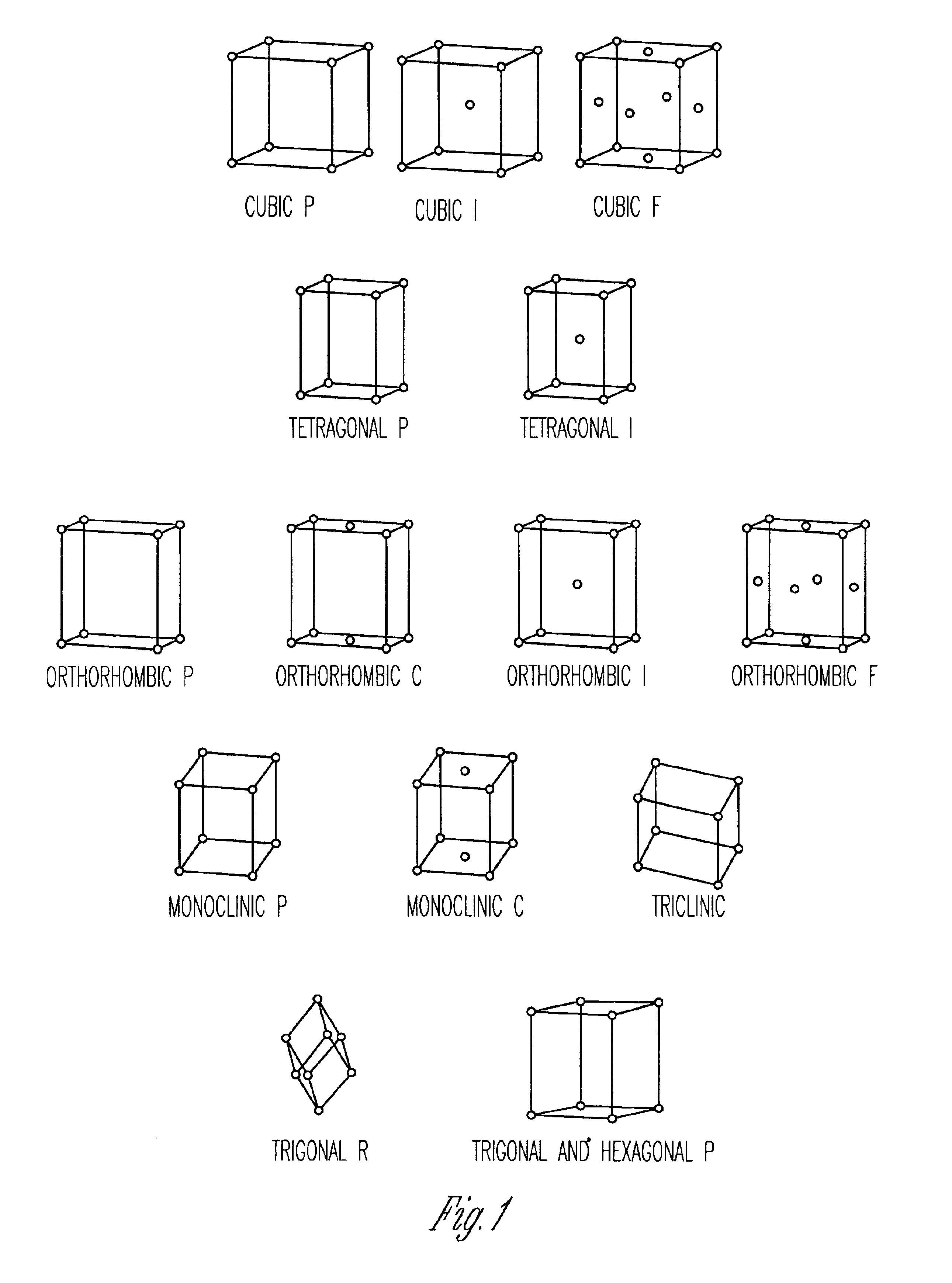
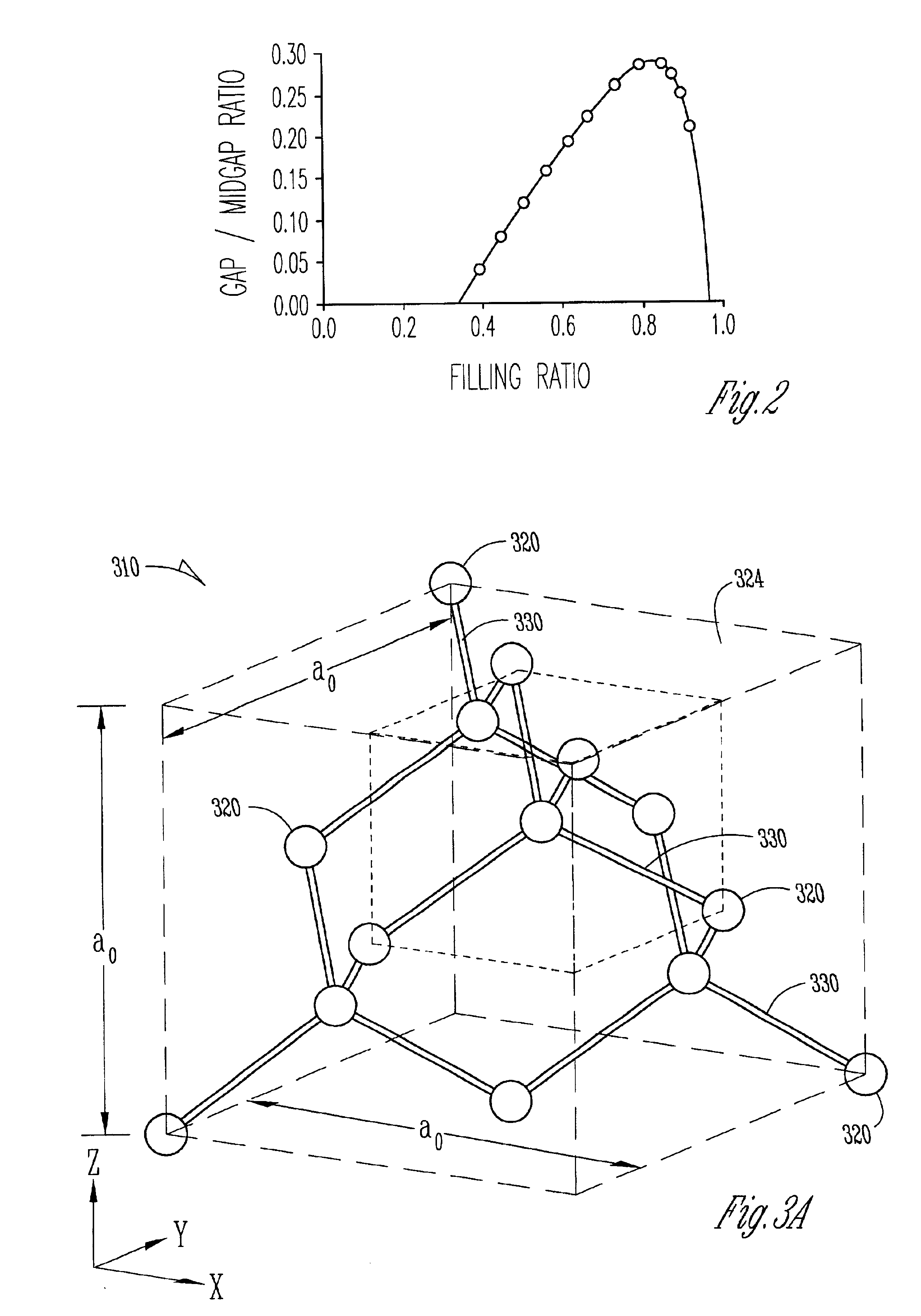
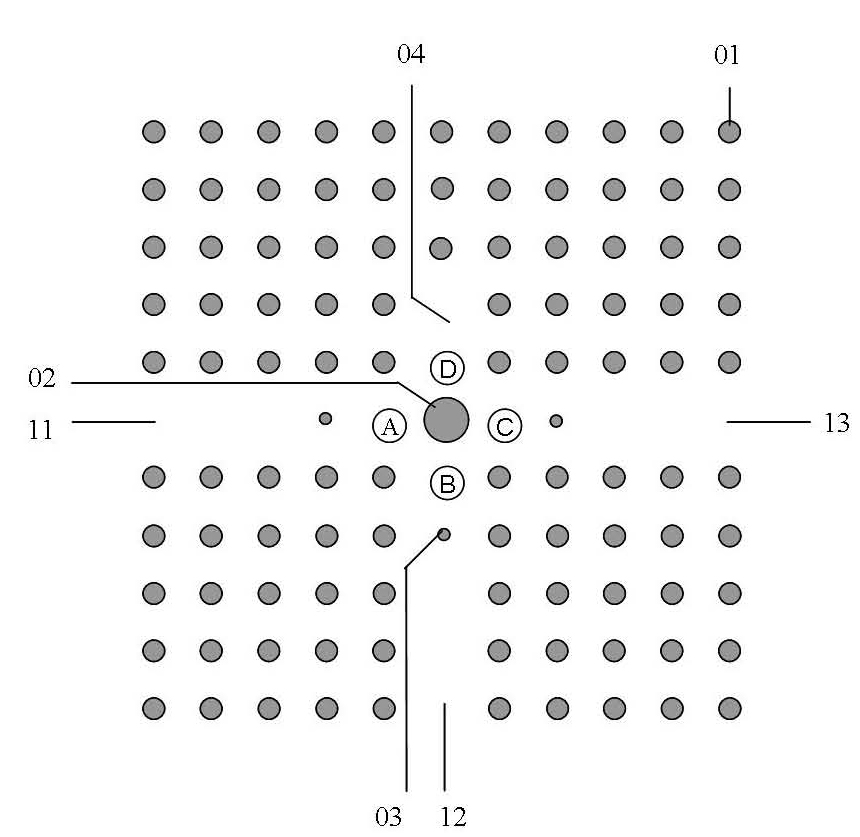
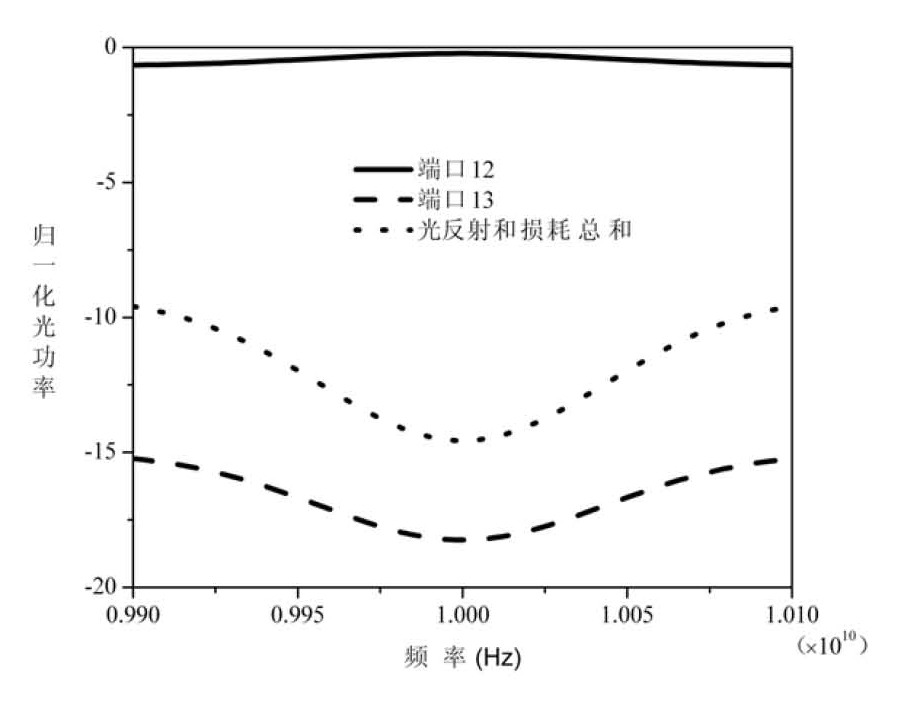
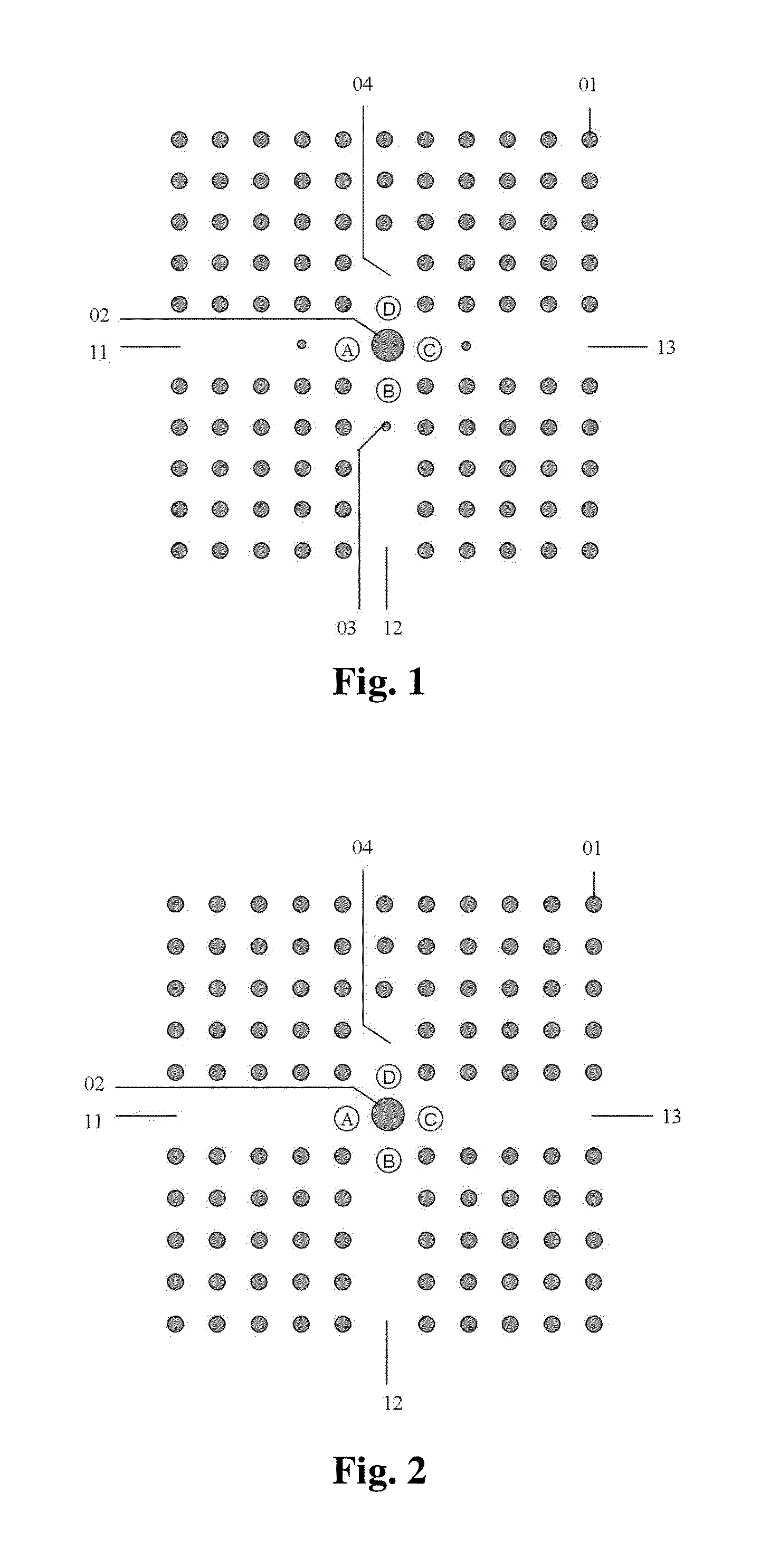
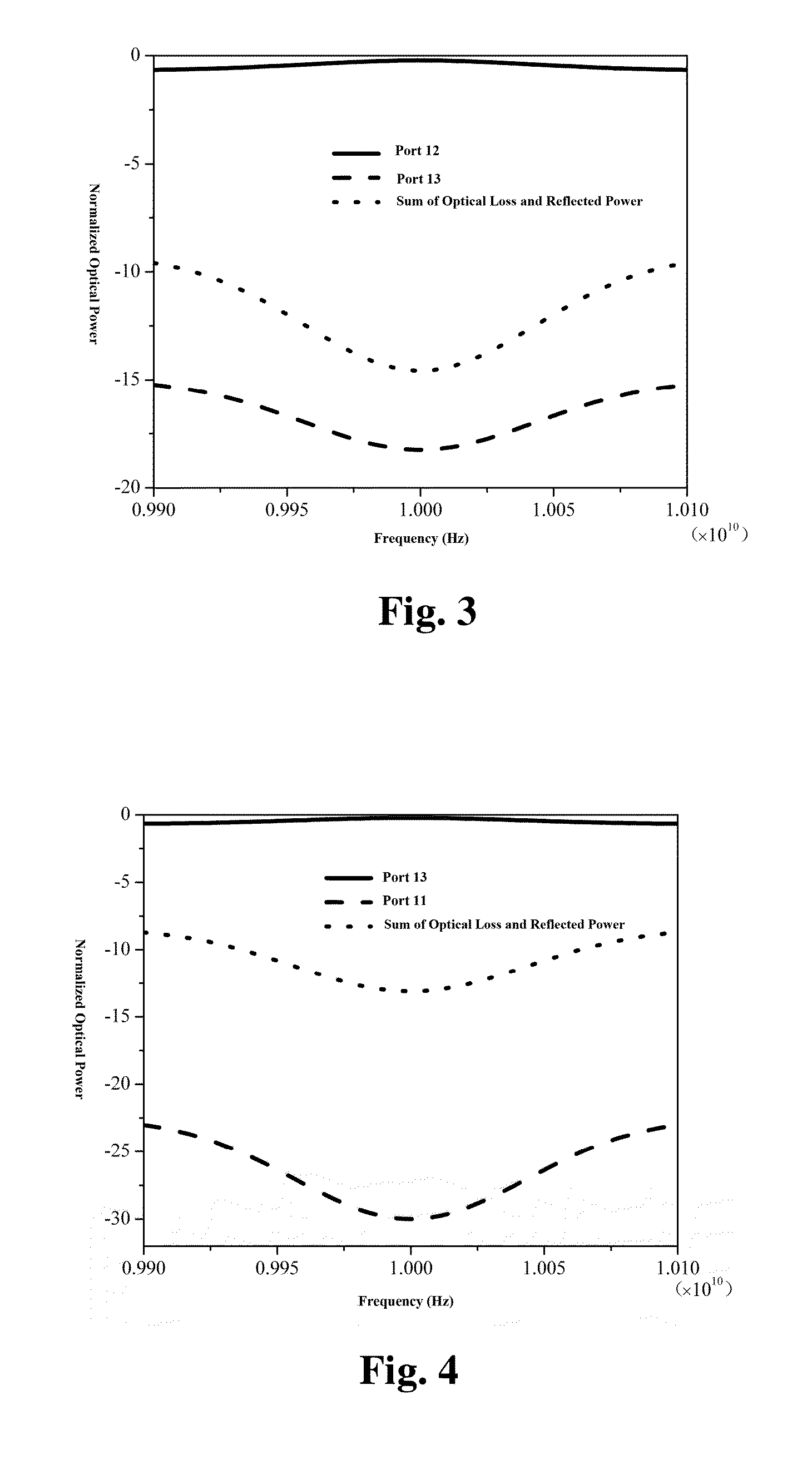
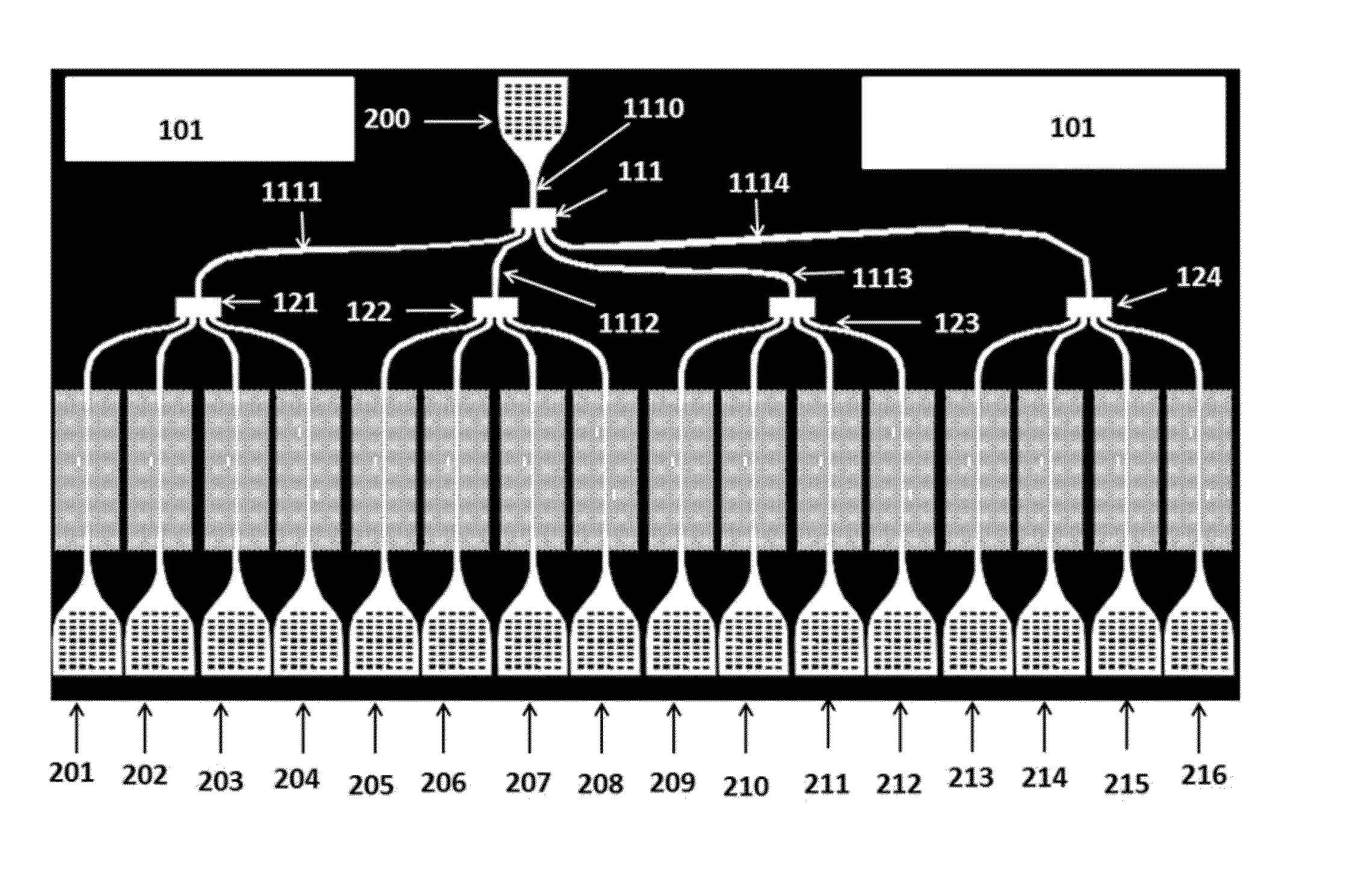
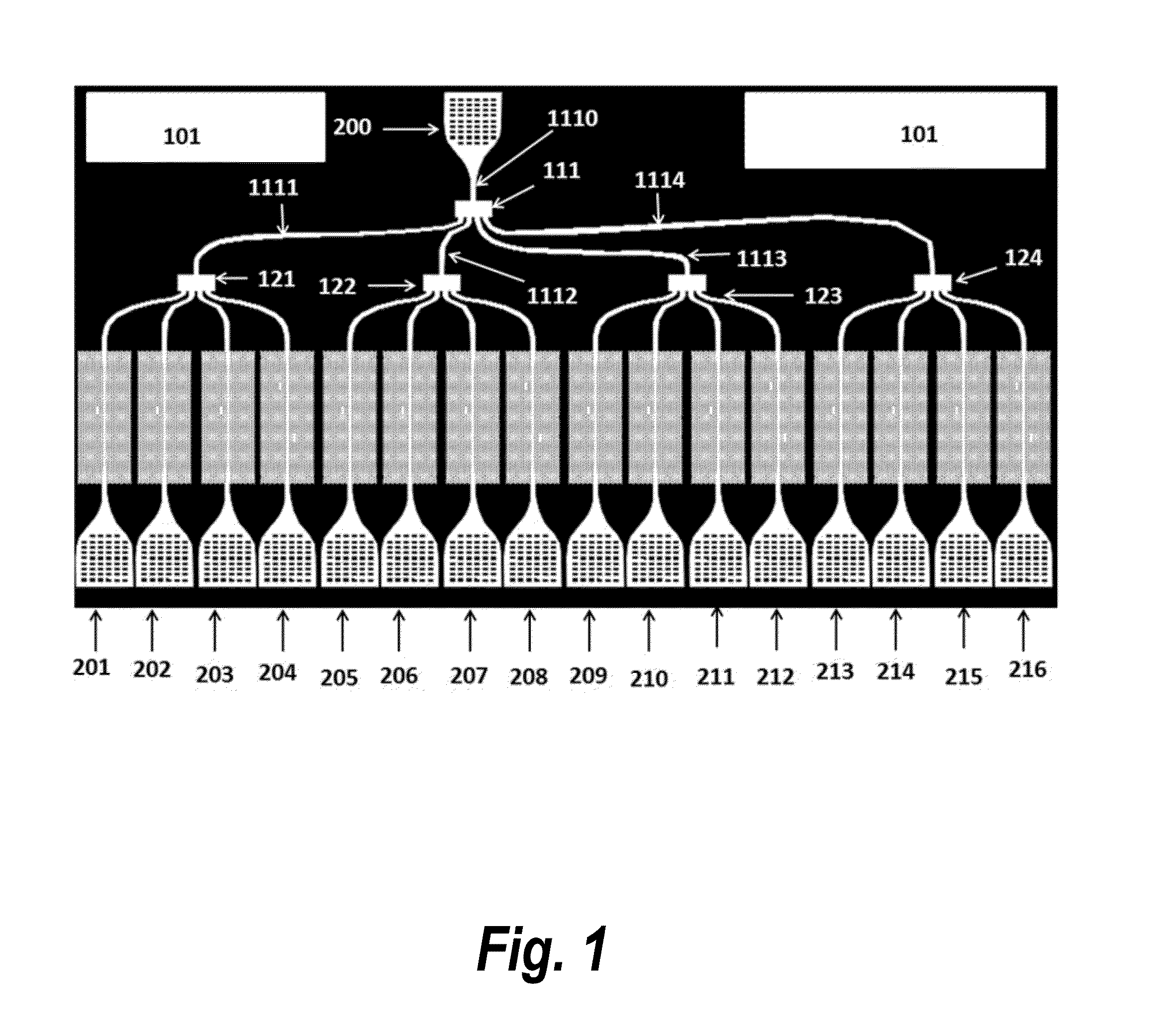
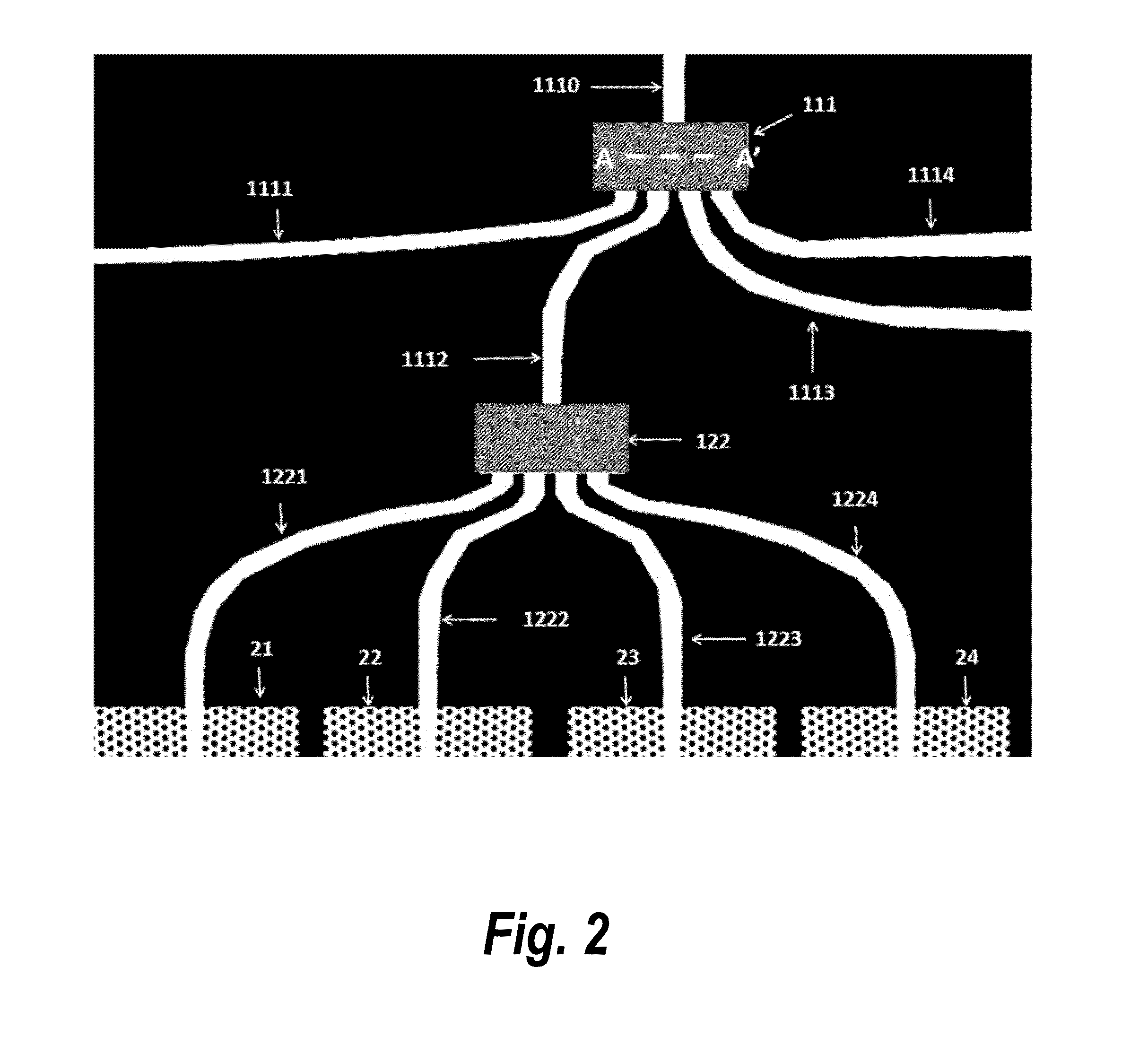
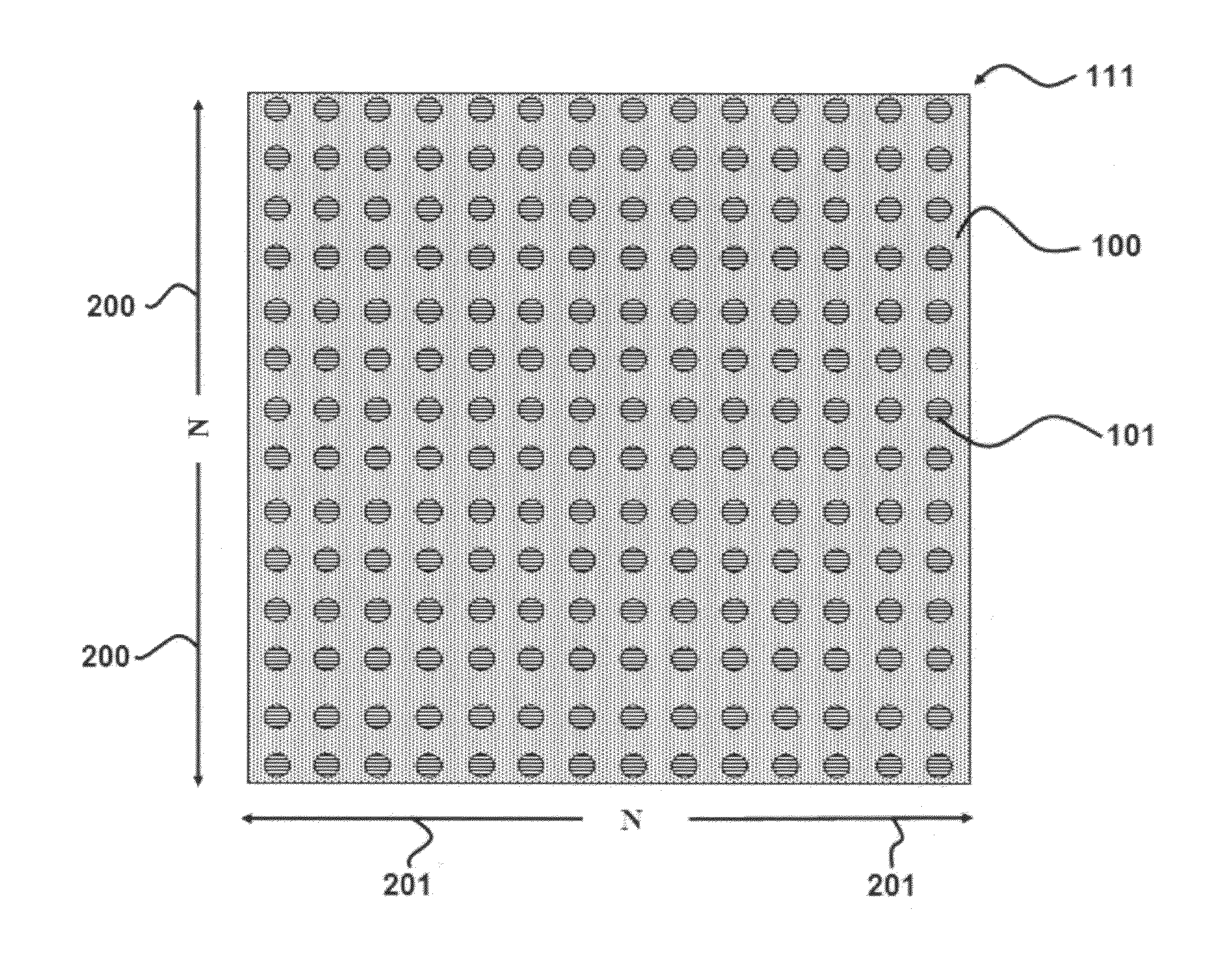
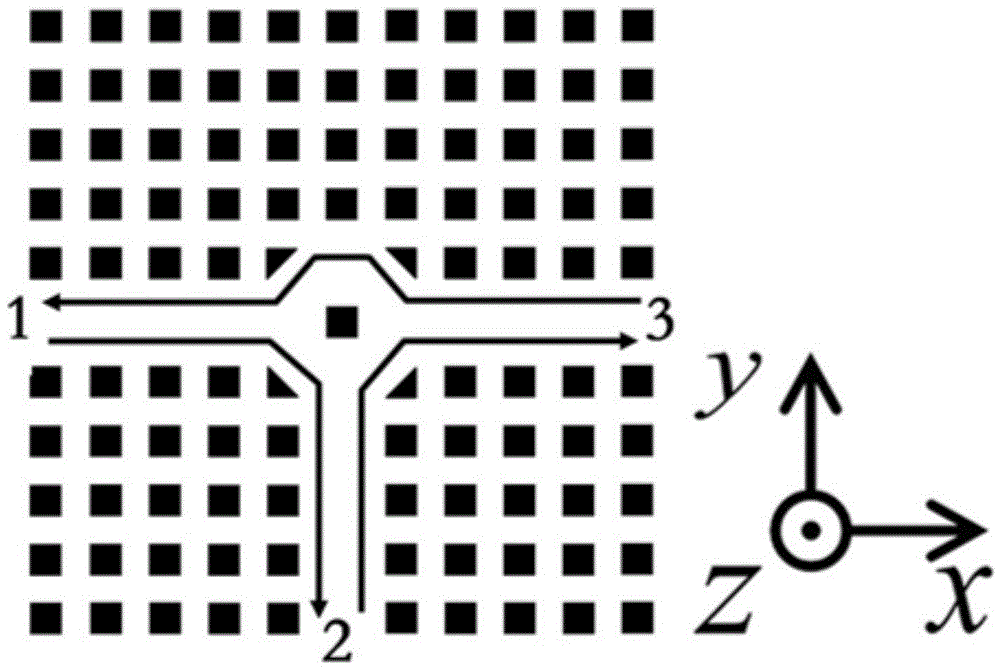
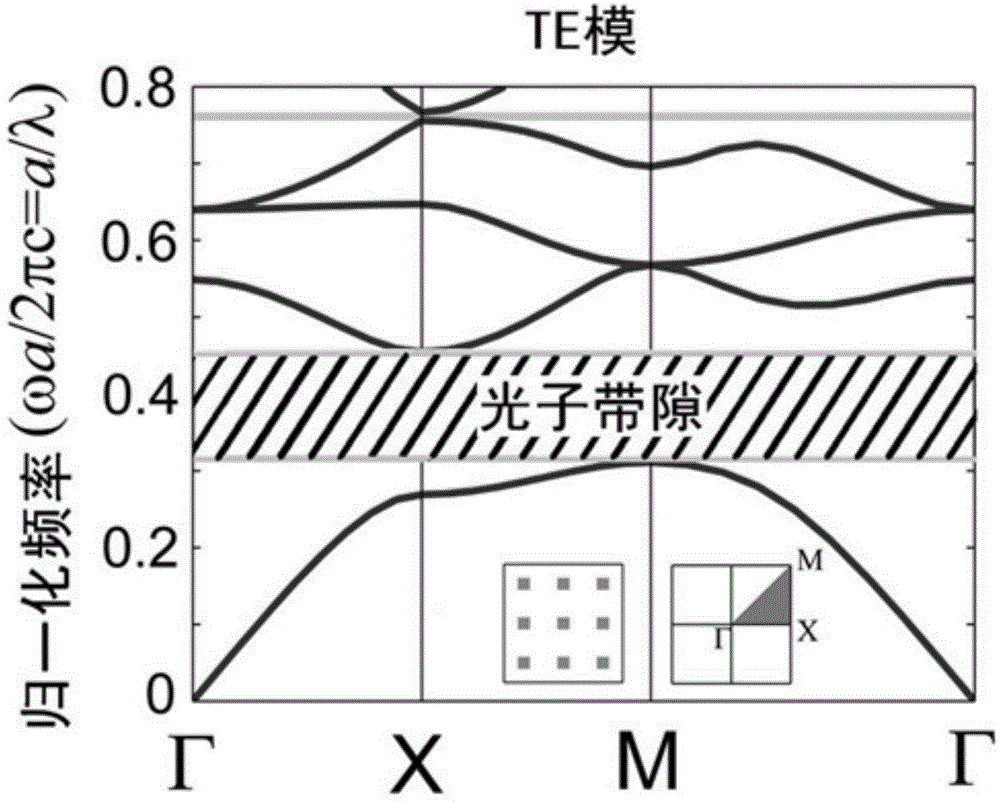
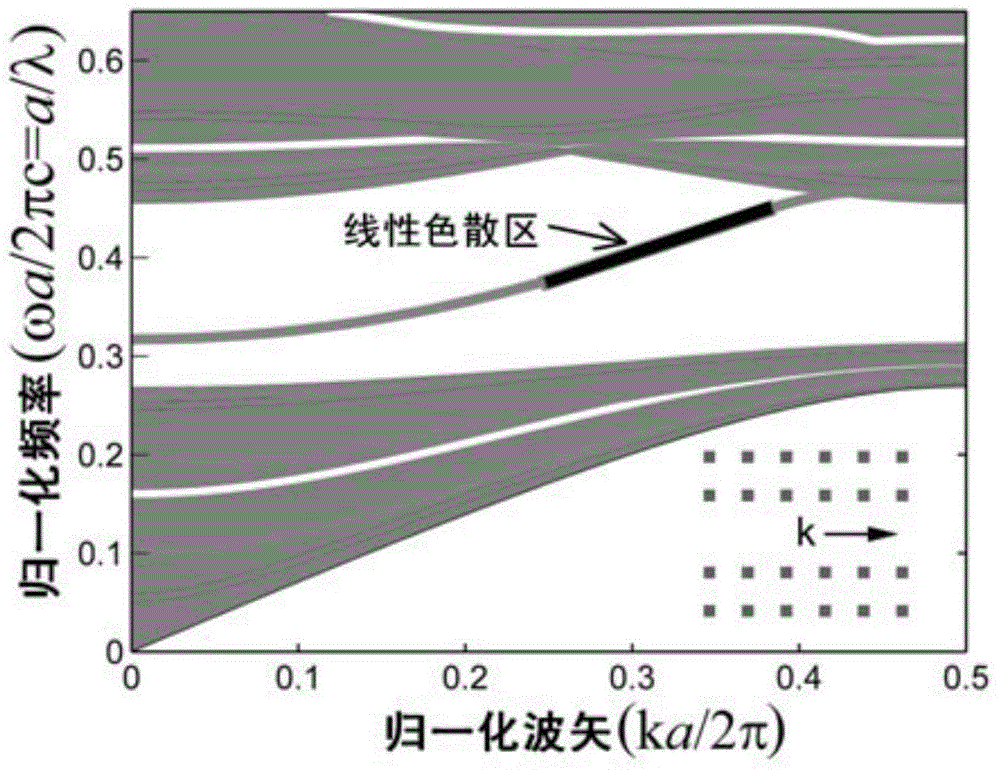
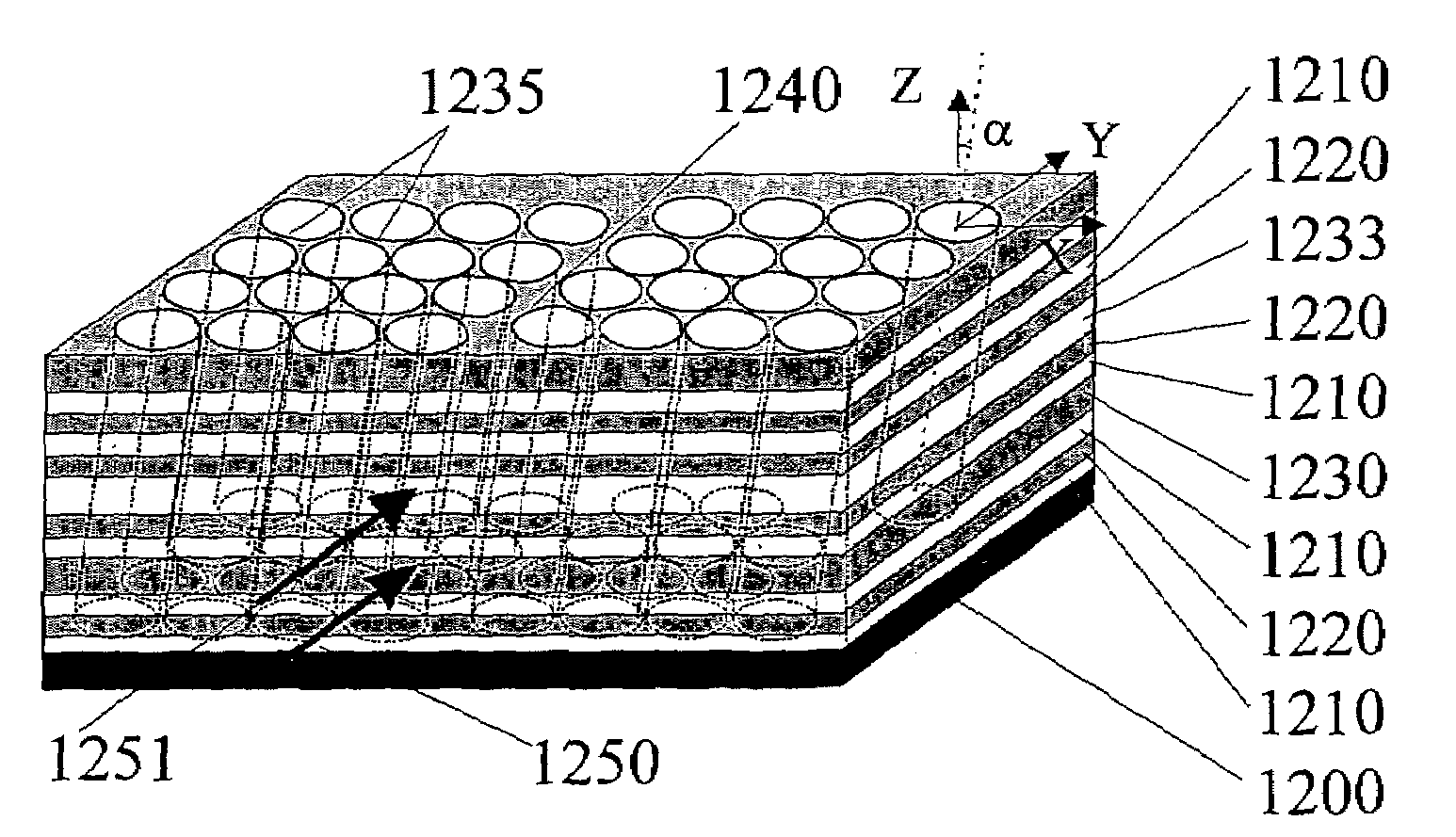
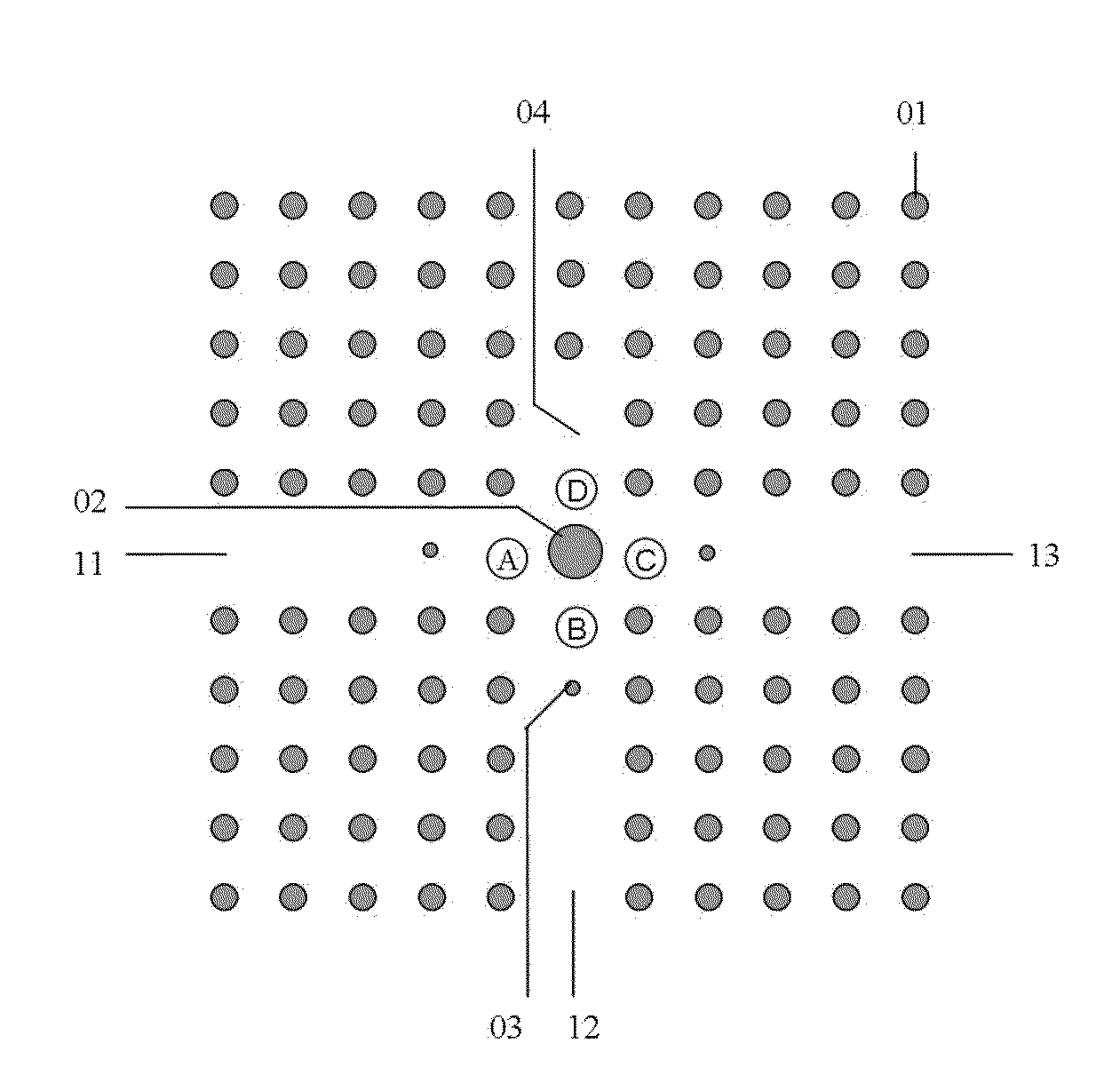Patents
Literature
286 results about "Photonic crystal waveguides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Active photonic crystal waveguide device and method
InactiveUS20020021878A1Reduce device sizeNanoopticsCoupling light guidesOptical propertyPhotonic bandgap
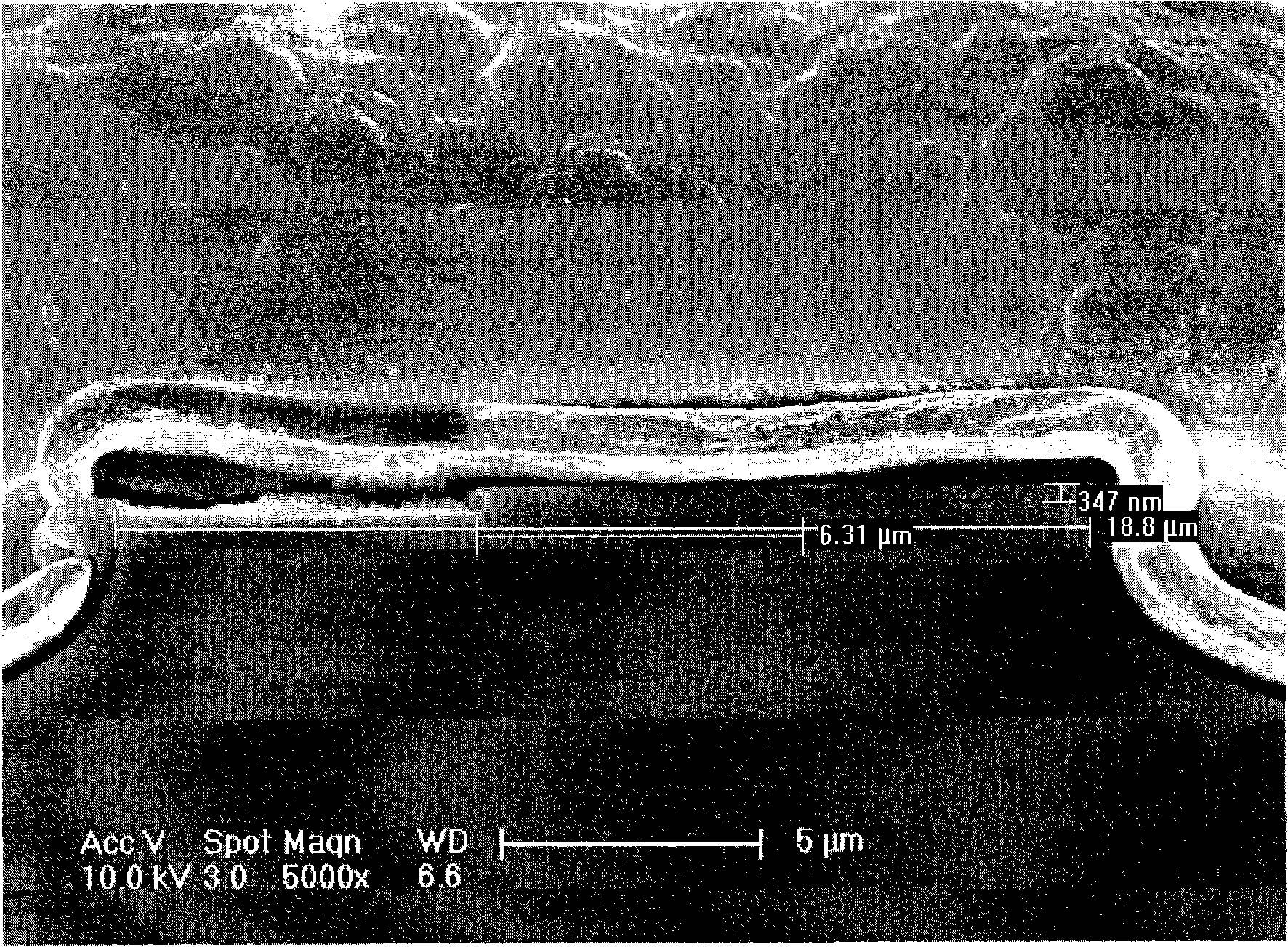
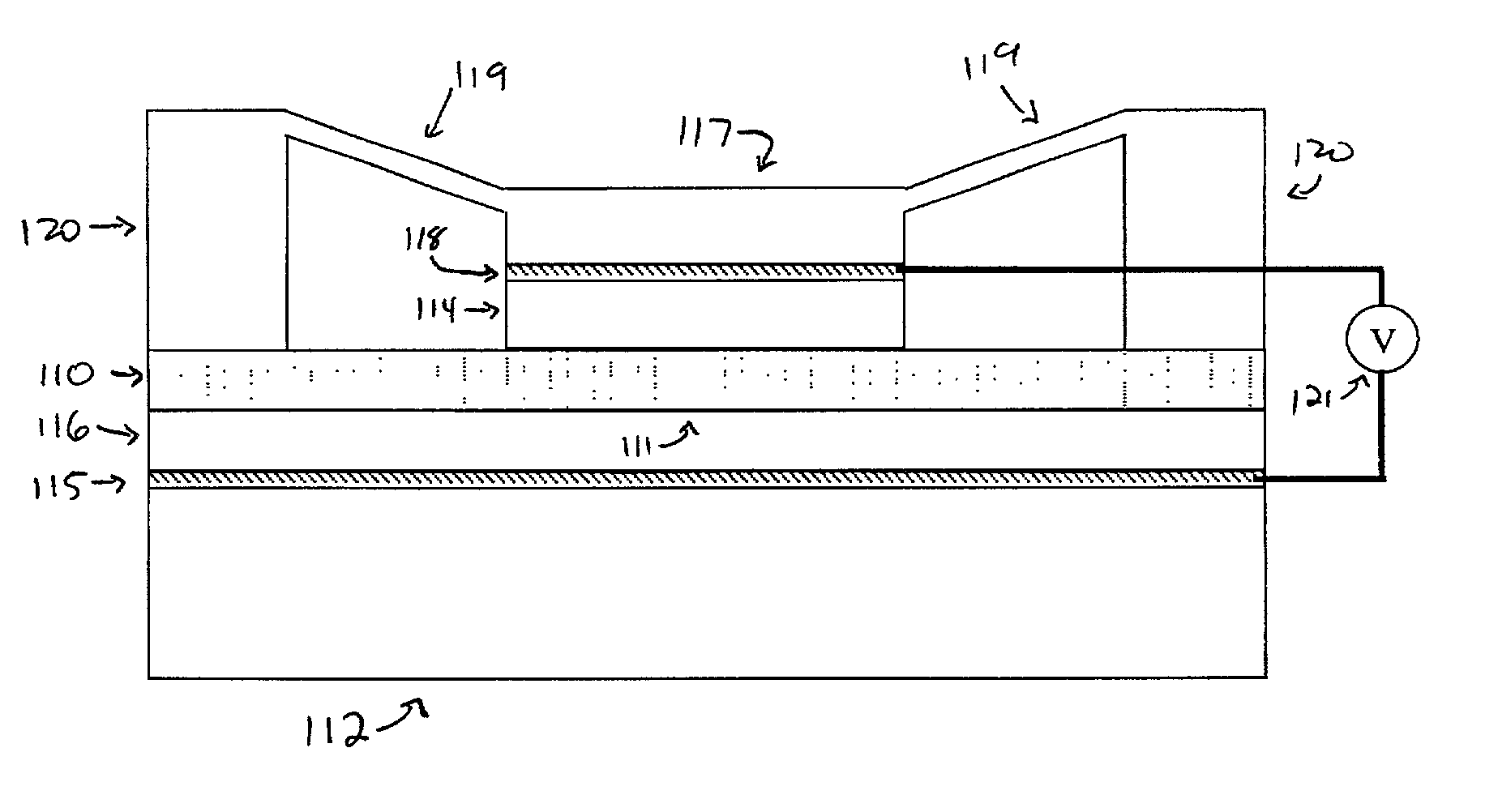
An active photonic crystal device for controlling an optical signal is disclosed. The device includes a planar photonic crystal with a defect waveguide bounded on the top and bottom by an upper cladding region and a lower cladding region. An optical signal propagating in the defect waveguide is confined in the plane of the photonic crystal by the photonic bandgap, and in the direction normal to the photonic crystal by the upper clad region and the lower clad region. The propagation of the optical signal in the defect waveguide is controlled by varying the optical properties at least one of the upper clad region or the lower clad region. The variation of the optical properties of the controllable regions may be achieved using a thermo-optic effect, an electro-optic effect, a stress-optic effect, or a mechano-optic effect, or by moving a material into or out of the controllable region.
Owner:CORNING INC
Three-dimensional photonic crystal waveguide structure and method
InactiveUS6898362B2Polycrystalline material growthLaser optical resonator constructionPhotonic bandgapSolid substrate
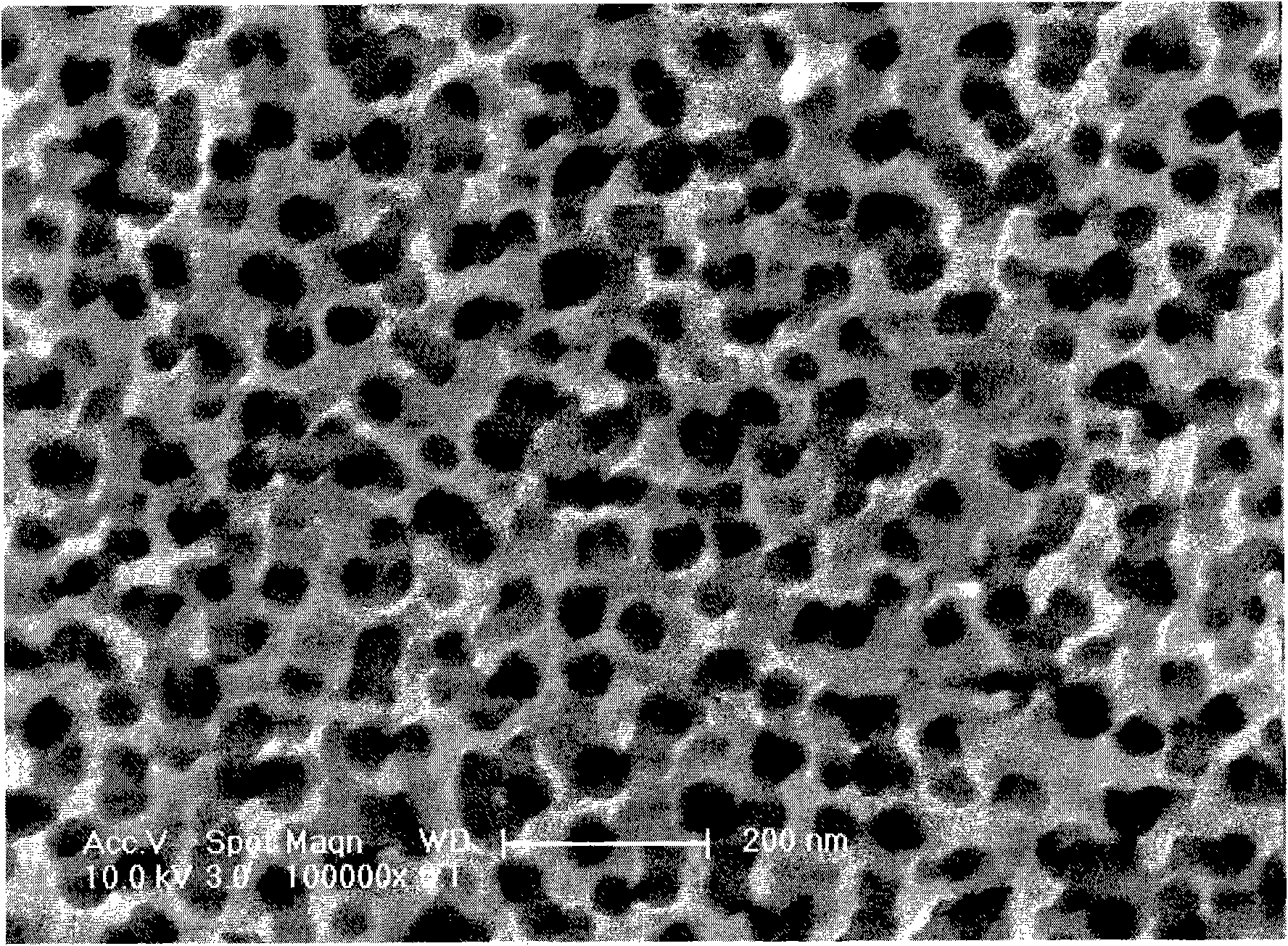
A waveguide structure formed with a three-dimensional (3D) photonic crystal is disclosed. The 3D photonic crystal comprises a periodic array of voids formed in a solid substrate. The voids are arranged to create a complete photonic bandgap. The voids may be formed using a technique called “surface transformation,” which involves forming holes in the substrate surface, and annealing the substrate to initiate migration of the substrate near the surface to form voids in the substrate. A channel capable of transmitting radiation corresponding to the complete bandgap is formed in the 3D photonic crystal, thus forming the waveguide. The waveguide may be formed by interfacing two 3D photonic crystal regions, with at least one of the regions having a channel formed therein. The bandgap wavelength can be chosen by arranging the periodic array of voids to have a lattice constant a fraction of the bandgap wavelength.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Photonic crystal magneto-optical circulator and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102043261AWell formedCompact structureOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsPhotonic crystalCross connection
