Method for in-situ sampling, separating enriching and measuring heavy metal ion in water body
A technology for heavy metal ions and water bodies, which can be used in measurement devices, sampling devices, chemical method analysis, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
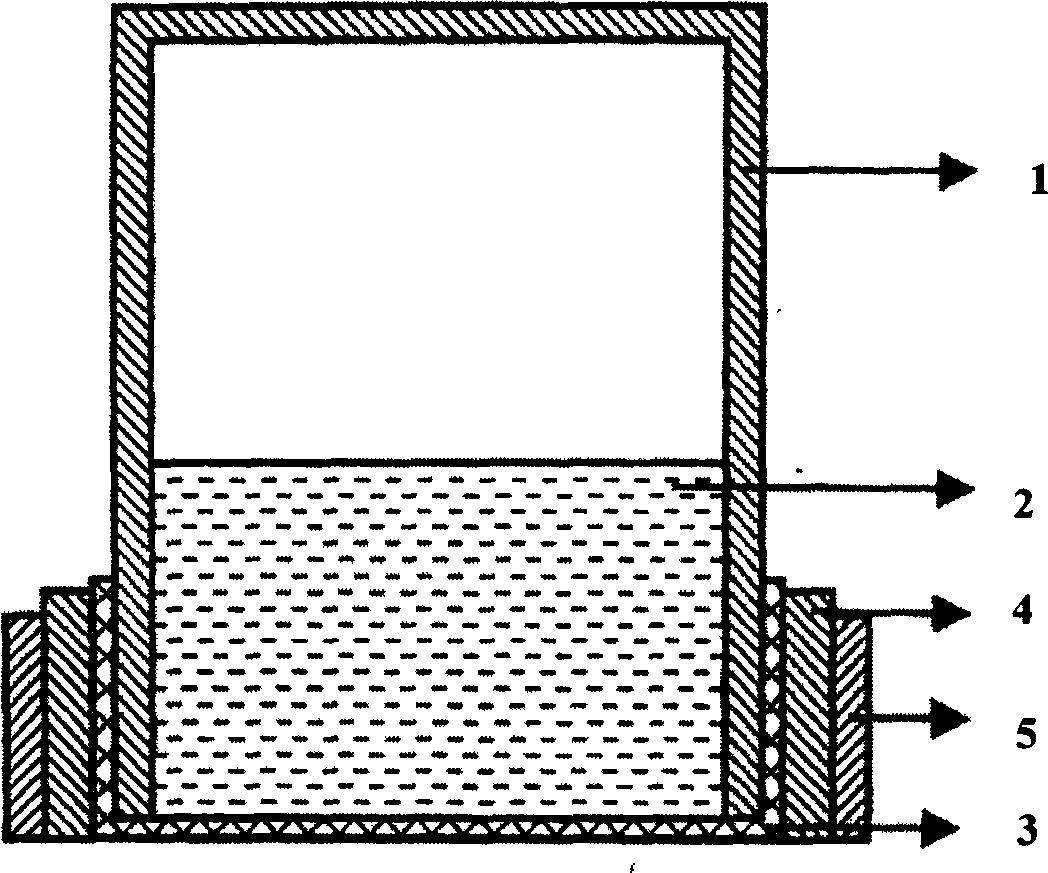
[0031] Take 2mL of 0.0001M carboxymethyl cellulose (calculated according to the concentration of carboxyl group) into a polypropylene device with a volume of 2mL, seal the device with a dialysis membrane, and put the device into a water body polluted by heavy metals for 1h Take it out, use atomic absorption spectrometry to measure the concentration of heavy metals, and calculate the average concentration of heavy metals in water during the storage time.
Embodiment 2
[0033] Take 2mL of 0.0001M carboxymethyl cellulose (calculated according to the concentration of carboxyl groups) into a polypropylene device with a volume of 2mL, seal the device with chromatographic paper, a total of 3 devices, and put the device into a water body polluted by heavy metals for 1h Take it out, use atomic absorption spectrometry to measure the concentration of heavy metals, and calculate the average concentration of heavy metals in water during the storage time.
Embodiment 3
[0035] Take 2mL of 0.0001M carboxymethyl cellulose (calculated according to the concentration of carboxyl groups) into a polypropylene device with a volume of 2mL, seal the device with a collodion film, a total of 3 devices, and put the device into a water body polluted by heavy metals Put it aside for 1 hour and take it out, use atomic absorption spectrometry to measure the concentration of heavy metals, and calculate the average concentration of heavy metals in water during the storage time.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com