Patents
Literature
39 results about "Optical absorption spectra" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Optical absorption spectra of minerals result from the interaction with electromagnetic radiation in the energy range of 40 000 cm^(-1) to 4000 cm^(-1) corresponding to the wavelength range of 250 nm to 2500 nm.
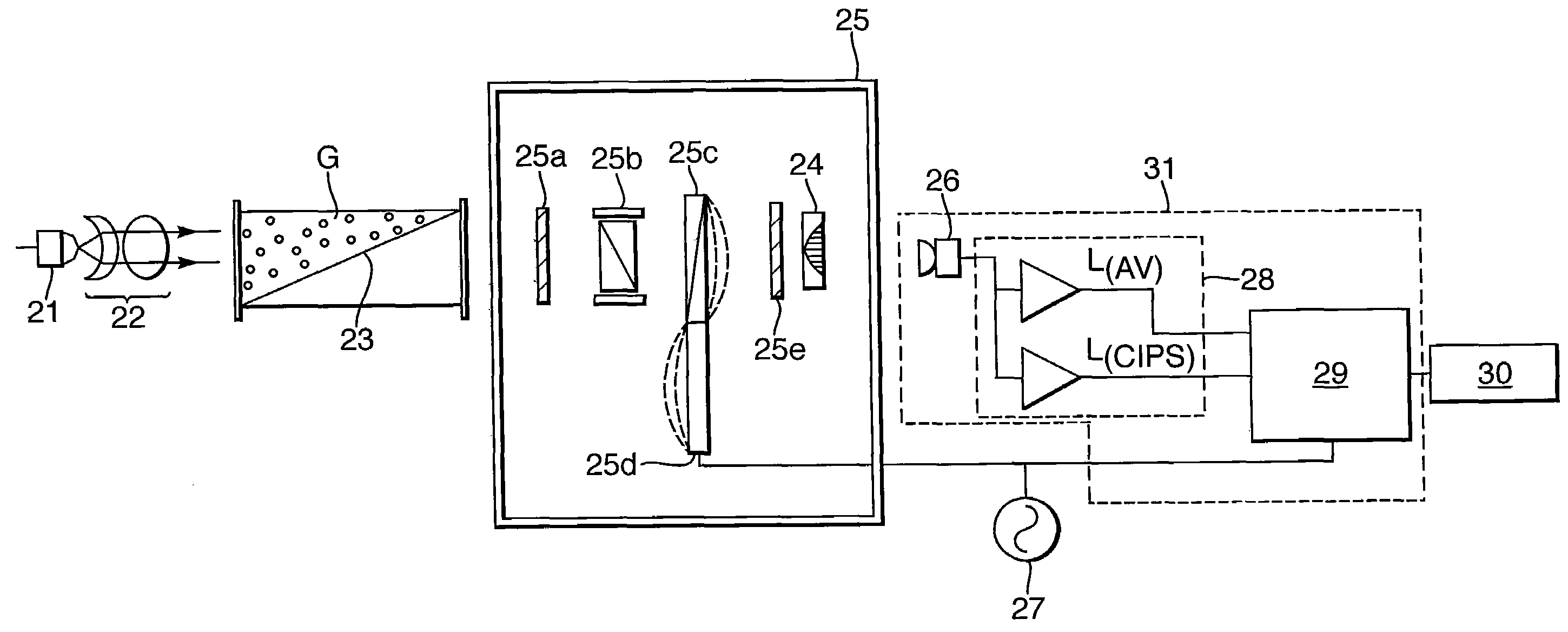
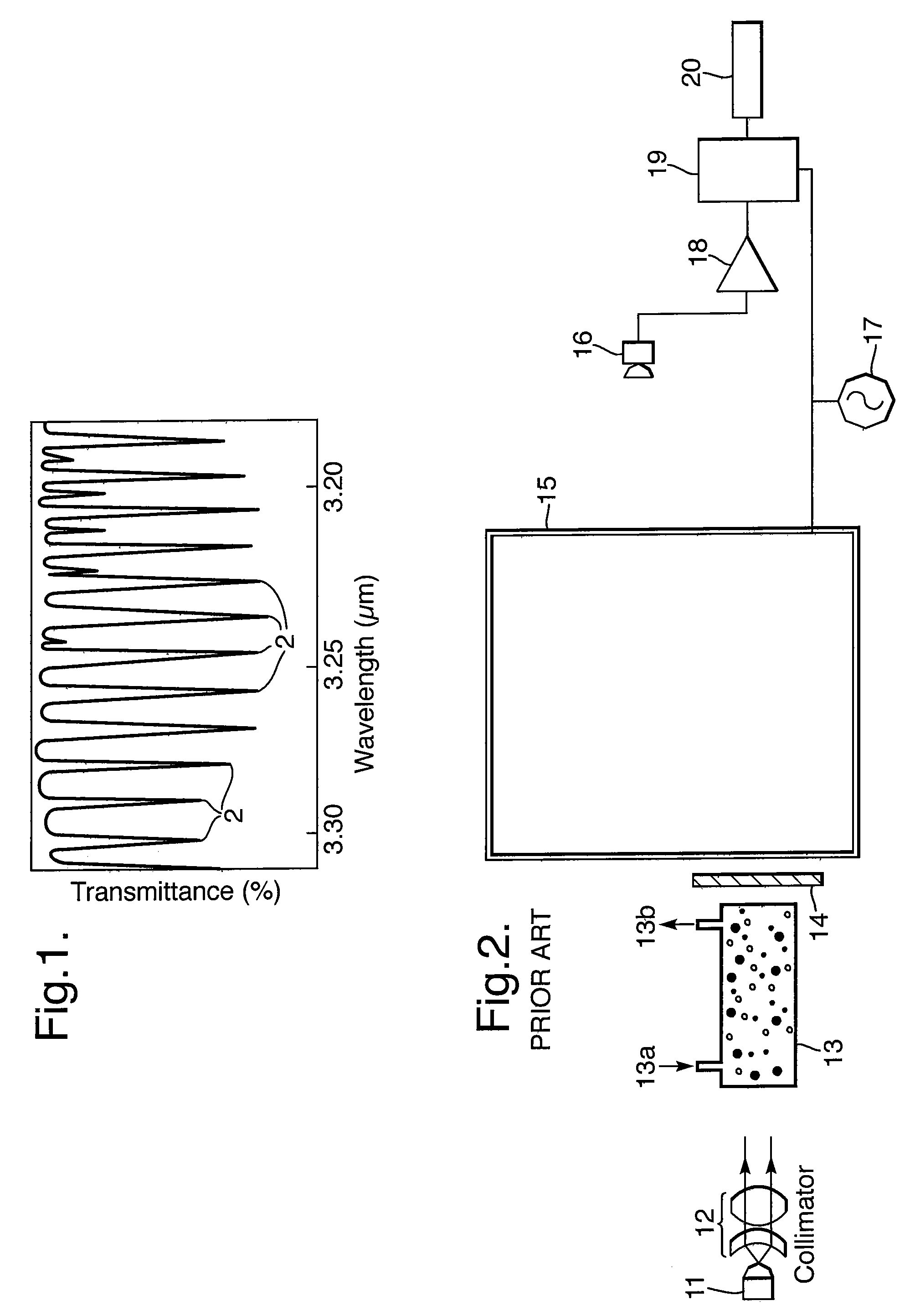
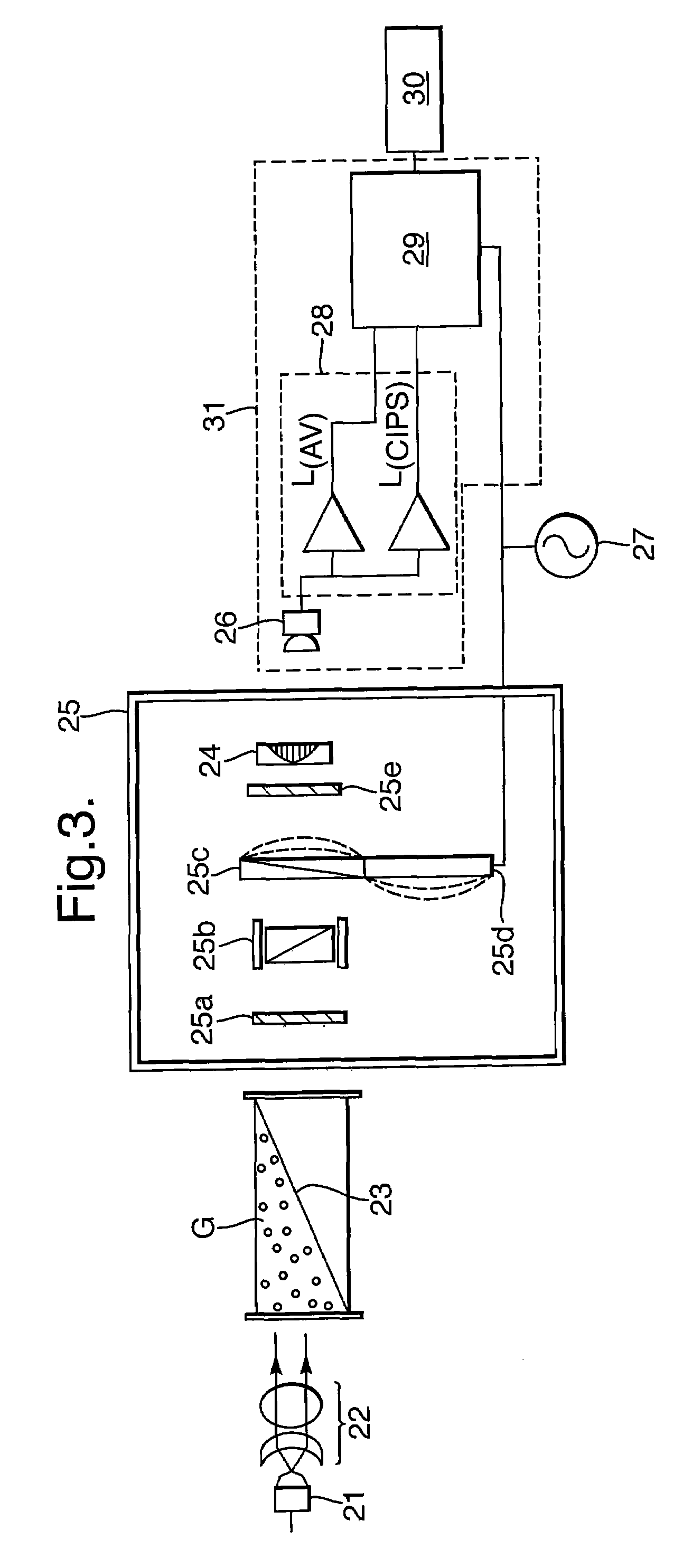
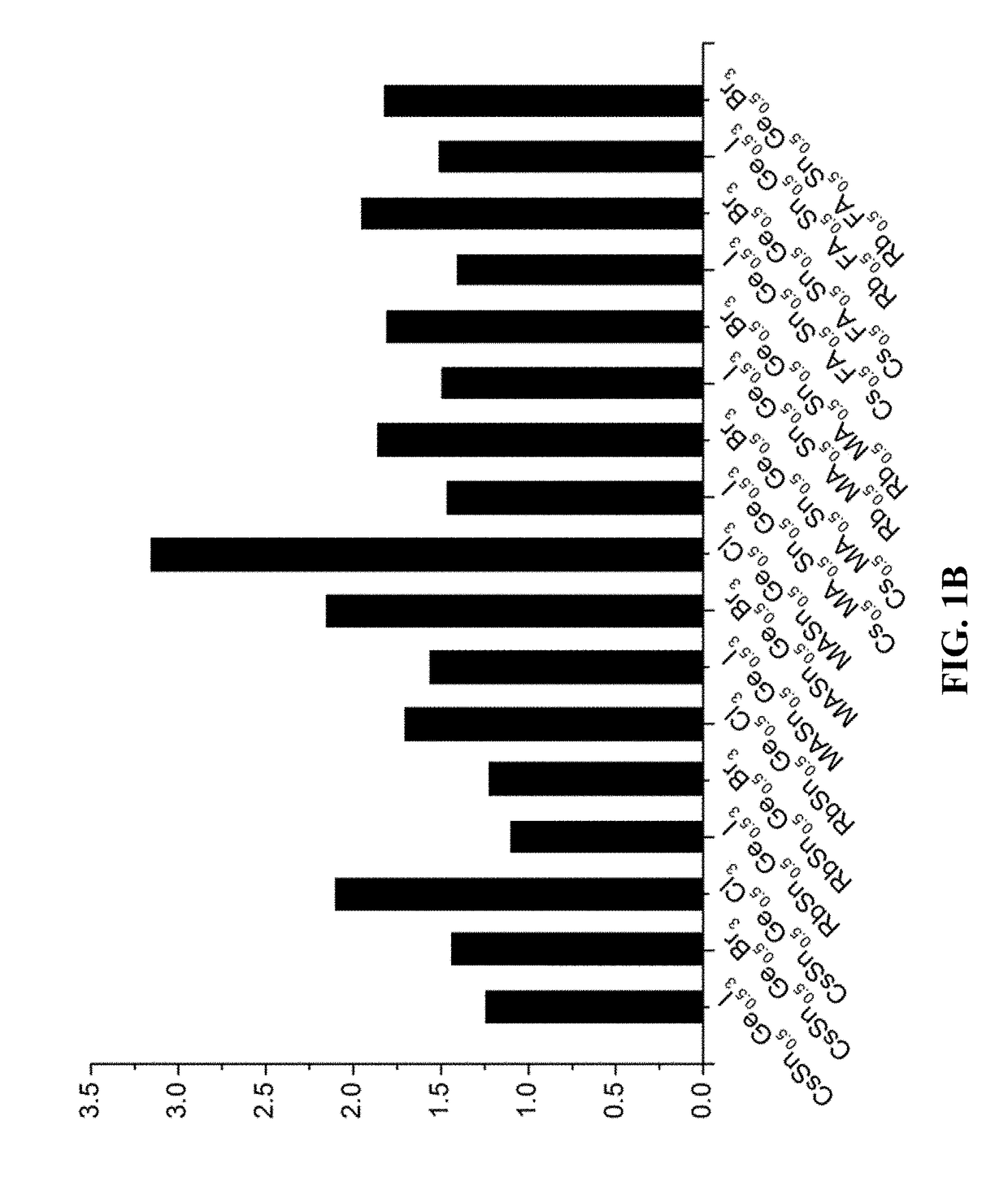
Multivariate optical elements for optical analysis system
A method of developing a multivariate optical element for an optical analysis system includes forming an optically absorptive spectral element having an optically absorptive material, the optically absorptive material being absorbing in a predetermined spectral region; and utilizing the optically absorptive spectral element in the optical analysis system.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Novel multivariate optical elements for optical analysis system
A method of developing a multivariate optical element for an optical analysis system includes forming an optically absorptive spectral element having an optically absorptive material, the optically absorptive material being absorbing in a predetermined spectral region; and utilizing the optically absorptive spectral element in the optical analysis system.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
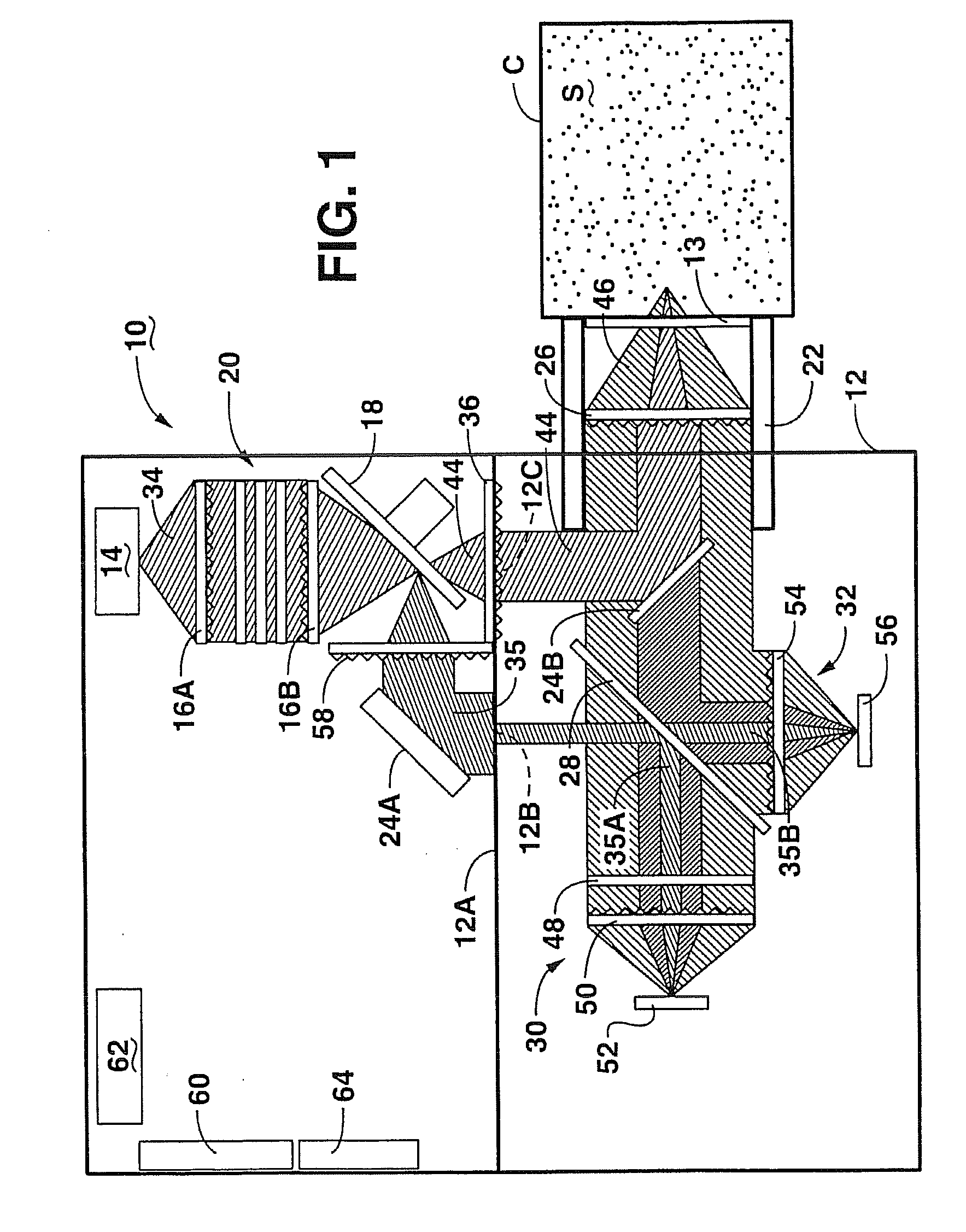
Graphene Optical Sensor
ActiveUS20120069338A1Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorAnalyteOptical absorption spectra
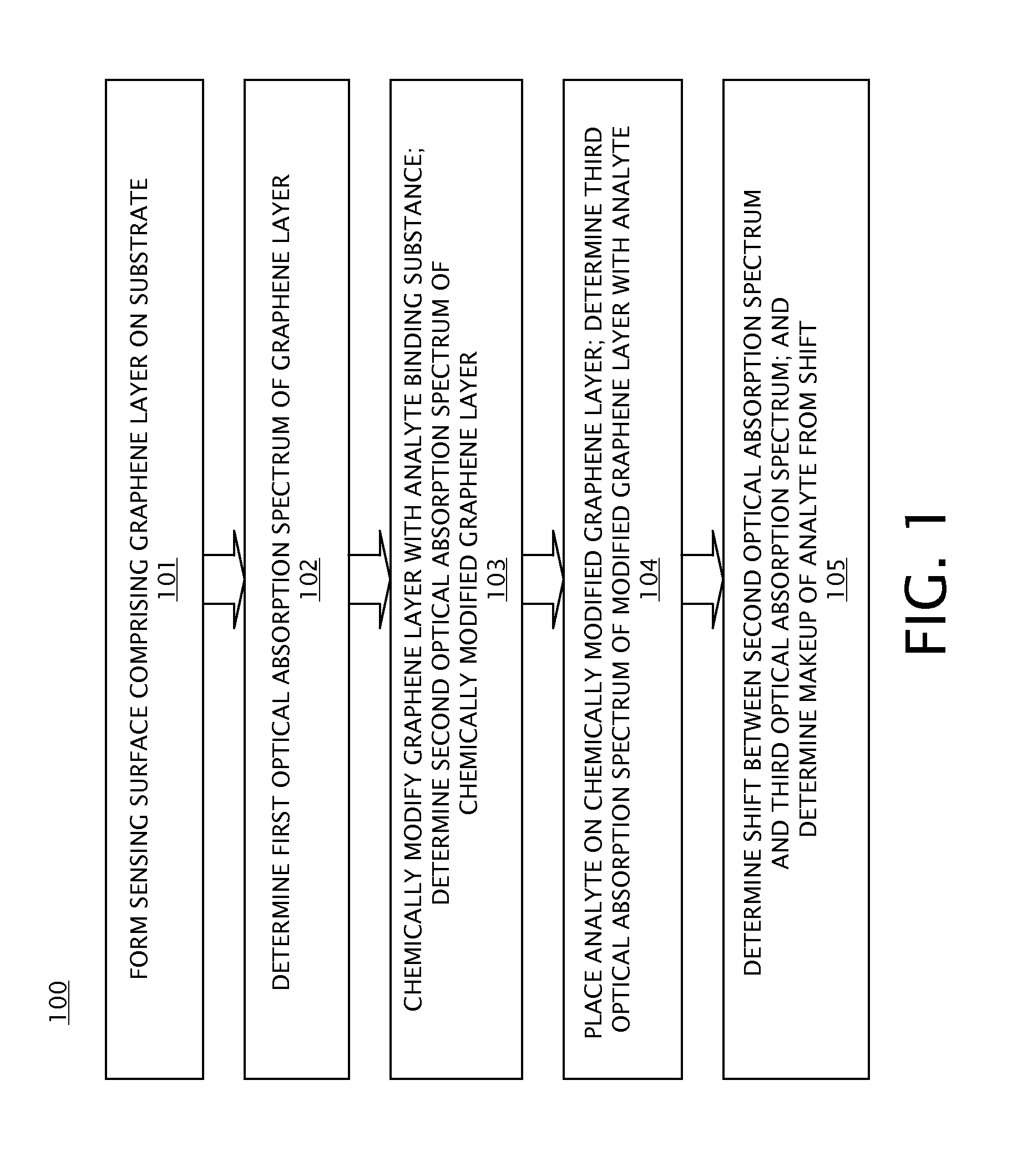
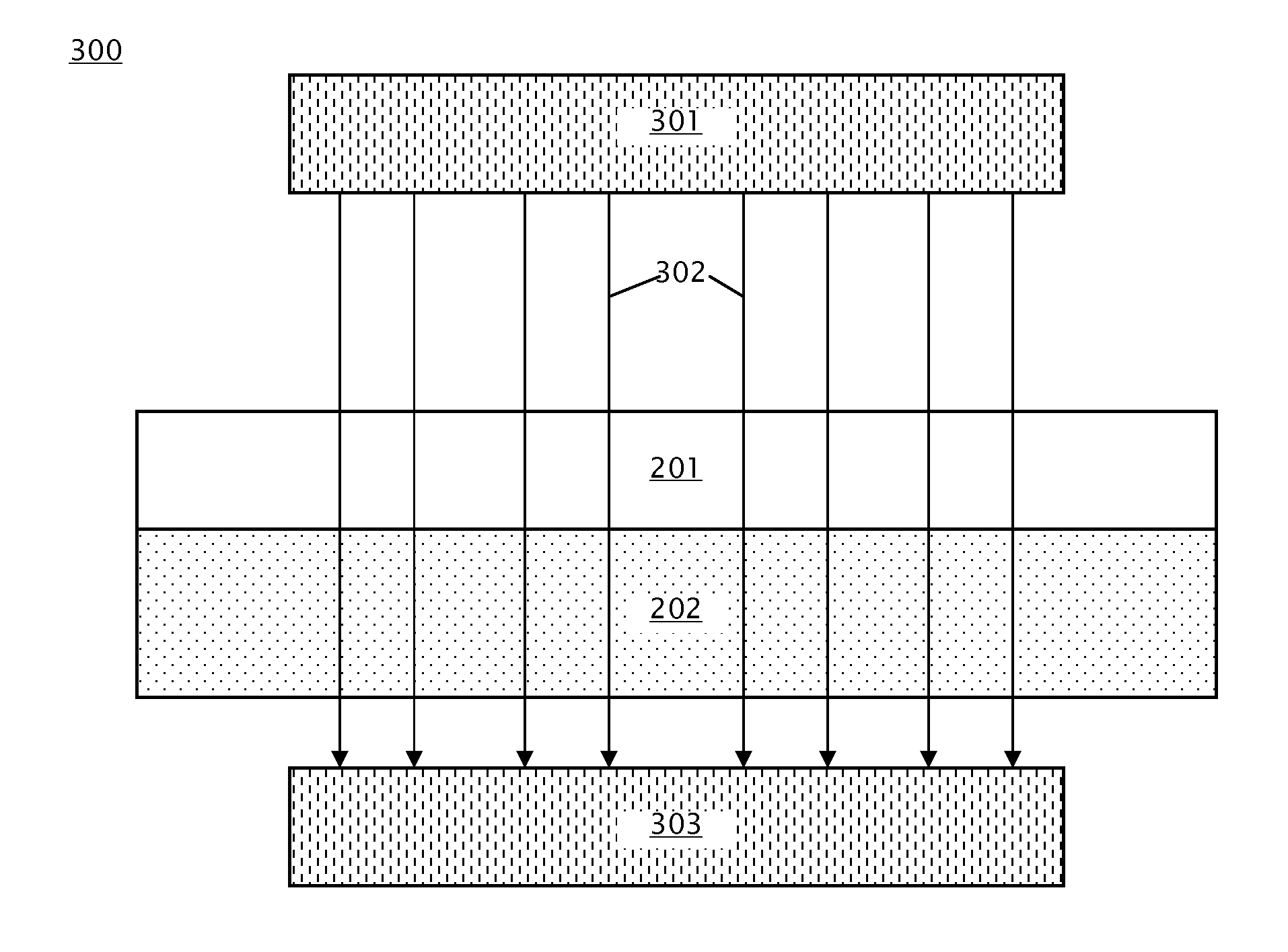
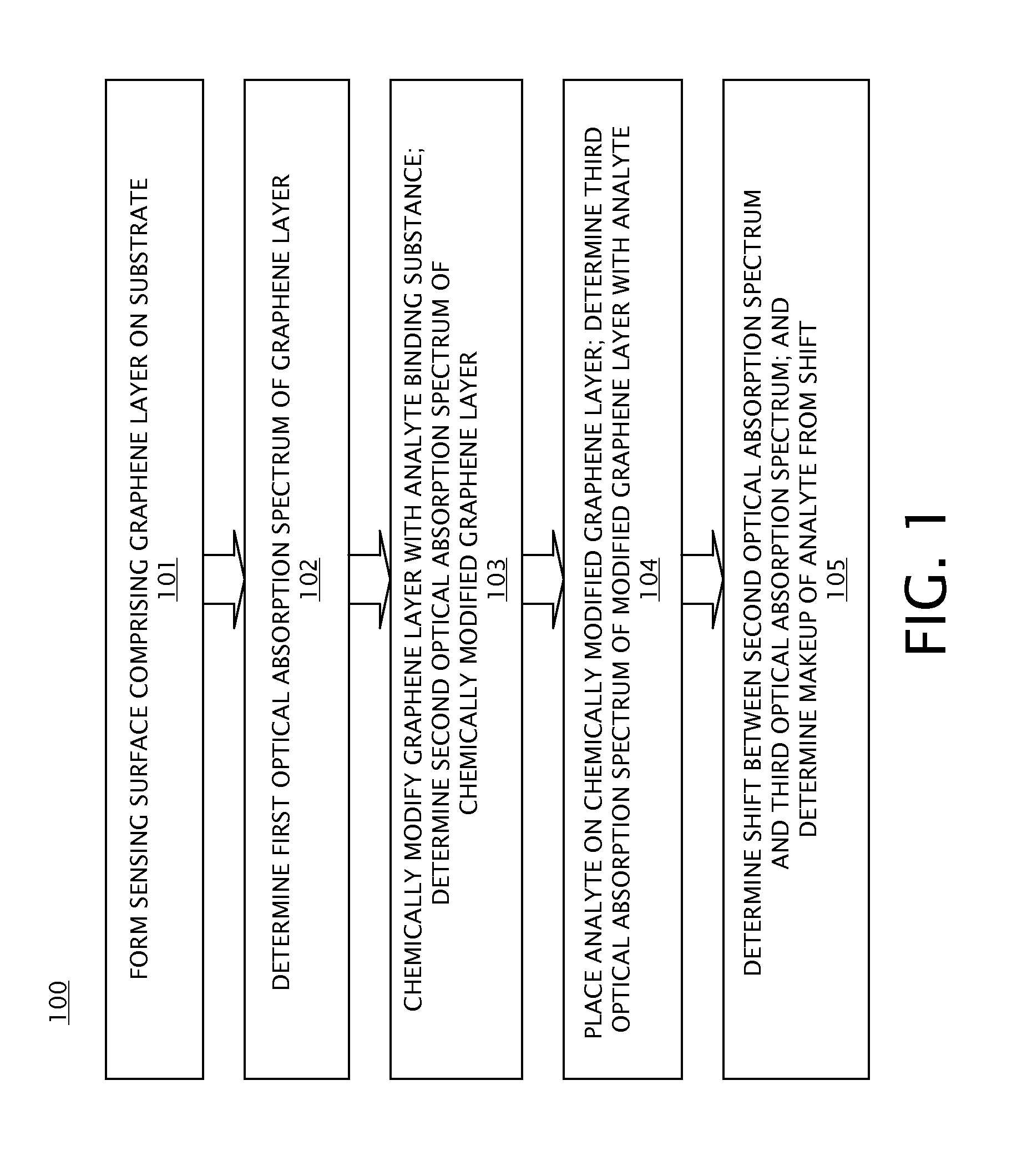
A method of using an optical sensor, the optical sensor comprising a sensing surface comprising graphene layer, the sensing surface located on a substrate, includes determining a first optical absorption spectrum for the graphene layer by a spectrophotometer; adding an analyte, the analyte selected to cause a shift in the first optical absorption spectrum, to the graphene layer; determining a second optical absorption spectrum for the modified graphene layer by a spectrophotometer; determining a shift between the first optical absorption spectrum and the second optical absorption spectrum; and determining a makeup of the analyte based on the determined shift.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Photonic crystal slot waveguide miniature on-chip absorption spectrometer
ActiveUS20120044489A1Enhanced light absorptionEliminate needRadiation pyrometryCladded optical fibreAnalyteOptical absorption spectra
