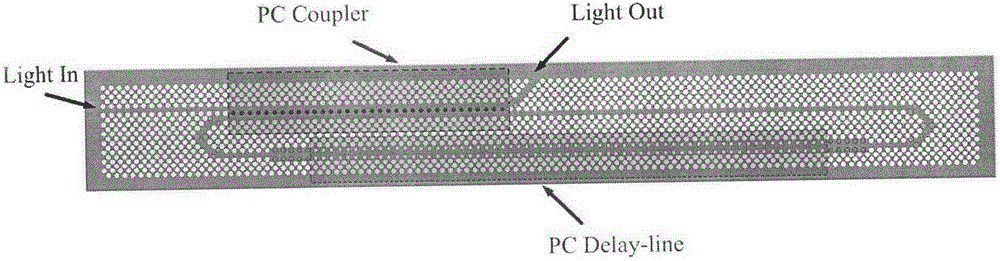
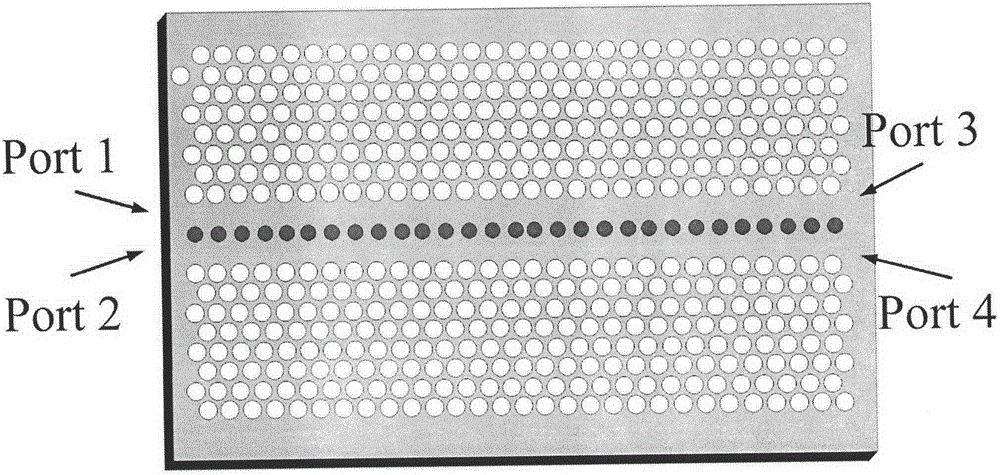
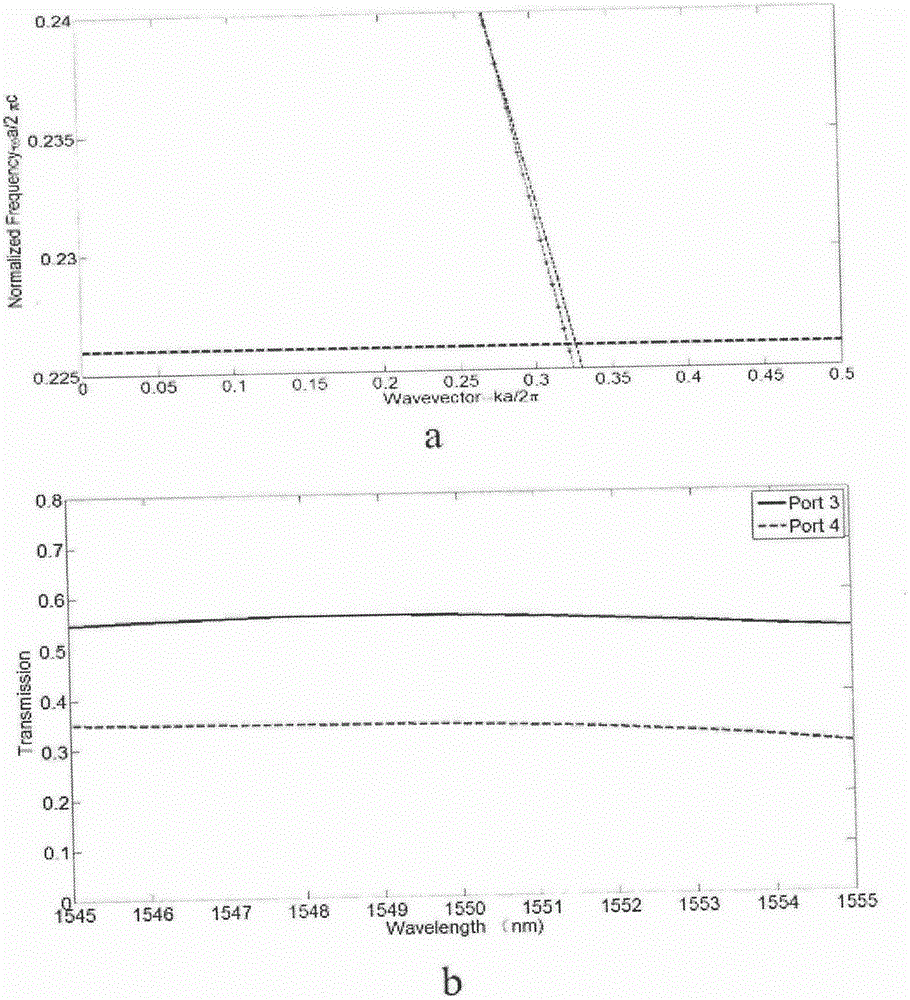
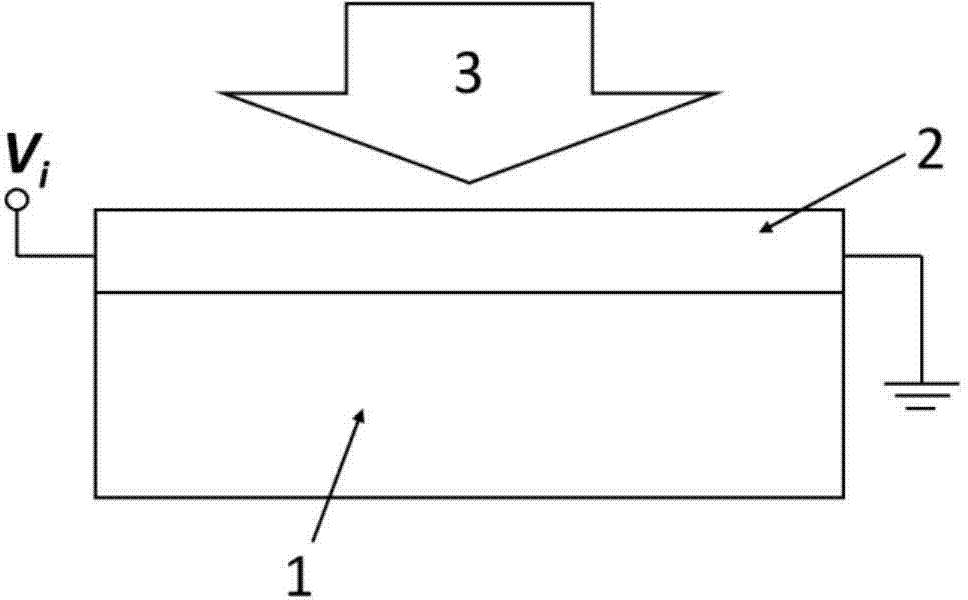
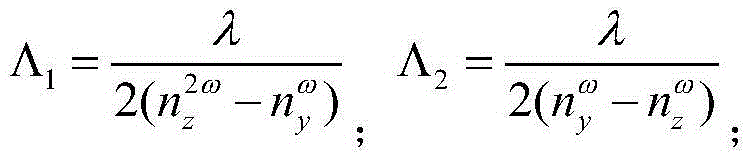Patents
Literature
222 results about "Slow light" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
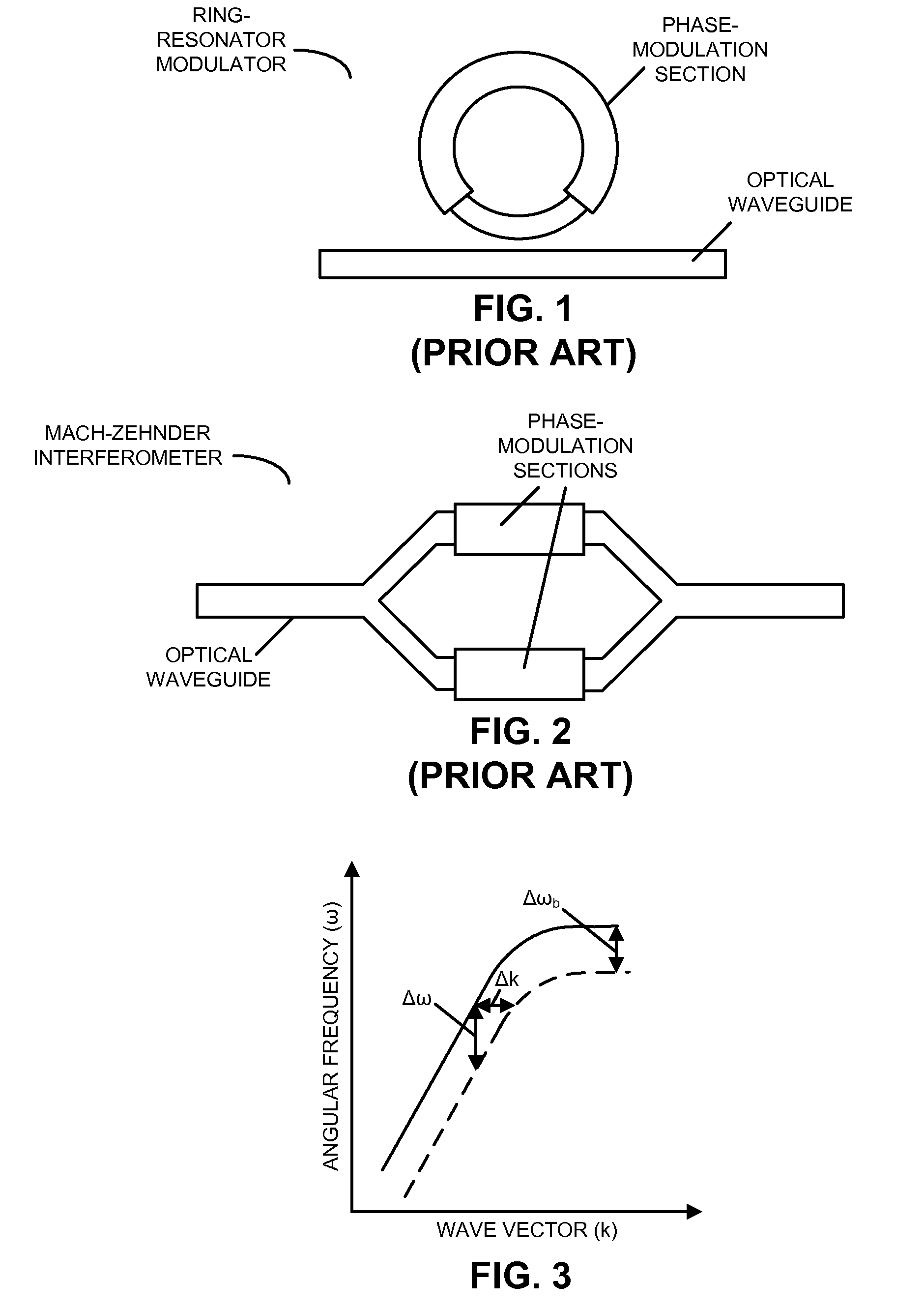
Slow light is the propagation of an optical pulse or other modulation of an optical carrier at a very low group velocity. Slow light occurs when a propagating pulse is substantially slowed down by the interaction with the medium in which the propagation takes place.
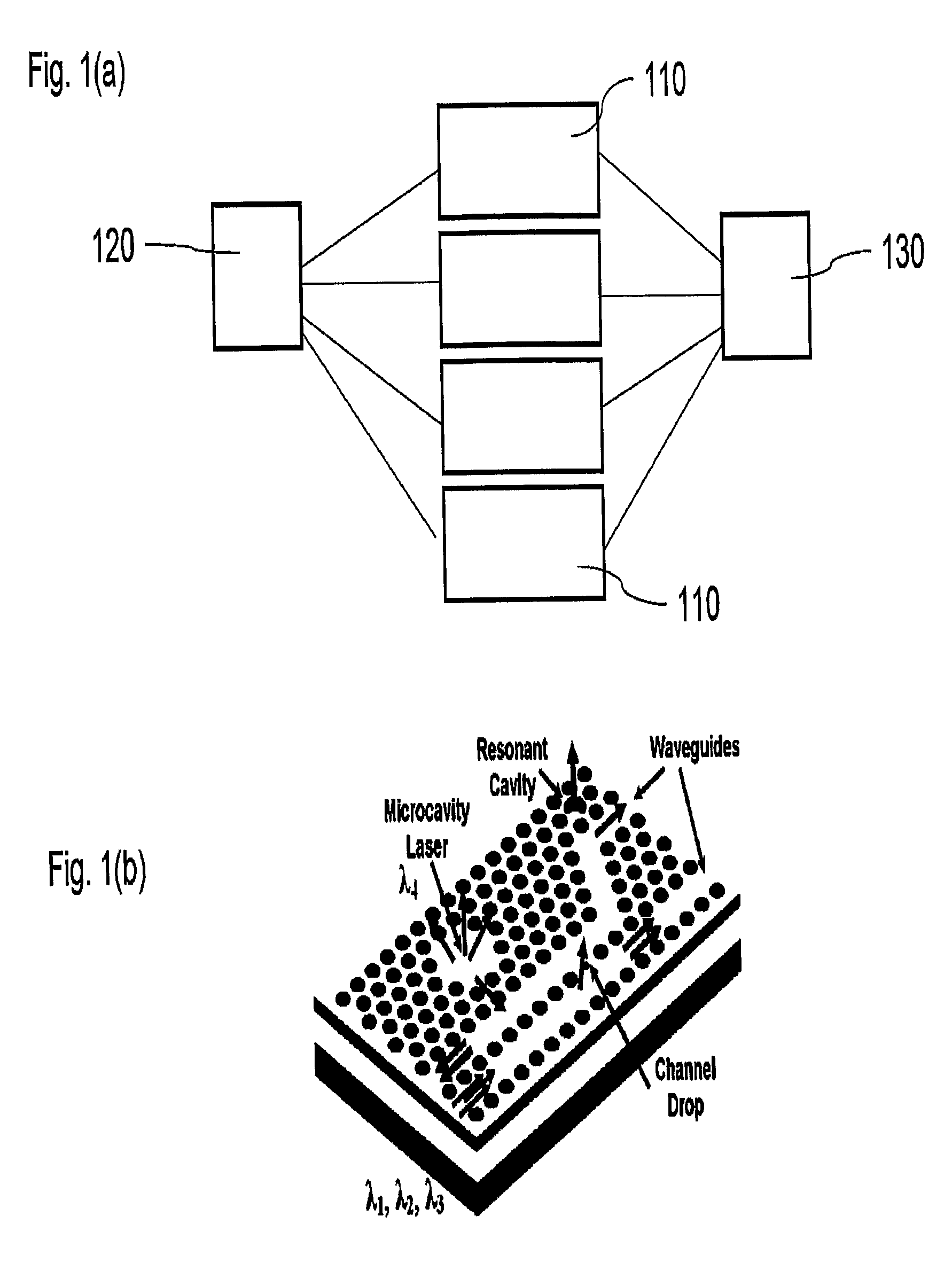
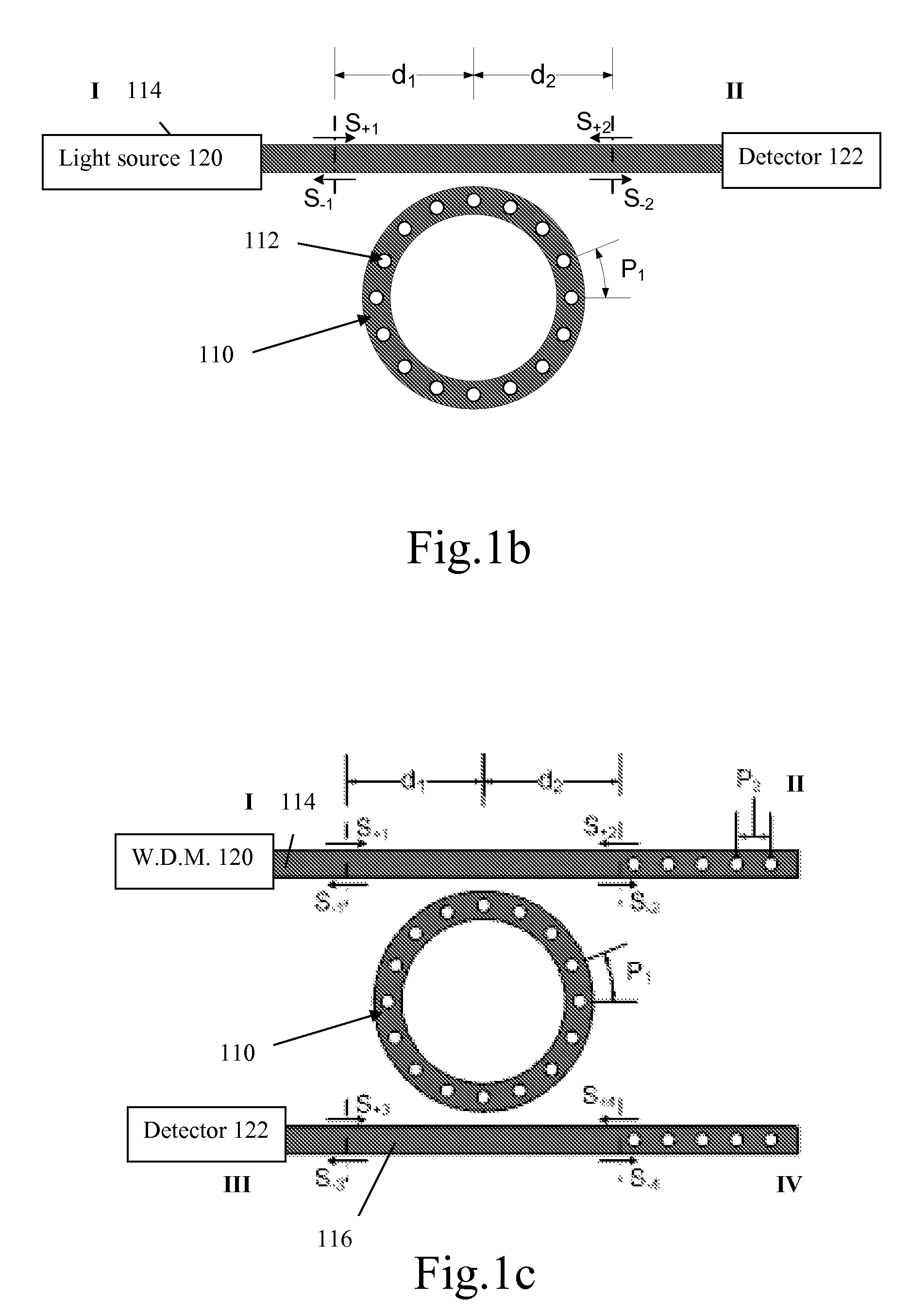
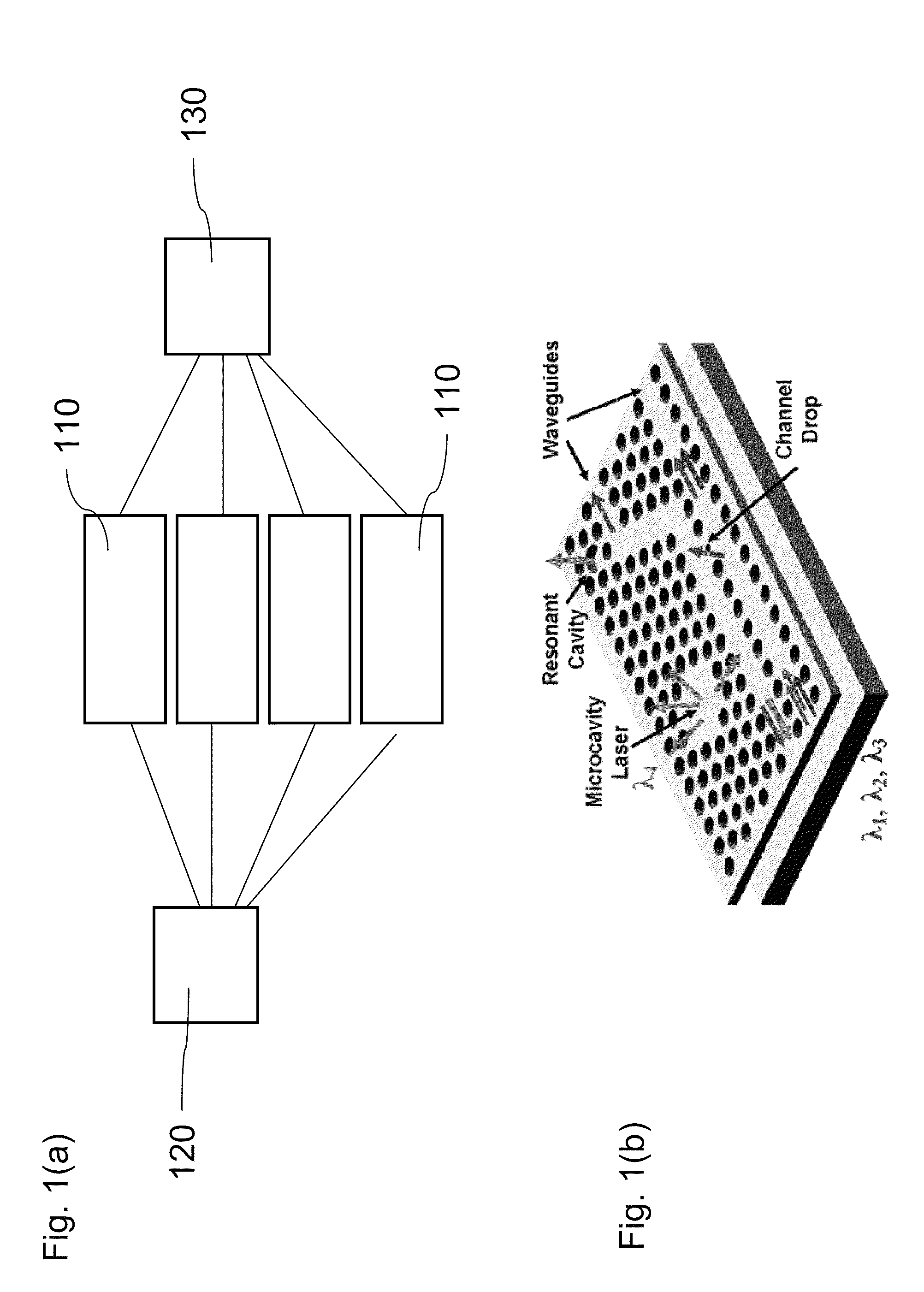
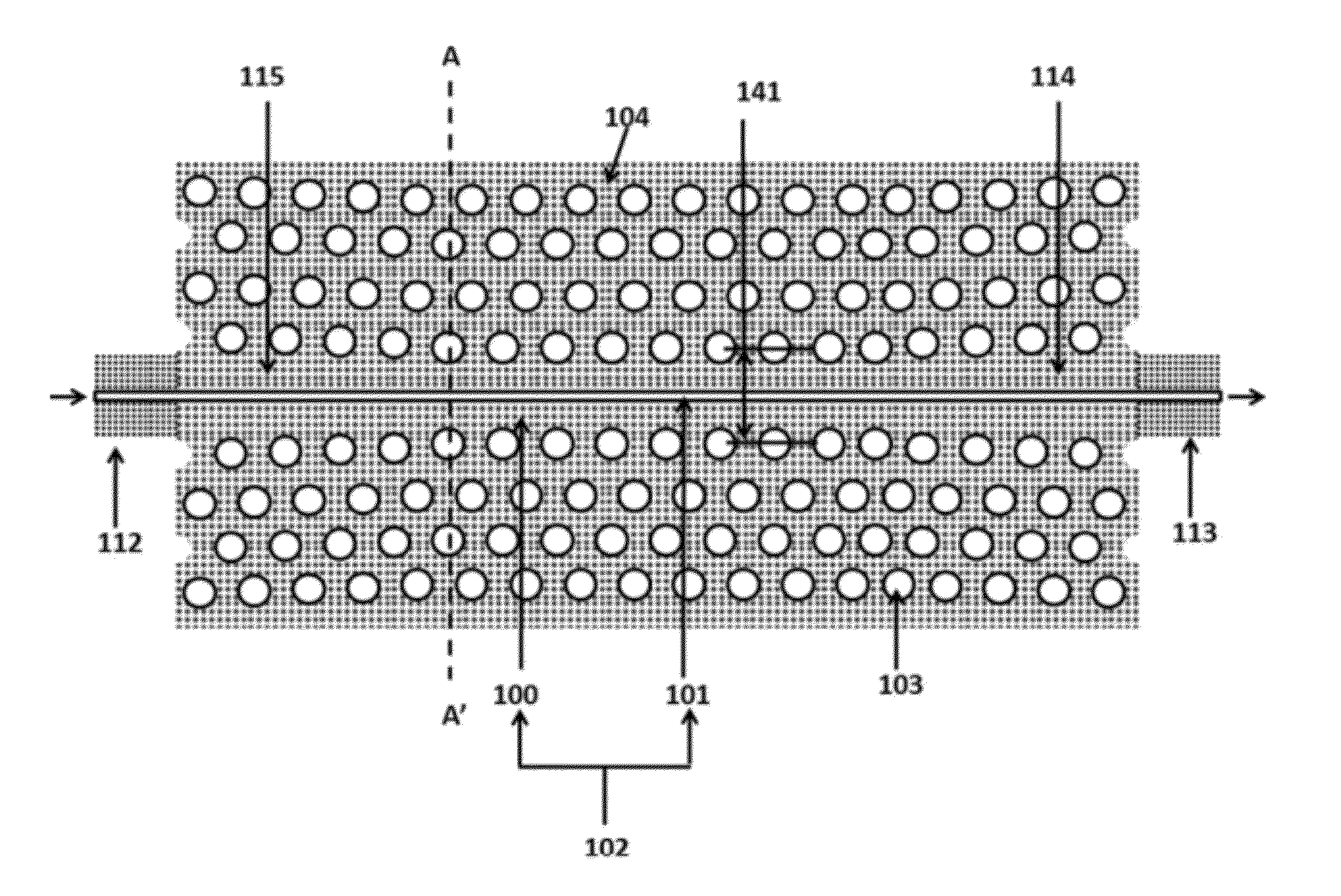
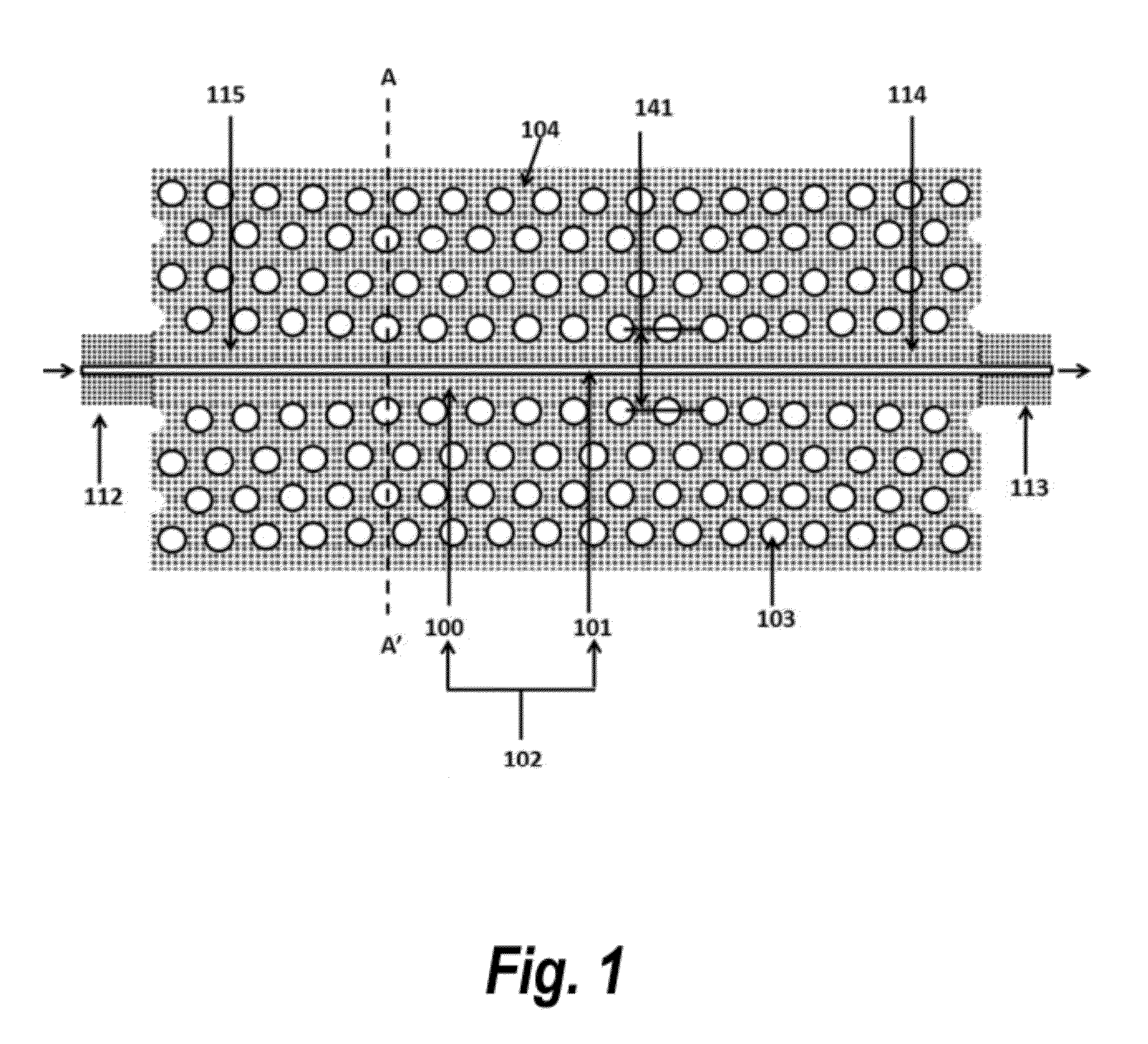
Two-dimensional surface normal slow-light photonic crystal waveguide optical phased array
ActiveUS20120013962A1High thermo-optic coefficientPromote formationCladded optical fibreNanoopticsRefractive indexLaser light
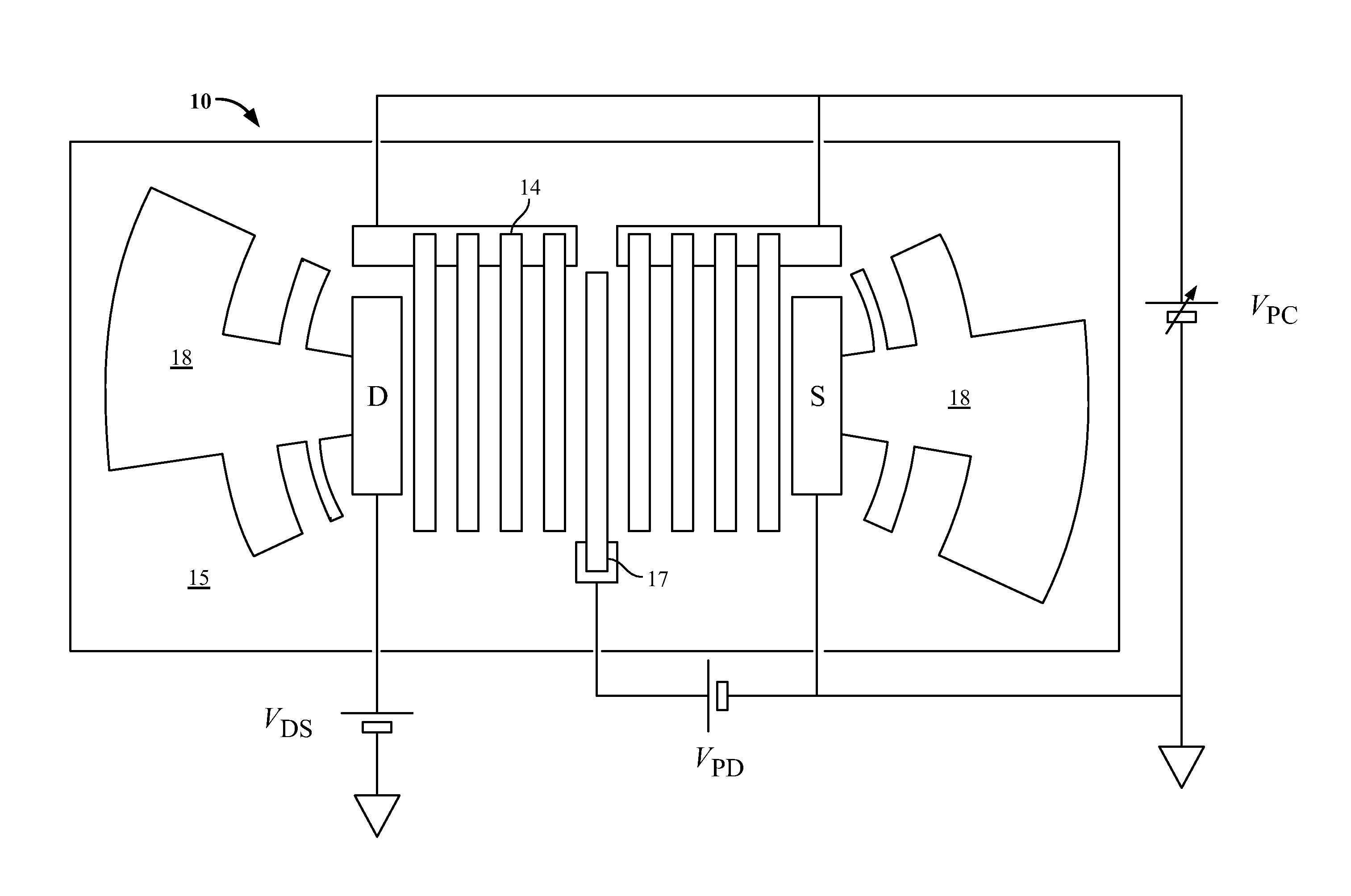
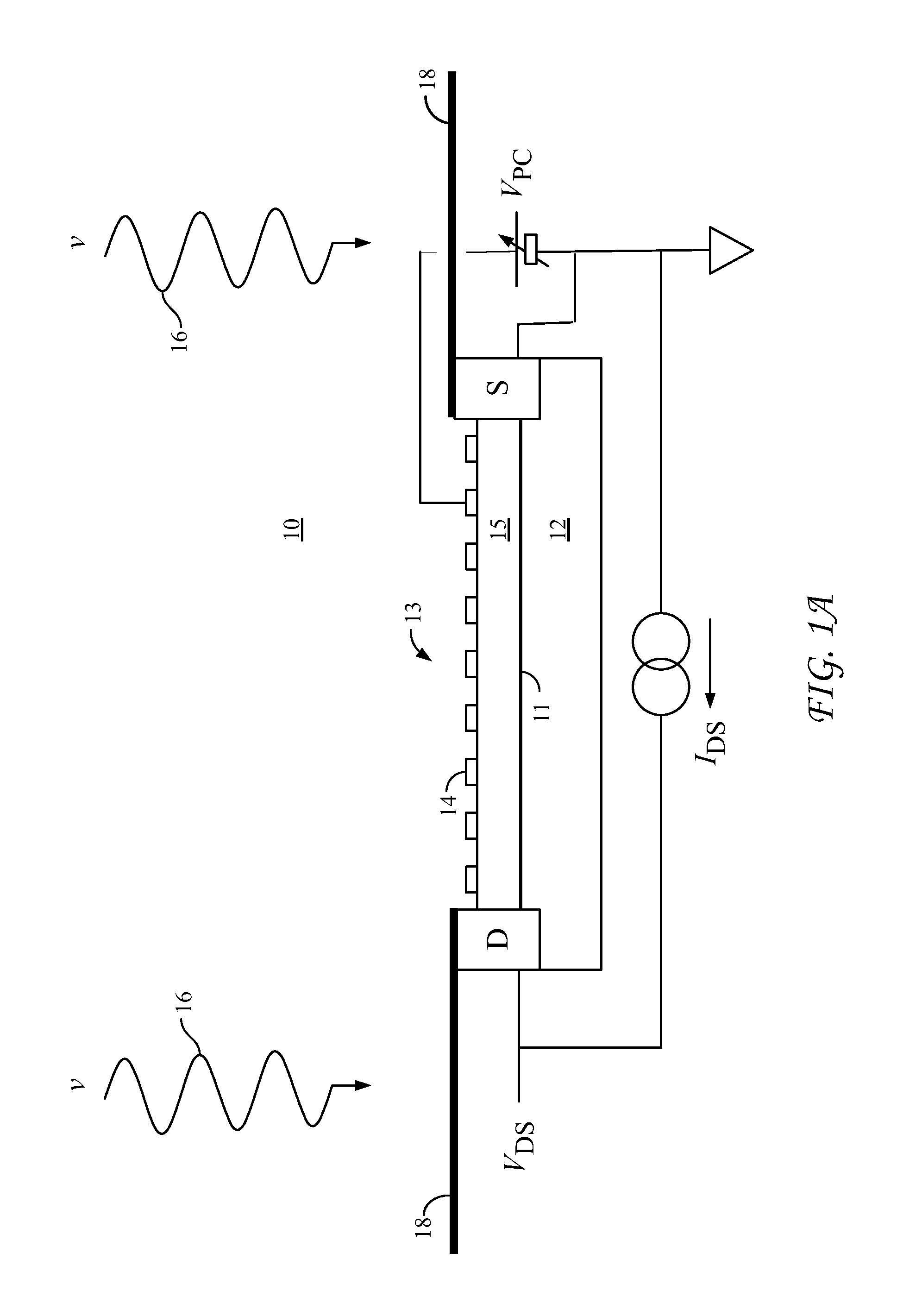
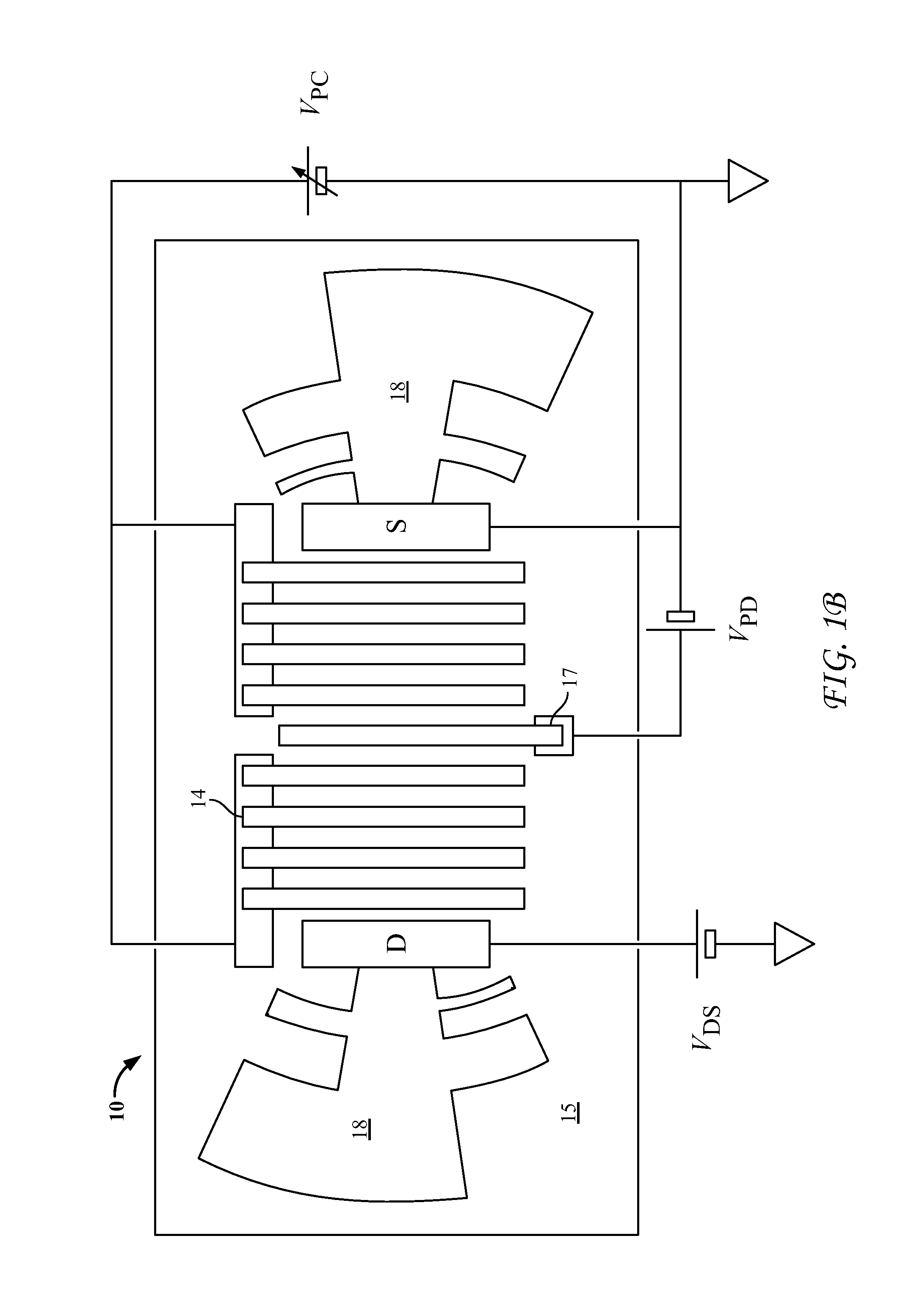
Methods and devices for optical beam steering are disclosed including coupling a laser light into an apparatus comprising a first substrate; an array of air core photonic crystal waveguides; columnar members etched around each air core waveguide; a pair of metal electrodes around the columnar members; a trench around the pair of metal electrodes surrounding each air core photonic crystal waveguide; a second substrate coupled to the first substrate comprising electrical interconnection lines; and a holographic fanout array comprising a third substrate; a photopolymer film coated on the third substrate; a hologram written in the photopolymer film configured to couple the laser