Method of measuring lead content in shredded squid by microwave digestion-atomic absorption spectroscopy
A technique of atomic absorption spectroscopy and microwave digestion, which is applied in the field of quantitative analysis for the determination of lead in squid shreds, can solve the problems of unguaranteed accuracy, unsatisfactory signal stability, etc., and achieve high temperature rise and increased stability , the effect of improving the accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
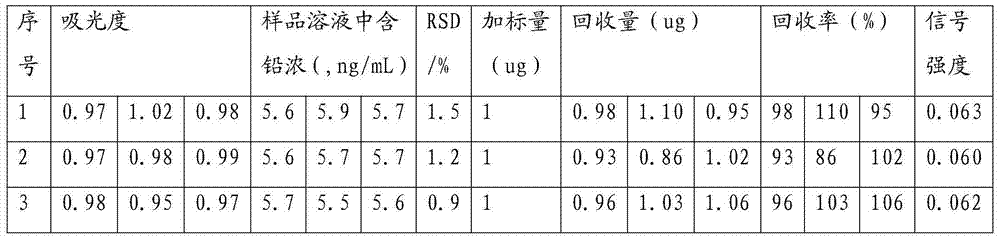
Embodiment 1
[0042] Accurately weigh 0.5g of crushed squid shredded sample into a clean and dry microwave digestion tank, add 6mL of 70% nitric acid and 2mL of 30% hydrogen peroxide, cover and seal it overnight, and put it into a microwave digestion apparatus with a digestion pressure of 2.5MPa the next day In the microwave digestion instrument, heat at 140°C for 5 minutes, 200°C for 5 minutes, 200°C for 20 minutes, and 0°C for 5 minutes to assist digestion. After the digestion program is over, take out the digestion tank and cool it to room temperature in a fume hood. Transfer the solution to a polytetrafluoroethylene beaker, wash the digestion tank several times with a small amount of water, put it into the beaker, place it on a hot plate to heat and catch the acid, and when the solution evaporates to 2mL, remove the beaker and transfer the test solution to a capacity of 25mL bottle, dilute to volume with twice distilled water to obtain a sample solution.
[0043] Drawing of working curv...
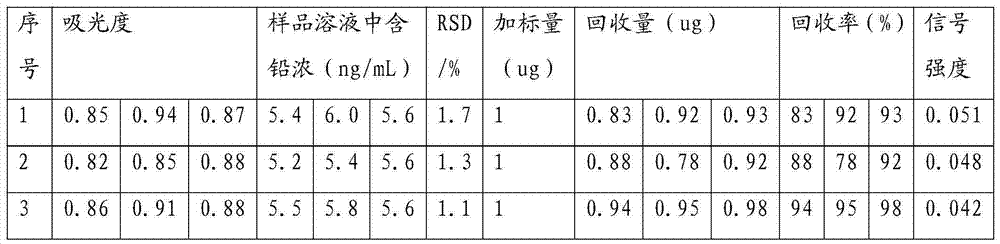
Embodiment 2
[0054]The only difference from Example 1 is that the matrix modifier added is 3.75uL 2% ammonium dihydrogen phosphate solution, 1.5uL 1% nitric acid solution, 0.75uL 1% ascorbic acid solution (that is, the volume ratio is 5:2:1)
[0055] Other experimental conditions are consistent with embodiment 1. Specifically:
[0056] Drawing of working curve:
[0057] Take 0.0, 5.0, 10.0, 15.0, 20.0, 25.0mL lead standard solution with a concentration of 0.05ug / mL in a 50mL volumetric flask, add 3.75uL 2% ammonium dihydrogen phosphate solution, 1.5uL 1% nitric acid solution, 0.75uL1 % ascorbic acid solution (i.e. the volume ratio is 3:2:1), constant volume with 1% nitric acid, the lead concentration A is 0.0mg / mL, 0.005ug / mL, 0.01ug / mL, 0.015ug / mL, 0.020ug / mL, 0.025ug / mL series of standard solutions, and then measure the absorbance C of the series of standard solutions according to the above-mentioned graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometer measurement conditions, as follows: C=...
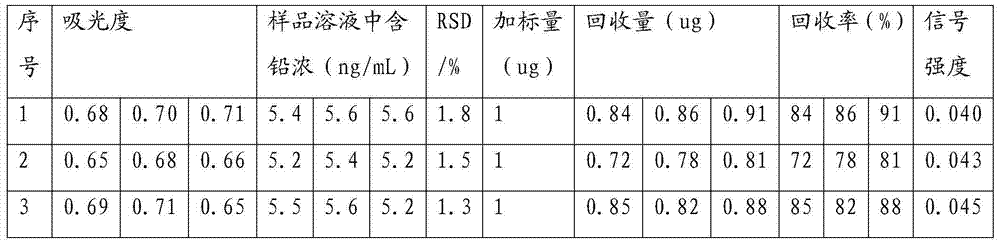
Embodiment 3
[0066] The difference from implementation 1 is that no matrix modifier is added.
[0067] Other other experimental conditions are consistent with embodiment 1. Specifically:
[0068] Drawing of working curve:
[0069] Take 0.0, 5.0, 10.0, 15.0, 20.0, 25.0mL of lead standard solution with a concentration of 0.05ug / mL in a 50mL volumetric flask, and dilute to volume with 1% nitric acid to obtain a lead concentration A of 0.0mg / mL respectively , 0.005ug / mL, 0.01ug / mL, 0.015ug / mL, 0.020ug / mL, 0.025ug / mL series of standard solutions, and then measure the absorbance C of the series of standard solutions according to the above-mentioned graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometer measurement conditions , as follows: C=0, 0.63, 1.26, 1.89, 2.52, 3.15.
[0070] According to the corresponding relationship between A and C, a linear regression equation is obtained through mathematical fitting, as follows:
[0071] A=0.00794C (ug / mL), the correlation coefficient is r=0.9989.
[00...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com