The invention relates to a photonic crystal magneto-optical circulator comprising a first medium material columns in an air background, the first medium material columns are arranged in the shape of two-dimensional tetragonal lattice; the photonic crystal magneto-optical circulator also comprises a photonic crystal waveguide which includes a transverse photonic crystal waveguide and a longitudinal photonic crystal waveguide which are mutually intercrossed, a second medium material column used for guiding light and positioned at the cross connection of the transverse photonic crystal waveguideand the longitudinal photonic crystal waveguide, four identical magneto-optical material columns uniformly positioned around the second medium material columns, and at least three identical third medium material columns respectively positioned outside the three magneto-optical material columns. The photonic crystal magneto-optical circulator provided by the invention can respectively realize single direction optical circulating transmission among three ports arranged in the shape of T and among four ports arranged in the shape of a cross. The photonic crystal magneto-optical circulator provided by the invention is advantageous in that it has a concise form and a compact structure, and is suitable for serving as an anti-interference component in a photonic crystal integrated optical circuit.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Photonic Crystal Magneto-Optical Circulator and Manufacturing Method Thereof
InactiveUS20130223805A1Valid matchWell formedOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical articlesElectricityDielectric
The invention relates to a photonic crystal magneto-optical circulator, which comprises first dielectric material columns in an air background, wherein the first dielectric material columns are arranged in the form of two-dimensional square lattice. The photonic crystal magneto-optical circulator also comprises a “T-shaped” or a “cross-shaped” photonic crystal waveguide, a second dielectric material column, four same magneto-optical material columns and at least three same third dielectric material columns, wherein the “T-shaped” or a “cross-shaped” photonic crystal waveguide comprises a horizontal photonic crystal waveguide and a vertical photonic crystal waveguide which are intercrossed; the second dielectric material column is arranged at a cross-connected position of the horizontal photonic crystal waveguide and the vertical photonic crystal waveguide and has the function of light guiding; the four same magneto-optical material columns are uniformly arranged on the periphery of the second dielectric material column; and at least three same third dielectric material columns.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Packaged chip for multiplexing photonic crystal waveguide and photonic crystal slot waveguide devices for chip-integrated label-free detection and absorption spectroscopy with high throughput, sensitivity, and specificity
ActiveUS20130005606A1Most efficientPrecise positioningRadiation pyrometryColor measuring devicesSlot-waveguidePhotonic crystal
Systems and methods for chip-integrated label-free detection and absorption spectroscopy with high throughput, sensitivity, and specificity are disclosed. The invention comprises packaged chips for multiplexing photonic crystal waveguide and photonic crystal slot waveguide devices. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:OMEGA OPTICS
Two-dimensional surface normal slow-light photonic crystal waveguide optical phased array
ActiveUS20120013962A1High thermo-optic coefficientPromote formationCladded optical fibreNanoopticsRefractive indexLaser light
Methods and devices for optical beam steering are disclosed including coupling a laser light into an apparatus comprising a first substrate; an array of air core photonic crystal waveguides; columnar members etched around each air core waveguide; a pair of metal electrodes around the columnar members; a trench around the pair of metal electrodes surrounding each air core photonic crystal waveguide; a second substrate coupled to the first substrate comprising electrical interconnection lines; and a holographic fanout array comprising a third substrate; a photopolymer film coated on the third substrate; a hologram written in the photopolymer film configured to couple the laser light into the third substrate; and an array of holograms recorded in the photopolymer film configured to couple a portion of the laser light into the waveguides; and passing a current through the electrodes to induce a refractive index change in the first substrate to control the phase of the portion of the laser light that passes through each waveguide. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:OMEGA OPTICS
