Patents
Literature
1114 results about "Surface plasmon polariton" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
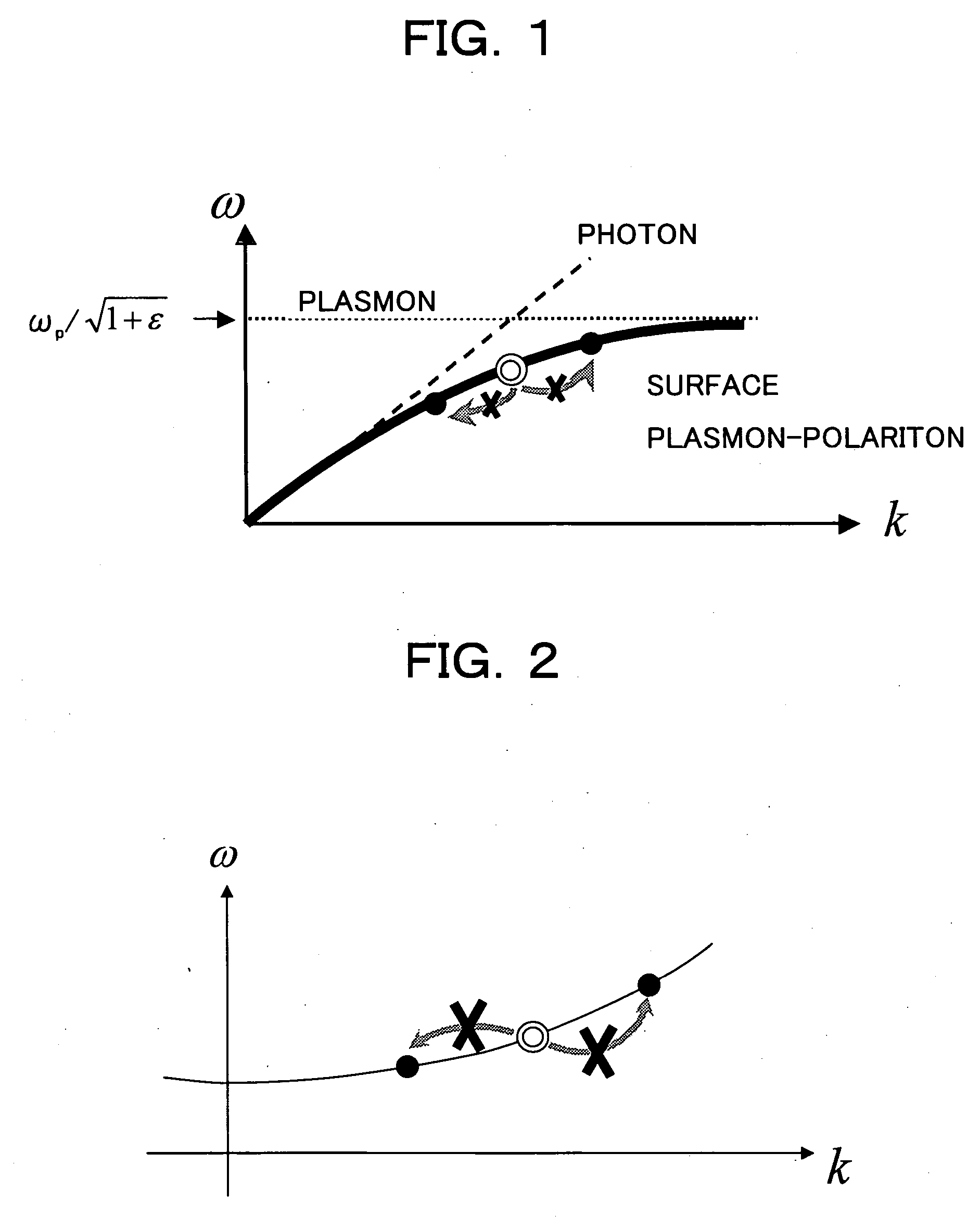
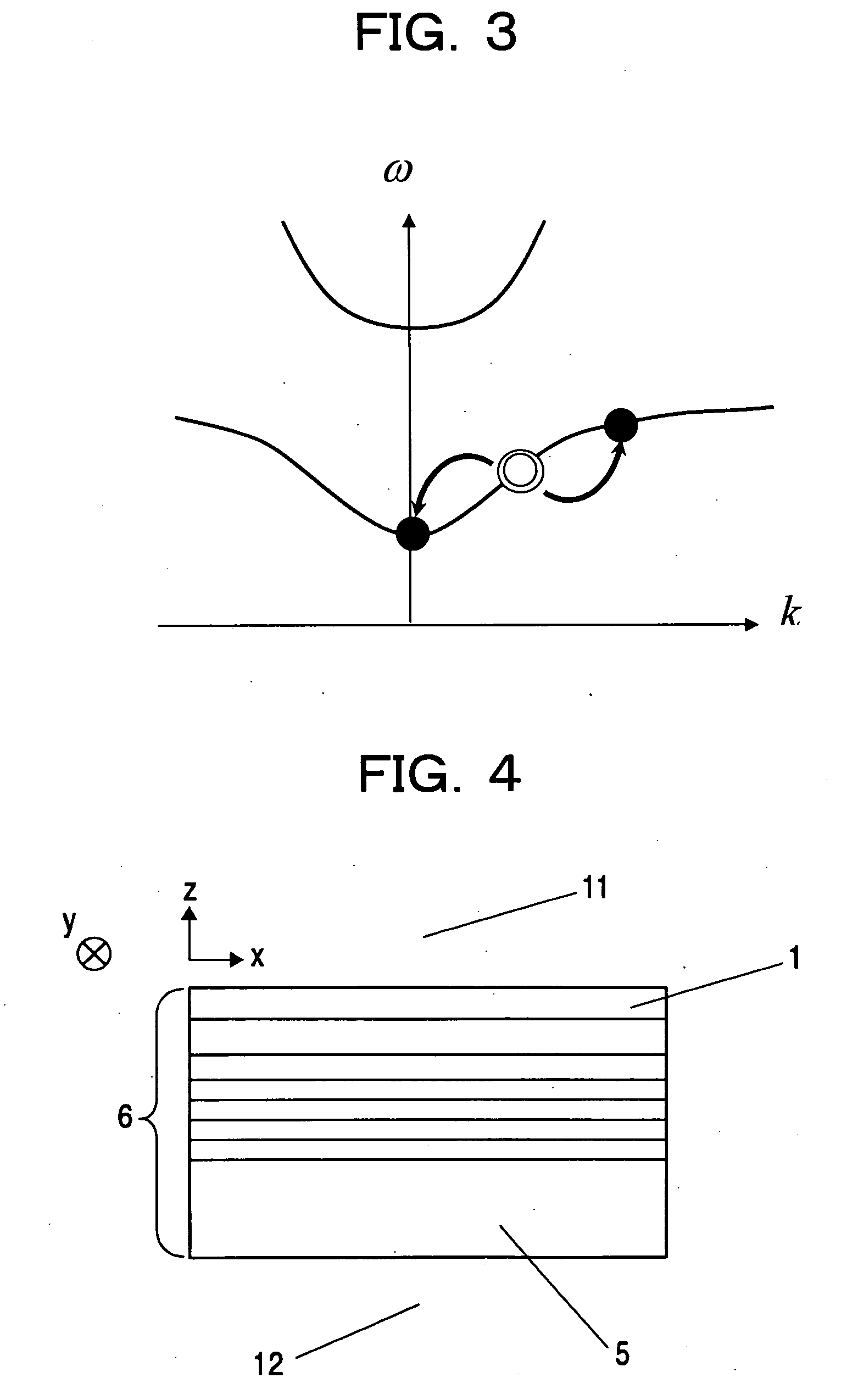
Surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) are electromagnetic waves that travel along a metal–dielectric or metal–air interface, practically in the infrared or visible-frequency. The term "surface plasmon polariton" explains that the wave involves both charge motion in the metal ("surface plasmon") and electromagnetic waves in the air or dielectric ("polariton").
Surface plasmon devices
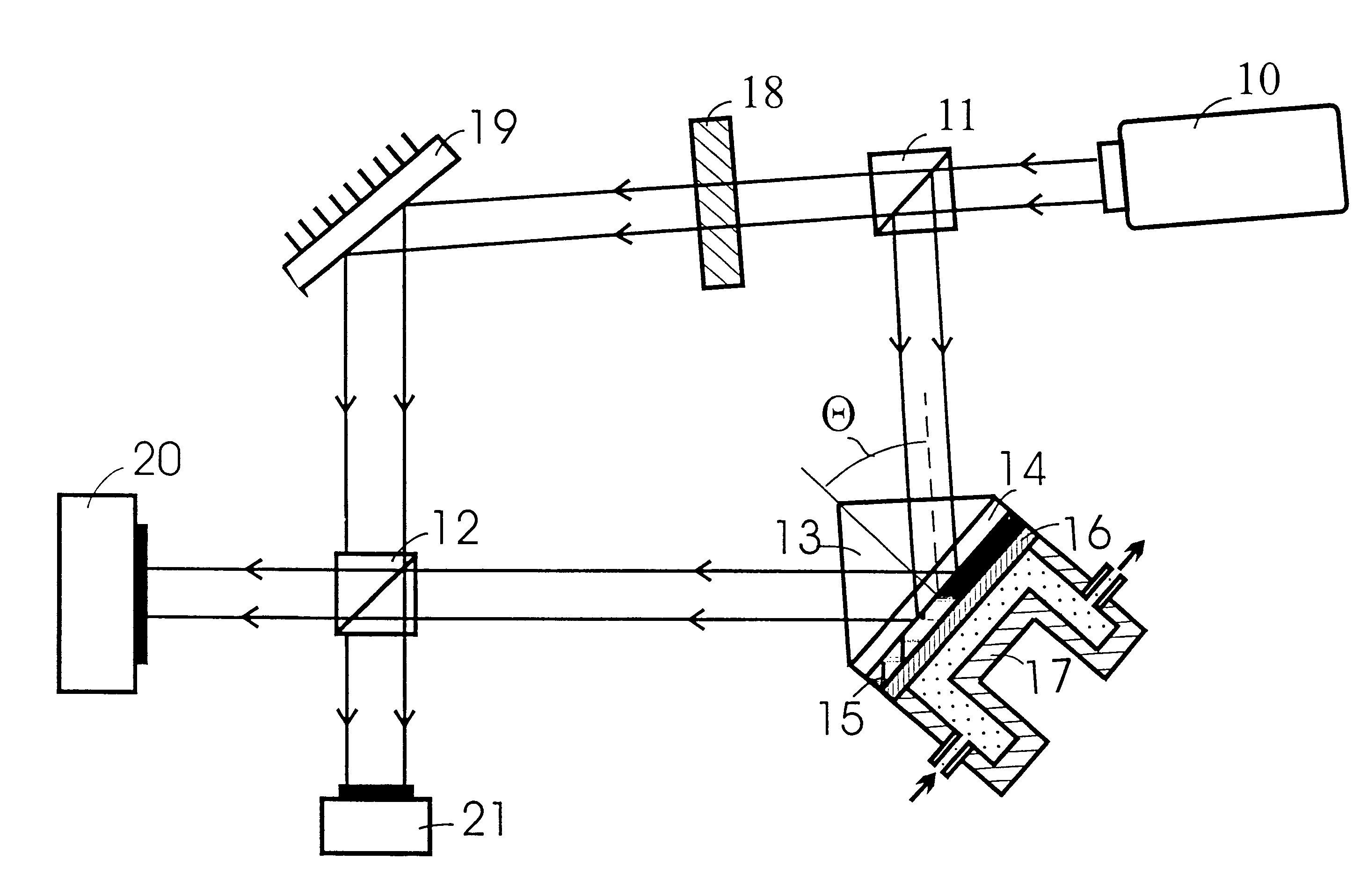
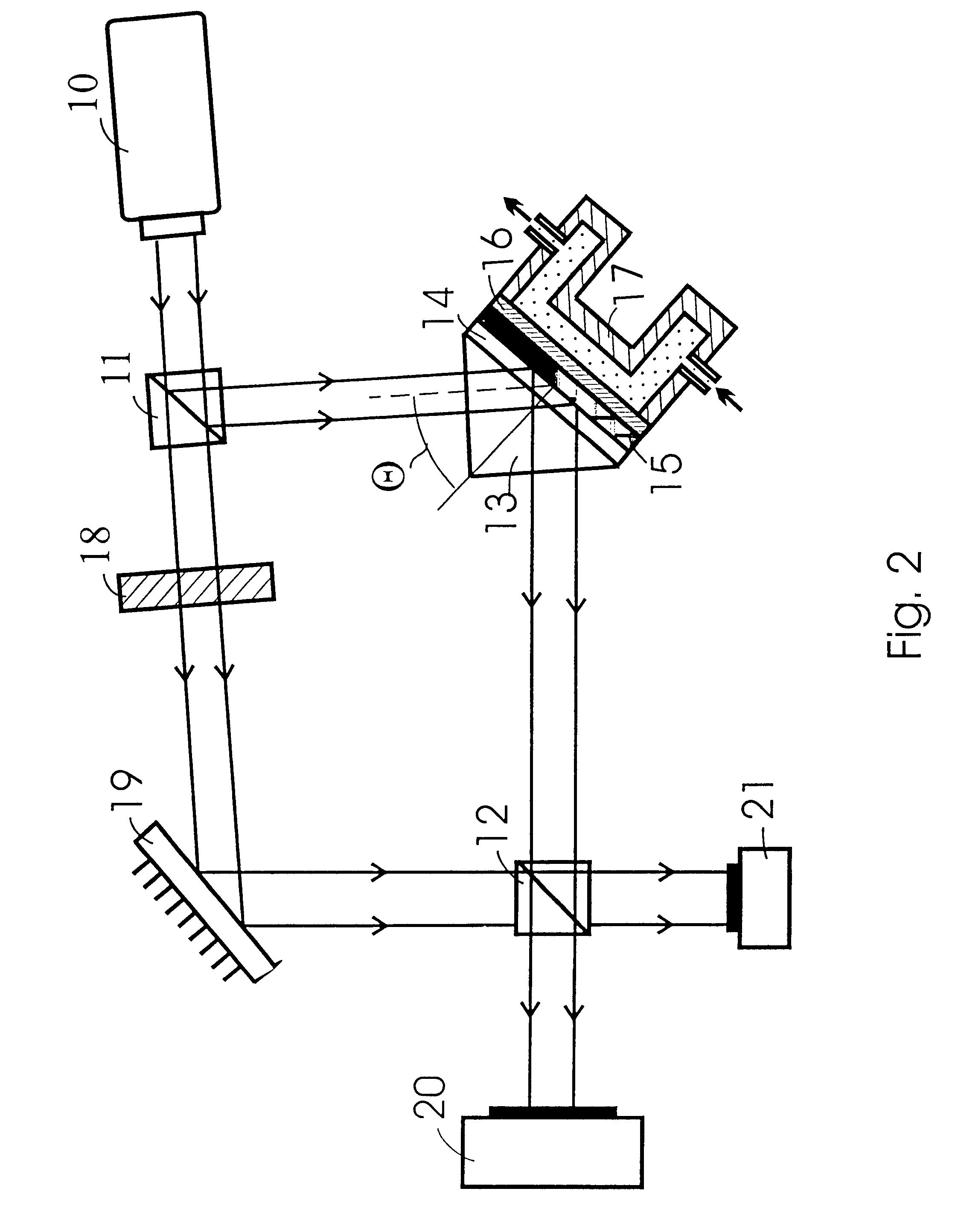
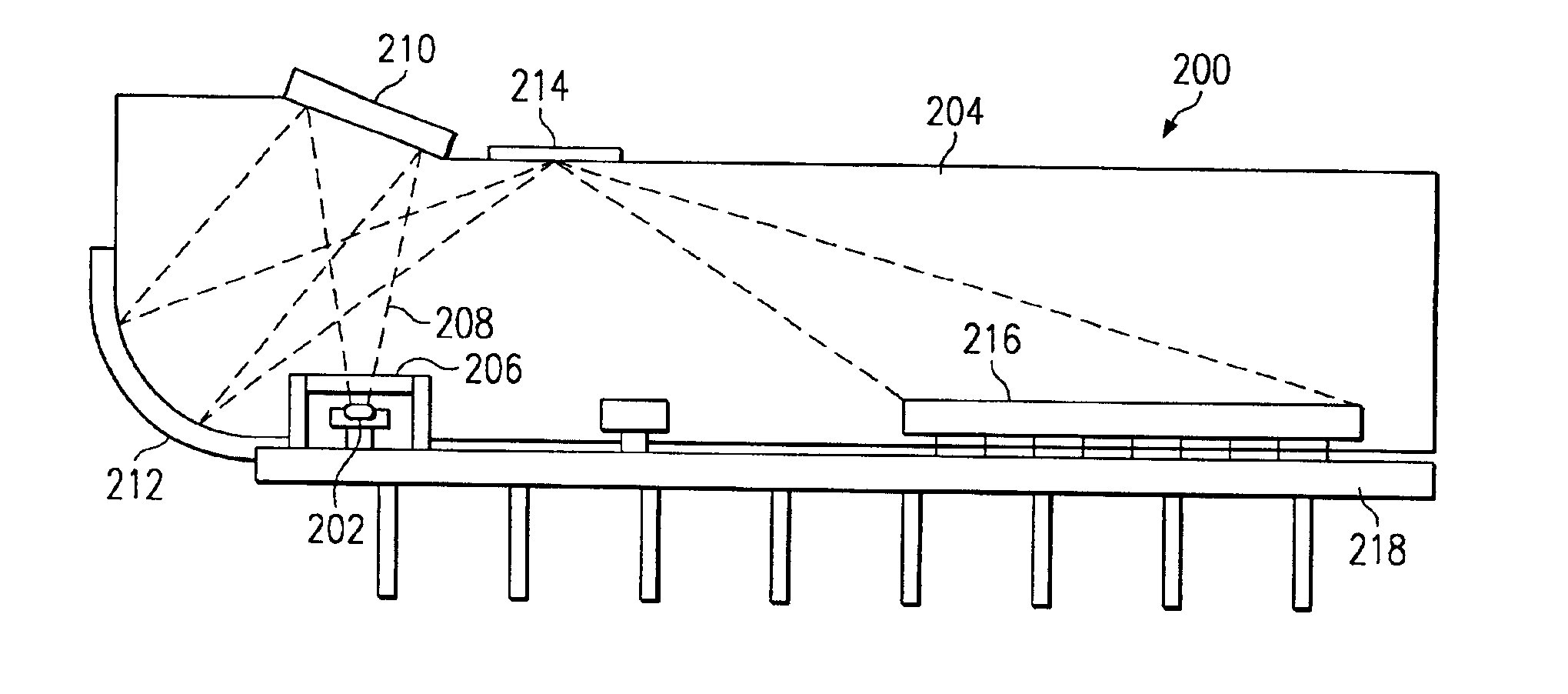
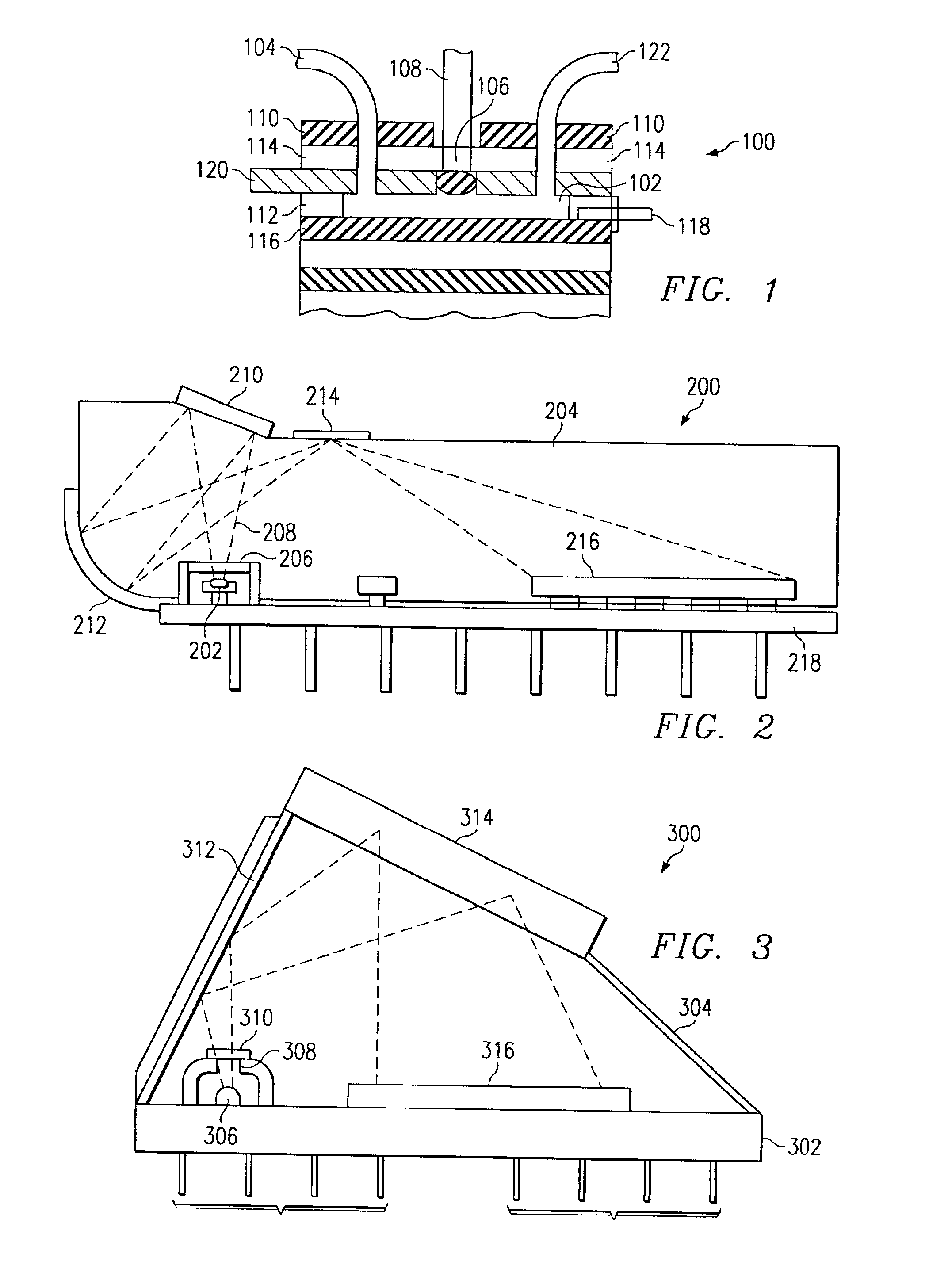
InactiveUS7010183B2Laser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionSoftware engineeringEngineering
A device including an input port configured to receive an input signal is described. The device also includes an output port and a structure, which structure includes a tunneling junction connected with the input port and the output port. The tunneling junction is configured in a way (i) which provides electrons in a particular energy state within the structure, (ii) which produces surface plasmons in response to the input signal, (iii) which causes the structure to act as a waveguide for directing at least a portion of the surface plasmons along a predetermined path toward the output port such that the surface plasmons so directed interact with the electrons in a particular way, and (iv) which produces at the output port an output signal resulting from the particular interaction between the electrons and the surface plasmons.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Wavelength tunable surface plasmon resonance sensor
InactiveUS7030989B2Convenient timeSmall amount of sampleScattering properties measurementsRefractive indexSurface plasmon resonance sensor
This invention provides methods, devices and device components for sensing, imaging and characterizing changes in the composition of a probe region. More particularly, the present invention provides methods and devices for detecting changes in the refractive index of a probe region positioned adjacent to a sensing surface, preferably a sensing surface comprising a thin conducting film supporting surface plasmon formation. In addition, the present invention provides methods and device for generating surface plasmons in a probe region and characterizing the composition of the probe region by generating one or more surface plasmon resonances curves and / or surface plasmon resonance images of the probe region.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Plasmon-photon coupled optical devices
InactiveUS20050275934A1Avoid spreadingImprove transmittanceBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansAngle of incidenceRefractive index
The present invention is directed to optical devices. More specifically, the disclosed devices include a film defining a periodic array of surface elements so as to give rise to surface plasmon polaritons. The film also includes at least a single aperture having a diameter less than the wavelength of light. In one embodiment, the surface elements can be an array of anisotropic apertures and the films can act as a polarizer. The disclosed devices can also include a material having a variable refractive index substantially adjacent to the metal film. For example, the refractive index of the adjacent material can vary according to some characteristic of the light incident to the device, for instance, the intensity or the angle of incidence of the light. In this embodiment, resonant coupling of incident light with the SPP, and hence transmittivity of the device, can depend upon the nature of incident light. The disclosed devices can be useful in, for example, remote polarizers, polarization mode dispersion, isolators, multi-color displays, switches, such as can be controlled according to incident sunlight, or optical filters, such as for eye protection devices, filtering out possibly harmful light.
