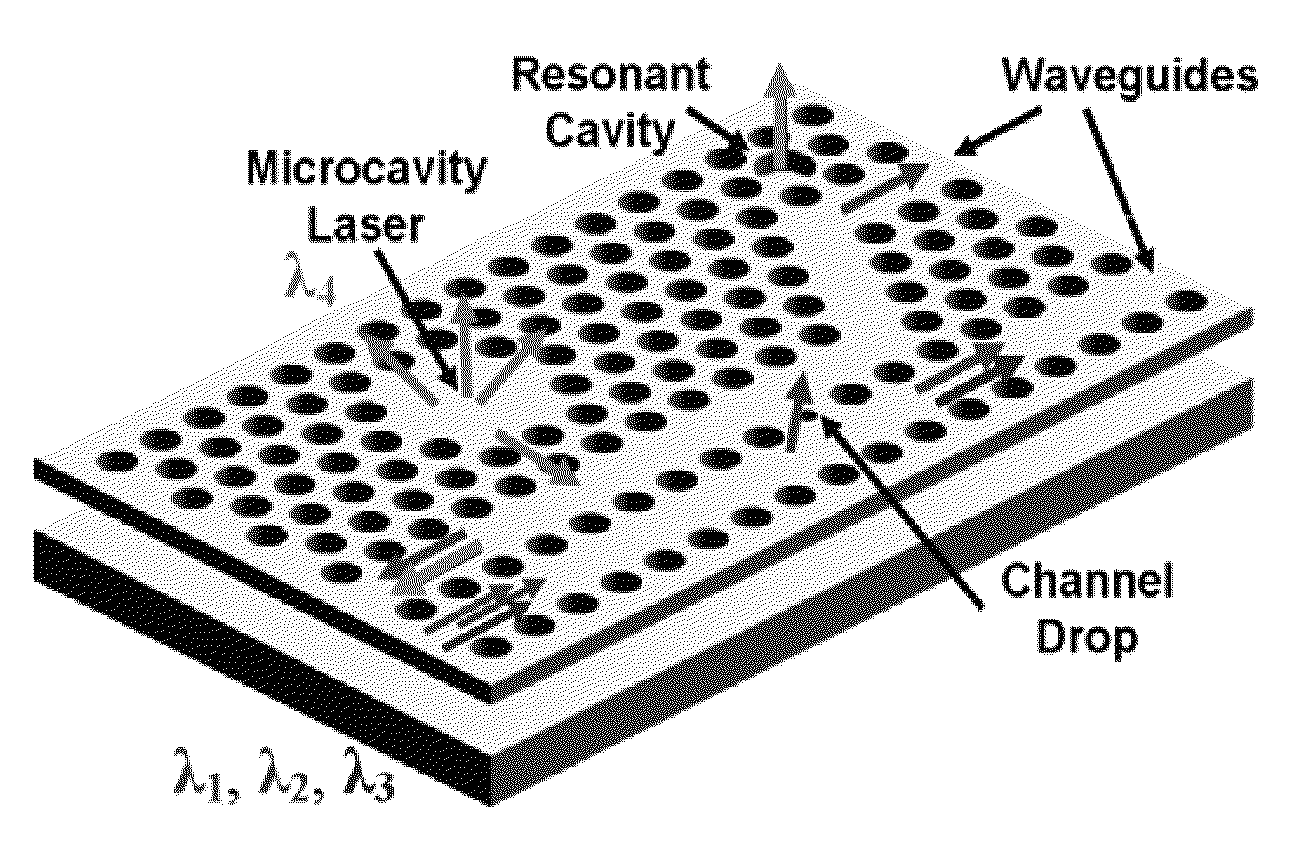
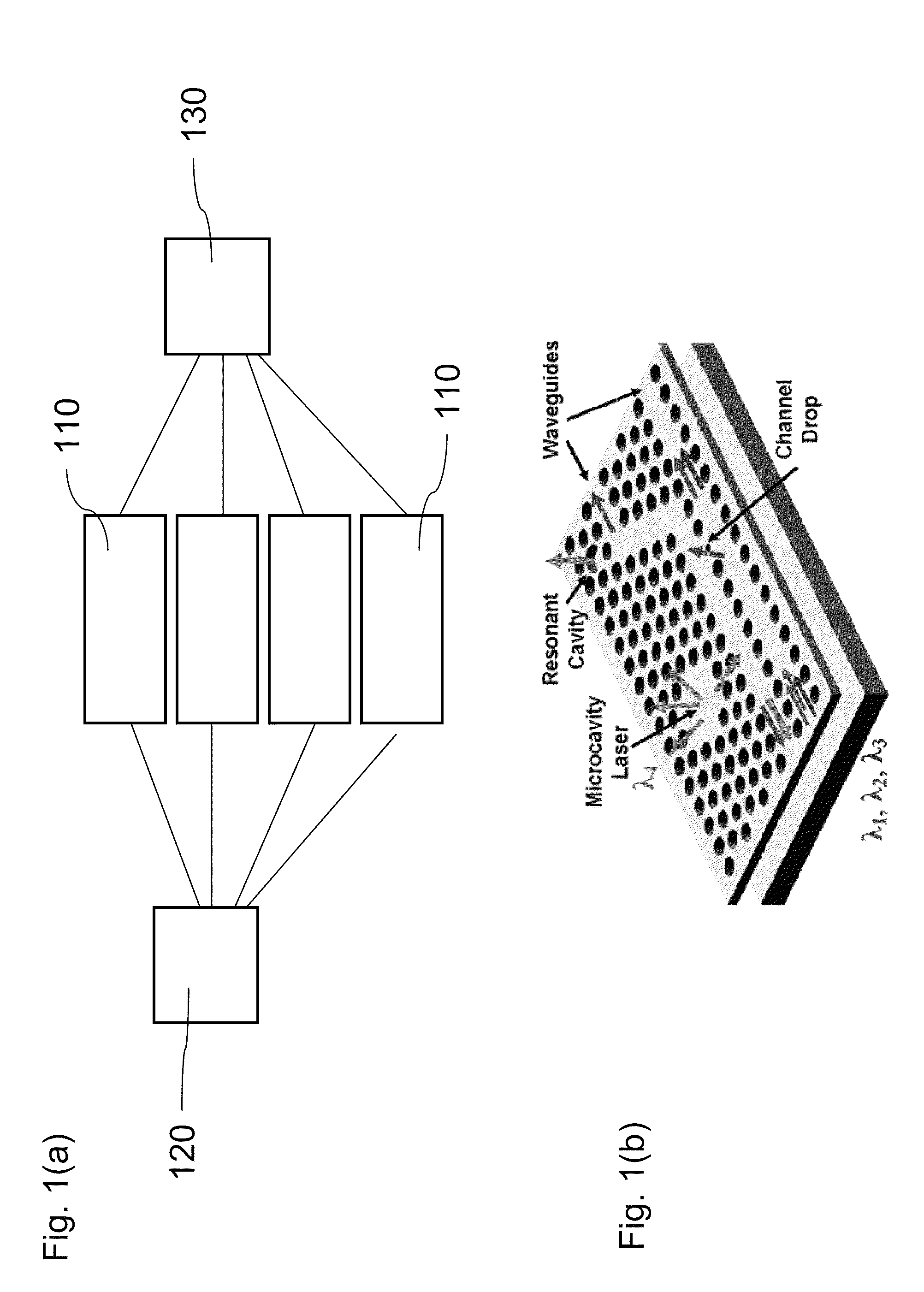
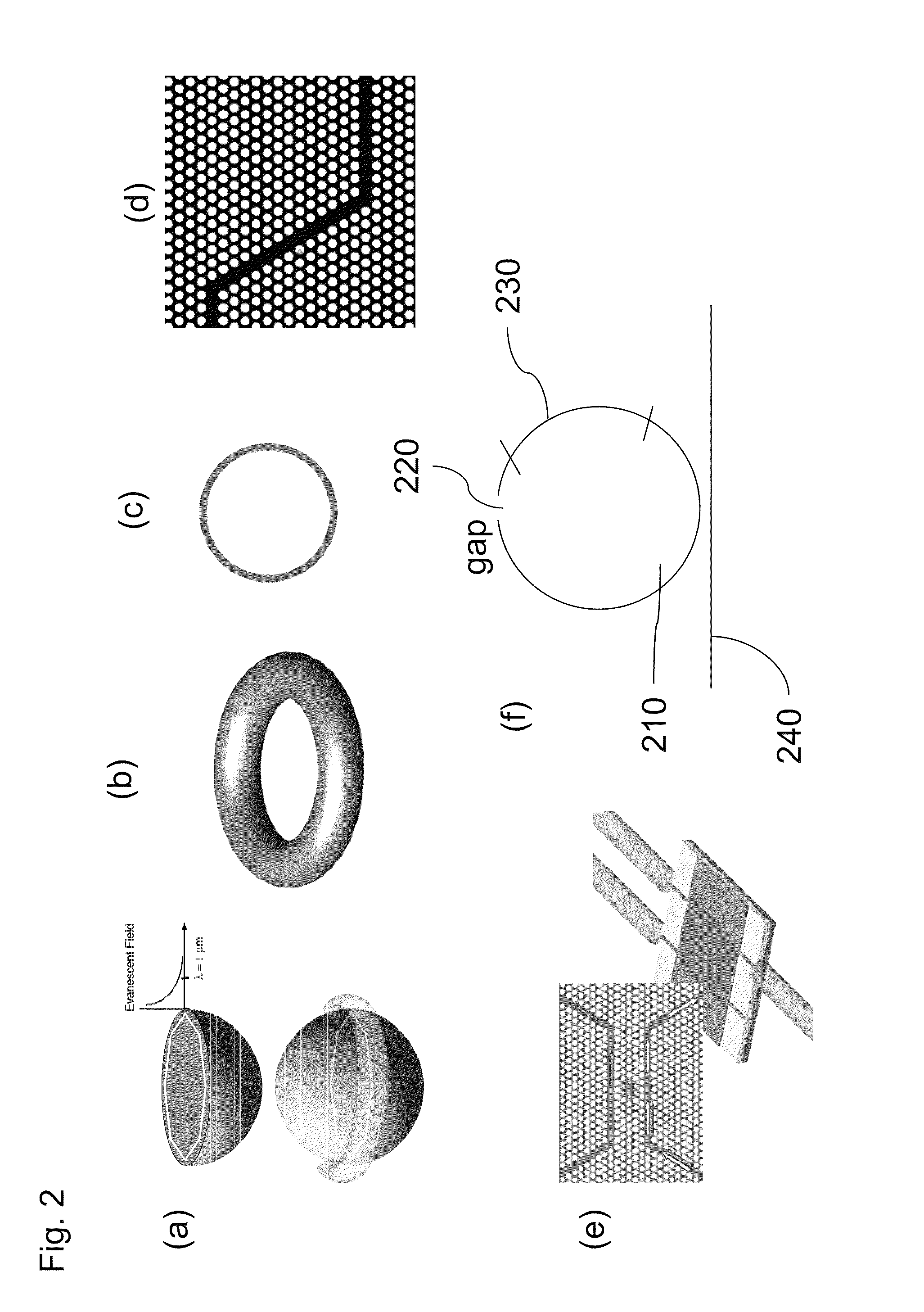
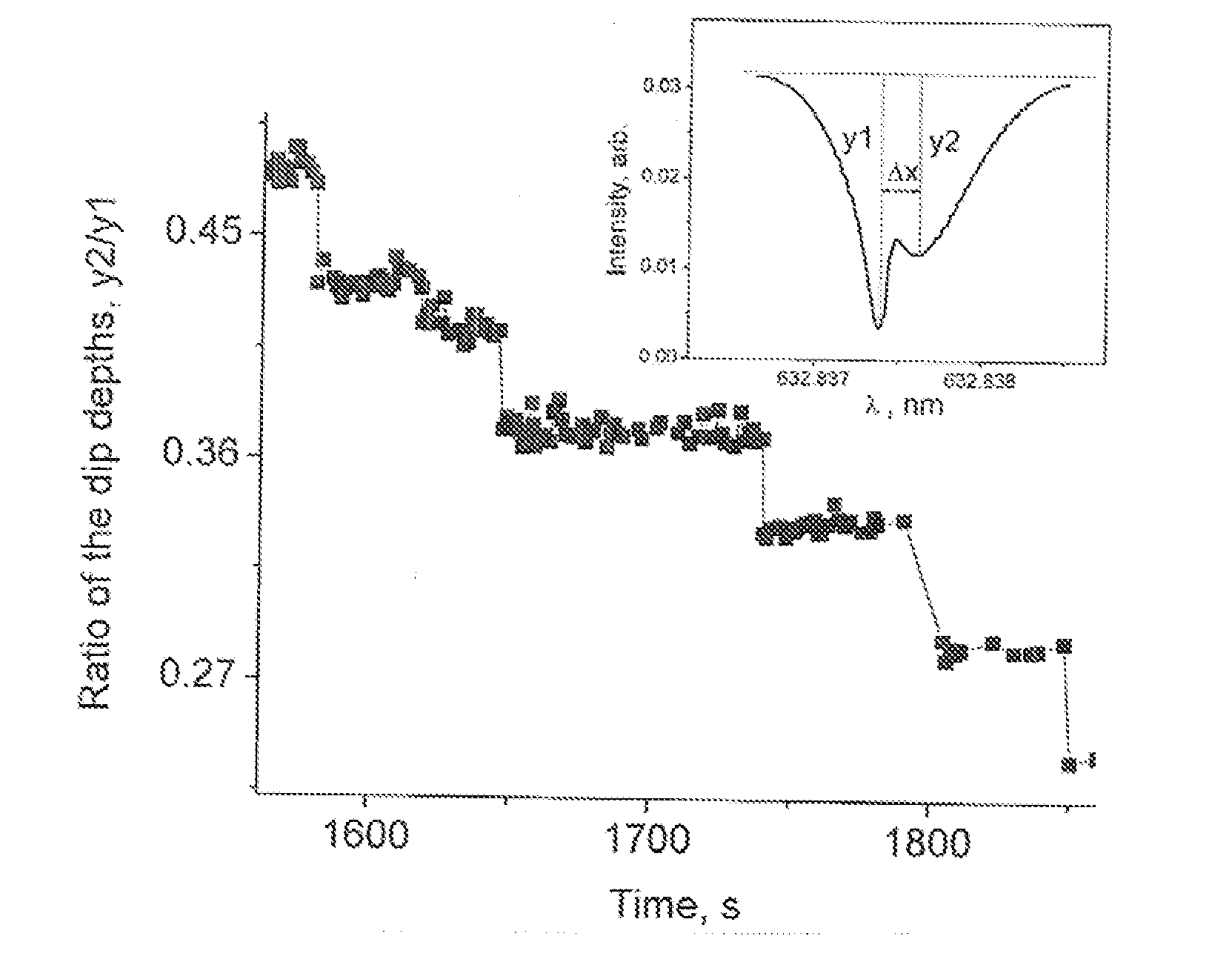
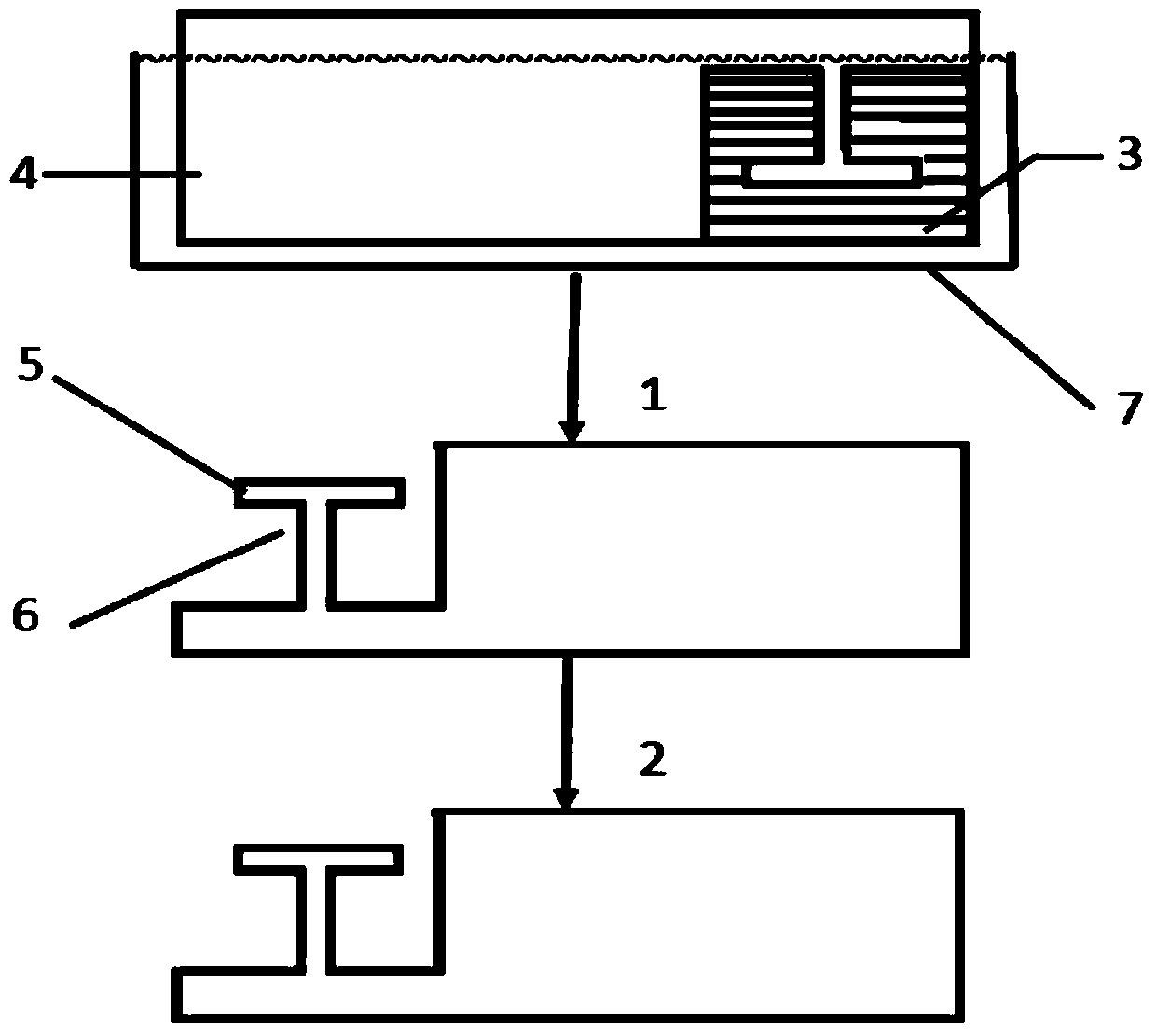
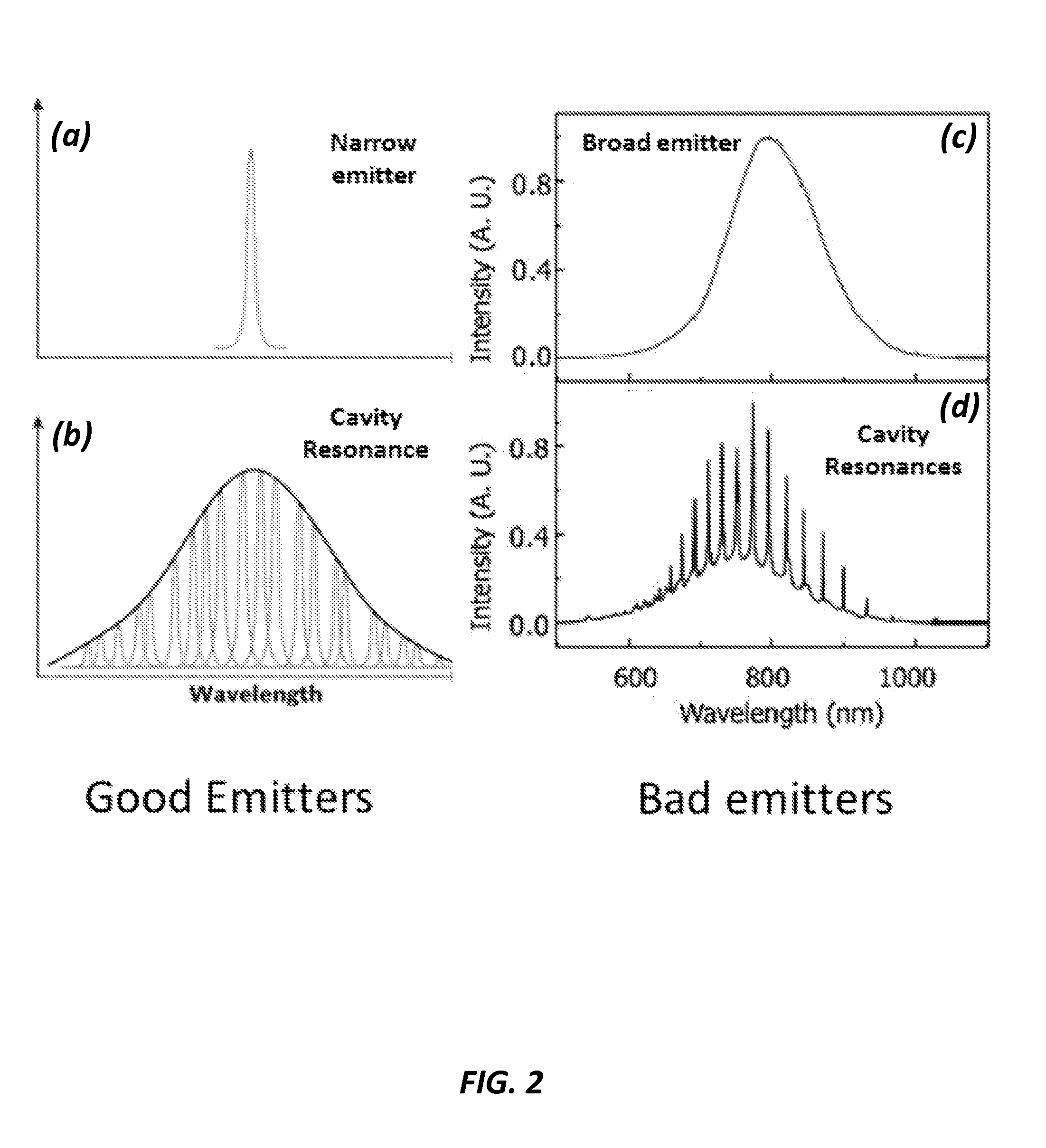
Patents
Literature
61 results about "Mode volume" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
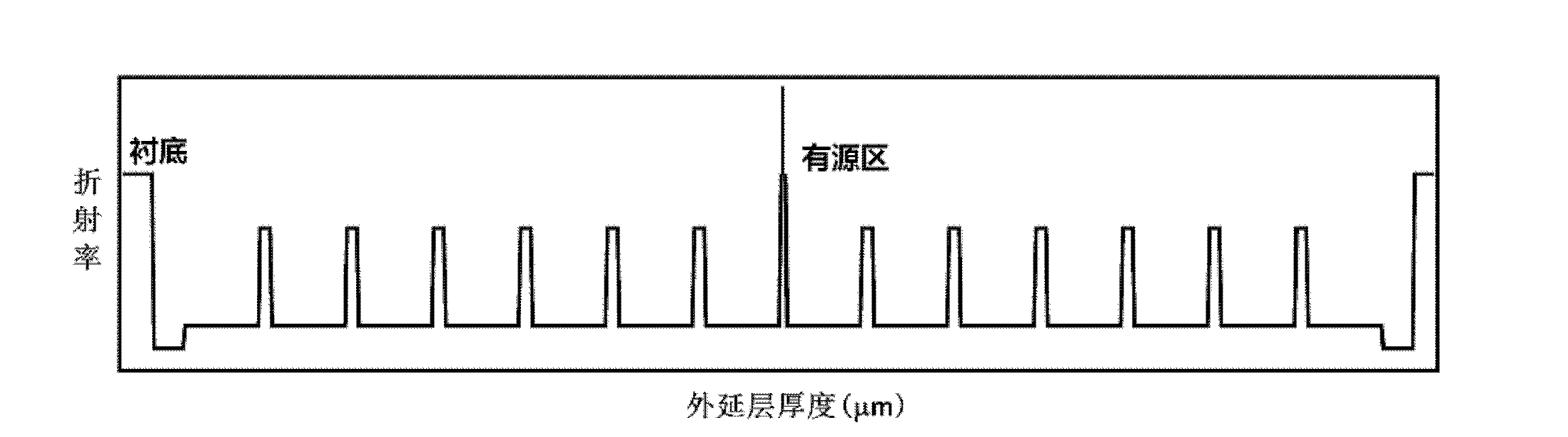
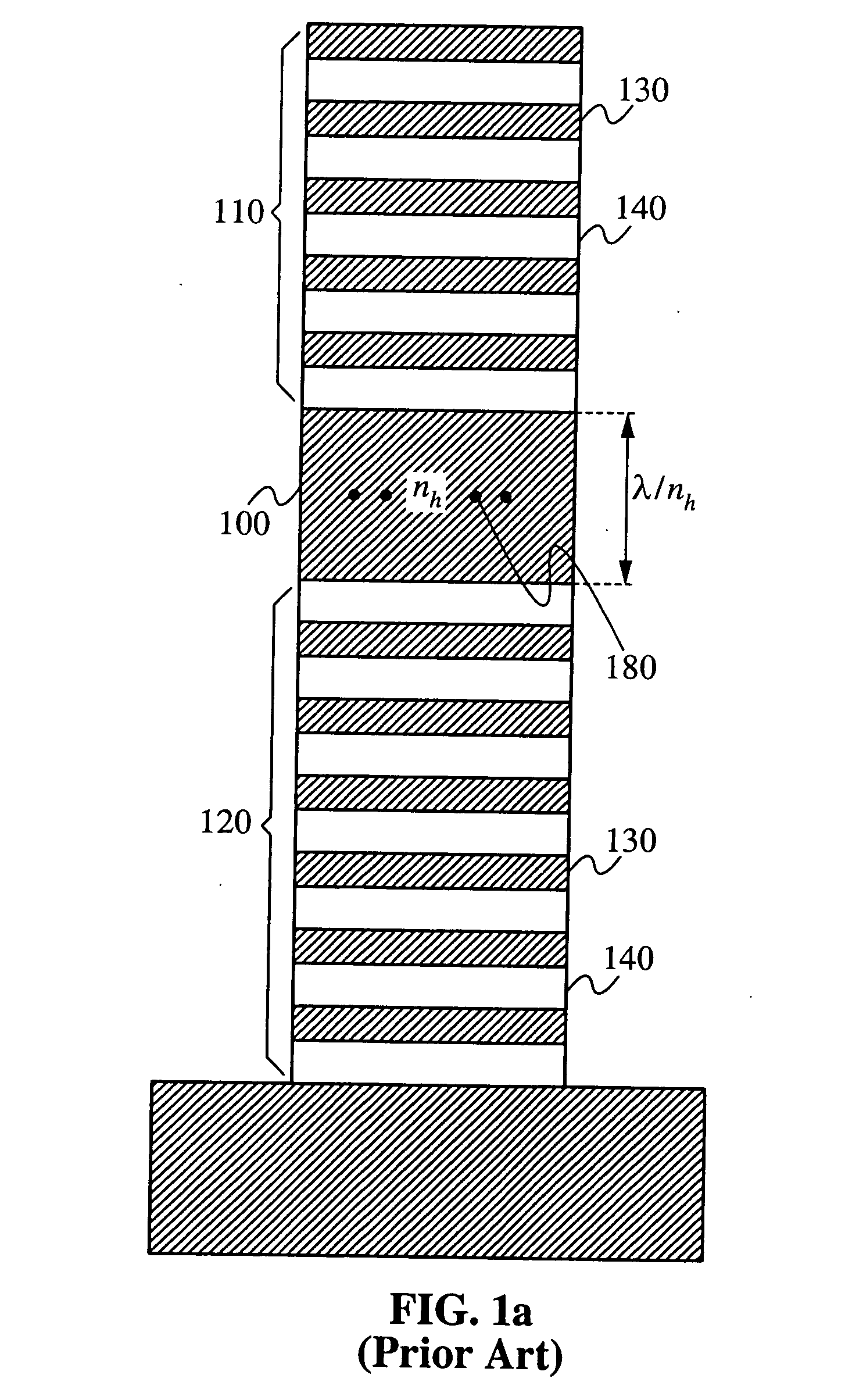
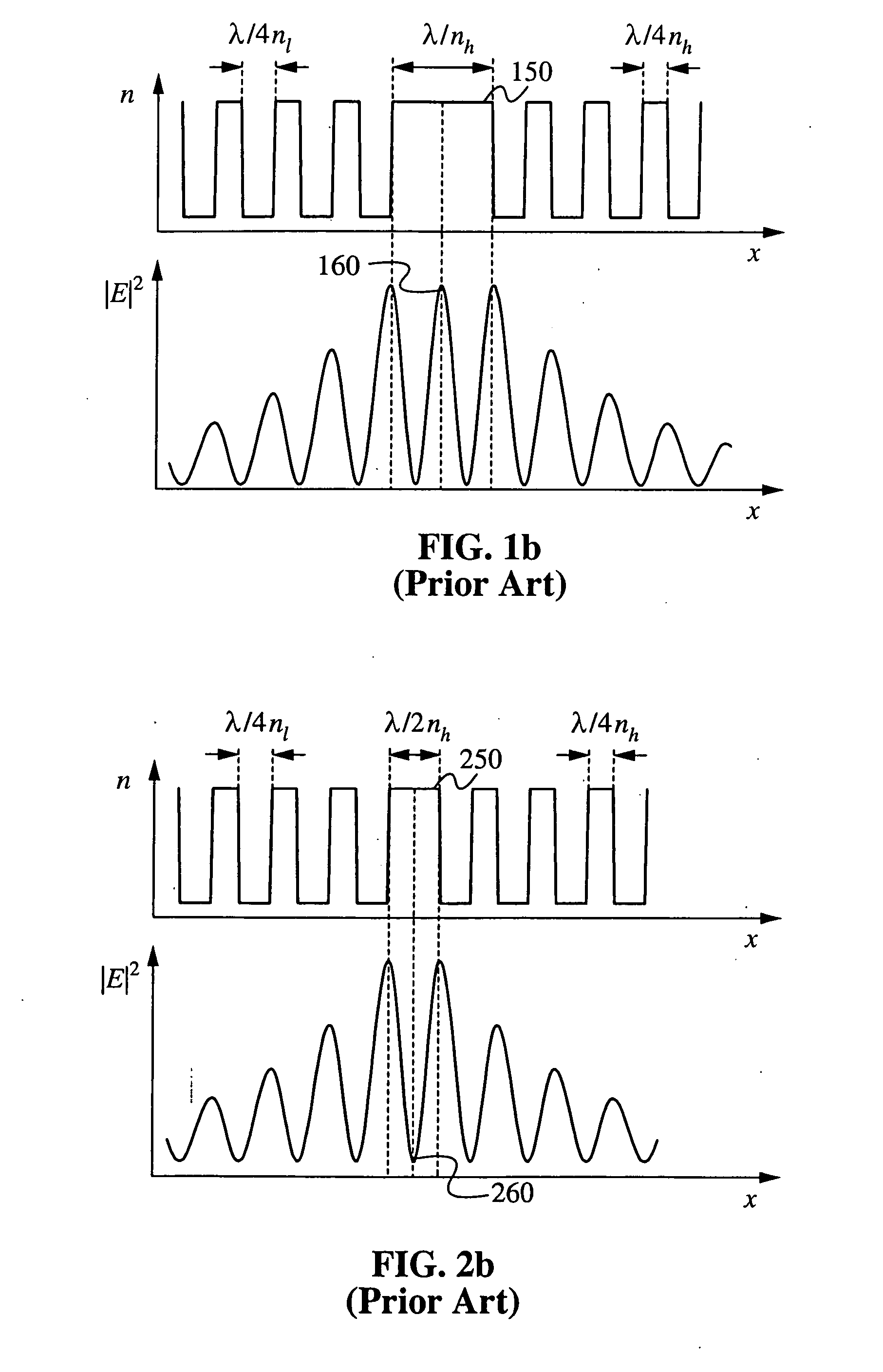