light into the third substrate; and an array of holograms recorded in the photopolymer film configured to couple a portion of the laser light into the waveguides; and passing a current through the electrodes to induce a refractive index change in the first substrate to control the phase of the portion of the laser light that passes through each waveguide. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:OMEGA OPTICS
Dynamic Terahertz Switch Using Periodic Corrugated Structures
InactiveUS20120019901A1Ease of lightOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsManufacturing technologyElectrical conductor
A subwavelength terahertz (THz) switch using an artificially designed conductor metamaterial is discussed in this invention. Theoretically, slow-light EM wave propagating at THz speed imitates the strongly localized surface plasmon modes and henceforth is called Spoof Surface Plasmon Polariton (SSPP) mode in this invention. The SSPP mode of slow-light EM propagation can be easily tailored by changing the refractive index of the dielectric materials inside the metallic gap structure engineered as a periodic array of grooves. Thus, the incorporation of electro-optical material which has birefringence such as a nematic liquid crystal (N-LC) or multiple-refractive indices into the metallic gap leads to a highly compact and efficient terahertz switch being controlled by a low-voltage signal. The optimal design of the SSPP switch enabled by this novel method shows many interesting properties including 1) strong subwavelength localization; 2) relatively high extinction (On / Off switching) ratio; and 3) small damping attenuation. The THz dynamic switches can be used to construct linear switches, Y junction switches and Mach-Zehnder interferometers by using micromachining and other fabrication techniques.