Methods and systems for label-free on-chip optical absorption spectrometer consisting of a photonic crystal slot waveguide are disclosed. The invention comprises an on-chip integrated optical absorption spectroscopy device that combines the slow light effect in photonic crystal waveguide and optical field enhancement in a slot waveguide and enables detection and identification of multiple analytes to be performed simultaneously using optical absorption techniques leading to a device for chemical and biological sensing, trace detection, and identification via unique analyte absorption spectral signatures. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:OMEGA OPTICS
Graphene optical sensor
ActiveUS8395774B2Radiation pyrometryMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorAnalyteOptical absorption spectra
A method of using an optical sensor, the optical sensor comprising a sensing surface comprising graphene layer, the sensing surface located on a substrate, includes determining a first optical absorption spectrum for the graphene layer by a spectrophotometer; adding an analyte, the analyte selected to cause a shift in the first optical absorption spectrum, to the graphene layer; determining a second optical absorption spectrum for the modified graphene layer by a spectrophotometer; determining a shift between the first optical absorption spectrum and the second optical absorption spectrum; and determining a makeup of the analyte based on the determined shift.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP +1
Compact optical gas detection system and apparatus
ActiveUS20180348121A1Small sizeImprove the environmentTransmissivity measurementsWater vaporOptical absorption spectra
System and apparatus for portable gas detection. Specifically, this disclosure describes apparatuses and systems for optical gas detection in a compact package. There is a need for a very compact, low-power, gas detection system for gases such as CO2, NOx, water vapor, methane etc. This disclosure provides an ultra-compact and highly efficient optical measurement system based on principals of optical absorption spectroscopy. It reduces the size of the instrument as well its power consumption by more than an order of magnitude making it possible to deploy it widely. There is an identified need for large number of distributed gas sensors to improve human health, environment, and save energy usage.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
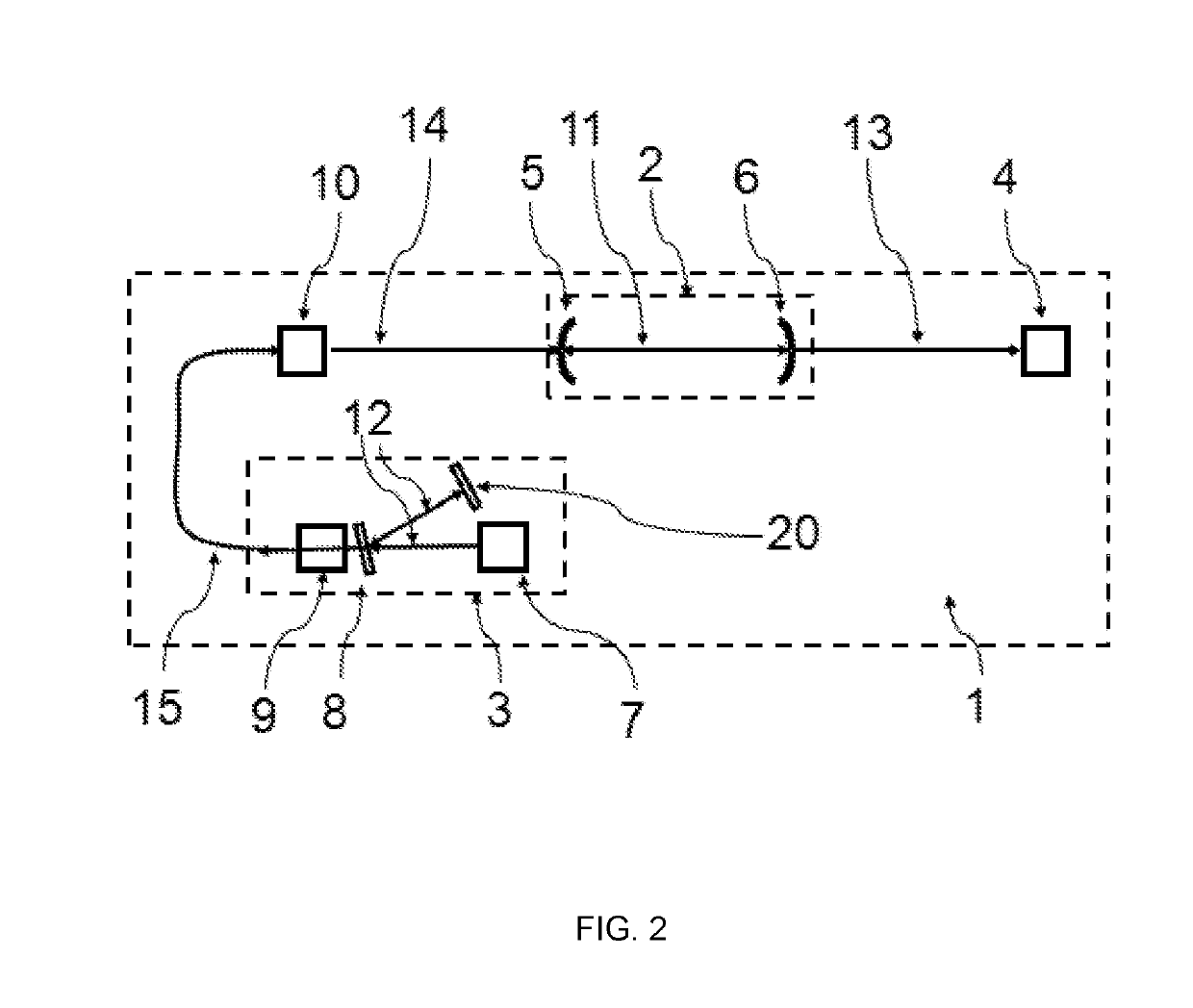