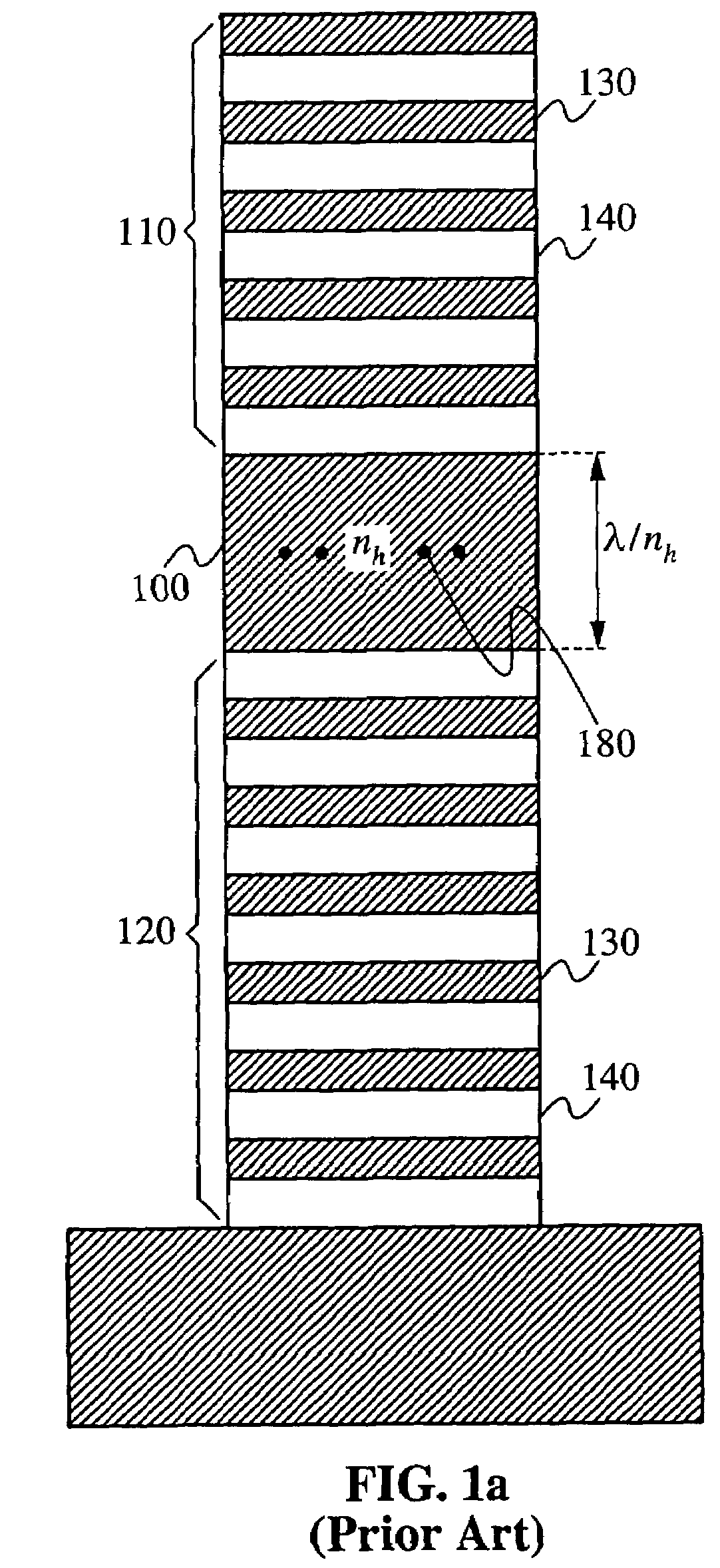
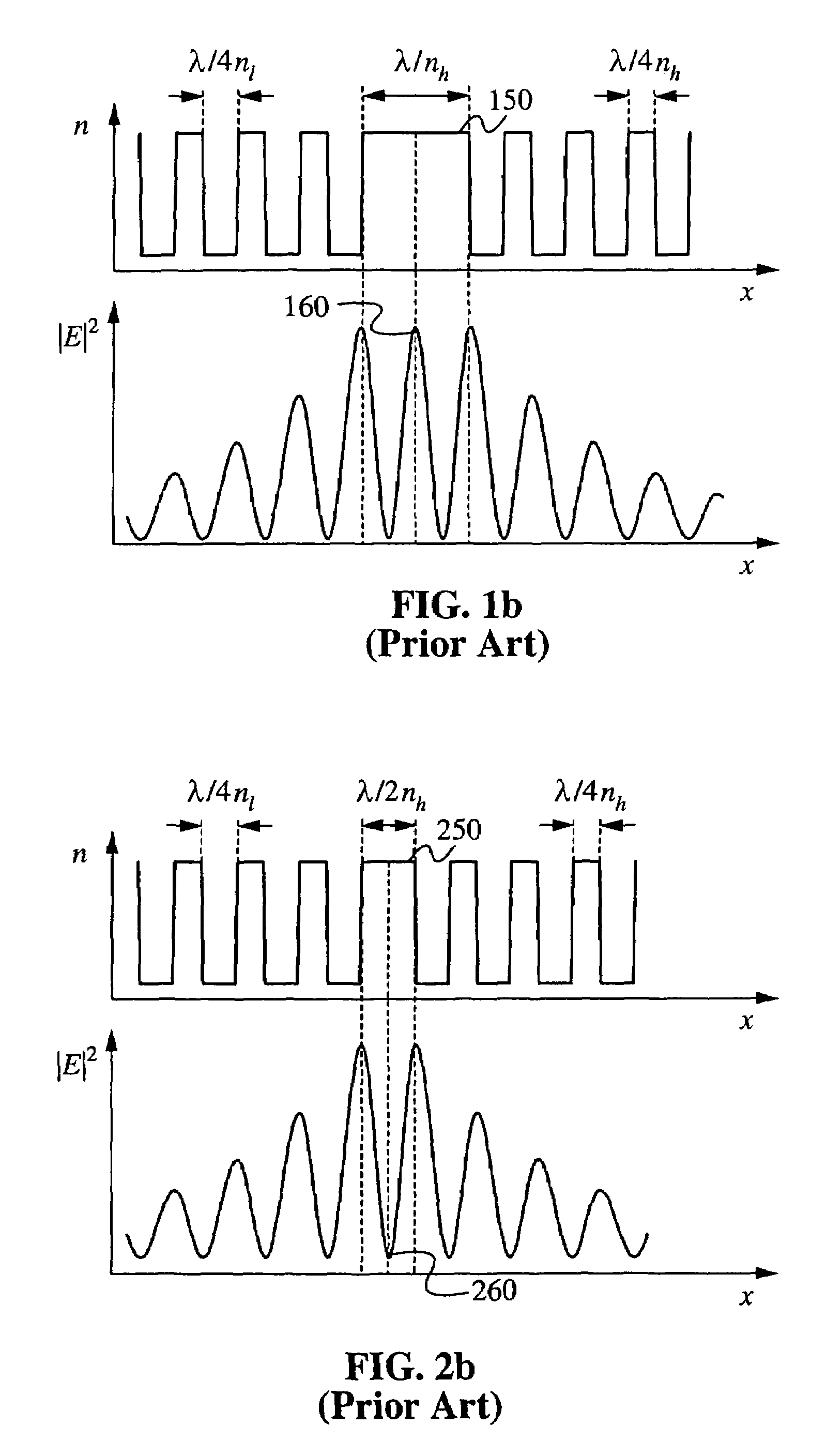
In fiber optics, mode volume is the number of bound modes that an optical fiber is capable of supporting. The mode volume M is approximately given by 4V2/π² and V2/2(g/g+2), respectively for step-index and power-law index profile fibers, where g is the profile parameter, and V is the normalized frequency, which must be greater than 5 for this approximation to be valid.
