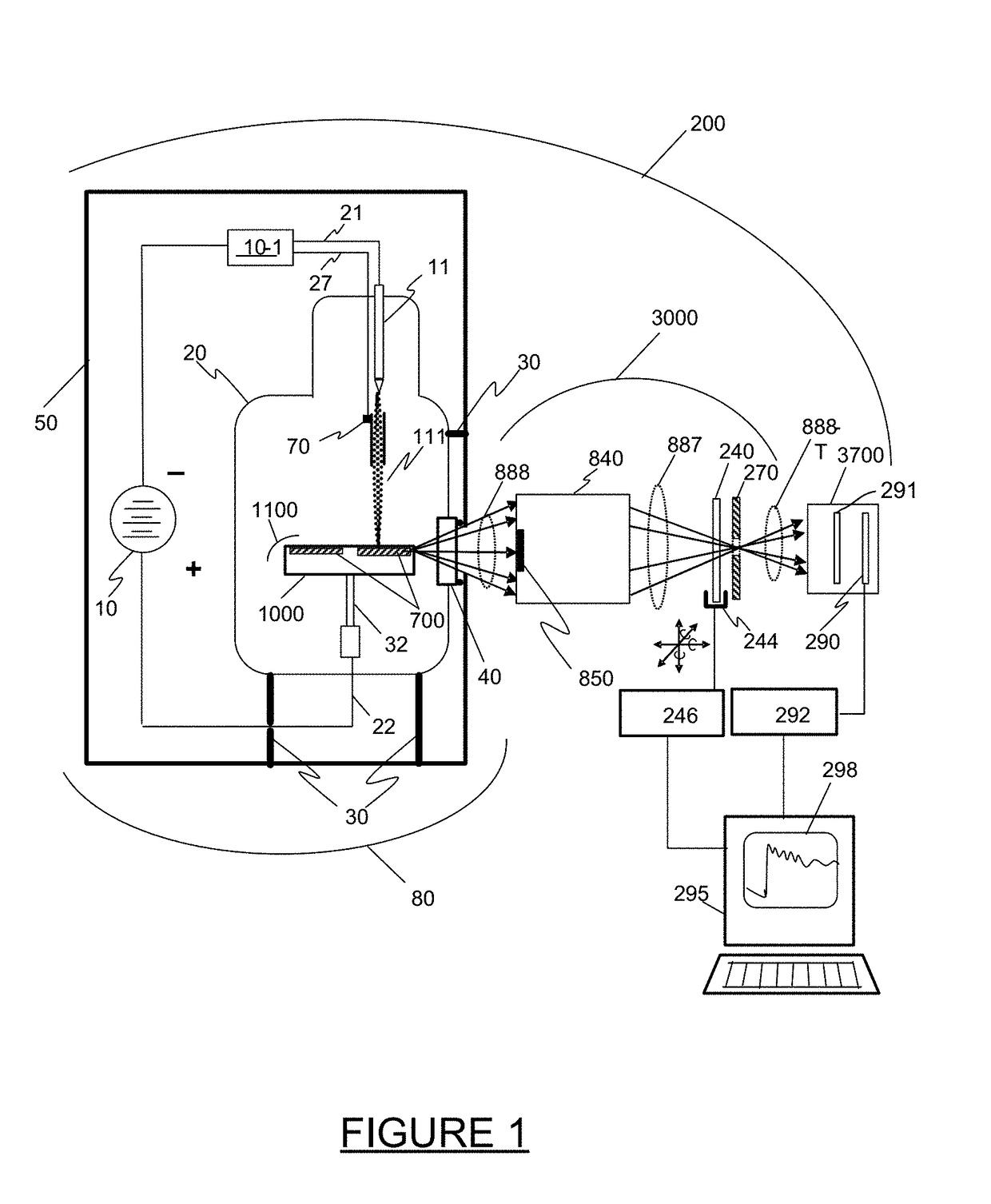
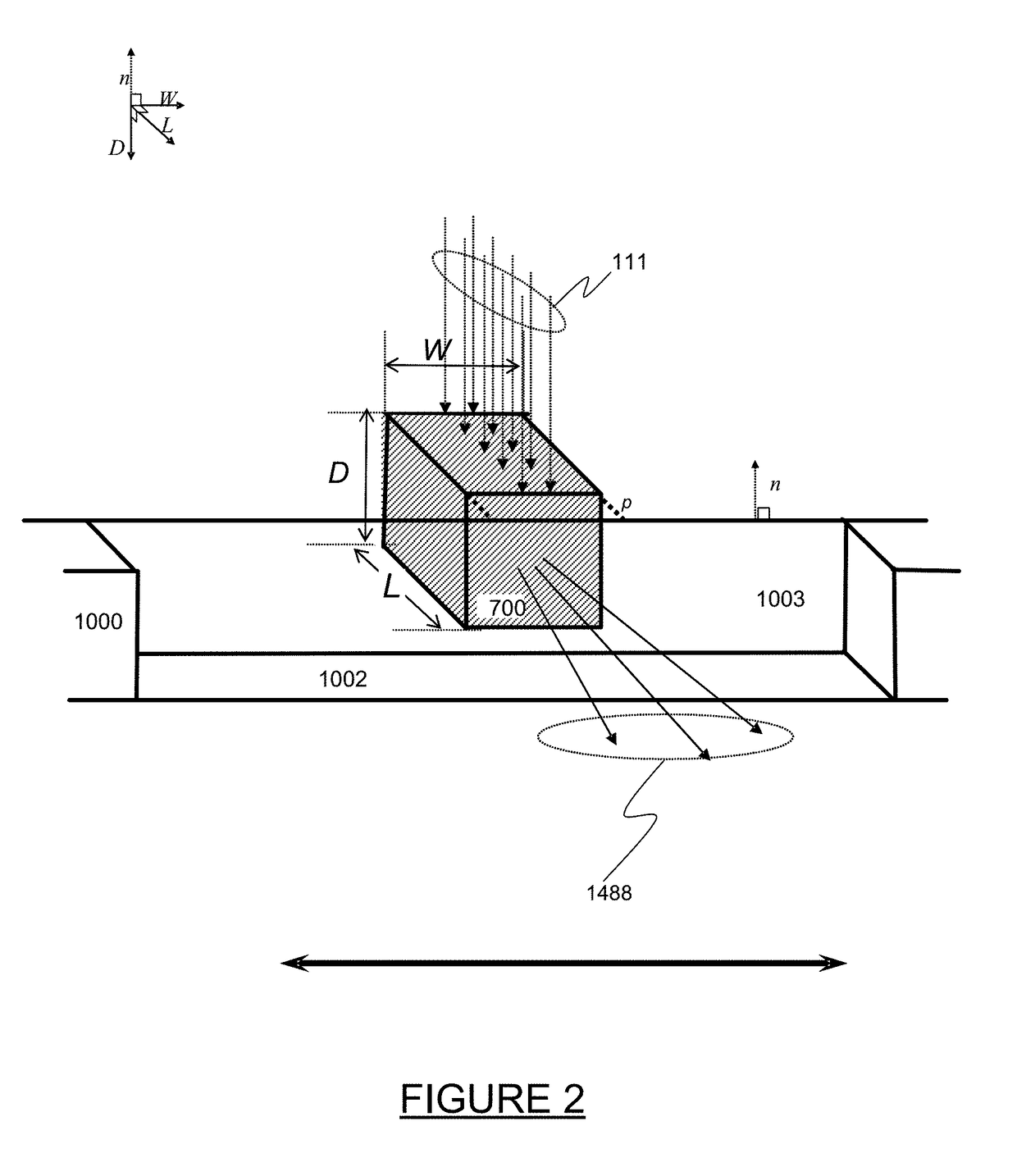
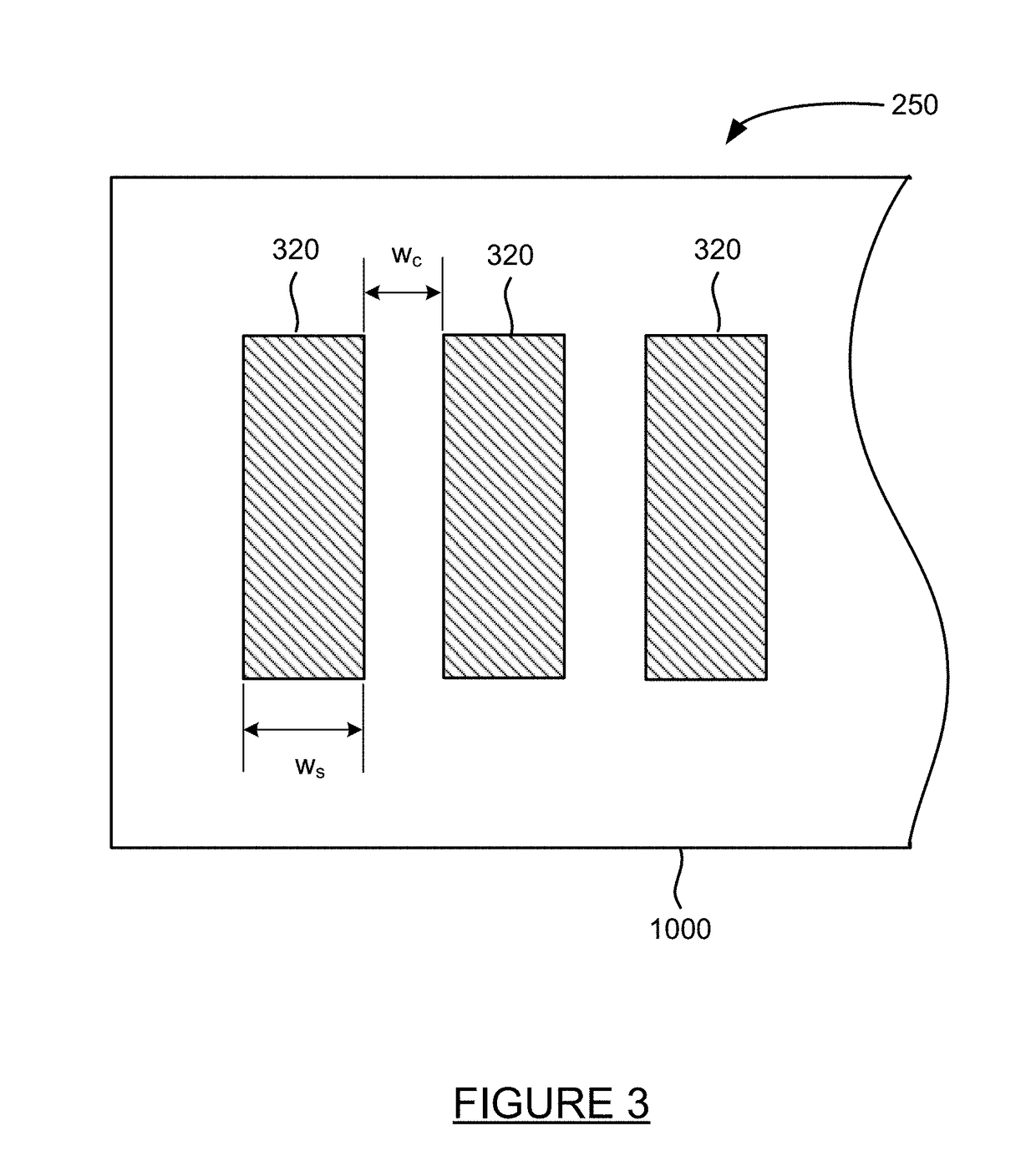
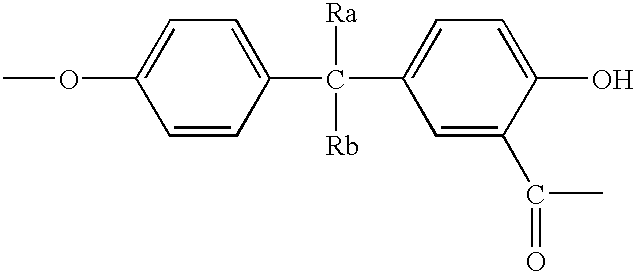
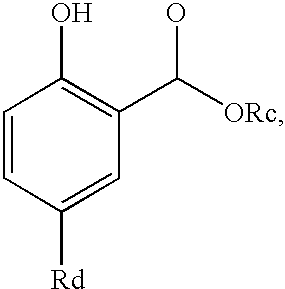
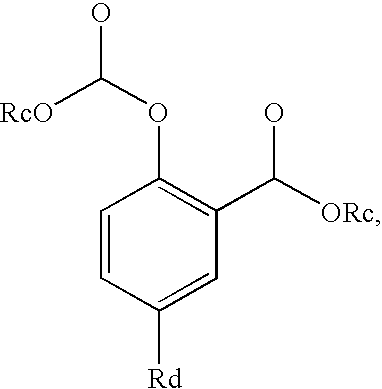
Patents
Literature
269 results about "Atomic absorption spectroscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) and atomic emission spectroscopy (AES) is a spectroanalytical procedure for the quantitative determination of chemical elements using the absorption of optical radiation (light) by free atoms in the gaseous state. Atomic absorption spectroscopy is based on absorption of light by free metallic ions.
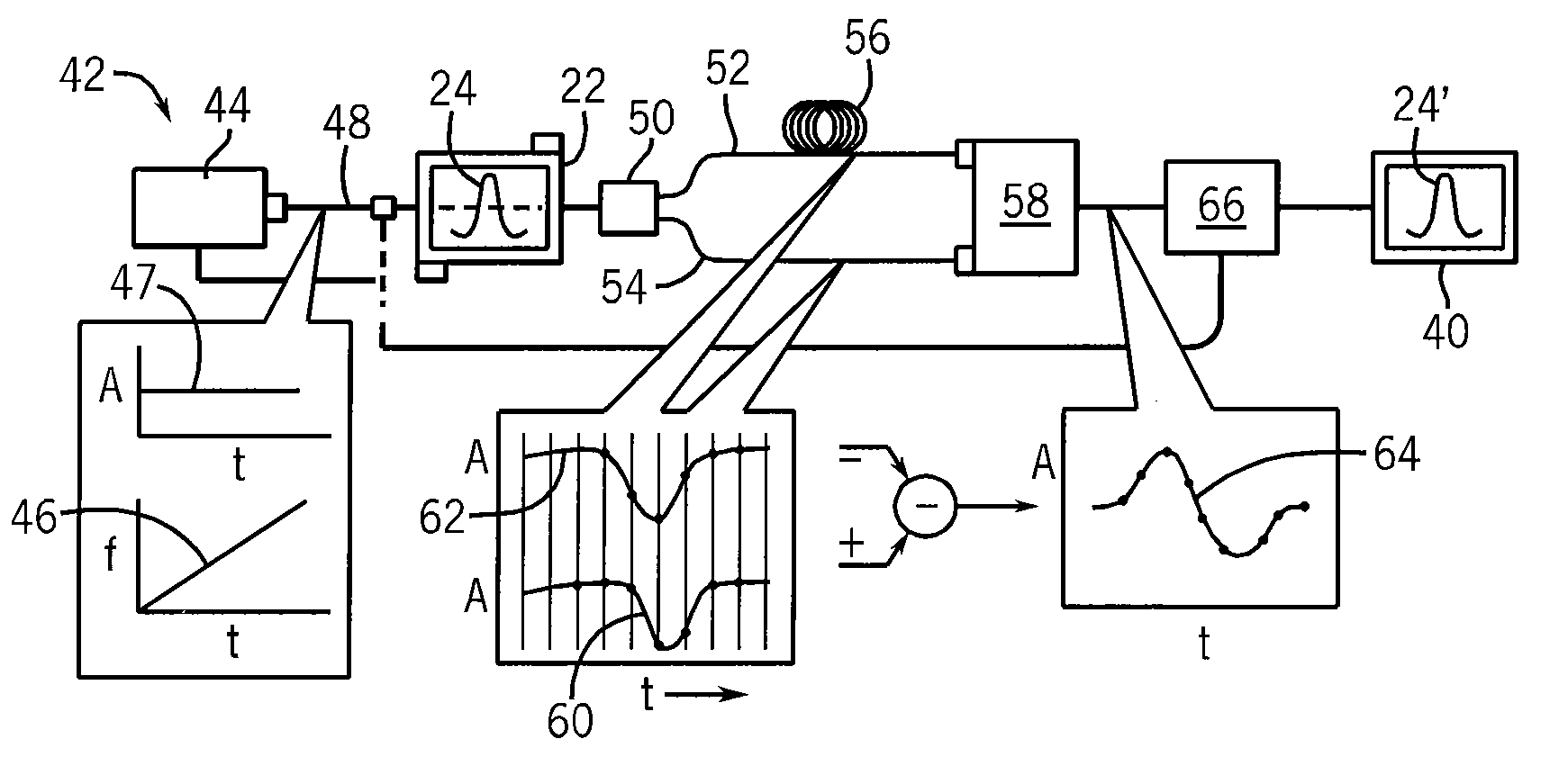
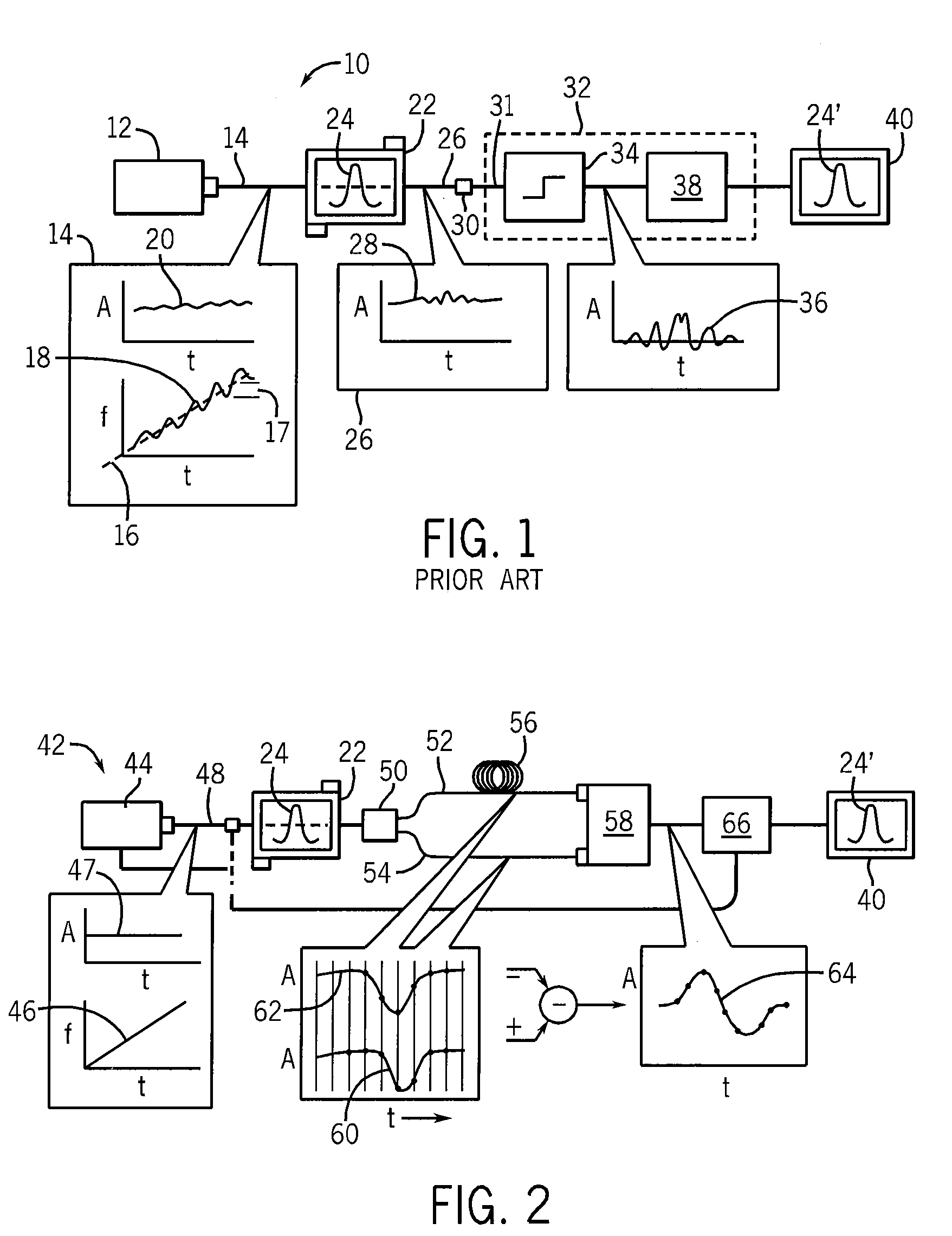
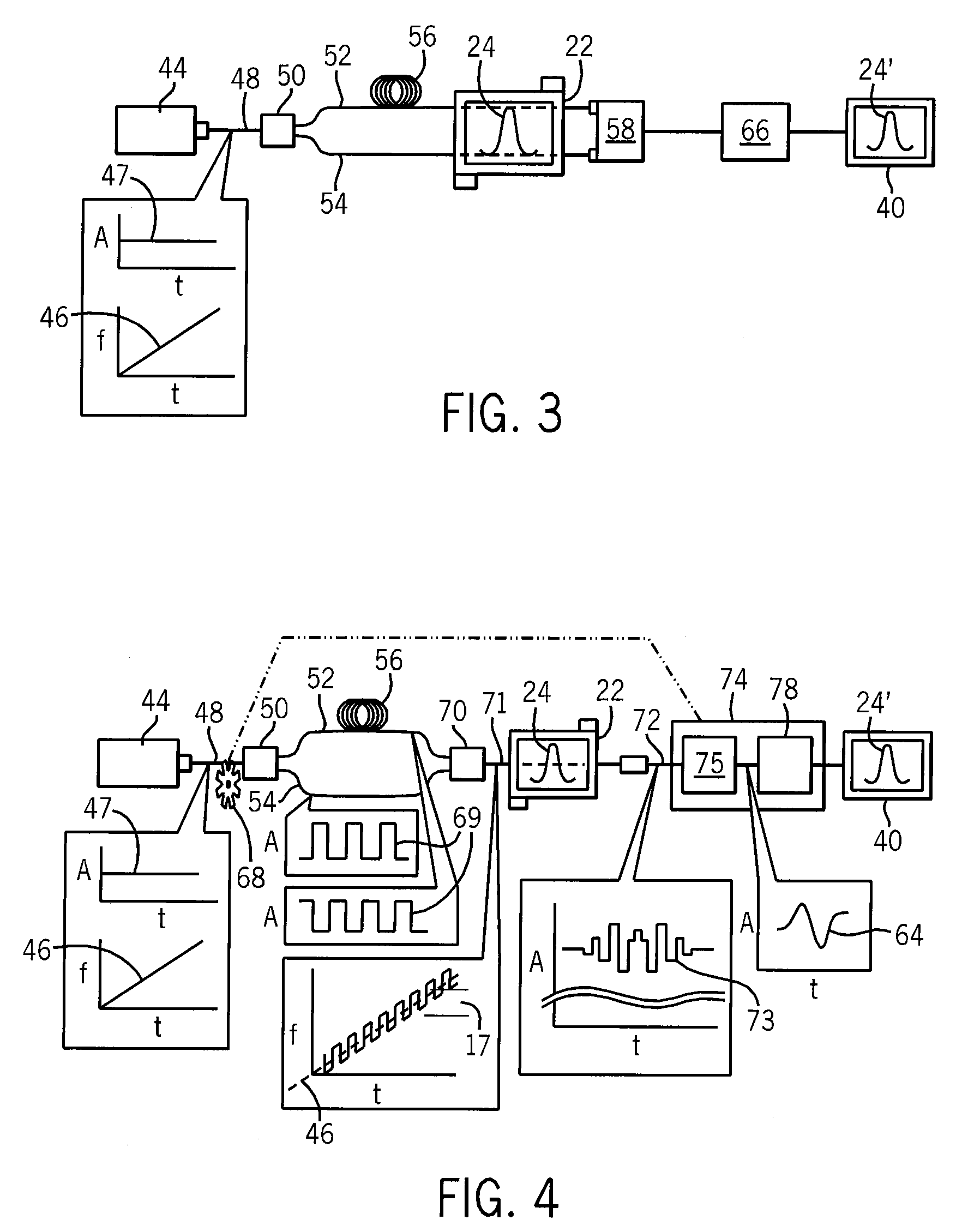
Cavity-enhanced liquid absorption spectroscopy
ActiveUS6839140B1Avoid interferenceSuppress interferenceColor/spectral properties measurementsAtomic absorption spectroscopySpectroscopy
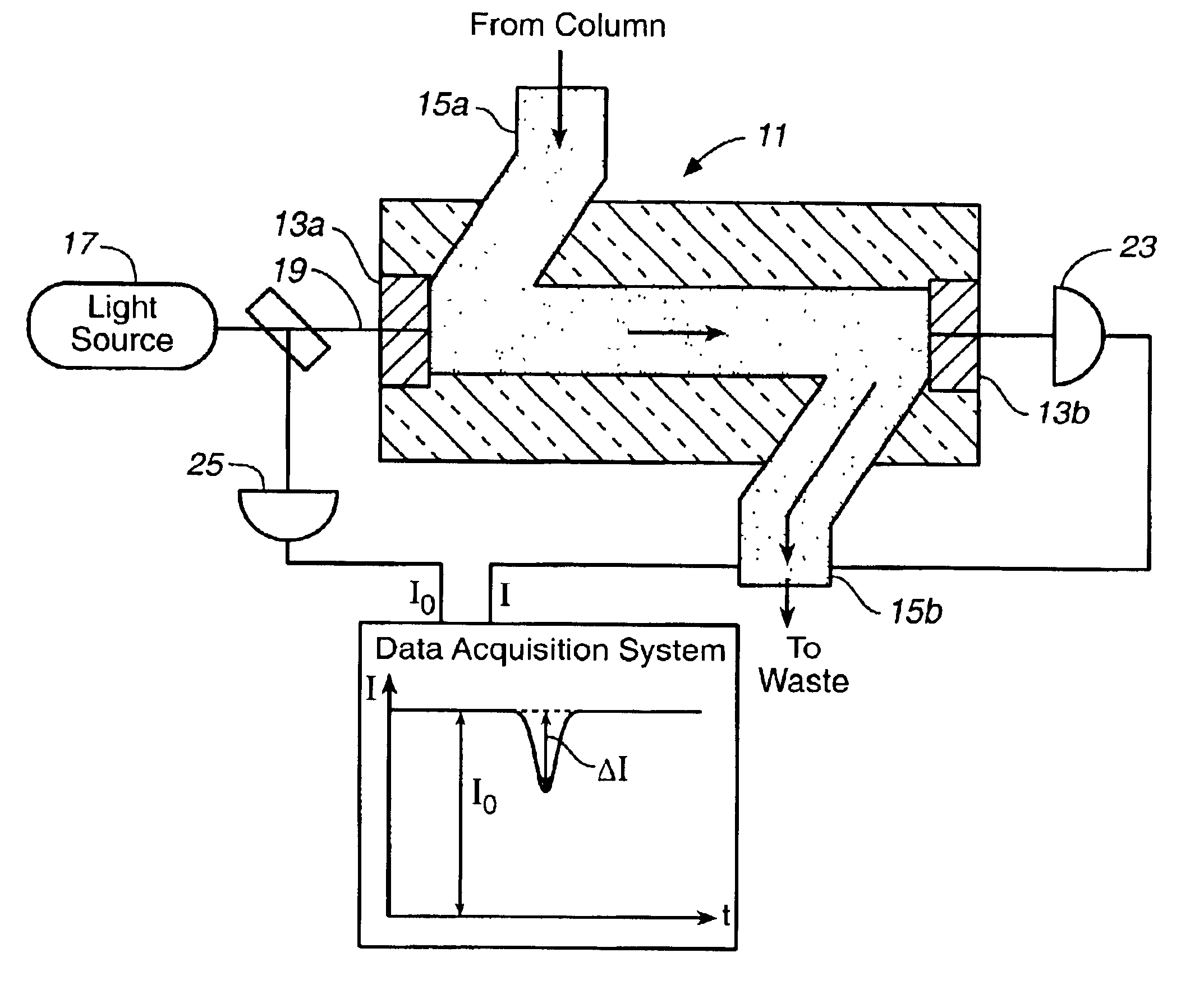
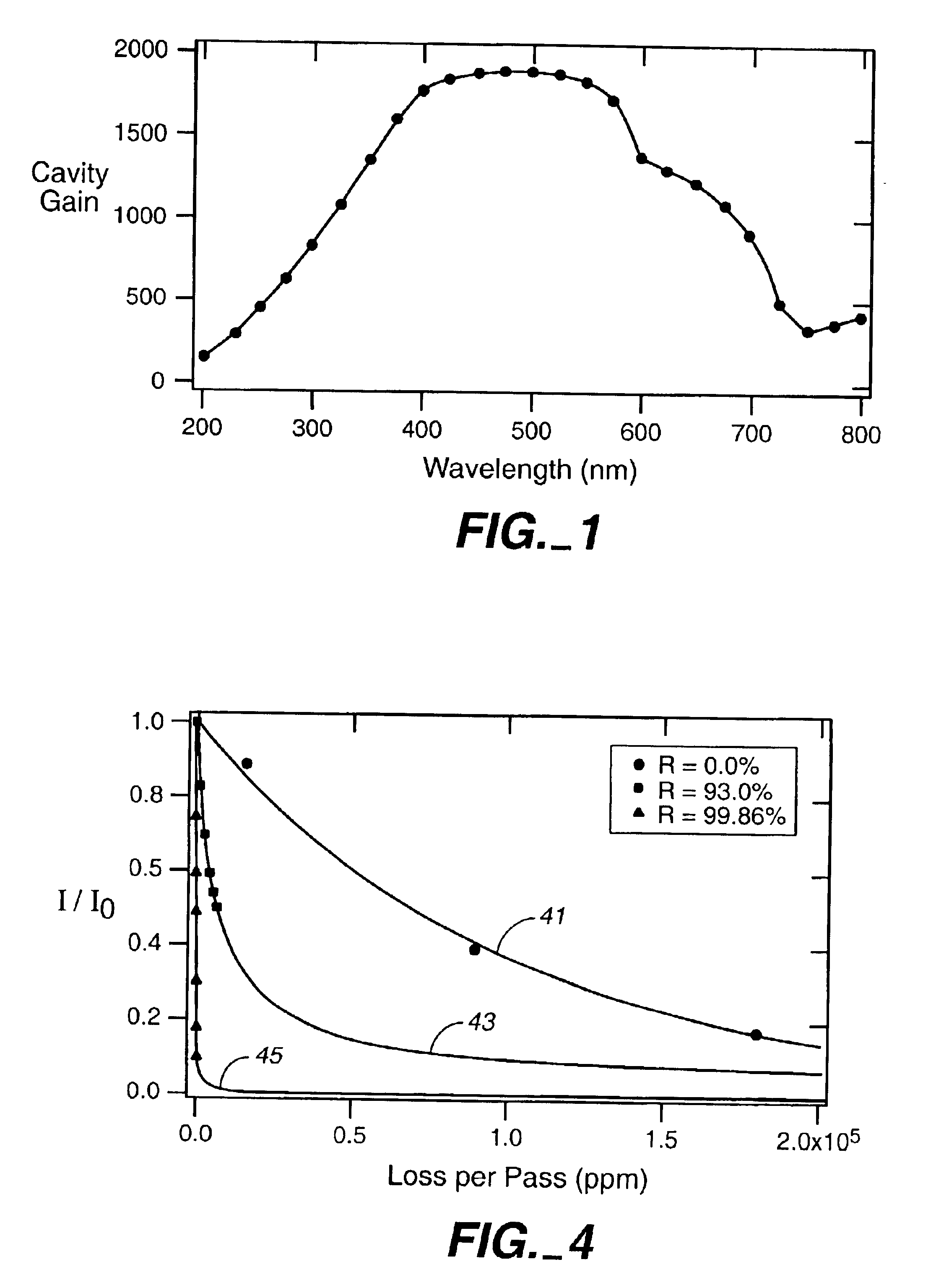
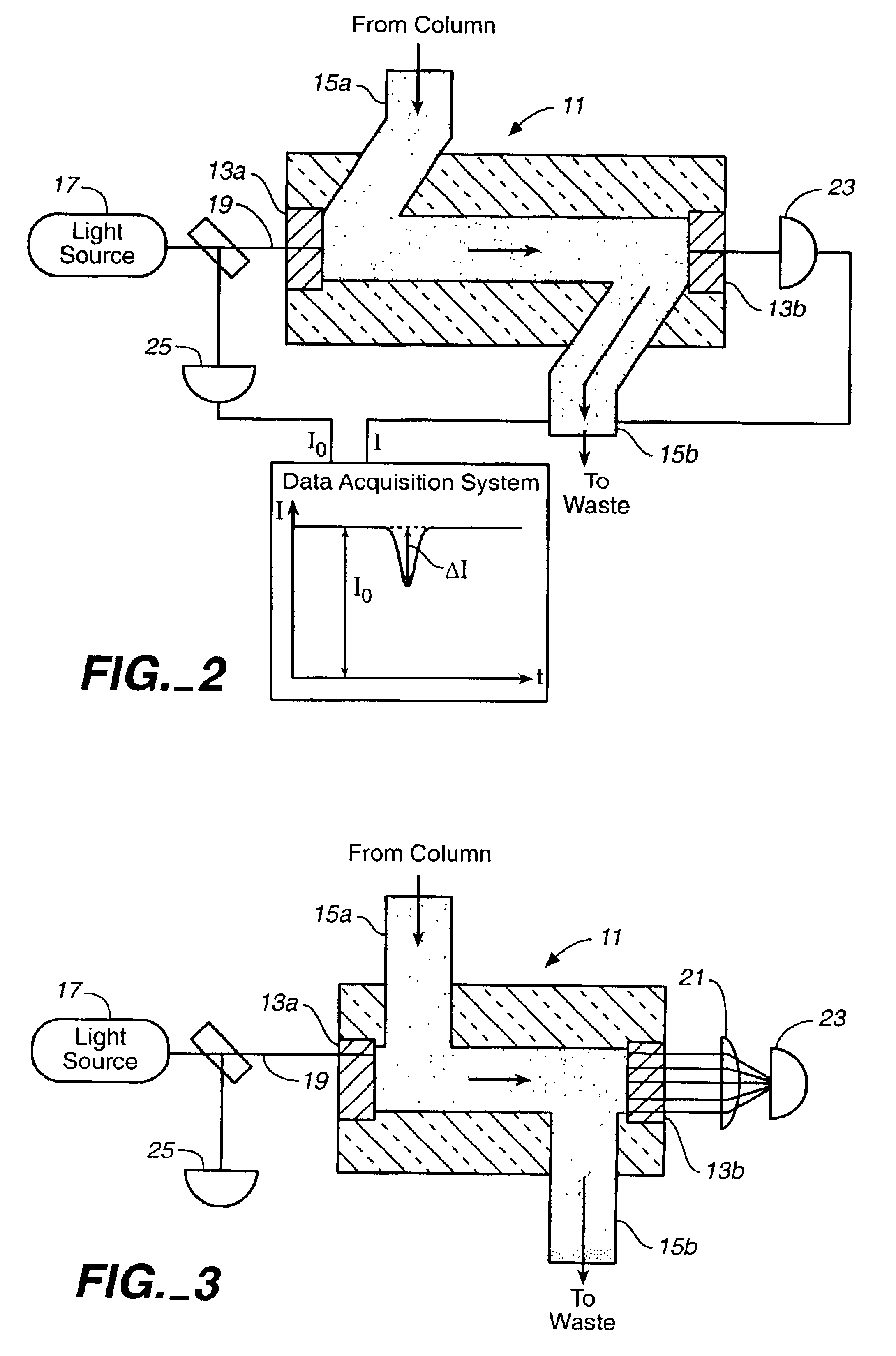
An integrated-cavity output spectroscopy (ICOS) instrument adapted for measuring liquid samples has a low-scatter flow cell arrangement passing through a stable optical cavity defined by an