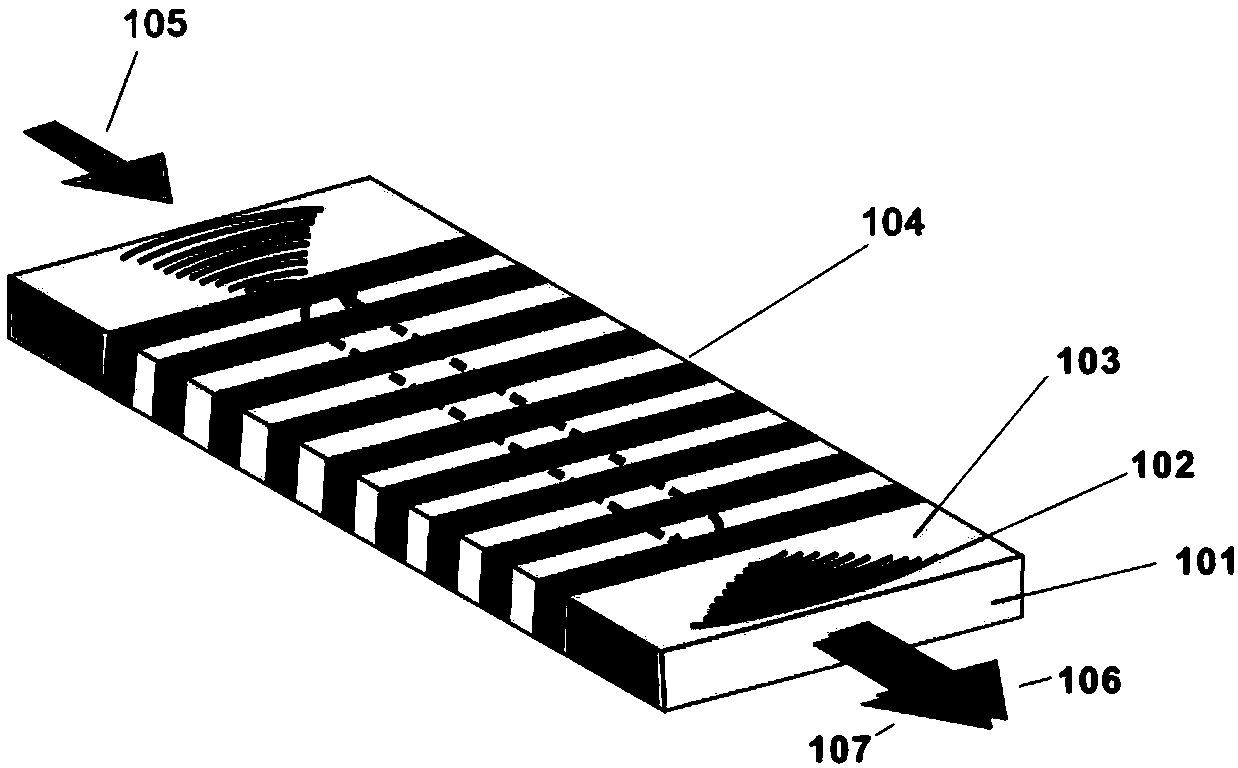
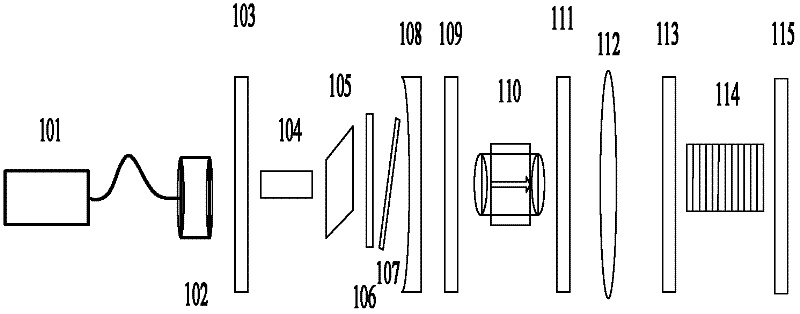
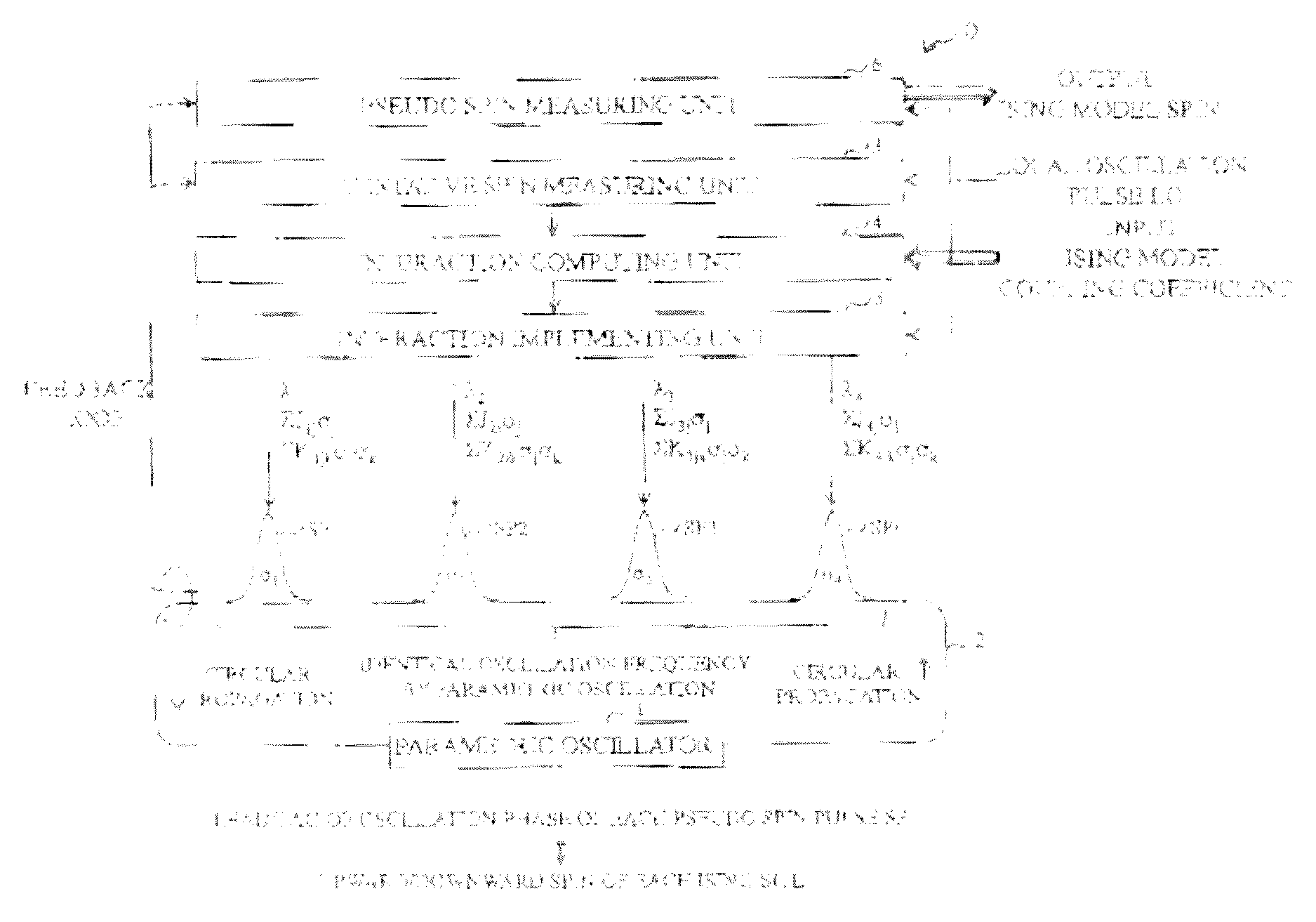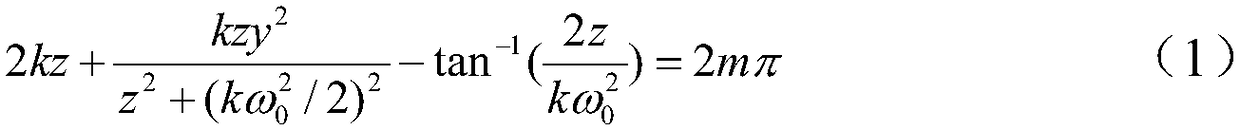Patents
Literature
147 results about "Parametric oscillation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