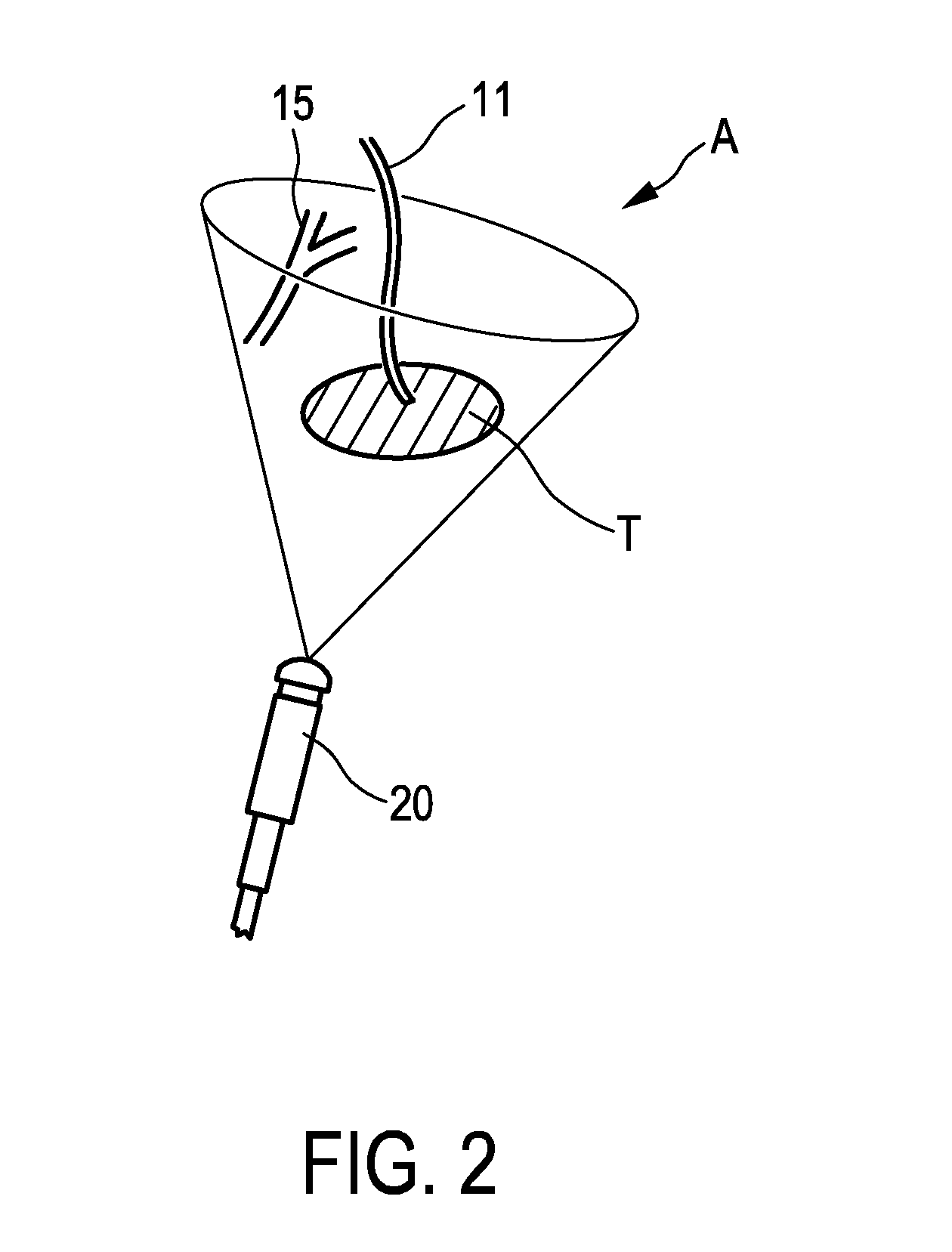
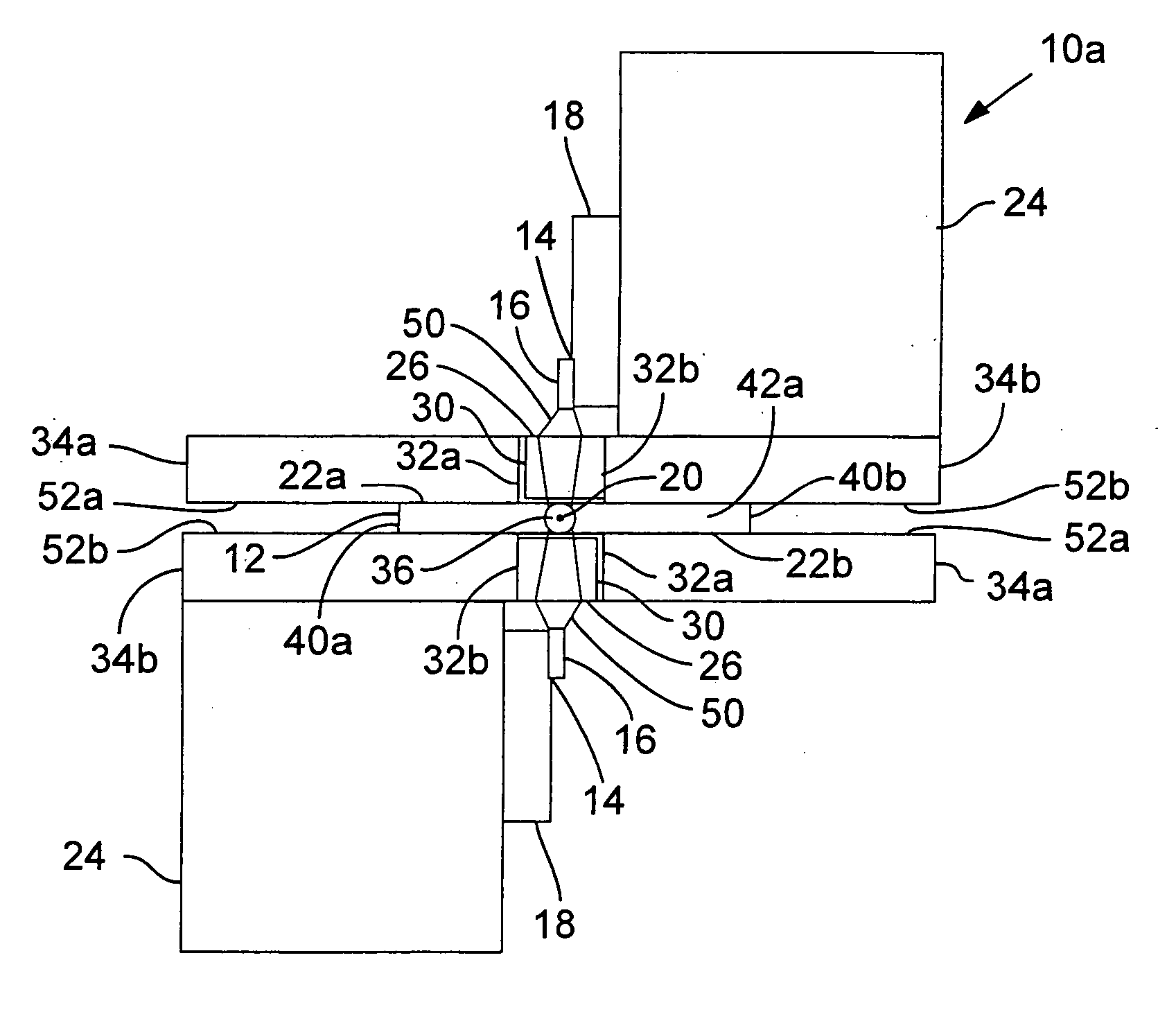
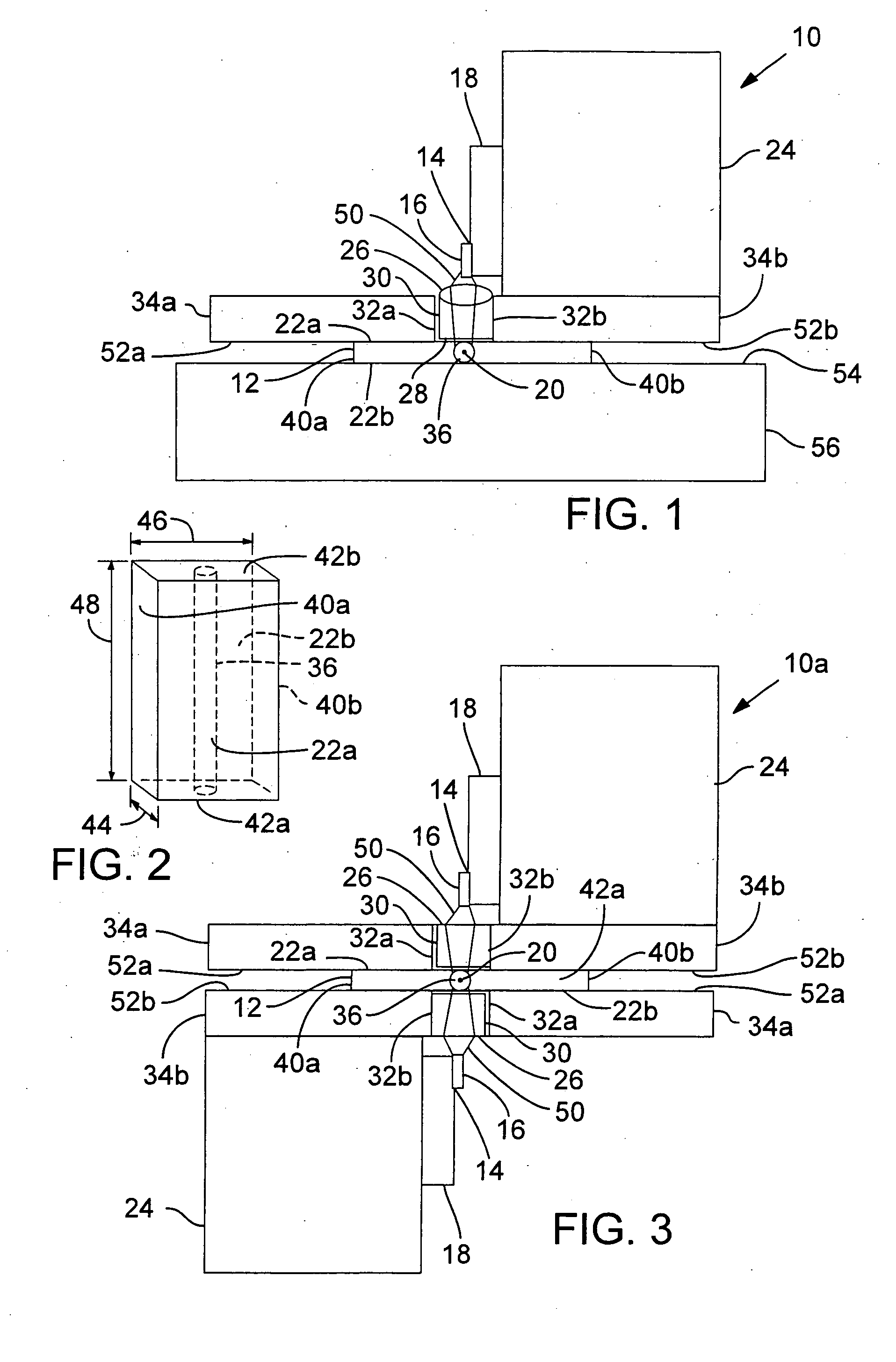
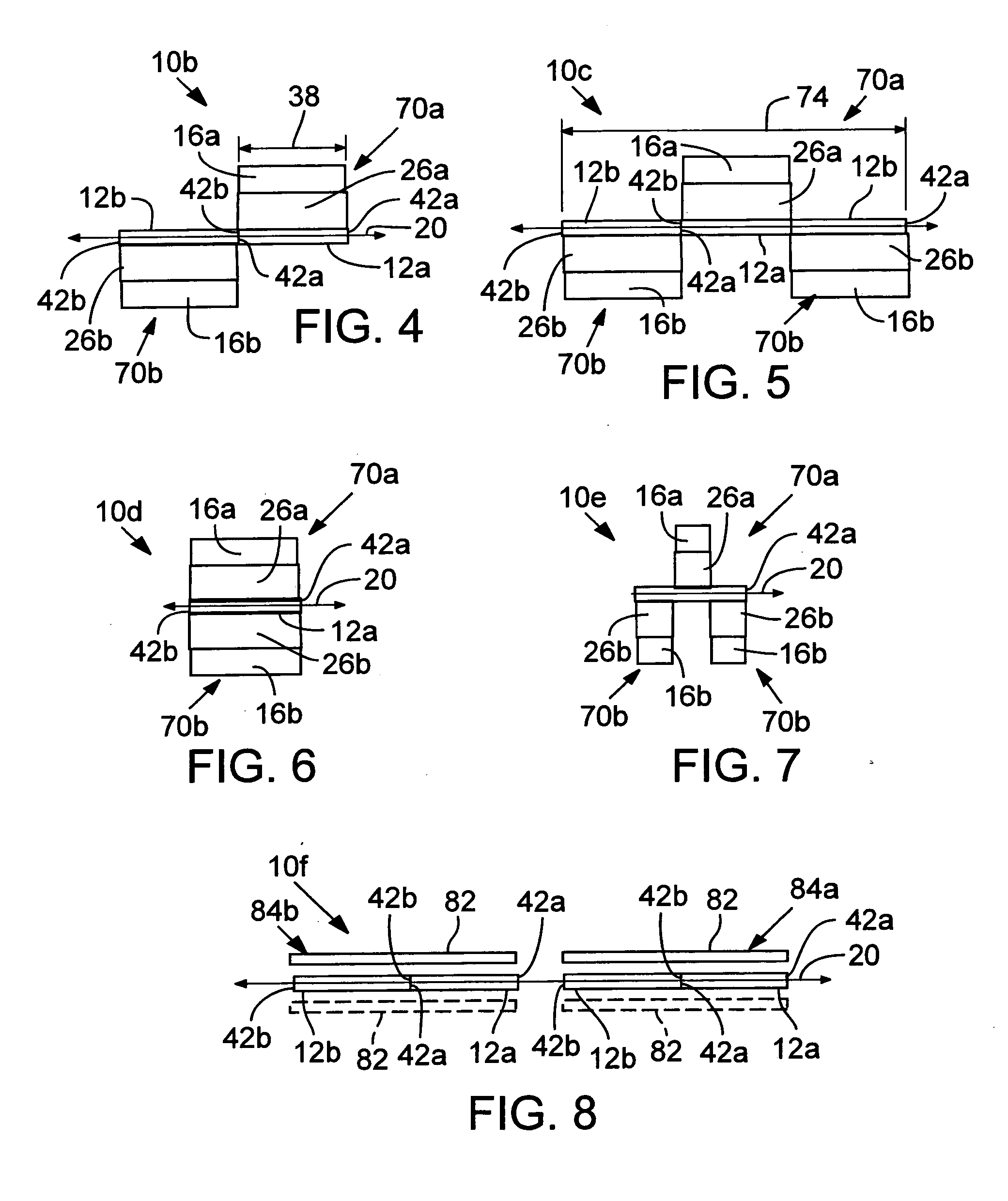
Anti-drawback medical valve
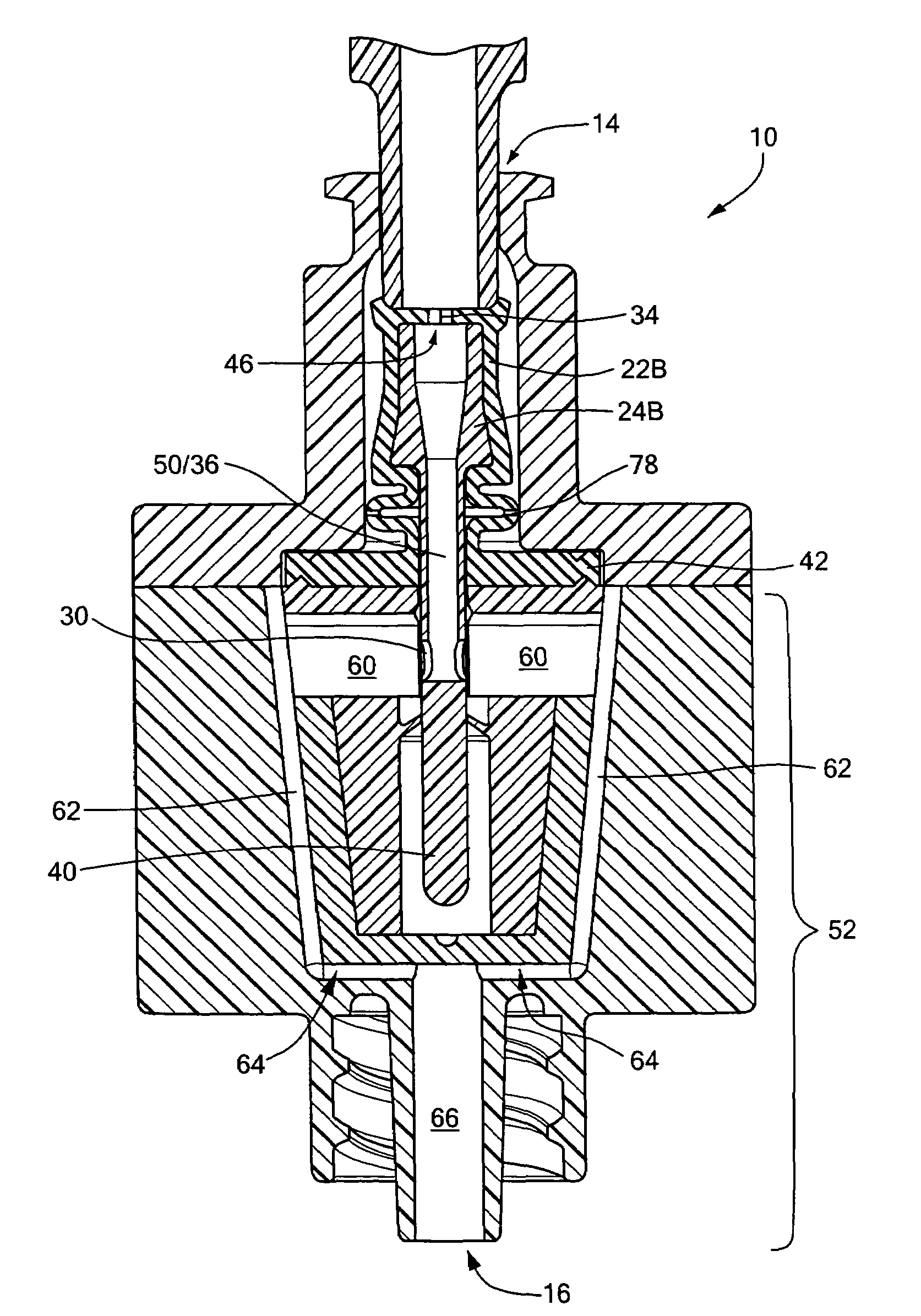
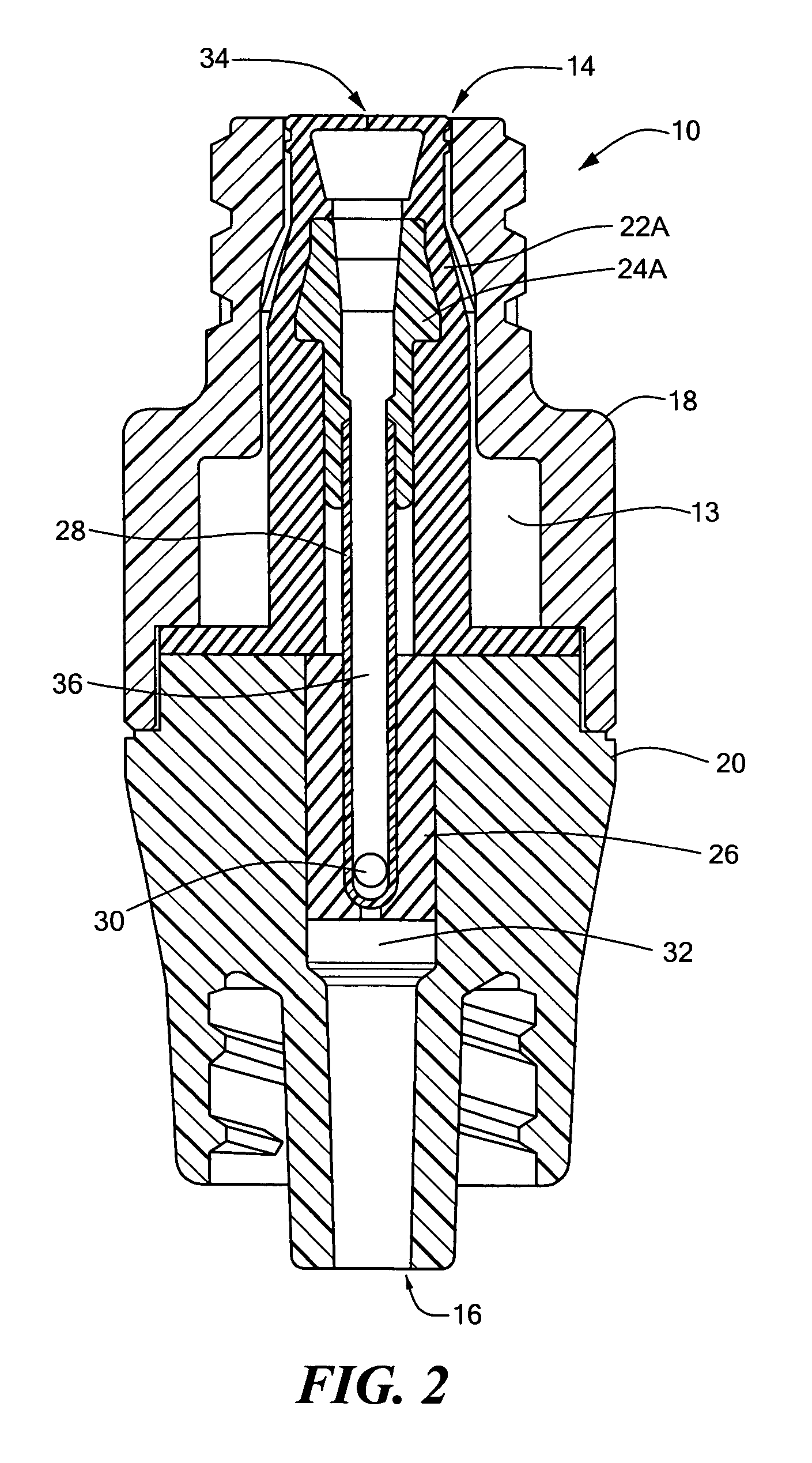
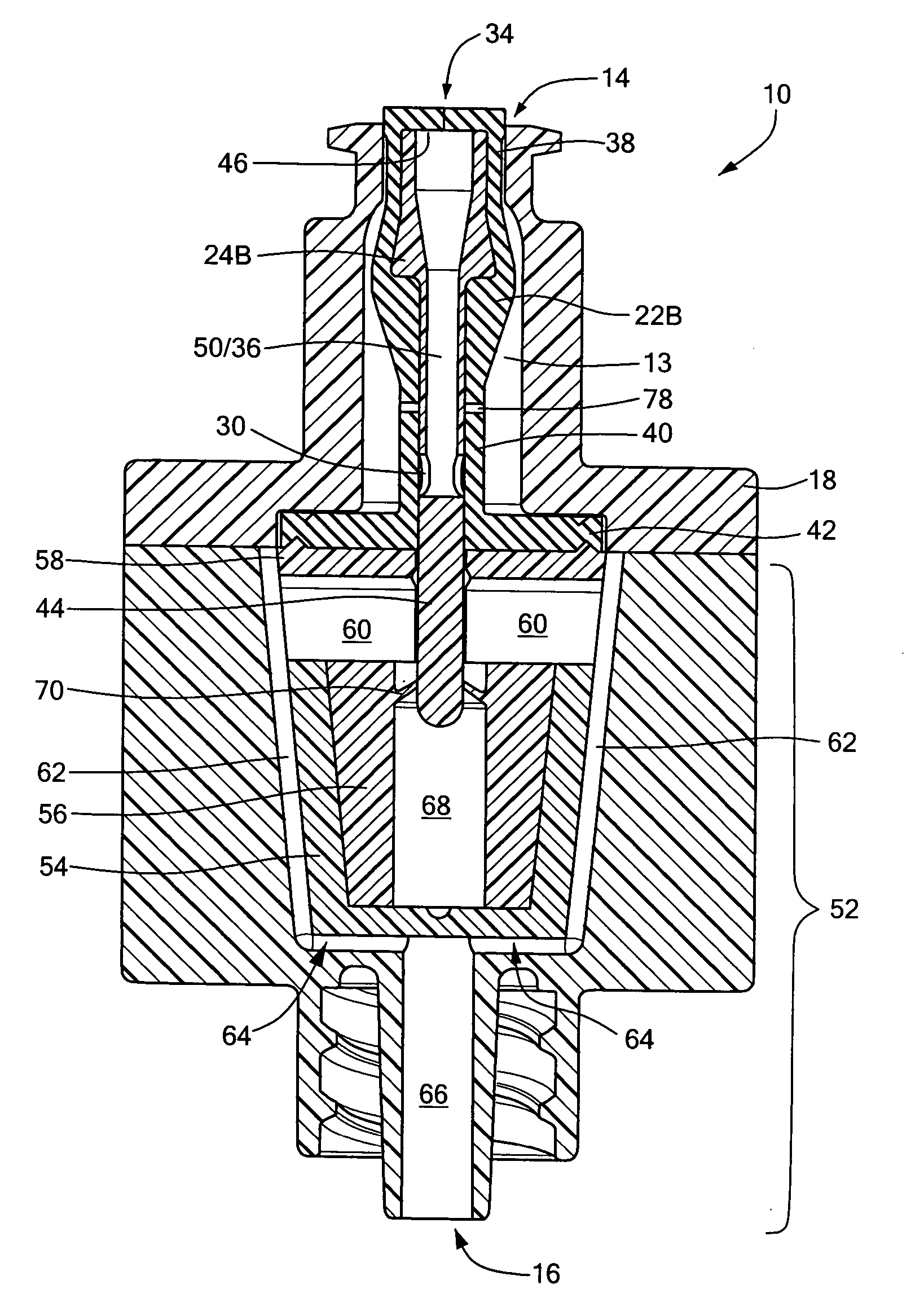
InactiveUS7753892B2Constant volumeAvoid flowHaemostasis valvesCatheterMechanical engineeringMedical treatment
A medical valve has an interior flow path having a volume that is substantially the same when in either the closed mode (when the valve is closed) or the open mode (when the valve is open). To those ends, the medical valve has a housing forming an interior, and a valve mechanism (within the interior) having a substantially rigid translating member with a bore. The interior of the housing has a flow path that includes at least a portion of the bore of the translating member. As noted above, the open mode volume is substantially equal to the closed mode volume.