arrangement of two or more mirrors. The flow cell provides a sample volume within the cavity of at most one microliter at any given time. The optical cavity has an effective cavity length of at most one centimeter and mirror radii of curvature for the stable cavity arrangement are much longer than the cavity length. A light beam with stable characteristics is introduced into the cavity, passes through the liquid sample cell multiple times, and a detector measures a portion of the light from the cavity. The light measurement is analyzed to determine absorption by the liquid sample, and related information.
Owner:LOS GATOS RES
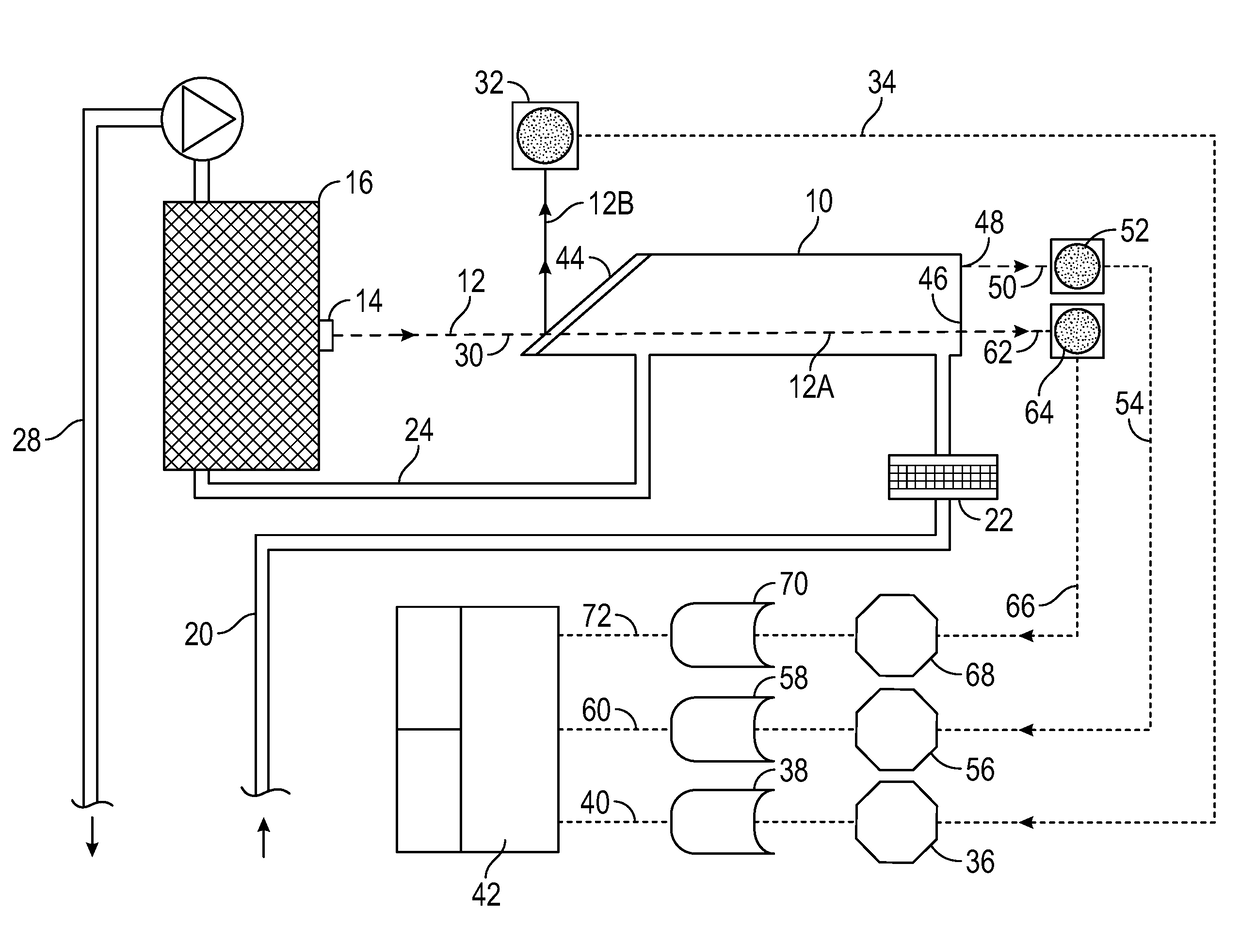
Method and device for detecting gases by absorption spectroscopy
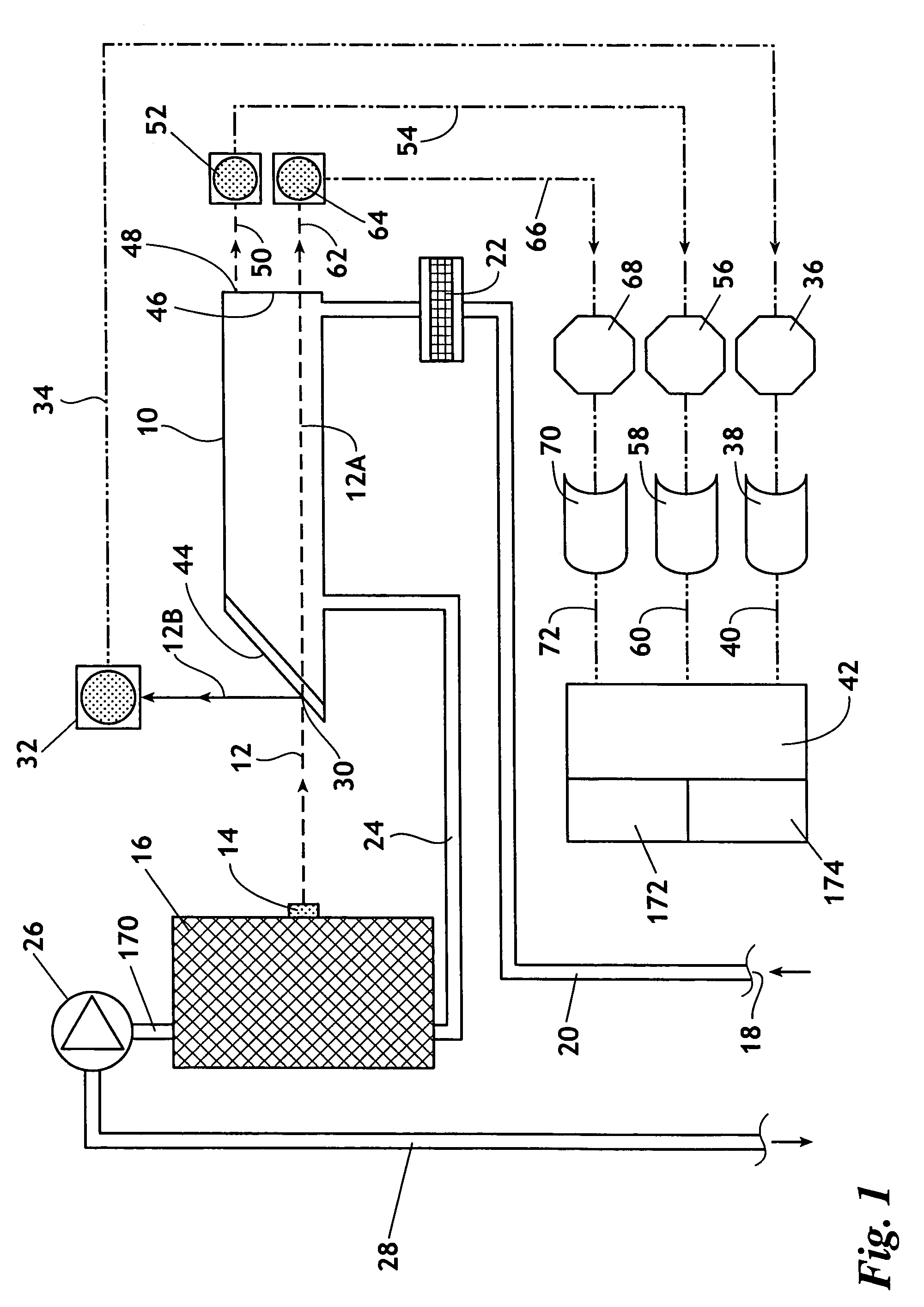
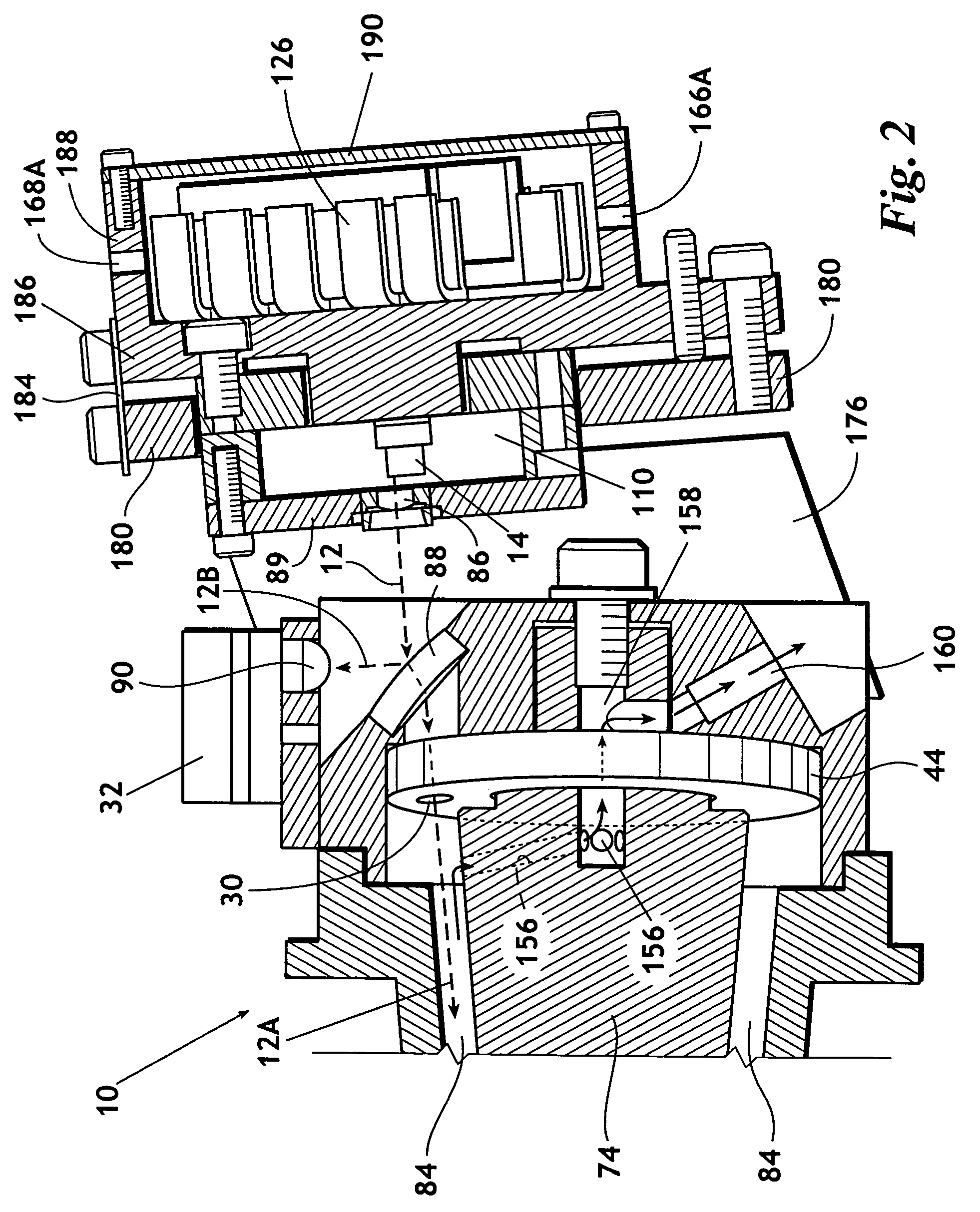
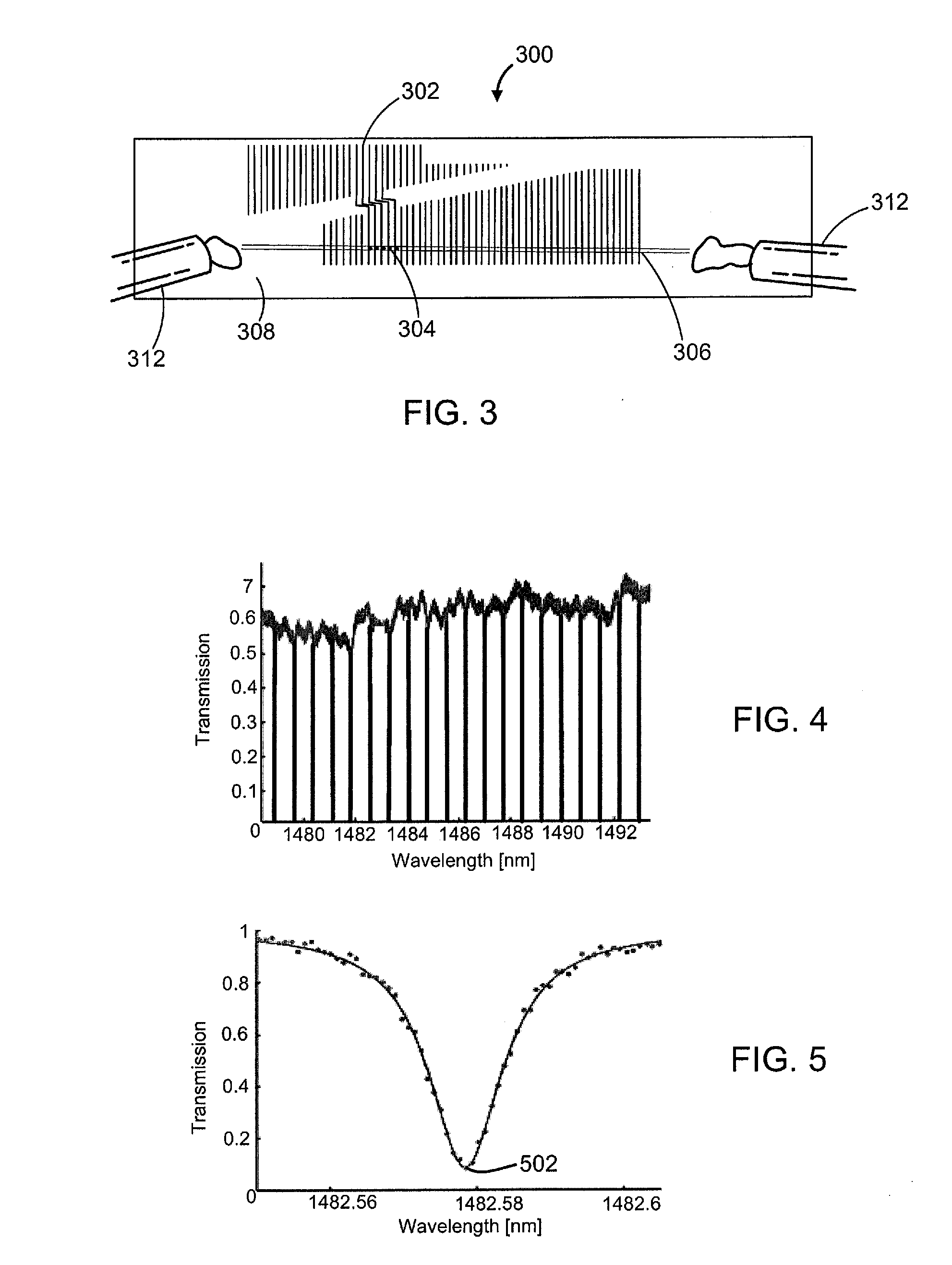
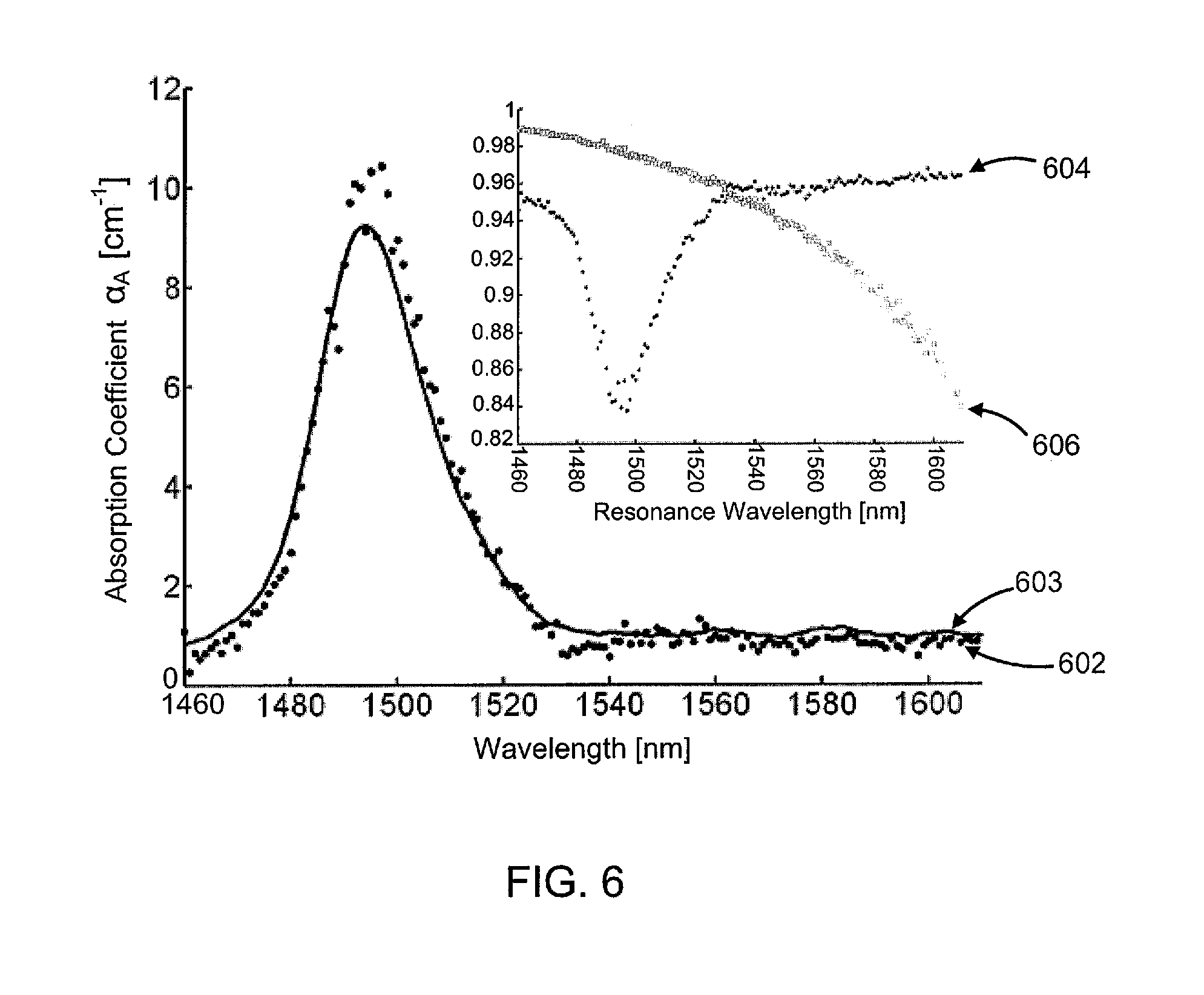
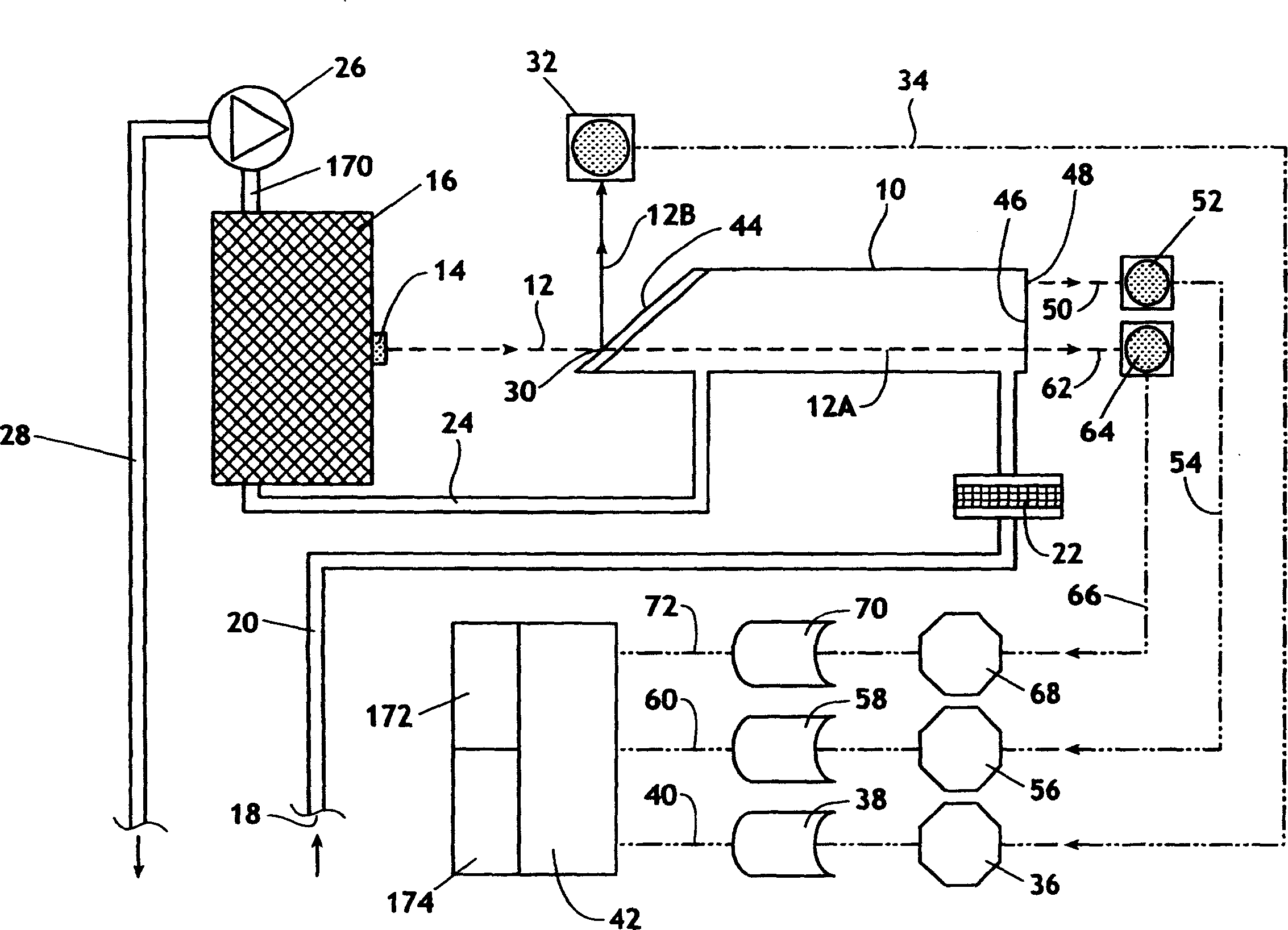
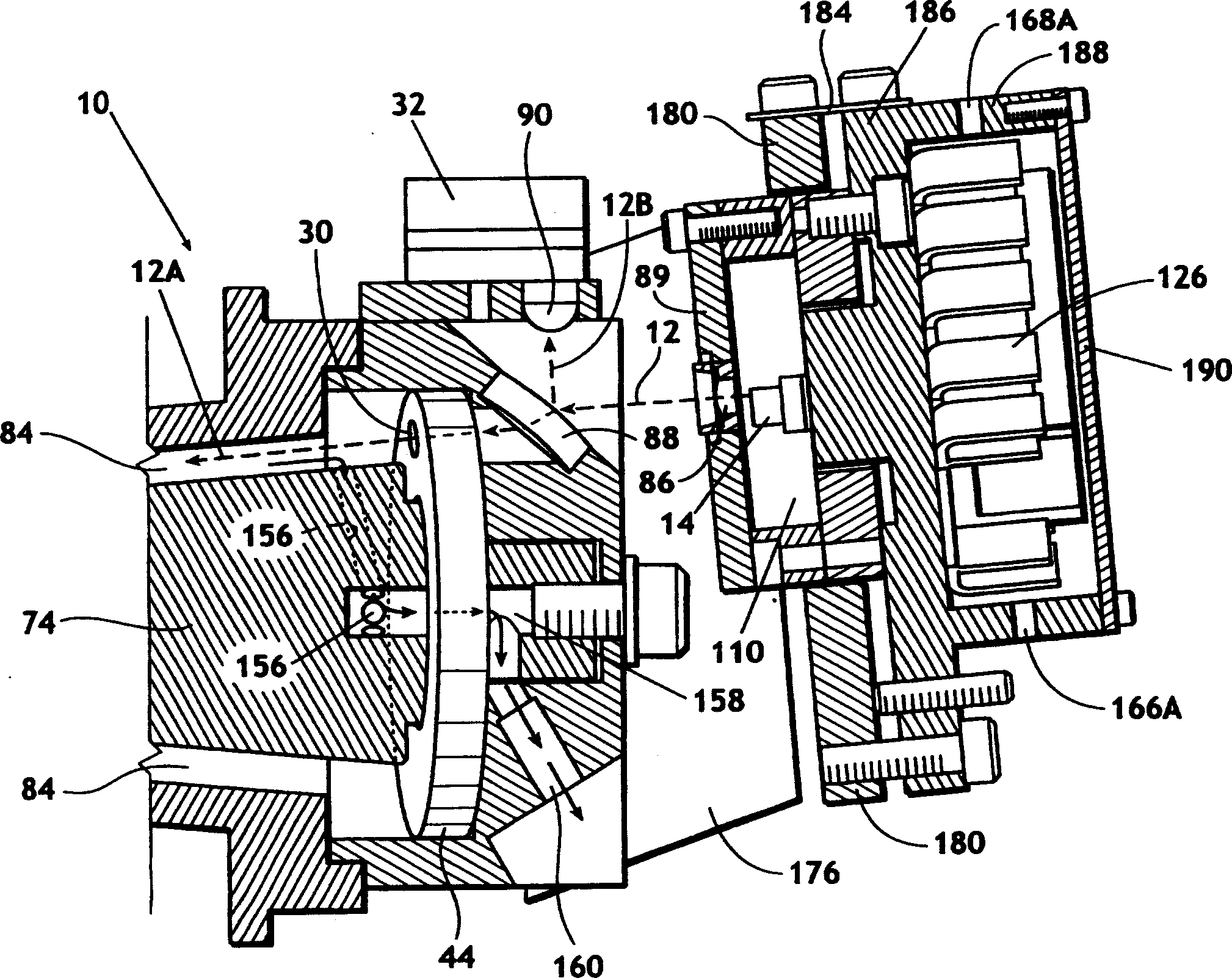
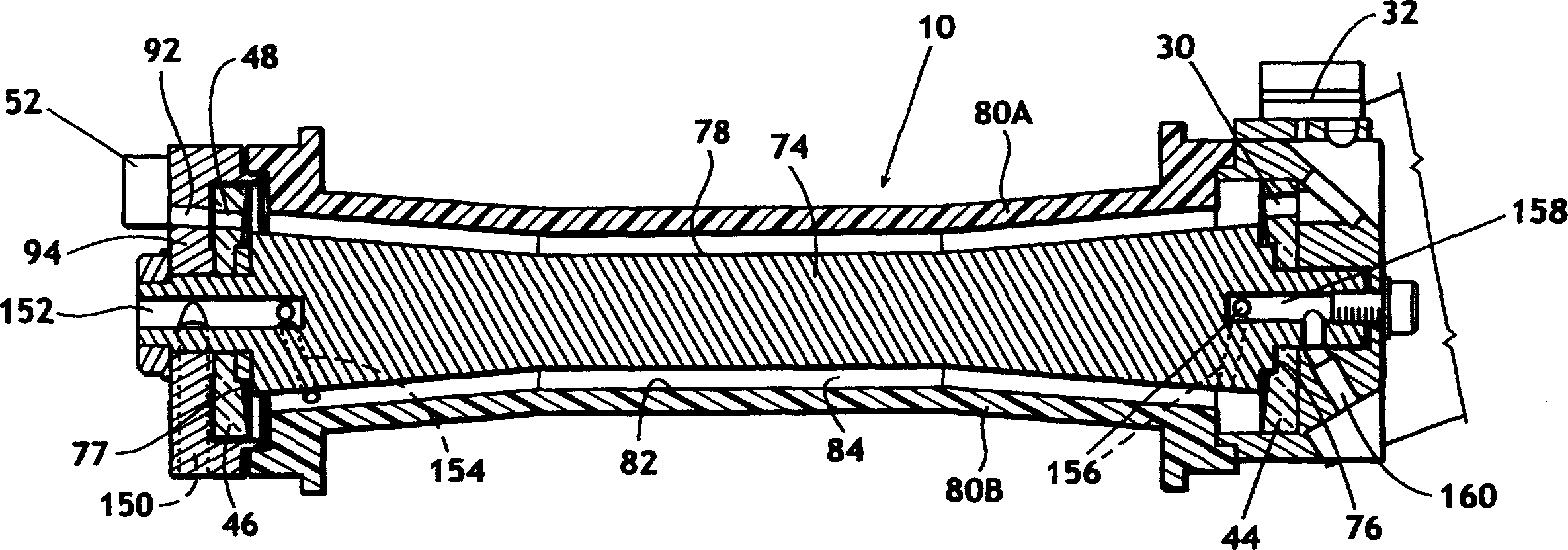
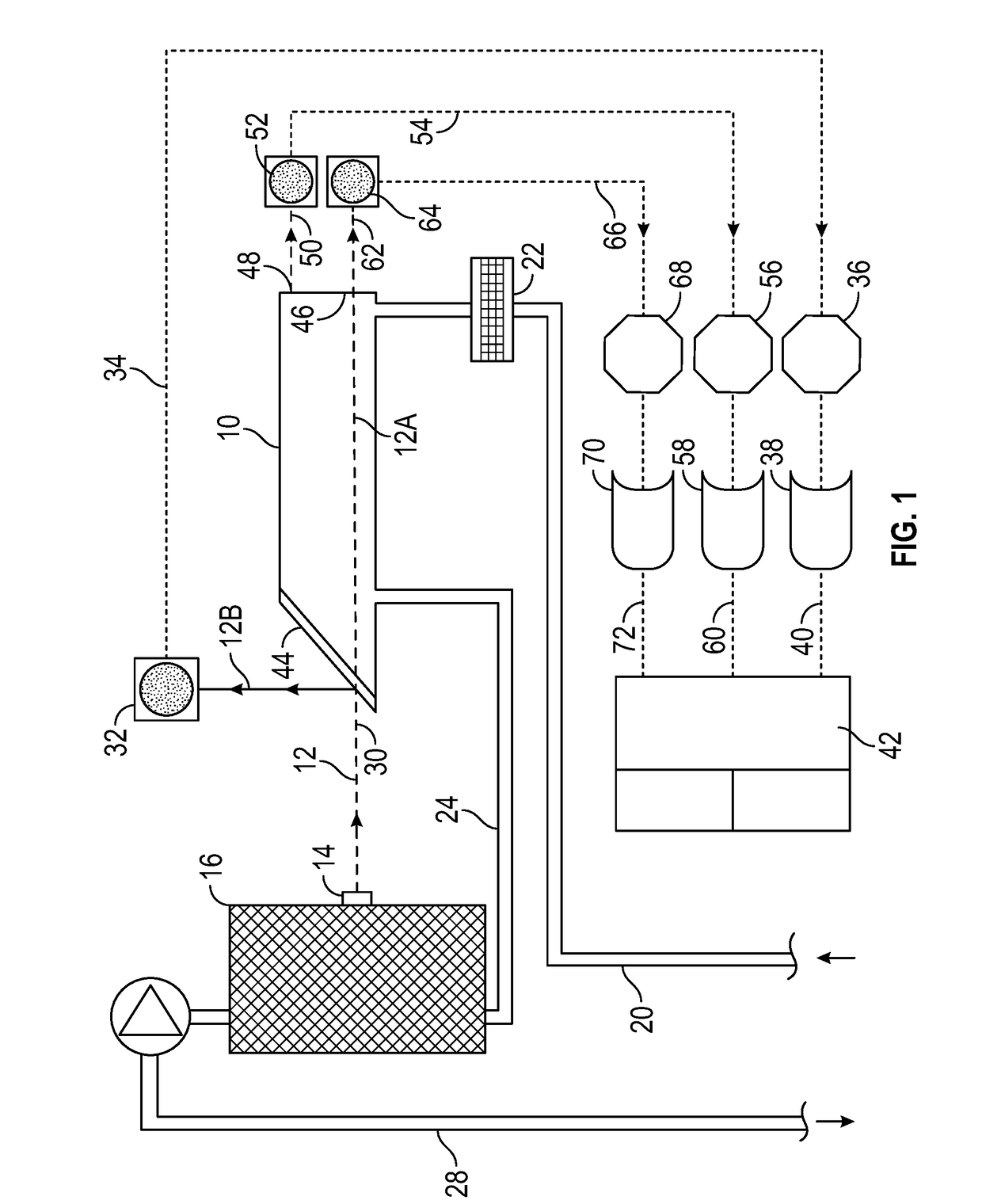
InactiveUS7352463B2Increase the itineraryImprove portabilityTransmissivity measurementsWavelengthAbsorption spectroscopy
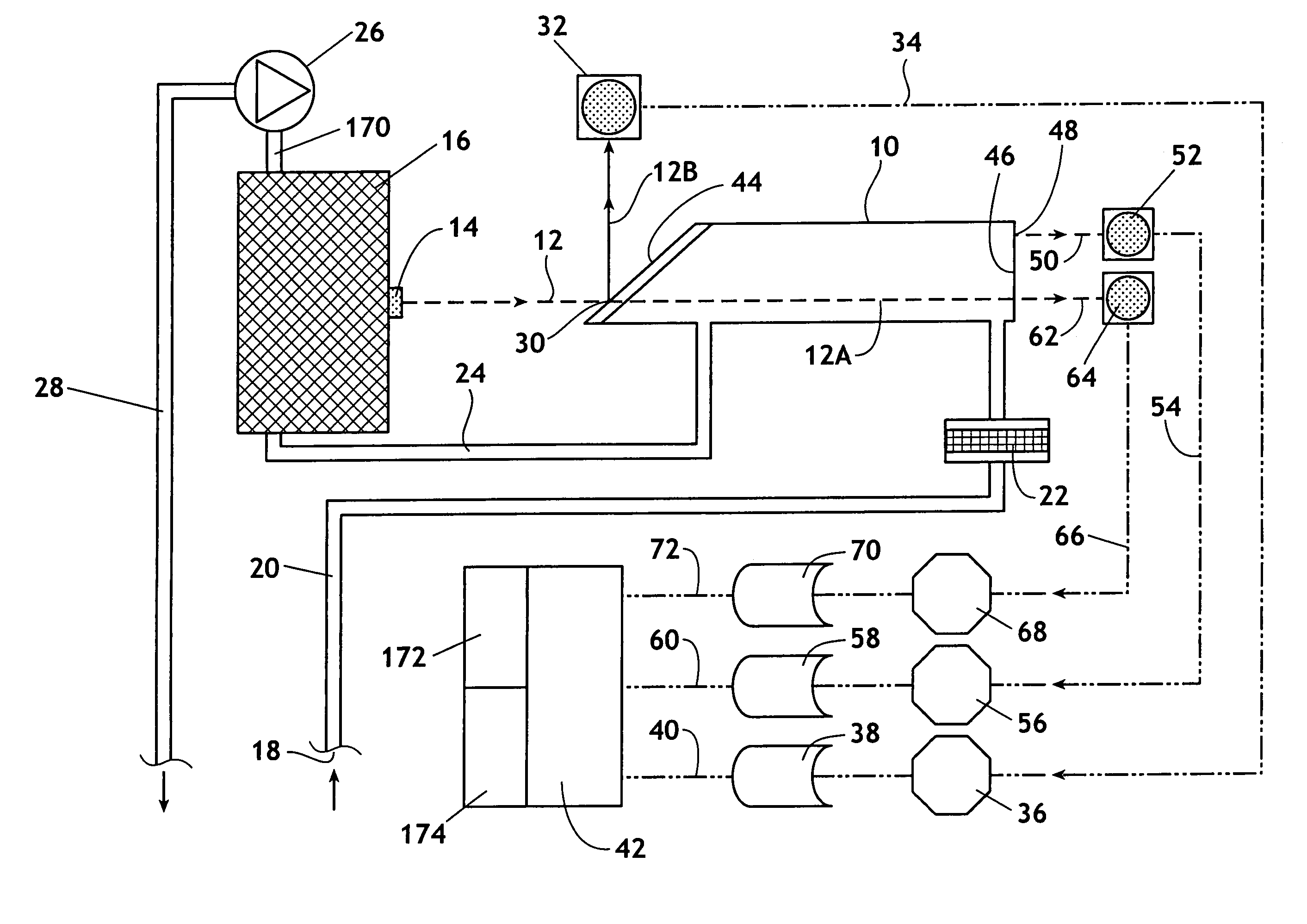
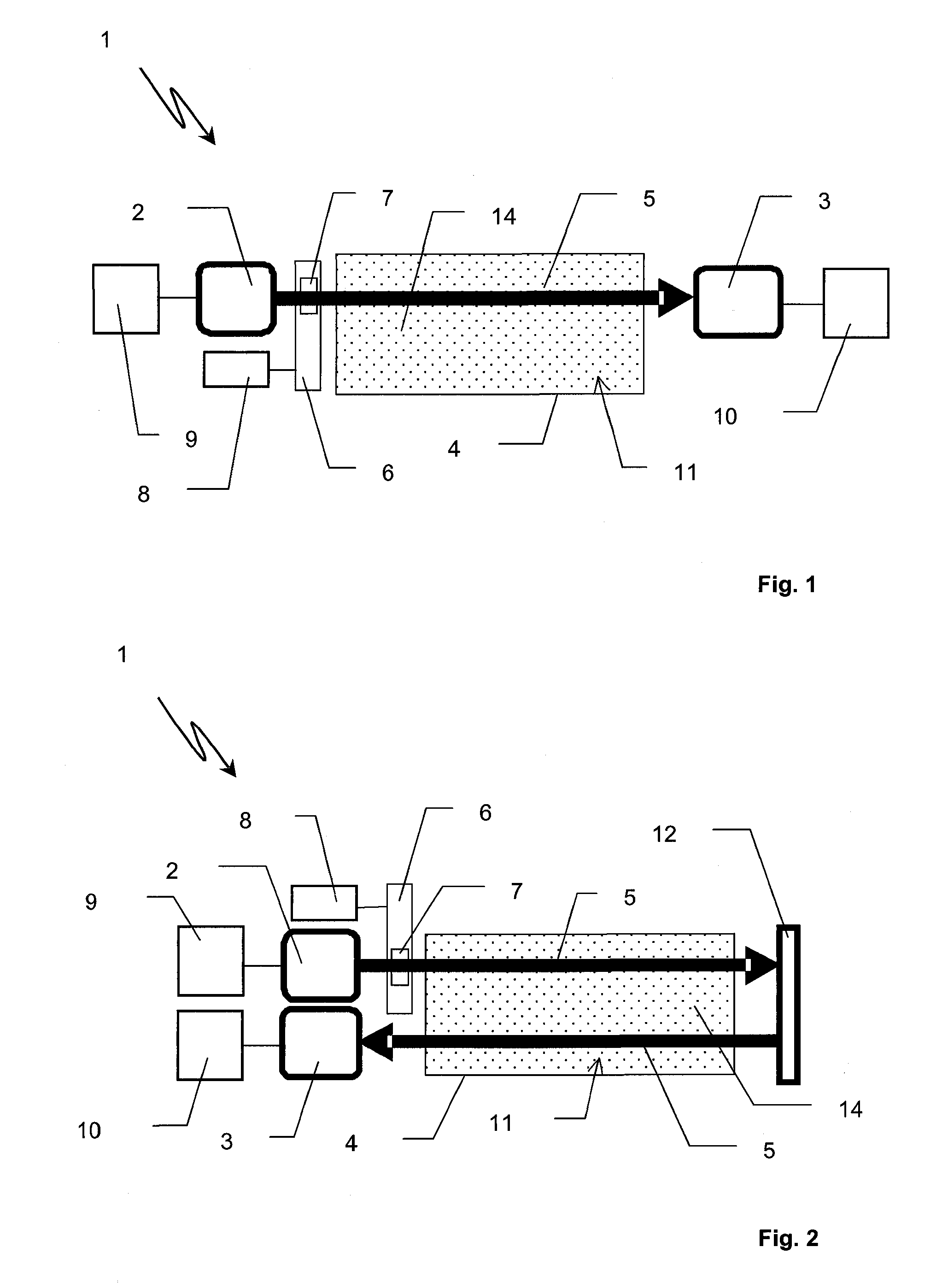
A method and device for measuring a concentration of a preselected gas in a gas sample are disclosed. The device comprises a Herriott type multipass cell (10) having a center axle (74) and a housing (80A, 80B) surrounding and spaced from the axle to provide a tubular sample cavity (84). The gas sample is pumped through the sample cavity via apertures (154, 156) provided in opposed ends of the axle. A first mirror (44) and a second mirror (46) are supported at opposed ends of the axle. A light source, e.g. a laser or LED, is provided for emitting a light beam into the sample cavity via an entry aperture (30) in the first mirror, the light beam having a wave length at which the preselected gas strongly absorbs. The beam is reflected between the mirrors for a number of times before exiting the cell via an exit aperture (48) in the second mirror and impinging on a detector (52). The device further comprises a reference detector (32) for monitoring the intensity of the unattenuated light beam and a detector for detecting the intensity of light transmitted through the second mirror after a single pass through the cell. The light source is operatively connected to a heat control assembly having a heat sink and the gas sample is passed said heat sink to augment temperature control of the light source.