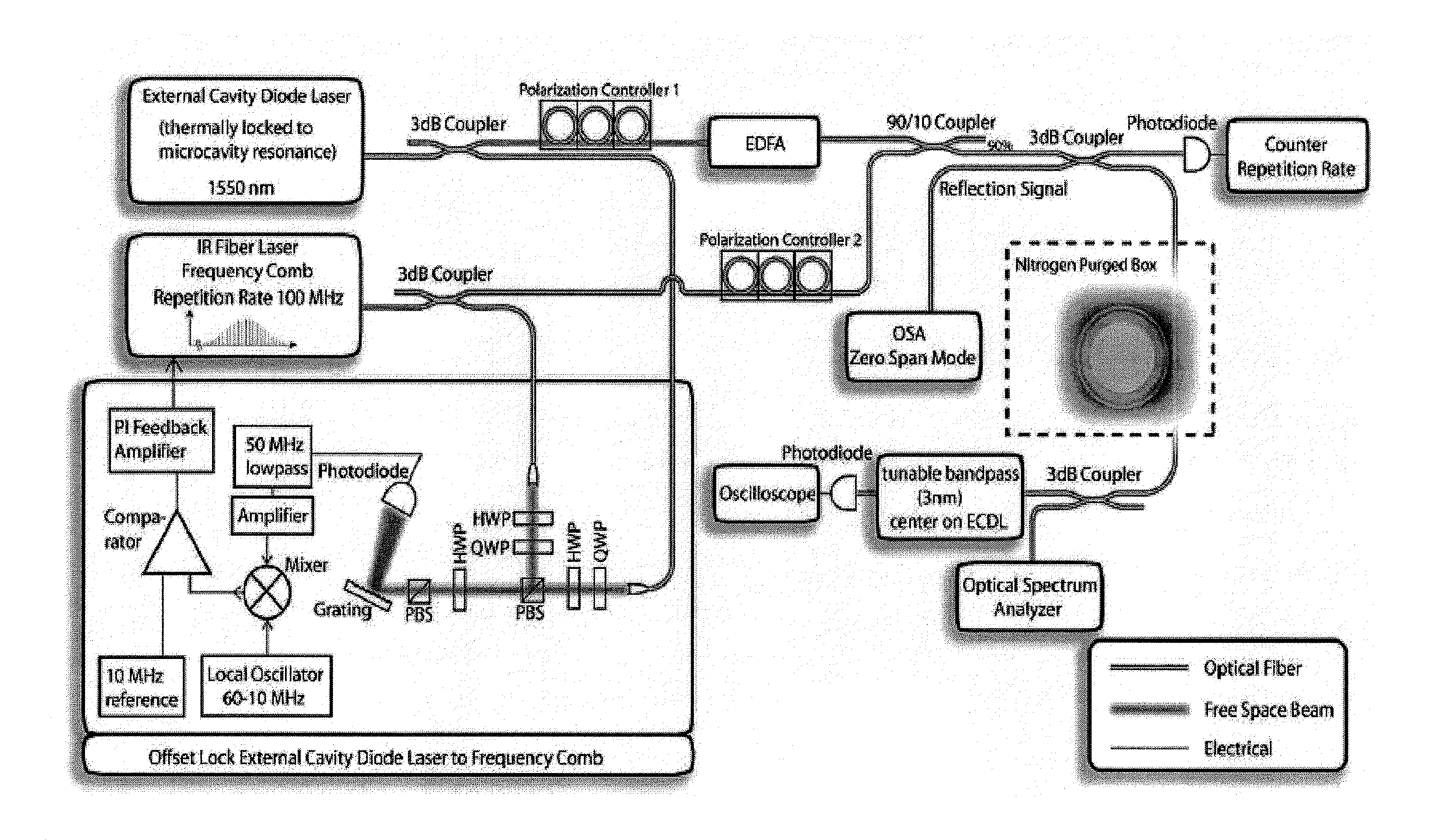
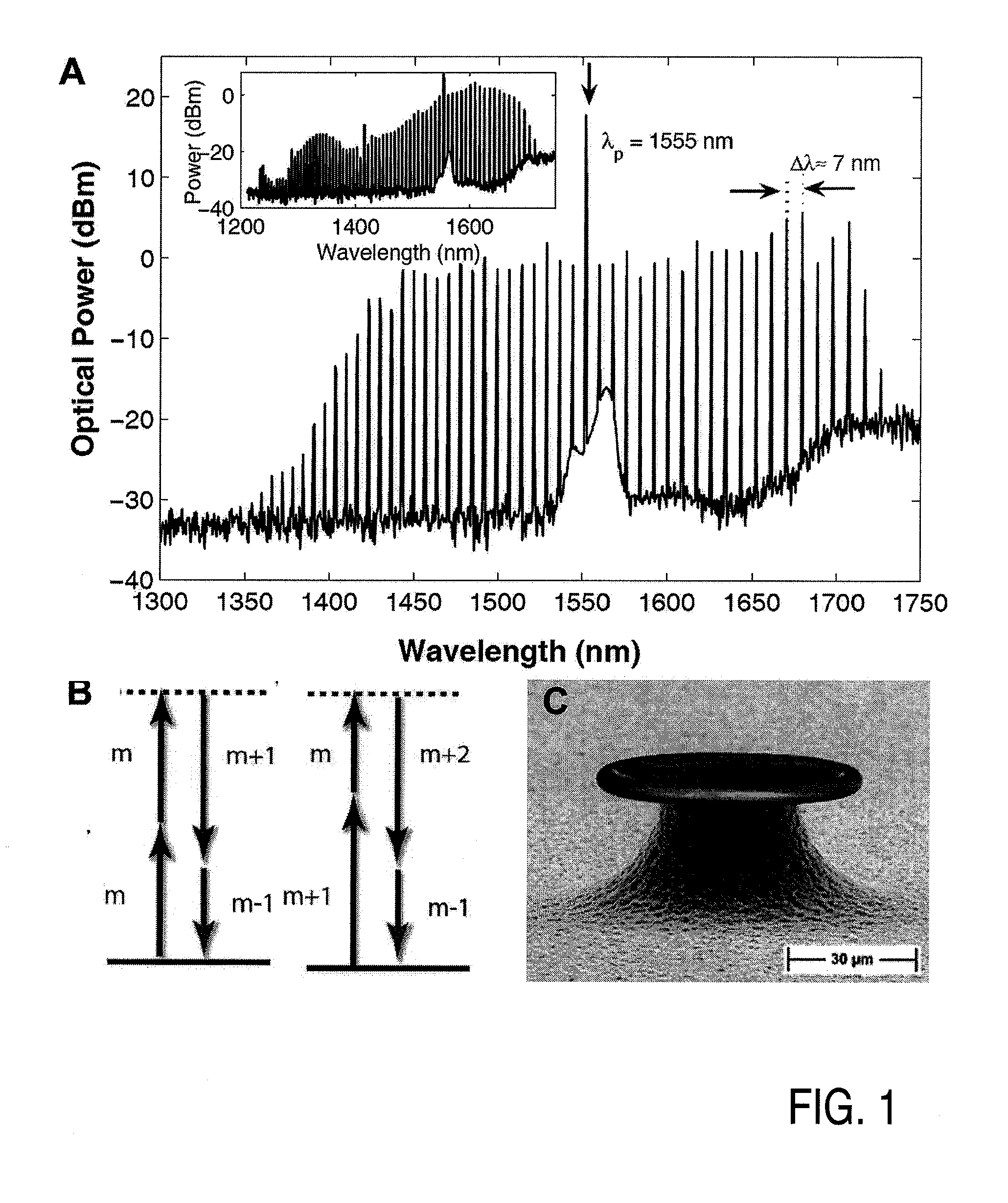
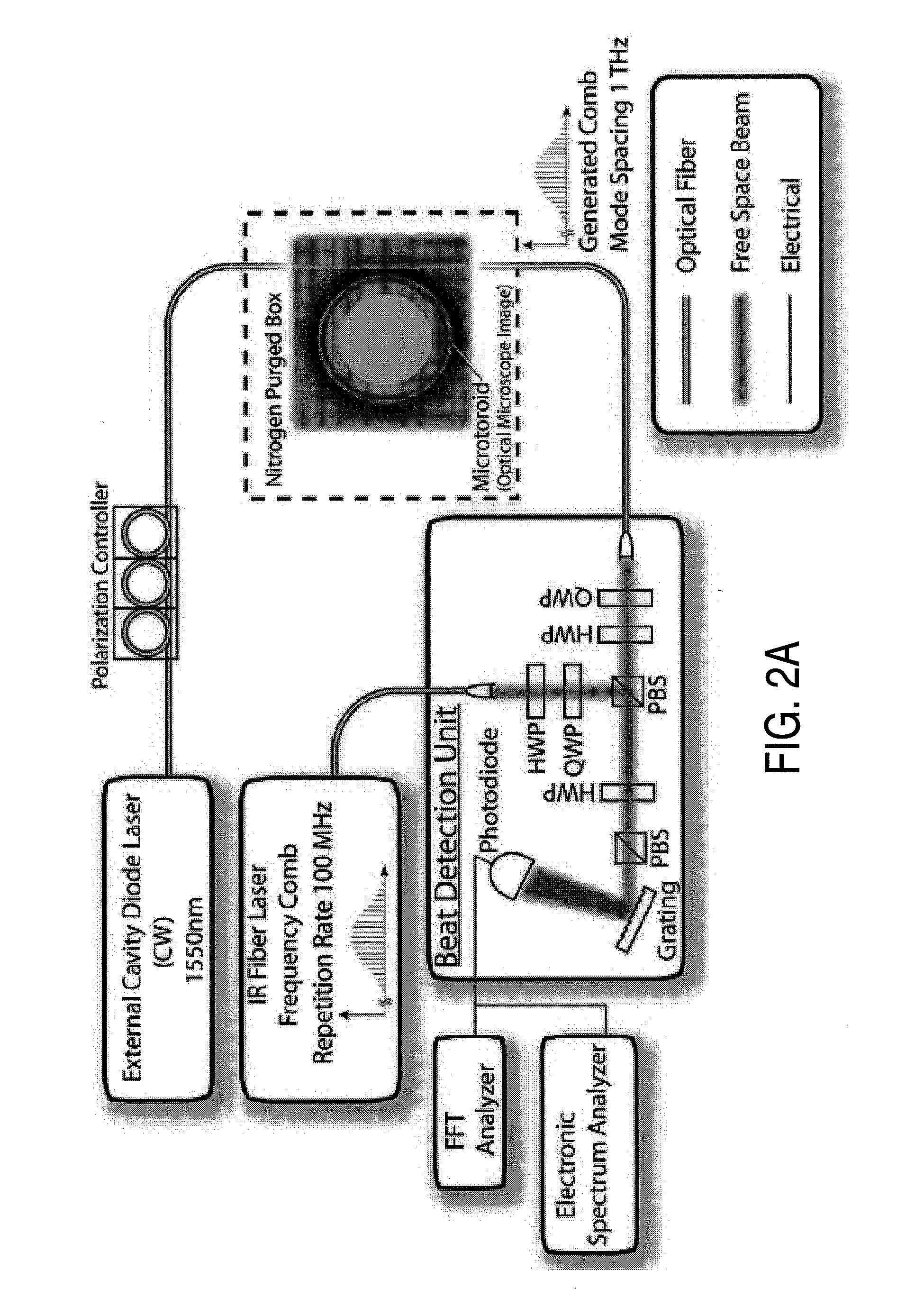
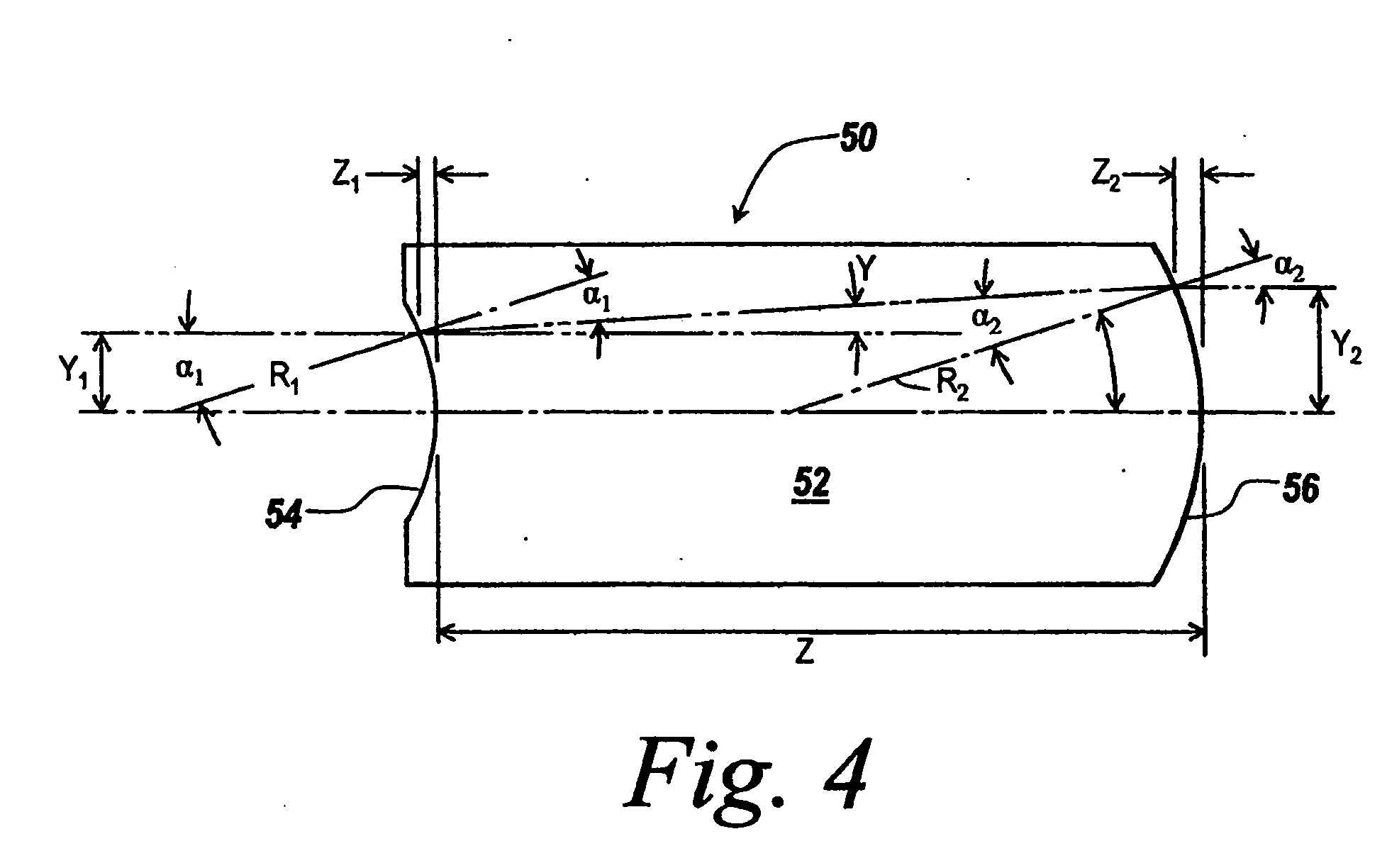
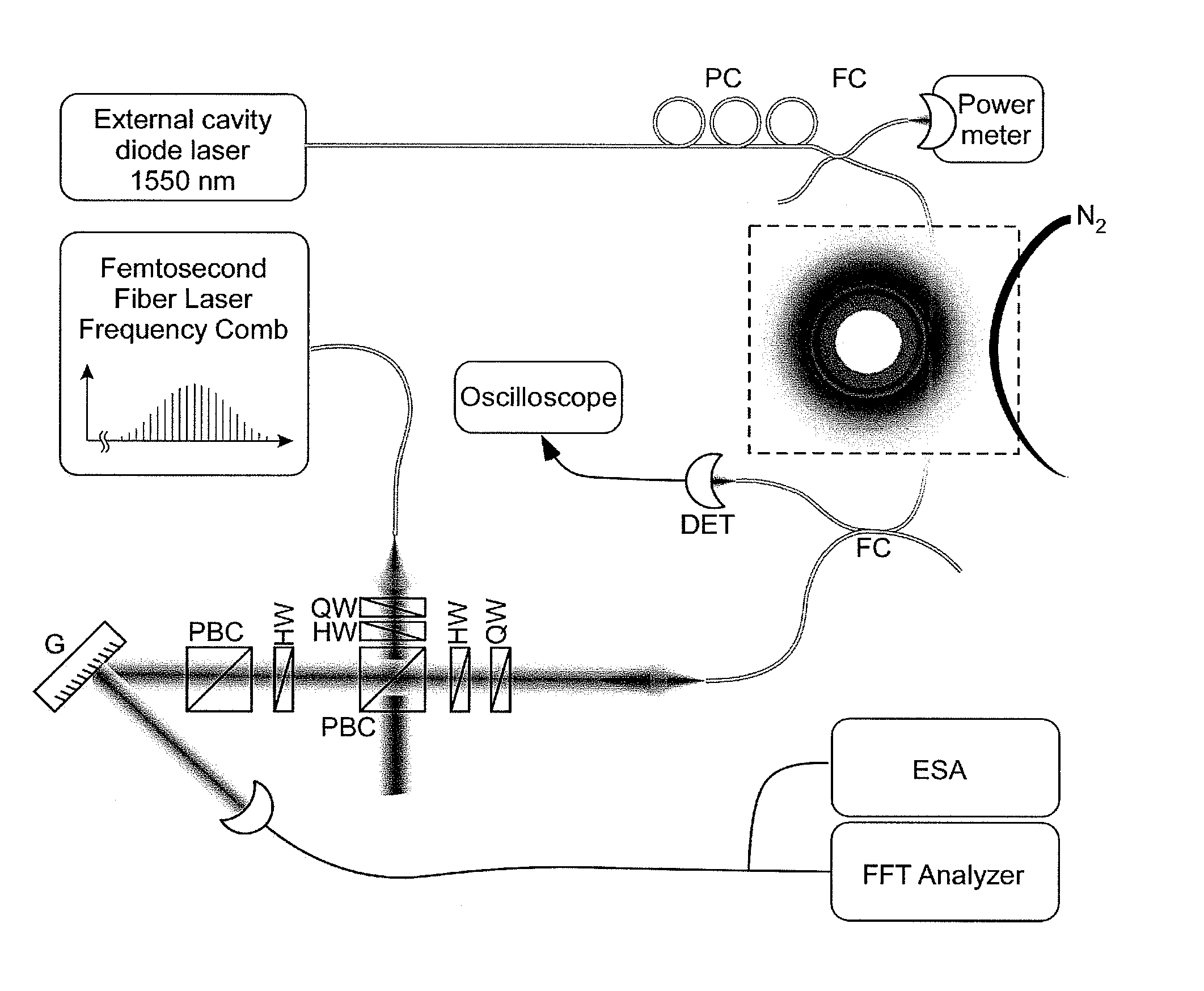
