Patents
Literature
255results about How to "Increase ionic strength" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Immunoassay device with immuno-reference electrode
InactiveUS20060160164A1Reduce distractionsIncrease ionic strengthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsImmune profilingImmobilized Antibodies
An electrochemical immunosensor system with reduced interference, comprising: a first immunosensor that generates an electrochemical signal based on the formation of a sandwich between an immobilized antibody, a target analyte and a labeled antibody, wherein a portion of the signal arises from non-specific binding of the labeled antibody in the region of the first immunosensor, and a second immunosensor that acts as an immuno-reference sensor and generates a signal that is the same as or predictably related to the degree of non-specific binding which occurs in the region of the first immunosensor, and has an immunocomplex between an immobilized antibody and an endogenous or exogenous protein that is in the sample and that is not the target analyte.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
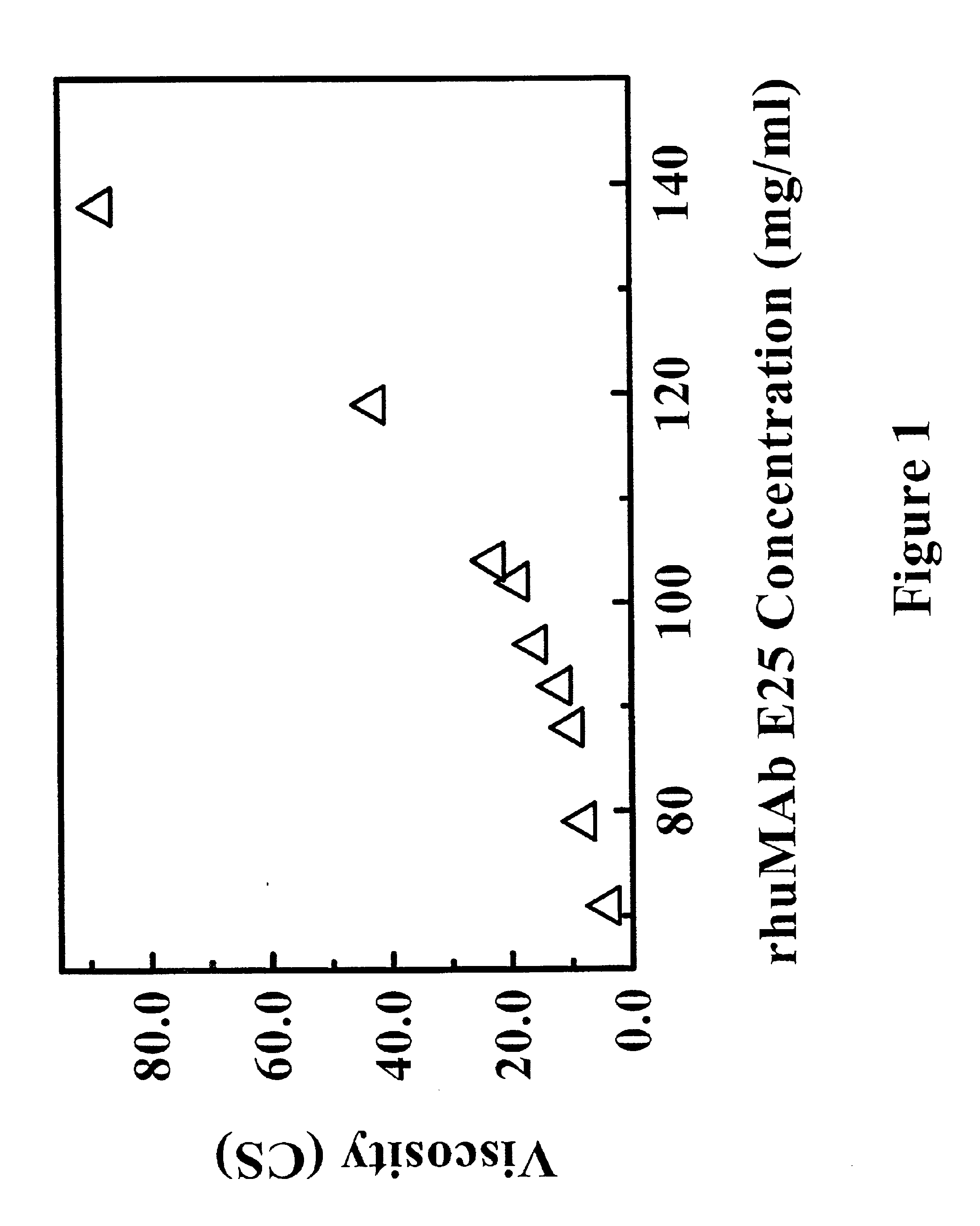
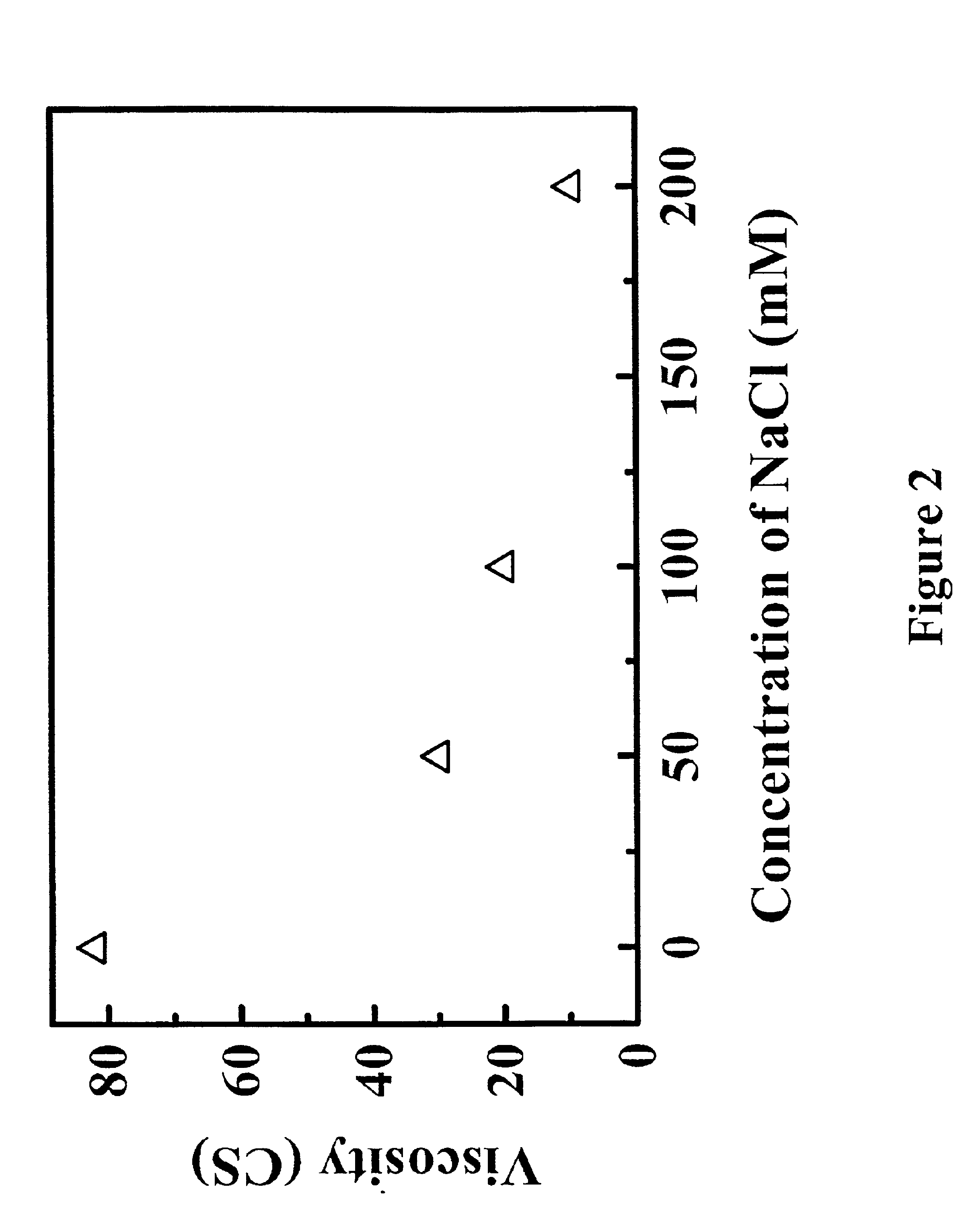
