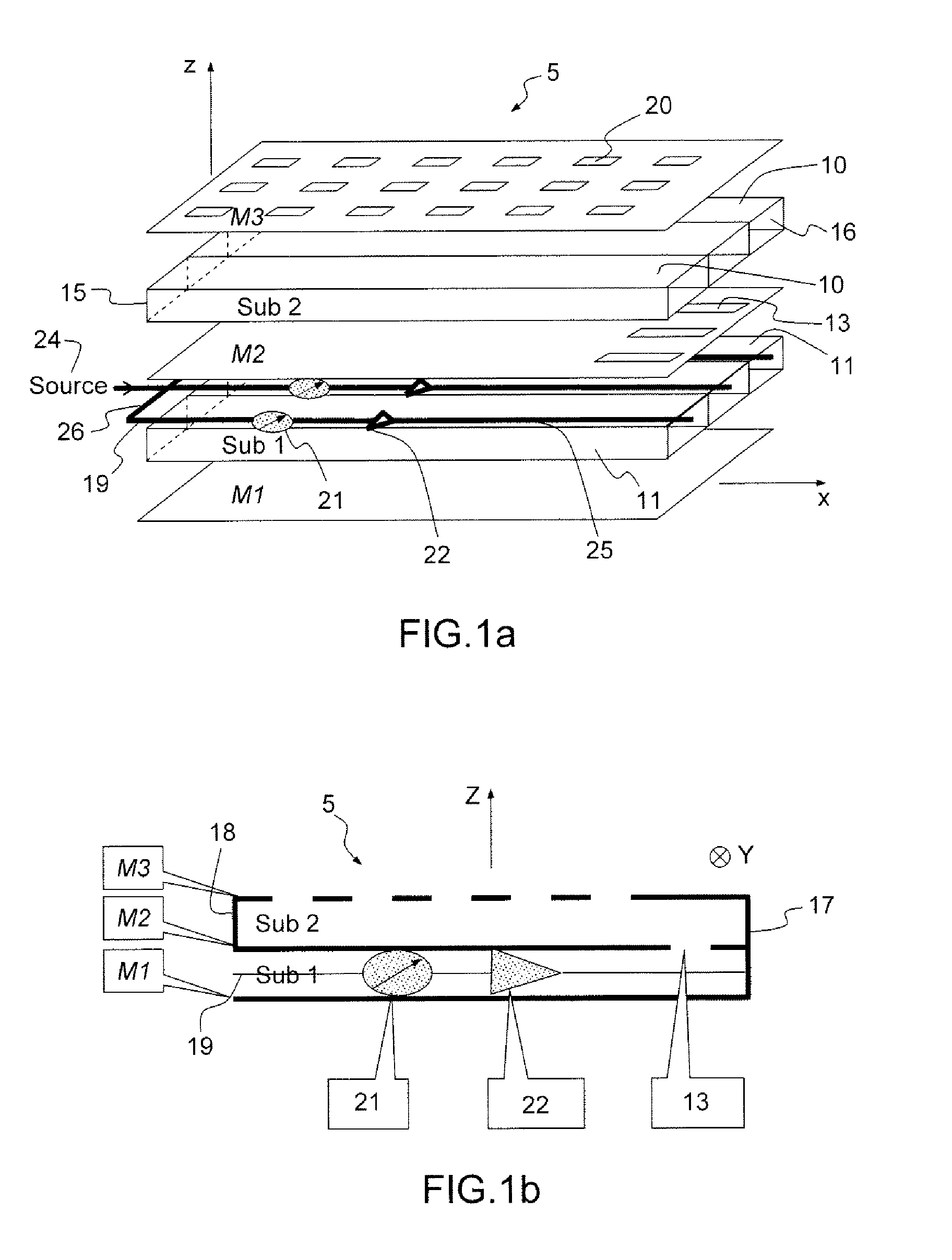
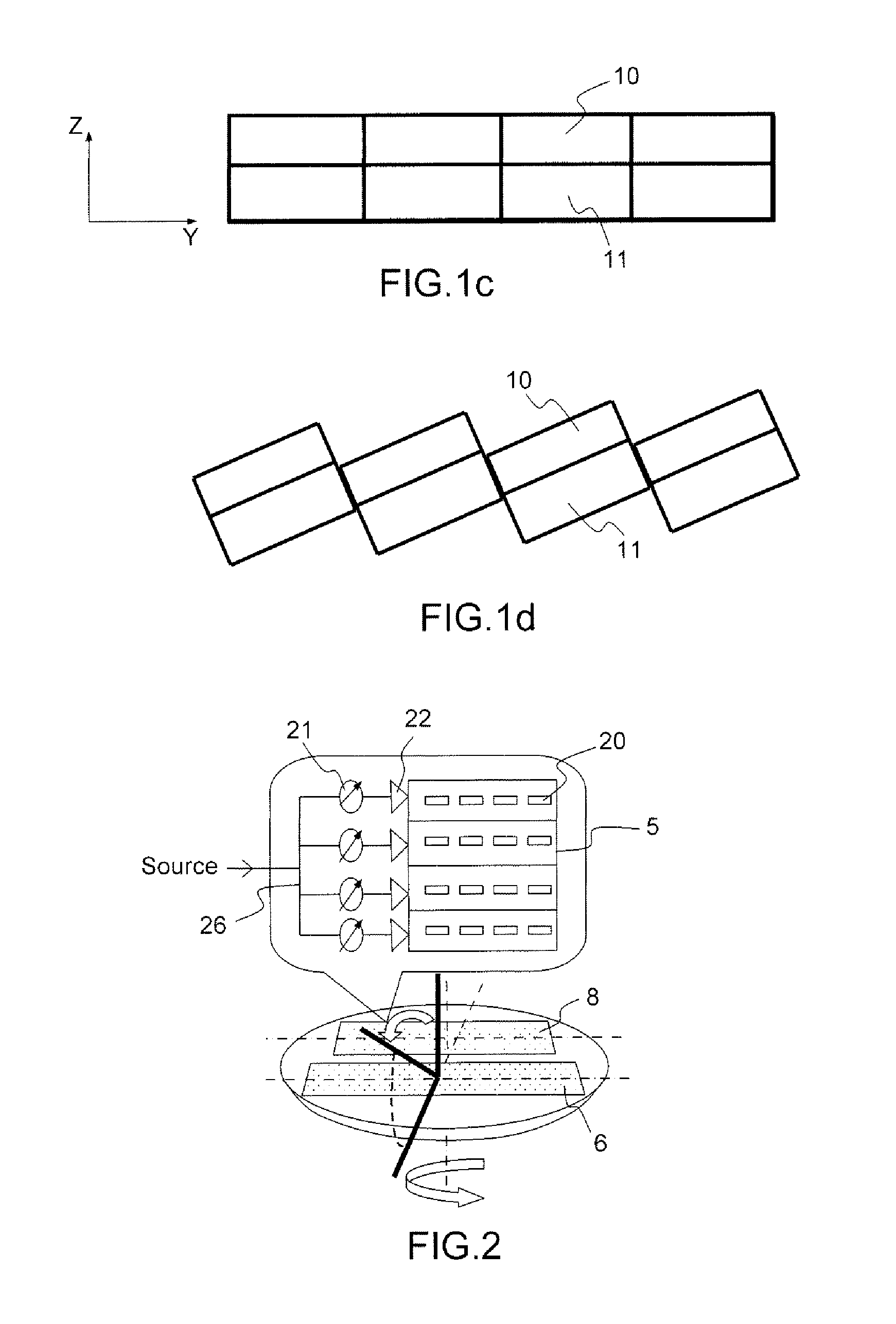
InactiveUS8976072B2Easy to implementLow costAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesLinear waveguide fed arraysSlot-waveguideSlotted waveguide
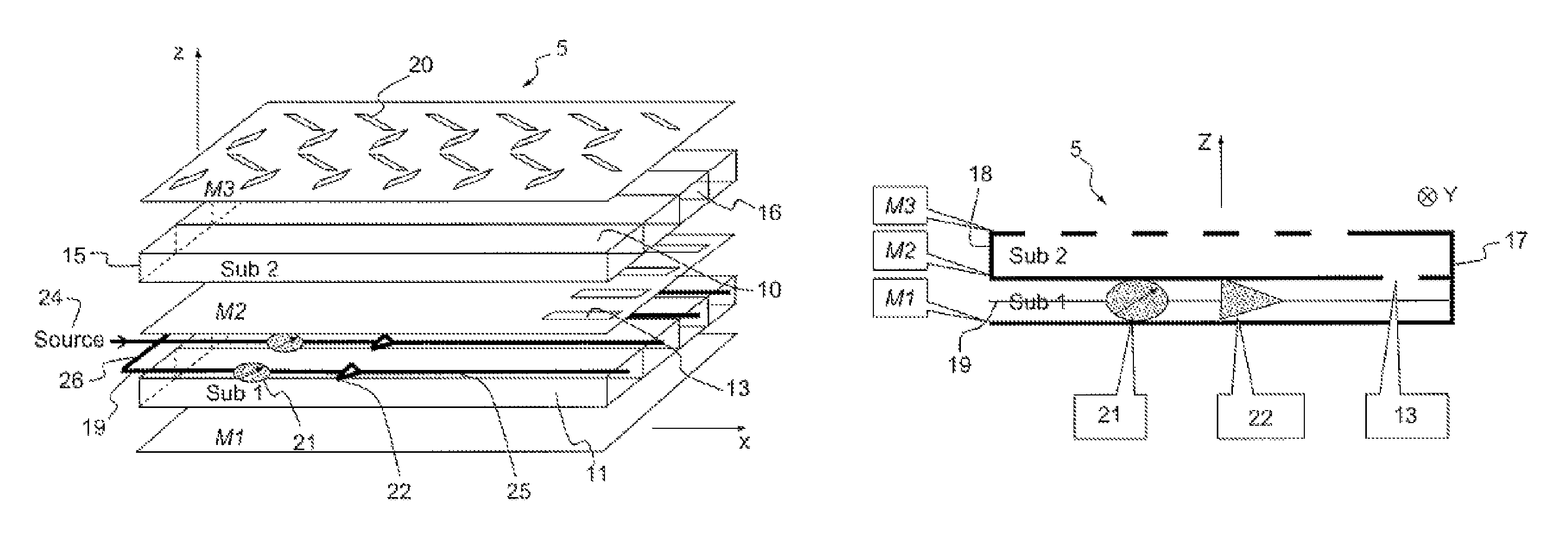
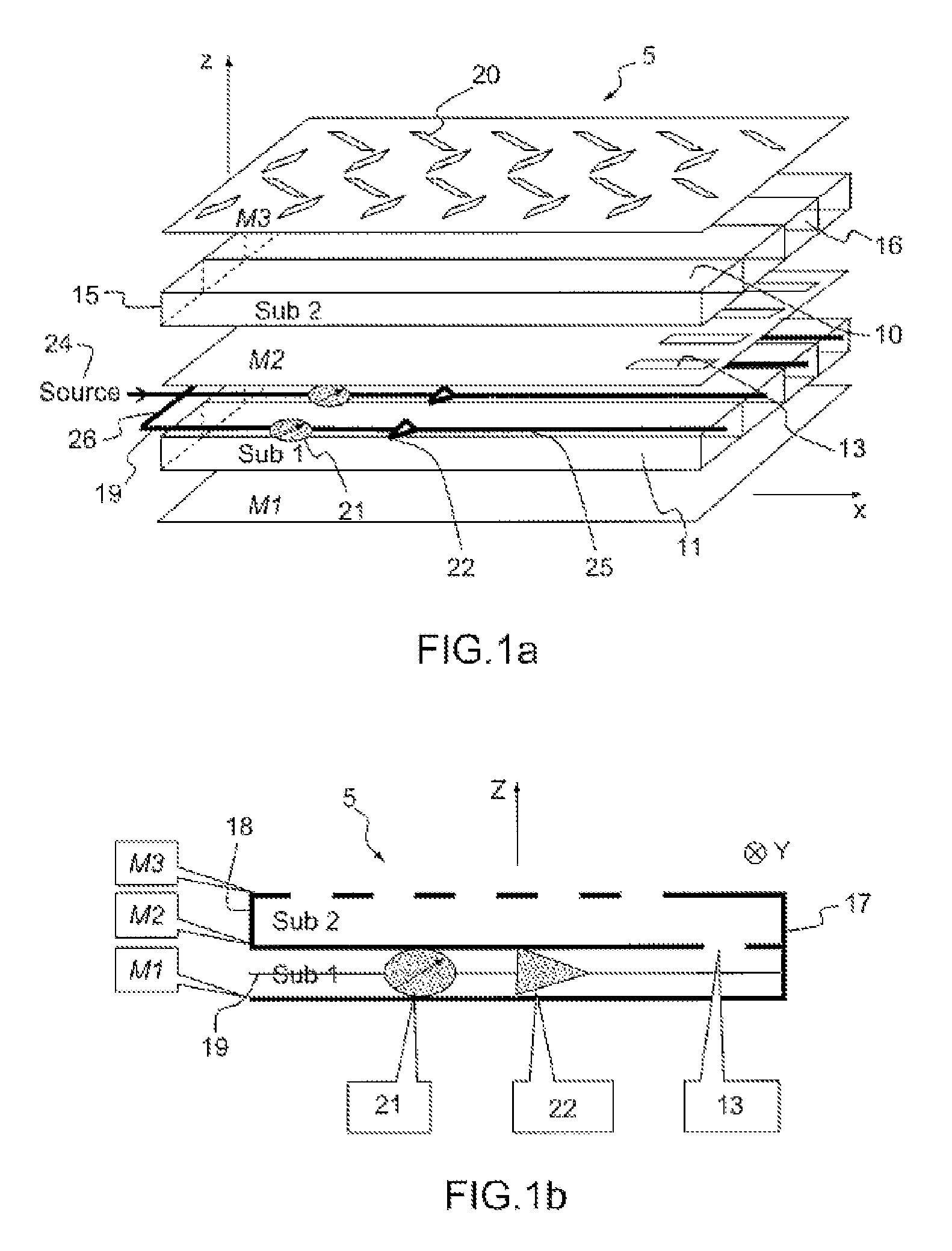
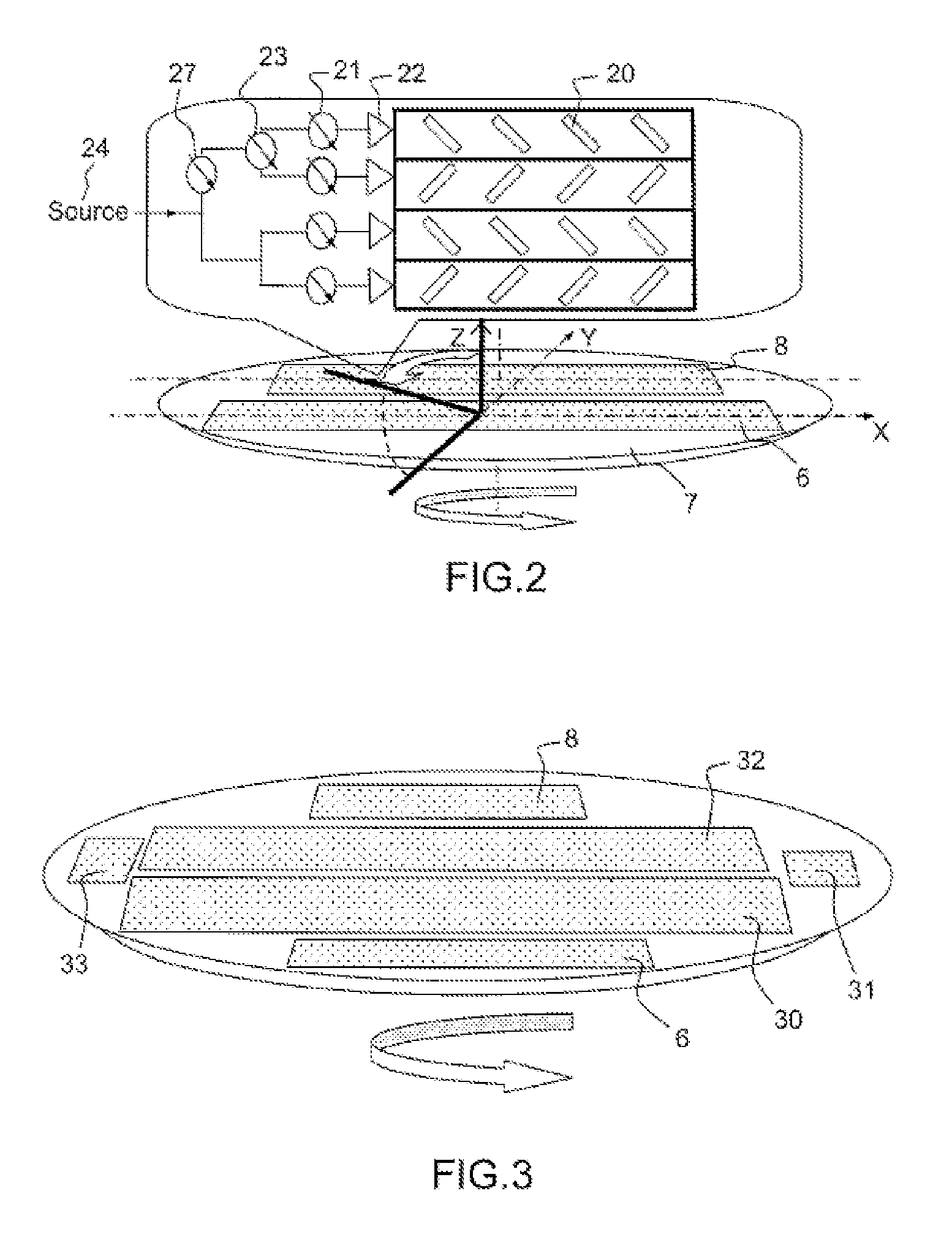
A flat scanning antenna comprises at least one slotted waveguide array comprising two dielectric substrates, one superposed above the other. The two substrates comprise the same number of waveguides, which are in mutual correspondence and communicate between them, pairwise, via corresponding coupling slots. Each waveguide of the upper substrate further includes a plurality of radiating slots, all the radiating slots being mutually parallel and oriented in the same direction and each waveguide of the lower substrate includes an individual internal supply circuit comprising an individual phase-shift / amplification electronic circuit.
Owner:THALES SA
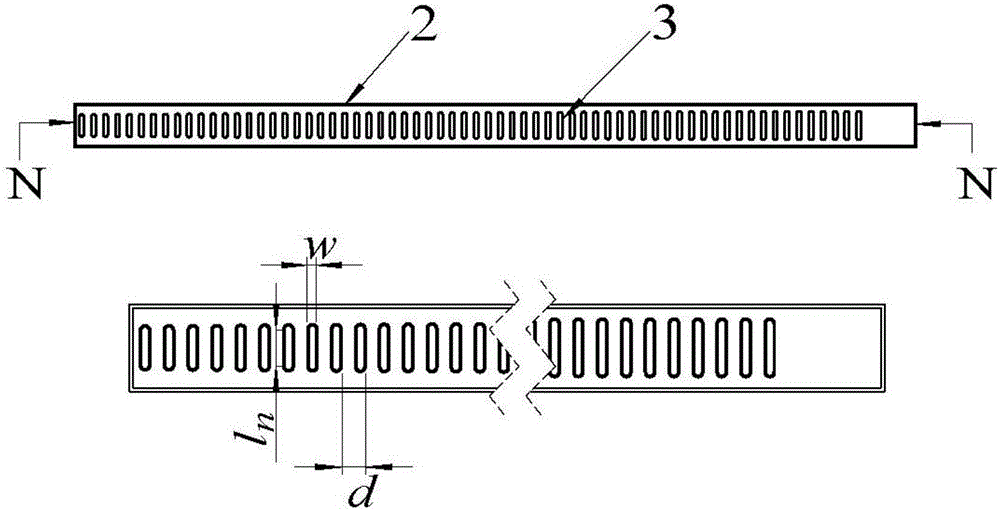
One-dimensional waveguide narrow slot antenna capable of scanning
ActiveCN103326125AUniform radiationSimple structureWaveguide mouthsRadiating element housingsSlot-waveguideBeam scanning
The invention discloses a one-dimensional waveguide narrow slot antenna capable of scanning in order to solve the problems that an existing waveguide narrow slot array antenna unit is not even in radiation, difficult to achieve beam scanning in the single frequency condition, not high in power capacity and the like. The one-dimensional waveguide narrow slot antenna capable of scanning is composed of a rectangular slot waveguide, a sliding panel and a stepping motor. The rectangular slot waveguide is composed of a first narrow wall, a second narrow wall and two wide walls, one end of the rectangular slot waveguide is provided with a microwave feed-in port, the other end of the rectangular slot waveguide is connected with a matched load, n slots are formed in the first narrow wall of the rectangular slot waveguide, and the stepping motor is fixedly arranged on the second narrow wall. The sliding panel is