Apparatus and method for switching, modulation and dynamic control of light transmission using photonic crystals
ActiveUS7421179B1Reduce power consumptionLow heat generationNanoopticsOptical waveguide light guidePhotonicsSilicon oxide
Owner:OMEGA OPTICS
Photonic crystal microarray device for label-free multiple analyte sensing, biosensing and diagnostic assay chips
ActiveUS20110028346A1Increase measurement throughputHigh sensitivityLibrary screeningMaterial analysis by optical meansMultiple speciesThroughput
Methods and systems for label-free multiple analyte sensing, biosensing and diagnostic assay chips consisting of an array of photonic crystal microcavities along a single photonic crystal waveguide are disclosed. The invention comprises an on-chip integrated microarray device that enables detection and identification of multiple species to be performed simultaneously using optical techniques leading to a high throughput device for chemical sensing, biosensing and medical diagnostics. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:OMEGA OPTICS
Photonic crystal waveguide based superefficient compact T-shaped circulator
The invention discloses a photonic crystal waveguide based superefficient compact T-shaped circulator. The photonic crystal waveguide based superefficient compact T-shaped circulator comprises a T-shaped photonic crystal waveguide with three end openings; a square magneto-optical dielectric rod is arranged in the center of the T-shaped photonic crystal waveguide; four square dielectric rods are arranged at four corners in the center of the crisscrossing waveguide; angles of the four square dielectric rods are cut to form into isosceles right triangles with the length of right angle sides to be identical to that of sides of background square dielectric rods to form into corner dielectric rods; the corner dielectric rods and left parts at corresponding lattice point positions of the corner dielectric rods are coincided or not; the insertion loss of the circulator is from 0.02db to 1db and the isolation of the two end openings is larger than 14db. The photonic crystal waveguide based superefficient compact T-shaped circulator has the advantages of being small in size, high in integration level, high in electromagnetic wave transmission efficiency, beneficial to integration and efficient and allowing circuiting and being widely applied to microwave, terahertz and light communication wave bands.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Integrated photonic crystal structure and method of producing same
InactiveUS7194174B2Effectively reflecting and transmitting and filtering and confiningIncrease the gapNanoopticsCoupling light guidesRadiation lossRefractive index
An integrated photonic crystal (IPC) structure and method of producing the same in which the IPC structure includes a first layered sub-structure with a surface and a one-dimensional periodic refractive index variation along the direction perpendicular to the surface, and a second sub-structure with a plurality of essentially straight identical passages arranged in a two-dimensional periodic pattern cutting through the layered structure at an angle α. First and second defects in the first and second sub-structures, respectively, enable electromagnetic modes to be localized in the vicinity of the defects and allow photonic crystal waveguide to be constructed that can control and filter light very efficiently and minimize radiation losses.
