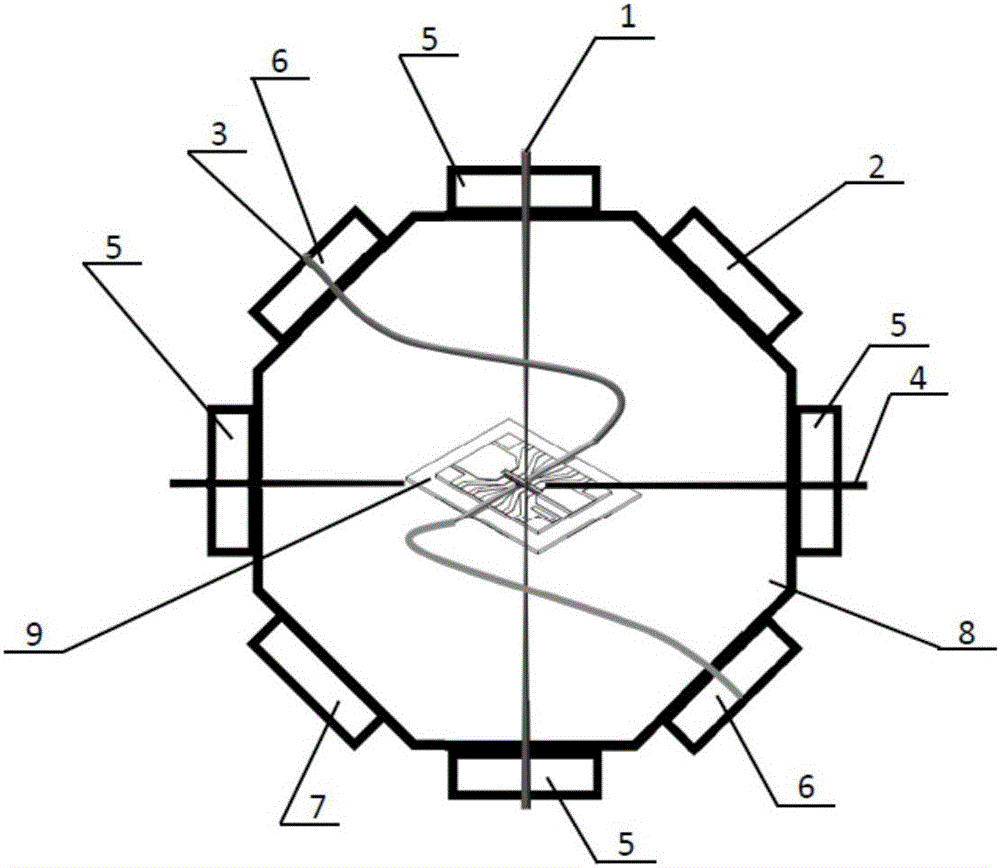
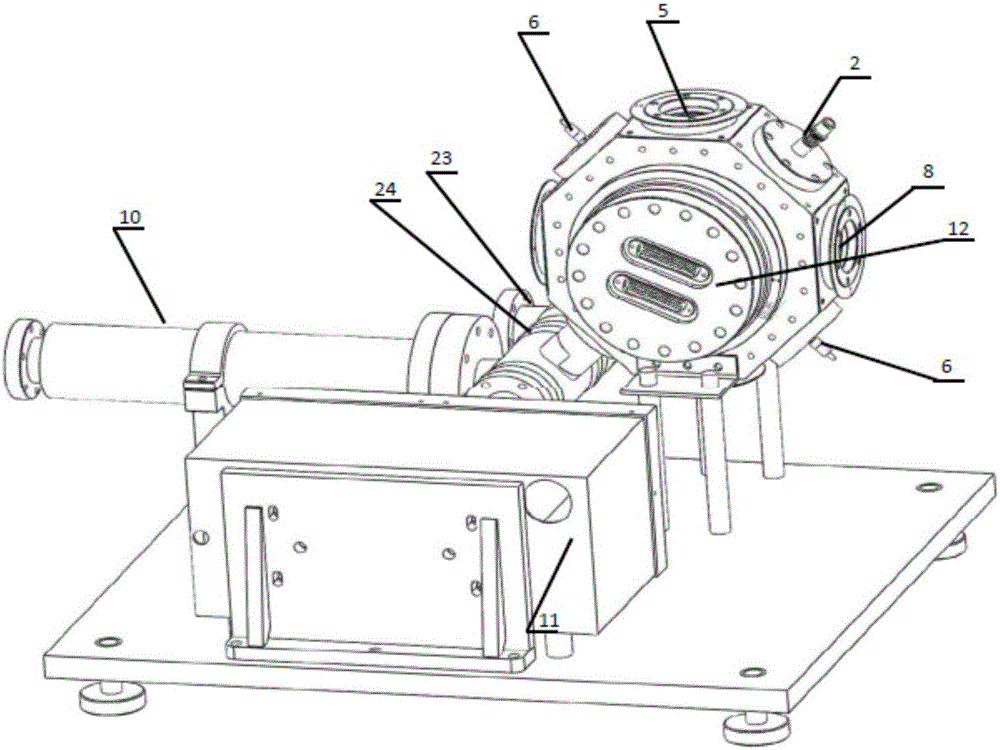
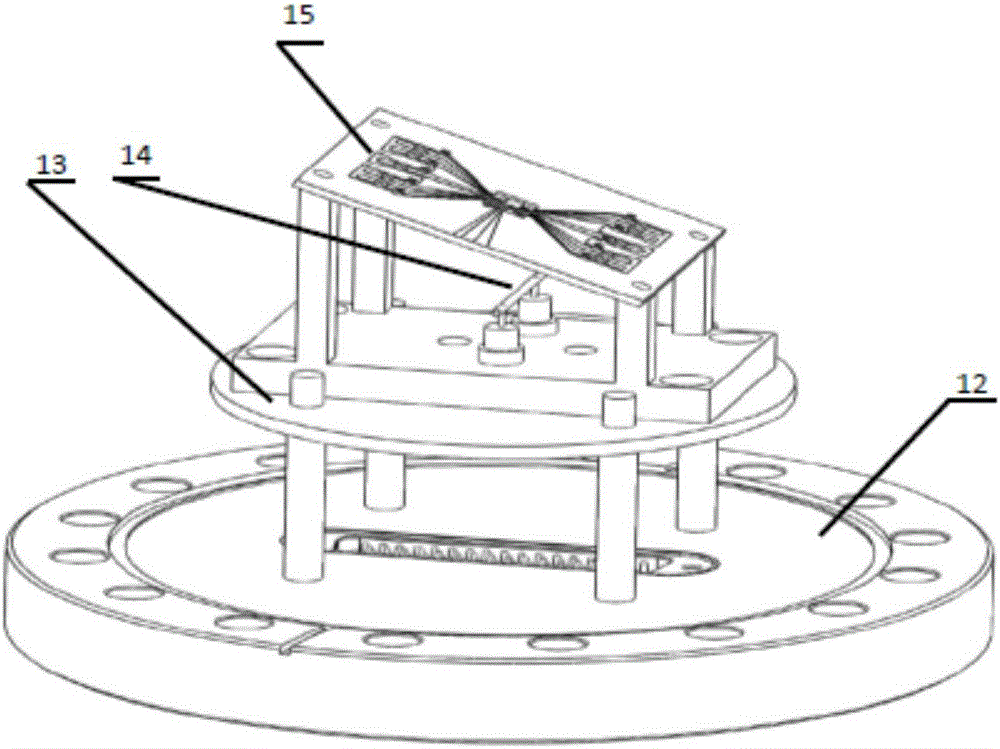
Patents
Literature
250 results about "Optical microcavity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An optical microcavity or microresonator is a structure formed by reflecting faces on the two sides of a spacer layer or optical medium, or by wrapping a waveguide in a circular fashion to form a ring. The former type is a standing wave cavity, and the latter is a traveling wave cavity. The name microcavity stems from the fact that it is often only a few micrometers thick, the spacer layer sometimes even in the nanometer range. As with common lasers this forms an optical cavity or optical resonator, allowing a standing wave to form inside the spacer layer, or a traveling wave that goes around in the ring.
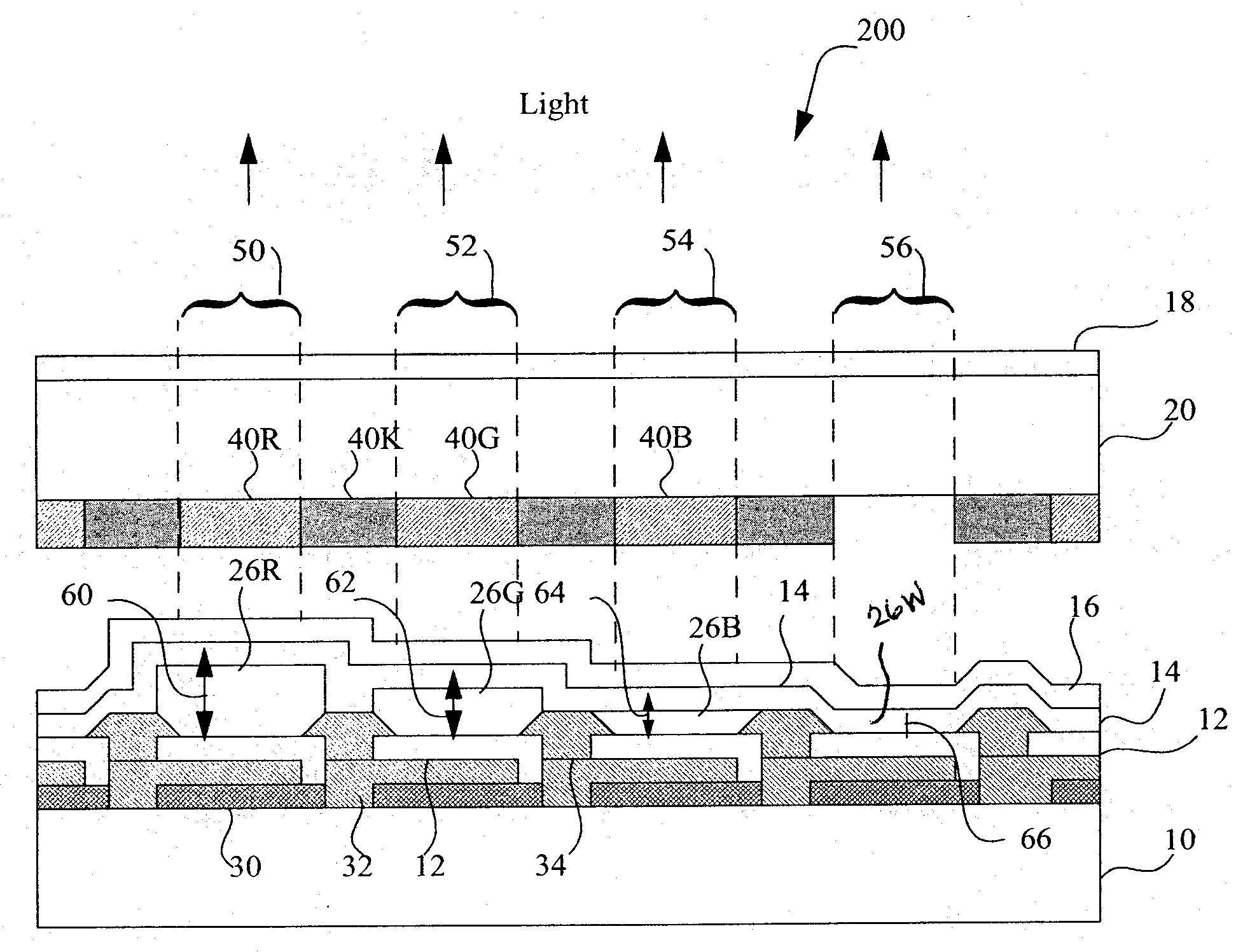
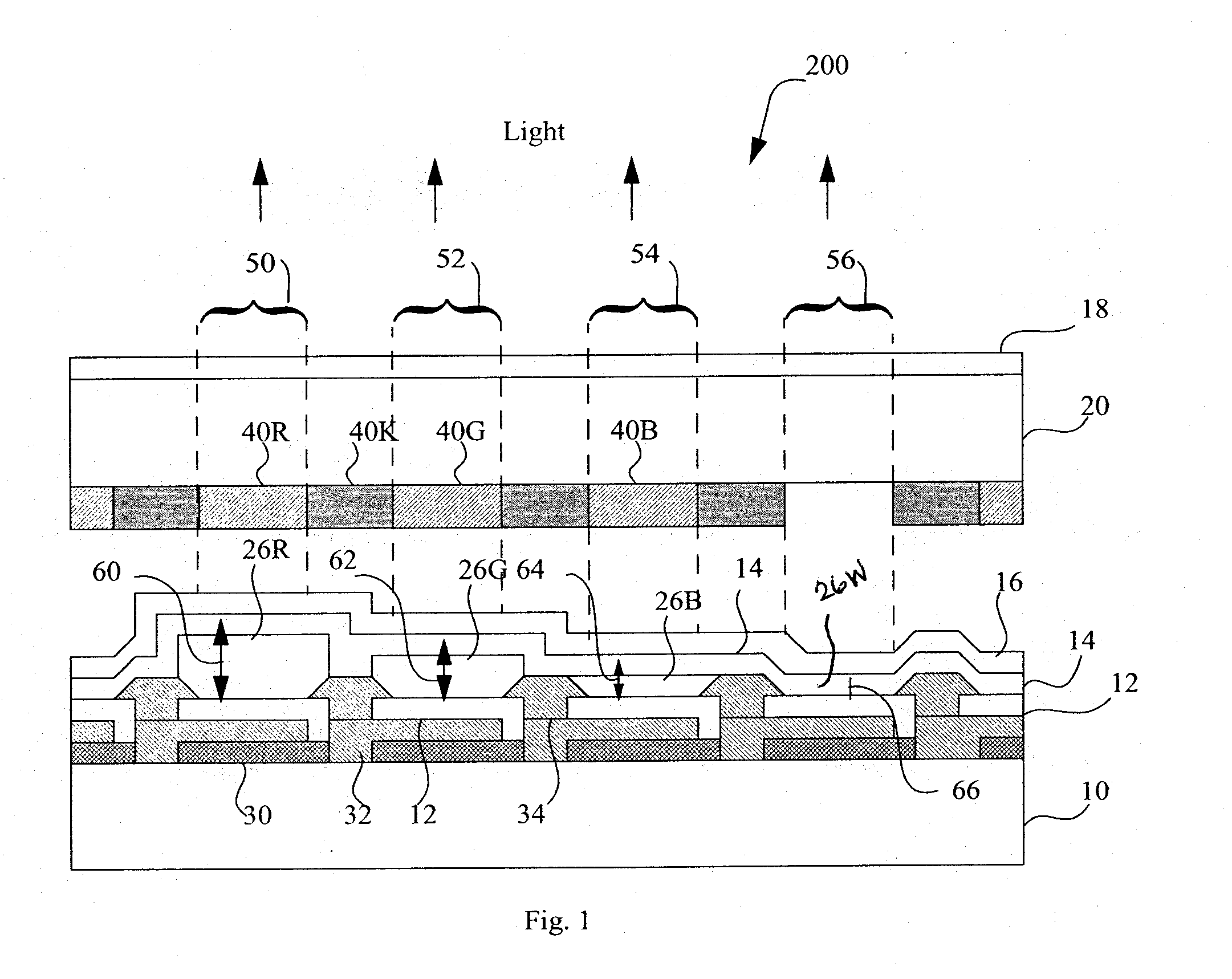
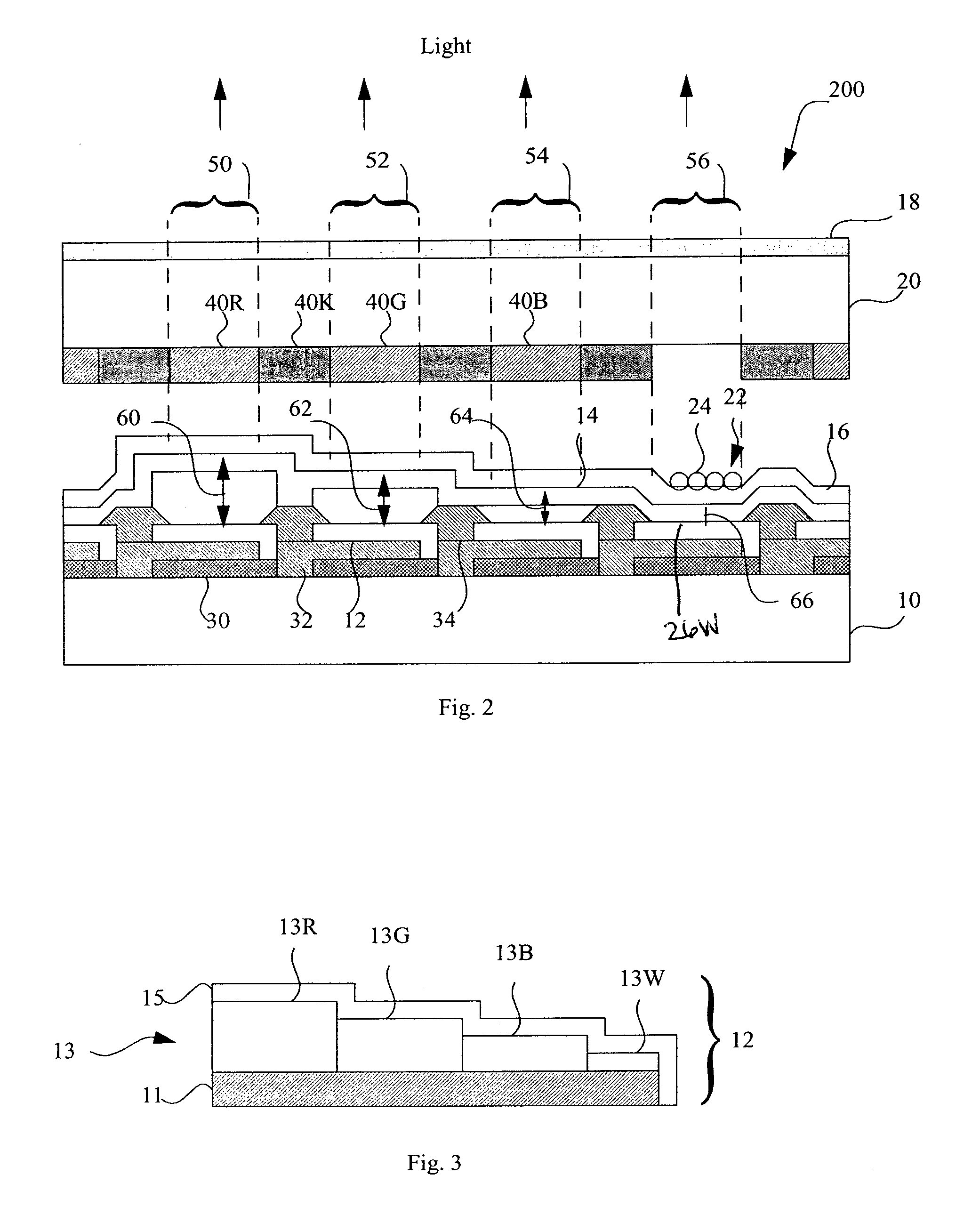
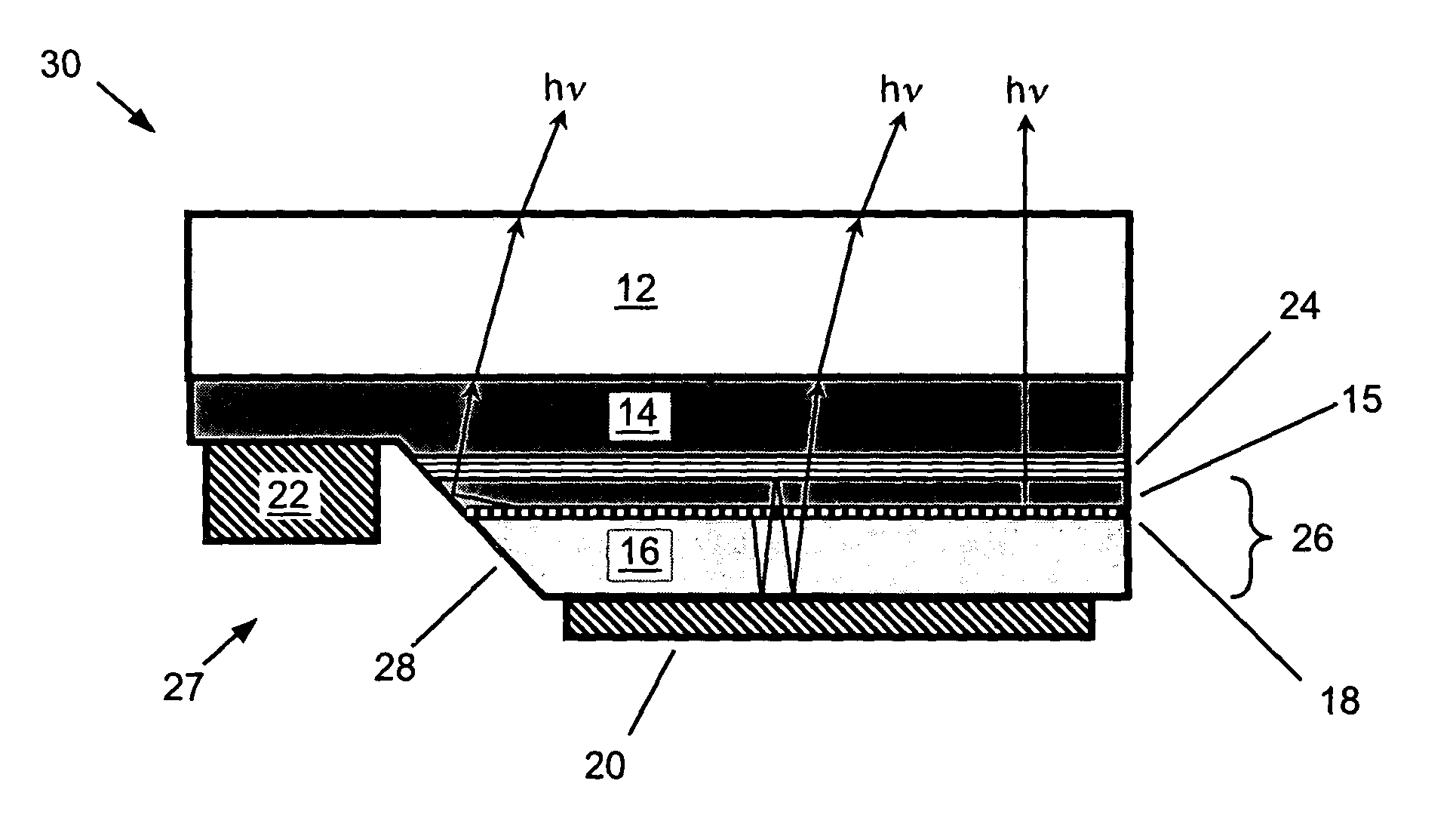
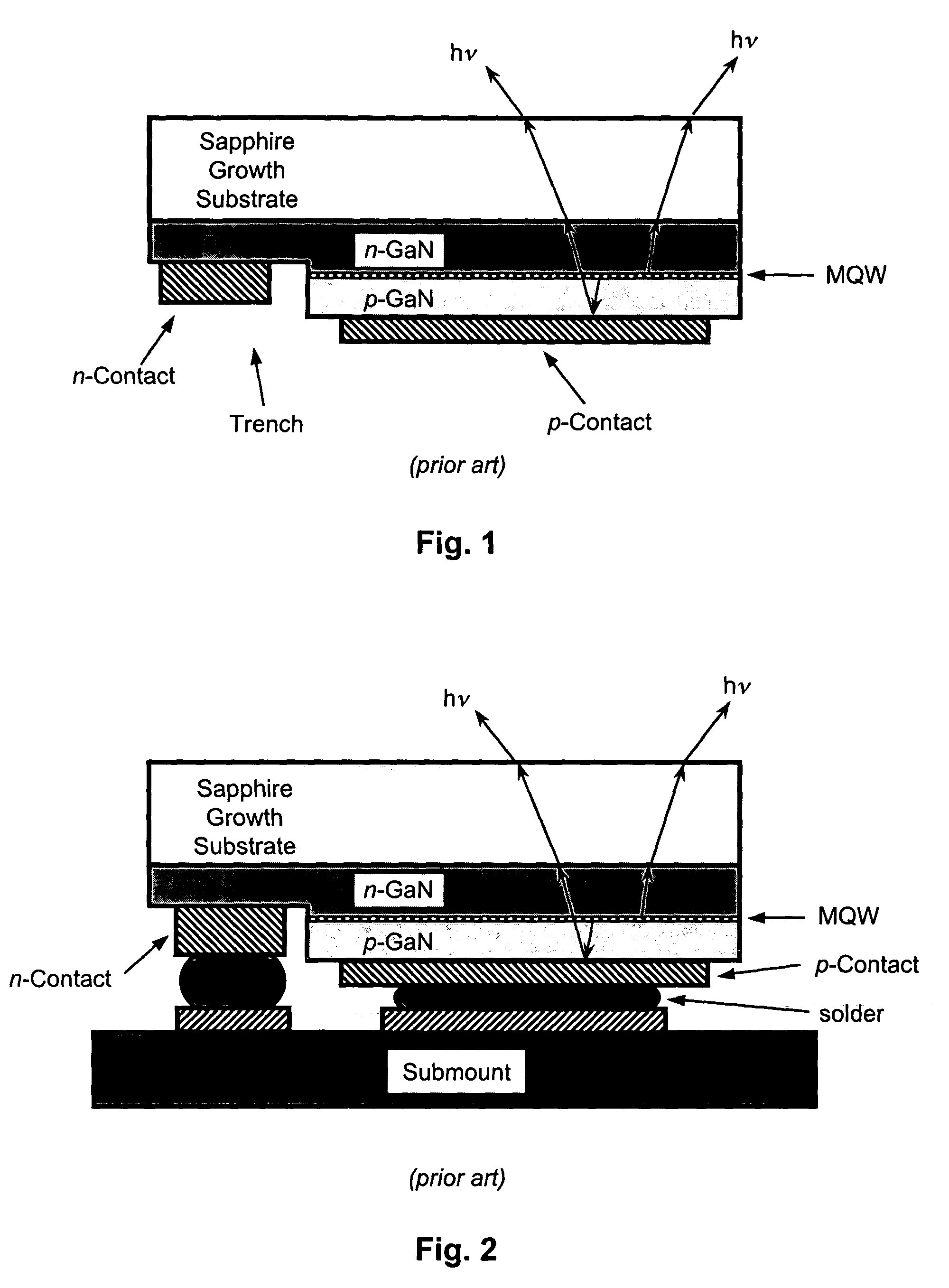
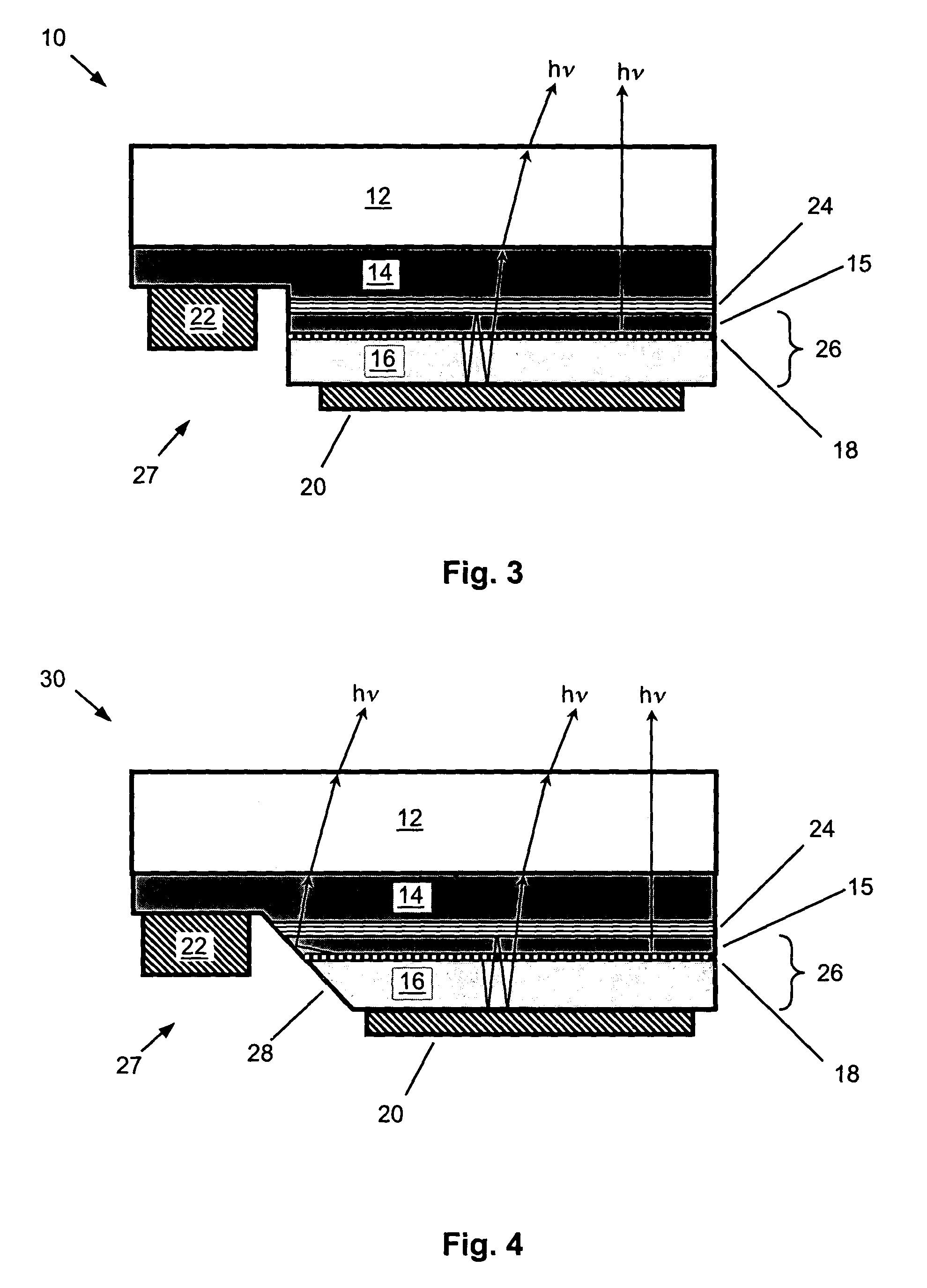
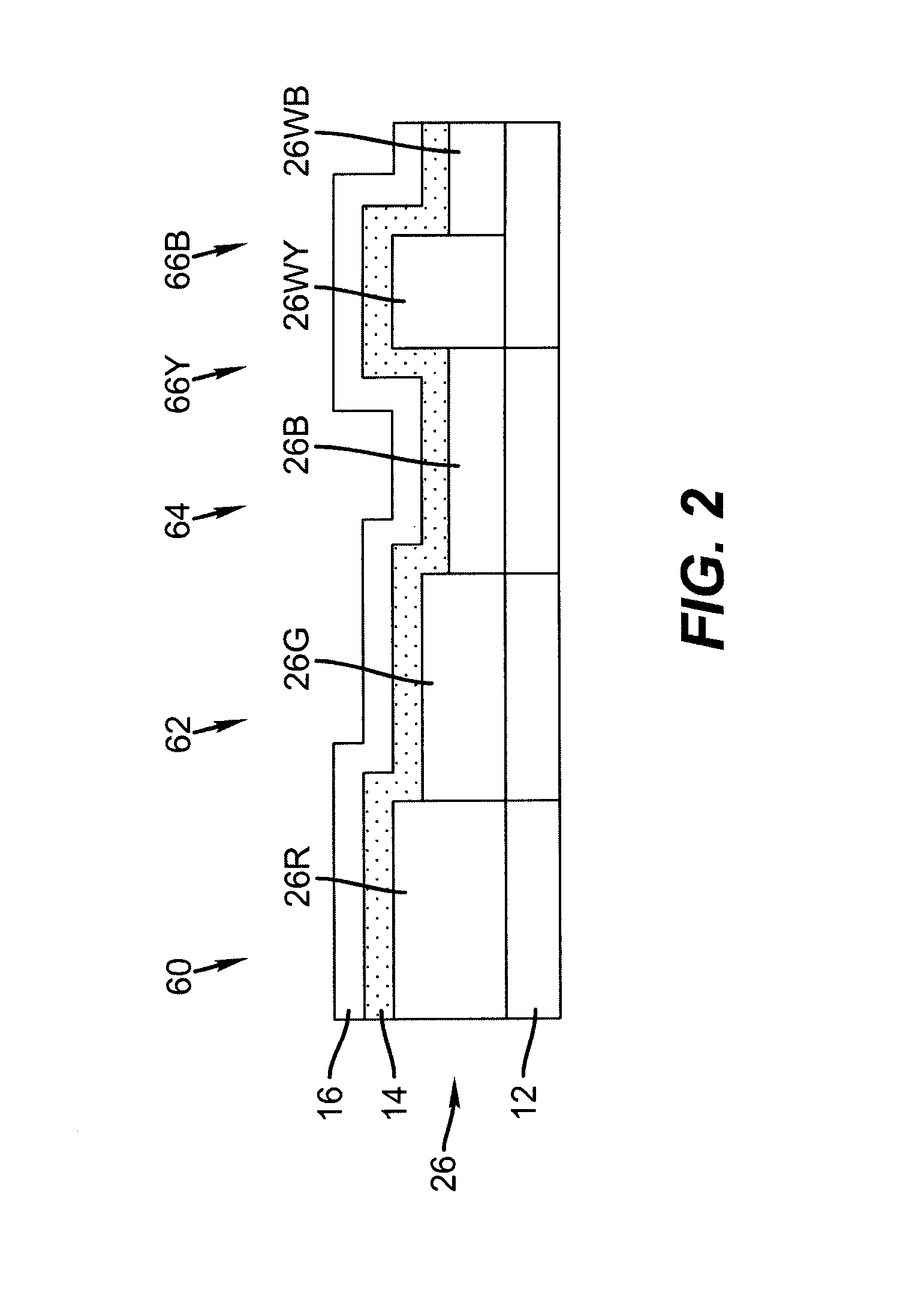
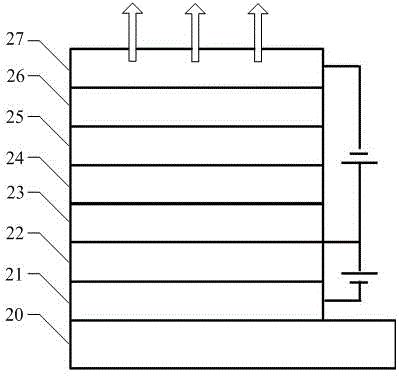
LED device having improved contrast
ActiveUS20090051283A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsLight-emitting diodeOptical microcavity
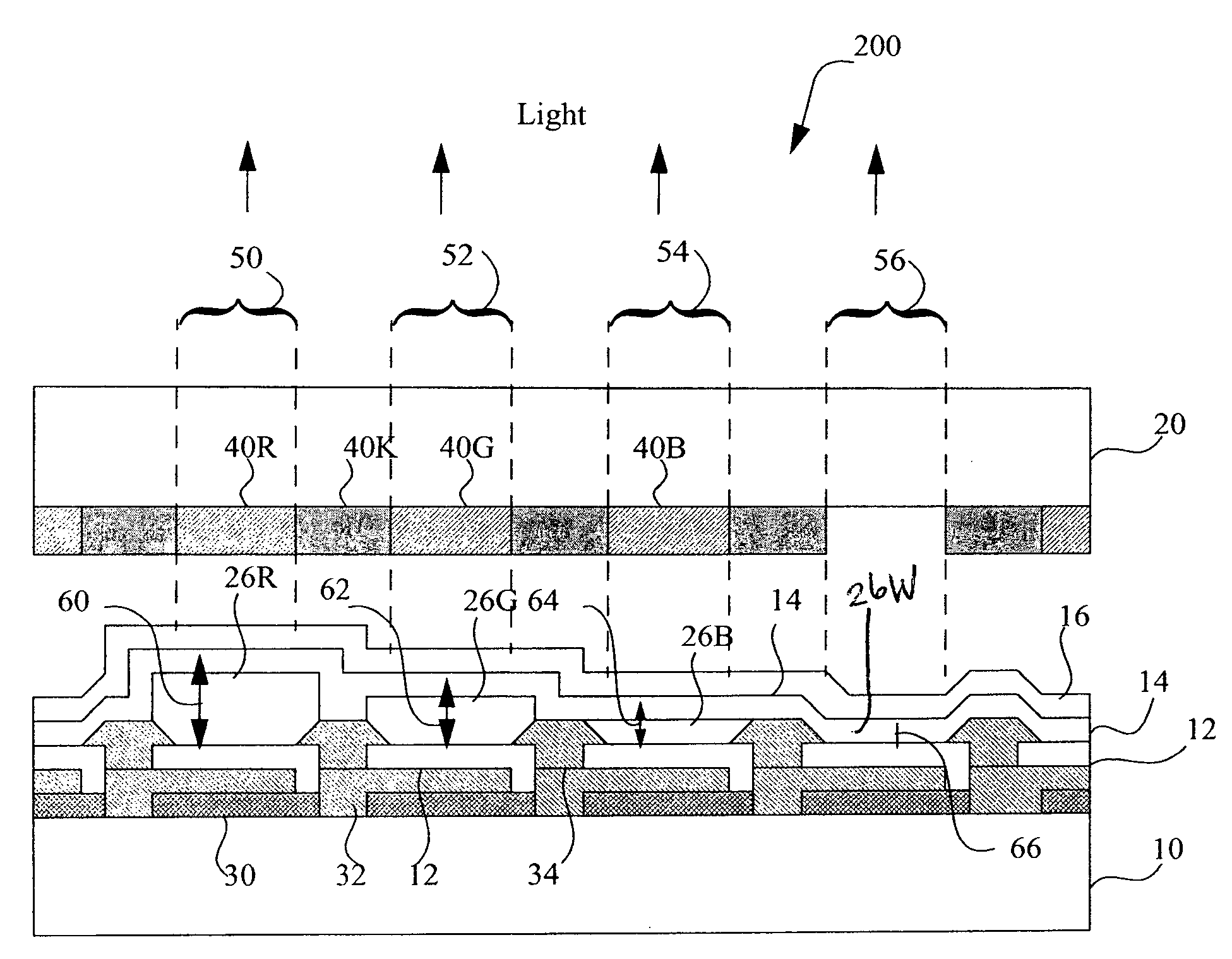
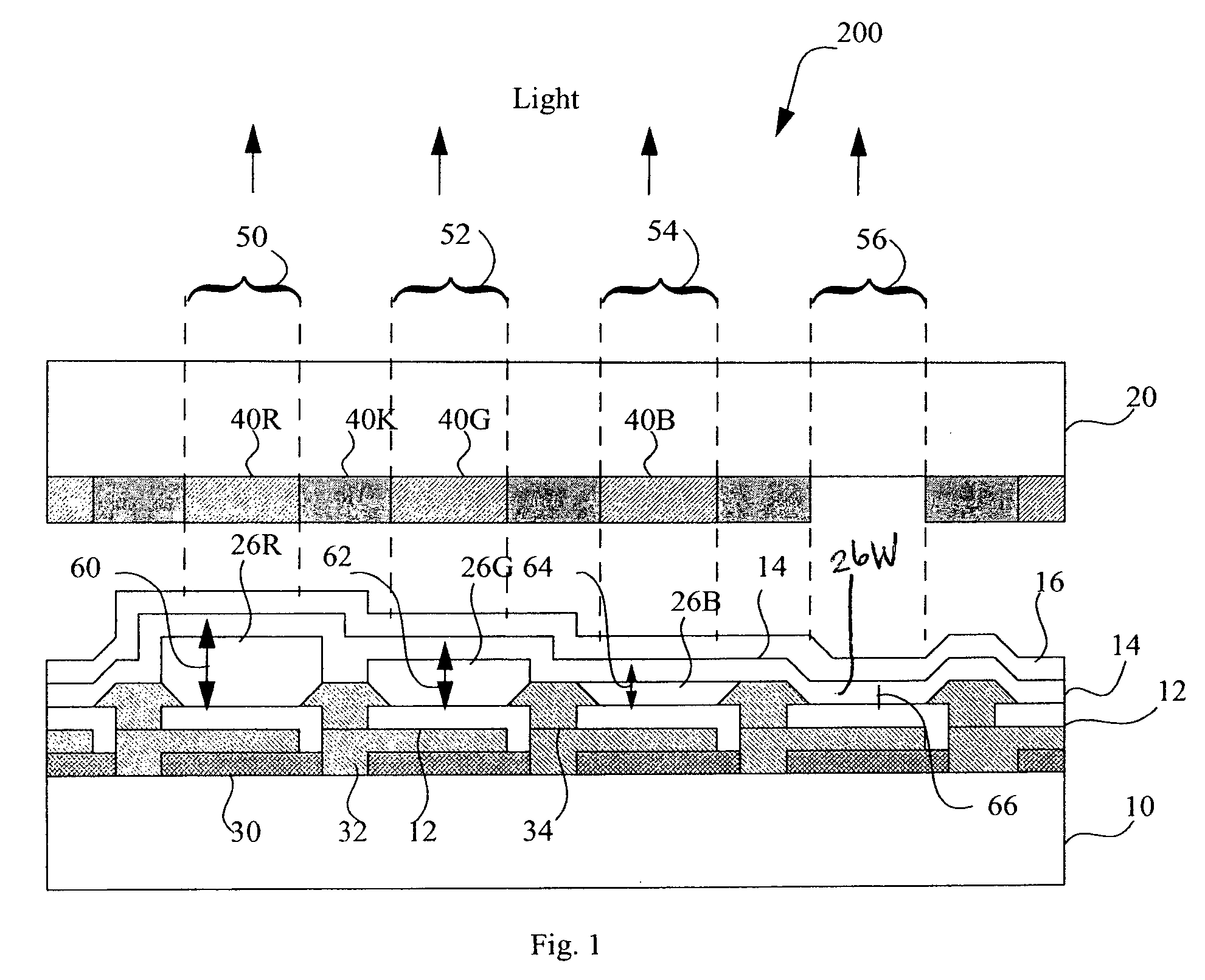
A light-emitting diode device, including a substrate; and a reflective electrode and a semi-transparent electrode formed over the substrate and an unpatterned white light-emitting layer formed between the reflective electrode and the semi-transparent electrode, the reflective electrode, semi-transparent electrode, and unpatterned white-light-emitting layer forming an optical microcavity, and wherein either the reflective or semi-transparent electrodes is patterned to form a plurality of independently controllable light-emitting elements with at least one light-emitting element having no color filter. Color filters are formed over a side of the semi-transparent electrodes opposite the unpatterned white light-emitting layer in correspondence with the light-emitting elements, the color filters having at least two different colors. Additionally, a reflected-light absorbing layer is located over all of the light-emitting elements.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Flip-chip light emitting diode with resonant optical microcavity