Owner:MAZUMDER PINAKI
Variable semiconductor all-optical buffer using slow light based on electromagnetically induced transparency
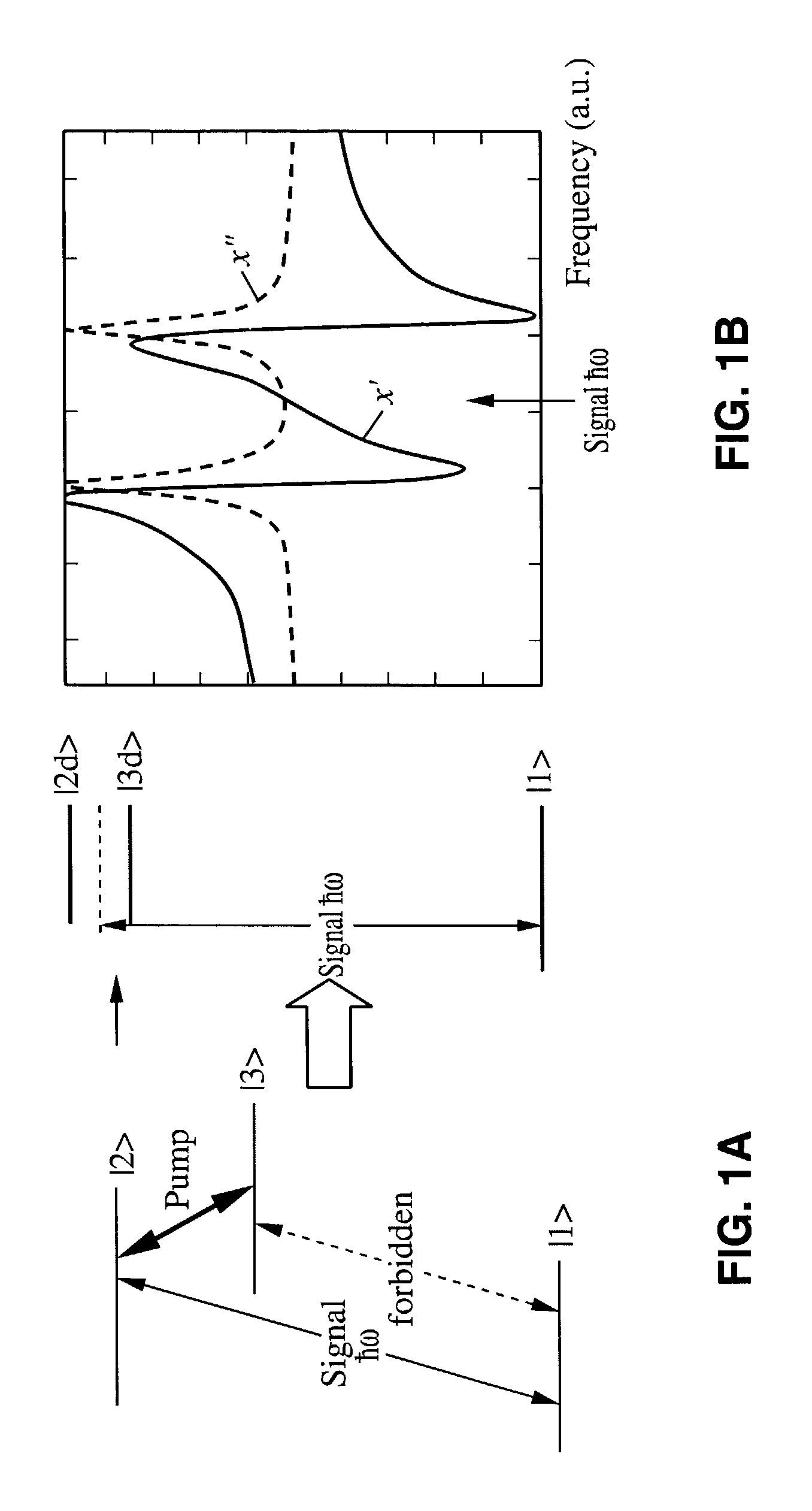
A variable semiconductor all-optical buffer and method of fabrication is provided where buffering is achieved by slowing down the optical signal using a control light source to vary the dispersion characteristic of the medium based on electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT). Photonic bandgap engineering in conjunction with strained quantum wells (QWs) and quantum dots (QDs) achieves room temperature operation of EIT. Photonic crystals are used to sharpen the spectral linewidths in a quantum well structure due to its density of states and in a quantum-dot structure caused by the inhomogeneity of the dot size, typically observed in state-of-the-art QD materials. The configuration facilitates monolithic integration of an optical buffer with an amplifier and control laser to provide advantages over other material systems as candidates for optical buffers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
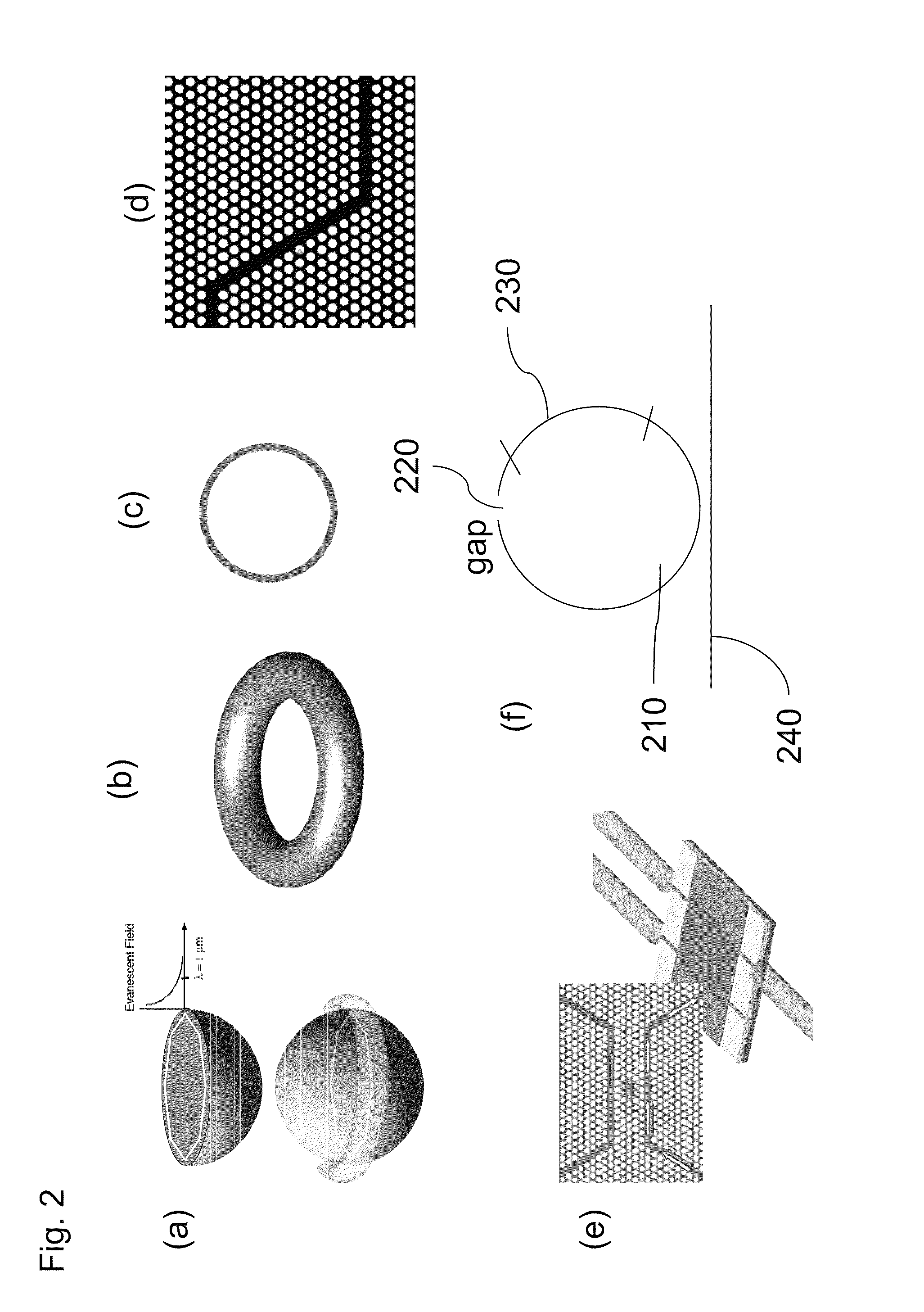
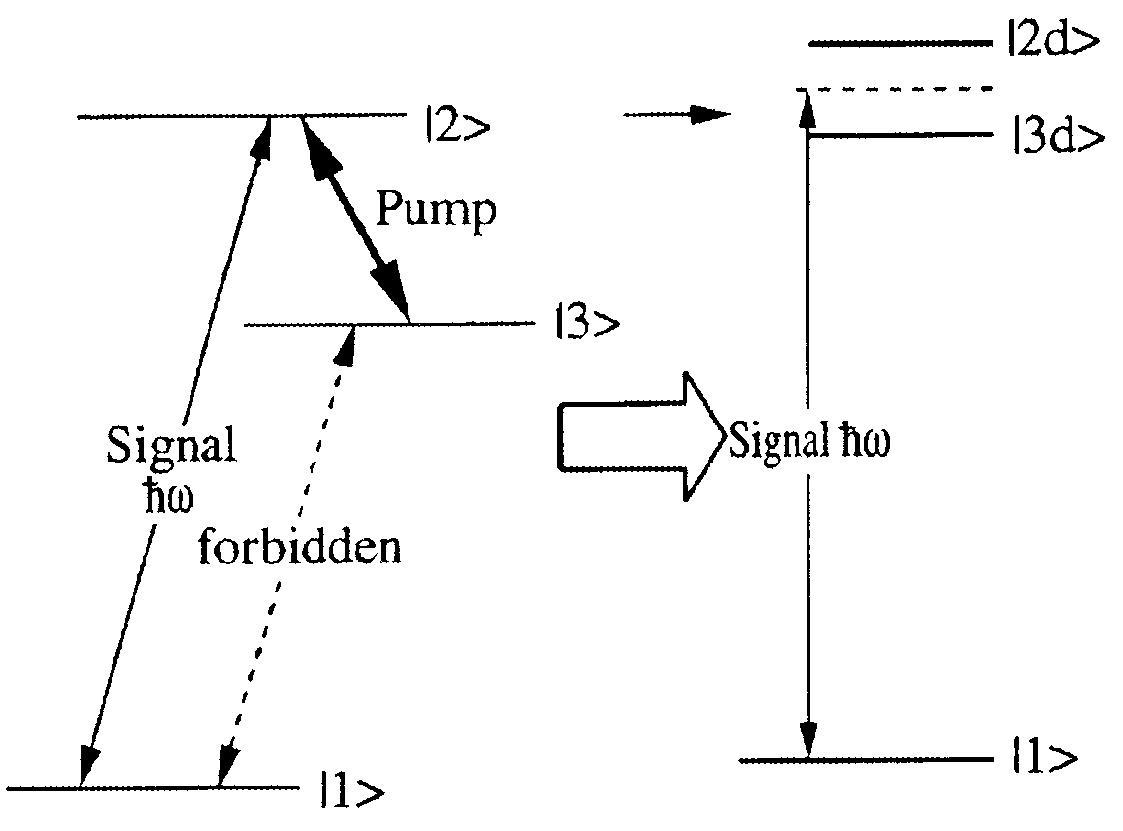
Methods and devices for measurements using pump-probe spectroscopy in high-q microcavities
InactiveUS20090237666A1Improve Sensing PerformanceRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometrySpectroscopyPump probe
The use of optical microcavities, high-Q resonators and slow-light structures as tools for detecting molecules and probing conformations and measuring polarizability and anisotropy of molecules and molecular assemblies using a pump-probe approach is described. Resonances are excited simultaneously or sequentially with pump and probe beams coupled to the same microcavity, so that a pump beam wavelength can be chosen to interact with molecules adsorbed to the microcavity surface, whereas a probe beam wavelength can be chosen to non-invasively measure pump-induced perturbations. The induced perturbations are manifest due to changes of resonance conditions and measured from changes in transfer characteristics or from changes of the scattering spectra of a microcavity-waveguide system. The perturbations induced by the pump beam may be due to polarizability changes, changes in molecular conformation, breakage or formation of chemical bonds, triggering of excited states, and formation of new chemical species. Furthermore, heat may be generated due to absorption of the pump beam. Furthermore, the use resonant modes with different states of polarization allows for measurements of polarizability and its anisotropy in samples interacting with the optical device.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Tunable plasmonic crystal
ActiveUS9105791B1High electron mobilityHigh hole mobilitySemiconductor devicesWavelengthMetal electrodes
A tunable plasmonic crystal comprises several periods in a two-dimensional electron or hole gas plasmonic medium that is both extremely subwavelength (˜λ / 100) and tunable through the application of voltages to metal electrodes. Tuning of the plasmonic crystal band edges can be realized in materials such as semiconductors and graphene to actively control the plasmonic crystal dispersion in the terahertz and infrared spectral regions. The tunable plasmonic crystal provides a useful degree of freedom for applications in slow light devices, voltage-tunable waveguides, filters, ultra-sensitive direct and heterodyne THz detectors, and THz oscillators.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC +1
Methods, materials and devices for light manipulation with oriented molecular assemblies in micronscale photonic circuit elements with high-q or slow light
InactiveUS20090136181A1Remarkable effectEnhanced interactionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingNanowireFluorescence
An optical device that comprises an input waveguide, an output waveguide, a high-Q resonant or photonic structure that generate slow light connected to the input waveguide and the output waveguide, and an interface, surface or mode volume modified with at least one material formed from a single molecule, an ordered aggregate of molecules or nanostructures. The optical device may include more than one input waveguide, output waveguide, high-Q resonant or photonic structure and interface, surface or mode volume. The high-Q resonant or photonic structure may comprise at least one selected from the group of: microspherical cavities, microtoroidal cavities, microring-cavities, photonic crystal defect cavities, fabry-perot cavities, photonic crystal waveguides. The ordered aggregate of molecules or nanostructures comprises at least one selected from the group of: organic or biological monolayers, biological complexes, cell membranes, bacterial membranes, virus assemblies, nanowire or nanotube assemblies, quantum-dot assemblies, one or more assemblies containing one or more rhodopsins, green fluorescence proteins, diarylethers, lipid bilayers, chloroplasts or components, mitochondria or components, cellular or bacterial organelles or components, bacterial S-layers, photochromic molecules. Further, the molecular aggregate may exhibit a photoinduced response.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