Owner:IGNIS PHOTONYX AS
Integrated photon crystal double waveguide back coupling fluid refractive index sensor
InactiveCN101021593AEasy plane integrationHigh Sensitivity FeaturesPhase-affecting property measurementsCoupling light guidesLight energyPhotonic crystal structure
The invention belongs to the photoelectronic technical field, characterized in that: it adopts electron beam exposure and dry-etching process to form a photon crystal double-waveguide structure on semiconductor, where the two ends of the photon crystal waveguide are connected with light guide connection light waveguides and it removes part of the sacrificial layer by wet etching process to form a bridge support structure. By reverse coupling action of the photon crystal double waveguide, the light of evenly symmetric transmission mode cross over frequency can be reversely coupled from straight-through waveguide into coupling waveguide so as to cause the transmission spectrum of the straight-through waveguide has obvious hollows. When the detected fluid fills periodical holes of photon crystal or upper and lower spaces of the photon crystal layer, dispersion characteristic of the transmission mode in the photon crystal double waveguide is changed, or changed by external force, which can cause variation of evenly symmetric transmission mode cross over frequency so as to cause variation of transmission spectrum of the straight-through waveguide, thus implementing microflow refractivity detection and sensing of high sensitivity and integrated photon crystal structure.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
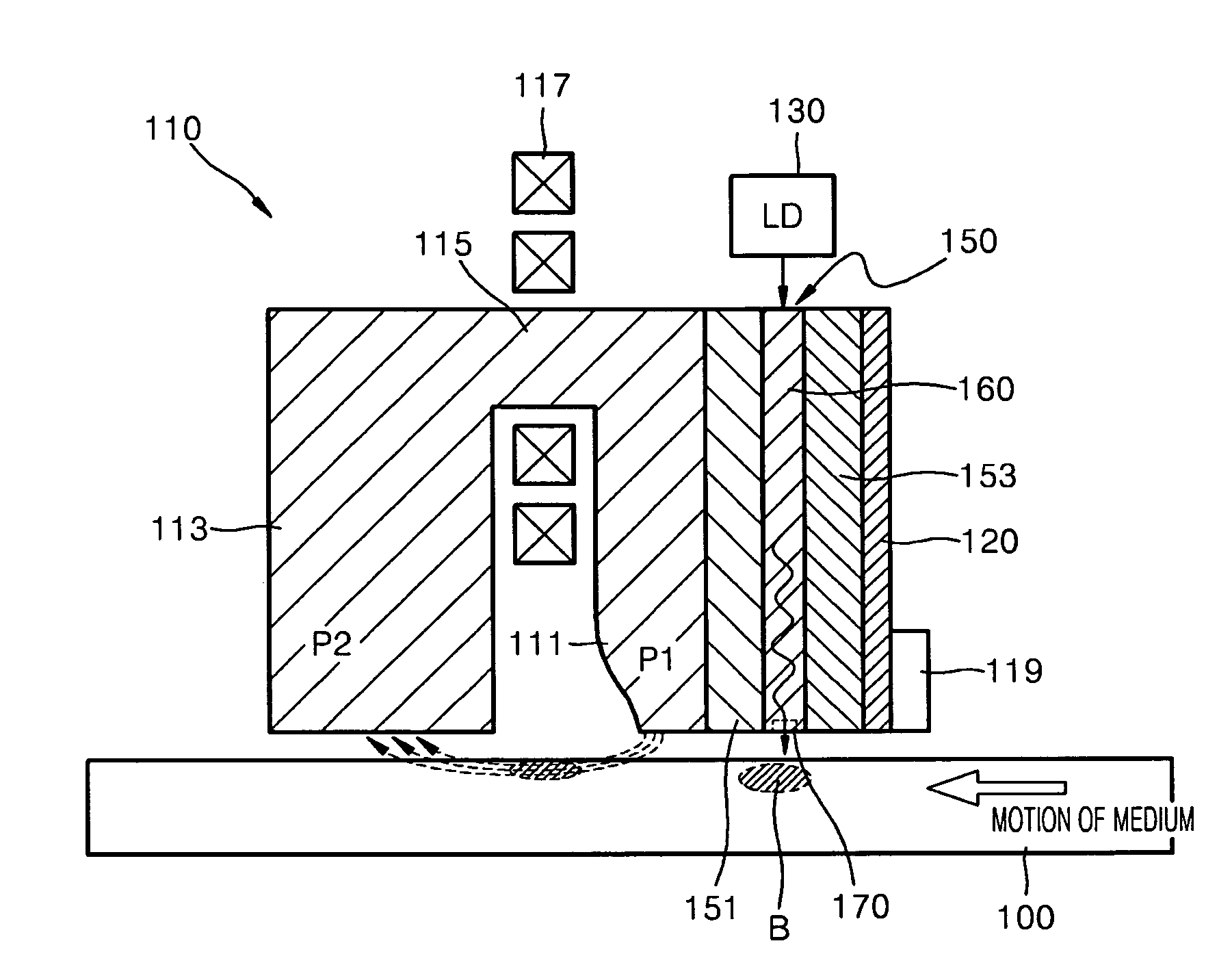
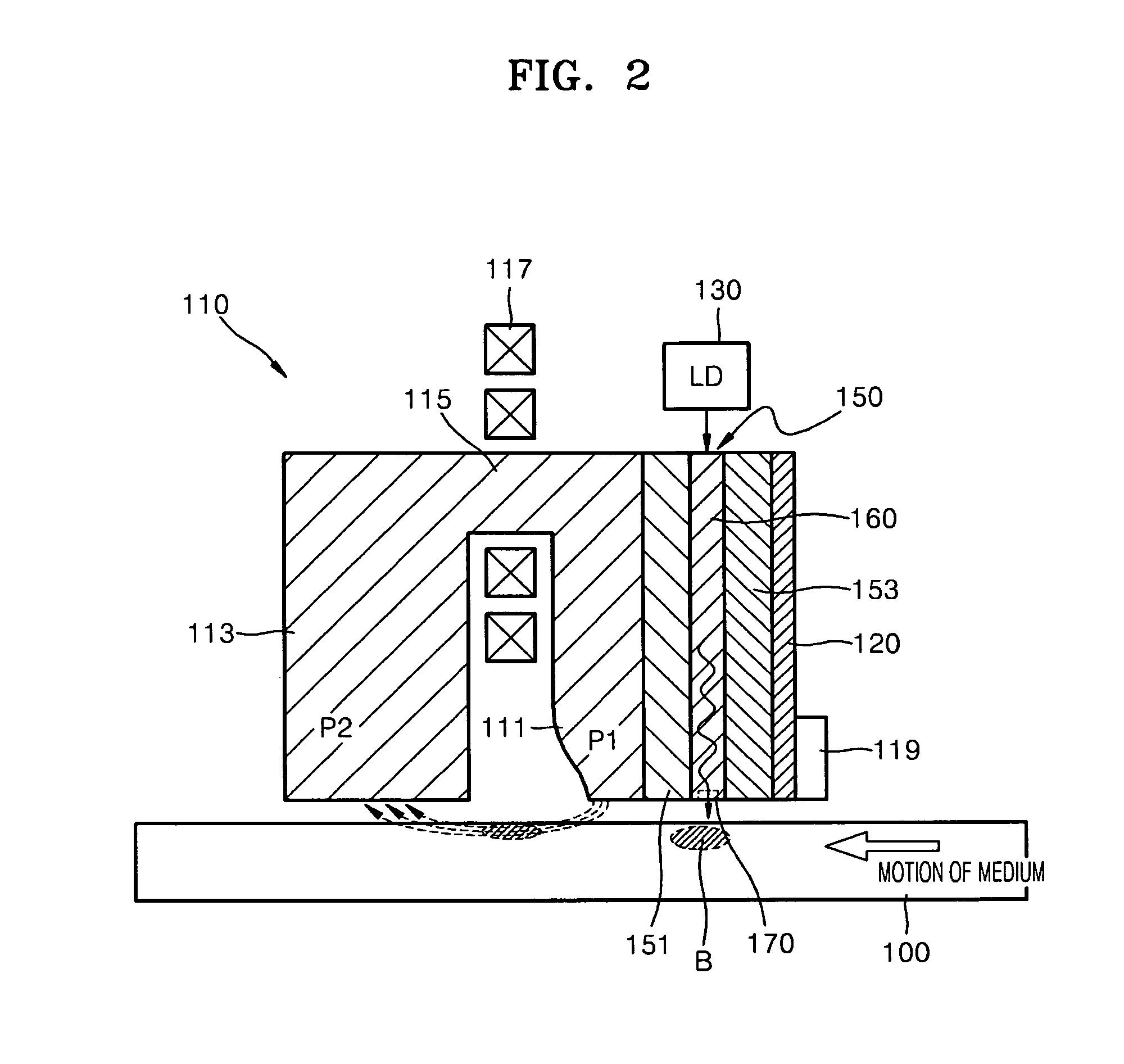
Heat-assisted magnetic recording head and method of manufacturing the same
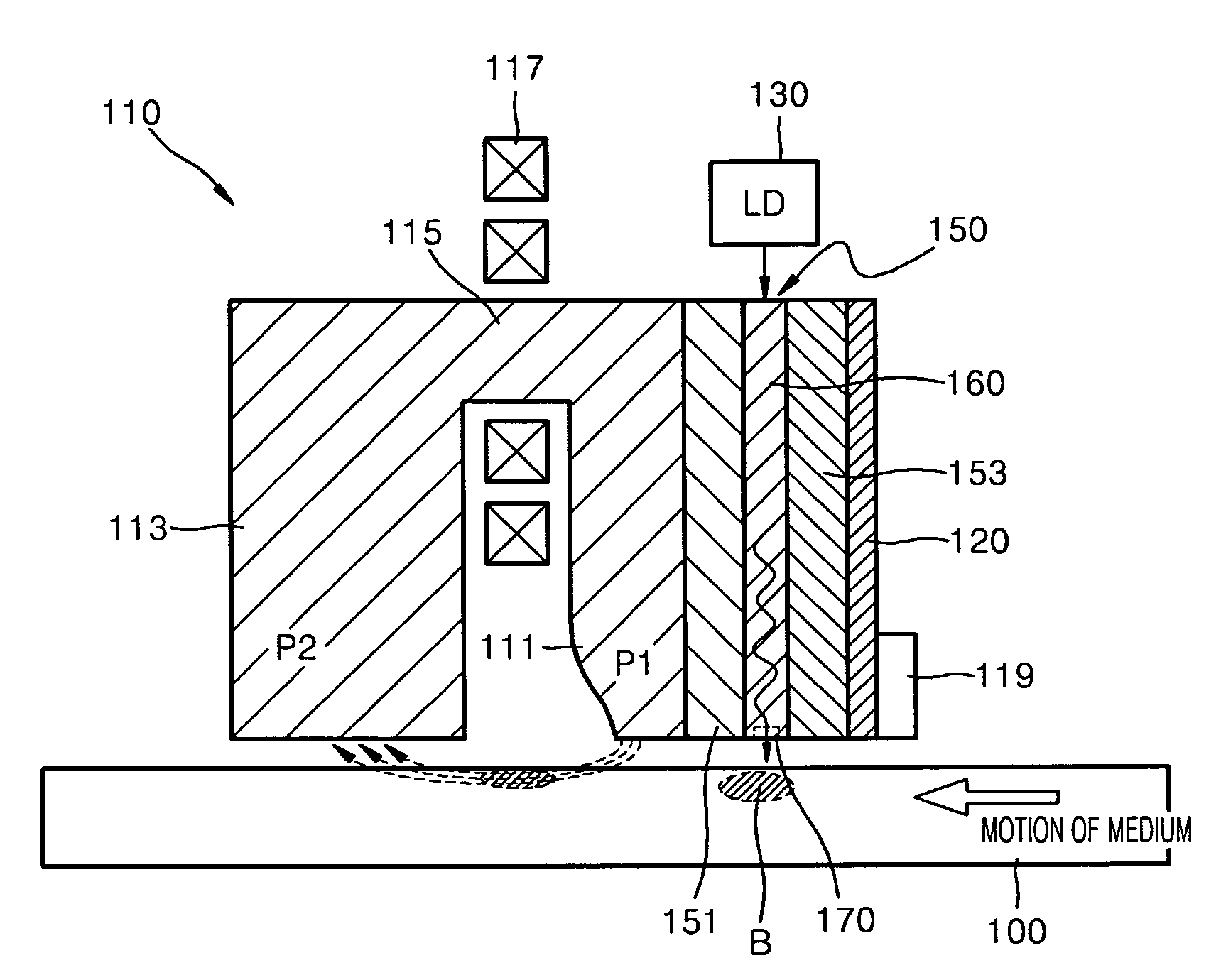
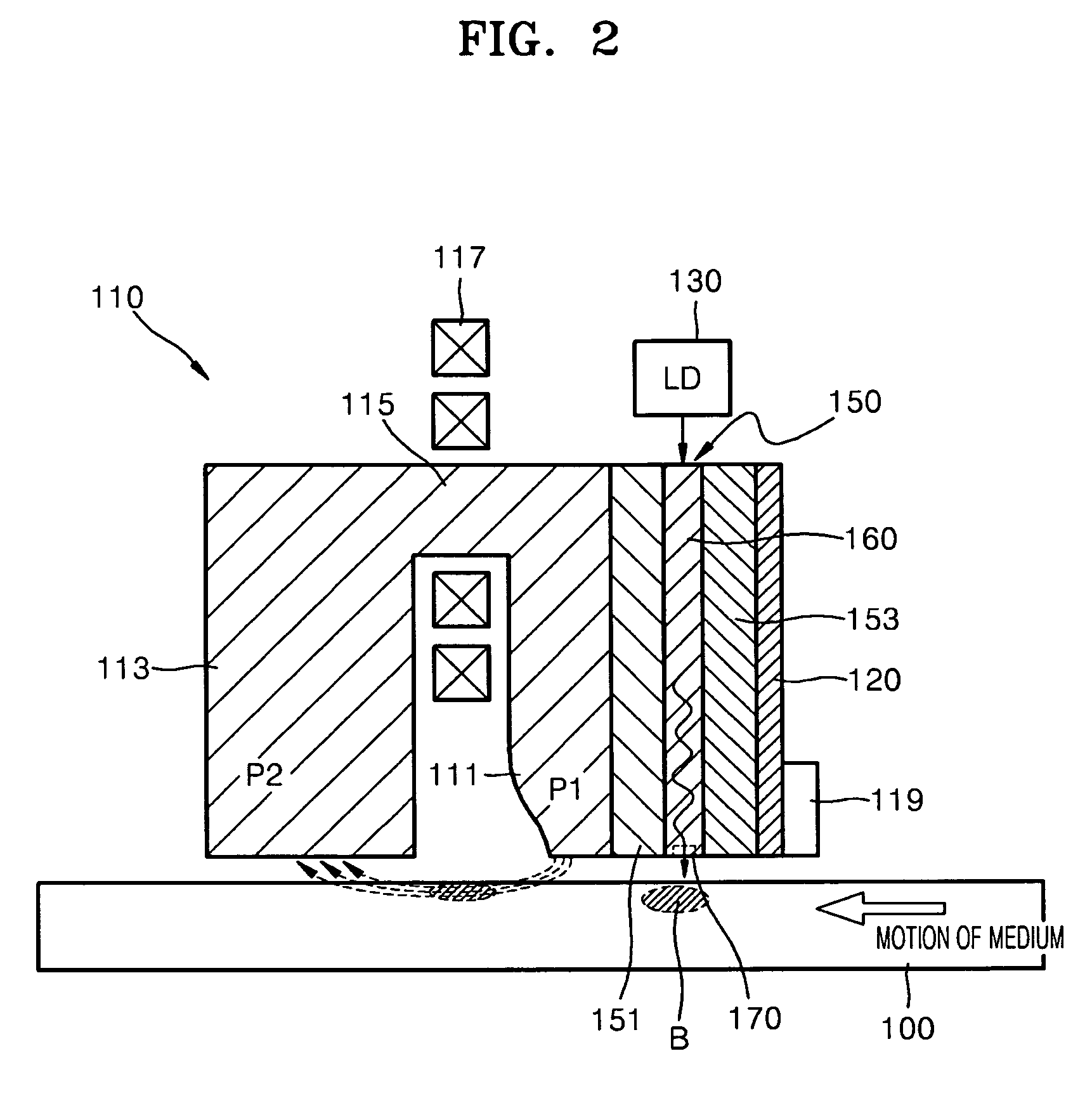
InactiveUS7710686B2High densitySmall sizeRecord information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing methodsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingLight guide
A heat-assisted magnetic recording head (HAMR) head includes a magnetic recording head including a recording pole for applying a magnetic recording field on a magnetic recording medium and a return pole magnetically connected to the recording pole to form a magnetic path, a light source for emitting light, and an optical transmission module including an photonic crystal waveguide disposed at a side of the magnetic recording head to guide light incident from the light source and a nano aperture for enhancing an optical field by varying an intensity distribution of the light guided through the photonic crystal waveguide.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Heat-assisted magnetic recording head and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20070159718A1High densitySmall sizeRecord information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing methodsHeat-assisted magnetic recordingLight guide
A heat-assisted magnetic recording head (HAMR) head includes a magnetic recording head including a recording pole for applying a magnetic recording field on a magnetic recording medium and a return pole magnetically connected to the recording pole to form a magnetic path, a light source for emitting light, and an optical transmission module including an photonic crystal waveguide disposed at a side of the magnetic recording head to guide light incident from the light source and a nano aperture for enhancing an optical field by varying an intensity distribution of the light guided through the photonic crystal waveguide.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Methods, materials and devices for light manipulation with oriented molecular assemblies in micronscale photonic circuit elements with high-q or slow light
InactiveUS20090136181A1Remarkable effectEnhanced interactionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingNanowireFluorescence
An optical device that comprises an input waveguide, an output waveguide, a high-Q resonant or photonic structure that generate slow light connected to the input waveguide and the output waveguide, and an interface, surface or mode volume modified with at least one material formed from a single molecule, an ordered aggregate of molecules or nanostructures. The optical device may include more than one input waveguide, output waveguide, high-Q resonant or photonic structure and interface, surface or mode volume. The high-Q resonant or photonic structure may comprise at least one selected from the group of: microspherical cavities, microtoroidal cavities, microring-cavities, photonic crystal defect cavities, fabry-perot cavities, photonic crystal waveguides. The ordered aggregate of molecules or nanostructures comprises at least one selected from the group of: organic or biological monolayers, biological complexes, cell membranes, bacterial membranes, virus assemblies, nanowire or nanotube assemblies, quantum-dot assemblies, one or more assemblies containing one or more rhodopsins, green fluorescence proteins, diarylethers, lipid bilayers, chloroplasts or components, mitochondria or components, cellular or bacterial organelles or components, bacterial S-layers, photochromic molecules. Further, the molecular aggregate may exhibit a photoinduced response.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Method and apparatus for thermo-optic modulation of optical signals