InactiveUS6969874B1Improve efficiencyAccelerate emissionsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesDielectric substrateGallium nitride
A flip-chip light emitting diode with enhanced efficiency. The device structure employs a microcavity structure in a flip-chip configuration. The microcavity enhances the light emission in vertical modes, which are readily extracted from the device. Most of the rest of the light is emitted into waveguided lateral modes. Flip-chip configuration is advantageous for light emitting diodes (LEDs) grown on dielectric substrates (e.g., gallium nitride LEDs grown on sapphire substrates) in general due to better thermal dissipation and lower series resistance. Flip-chip configuration is advantageous for microcavity LEDs in particular because (a) one of the reflectors is a high-reflectivity metal ohmic contact that is already part of the flip-chip configuration, and (b) current conduction is only required through a single distributed Bragg reflector. Some of the waveguided lateral modes can also be extracted with angled sidewalls used for the interdigitated contacts in the flip-chip configuration.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
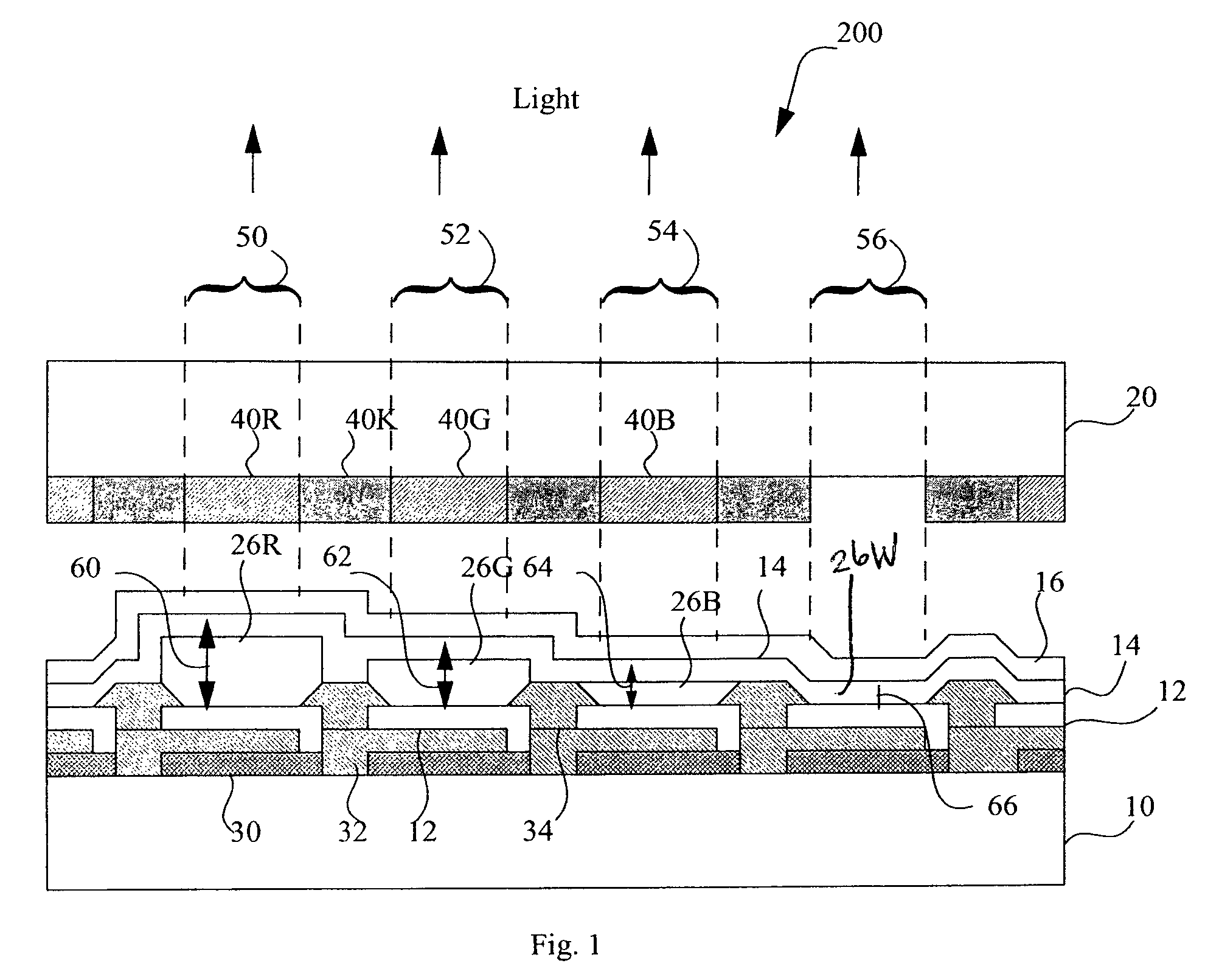
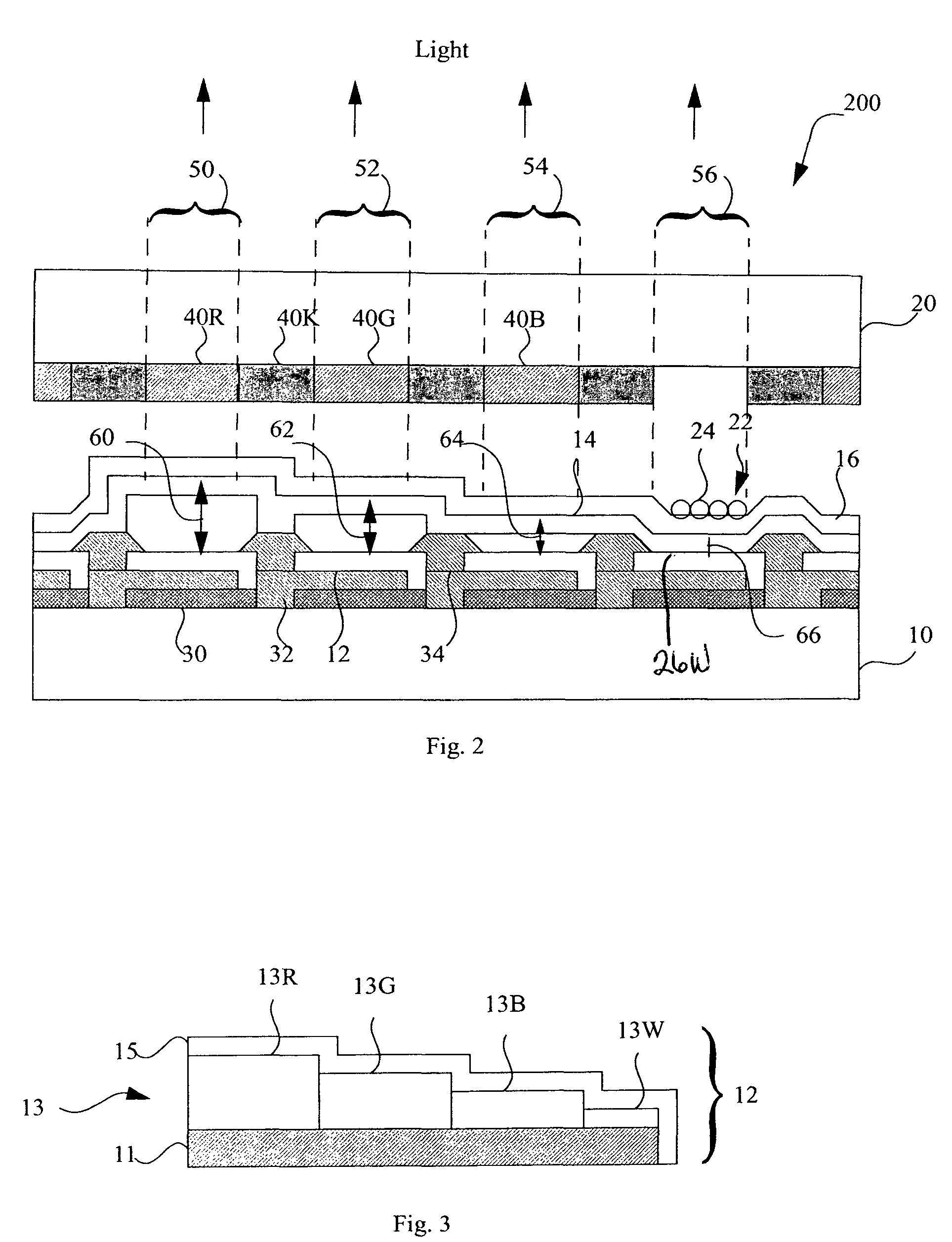
LED device having improved light output
ActiveUS20090072693A1Improve light outputImprove manufacturabilityIncadescent screens/filtersElectric discharge tubesOptical cavityLength wave
A white light-emitting microcavity light-emitting diode device, comprising:a) A reflective electrode and a semi-transparent electrode formed over a substrate and an unpatterned white-light-emitting layer formed between the reflective electrode and the semi-transparent electrode, the reflective electrode, semi-transparent electrode, and unpatterned white-light-emitting layer forming an optical cavity. Either the reflective or semi-transparent electrode is patterned to form independently-controllable light-emitting sub-pixel elements.b) Color filters are formed over a side of the semi-transparent electrodes opposite the unpatterned white light-emitting-layer in correspondence with the independently-controllable light-emitting elements to form colored