Owner:ECOTEC INT HLDG LLC
High brightness X-ray absorption spectroscopy system
InactiveUS9448190B2Increase brightnessImprove thermal conductivityRadiation/particle handlingX-ray tube electrodesHigh energyDesign for X
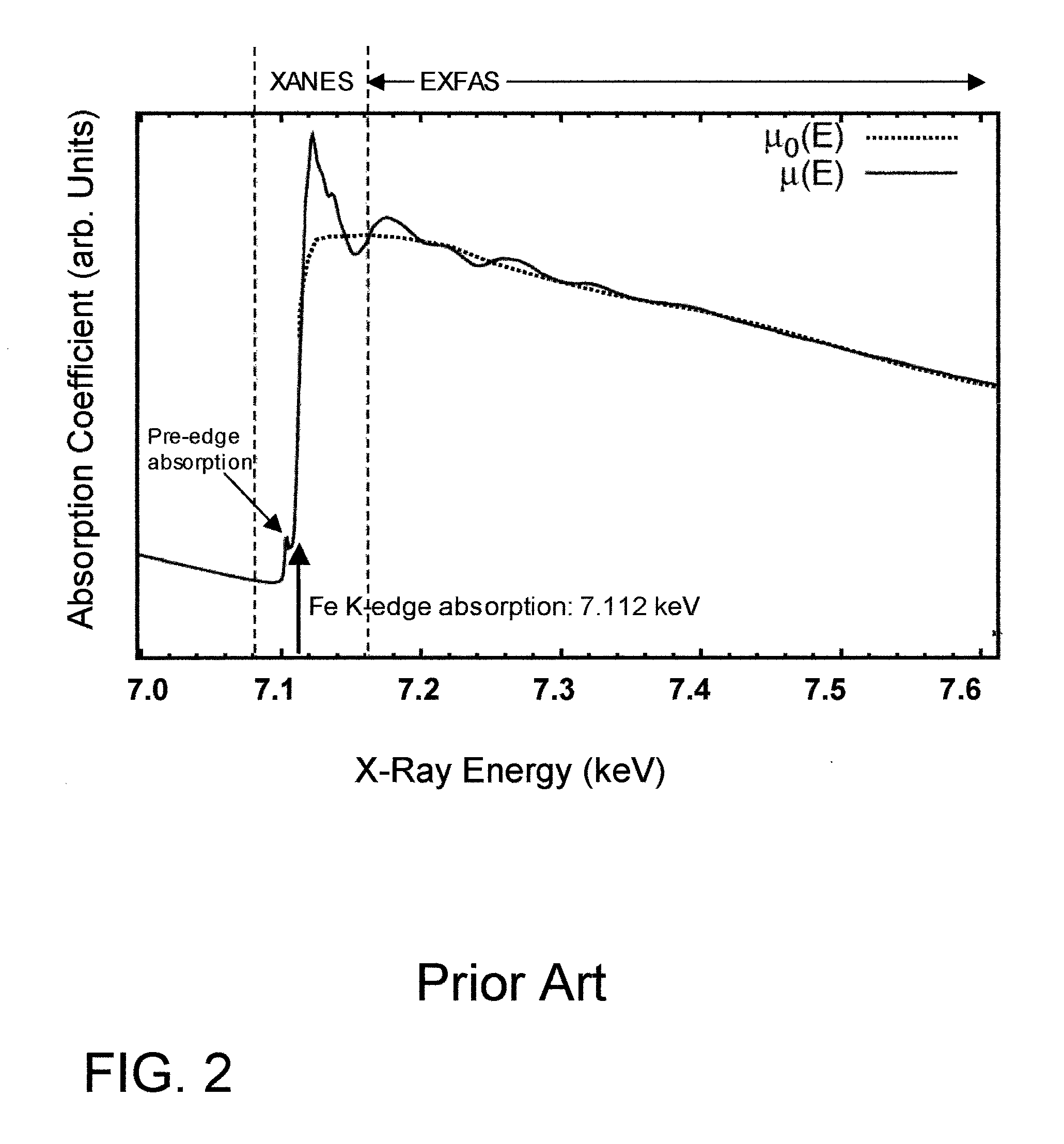
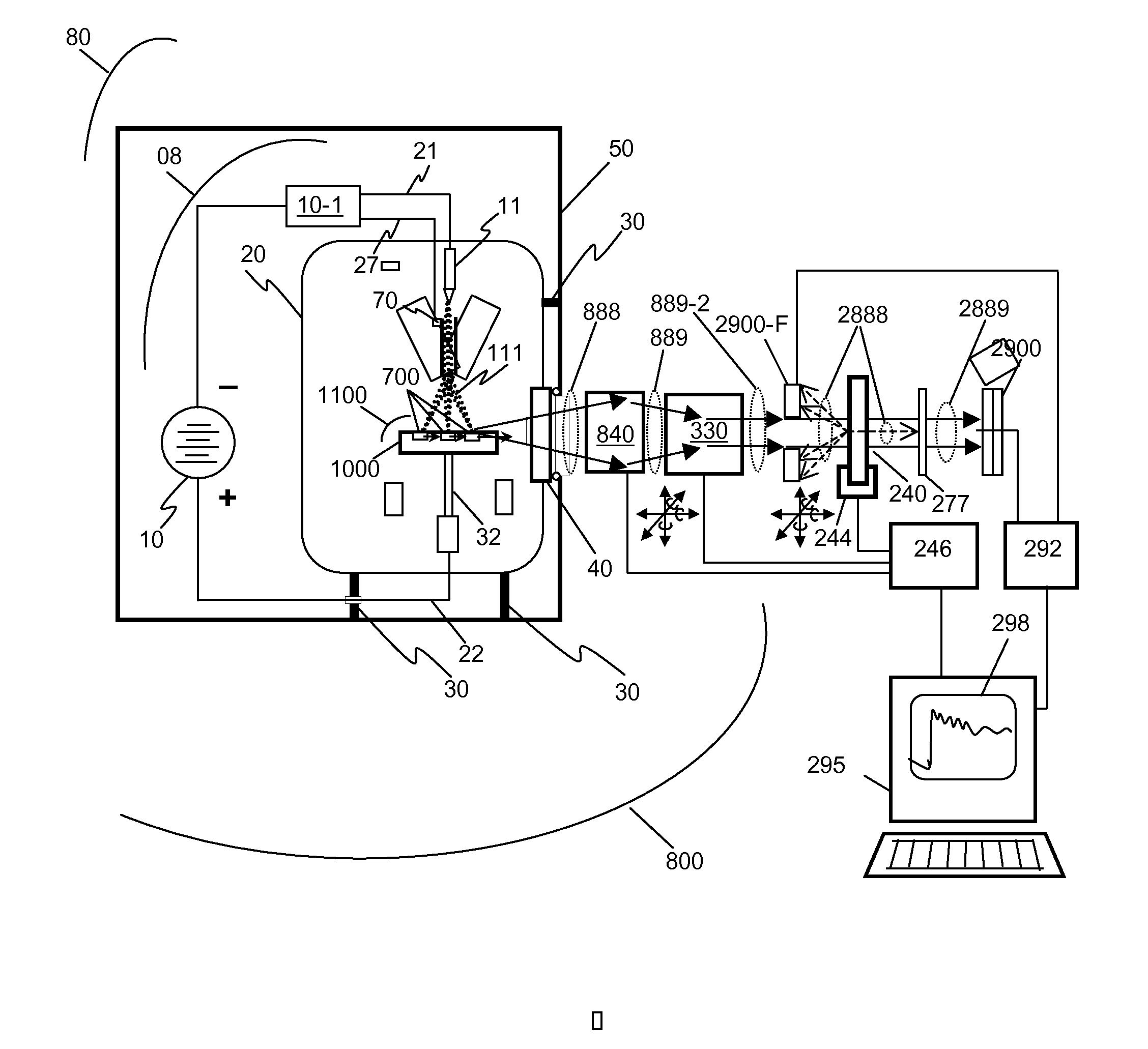
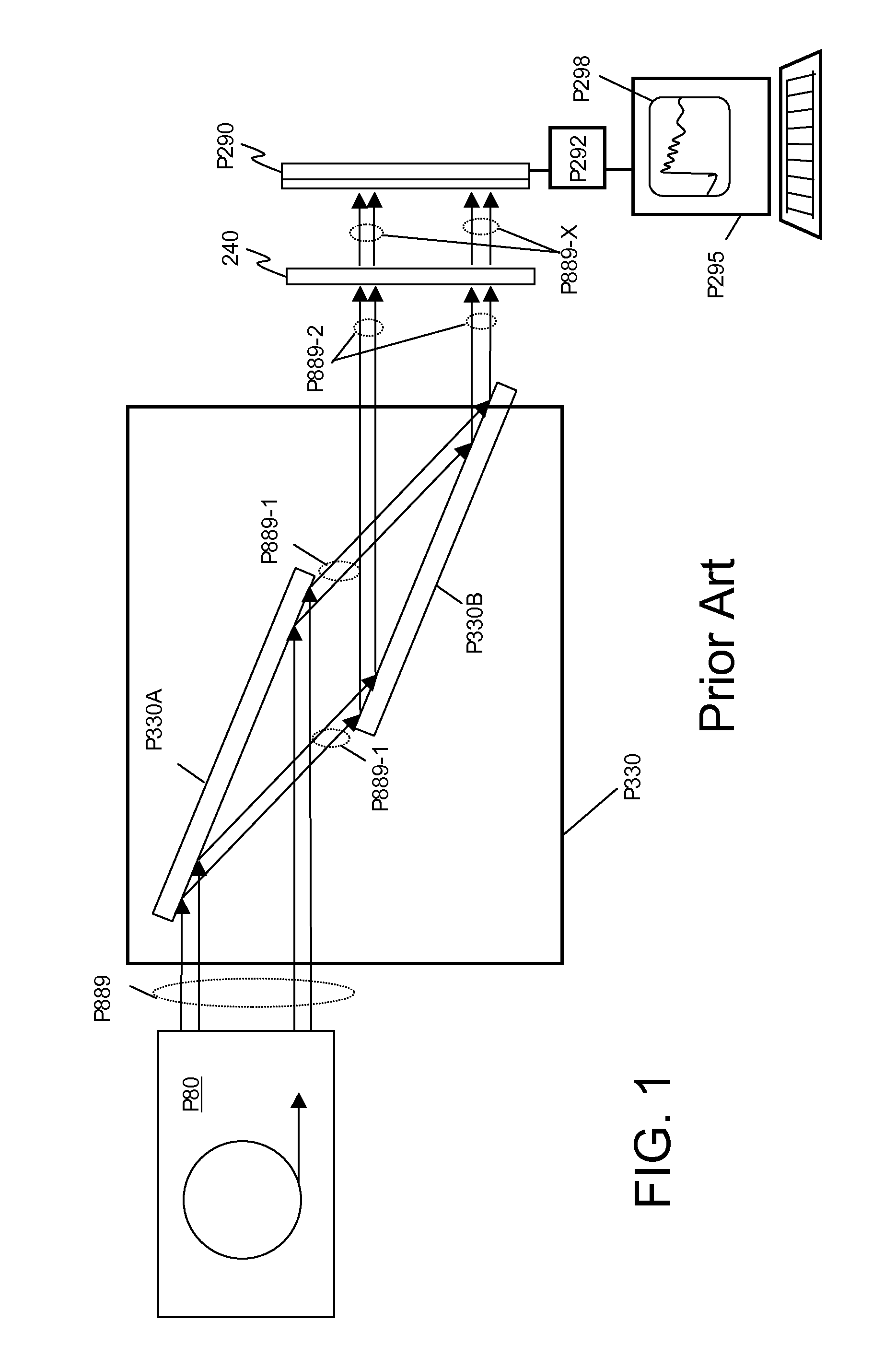
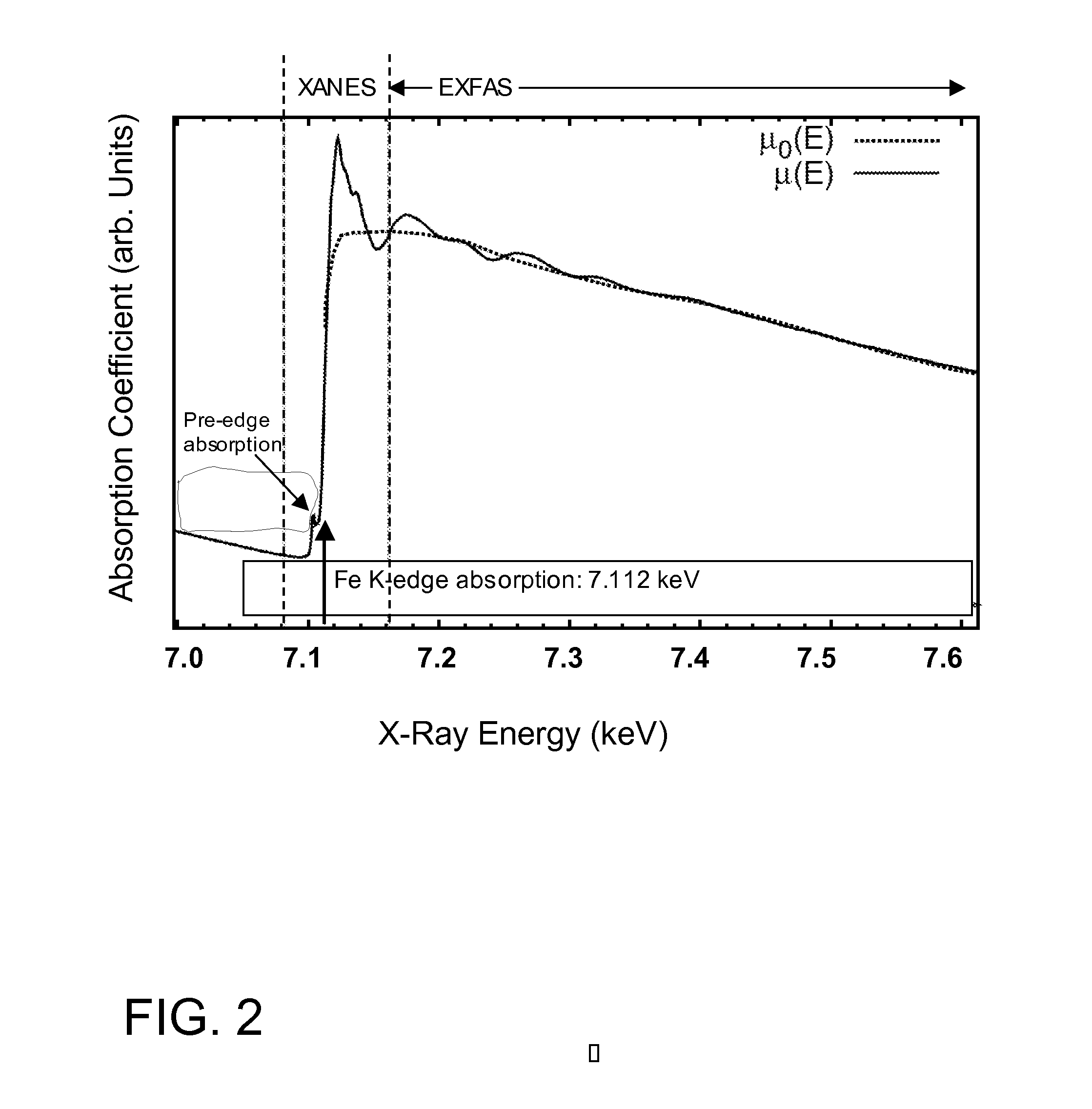
This disclosure presents systems for x-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) measurements that have x-ray flux and flux density several orders of magnitude greater than existing compact systems. These are useful for laboratory or field applications of x-ray absorption near-edge spectroscopy (XANES) or extended x-ray fine absorption structure (EXFAS) spectroscopy. The higher brightness is achieved by using designs for x-ray targets that comprise a number of aligned microstructures of x-ray generating materials fabricated in close thermal contact with a substrate having high thermal conductivity. This allows for bombardment with higher electron density and / or higher energy electrons, leading to greater x-ray brightness and high flux. The high brightness x-ray source is then coupled to an x-ray reflecting optical system to collimate the x-rays, and a monochromator, which selects the exposure energy. Absorption spectra of samples using the high flux monochromatic x-rays can be made using standard detection techniques.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
Packaged chip for multiplexing photonic crystal waveguide and photonic crystal slot waveguide devices for chip-integrated label-free detection and absorption spectroscopy with high throughput, sensitivity, and specificity
ActiveUS20130005606A1Most efficientPrecise positioningRadiation pyrometryColor measuring devicesSlot-waveguidePhotonic crystal
Systems and methods for chip-integrated label-free detection and absorption spectroscopy with high throughput, sensitivity, and specificity are disclosed. The invention comprises packaged chips for multiplexing photonic crystal waveguide and photonic crystal slot waveguide devices. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:OMEGA OPTICS
High brightness x-ray absorption spectroscopy system
InactiveUS20150357069A1Increase brightnessImprove thermal conductivityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray spectral distribution measurementHigh energyDesign for X
This disclosure presents systems for x-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) measurements that have x-ray flux and flux density several orders of magnitude greater than existing compact systems. These are useful for laboratory or field applications of x-ray absorption near-edge spectroscopy (XANES) or extended x-ray fine absorption structure (EXFAS) spectroscopy.The higher brightness is achieved by using designs for x-ray targets that comprise a number of aligned microstructures of x-ray generating materials fabricated in close thermal contact with a substrate having high thermal conductivity. This allows for bombardment with higher electron density and / or higher energy electrons, leading to greater x-ray brightness and high flux.The high brightness x-ray source is then coupled to an x-ray reflecting optical system to collimate the x-rays, and a monochromator, which selects the exposure energy. Absorption spectra of samples using the high flux monochromatic x-rays can be made using standard detection techniques.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
Laser-triggered plasma apparatus for atomic emission spectroscopy
Multiple energy sources, such as a laser and electrical current, are employed, in close coordination, spatially and temporally, to clean a sample, vaporize its material and excite vapor atoms for the purpose of atomic emission spectroscopy. These methods permit better monitoring and control of the individual processes in real time, lead to higher consistency and higher quality optical emission spectra, and enhance the measurements of non-conducting solids, liquids and gases. Additionally, a portable instrument is provided with both laser source and spectrometer optically coupled to a hand-holdable unit.
Owner:THERMO NITON ANALYZERS
Quartz member for semiconductor manufacturing equipment and method for metal analysis in quartz member
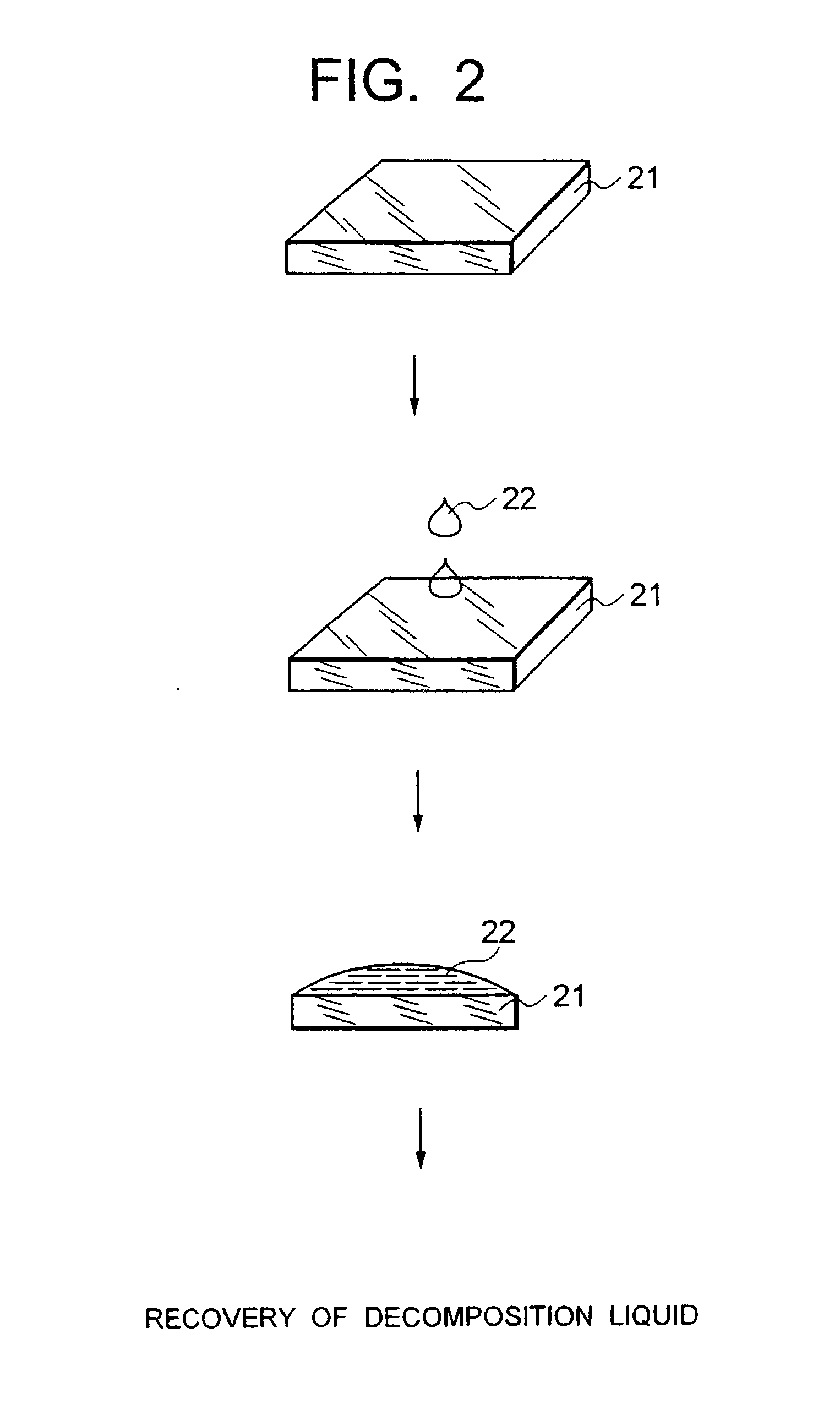
InactiveUS20030000458A1Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityAfter-treatment apparatusFrom solid stateDecompositionContamination
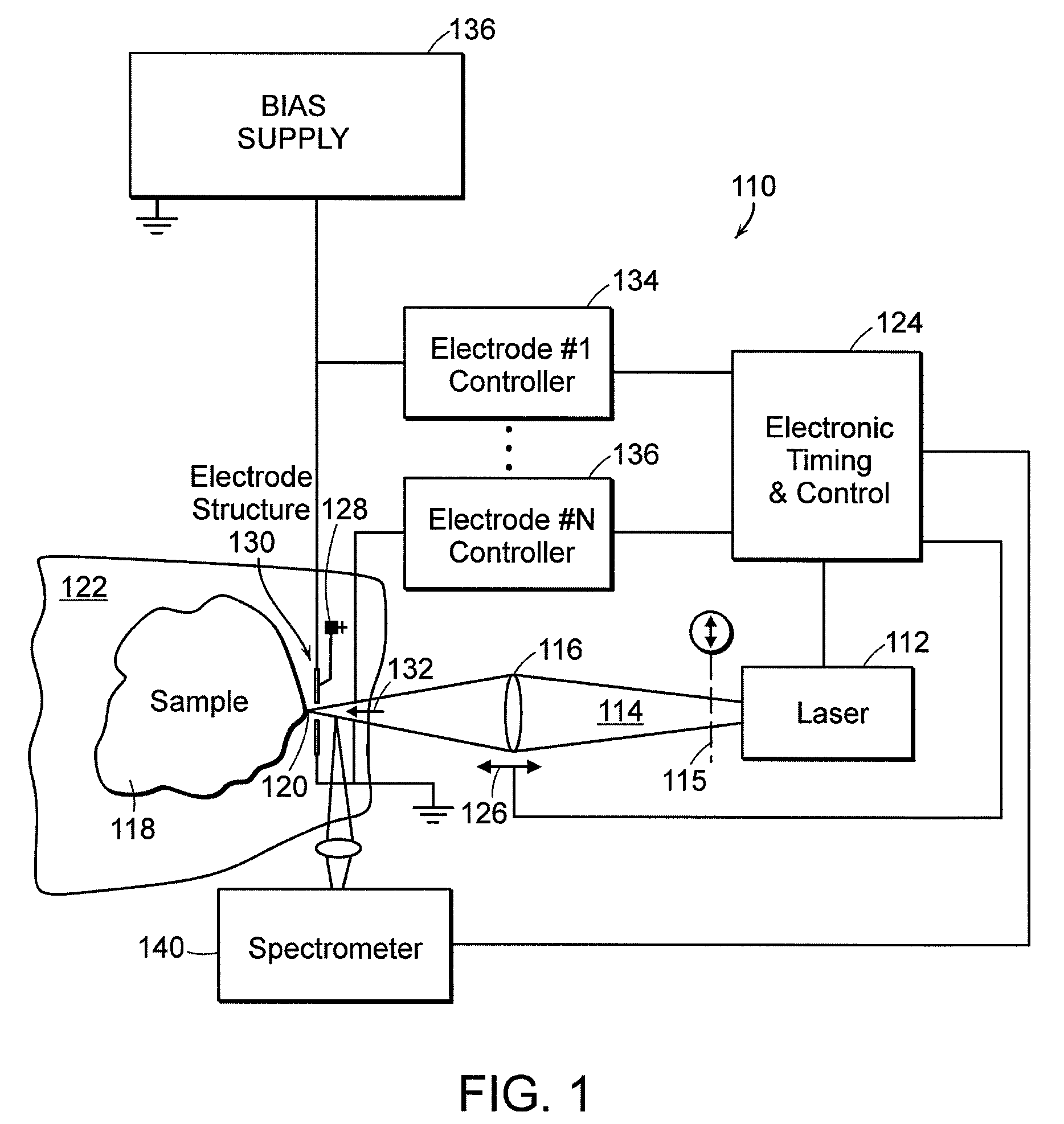
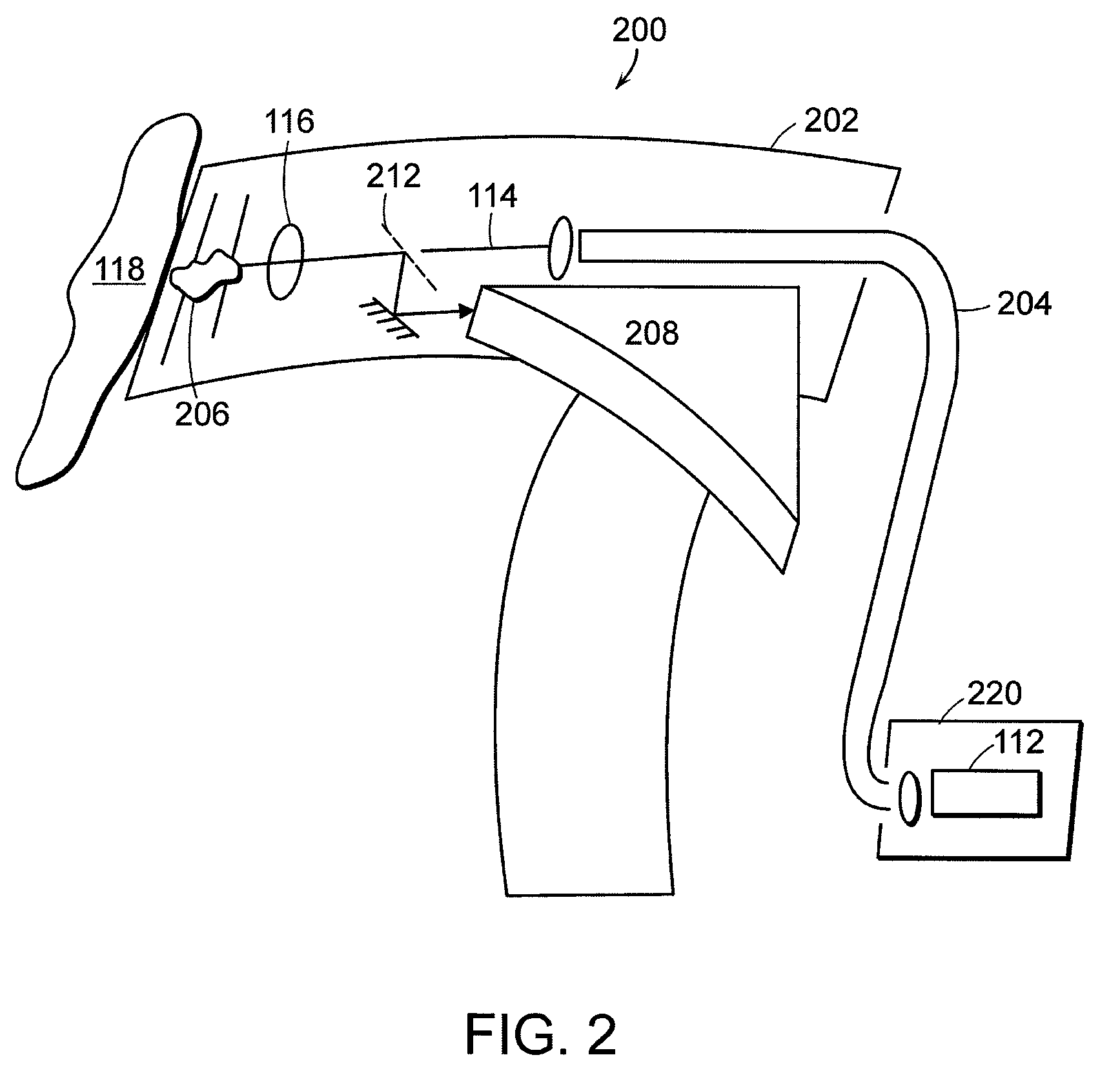
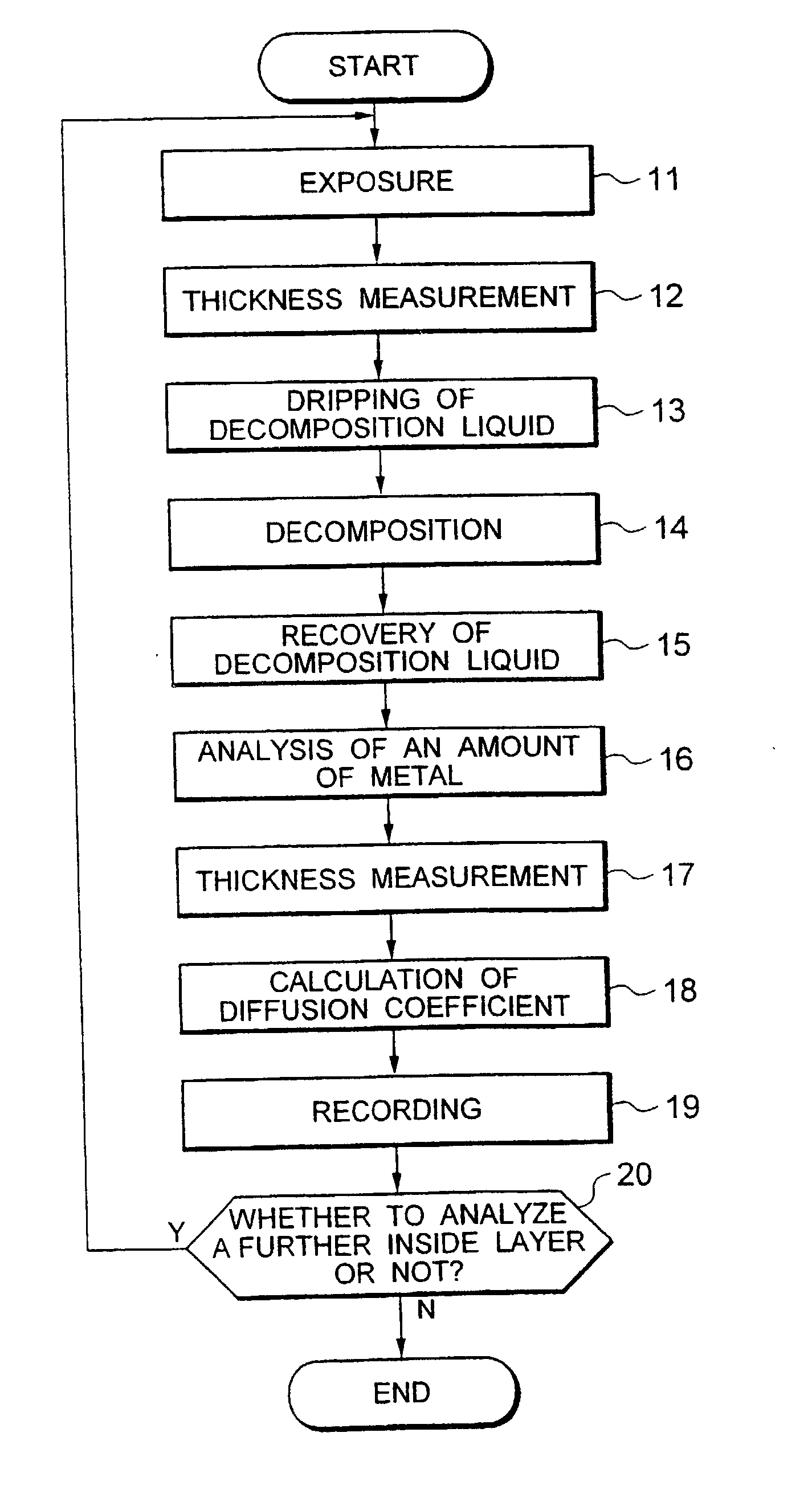