Owner:CLEMSON UNIV RES FOUND
System, method and apparatus for RF directed energy
InactiveUS7820990B2Electric discharge tubesHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionLength waveField of view
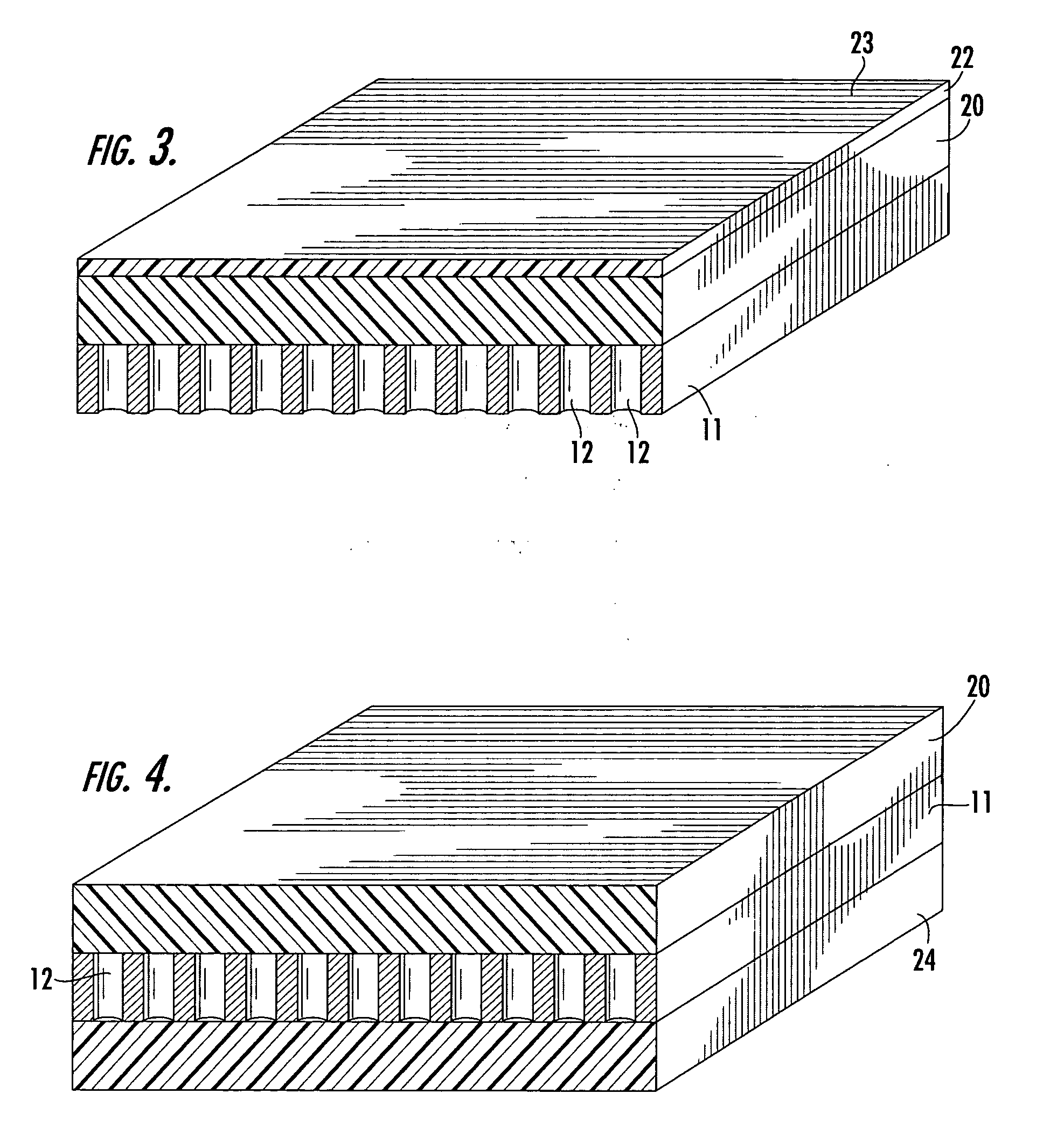
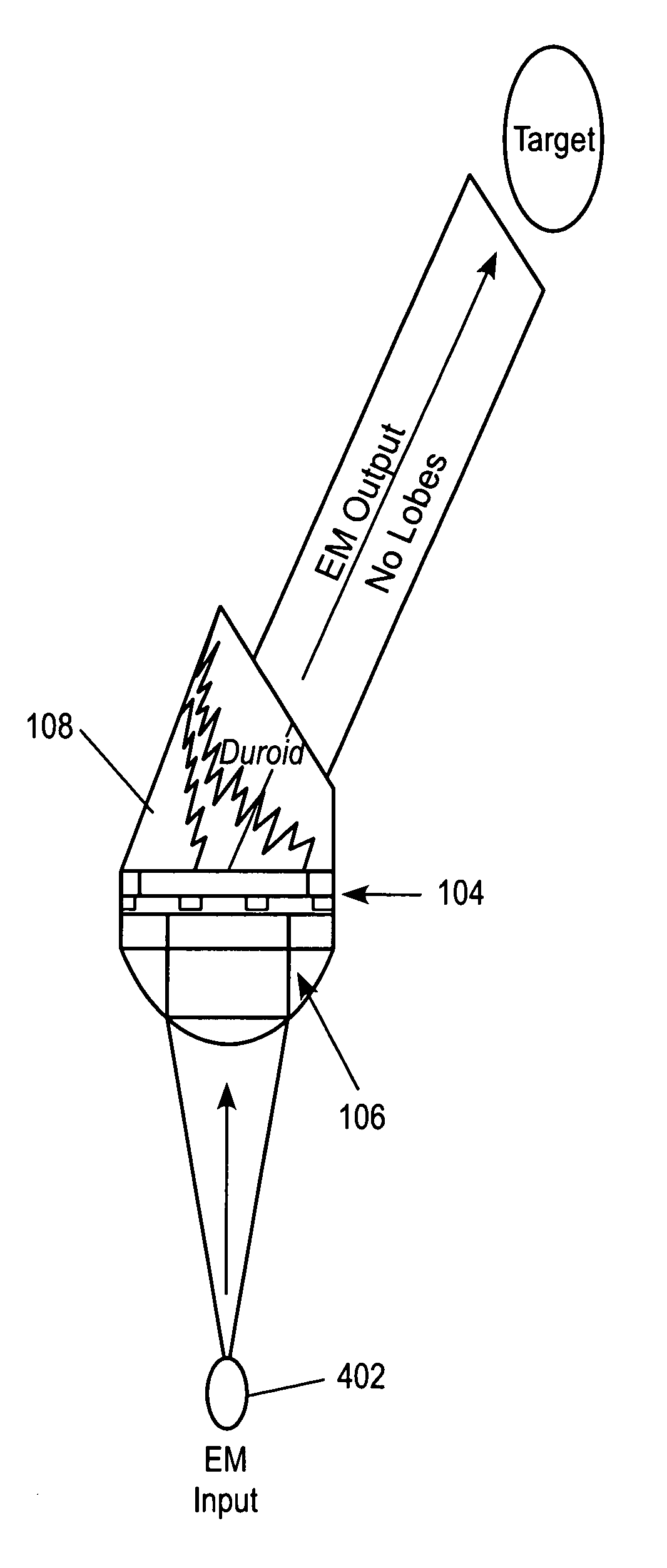
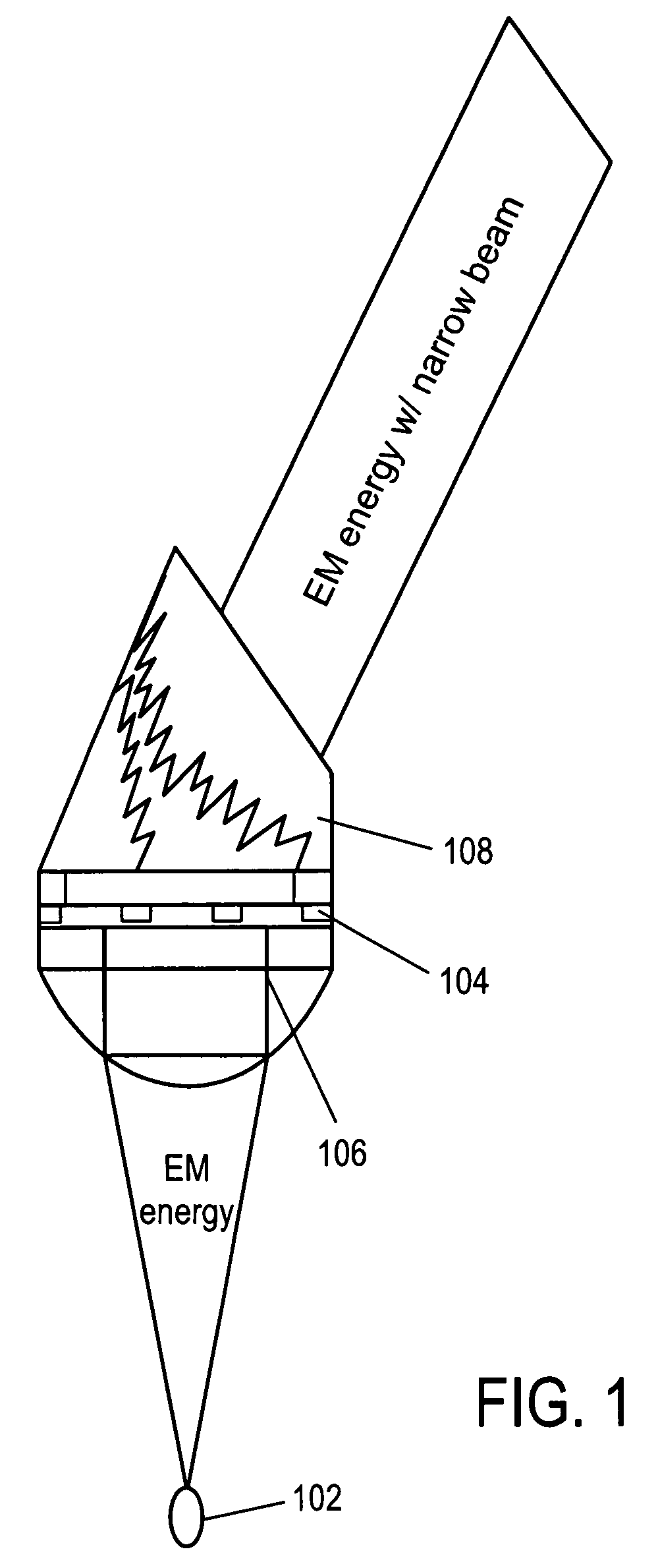
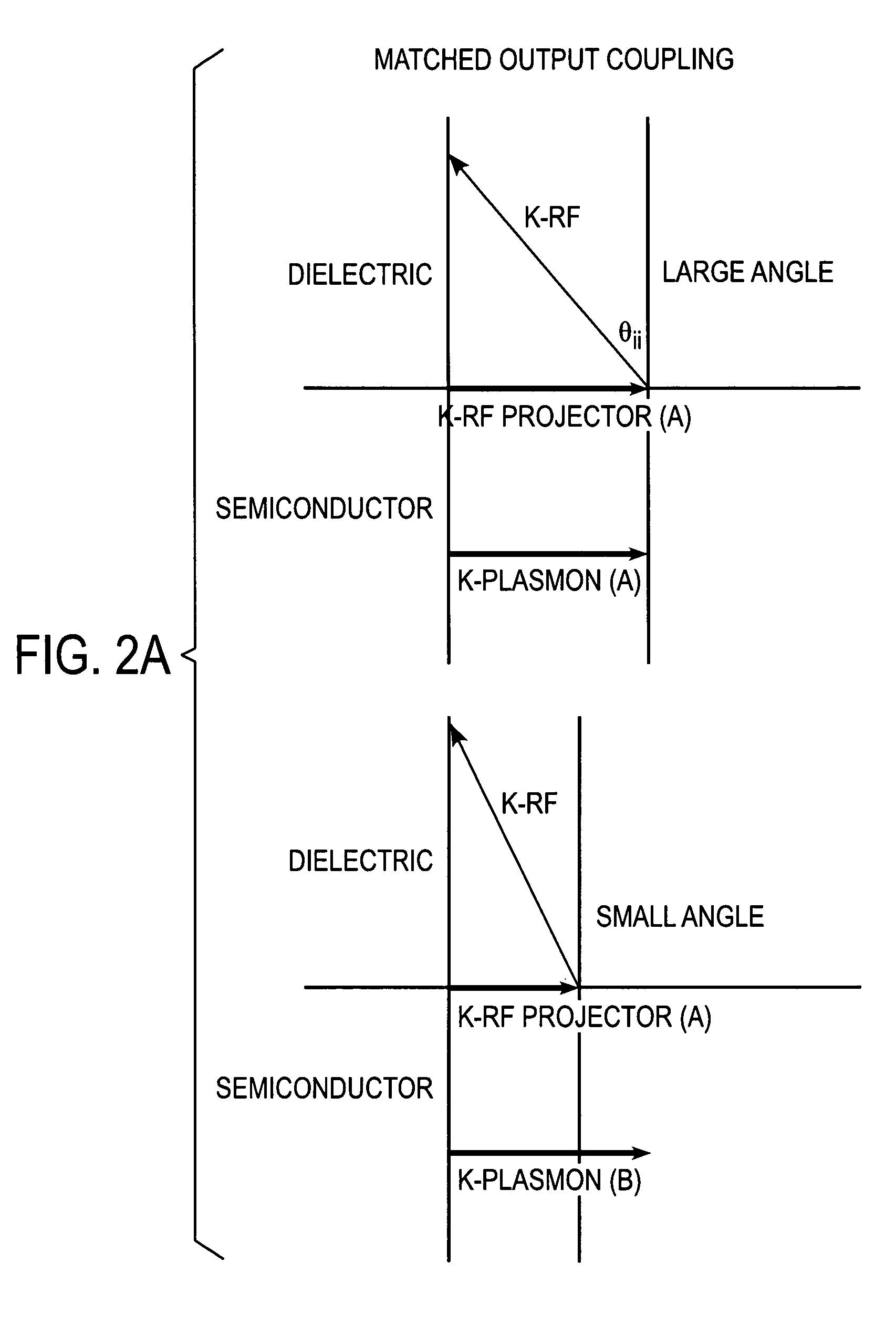
Systems and methods are disclosed for emitting electromagnetic (EM) energy. A source emits EM energy that is incident on a first material. The first material transmits EM energy to a second material. The second material can have a first surface adjacent to the first material and a thickness and shape selected to stimulate surface plasmon polaritons on the first surface of the second material to resonate the EM energy transmitted from the first material such that the resonated EM energy has an EM wavelength in a narrow field of view with substantially no sidelobes.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Surface plasmon coupled nonequilibrium thermoelectric devices
InactiveUS20050247337A1Easy maintenanceEasy to manufactureThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectElectric discharge tubesThermal energyElectron temperature
A surface-plasmon-coupled thermoelectric apparatus includes a first surface-plasmon substrate and a thermoelectric substrate electrically coupled to a plurality of electrodes. The substrates are electrically isolated from each other, and a first face of the thermoelectric substrate opposes a first face of the first surface-plasmon substrate to define a phonon insulating gap. A method of transferring thermal energy across the phonon insulating gap includes creating a first surface-plasmon polariton at the first surface-plasmon substrate when the first surface-plasmon substrate is coupled to a first thermal reservoir. Also included is creating a nonequilibrium state between the electron temperature and the phonon temperature at a first face of the thermoelectric substrate, when a second face of the thermoelectric substrate is coupled to a second thermal reservoir. Also included is coupling the first surface plasmon polariton with electrons in the thermoelectric substrate across the phonon insulating gap, thereby transferring thermal energy between the thermal reservoirs through the phonon insulating gap.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD +1
Near-field light generating element utilizing surface plasmon
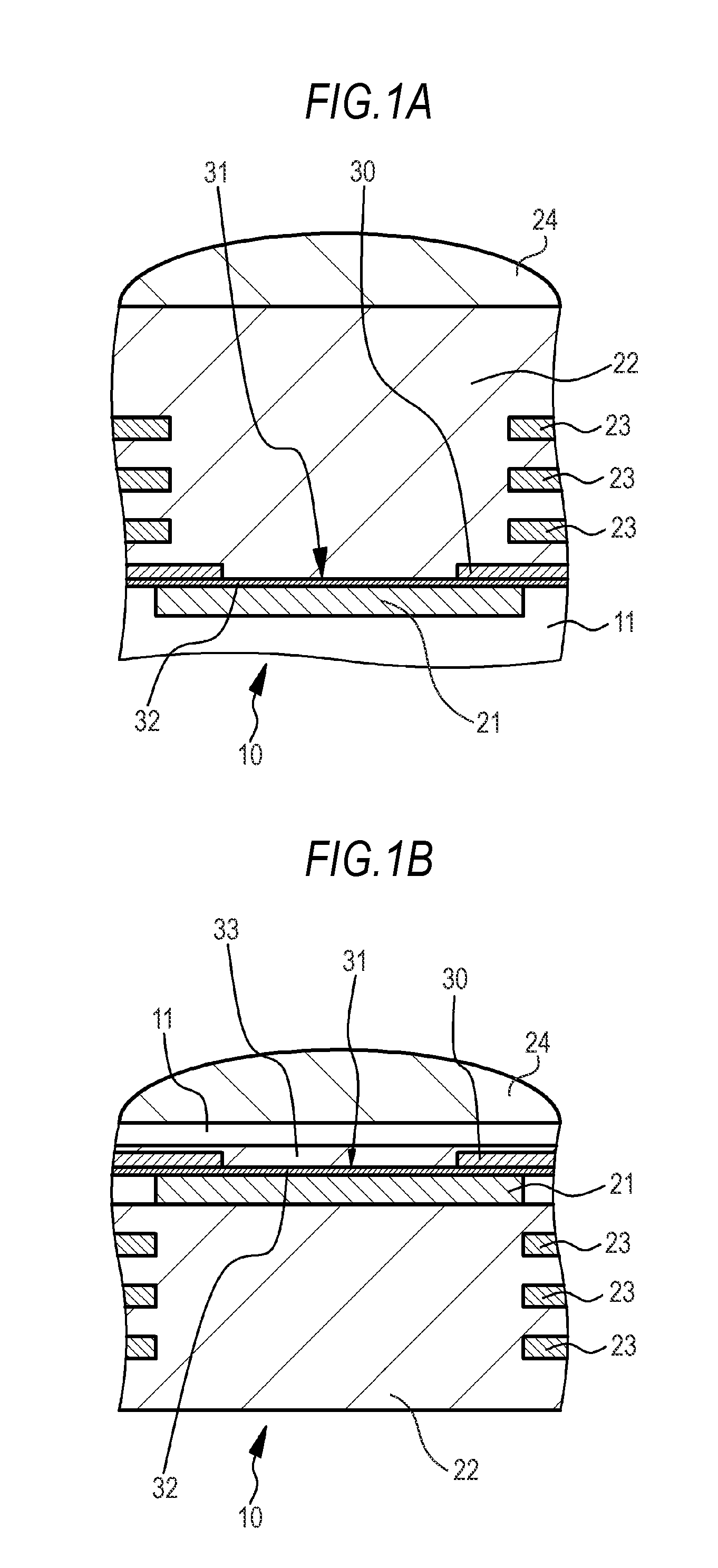
ActiveUS8000178B2Avoid excessive heatAppropriate heatCombination recordingArm with optical waveguideSurface plasmonMagnetic poles