sub-pixels. At least one independently-controllable light-emitting element has at least two commonly-controlled portions that together emit substantially white light to form a white sub-pixel.c) The optical cavity of one or more of the commonly-controlled portions of the white sub-pixel comprises optical microcavities tuned to emit light at a different complementary wavelength at an emission angle.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
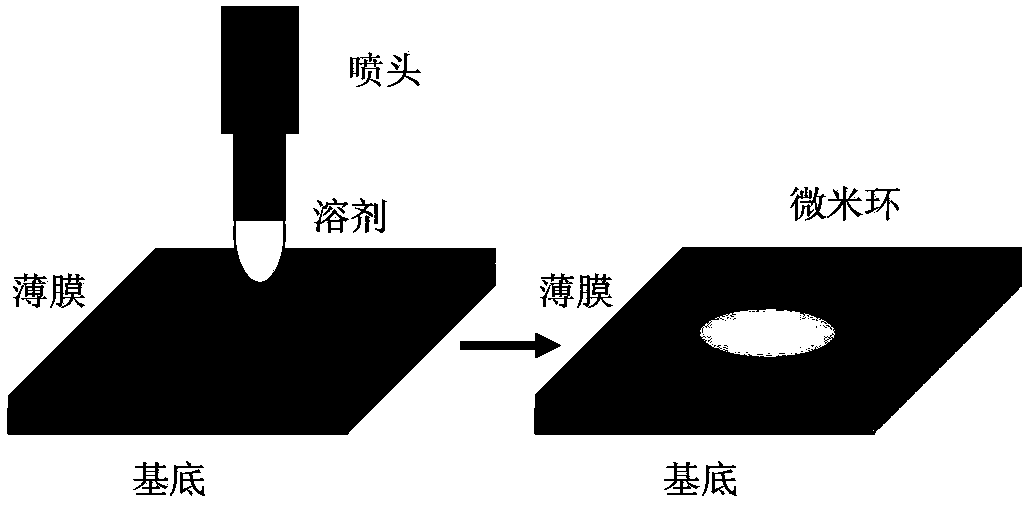
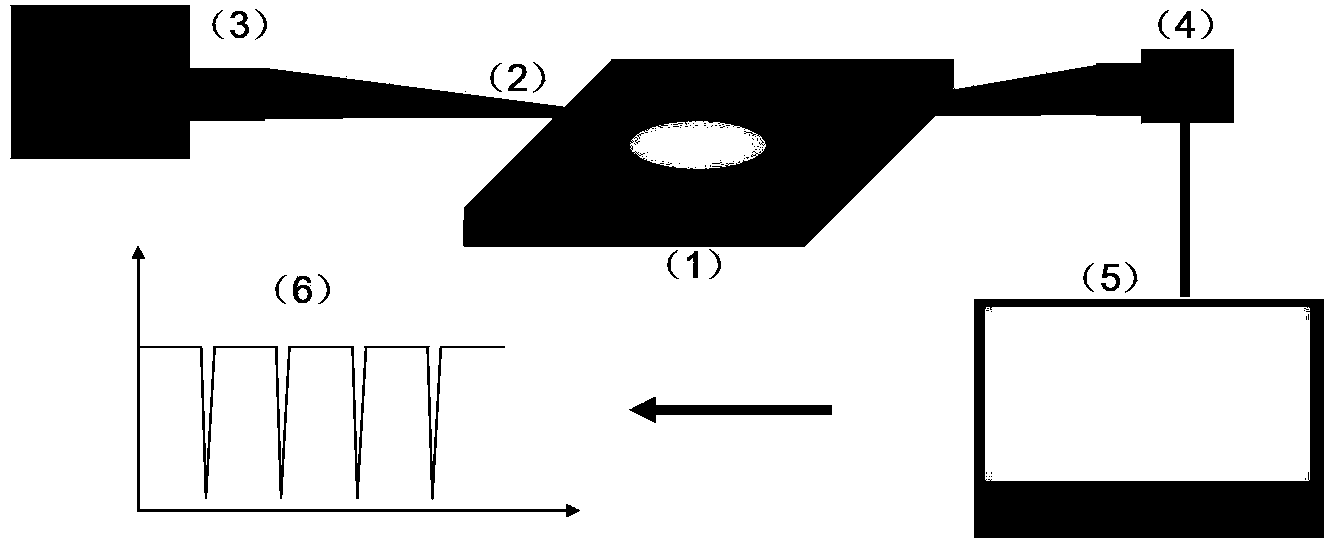
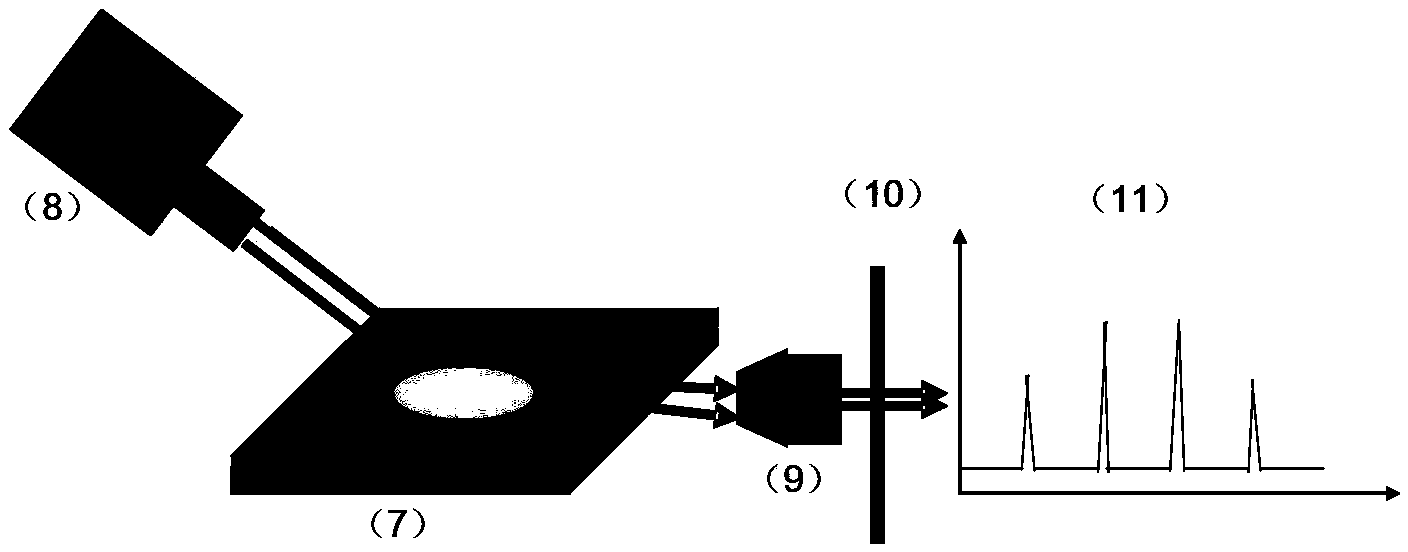
Whispering gallery mode photonic device and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104253372ARealize the coupling effectSolve patterningOptical resonator shape and constructionWhispering galleryArray data structure
The invention provides a whispering gallery mode photonic device and a preparation method thereof. According to the preparation method of a micro ring array structure, solvent droplets are utilized to dissolve a polymer film, so that a "coffee ring effect" can be generated, and therefore, polymer can be accumulated at the periphery of liquid so as to form an annular structure of which the height is obviously different from the height of the film, and conduction and confinement of light in the polymer structure can be realized; and light signals are inputted to the micron ring structure through utilizing excitation, scattering or near field coupling modes, so that a resonance effect in a whispering gallery mode can be realized. The prepared micron ring structure can be adopted as a high-quality factor optical micro cavity, so that a modulation-mode spectrum can be obtained, the width of spectral lines of the spectrum being significantly narrowed; a whispering gallery-mode light amplification stimulated emission can be realized through optical gain; and in a multi-ring coupled array structure, light signal processing and high sensitive response to outside stimuli can be realized according to the wavelength change information of the modulated spectrum and laser modes.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
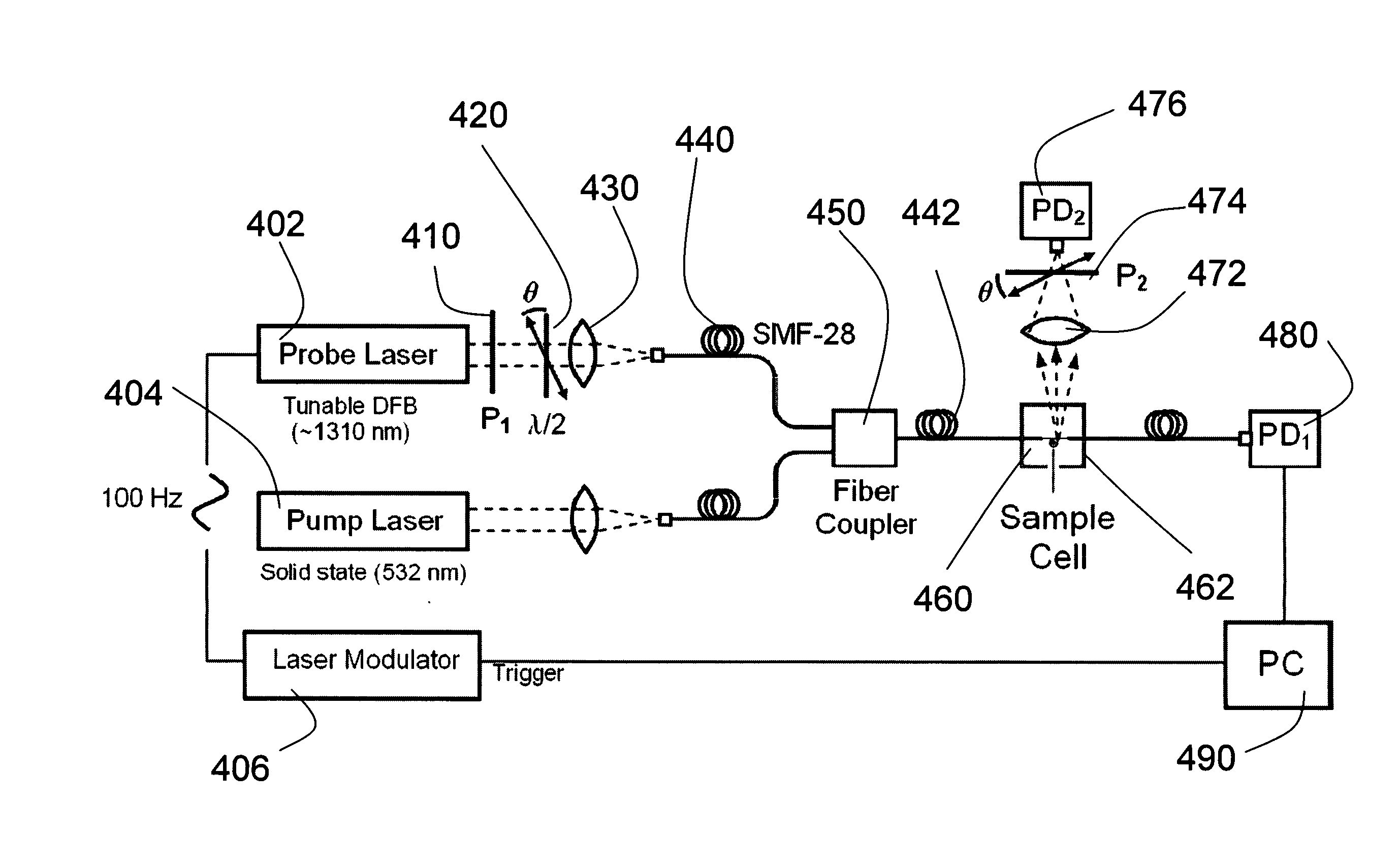
Methods and devices for measurements using pump-probe spectroscopy in high-q microcavities
InactiveUS20090237666A1Improve Sensing PerformanceRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometrySpectroscopyPump probe