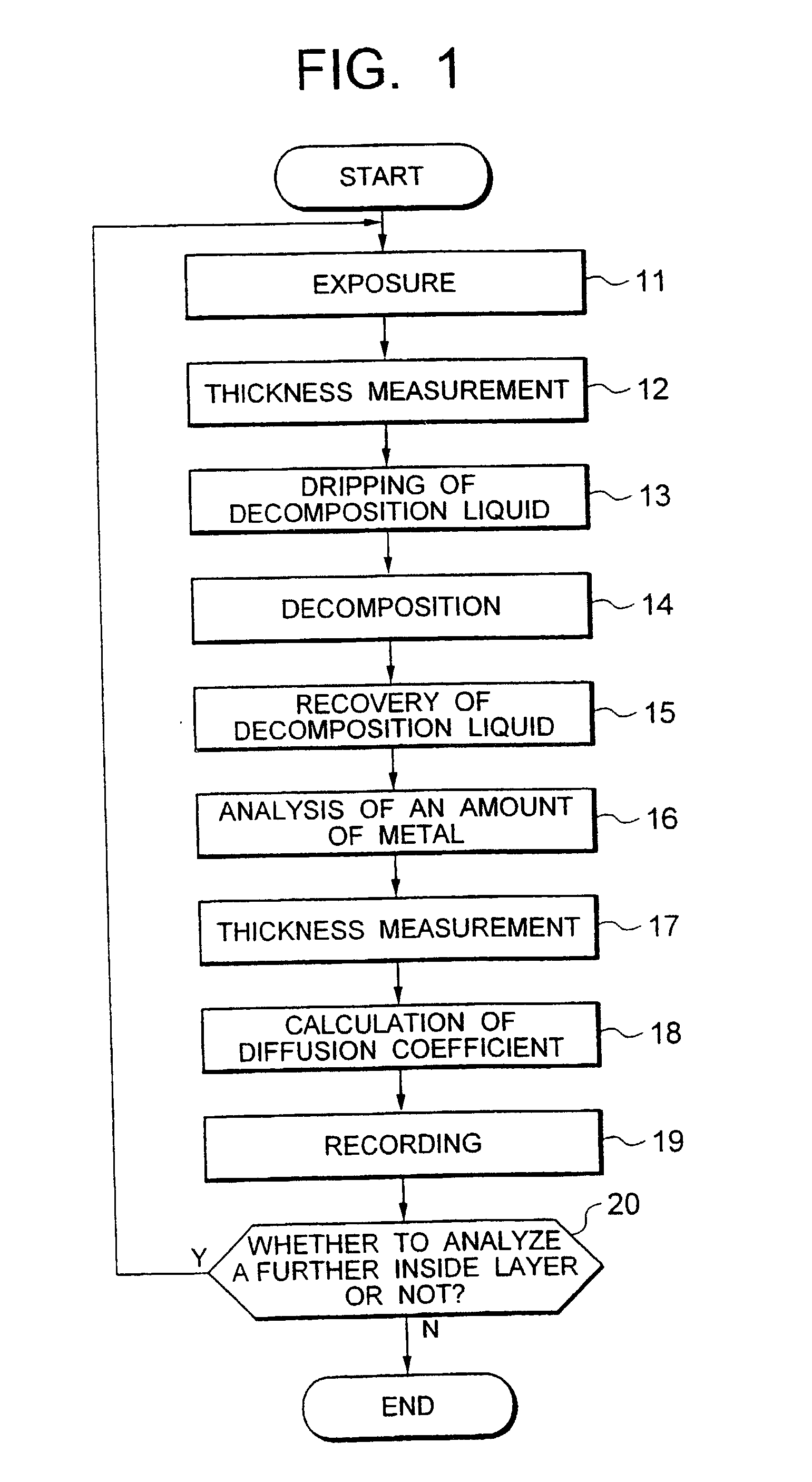
Quartz member such as a quartz tube for semiconductor manufacturing equipment capable of heat treating a substrate to be treated without causing contamination, a manufacturing method of such quartz member, thermal treatment equipment furnished with such quartz member, and an analysis method of metal in quartz member are provided. A quartz specimen is immersed in hydrofluoric acid to expose a layer to be analyzed located at a prescribed depth. On an exposed surface, a decomposition liquid such as hydrofluoric acid or nitric acid is dripped to decompose only an extremely thin layer to be analyzed, followed by recovering of the decomposition liquid. The decomposition liquid is quantitatively analyzed by use of atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) or the like to measure an amount of metal contained in the decomposition liquid. From a difference of thicknesses before and after the decomposition and an area of dripped decomposition liquid, a volume of a decomposed layer to be analyzed is obtained. From this and the amount of metal contained in the decomposition liquid, a concentration of metal contained in the layer to be analyzed, in addition a diffusion coefficient of a layer to be analyzed is calculated. With thus obtained diffusion coefficient as an index, quartz material in which metal diffuses with difficulty is sorted out. With thus sorted quartz material, a quartz member used for semiconductor manufacturing equipment such as a quartz tube is manufactured.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Detection of contamination in imaging systems by fluorescence and/or absorption spectroscopy
InactiveUS7087907B1Improve efficiencySignificant timePhotomechanical apparatusOptically investigating flaws/contaminationMulti pollutantFluorescence
Process and system for detection of contamination in an imaging system, including providing an imaging system having one or more element having a surface for reflecting or refracting first incident radiation; mounting with respect to at least one of the one or more element one or more detector capable of sensing third radiation emitted or transmitted by one or more contaminant on the surface of the one or more element when second radiation is absorbed by the one or more contaminant; applying the first incident radiation and / or the second radiation to the at least one element; and detecting with the one or more detector the third radiation emitted or transmitted by the one or more contaminant.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Background-free absorption spectroscopy using spectral differentiator
ActiveUS8149415B2Reduce impactControl depthRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryDifferentiatorAtomic absorption spectroscopy
An absorption spectrometer provides improved rejection of background radiation signal by employing a frequency-swept laser signal without frequency dithering and performing an effective differentiation of output light from a test cell to eliminate these constant or slowly varying background radiation levels.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
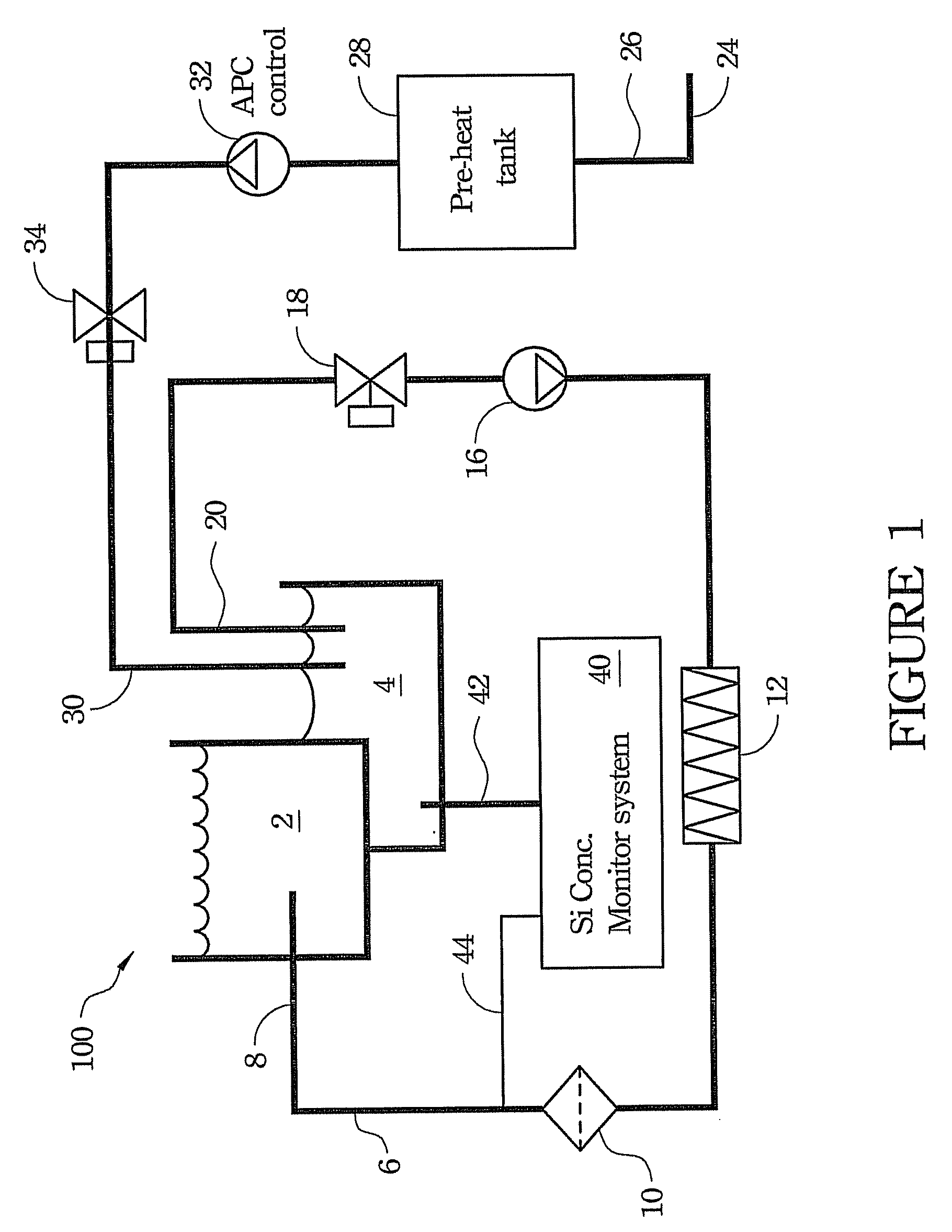
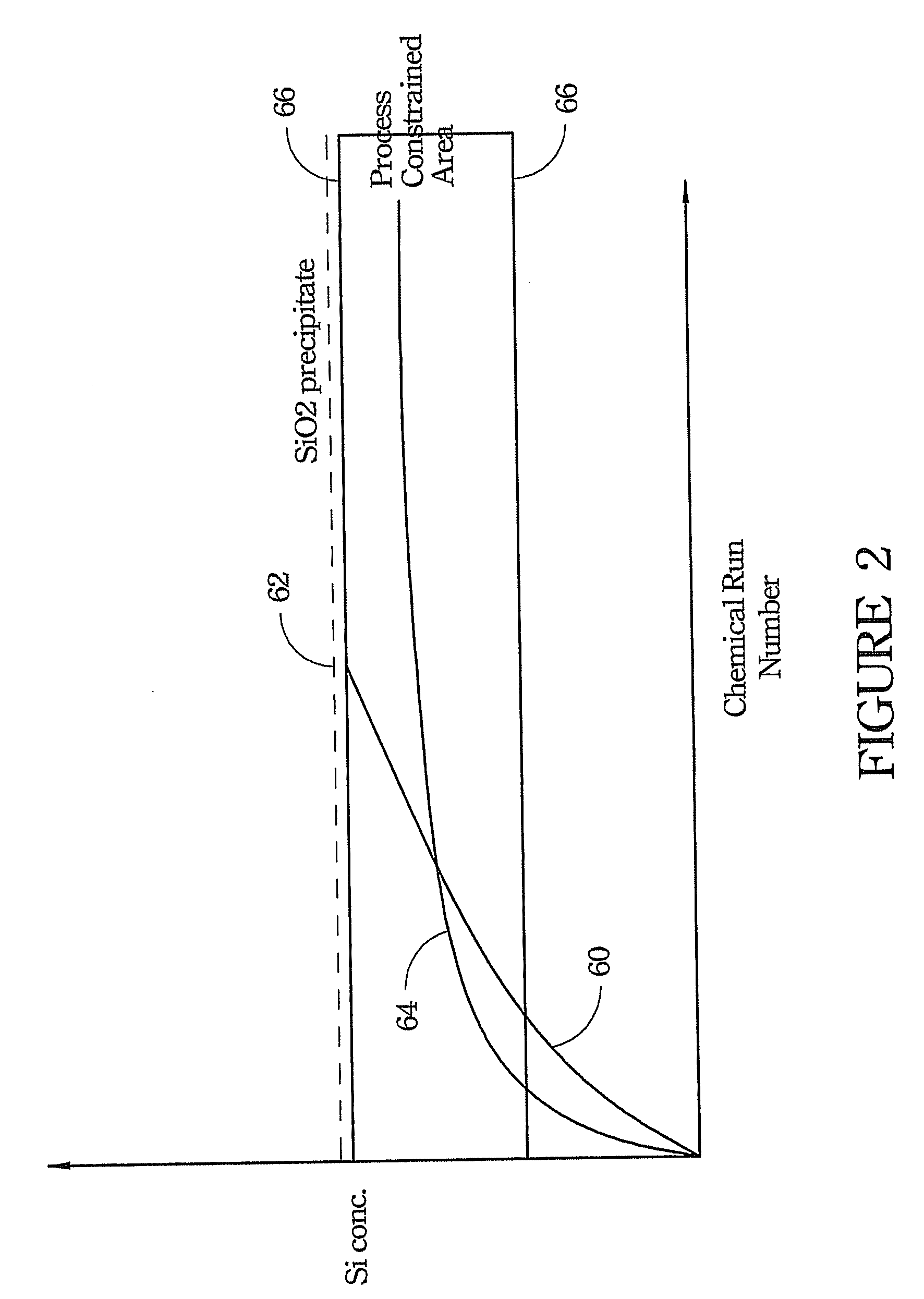
Apparatus and method for controlling silicon nitride etching tank
ActiveUS20080179293A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDecorative surface effectsO-Phosphoric AcidSteady state temperature
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
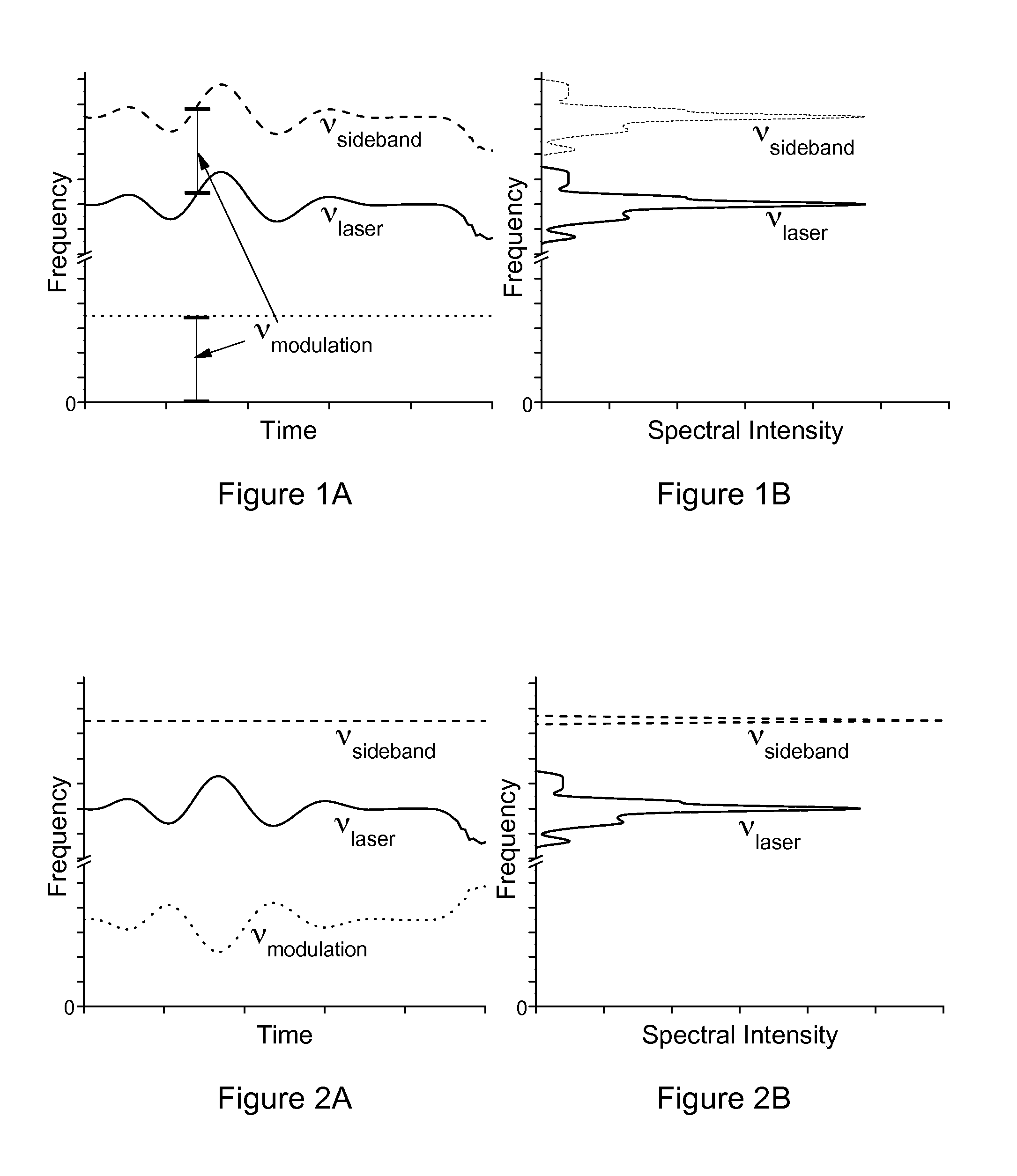
Cavity enhanced absorption spectroscopy with a laser modulation side-band frequency locked to the cavity
A cavity enhanced absorption spectrometer (CEAS) and method for controlling the same. The CEAS includes a coherent electro-magnetic radiation source, an electro-magnetic modulator that creates a sideband with an adjustable frequency that is offset from the radiation source frequency by imparting an adjustable frequency modulation to the radiation. The CEAS also includes a RF source that drives the electro-magnetic modulator and a cavity enhanced absorption resonator (CEAR) that receives the sideband. A detector measures the proximity of the frequency of the sideband relative to the resonant frequency of the CEAR and generates a proximity detector signal, which is converted by a controller to a control signal that controls at least one of the RF source and the resonant frequency of the CEAR such that the frequency of the sideband and the resonant frequency of the CEAR are adjusted to maintain a predetermined proximity therebetween.