Owner:NP MEDICAL
Anti-drawback medical valve
A medical valve has an interior flow path having a volume that is substantially the same when in either the closed mode (when the valve is closed) or the open mode (when the valve is open). To those ends, the medical valve has a housing forming an interior, and a valve mechanism (within the interior) having a substantially rigid translating member with a bore. The interior of the housing has a flow path that includes at least a portion of the bore of the translating member. As noted above, the open mode volume is substantially equal to the closed mode volume.
Owner:NP MEDICAL
Bragg refractive waveguide edge transmitting semiconductor laser with low horizontal divergence angle
ActiveCN102324696AReduce complexityImprove coupling efficiencyOptical wave guidanceFull waveRefractive index
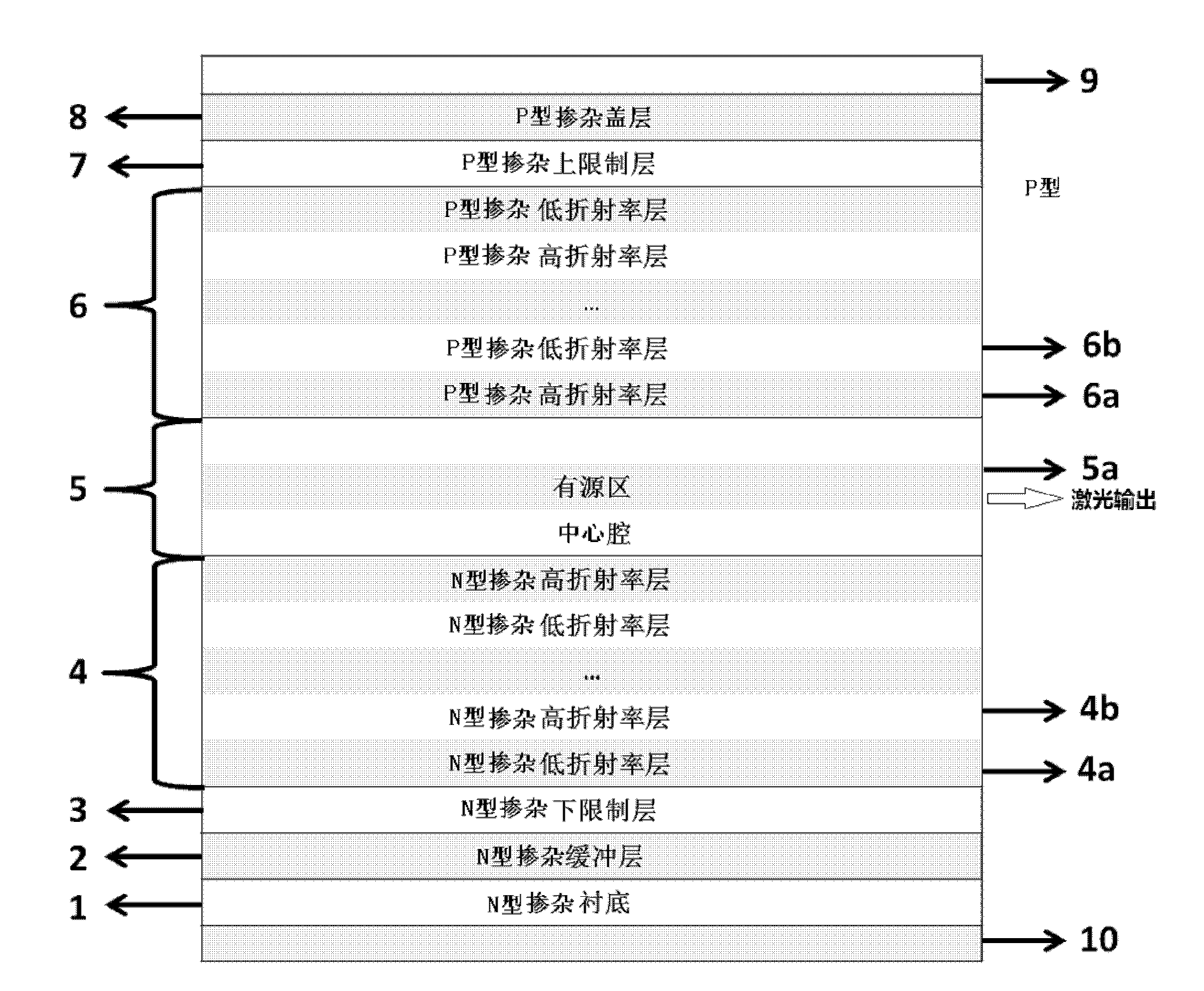
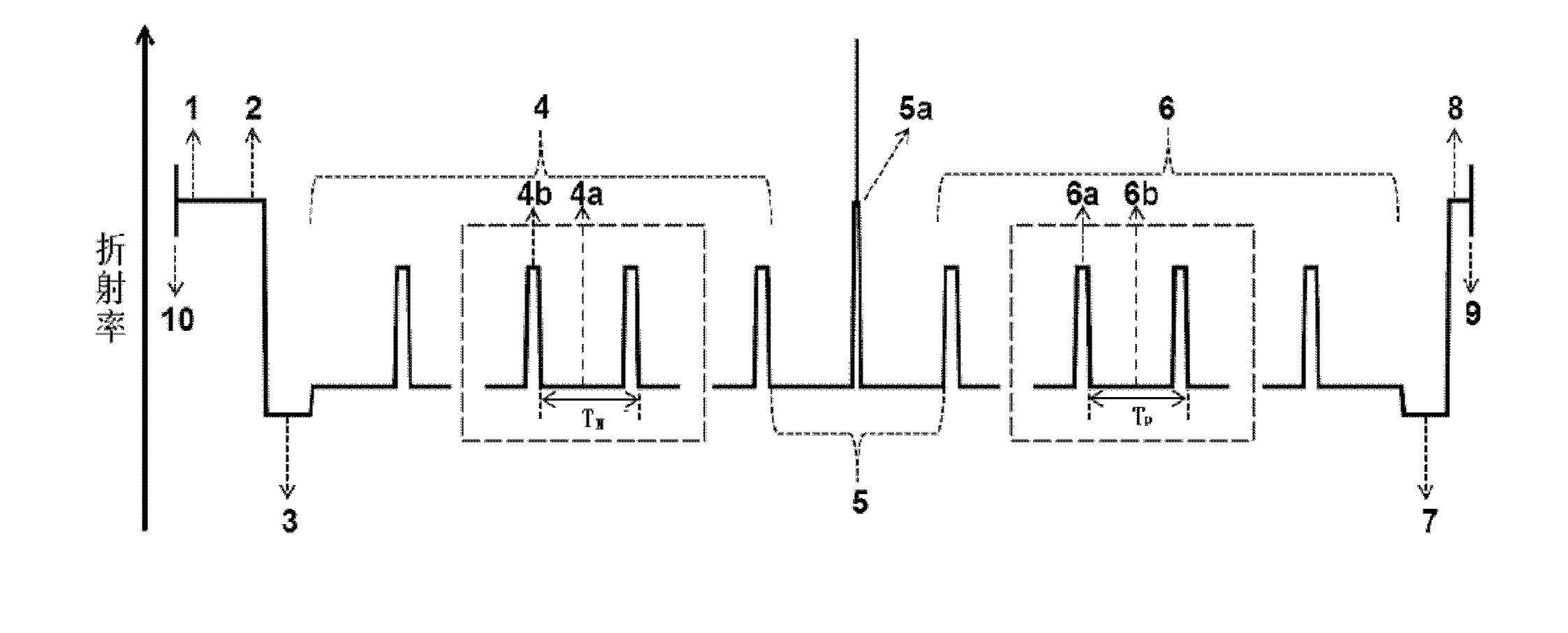
The invention relates to a Bragg refractive waveguide edge transmitting semiconductor laser with a low horizontal divergence angle, wherein the P electrode of the laser is placed on the top face of a cover layer and is electrically connected onto the cover layer; the N electrode is positioned on the back face of a substrate and is electrically connected to the substrate; a center cavity is positioned between an upper waveguide layer and a lower waveguide layer; an active area is inserted in the center cavity; a Bragg refractive waveguide formed by periodically distributing a plurality of layers of N-doped materials with a high refractive index and a low refractive index is adopted in the lower waveguide layer on; and a Bragg refractive waveguide formed by periodically distributing a plurality of layers of P-doped materials with a high refractive index and a low refractive index is adopted in the upper waveguide layer. The Bragg refractive waveguide edge transmitting semiconductor laser with the low horizontal divergence angle has the advantages that: effects such as catastrophic damage, hole burning, electric heat overburning, beam filamentization and the like on the end face of the traditional edge transmitting semiconductor laser can be effectively improved, and the laser can realize the large mode-volume and stable single-transverse-mode work because of the great gain loss difference between a basic mode and a high-order mode, the full wave at half maximum (FWHM) of the transverse far-field divergence angle of the laser can reach below 10 DEG.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods, materials and devices for light manipulation with oriented molecular assemblies in micronscale photonic circuit elements with high-q or slow light
InactiveUS20090136181A1Remarkable effectEnhanced interactionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingNanowireFluorescence
An optical device that comprises an input waveguide, an output waveguide, a high-Q resonant or photonic structure that generate slow light connected to the input waveguide and the output waveguide, and an interface, surface or mode volume modified with at least one material formed from a single molecule, an ordered aggregate of molecules or nanostructures. The optical device may include more than one input waveguide, output waveguide, high-Q resonant or photonic structure and interface, surface or mode volume. The high-Q resonant or photonic structure may comprise at least one selected from the group of: microspherical cavities, microtoroidal cavities, microring-cavities, photonic crystal defect cavities, fabry-perot cavities, photonic crystal waveguides. The ordered aggregate of molecules or nanostructures comprises at least one selected from the group of: organic or biological monolayers, biological complexes, cell membranes, bacterial membranes, virus assemblies, nanowire or nanotube assemblies, quantum-dot assemblies, one or more assemblies containing one or more rhodopsins, green fluorescence proteins, diarylethers, lipid bilayers, chloroplasts or components, mitochondria or components, cellular or bacterial organelles or components, bacterial S-layers, photochromic molecules. Further, the molecular aggregate may exhibit a photoinduced response.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Methods, materials and devices for light manipulation with oriented molecular assemblies in micronscale photonic circuit elements with High-Q or slow light