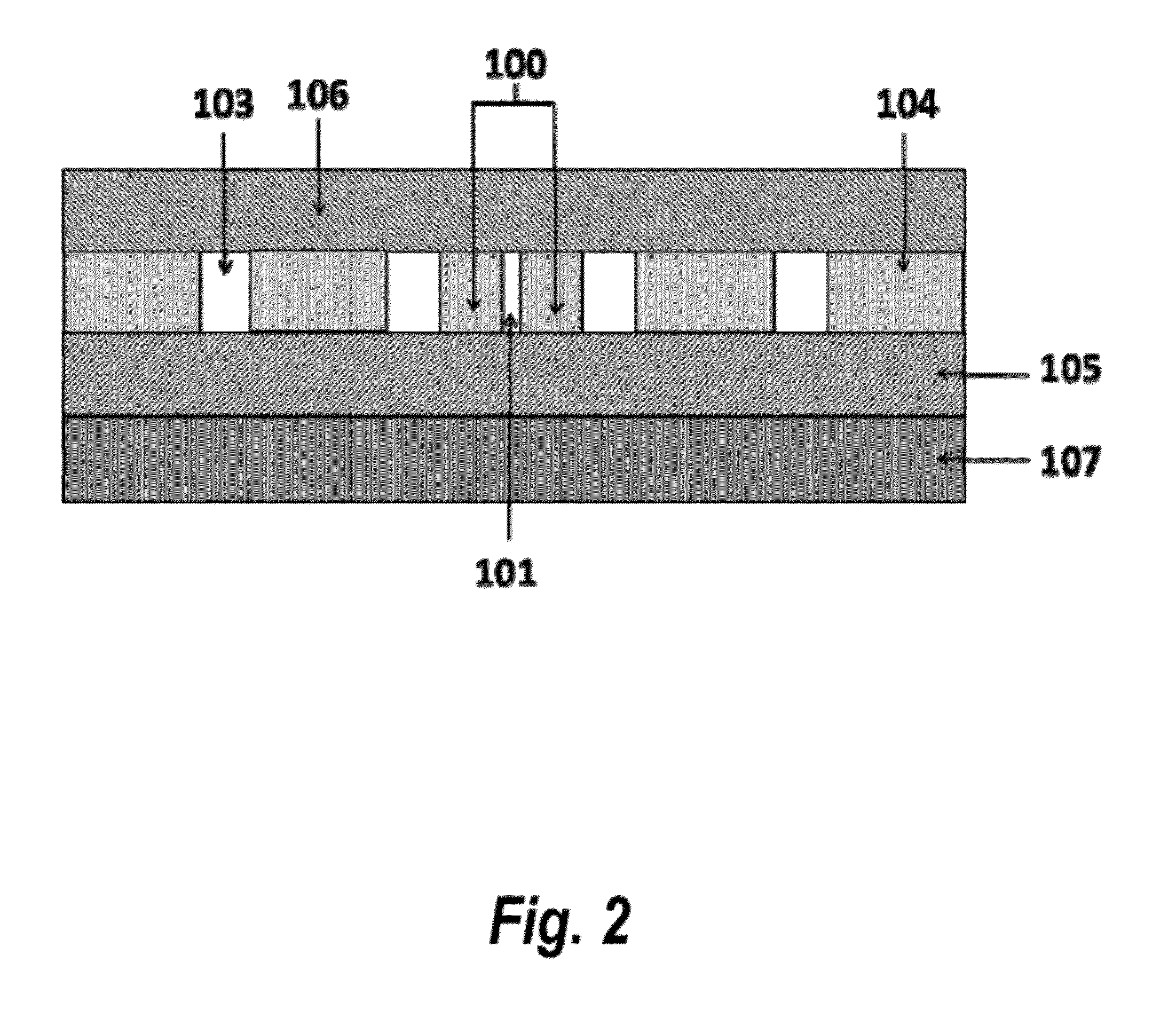
Electro-Optical Modulator Structure
InactiveUS20090220184A1Improve performanceSmall sizeMaterial analysis by optical meansNanoopticsSlow lightSemiconductor chip
The present invention discloses an ultra-compact optical modulator comprising at least one resonator on a semiconductor chip. The EO modulator modulates incoming light having a certain wavelength range and comprises a waveguide layer accommodating at least one resonator having a periodic complex refraction index distribution structure defining a periodic defect band-edge and a cladding layer; and at least one electrode; the waveguide layer, the cladding layer and the electrode forming a capacitor structure; such that when an external voltage is applied to the capacitor structure the free carrier concentration in the waveguide layer is controlled, enabling a modulation of the resonator's refractive index; wherein the periodic defect band-edge is selected to be within the wavelength range, enabling a slow-light propagation of the incoming light within the waveguide layer.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Photonic crystal slot waveguide miniature on-chip absorption spectrometer
ActiveUS20120044489A1Enhanced light absorptionEliminate needRadiation pyrometryCladded optical fibreAnalyteOptical absorption spectra
Methods and systems for label-free on-chip optical absorption spectrometer consisting of a photonic crystal slot waveguide are disclosed. The invention comprises an on-chip integrated optical absorption spectroscopy device that combines the slow light effect in photonic crystal waveguide and optical field enhancement in a slot waveguide and enables detection and identification of multiple analytes to be performed simultaneously using optical absorption techniques leading to a device for chemical and biological sensing, trace detection, and identification via unique analyte absorption spectral signatures. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:OMEGA OPTICS
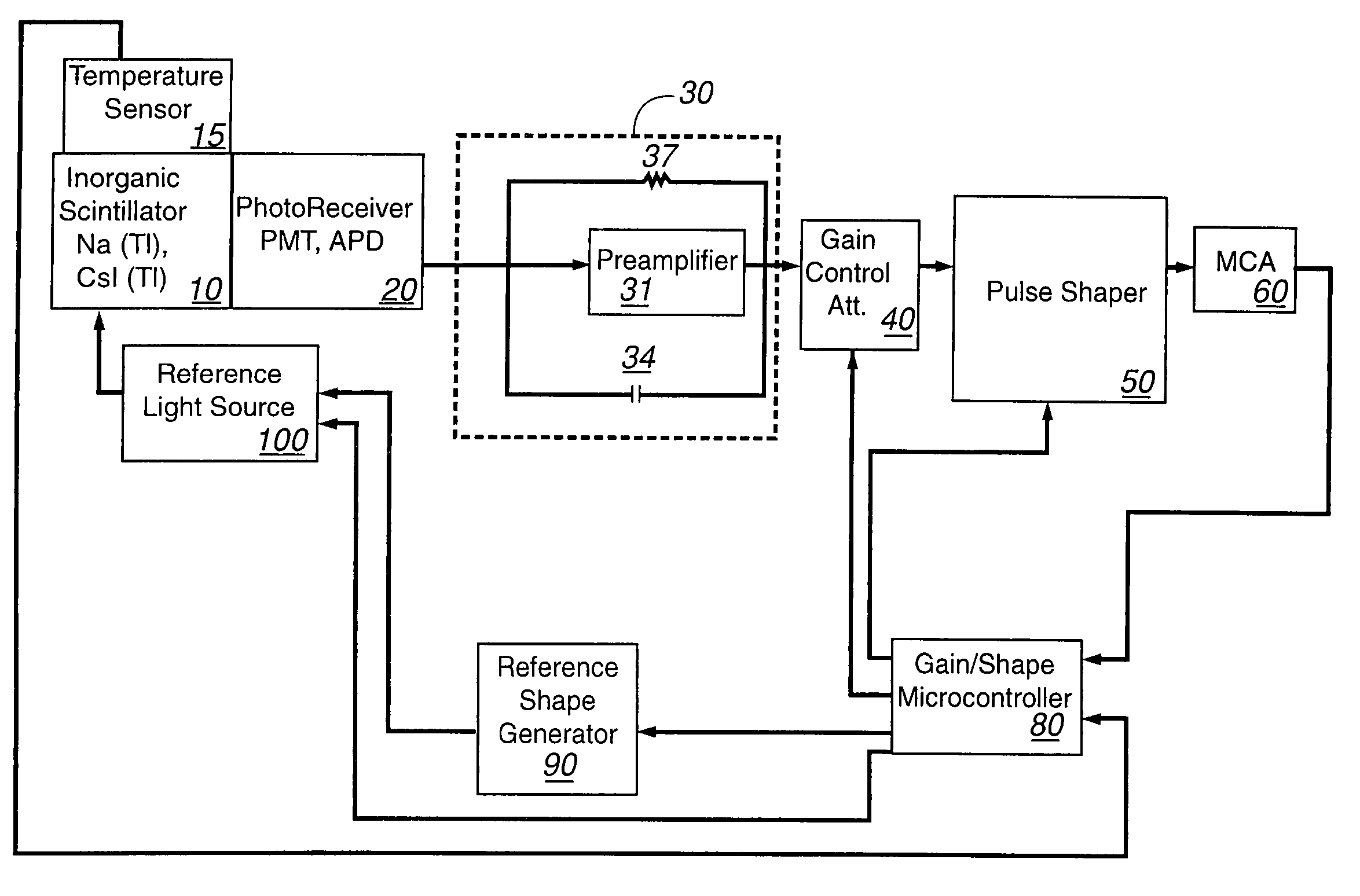
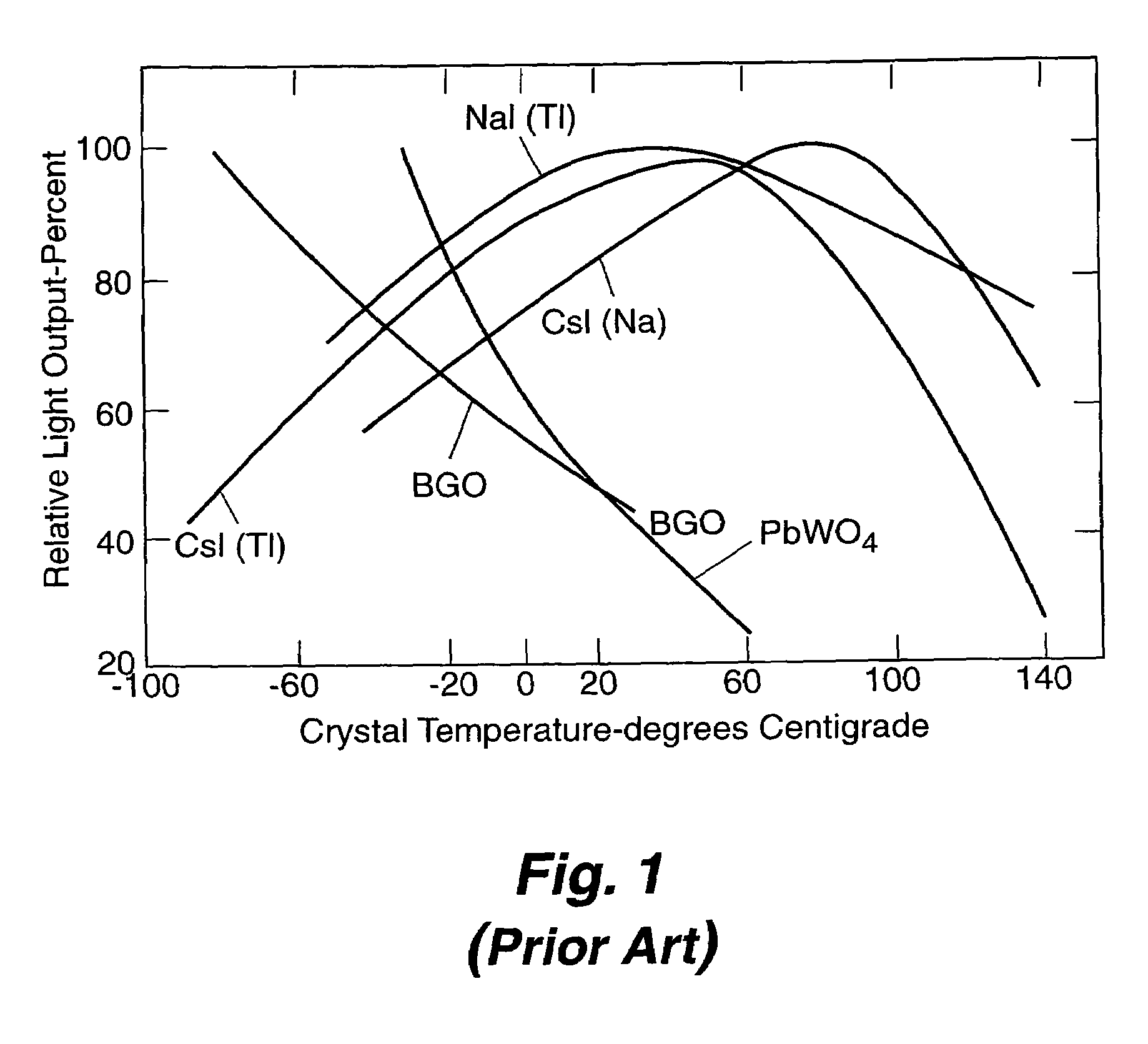
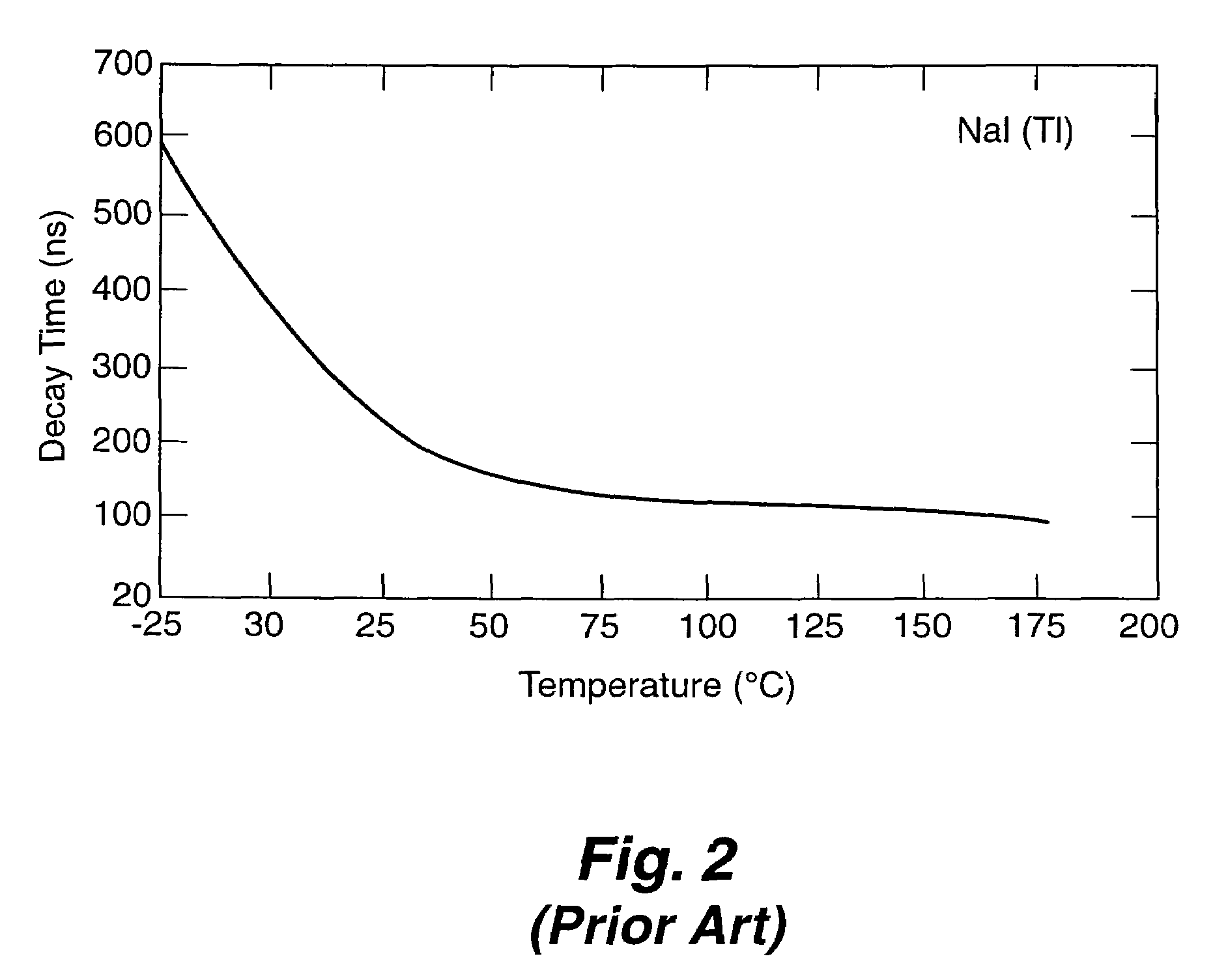
Apparatus and method for temperature correction and expanded count rate of inorganic scintillation detectors
InactiveUS7081626B2Increase count rateMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementCounting rateSlow light
The present invention includes an apparatus and corresponding method for temperature correction and count rate expansion of inorganic scintillation detectors. A temperature sensor is attached to an inorganic scintillation detector. The inorganic scintillation detector, due to interaction with incident radiation, creates light pulse signals. A photoreceiver processes the light pulse signals to current signals. Temperature correction circuitry that uses a fast light component signal, a slow light component signal, and the temperature signal from the temperature sensor to corrected an inorganic scintillation detector signal output and expanded the count rate.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Methods, materials and devices for light manipulation with oriented molecular assemblies in micronscale photonic circuit elements with High-Q or slow light
An optical device that comprises an input waveguide, an output waveguide, a high-Q resonant or photonic structure that generate slow light connected to the input waveguide and the output waveguide, and an interface, surface or mode volume modified with at least one material formed from a single molecule, an ordered aggregate of molecules or nanostructures. The optical device may include more than one input waveguide, output waveguide, high-Q resonant or photonic structure and interface, surface or mode volume. The high-Q resonant or photonic structure may comprise at least one selected from the group of: microspherical cavities, microtoroidal cavities, microring-cavities, photonic crystal defect cavities, fabry-perot cavities, photonic crystal waveguides. The ordered aggregate of molecules or nanostructures comprises at least one selected from the group of: organic or biological monolayers, biological complexes, cell membranes, bacterial membranes, virus assemblies, nanowire or nanotube assemblies, quantum-dot assemblies, one or more assemblies containing one or more rhodopsins, green fluorescence proteins, diarylethers, lipid bilayers, chloroplasts or components, mitochondria or components, cellular or bacterial organelles or components, bacterial S-layers, photochromic molecules. Further, the molecular aggregate may exhibit a photoinduced response.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