The use of optical microcavities, high-Q resonators and slow-light structures as tools for detecting molecules and probing conformations and measuring polarizability and anisotropy of molecules and molecular assemblies using a pump-probe approach is described. Resonances are excited simultaneously or sequentially with pump and probe beams coupled to the same microcavity, so that a pump beam wavelength can be chosen to interact with molecules adsorbed to the microcavity surface, whereas a probe beam wavelength can be chosen to non-invasively measure pump-induced perturbations. The induced perturbations are manifest due to changes of resonance conditions and measured from changes in transfer characteristics or from changes of the scattering spectra of a microcavity-waveguide system. The perturbations induced by the pump beam may be due to polarizability changes, changes in molecular conformation, breakage or formation of chemical bonds, triggering of excited states, and formation of new chemical species. Furthermore, heat may be generated due to absorption of the pump beam. Furthermore, the use resonant modes with different states of polarization allows for measurements of polarizability and its anisotropy in samples interacting with the optical device.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Method, chip, device and system for effecting and monitoring nucleic acid accumulation
InactiveUS6465241B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMonitors radiationWaveguide
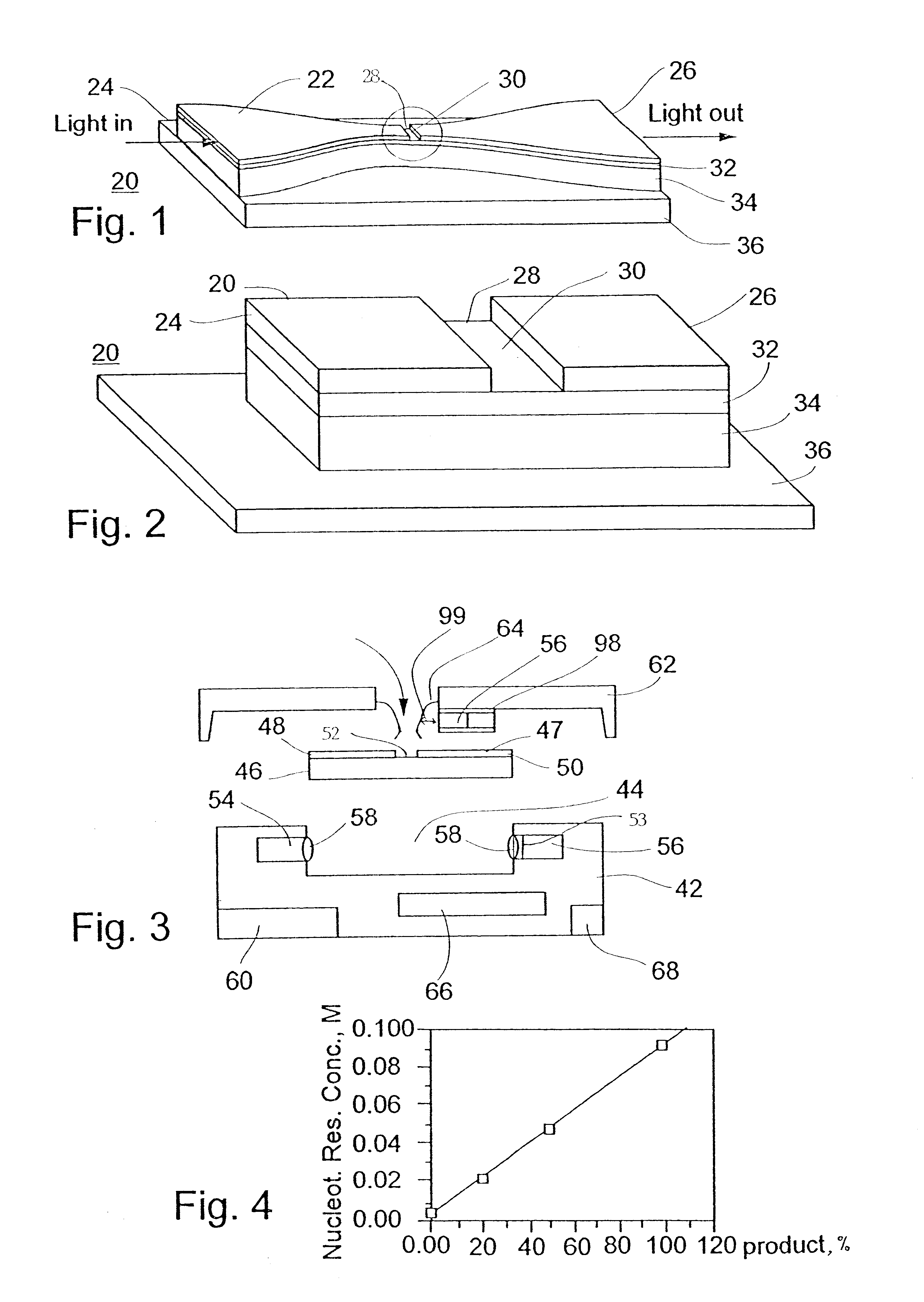
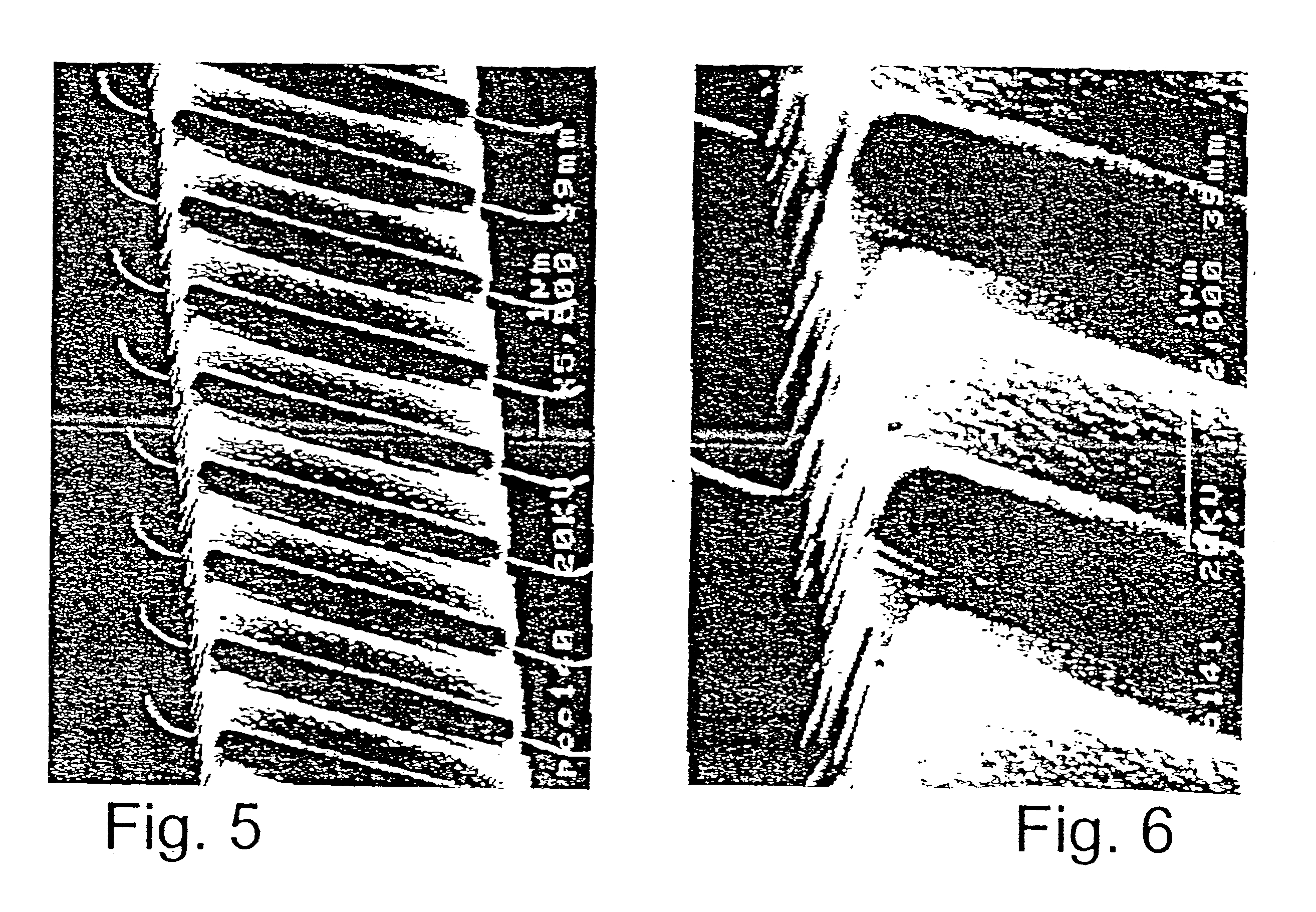
A nucleic acid accumulation analyzing chip comprising an optical waveguide having a radiation input port and a radiation output port, the optical waveguide being formed with at least one optical microcavity along its optical path, at least one oligonucleotide being immobilized to the optical waveguide in the microcavity, such that when the at least one oligonucleotide is contacted with reaction reagents under conditions allowing a nucleic acid accumulation reaction to take place, accumulated nucleic acid is detectable by providing radiation at the radiation input port of the optical waveguide and monitoring radiation signal modulation at the radiation output port of the optical waveguide.