Provided is a surface plasmon antenna that can be set so that the emitting position on the end surface of the plasmon antenna where near-field light is emitted is located sufficiently close to the end of a magnetic pole. The surface plasmon antenna comprises an edge having a portion for coupling with a light in a surface plasmon mode. The edge is provided for propagating surface plasmon excited by the light and extends from the portion to a near-field light generating end surface that emits near-field light. The edge for propagating surface plasmon is a very narrow propagation region. Therefore, the near-field light generating end surface, which appears as a polished surface processed through polishing in the manufacturing of the plasmon antenna, can be made a shape with a very small size, and further can be set so that surface plasmon propagates to reach the end surface reliably.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Pinpoint enhanced dark-field microscope, electrochemical testing device and leveling system
InactiveCN102798735AAchieve positioningAchieve levelingScanning probe microscopyDesorptionMetal particle
The invention provides a pinpoint enhanced dark-field microscope, an electrochemical testing device and a leveling system. The pinpoint enhanced dark-field microscope is characterized by using an optical fiber probe, wherein metal nanometer particles for decoration are arranged at the pinpoint of the optical fiber probe, incident lights are transmitted inside the optical fiber probe which is provided with the metal nanometer particles for decoration, and the distance between the pinpoint and a sample adopts a light intensity control mode; and the pinpoint enhanced dark-field microscope is a localized surface plasmon resonance dark-field coupling device which utilizes the near-field coupling function of the nanometer metal particles at the pinpoint of the probe and a metal substrate material. The microscope can be used for researching basic surface and interface chemical problems such as a double-electric-layer structure of a substrate surface, adsorption / desorption behaviors and multi-phase catalysis. In addition, based on the LSPR (Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance) distance sensitiveness principle, the pinpoint enhanced dark-field microscope can be applied to a three-probe horizontal sensor to perform self-adaptive leveling on a nanometer processing platform.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
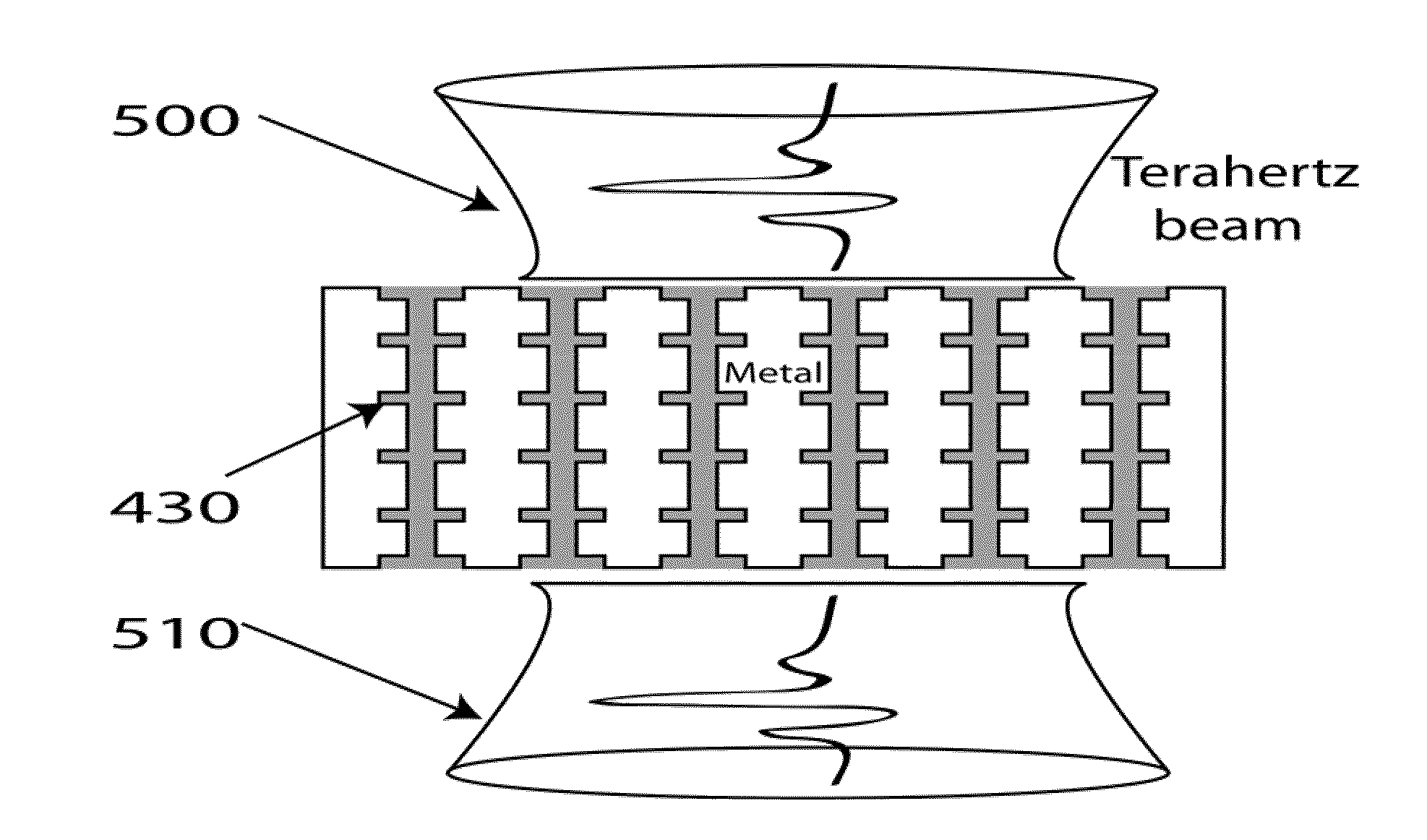
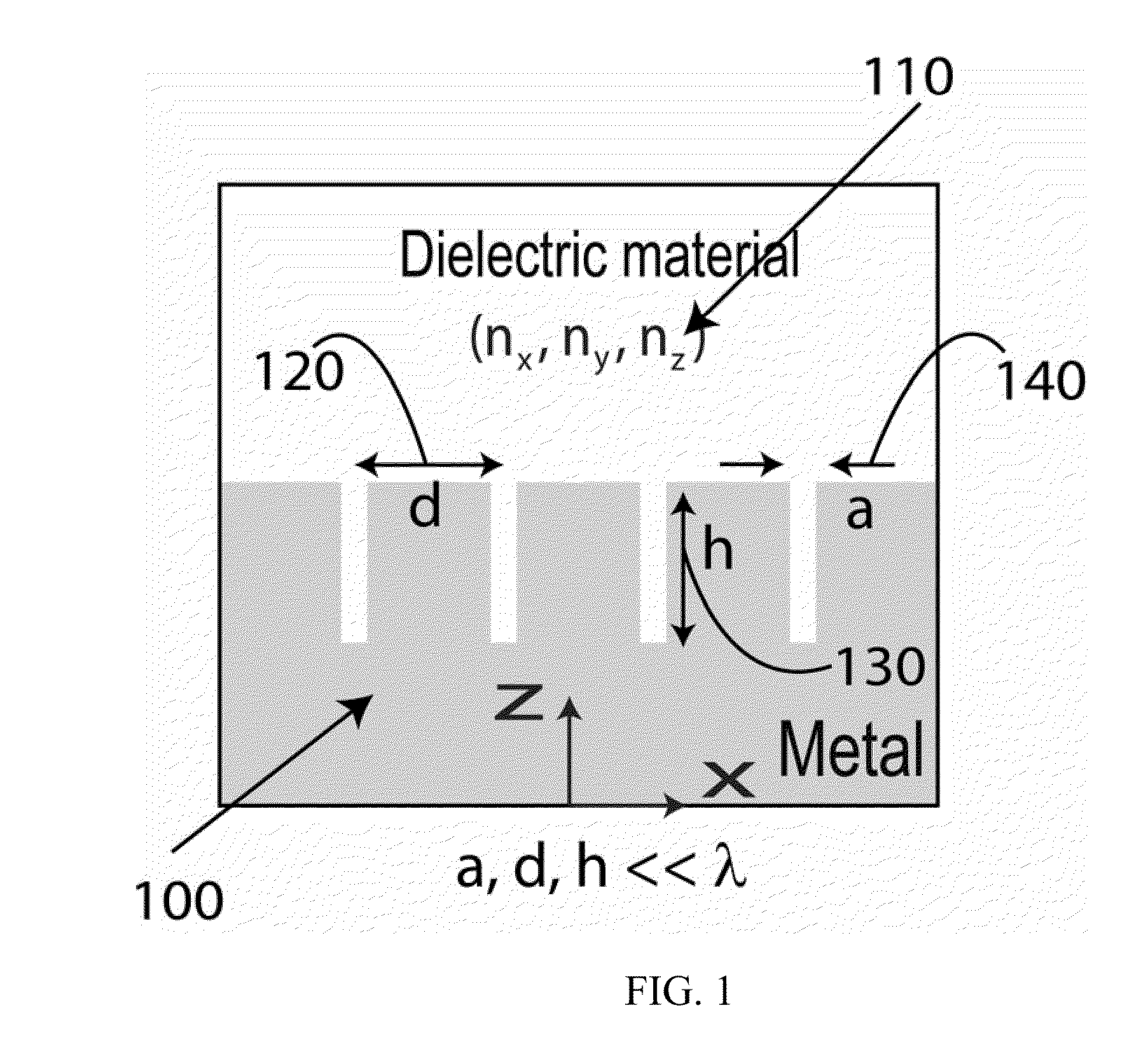
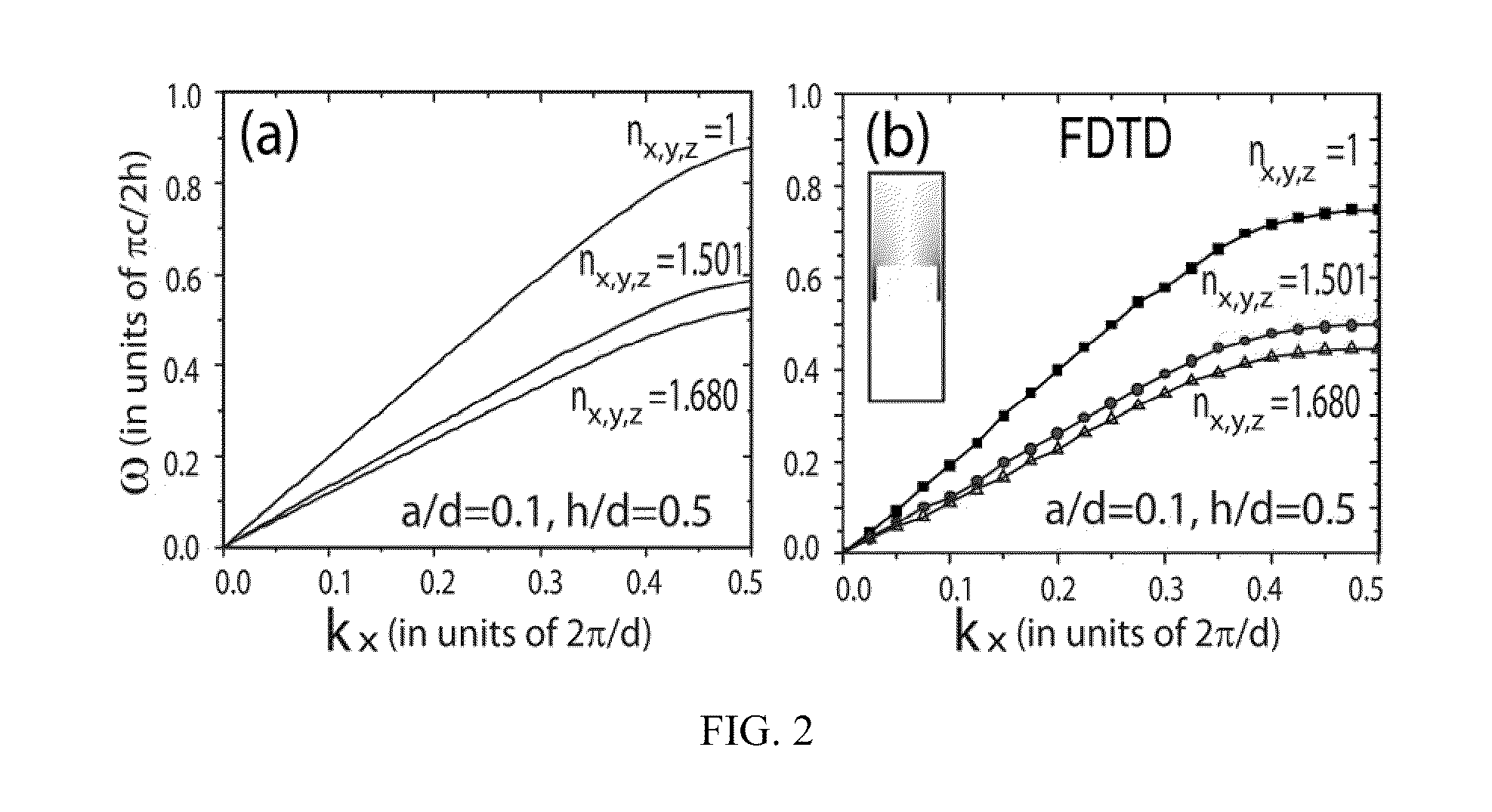
Dynamic Terahertz Switch Using Periodic Corrugated Structures
InactiveUS20120019901A1Ease of lightOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsManufacturing technologyElectrical conductor
A subwavelength terahertz (THz) switch using an artificially designed conductor metamaterial is discussed in this invention. Theoretically, slow-light EM wave propagating at THz speed imitates the strongly localized surface plasmon modes and henceforth is called Spoof Surface Plasmon Polariton (SSPP) mode in this invention. The SSPP mode of slow-light EM propagation can be easily tailored by changing the refractive index of the dielectric materials inside the metallic gap structure engineered as a periodic array of grooves. Thus, the incorporation of electro-optical material which has birefringence such as a nematic liquid crystal (N-LC) or multiple-refractive indices into the metallic gap leads to a highly compact and efficient terahertz switch being controlled by a low-voltage signal. The optimal design of the SSPP switch enabled by this novel method shows many interesting properties including 1) strong subwavelength localization; 2) relatively high extinction (On / Off switching) ratio; and 3) small damping attenuation. The THz dynamic switches can be used to construct linear switches, Y junction switches and Mach-Zehnder interferometers by using micromachining and other fabrication techniques.