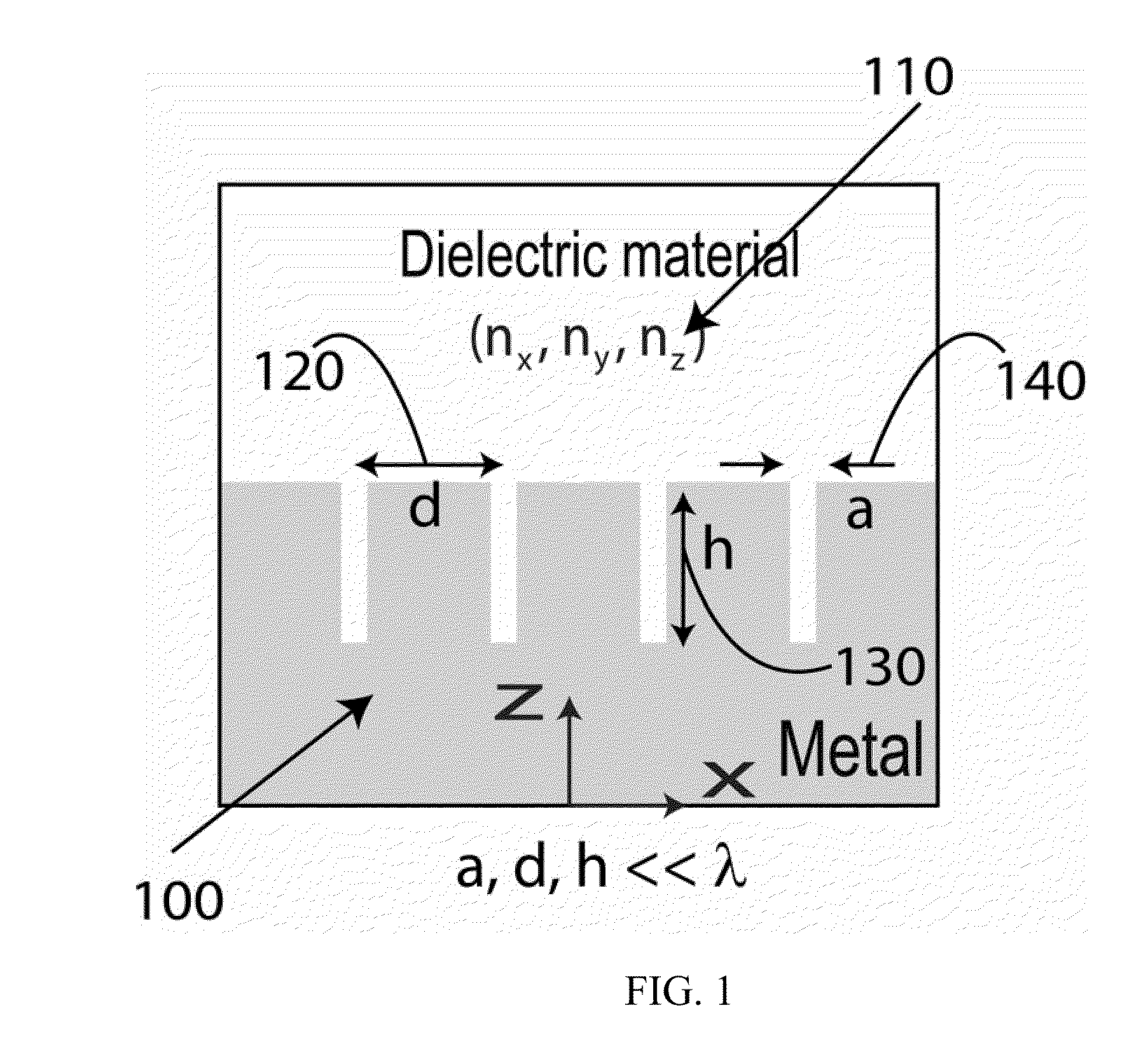
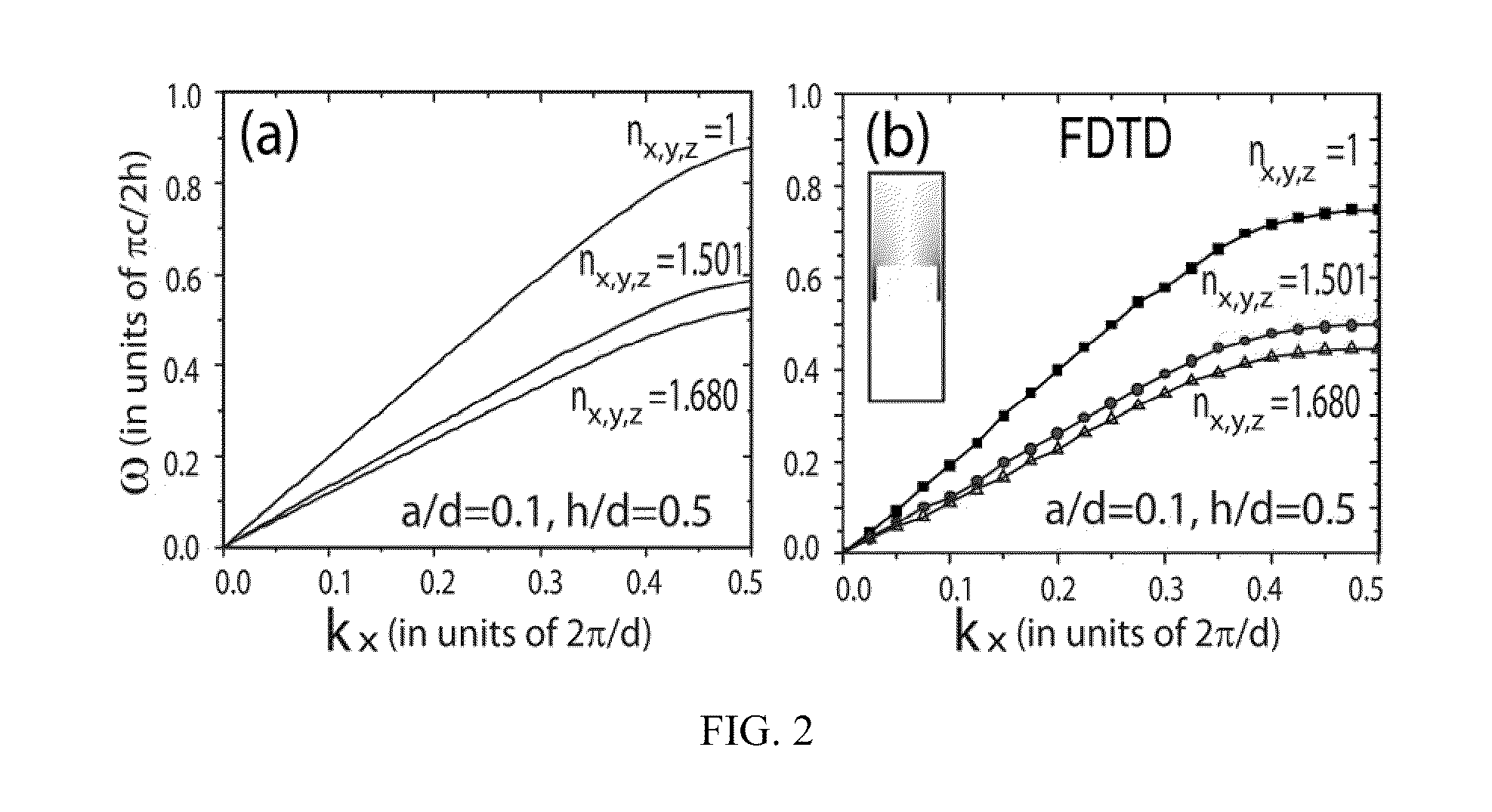
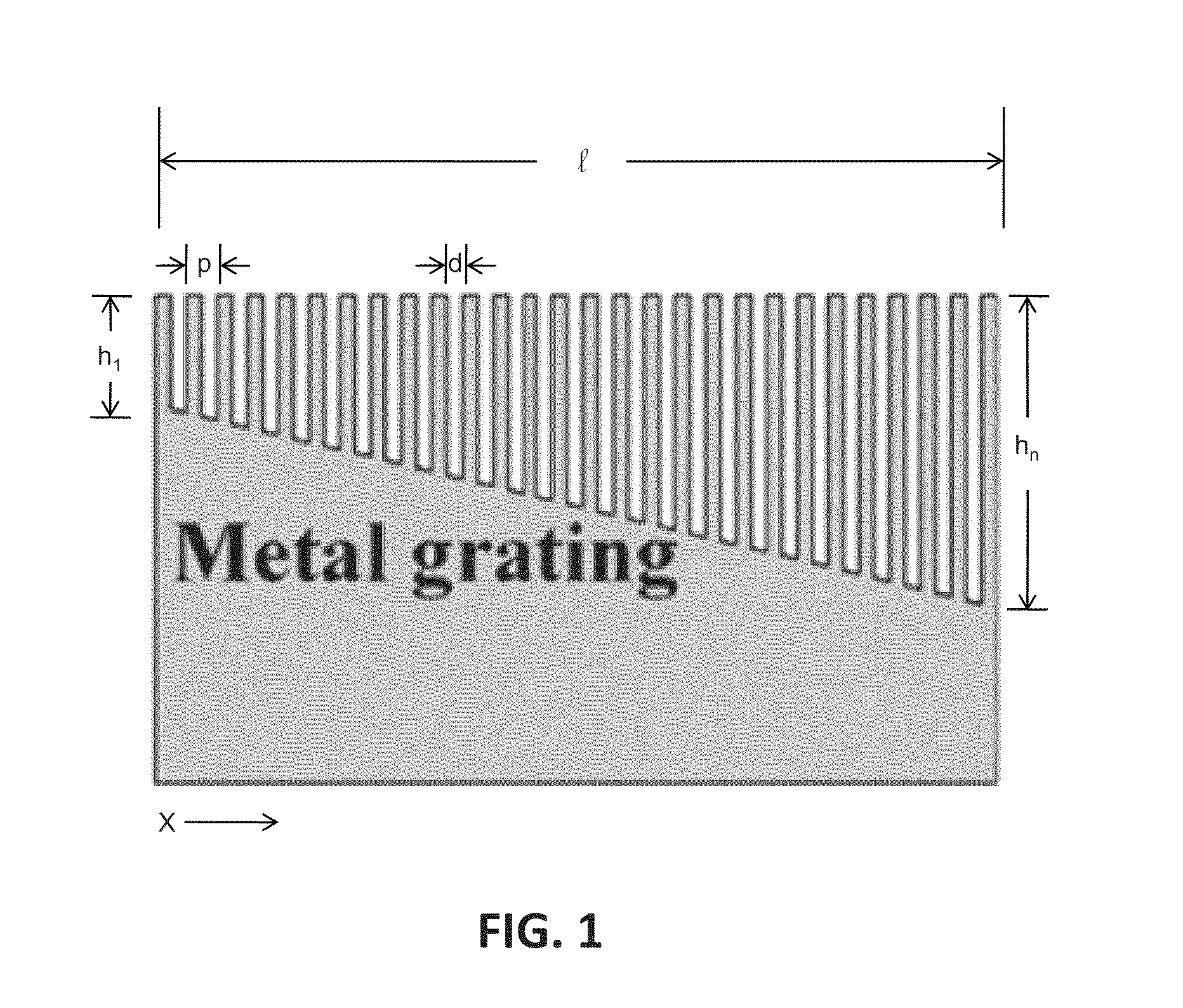
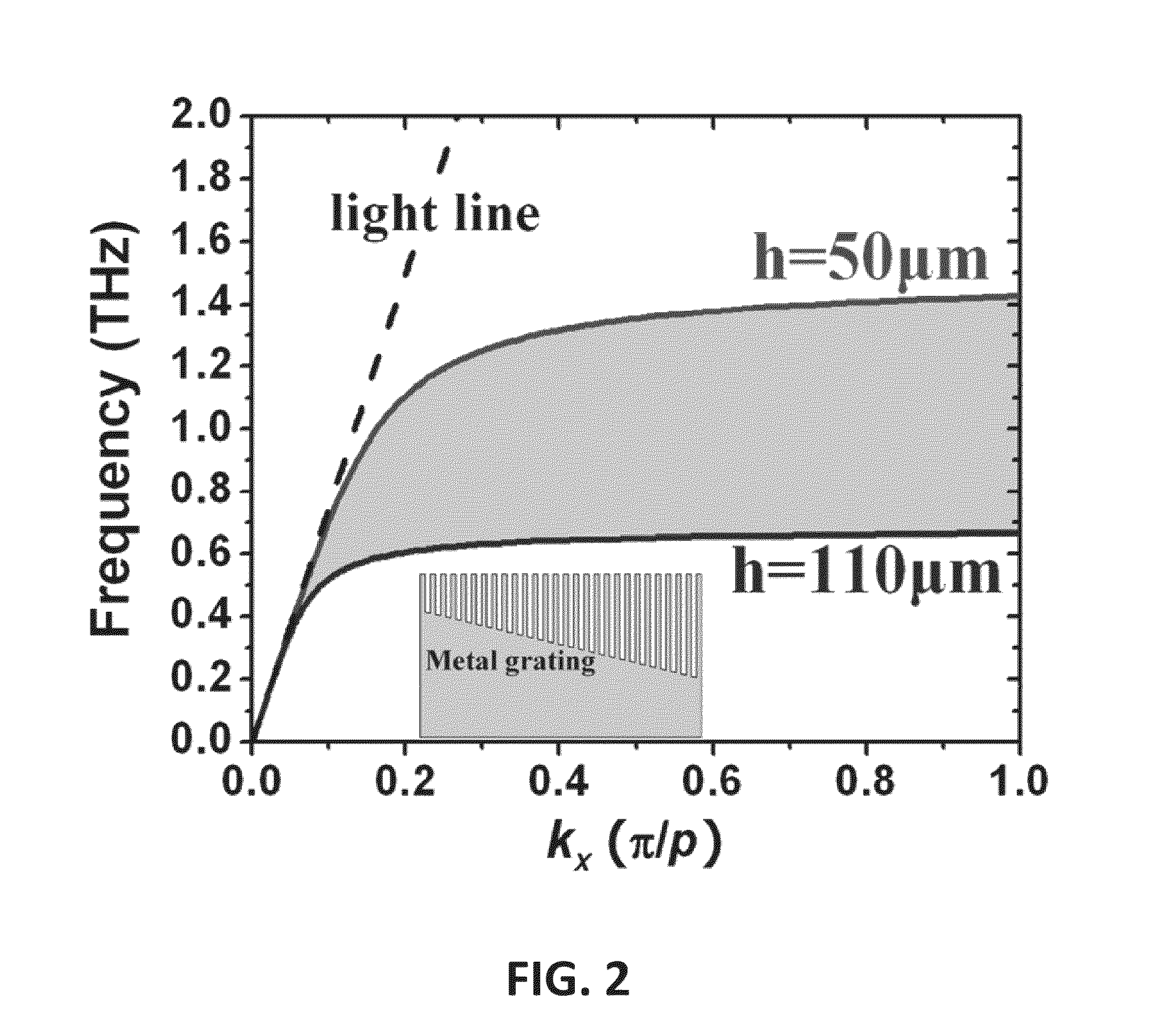
Ultra-wide band slow light structure using plasmonic graded grating structures
A slow light system includes a substrate and a metal layer formed thereon, the metal layer having a graded grating structure formed at a surface thereof, wherein the grating depth of the grating structure is sized such that surface-plasmon polariton dispersion behavior of the grating structure differs at different respective locations along the grating structure. Different wavelengths of incident light waves can be slowed at the respective locations along the grating structure.
Owner:LEHIGH UNIVERSITY
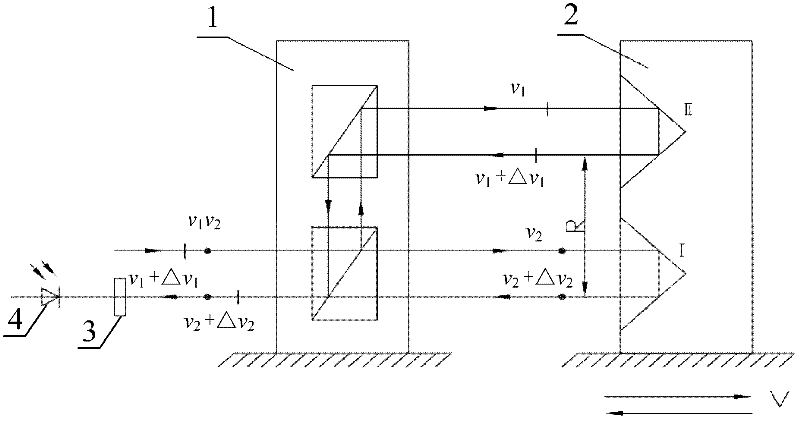
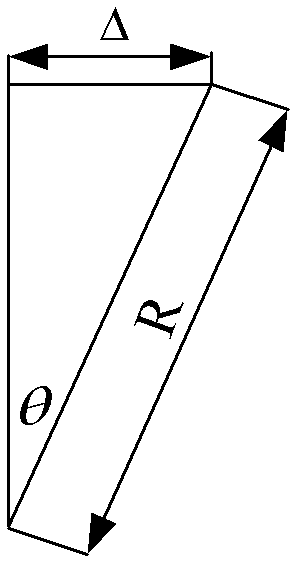
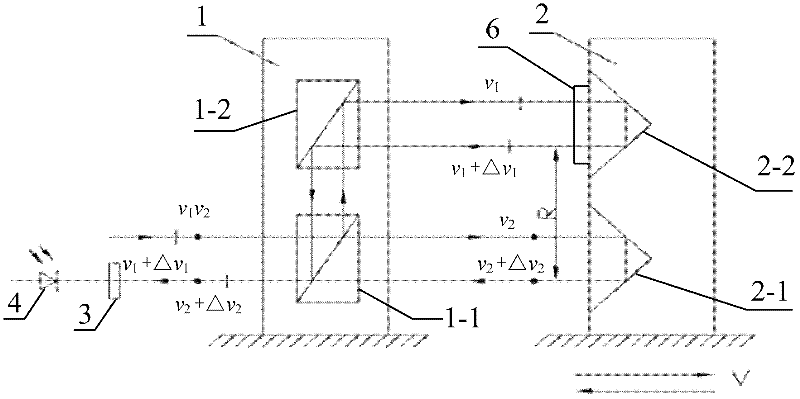
Angle measuring device and angle measuring method of double-frequency laser interferometer based on slow-light material
InactiveCN102564354AHigh detection sensitivityUsing optical meansSpectral hole burningPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention provides an angle measuring device and an angle measuring method of a double-frequency laser interferometer based on a slow-light material, which relates to an angle measuring device and an angle measuring method of the double-frequency laser interferometer. The angle measuring device provided by the invention aims at solving the problem of low angle measuring sensitivity of the angle measuring device of the existing double-frequency laser interferometer. Double-frequency laser is divided into polarized light with frequency at v1 and polarized light with frequency at v2 through a polarization spectroscope in a polarization direction. The polarized light with the frequency at v1 enters a pyramid prism 1 to be reflected to the polarization spectroscope through the pyramid prism 1; the polarized light with the frequency at v2 is reflected to the slow-light material sequentially through a common corner reflector, the slow-light material and a pyramid prism 2 and then is reflected to the polarization spectroscope sequentially through the slow-light material and the common corner reflector to converge with polarized light reflected through the pyramid prism 1 at the position of the polarization spectroscope so as to form beat frequency; and converged light enters an optical detection face of a photoelectric detector after being subjected to transmission of a polarization reducing device. The angle measuring device and the angle measuring method provided by the invention are applicable to the electromagnetic induction transparency technology and the spectral hole burning technology.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for realizing integration of polarizing beam splitter and slow light device by using bend waveguide
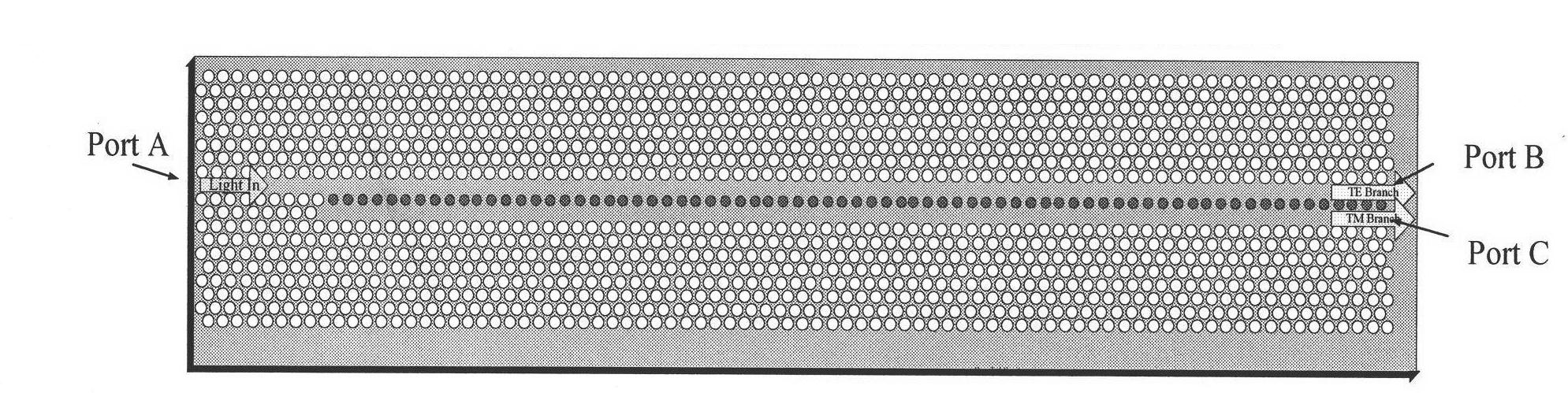
InactiveCN102200613AGood beam splitting performanceChange working frequency bandCoupling light guidesManufacturing technologyBeam splitter
The invention relates to a method for realizing integration of a polarizing beam splitter and a slow light device by using a bend waveguide, belonging to the technical field of micro optical integration. In the invention, the polarizing beam splitter and a coupled-cavity waveguide slow light device are integrated on the same flat plate by using the bend waveguide with two turn angles of 60 degrees for the first time. In the invention, a flat-plate structure based on a two-dimensional photonic crystal is designed; and the structure of the device is designed in such a way that each module of an integrated device works at the same frequency, thus high efficient coupling between the polarizing beam splitter and the bend waveguide as well as the slow light device is realized. The basic structure of the flat-plate structure is a photonic crystal GaAlAs (Gallium-Aluminum-Arsenic) flat-plate structure based on an air-vent triangular lattice, which is much closer to a traditional widely-applied photonic crystal manufacturing technology based on SOI (Silicon-On-Insulator) and has the characteristic of very good realizability. In addition, the polarizing beam splitter and the coupled-cavity waveguide slow light device are connected with each other by using the bend waveguide in the design of the scheme so as to provide a new method for realizing the micro PIC (Programmable Interrupt Controller).