Optical absorption spectroscopy with multi-ass cell with adjustable optical path length
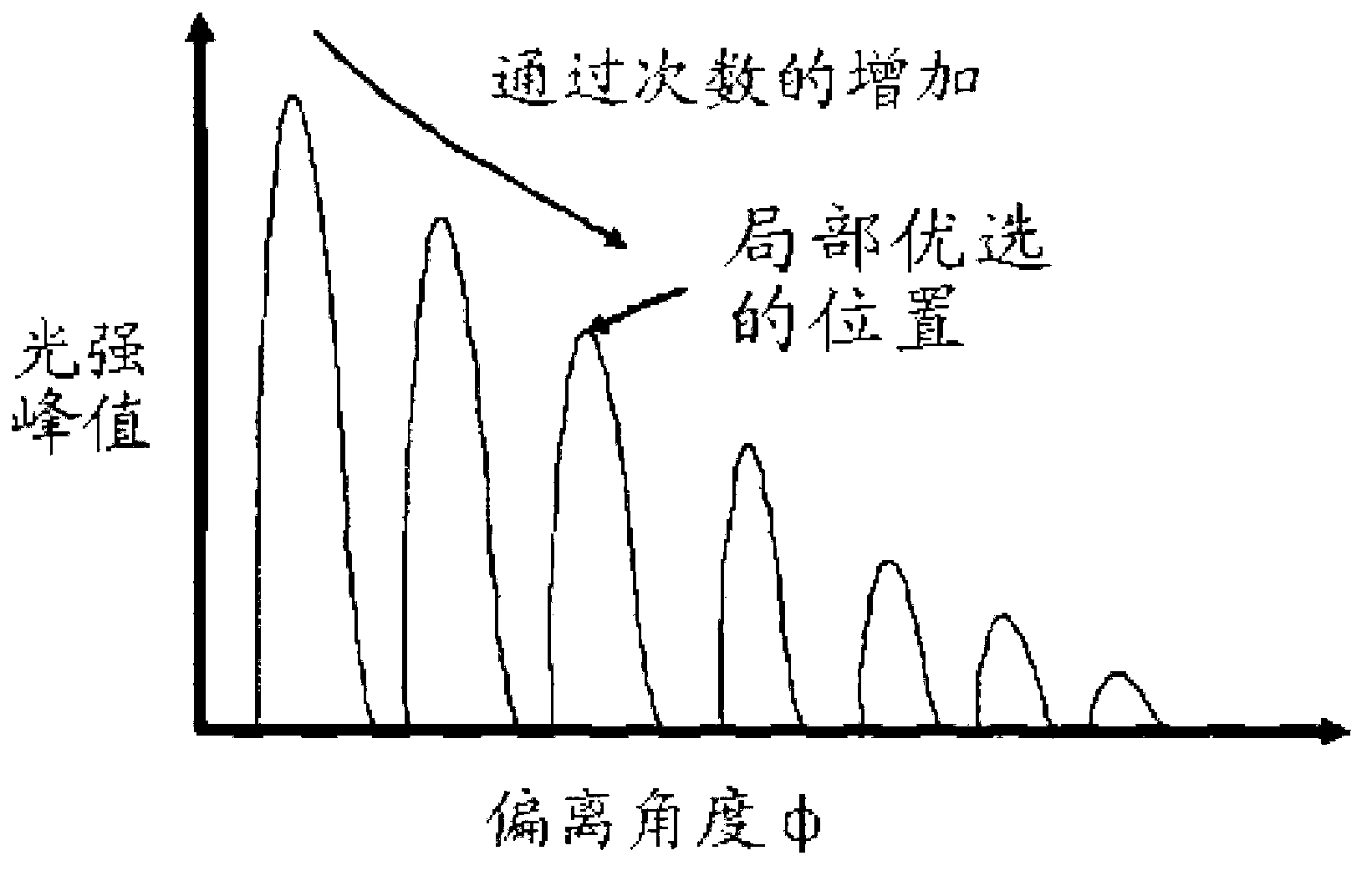
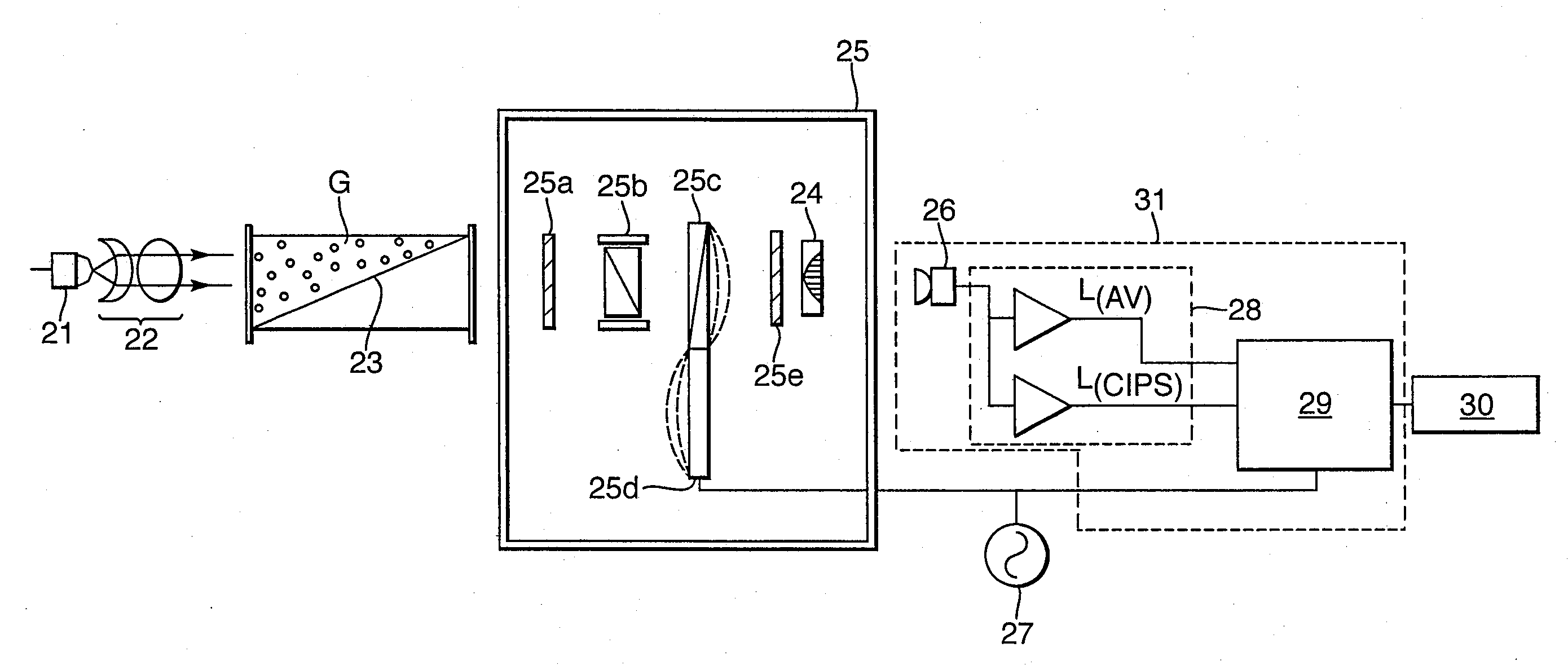
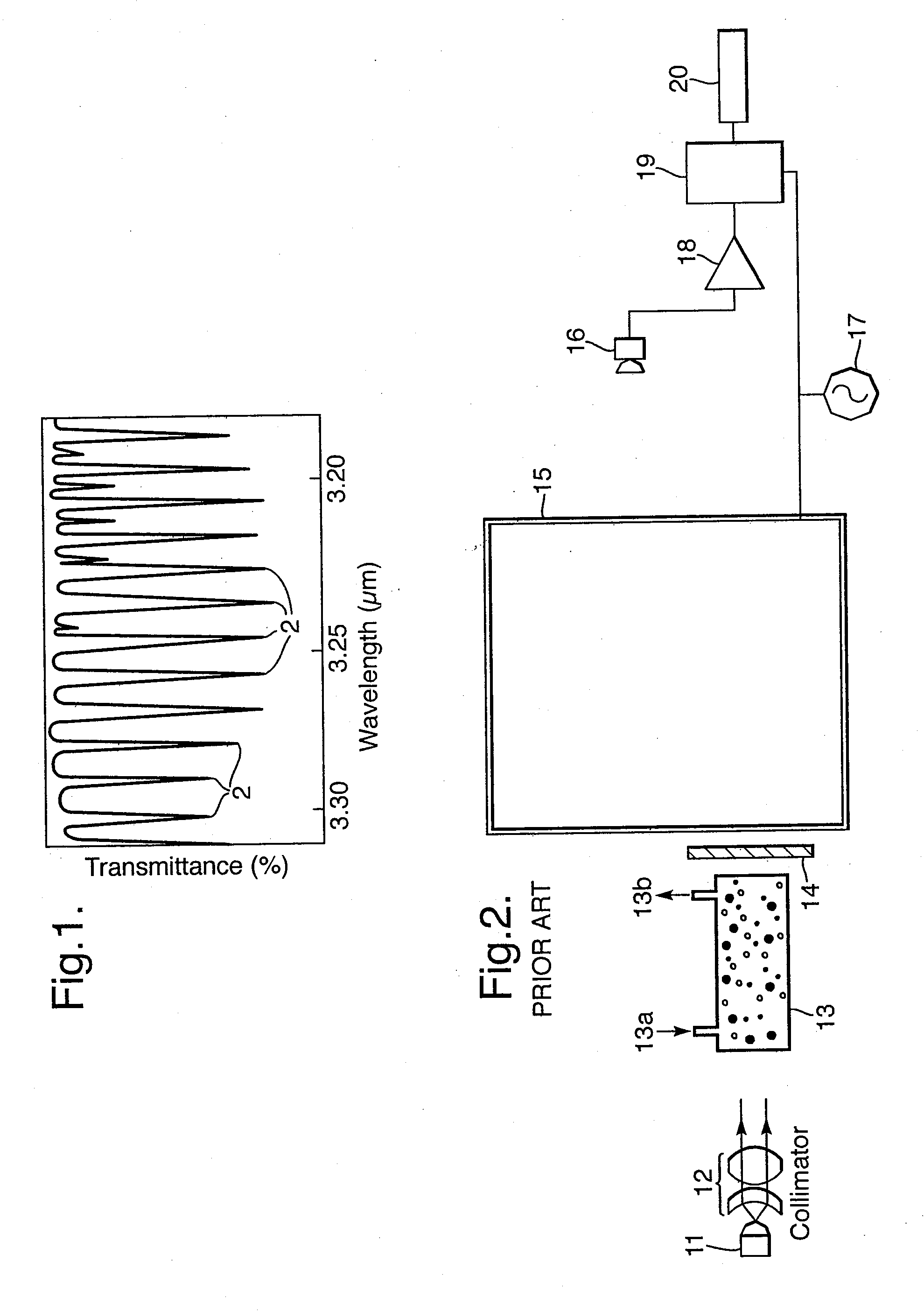
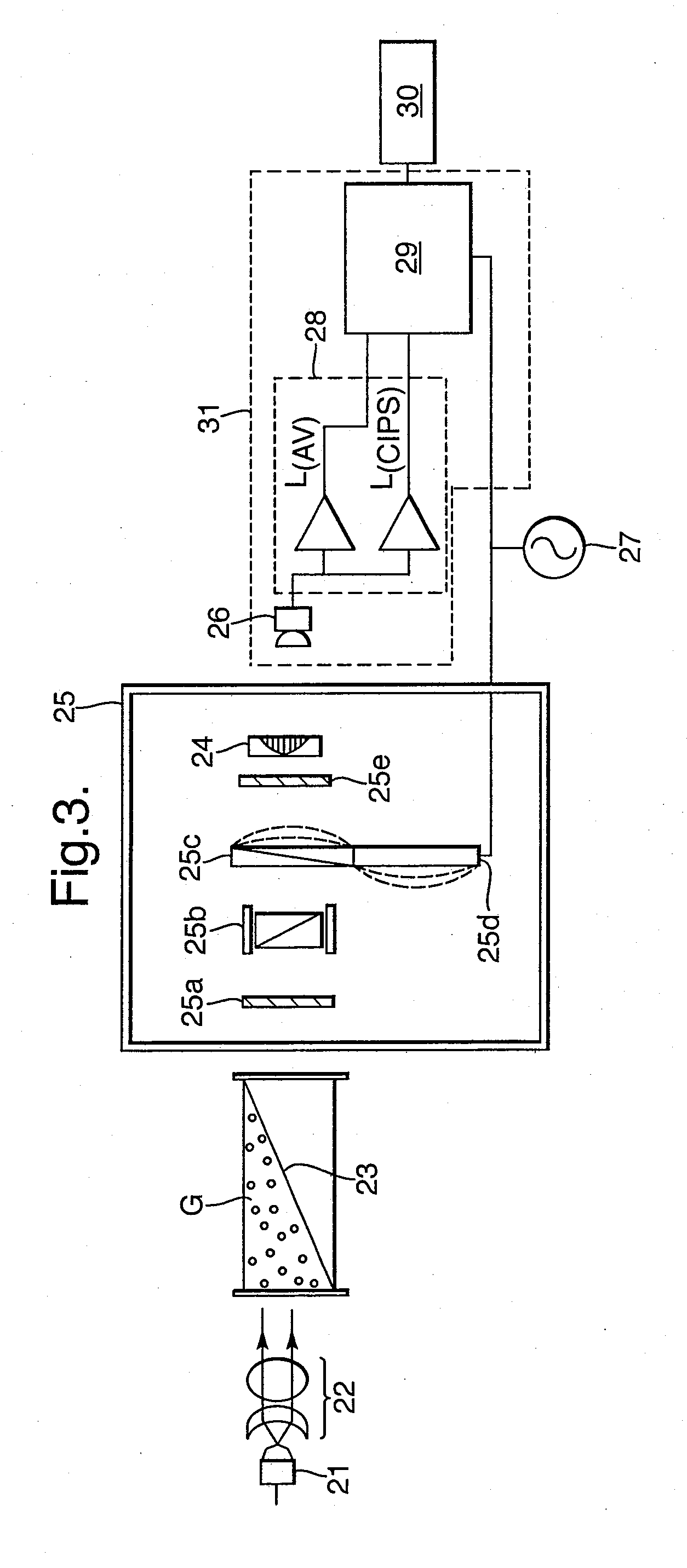
InactiveCN103221793AAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyColor/spectral properties measurementsPath lengthX-ray absorption spectroscopy
An optical absorption spectroscopy apparatus comprises a light source, a detector for detecting an optical absorption spectrum of light transmitted from the source through a sample volume and one or more reflectors for reflecting the transmitted light multiple times through the sample volume. An adjuster device is provided for adjusting at least one optical element so as to vary the path length of the transmitted light by controlling the number of times the light is reflected through the sample volume. Drive means is provided for driving the adjuster device, so enabling the detector to detect the transmitted light at a range of different path lengths.
Owner:DUVAS TECH
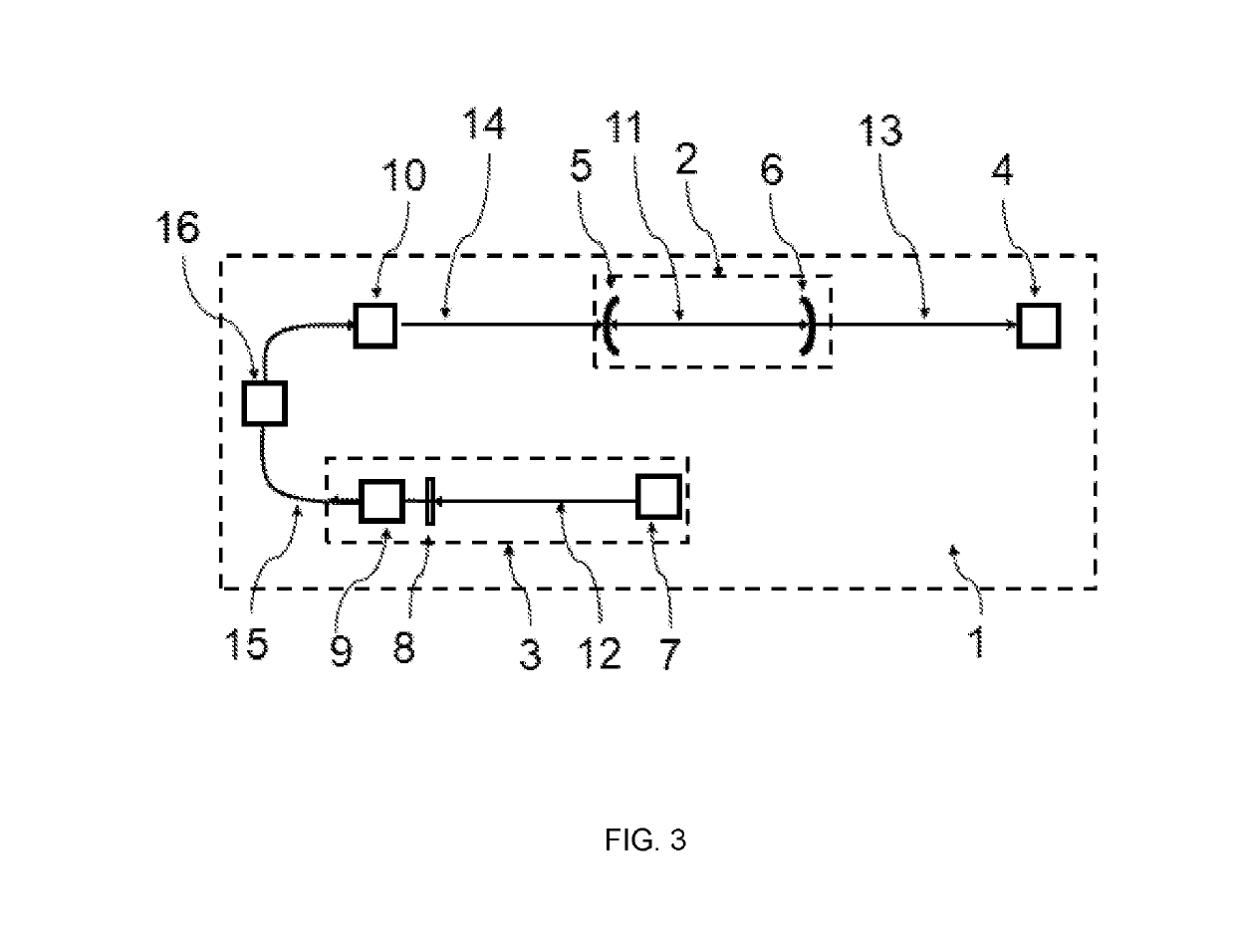
Optical Absorption Spectrometer and Method for Measuring Concentration of a Substance
InactiveUS20090257064A1High sensitivityAccurate measurementRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryOptical absorption spectraSpectrometer
An optical absorption spectrometer is provided for determining the concentration of a substance within a sample. The optical absorption spectrometer comprises a first radiation source for supplying radiation to the sample to be measured; at least one cavity for containing the sample during measurement; and a detector assembly for detecting radiation transmitted along first and second optical paths through the sample, the length of the first optical path being greater than that of the second optical path.
Owner:BAH HLDG
Optical absorption spectrometer and method for measuring concentration of a substance
ActiveUS7570360B1Accurate measurementReduce dependenceRadiation pyrometryAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceOptical absorption spectraSpectrometer
An optical absorption spectrometer is provided for determining the concentration of a substance within a sample. The optical absorption spectrometer comprises a first radiation source for supplying radiation to the sample to be measured; at least one cavity for containing the sample during measurement; and a detector assembly for detecting radiation transmitted along first and second optical paths through the sample, the length of the first optical path being greater than that of the second optical path.