ActiveUS20050084213A1NanoopticsCoupling light guidesElectrical resistance and conductanceElectricity
The present invention is a method and an apparatus for thermo-optic control of optical signals using photonic crystal structures. In one embodiment, a first portion of a split signal is modulated by propagating the signal through a photonic crystal waveguide in which two electrical contacts are laterally spaced from the waveguide region by a plurality of apertures formed through the photonic crystal substrate. A voltage applied across the electrical contacts causes resistive heating of the proximate photonic crystal waveguide through which the signal propagates, thereby modulating the temperature relative to an un-modulated second portion of the split signal that is used as a reference.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
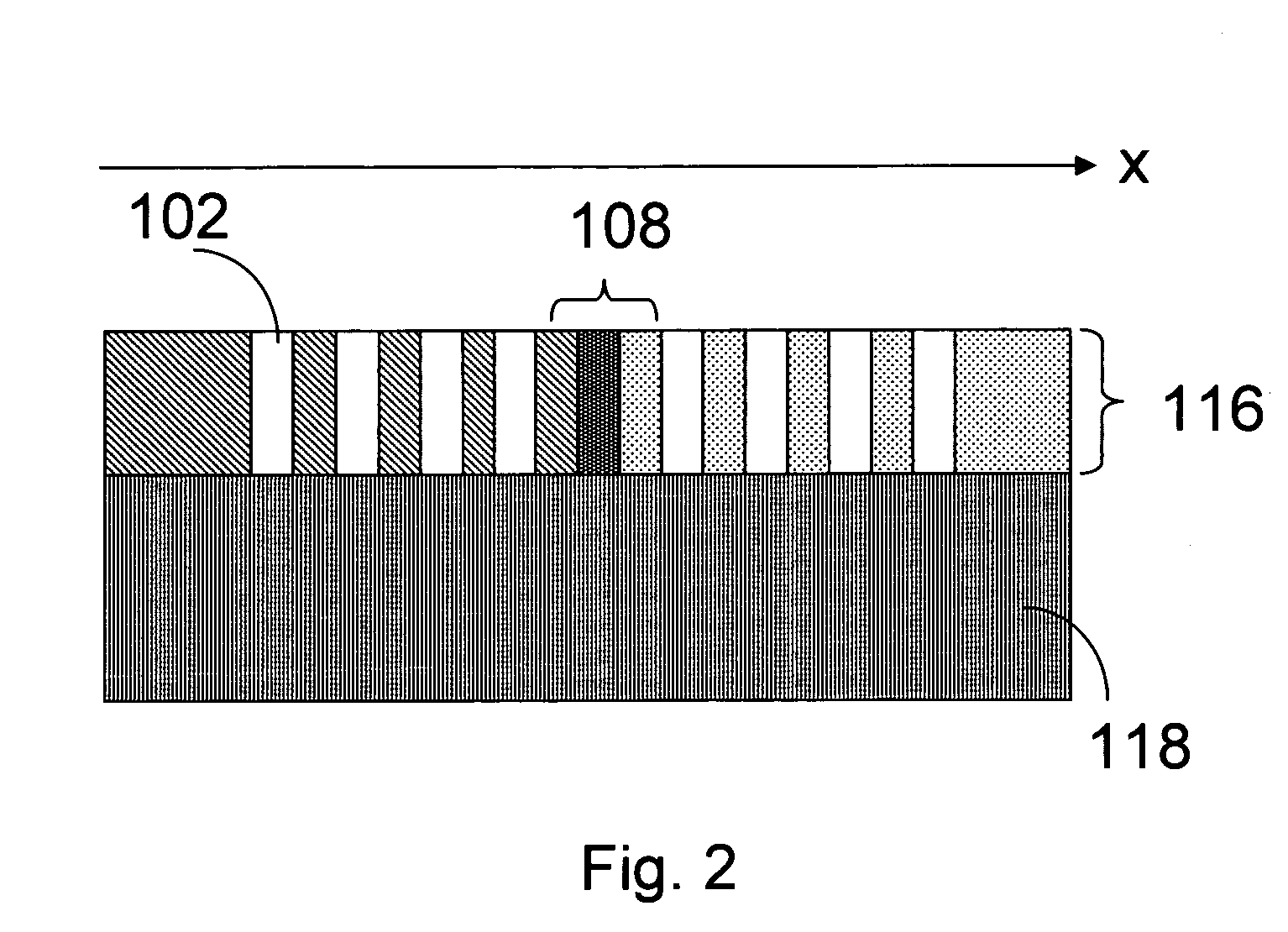
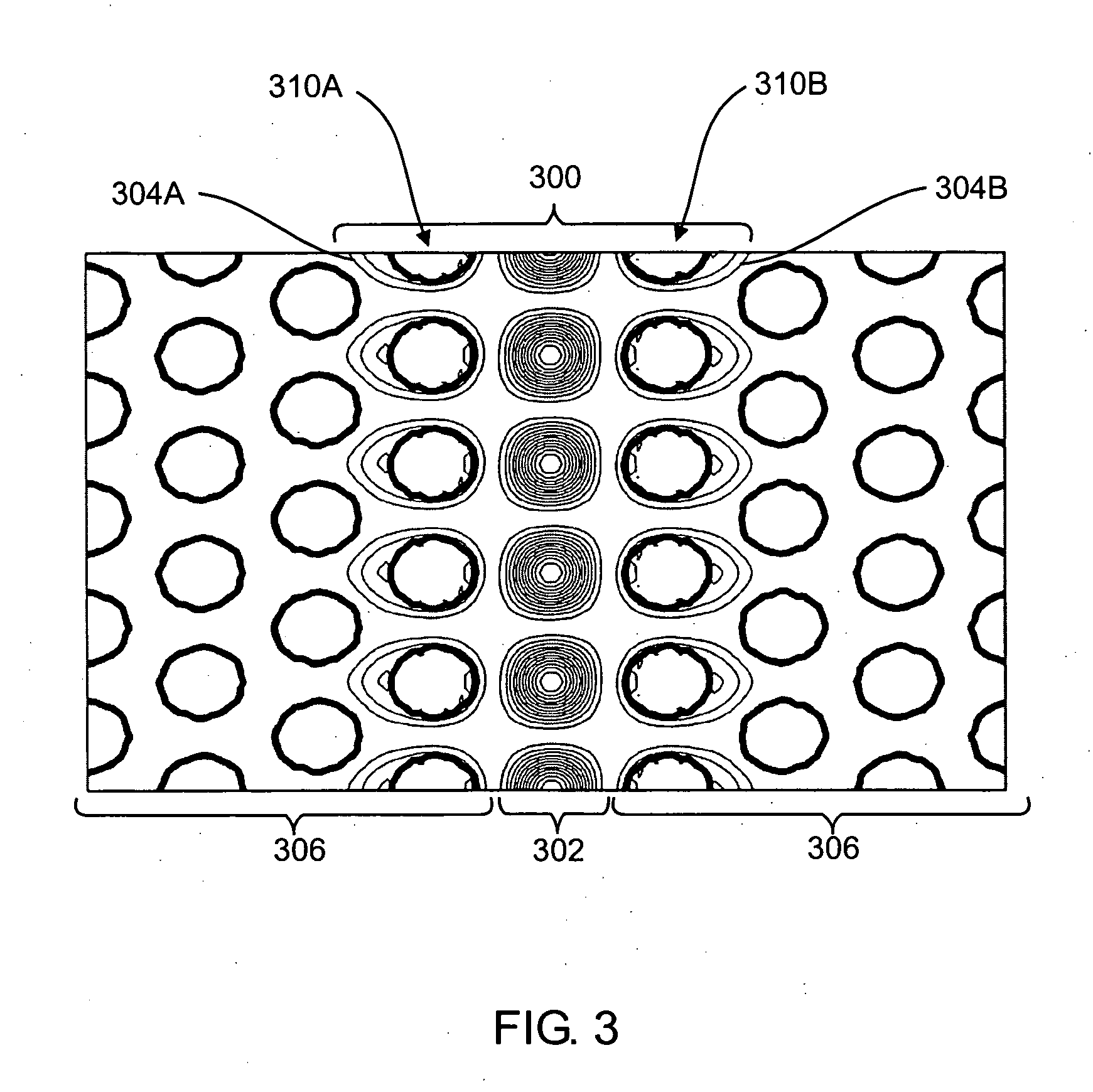
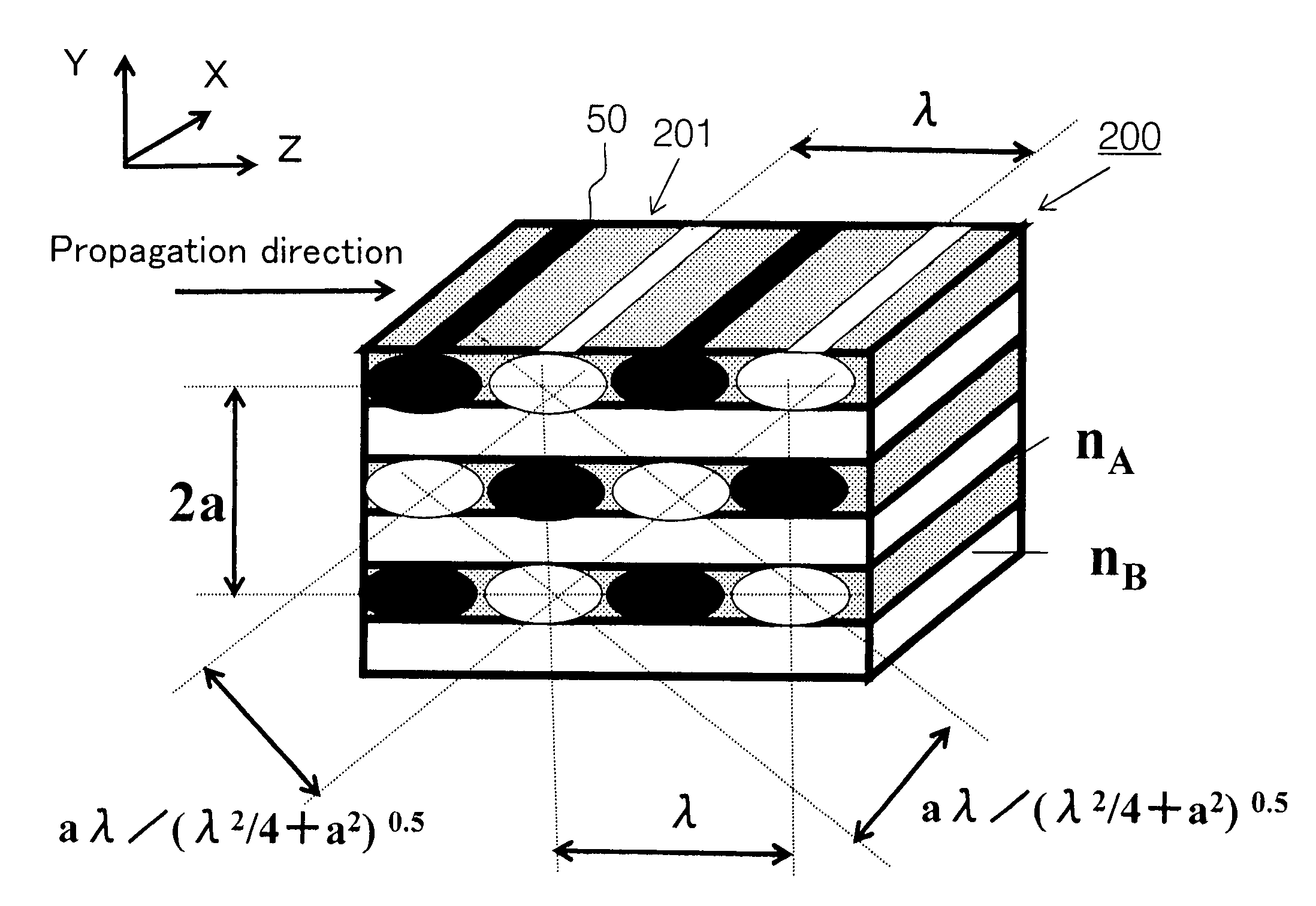
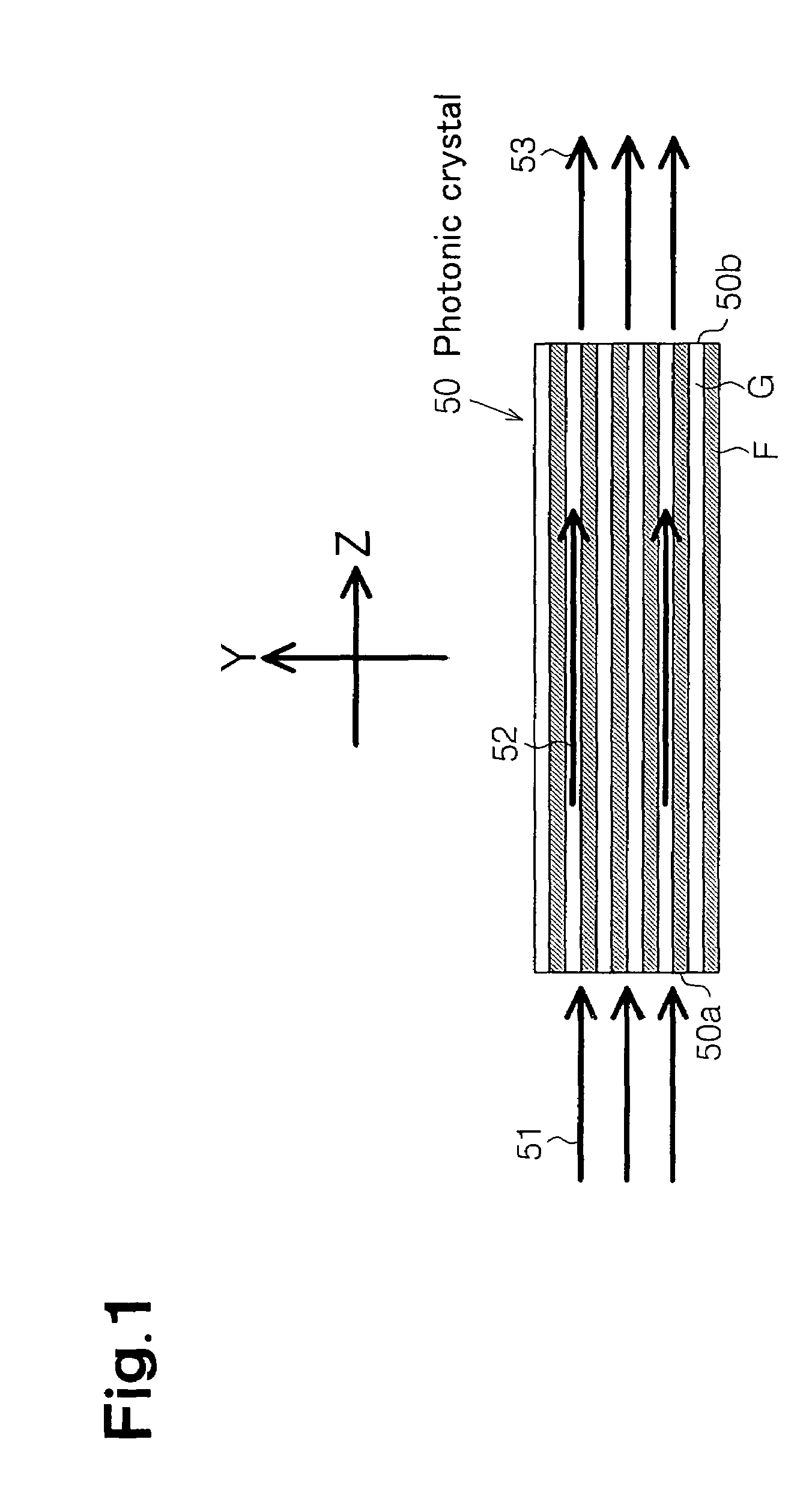
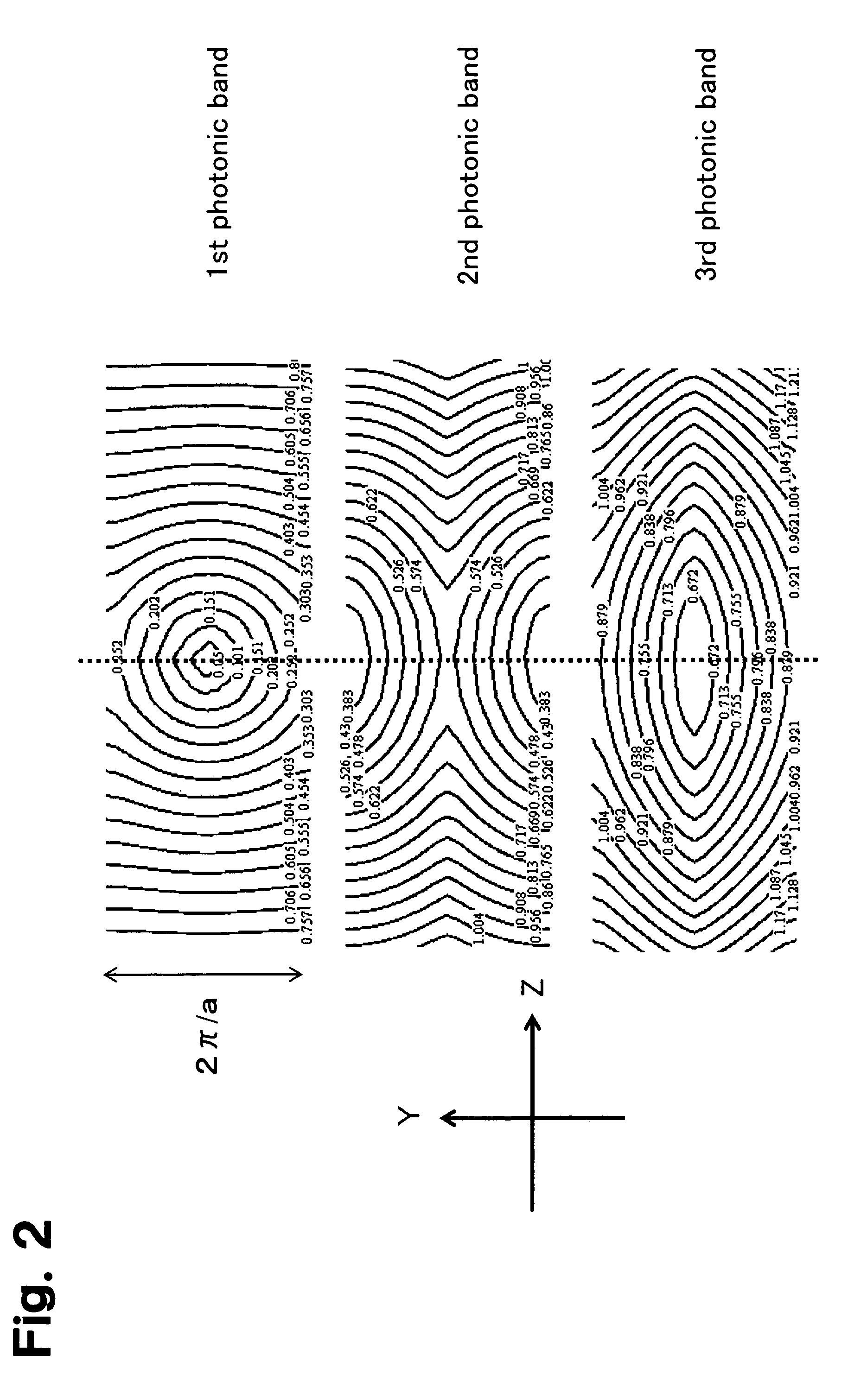
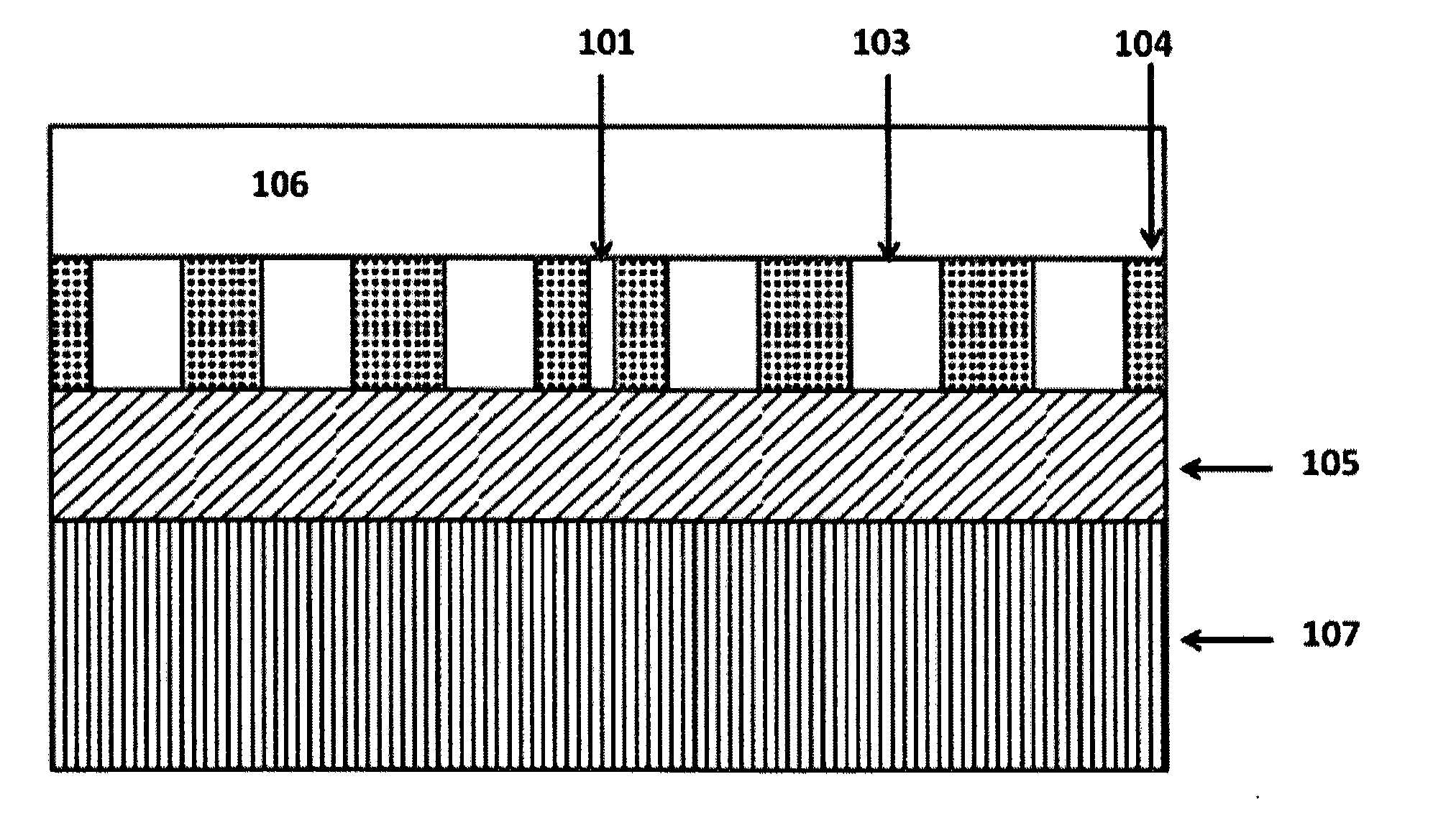
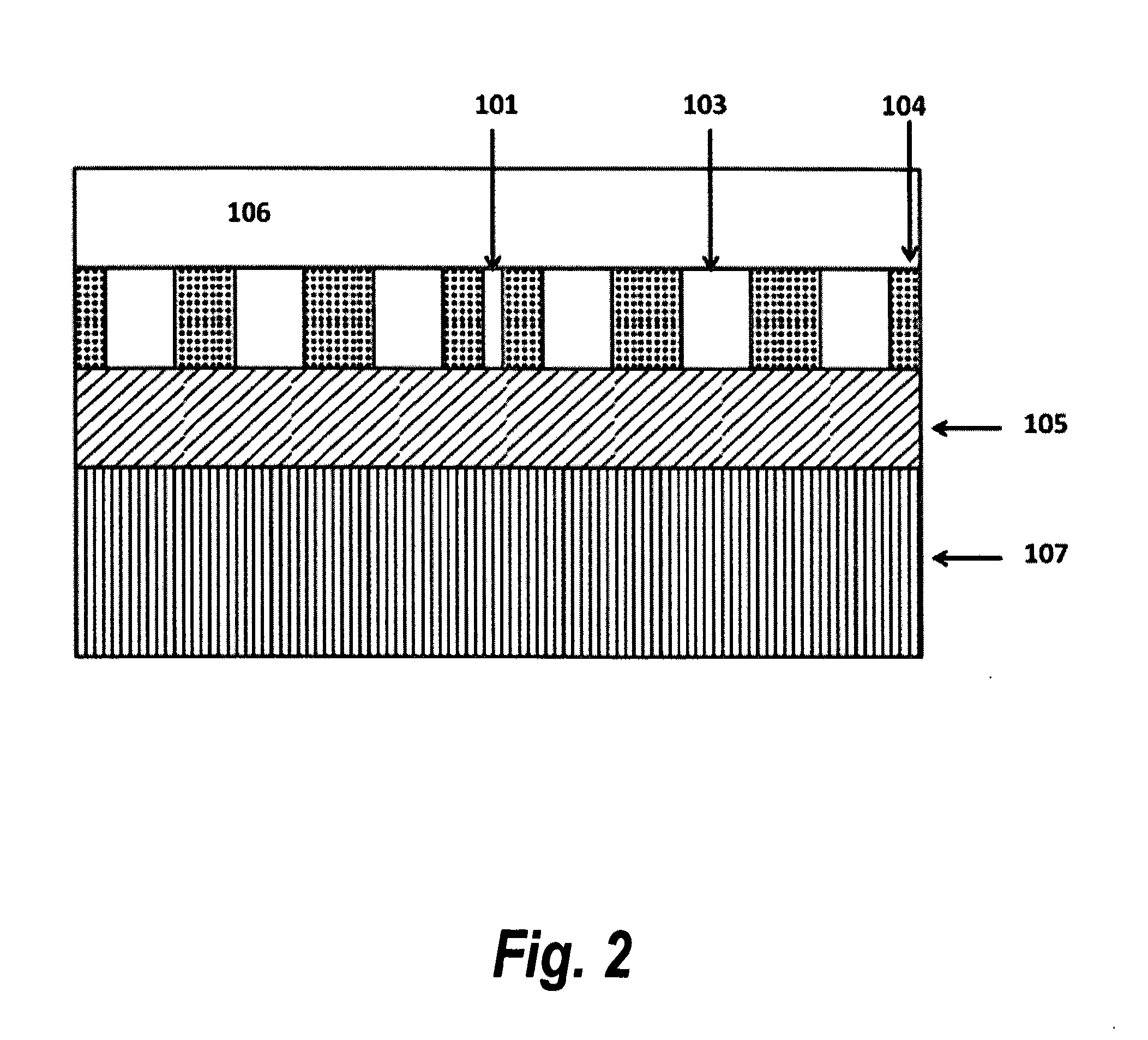
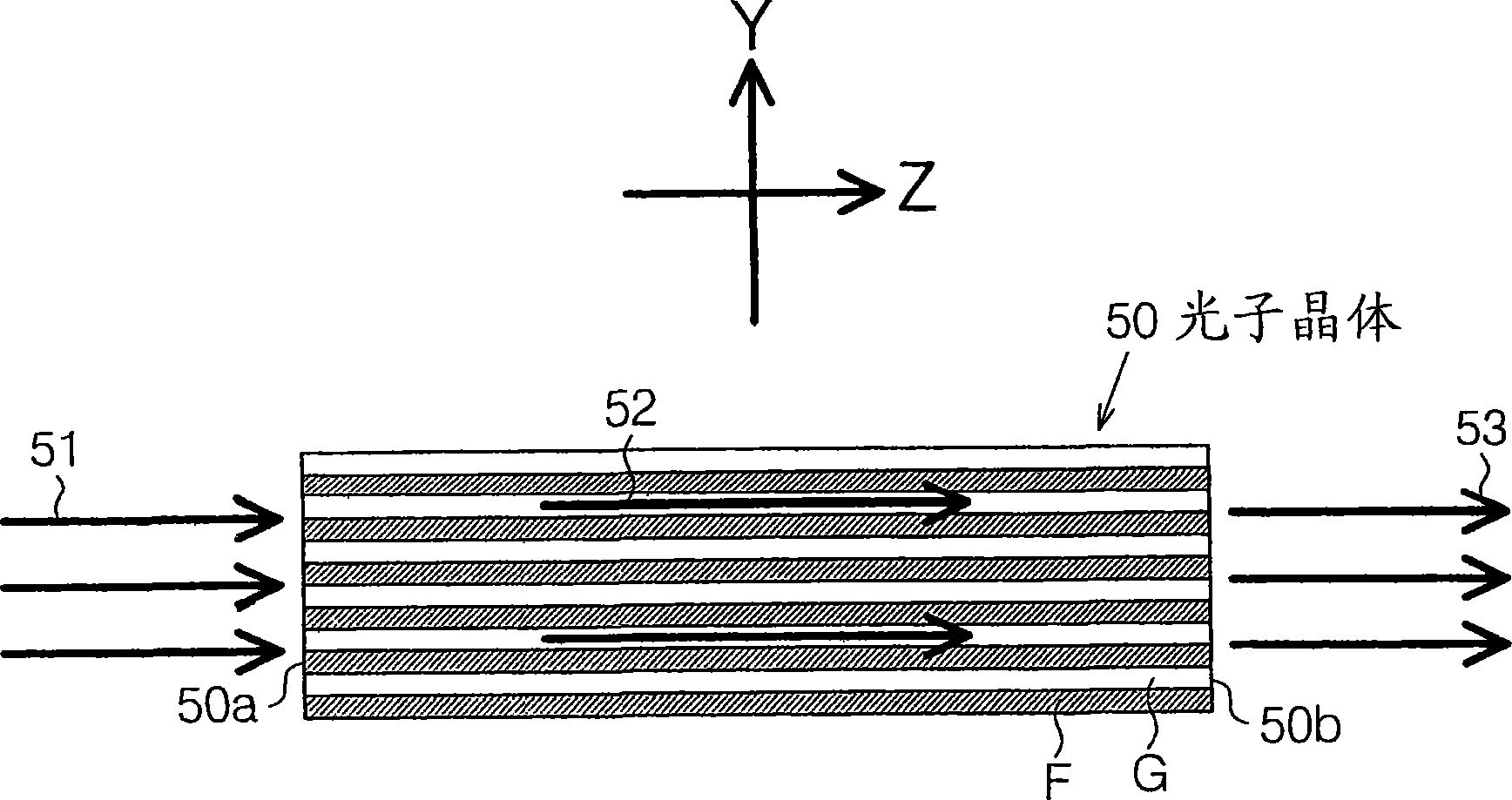
Photonic crystal waveguide, homogeneous medium waveguide, and optical device
A photonic crystal waveguide and a homogeneous medium waveguide for enabling a steep bend and arrangement at an arbitrary angle with low propagation loss. A photonic crystal waveguide has a core formed by a photonic crystal having periodicity in the Y-direction. Electromagnetic wave is propagated by a band on the Brillouin zone boundary of the photonic band structure of the core. A side face of the core parallel to the Y-direction is in contact with a homogeneous medium having a refractive index of ns, and the condition of λ0 / ns>aλ / (λ2 / 4+a2)0.5 is satisfied when the wavelength in vacuum of the electromagnetic wave is represented by λ0, the period of the photonic crystal is represented by a, and the period in the XZ-plane direction of the wave propagated through the core is represented by λ.
Owner:NIPPON SHEET GLASS CO LTD
Quantum cascade laser with photonic quasi-crystal waveguide and manufacture method thereof
The invention relates to a quantum cascade laser with a photonic quasi crystal waveguide, comprising a substrate, a lower waveguide layer, a quantum cascade active area structure, an upper waveguide layer, an upper cladding, an upper covering layer, a high-doping ohmic contact layer, a photonic quasi crystal structure array, an electric insulation layer, a front electrode and a back electrode, wherein the lower waveguide layer is grown on the substrate, the middle of the lower waveguide layer is provided with a boss, and a ridge-shaped double-groove table-board structure is formed at both sides of the boss; the quantum cascade active area structure is grown on the boss of the lower waveguide layer; the upper waveguide layer is grown on the quantum cascade active area structure; the upper cladding is grown on the upper waveguide layer; the upper covering layer is grown on the upper cladding; the high-doping ohmic contact layer is grown on the upper covering layer; the photonic quasi crystal structure array is manufactured at both sides of the upper covering layer and the high-doping ohmic contact layer, the middle width is 2-10 mu m, and the widths of the photonic quasi crystal structure array at both sides are the same and are respectively 5-24 mu m; the electric insulation layer is deposited on the ohmic contact layer and covers the upper surface and the side wall of the whole ridge-shaped table-board, and the central part of the ridge-shaped table-board, covered with the insulation layer, is reserved with an electric injection window; the front electrode is manufactured on the insulation layer; and the back electrode is grown on the back of the substrate.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multimode interference coupler for use with slot photonic crystal waveguides
ActiveUS20100226608A1Compact structureEffective and practicalPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMultimode interferenceCondensed matter physics
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
T-shaped polarization beam splitter with photonic crystal waveguide
InactiveCN102650714ASuitable for integrationSmall structureNanoopticsCoupling light guidesBeam splitterOptical polarization
The invention discloses a T-shaped polarization beam splitter with a photonic crystal waveguide. The T-shaped polarization beam splitter comprises the photonic crystal waveguide with a complete forbidden band. After incident waves in any polarization directions are input to the polarization beam splitter by the input end of the photonic crystal waveguide, a transverse electric (TE) component is output from a TE output end, whereas a transverse magnetic (TM) component is output from the TM output end of the beam splitter. The T-shaped polarization beam splitter disclosed by the invention is small in structural size, high in degree of polarization, high in optical transmission efficiency, convenient in integration and high in efficiency and is suitable for integrating optical paths on a large scale, and the function of different-wavelength polarization beam splitting can be realized.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Photonic crystal element