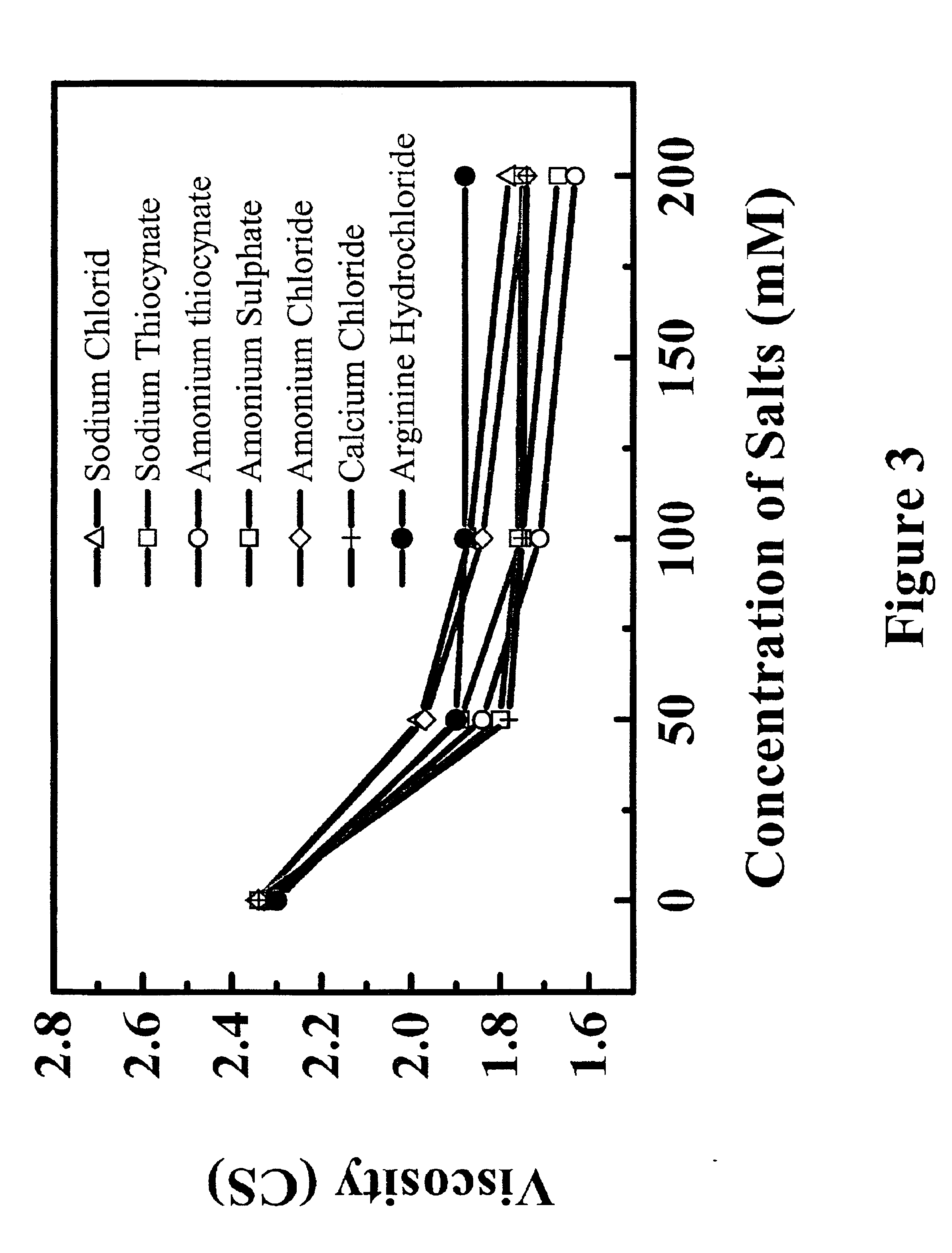
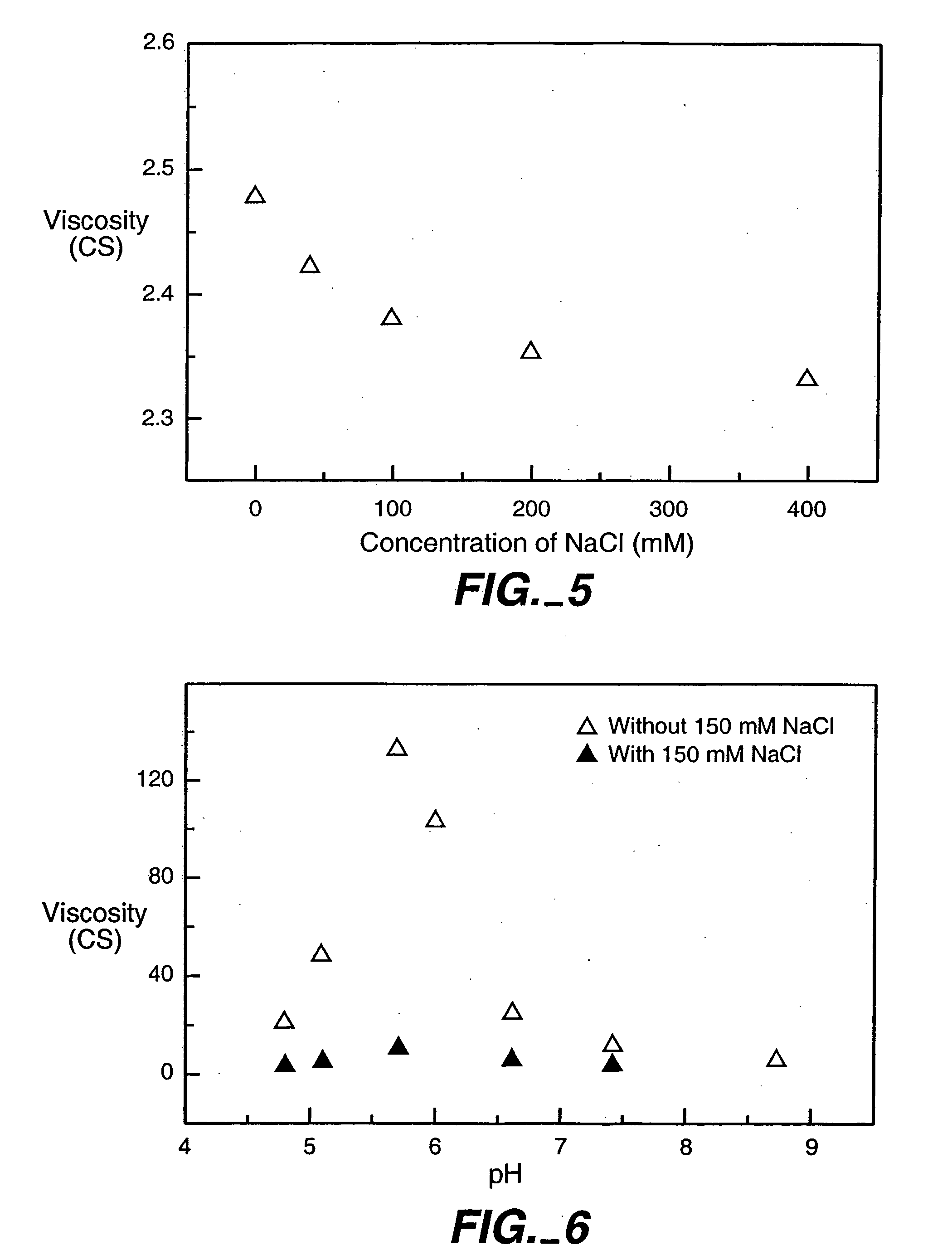
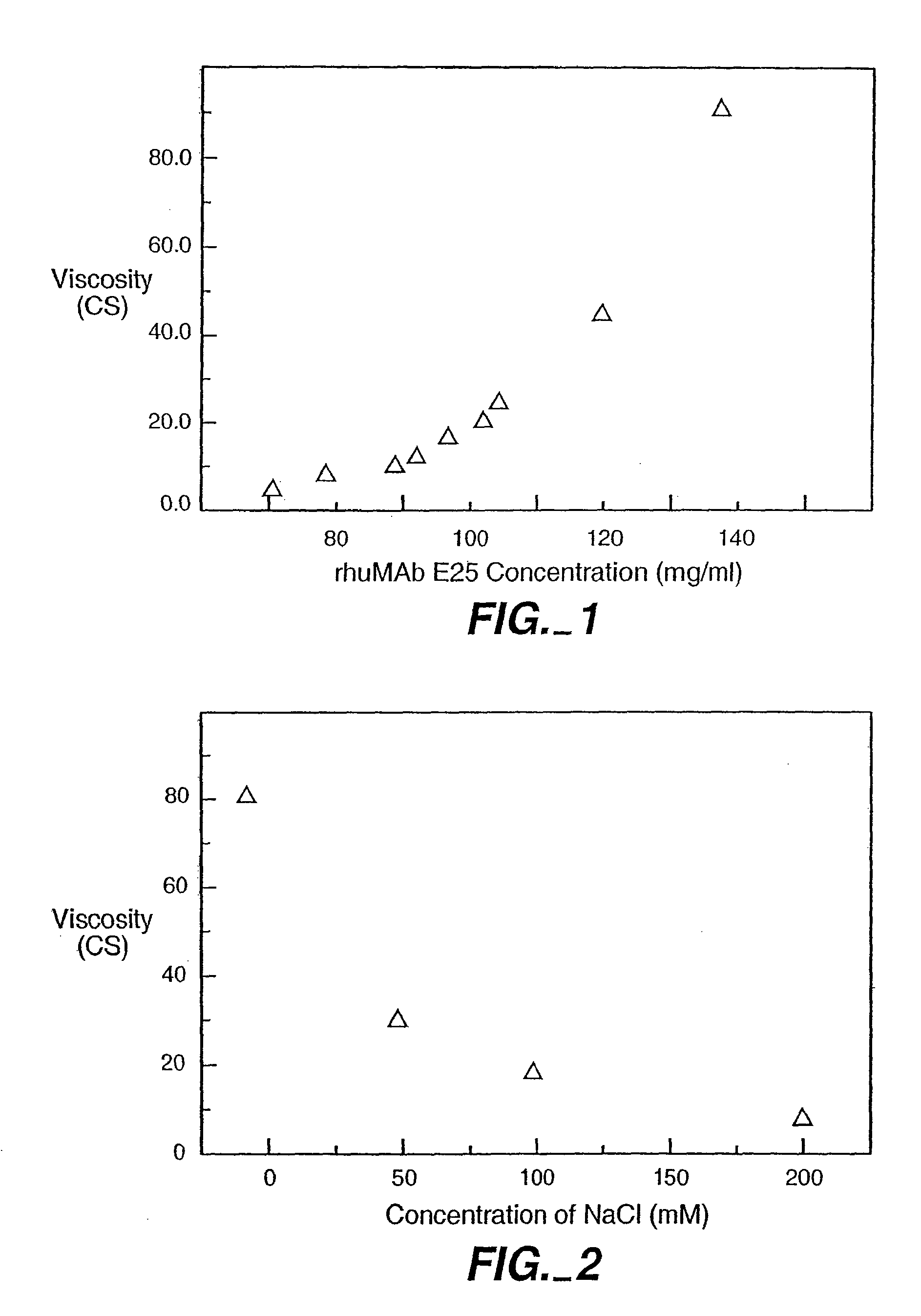
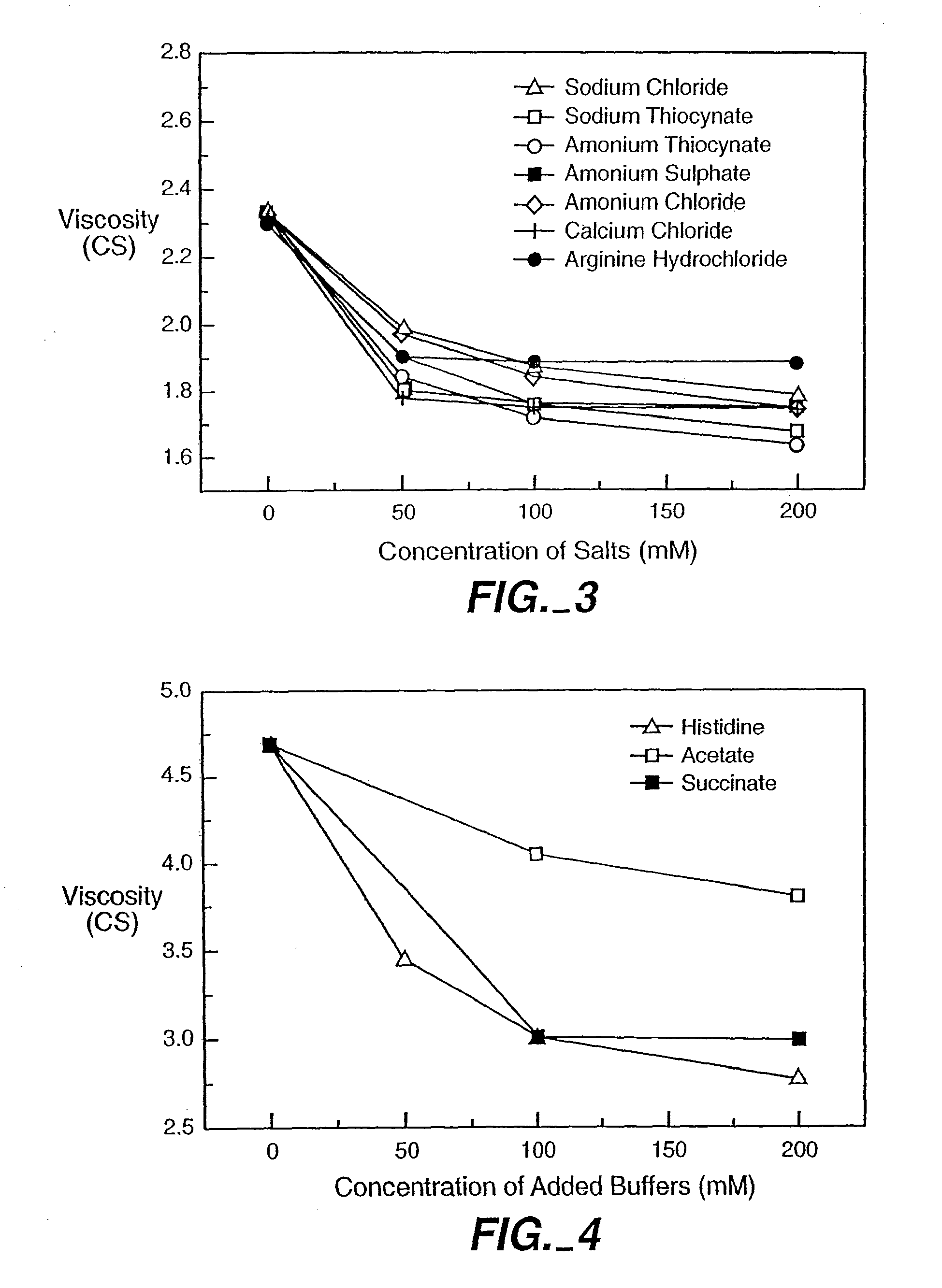
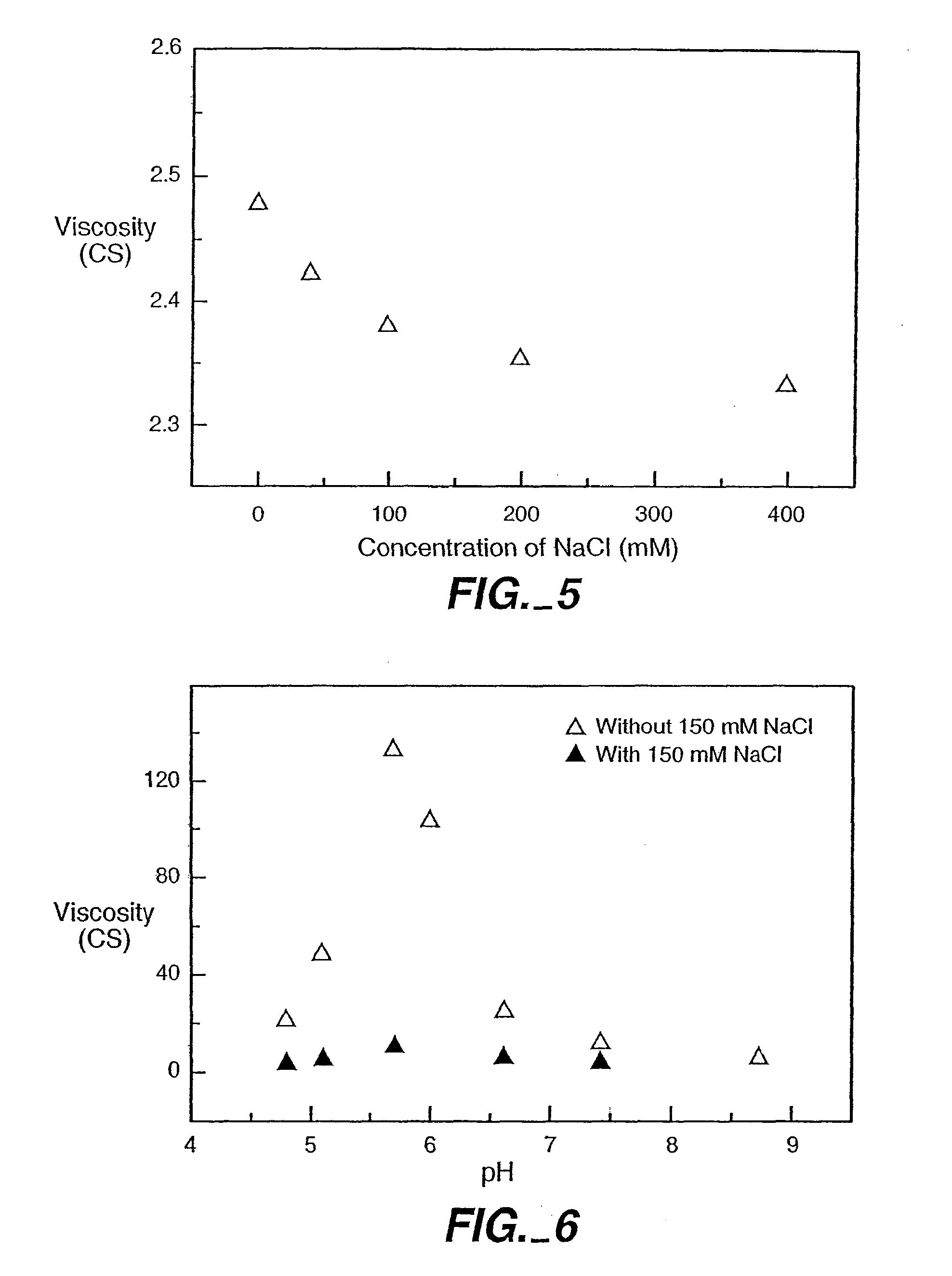
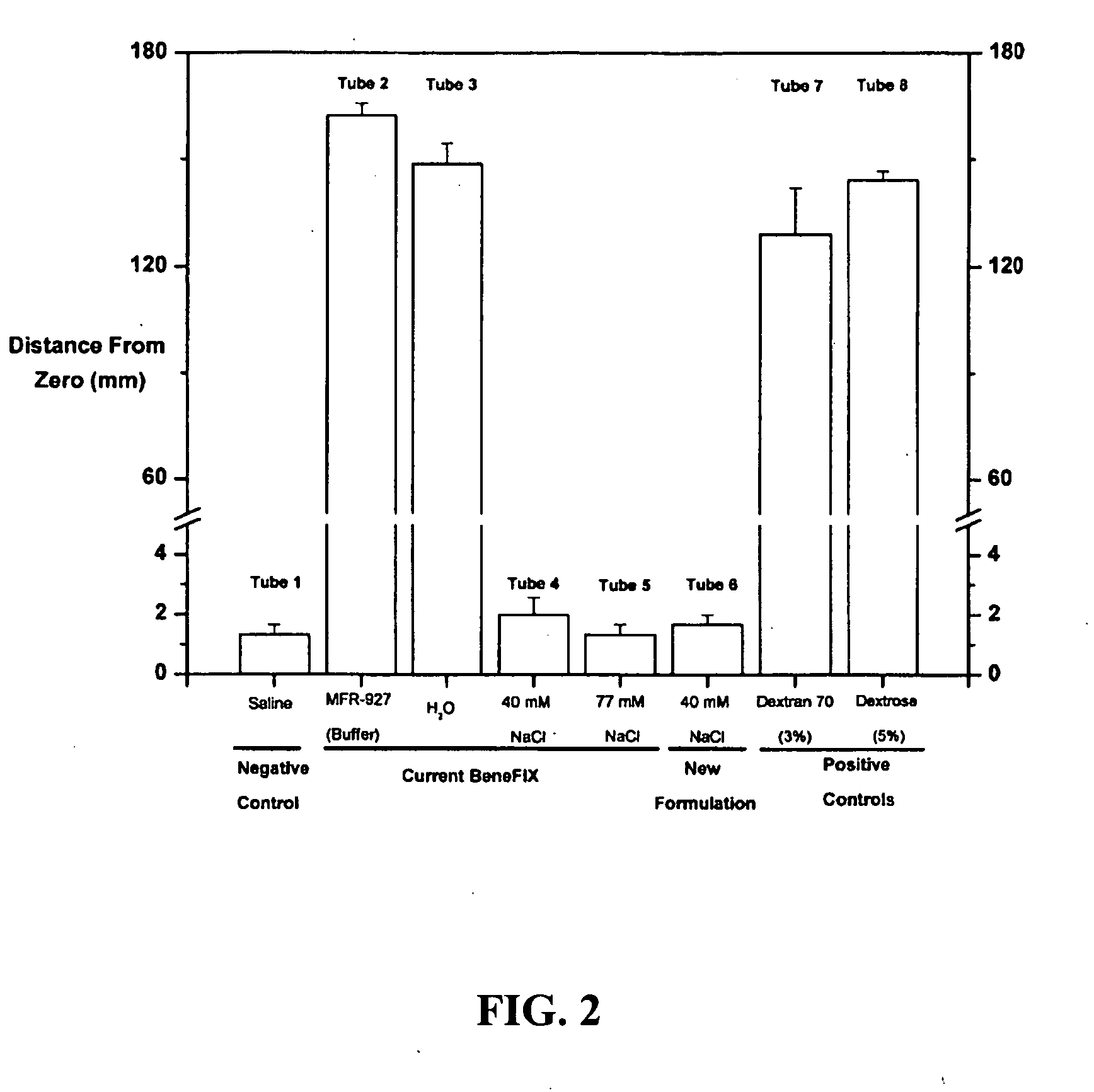
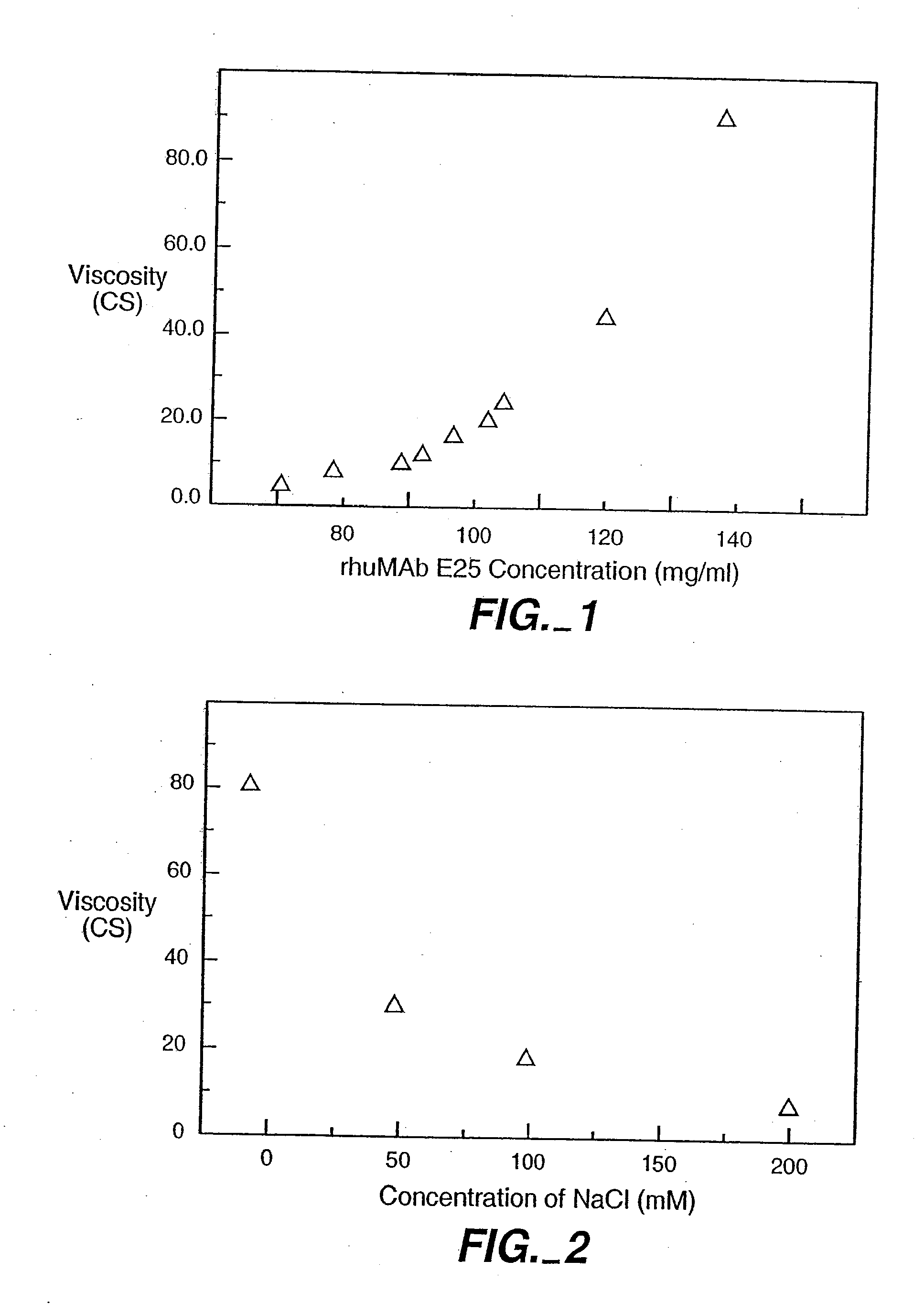
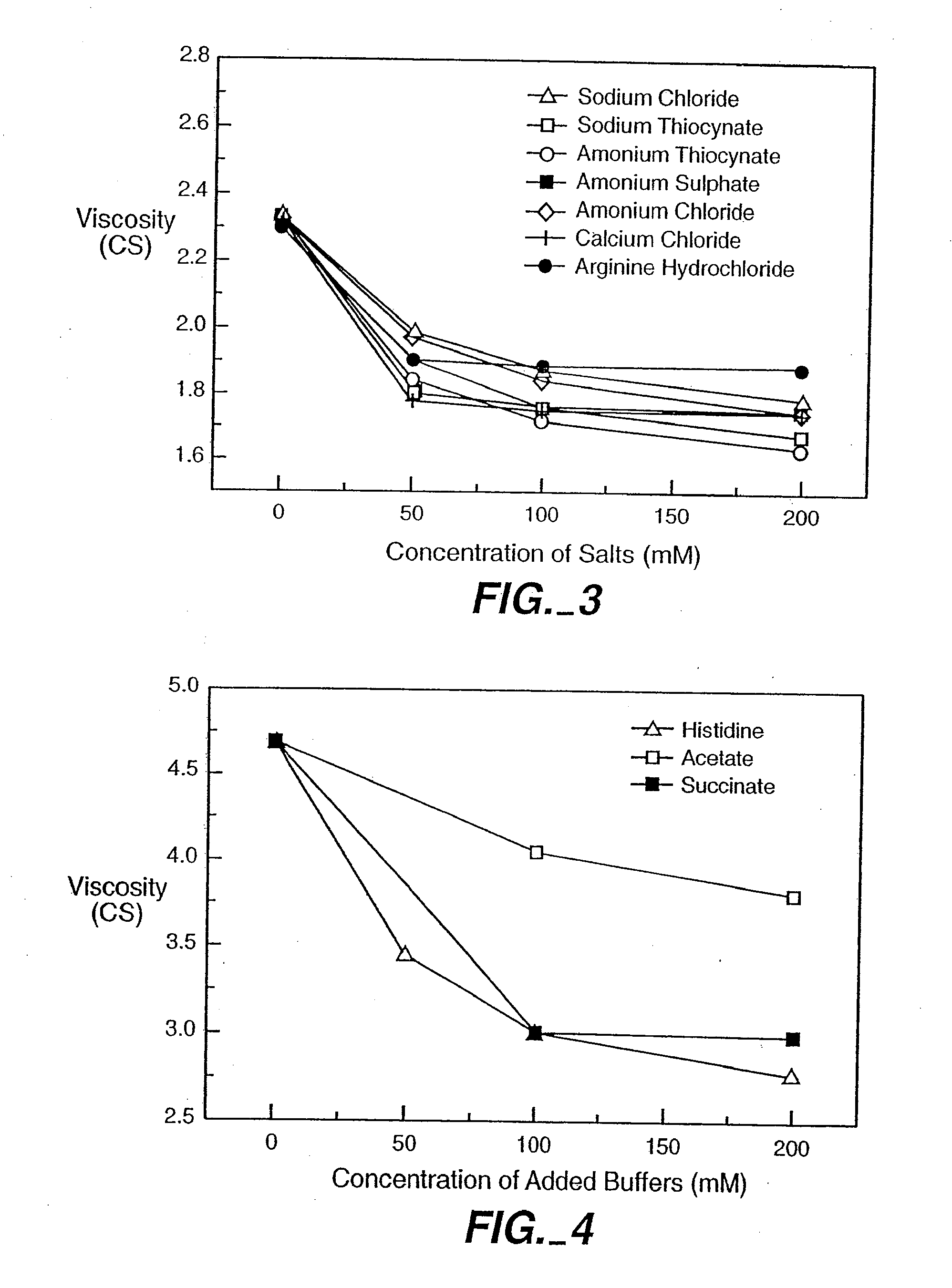
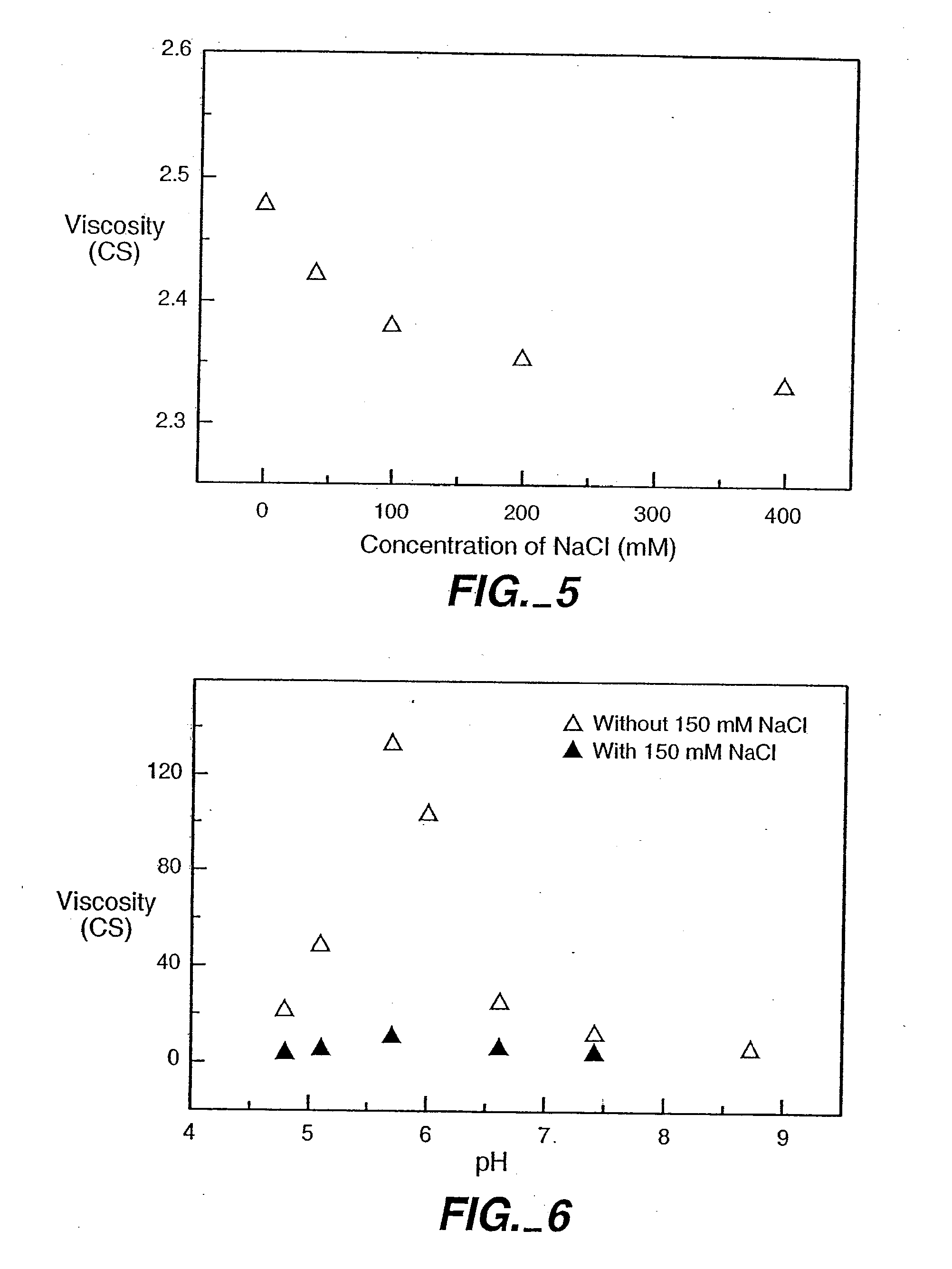
Reduced-viscosity concentrated protein formulations
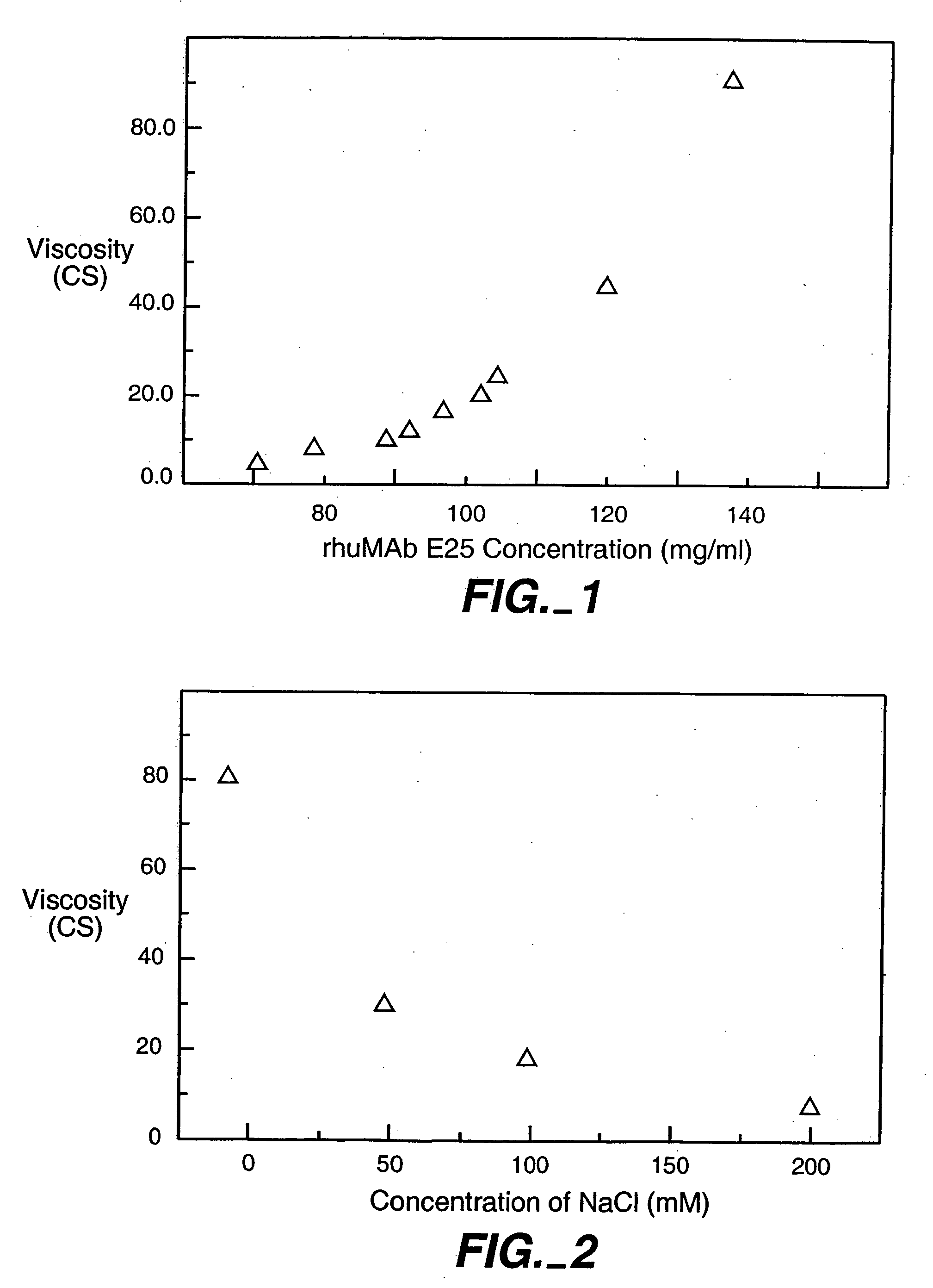
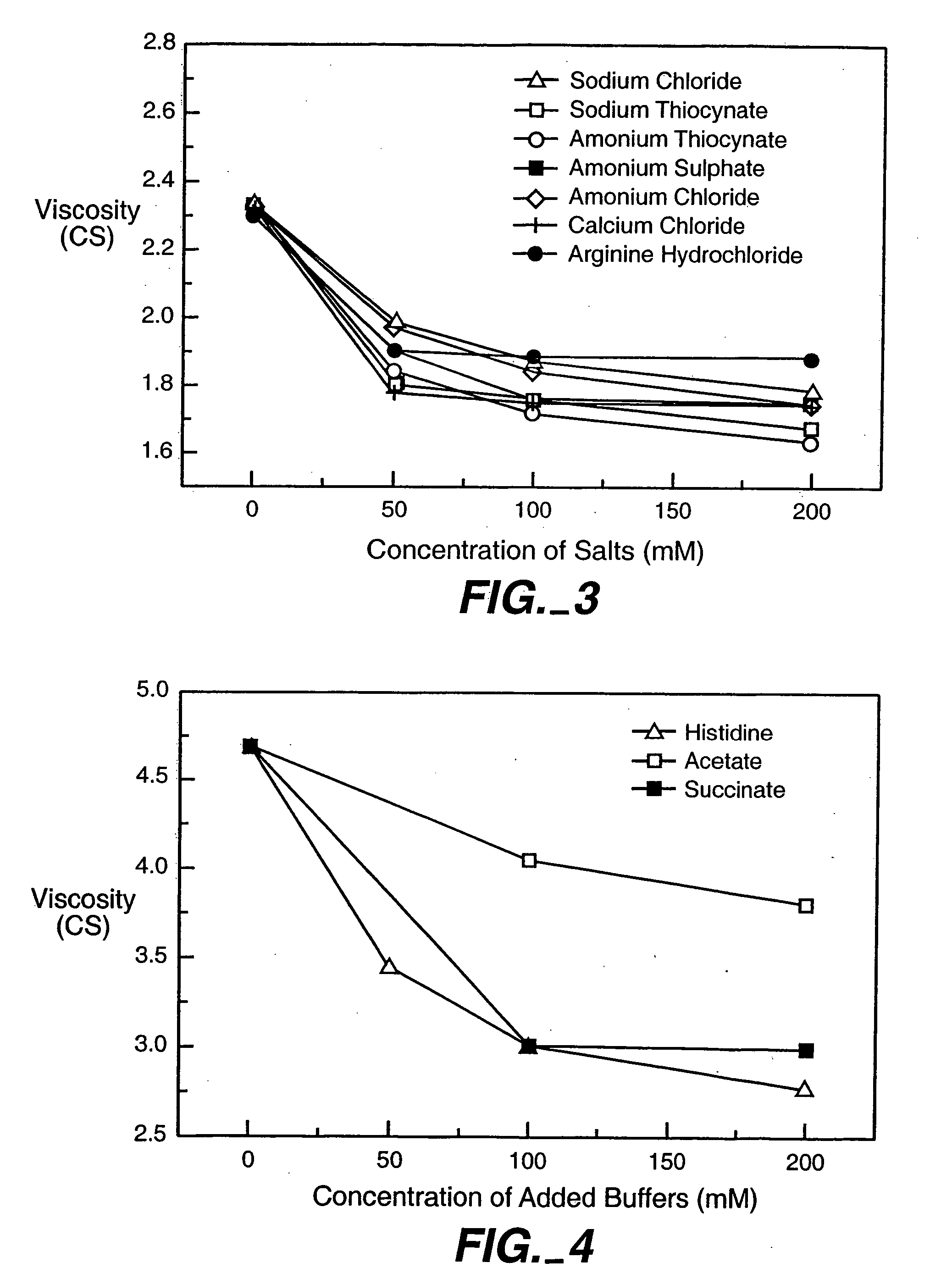
InactiveUS6875432B2Low viscosityCompromising stability and biological activityPeptide/protein ingredientsInorganic non-active ingredientsConcentration proteinChemistry
The present application concerns concentrated protein formulations with reduced viscosity, which are particularly suitable for subcutaneous administration. The application further concerns a method for reducing the viscosity of concentrated protein formulations.
Owner:GENENTECH INC +1
Immunoassay device with immuno-reference electrode
InactiveUS7723099B2Increase ionic strengthReduce distractionsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein insertionNon specific