Owner:BAH HLDG
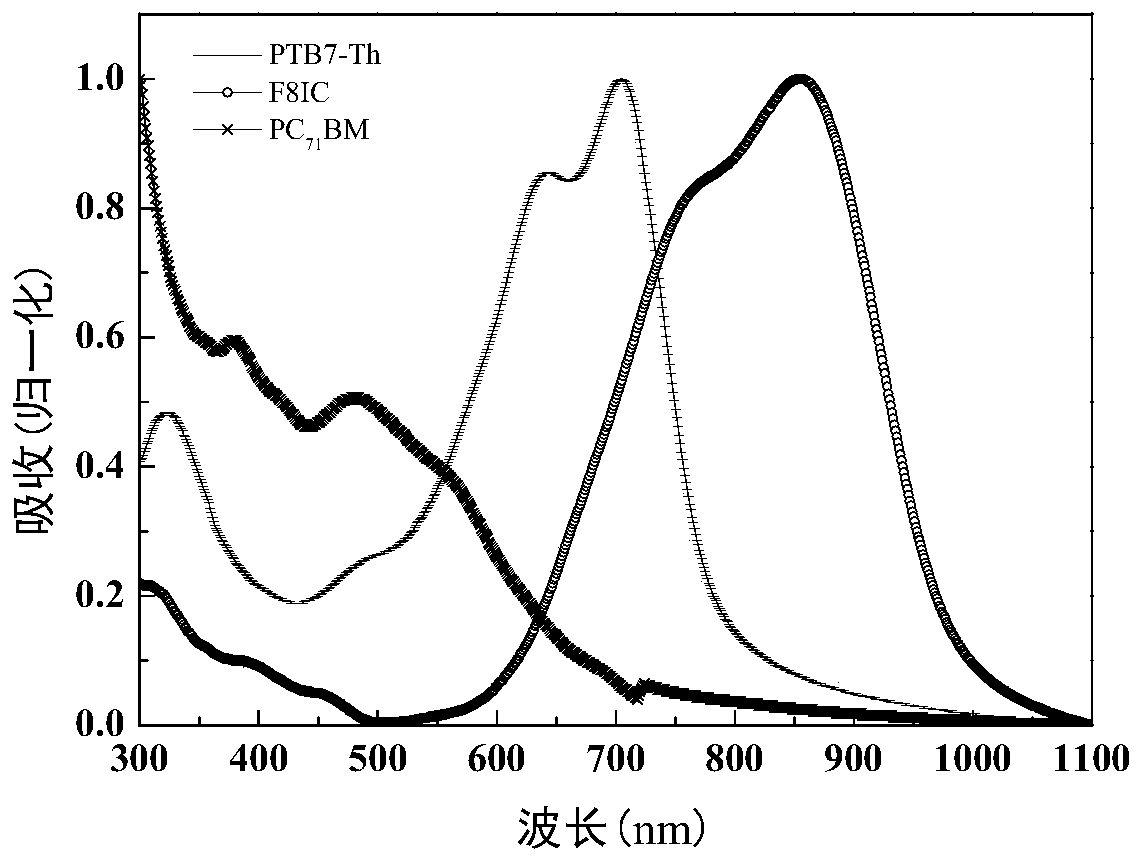
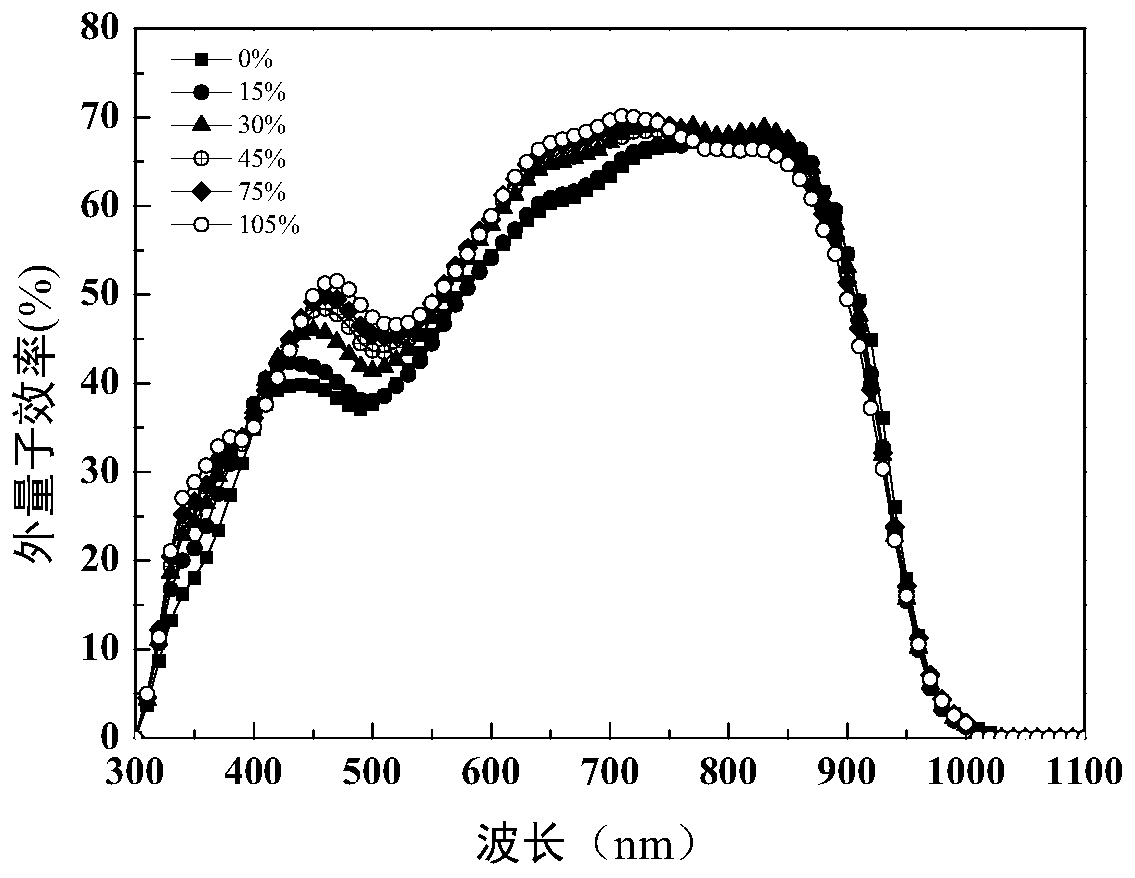
High-efficiency ternary organic solar cell and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109980090AEasy to makeImprove photoelectric energy conversion efficiencyFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesScreen printingOrganic solar cell
The invention discloses a high-efficiency ternary organic solar cell and a preparation method thereof. The active layer of the organic solar cell is obtained by blending a donor material and a receptor material. A ternary organic solar cell containing both non-fullerene and fullerene receptors is prepared by introducing a third component, fullerene acceptor, into the active layer of a binary non-fullerene organic solar cell. The addition of the fullerene receptor not only broadens the optical absorption spectrum of a device and increases the short-circuit current density, but also modifies theshape of the active layer, and finally improves the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the organic solar cell. Further, the active layer of the ternary organic solar cell can be processed at roomtemperature, and a solution can be formed into a film by spin coating, blade coating, and screen printing. Without any physical optimization method, the method can improve the efficiency of the device, reduces the manufacturing cost of the organic solar cell, and is suitable for the roll-to-roll production process.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
White cell for fluid detection
InactiveUS20150062572A1Radiation pyrometryAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyWhite blood cellOptical absorption spectra
An optical absorption spectroscopy apparatus includes a field mirror and at least one object mirror configured to reflect transmitted light multiple times between the field minor and the at least one object mirror through a sample volume. At least one fold mirror is configured to allow the transmitted light to double pass across the field mirror. The apparatus can further include a light source and a detector configured to detect an optical absorption spectrum of the light transmitted from the light source through a sample volume.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Optical absorption spectroscopy based gas analyzer systems and methods
InactiveUS20190025203A1Absorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyColor/spectral properties measurementsResonant cavityExternal cavity laser
The present invention provides a system for measuring concentrations of trace gases in gas mixtures using the absorption spectroscopy method. The system comprising: a resonant optical cavity, a continuous-wave stepwise tunable external cavity laser having a DFB laser as a gain media; a detector system for measuring an absorption of laser light by the gas in the resonant optical cavity, wherein the roundtrip optical cavity length of the external cavity laser are the roundtrip optical cavity length of the resonant cavity are close
Owner:KOULIKOV SERGUEI
Photonic crystal slot waveguide miniature on-chip absorption spectrometer
ActiveUS8282882B2Enhanced light absorptionEliminate needRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSlot-waveguideAnalyte
Methods and systems for label-free on-chip optical absorption spectrometer consisting of a photonic crystal slot waveguide are disclosed. The invention comprises an on-chip integrated optical absorption spectroscopy device that combines the slow light effect in photonic crystal waveguide and optical field enhancement in a slot waveguide and enables detection and identification of multiple analytes to be performed simultaneously using optical absorption techniques leading to a device for chemical and biological sensing, trace detection, and identification via unique analyte absorption spectral signatures. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:OMEGA OPTICS
Optical absorption spectroscopy based gas analyzer systems and methods
ActiveUS20190265160A1Analysis by thermal excitationAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyResonant cavityExternal cavity laser
The present invention provides a system for measuring concentrations of trace gases in gas mixtures using the absorption spectroscopy method. The system comprising: a resonant optical cavity, a continuous-wave stepwise tunable external cavity laser having a DFB laser as a gain media; a detector system for measuring an absorption of laser light by the gas in the resonant optical cavity, wherein the roundtrip optical cavity length of the external cavity laser are the roundtrip optical cavity length of the resonant cavity are close
Owner:KOULIKOV SERGUEI
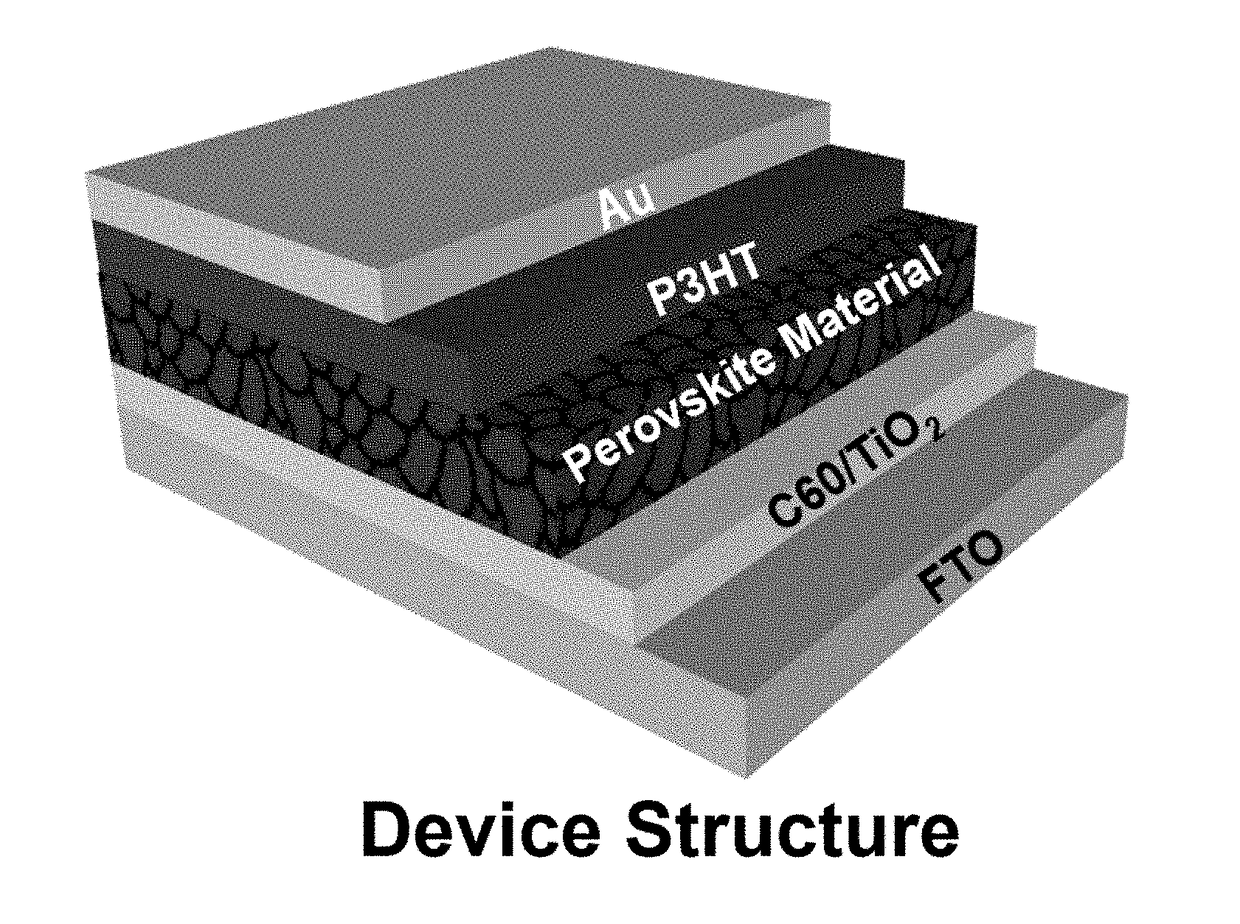
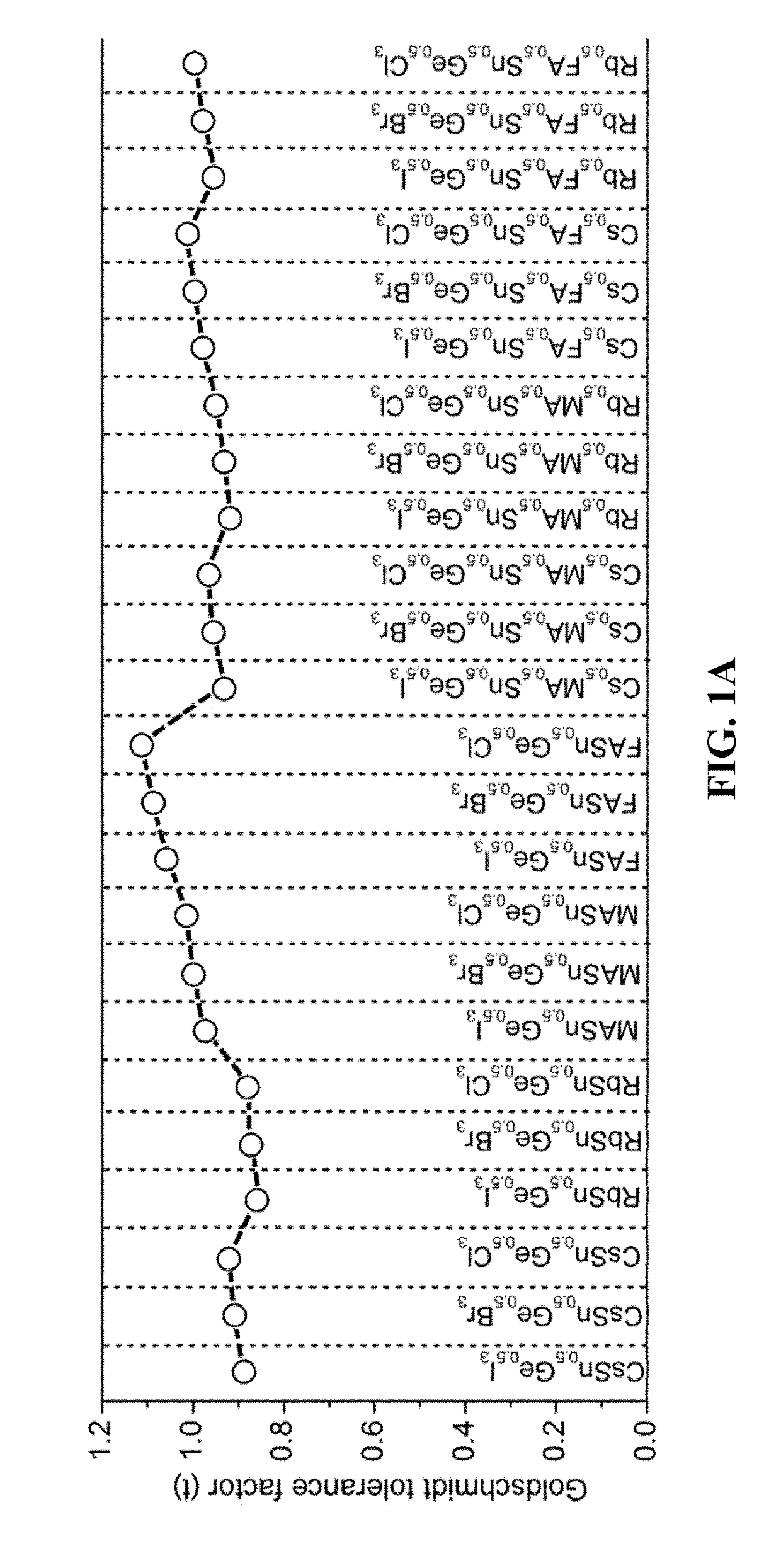
Mixed tin and germanium perovskites
InactiveUS20180254362A1Large positive valueSmall positive valueSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical absorption spectraPhotochemistry
Perovskite materials useful in the manufacture of photovoltaic cells are provided. The perovskite materials have the formula AB′0.5B″0.5X3 or A′0.5A″0.5B′0.5B″0.5X3, wherein A, A′, and A″ are organic or inorganic cations, X is a halogen ion, B′ is tin, and B″ is germanium. Embodiments of the mixed tin and germanium halide perovskite materials possess a direct bandgap within the optimal range of 0.9-1.6 eV and have an optical absorption spectrum that is comparable to the state-of-the-art methylammonium lead iodide perovskites. The perovskite materials provided herein have been formulated to be lead-free.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY +1
Laser stimulated atom probe characterization of semiconductor and dielectric structures
InactiveUS20050017174A1Rapid pulseImprove optical absorptionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationNanotechnologySemiconductor materialsOptical absorption spectra
A laser stimulated atom probe for atom probe imaging of dielectric and low conductivity semiconductor materials is disclosed. The laser stimulated atom probe comprises a conventional atom probe providing a field emission tip and ion detector arrangement, a laser system providing a laser short laser pulse and synchronous electronic timing signal to the atom probe, and an optical system for delivery of the laser beam onto the field emitting tip apex. The conventional atom probe is employed in a manner similar to that used for investigation of high conductivity materials. However, the electric field is held static while the laser is pulsed to provide pulsing of the ion emission rate. The laser pulsing is accomplished in a manner similar to prior implementations of pulsed laser atom probe spectroscopy. The laser pulses provide a trigger signal to enable recording the time of flight in the atom probe. The laser operates at a wavelength in the UV in order to enhance the optical absorption in semiconductor or dielectric field emission tips. The increased optical absorption allows efficient thermal pumping of the field evaporation rate. The tip apex field is also used to redshift the optical absorption spectra of the dielectric or semiconducting material under investigation, further enhancing the optical absorption. Due to the enhanced absorption, it is also possible to realize a photo ionization mechanism, wherein the laser stimulates electronic transitions from the more extended surface atoms, thereby ionizing the surface atom. The laser source is collimated by a collimation lens, reflected using dielectric mirrors, directed onto the sample tip using a focusing lens arrangement, collected from the tip using a collection lens, and directed into a beam stop. The laser beam diameter at focus is approximately 3-30 microns, thus, individual emission tips may be scanned from a field of tips illuminated by the laser pulse.