A waveguide stub is connected to a pillar-type square-lattice photonic crystal waveguide. Within the waveguide stub, the diameter of a defect is made larger than that of the original photonic crystal waveguide thereby reducing the group velocity of a guided light. The original waveguide and the waveguide stub are smoothly connected via a taper waveguide. Because of low group velocity of light in the waveguide stub, free spectral range (FSR) decreases thereby allowing the size of the waveguide stub to be reduced.
Owner:NEC CORP
Photonic crystal waveguide based superefficient compact cross circulator
InactiveCN104101948ASmall structureHighly integratedOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsRight triangleMicrowave
The invention discloses a photonic crystal waveguide based superefficient compact cross circulator. The photonic crystal waveguide based superefficient compact cross circulator comprises a crisscrossing photonic crystal waveguide with four end openings; a square magneto-optical dielectric rod is arranged in the center of the crisscrossing photonic crystal waveguide; four square dielectric rods are arranged at four corners in the center of the crisscrossing waveguide; angles of the four square dielectric rods are cut to form into isosceles right triangles with the length of right angle sides to be identical to that of sides of background square dielectric rods to form into corner dielectric rods; the corner dielectric rods and left parts at corresponding lattice point positions of the corner dielectric rods are coincided or not; the insertion loss of the circulator is from 0.02db to 1db and the isolation of an isolation end and an input end is larger than 14db. The photonic crystal waveguide based superefficient compact cross circulator has the advantages of being small in size, high in integration level, high in electromagnetic wave transmission efficiency, beneficial to integration and efficient and allowing circuiting and being widely applied to microwave, terahertz and light communication wave bands.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
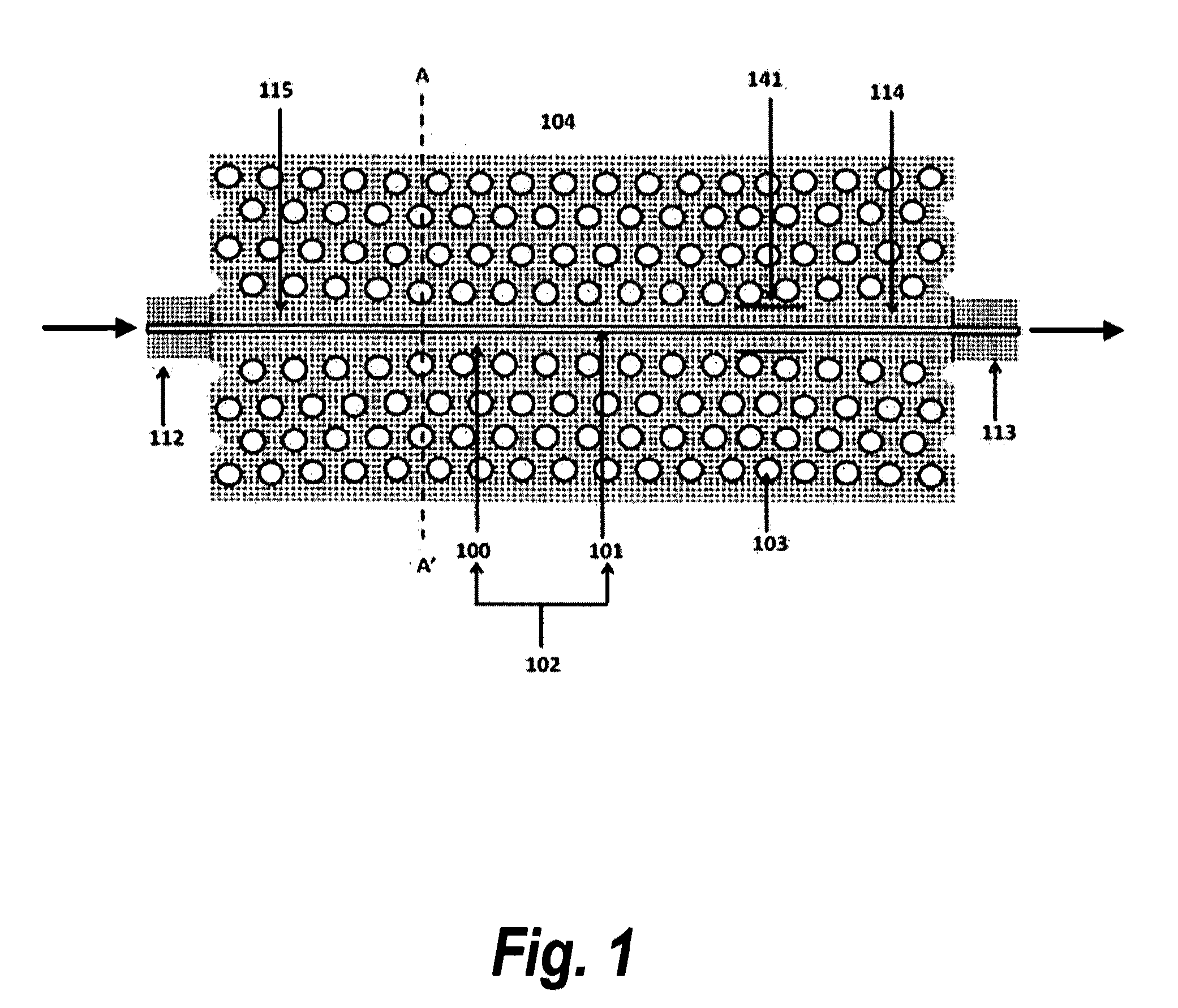
Displacement sensor based on photonic crystal waveguides
A displacement sensor comprising at least one pair of co-planar photonic crystal waveguide (PCWG) sections aligned along or parallel to a common axis and separated by a gap, one PCWG section of a pair operative to perform a displacement relative to the other section of the pair. In some embodiments, the sensor is linear, comprising two PCWG sections sperated by a gap that forms a cross PCWG, the displacement sensing performed preferrably differentially between two edges of the cross PCWG. In other embodiments, the sensor includes Mach Zehnder Interferometer (MZI) configurations with gaps between fixed and moving PCWG sections. Displacement induced changes in the gap widths are reflected in changes in an output parameter of the MZI.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Photonic crystal slot waveguide miniature on-chip absorption spectrometer
ActiveUS20120044489A1Enhanced light absorptionEliminate needRadiation pyrometryCladded optical fibreAnalyteOptical absorption spectra
Methods and systems for label-free on-chip optical absorption spectrometer consisting of a photonic crystal slot waveguide are disclosed. The invention comprises an on-chip integrated optical absorption spectroscopy device that combines the slow light effect in photonic crystal waveguide and optical field enhancement in a slot waveguide and enables detection and identification of multiple analytes to be performed simultaneously using optical absorption techniques leading to a device for chemical and biological sensing, trace detection, and identification via unique analyte absorption spectral signatures. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:OMEGA OPTICS
Photonic crystal waveguide, homogeneous medium waveguide, and optical device
A photonic crystal waveguide and a homogeneous medium waveguide that can be bent sharply and placed at a free angle and have a low propagation loss. The photonic crystal waveguide (200) has a core composed of a photonic crystal (50) having a periodicity in the Y-direction. An electromagnetic wave propagates along a band on the border of the Brillouin zone of the photonic band structure of the core. The side surface parallel to the Y-direction of the core is in contact with a homogeneous medium of refractive index ns. A condition lambda0 / ns>alambda / (lambda<2> / 4+a<2>)<0.5> is satisfied where lambda0 is the wavelength of the electromagnetic wave in the vacuum space, a is the period of the photonic crystal, and lambda is the period in an X-Z plane direction of the wave propagating through the core. This condition is essential to prevent light from leaking from the side surface of the photonic crystal waveguide (200). Therefore, satisfying the condition confines the wave propagating through the core inside the side surface when the propagation angle phi=0 DEG .