An optical device that comprises an input waveguide, an output waveguide, a high-Q resonant or photonic structure that generate slow light connected to the input waveguide and the output waveguide, and an interface, surface or mode volume modified with at least one material formed from a single molecule, an ordered aggregate of molecules or nanostructures. The optical device may include more than one input waveguide, output waveguide, high-Q resonant or photonic structure and interface, surface or mode volume. The high-Q resonant or photonic structure may comprise at least one selected from the group of: microspherical cavities, microtoroidal cavities, microring-cavities, photonic crystal defect cavities, fabry-perot cavities, photonic crystal waveguides. The ordered aggregate of molecules or nanostructures comprises at least one selected from the group of: organic or biological monolayers, biological complexes, cell membranes, bacterial membranes, virus assemblies, nanowire or nanotube assemblies, quantum-dot assemblies, one or more assemblies containing one or more rhodopsins, green fluorescence proteins, diarylethers, lipid bilayers, chloroplasts or components, mitochondria or components, cellular or bacterial organelles or components, bacterial S-layers, photochromic molecules. Further, the molecular aggregate may exhibit a photoinduced response.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
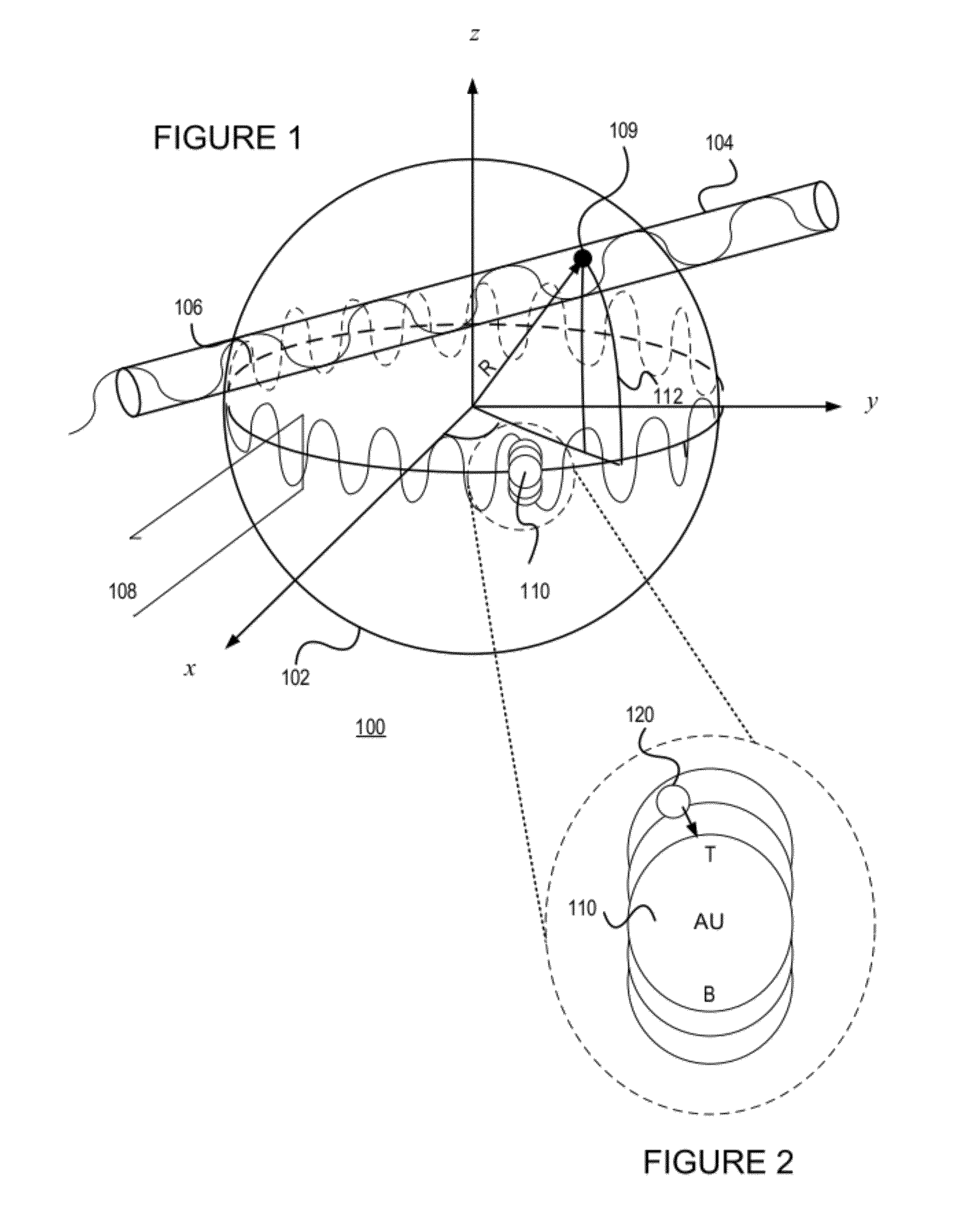
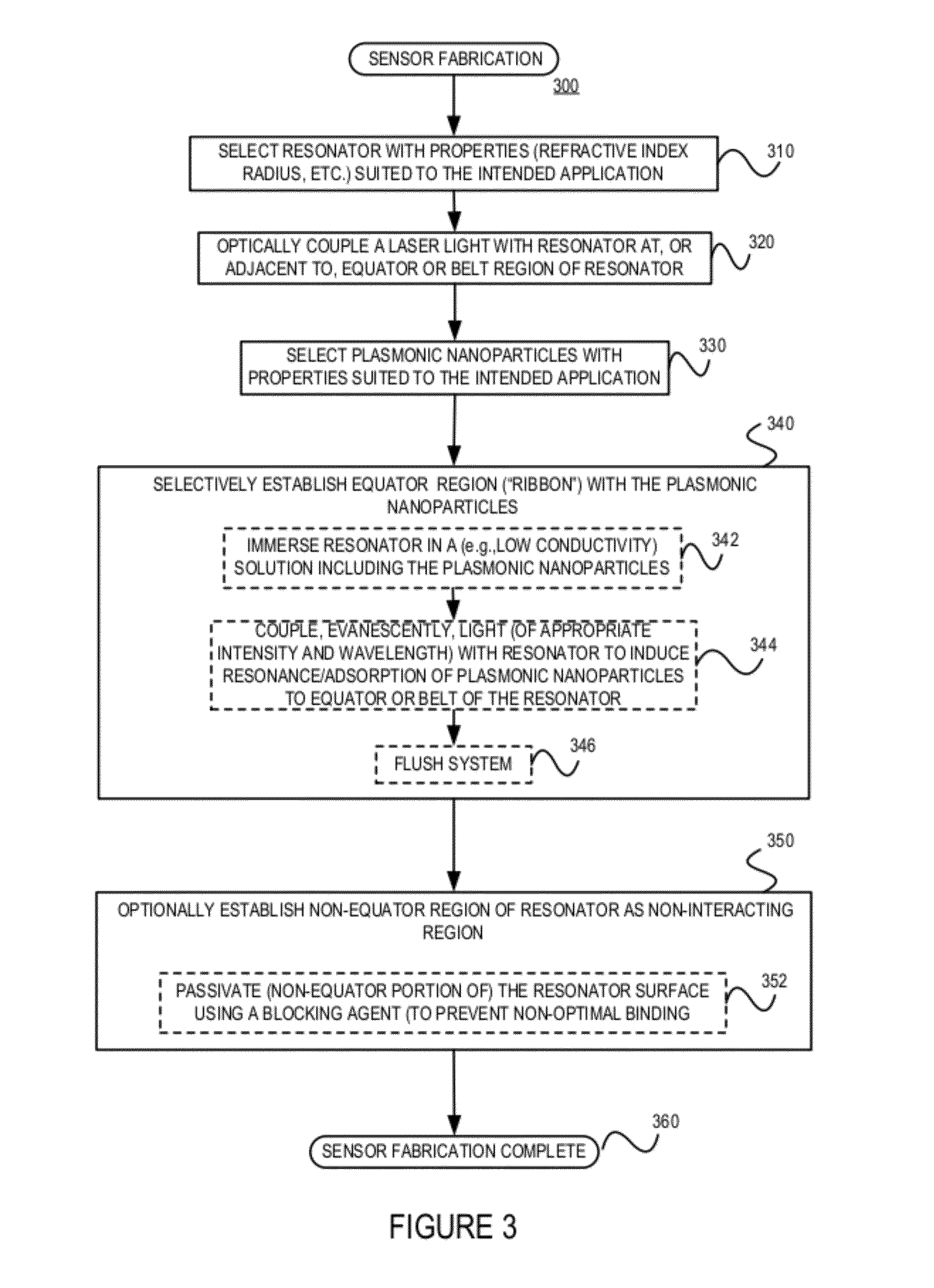
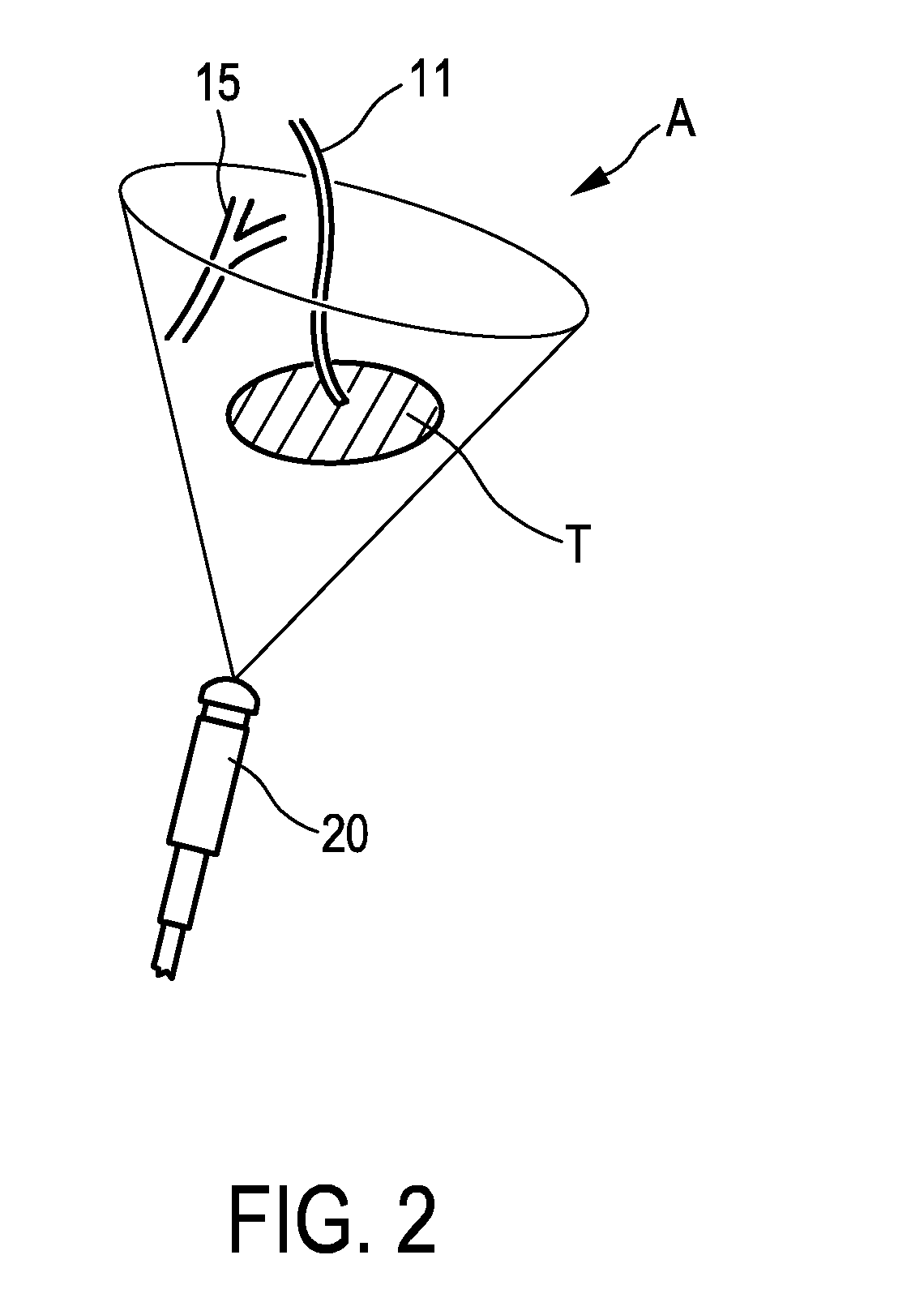
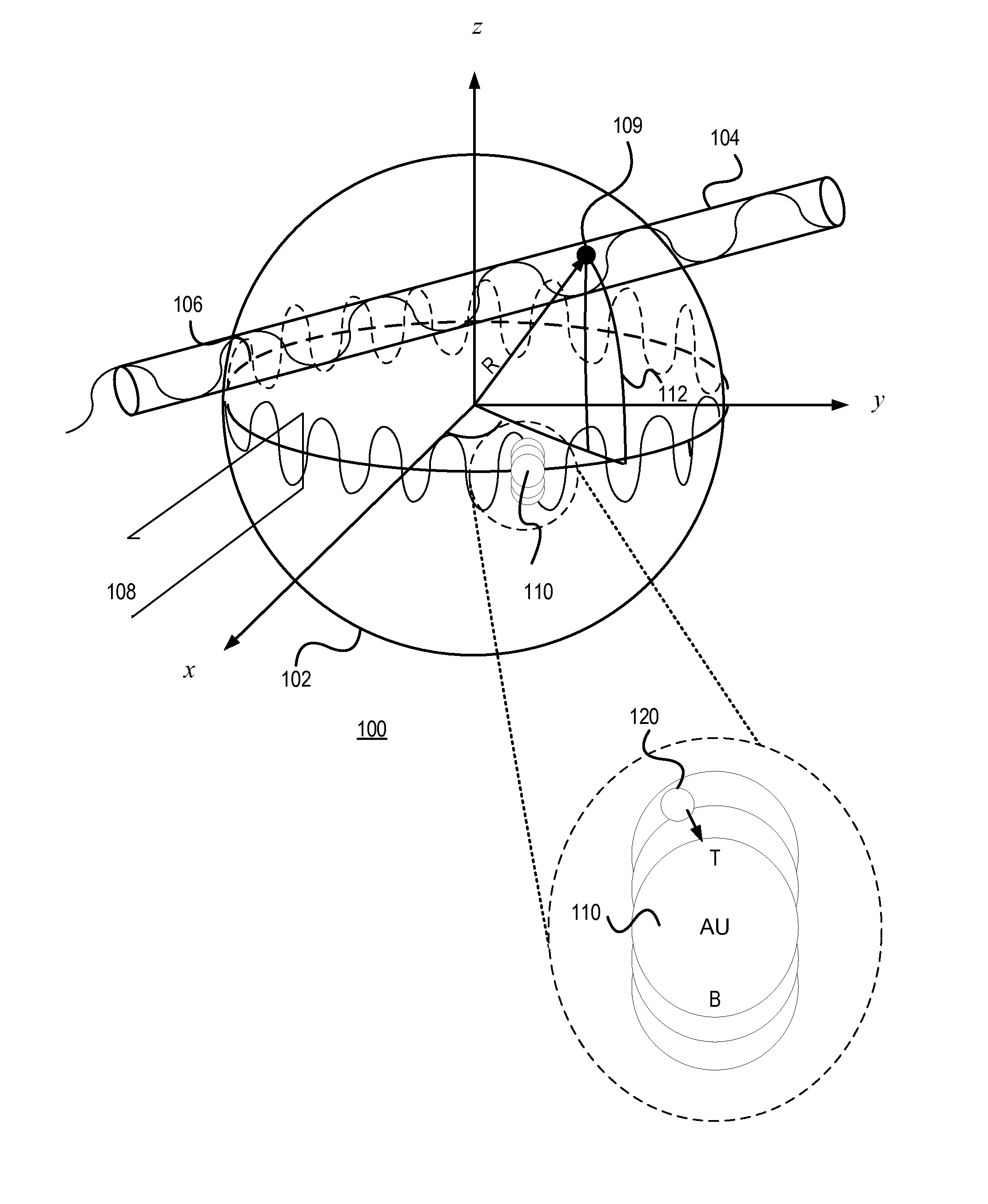
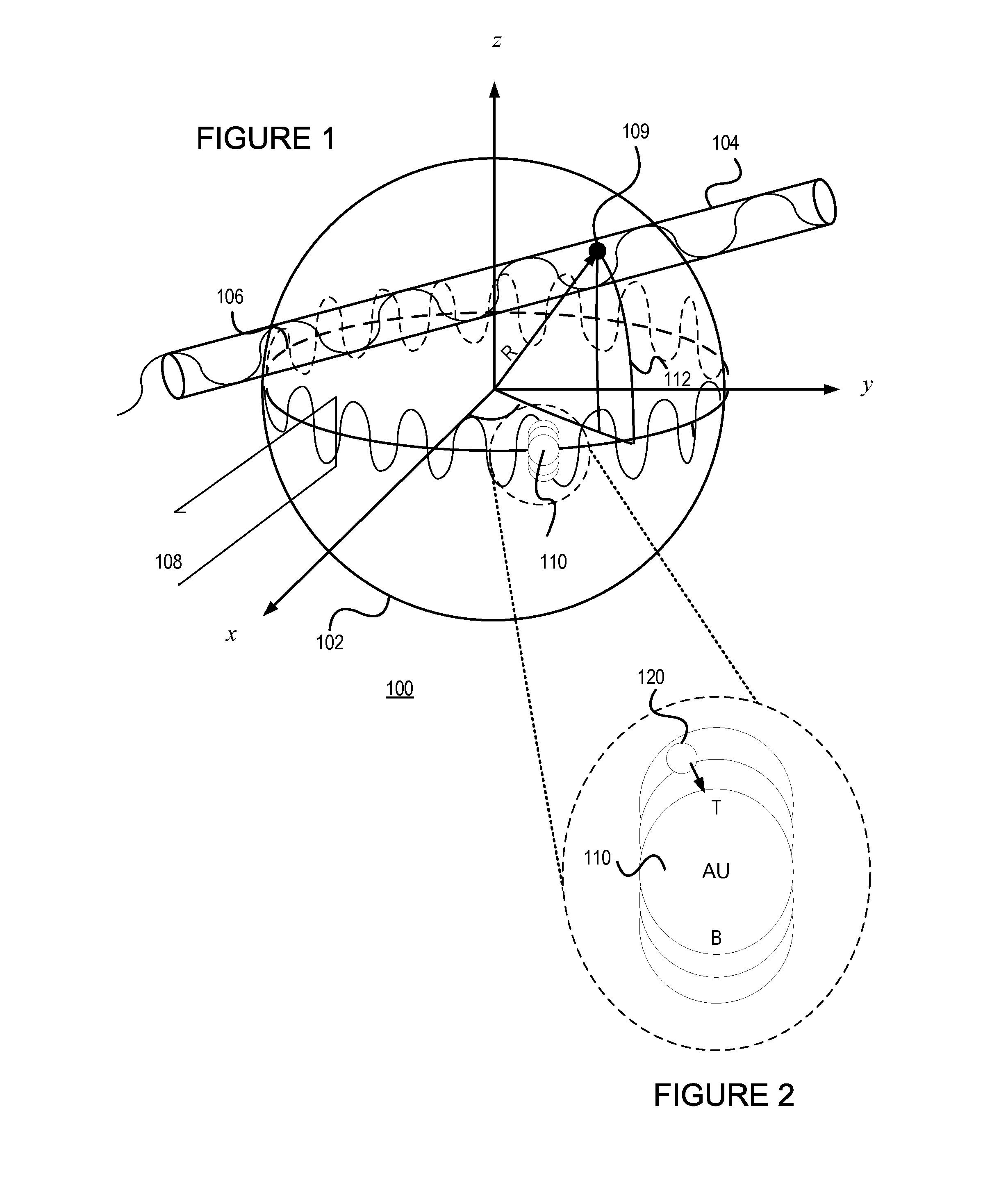
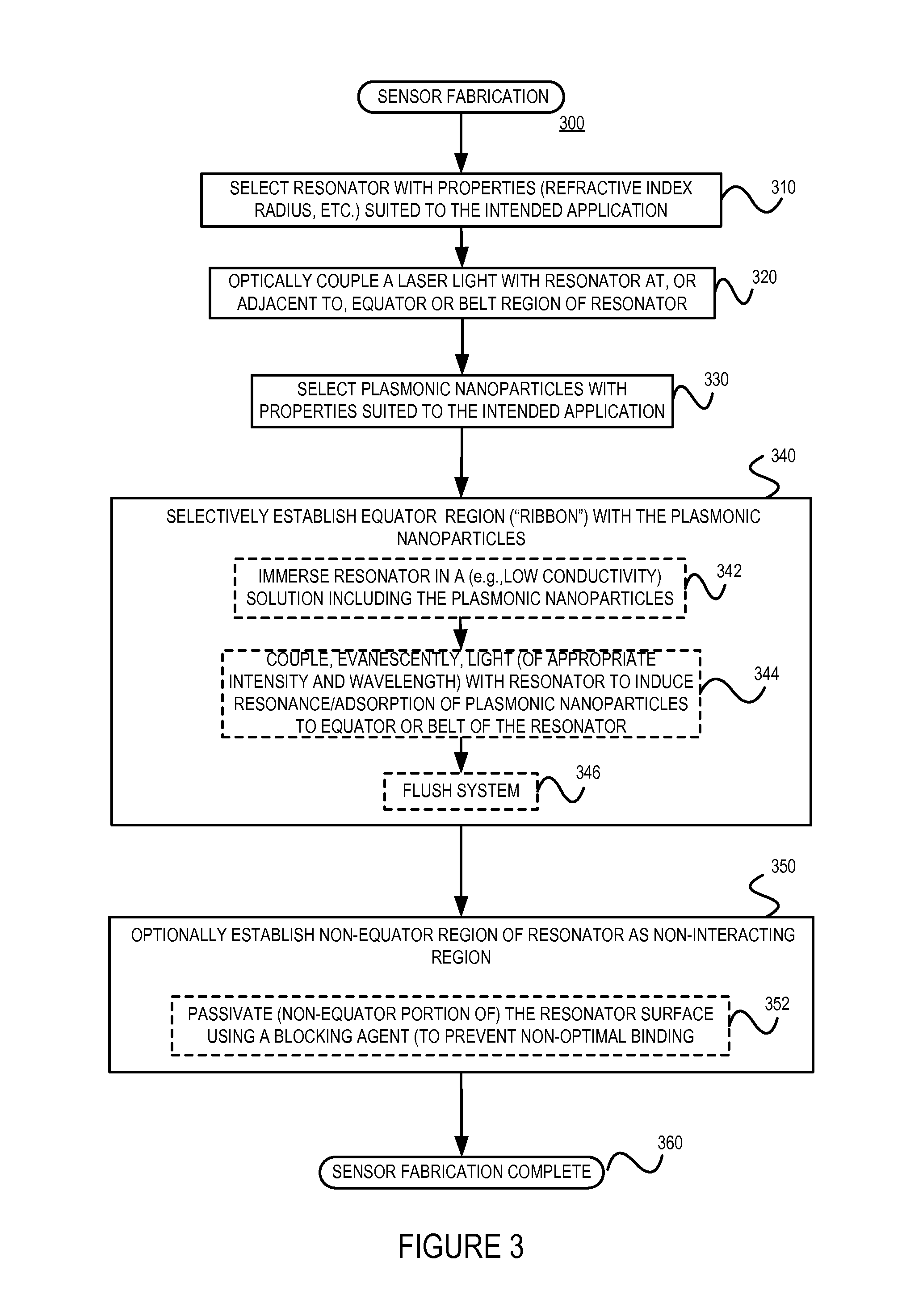
Plasmonic enhancement of whispering gallery mode biosensors
ActiveUS20120069331A1Reduce conductivityRadiation pyrometryMicrobiological testing/measurementWhispering galleryResonance
A sensor for determining the presence or concentration of a target entity in a medium is described, and includes (a) an optical waveguide; (b) a microresonator optically coupled with the optical waveguide such that light within the optical waveguide induces a resonant mode within the microresonator at an equator region (or a mode volume); and (c) at least one plasmonic nanoparticle adsorbed onto a surface area of the microresonator within the equator region (or the mode volume) such that light inducing a resonant mode within the microresonator also causes a plasmonic resonance in the at least one plasmonic nanoparticle. Detection methods for using such sensors are also described. Finally, methods, involving the use of carousel forces, for fabricating such sensors are also described.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Design method of semiconductor diode both-end pumping high power UV laser
InactiveCN101232148AReduce coupling lossExtend working lifeActive medium materialHigh power lasersPlane mirror
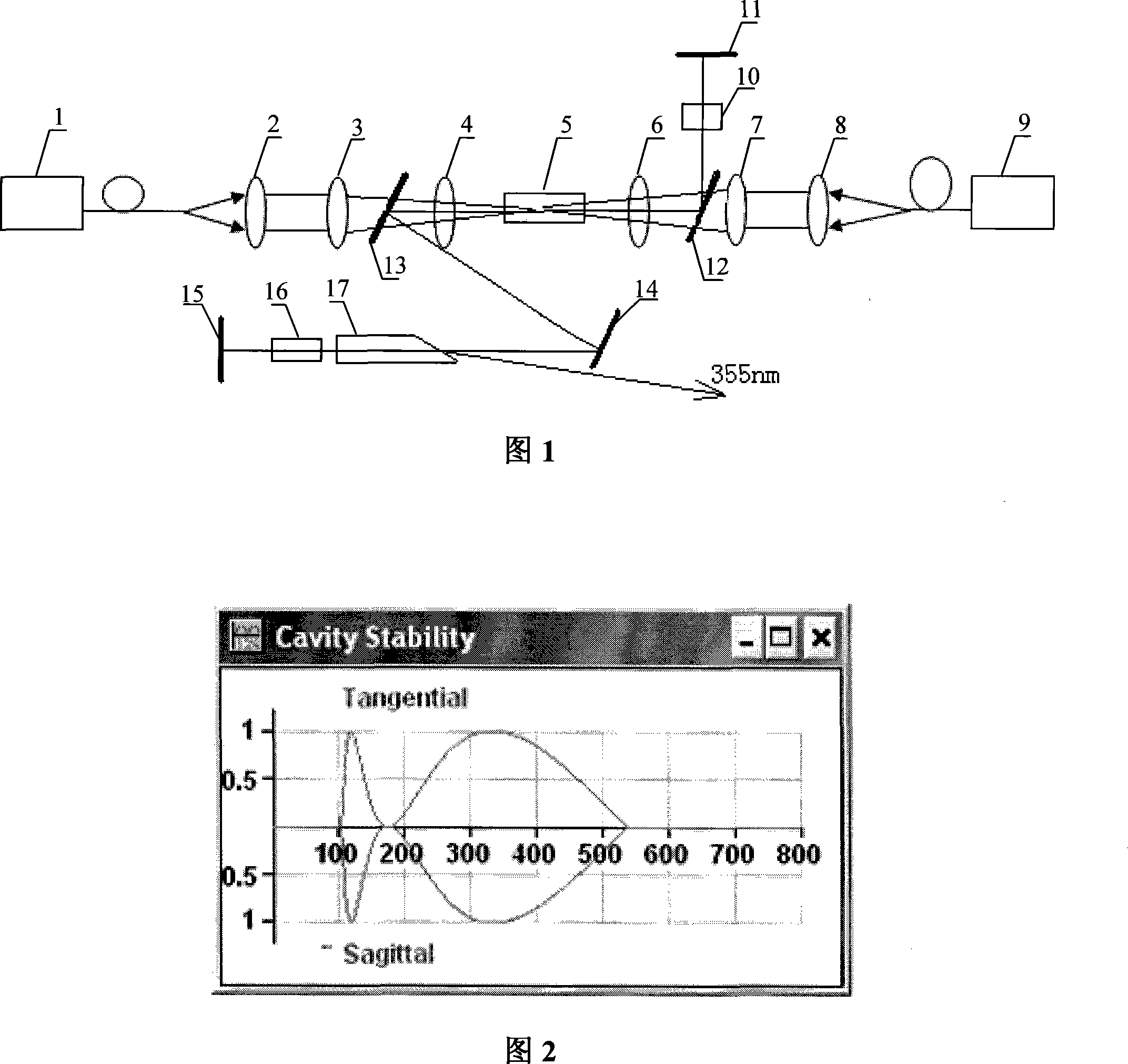
The invention provides a design method of a semiconductor diode double-end-pumped high-power UV laser, which comprises following steps: constituting a double-end-pumped laser crystal by using two semiconductor diodes; outputting a pumped beam with 808 nm; coupling the pumped beam by an aspherical optical coupling system and a lens to a laser crystal to generate a laser beam with 1064 nm; oscillating the laser beam in a resonant cavity consisting of five planar mirrors; modulating with Q switch; converting the modulated fundamental frequency light with 1,064 nm into a frequency-doubled light with 532 nm by a frequency-doubling crystal; mixing the unconverted fundament frequency light with 1,064 nm with the frequency-doubled light with 532 nm by a frequency-tripling crystal to obtain a UV laser with 355 nm; and outputting the UV laser from a surface of the frequency-tripling crystal cut by Brewster angle. According to the scheme, the laser cavity has the advantages of large mode volume, smaller laser spot at the frequency-doubling crystal, greatly reducing intracavity loss by cutting the frequency-tripling crystal with Brewster angle and high power laser output.