Owner:CHISM II WILLIAM W
Method for the Chip-Integrated Spectroscopic Identification of Solids, Liquids, and Gases
ActiveUS20120327398A1Enhanced light absorptionEliminate needRadiation pyrometryColor measuring devicesSlot-waveguideAnalyte
Methods and systems for a label-free on-chip optical absorption spectrometer consisting of a photonic crystal slot waveguide are disclosed. The invention comprises an on-chip integrated optical absorption spectroscopy device that combines the slow light effect in photonic crystal waveguide and optical field enhancement in a slot waveguide and enables detection and identification of multiple analytes to be performed simultaneously using optical absorption techniques leading to a device for chemical and biological sensing, trace detection, and identification via unique analyte absorption spectral signatures. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:OMEGA OPTICS
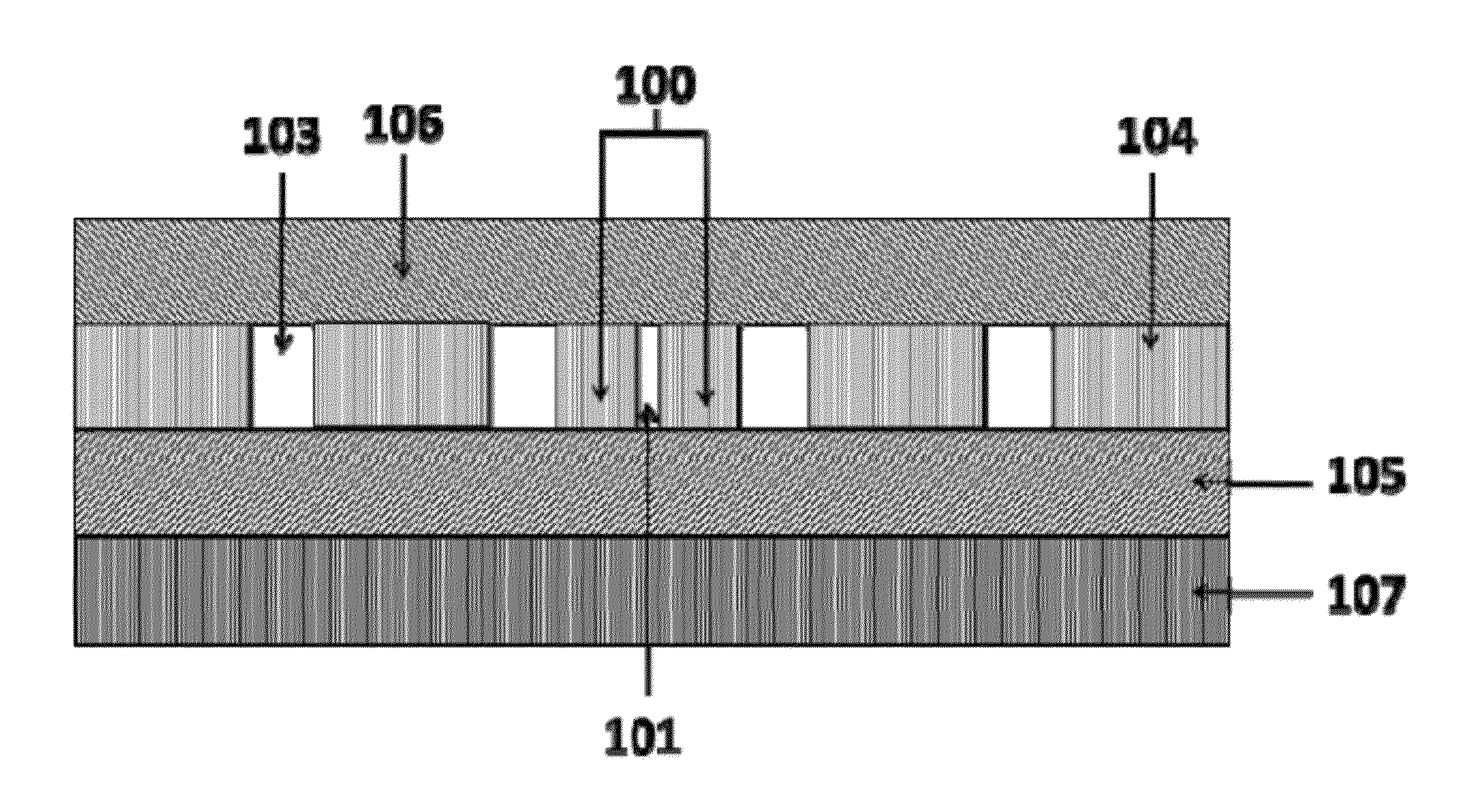
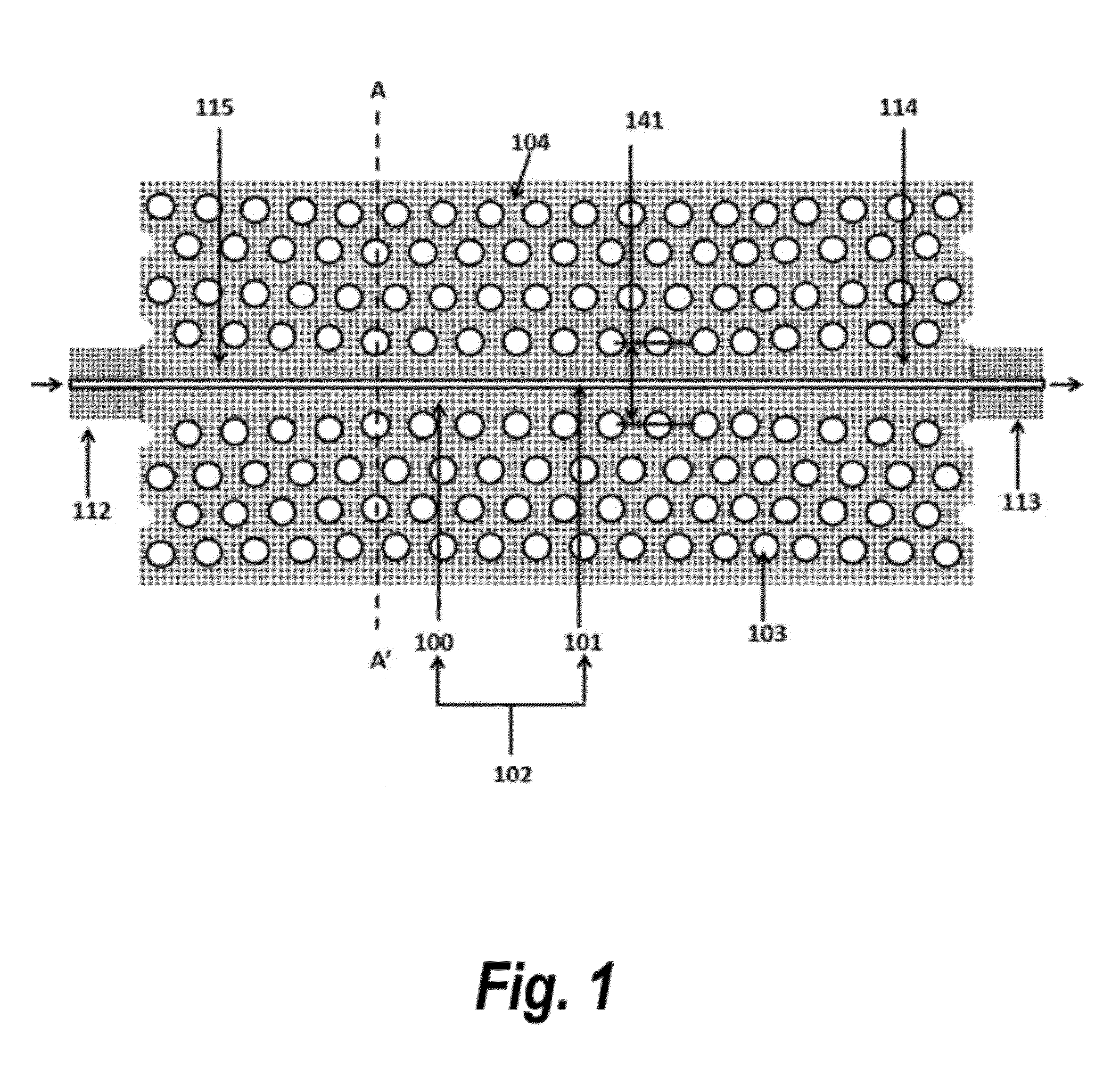
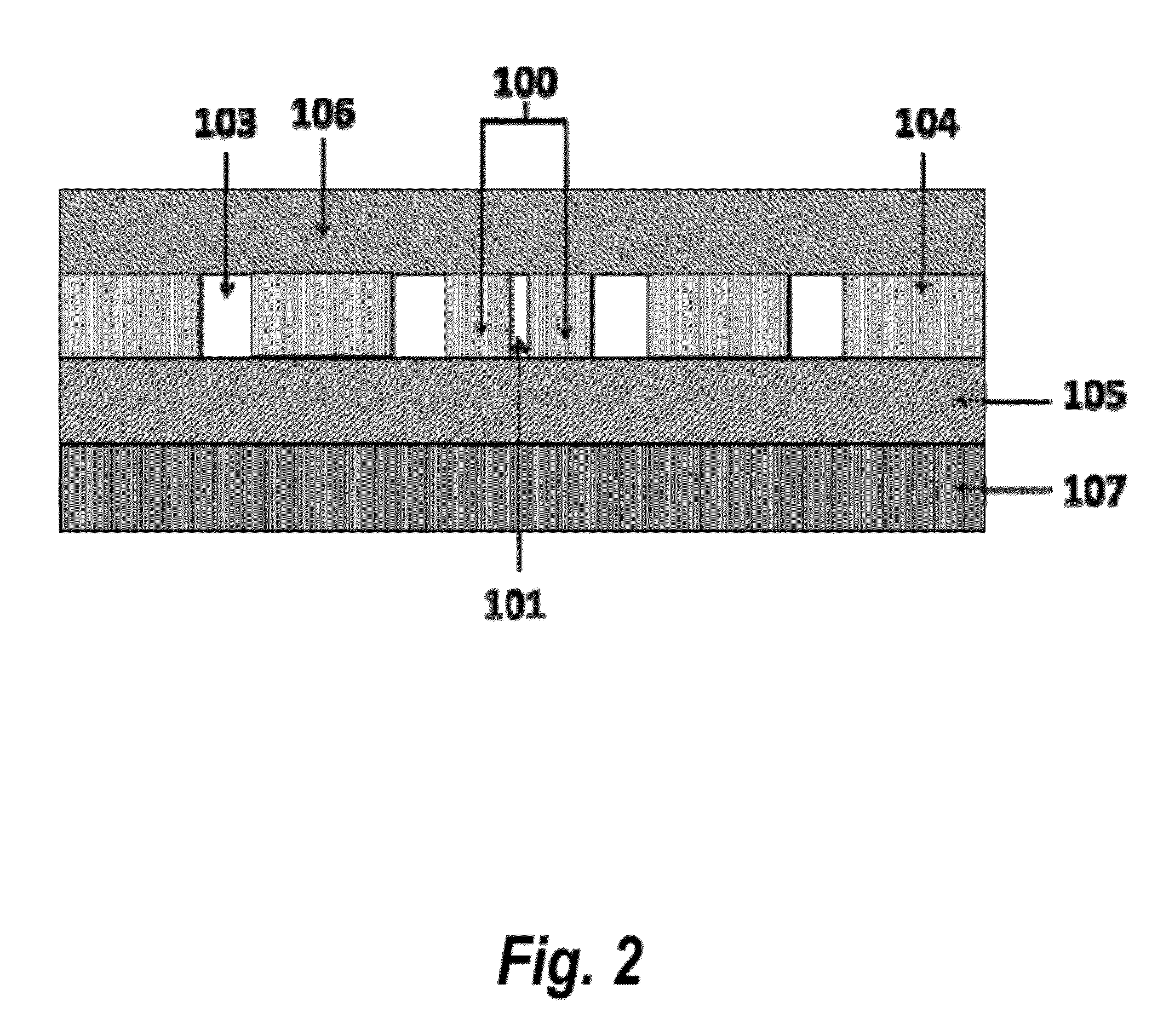
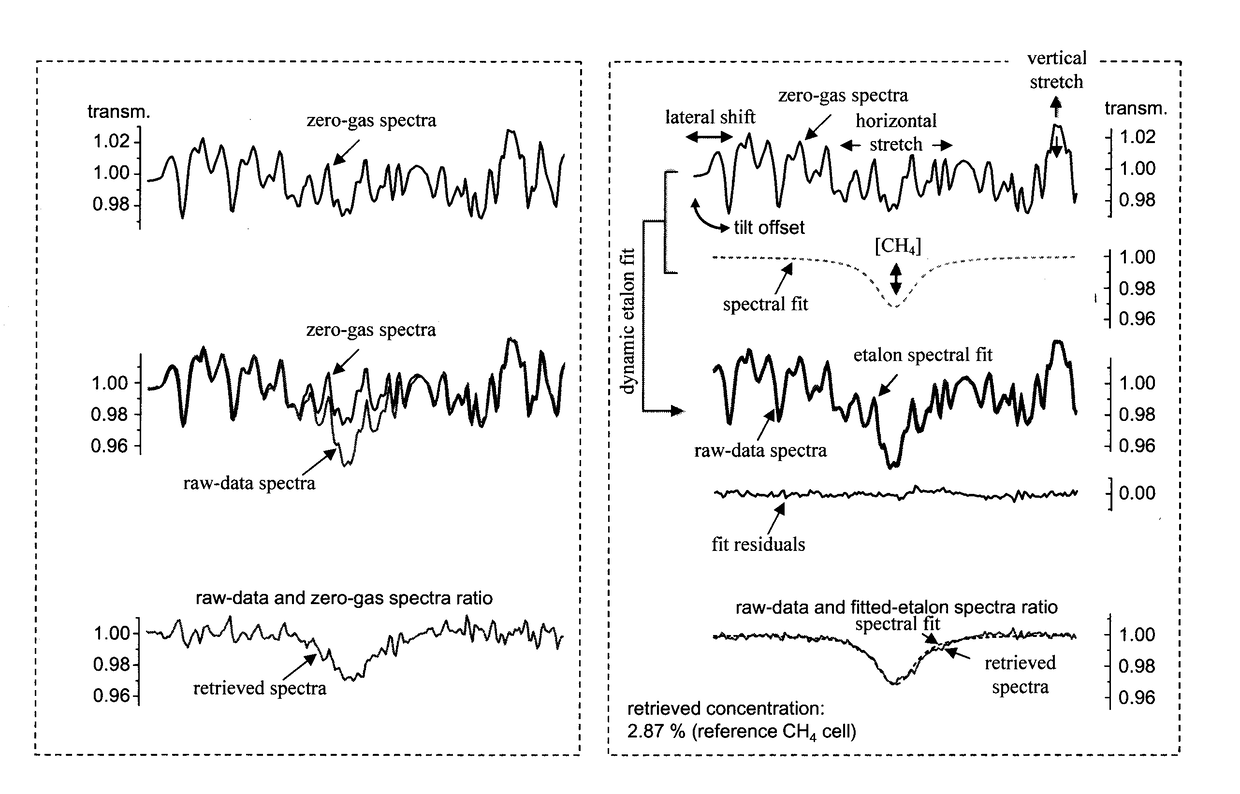
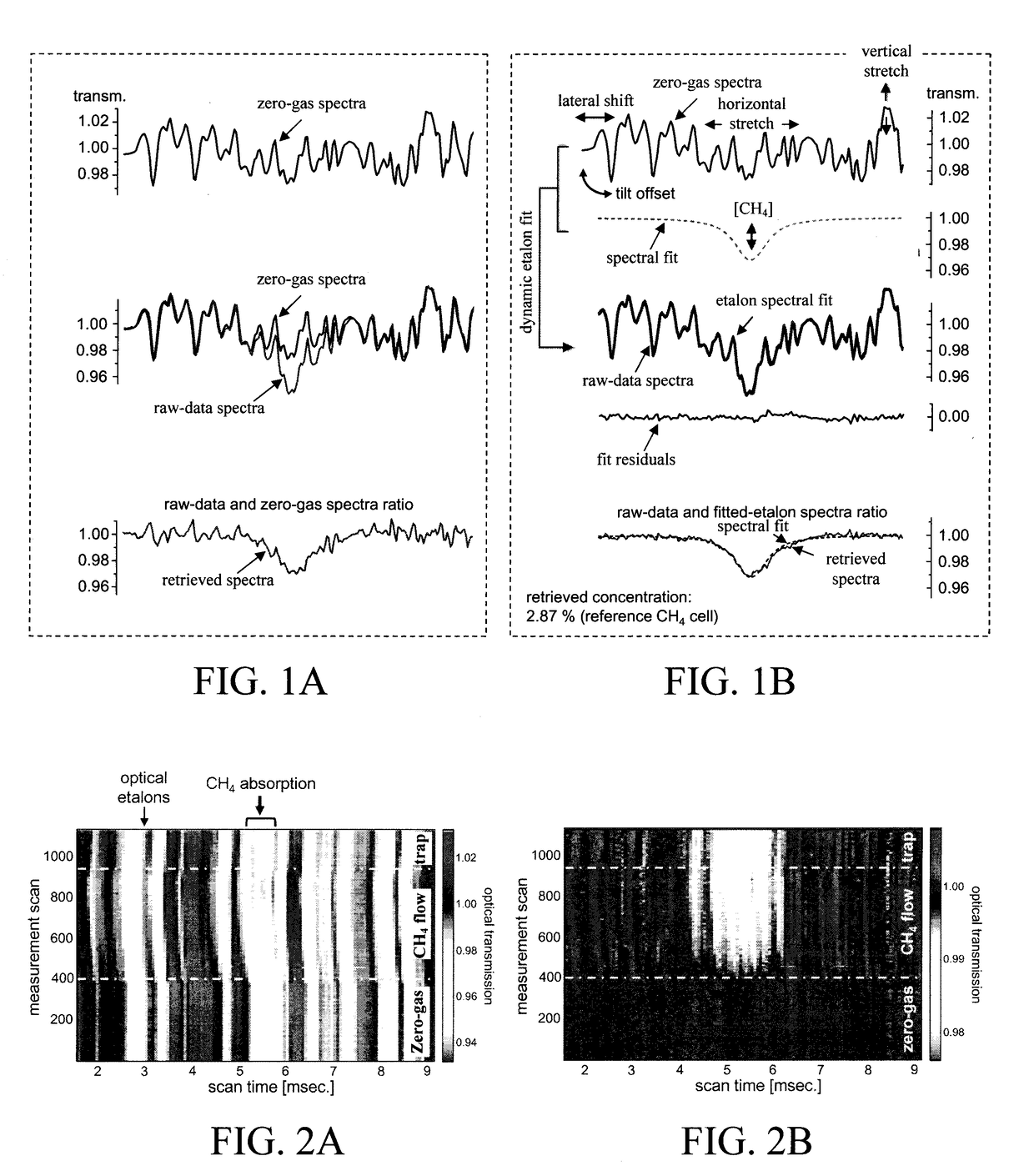
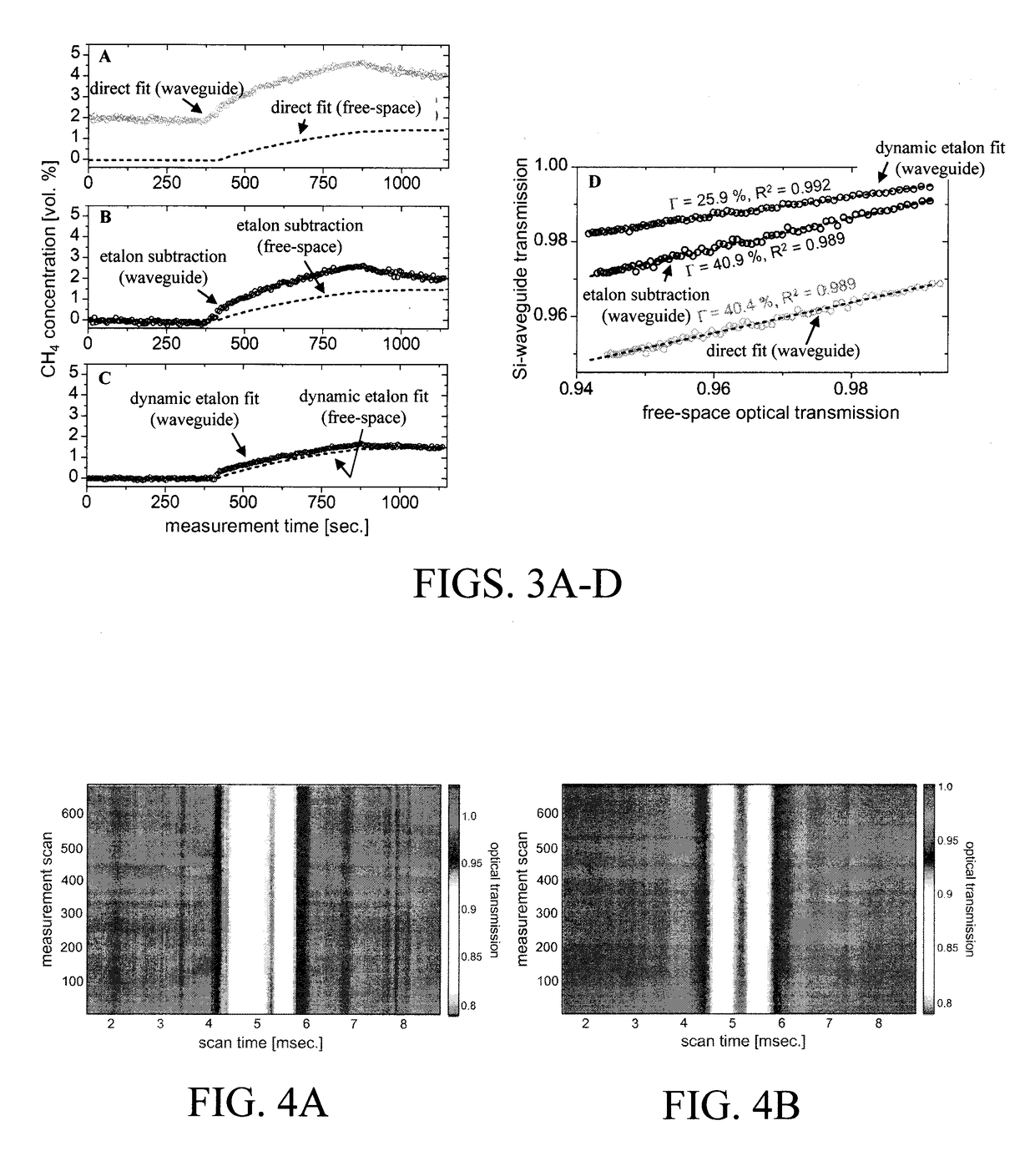
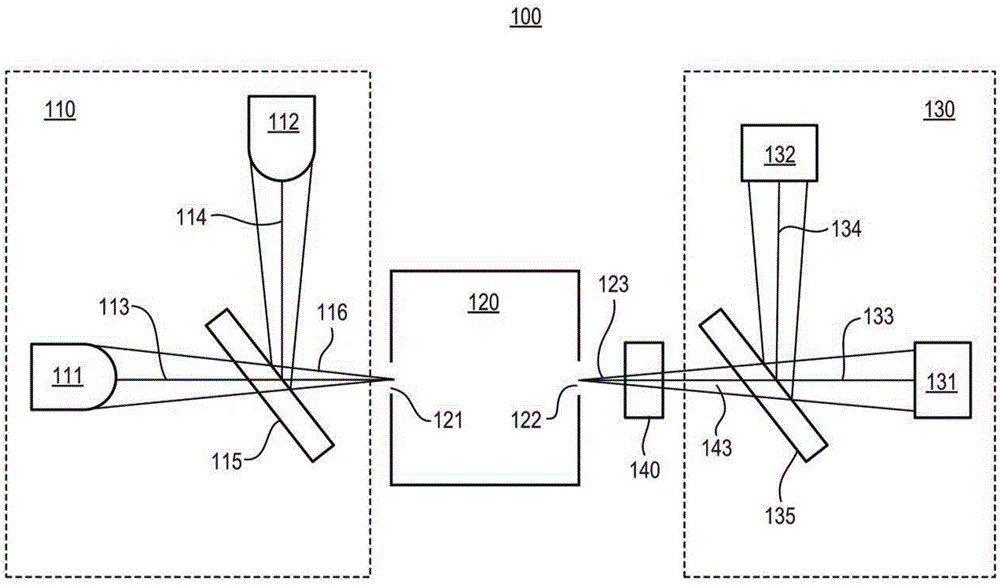
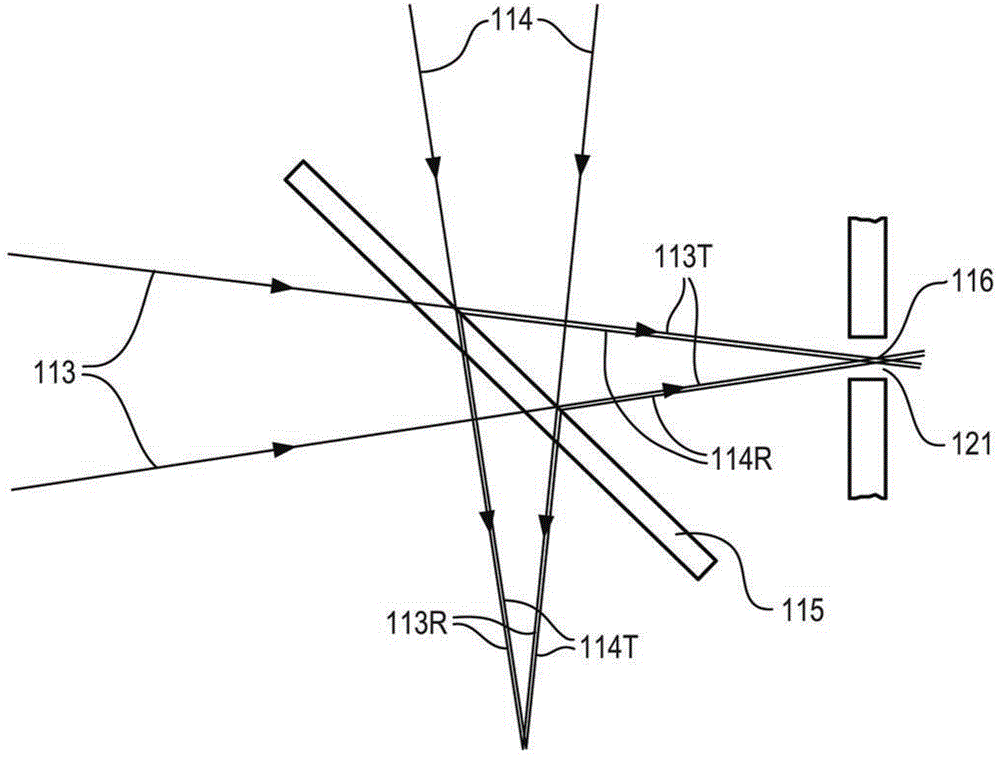
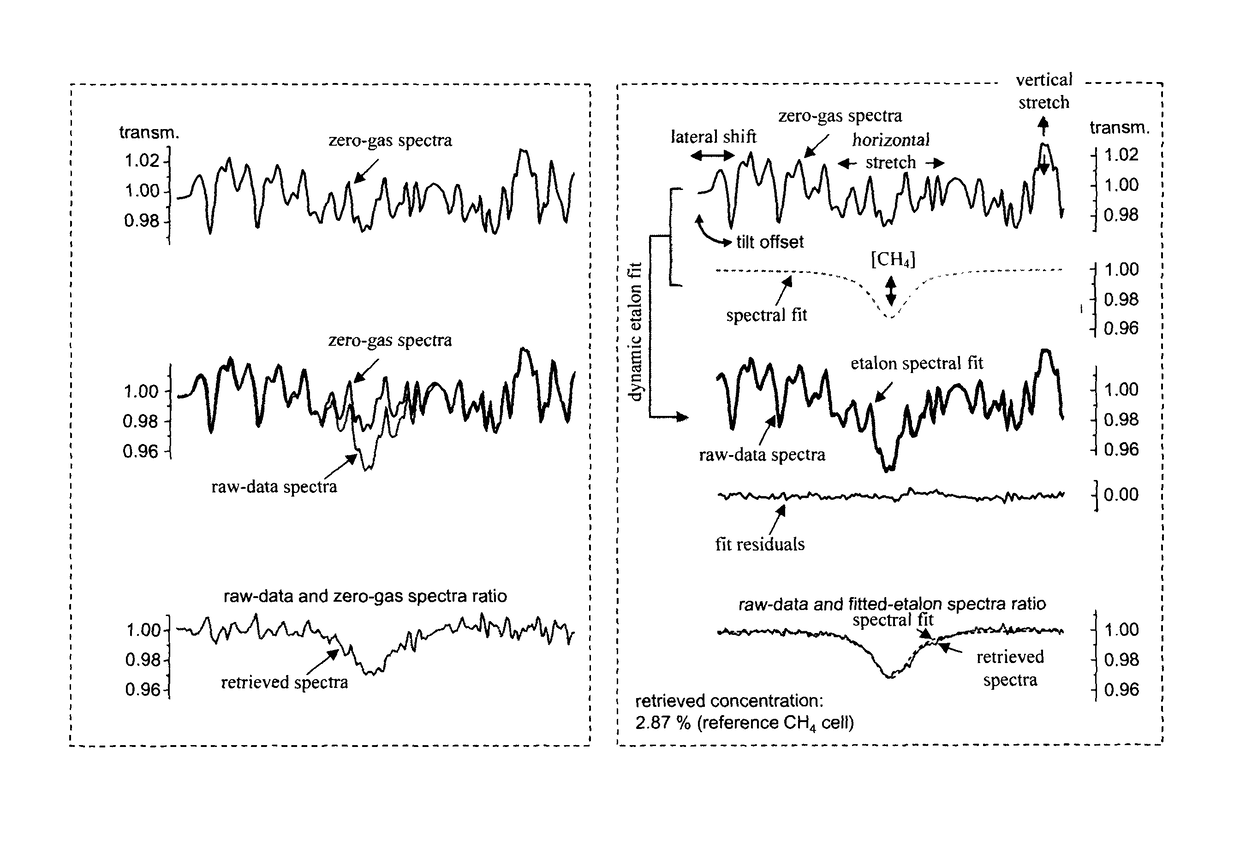
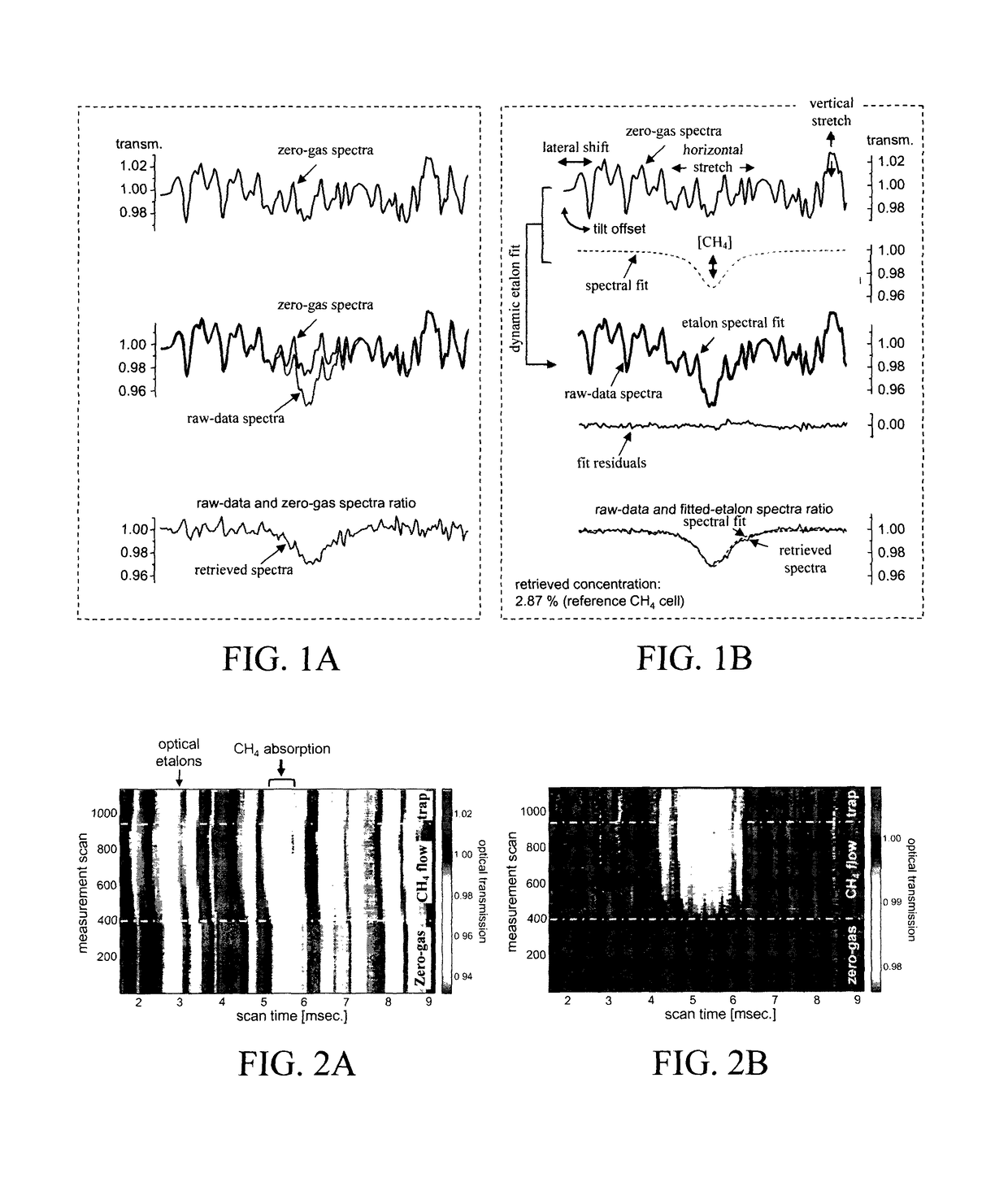
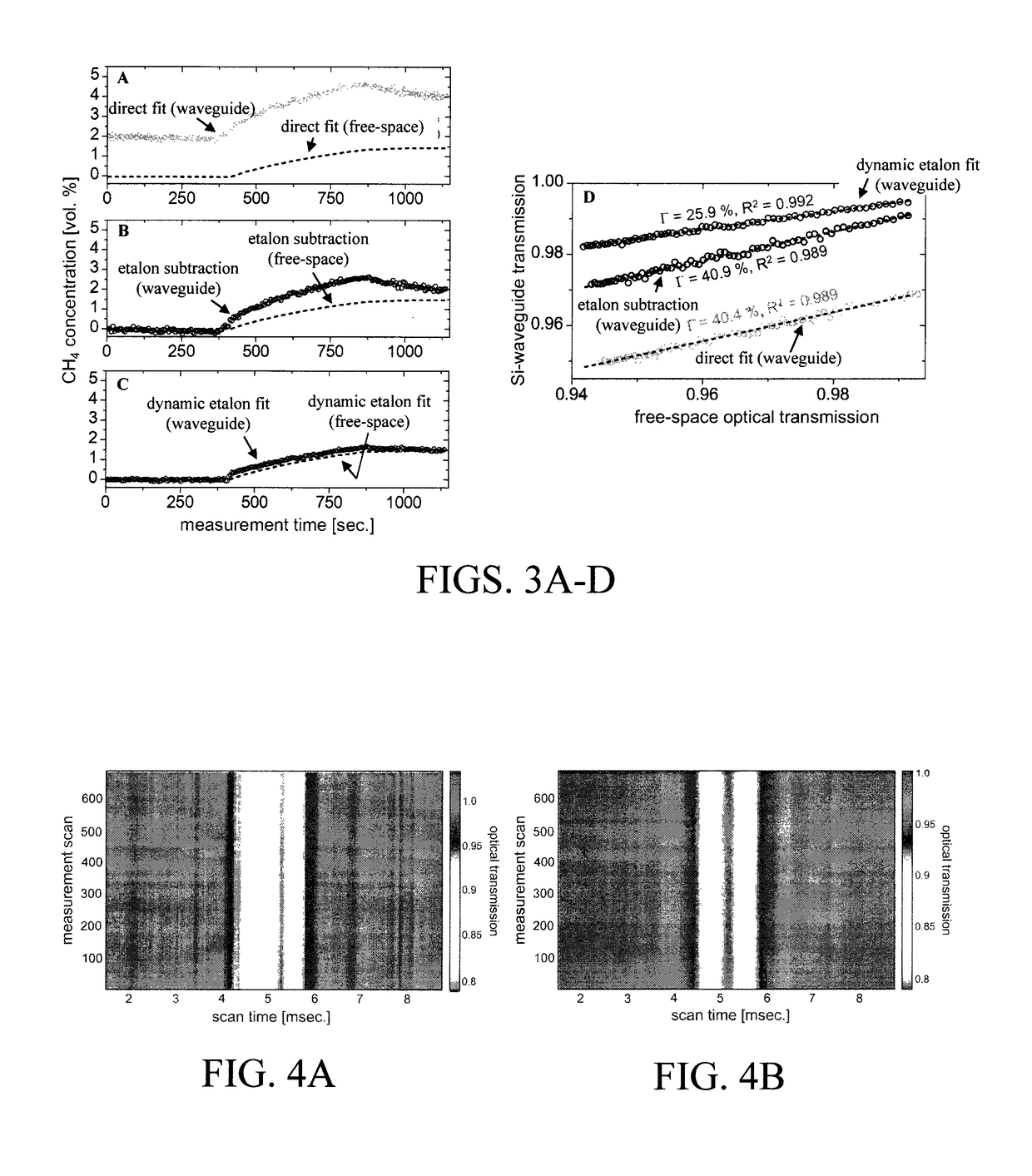
Ensuring Stable, Precise, and Accurate Optical Absorption Spectroscopic Trace Gas Concentration Measurements in the Presence of Time-Varying Etalons
ActiveUS20170146448A1Improved optical absorption measurementReduce background noiseColor/spectral properties measurementsAnalyteOptical absorption spectra
Provided herein are techniques for improved optical absorption measurements in the presence of time-varying etalons. In one aspect, a method for dynamic etalon fitting for adaptive background noise reduction in an optical sensor is provided. The method includes the steps of: obtaining a zero-gas spectrum measured using the optical sensor; obtaining an analyte gas spectrum of a target trace gas measured using the optical sensor; comparing the zero-gas spectrum and the analyte gas spectrum using fit parameters that compensate for drifting etalons in the optical sensor; and dynamically extracting the drifting etalons from the analyte gas spectrum to retrieve concentration of the target trace gas.
Owner:IBM CORP
Optical absorption spectrometry system including dichroic beam combiner and splitter
InactiveCN104655279AMaterial analysis by optical meansAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyOptical absorption spectraLight beam