Owner:NIPPON SHEET GLASS CO LTD
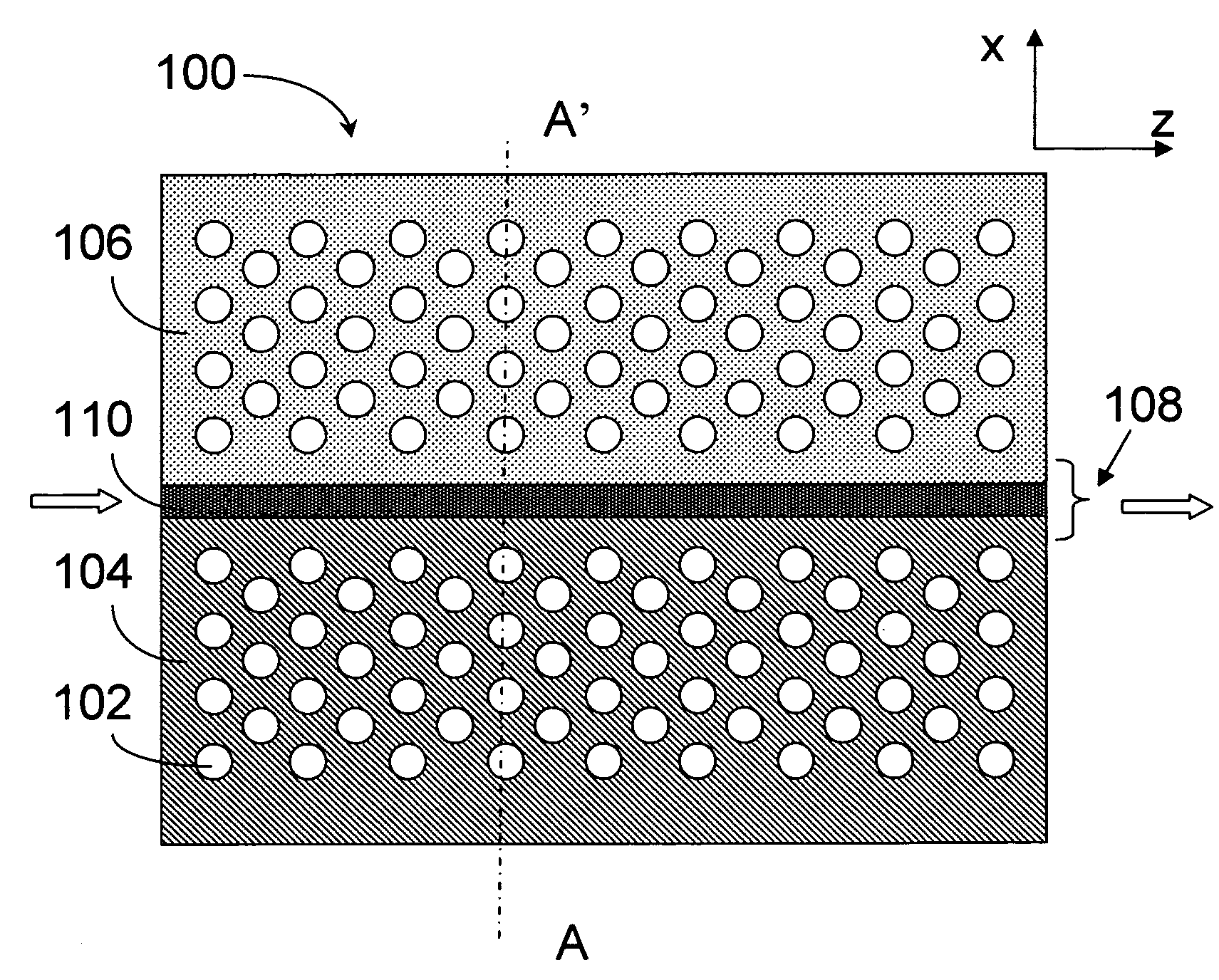
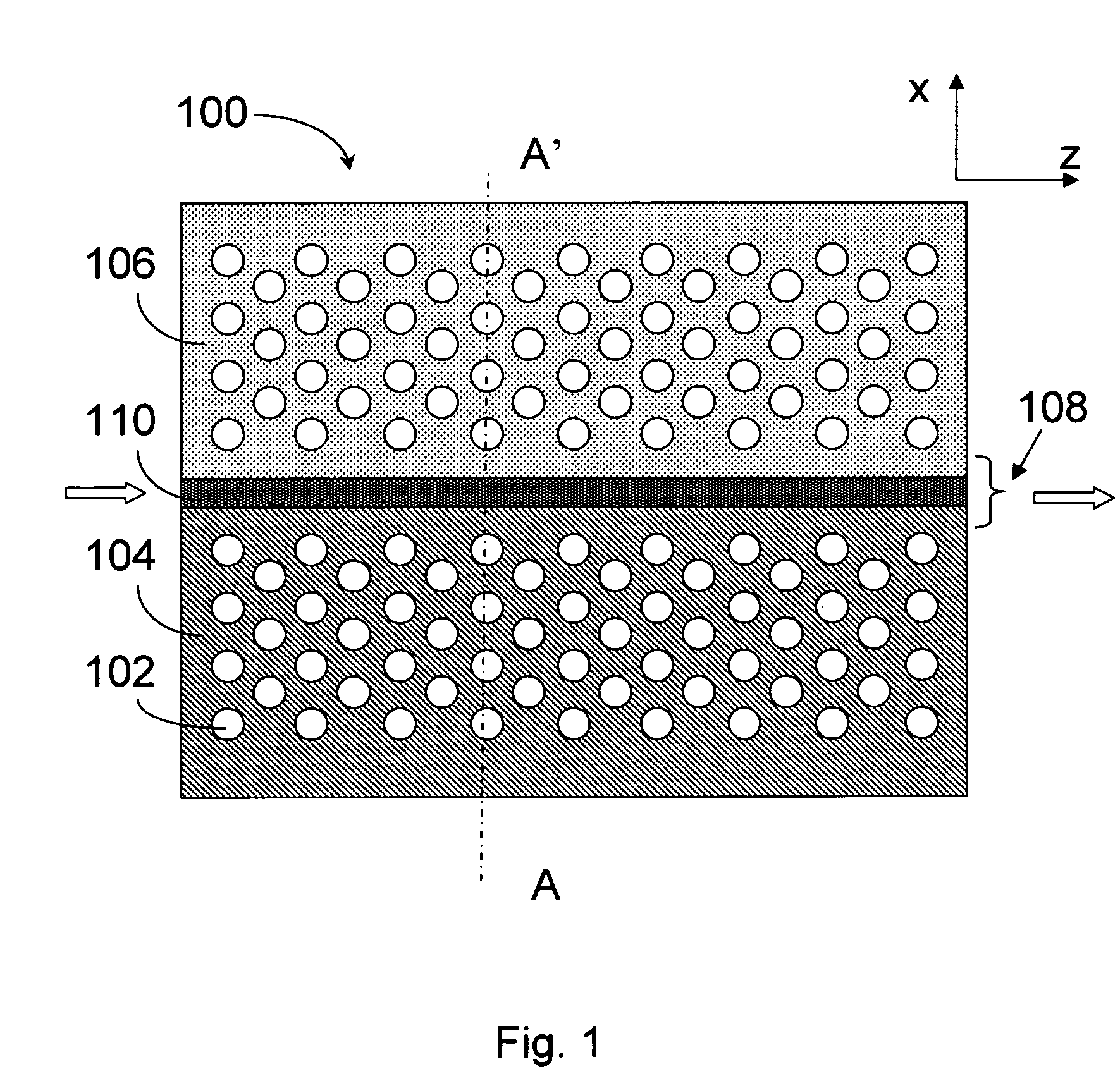
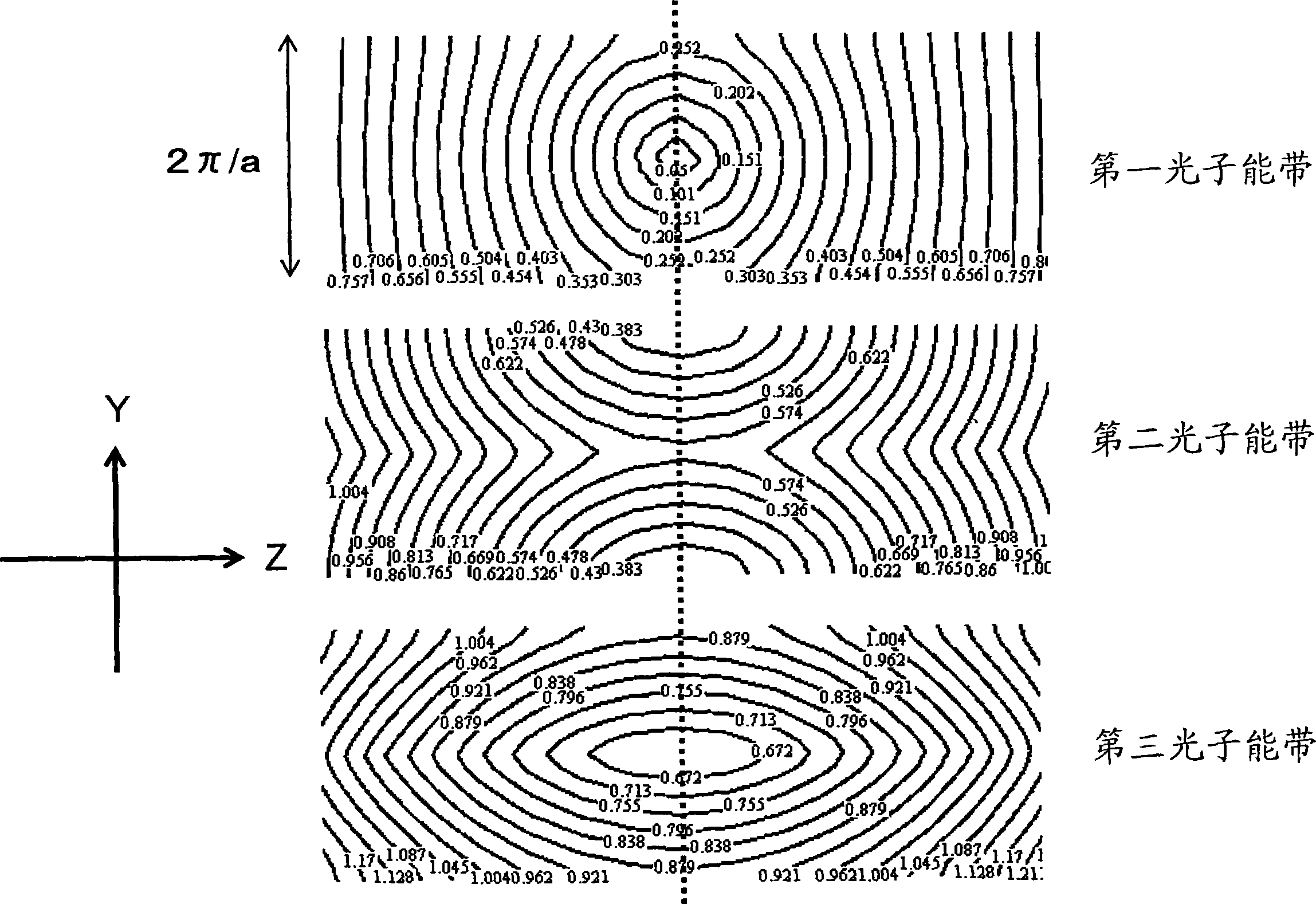
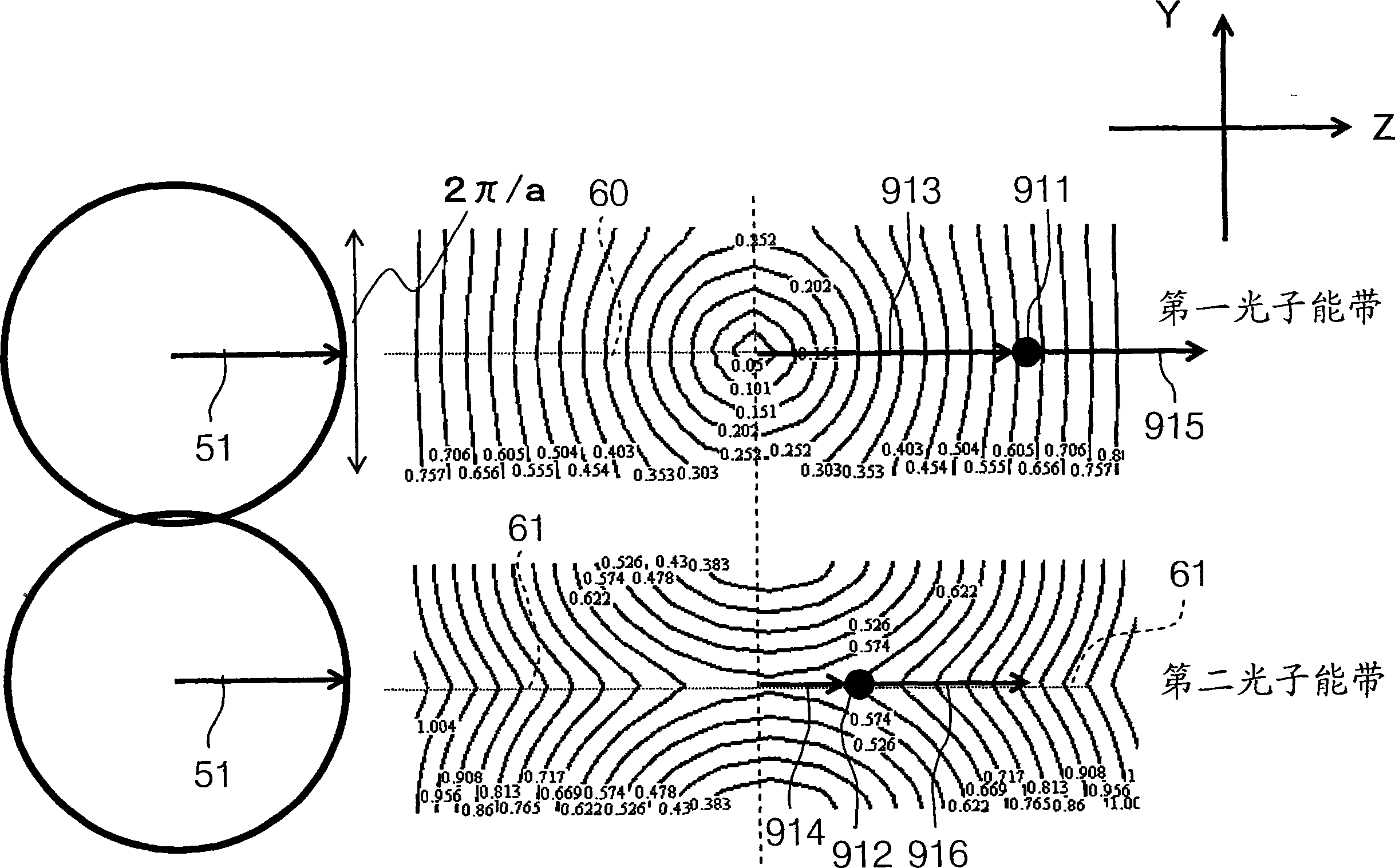
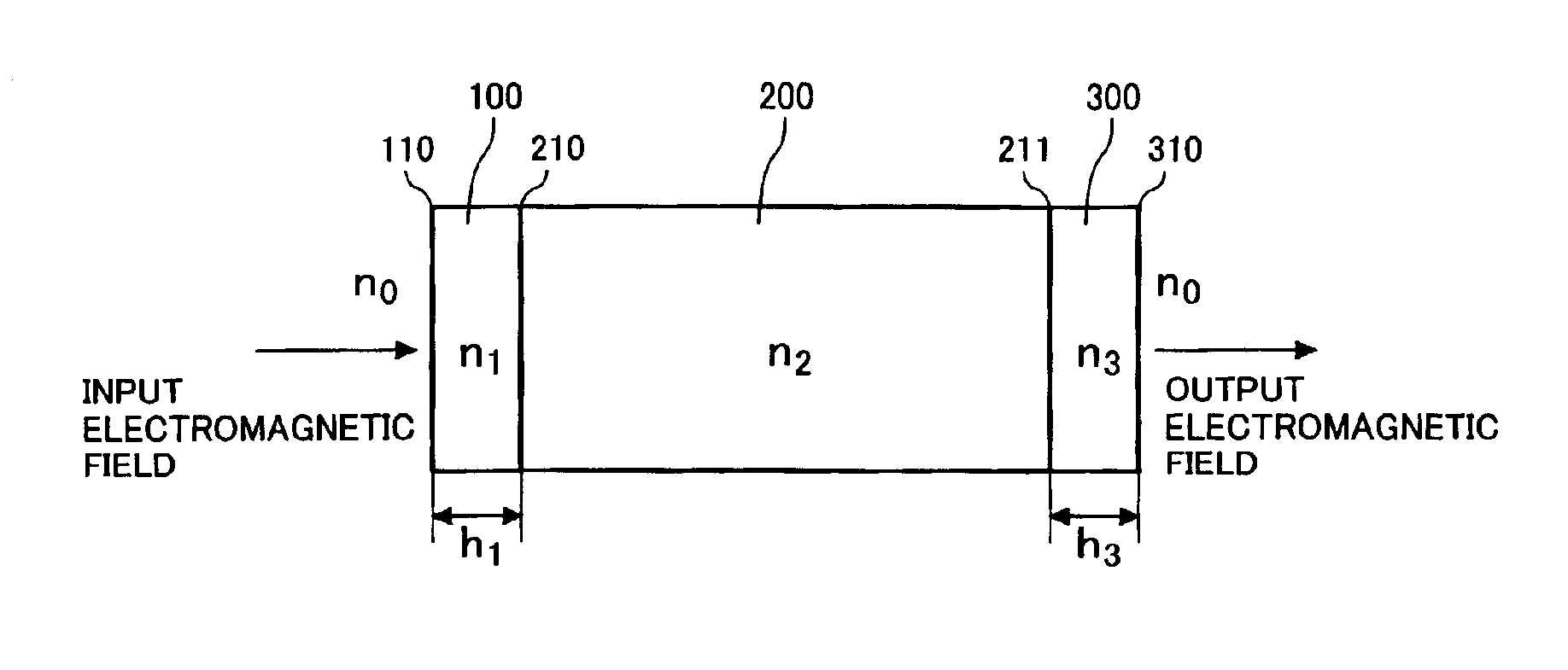
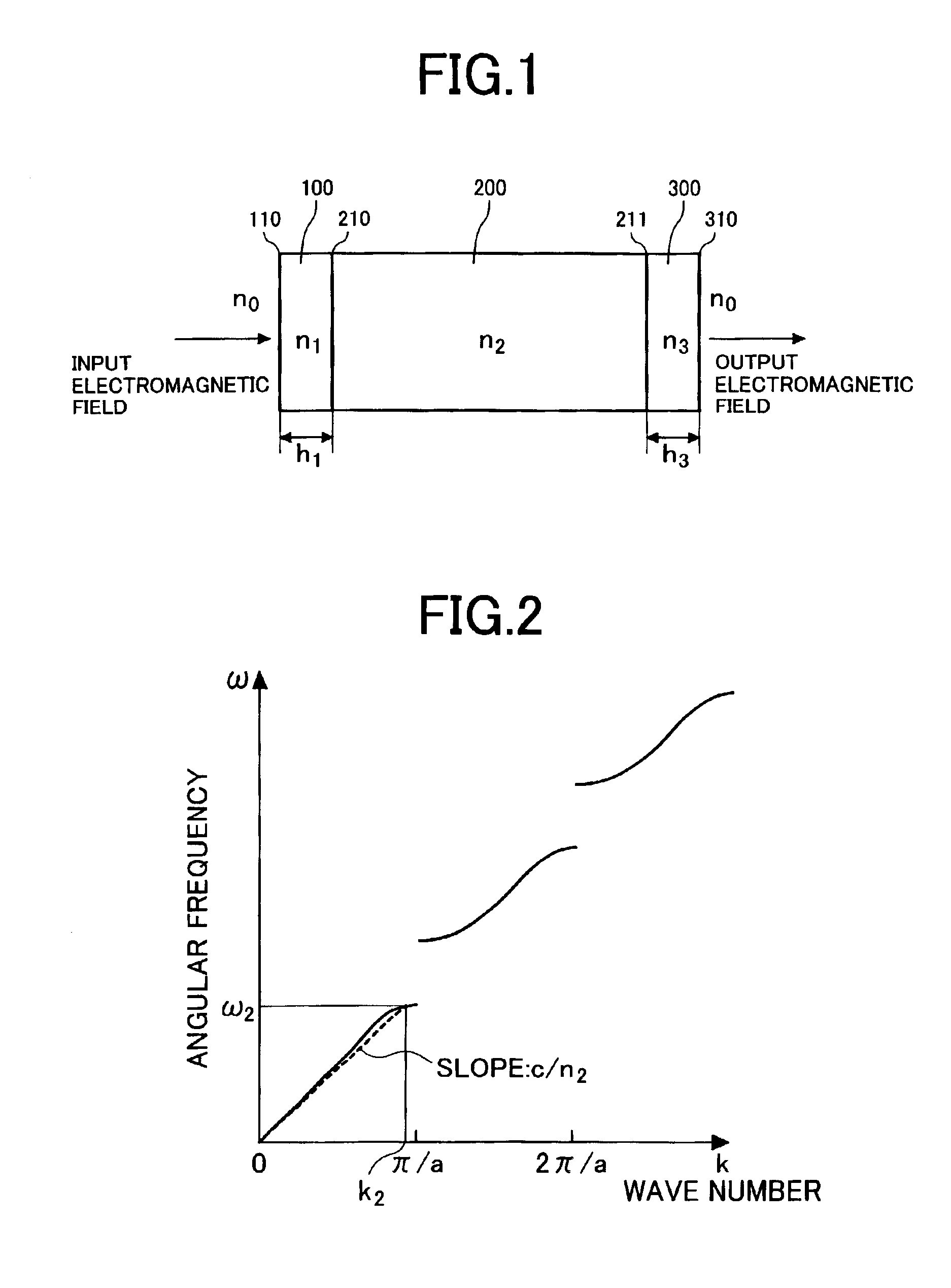
Photonic crystal and photonic-crystal waveguide
InactiveUS6879766B2Reduce reflection lossReflection lossCladded optical fibreNanoopticsReflection lossPhotonic crystal
The present invention provides a technique of reducing an incident / outgoing loss of a photonic crystal. On each of incident / outgoing sides of a photonic crystal, an antireflection layer made of a photonic crystal is disposed. At the incident side of a photonic crystal 200 having an effective refractive index n2, a photonic crystal 100 having an effective refractive index n1 satisfying the relation of n1<n2 is disposed, and the thickness of the photonic crystal 100 is controlled so that reflection components from interfaces 210 and 110 cancel each other out by interference, thereby reducing a total reflection loss on the incident side. The outgoing side is similarly constructed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Three-dimensional photonic crystal waveguide structure and method
InactiveUS7054532B2Polycrystalline material growthLaser optical resonator constructionPhotonic bandgapSolid substrate
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Single-mode large-power THz quantum cascade laser (QCL) and manufacturing technology thereof
InactiveCN102570307AIncrease output powerGuaranteed single-mode narrow linewidthOptical wave guidanceLaser active region structureGratingManufacturing technology
The invention provides a single-mode large-power THz quantum cascade laser (QCL) and a manufacturing technology thereof. The single-mode large-power THz QCL comprises a two-dimensional photonic crystal waveguide located on a center and a first order grating waveguide distributed around the two-dimensional photonic crystal waveguide. By using the single-mode large-power THz QCL of the invention, output power of the THz laser of the center area waveguide can be substantially increased; a single-mode narrow line width of the THz laser can be guaranteed; a working mode set by the laser is only fed back; a lateral high-order mode can be inhibited; a quality factor of a photonic crystal resonator can be increased simultaneously.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical active device