embedded between the first narrow wall and the second narrow wall, and the sliding panel can slide in the direction perpendicular to the second narrow wall of the waveguide. According to the one-dimensional waveguide narrow slot antenna cable of scanning, each slot unit basically achieves even radiation, the purpose that the microwave beams scan in the one-dimensional direction under the single frequency working condition is achieved, large-scale array arranging capacity and high-power microwave field application potential are achieved, the structure is simple, and operating is convenient.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
High-power microwave dense-slot waveguide antenna
ActiveCN106058476AReduce equivalent resistanceImprove radiation efficiencySlot antennasSlot-waveguideMicrowave technology
The invention relates to the field of high-power microwave technologies, in particular to a high-power microwave dense-slot waveguide antenna. Specific to the technical problem that an existing high-power microwave antenna with a low compactness degree cannot be applied to certain environments, the invention provides a high-power microwave waveguide slot antenna which is compact in structure and has relatively high power capacity and an arraying prospect. According to the characteristics of a large number of slots within a unit length of the waveguide slot antenna and relatively low coupling power allocated to the slots, relatively high power capacity is realized. Meanwhile, a relatively low antenna is designed according to the characteristics that the slots are formed in wide edges and waveguide narrow edges can be relatively small, so that actual applications are satisfied. Through adoption of the high-power microwave dense-slot waveguide antenna, the defects of low power capacity and relatively large size in a conventional waveguide slot antenna can be overcome, and an effective technical scheme is provided for projects.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Optical fiber and silicon waveguide coupling structure based on polymer waveguides and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN104459890AGuaranteed reliabilityImprove coupling efficiencyCoupling light guidesSilicon dioxideStructure based