Owner:SUZHOU DELPHI LASER
Chip-integrated 2-micrometer wavelength micro laser
ActiveCN104466657AWith chip integrationWith miniaturizationActive medium materialCarbon dioxide laser lightPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a chip-integrated 2-micrometer wavelength micro laser. The chip-integrated 2-micrometer wavelength micro laser comprises a rare earth doping monox micro ring core cavity and a micro-nano fiber, wherein the micro-nano fiber is located on one side of the monox micro ring core cavity. The monox micro ring core cavity is prepared through the following steps that (1) a rare earth doping monox film is prepared on the surface of a silicon wafer through a sol-gel method; (2) a monox micro disc cavity is prepared on the surface of the monox film through a photoetching process and an etching process; (3) heating reflux treatment is carried out on the monox micro disc cavity through a carbon dioxide laser to obtain the monox micro ring core cavity. The 2-micrometer wavelength micro laser prepared through the sol-gel rare earth doping method has the advantages of being integrated in chip, micro, stable, low in threshold and the like, the energy mode volume in the cavity can be optimized according to the carbon dioxide laser reflux power and time, and a laser with a higher quality is obtained.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
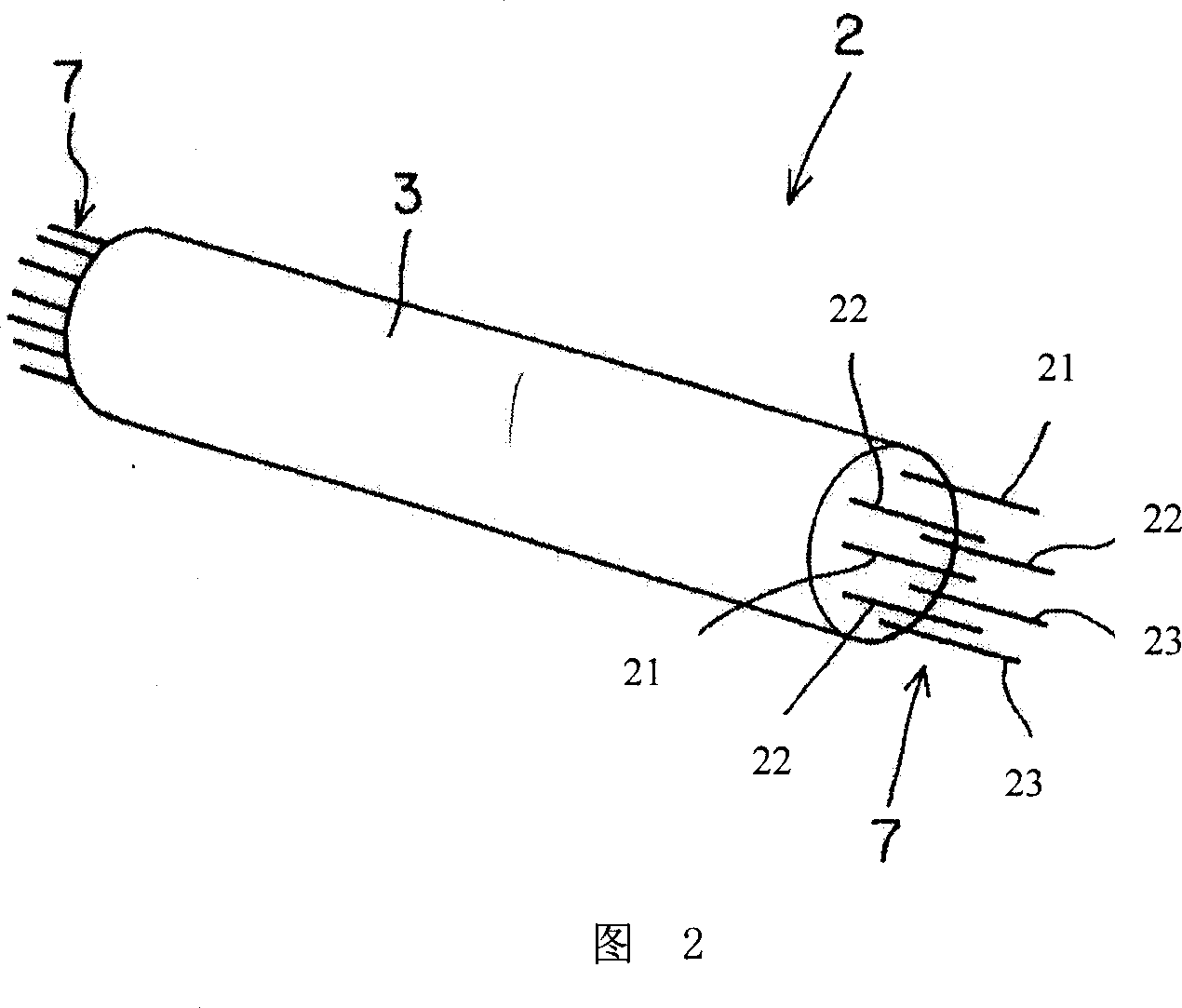
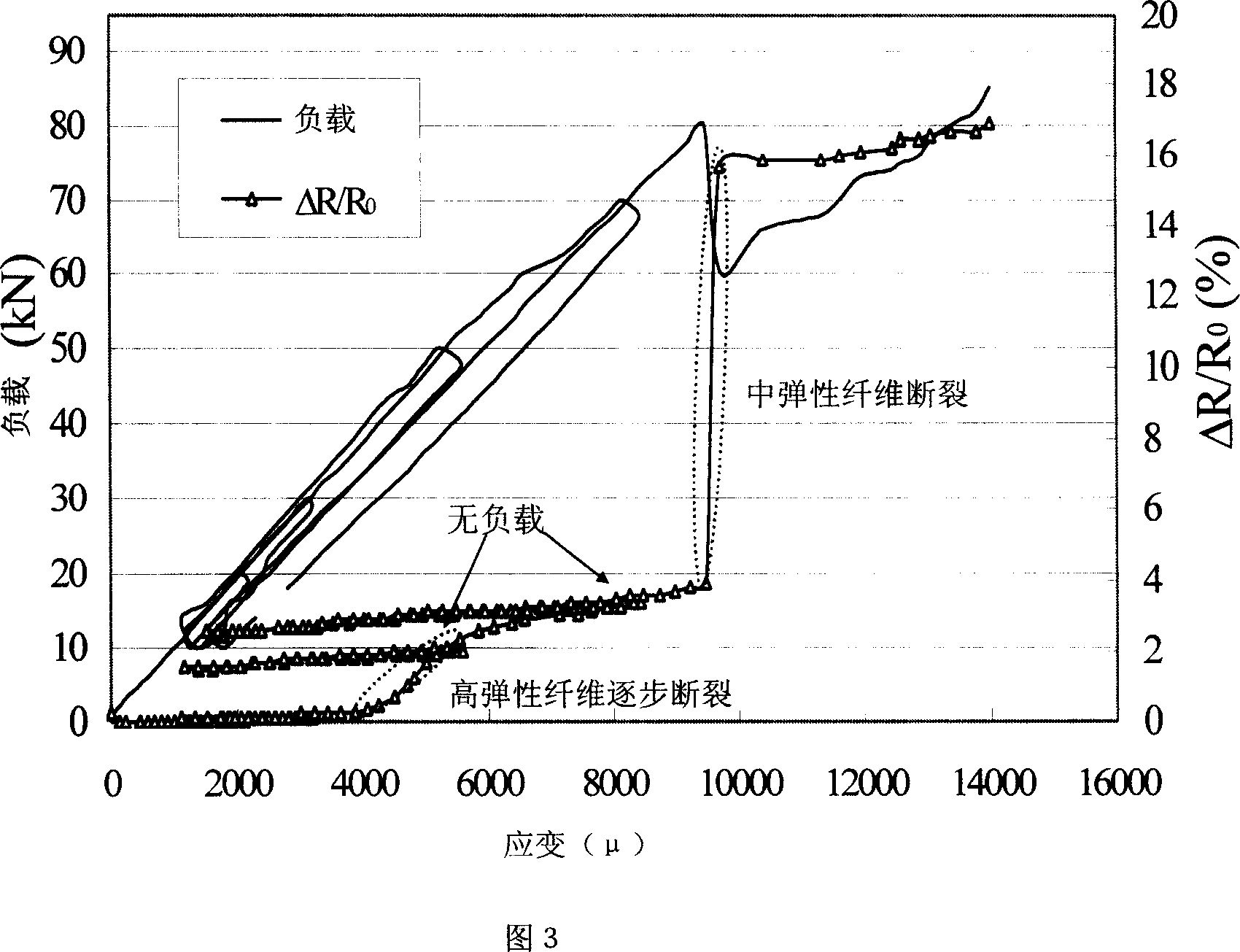
Farraginous carbon fiber composite material, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN1924124AImprove resistance change rateAvoid the defect of losing the sensing functionFibre treatmentForce measurementFiberHigh intensity
This invention discloses one mixture carbon fiber compound materials and its application, which comprises the following parts: spring mode volume as 500-650GPa carbon fiber A; spring mode as 360- 450GPa carbon fiber B and string intensity as 3200-5000MPa carbon fiber C. Due to used carbon fiber of high intensity and rigidity, it comprises good conductivity and piezoelectricity effect.
Owner:吴智深 +1
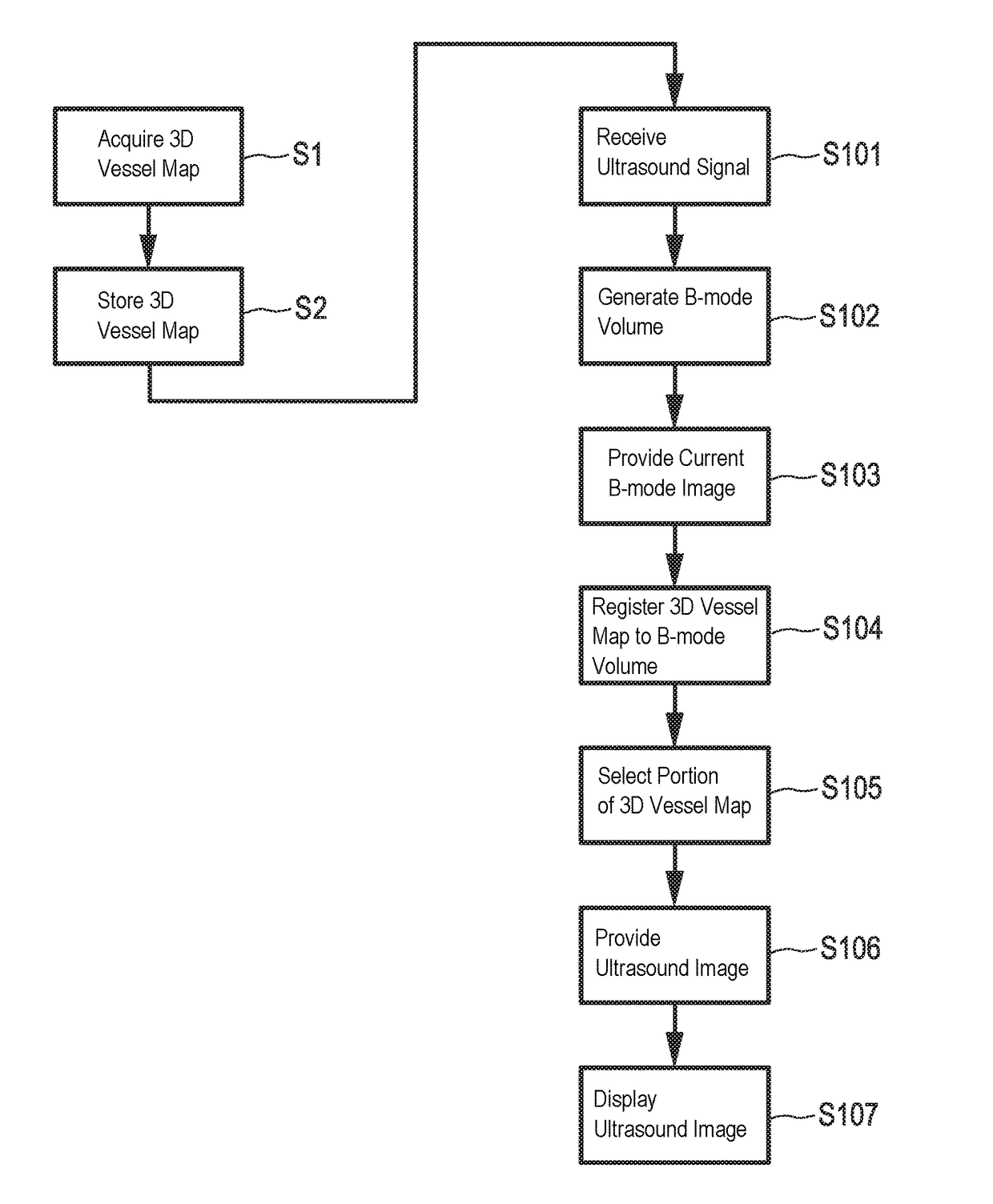
Ultrasound imaging system and method for image guidance procedure
ActiveUS9715757B2Faster frame rateImprove usability and reliabilityReconstruction from projectionImage analysisUltrasound imagingImaging processing
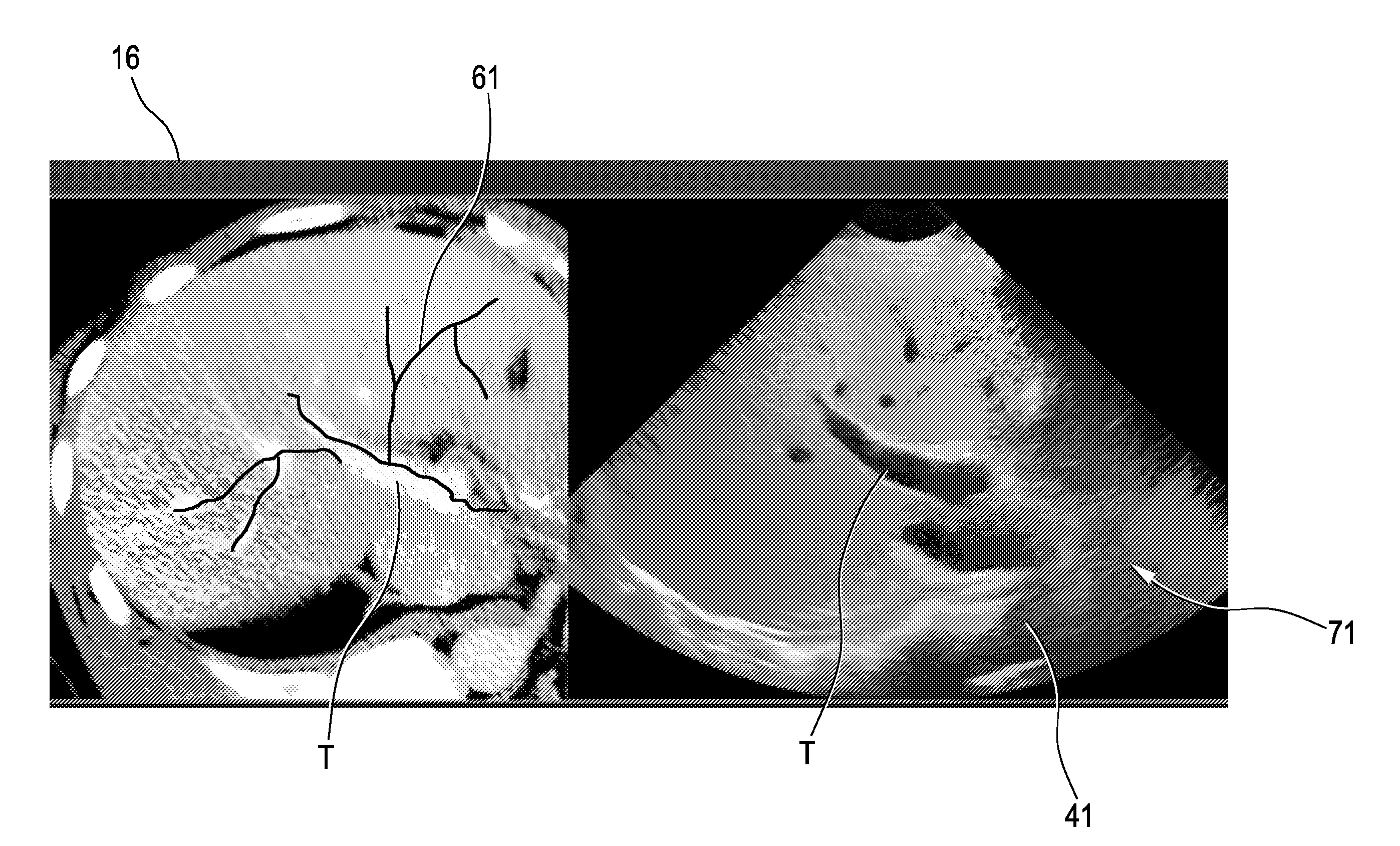
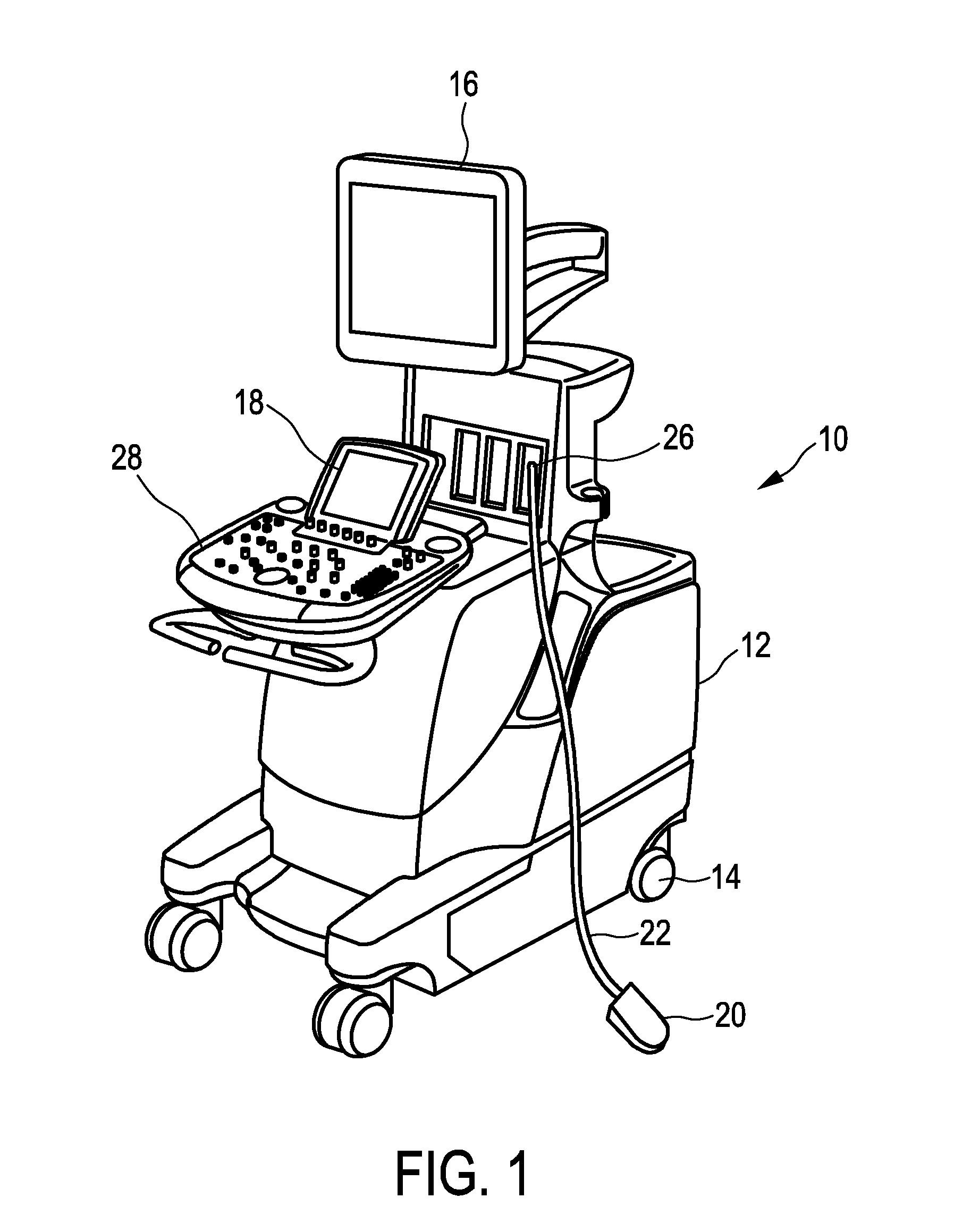
The present invention relates to an ultrasound imaging system (10) comprising an ultrasound probe (20) having a transducer array (21) configured to provide an ultrasound receive signal. The system further comprises a B-mode volume processing unit (30) configured to generate a B-mode volume (31) based on the ultrasound receive signal, and a B-mode image processing unit (40) configured to provide a current B-mode image (41) based on the B-mode volume (31). The system further comprises a memory (50) configured to store a previously acquired 3D-vessel map (51). Also, the system comprises a registration unit (60) configured to register the previously acquired 3D-vessel map (51) to the B-mode volume (31) and to select a portion (61) of the 3D-vessel map corresponding to the current B-mode image (41). Further, the system comprises a display configured to display an ultrasound image (71) based on the current B-mode image (41) and the selected portion (61) of the 3D-vessel map (51). The present invention further relates to a method for providing such ultrasound image with vessel information and a corresponding computer program.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Plasmonic enhancement of whispering gallery mode biosensors
ActiveUS8493560B2Radiation pyrometryMicrobiological testing/measurementWhispering galleryEngineering
A sensor for determining the presence or concentration of a target entity in a medium is described, and includes (a) an optical waveguide; (b) a microresonator optically coupled with the optical waveguide such that light within the optical waveguide induces a resonant mode within the microresonator at an equator region (or a mode volume); and (c) at least one plasmonic nanoparticle adsorbed onto a surface area of the microresonator within the equator region (or the mode volume) such that light inducing a resonant mode within the microresonator also causes a plasmonic resonance in the at least one plasmonic nanoparticle. Detection methods for using such sensors are also described. Finally, methods, involving the use of carousel forces, for fabricating such sensors are also described.