In an optical device, a slab layer has an active layer sandwiched between two cladding layers. Periodic air holes are present in the slab layer. A linear defect region is present in a part of the air hole structures. As a result, laser oscillation is generated at the band end in a two-dimensional photonic crystal waveguide mode.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP +1
Method and apparatus for thermo-optic modulation of optical signals
The present invention is a method and an apparatus for thermo-optic control of optical signals using photonic crystal structures. In one embodiment, a first portion of a split signal is modulated by propagating the signal through a photonic crystal waveguide in which two electrical contacts are laterally spaced from the waveguide region by a plurality of apertures formed through the photonic crystal substrate. A voltage applied across the electrical contacts causes resistive heating of the proximate photonic crystal waveguide through which the signal propagates, thereby modulating the temperature relative to an un-modulated second portion of the split signal that is used as a reference.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
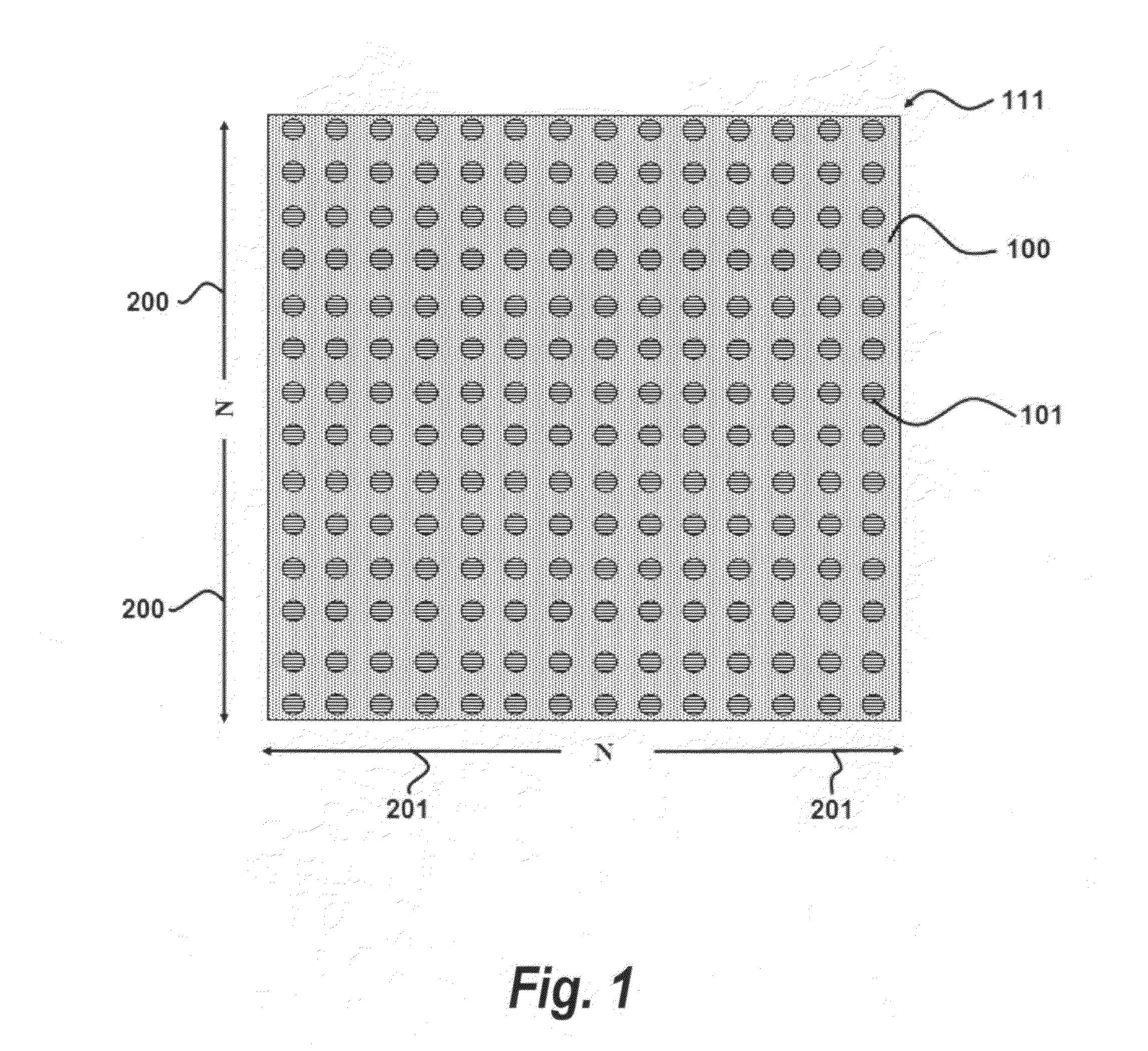
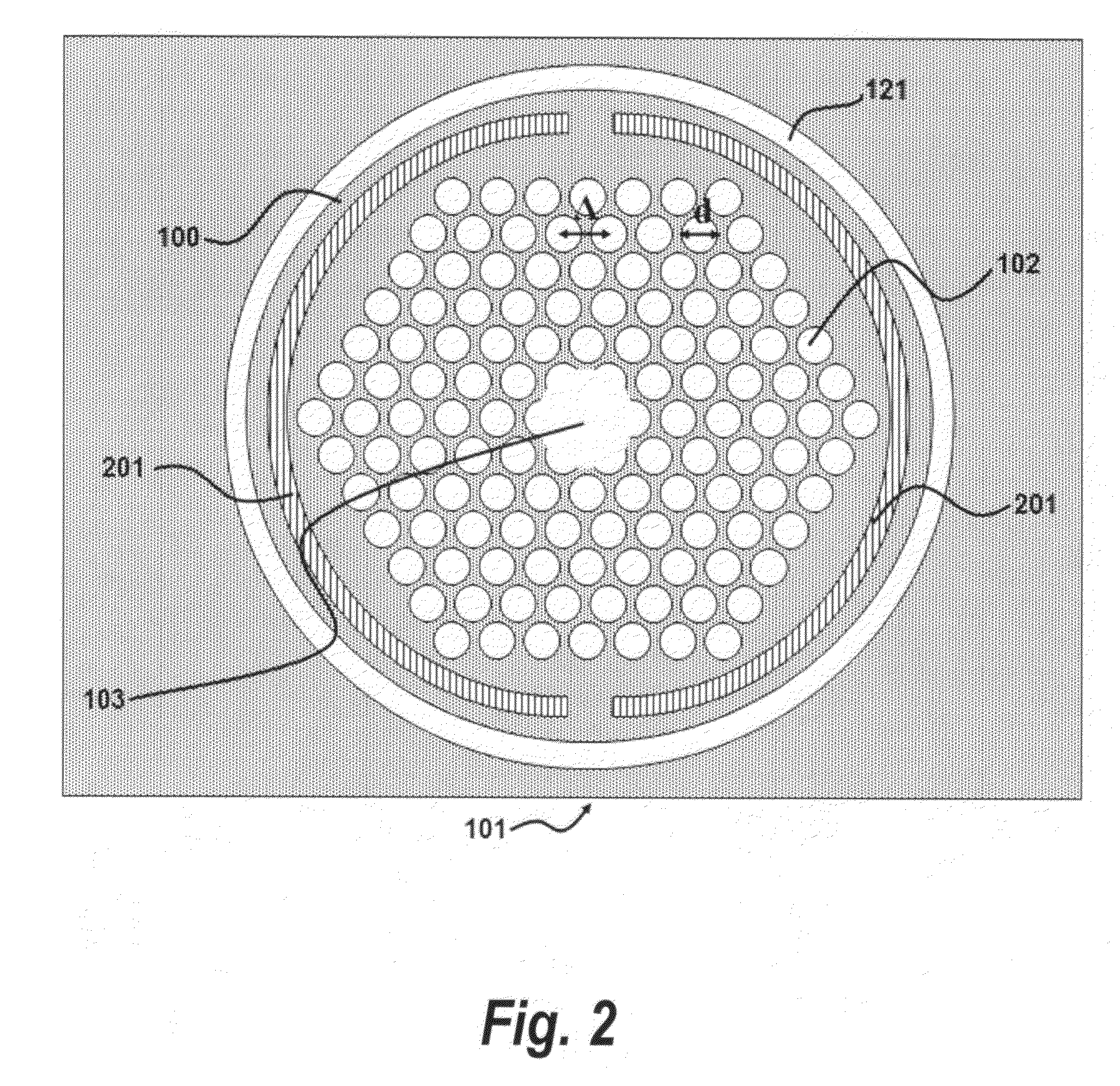
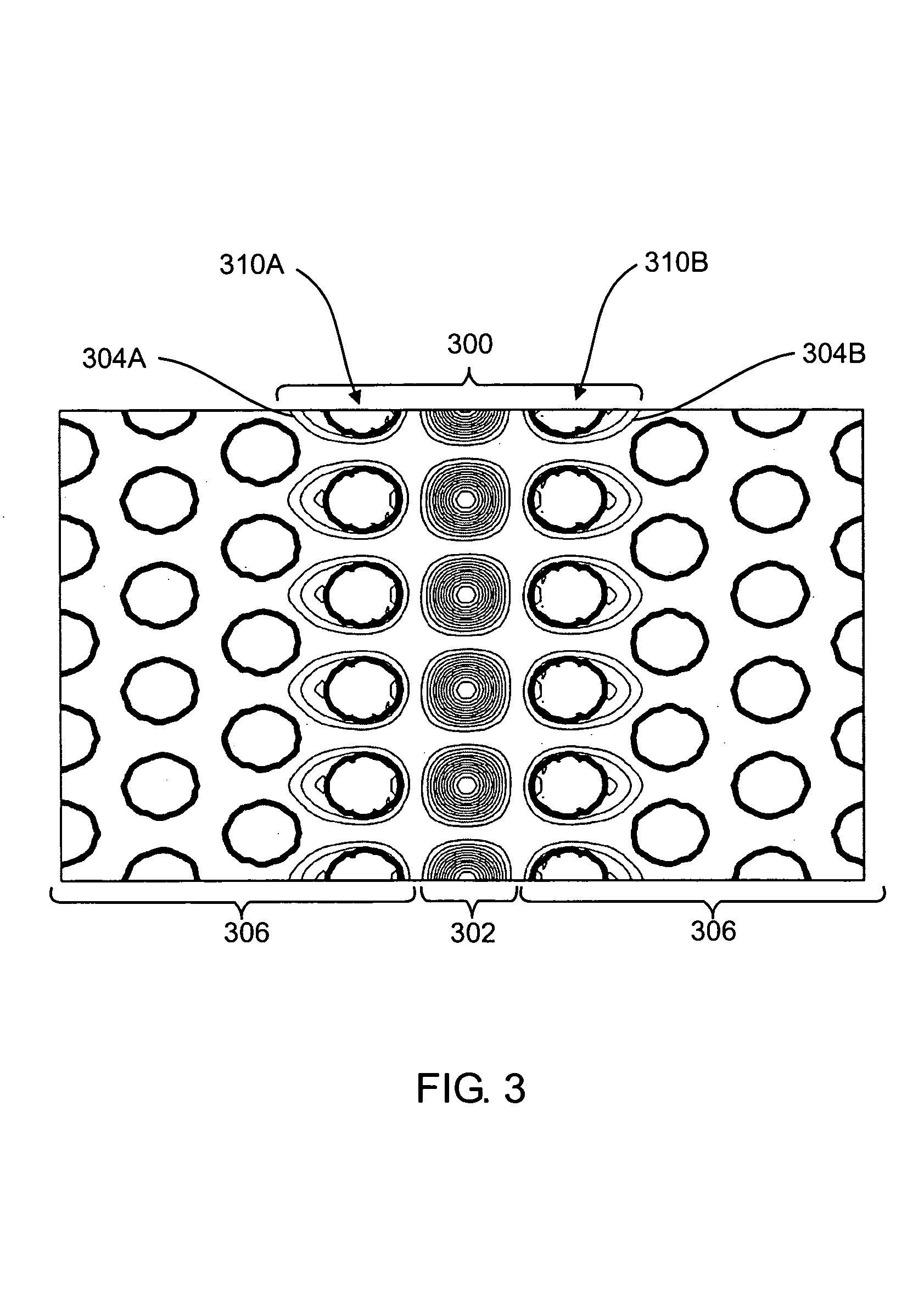
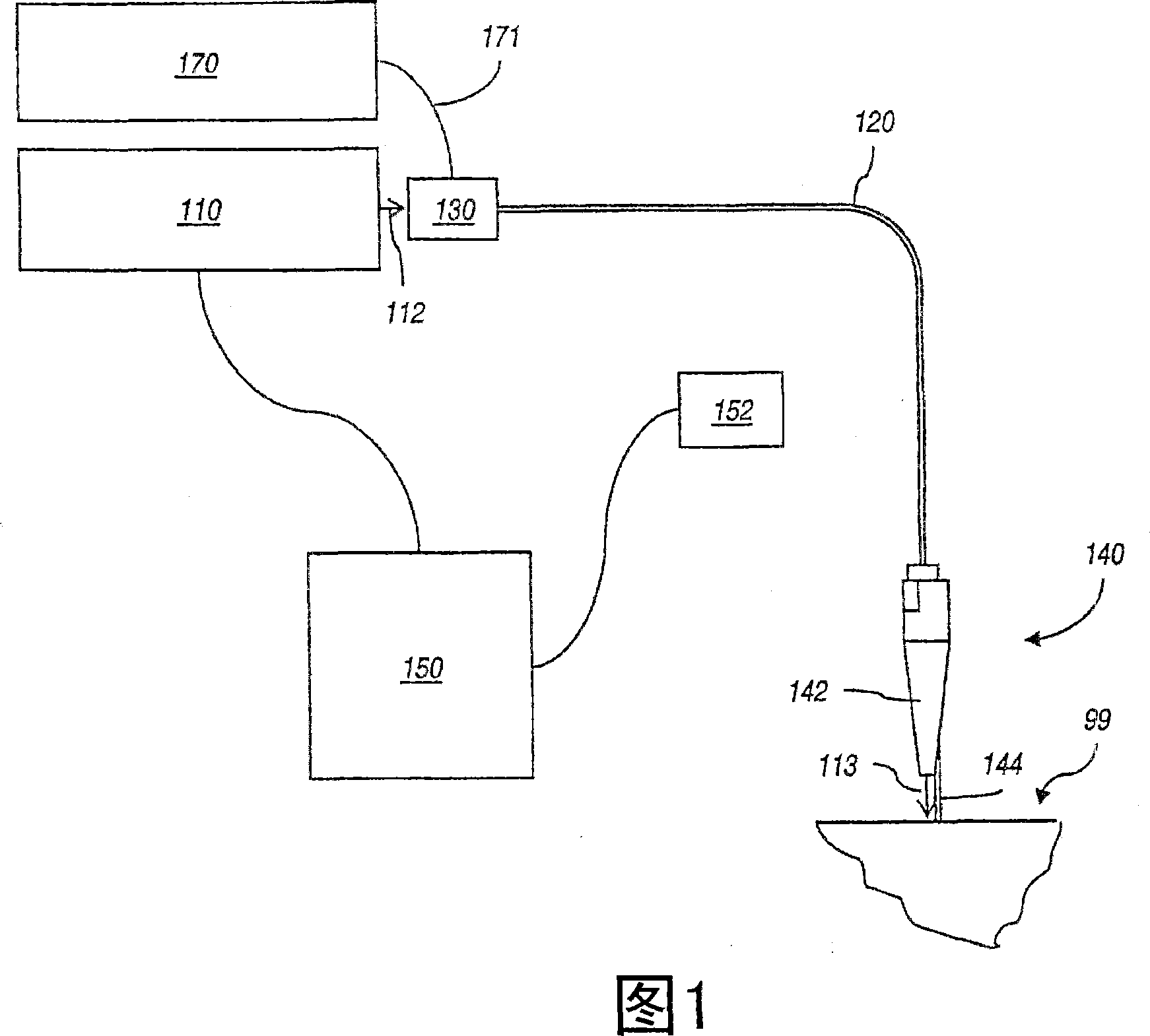
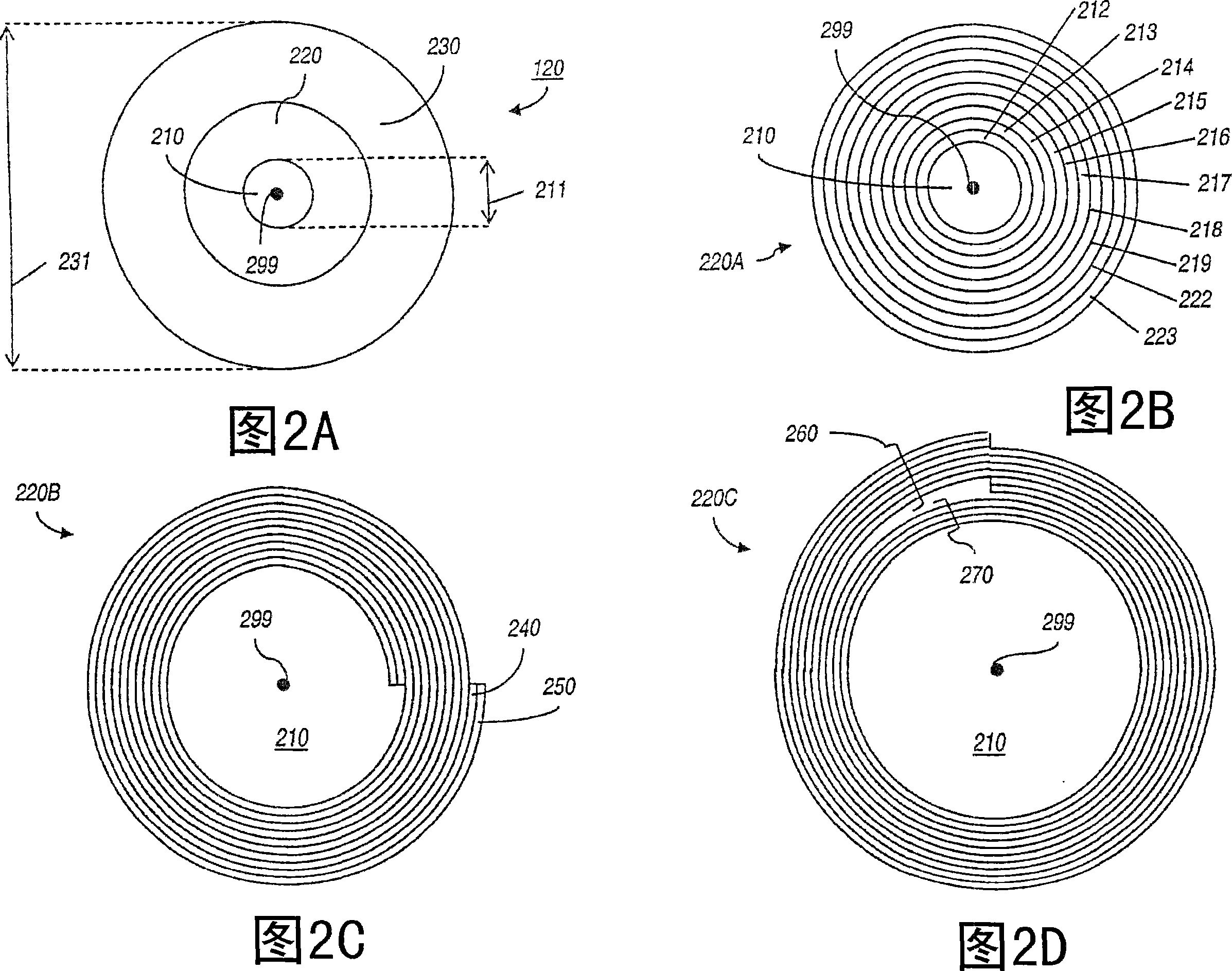
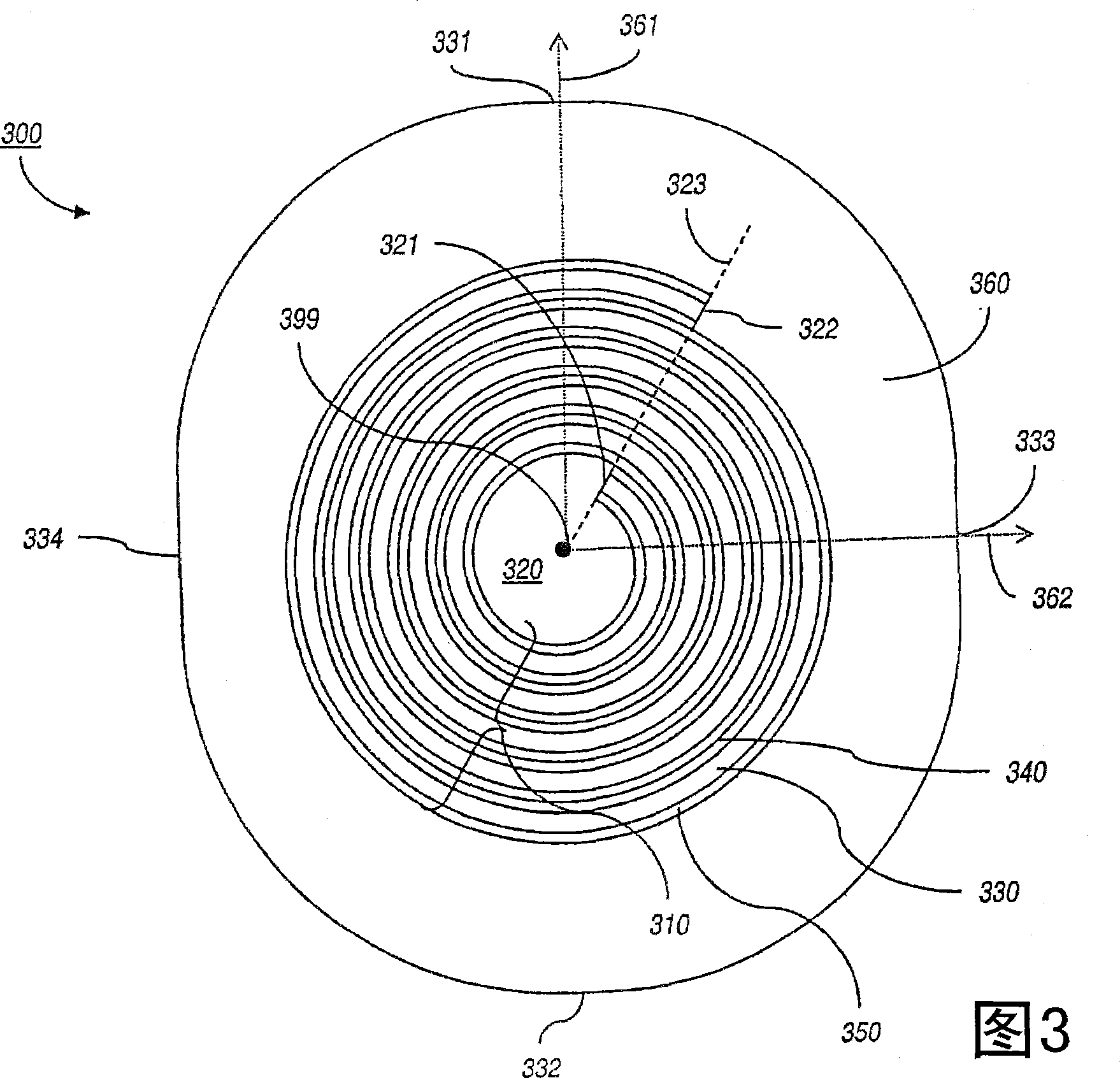
Photonic crystal waveguides and medical treatment systems containing the same
In general, in one aspect, the invention features systems, including a photonic crystal fiber including a core extending along a waveguide axis and a dielectric confinement region surrounding the core, the dielectric confinement region being configured to guide radiation along the waveguide axis from an input end to an output end of the photonic crystal fiber. The systems also includes a handpiece attached to the photonic crystal fiber, wherein the handpiece allows an operator to control the orientation of the output end to direct the radiation to a target location of a patient.
Owner:全波导公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com