Owner:RAMOT UNIV AUTHORITY FOR APPLIED RES & INDAL DEVMENT
LED device having improved light output
ActiveUS20090051284A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsLight-emitting diodeOptical microcavity
An light-emitting diode device, including a substrate; and a reflective electrode and a semi-transparent electrode formed over the substrate and an unpatterned white light-emitting layer formed between the reflective electrode and the semi-transparent electrode, the reflective electrode, semi-transparent electrode, and unpatterned white-light-emitting layer forming an optical microcavity, and wherein either the reflective or semi-transparent electrodes is patterned to form a plurality of independently controllable light-emitting elements with at least one light-emitting element having no color filter. Color filters are formed over a side of the semi-transparent electrodes opposite the unpatterned white light-emitting layer in correspondence with the light-emitting elements, the color filters having at least two different colors.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
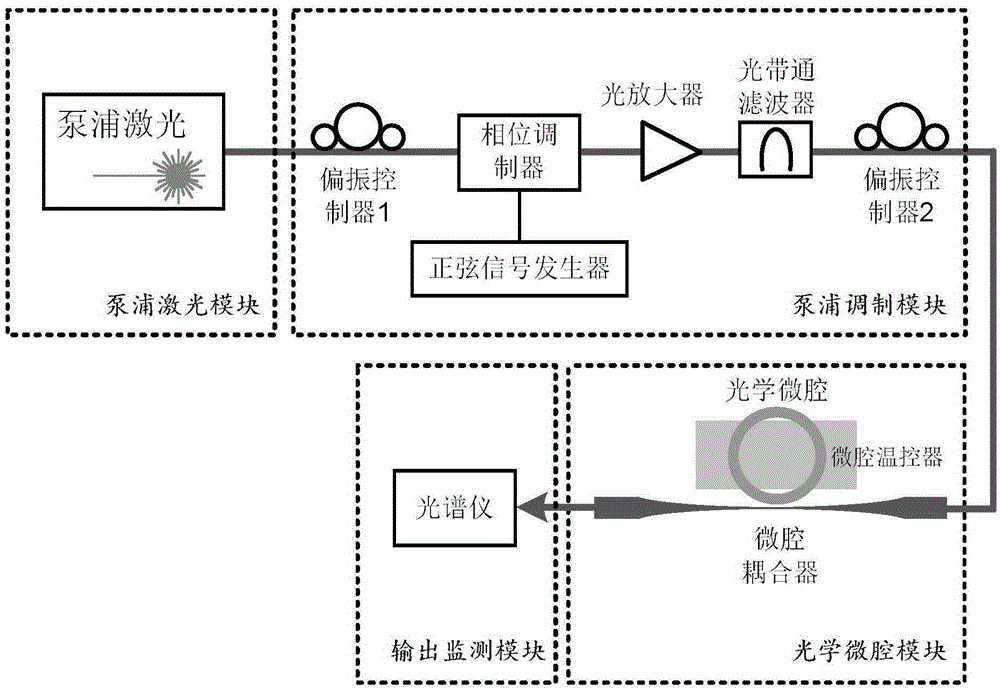
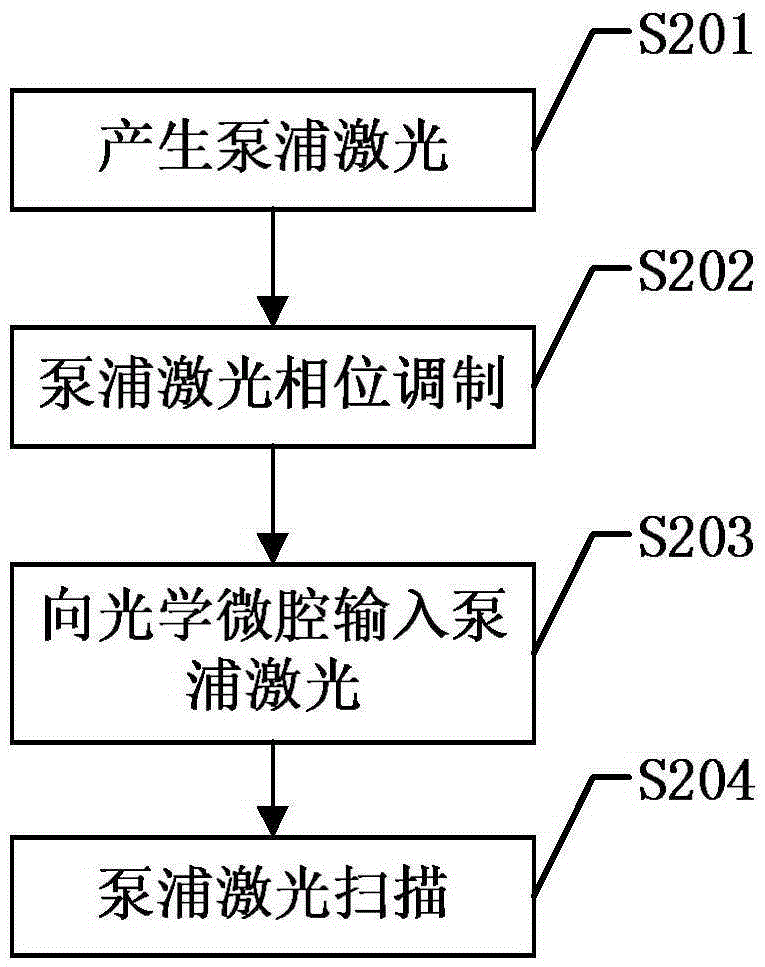
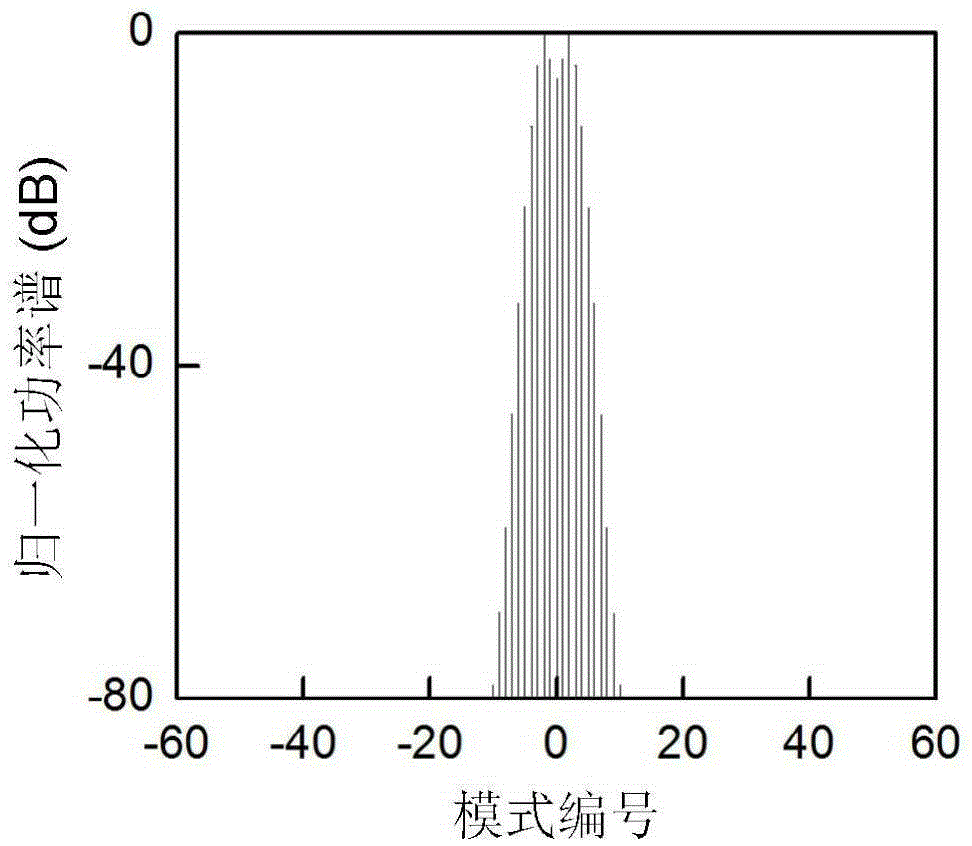
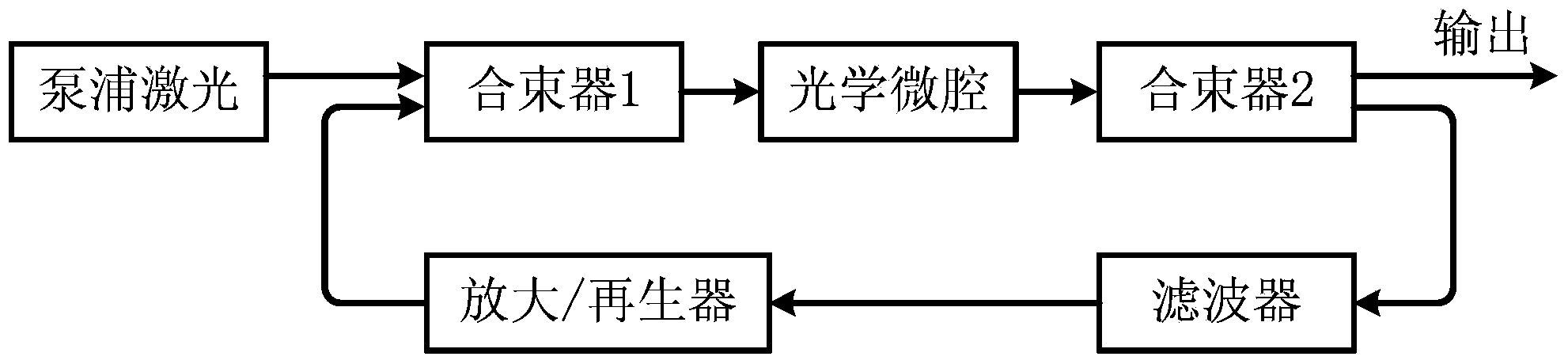
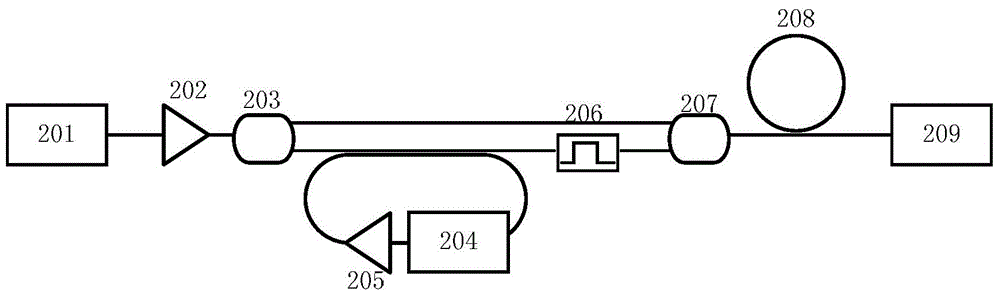
Certainty soliton mode locking method for Kerr optical frequency comb in optical microcavity
The invention discloses a certainty soliton mode locking method for a Kerr optical frequency comb in an optical microcavity. A pump laser power is set to be less than optical microcavity parametric oscillation threshold valve power; the generated pump laser is modulated; the frequency of a modulating signal is accordant with free frequency spectrum width of the optical microcavity; the amplitude of the modulating signal is obtained by calculating three-order dispersion value of the optical microcavity; the pump laser, after being subjected to phase modulation, enters the optical microcavity through a microcavity coupler in a coupling manner; the coupling coefficient is controlled to enable the optical microcavity to work in a critical coupling state; the pump laser is scanned from a long wavelength direction to a short wavelength direction in the optical microcavity; the spectrum of the output pump laser is collected at the output end of the optical microcavity; and in case that the current pump laser spectrum comprises a smooth envelope, the soliton mode locking is finished, and the scanning is stopped. According to the certainty soliton mode locking method for the Kerr optical frequency comb in the optical microcavity, the problems of high randomness, low reliability, high probability of disturbance and the like of the existing Kerr optical frequency comb mode locking scheme are overcame, so that the rapid and accurate soliton mode locking is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
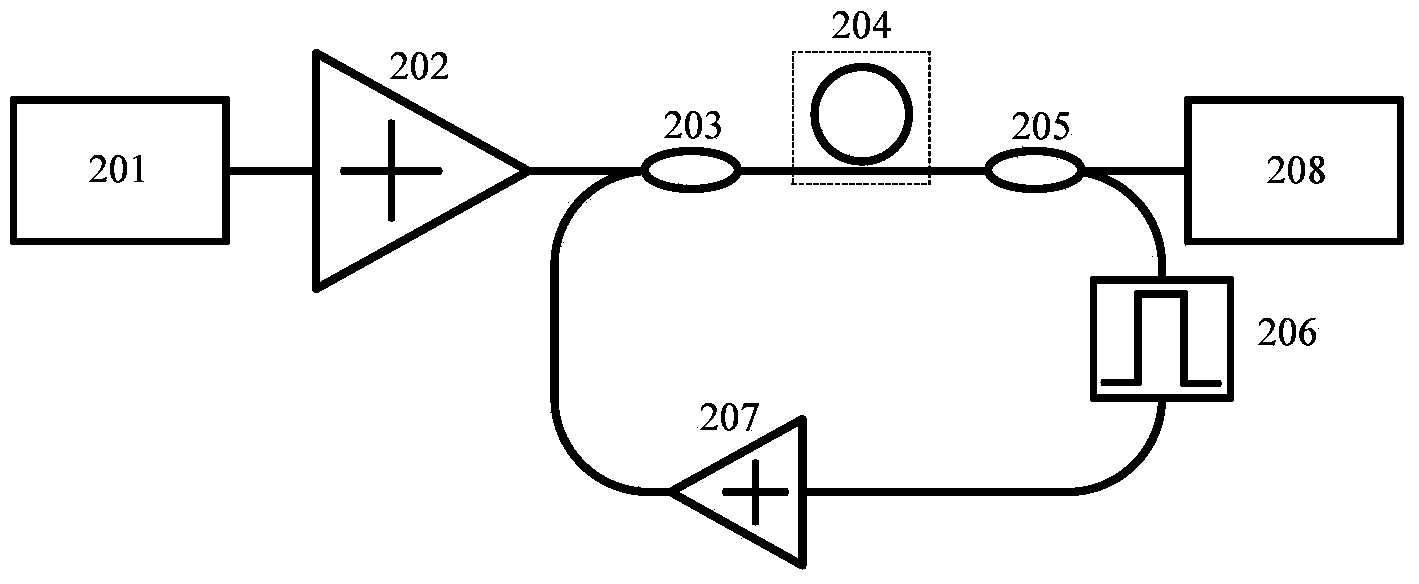
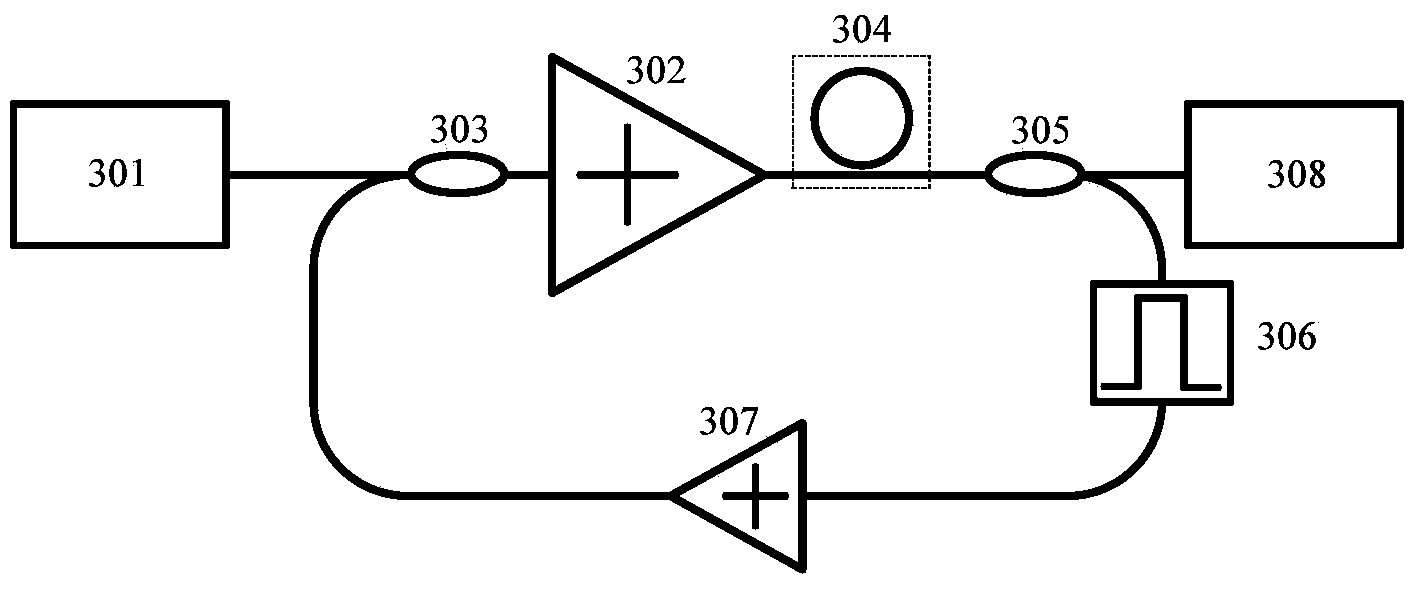
Optical micro-cavity light-frequency comb generating system based on comb tooth feedback control and regulation
InactiveCN103838055AImprove coherenceReduce RF NoiseLaser detailsNon-linear opticsFrequency combOptical field
The invention discloses an optical micro-cavity light-frequency comb generating system based on comb tooth feedback control and regulation, and belongs to the optical field. The system comprises a pumping laser, an optical micro-cavity, a feedback regulation and control loop and the like. After parts of comb teeth in light-frequency comb signals generated in the optical micro-cavity are filtered, amplified or regenerated by the feedback regulation and control loop, the feedback regulation and control loop and the pumping laser stimulate the optical micro-cavity together, and the high performance of an optical micro-cavity light-frequency comb is realized by the formed feedback regulation and control loop. Compared with the existing system for generating a light-frequency comb by using a single pumping layer, the optical micro-cavity light-frequency comb generating system has the advantages that the threshold value generated by the light-frequency comb can be reduced, the coherence is increased, controlled comb tooth gaps are formed, and tolerance on pumping conditions is improved. Moreover, the optical micro-cavity light-frequency comb generating system is simple in structure and high in repeatability; and the performance improvement effect of the system is remarkable.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Meta material- microcavity composite structure and preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN105093777AChange the effective refractive indexNonlinear Refractive Index EnhancementNon-linear opticsInter layerResonance
The invention discloses a meta material-microcavity composite structure and a preparation method and use thereof. The composite structure, from up to down, successively includes: a three-layer composite structure, from up to down, including meta materials, two-dimensional materials and optical microcavities, wherein the upper layer meta materials is provided with a plurality of resonance units arranged periodically. Pump lights incident into the meta materials to cause a change of a nonlinear refractive index of the two-dimensional materials, and a local field enhancement effect of the meta materials stimulated by the pump lights and a local field enhancement effect of the optical microcavities are together to improve the nonlinear refractive index of the two-dimensional materials to allow the effective refractive index around the meta materials to be changed, thereby a transmission state of that lights through composite structure is changed. According to the invention, the nonlinear refractive index of the materials is improved, the response time is reduced, and all-optical adjustability is enhanced. The production process is simple, available materials are wide, and the composite structure of the invention may be used for the all-optical switches or the sensors.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
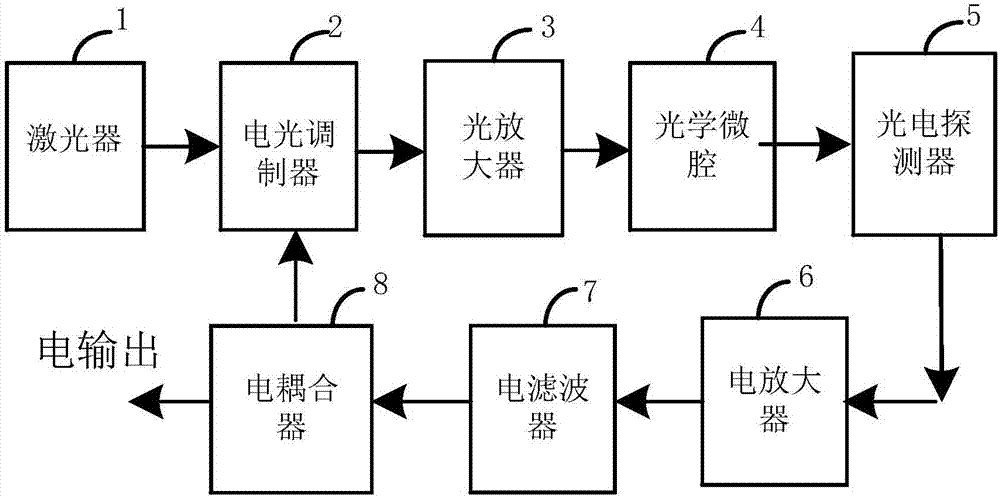
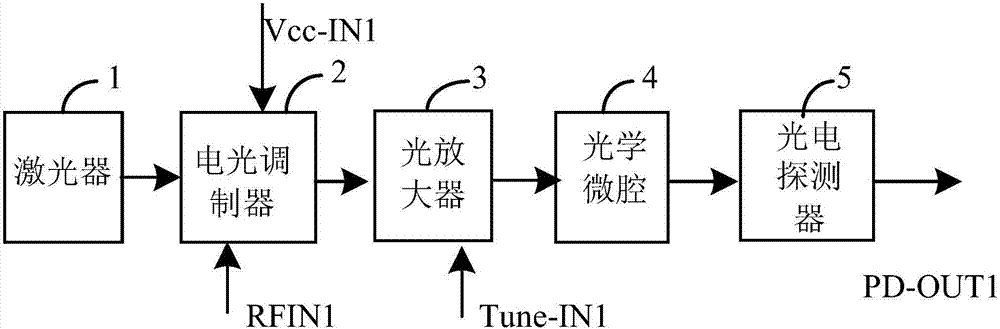
Light and small type ultra-low phase noise photoelectric oscillator and optical micro-cavity manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN106921106AAchieve ultra-low phase noiseRealize light and smallSolid masersPhase noiseOptical microcavity
The invention provides a light and small type ultra-low phase noise photoelectric oscillator and an optical micro-cavity manufacturing method thereof. The oscillator comprises a laser, an electrooptical modulator, an optical micro-cavity, a photoelectric detector, an electric amplifier, an electric filter and an electric coupler. An optical signal output by the laser is subjected to modulation and output by the electrooptical modulator, the optical signal amplification by the optical amplifier, optical delay and optical energy storage by the optical micro-cavity, and the photoelectric conversion by the photoelectric detector. The converted electric signal passes the electric amplifier and the electric filter, and is fed back to the electrooptical modulator through the electric coupler. According to the invention, by use of the photoelectric link de-noising technology, and taking low-loss and high Q value optical micro-cavity as an energy storing element, ultra-low phase noise of the microwave signals output by the photoelectric oscillator is achieved; and by use of the micro type optical micro-cavity, small and light photoelectric oscillator is achieved.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 38 RES INST
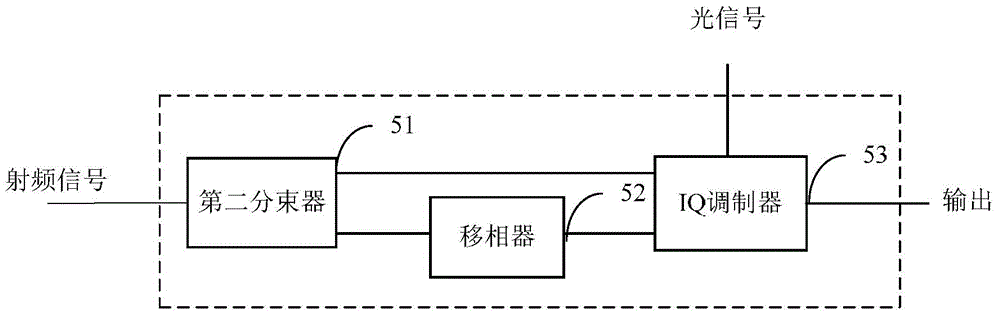
A tunable optical micro-cavity Raman laser and a tunable optical micro-cavity doped laser
InactiveCN104934850ASimple structureReduce volumeLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionWavelength-division multiplexingOptical microcavity