The invention discloses an optical fiber and silicon waveguide coupling structure based on polymer waveguides and a manufacturing method of the optical fiber and silicon waveguide coupling structure. The optical fiber and silicon waveguide coupling structure based on the polymer waveguides comprises an SOI wafer and an optical fiber arranged on the SOI wafer, the polymer straight waveguide and the polymer tapered waveguide are arranged on a buried oxide layer of the SOI wafer in sequence from right to left, the narrower end of the polymer tapered waveguide is connected with the polymer straight waveguide, and the wider end of the polymer tapered waveguide is aligned with a fiber core of the optical fiber; the silicon waveguide is arranged on upper layer silicon, the left end of the silicon waveguide is a back taper structure with a gradually changing width, the right end of the silicon waveguide is of a straight silicon waveguide back taper structure, part of the straight silicon waveguide wrapped in the polymer straight waveguide, and other parts of the straight silicon waveguide is covered with a silicon dioxide covering layer; a V-shaped groove is formed in the top surface of the left end of the SOI wafer, the silicon dioxide covering layer, the upper layer silicon and the buried oxide layer sequentially penetrate through the V-shaped groove in the depth direction, and the bottom end of the V-shaped groove is located at substrate silicon; the optical fiber is fixed in the V-shaped groove. The optical fiber and silicon waveguide coupling structure based on the polymer waveguides and the manufacturing method of the optical fiber and silicon waveguide coupling structure not only improve coupling efficiency, reduce process complexity and guarantee the reliability of the optical fiber coupling structure.
Owner:WUHAN POST & TELECOMM RES INST CO LTD
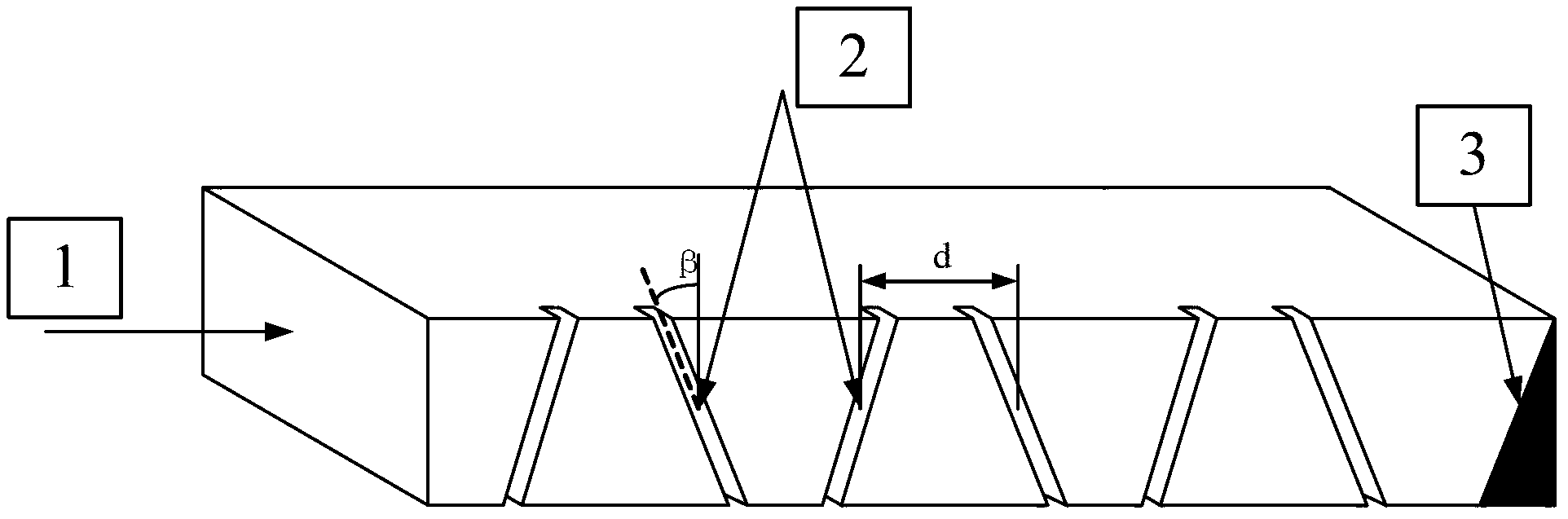
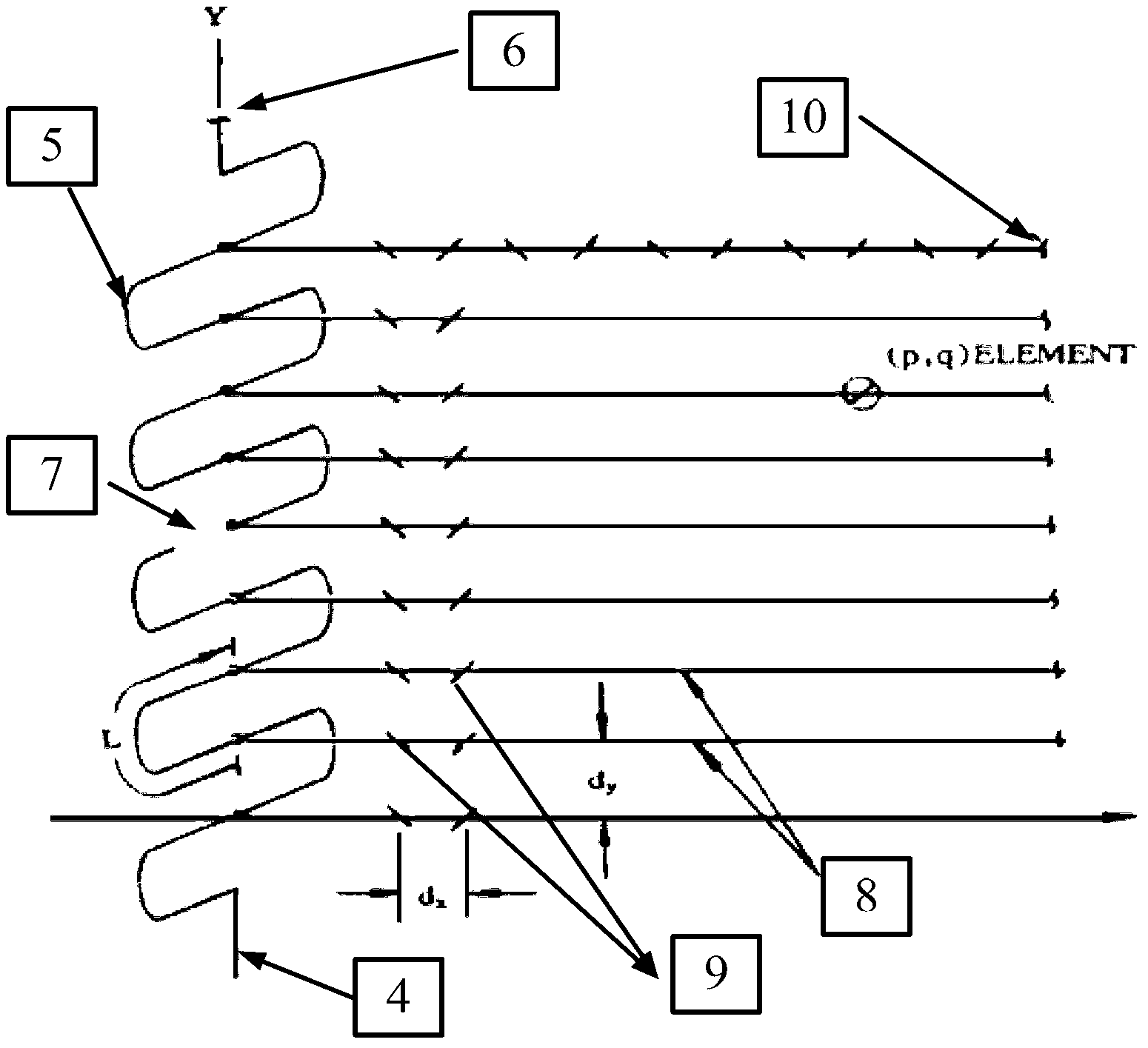
An Amplitude-Phase Weighted Narrow-Side Waveguide Slot Array Antenna
