Photonic crystal waveguide, homogeneous medium waveguide, and optical device
A photonic crystal waveguide and photonic crystal technology, applied in the direction of optical waveguide light guide, laser components, optics, etc., can solve the problems of arranging waveguides and design restrictions, and achieve the effect of small waveguide width and compact size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
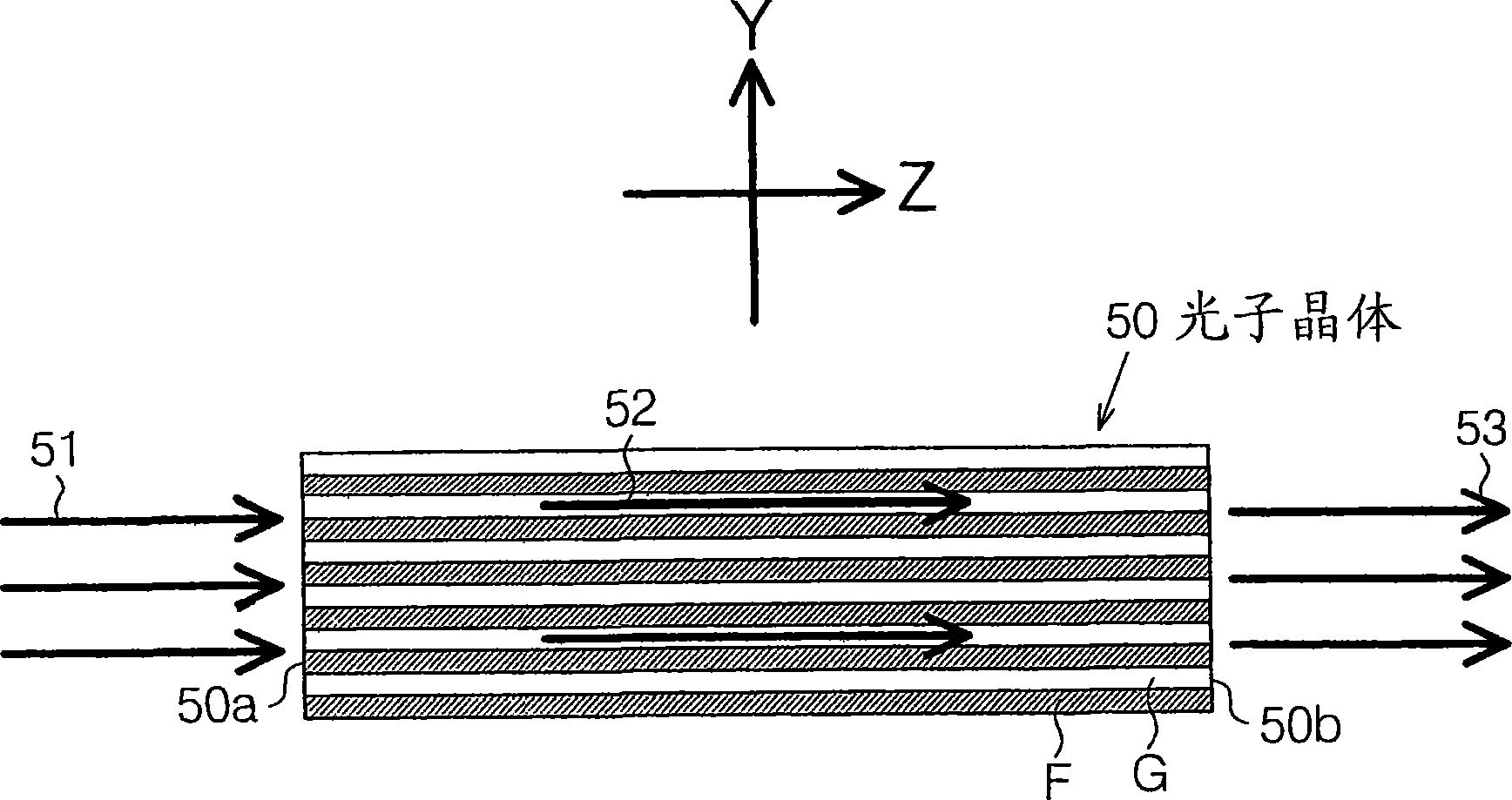
[0373] When the above-mentioned one-dimensional photonic crystal is used in the design (for example, as Figure 20 In the case of the optical device shown), it is preferable to form the photonic crystal in the shape of a waveguide, because this facilitates the connection with the optical fiber, and facilitates the control of the above-mentioned characteristics ("extraordinarily large wavelength dispersion" and "group velocity anomaly") The electrodes are arranged.
[0374] by using according to Figure 21 The photonic crystal waveguide 200 of the first embodiment shown is formed Figure 20 Optics shown. The photonic crystal waveguide 200 is formed in a waveguide shape on a suitable substrate 90 by using a one-dimensional photonic crystal as a core. For the photonic crystal forming the core of the photonic crystal waveguide 200 assigned with figure 1 The photonic crystal 50 has the same reference numerals, and its repeated description is omitted.