Owner:ENTANGLEMENT TECH
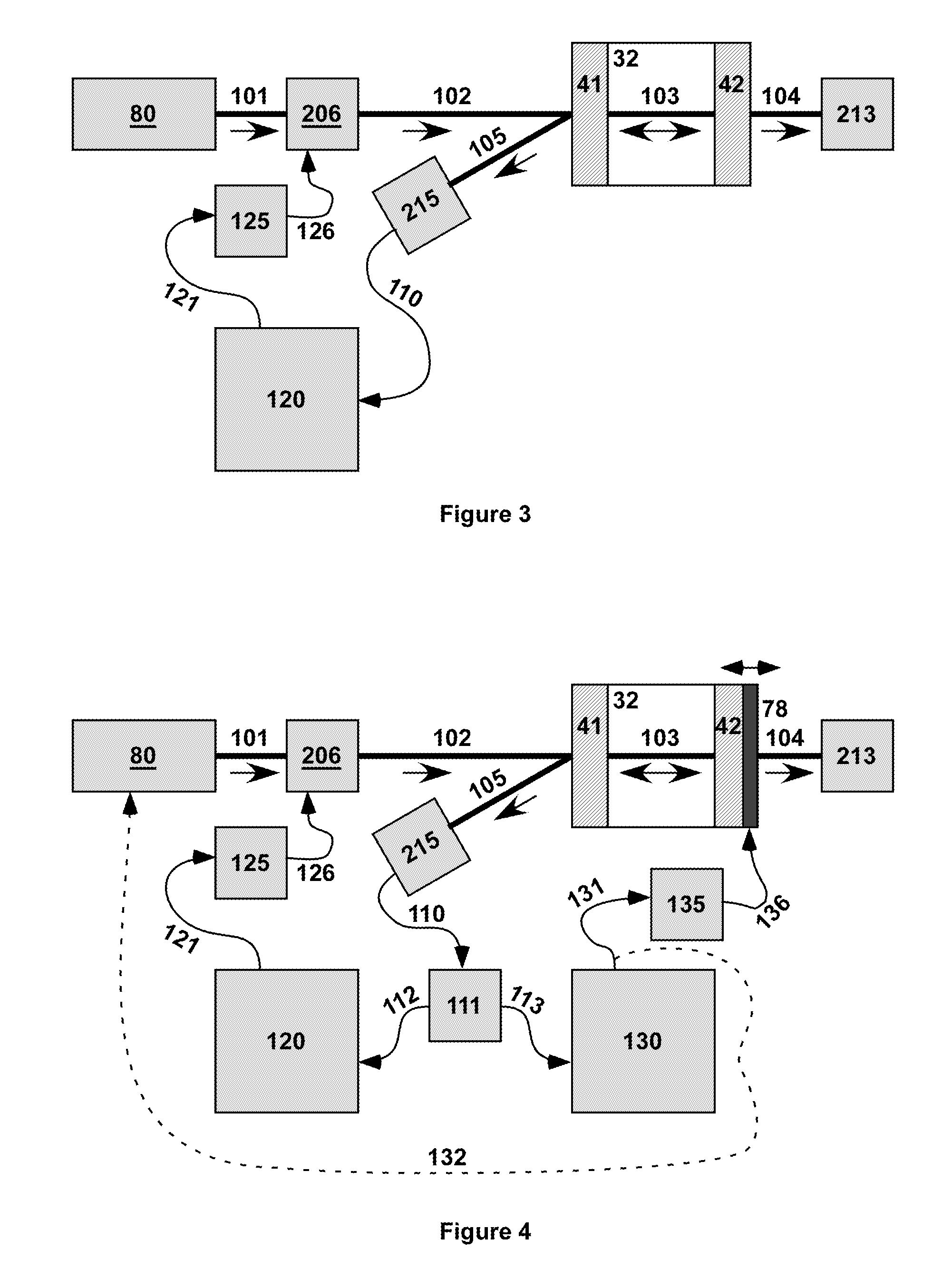
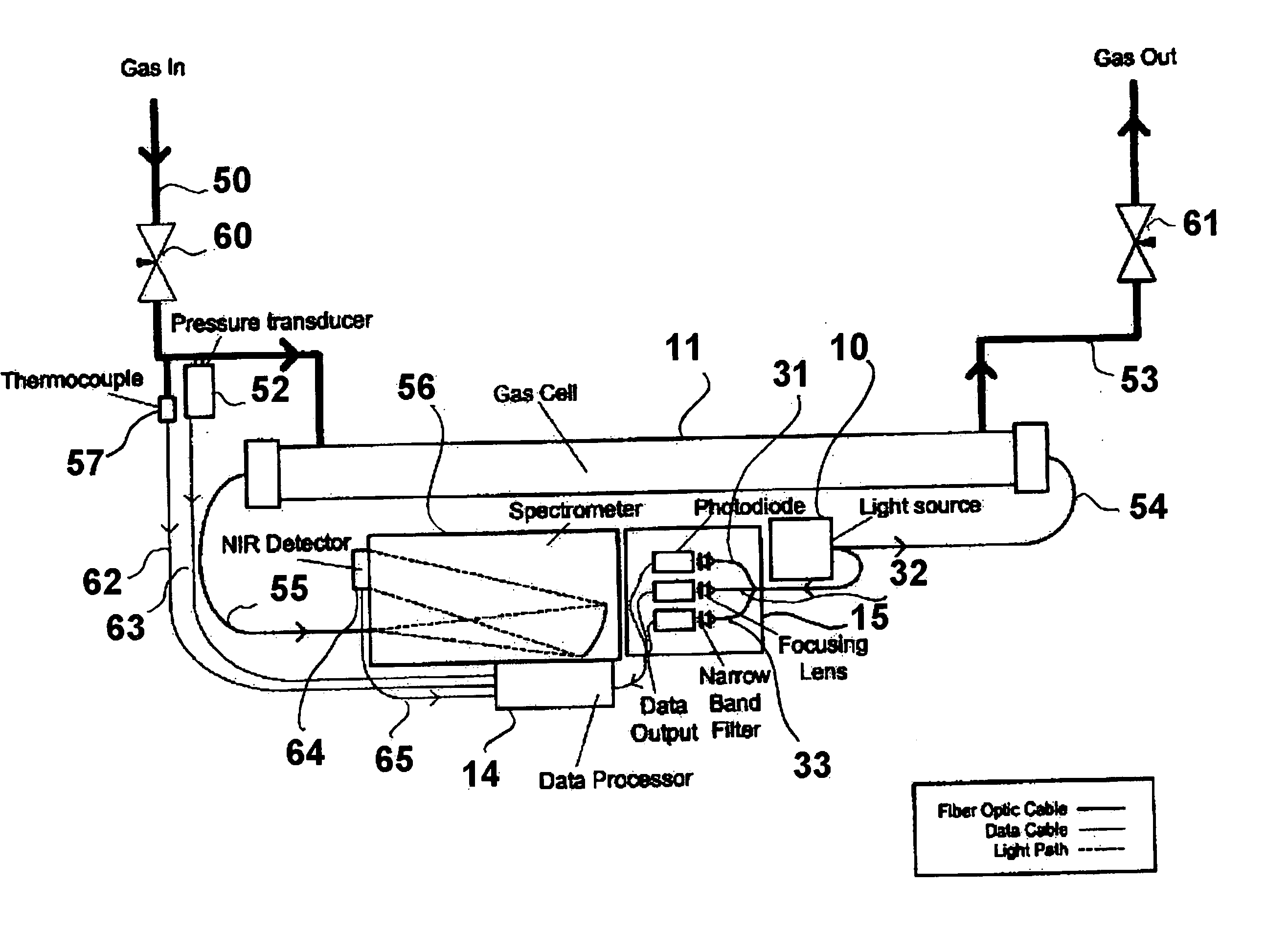
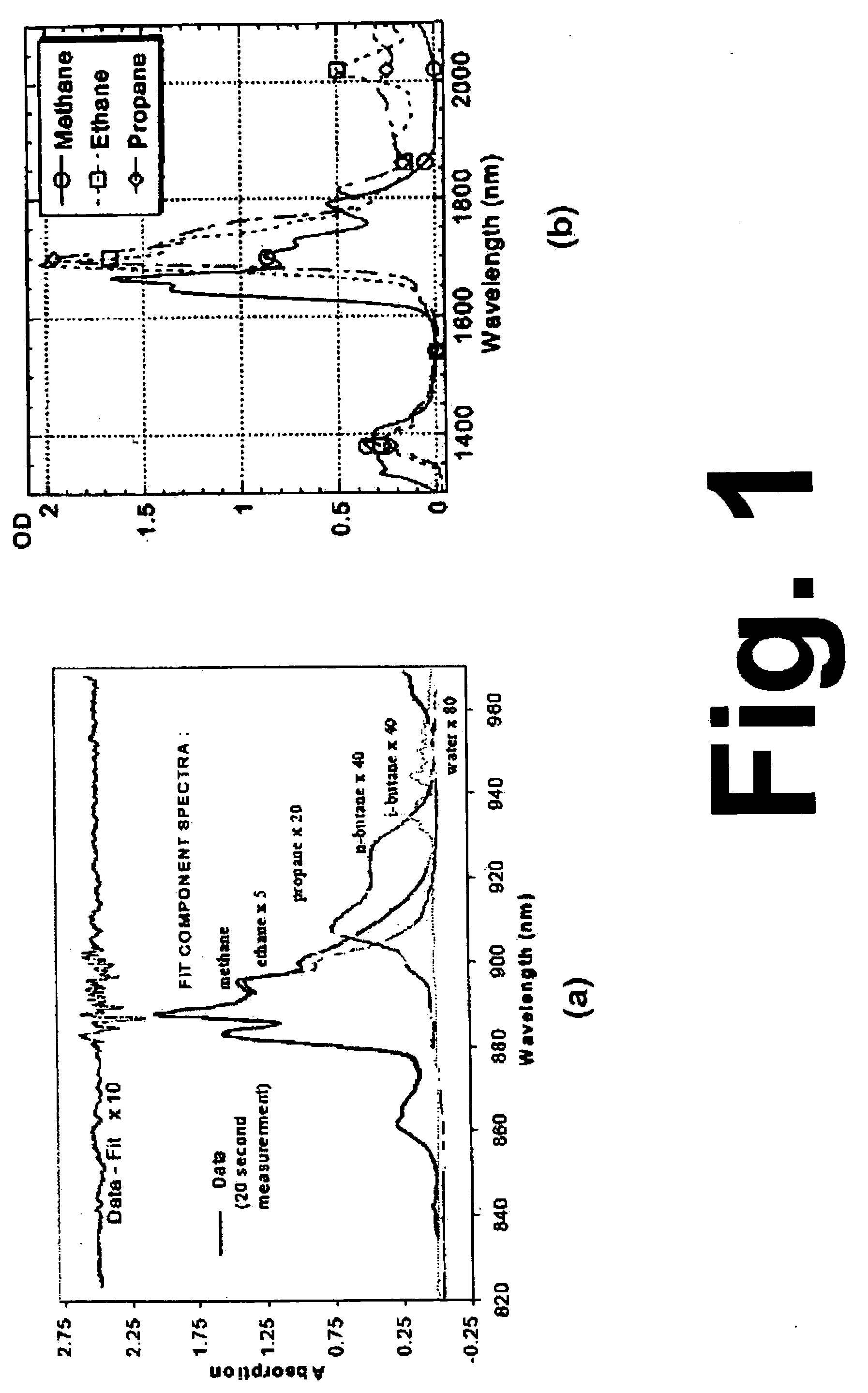
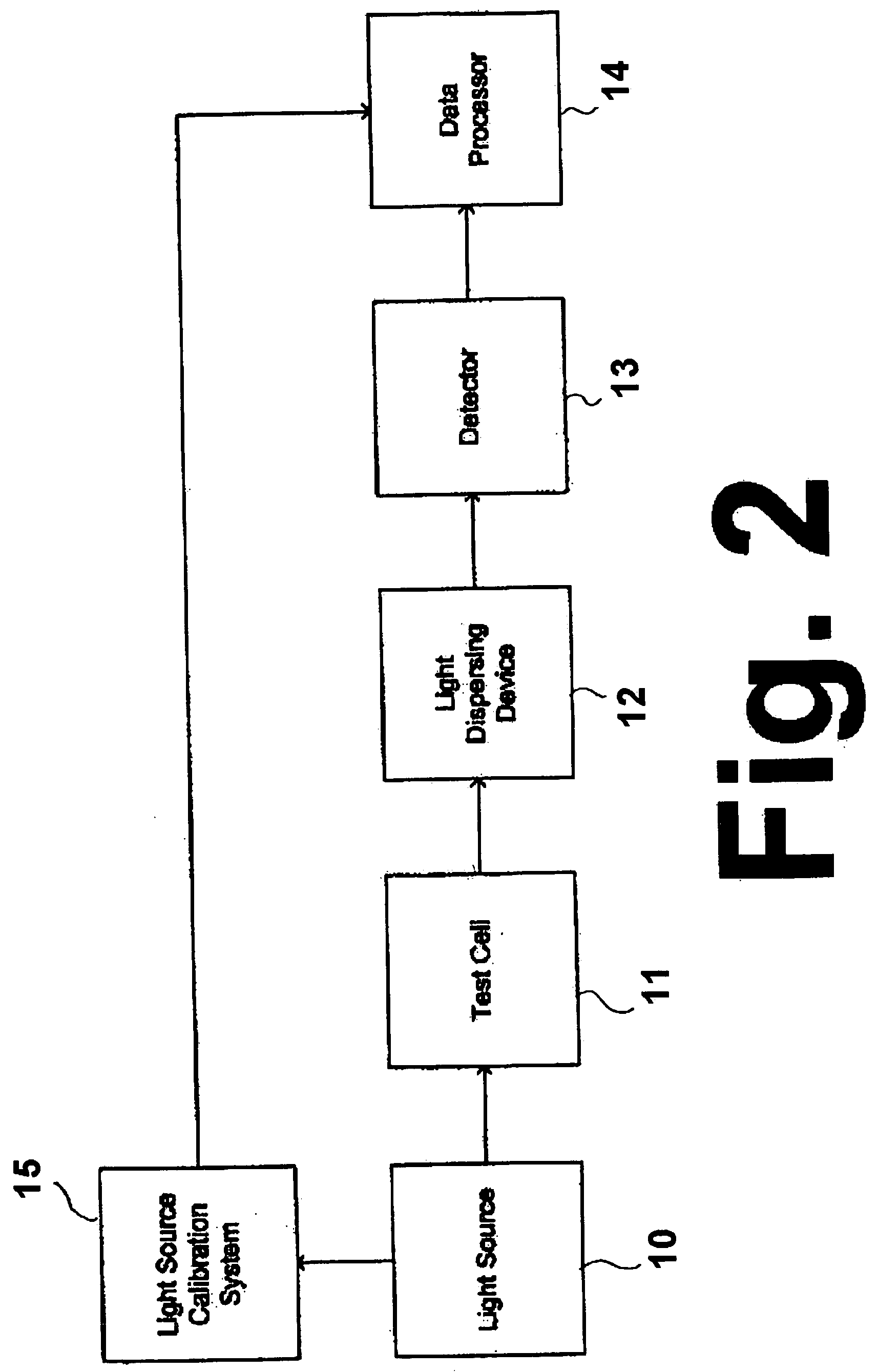
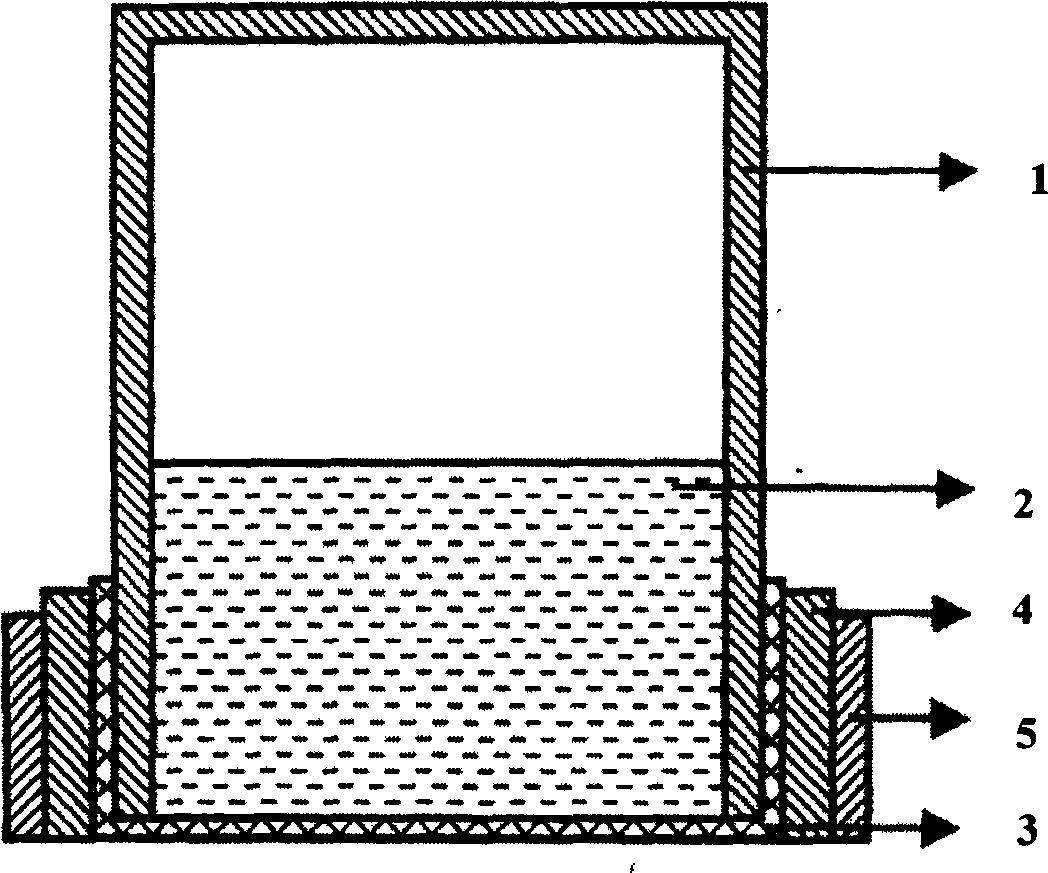
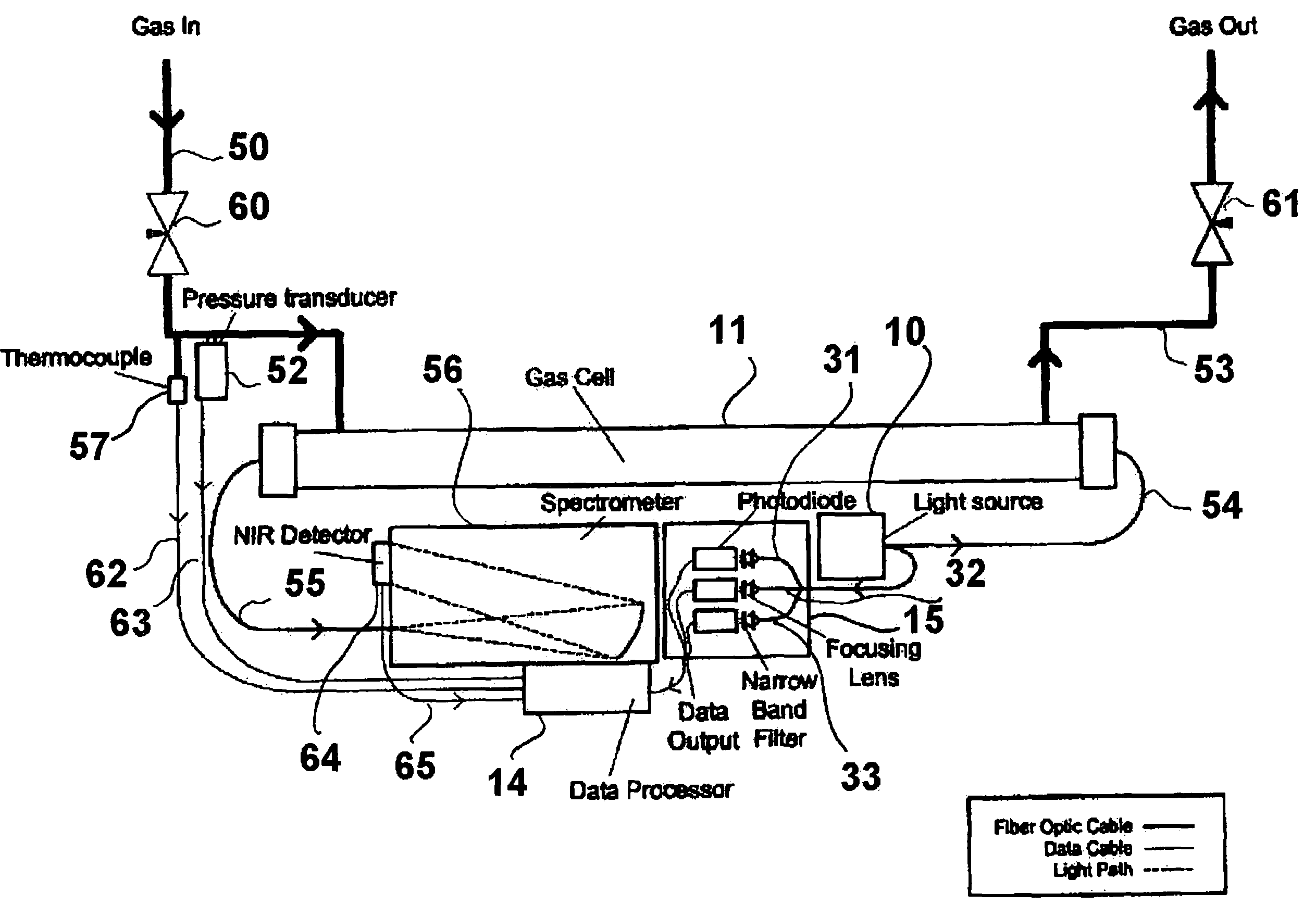
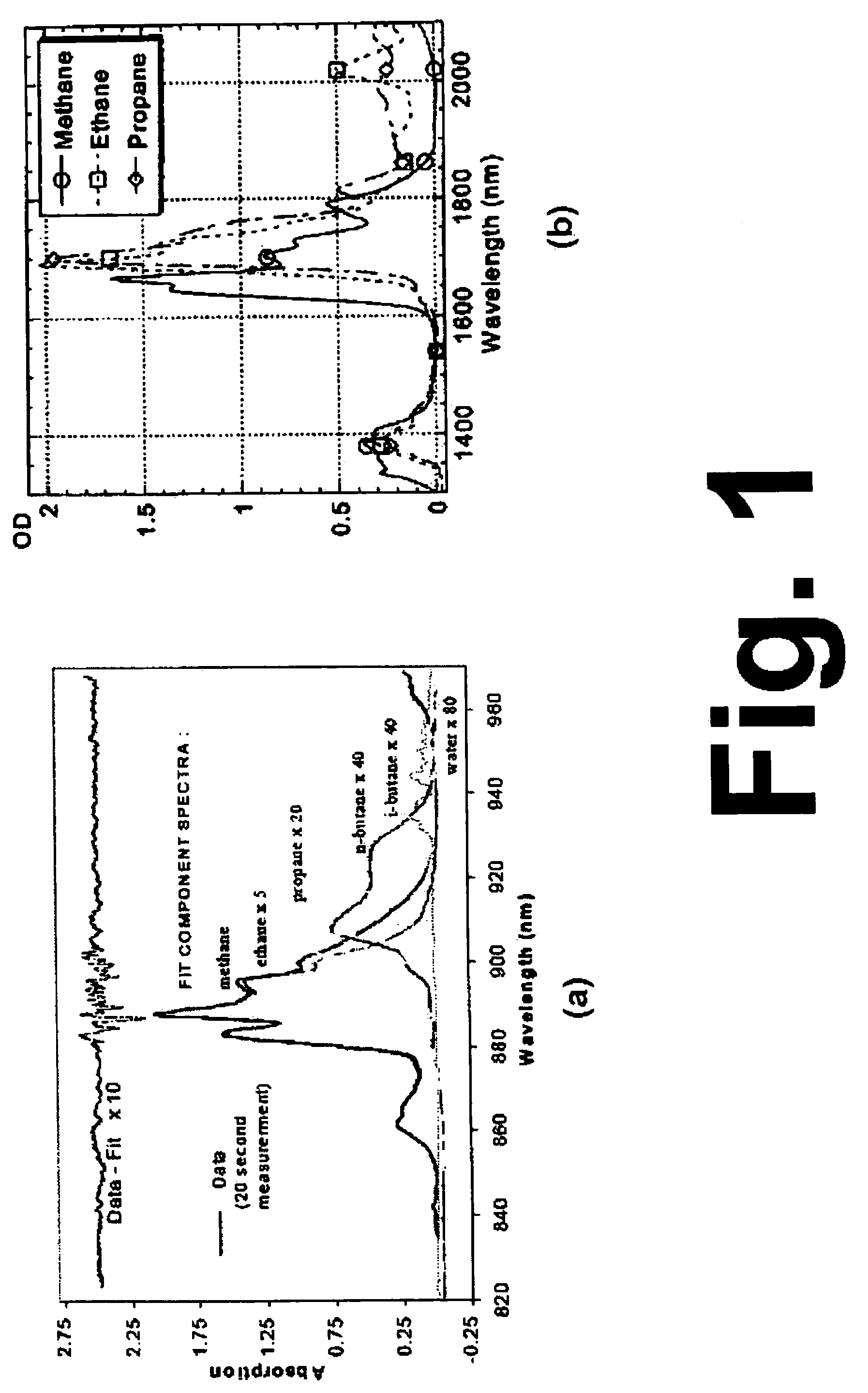
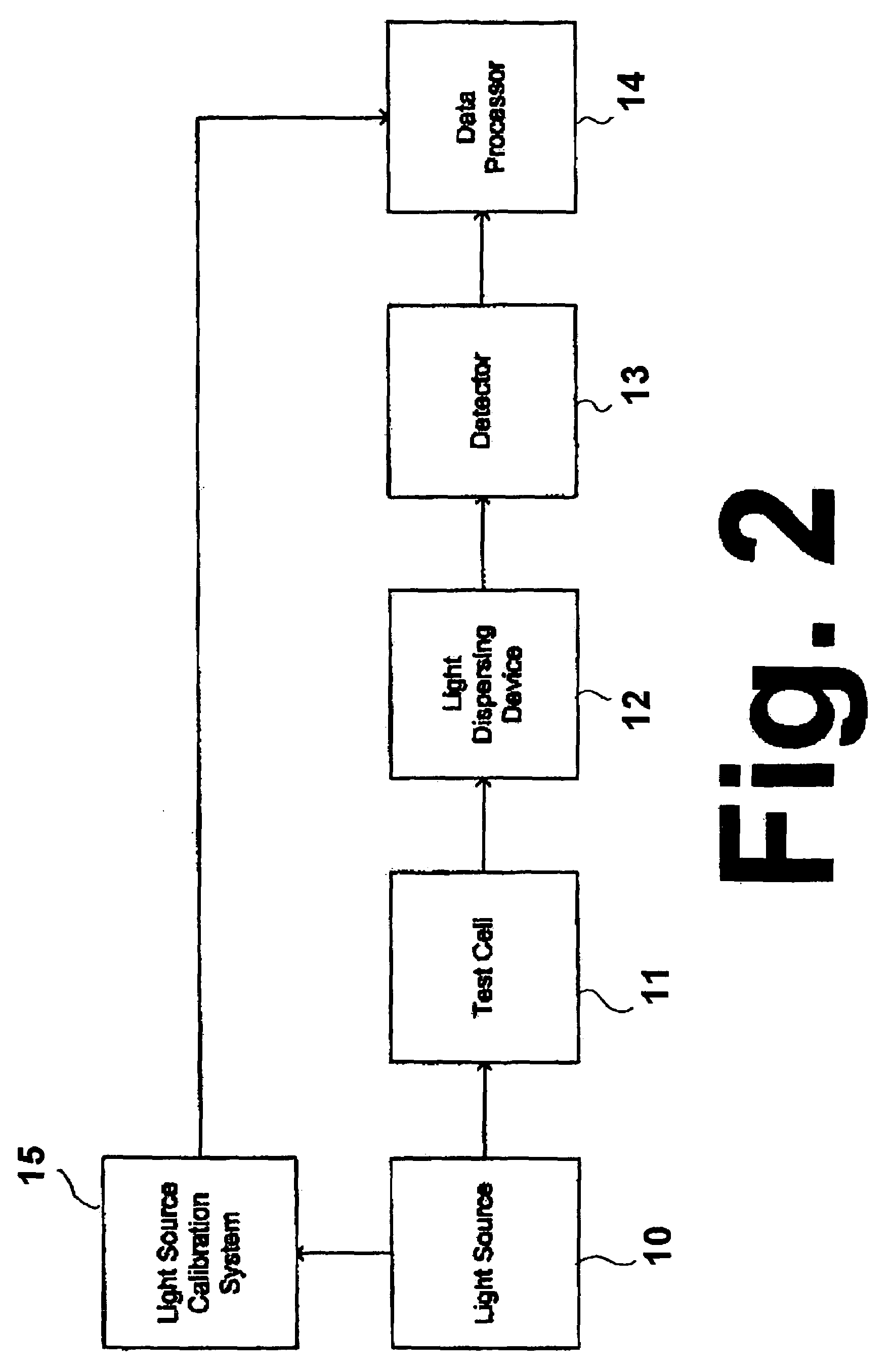
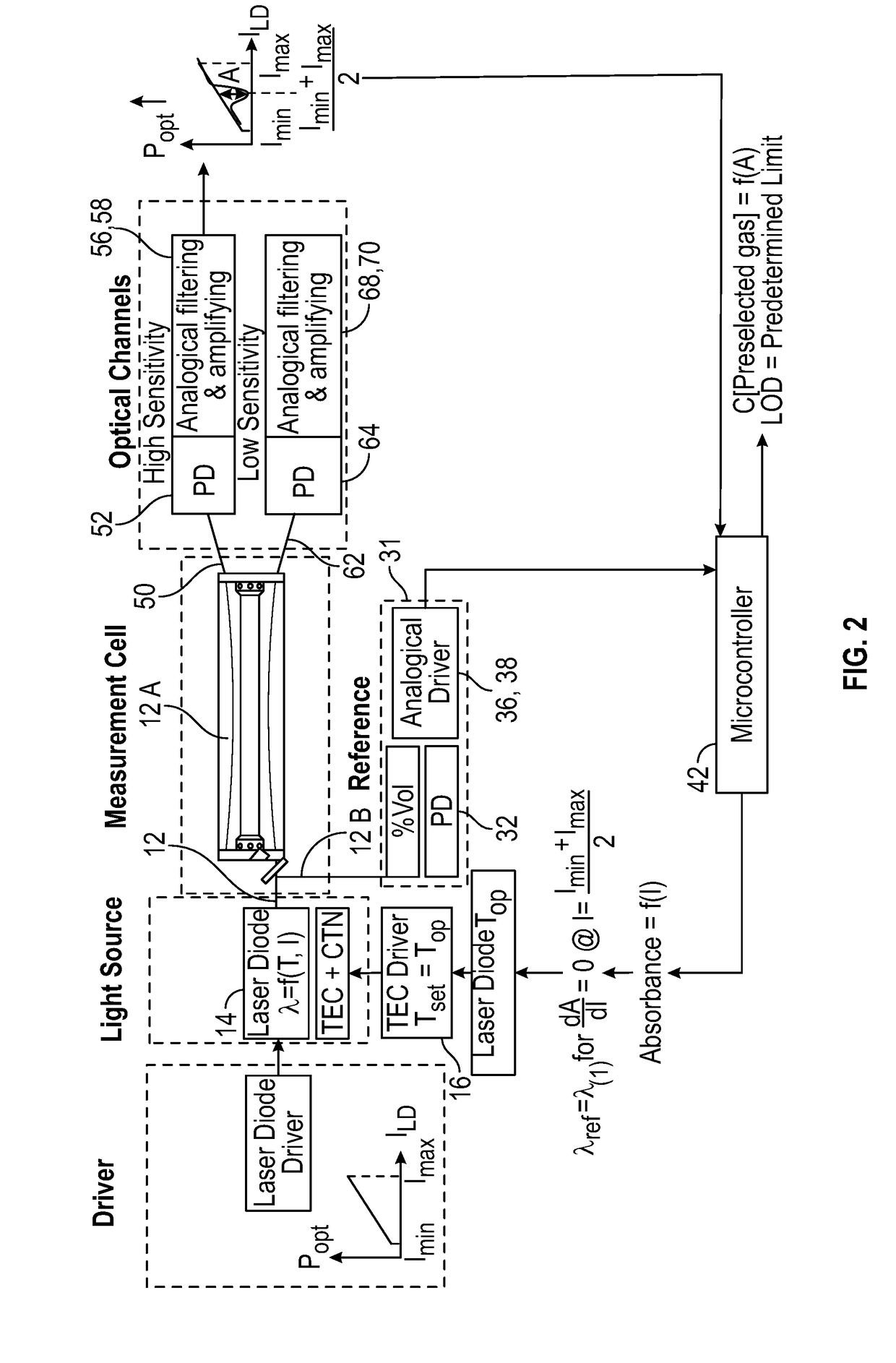
Method and apparatus for optically measuring the heating value of a multi-component fuel gas using nir absorption spectroscopy
ActiveUS20060092423A1Lower initial costReduce maintenance costsThermometer detailsPhotometry using reference valueOn boardLighting spectrum
A method and system for measuring heat energy of a combustible fluid in which light having wavelengths in the near-infrared is directed into a test cell containing the combustible fluid and portions of the light not absorbed by the combustible fluid and passing out of the cell are spatially dispersed by wavelength, forming a light spectrum that is projected onto a detector. The light spectrum is digitized and inputted into a data processing unit in which it is compared to the actual spectrum of the light source stored in the system to determine the absorbance spectrum of the combustible fluid. The system is spectrally calibrated by identifying known spectral features of the combustible gas absorbance spectrum. To correct for deviations in the original light source spectrum, a light source calibration system is employed. Upon determination of the absorbance spectrum of the combustible fluid, the heating value of the combustible fluid is determined by comparing the absorbance spectrum to a plurality of spectra located within an on-board database.