An optical absorption spectrometry system includes first and second light sources, a dichroic beam combiner and a wavelength selective module. The first light source emits first light having first wavelengths within a first wavelength range, and the second light source emits second light having second wavelengths within a second wavelength range different from the first wavelength range. The dichroic beam combiner includes a predetermined first reflectance / transmission transition region, the dichroic beam combiner being configured to transmit a first portion of the first light and to reflect a second portion of the second light to provide combined light. The wavelength selective module is configured to disperse the combined light received at an entrance aperture, to select a sample wavelength range of the dispersed light as sample light, and to output the sample light having the selected sample wavelength range from an exit aperture for illuminating a sample.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Difluorobithiophene-based donor-acceptor polymers for electronic and photonic applications
ActiveCN107074830AImprove solubilityEasy to processGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsConductive materialOptical absorption spectraPolymer solution
An organic compound, a donor-acceptor conjugated polymer, a formulation and a thin film, wherein a solution of the donor-acceptor conjugated polymer exhibits a peak optical absorption spectrum red shift of at least 100 nm when the donor-acceptor conjugated polymer solution is cooled from 140 DEG C to room temperature.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and apparatus for increased purge efficacy in optical absorption spectroscopic measurements of gases in sealed containers
ActiveUS20130293892A1Rapidly and efficiently removedSpeed up the removal processColor/spectral properties measurementsOptical absorption spectraLight beam
A system and method for nondestructive detection of gas in a sealed container. The system includes a light source housed in a light source housing and configured to emit a light beam for absorption in a substance to be measured, a detector housed in a detector housing and configured to detect the emitted light beam, a zone that accepts one or more of the sealed containers, each container being substantially optically transparent and containing the substance to be measured, the zone located between the detector and the light source, the light source configured to transmit the light beam through the zone, and a light source purging system comprising a light source channel surrounding the light source and positioned between the light source and the detector housing, the light source channel configured to expel purge gas from a purge gas source into the zone.