Owner:POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE OF NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
Method for improving collection efficiency of diamond NV color center fluorescence
ActiveCN109884013AAchieve excitationFor efficient collectionFluorescence/phosphorescenceQuantum sensorFiber
The invention discloses a method for improving collection efficiency of diamond NV color center fluorescence. The method comprises the following steps of forming an optical resonator by coupling a nano-diamond and a microsphere cavity based on the Purcell effect, integrating a microwave antenna thereon to prepare a microsphere cavity (200-500 microns) containing the nano-diamond, exciting the diamond NV color center to generate fluorescence by 532nm laser, and enhancing and collecting the fluorescence using a whispering wall mode such that the fluorescence generated by the diamond NV color center can be continuously circulated in the microsphere cavity, thereby establishing a strong light field and directly achieving the collection of fluorescence using the fiber connected to the sphere cavity. The method combines nano-diamond with optical microcavity with low requirements on preparation process, has the characteristics such as low cost, small mode volume and high energy density, realizes excitation and efficient collection of diamond NV color center fluorescence, and is expected to realize integrated application of NV color center based high sensitivity quantum sensors.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Narrow-linewidth microcavity brillouin laser with suppressed temperature fluctuations
ActiveUS20190341739A1Suppress noiseAddress limitationsLaser using scattering effectsActive medium shape and constructionLine widthCenter frequency
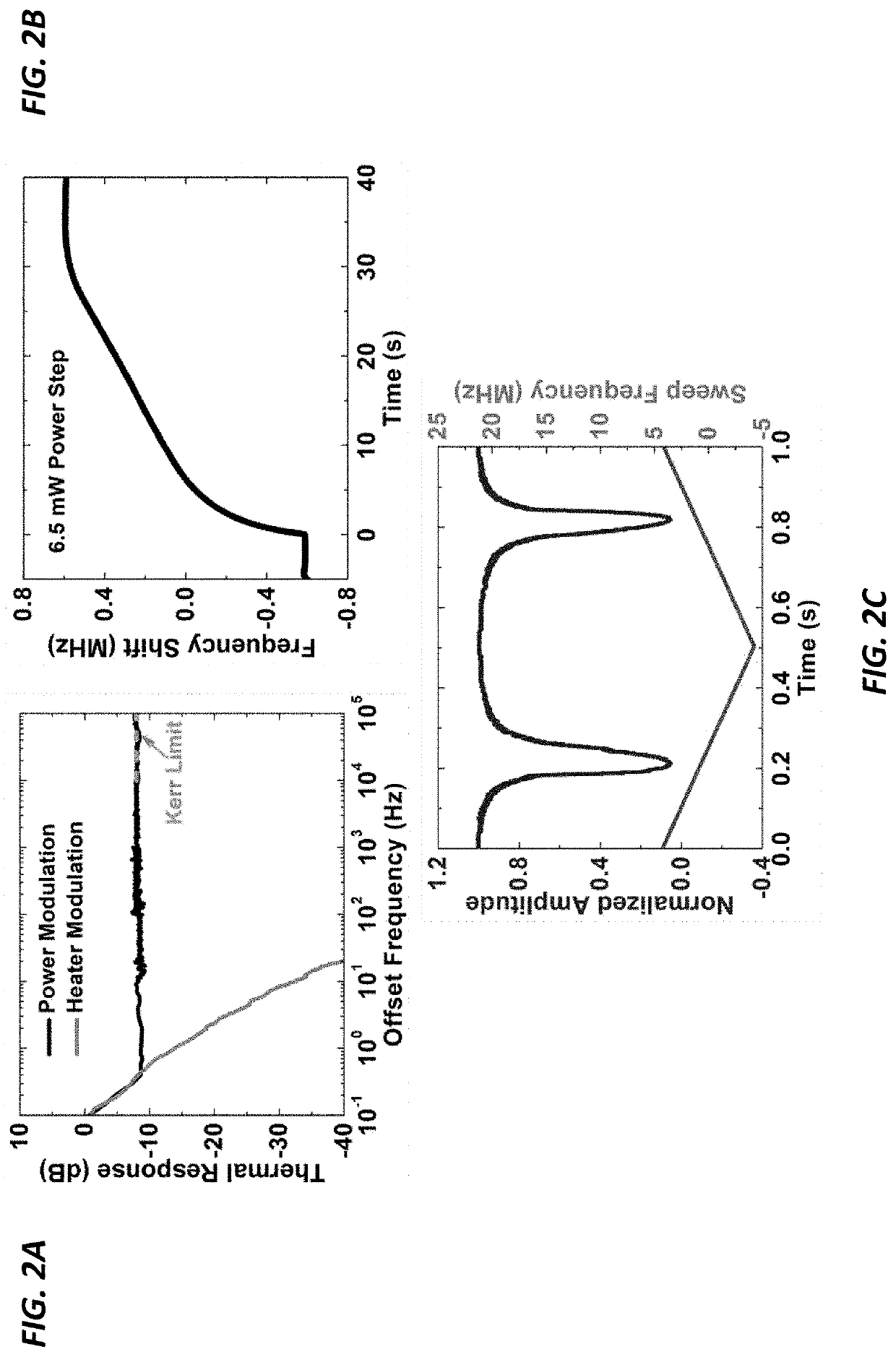
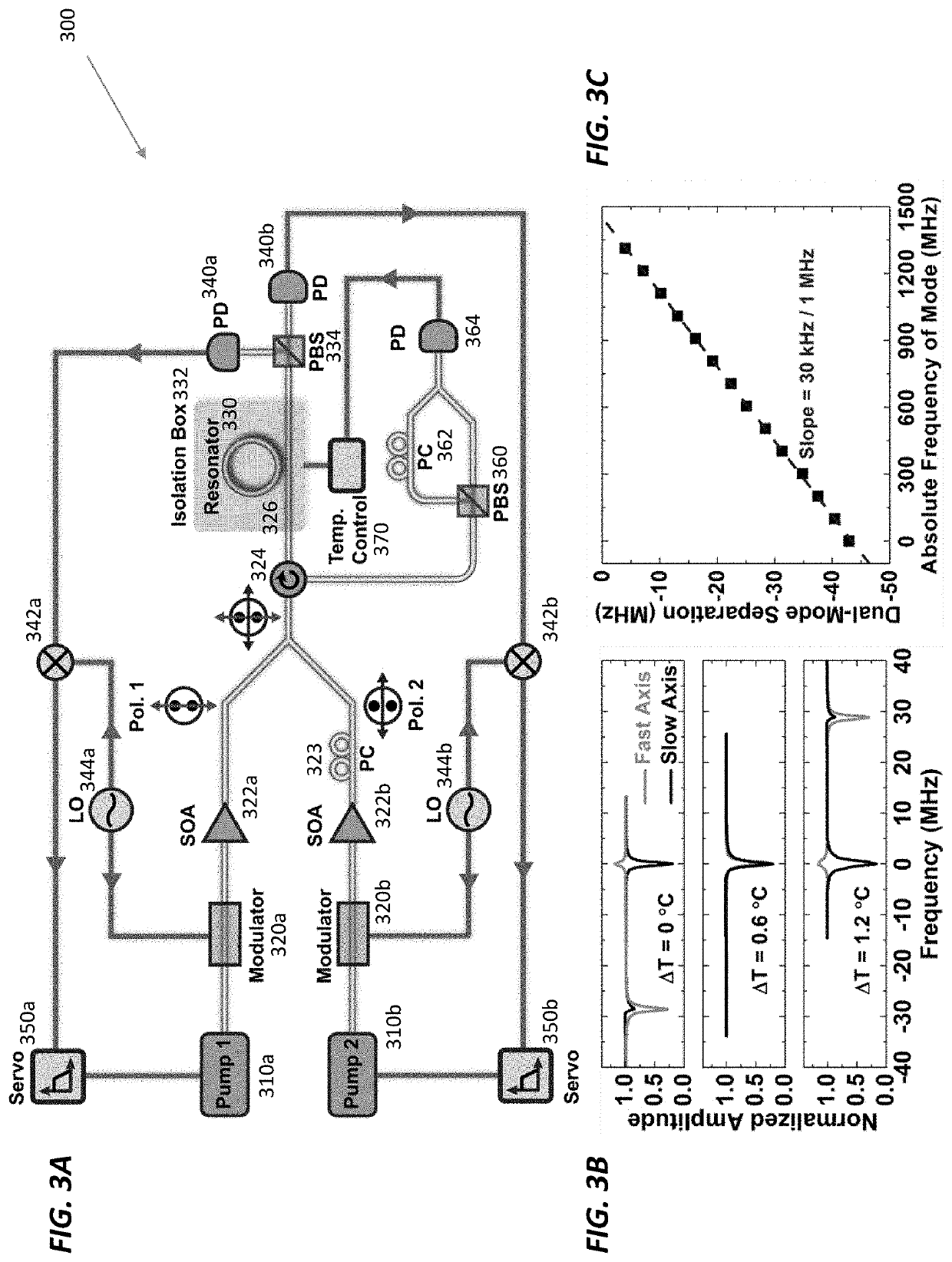
Ultrastable lasers serve as the backbone for advanced scientific experiments and enable atomic spectroscopy and laser interferometry at high levels of precision. But is not clear how to realize an ultrastable laser that is compact and portable for field use. An ultrastable laser source should be insensitive to both short- and long-term fluctuations in temperature, which ultimately broaden the laser linewidth and cause drift in the laser's center frequency. Fortunately, using a large mode-volume optical resonator, which suppresses the resonator's fast thermal fluctuations, together with the stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) optical nonlinearity presents a powerful combination that enables the ability to lase with an ultra-narrow linewidth of 20 Hz. The laser's long-term temperature drift is compensated by using the narrow Brillouin line to sense minute changes in the resonator's temperature (e.g., changes of 85 nK). The precision of this temperature measurement enables the stabilization of resonators against environmental perturbations.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Two-groove wide-ridge type semiconductor light amplifier and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105514801AAchieve single-mode outputIncrease output powerLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersQuantum wellOhmic contact
The invention relates to a two-groove wide-ridge type semiconductor light amplifier, which comprises a substrate and an epitaxial layer growing on the substrate, wherein the upper part of the epitaxial layer comprises an n type waveguide layer, an active area quantum well layer, a p type covering layer and an ohmic contact layer; the active area quantum well layer is arranged at the upper part of the n type waveguide layer; the p type covering layer and the ohmic contact layer are arranged at the upper part of the active area quantum well layer; the partial region of the ohmic contact layer is vertically and downwards etched into the n type waveguide layer to form a two-groove limitation ridge type structure; two grooves are two mutually parallel grooves; the width of the ridge type structure is identical to the thickness of a ridge type waveguide. A waveguide coupling mode is adopted; a coplanar waveguide is used as a filter; the single-mode output in the large-mode volume is realized; the output power is increased; meanwhile, the coupling efficiency is also improved.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical chaos generating device based on silicon photon microcavity
ActiveCN106654855AFacilitate direct handlingReduce manufacturing costLaser optical resonator constructionLaser output parameters controlErbium dopingFiber amplifier
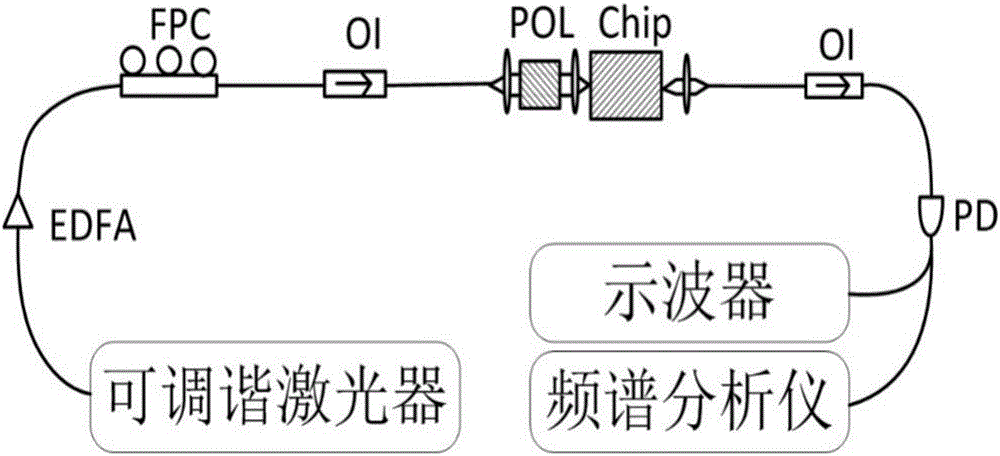
The invention relates to an optical chaos generating device based on a silicon photon microcavity. The optical chaos generating device comprises a tunable laser, an erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA), a fiber polarization controller (FPC), an optical isolator (OI), a polarizing plate, a silicon photon microcavity and a photodetector (PD). The optical chaos generating device based on a silicon photon microcavity generates optical chaos by using the silicon photon microcavity, enables the optical chaos to be fully integrated with CMOS, has low manufacturing cost, is suitable for large-scale mass production, has a smaller model volume, a higher quality factor, high local energy density, good light control performance, is conducive to direct operation of light processing, achieves low-threshold operation, is fully integrated and good in actual stability.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
A loop concave output mirror laser resonance cavity
InactiveCN101262113AIncrease powerImprove output beam qualityOptical resonator shape and constructionResonant cavityDivergence angle
The invention discloses a laser resonant cavity with an annular and a concave output mirror, which comprises a reflecting mirror, a laser medium and an output mirror; the output mirror is an annular concave mirror of which the working surface comprises one or a plurality of homocentric, annular and circular arc shaped concave cambers; the central part of the working surface of the output mirror can also be a circular working surface or the central part of the out mirror can be non-working surface or hollowness; an annular and concave reflecting mirror can also be adopted by the laser resonant cavity of the invention. The laser resonant cavity provided by the invention has the advantages of simple processing, convenient adjustment, steady operation, large available mode volume, very small divergence angle and good beam quality, thus being able to be applicable to gas lasesr or solid lasers with medium and high power, in particular to large volume gain medium and cylindrical and toroidal gain medium.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Ultrasound imaging system and method for image guidance procedure
ActiveUS20150294497A1Increased and sufficient frame rateFaster frame rateReconstruction from projectionImage analysisUltrasound imagingImaging processing
The present invention relates to an ultrasound imaging system (10) comprising an ultrasound probe (20) having a transducer array (21) configured to provide an ultrasound receive signal. The system further comprises a B-mode volume processing unit (30) configured to generate a B-mode volume (31) based on the ultrasound receive signal, and a B-mode image processing unit (40) configured to provide a current B-mode image (41) based on the B-mode volume (31). The system further comprises a memory (50) configured to store a previously acquired 3D-vessel map (51). Also, the system comprises a registration unit (60) configured to register the previously acquired 3D-vessel map (51) to the B-mode volume (31) and to select a portion (61) of the 3D-vessel map corresponding to the current B-mode image (41). Further, the system comprises a display configured to display an ultrasound image (71) based on the current B-mode image (41) and the selected portion (61) of the 3D-vessel map (51). The present invention further relates to a method for providing such ultrasound image with vessel information and a corresponding computer program.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Method for generating third-harmonic-generation ultraviolet laser through fold resonating cavity
InactiveCN103682974AReduce absorptionEasy to operateOptical resonator shape and constructionUltravioletFundamental frequency
The invention discloses a method for generating a third-harmonic-generation ultraviolet laser through a fold resonating cavity. Laser crystal is pumped from the side face of a laser diode, simulated radiation is generated, fundamental frequency light generation is formed in the cavity, fundamental frequency light is converted into pulsed light through a Q switch, the power density of the fundamental frequency light is improved, second harmonics are generated by the fundamental frequency light through frequency doubling crystal, the ultraviolet laser is generated by the remaining fundamental frequency light and the generated second harmonics under the action of sum frequency crystal and is output out of the cavity through an output mirror; ultraviolet emergent light in one direction is reflected to the resonating cavity for vibration in a continued mode by an ultraviolet reflecting mirror outside the fold resonating cavity, so that the ultraviolet light is only output in one direction and loss of the ultraviolet light is reduced. The method of inner-cavity frequency doubling and sum frequency is applied to the fold resonating cavity, the high power density inside the cavity and the large mode volume are utilized, and therefore the ultraviolet laser conversion efficiency is improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
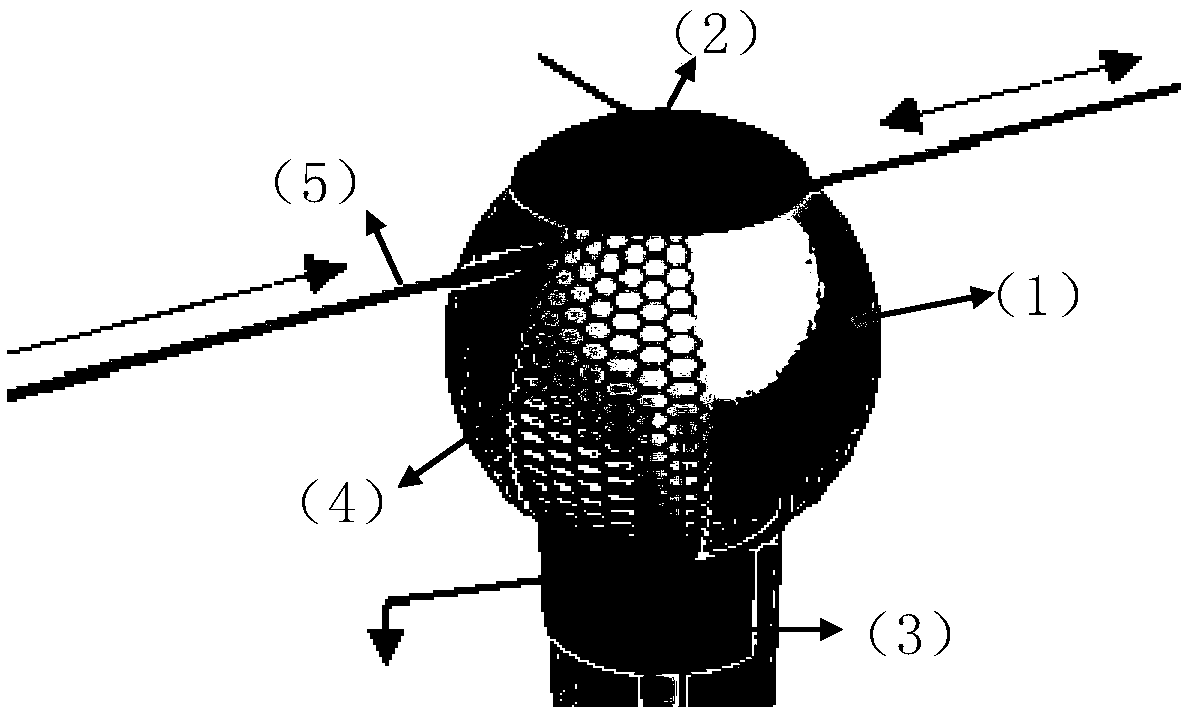
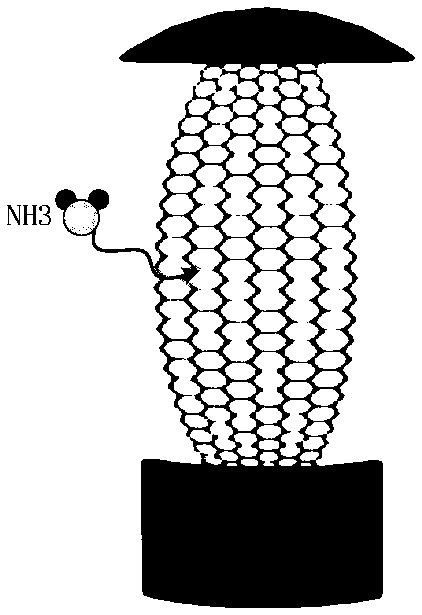
Graphene embedded echo-wall microsphere cavity monomolecular gas sensor
ActiveCN109164051AReduced mode volumeEasy accessColor/spectral properties measurementsElectricityResonant cavity
The invention belongs to the field of sensing, and in particular relates to a graphene embedded echo-wall microsphere cavity monomolecular gas sensor based on graphene singular points. According to the invention, the mode volume of microspheres is effectively reduced through gold electrodes on the microspheres, the number of resonant modes is greatly reduced, and the graphene embedded echo-wall microsphere cavity monomolecular gas sensor relies on physical adsorption of graphene and characteristics of the electrically adjustable Fermi level, microsphere cavities can be precisely controlled towork at the singular points through electrically regulated supermaterial graphene to improve the sensing response speed and sensitivity, and furthermore, resonant cavities with high-quality factors can greatly reduce the sensing power consumption: the response time is only one thousandth of that of an electrochemical gas sensor, the sensitivity can be 10,000 or more than 10,000 times that of the traditional optical gas sensor, and the sensing power consumption is as low as 70 nanowatt. Optical fiber communication networks can be conveniently accessed by using common single-mode optical fiber connectors. By adopting the graphene embedded echo-wall microsphere cavity monomolecular gas sensor disclosed by the invention, the sensing sensitivity achieves the monomolecular weight level and the sensing power consumption is lower on the basis of ensuring small sensor size, simple structure and fast response.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
GaN-based metal-ultrathin oxide-semiconductor composite structure nanolaser and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106785913AUniform diameter and lengthSmall optical mode volumeLaser detailsLaser active region structureBiological imagingLaser light