An electrochemical immunosensor system with reduced interference, comprising: a first immunosensor that generates an electrochemical signal based on the formation of a sandwich between an immobilized antibody, a target analyte and a labeled antibody, wherein a portion of the signal arises from non-specific binding of the labeled antibody in the region of the first immunosensor, anda second immunosensor that acts as an immuno-reference sensor and generates a signal that is the same as or predictably related to the degree of non-specific binding which occurs in the region of the first immunosensor, and has an immunocomplex between an immobilized antibody and an endogenous or exogenous protein that is in the sample and that is not the target analyte.
Owner:ABBOTT POINT CARE
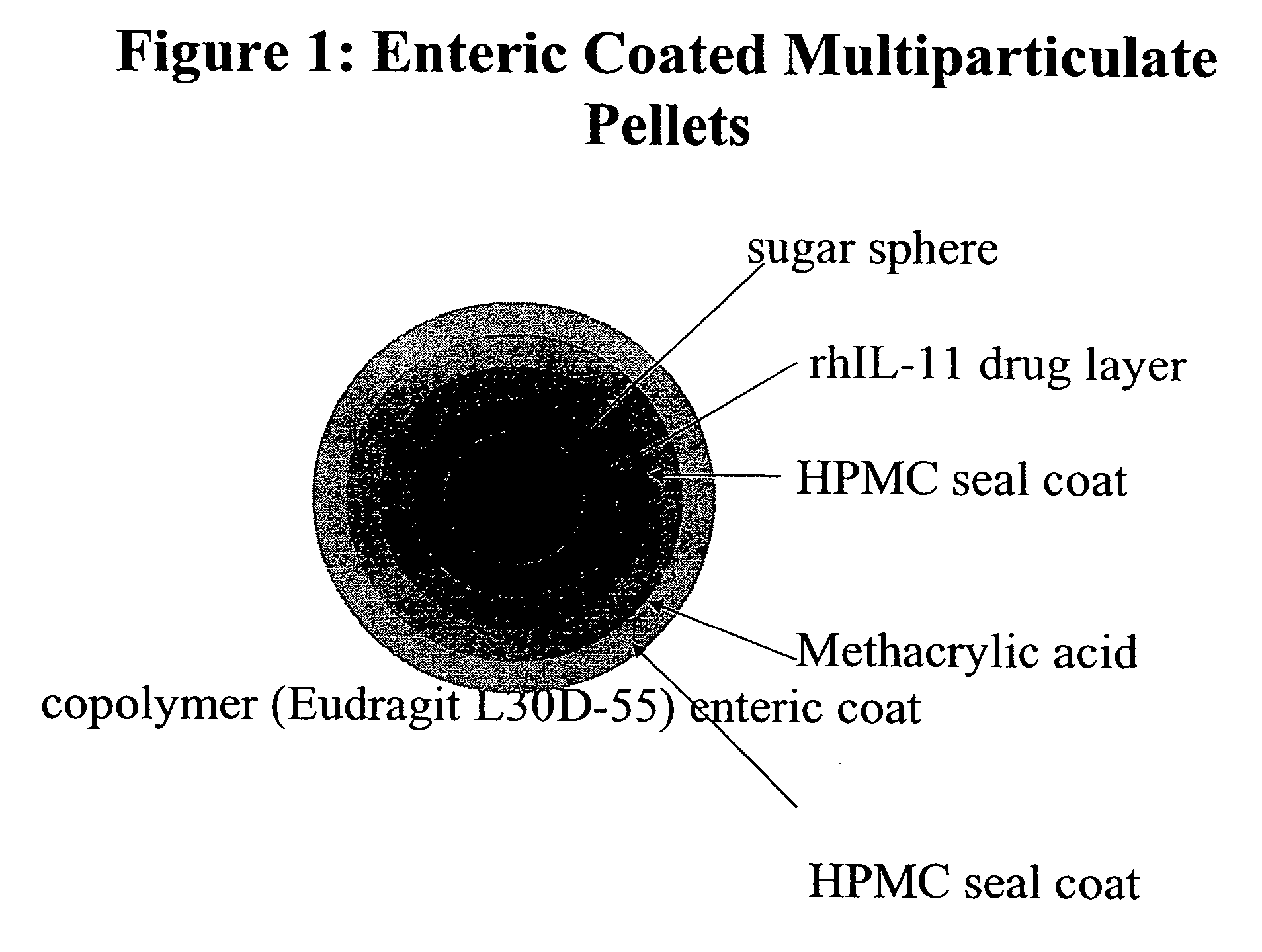
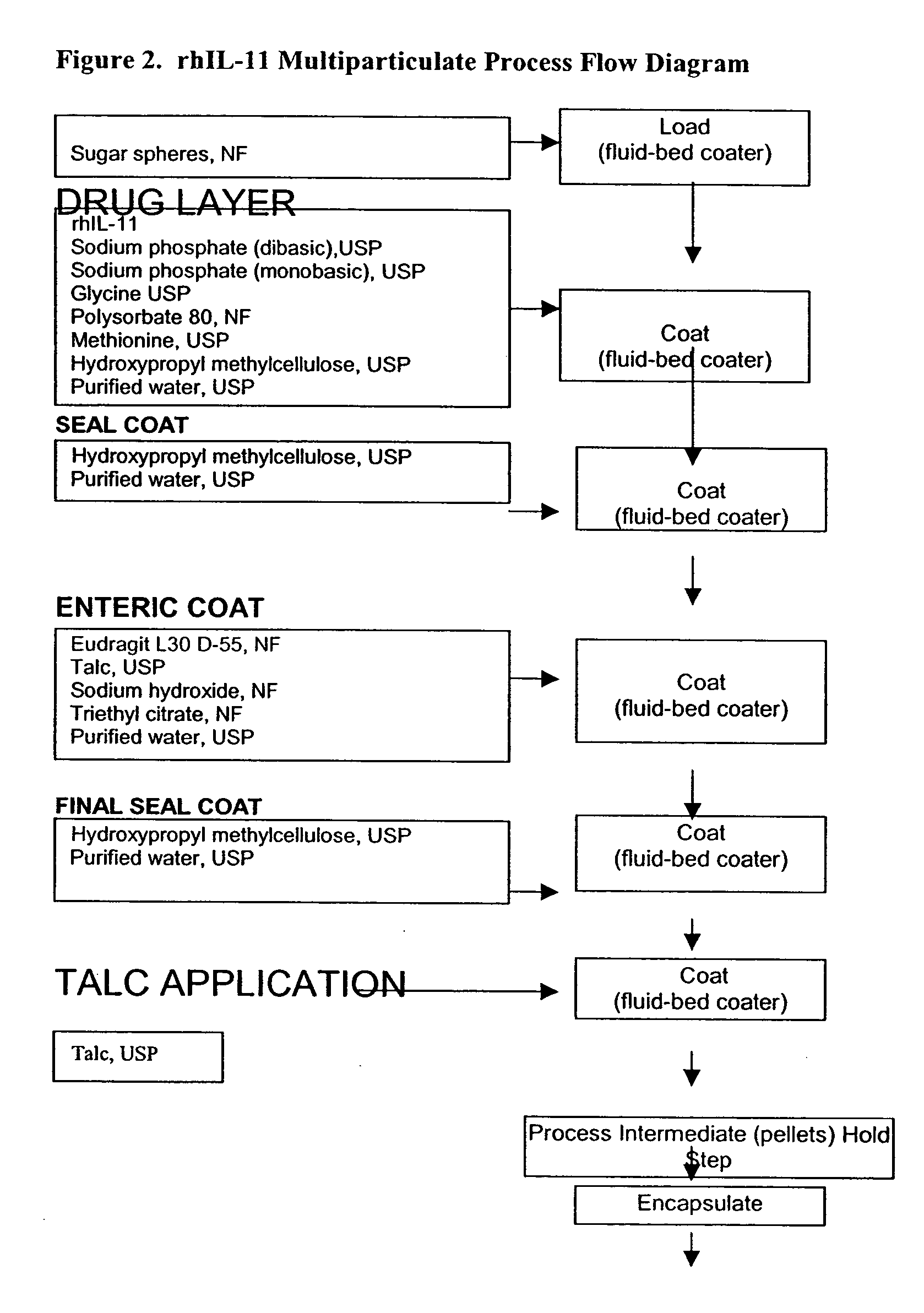
Delayed release formulations for oral administration of a polypeptide therapeutic agent and methods of using same
InactiveUS20040126358A1Increase ionic strengthReduced strengthAntipyreticAnalgesicsOral medicationWhite blood cell
The invention provides compositions containing polypeptides, including therapeutic polypeptides such as interleukin-11, that are suitable for oral administration.