Owner:MAZUMDER PINAKI
Plasmon-photon coupled optical devices
InactiveUS7110154B2Improve transmittanceTransmittivity of high intensity light is limitedBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansAngle of incidenceRefractive index
The present invention is directed to optical devices. More specifically, the disclosed devices include a film defining a periodic array of surface elements so as to give rise to surface plasmon polaritons. The film also includes at least a single aperture having a diameter less than the wavelength of light. In one embodiment, the surface elements can be an array of anisotropic apertures and the films can act as a polarizer. The disclosed devices can also include a material having a variable refractive index substantially adjacent to the metal film. For example, the refractive index of the adjacent material can vary according to some characteristic of the light incident to the device, for instance, the intensity or the angle of incidence of the light. In this embodiment, resonant coupling of incident light with the SPP, and hence transmittivity of the device, can depend upon the nature of incident light. The disclosed devices can be useful in, for example, remote polarizers, polarization mode dispersion, isolators, multi-color displays, switches, such as can be controlled according to incident sunlight, or optical filters, such as for eye protection devices, filtering out possibly harmful light.
Owner:CLEMSON UNIV RES FOUND
OLED device having improved light output
ActiveUS20070063628A1Improve light outputMaintain clarityIncadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensReflective layerLight-emitting diode
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Illumination device
ActiveUS20130286633A1Improving wavelength conversion processEnhanced couplingProjectorsDiffraction gratingsResonancePhosphor
Proposed is an illumination device (100), comprising a light source (110) such as an LED or a laser diode, a wavelength conversion medium (120) such as a phosphor, and a periodic antenna array (300) made of a highly polarisable material such as a metal. The light source emits primary wavelength light that at least partially is converted in secondary wavelength light by the wavelength conversion medium. The periodic antenna array is positioned in close proximity to the wavelength conversion medium and functions to enhance the efficiency of the absorption and / or emission processes in the wavelength conversion medium through the coupling of the incident primary wavelength light or the emitted secondary light to surface lattice resonances that arise from the diffractive coupling of localized surface plasmon polaritons in the individual antennas of the array. This is especially advantageous for forming low étendue illumination device suitable for use in projection systems, or for controlling the directionality, the polarization, and / or the color of the secondary wavelength light.
Owner:LUMILEDS
Sensor system with surface-plasmon-polariton (SPP) enhanced selective fluorescence excitation and method
InactiveUS20090045351A1Enhanced selected fluorescence excitationIncrease choicePhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansLight beamFluorescence microscope
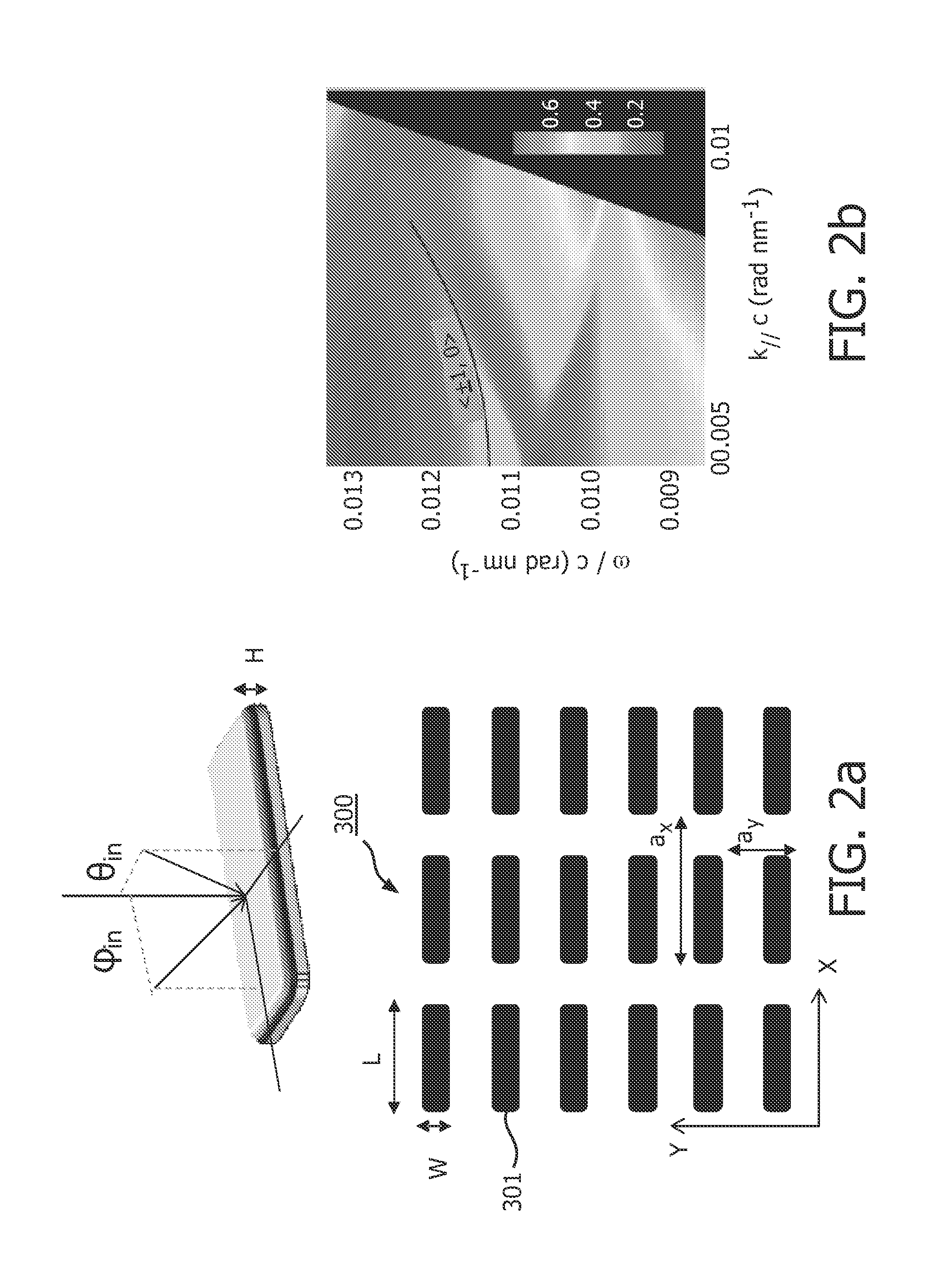
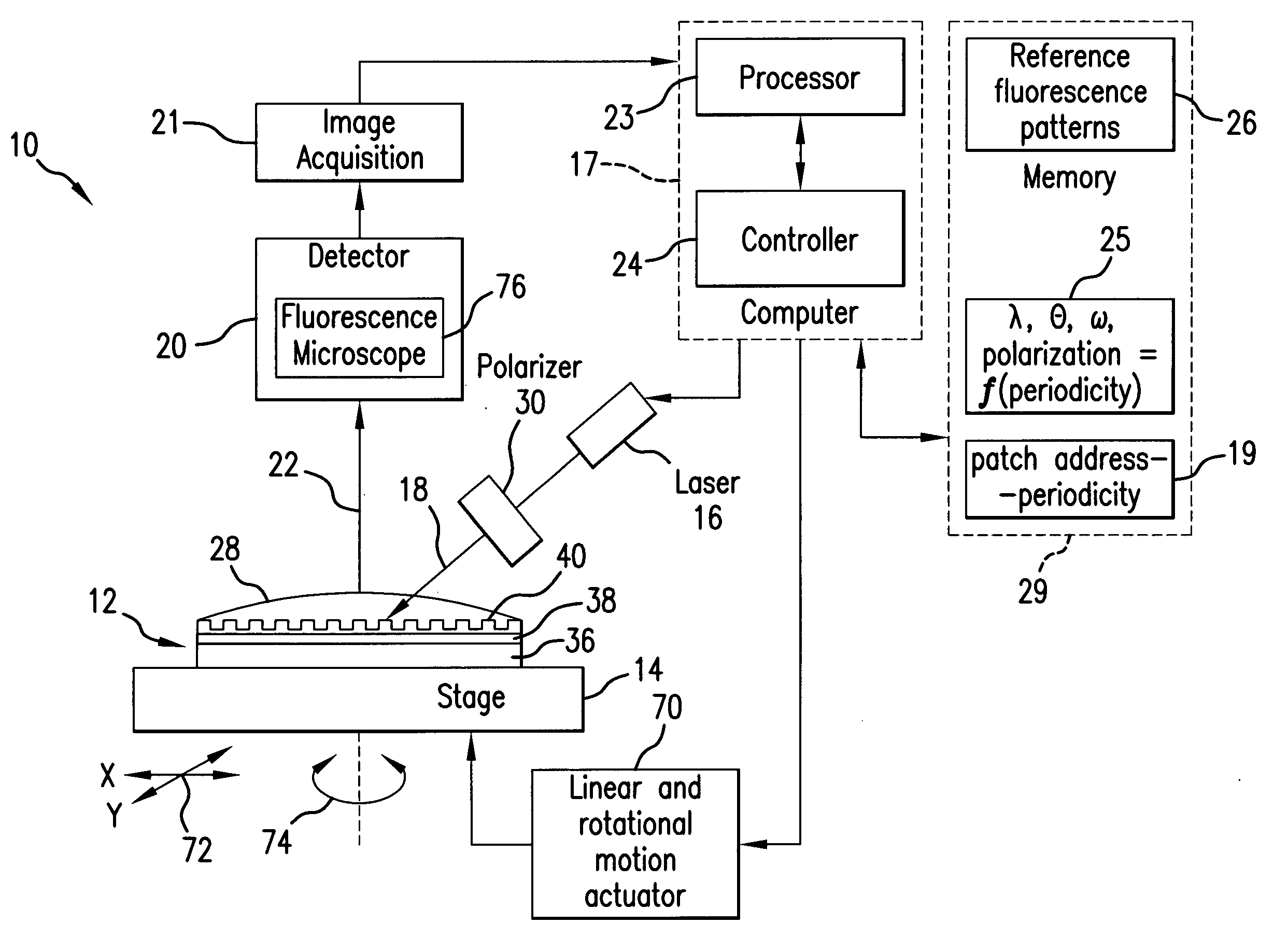
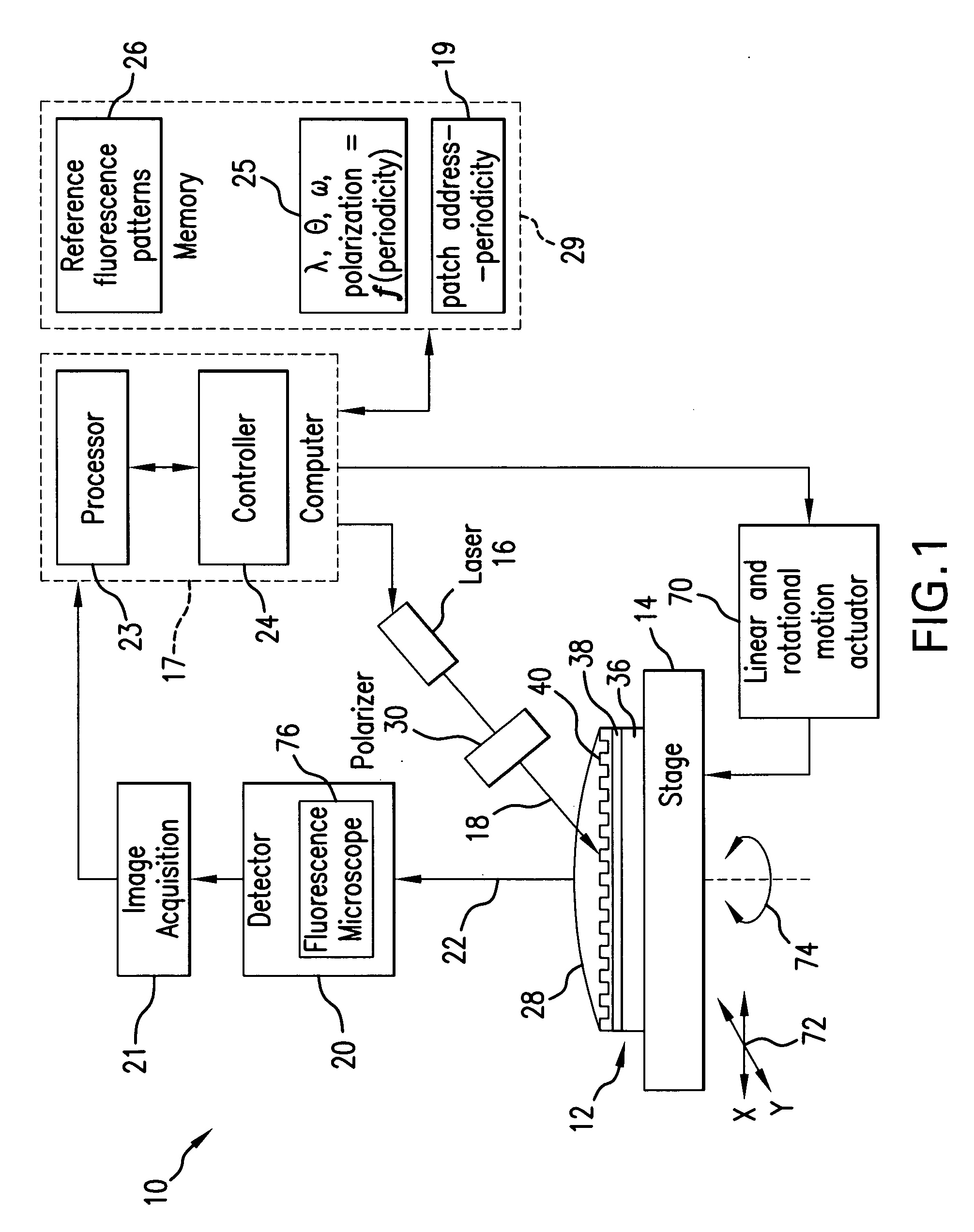
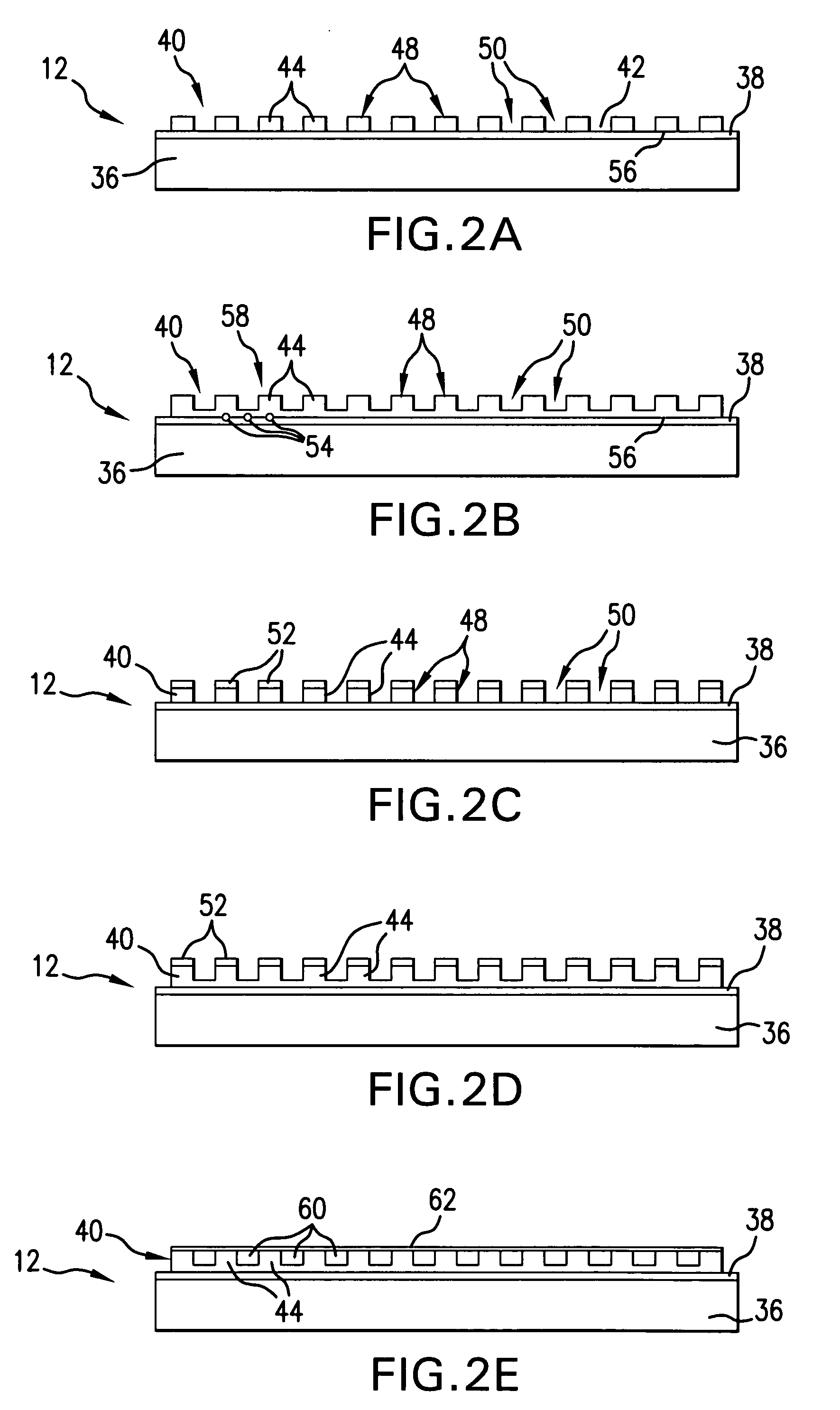
In a sensor system, an active sensor chip includes an array of periodically-patterned dielectric active sensor patches of different periodicities and geometries formed on a metal film. A specimen under study is positioned on each patch, and the active sensor chip is interrogated by illumination the patches in a predetermined sequence to result in a fluorescence response from each patch enhanced by SPP. The intensity of the fluorescence response is controlled by varying the wavelength, incidence angle, azimuthal orientation and polarization direction of the excitation light beam as the function of the periodicity of the illuminated patch. The system is compatible with commercial fluorescence microscopes and scanned laser interrogation systems.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
Method of examining biological, biochemical, and chemical characteristics of a medium and apparatus for its embodiment
InactiveUS6628376B1High sensitivityWide dynamic rangeSamplingScattering properties measurementsImage resolutionOrder form
Examinations of biological, biochemical, and chemical characteristics of media, mainly of biologic origin, or media that are in contact with biological objects whose living is influenced by the media characteristics. One excites surface plasmon polaritons on a metal layer covered with a material sensitive to the examined characteristics of a medium, produces an interference with a beam of radiation reflected under these conditions and a reference beam, records parameters of a spatial intensity distribution in the resulting interference pattern, and judges the examined characteristics on the basis of the recorded parameters. The proposed method and apparatus ensure the technical result that consists in upgrading of sensitivity and resolution of measurements, at least, by two orders.