Owner:GAS TECH INST
Method for in-situ sampling, separating enriching and measuring heavy metal ion in water body
InactiveCN101021515ASelectiveWithdrawing sample devicesTesting waterChemical reactionPhysical chemistry
A method to sample in situ, separate, enrich and measure heavy metal ion in waters. Its steps contain: (1) Puts some high-molecular compound being capable of occurring chemical reaction with heavy metal ion into device and uses a semi-permeable membrane being able to permeate heavy metal ion to cover it. (2) Puts device into waters and detaches it from waters by membrane. (3) Sets in waters for a period of time. Recur to osmosis of membrane, heavy metal ion enters into back of device to occur chemical reaction with high-molecular compound. (4) Takes out device located in waters to measure concentration and mean concentration of heavy metal in waters by atomic absorption spectrometry. It is characterized in that simple, economical, providing concentration and measurement in situ for much heavy metal, has selectivity.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method and apparatus for optically measuring the heating value of a multi-component fuel gas using nir absorption spectroscopy
ActiveUS7248357B2Low costThermometer detailsPhotometry using reference valueOn boardLighting spectrum
Owner:GAS TECH INST
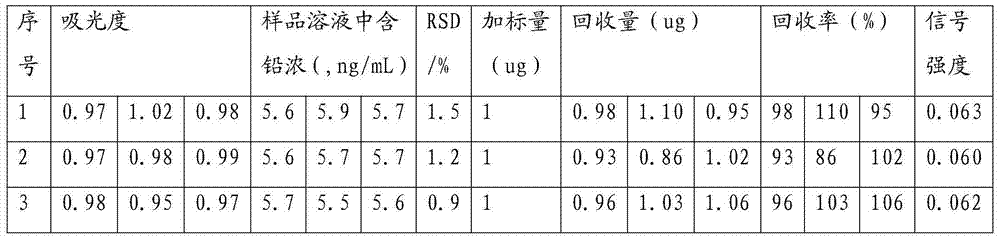
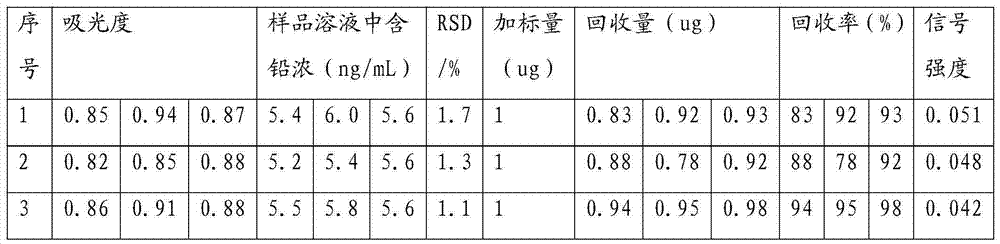
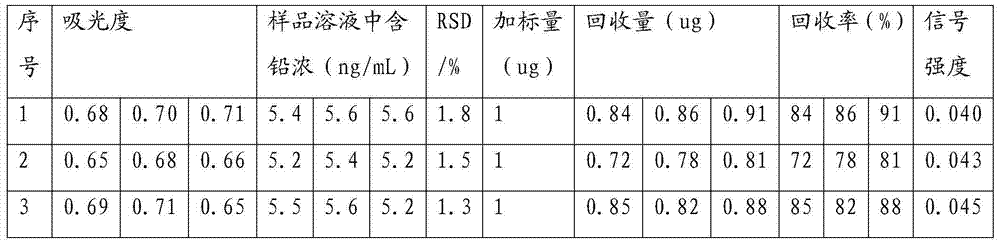
Method of measuring lead content in shredded squid by microwave digestion-atomic absorption spectroscopy
InactiveCN103499475AReduce distractionsImprove accuracyPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by thermal excitationAtomic absorption spectroscopyAbsorbance
The invention provides a method of measuring lead content in shredded squid by microwave digestion-atomic absorption spectroscopy. The method is characterized in that a shredded squid sample is pre-treated by adopting microwave digestion; mixed liquor of 2% ammonium dihydrogen phosphate liquor, 1% nitric acid liquor and 1% ascorbic acid liquor which are in a volume ratio of (3-5):2:1 is used as a matrix modifier; in an absorbance measuring process, the matrix modifier, sample liquor and standard liquor are measured at the same time, so that interferences of matrix can be lowered while lead is measured, accuracy of the measuring method can be improved, and signal stability can be increased. The whole test process is simple, sensitive and accurate, can be used for measuring the lead content in the shredded squid and is further widely applicable to a lead content test of diet consumables of drink, soy sauce, rice, flour, powered milk and the like in addition to being.
Owner:SUZHOU GUOHUAN ENVIRONMENT DETECTION
Cavity-enhanced on-chip absorption spectroscopy
ActiveUS20100124787A1Analysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionBiological testingLine widthWaveguide
Embodiments of optofluidic devices or methods according to the application can provide on-chip, label-free, massively parallel analysis of analytes. An embodiment of the optofluidic device can comprise a microresonator, a waveguide optically coupled to the microresonator, and a fluidic channel that exposes an analyte to an evanescent field from the microresonator, wherein the light signal has a linewidth lesser than the width of at least one resonance of the light signal propagating in the microresonator. The light signal can be tuned across a spectrum of light wavelengths, wherein the spectrum of wavelengths includes one or more wavelengths defining the at least one resonance in the microresonator. The light transmission through the waveguide over the spectrum of wavelengths of the input light can be detected, and an absorption spectrum of the analyte can be determined.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
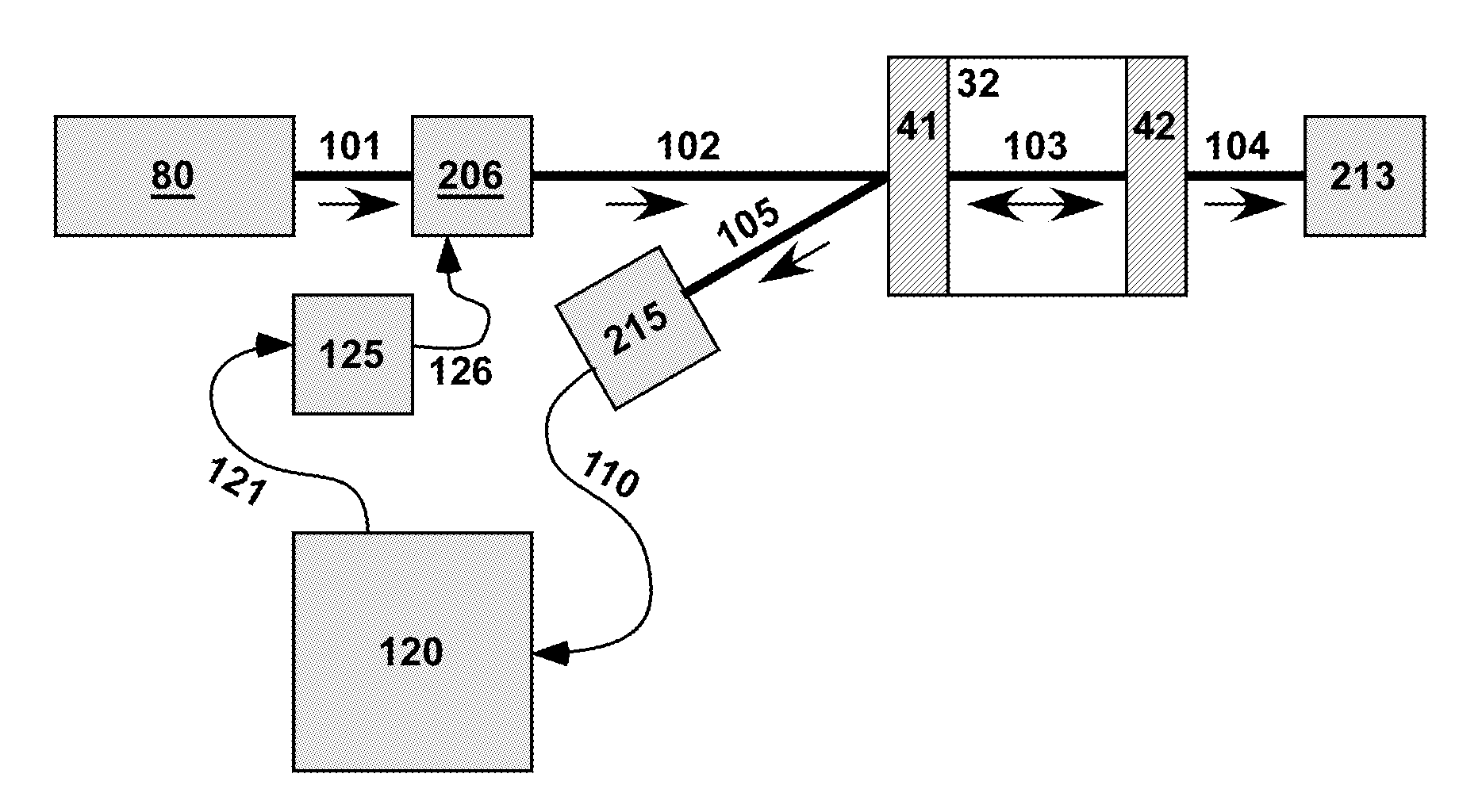
Device and method for detecting gases by absorption spectroscopy
InactiveCN1659428AQuick investigationDraw quickly and preciselyAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyColor/spectral properties measurementsTemperature controlX-ray absorption spectroscopy
A method and device for measuring a concentration of a preselected gas in a gas sample are disclosed. The device comprises a Herripott type multipass cell having a center axle and a housing surrounding and spaced from the axle to provide a tubular sample cavity. The gas sample is pumped through the sample cavity via apertures provided in opposed ends of the axle. A first mirror and a second mirror are supported at opposed ends of the axle. A light source, e.g. a laser or LED, is provided for emitting a light beam into the sample cavity via en entry aperture in the first mirror, the light beam having a wave length at which the preselected gas strongly absorbs. The beam is reflected between the mirrors for a number of times before exiting the cell via an exit aperture in the second mirror and impinging the intensity of the unattenuated light beam and a detector for detecting the intensity of light transmitted through the second mirror after a single pass through the cell. The light source is operatively connected to a heat control assembly having a heat sink and the gas sample is passed said heat sink to augment temperature control of the light source.
Owner:TDW DELAWARE INC
Optical absorption meter
InactiveUS20120201268A1Breakthrough sensitivityDecrease sample heat capacityThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsCryogenic temperature measurementLuminosityAtomic absorption spectroscopy
An optical absorption calorimeter performs absorbance measurements at low cryogenic temperatures, such as above 0K to 5K (e.g. near liquid helium temperature), using high-resolution thermometry with SQUID readout to probe optical absorption to better than 1 ppb. This improved sensitivity yields improved performance in calorimetric absorption spectroscopy by lowering the required excitation power, improving the spectral resolution, and opening up the full spectrum, from near-IR to near-UV and beyond for analysis.
Owner:STC UNM
Method of performing x-ray spectroscopy and x-ray absorption spectrometer system
ActiveUS20190011379A1Efficient removalIncrease brightnessMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray tube electrodesSingle crystalX-ray detector
A method for performing x-ray absorption spectroscopy and an x-ray absorption spectrometer system to be used with a compact laboratory x-ray source to measure x-ray absorption of the element of interest in an object with both high spatial and high spectral resolution. The spectrometer system comprises a compact high brightness laboratory x-ray source, an optical train to focus the x-rays through an object to be examined, and a spectrometer comprising a single crystal analyzer (and, in some embodiments, also a mosaic crystal) to disperse the transmitted beam onto a spatially resolving x-ray detector. The high brightness / high flux x-ray source may have a take-off angle between 0 and 105 mrad. and be coupled to an optical train that collects and focuses the high flux x-rays to spots less than 500 micrometers, leading to high flux density. The coatings of the optical train may also act as a “low-pass” filter, allowing a predetermined bandwidth of x-rays to be observed at one time while excluding the higher harmonics.
Owner:SIGRAY INC
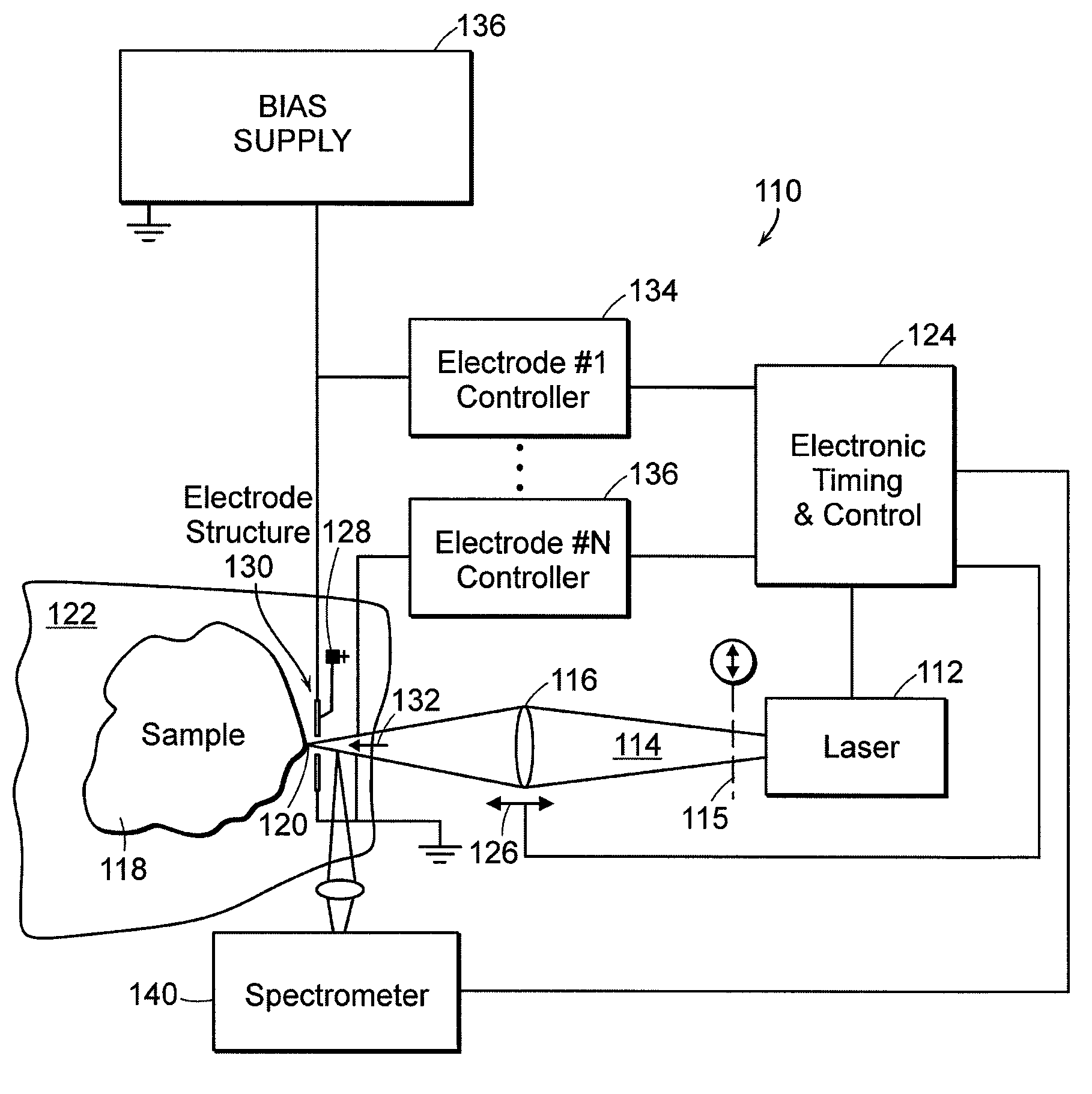
Method and apparatus for in situ determination of molten polycarbonate composition using electronic absorption spectroscopy
InactiveUS20030053050A1High signal resolutionReduce errorsRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by optical meansEnd-groupAtomic absorption spectroscopy
The present invention relates to methods and devices for in-situ measurement of reaction components of interest during manufacturing of polycarbonate by melt polymerization. The present invention describes irradiating a molten polymer sample with UV / visible light, and generating an absorbance profile correlated to Fries products as well as uncapped phenolic groups in the sample. The methods and apparatus of the invention are suitable for monitoring of Fries products in reactions ranging in size from small scale combinatorial formats to production scale reactors. Also included in methods of the invention are univariate and multivariate analysis for prediction of linear Fries, branched Fries and uncapped phenolic end-groups in unknowns.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
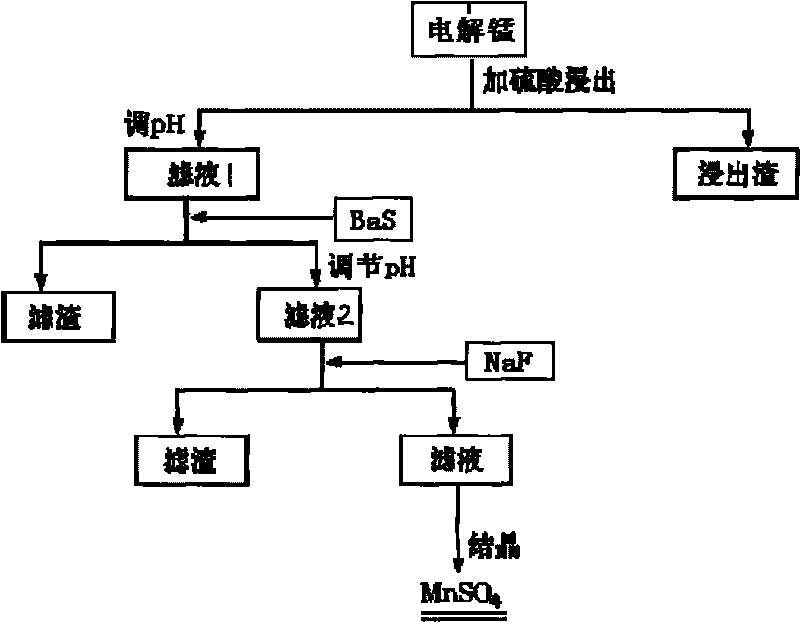
Preparation method of electronic grade high-purity manganese sulfate monohydrate
The invention discloses a method for preparing manganese sulfate monohydrate by taking electrolytic manganese and industrial sulphuric acid as raw material; the method comprises the following steps: (1) the electrolytic manganese is ground and sieved to obtain manganese powder; the manganese powder is added in the industrial sulphuric acid and is heated to 80-90 DEG C and reacts for 4-12h continuously under the stirring condition, so as to obtain manganese sulphate suspension; the heavy metallic salt content in the manganese sulphate suspension is measured by atomic absorption spectroscopy; (2) the pH of the suspension is adjusted to 3-4, barium sulphide is added and filtration is carried out, so as to obtain filtrate 1; (3) lime stone is added in the filtrate 1, after the pH value is adjusted to be 5-6 and is placed still, so as to obtain the filtrate 2; (4) sodium fluoride is added in the filtrate 2 for reacting 20-26 hours and then is filtered, so as to obtain manganese sulphate solution; (5) after the manganese sulphate solution is concentrated and recrystallized, centrifugal separation, washing, drying and crashing are carried out, thereby obtaining the manganese sulfate monohydrate; the method has simple production process, easy operation, no pollution and low equipment requirements.
Owner:GUANGDONG GUANGHUA SCI TECH
Laser absorption spectroscopy system and method for discrimination of a first and a second gas
ActiveUS20180059003A1High sensitivityDetection of fluid at leakage pointColor/spectral properties measurementsHigh absorptionIsotope
A system and method to discriminate between a first preselected gas and at least one other preselected gas use of an absorption spectroscopy analyzer that includes a Herriott cell and a temperature sensitive light source. The light source operates at a temperature that emits a beam at a wavelength that corresponds to high absorption by a first preselected gas. When a predetermined level of this gas is detected in a gas sample, the analyzer changes the operating temperature of the light source to emit a beam at a wavelength that corresponds to high absorption by a second preselected gas. The second preselected gas can be a different isotope of the first preselected gas.
Owner:ECOTEC SOLUTIONS
In-line cell for absorption spectroscopy
InactiveUS6084668AWithdrawing sample devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansLight reflectionAtomic absorption spectroscopy
Provided is a novel in-line cell useful in absorption spectroscopy. The cell includes a sample region, a light entry port and a light exit port being the same or separate ports. Each port is in communication with the sample region and contains a light transmissive window. A mirror having a light reflective surface faces the sample region, and a heater effective to heat the light transmissive window in the light entry port and / or said light exit port is provided. The cell can be used to determine the concentration of molecular gas impurities in a sample. Particular applicability is found in semiconductor manufacturing in a semiconductor processing tool.
Owner:AIR LIQUIDE AMERICA INC
Method and device for measuring sulfur content in coal by ultraviolet absorption spectroscopy
ActiveCN101806727AEliminate absorptionQuick analysisColor/spectral properties measurementsDecompositionWater vapor
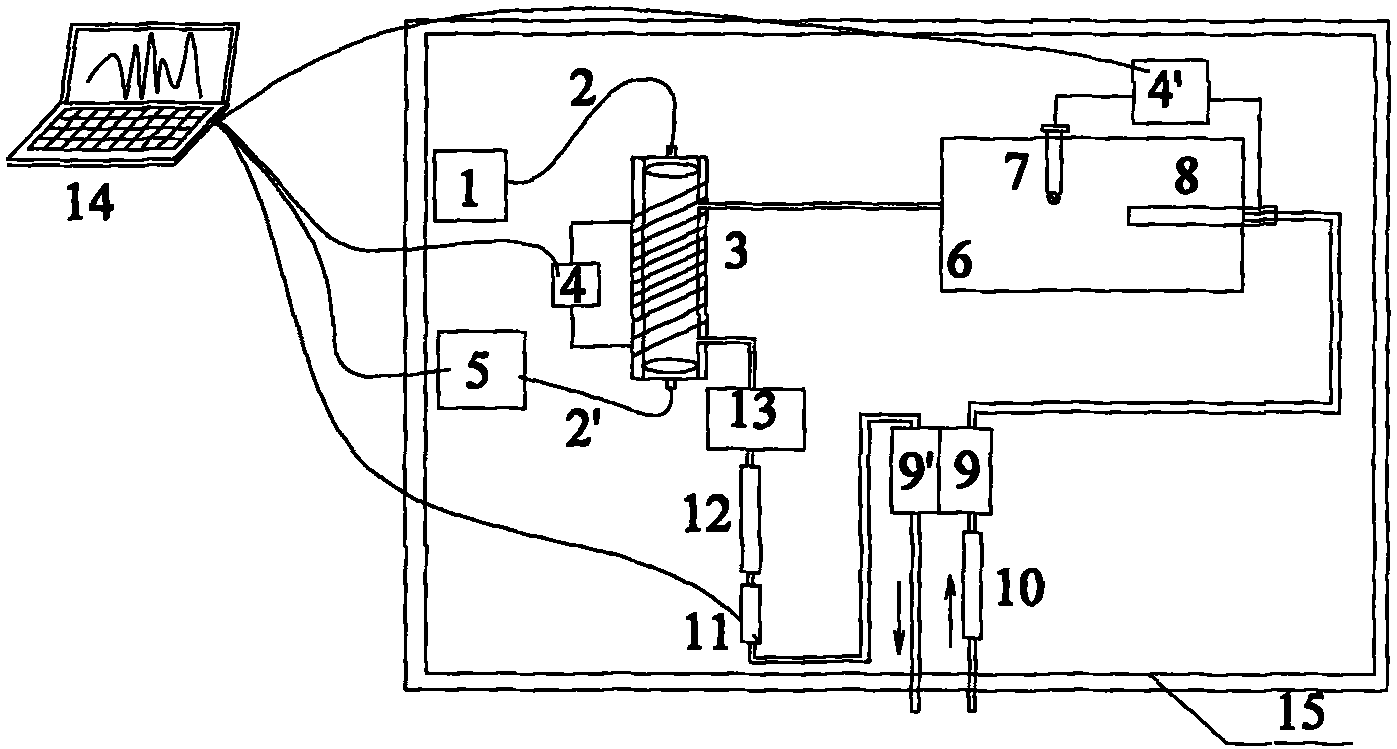
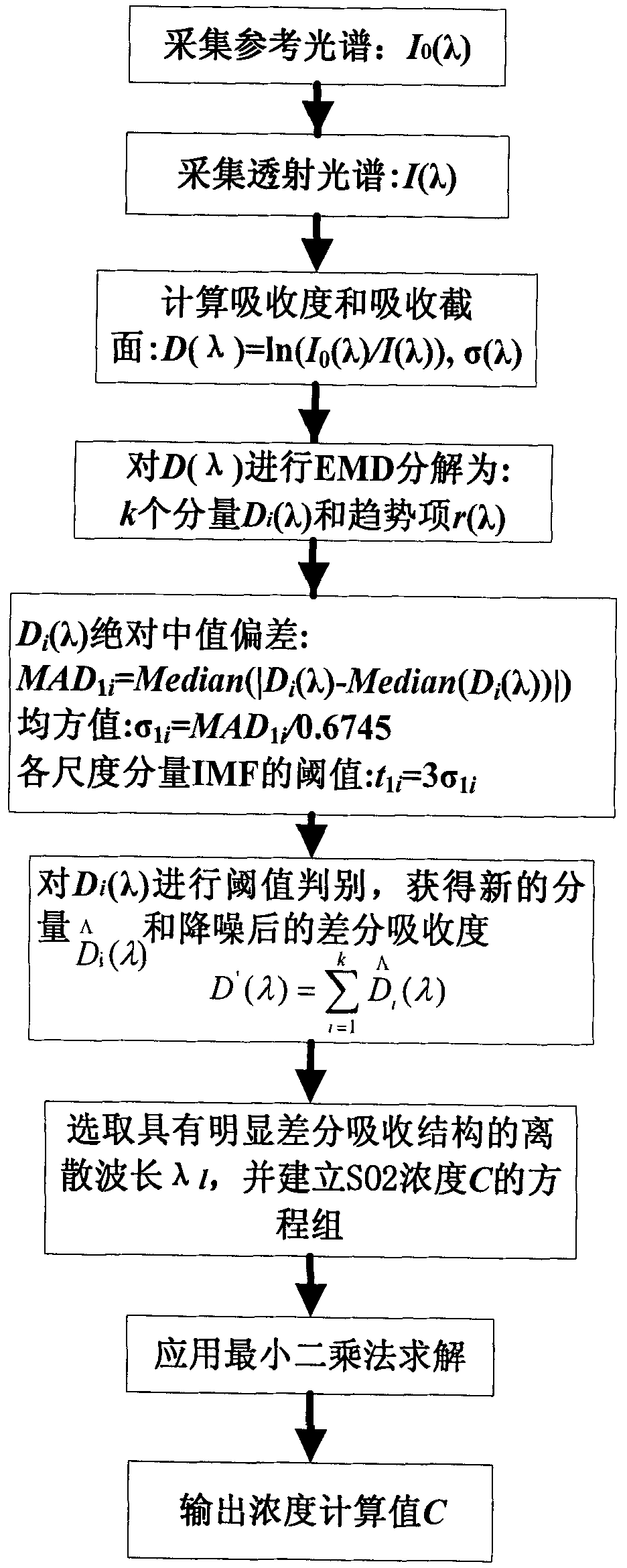
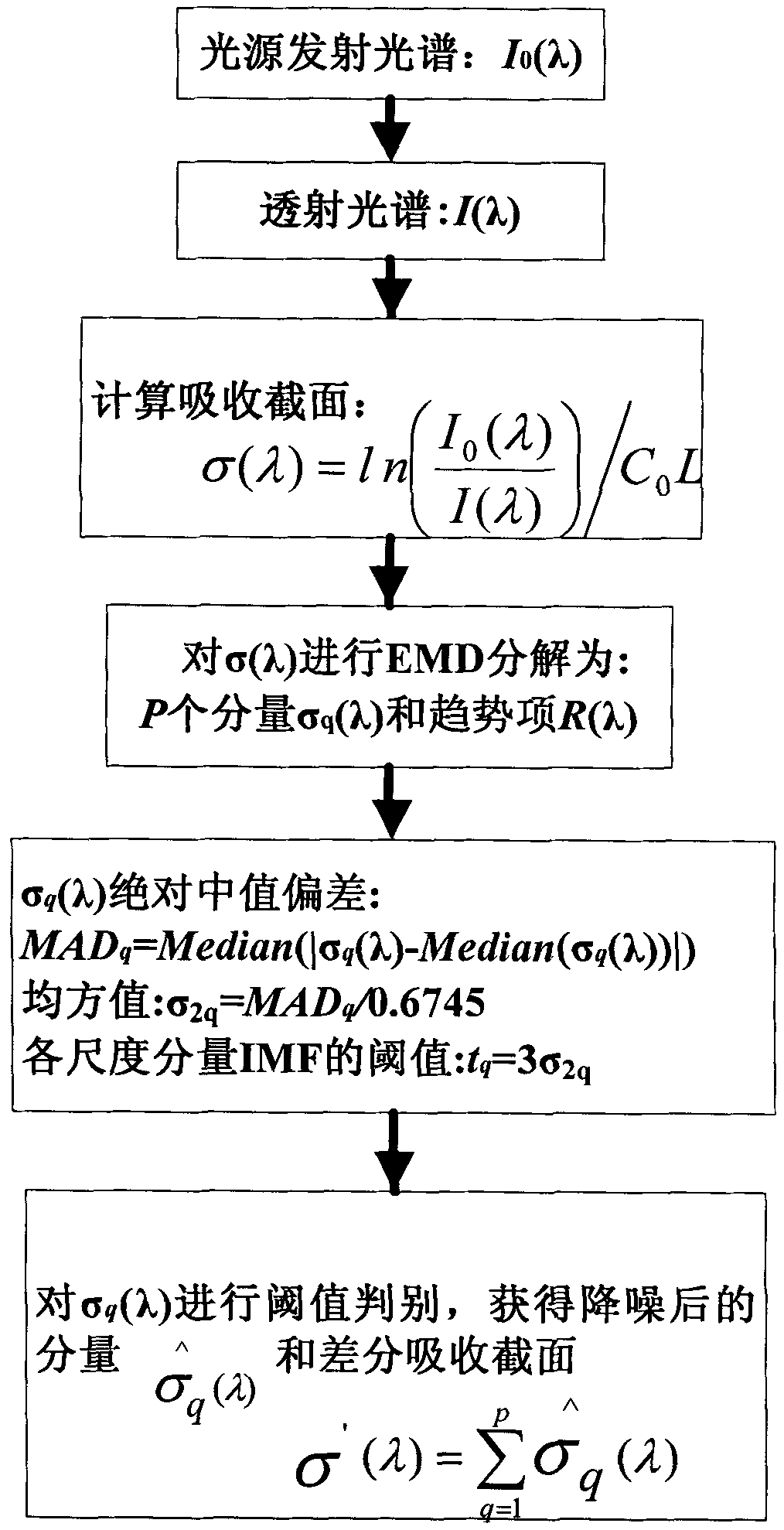
The invention discloses a method and a device for measuring sulfur content in coal by ultraviolet absorption spectroscopy. In the measurement method, the decomposition scale and a threshold are determined adaptively by combining empirical mode decomposition with 3sigma criterion, and non-stationary characteristics of differential absorption degree per se can be fully retained, so the spectral interference problem caused by dust, water vapor and background gas in combustion gas is effectively solved; the instantaneous concentration of SO2 is obtained through calculation according to the differential absorption degree after noise reduction and trend term removal, and the total sulfur content accumulated in the coal sample combustion gas is calculated through the gas flow; the sulfur content in the coal can be obtained by dividing the coal sample amount by the total sulfur content separated from the coal sample combustion; and the pretreatment process needed to be performed on the combustion gas by coulometric titration and an infrared absorption method is avoided. The device for measuring the sulfur content in the coal by the ultraviolet absorption spectroscopy comprises a combustion furnace, a measuring chamber, an ultraviolet light source, a spectrometer, an air purifying device, a flow meter, a waste gas treatment device, a computer, and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Optical absorption spectroscopy with multi-ass cell with adjustable optical path length
InactiveCN103221793AAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyColor/spectral properties measurementsPath lengthX-ray absorption spectroscopy
An optical absorption spectroscopy apparatus comprises a light source, a detector for detecting an optical absorption spectrum of light transmitted from the source through a sample volume and one or more reflectors for reflecting the transmitted light multiple times through the sample volume. An adjuster device is provided for adjusting at least one optical element so as to vary the path length of the transmitted light by controlling the number of times the light is reflected through the sample volume. Drive means is provided for driving the adjuster device, so enabling the detector to detect the transmitted light at a range of different path lengths.