The invention discloses a GaN-based metal-ultrathin oxide-semiconductor composite structure nanolaser, which comprises a substrate and an InGaN / Ga quantum well nano-column, wherein the structure of the substrate sequentially comprises a SiO2-Si substrate, a metal layer and an ultrathin oxide layer; the InGaN / Ga quantum well nano-column is put on the surface of the ultrathin oxide layer and structure of the InGaN / Ga quantum well nano-column sequentially comprises a sapphire substrate layer, an n-type GaN layer, an In<x>Ga<x-1>N / GaN quantum well active layer and a p-type GaN layer. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the GaN-based metal-ultrathin oxide-semiconductor composite structure nanolaser. The nanolaser has the advantages that (1) the nanolaser has very small optical mode volume and can break through a diffraction limit of light, and the submicron-sized laser can be achieved; (2) the laser has an extremely low lasing threshold and an MUTOS laser light structure can lase under an optical pump of 0.15kW / cm<2>; and (3) the mode of laser light can be regulated and controlled and single-mode and multi-mode laser light transmission is achieved. The laser structure has potential application value in the aspects of ultra-high resolution intelligent displaying, complicated biological imaging, and photoelectric interconnection of a silicon-based integration circuit and a photoelectronic device.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Semiconductor optical amplifier
ActiveCN106785915APhoton density increaseIncreased pattern volumeLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersUltravioletDivergence angle
The invention discloses a semiconductor optical amplifier, and especially relates to a GaAs-based semiconductor optical amplifier having a parabola-shaped curved-surface waveguide structure. Material of the semiconductor optical amplifier is a GaAs-based material system. An N-type AlxGa1-xAs buffer layer, an N-type AlGaAsSb lower limit layer, an N-type N-AlxGa1-xAs lower waveguide layer, an InxGa1-xAs quantum well active region, a P-type AlxGa1-xAs upper waveguide layer and a P-type AlGaAsSb upper limit layer are epitaxially prepared on an N-type GaAs substrate in sequence. The upper waveguide layer of the semiconductor optical amplifier is in the parabola-shaped curved-surface structure; such structure can enable a parabola-shaped curved-surface tip to have higher photon density, thereby improving mode volume of the semiconductor optical amplifier and enabling the semiconductor optical amplifier to have higher gain; and meanwhile, the parabola-shaped curved-surface waveguide structure facilitates compressing divergence angle of the semiconductor optical amplifier, thereby realizing high-power output and improving fiber coupling efficiency. The parabola-shaped curved-surface structure of the upper waveguide layer of the semiconductor optical amplifier is prepared through electron beam lithography or ultra-violet lithography, and then, through a dry method and wet method combined etching process.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Diode-pumped, solid-state laser with chip-shaped laser medium and heat sink
InactiveUS20060285571A1Improve matchAdequate pumping coupling efficiencyActive medium materialActive medium shape and constructionOptoelectronicsSolid-state laser
A chip-shaped laser medium (12) is side pumped to improve mode matching between the pumping energy (50) and lasing mode volume (36). The chip thickness (44) and laser medium doping level can be designed and controlled to ensure adequate pumping coupling efficiency. The chip shape can also be employed to provide greater chip surface areas (22) for cooling the laser medium (12). The laser pumping package (70), gain module (101), and chip-shaped design can be scalable to offer higher pumping power and high output power. Different orientations of the gain modules (101) with respect to each other can be used to provide better lasing mode quality.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
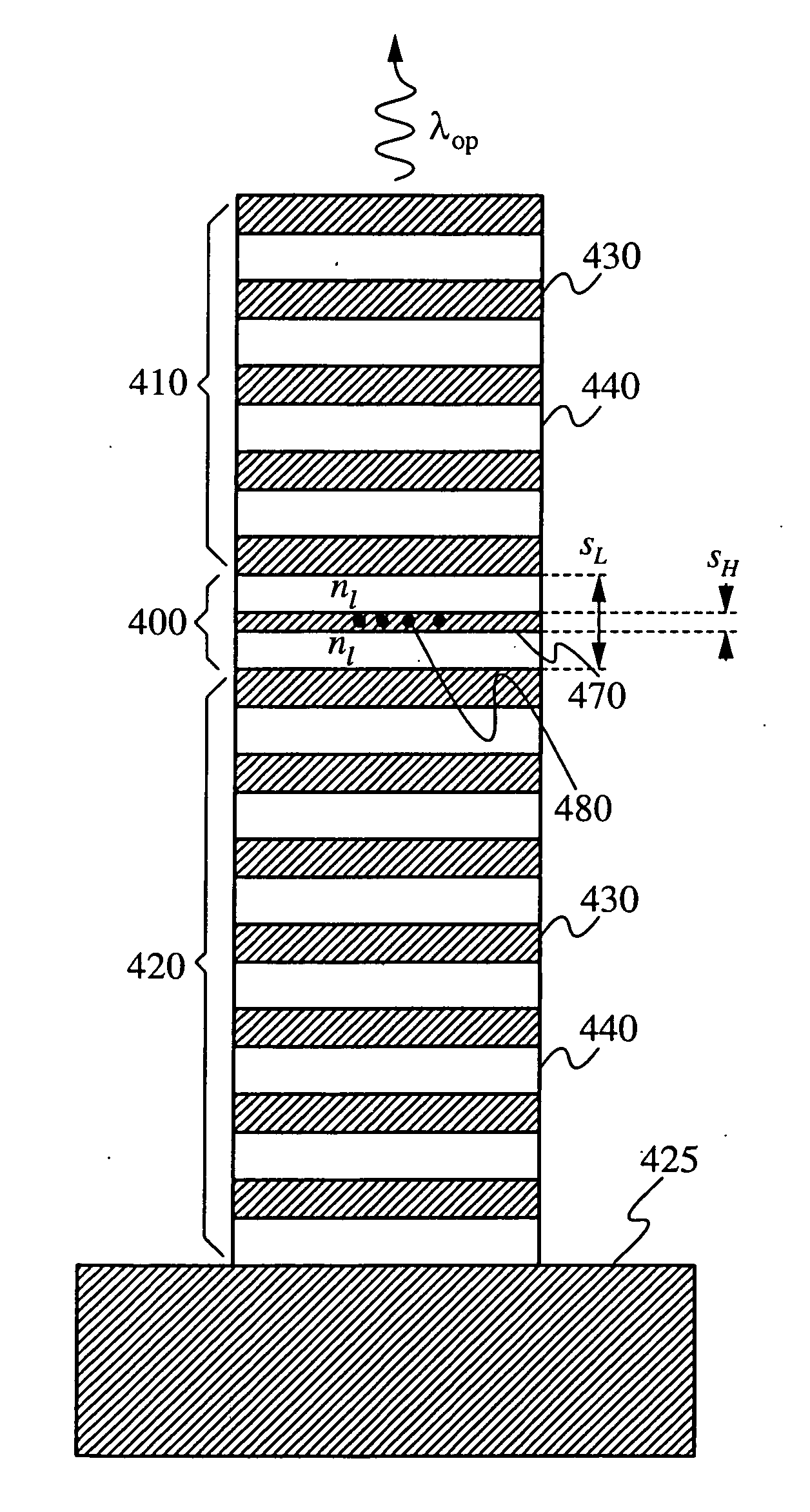
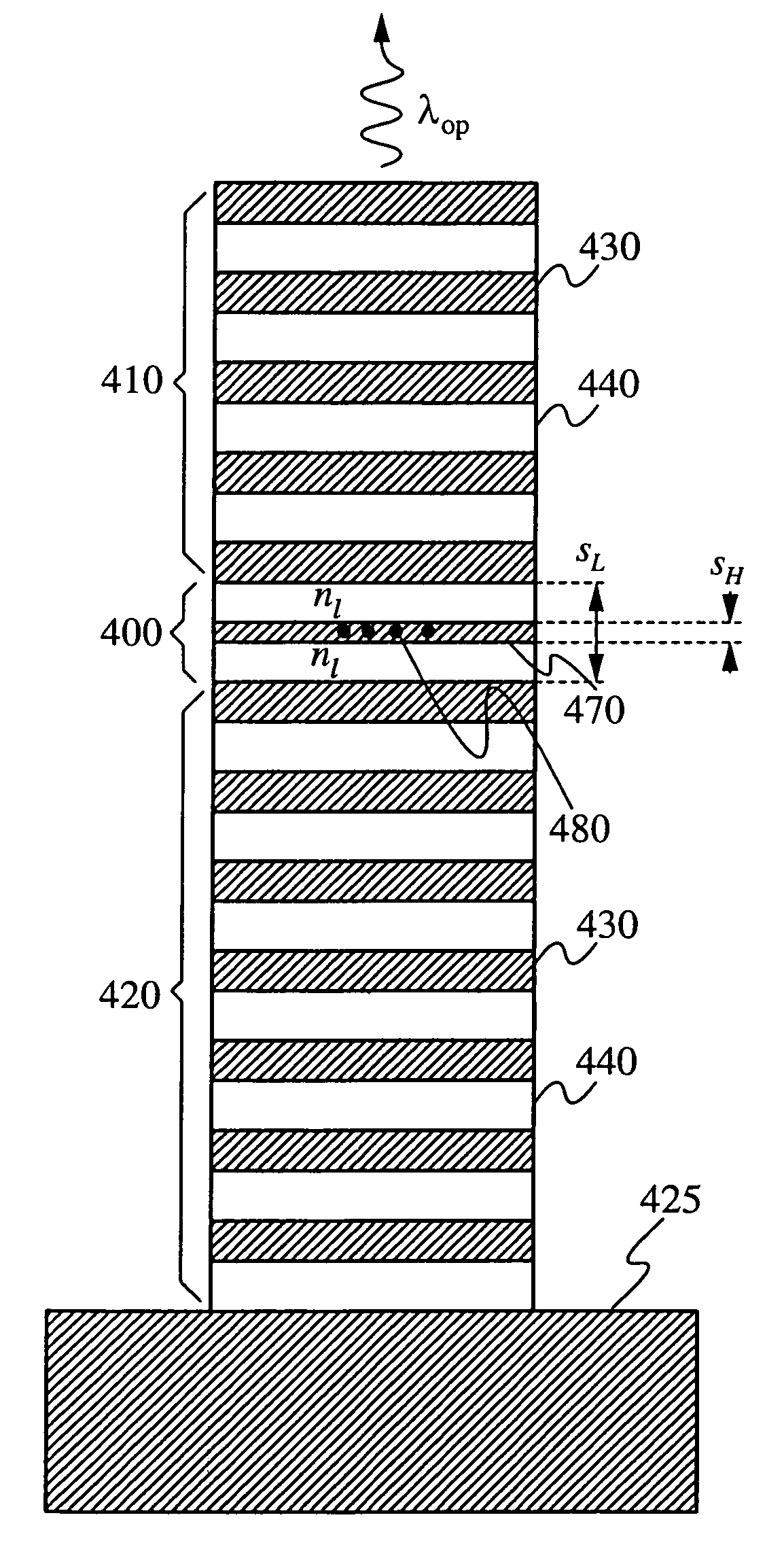
Half-wavelength micropost microcavity with electric field maximum in the high-refractive-index material
InactiveUS20070183471A1Strong interactionRaise the ratioQuantum computersLaser active region structureRefractive indexQuantum network
A micropost microcavity device has a maximum field intensity at the center of a high-index spacer as well as a small mode volume. The device has an approximately half-wavelength thick low-index spacer [400] sandwiched between two quarter wave stacks [410, 420]. The low-index spacer has a high-index subspacer layer [470] positioned at its center. The subspacer layer has a thickness smaller than a quarter wavelength. As a result, the electric field intensity remains a maximum at the center of the spacer where the high-index subspacer is positioned. A quantum dot or other active region [480] may be embedded within the subspacer [470]. The microcavity devices provide, for example, single photon sources, single dot lasers, low-threshold quantum dot or quantum well lasers, or devices for strong coupling between a single quantum dot and the cavity field which can be used as components of photonic integrated circuits, quantum computers, quantum networks, or quantum cryptographic systems.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Surface phasmon coaxial optical waveguide structure
InactiveCN101363939AReduce lossImprove radiation efficiencyCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideResonant cavityBroadband
The invention discloses a surface plasmon coaxial optical wave guide structure which relates to an optical wave guide. The surface plasmon coaxial optical wave guide structure is good for the light signal transmission. A cylindrical core layer and a tubular shell layer are arranged; the cylindrical core layer is a metal core layer; and the shell layer is a wide band-gap media shell layer. The surface plasmon coaxial optical wave guide structure taking metal as the core layer enlarges the transmitted light signal in the wave guide, and provides a resonant cavity with small mode volume, thereby improving fineness and facilitating transmission efficiency of the objective light signal.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for implementing annular cavity whispering gallery mode by photonic crystal structure
InactiveCN101499616AHigh quality factorEasy to integrateLaser optical resonator constructionActive medium materialWhispering gallerySemiconductor materials
The invention discloses a method for adopting a photonic crystal structure to realize the whispering gallery mode of a ring cavity. In the method, 12 photonic crystal air holes are removed from a complete triangular lattice photonic crystal in the semiconductor material; 6 photonic crystal air holes are added at the annular corners; and then the ring cavity of the photonic crystal can be formed. The whispering gallery mode of the ring cavity produced in the method has good quality factors, and the mode is only a plurality of microns in size, thereby solving the problem that the whispering gallery mode is difficult to be integrated to a small scale size.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Half-wavelength micropost microcavity with electric field maximum in the high-refractive-index material
InactiveUS7292613B2Strong interactionRaise the ratioQuantum computersLaser active region structureElectrical field strengthRefractive index
A micropost microcavity device has a maximum field intensity at the center of a high-index spacer as well as a small mode volume. The device has an approximately half-wavelength thick low-index spacer [400] sandwiched between two quarter wave stacks [410, 420]. The low-index spacer has a high-index subspacer layer [470] positioned at its center. The subspacer layer has a thickness smaller than a quarter wavelength. As a result, the electric field intensity remains a maximum at the center of the spacer where the high-index subspacer is positioned. A quantum dot or other active region [480] may be embedded within the subspacer [470]. The microcavity devices provide, for example, single photon sources, single dot lasers, low-threshold quantum dot or quantum well lasers, or devices for strong coupling between a single quantum dot and the cavity field which can be used as components of photonic integrated circuits, quantum computers, quantum networks, or quantum cryptographic systems.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
On-chip integrated cascade amplification semiconductor laser
ActiveCN109873295ARealize disseminationAchieving single-stage amplificationOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsGratingLuminous flux
The invention discloses an on-chip integrated cascade amplification semiconductor laser. The on-chip integrated cascade amplification semiconductor laser comprises a ridge type area, an on-chip DBR grating structure, a tapered type area and an epitaxial waveguide; the DBR grating structure is arranged on the ridge type area, the ridge type area is a ridge type waveguide structure, the tapered typearea is a gain waveguide structure; the epitaxial waveguide has a first-order ladder thickness; the ridge type area is arranged at a thin side of the epitaxial waveguide, the tapered type area is arranged at a thick side of the epitaxial waveguide, and the ridge type area and the tapered type area are cascaded. The laser of the design can more sufficiently utilize the tapered type area gain in comparison with a laser amplification way of traditionally utilizing the tapered gain structure; the base model feature is maintained when the mode volume is extended based on the iso-luminous flux principle, the optical quality of the near diffraction limit laser is guaranteed, and the brightness is greatly improved.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED ELECTRONICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Fabrication method for electro-optical tuning whispering gallery mode microcavity of integrated electrode
InactiveCN106374335AHigh Q valueIncrease the refractive index ratioLaser optical resonator constructionChemical platingWhispering gallery
A method for fabricating an electro-optical tuning whispering gallery mode microcavity of an integrated electrode by a femtosecond laser microprocessing technology comprises the steps of helping to induce electrode chemical plating by a femtosecond laser, etching a microcavity structure by the femtosecond laser, grinding focused ion beam and performing chemical corrosion. In the three-dimensional whispering gallery mode optical microcavity fabricated according to the method, continuous total internal reflection of light is achieved by the ratio between refractive indexes of a cavity and an external environment, the three-dimensional whispering gallery mode optical microcavity has extremely high surface smoothness, and a small mode size and a high quality factor (larger than 10<5>) are supported; and meanwhile, accurate control on an electric field around the microcavity can be achieved by a transversely-integrated electrode, continuous adjustment of the refractive indexes is achieved by an electro-optical effect of a cavity material, and the purpose of mode cavity tuning in a whispering gallery mode is further achieved. The method is applicable to various dielectric thin film materials with electro-optical effects.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method for three-dimensional crystal optics echo wall micro-cavity
ActiveCN103738915AIncrease varietyIncrease roughnessMicrostructural devicesLaser beam welding apparatusSurface finishTotal internal reflection
The invention provides a preparation method for a three-dimensional crystal optics echo wall micro-cavity. The preparation method comprises the steps: carrying out femtosecond laser selective ablation on crystals soaked in liquid and grinding the lateral wall of the micro-cavity by using a focused ion beam. The three-dimensional crystal optics echo wall micro-cavity prepared by adopting the method provided by the invention can be used for limiting light through continuous total internal reflection of the cavity and an outside face, and has the advantages of extremely high surface smoothness, small mode volume and high quality factor. The preparation method is applicable to various crystal materials, glass and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Confocal and Concave 1D Photonic Crystal Resonant Cavities with Ultra-low Mode Volume
A 1D nanobeam photonic crystal cavity is provided that includes a substrate, where the substrate includes a dielectric medium, and a series of cutout features in the substrate, where each cutout feature includes a first curved surface and a second curved surface, where the first curved surface and the second curved surface form a meniscus shape, where the series of cutout features include an array of sizes of the meniscus shape cutouts, where edges of the meniscus shape and the array of sizes are disposed to form a pair of opposing parabolic dips proximal to a central region of the series of cutout features.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com