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
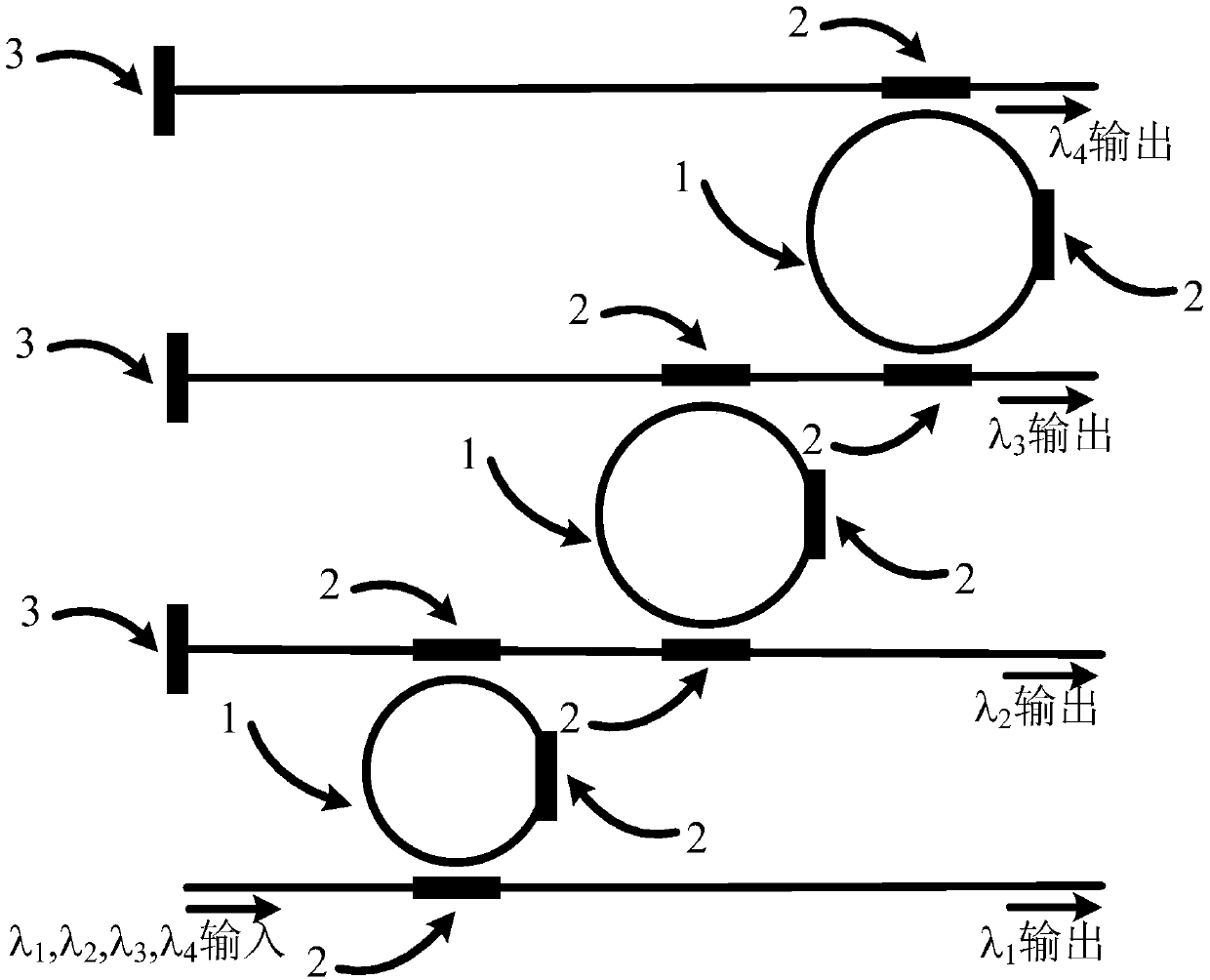
Reflective microring resonator, multi-wavelength light delayer and photon beam-forming chip
The invention discloses a reflective microring resonator. The reflective microring resonator comprises an upper download type microring resonator, wherein the upper download type microring resonator comprises a microring and a channel waveguide coupled with the microring, a download end of the upper download type microring resonator is provided with a light reflection structure, and the reflectivemicroring resonator further comprises a coupling control module used for controlling the coupling amount of the microring and the channel waveguide to make a group delay state of resonant light in two directions in the reflective microring resonator satisfy the fast and slow light cancellation condition. The invention further discloses a multi-wavelength light delayer, a photon beam-forming method and a photon beam-forming chip. The reflective microring resonator is advantaged in that true wideband light delay can be achieved, and the delay amount can be flexibly adjusted.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
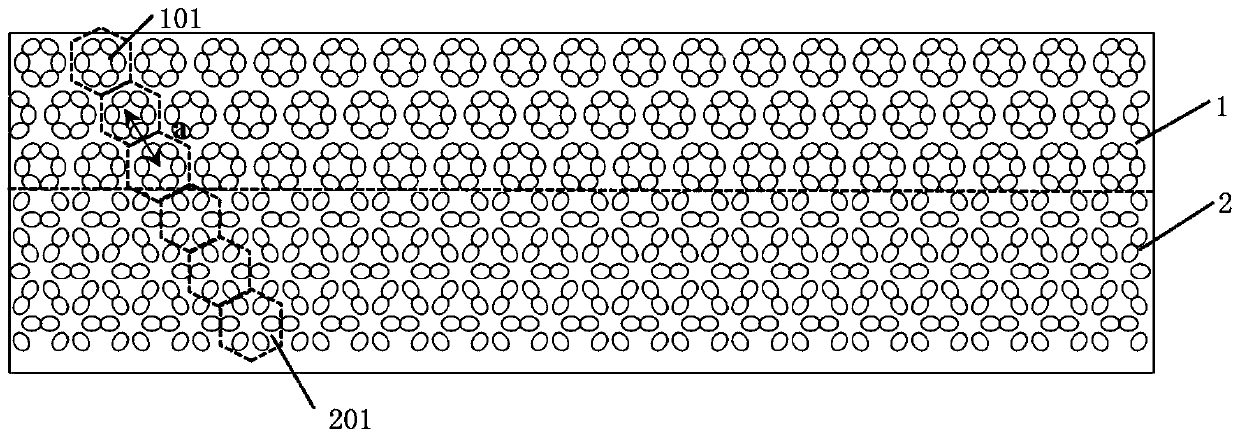
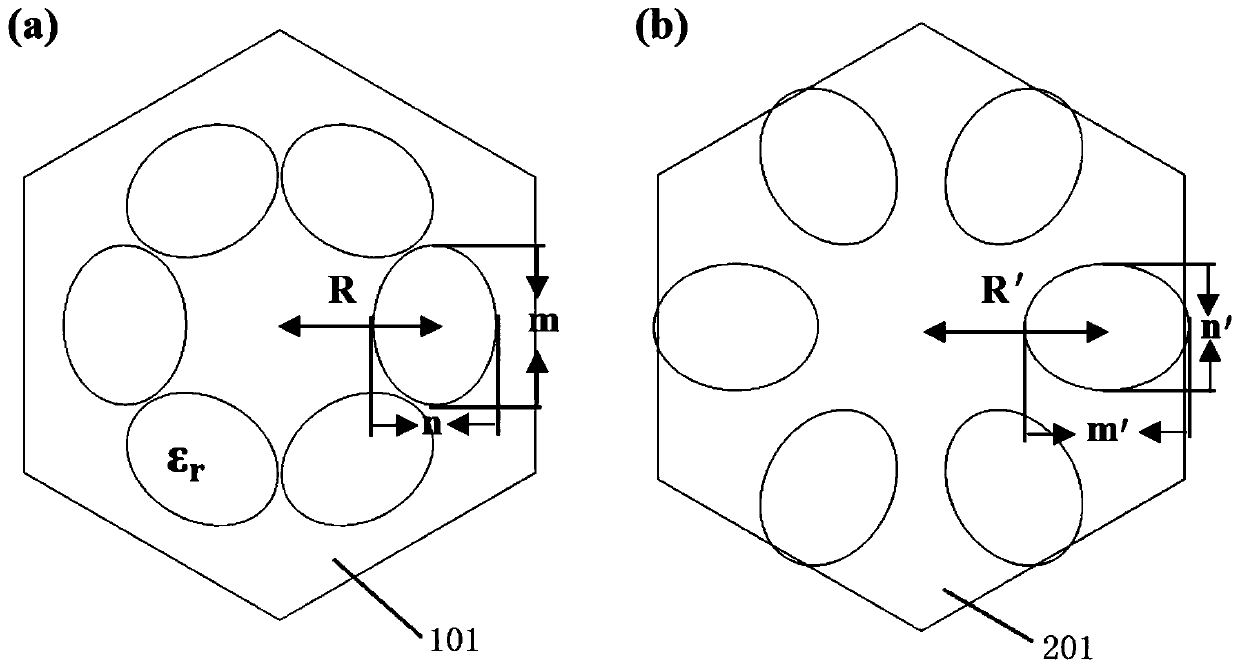
Photonic crystal slow light waveguide based on honeycomb structure
ActiveCN110161621AReduce manufacturing costRealize slow light transmissionCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideDielectric cylinderSlow light
The invention provides a photonic crystal slow light waveguide based on a honeycomb structure. The photonic crystal slow light waveguide based on the honeycomb structure comprises a topology mediocrestructure and a topology non-mediocre structure, and the other part is composed of crystal cells which are arranged and have topology non-mediocre property. A relatively mild energy band appears in afirst Brillouin zone in an energy band structure, and transmission group velocity of light at the frequency is close to 0, so that slow light transmission is realized. An elliptical dielectric cylinder is made from a common dielectric material silicon, and production cost is low.
Owner:南通宁竞信息科技有限公司
Fabrication Tolerant Design for the Chip-Integrated Spectroscopic Identification of Solids, Liquids, and Gases
ActiveUS20120328233A1Enhanced light absorptionEnhanced optical fieldNanoopticsColor/spectral properties measurementsAbsorption spectroscopySpectrometer
Methods and systems for a label-free on-chip optical absorption spectrometer consisting of a photonic crystal slot waveguide are disclosed. The invention comprises an on-chip integrated optical absorption spectroscopy device that combines the slow light effect in photonic crystal waveguide and optical field enhancement in a slot waveguide and enables detection and identification of multiple analytes to be performed simultaneously using optical absorption techniques leading to a device for chemical and biological sensing, trace detection, and identification via unique analyte absorption spectral signatures. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:OMEGA OPTICS
Variable semiconductor all-optical buffer using slow light based on electromagnetically induced transparency
A variable semiconductor all-optical buffer and method of fabrication is provided where buffering is achieved by slowing down the optical signal using a control light source to vary the dispersion characteristic of the medium based on electromagnetically induced transparency (EIT). Photonic bandgap engineering in conjunction with strained quantum wells (QWs) and quantum dots (QDs) achieves room temperature operation of EIT. Photonic crystals are used to sharpen the spectral linewidths in a quantum well structure due to its density of states and in a quantum-dot structure caused by the inhomogeneity of the dot size, typically observed in state-of-the-art QD materials. The configuration facilitates monolithic integration of an optical buffer with an amplifier and control laser to provide advantages over other material systems as candidates for optical buffers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Adjustable light pulse time-delay device with wide bandwidth and multiple gains based on stimulated brillouin scatter
A pulse delay device of adjustable light based on multigrain spectral band width excited by Brillouin scattering is prepared as connecting laser source to pumping light source being connected to adjustable attenuator, connecting said attenuator to the second optical fiber circulator (TSOFC) being connected to the second single-mode optical fiber, connecting laser source to detection pulse light source being connected to optical fiber isolator, connecting said isolator to the third polarized controller being connected to the second single-mode optical fiber, and using the third port of TSOFC as output end.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Two-dimensional surface normal slow-light photonic crystal waveguide optical phased array
ActiveUS8200055B2High thermo-optic coefficientPromote formationCladded optical fibreNanoopticsRefractive indexLaser light
Methods and devices for optical beam steering are disclosed including coupling a laser light into an apparatus comprising a first substrate; an array of air core photonic crystal waveguides; columnar members etched around each air core waveguide; a pair of metal electrodes around the columnar members; a trench around the pair of metal electrodes surrounding each air core photonic crystal waveguide; a second substrate coupled to the first substrate comprising electrical interconnection lines; and a holographic fanout array comprising a third substrate; a photopolymer film coated on the third substrate; a hologram written in the photopolymer film configured to couple the laser light into the third substrate; and an array of holograms recorded in the photopolymer film configured to couple a portion of the laser light into the waveguides; and passing a current through the electrodes to induce a refractive index change in the first substrate to control the phase of the portion of the laser light that passes through each waveguide. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:OMEGA OPTICS
