Illumination device
a technology of a spherical device and a spherical tube, which is applied in the direction of semiconductor devices for light sources, lighting and heating apparatus, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of high local heat dissipation, emission directionality problems, and difficulty in limiting usefulness, so as to enhance the excitation of the wavelength conversion medium, improve the wavelength conversion process, and improve the coupling of the primary
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
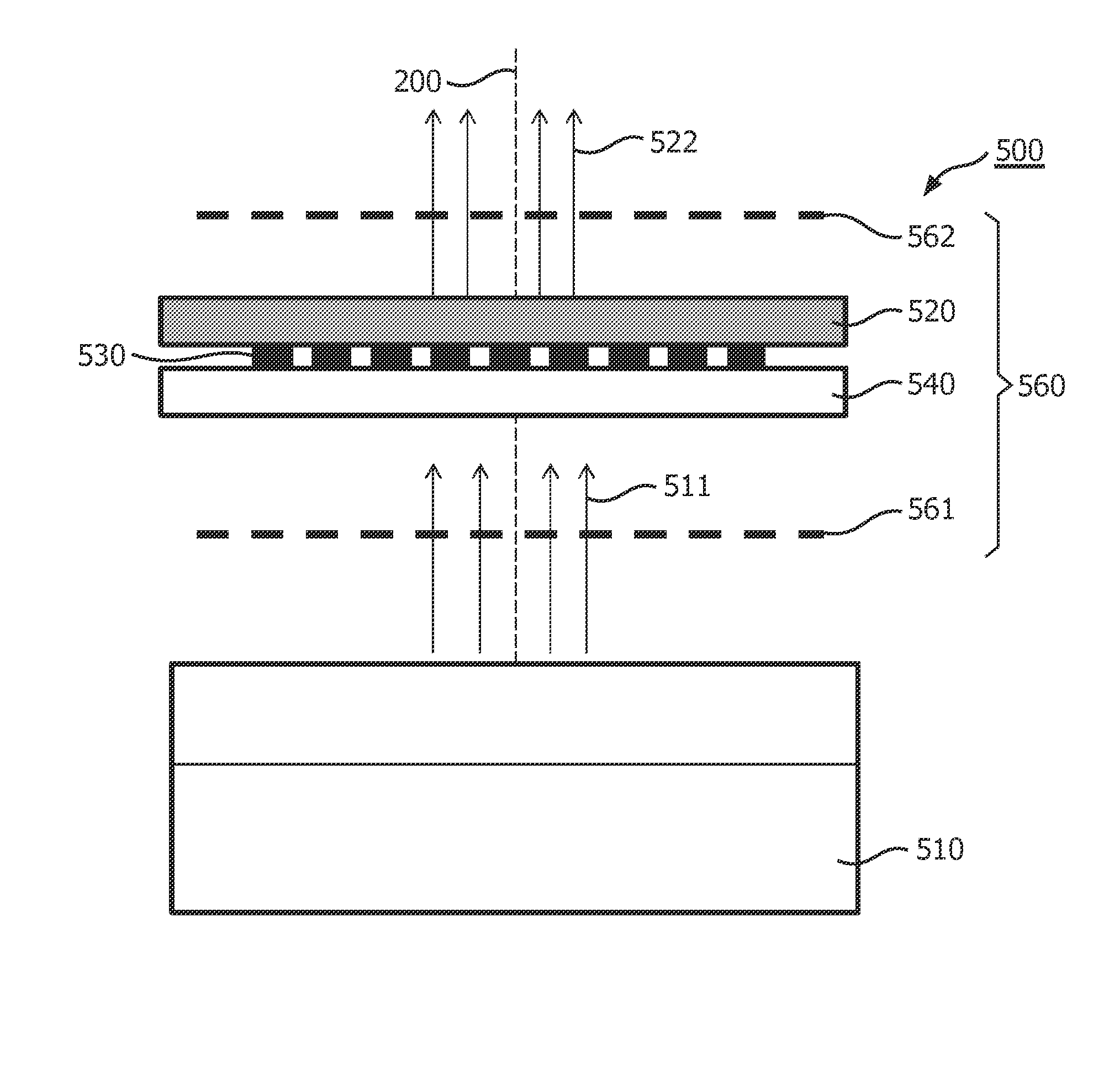