Owner:NIKITIN PETR IVANOVICH
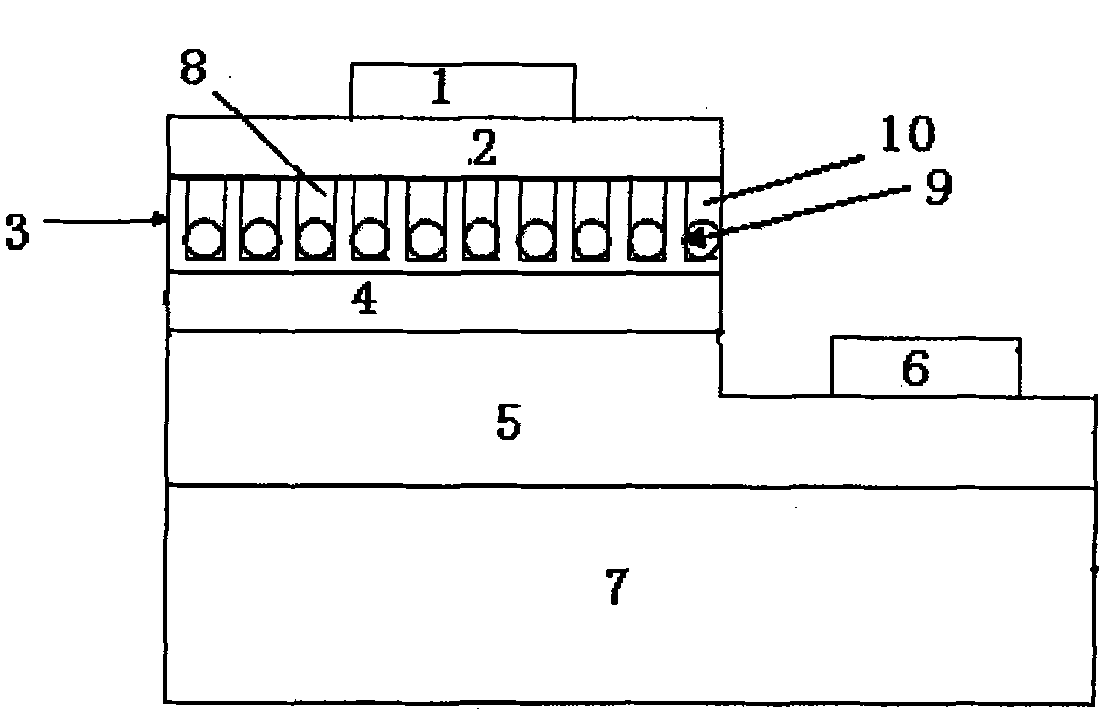
Structure of P-type GaN layer of GaN-based light-emitting diode chip
The invention provides a structure of a P-type GaN layer of a GaN-based light-emitting diode (LED) chip, wherein the P-type GaN layer is provided with pores, the distance from the bottoms of pores to the quantum-well active area of the LED chip is 10-100nm, metal particles are filled in the pores, and transparent dielectric films are filled at the pore openings to block the metal particles. The P-type GaN layer of the invention is provided with nano-pores, each pore is provided with a metal particle; the metal particle-active layer dielectric heterostructure is transplanted at the nanoscale to form the dielectric heterostructure coupled by the nanometer metal particles and the quantum-well active area; and the coupling of the surface plasmon polariton (SPP) and excitons increases the luminous efficiency of the GaN-based LED.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
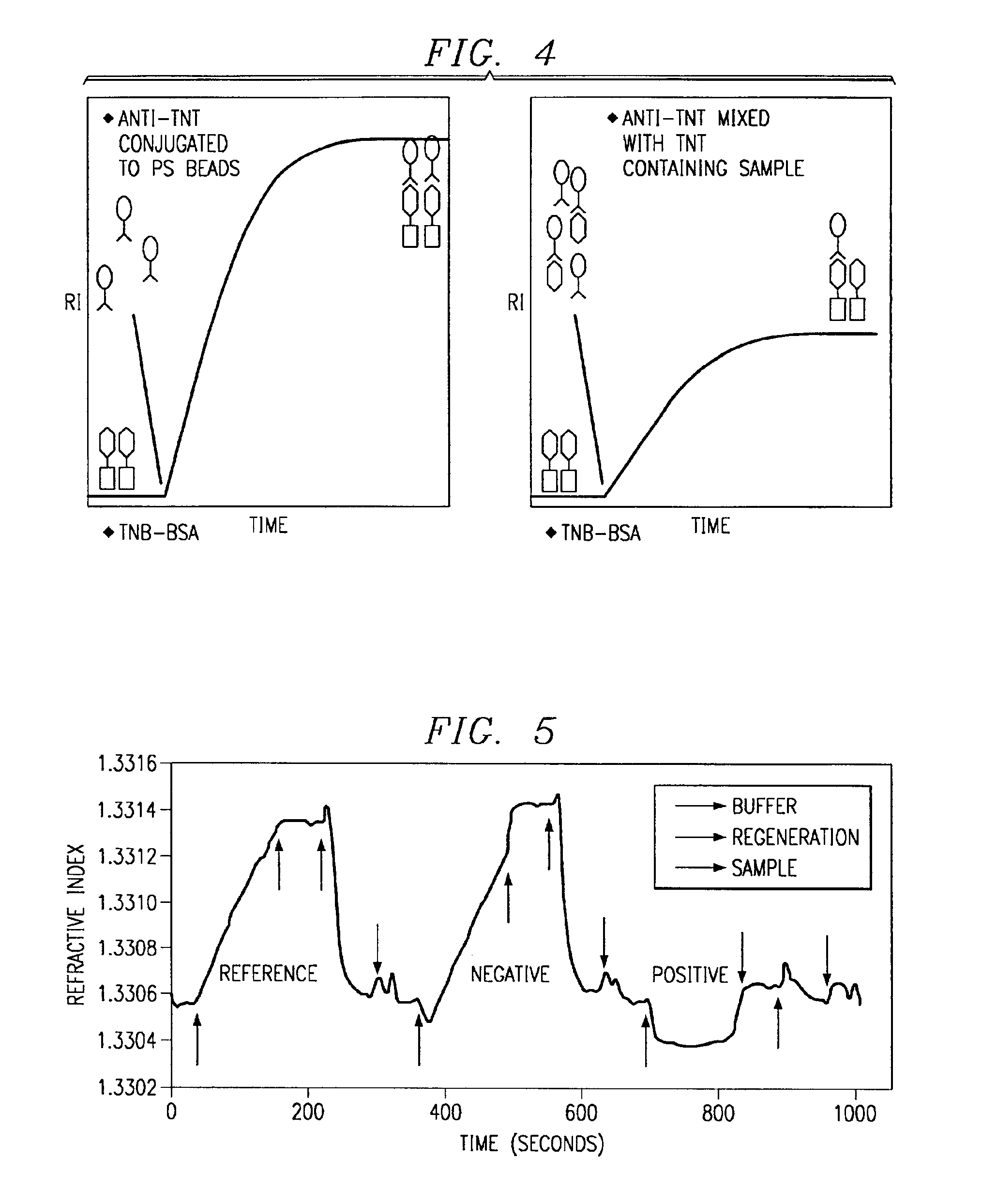
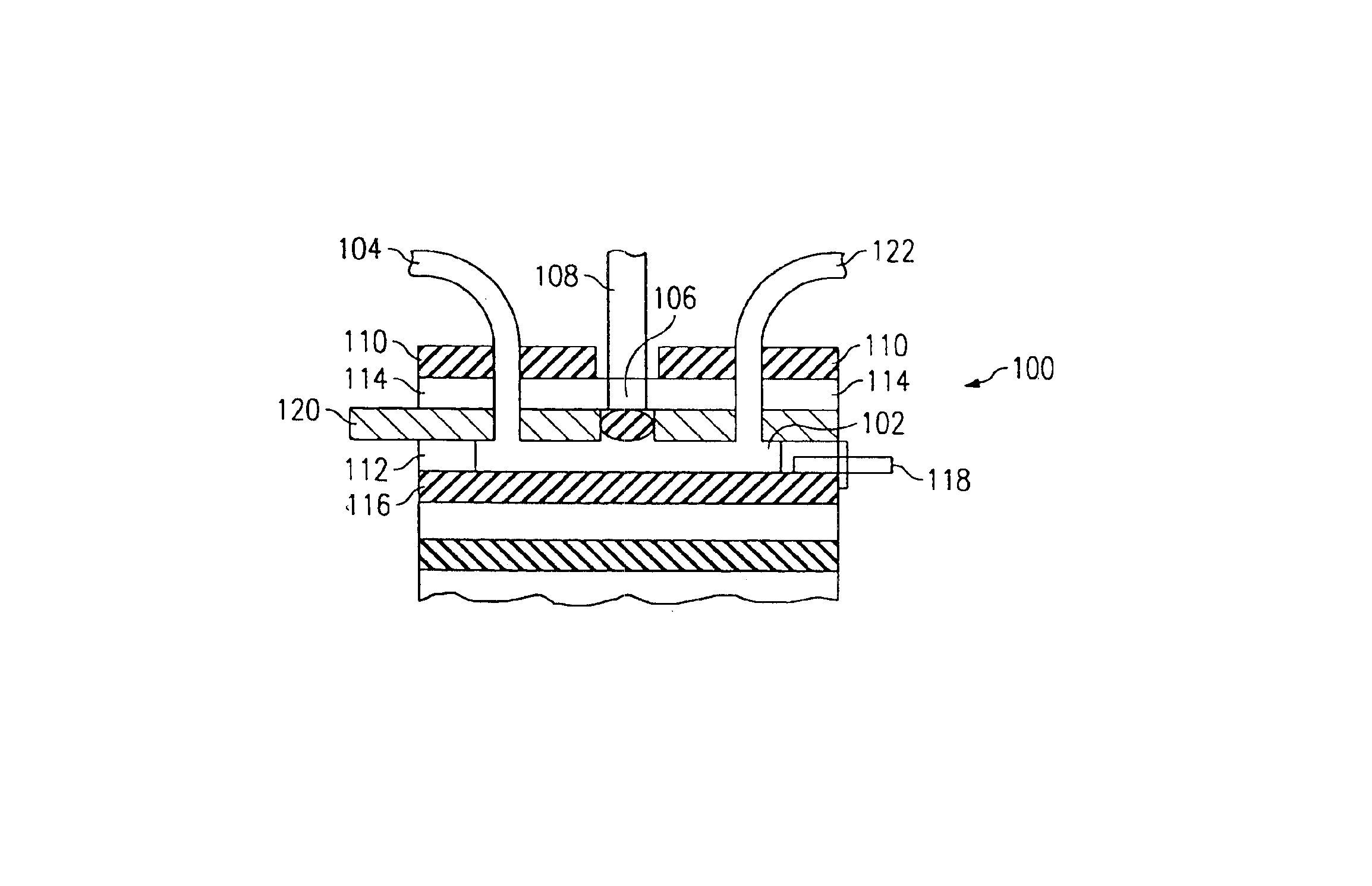
System for directed molecular interaction in surface plasmon resonance analysis
InactiveUS6862398B2High sensitivityEfficient and high-volume and mass productionChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceScattering properties measurementsAnalyteSurface plasmon resonance sensor
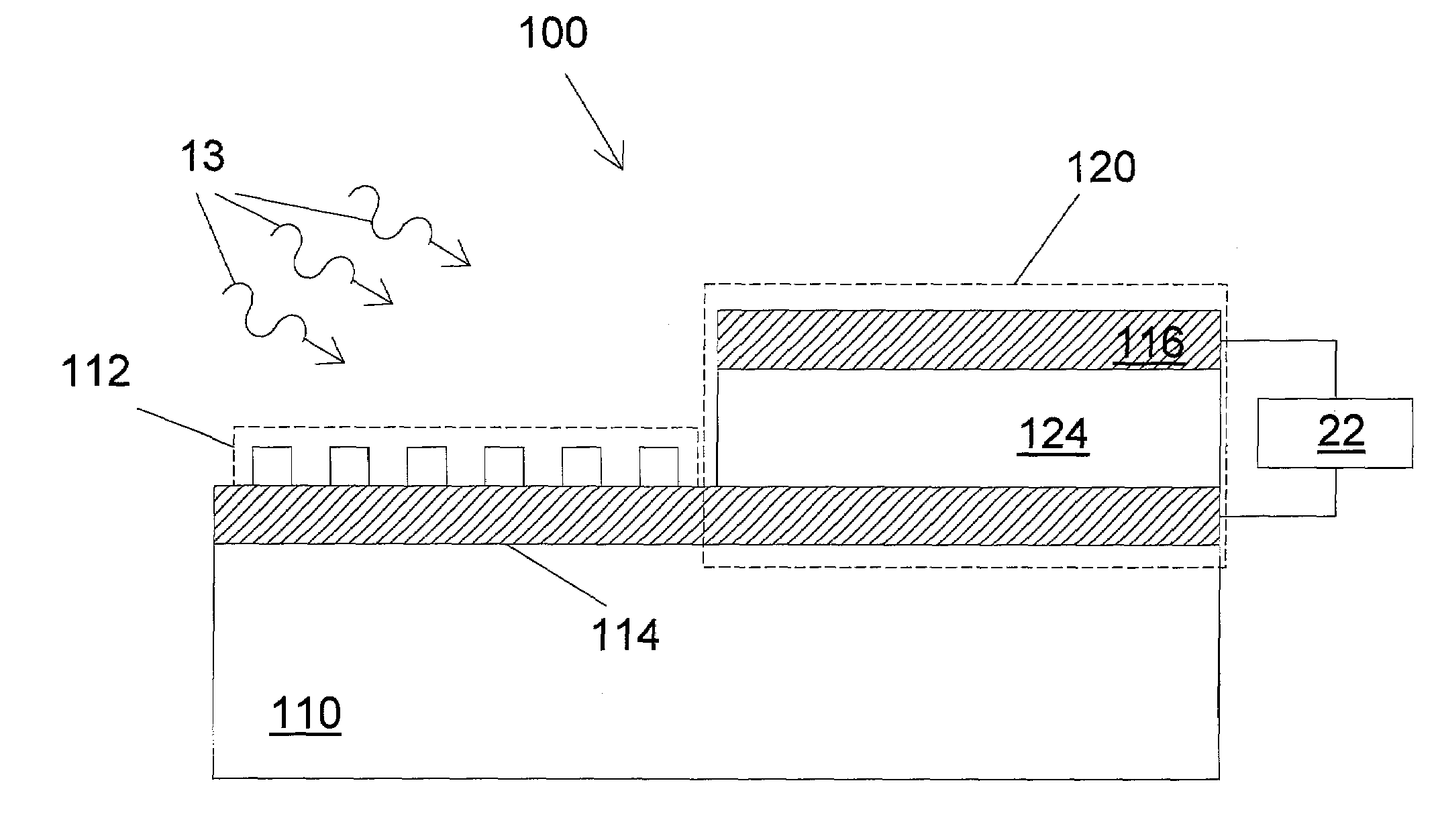
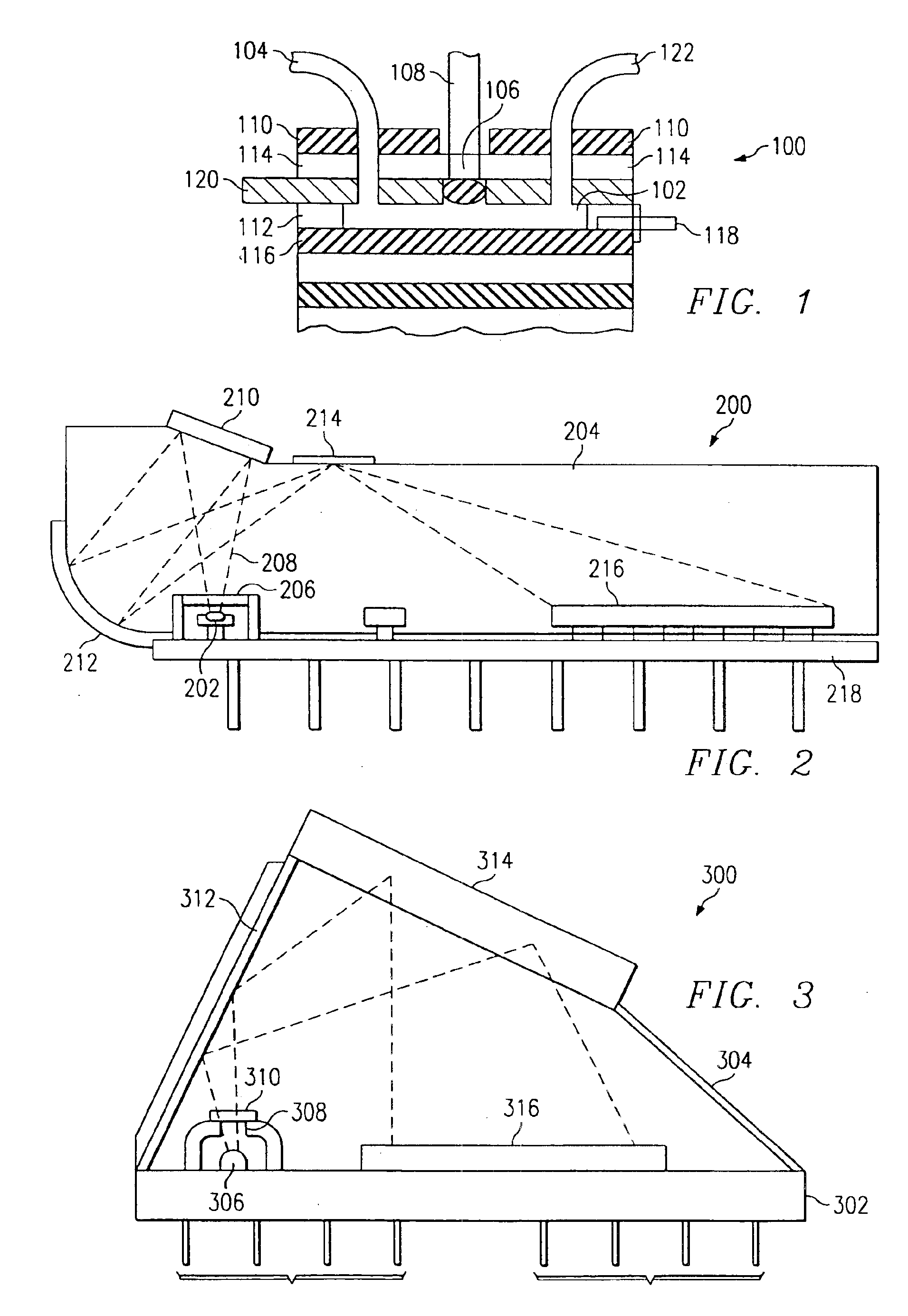