Owner:LIGHTHOUSE INSTR
Glass panel unit and glass window
ActiveUS20190055775A1Improve stabilityLess easily recognizableClimate change adaptationSynthetic resin layered productsOptical absorption spectraUltraviolet
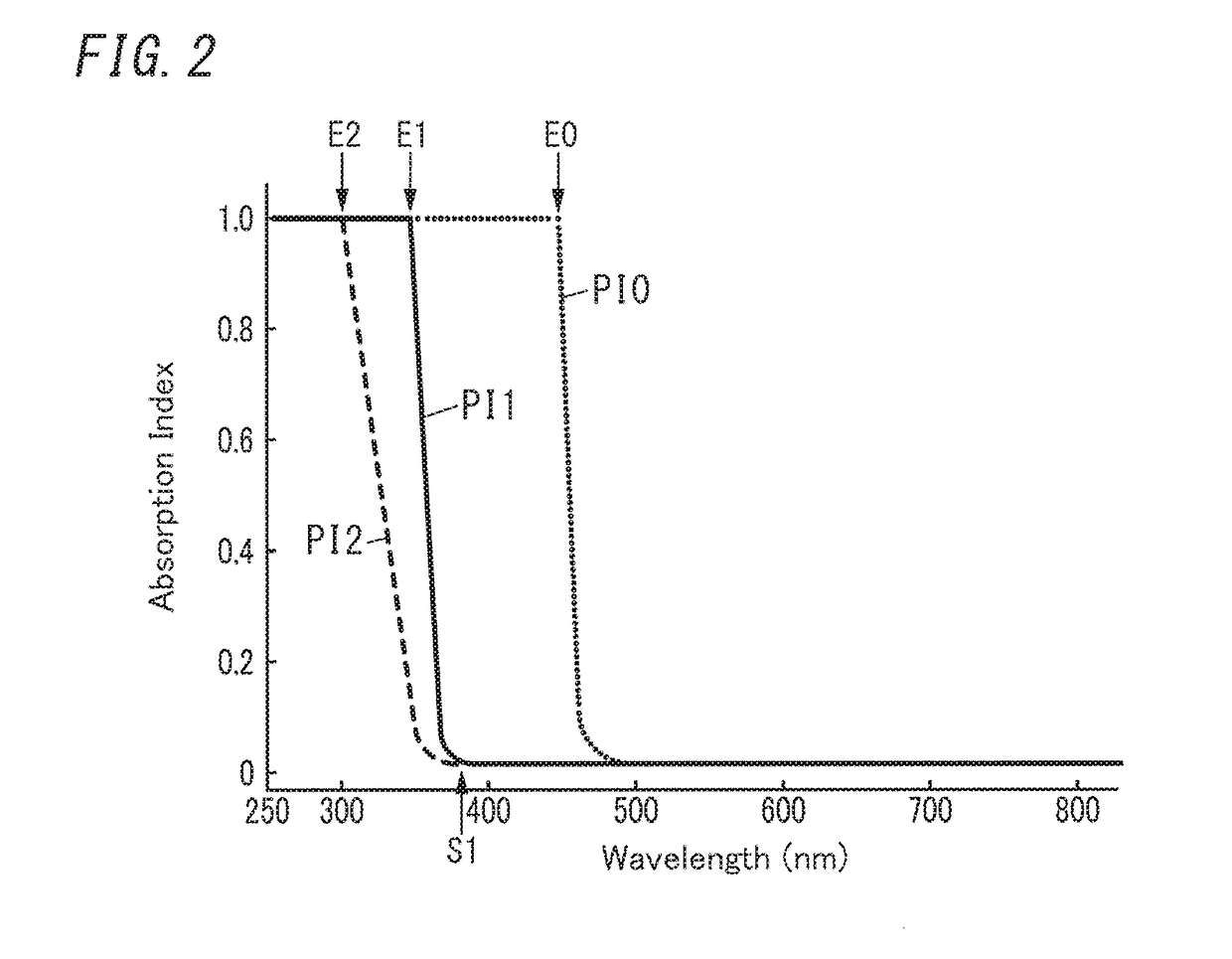
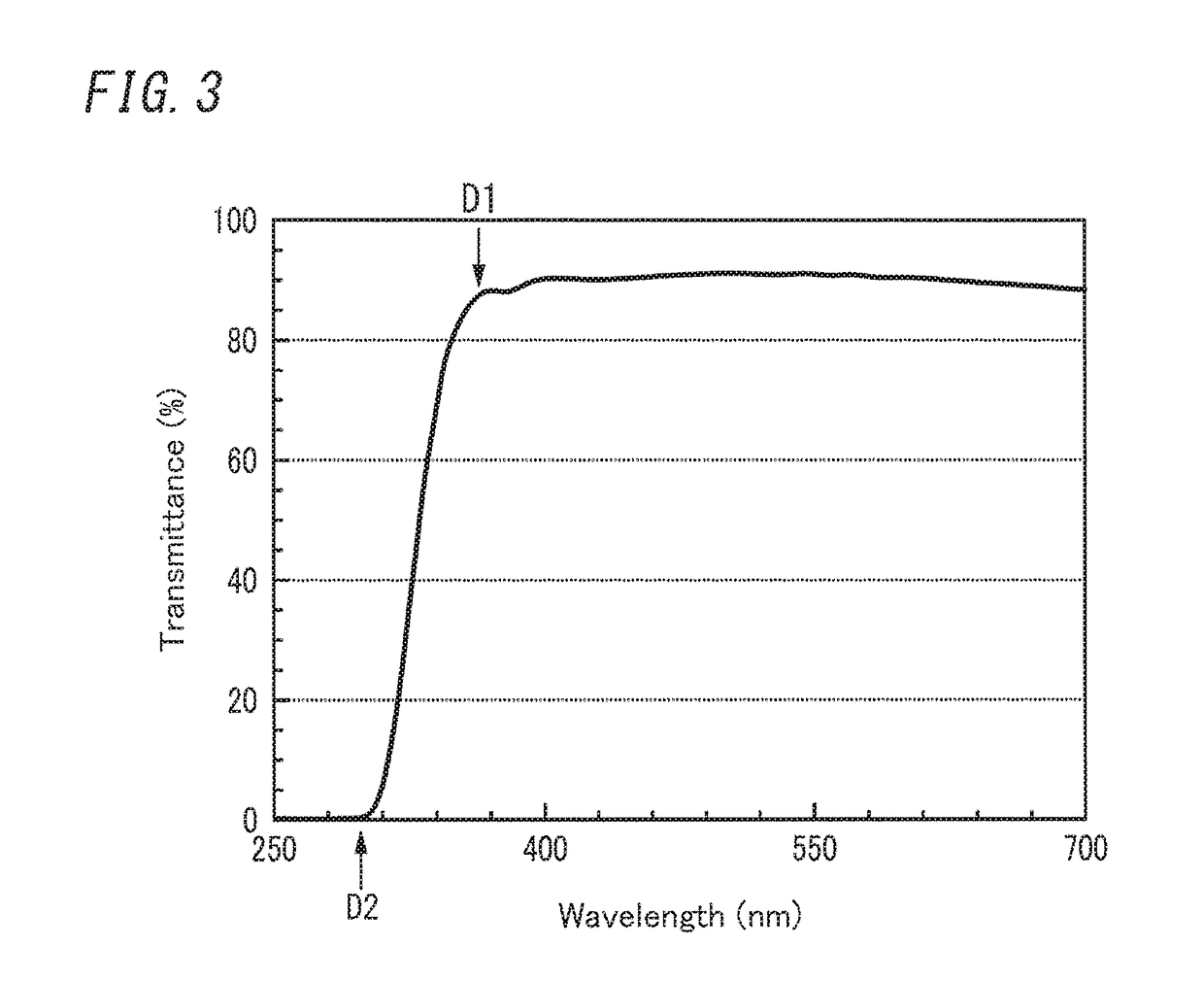
Disclosed herein is a glass panel unit including: a first panel including at least a first glass plate; a second panel arranged to face the first panel and including at least a second glass plate; a frame member formed in a shape of a frame corresponding in shape to respective peripheral portions which extend along edges of the first panel and the second panel, and bonded to the peripheral portions; and at least one spacer provided in a vacuum space between the first panel and the second panel. The at least one spacer contains a polyimide. The polyimide has an absorption edge at which an absorption index decreases in an optical absorption spectrum ranging from an ultraviolet ray to visible radiation. The absorption edge is equal to or less than 400 nm.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Ensuring stable, precise, and accurate optical absorption spectroscopic trace gas concentration measurements in the presence of time-varying etalons
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
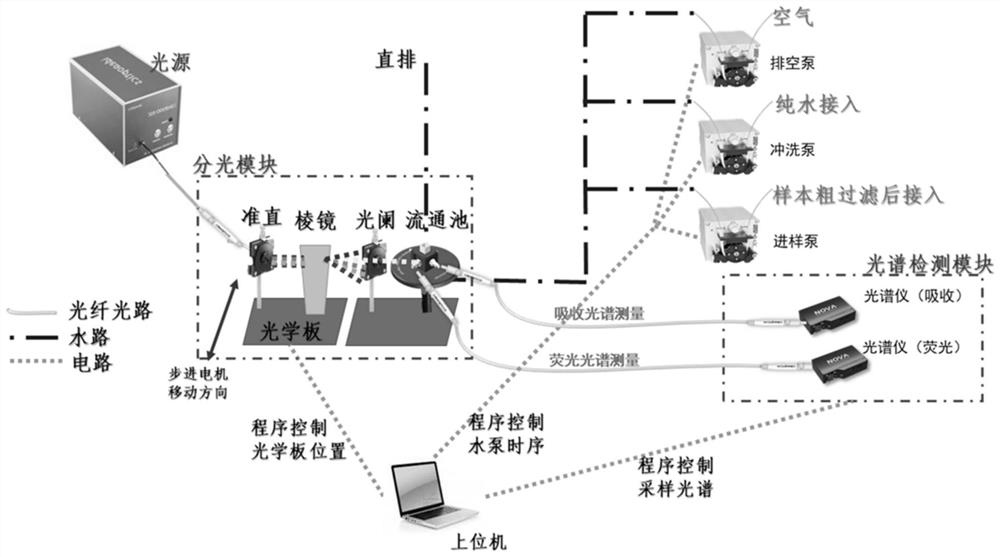
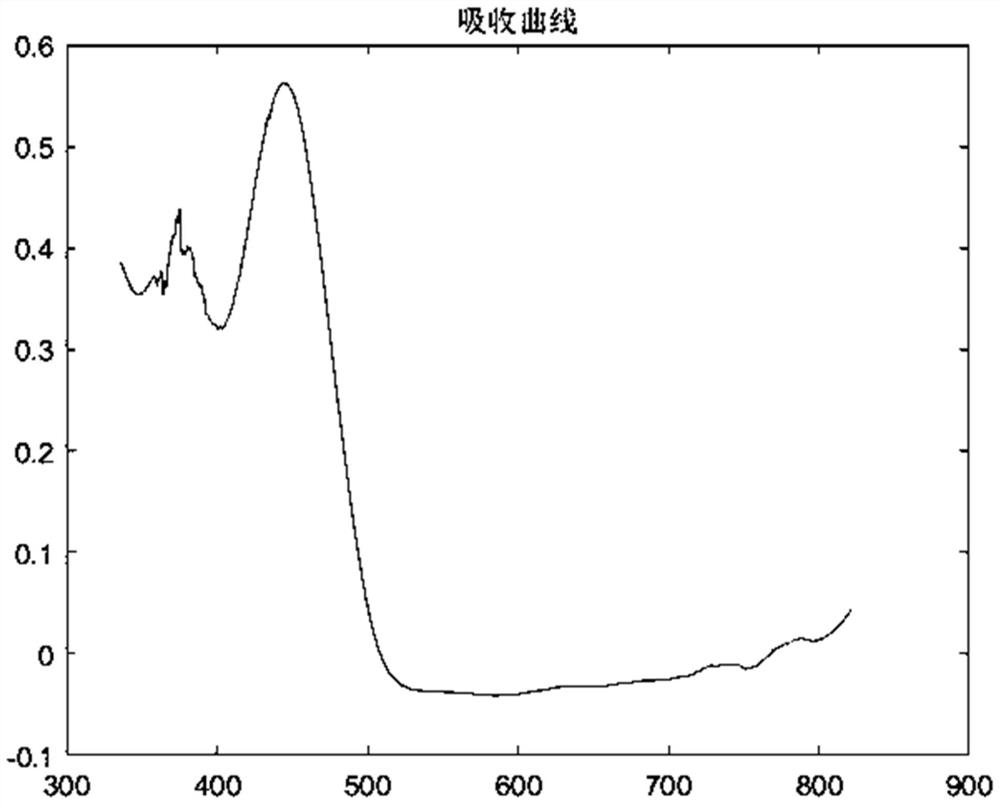
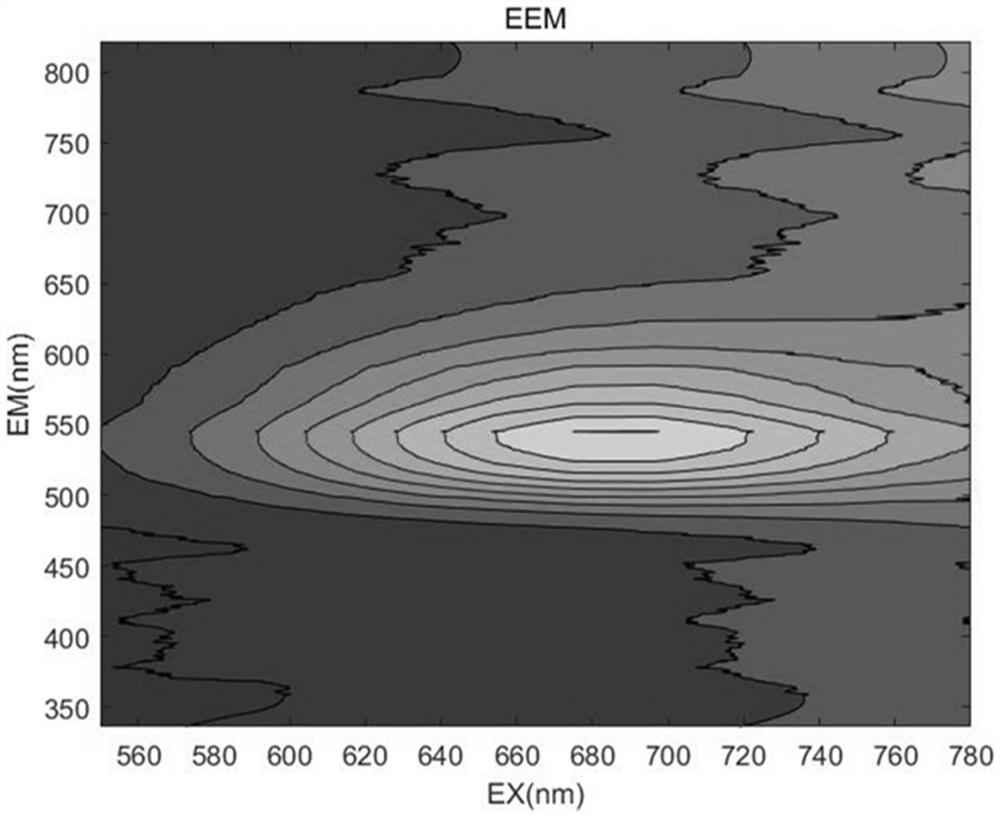
Discrete three-dimensional fluorescence/visible light absorption spectrum detection device for judging water quality pollution
PendingCN114166747ALow costEasy to carryColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceContinuous measurementOptical absorption spectra
The invention discloses a discrete three-dimensional fluorescence / visible light absorption spectrum detection device for discriminating water quality pollution, which integrates a water path, a circuit and a light path, adopts a small spectrometer and a prism light splitting module, and is low in cost and convenient to carry and maintain; a discrete three-dimensional fluorescence spectrum and an absorption spectrum can be obtained at the same time in one-time on-site detection, and a characteristic peak is enhanced by utilizing the relevance of light absorption and fluorescence mechanisms. After circulating sampling is set, uninterrupted in-situ continuous measurement can be achieved, obtained spectral data cover water quality abnormal information and pollution type information at different times, and the data obtained through the device can be used for rapidly judging whether pollution exists or not and the pollution type. Through a side cloud cooperation mode, detected bottom layer data does not need to be uploaded to a cloud end for analysis, computing resources can be shared by a plurality of detection devices, the network flow of water quality analysis is saved, and the processing speed and the operation efficiency are improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Hydroxygallium phthalocyanine pigment and process for the production thereof, electrophotographic photoreceptor, process cartridge, electrophotographic device and image formation method
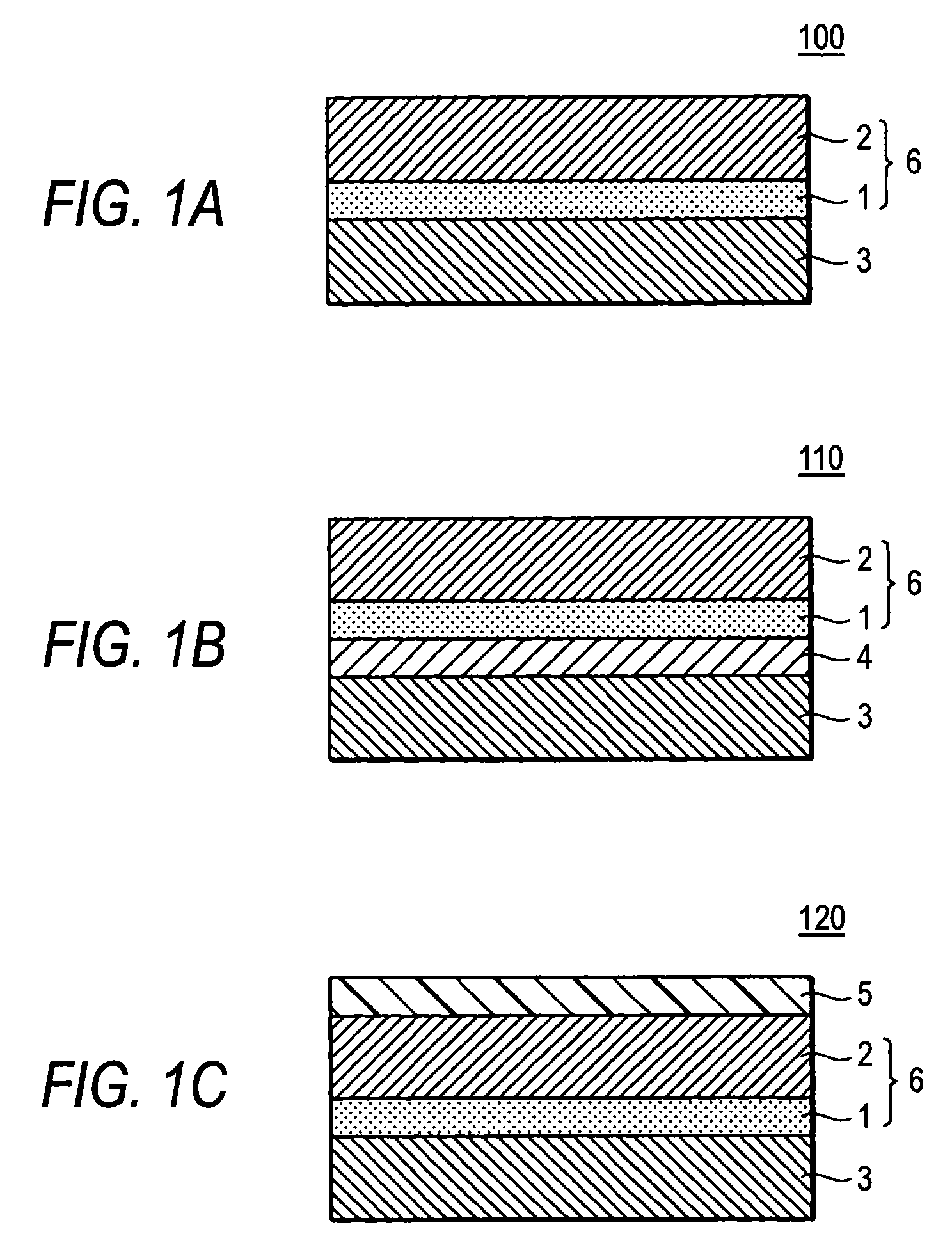
ActiveUS7381512B2Maintain good propertiesQuality improvementReactive dyesPorphines/azaporphinesOptical absorption spectraImage formation
A hydroxygallium phthalocyanine pigment is characterized by having a maximum peak wavelength within a range of from 810 nm to 839 nm in optical absorption spectrum in a wavelength range of from 600 nm to 900 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
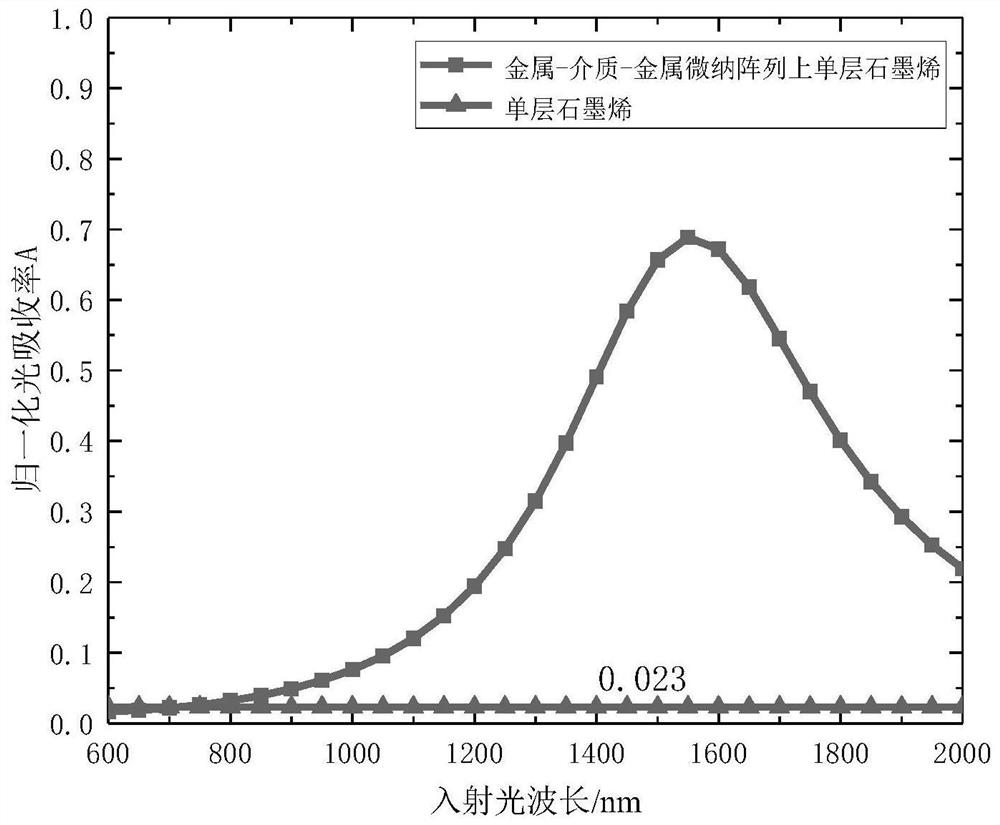
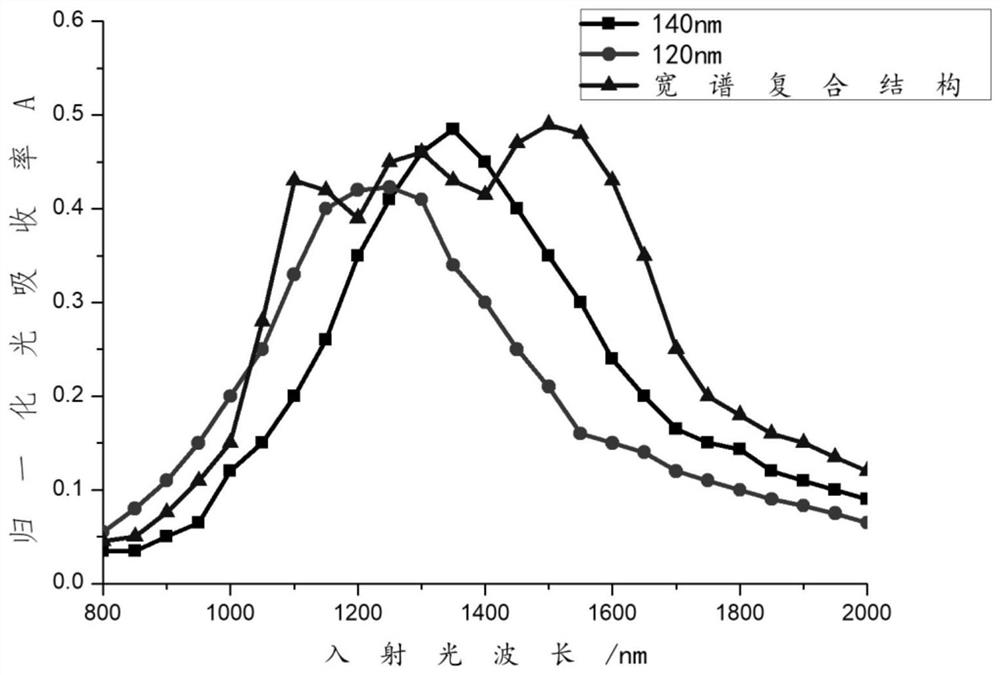
A tunable near-infrared three-array periodic broadband light absorption enhancement structure
ActiveCN111244199BMeet application needsSemiconductor devicesOptical absorption spectraElectrical connection
Owner:苏州众为光电有限公司
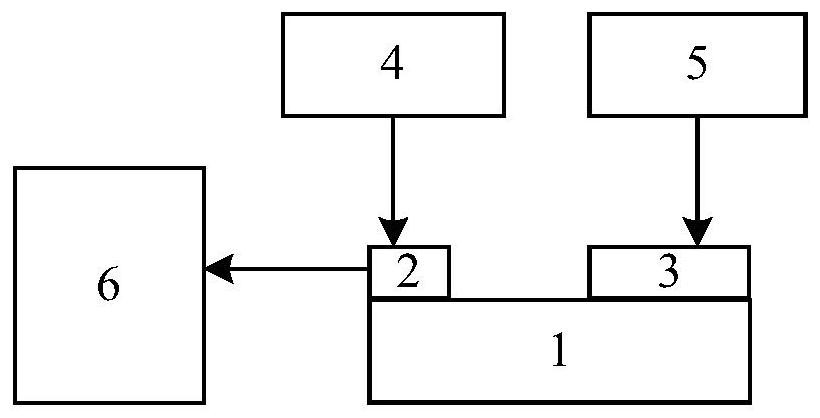
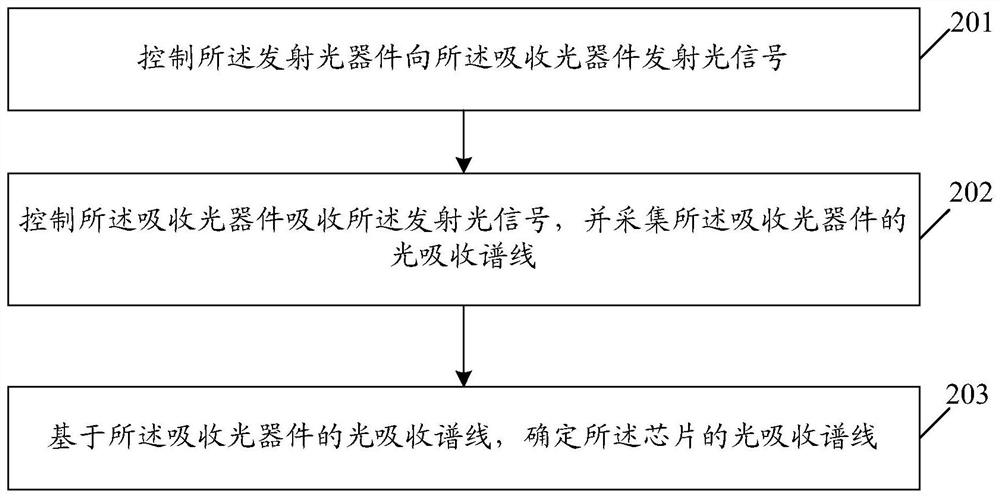
Chip absorption spectrum measuring method, device and equipment and storage medium
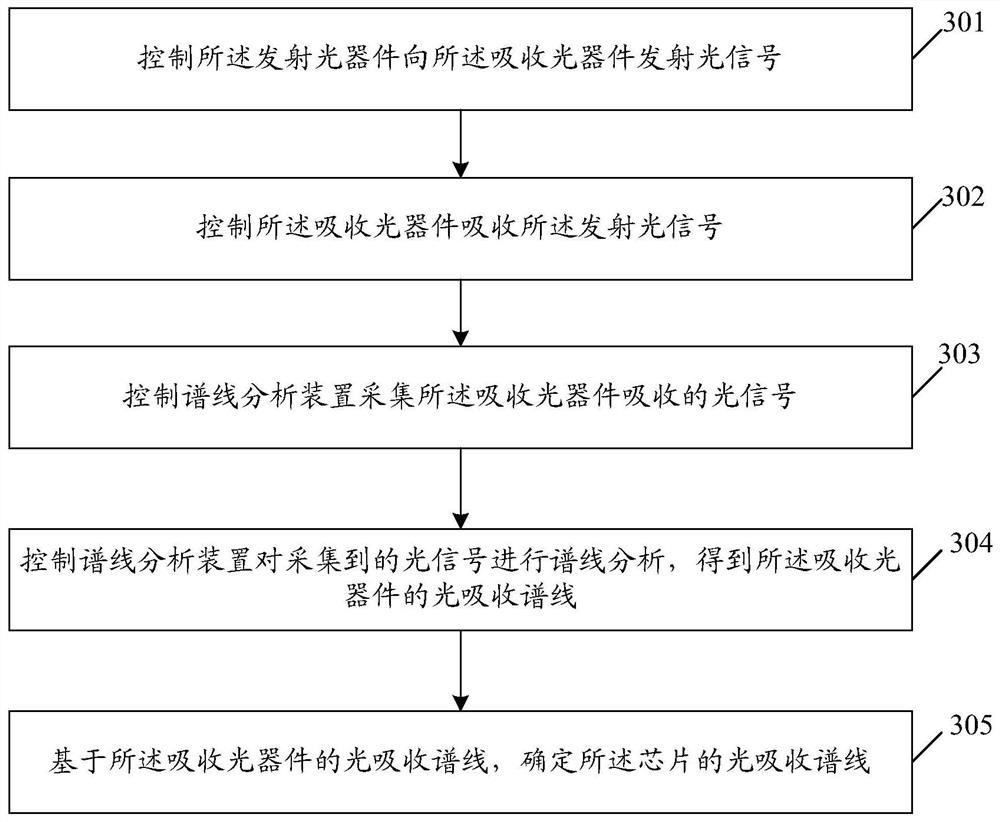
InactiveCN112229518AAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyOptical absorption spectraLight signal