[0375] After converting ...
no. 2 example
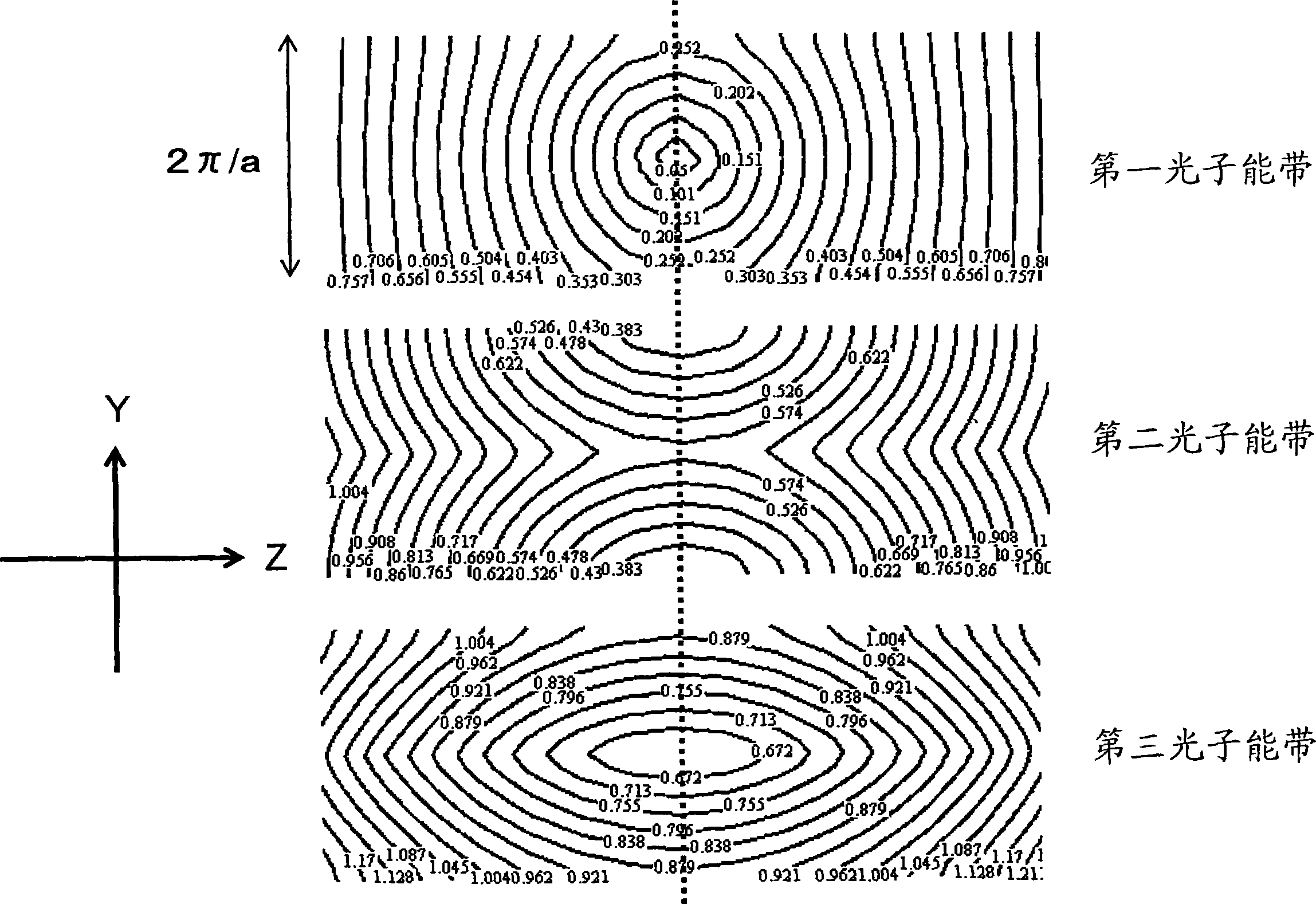
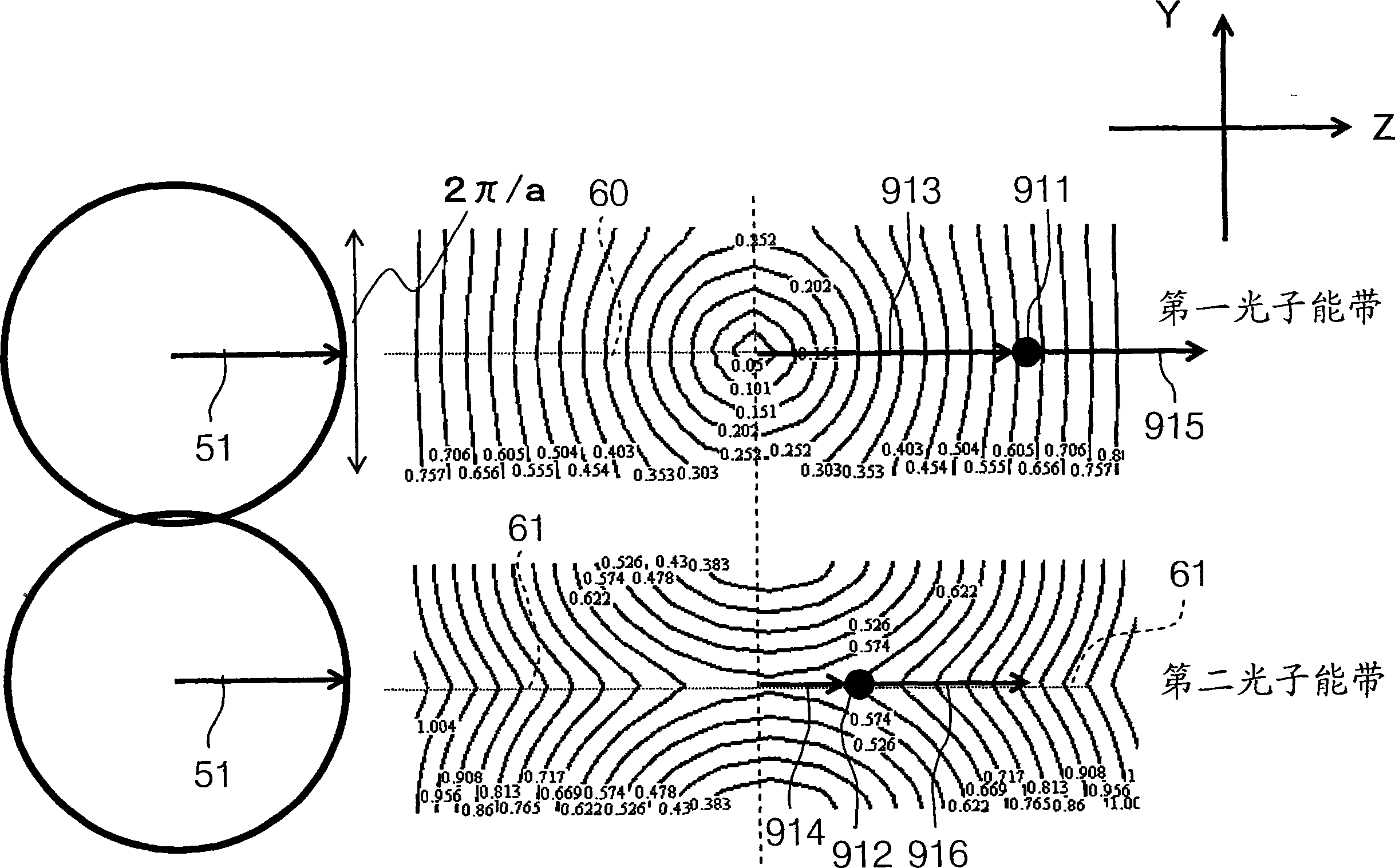
[0511] The following applies to the propagating light using the photon energy band at the center of the Brillouin zone, described in the first embodiment above and Figure 21 and 22 Confinement conditions in various directions of the illustrated photonic crystal waveguide 200 are described.
[0512] (Y direction mode)
[0513] Unlike the above propagation using "bands on the boundary of the Brillouin zone", in Figure 26 The second up-band propagating mode shown is the zeroth order mode with N=0. Do not use Figure 25 The "zero-order mode on the first energy band" is shown because its characteristics are close to those of ordinary plane waves.
[0514] (Single-mode condition in Y direction)
[0515] If the effective refractive index of the propagating mode is larger than that of the upper and lower cladding medium, confinement can be achieved due to the difference in refractive index. However, if the effective refractive index of the propagating mode is small, then in ...
no. 3 example
[0568] Next, a description will be given of a third embodiment in which the present invention is applied to a waveguide whose core is formed of a uniform material. Such as Figure 40 As shown, the homogeneous dielectric waveguide 300 according to this embodiment consists of a refractive index n with a finite thickness in one direction (Y direction) 0 It is formed of a uniform material, and includes a core 301 and a cladding 342 that propagate electromagnetic waves in a direction (XZ plane direction) perpendicular to the one direction.
[0569] The cladding 342 on the opposite surface perpendicular to the Y direction of the core 301 is formed of a one-dimensional photonic crystal having periodicity in the Y direction (the one direction). The cladding 342 is a confinement cladding for preventing electromagnetic waves propagating through the core 301 from leaking out from surfaces (top and bottom surfaces) perpendicular to the Y direction.
[0570] In such a configuration of th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angle of incidence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com