Owner:WYETH LLC
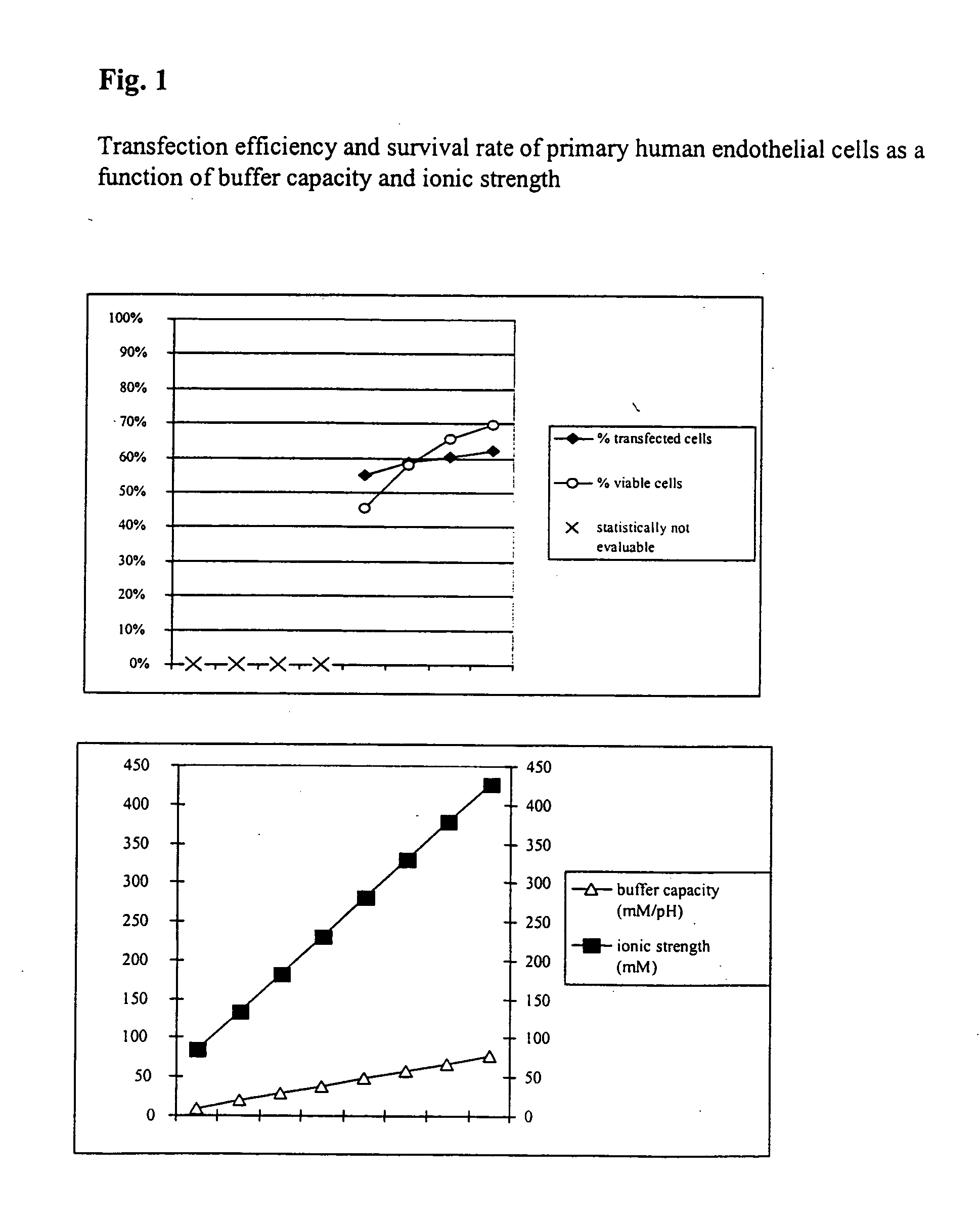
Buffer solution for electroporation and a method comprising the use of the same
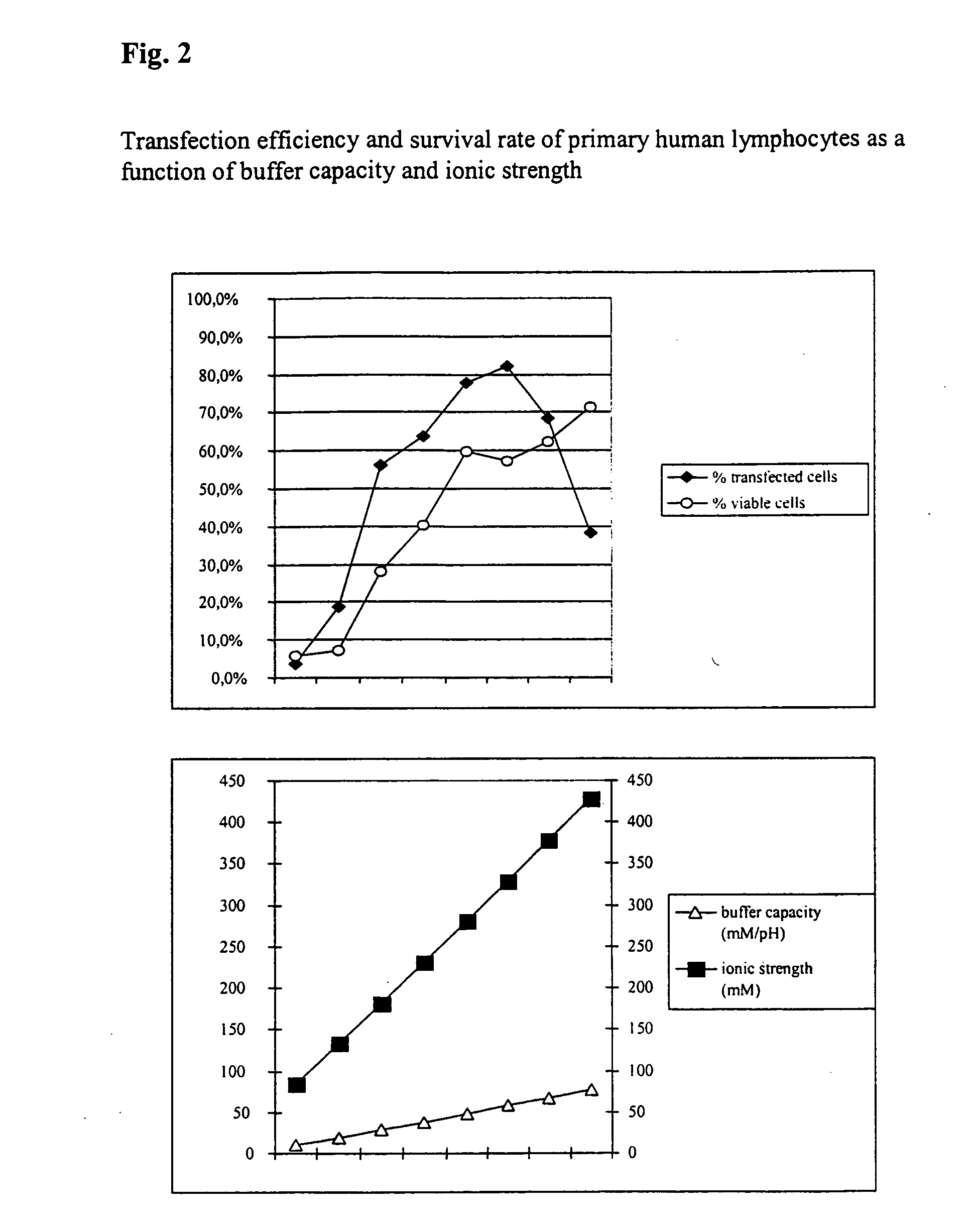
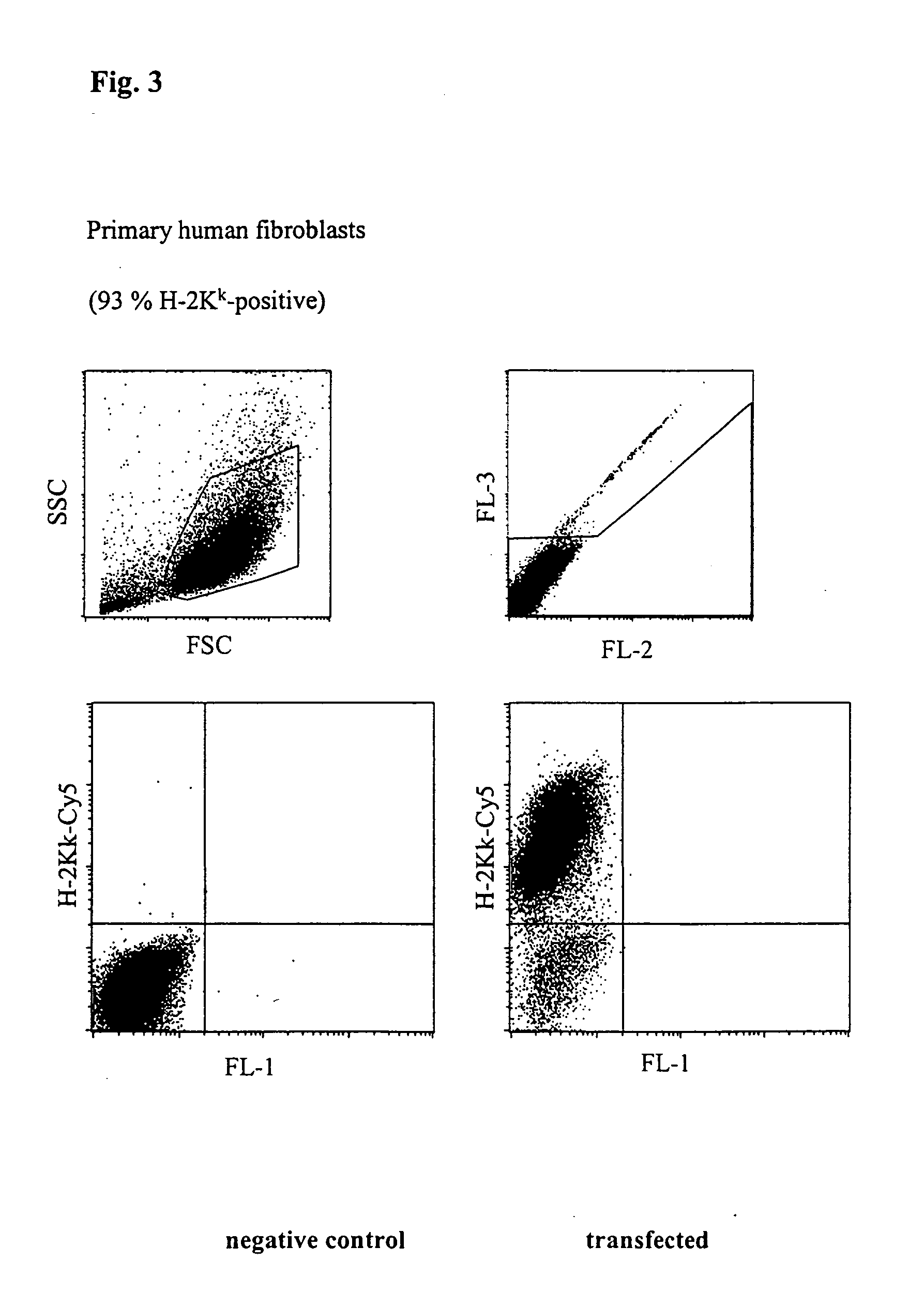
InactiveUS20050064596A1High transfection efficiencyReduce cell deathPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsElectroporationIon
The invention relates to a buffer solution for suspending animal or human cells and for dissolving biologically active molecules in order to introduce said biologically active molecules into the cells using an electric current and to a method for introducing biologically active molecules into animal or human cells using an electric current and a buffer solution. The inventive buffer solution has a buffering capacity of at least 20 mmol*I−1*pH−1 and an ionic strength of at least 200 mmol*I−1 during a change to the pH value from pH 7 to pH 8 and at a temperature of 25° C. The use of a buffer solution of this type in the corresponding method allows biologically active molecules to be introduced into animal and human cells with a high degree of transfection efficiency and at the same time a low cell mortality. Different cell types, in particular dormant and actively dividing cells of low activity, can be successfully transfected in said buffer solution.
Owner:LONZA COLOGNE
Beneficial Effects of Increasing Local Blood Flow
InactiveUS20090105336A1Increase oxygenationImprove tissue nutritionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsTopical creamArginine
The present invention provides a treatment for enhancing the ability of the body to heal wounds. A topical cream is described which improves blood flow by the transdermal delivery of the nitric oxide precursor L-Arginine either alone or with an adjunct, theophylline. The delivery of the active agents is accomplished by use of a vehicle which contains a hostile biophysical environment which is also hostile to hydrogen bond formation.
Owner:STRATEGIC SCI & TECH
Reduced-viscosity concentrated protein formulations
InactiveUS20050175603A1Low viscosityCompromising stability and biological activityPeptide/protein ingredientsInorganic non-active ingredientsConcentration proteinChemistry
The present application concerns concentrated protein formulations with reduced viscosity, which are particularly suitable for subcutaneous administration. The application further concerns a method for reducing the viscosity of concentrated protein formulations.
Owner:GENENTECH INC +1
Alphavirus particles and methods for preparation
ActiveUS7078218B2Improve salt wash recoveryIncrease ionic strengthSsRNA viruses positive-senseGenetic material ingredientsHigh densityPotassium
Provided herein are methods for producing alphavirus replicon particles in high yield; replicon RNAs are electroporated into permissive cells, where the cells are at a relatively high density, together with at least one helper nucleic acid providing the necessary functions for packaging. After a growth period in appropriate medium, alphavirus replicon particles are harvested from the surfaces of the cells in which they were produced using a salt wash in which the salt concentration is from about 0.2 to about 5 M sodium chloride, calcium chloride, magnesium chloride, potassium chloride, ammonium acetate, ammonium bicarbonate, among others. After dilution, if necessary, the particles can be purified by a suitable chromatographic technique.
Owner:ALPHAVAX INC
Compositions and methods to prevent AAV vector aggregation
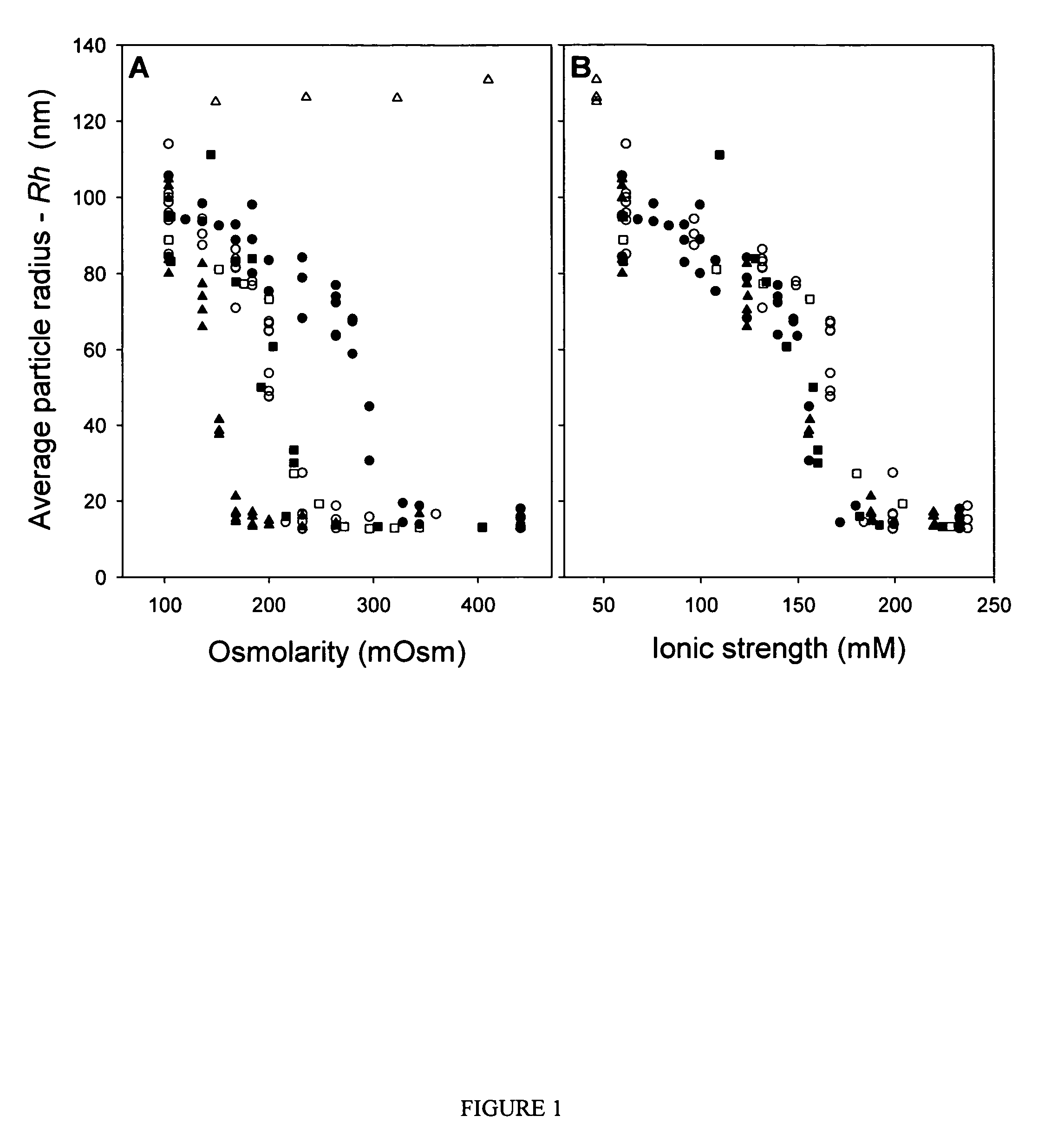
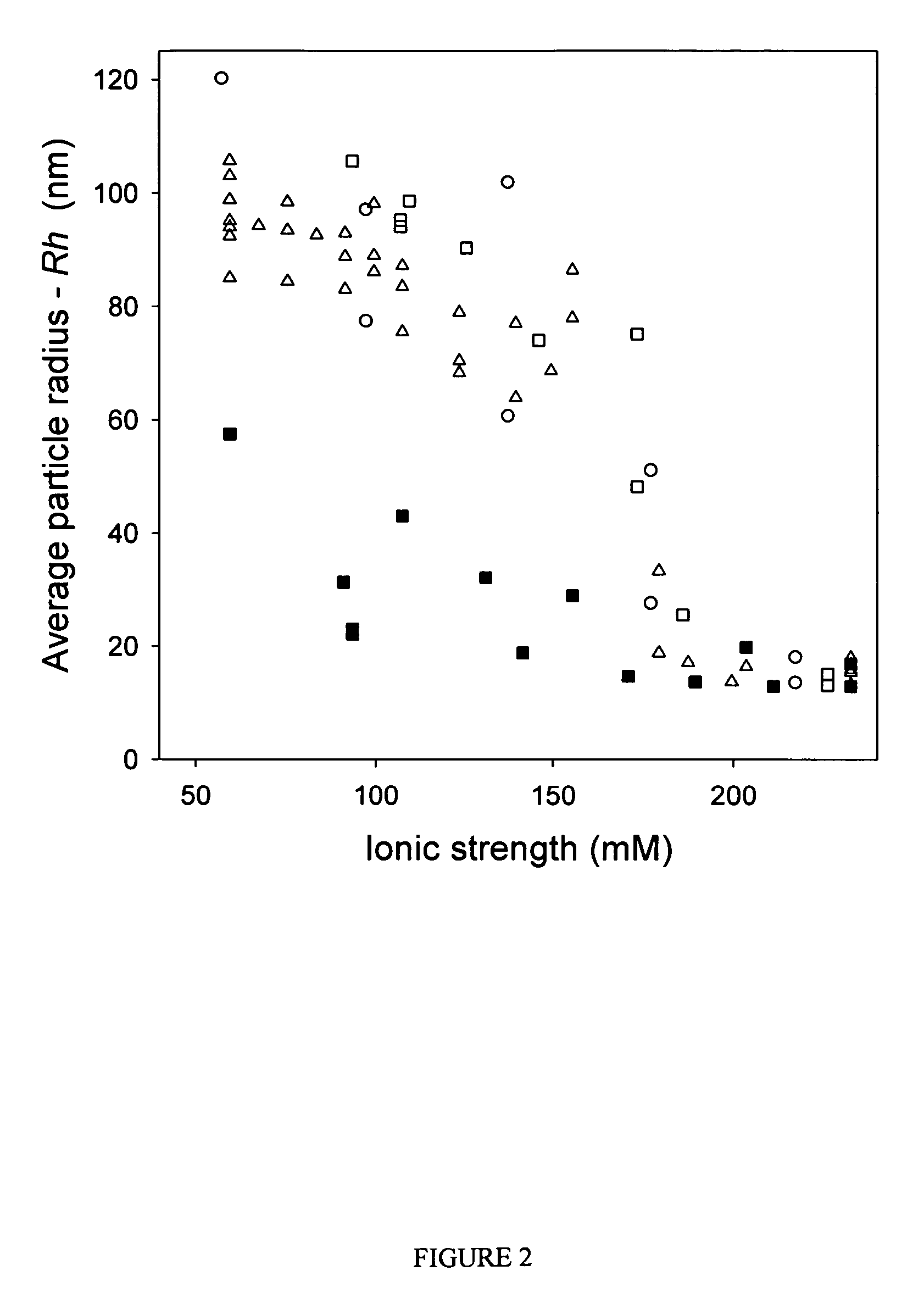
ActiveUS7704721B2Increase ionic strengthImprove efficiencyRecovery/purificationSsDNA virusesFreeze thawingIonic strength
Compositions and methods are provided for preparation of concentrated stock solutions of AAV virions without aggregation. Formulations for AAV preparation and storage are high ionic strength solutions (e.g. μ˜500 mM) that are nonetheless isotonic with the intended target tissue. This combination of high ionic strength and modest osmolarity is achieved using salts of high valency, such as sodium citrate. AAV stock solutions up to 6.4×1013 vg / mL are possible using the formulations of the invention, with no aggregation being observed even after ten freeze-thaw cycles. The surfactant Pluronic® F68 may be added at 0.001% to prevent losses of virions to surfaces during handling. Virion preparations can also be treated with nucleases to eliminate small nucleic acid strands on virions surfaces that exacerbate aggregation.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Method for anion-exchange adsorption and anion-exchangers
InactiveUS6702943B1Reduced ligand contentSolve insufficient capacityIon-exchanger regenerationOrganic anion exchangersHydrogenDesorption
A method for the removal of a substance carrying a negative charge and being present in an aqueous liquid (I). The method comprises the steps of: (i) contacting the liquid with a matrix carrying a plurality of ligands comprising a positively charged structure and a hydrophobic structure, and (ii) desorbing the substance. The characterizing feature is that (I) each of said ligands together with a spacer has the formula: -SP-[Ar-R1-N<+>(R2R3R4)] where (A) [Ar-R1-N<+>(R2R3R4)] represents a ligand a) Ar is an aromatic ring, b) R1 is [(L)nR'1]m where n and m are integers selected amongst zero or 1; L is amino nitrogen, ether oxygen or thioether sulphur; R'1 is a linker selected among 1) hydrocarbon groups; 2) -C(=NH)-; c) R2-4 are selected among hydrogen and alkyls; (B) SP is a spacer providing a carbon or a heteroatom directly attached to Ar-R1-N<+>(R2R3R4); (C)-represents that SP replaces a hydrogen in (Ar-R1-N<+>(R2R3R4); (D)-represents binding to the matrix; and (II) desorption. There is also described (a) anion-exchangers having high breakthrough capacities, (b) a screening method and (c) a desalting protocol.