The invention relates to the field of lasers and specifically relates to a tunable optical micro-cavity Raman laser and a tunable optical micro-cavity doped laser. The tunable optical micro-cavity Raman laser comprises a first pump source, an optical micro-cavity, a coupling device and a temperature control apparatus. The first pump source and the optical micro-cavity are connected via the coupling device, and the optical micro-cavity is in a temperature control scope of the temperature control apparatus. The tunable optical micro-cavity doped laser comprises a second pump source generating 980nm or 1480nm pump light, a doped optical micro-cavity, a coupling device, a wavelength division multiplexer and a temperature control apparatus. The second pump source, the doped optical micro-cavity and the wavelength division multiplexer are connected through the coupling device, and the doped optical micro-cavity is in the temperature control scope of the temperature control apparatus. According to the invention, the structure is simple; the size is small; the Q-value is high; and subsequent integration application is provided with convenience. Tuning of wavelengths of emitting laser is realized through controlling of the temperature of the micro-cavity. The tuning mechanism is simple, convenient and efficient.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Perovskite photoelectric detector with optical micro cavity structure and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109841739AAchieving Narrow AbsorptionNarrowed detection half-wave peak widthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHole transport layerMetal electrodes
The invention belongs to the technical field of visible light detection, and specifically discloses a perovskite photoelectric detector with an optical micro cavity structure and a preparation methodthereof. The perovskite photoelectric detector comprises a glass substrate, a transparent conductive electrode layer, a light reflection layer, a hole transport layer, a perovskite sensitive layer, anelectron transport layer, a hole barrier layer and a metal electrode layer arranged in turn from bottom to top. The perovskite sensitive layer comprises multiple materials selected from a typical halogen perovskite material with a chemical formula of ABX<3>, a monovalent cation substituted perovskite material with a chemical formula of A<x><1>A<1-x><2>BM (0<x<1), a halogen substituted solid solution perovskite material with a chemical formula of ABM<x><1>M<3-x><2> (0<x<3), a metal substituted solid solution perovskite material with a chemical formula of AB<x><1>B<1-x><2>M (0<x<1) and a two-dimensional perovskite material. The thickness of the perovskite sensitive layer is 50-5000nm. By arranging the perovskite sensitive layer materials and making the perovskite film thick, a charge narrowing absorption effect is achieved, the detection half-wave peak width of the detector can be narrowed, and the detection performance of the detector can be improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
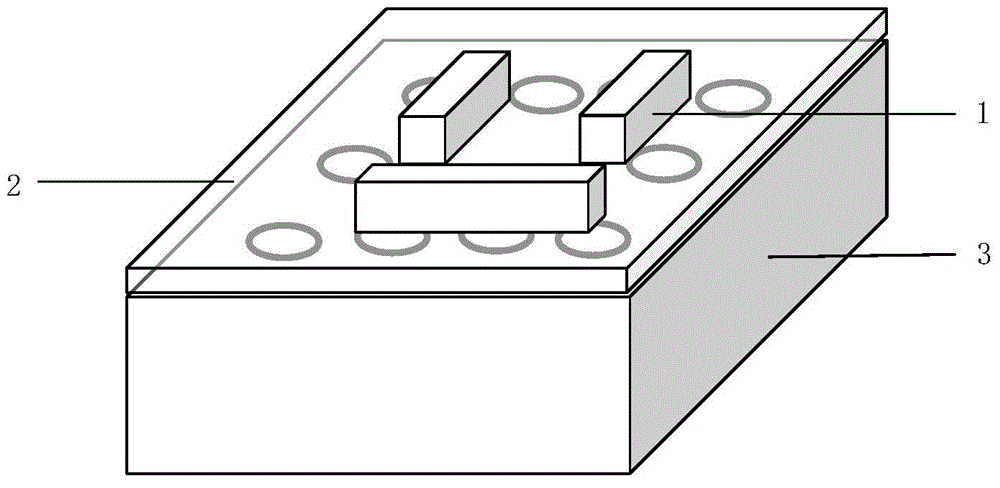
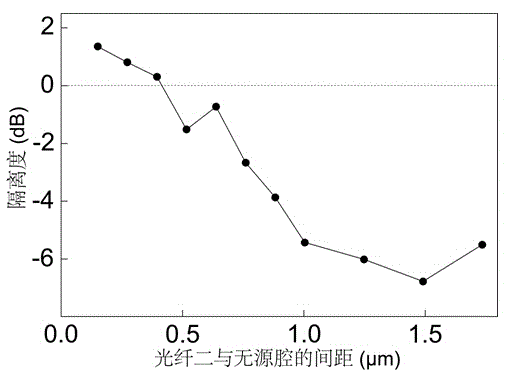
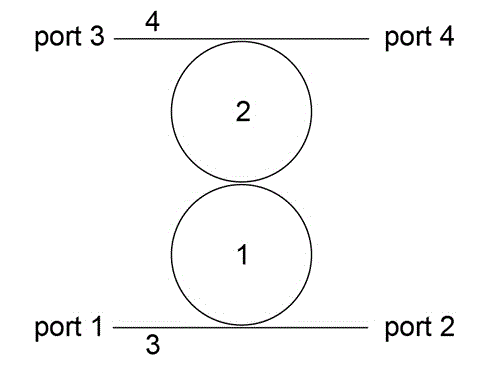
On-chip tunable optical isolator based on active-passive optical micro cavity coupling system
ActiveCN104133270AHigh sensitivityLarge adjustment rangeCoupling light guidesOptical isolatorCoupling system
The invention discloses an on-chip tunable optical isolator based on an active-passive optical micro cavity coupling system. The on-chip tunable optical isolator comprises an active optical micro cavity (1), a passive optical micro cavity (2), a first optical fiber (3) and a second optical fiber (4). The first optical fiber (3) is coupled to the active optical micro cavity (1). The active optical micro cavity (1) is coupled to the passive optical micro cavity (2). The second optical fiber (4) is coupled to the passive optical micro cavity (2). The optical isolator of the invention has the characteristics of high sensitivity, wide tunable range, simple preparation and easy integration.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
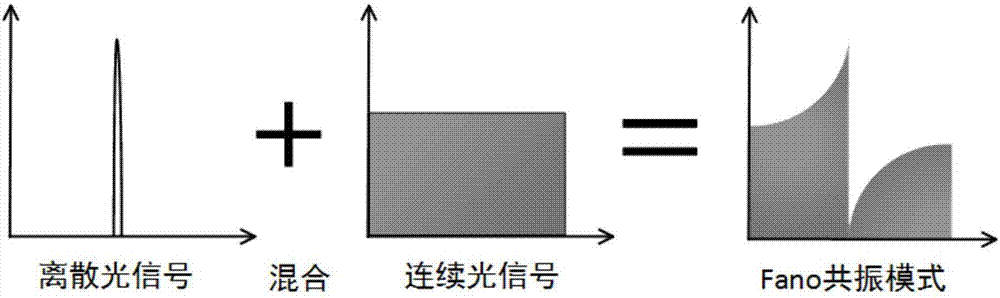
Fano resonance sensing apparatus based on axisymmetric optical micro-cavity, and apparatus thereof
ActiveCN107389610AEasy to makeSimple manufacturing processPhase-affecting property measurementsSemiconductor materialsRefractive index
The invention provides a Fano resonance sensing apparatus based on an axisymmetric optical micro-cavity. The Fano resonance sensing apparatus comprises an axisymmetric optical micro-cavity and a coupled waveguide, wherein the axisymmetric optical micro-cavity has a columnar shape and comprises a straight cylinder type solid cylinder micro-cavity, a straight cylinder type hollow cylinder micro-cavity, a microbubble-like solid cylindrical micro-cavity, a microbubble-like hollow cylindrical micro-cavity, a micro ring cavity, a metal-coated cylindrical micro-cavity and the like, the material of the micro-cavity is silicon dioxide, a macromolecule polymer, an optic crystal, a semiconductor material and the like, and the coupled waveguide is optical fibers with a diameter of 0.5-1.5 [mu]m, a coupled prism having high refractive index, an on-chip integrated waveguide and the like. According to the present invention, the discrete high-order echo wall mode in the micro-cavity and the continuous background light are subjected to offset interference, such that the dynamically-changing Fano resonance spectrum can be stably and effectively produced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Optical microcavity for a high-contrast display
ActiveUS20170293169A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhoton recyclingDisplay device
An optical microcavity for a high-contrast display comprises an enclosed cavity having a front wall and a back wall, where the front wall comprises a pinhole opening for emission of light from the cavity and the back wall is configured to generate or transmit light into the cavity. An outer surface of the front wall absorbs some or substantially all optical wavelengths of externally incident light so as to appear black or colored. An inner surface of the front wall comprises a light reflectivity of greater than 90% to promote photon recycling within the cavity and light emission through the pinhole opening.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Frequency stabilization type photoproduction microwave signal source based on optical microcavity
InactiveCN104466620AImprove frequency stabilityImprove coherenceSolid masersFrequency stabilizationPhase noise
The invention discloses a frequency stabilization type photoproduction microwave signal source based on an optical microcavity, and relates to the field of optical communication devices. The frequency stabilization type photoproduction microwave signal source comprises an optical loop and an optical coupler, wherein the optical loop is mainly composed of the optical microcavity, a band-pass filter, an optical amplifier and an optical coupler. The optical microcavity is used for forming periodic comb filtering with fixed frequency space; the band-pass filter is used for selecting two optical signals with adjacent frequencies from multi-frequency optical signals output from the optical microcavity; the optical amplifier is used for generating optical power gains in the optical loop, achieving hot shooting of the two optical signals with the adjacent frequencies, and forming double-frequency lasers; the optical coupler is used for outputting part of optical power coupling of the double-frequency lasers; a photoelectric detector is used for receiving the double-frequency lasers output by the optical couplers and obtaining photoproduction microwave signals with an optical beat frequency effect. By means of the frequency stabilization type photoproduction microwave signal source, the frequency stability of the microwave signals is improved, and the phase noise of the photoproduction microwave signals is restrained.