The invention discloses a chip absorption spectrum measurement method, device and equipment, and a storage medium. A chip comprises an emission optical device and an absorption optical device. The transmitting optical device is used for transmitting an optical signal to the absorbing optical device; the method comprises the following steps: controlling an emission optical device to emit an opticalsignal to an absorption optical device; controlling an absorption optical device to absorb the emitted optical signal, and collecting a light absorption spectral line of the absorption optical device; and determining a light absorption spectral line of the chip based on the light absorption spectral line of the absorption optical device. In this way, an optical signal can be directly emitted to the absorption optical device through the emission optical device of the chip so as to acquire the light absorption spectral line of the absorption optical device. Since the light absorption capabilityof the chip mainly depends on the light absorption capability of the absorption optical device, the light absorption spectral line of the chip can be determined according to the light absorption spectral line of the absorption optical device.
Owner:WUHAN TELECOMM DEVICES
All-optical monolithic integrated optoelectronic device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN104716153BEffective combinationAvoid mismatchSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesOptical absorption spectraLength wave
The present invention provides an all-optical GaN / GaInP / GaAs monolithic integrated device and a manufacturing method thereof. The bandgap energies of the all-optical monolithic integrated device are 3.5 / 1.9 / 1.4 ev, respectively, increasing between GaAs and GaN The bandgap of GaInP in the middle layer is 1.9ev and the wavelength is in the range of red light. The all-optical monolithic integrated device can absorb and utilize different energy spectra similar to its bandgap, which are blue light, yellow light and red light respectively, so as to realize all-optical scope.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Common CT computer imaging omics stone component analysis system and method
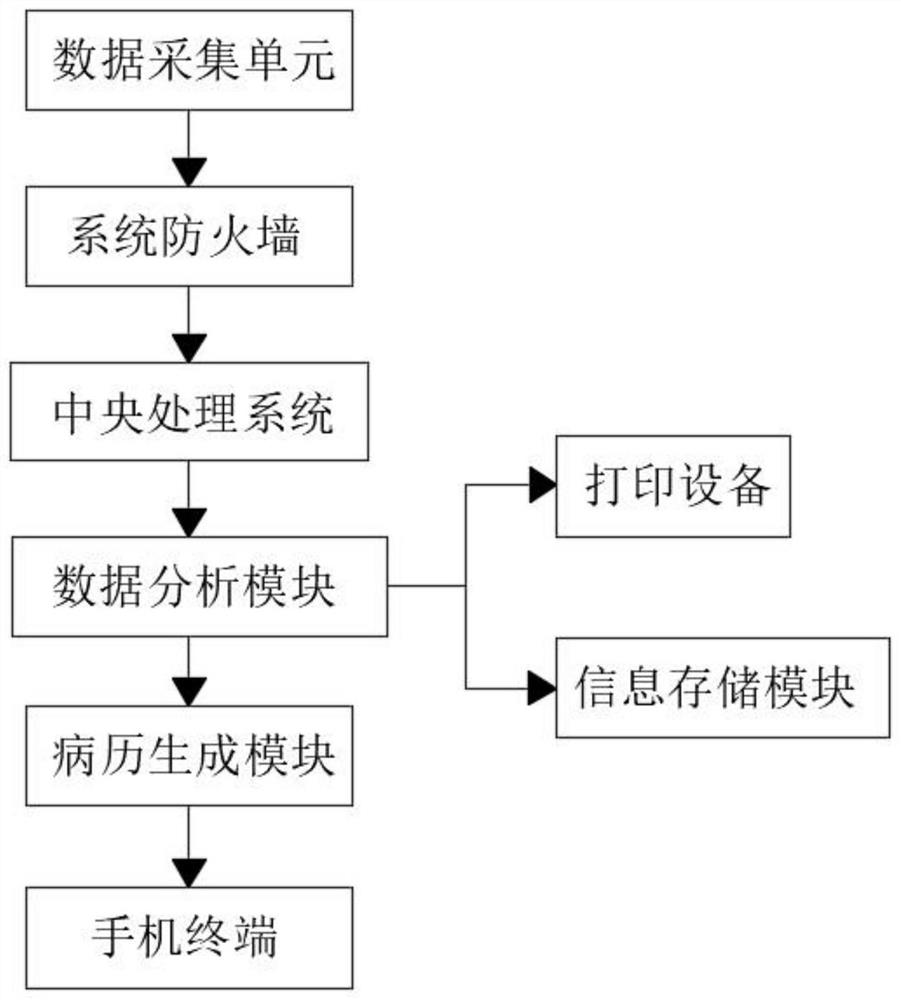
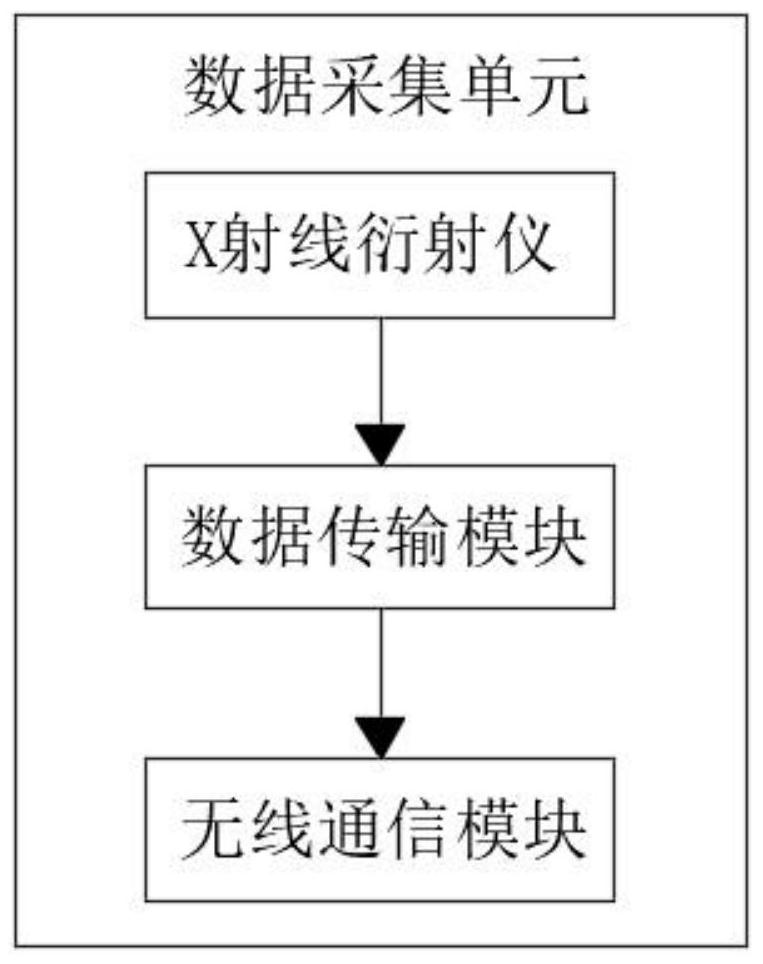
InactiveCN112595735AAnalysis and detection are accurateEffective detection and analysisMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAlgorithmOptical absorption spectra
The invention relates to the technical field of medical images, in particular to a common CT computer imaging omics stone component analysis system and method, and the system comprises a central processing system, a data collection unit, a data analysis module, printing equipment and a mobile phone terminal. The input end of the central processing system is unidirectionally and electrically connected with a system firewall, and the data collection unit is connected with the system firewall through a wireless network. Calculus components are analyzed through CT computer imaging omics and compared with data in a database, the defects of an existing calculus analysis method are overcome, and the calculus analysis method has the advantages that calculus can be detected and analyzed more accurately and effectively, data are prevented from being lost in the transmission process, and then detection errors can be reduced. The problem that at present, infrared spectrum detection analysis is mainly adopted for calculus component analysis, the infrared light absorption band characteristic of a calculus sample is not high enough, and certain errors exist in detection of some calculus components is solved.
Owner:澧县人民医院
Method and apparatus for increased purge efficacy in optical absorption spectroscopic measurements of gases in sealed containers
InactiveUS9176050B2Rapidly and efficiently removedSpeed up the removal processColor/spectral properties measurementsOptical absorption spectraLight beam
A system and method for nondestructive detection of gas in a sealed container. The system includes a light source housed in a light source housing and configured to emit a light beam for absorption in a substance to be measured, a detector housed in a detector housing and configured to detect the emitted light beam, a zone that accepts one or more of the sealed containers, each container being substantially optically transparent and containing the substance to be measured, the zone located between the detector and the light source, the light source configured to transmit the light beam through the zone, and a light source purging system comprising a light source channel surrounding the light source and positioned between the light source and the housing, the light source channel configured to expel purge gas from a purge gas source into the zone.
Owner:LIGHTHOUSE INSTR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com