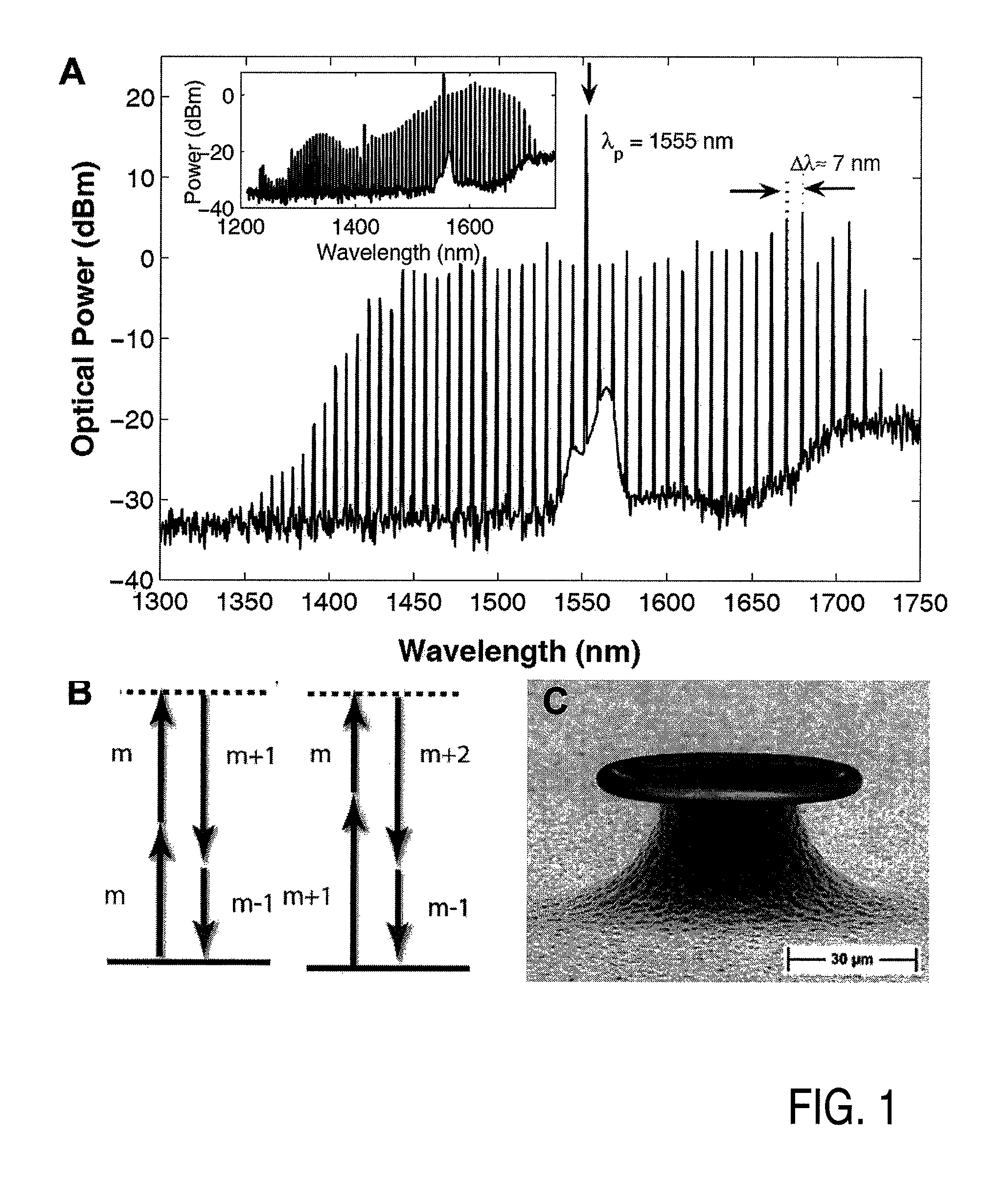
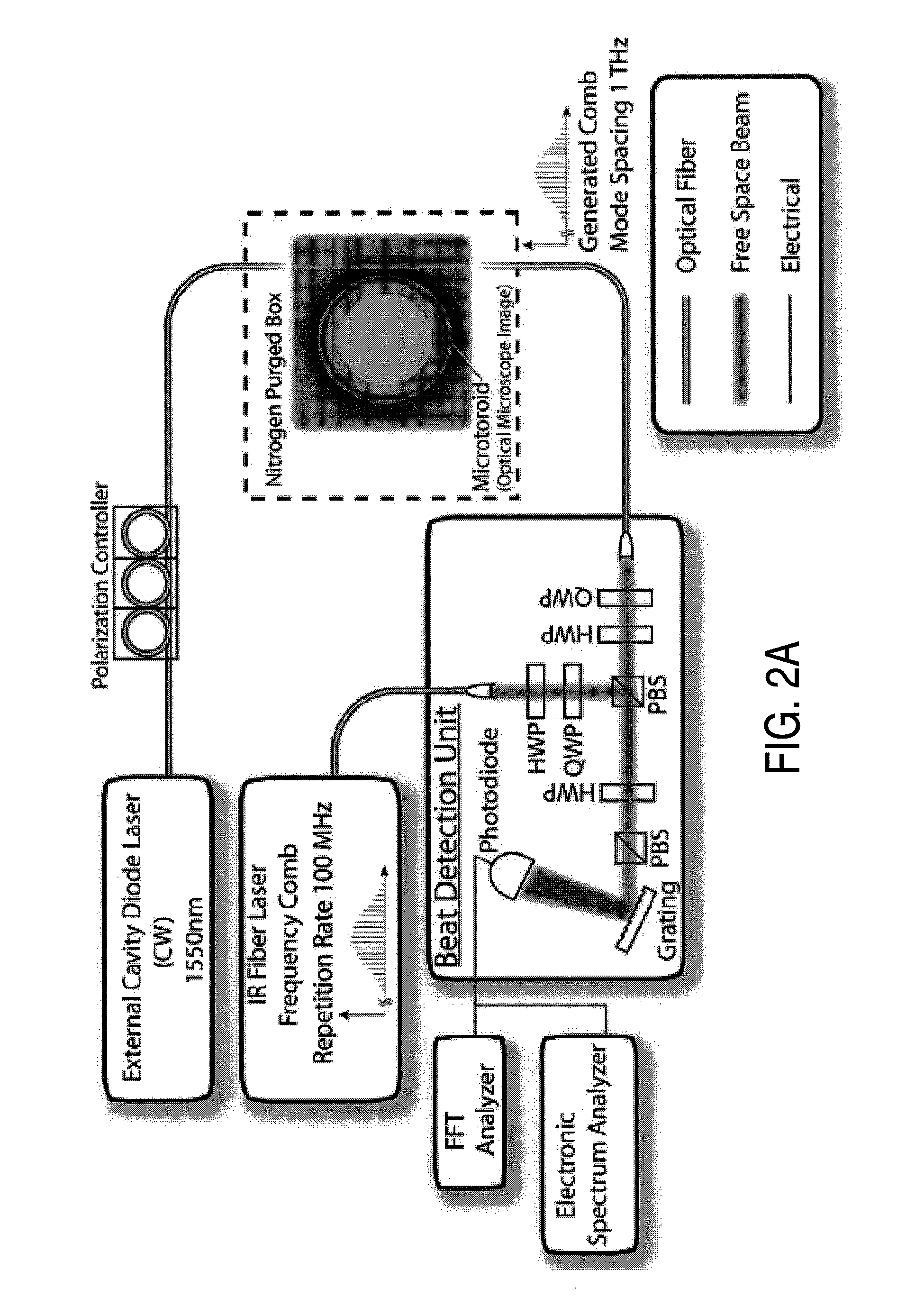
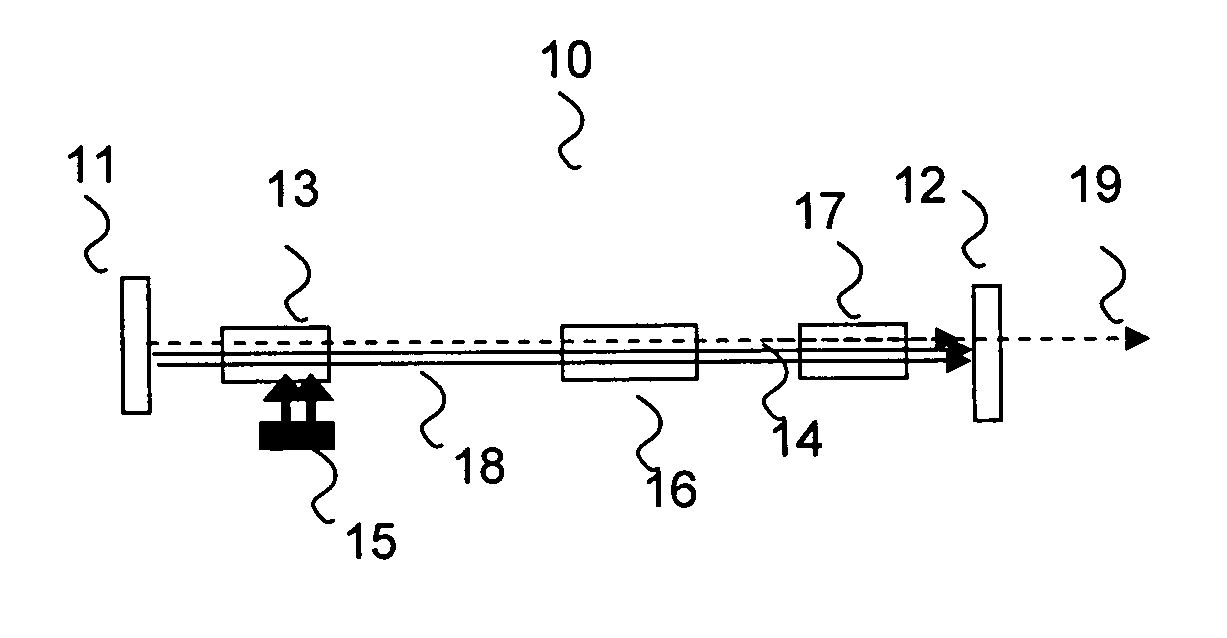
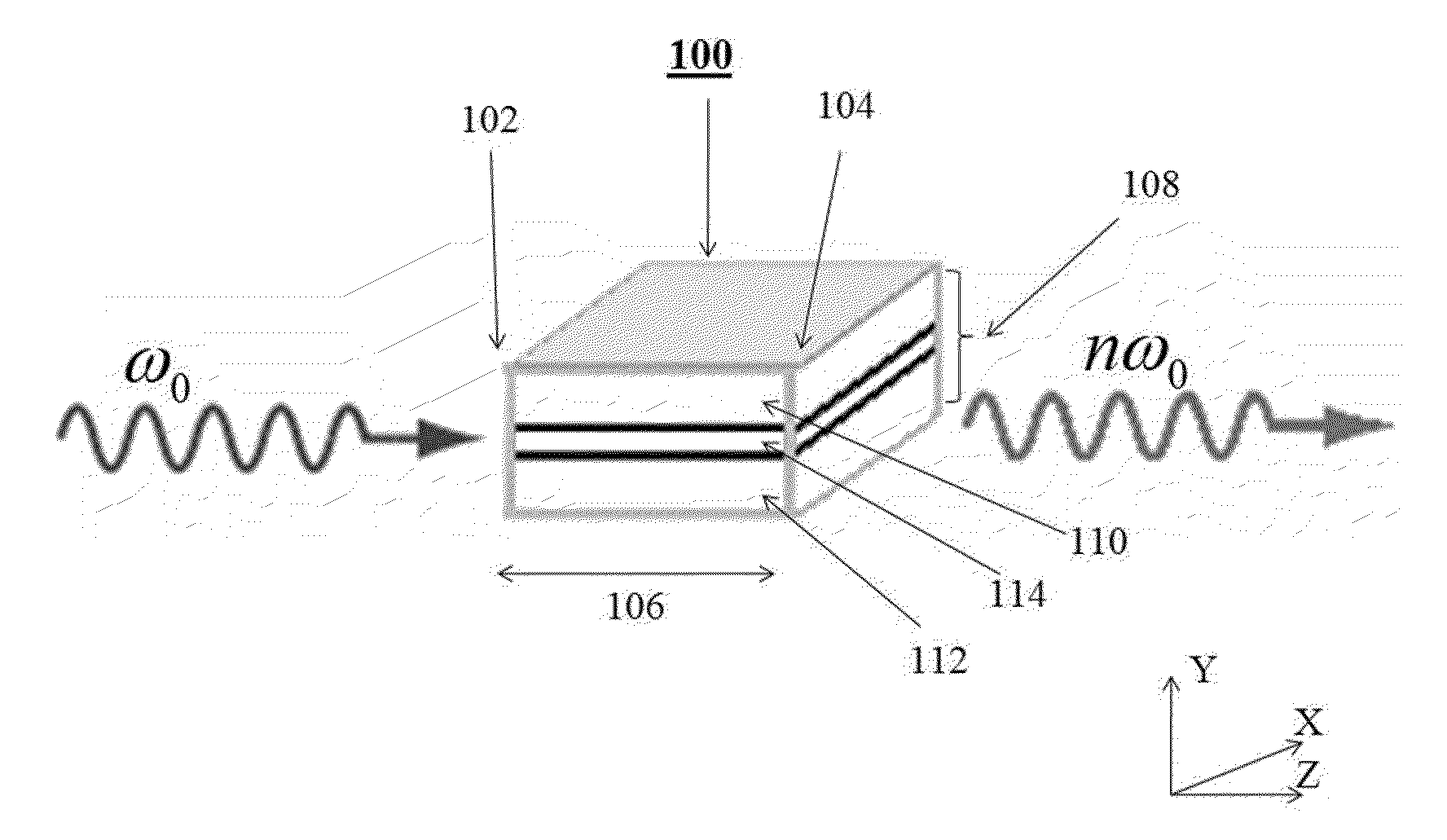
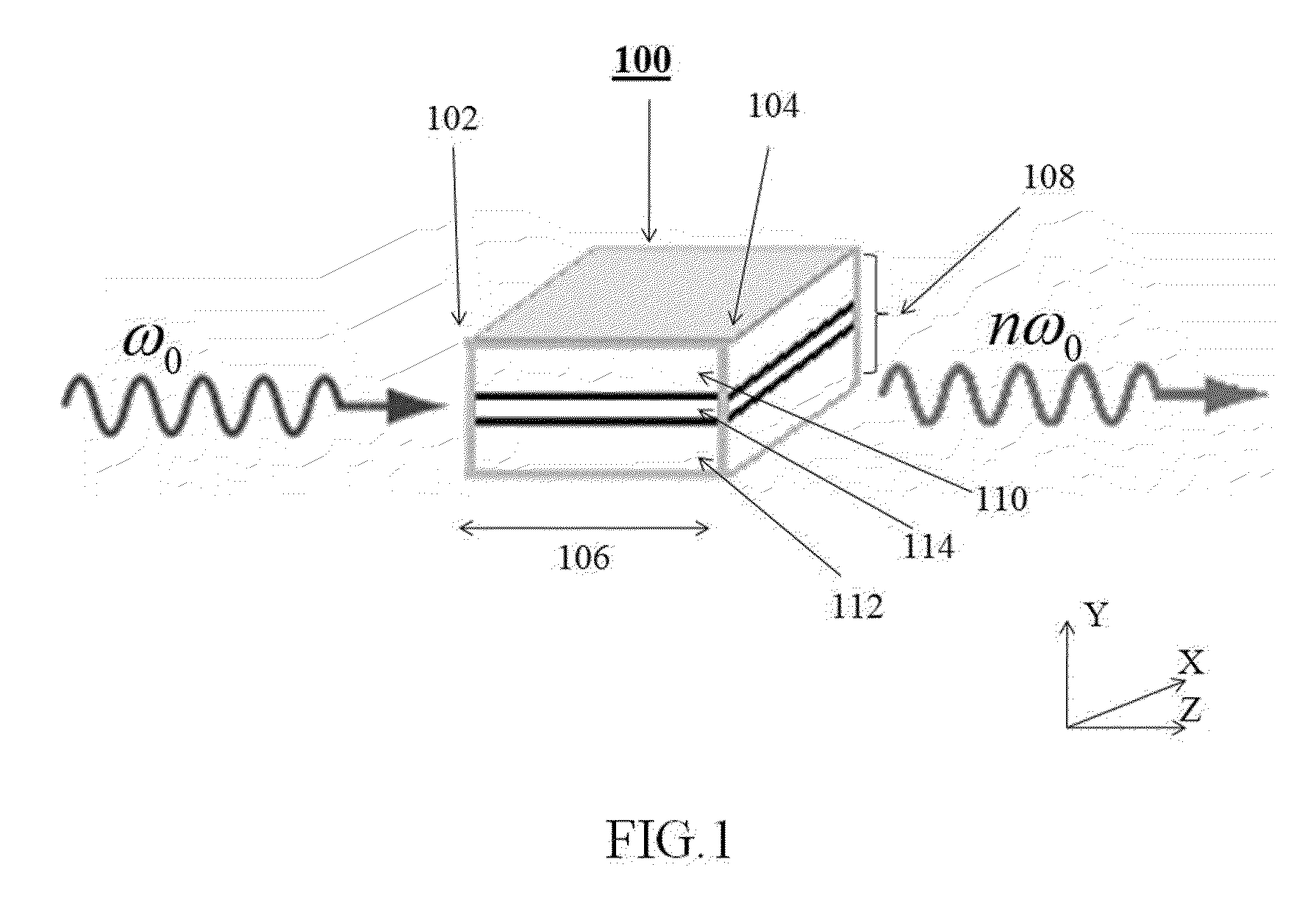
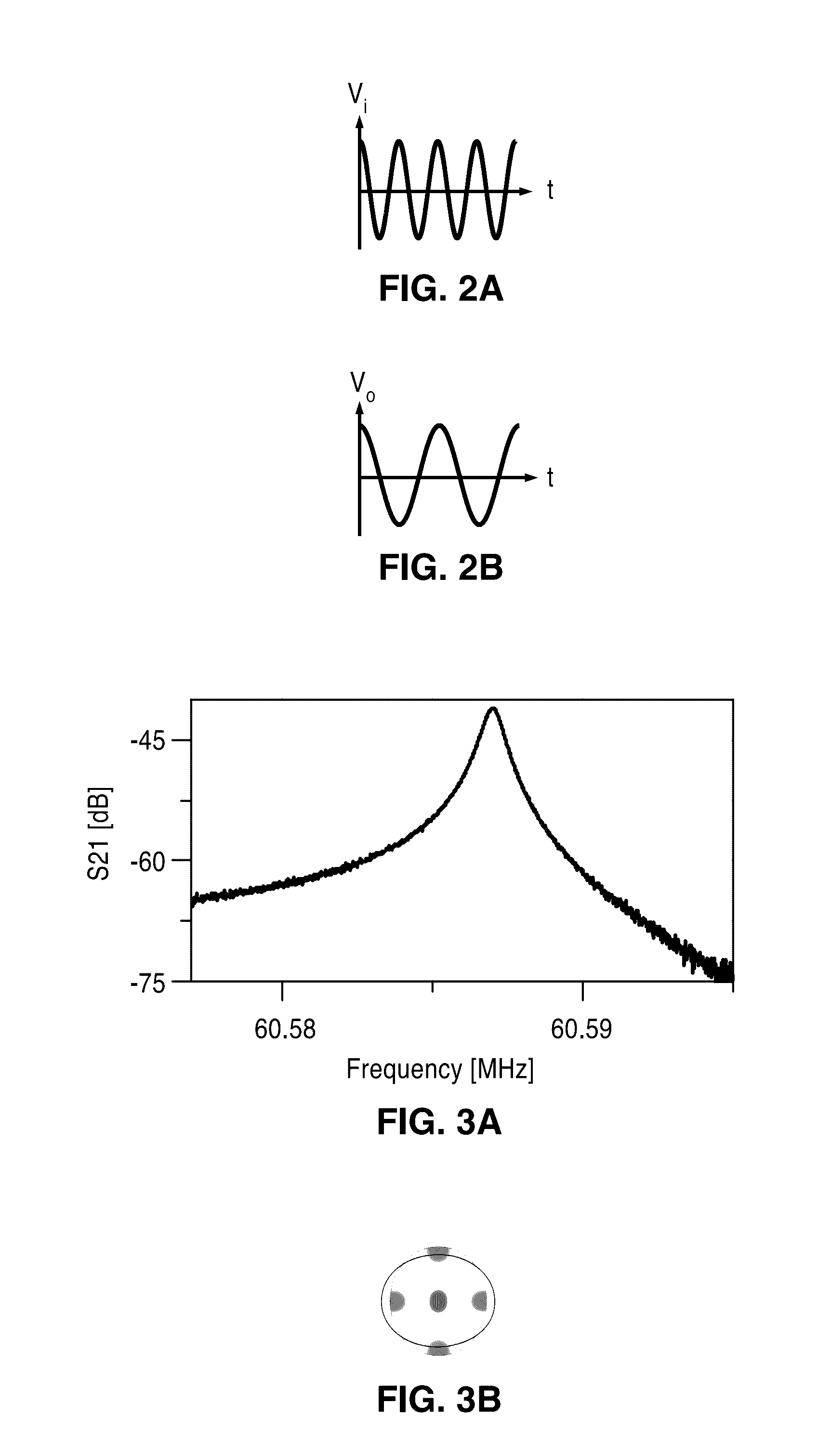