ActiveCN102299421ACompact structureLow profileAntenna arraysAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesSlot-waveguideAzimuth direction
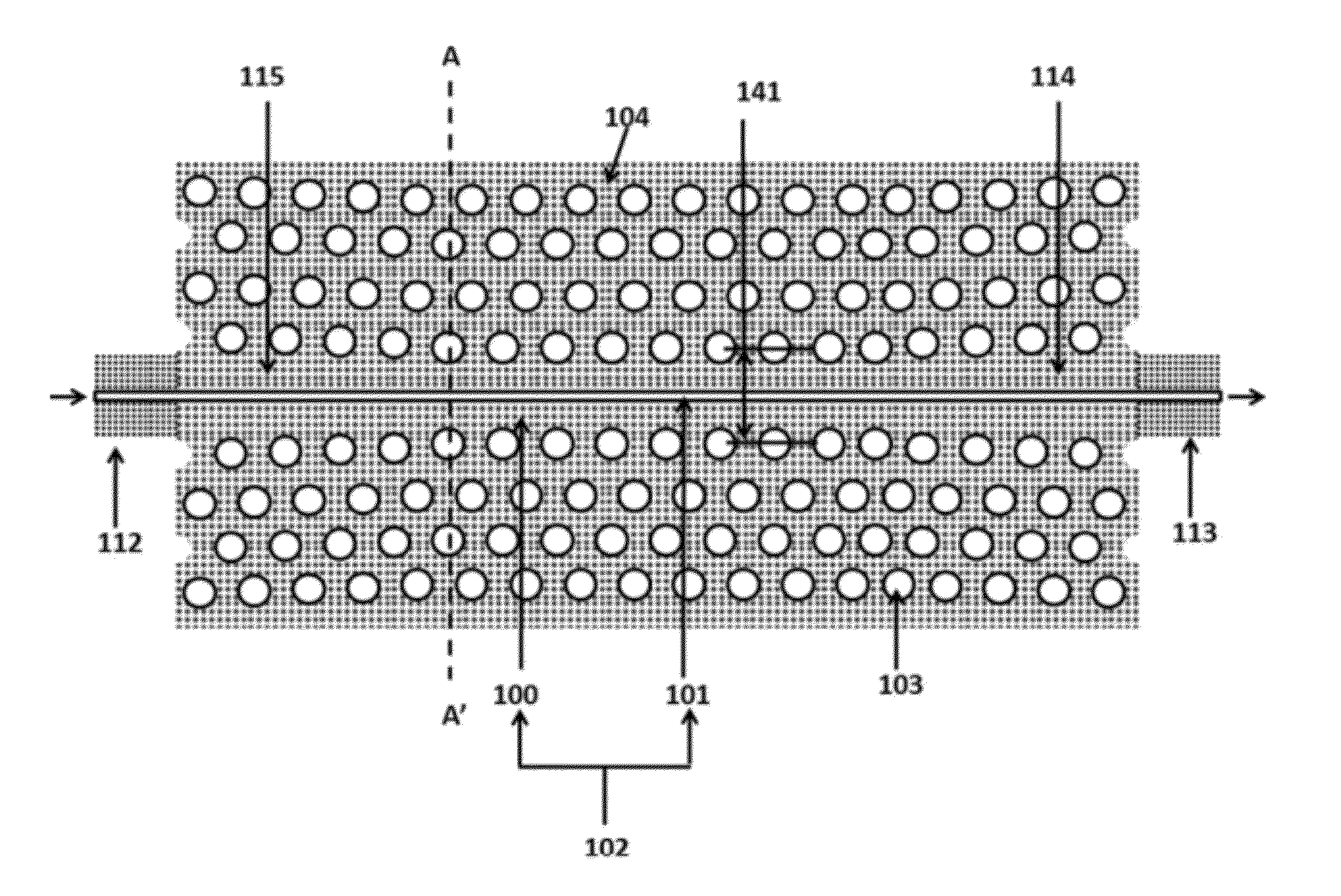
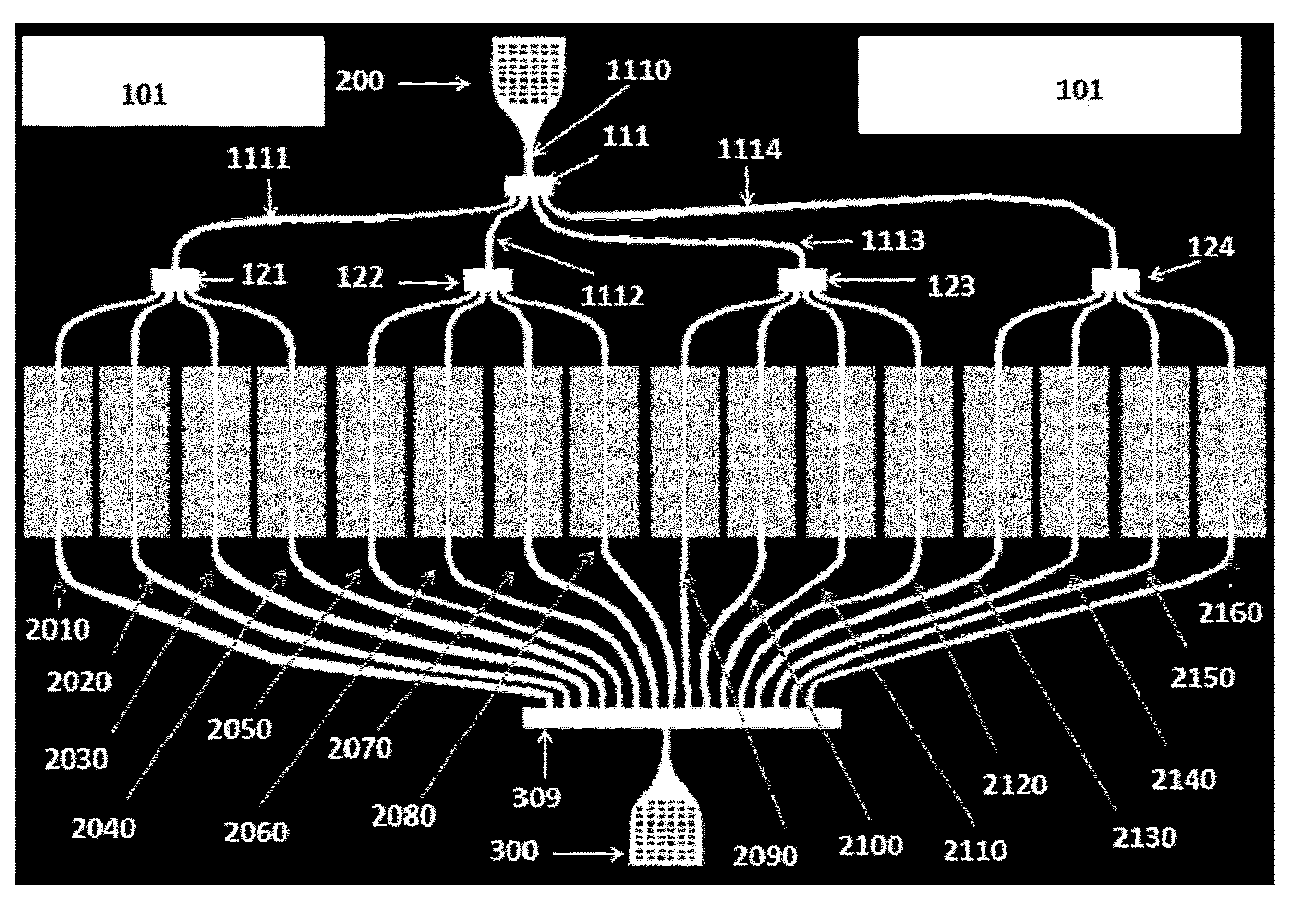
The invention discloses an amplitude-phase weighed narrow waveguide slot array antenna, comprising a waveguide narrow radiating array surface (1) and an integrated amplitude-phase weighed shaping waveguide narrow feed network (2), wherein the range of the waveguide narrow radiating array surface (1) comprises 6-14 narrow slotting waveguides (11); the azimuth direction of the waveguide narrow radiating array surface (1) comprises 2-100 radiating slots (12); and the integrated amplitude-phase weighed shaping waveguide narrow feed network (2) comprises a feed transmission waveguide (23), amplitude-phase simultaneous weighing feed coupling slots (24) and an excessive connecting waveguide (26). For the radiating array surface of the antenna, slots which are inclined alternately are arranged at a waveguide narrow edge for in-phase radiation, and the feed network realizes different amplitude-phase allocations by slots which are inclined in the same direction at the waveguide narrow edge, thus reducing the structural complexity of the feed network and the transmission loss effectively and decreasing the processing difficulty and processing cost of the antenna system.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Fabrication Tolerant Design for the Chip-Integrated Spectroscopic Identification of Solids, Liquids, and Gases
ActiveUS20120328233A1Enhanced light absorptionEnhanced optical fieldNanoopticsColor/spectral properties measurementsAbsorption spectroscopySpectrometer
Methods and systems for a label-free on-chip optical absorption spectrometer consisting of a photonic crystal slot waveguide are disclosed. The invention comprises an on-chip integrated optical absorption spectroscopy device that combines the slow light effect in photonic crystal waveguide and optical field enhancement in a slot waveguide and enables detection and identification of multiple analytes to be performed simultaneously using optical absorption techniques leading to a device for chemical and biological sensing, trace detection, and identification via unique analyte absorption spectral signatures. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:OMEGA OPTICS