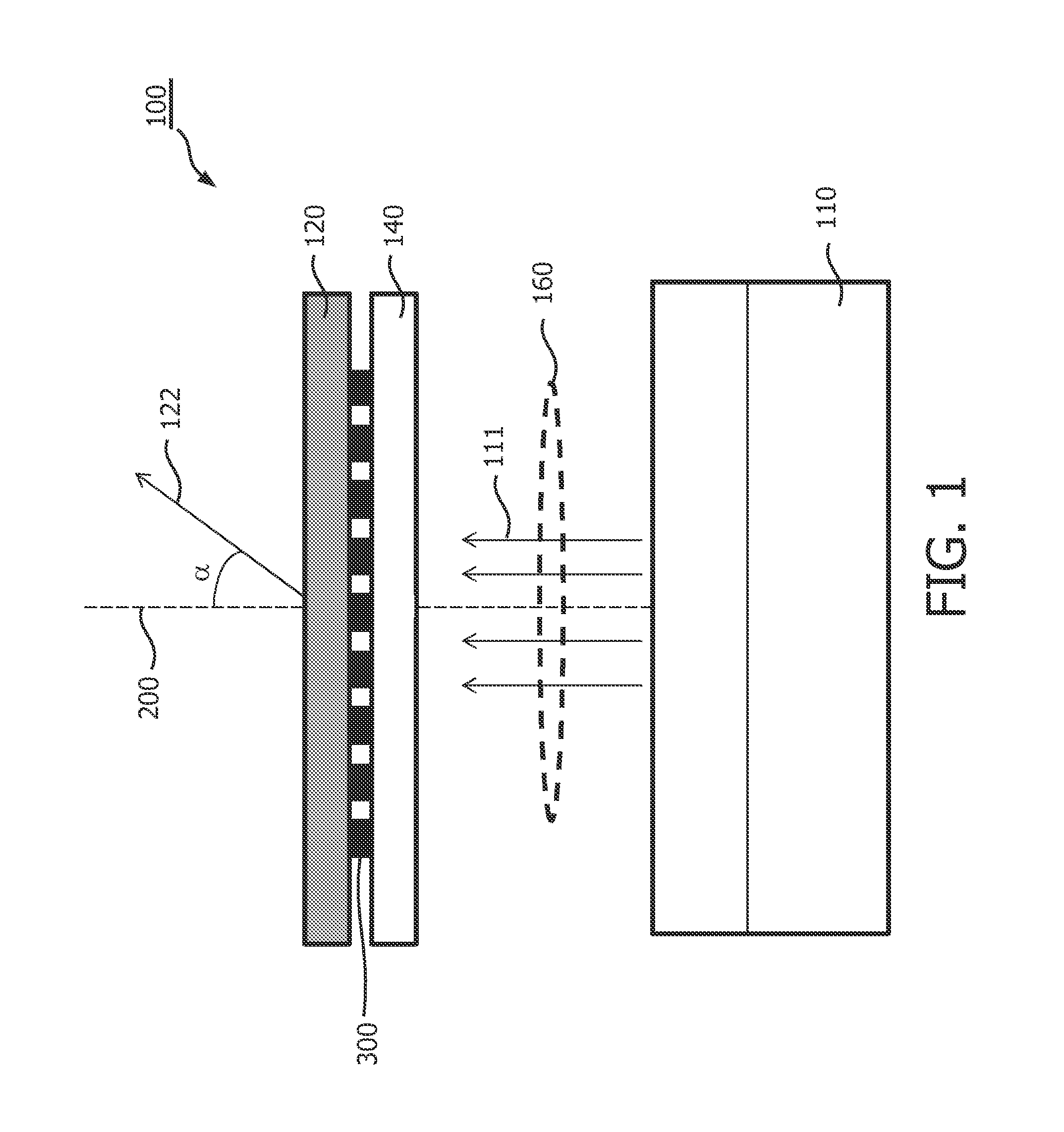
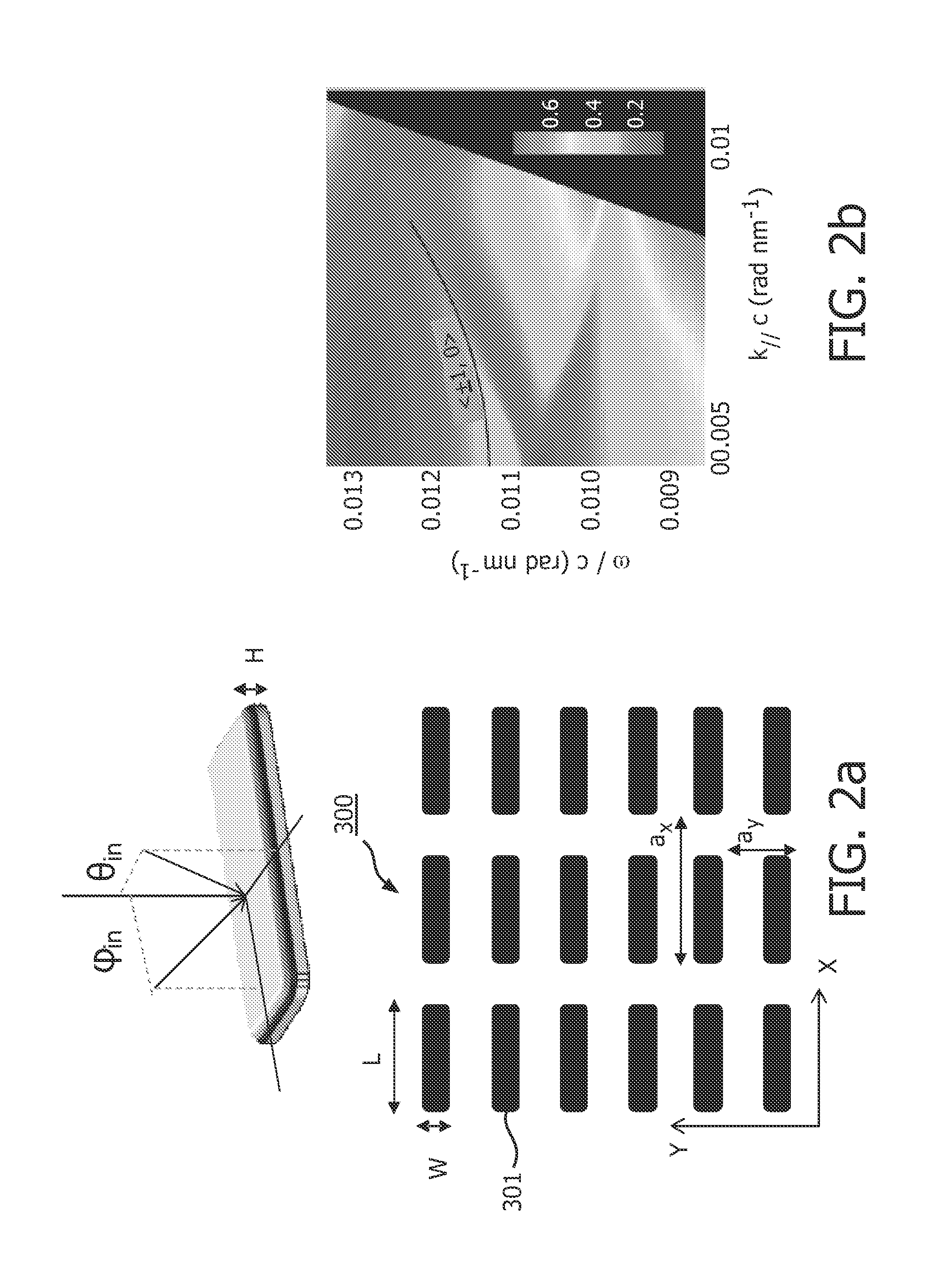
[0032]FIG. 1 shows an illumination device 100 in accordance with the invention. The illumination device 100 comprises a light source 110, for instance a semiconductor light source such as a (inorganic or organic) light emitting diode (LED), a resonant cavity light emitting diode, a laser diode (LD), such as a vertical cavity laser diode or an edge emitting laser diode. Material systems currently of interest in the manufacture of such semiconductor light sources capable of operating in the visible spectrum include Group III-V semiconductors. In particular binary, ternary, and quaternary alloys of gallium, aluminium, indium, and nitrogen, also referred to as III-nitride materials, are of interest. Typically, III-nitride semiconductor light sources are fabricated by epitaxially growing a stack of semiconductor layers of different composition and dopant concentrations on a sapphire, silicon carbide, III-nitride, or other suitable substrate by metal-organic chemical vapour deposition, mo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com