Disclosed is apparatus and method for controlled surface plasmon resonance analysis having a surface plasmon resonance sensor (200) with a derivatized surface plasmon layer (116) in optical communication with the sensor, derivatizing the surface plasmon layer and placing an analyte detection chamber (102) in fluid communication with the derivatized surface plasmon layer. The chamber is adapted (118, 120) for the generation of a molecular interaction bias across the chamber. A conjugate is provided between an analyte and a bias responsive element, wherein the analyte is reactive with the derivatized surface plasmon layer and the bias responsive element changes the response of the analyte to the molecular interaction bias. A conjugated analyte may be introduced into the chamber, generating a molecular interaction.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
OLED device having enhancement layer(s)
ActiveUS20170133631A1Lower emission rateLow efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRadiative transferExcited state
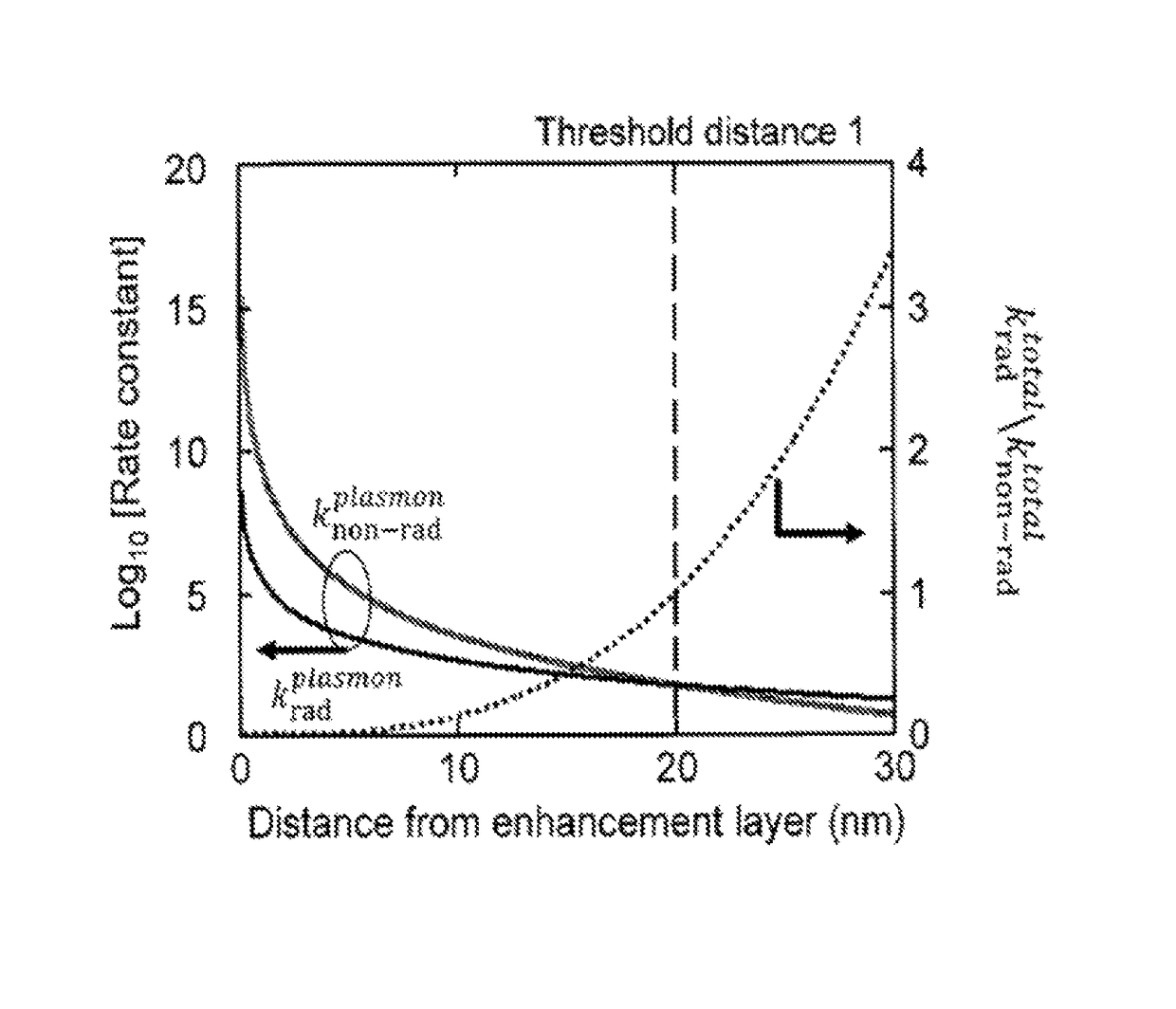
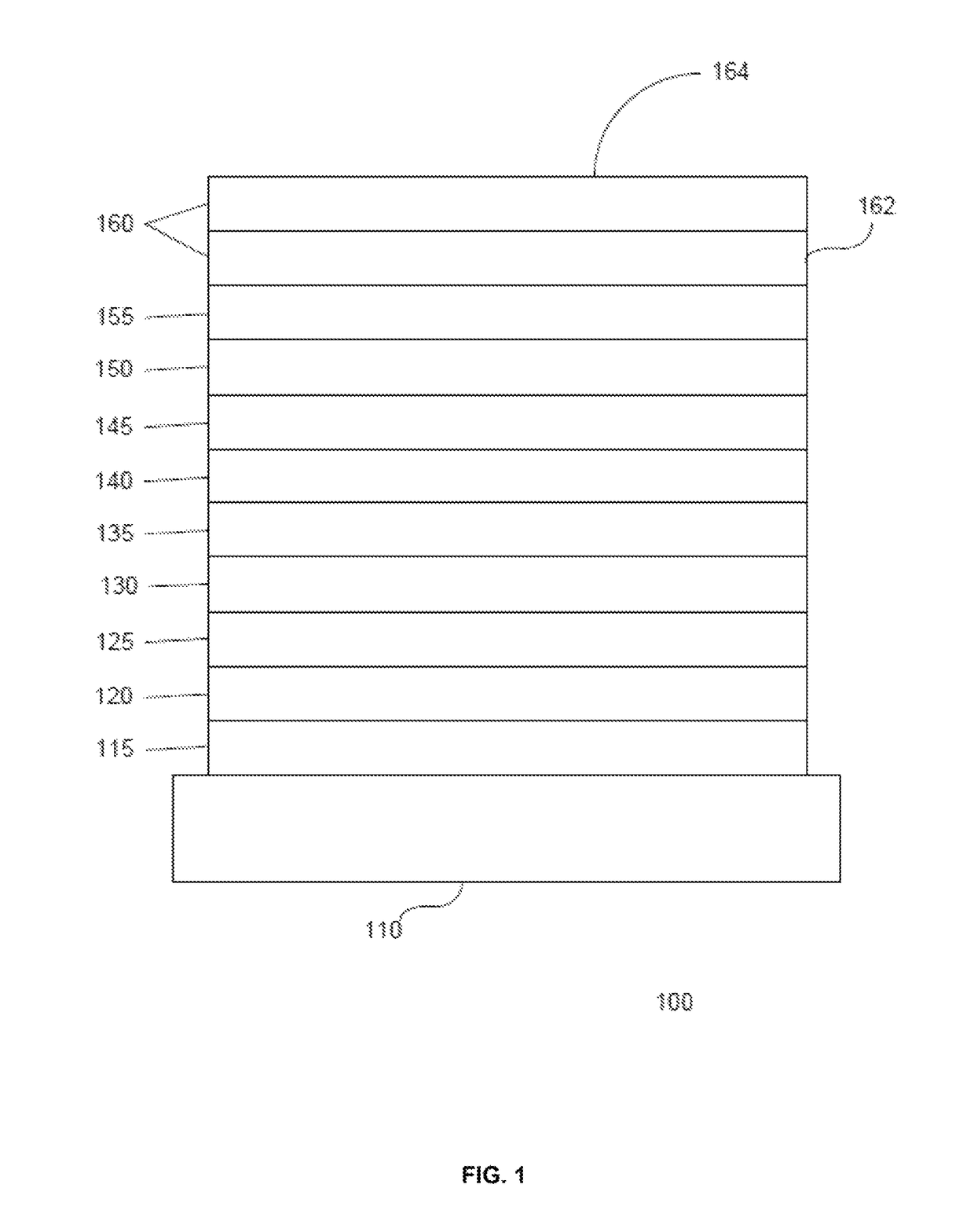
A method for improving the operation of an OLED includes maximizing on-radiative transfer of excited state energy from the OLED's organic emissive material to surface plasmon polaritons in an enhancement layer by providing the enhancement layer no more than a threshold distance away from the organic emissive layer; and emitting light into free space from the enhancement layer by scattering the energy from the surface plasmon polaritons through an outcoupling layer that is provided proximate to the enhancement layer but opposite from the organic emissive layer.