Slot Waveguide with Structural Modulation
ActiveUS20190067830A1Reduced propagation lossLarge mode overlapIndividually energised antenna arraysElectromagnetic transmittersSlot-waveguideElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:OMEGA OPTICS
Compact wide scan periodically loaded edge slot waveguide array
InactiveUS6781554B2Radio wave direction/deviation determination systemsIndividually energised antenna arraysSlot-waveguideEngineering
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Multimode interference biological chemical sensor based on silicon slot waveguides
InactiveCN102565000AGood manufacturing toleranceEasy to manufacturePhase-affecting property measurementsSlot-waveguideHigh bandwidth
The invention discloses a multimode interference biological chemical sensor based on silicon slot waveguides, which is characterized by comprising an input waveguide (1), two output waveguides, namely, a first output waveguide (3) and a second output waveguide (4), and a multimode interference waveguide (5), wherein the input waveguide (1) is used for inputting optical signals, the input waveguide (1) is connected with the first output waveguide (3) and the second waveguide (4) through the multimode interference waveguide (5), the multimode interference waveguide (5) is tapered, single wavelength optical signals are input through the input waveguide (1) and subjected to multimode interference in an area of the multimode interference waveguide (5), input lights are subjected to self-imaging length regeneration on the basis of the self-imaging effect of multimode interference, and the self-imaging length is selected as the length of the sensor. The multimode interference biological chemical sensor based on silicon slot waveguides has the advantages of compact structure, insensitive polarization, high bandwidth, good fabrication tolerance and large working range.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Mode transformers for low index high confinement waveguides