Owner:DUVAS TECH
Process and measuring equipment for improving the signal resolution in gas absorption spectroscopy
InactiveUS20120281221A1Raise the possibilityHigh refractive indexTransmissivity measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsLaser lightOptical path length
Process and measuring equipment for improving the signal resolution in gas absorption spectroscopy, wherein the measuring equipment includes a laser light source, a light detector and a measuring chamber arranged in between, and furthermore a light source control unit and a light detector evaluation unit. To improve the signal resolution, the noise intensity of the measuring equipment is reduced by averaging over time the interfering signal portions caused by back-reflections, etalons respectively self-mixing effects. This is accomplished by a light modulator arranged downstream the laser light source that continuously periodically influences the optical path length of the light beam. Thereto the light modulator includes an optical element with an adjustable refractory index that continuously cyclically alters the phase of the laser light of the light beam.
Owner:AXETRIS AG
Method of marking a product, marked product resulting thereof, and method of identifying same
ActiveUS20060228802A1Significant variabilityWork reliablyAnalysis using chemical indicatorsTesting/calibration apparatusIon chromatographyMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
A method and means for identifying the authenticity and the genuine nature of a solid or liquid bulk material, by incorporating a marking composition containing at least one trace ion into the said bulk material, whereby the total concentration of the incorporated trace ions in the market bulk material is chosen to be lower than the corresponding concentration of the same ions in standard sea water. The authenticity and the genuine nature or the adulteration level of the marked bulk material can be tested in-the-field using electrochemical sensors, and confirmed in the laboratory using a method such as atomic absorption spectroscopy, ion chromatography or mass spectrometry.
Owner:SICPA HLDG SA
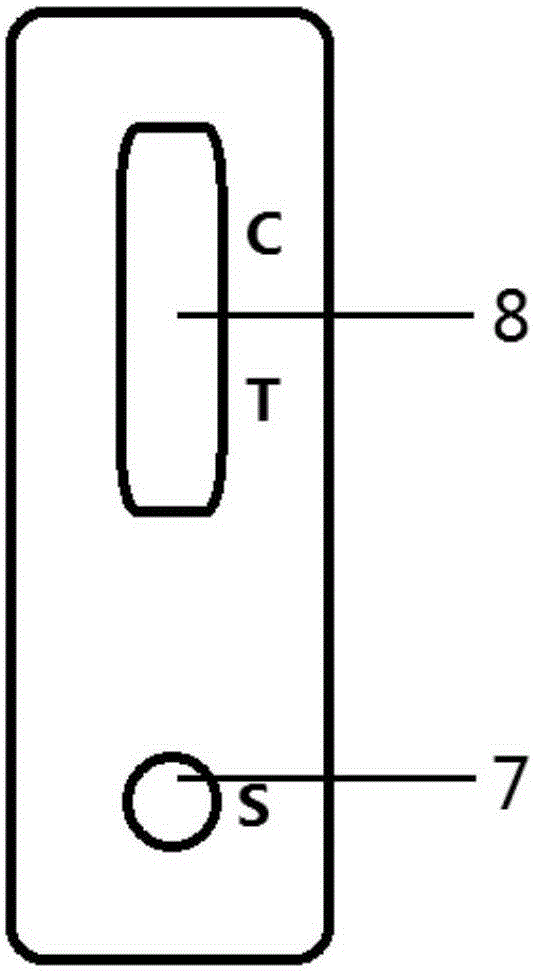
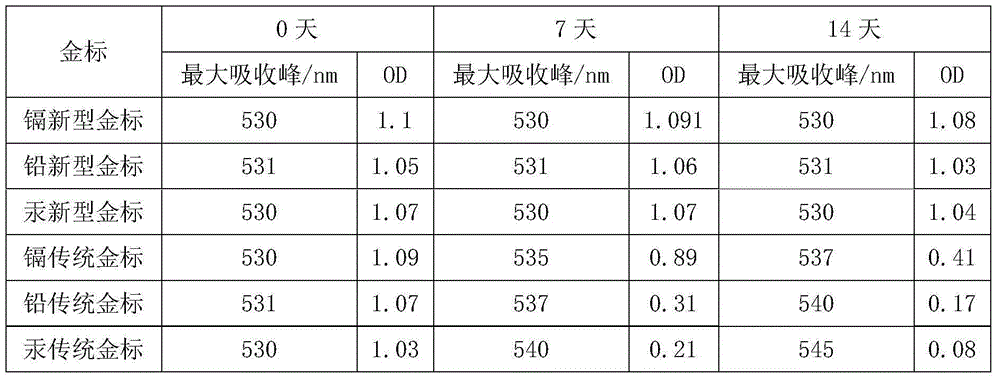
Heavy metal quantitative detecting system and method for quantitatively detecting heavy metal
ActiveCN105203765AAccurate Orientation DetectionLow costMaterial analysisPhysical chemistryAtomic absorption spectroscopy
The invention discloses a modified colloidal gold preparation method and a gold-labeled antibody preparation method, and further discloses a colloidal gold immunochromatography kit, a heavy metal quantitative detecting system with the kit, and a method for quantitatively detecting heavy metal. A gold-labeled antibody formed by modified colloidal gold and an antibody is stable and is not influenced by the acid environment; when the immunochromatography kit is prepared from the modified colloidal gold, in the acid conditions, heavy metal can still be accurately detected in an oriented mode, traditional atomic absorption spectrometry can be replaced, cost is low, and application prospects are good.
Owner:成都安普诺生物科技有限公司
Packaged chip for multiplexing photonic crystal waveguide and photonic crystal slot waveguide devices for chip-integrated label-free detection and absorption spectroscopy with high throughput, sensitivity, and specificity
ActiveUS8636955B2High throughput measurementImprove throughputRadiation pyrometryColor measuring devicesPhotonThroughput
Systems and methods for chip-integrated label-free detection and absorption spectroscopy with high throughput, sensitivity, and specificity are disclosed. The invention comprises packaged chips for multiplexing photonic crystal waveguide and photonic crystal slot waveguide devices. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:OMEGA OPTICS
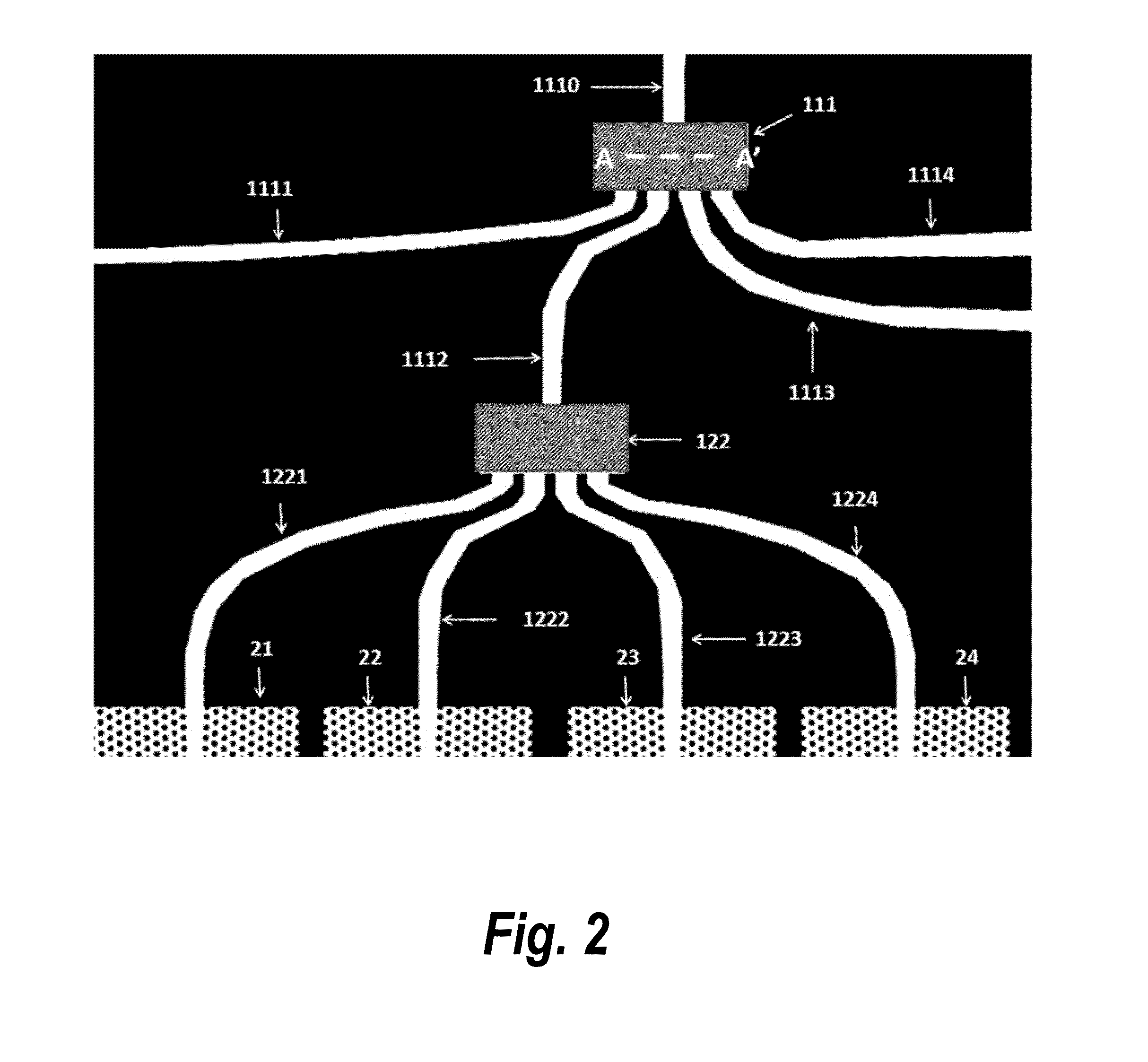
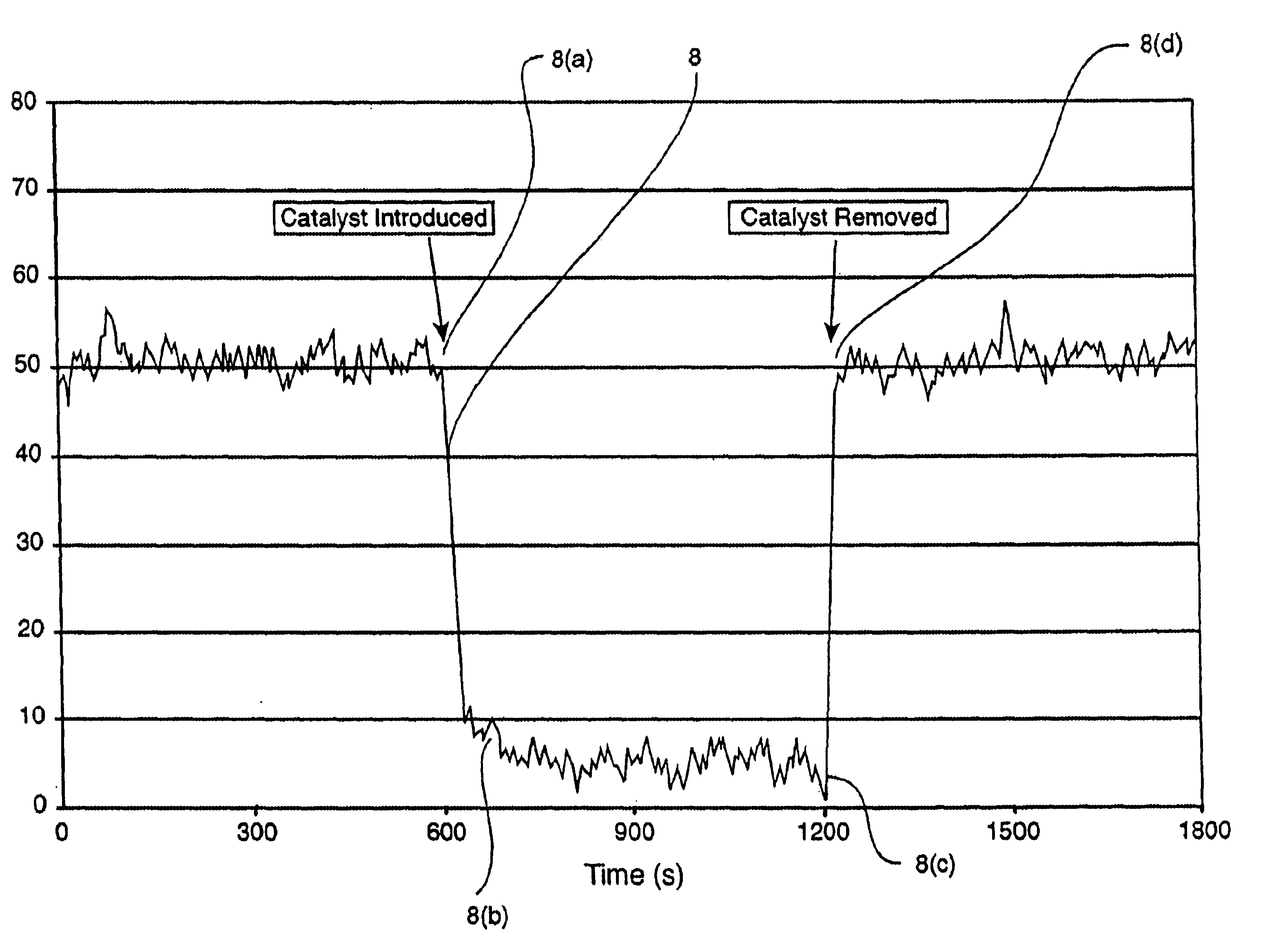
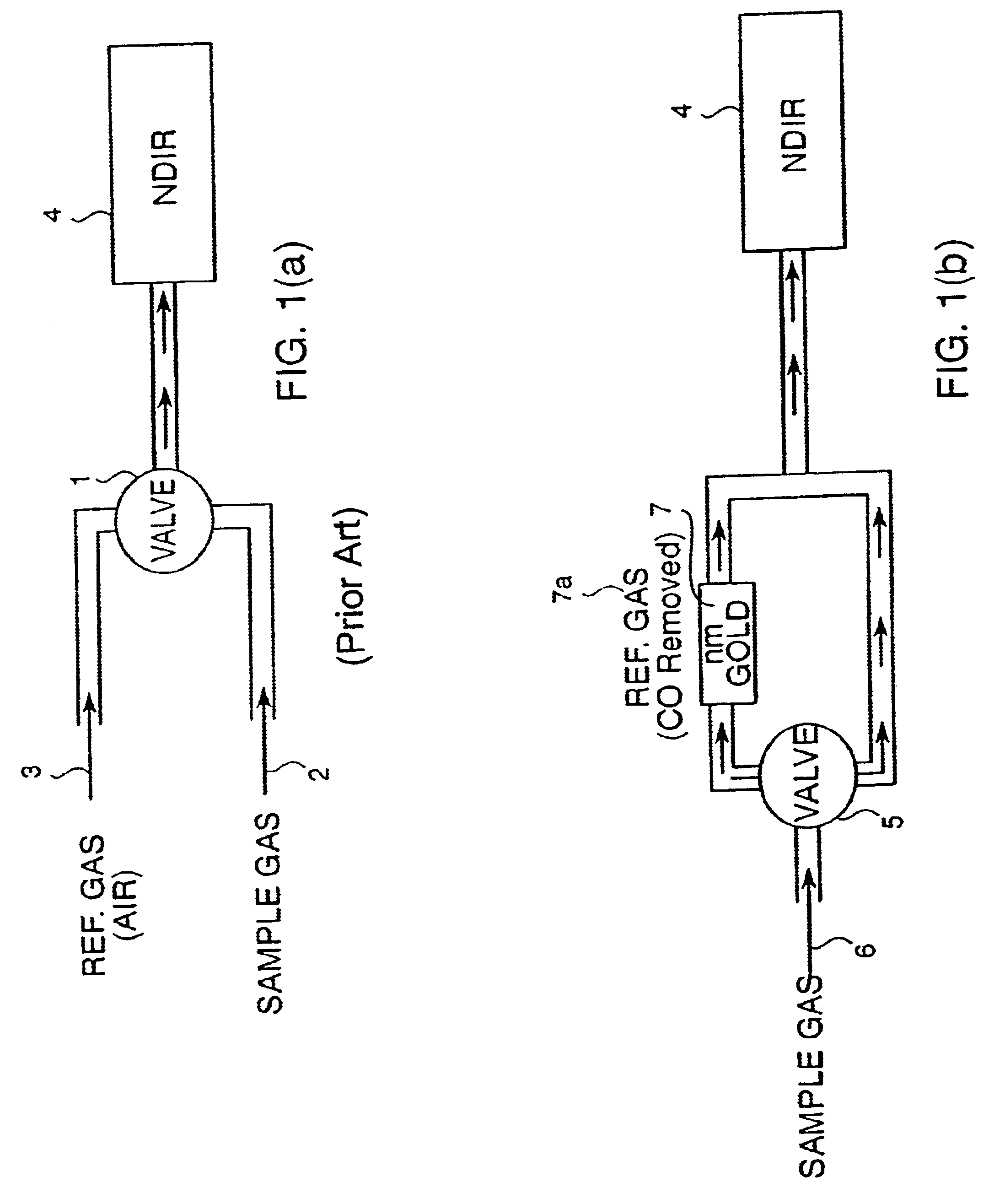
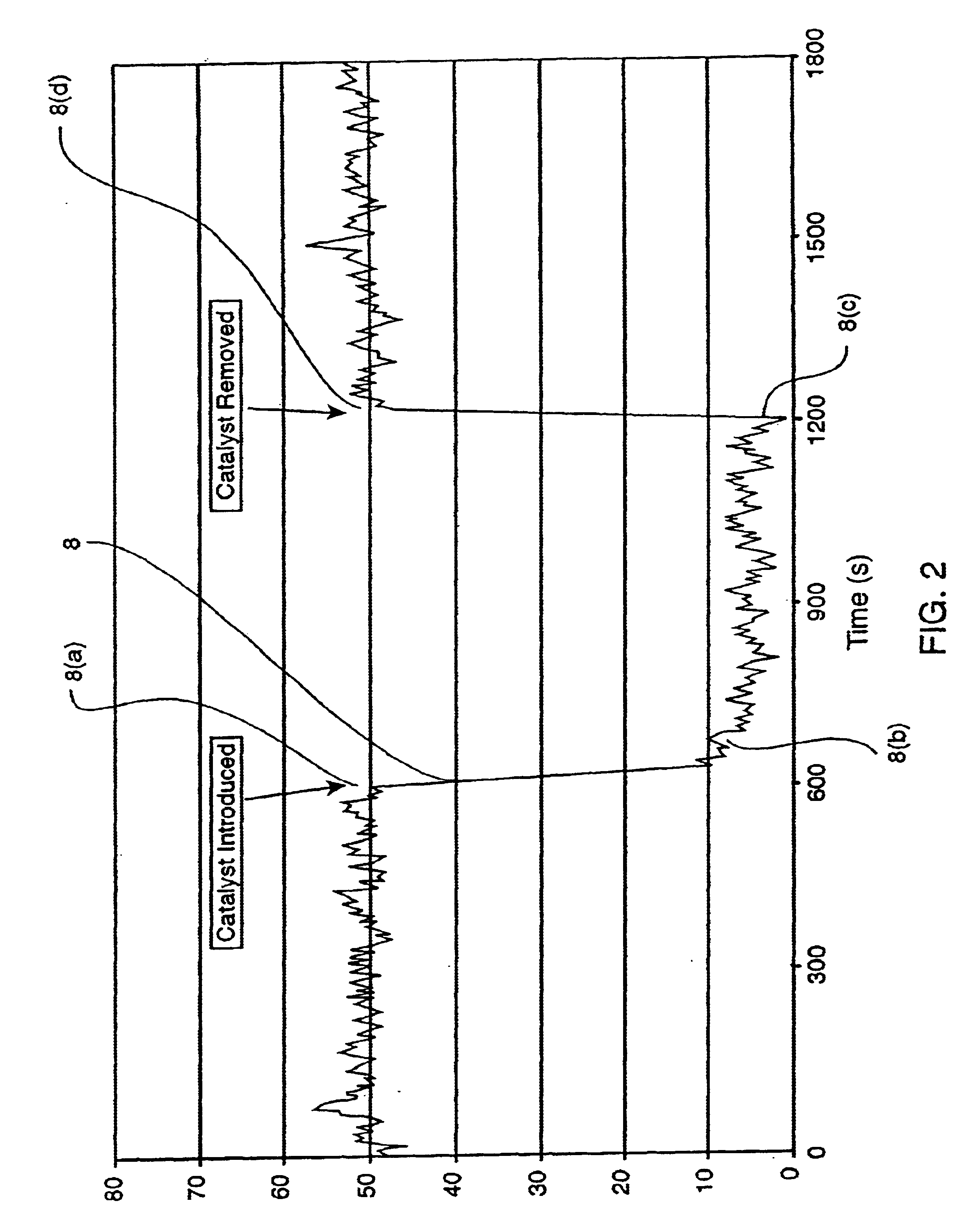
Method for improved detection of carbon monoxide by infrared absorption spectroscopy
A method for detecting the presence and amount of carbon monoxide, comprising the use of infrared spectroscopy to compare the spectra of the test gas containing carbon monoxide and the reference gas. The reference gas is the test gas from which carbon monoxide had been removed by conversion using catalysts. The presence and quantity of carbon monoxide is determined by deducting the spectrum of the reference gas from the spectrum of the test gas. The catalysts comprise nanoparticles of gold precipitated on a metal oxide or hydroxide carrier. An apparatus implementing this method.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com