Owner:WUHAN POST & TELECOMM RES INST CO LTD
Optical microcavity optical frequency comb generation apparatus and generation method based on injected seed light
ActiveCN104977775ALow toleranceFix stability issuesLaser detailsNon-linear opticsBeam splitterAudio power amplifier
The invention discloses an optical microcavity optical frequency comb generation apparatus and generation method based on injected seed light. The optical microcavity optical frequency comb generation apparatus comprises pumping laser, a first optical amplifier, a first beam splitter, a fiber loop, an optical filter, a binding device and an optical microcaity, wherein an input end of the first amplifier is connected to the pumping laser; an input end of the first beam splitter is connected to an output end of the first optical amplifier; one end of the fiber loop is connected to a second output end of the first beam splitter; an input end of the optical filter is connected to the other end of the fiber loop; a first input end of the binding device is connected to the first output end of the first beam splitter; a second input end of the binding device is connected to an output end of the optical filter; an input end of the optical microcavity is connected to the output end of the binding device; output of the pumping laser is divided into two parts by the first beam splitter after amplification by the first optical amplifier, including pumping light and seed light orderly passing through the fiber loop and the optical filter; and the pumping light and the seed light are injected into the optical microcavity via the binding device, and then optical frequency comb with controllable comb gaps is produced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
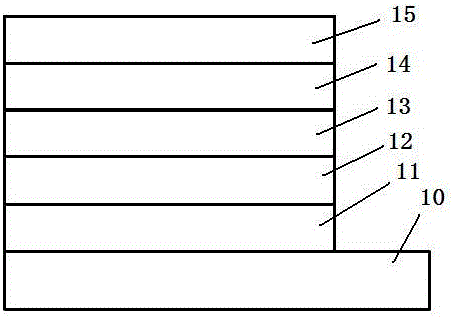
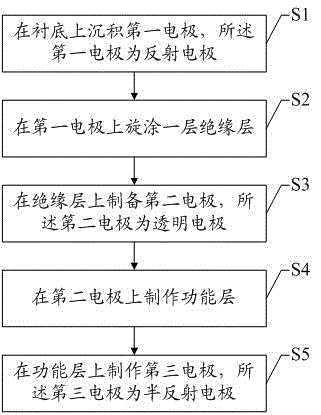
Top emission quantum-dot light-emitting diode (QLED) field-effect transistor with micro-cavity structure and fabrication method of top emission QLED filed-effect transistor
InactiveCN106654031AStructural Improvement and OptimizationHigh selectivitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInsulation layerQuantum dot
The invention discloses a top emission quantum-dot light-emitting diode (QLED) field-effect transistor with micro-cavity structure and a fabrication method of the top emission QLED filed-effect transistor. The top emission QLED field-effect transistor comprises a substrate, a first electrode, an insulation layer, a second electrode, a functional layer and a third electrode, wherein the first electrode is a reflection electrode, the second electrode is a transparent electrode, and the third electrode is a half-reflection electrode. Structure improvement and optimization are performed on the electrodes of top emission QLED field-effect transistor, an optical micro-cavity is formed in the device; and by means of an interference effect, light selection is achieved, the monochromaticity of emergent light wavelength corresponding to the cavity length of the optical micro-cavity and the luminous efficiency of a vertical direction are improved.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
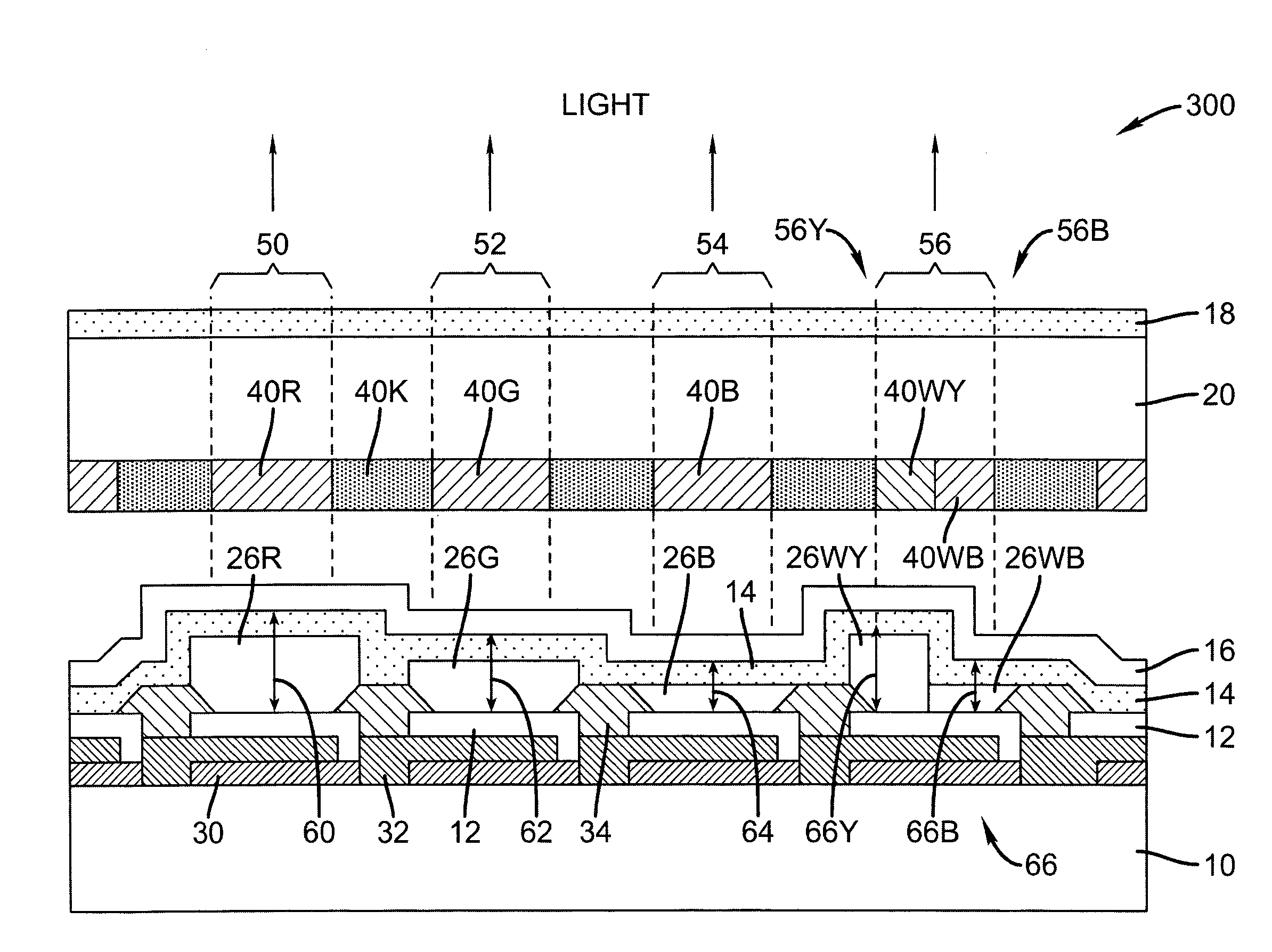
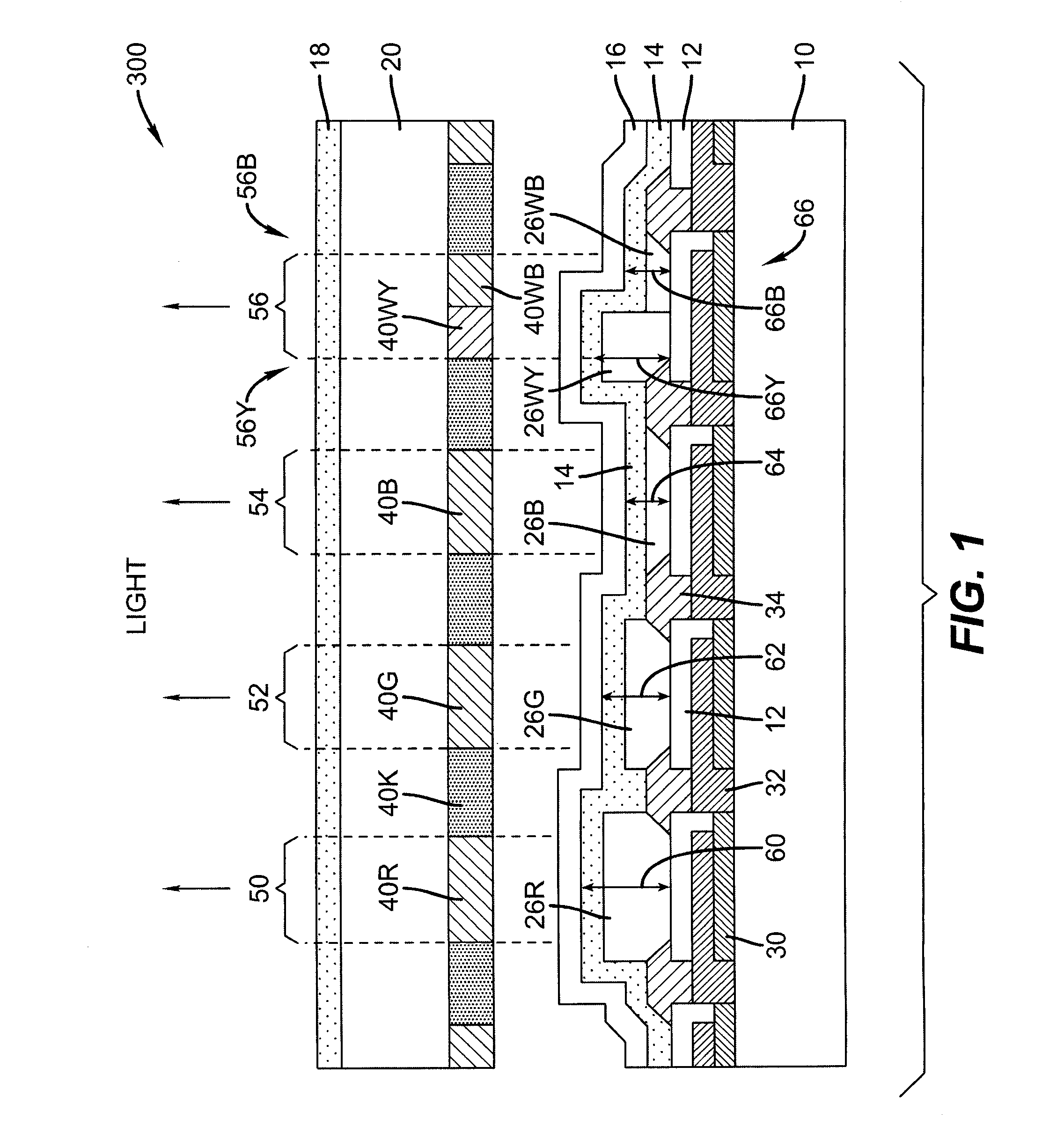
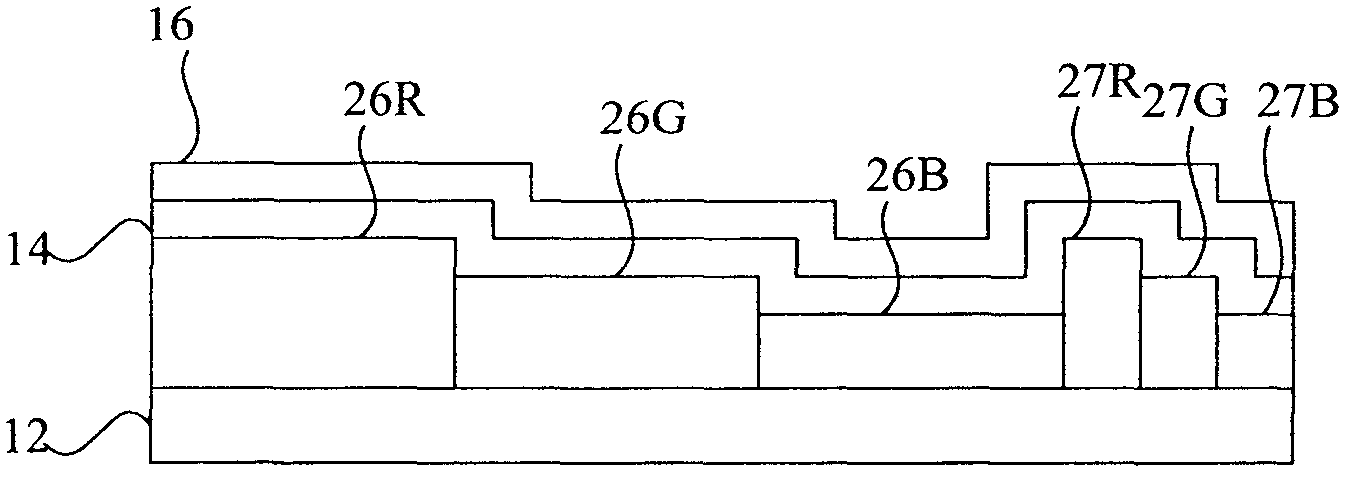
Light emitting diode device incorporating a white light emitting layer in combination with a plurality of optical microcavities
ActiveUS7888858B2Discharge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsLight-emitting diodeOptical microcavity
An light-emitting diode device, including a substrate; and a reflective electrode and a semi-transparent electrode formed over the substrate and an unpatterned white light-emitting layer formed between the reflective electrode and the semi-transparent electrode, the reflective electrode, semi-transparent electrode, and unpatterned white-light-emitting layer forming an optical microcavity, and wherein either the reflective or semi-transparent electrodes is patterned to form a plurality of independently controllable light-emitting elements with at least one light-emitting element having no color filter. Color filters are formed over a side of the semi-transparent electrodes opposite the unpatterned white light-emitting layer in correspondence with the light-emitting elements, the color filters having at least two different colors.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Single photon source based on single trapped ion
ActiveCN106683976AAchieving Doppler Limit CoolingPrecise Control of CouplingLamp detailsPhotonic quantum communicationFiberLine width
The present invention discloses a single photon source based on a single trapped ion. The source comprises a vacuum chamber, an ion trap chip and a calcium atomic furnace. The ion trap chip comprises an arsenic silicate substrate, a first silicon dioxide layer and a second silicon dioxide layer. The arseno silicate substrate is provided with a substrate through hole, the opposite side walls of the substrate through hole are respectively provided with fiber fixing grooves, the two fiber fixing grooves are respectively provided with two multimode fibers having the same optical axis, the opposite end surfaces of the two multimode fibers are concave surfaces, the surfaces of the concave surfaces are provided with dielectric films, the focal points of the concave surfaces of the two multimode fibers are overlapped, and an optical microcavity is formed between the concave surfaces of the two multimode fibers. The single photon source based on the single trapped ion realizes the Doppler limitation cooling of the single ion. The single photon source has higher generation efficiency and facilitates the connection with the current optical communication system to allow the prepared single photon line width to reach the natural line width of ion energy level transition.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
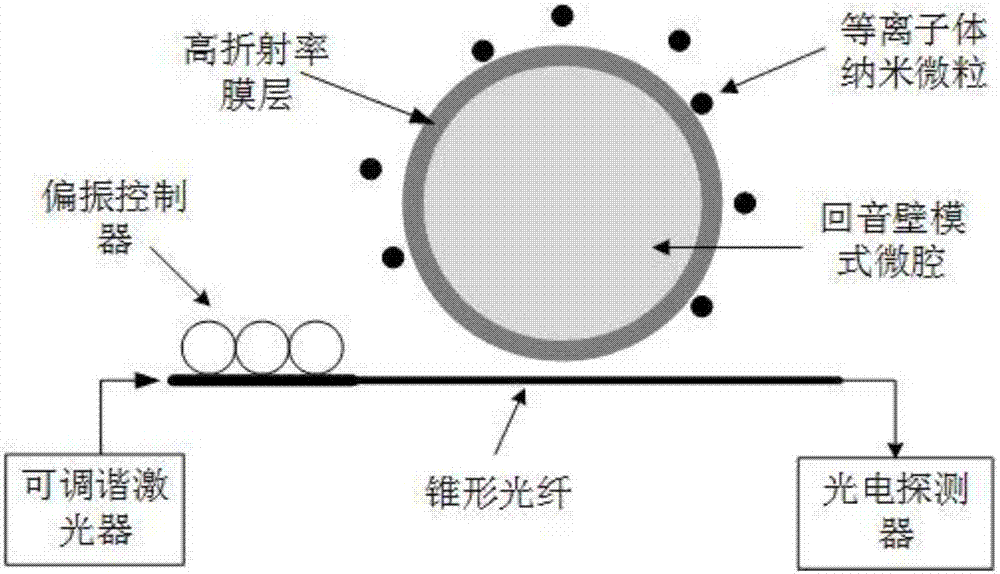
Surface plasma enhanced type mixture medium echo wall mode microcavity sensor
PendingCN107202774AEvanescent field strengthHigh Q valueMaterial analysis by optical meansRefractive indexMicroparticle
The invention discloses a surface plasma enhanced type mixture medium echo wall mode microcavity sensor. The surface plasma enhanced type mixture medium echo wall mode microcavity sensor comprises a tunable laser, a polarization controller, a conical optical fiber, a mixed medium microcavity, plasma nanoparticles and a photoelectric detector; laser output by the tunable laser enters the mixed medium microcavity through the conical optical fiber and performs total reflection in the mixed medium microcavity to form echo wall mode resonance; the polarization controller is used for controlling laser polarization state input into the conical optical fiber; the photoelectric detector is used for recording and analyzing an echo wall mode transmission spectrum at the output end of a coupling system consisting of the conical optical fiber and the mixed medium microcavity; the mixed medium microcavity is formed by plating a high-refractive-index film layer on the surface of an optical microcavity; the plasma nanoparticles are attached to the surface of the mixed medium microcavity; the mixed medium microcavity is placed in measured physical quantity. The surface plasma enhanced type mixture medium echo wall mode microcavity sensor has the advantages of compact structure, high sensitivity, high response speed and the like, and has potential application value in the field of biochemical trace real-time detection.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Cantilever beam type accelerometer based on photonic crystal microcavity
InactiveCN101782594AVerify feasibilityStrengthen the teamTelevision system detailsImpedence networksAccelerometerPhotonics
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Efficient organic light-emitting diode and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN104269495AImprove current efficiencyImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectron transferLight-emitting diode
The invention relates to an efficient organic light-emitting diode and a manufacturing method of the efficient organic light-emitting diode. The efficient organic light-emitting diode is of a microcavity structure. The efficient organic light-emitting diode structurally comprises a substrate, a metal anode, a hole injection layer, a hole transmission layer, an electron transfer layer / light-emitting layer and an electron injection layer / metal cathode from bottom to top in sequence. The microcavity structure is formed by bimetallic electrode aluminum, by the adoption of the optical microcavity of the structure, efficient organic light-emitting devices can be manufactured both in a top light-emitting component structure and a bottom light-emitting component structure, and the luminescent spectrum can be narrowed. Or the efficient organic light-emitting diode structurally comprises the substrate, the metal cathode / electron injection layer, the electron transfer layer / light-emitting layer, the hole transmission layer, the hole injection layer and the metal anode from bottom to top in sequence. Due to the fact that the bimetallic electrode structure is adopted by the optical microcavity, the efficient organic light-emitting diode is obtained through the microcavity effect, and the characteristic of higher spectrum color purity is shown at the same time.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for improving collection efficiency of diamond NV color center fluorescence