Owner:UNIVERSAL DISPLAY
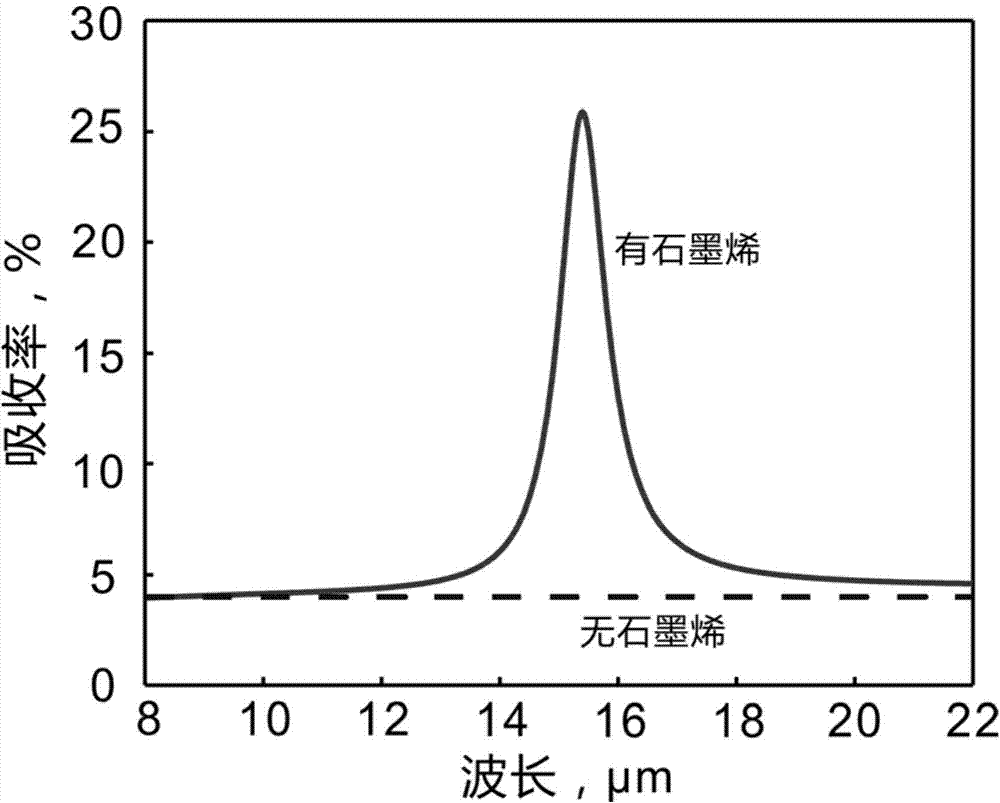
Photoelectric material adjustable absorption enhancing layer based on graphene surface plasmon
InactiveCN104851929ARich sourcesImprove optical absorptionSemiconductor devicesMicro nanoDoped graphene
The invention belongs to the field of photoelectric technology, and specifically relates to a photoelectric material adjustable absorption enhancing layer based on graphene surface plasmon. Graphene forming the enhancing layer is a thin film formed by single-layer graphene and having micro-nano scale structural features, graphene is doped to a certain concentration, and the Fermi level Ef of the graphene is larger than 0.1eV or smaller than -0.1eV, so that the graphene becomes a surface plasmon material; and the micro-nano structure is used for realizing wave-vector matching between incident light and a graphene surface plasmon mode, and under irradiation of the incident light, the doped graphene micro-nano structure generates surface plasmon, thereby realizing a local area of focusing. The absorption enhancing layer is applied to the upper side of photoelectric material used by photoelectric devices such as a solar cell and a photoelectric detector, can improve the absorption efficiency of the photoelectric material, and can realize active regulation and control of absorption characteristics of the photoelectric material, thereby expanding application of the photoelectric material in fields of spectrum-adjustable selective detection and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
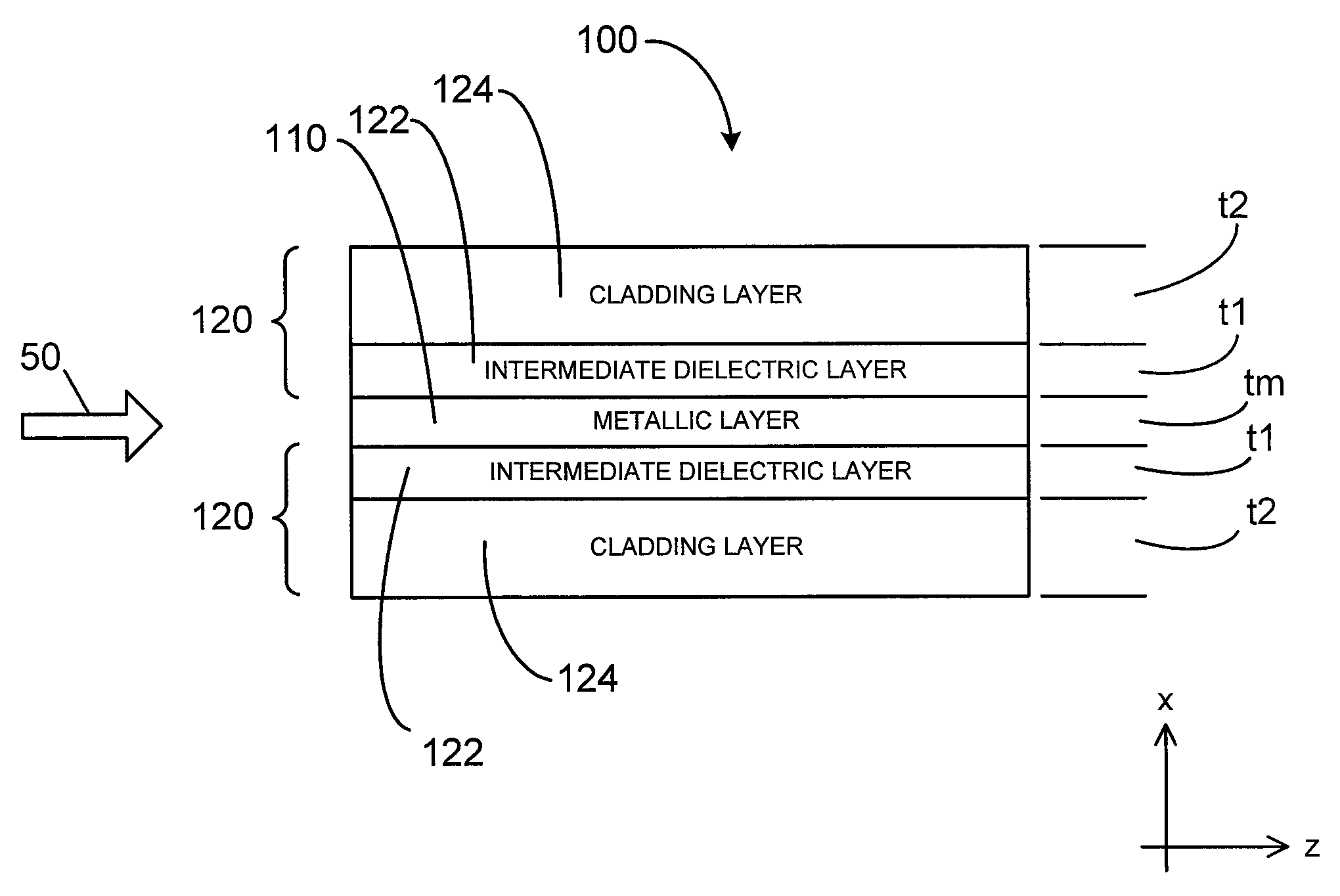
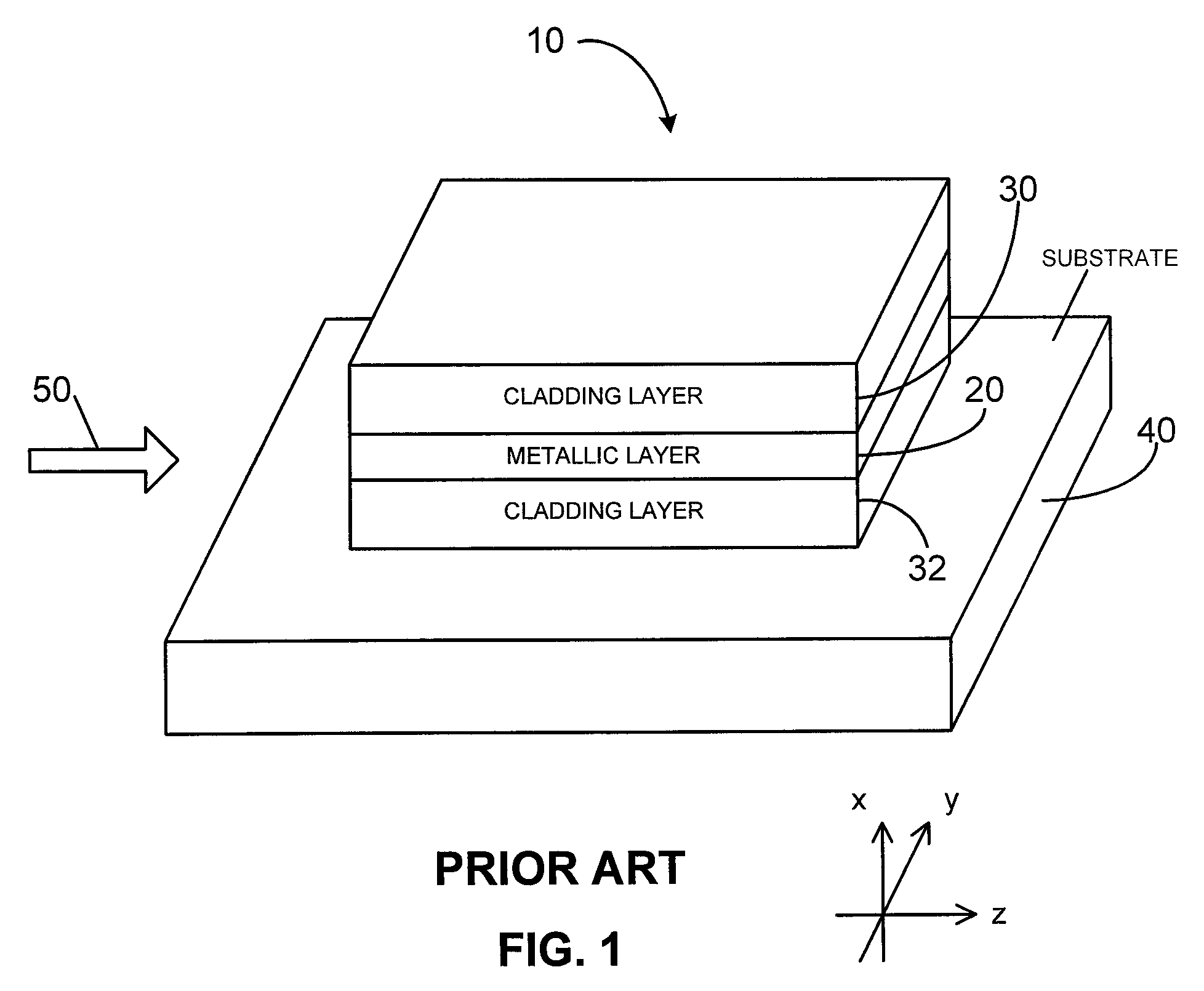
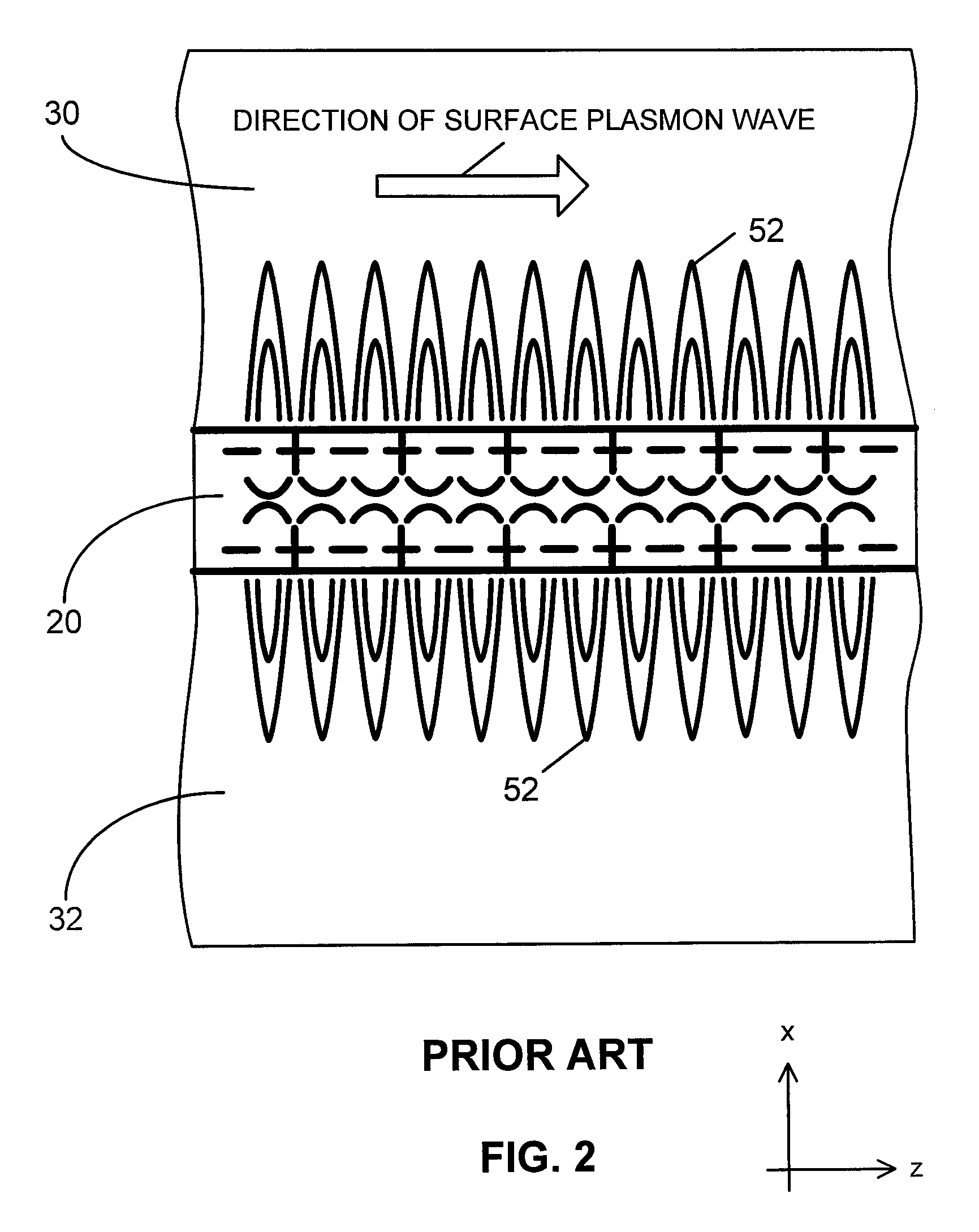
Waveguides for ultra-long range surface plasmon-polariton propagation
The disclosure relates to surface plasmon-polariton waveguides, which can guide ultra-long range surface plasmon-polariton waves. The attenuation of an ultra-long range surface plasmon-polariton waves is much lower than the attenuation of the conventional long range surface plasmon-polariton waves guided with the same kind of metal film or metal strip at the same plasmon-polariton frequency. An exemplary ultra-long range surface plasmon-polariton waveguide disclosed in this disclosure comprises a metal layer, such as a metal film or finite width metal strip, intermediate dielectric layers adjacent to the metal layer, and outer cladding dielectric material. The intermediate dielectric layers redistribute the electromagnetic energy distribution of the surface plasmon-polariton waves so that less of the energy propagates in the metal layer. Therefore, the attenuation of the surface plasmon-polariton wave is reduced. The propagation distance of the ultra-long range surface plasmon-polariton wave can be designed to a desired value by adjusting the thickness and the material property of the intermediate dielectric layers and other parameters related to the waveguide.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA
OLED device having enhancement layer(s)
ActiveUS9960386B2Easy to operateMaximizing non-radiative transferSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingExcited stateRadiative transfer
A method for improving the operation of an OLED includes maximizing on-radiative transfer of excited state energy from the OLED's organic emissive material to surface plasmon polaritons in an enhancement layer by providing the enhancement layer no more than a threshold distance away from the organic emissive layer; and emitting light into free space from the enhancement layer by scattering the energy from the surface plasmon polaritons through an outcoupling layer that is provided proximate to the enhancement layer but opposite from the organic emissive layer.
Owner:UNIVERSAL DISPLAY
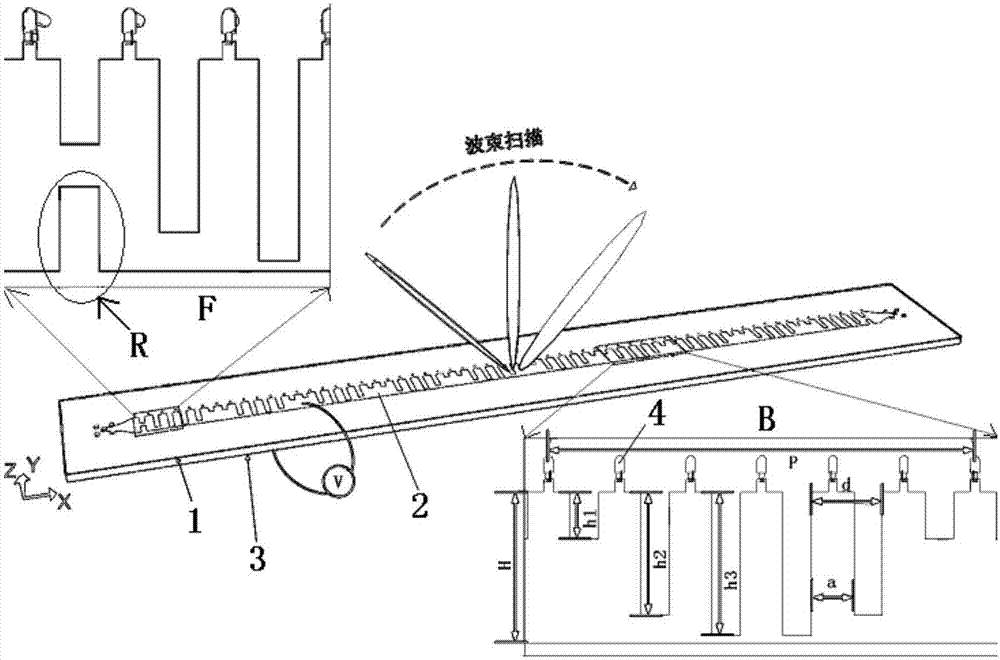
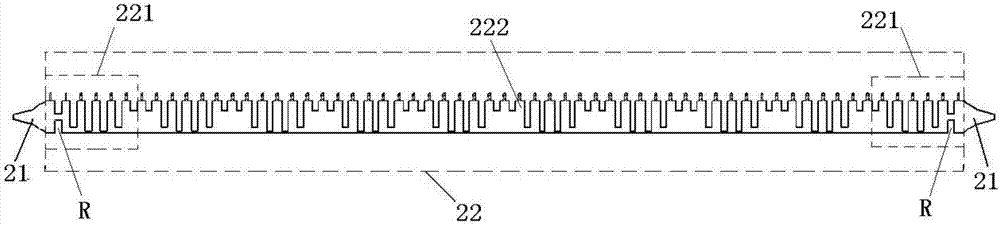
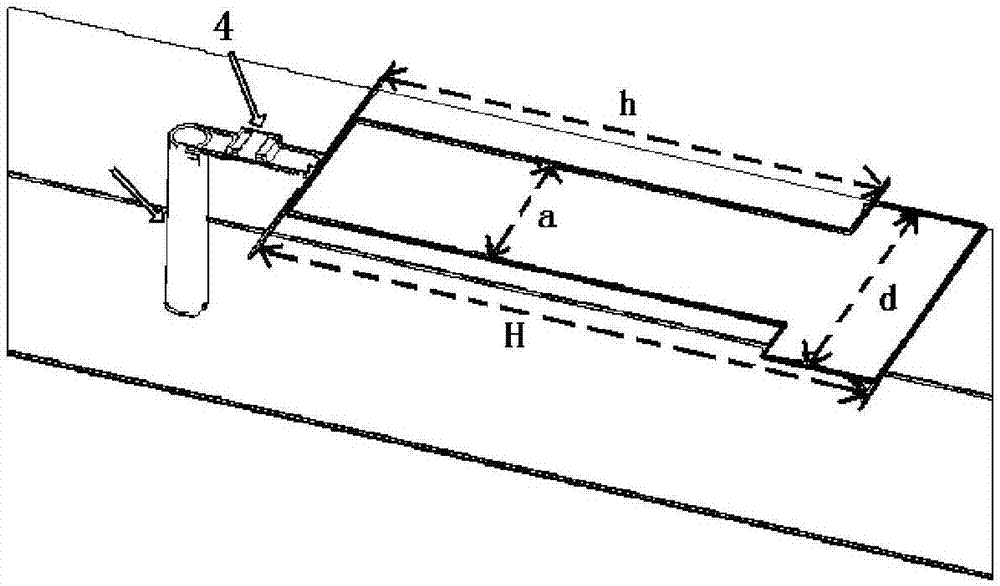
Fixed frequency beam scanning leaky-wave antenna and beam scanning method thereof
ActiveCN107425282AEasy to manufactureEasy to operateAntenna earthingsAntennas earthing switches associationDielectric substrateBeam scanning
The invention discloses a fixed frequency beam scanning leaky-wave antenna and a beam scanning method thereof. The antenna comprises a dielectric substrate, a metal strip and a metal floorboard positioned on front and back surfaces of the dielectric substrate, and a plurality of variable capacitance diode positioned on the front surface of the dielectric substrate, wherein the metal strip comprises a set of arc-shaped gradient microstrip structures and an artificial surface plasmon structure positioned between the gradient microstrip structures; the artificial surface plasmon structure comprises transition sections connected with the gradient microstrip structures and a plurality of groove units with periodically changed groove depth positioned between the transition sections; and the metal strip is connected with the metal floorboard via the variable capacitance diode and through holes. According to the antenna and the beam scanning method thereof provided by the invention, modulation on average surface impedance is achieved by adjusting the capacitance value of the variable capacitance diode, and fixed frequency beam scanning can be achieved along with the change of voltage; in addition, the antenna is simple to manufacture, convenient to operate and prone to integrate; and only a photoetching step is needed, so that cost is saved, machining errors caused by a multi-layer structure are avoided.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Laser stripping film LED (Light-Emitting Diode) and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103311395AReduce thermal resistanceImprove light extraction efficiencySemiconductor devicesUltraviolet lightsEvaporation
The invention discloses a laser stripping film LED (Light-Emitting Diode) and a preparation method thereof. A chip unit of the laser stripping film LED comprises a type n layer, a quantum well, a type p layer, a periodical metal nanometer structure, an electrode p, an insulating layer and an electrode n, wherein the type p layer is formed on the quantum well; the periodical metal nanometer structure is embedded into the type p layer; the abovementioned structures inversely cover on a substrate; and a bonding pad p is arranged at one corner of a chip. According to the laser stripping film LED, the coupling resonance functions of surface plasmons and a quantum well structure are utilized, so that the radiation compounding efficiency and light-emitting efficiency of the LED are increased greatly under bulk injection, and meanwhile, certain effects are achieved on green-yellow light and ultraviolet light LEDs with low light-emitting efficiency; laser scribing and corroding methods are adopted for partitioning the chip unit, so that the warping of an epitaxial wafer is reduced, and the processing difficulty and cost are lowered; and specific to the bonding pad p, a protection layer and silver layer evaporation process is adopted, so that the manufacturing process of the bonding pad p is simplified, and the process cost is lowered; and a hot phosphoric acid coarsening method is adopted, so that the process cost is lowered, and the light-emitting efficiency of the LED is increased.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
System for directed molecular interaction in surface plasmon resonance analysis
InactiveUS6870627B2High sensitivityEfficient and high-volume and mass productionCombination devicesRadiation pyrometryAnalyteSurface plasmon resonance sensor
Disclosed is apparatus and method for controlled surface plasmon resonance analysis having a surface plasmon resonance sensor (200) with a derivatized surface plasmon layer (116) in optical communication with the sensor, derivatizing the surface plasmon layer and placing an analyte detection chamber (102) in fluid communication with the derivatized surface plasmon layer. The chamber is adapted (118, 120) for the generation of a molecular interaction bias across the chamber. A conjugate is provided between an analyte and a bias responsive element, wherein the analyte is reactive with the derivatized surface plasmon layer and the bias responsive element changes the response of the analyte to the molecular interaction bias. A conjugated analyte may be introduced into the chamber, generating a molecular interaction.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Optical converter
InactiveUS20070146866A1Function increaseAvoid overall overheatingLight demodulationNon-linear opticsOptical radiationLight beam
A device for conversion or amplification of the frequency of optical radiation, both continuous wave and pulsed, with a cheap and compact structure. The device includes a multilayer structure including a metal layer and a dielectric layer, and a transparent dielectric material disposed on the top layer of the multilayer structure. An incident beam is coupled by a coupling device, utilizing a specific surface plasmon-polariton mode, and thereby output beams reflected from a sample are modulated or amplified.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Process for processing surface plasmon polariton coupled nano array based on scallop effect
ActiveCN104495742AOptimized Design Coupling StructureConvenient researchDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingDiffraction effectNano structuring