Ultra-wide band slow light structure using plasmonic graded grating structures
A slow light system includes a substrate and a metal layer formed thereon, the metal layer having a graded grating structure formed at a surface thereof, wherein the grating depth of the grating structure is sized such that surface-plasmon polariton dispersion behavior of the grating structure differs at different respective locations along the grating structure. Different wavelengths of incident light waves can be slowed at the respective locations along the grating structure.
Owner:LEHIGH UNIVERSITY
High-sensitivity resonance type optical fiber peg-top based on slow light group velocity
InactiveCN101126642AHigh sensitivityLow costSagnac effect gyrometersCoupling light guidesBeam splitterRefractive index
The utility model relates to a resonator fiber optic gyro with high sensitivity, belonging to the technical field of a fiber optic gyro, which aims at overcoming the problems that low sensibility (0.1 degree / hour) exists upon prior resonator fiber optic gyro and can not meet attitude tracking of short range / midrange missiles and commercial aircrafts, more particularly can not meet areas such as space positioning and submarine navigation with high requirement for sensibility. The utility model is characterized in that a laser output end of a frequency conversion laser (1) is connected with a dispersion fiber ring resonator (11) through a group speed control system (2), a fiber beam splitter (3), a first lithium niobate phase modulator (4), a second lithium niobate phase modulator (5), a first optical fiber coupler (6), a second optical fiber coupler (7) and a third optical fiber coupler (10). The utility model has the advantages of high sensibility up to ng times (The ng is group speed refractive index), low production cost, simple structure and small size.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
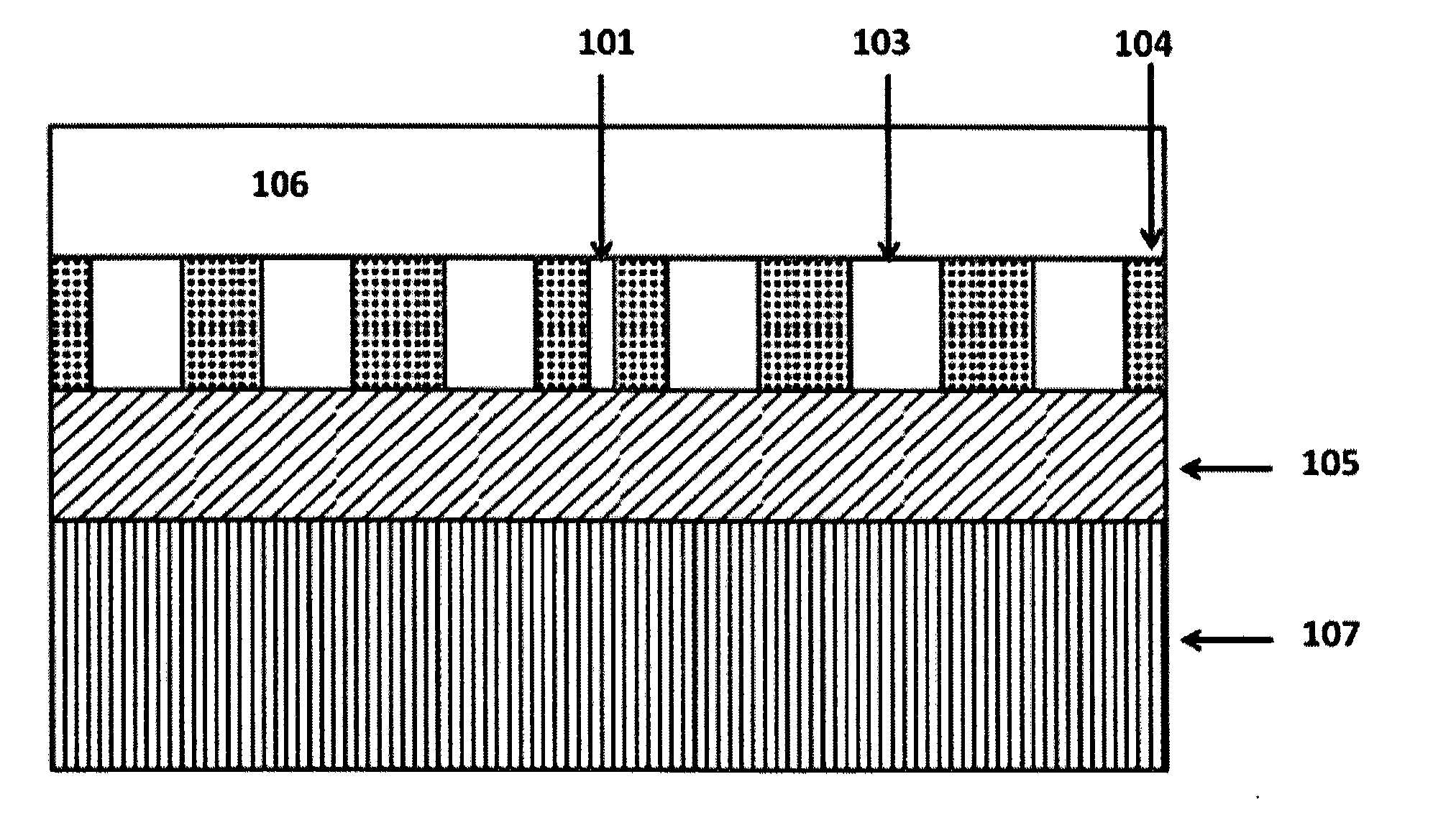
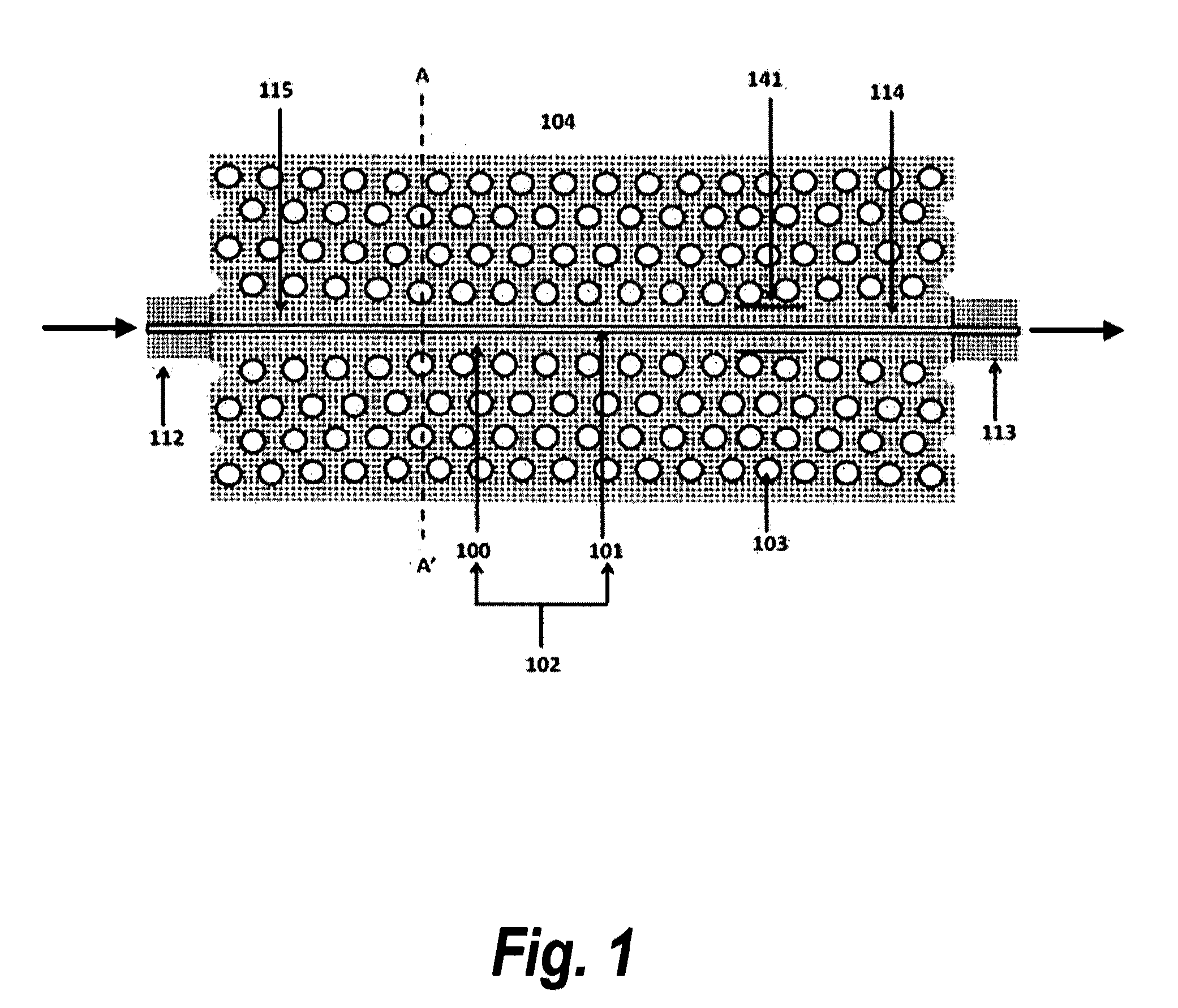
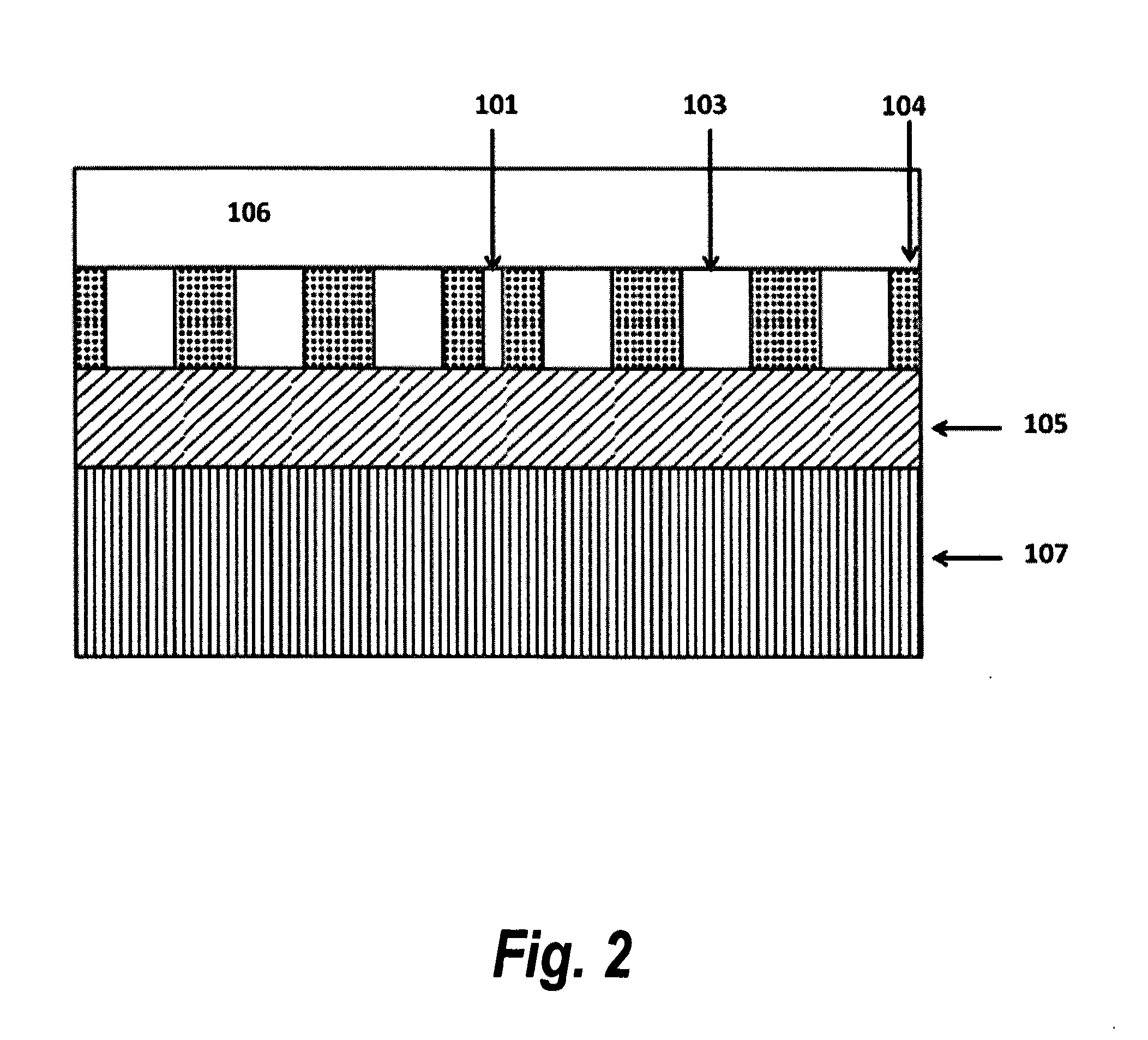
Photonic crystal rectangular coupled cavity zero dispersion slow optical wave guide
InactiveCN101887145AAchieving Slow Light PropagationAchieve single-mode outputOptical light guidesDielectric cylinderSlow light
The invention provides a dielectric cylinder photonic crystal zero dispersion slow optical wave guide which comprises a substrate, a plurality of coupled cavities, a plurality of dielectric cylinders and an excitation source, wherein each coupled cavity is a rectangular cylinder, and the coupled cavities are vertically manufactured above the middle part of the substrate in a row and are used for regulating a slow light mode; each dielectric cylinder is a cylinder, and the dielectric cylinders are vertically manufactured above the substrate in a plurality of rows, are arranged at both sides of the coupled cavities and are used for laterally limiting a light field; and the excitation source is arranged at one side of the substrate, is relative to the coupled cavities in a row and excites the slow light mode to generate.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multiplier enhancing method based on periodically poled lithium niobate
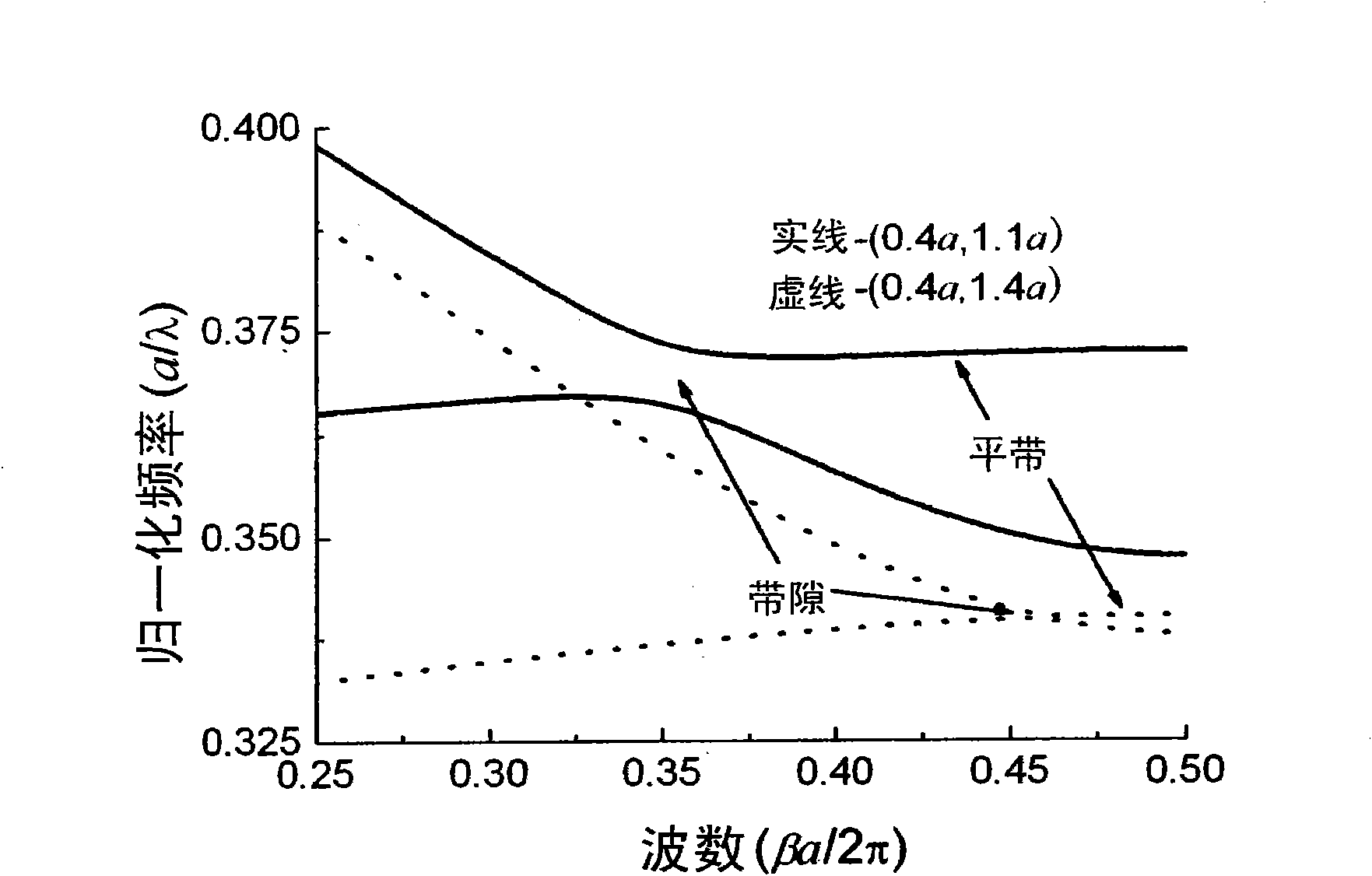
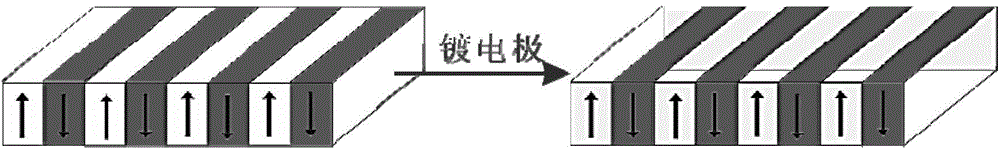
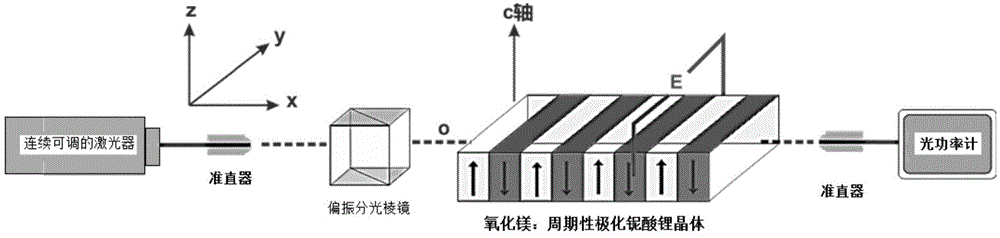
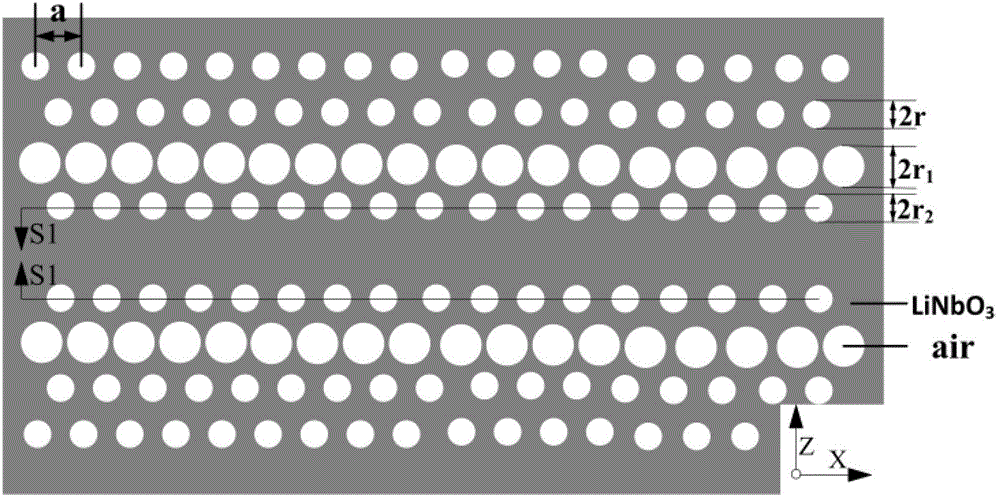
InactiveCN103605248AImprove conversion efficiencyChange cycleNon-linear opticsInformation processingSlow light
The invention provides a multiplier enhancing method based on periodically poled lithium niobate, and belongs to the technical field of optical information processing. The method includes firstly, performing room temperature electric field polarization on lithium niobate crystals, changing the polarization direction of the electric domain in a negative domain region of the +Z face of the crystals, and performing vacuum coating sputter electrode on two Y-directional sides of the crystals; then irradiated the crystals with a normal light and applying voltage of the two Y-directional sides of the lithium niobate crystals through a high voltage source simultaneously, and realizing ordinary light multiplier enhancement through produced slow light effects. According to the method, the quasi-phase matching technique (QPM) is creatively combined with effective light power enhancement resulted from the slow light effects.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
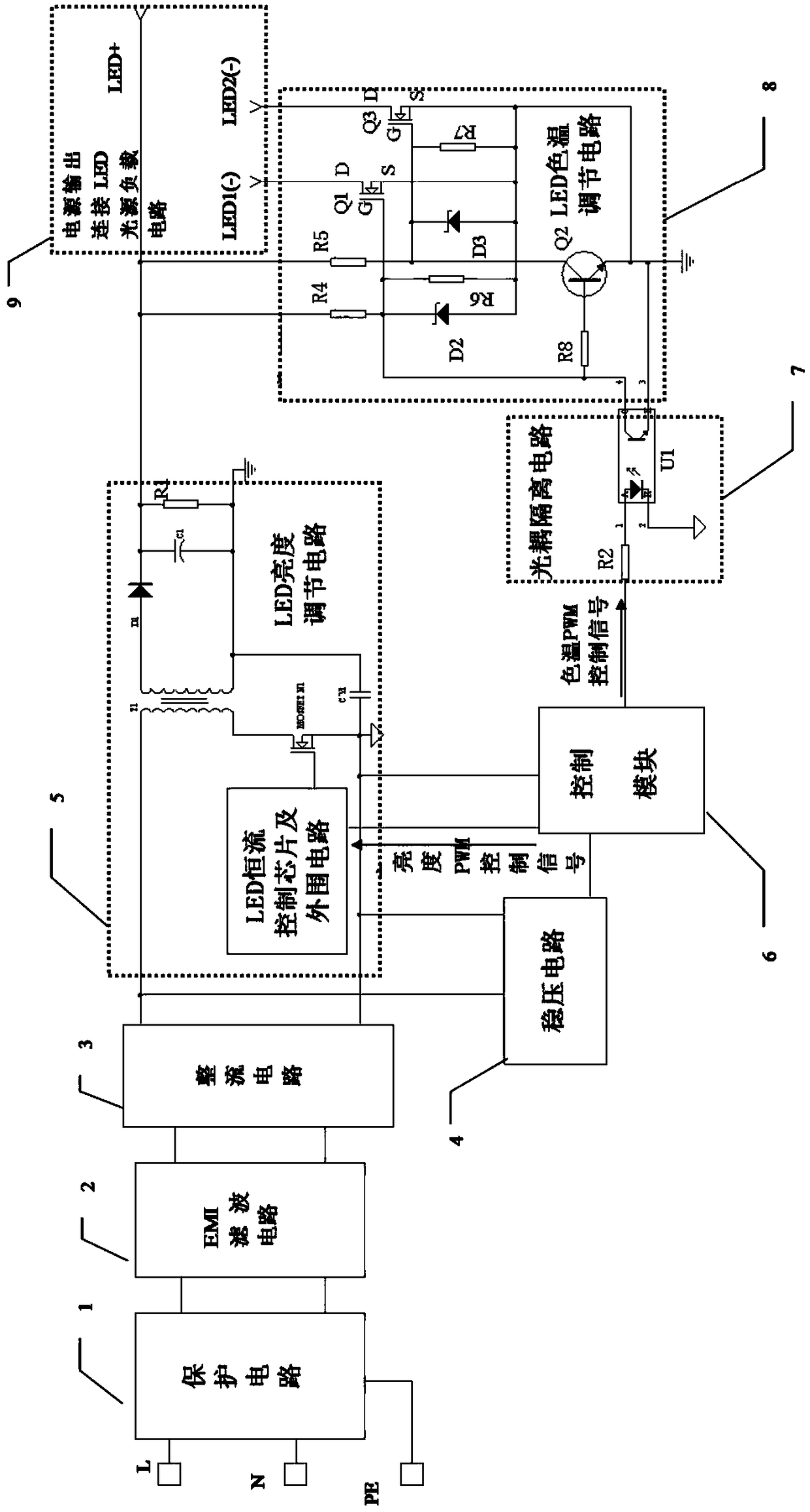
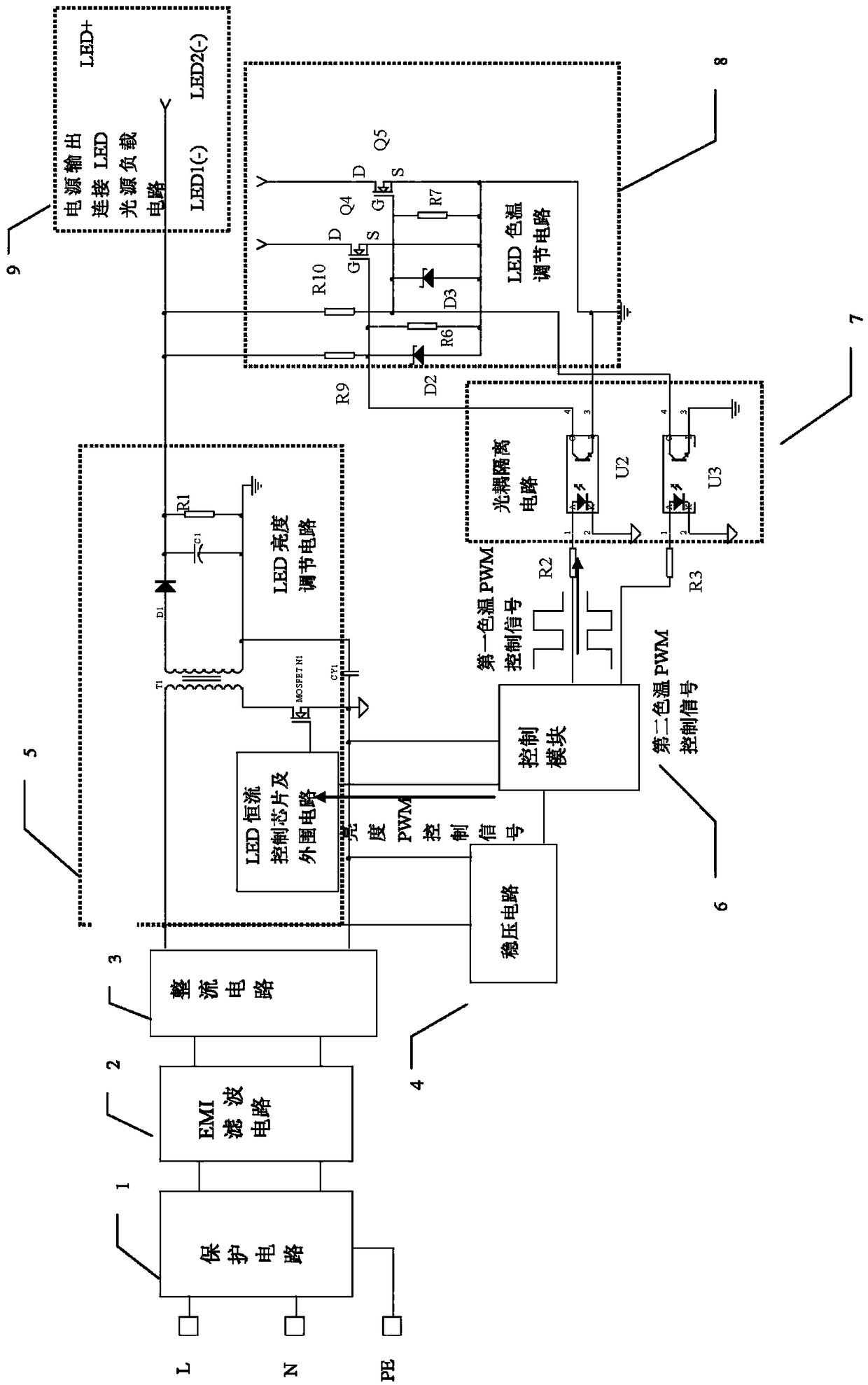
Dimming and color-regulating LED isolation constant current driving power supply
PendingCN108770136AStrong load compatibilityReduce power consumptionElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesControl signalEngineering
The invention discloses a dimming and color-regulating LED isolation constant current driving power supply. The power supply comprises a protection circuit, an EMI filtering circuit, a rectifying circuit, a voltage stabilizing circuit, an optical coupler isolation circuit, a control module, an LED light source, an LED color temperature regulating circuit, and an LED brightness regulating circuit,wherein AC mains supply provides a bus DC high voltage after sequentially passing through the protection circuit, the EMI filtering circuit and the rectifying circuit; the control module sends two independent PWM control signals; one signal directly controls a dimming pin of a dimming LED constant current control chip in a dimming LED isolation driving circuit to carry out load dimming on the LEDlight source; and the other signal is converted into two PWM control signals with completely opposite phases through optical couplers and other simple peripheral elements, and the two PWM control signals control quick starting and closing of output switching MOS tubes to regulate output current proportions of light beads with a pure white color temperature and light beads with a warm white color temperature. The dimming and color-regulating LED isolation constant current driving power supply provided by the invention has the advantages of high load compatibility, slow light attenuation of thelight beads, and low energy consumption.