The mode transforming structure includes a first waveguide structure. A slot waveguide region is coupled to the first waveguide structure. The slot waveguide region includes one or more complementary tapered pairs so near lossless transforming between the first waveguide structure and the slot waveguide region occurs so as to allow optical modes to be transferred between the first waveguide and the slot waveguide region.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method for preparing intermediate and long infrared undercut type optical waveguides based on silicon on insulator (SOI) materials
InactiveCN103033880AEasy to buyQuality improvementOptical light guidesSlot-waveguideRefractive index
The invention discloses a method for preparing intermediate and long infrared undercut type optical waveguides based on silicon on insulator (SOI) materials. A row of square holes are formed in two sides of a ridge waveguide on an SOI piece, parallel to the ridge waveguide, and distributed at intervals. A high-loss oxygen buried layer under the ridge waveguide is hollowed out through the square holes so that an intermediate and long infrared undercut type ridge waveguide structure is achieved. Or slots are etched at the center of the ridge waveguide on the SOI piece, and a high-loss oxygen buried layer under the slot type waveguide is hollowed out trough the slots so that an intermediate and long infrared undercut type slot waveguide structure is achieved. Two manufactured waveguide structures through the method have low transmission loss, and a light field of the undercut type slot waveguide is mainly limited in the slots with a low refractive index. If chemical materials which can absorb existing characteristics of intermediate and long infrared bands are filled in the slots, an intermediate and long infrared absorption type sensor can be formed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
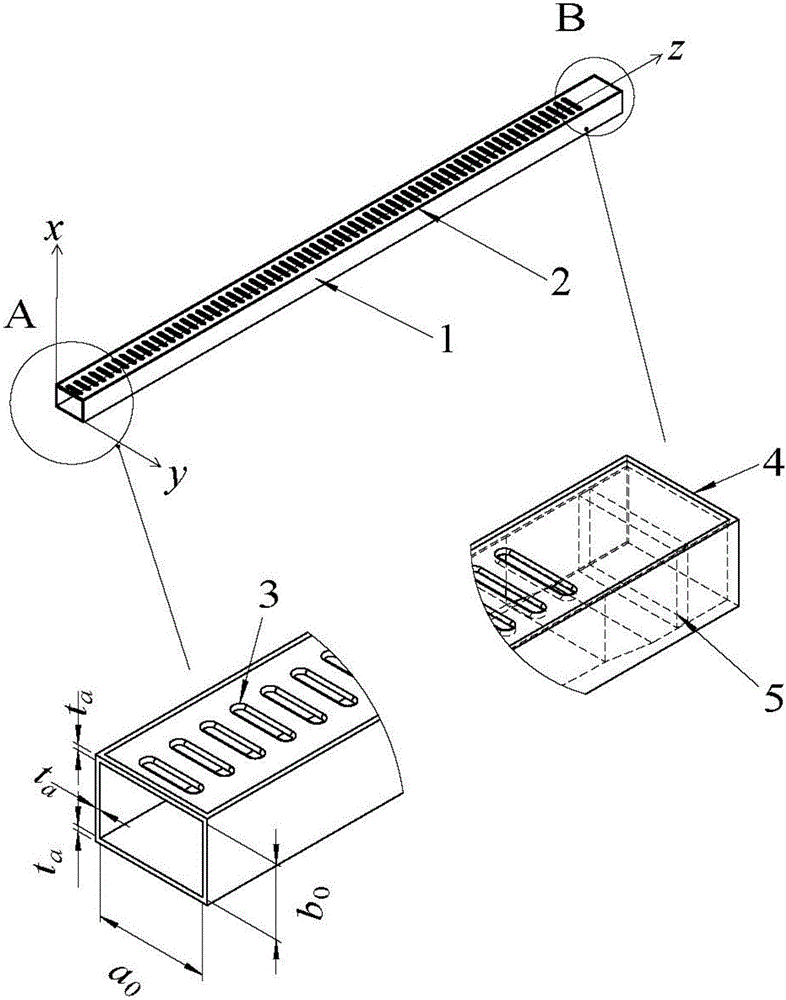
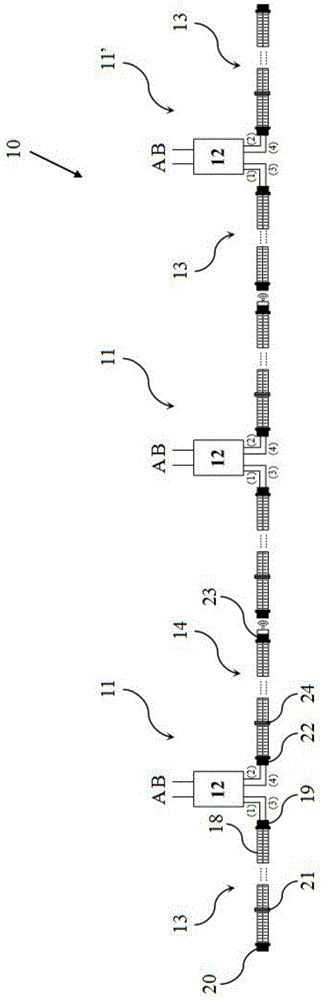
Dual-frequency common-caliber waveguide slot waveguide antenna and design method thereof, and antenna array