The invention discloses a method for preparing a surface plasmon polariton coupled nano array. The method comprises the following steps: performing deep reactive ion etching on a substrate by adopting a nano-scale etching mask which is manufactured by electron beam exposure, and then performing metallic membrane plating to obtain a three-dimensional 'metal nano structure array-nano space layer-metallic film' structure. The metallic nano structure generates local electromagnetic field resonance of photon and free electron to generate a very strong local surface plasmon polariton, and a diffraction effect provides wave vector compensation to excite a propagating type surface plasmon polariton of the metallic film so as to form local surface plasmon polariton-propagating type surface plasmon polariton coupling, so that light is restrained in a nano scale to initiate very strong surface local near field enhancement between a metal and a medium interface. The structure manufactured by the process disclosed by the invention can promote new mechanism exploration of the surface plasmon polariton, and has important application prospects in the fields of metamaterials, ultrahigh-sensitivity optical biosensing and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Transmission line, and leaky-wave antenna multiplexing device and beam scanning method thereof
ActiveCN107425275ARealize beam fixed-frequency scanningEasy to manufactureRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsPeriodic alternatingDielectric substrate
The invention discloses a transmission line, a leaky-wave antenna multiplexing device and a beam scanning method thereof. The device comprises a dielectric substrate, a metal strip and a metal floorboard positioned on the front and back surfaces of the dielectric substrate, and periodically alternatively arranged capacitors and variable capacitance diodes for connecting the metal floorboard and the metal strip via the through holes. The metal strip comprises gradient microstrip line structures at two ends and an artificial surface plasmon structure positioned therebetween. When the capacitance value of the variable capacitance diode is identical with that of the fixed capacitor, the surface impedance of the device is identical, and thus the function of the transmission line is achieved; when the capacitance value of the variable capacitance diode is not identical with that of the fixed capacitor, the surface impedance of the device is periodically modulated, and thus the radiation function of the leaky-wave antenna is achieved. Voltage is used as a regulation means, and fixed frequency beam scanning can be achieved along with the change of the voltage; the device is simple to manufacture, convenient to operate and prone to integrate; only a photoetching step is needed, so that cost is saved, and machining errors caused by a multi-layer structure are avoided.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Surface plasmon crystal transducer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101551330AStructural parameters are adjustableSimple preparation processIndividual molecule manipulationScattering properties measurementsMicrosphereTransducer
The invention discloses a surface plasmon crystal transducer and a manufacturing method thereof. The transducer comprises a quasi-three-dimensional metal hemispherical shell membrane with periodic fluctuation surface; the metal hemispherical shell membrane is formed by metal nano hollow hemispherical shells and forms two-dimensional hexagonal close piling arrangement; the adjacent hemispherical shells are connected with each other; and microscopic holes are arranged among any three adjacent hemispherical shells. The manufacturing method of the transducer comprises the following steps of: adopting colloidal crystal obtained by micron or submicron medium microspheres through self-assembly technology as a template; utilizing a physical or chemical deposition method to deposit metal nanoparticles on the surface of the microspheres of the template till the deposition amount of the metal leads the nanoparticles to form a continuous metal hemispherical shell membrane; and utilizing a physical or chemical method to remove the colloidal crystal template so as to obtain the surface plasmon crystal transducer formed by the metal nano hollow hemispherical shells. The invention has the advantages of simple manufacturing process, low cost, good stability, high sensitivity, repeatability and simple operation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Manufacturing method of surface-plasmon-enhanced GaN-based nanopore LED
InactiveCN104051587AClose coupling distanceExcellent electrical propertiesSemiconductor devicesPower flowNanoparticle
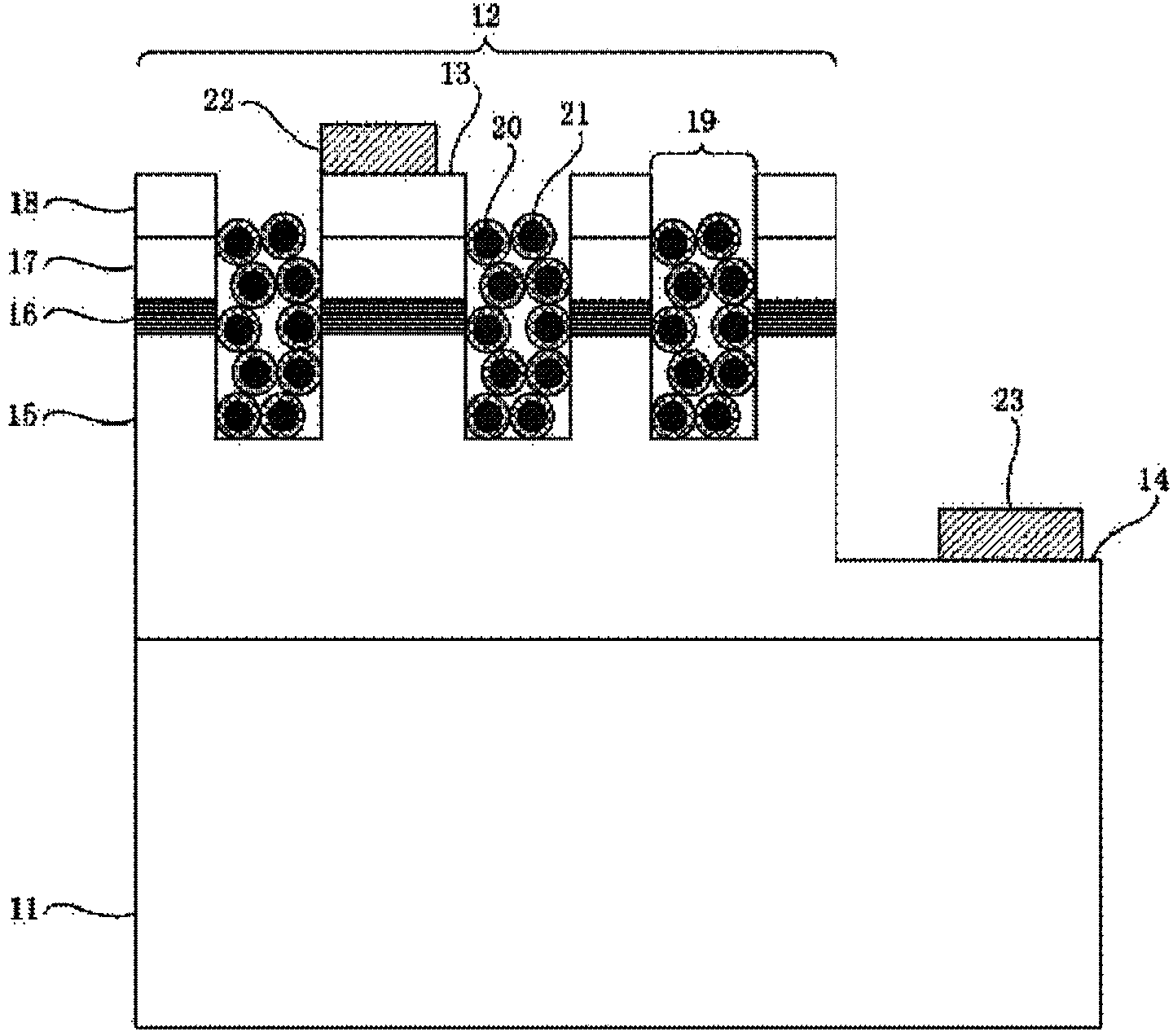
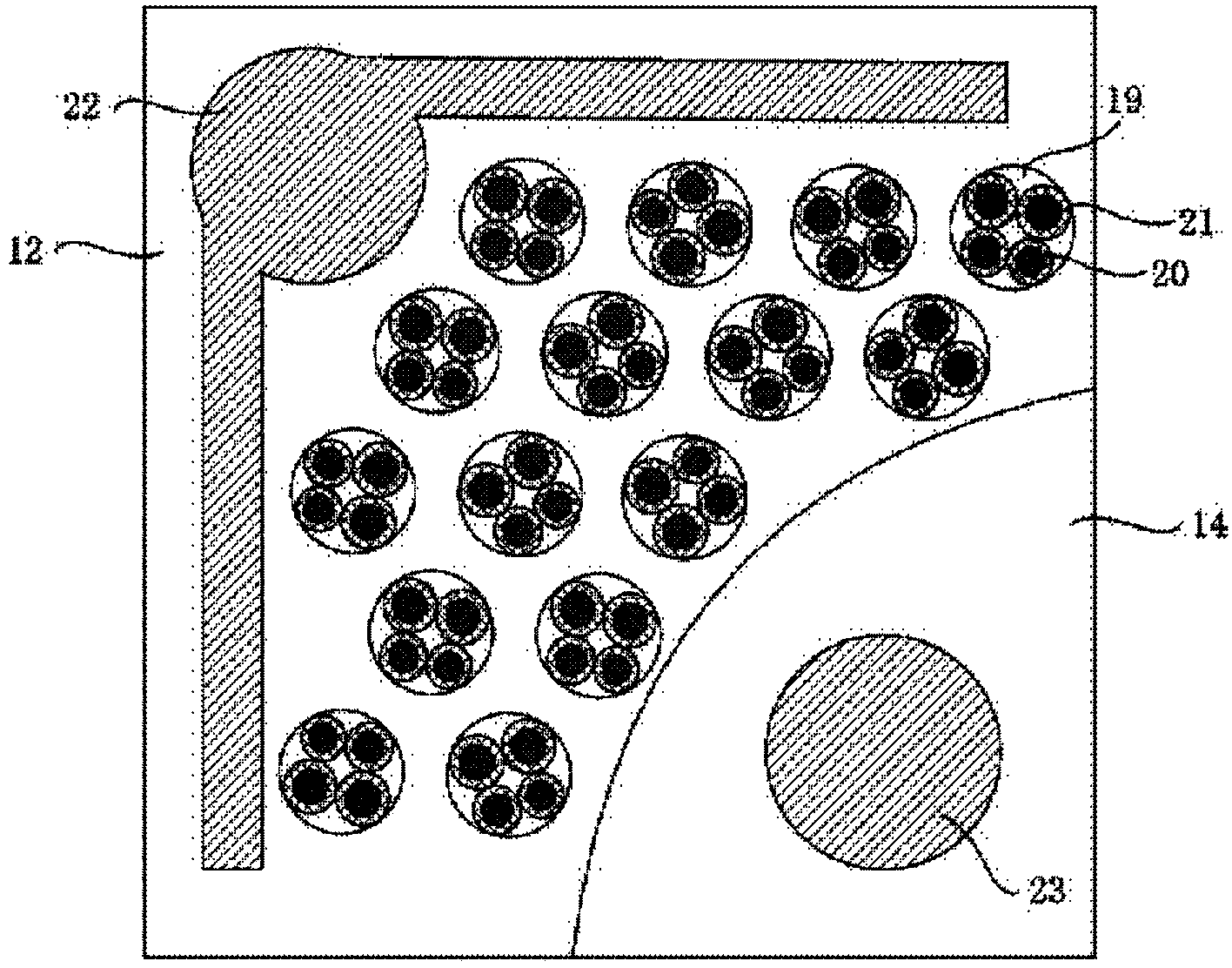
A manufacturing method of a surface-plasmon-enhanced GaN-based nanopore LED includes the following steps of firstly, sequentially growing an n-type InAlGaN layer, a non-doped or doped multi-quantum-well layer, a p-type InAlGaN layer and a current expansion layer on a substrate; secondly, conducting downward etching on the current expansion layer into the n-type InAlGaN layer through a photo-etching and dry-etching process so that a GaN-based LED structure nanopore array can be formed; thirdly, conducting downward etching on the portion, located on one side of the GaN-based LED structure nanopore array, of the upper surface of the current expansion layer to form a tabletop, wherein the etching depth is larger than the depth of nanopores of the GaN-based LED structure nanopore array; fourthly, manufacturing a p electrode on part of the upper surface of the current expansion layer through a photo-etching, evaporating and adhesive tape stripping process; fifthly, manufacturing an n electrode on the tabletop; sixthly, filling the nanopores of the GaN-based LED structure nanopore array with multiple spherical metal nanometer particles with non-conductive film wrapping on the outer surfaces to form a nuclear shell metal nanometer spherical layer, and completing manufacturing.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fluorescence enhanced microarray biochip based on micro/nano periodic structures and method for preparing same
InactiveCN102901715ALow costImprove throughputDecorative surface effectsScattering properties measurementsFluorescenceStructure based
The invention relates to a fluorescence enhanced microarray biochip based on micro / nano periodic structures and a method for preparing the same. According to the chip, the micro / nano periodic structures based on the surface plasmon resonance enhanced fluorescence technology serve as a substrate material of the microarray biochip; a series of micro / nano periodic structures are processed on a glass or / and polymer substrate, wherein the period is 400-800 nm, and the depth is 20-100 nm; and multiple layers of functional films are deposited on the glass or / and polymer substrate to ensure that the glass or / and polymer substrate has the function of surface plasmon resonance coupling enhanced fluorescence. The fluorescence signal strength and sensitivity of biomolecule microarray analysis on a substrate are improved by about 10 times, so that the micro / nano periodic structures have the potential to become a brand new low-cost high-throughput and ultrasensitive microarray biochip substrate material. The fluorescence enhanced microarray biochip based on the micro / nano periodic structures has the characteristics that surface plasmon resonance enhanced fluorescence is combined with the microarray biochip technology, the microarray biochip is simple in structure, flexible and various in materials and suitable for mass production and high-throughput detection.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Two-dimensional solid-state imaging device
InactiveUS20100295143A1Increase the number of pixelsReduce the opening areaTransistorTelevision system detailsProjection imageResonance
A two-dimensional solid-state imaging device includes: pixel regions arranged in a two-dimensional matrix, wherein each pixel region has a plurality of subpixel regions, a metal layer with an opening of an opening size smaller than the wavelength of an incoming electromagnetic wave and a photoelectric conversion element are arranged with an insulating film interposed therebetween, at least one photoelectric conversion element is arranged in the opening provided at a portion of the metal layer in each subpixel region, a projection image of the opening is included in a light receiving region of the photoelectric conversion element, the opening is arrayed so as to cause a resonance state based on surface plasmon polariton excited by the incoming electromagnetic wave, and near-field light generated near the opening in the resonance state is converted to an electrical signal by the photoelectric conversion element.
Owner:SONY CORP
Thin-film solar battery based on imaged metal substrate and manufacturing method of battery
ActiveCN102709402ASimple processEasy to large areaFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationMetallic materialsElectromagnetic field
The invention provides a thin-film solar battery based on an imaged metal substrate and a manufacturing method of the battery. The imaged metal substrate of a first metal material is manufactured by adopting an anode oxidization method or a nano imprinting method which can produce in a large area at a low cost and an imaged metal thin film of a second metal material between the imaged metal substrate and a light absorption layer is additionally arranged. According to the invention, by utilizing diffusion to light of the imaged metal thin film and a surface plasmon effect of the imaged metal thin film, a light path of incidence photons in the light absorption layer is increased and a partial electric magnetic field is enhanced, so that the light can be sufficiently absorbed in the light absorption layer and the light absorption efficiency is enhanced; and therefore, the thickness of the light absorption layer is reduced, and the photon-generated carrier collection efficiency and the photoelectric conversion efficiency are improved. Meanwhile, the cost is accelerated to be reduced. The thin-film solar battery based on the imaged metal substrate and the manufacturing method of the battery have the advantages of simple process and easiness of realizing large-area and low-cost production application.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com