Owner:DONGGUAN BONTECK HARDWARE
Enhanced optical modulation using slow light
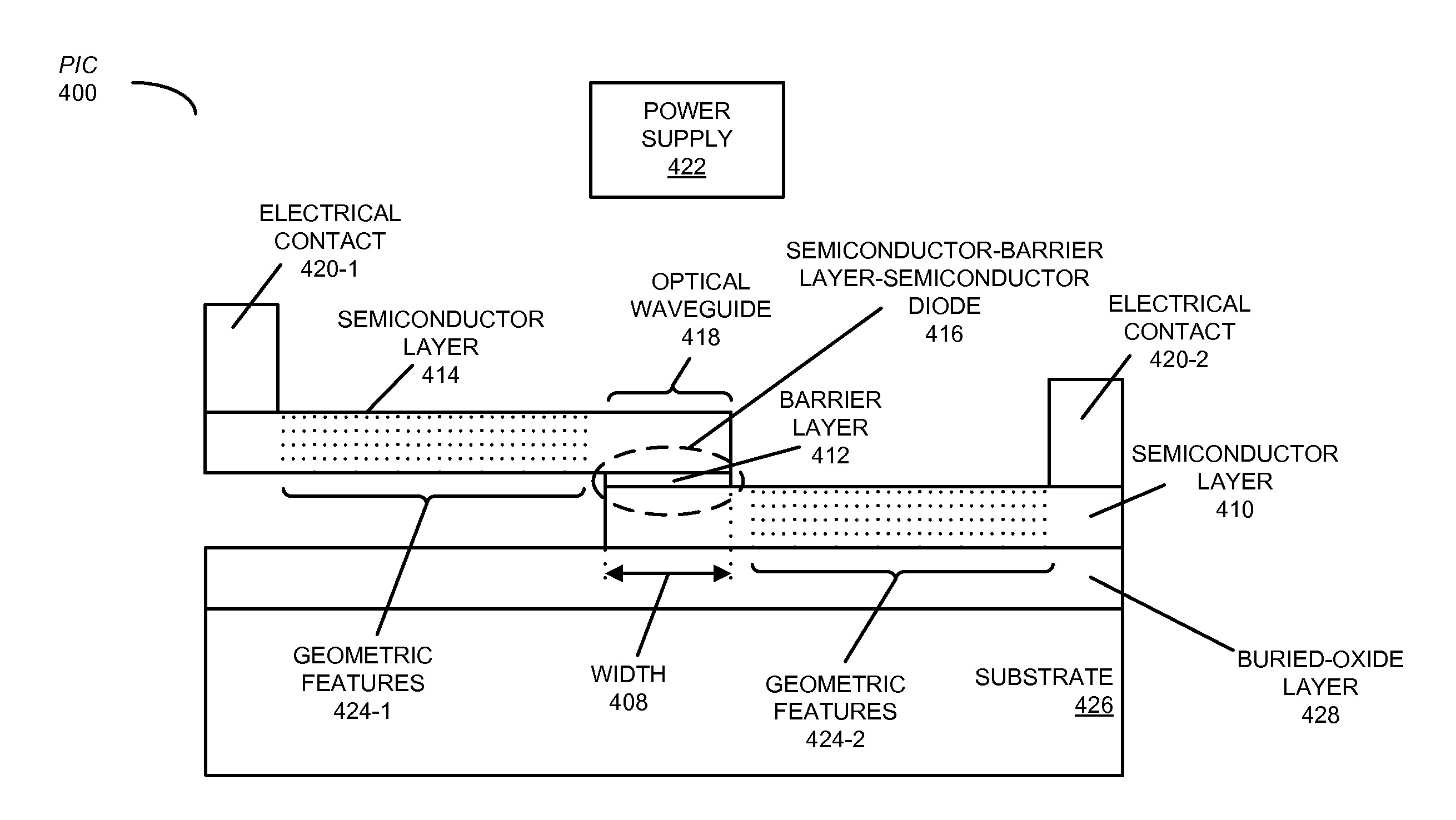
ActiveUS20150086219A1Electromagnetic transmittersOptical waveguide light guideElectrical conductorMach–Zehnder interferometer
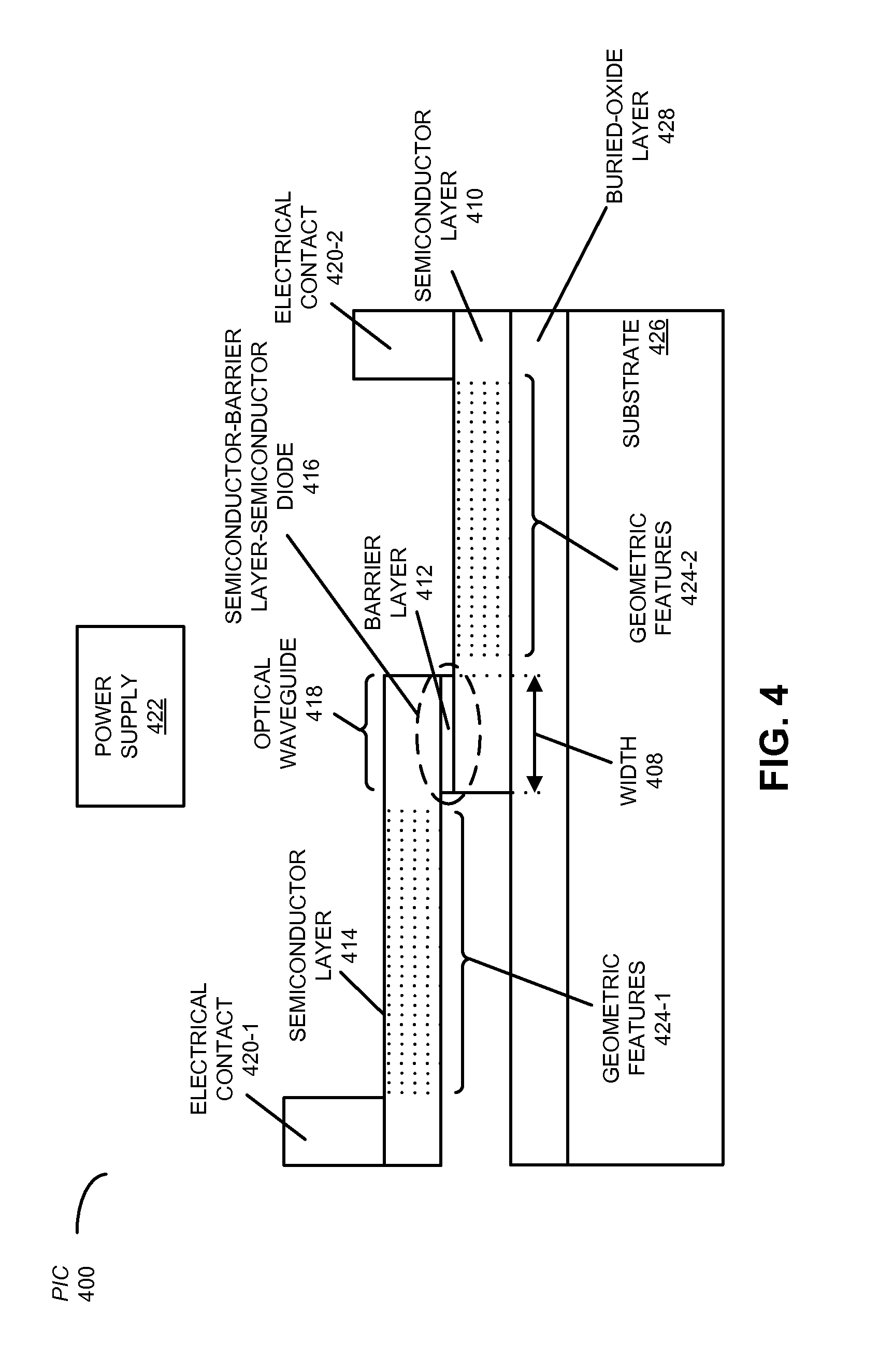
A photonic integrated circuit (PIC) is described. This PIC includes a semiconductor-barrier layer-semiconductor diode in an optical waveguide that conveys an optical signal, where the barrier layer is an oxide or a high-k material. Moreover, semiconductor layers in the semiconductor-barrier layer-semiconductor diode may include geometric features (such as a periodic pattern of holes or trenches) that create a lattice-shifted photonic crystal optical waveguide having a group velocity of light that is lower than the group velocity of light in the first semiconductor layer and the second semiconductor layer without the geometric features. The optical waveguide is included in an optical modulator, such as a Mach-Zehnder interferometer (MZI).
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Broadband light source optimization pump device used for SBS slow light detention
InactiveCN101247179ADynamically optimize performanceReduce complexityFibre transmissionCoupling light guidesSlow lightOptoelectronics
The present invention discloses a wideband light source optimizing pump arrangement for SBS slow light put-off, pump light source is provided in one or more than one channel slow light system, light path setting includes: wideband light source, first polarizer and character light device. Multiple relative stretching pump sources are outputted simultaneously with the design of the present invention by wideband light source executing periodicity filtering. The multiple pump source produced by same wideband light source can be used in multiple channel system and produces slow photo effect at the same time, and also can be used at the same time in a channel to optimizing final gain spectrum. The design of the invention reduces systemic complex degree and cost of facilities, simultaneously can dynamic optimizes systemic performance with different slow light.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for implementing microwave photonic filter based on photonic crystal
InactiveCN102722000AReduce volumeReduce lossOptical light guidesBandpass filteringFrequency spectrum
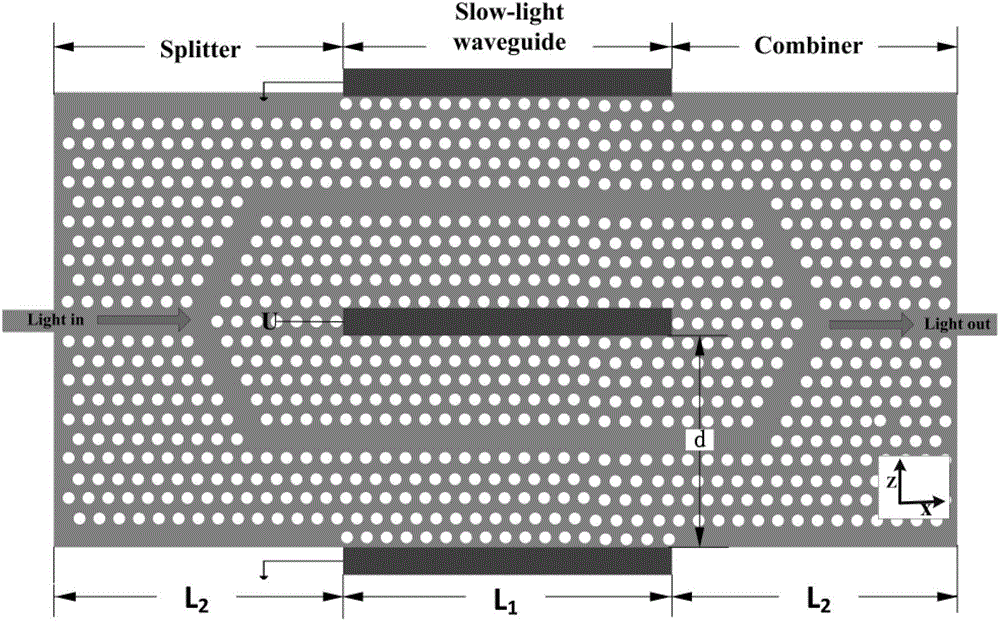
The invention relates to a method for implementing a microwave photonic filter based on a photonic crystal. A bent waveguide integrated coupling beam splitter and a slow light waveguide delay line are used on the same photonic crystal, so that a system function of the filter has the bandpass filter characteristic of trapped wave depth of 10dB in a free frequency spectral range of 130 GHz at 1,550 nanometers; and the function of filtering residual edge bands of a light generation millimeter wave signal can be realized. By using a bidimensional photonic crystal structure compared with an optical fiber ring structure, the size of the filter can be greatly reduced; and the method is favorable for minimizing and integrating the device.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Adjustable and controllable spatial electromagnetic induction transparent metamaterial device
The invention discloses an adjustable and controllable spatial electromagnetic induction transparent metamaterial device. The device comprises a substrate and a metal unit array which is positioned on the substrate and can be used for generating an electromagnetic induction transparent phenomenon, wherein the metal unit array comprises a plurality of metal units which are distributed in an array form; each metal unit comprises a first metal microstructure and a second metal microstructure; each first metal microstructure comprises a first metal pattern; each second metal microstructure comprises a second metal pattern; each first metal microstructure and / or each second metal microstructure further comprises a semiconductor element. By adopting the adjustable and controllable spatial electromagnetic induction transparent metamaterial device, the problem of incapability of easily and rapidly adjusting and controlling the working frequency of the electromagnetic induction transparent metamaterial in the prior art can be effectively solved, and a large modulation depth and a high switching speed can be realized. The device can be widely applied to the technical fields of slow light modulation, optical switches, sensors, wireless communication and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Integrated photonic crystal MZI modulator applied to 60 GHz ROF system
ActiveCN103336379AIncrease modulation bandwidthGood achievabilityOptical light guidesNon-linear opticsRadio over fiberModulation function
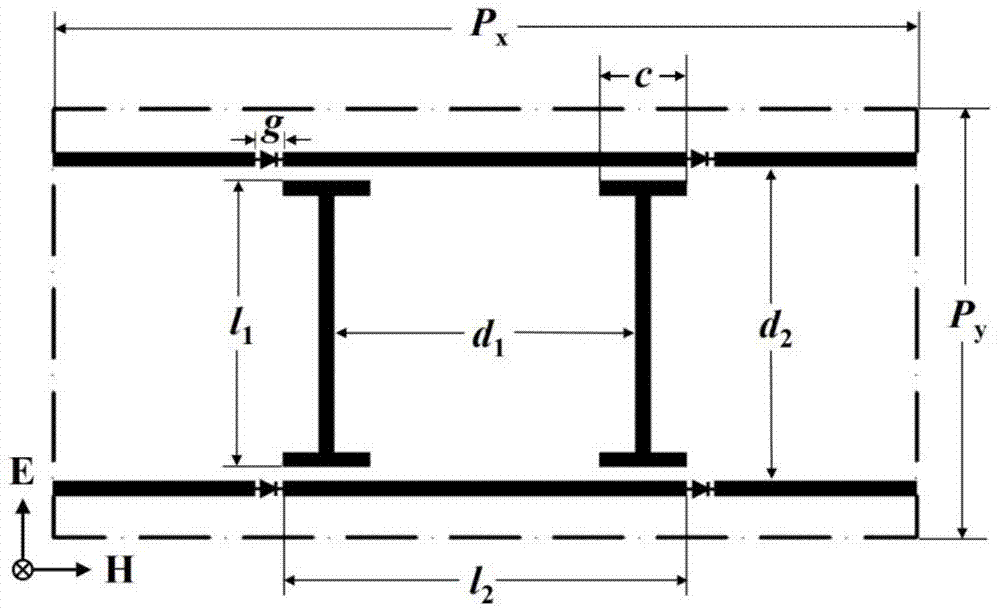
The invention relates to an implementation method of an MZI (Mach Zehnder Interferometer) electrooptical modulator applied to a 60 GHz ROF (Radio-Over-Fiber) system, and the MZI electrooptical modulator is based on the integration of a two-dimensional photonic crystal beamsplitter, combiner, a slow light waveguide and a coupling waveguide. According to the invention, lithium niobate photonic crystals adopting triangular patterned media background ventage structures are adopted, the photonic crystal beamsplitter, the combiner, the slow light waveguide and the coupling waveguide are integrated on the same photonic crystal board to realize the MZI electrooptical modulation function, the beamsplitter, the combiner, the slow light waveguide and the coupling waveguide are designed to optimize the integral structure and improve the device performance so as to implement the photonic crystal MZI electrooptical modulator. The combining structure is compact and has lower modulation voltage, and is suitable for a full-gloss integrated system. The invention provides an implementation method of a subminiature efficient photonic crystal MZI electrooptical modulator for full-gloss integrated networks and ROF systems.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
E-shaped all-dielectric super-surface electromagnetic induction transparent resonance device
ActiveCN107579328ASimple structural designReduce the speed of propagationPhase-affecting property measurementsResonatorsSlow lightRefractive index
The invention discloses an E-shaped all-dielectric super-surface electromagnetic induction transparent resonance device. The device comprises a substrate and E-shaped dielectric resonance units whichare located on the surface of the substrate and distributed in a two-dimensional periodicity mode, the substrate is made from dielectric materials, and the dielectric constant of the substrate is larger than 0 and smaller than or equal to 5; the dielectric constant of the E-shaped dielectric resonance units is larger than or equal to 6. Accordingly, the group refractive index can be increased, andthe slow light effect can be achieved. Meanwhile, the device can be used for high-sensitivity refractive index sensing devices.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com