Owner:CYTIVA BIOPROCESS R&D AB
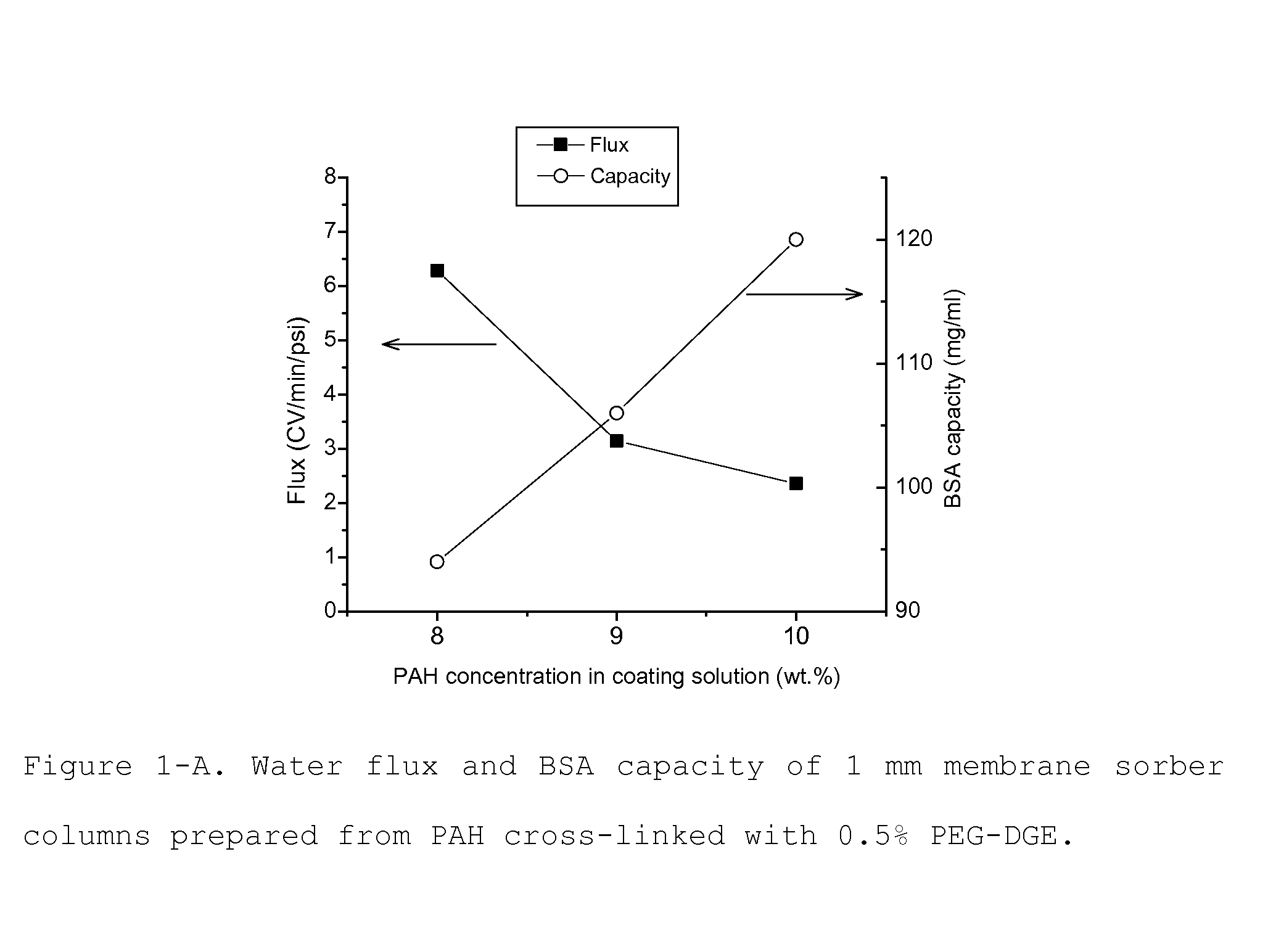
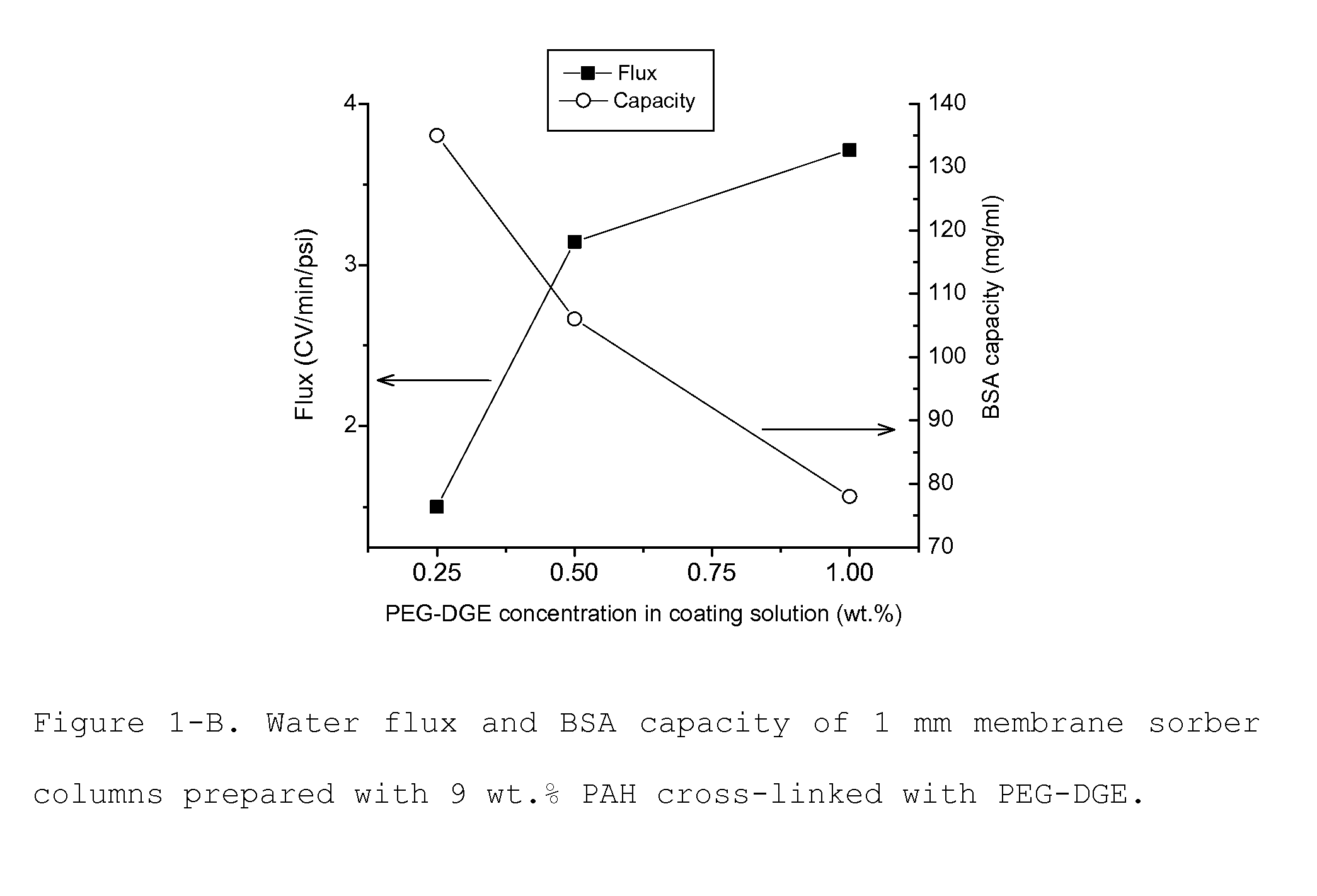
Media for membrane ion exchange chromatography based on polymeric primary amines, sorption device containing that media, and chromatography scheme and purification method using the same
ActiveUS20090050566A1Improve bindingGood removal effectCation exchanger materialsIon-exchanger regenerationPurification methodsSorbent
Media and devices, such as anion exchangers including such media, wherein the media is a membrane having a surface coated with a polymer such as a polyallylamine. The resulting membrane offers stronger binding of protein impurities and superior removal of host cell proteins from biological samples than conventional ligands based on quaternary ammonium salts, including trimethylammonium ligands. Also described is a chromatography scheme and method for purifying monoclonal antibodies, wherein the anion exchange sorber is placed downstream of an affinity column (such as Protein A or Protein G affinity column) and optionally one or more polishing devices such as cationic exchange columns. Little or no dilution of the cation exchanger pool (or affinity column exchange pool where no cation exchanger is used) is necessary to lower the conductivity of the sample. The sorber functions well to strongly bind host cell proteins and other impurities in biological samples even at high conductivities and pH.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
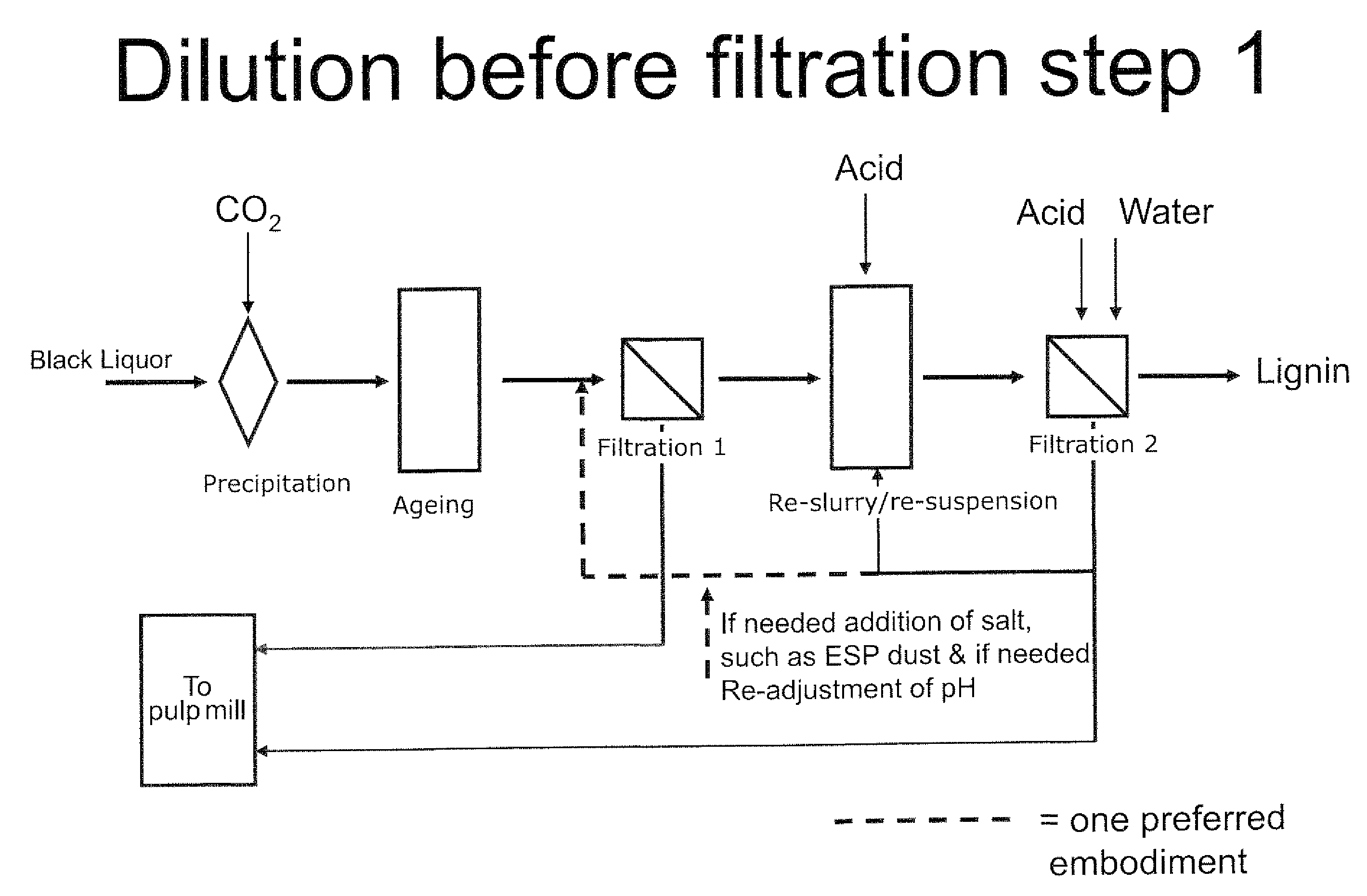
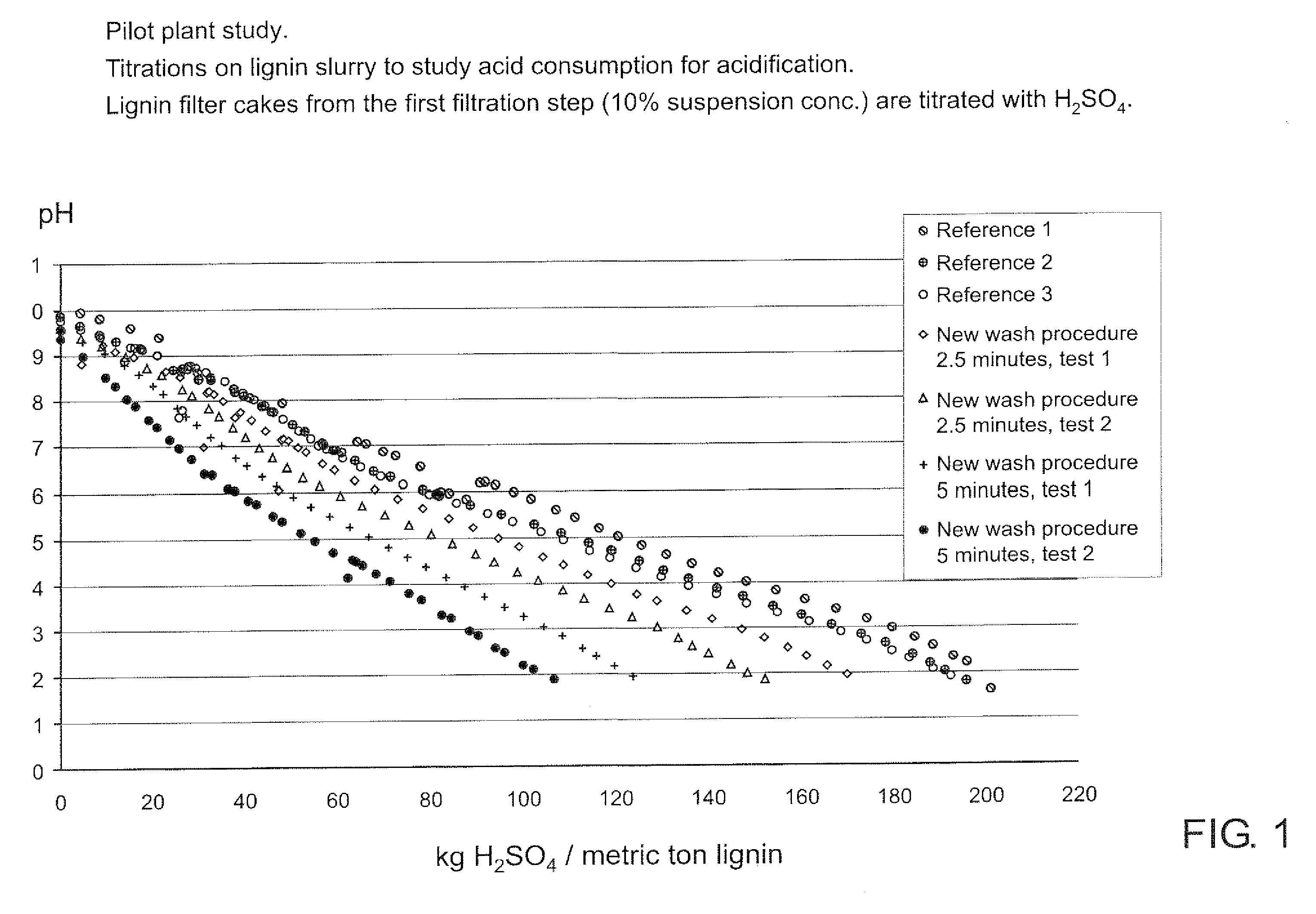
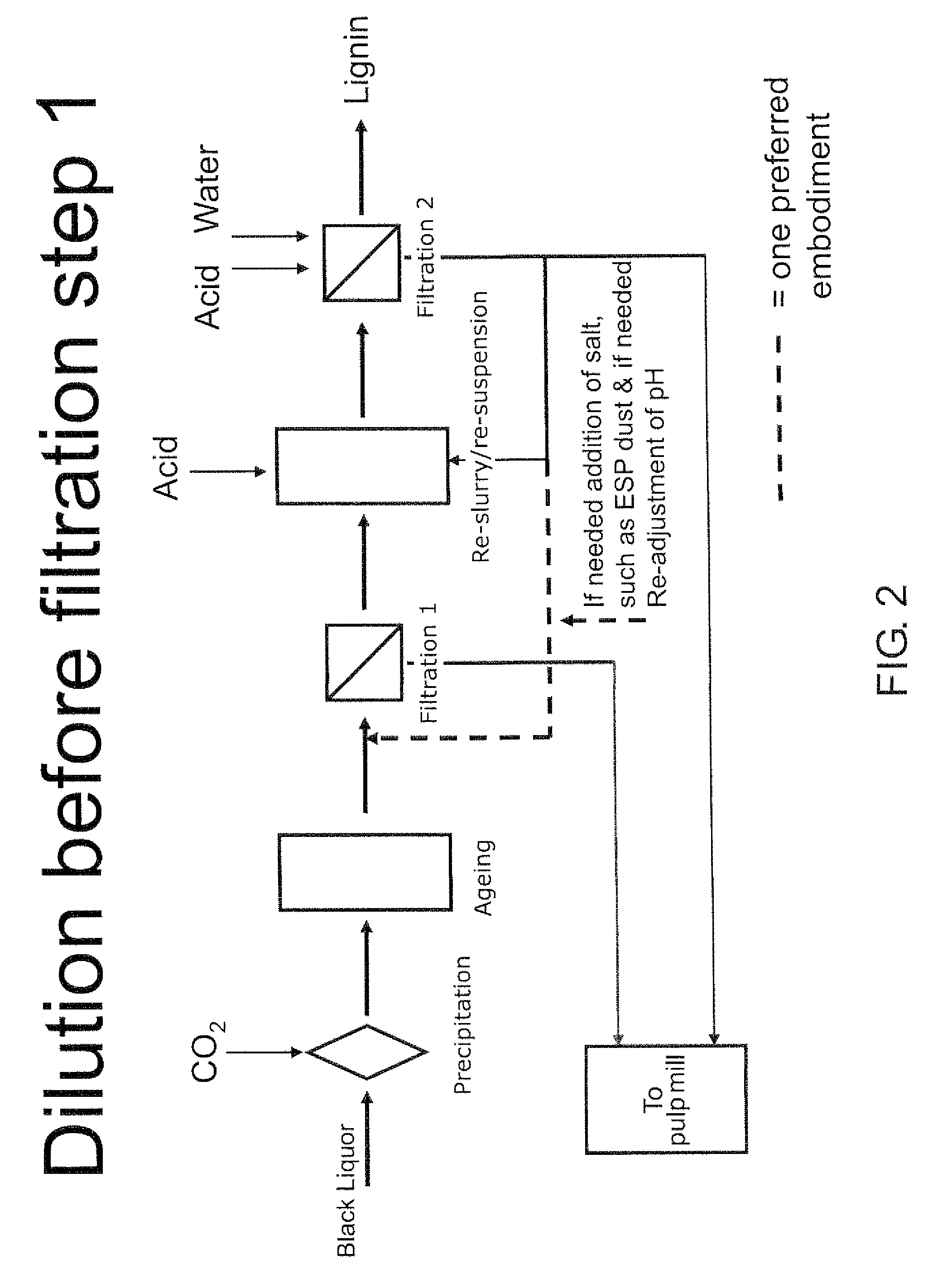
Method for separating lignin from black liquor, a lignin product, and use of a lignin product for the production of fuels or materials
ActiveUS20100325947A1Control balanceLower requirementSolid fuelsPulp by-products recoveryChemistryRecovery boiler
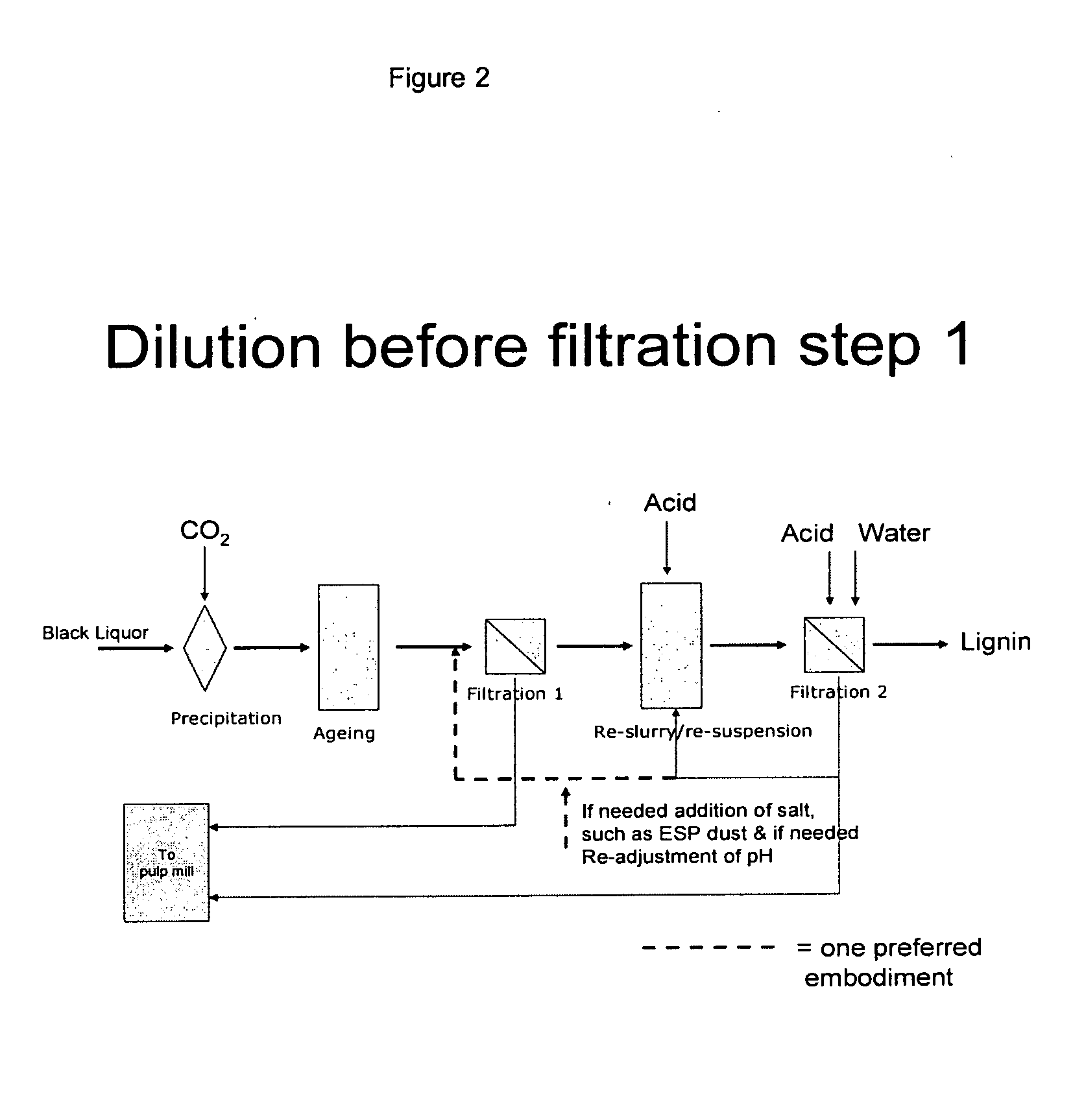
The method is for controlling a sodium and sulphur balance of a pulp mill while separating lignin from black liquor. Lignin is precipitated by using an acid followed by filtration. The lignin filter cake thus obtained is re-suspended in acidic liquid and dewatered to form a second cake. The filtrate obtained after dewatering of the second cake is returned for washing and suspension of the first cake. Sodium sulphate-rich ESP (electrostatic precipitator) dust produced in the recovery boiler is used in the washing of the precipitated lignin cake.
Owner:VALMET AB
Method
ActiveUS20080214796A1Lower requirementInhibition of dissolutionLignin derivativesPulp by-products recoveryBlack liquorPulp mill
A method for controlling the sodium and sulphur balance of a pulp mill while separating lignin from black liquor, and also a lignin product or an intermediate lignin product obtainable by the method. The present invention also provides use of a lignin product or an intermediate lignin product for the production of fuel (solid, gaseous or liquid) or materials.