ActiveCN110429378AImprove efficiencyHigh gainParticular array feeding systemsSimultaneous aerial operationsSlotted waveguideSlot-waveguide
The invention discloses a dual-frequency common-caliber waveguide slot waveguide antenna and a design method thereof, and an antenna array. The dual-frequency common-caliber waveguide slot waveguide antenna comprises a radiation port, a radiation sidewall, a first waveguide cavity, a second waveguide cavity, a Ku-band input port and a Ka-band input port; the radiation port, the radiation sidewall,the first waveguide cavity, the second waveguide cavity and the Ka-band input port are sequentially disposed from top to bottom, and the Ku-band input port is disposed on the first waveguide cavity.The dual-frequency common-caliber waveguide slot waveguide antenna and a design method thereof, and the antenna array are high in efficiency, high in gain, easy to process, dual-band and large in distance.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 38 RES INST
On-board directional flat-plate antenna, vehicle comprising such an antenna, and satellite telecommunication system comprising such a vehicle
InactiveUS9013359B2Improve compactnessEasy to implementPolarisation/directional diversityAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesSlot-waveguideOn board
An onboard directional plane antenna comprises at least one array of radiating-slot waveguides comprising an alternating succession of three superposed metallic plates and of two dielectric substrates. The two substrates each comprise at least four adjacent waveguides, corresponding and communicating with one another pairwise by way of coupling slots. Each waveguide of the upper substrate furthermore comprises a plurality of radiating slots passing through the upper metallic plate, all the radiating slots of one and the same waveguide being parallel to one another and oriented in one and the same direction, the radiating slots of two adjacent waveguides being disposed in chevrons. Each waveguide of the lower substrate comprises an internal individual feed circuit comprising an individual electronic circuit for phase shifting and amplification.