ActiveCN109884013AAchieve excitationFor efficient collectionFluorescence/phosphorescenceQuantum sensorFiber
The invention discloses a method for improving collection efficiency of diamond NV color center fluorescence. The method comprises the following steps of forming an optical resonator by coupling a nano-diamond and a microsphere cavity based on the Purcell effect, integrating a microwave antenna thereon to prepare a microsphere cavity (200-500 microns) containing the nano-diamond, exciting the diamond NV color center to generate fluorescence by 532nm laser, and enhancing and collecting the fluorescence using a whispering wall mode such that the fluorescence generated by the diamond NV color center can be continuously circulated in the microsphere cavity, thereby establishing a strong light field and directly achieving the collection of fluorescence using the fiber connected to the sphere cavity. The method combines nano-diamond with optical microcavity with low requirements on preparation process, has the characteristics such as low cost, small mode volume and high energy density, realizes excitation and efficient collection of diamond NV color center fluorescence, and is expected to realize integrated application of NV color center based high sensitivity quantum sensors.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
On-chip broadband coupling optical microcavity system and coupling method thereof
ActiveCN107508140AEffectively stimulate the whispering gallery modeHigh intrinsic quality factorLaser detailsSemiconductor laser optical deviceRadiation lossExcited state
The present invention discloses an on-chip broadband coupling optical microcavity system and a coupling method thereof. In the invention, a non-circular optical microcavity and an optical waveguide prepared on a chip are adopted, and the slight deformation of the non-circular optical microcavity causes the eigenstate echo wall mode originally distributed only in the edge of the circular optical microcavity to extend into the non-circular optical microcavity, forming a "tail"; laser and the "tail" of the non-circular optical microcavity are in phase matching, so as to stimulate the excited state echo wall mode of the non-circular optical microcavity; the echo wall mode of the non-circular optical microcavity can be refracted into the optical waveguide through its "tail"; the optical waveguide enables effective broadband excitation and collection of the echo wall mode in the non-circular optical microcavity, i.e., the completion of the effective broadband coupling of the optical waveguide and the non-circular optical microcavity; and the deformation of the non-circular optical microcavity is so little that the non-circular optical microcavity can maintain high intrinsic quality factors (> 10<4>) without introducing large radiation losses.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Free-space optical micro-cavity Raman laser sensing device and sensing method thereof
ActiveCN105024269AHigh sensitivityIncrease flexibilityLaser detailsNon-linear opticsFrequency spectrumWhispering gallery
The invention discloses a free-space optical micro-cavity Raman laser sensing device and a sensing method thereof. The sensing device comprises a laser light source, a first focusing object lens, an optical micro-cavity, a second focusing object lens, a first collimating lens, a second collimating lens, a first photoelectric detector, an oscilloscope, a filter sheet, a third focusing object lens, a second photoelectric detector and a base spectrum analyzer. Raman laser of an optical micro-cavity is triggered through free-space frequency-tunable laser, and by observing frequency of beat frequency of the Raman laser, information of nanoscale-dimension particles attached to the surface of the optical micro-cavity is obtained; in the free-space Raman laser sensing technology, a whispering gallery mode and the Raman laser can be directly triggered in the free space through the frequency-tunable laser; and through avoiding the technical problems due to the introduction of an optical fiber taper, the flexibility of the device is improved, and signal to noise ratio is reduced, so that sensitivity of the sensing device is improved, and detection limit is reduced.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Optical micro-cavity, force measuring device and method, modulus measuring method and display panel
ActiveCN106124096ASimple structureEasy to mass manufactureForce measurement by measuring optical property variationInput/output processes for data processingMeasurement devicePhotonic crystal
An embodiment of the invention provides an optical micro-cavity, a force measuring device, a force measuring method, a modulus measuring method and a display panel. The optical micro-cavity comprises a photoluminescence layer, a photonic crystal layer and a semi-transmitting and semi-reflecting layer, wherein the photoluminescence layer is configured to generate light; the photonic crystal layer is arranged on one side of the photoluminescence layer, and is configured to reflect the light generated by the photoluminescence layer and transmit excitation light used for the photoluminescence layer; and the semi-transmitting and semi-reflecting layer is arranged on the other side of the photoluminescence layer and opposite to the photonic crystal layer, and is configured to transmit and reflect the light generated by the photoluminescence layer partially. The force measuring device comprises the optical micro-cavity and at least one optical sensor. According to the embodiment, the optical micro-cavity, the force measuring device and the display panel provided by the invention are simple in structure and easy in batch manufacturing, and the force measuring method and the modulus measuring method provided by the invention are easy to implement.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Microcavity thermal effect compensation method in Kerr optical frequency comb soliton mode locking process
ActiveCN107508137AAvoid strong randomnessAvoid reliabilityLaser detailsThermal equilibrium stateMode-locking
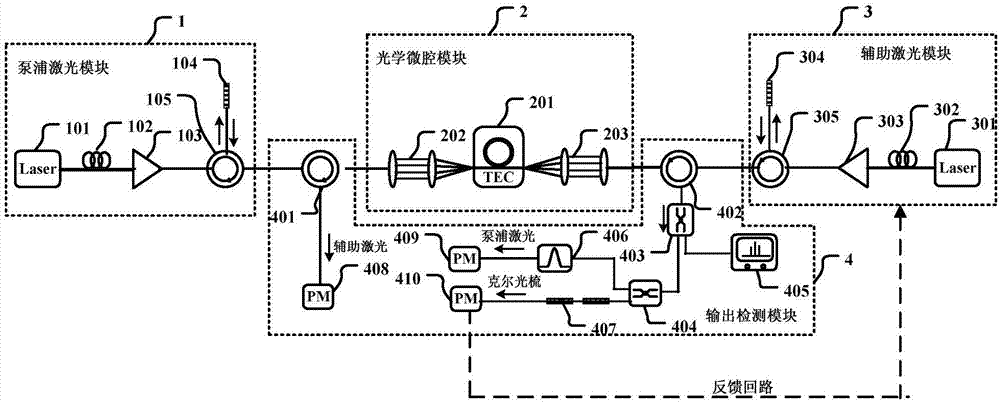
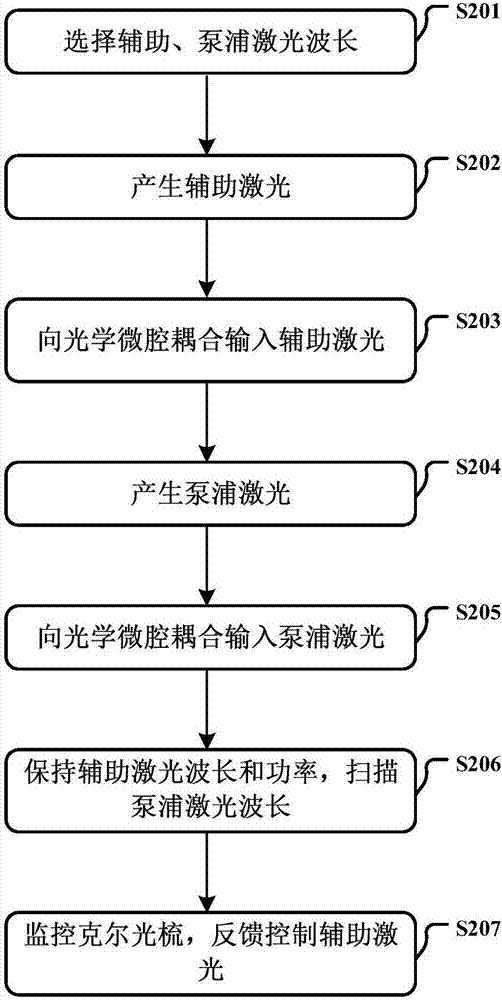
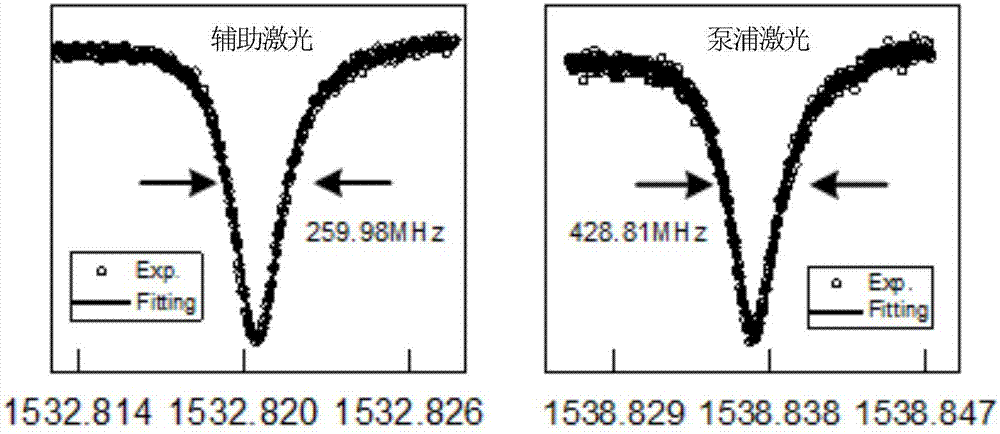
The present invention discloses a microcavity thermal effect compensation method in a Kerr optical frequency comb soliton mode locking process. Auxiliary laser is introduced into an optical microcavity and is employed to perform heating makeup of thermal effect in the soliton mode locking process to keep the thermal equilibrium state of the optical microcavity in the soliton mode locking process and perform certainty realization of the soliton mode locking in the optical microcavity each time so as to greatly simplify the soliton mode locking process in the optical microcavity and avoid the problems of the current Kerr optical frequency comb soliton mode locking process is high in randomness, bad in reliability and liable to disturbance, etc; and moreover, the optical power of the Kerr optical frequency comb is monitored to feed back and control the wavelength of the auxiliary laser, the soliton mode locking state can be stably existed for a long time, and when the soliton mode locking state is lost caused by external interference, the soliton mode locking state can be automatically recovered through control of the auxiliary laser so as to greatly improve the stability of the soliton mode locking state in the optical microcavity.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Apparatus and method for operating optical microcavity by light emitting diode
InactiveUS20120126143A1Lower the thresholdRadiation pyrometryPhotometryLight irradiationOptical cavity
An optical cavity mode apparatus comprising at least one microresonator; a light emitting diode for supplying light irradiation to the microresonator to stimulate the excitation level of the microresonator; and an optical detector to obtain spectra of the microresonator stimulated by the light emitting diode.
Owner:FUJIREBIO CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com