Owner:LIGNOBOOST
Method For Separating Lignin From A Lignin Containing Liquid/Slurry
InactiveUS20080051566A1Efficient separationImprove filtering effectLignin derivativesPulp by-products recoveryLignin degradationBlack liquor
A method for precipitating (separation) of lignin, using small amounts of acidifying agents, whereby a lignin product or an intermediate lignin product is obtained which can be used as fuel or chemical feed stock (or as a chemical or a raw material for further refining), from a lignin containing liquid / slurry, such as black liquor. A method for separation of lignin from a lignin containing liquid / slurry, such as black liquor, whereby a more pure lignin is obtained, a lignin product or an intermediate lignin product obtainable by the above methods, and use, preferably for the production of heat or for use as chemical, of the lignin product or intermediate lignin product are also disclosed.
Owner:LIGNOBOOST
Reduced-viscosity concentrated protein formulations
InactiveUS8703126B2Low viscosityCompromising stability and biological activityInorganic non-active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsConcentration proteinReduced viscosity
The present application concerns concentrated protein formulations with reduced viscosity, which are particularly suitable for subcutaneous administration. The application further concerns a method for reducing the viscosity of concentrated protein formulations.
Owner:GENENTECH INC +1
Superfine and spheroidizing rare-earth polish and preparing process thereof
ActiveCN101284983AIncrease ionic strengthIncrease surface chargeOther chemical processesIonDiammonium carbonate
The invention provides ultrafine spheroidized rare earth polishing powder and a process for making the same. The process comprises the following steps that: one of or the mixture of ammonia water, ammonium bicarbonate and ammonium carbonate is used as precipitant; ammonium salt and fluoride ions are added into precipitated slurry to adjust the ionic strength in mother liquid, so as to increase the surface electrical property of solid particles in the slurry; after high temperature aging, the ultrafine rare earth polishing powder with good dispersity and high spheroidization degree can be obtained by filtering the slurry, drying, burning, ball-milling and sieving filter cakes. The average particle size of the obtained polishing powder is between 0.02 mu m and 2.0 mu m, wherein the specific surface area BET is more than 0 and less than 10 m<2> / g, and the powder is in a well-dispersed spherical shape. The powder is used for polishing optical glass, crystal, display screens, etc., strong in cutting force, few in scratch and long in service time.
Owner:GRIREM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Protein a chromatography
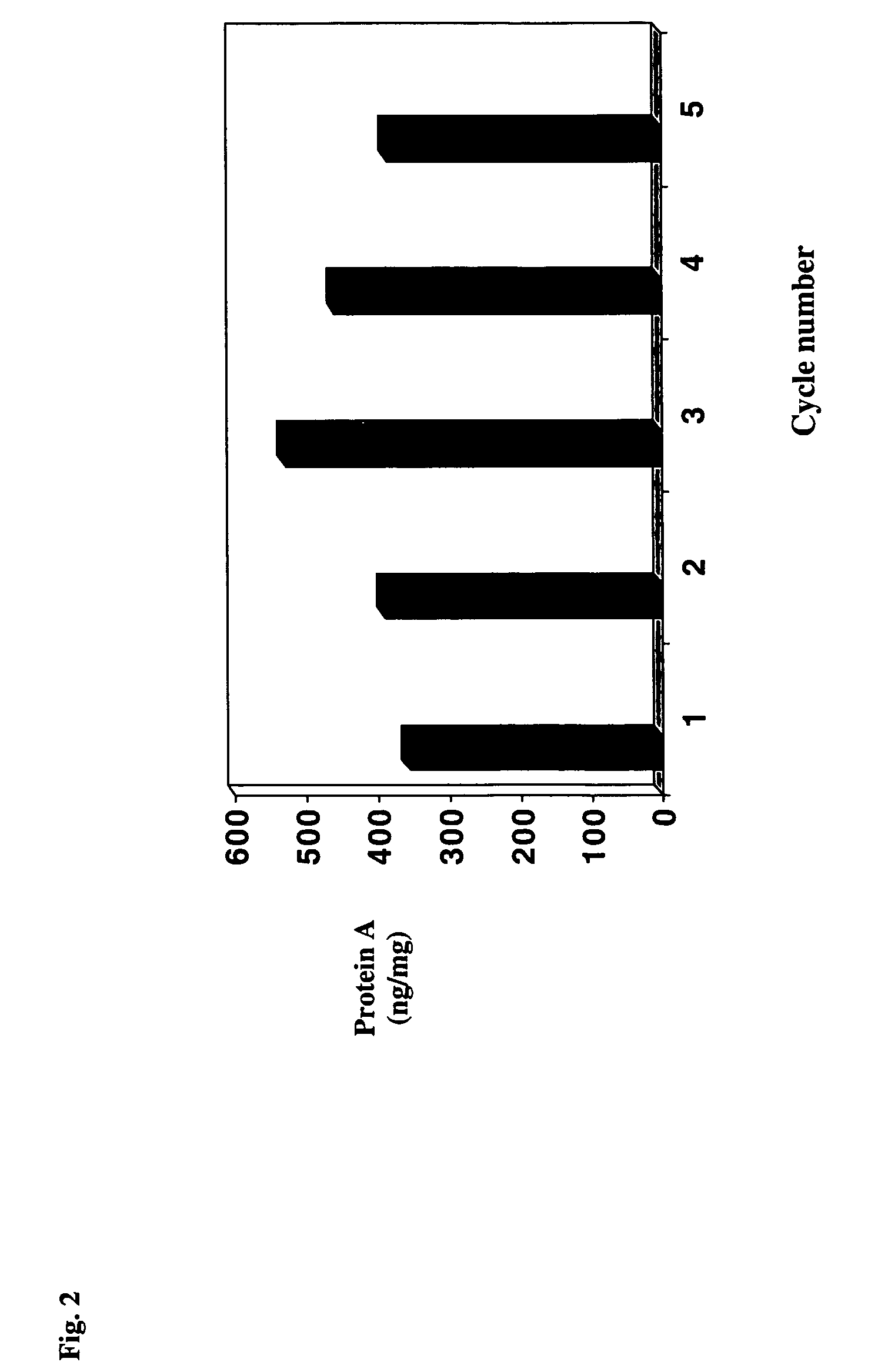
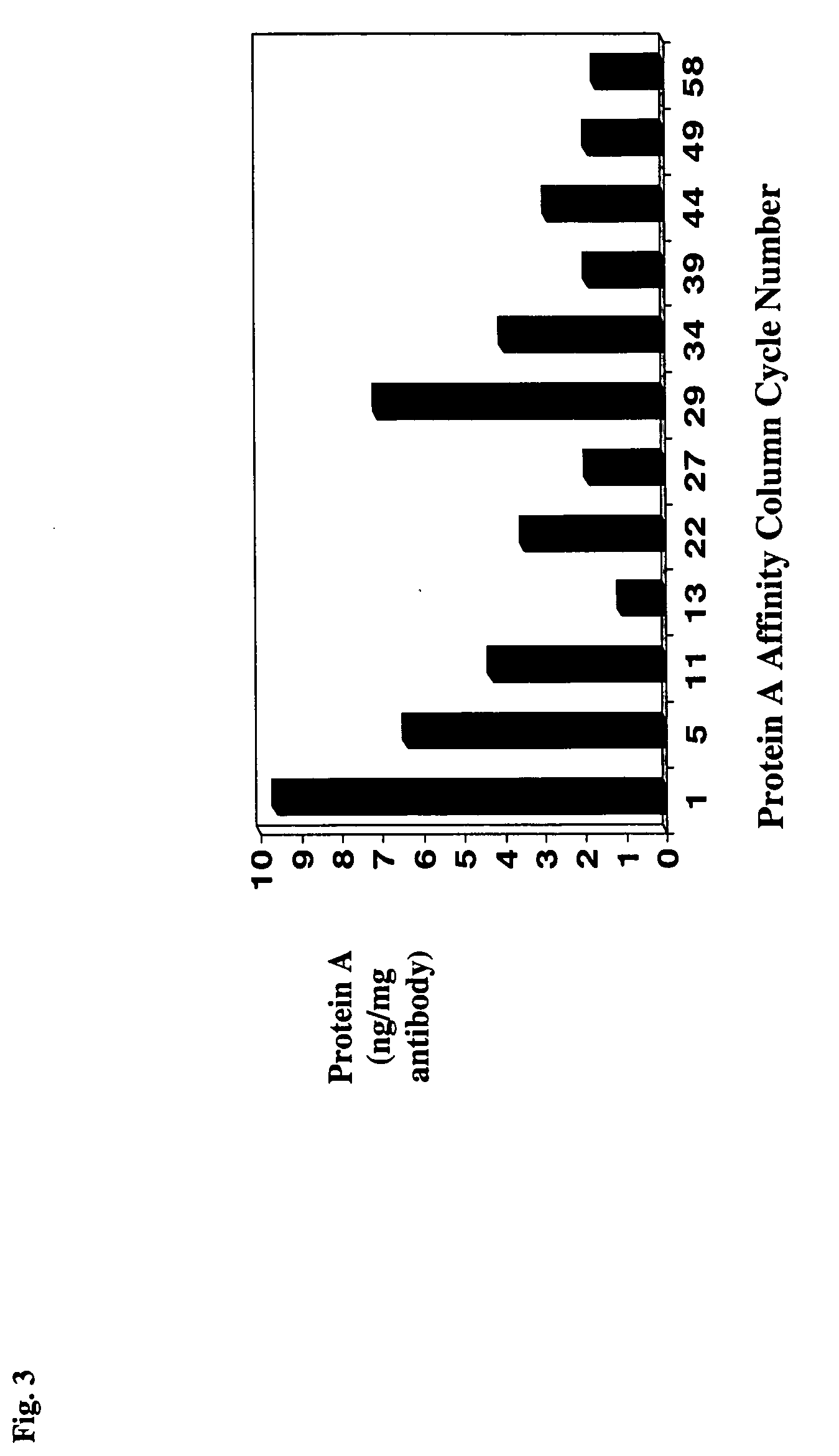
InactiveUS20060030696A1Increase ionic strengthThroughputSerum immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansProtein AChromatography
A novel method for selectively removing leaked protein A from antibody purified by means of protein A affnitiy chromatography is disclosed.
Owner:LONZA BIOLOGICS PLC
Stable silicone oil emulsion composition, article of manufacture, and method of fabric wrinkle control
InactiveUS6908962B1Convenient treatmentImprove performanceOther chemical processesMixing methodsWrinkleEmulsion
Silicone emulsion comprising: at least about 0.025% and less than about 10% of silicone oil; an active amount to emulsify said silicone oil and reduce surface tension of said composition of a surfactant system; and a an effective amount of a buffering system to maintain a pH of said composition to be at least about 6 for a period of at least about 3 months, are useful for controlling wrinkles in fabrics.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Anti-microbial granules
InactiveUS20060188580A1Reduce releaseIncrease ionic strengthPowder deliveryHeavy metal active ingredientsBiotechnologyEpoxy
Antimicrobial granules comprising granular materials coated with antimicrobial metal agents for use in various surface coating and grouting materials are provided. The antimicrobial granules have utility in imparting durable, safe, inexpensive and powerful antimicrobial properties to materials into which they are incorporated, such as epoxy coating and grouts for surgical theaters, public washrooms, and food processing plants. The granules further are capable of imparting a timed-release dosage of antimicrobial agents so that the effectiveness of the coating is palpable for extended periods.
Owner:CORRO SHIELD INT
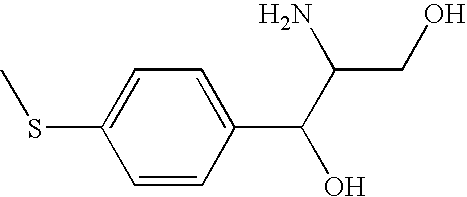
Sodium chloride solution for drug reconstitution or dilution
InactiveUS20070135343A1Prevent agglutinationIncrease ionic strengthBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHemolysisPresent method
The invention provides methods for preparing pharmaceutical formulations for injection such that upon injection the formulation does not cause erythrocyte agglutination, hemolysis, and / or cell shrinkage. To prevent agglutination, a pharmaceutical formulation ready for injection needs to have a sufficient ionic strength. To prevent hemolysis or cell shrinkage, a pharmaceutical formulation ready for injection needs to be about isotonic with respect to plasma. The invention provides methods that prepare pharmaceutical formulations for injection that have both the sufficient ionic strength to prevent agglutination and the requisite tonicity to prevent significant hemolysis or cell dehydration or shrinkage. The present methods involve the use of sodium chloride solutions that are about 25 mM to about 150 mM for reconstituting lyophilized cakes (or other non-liquid pharmaceutical formulations) into solution or for diluting pharmaceutical formulation solutions.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Reduced-viscosity concentrated protein formulations
InactiveUS20120076783A1Preventing self-associationLow viscosityInorganic non-active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsChemistryReduced viscosity
The present application concerns concentrated protein formulations with reduced viscosity, which are particularly suitable for subcutaneous administration. The application further concerns a method for reducing the viscosity of concentrated protein formulations.
Owner:GENENTECH INC +1
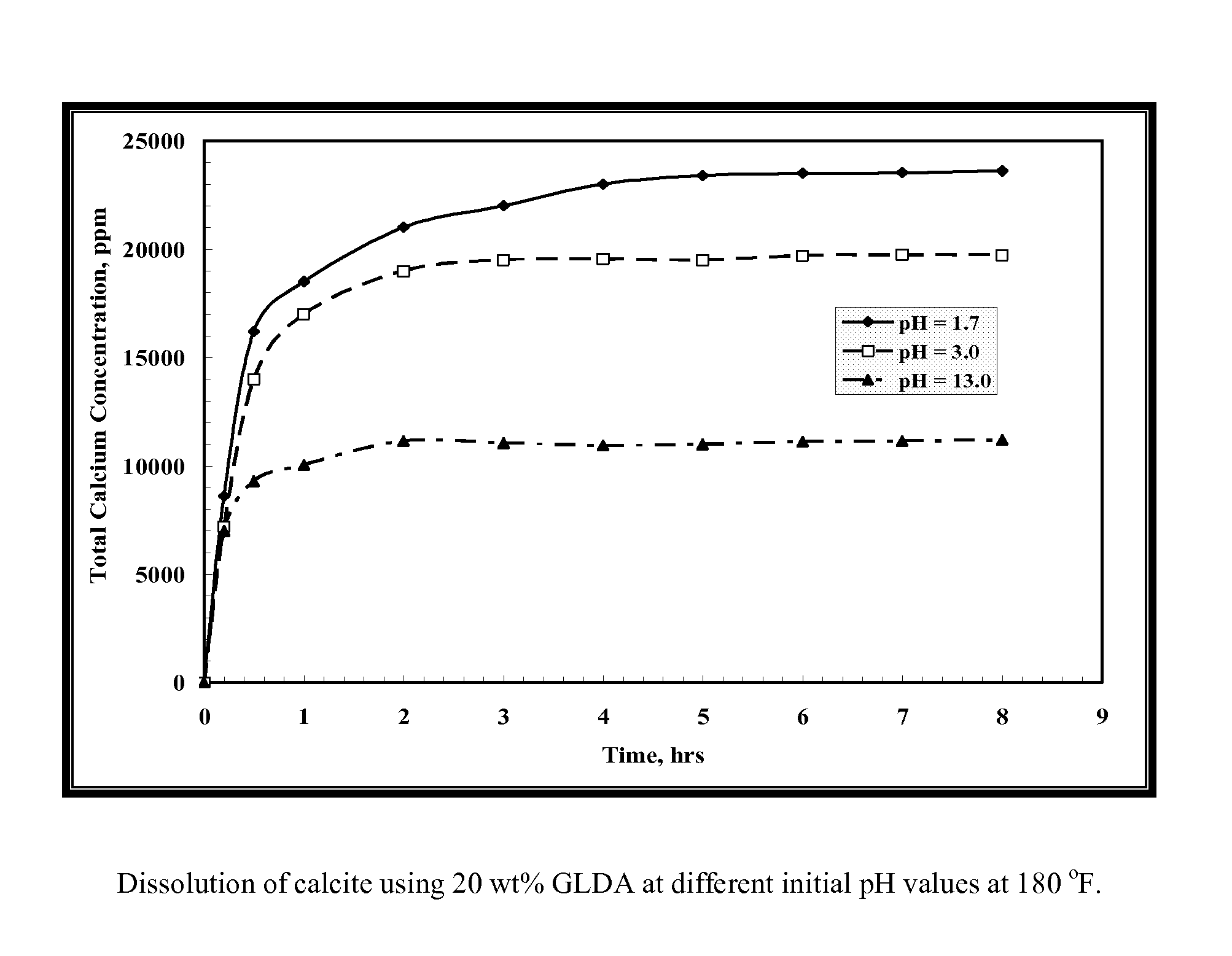
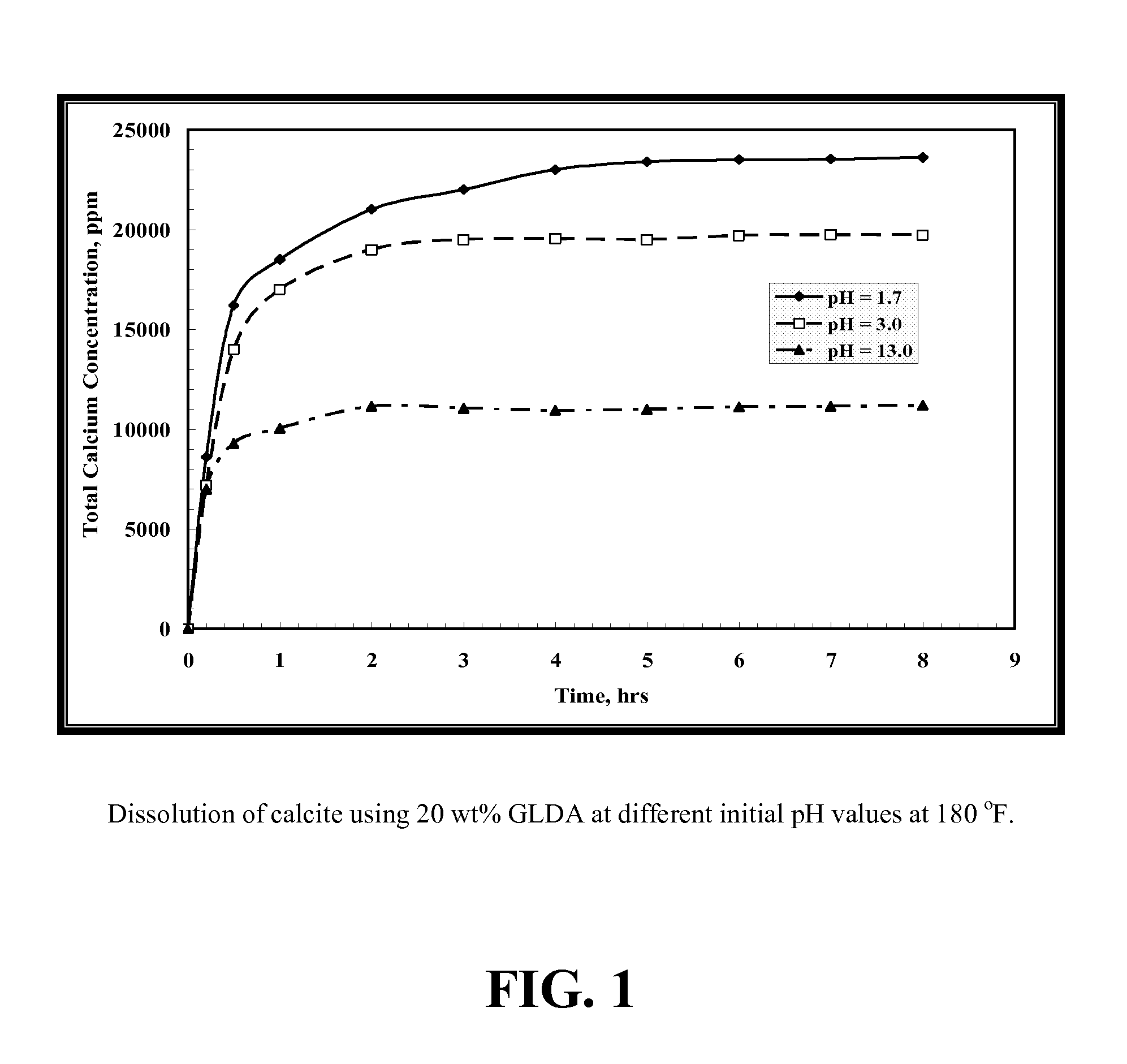
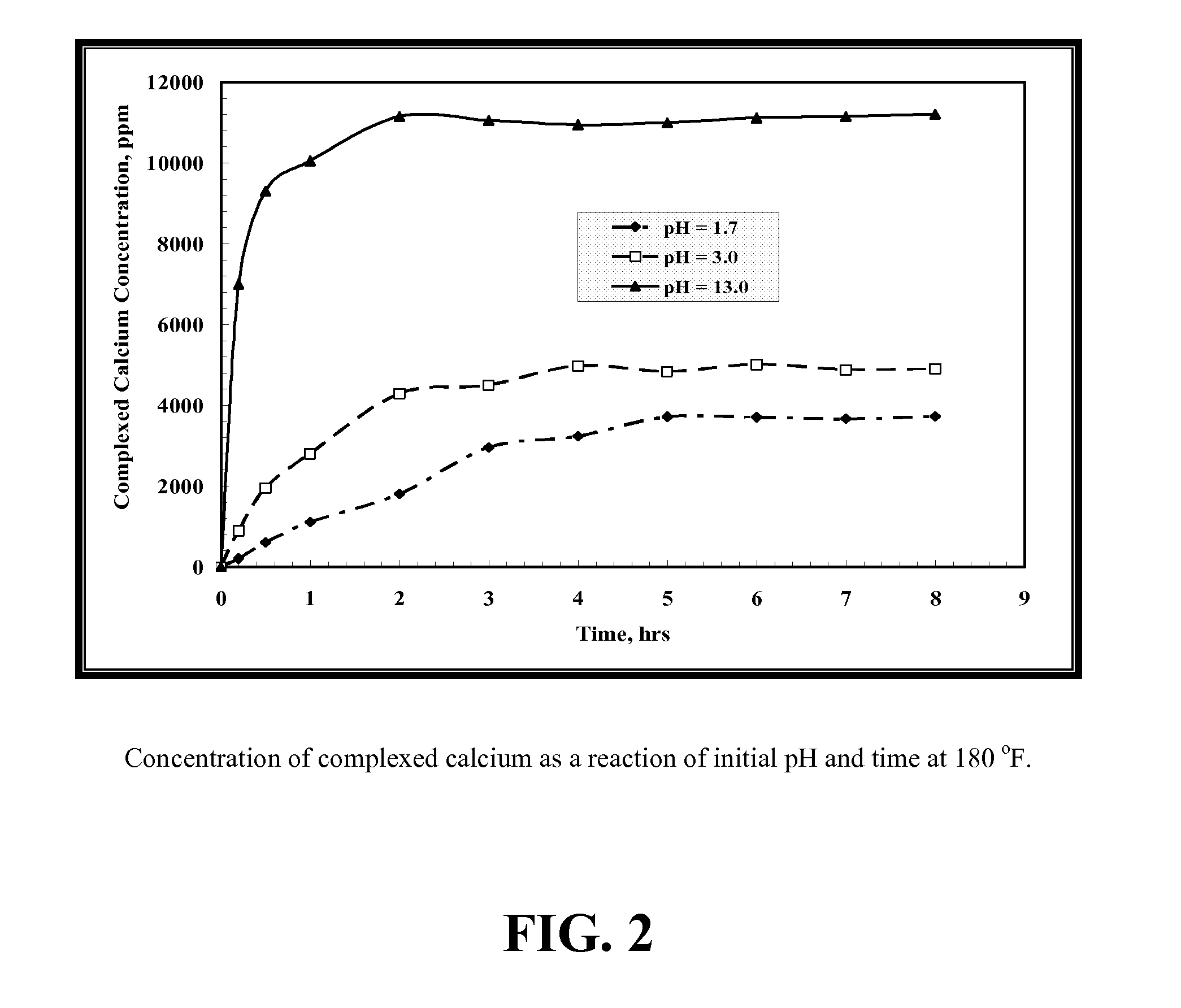
Environmentally friendly stimulation fluids, processes to create wormholes in carbonate reservoirs, and processes to remove wellbore damage in carbonate reservoirs
ActiveUS20120202720A1Reduce calcium concentrationChelating ability decreasedFlushingDrilling compositionDamage zoneWormhole
The present invention includes processes to create wormholes in carbonate reservoirs by contacting a formation with a solution comprising glutamic acid N,N-diacetic acid (GLDA) and / or a salt thereof, methylglycine-N,N-diacetic acid (MGDA) and / or a salt thereof, or a combination thereof. The present invention also includes processes to remove wellbore damage in a carbonate reservoir by contacting a damaged zone of the carbonate reservoir with a solution comprising GLDA and / or a salt thereof, methylglycine-N,N-diacetic acid (MGDA) and / or a salt thereof, or a combination thereof. The present invention further includes solutions comprising a salt and further comprising GLDA and / or a salt thereof, methylglycine-N,N-diacetic acid (MGDA) and / or a salt thereof, or a combination thereof.