Owner:THALES SA
Packaged chip for multiplexing photonic crystal waveguide and photonic crystal slot waveguide devices for chip-integrated label-free detection and absorption spectroscopy with high throughput, sensitivity, and specificity
ActiveUS8636955B2High throughput measurementImprove throughputRadiation pyrometryColor measuring devicesPhotonThroughput
Systems and methods for chip-integrated label-free detection and absorption spectroscopy with high throughput, sensitivity, and specificity are disclosed. The invention comprises packaged chips for multiplexing photonic crystal waveguide and photonic crystal slot waveguide devices. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:OMEGA OPTICS
Radio frequency superconducting cavity with slit waveguide structure for superconducting accelerator
InactiveCN101707850ARaise the ratioAttenuated Diode ModeAcceleratorsSlot-waveguideHigh volume manufacturing
Owner:PEKING UNIV
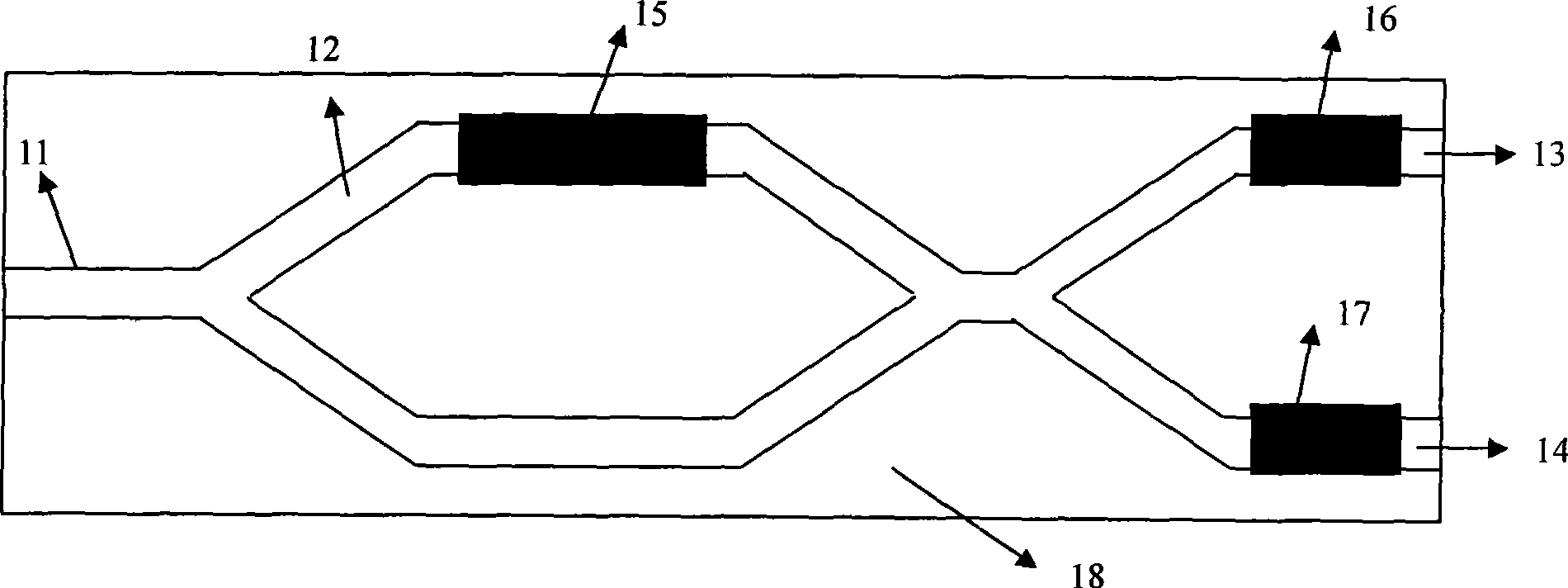
Low-crosstalk organic polymer waveguide optical switch
The invention discloses a low-crosstalk organic polymer waveguide switch and relates to a low-crosstalk termooptical waveguide switch device. All waveguide structures are embedded in a cladding (18). The input end of a Mach-Zehnder interference waveguide structure (12) is connected with the output end of an input waveguide (11). Two output ends of the Mach-Zehnder interference waveguide structure (12) are connected with the input end of an output waveguide (13) and the input end of an output waveguide (14) respectively. The top of the Mach-Zehnder interference waveguide structure (12) is provided with a first metal membrane thermode (15). The top of the output waveguide (13) is provided with a second metal membrane thermode (16). The top of the output waveguide (14) is provided with a third metal membrane thermode (17). The device controls the first metal membrane thermode (15) and the second metal membrane thermode (16) through current respectively or controls the first metal membrane thermode (15) and the third metal membrane thermode (17) through current respectively to realize a low-crosstalk optical switch function.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Slotted waveguide antenna, signal transmission device and signal continuous transmission system
The invention provides a slotted waveguide antenna that can be laid in an existing space, effectively isolates signals which cannot reach isolation requirements and separately transmits the signals, and also provides a signal transmission device and a signal continuous transmission system that both comprise the slotted waveguide antenna. The slotted waveguide antenna is characterized by comprising at least one slotted waveguide tube for transmitting electromagnetic wave signals, wherein the slotted waveguide tube at least comprises a first pipeline and a second pipeline parallel to each other, the surface of each of the first pipeline and the second pipeline is equipped with multiple slots that enable the electromagnetic wave signals to be transmitted between the inside of each pipeline and the outside of each pipeline, and the first pipeline and the second pipeline are respectively used for transmitting two types of electromagnetic wave signals, wherein the frequency interval between the two types of electromagnetic wave signals cannot reach preset isolation requirements.
Owner:中电科微波通信(上海)股份有限公司
Surface plasmon polariton waveguide
ActiveCN102736172AReduce absorption lossEnhanced Mode LocalityOptical waveguide light guideThin metalSlot-waveguide
The invention belongs to a waveguide technology and in particular relates to a surface plasmon polariton waveguide. The surface plasmon polariton waveguide comprises a substrate layer, two high-refractive-index dielectric layers, two low-refractive-index dielectric layers and a metal layer, wherein the two high-refractive-index dielectric layers, the two low-refractive-index dielectric layers and the metal layer are arranged above the substrate layer to form a lamination structure which consists of a first high-refractive-index dielectric, a first low-refractive-index dielectric, metal, a second low-refractive-index dielectric and a second high-refractive-index dielectric; and the lamination structure is horizontally placed or vertically laminated on the substrate layer. The surface plasmon polariton waveguide has the advantages that a surface plasmon polariton mode and the conventional slot waveguide mode are mixed; on the basis of the conventional slot waveguide, a central metal layer is added, and by using a metal-dielectrics surface plasmon polariton effect, mode locality is improved; and moreover, by using a thin metal layer long-range surface plasmon polariton effect, the absorption loss of the metal is reduced, so large propagation length of over 1 mm can be obtained.
Owner:ZHONGTIAN COMM TECH CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com