Owner:AKZO NOBEL CHEM INT BV
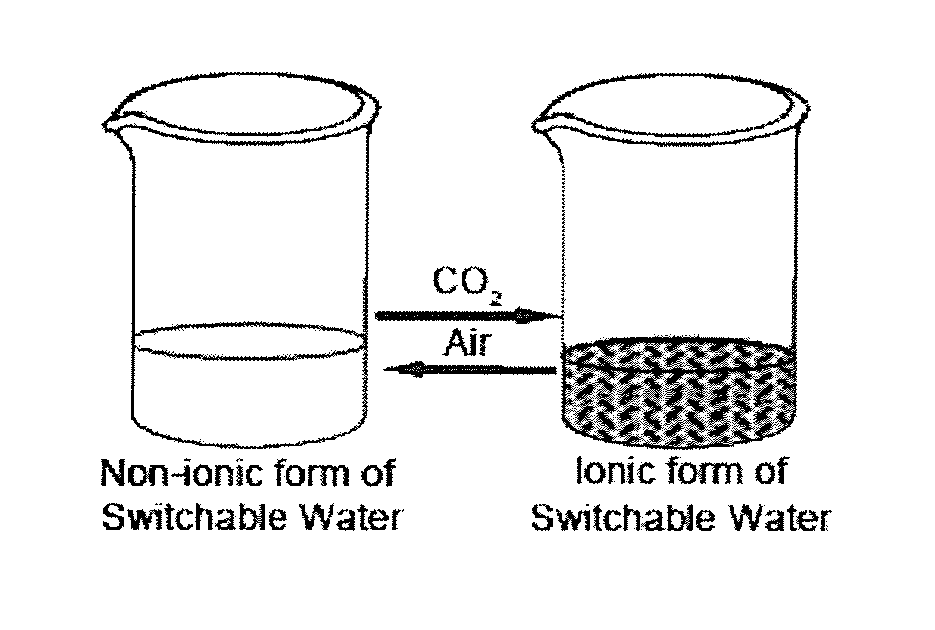
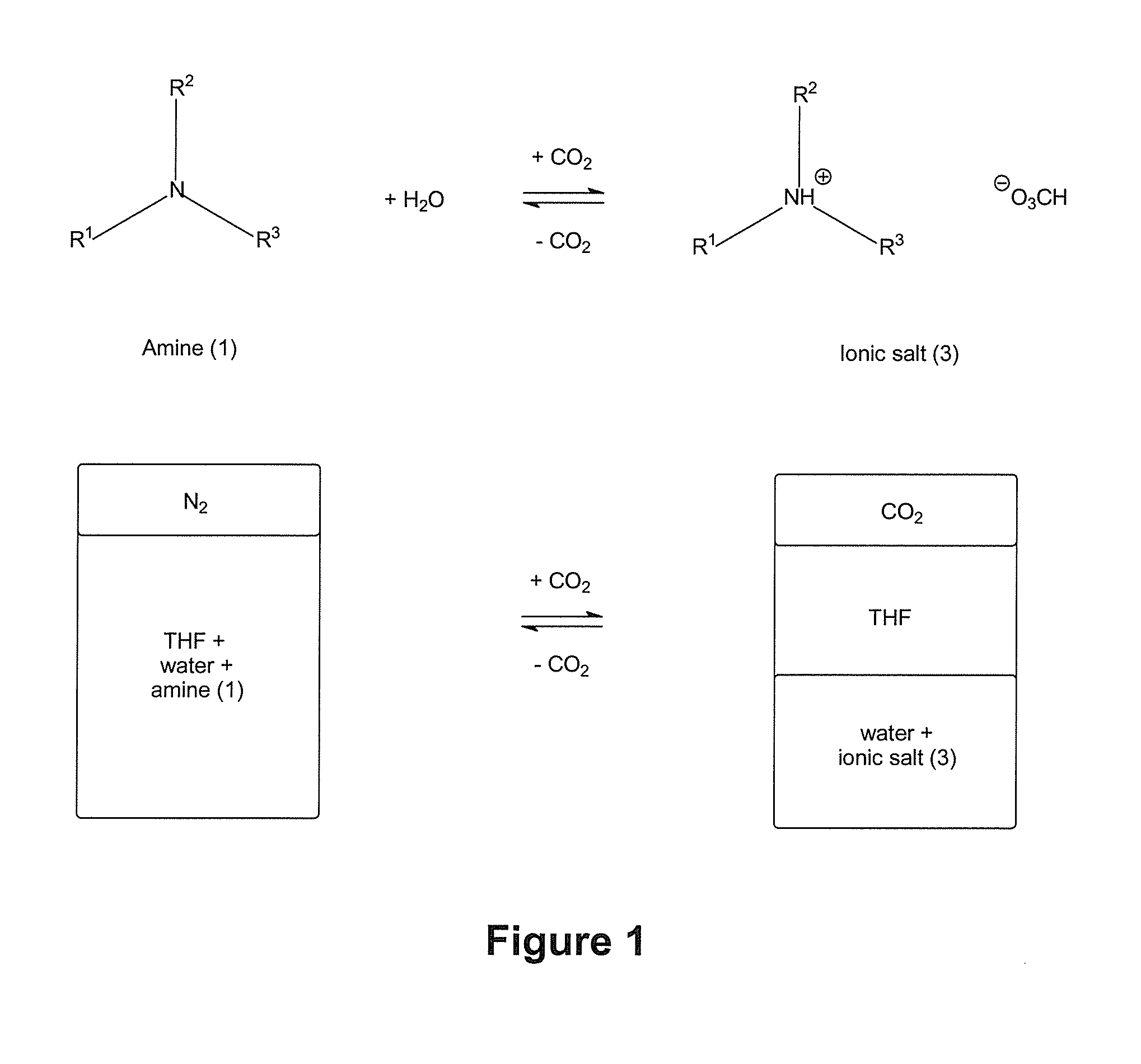
Systems and Methods for Use of Water with Switchable Ionic Strength
ActiveUS20140076810A1Increase ionic strengthChange viscosityWaste water treatment from quariesGeneral water supply conservationDistillationDesalination
Methods and systems for use of switchable water, which is capable of reversibly switching between an initial ionic strength and an increased ionic strength, is described. The disclosed methods and systems can be used, for example, in distillation-free removal of water from solvents, solutes, or solutions, desalination, clay settling, viscosity switching, etc. Switching from lower to higher ionic strength is readily achieved using low energy methods such as bubbling with C02, CS2 or COS or treatment with Bronsted acids. Switching from higher to lower ionic strength is readily achieved using low energy methods such as bubbling with air, inert gas, heating, agitating, introducing a vacuum or partial vacuum, or any combination or thereof.
Owner:QUEENS UNIV OF KINGSTON +1
Method for synthesizing fluorescence carbon dots with adjustable wave length in quantity and carbon quantum dots prepared through method
InactiveCN106995699ASignificantly progressiveThe synthesis method is simpleLuminescent compositionsPurification methodsMaterials science
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing fluorescence carbon dots with adjustable wave length in quantity and the carbon quantum dots prepared through the method, and relates to a preparation method of the carbon dots with higher synthesis fluorescence efficiency and mass yield and adjustable emission wavelength in a whole visible region by utilizing the same precursor as a carbon source. According to the preparation method for heat-treating the same carbon source by adopting different solvents and a fast precipitation purification method, the process is simple, high-efficient, green and environment-friendly, raw materials are cheap, and the reaction temperature is 160 to 250 DEG C. Each synthesized carbon quantum dot is formed by compounding a graphitized crystal lattice core and a layer of amorphous carbon shell, and has better solubility, stability and higher luminous efficiency in a common solvent; the diameter is gradually increased along with emission wavelength red shift and is 2 to 12nm. The synthesized carbon quantum dot as a novel luminescent material has the advantages of low production cost, high preparation yield, good light emitting stability low biotoxicity and favorable application prospect in application of photoelectric devices. The preparation method of the high-efficient near infrared fluorescence carbon dots brings convenience and chance for biological application of the carbon dots.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
In vitro method for disassmbly/reassembly of papillomavirus virus-like particles (VLPs). Homogeneous VLP and cavsomere compositions produced by said methods: use thereof as vehicle for improved purification, and delivery of active agents
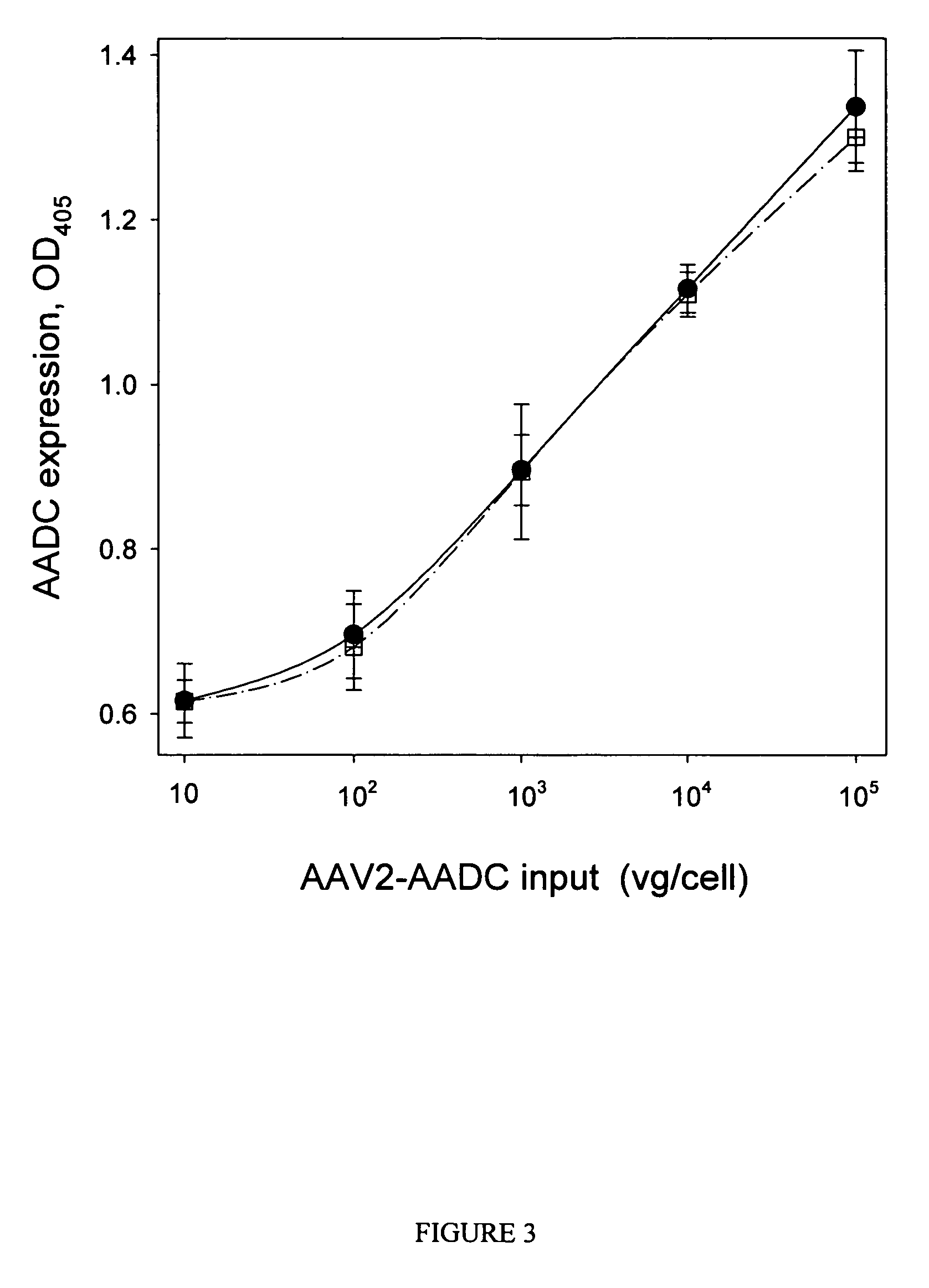
InactiveUS7351533B2Increase ionic strengthStabilize VLPsMicroencapsulation basedMicrobiological testing/measurementEpitopeDiagnostic agent
A method of disassembly / reassembly of papillomavinis VLPs is provided. The resultant VLPs have enhanced homogeneity, present conformational, neutralizing PV epitopes, and therefore are useful prophylactic and diagnostic agents. Further, these VLPs can be used to encapsulate desired moieties, e.g., therapeutic or diagnostic agents, or marker” DNAs, and the resultant VLPs used as in vivo delivery vehicles or as pseudovirions for evaluating vaccine efficacy.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Method for treating hydrochloric acid leachate of ferrotitanium materials
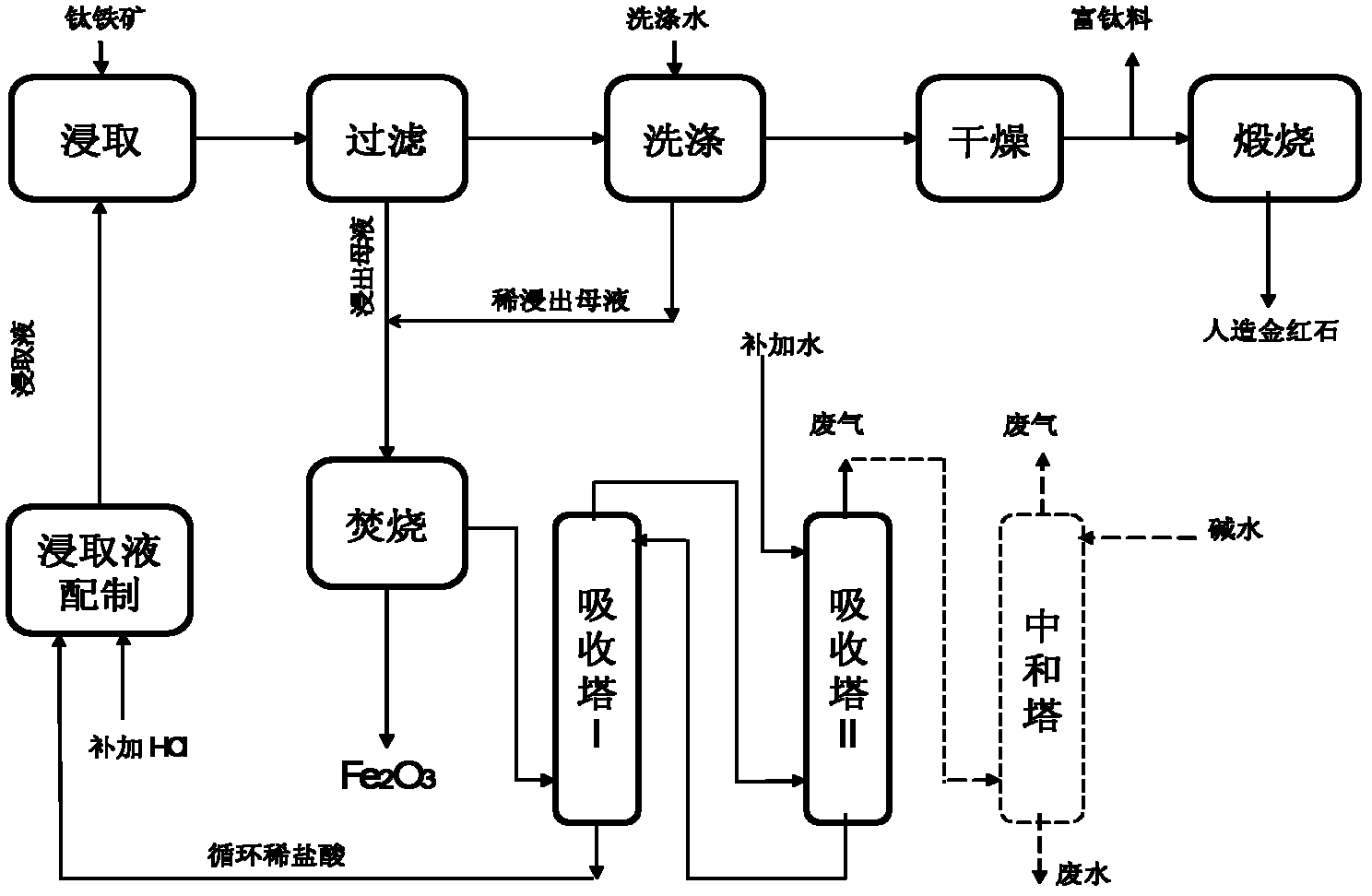
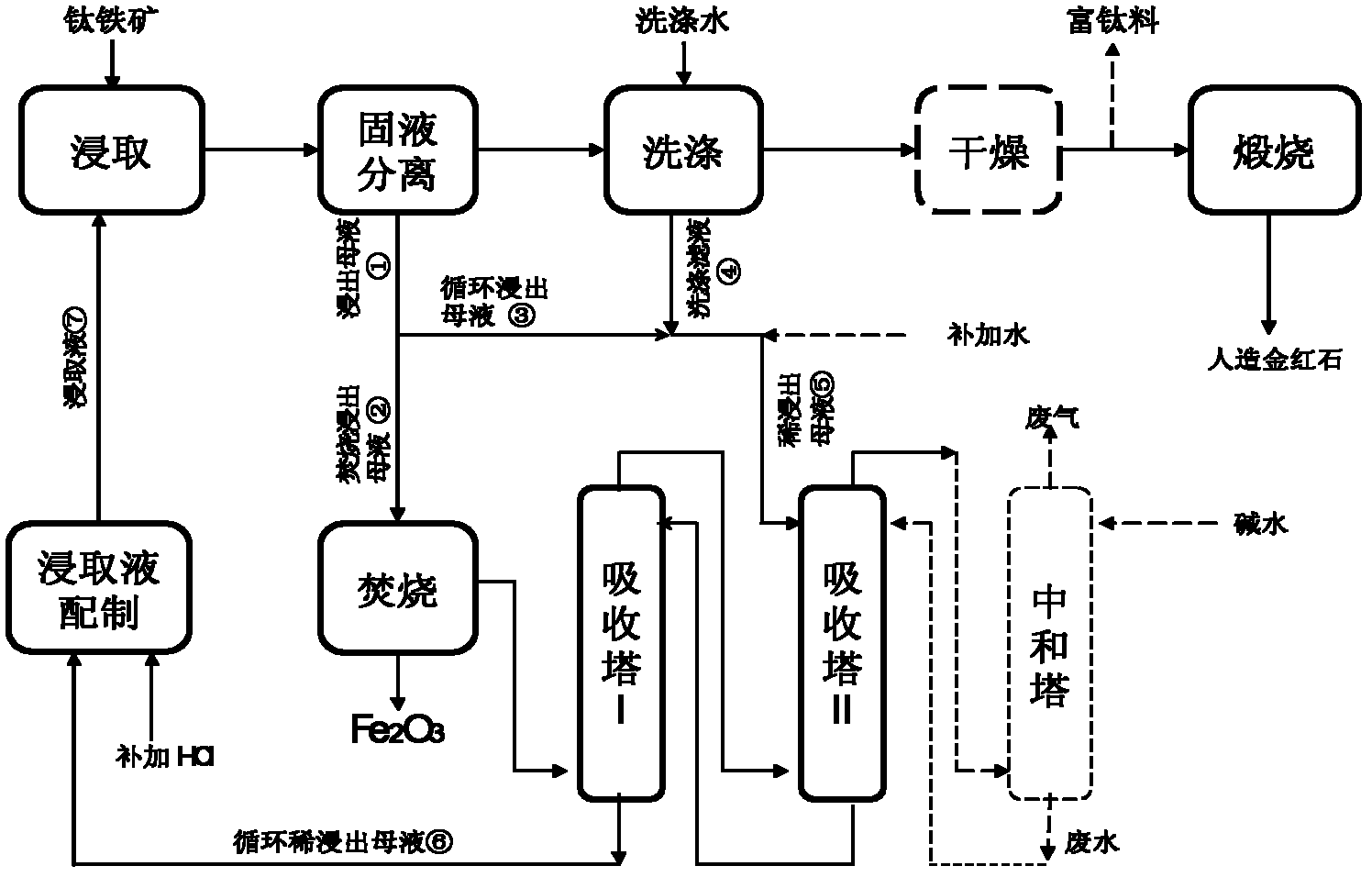
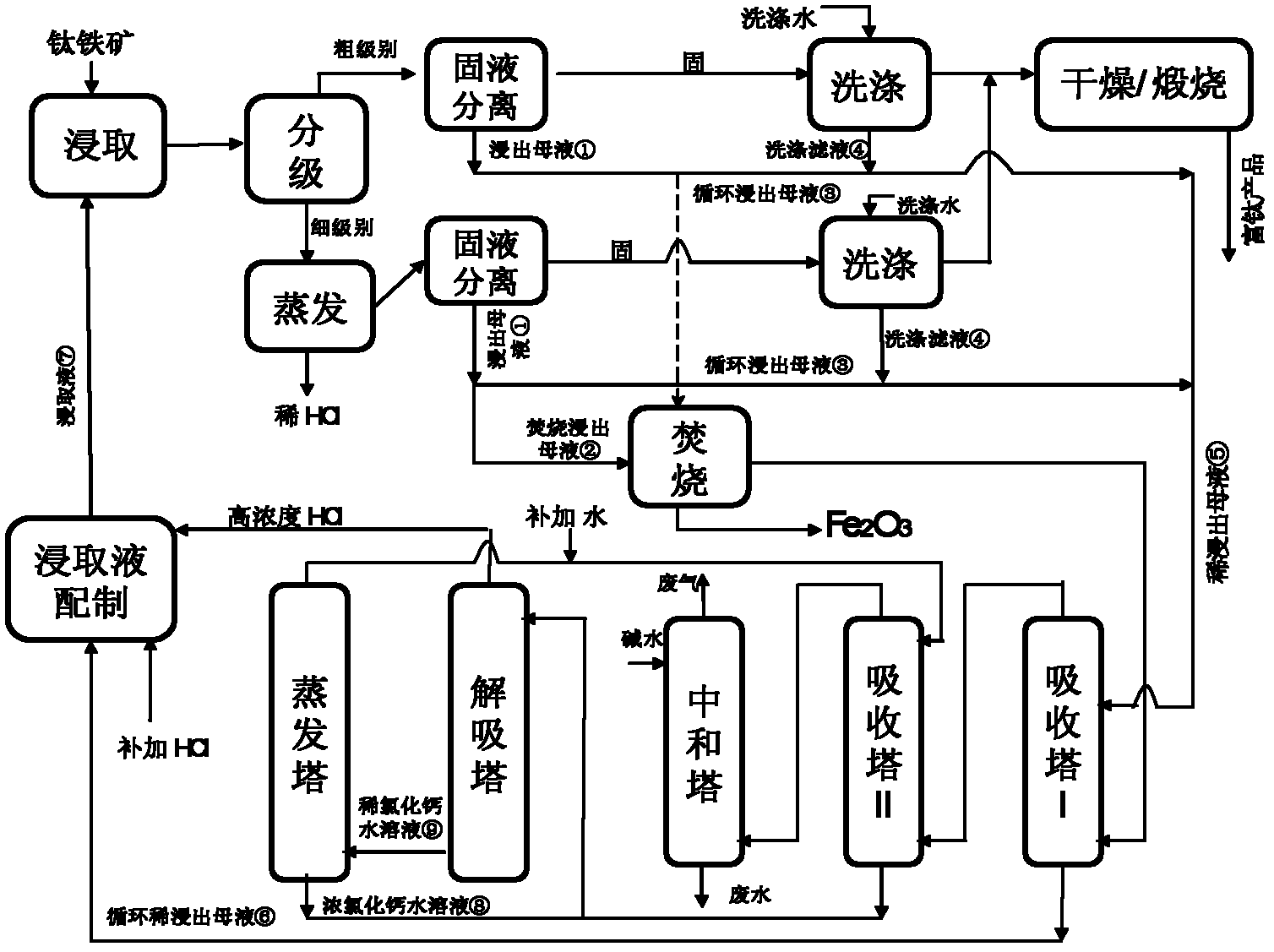
InactiveCN102352437AReduce incinerationReduce processing energy consumptionPregnant leach solutionMaterial balance
The invention provides a method for treating hydrochloric acid leachate of ferrotitanium materials. The method comprises the following steps of: dividing and burning leached mother liquid which is obtained by leaching the ferrotitanium materials by using hydrochloric acid leaching liquid; recovering hydrogen chloride obtained by burning for regeneration and cyclic utilization of the leaching liquid. By the method provided by the invention, the leachate is divided according to material balance of the leach elements (mainly comprising iron) of the hydrochloric acid leachate; and one part of theleachate after division is burned and the other part of the leachate is directly or indirectly absorbed by the hydrochloric acid to return to the leaching procedure, so that completely closed circuitcirculation is formed. By the method provided by the invention, the defect of overlarge energy consumption in the burning procedure after the ferrotitanium materials are leached by the conventional hydrochloric acid can be overcome and the burning quantity of the leached mother liquid can be reduced by 40 to 55 percent, so that the energy consumption of the whole process can be reduced by 35 to 45 percent. The method has a good industrial application prospect.
Owner:沙立林 +1
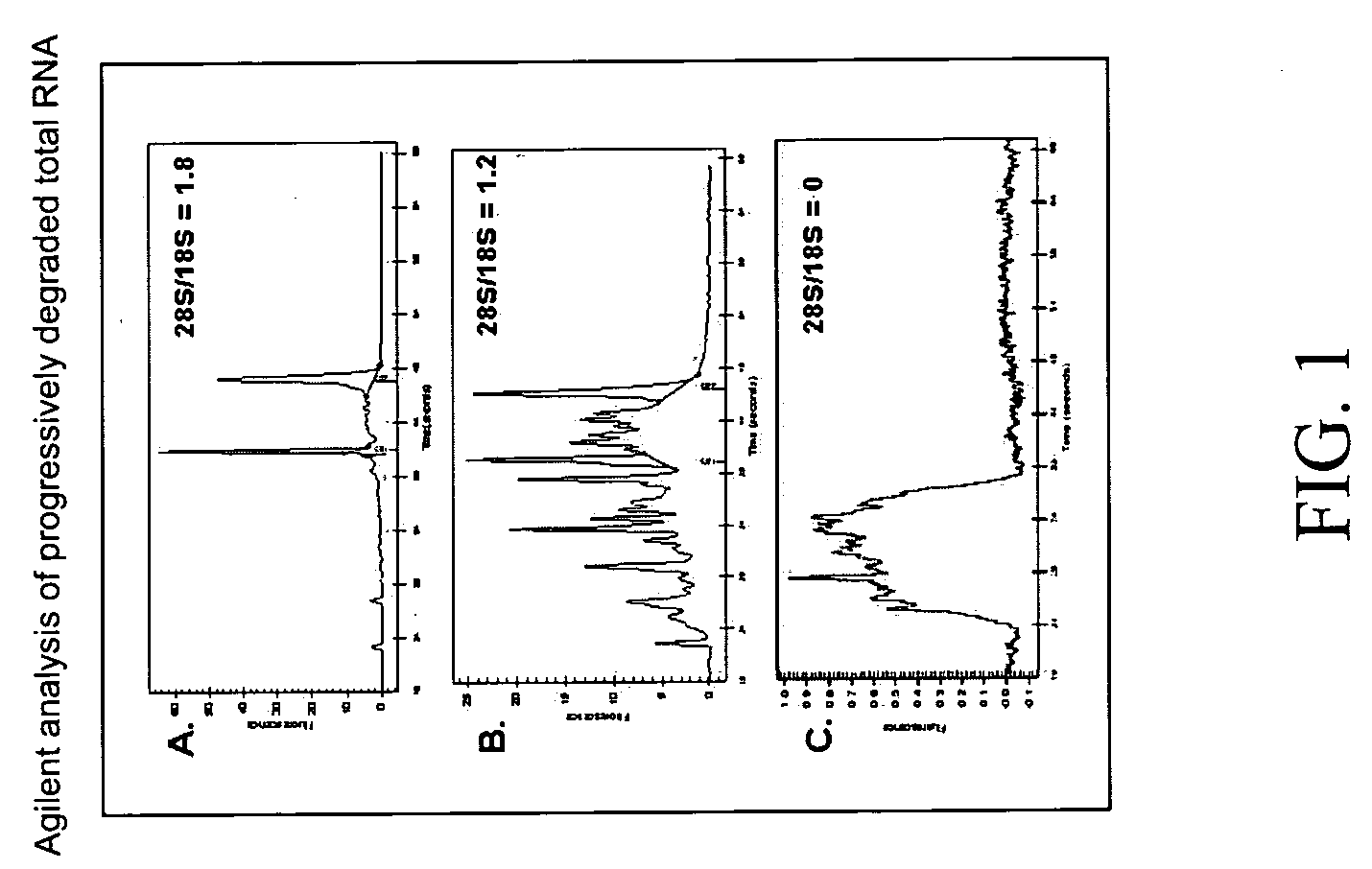
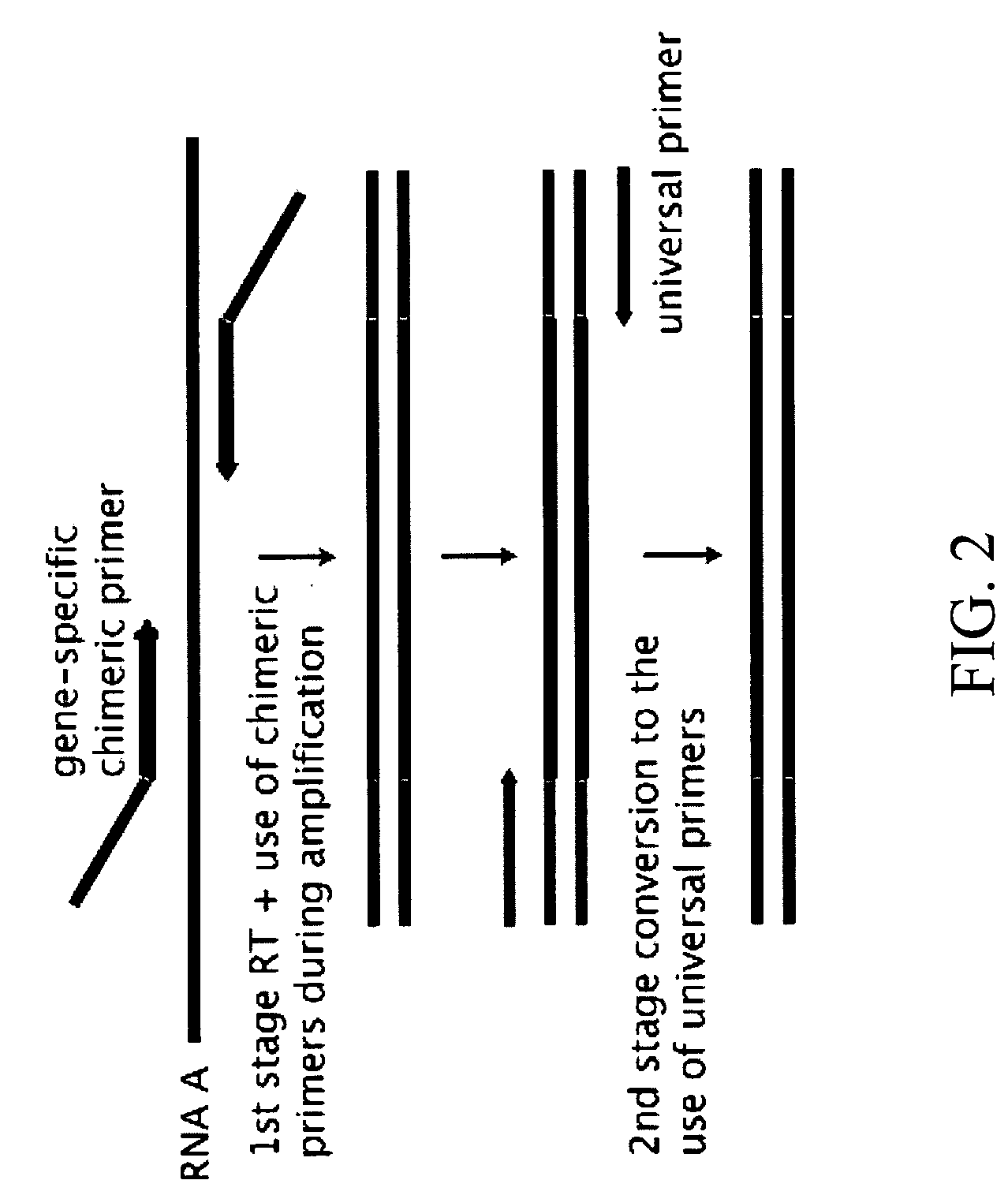
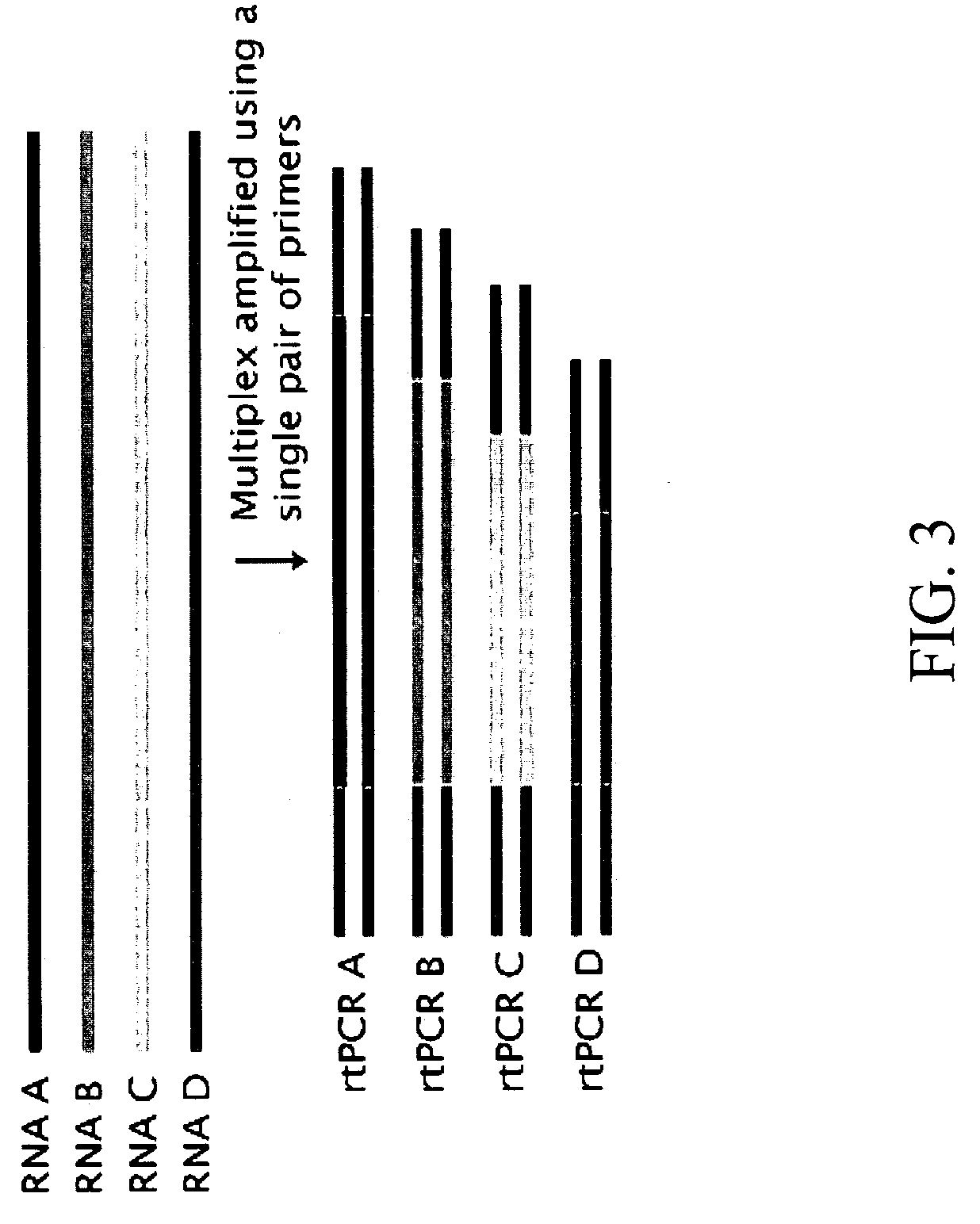
Compositions and methods for the analysis of degraded nucleic acids
InactiveUS20060281108A1Easy to detectEasy to quantifyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBioinformaticsGene expression profiling
The invention relates to compositions and methods for gene expression analysis. In some embodiments, the invention provides compositions and methods for amplifying targets in a degraded nucleic acid sample. In some embodiments, the invention provides methods for determining the quality of nucleic acids (e.g., the degree of degradation) in a nucleic acid sample. The invention also provides methods for producing a gene expression profile from a degraded RNA sample.
Owner:ALTHEADX
Media For Membrane Ion Exchange Chromatography Based On Polymeric Primary Amines, Sorption Device Containing That Media, And Chromatography Scheme And Purification Method Using The Same
InactiveUS20100200507A1Improve bindingGood removal effectIon-exchange process apparatusIon-exchanger regenerationPurification methodsSorbent
Media and devices, such as anion exchangers including such media, wherein the media is a membrane having a surface coated with a polymer such as a polyallylamine. The resulting membrane offers stronger binding of protein impurities and superior removal of host cell proteins from biological samples than conventional ligands based on quaternary ammonium salts, including trimethylammonium ligands. Also described is a chromatography scheme and method for purifying monoclonal antibodies, wherein the anion exchange sorber is placed downstream of an affinity column (such as Protein A or Protein G affinity column) and optionally one or more polishing devices such as cationic exchange columns. Little or no dilution of the cation exchanger pool (or affinity column exchange pool where no cation exchanger is used) is necessary to lower the conductivity of the sample. The sorber functions well to strongly bind host cell proteins and other impurities in biological samples even at high conductivities and pH.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Methods and compositions for treating subterranean formations using high ionic strength gelling agent polymers
InactiveUS20050065040A1Improve rheologyImproved viscosity propertiesFluid removalFlushingIonic strengthFluid composition
Methods, aqueous treating fluid compositions and high ionic strength gelling agent polymers for treating subterranean formations are provided. The aqueous treating fluid compositions are basically comprised of water and a high ionic strength sulfonated gelling agent polymer. The aqueous treating fluid compositions have superior properties compared to conventional treating fluids.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Solid phase technique for selectively isolating nucleic acids
InactiveUS20060003357A1High purityIncrease ionic strengthMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid reductionPurification methodsMagnetic bead
A method of isolating target nucleic acid molecules from a solution comprising a mixture of different size nucleic acid molecules, in the presence or absence of other biomolecules, by selectively facilitating the adsorption of a particular species of nucleic acid molecule to the functional group-coated surface of magnetically responsive paramagnetic microparticles is disclosed. Separation is accomplished by manipulating the ionic strength and polyalkylene glycol concentration of the solution to selectively precipitate, and reversibly adsorb, the target species of nucleic acid molecule, characterized by a particular molecular size, to paramagnetic microparticles, the surfaces of which act as a bioaffinity adsorbent for the nucleic acids. The target nucleic acid is isolated from the starting mixture based on molecular size and through the removal of magnetic beads to which the target nucleic acid molecules have been adsorbed. The disclosed method provides a simple, robust and readily automatable means of nucleic acid isolation and purification which produces high quality nucleic acid molecules suitable for: capillary electrophoresis, nucleotide sequencing, reverse transcription cloning the transfection, transduction or microinjection of mammalian cells, gene therapy protocols, the in vitro synthesis of RNA probes, cDNA library construction and PCR amplification.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com