Method and apparatus for optical frequency comb generation using a monolithic micro-resonator
An optical frequency comb generator includes a laser device arranged for generating input laser light having a predetermined input light frequency, a dielectric micro-resonator having a cavity exhibiting a third order nonlinearity, so that the micro-resonator is capable of optical parametric generation providing parametrically generated light, and a waveguide optically coupled to the micro-resonator, the waveguide being arranged for in-coupling the input laser light into the micro-resonator and out-coupling the parametrically generated light out of the micro-resonator, wherein the laser device, the waveguide and the micro-resonator being arranged for resonantly in-coupling the laser input light to a mode of the micro-resonator with a minimum power level so that an optical field inside the cavity exceeds a predetermined cascaded parametric oscillation threshold at which the parametrically generated light includes frequencies of frequency sidebands of the input light frequency and of the sidebands thereof.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
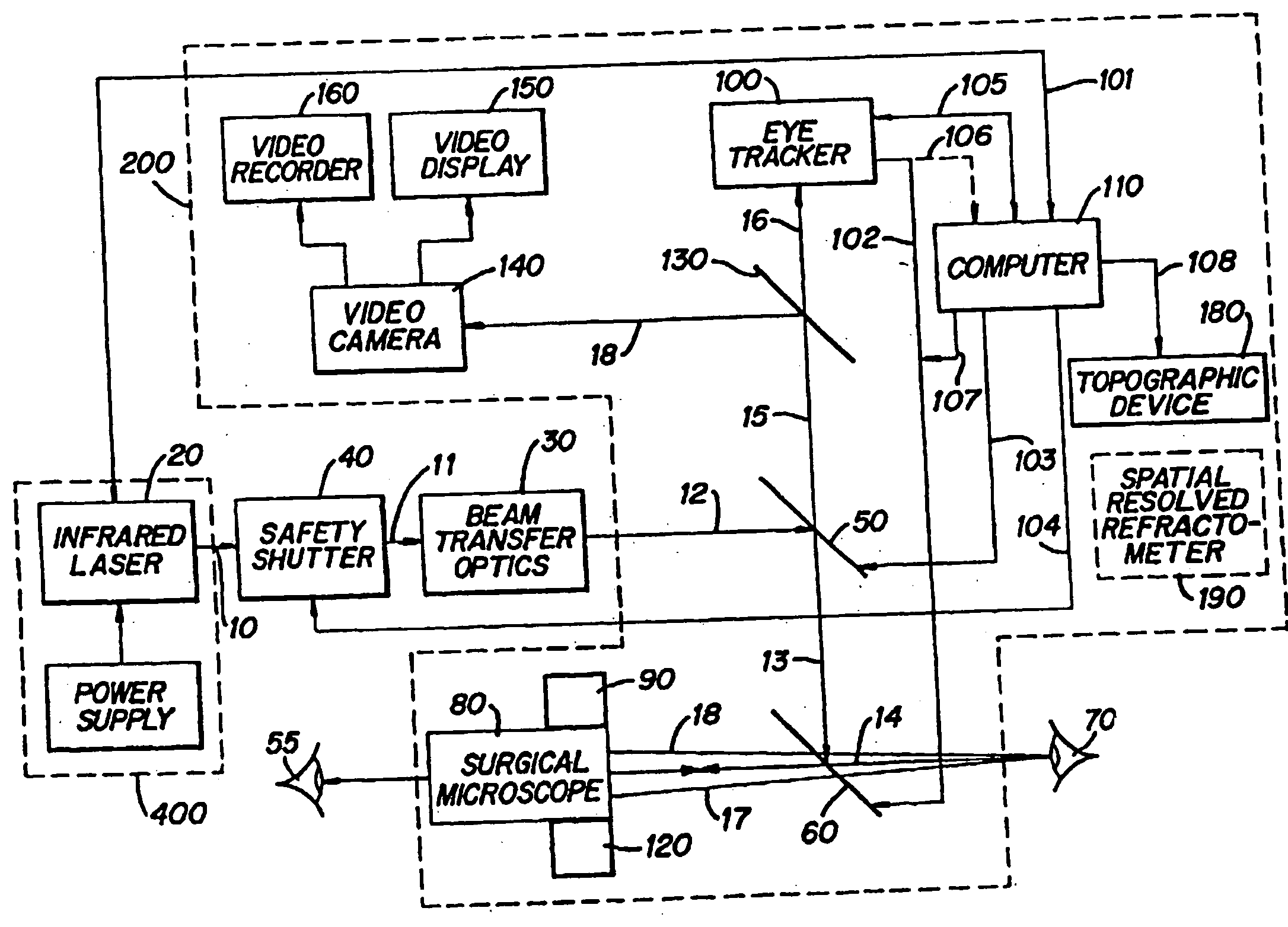
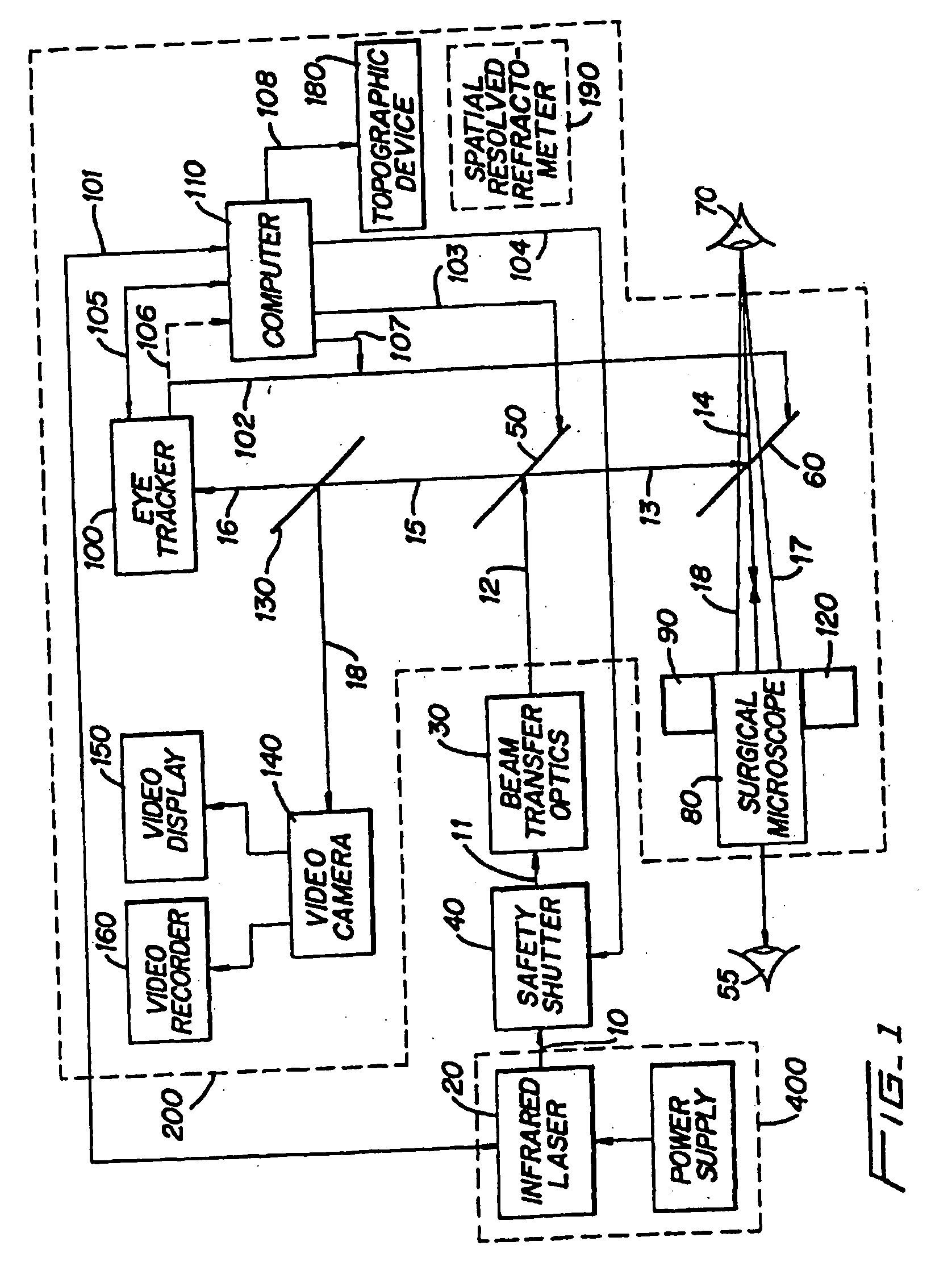
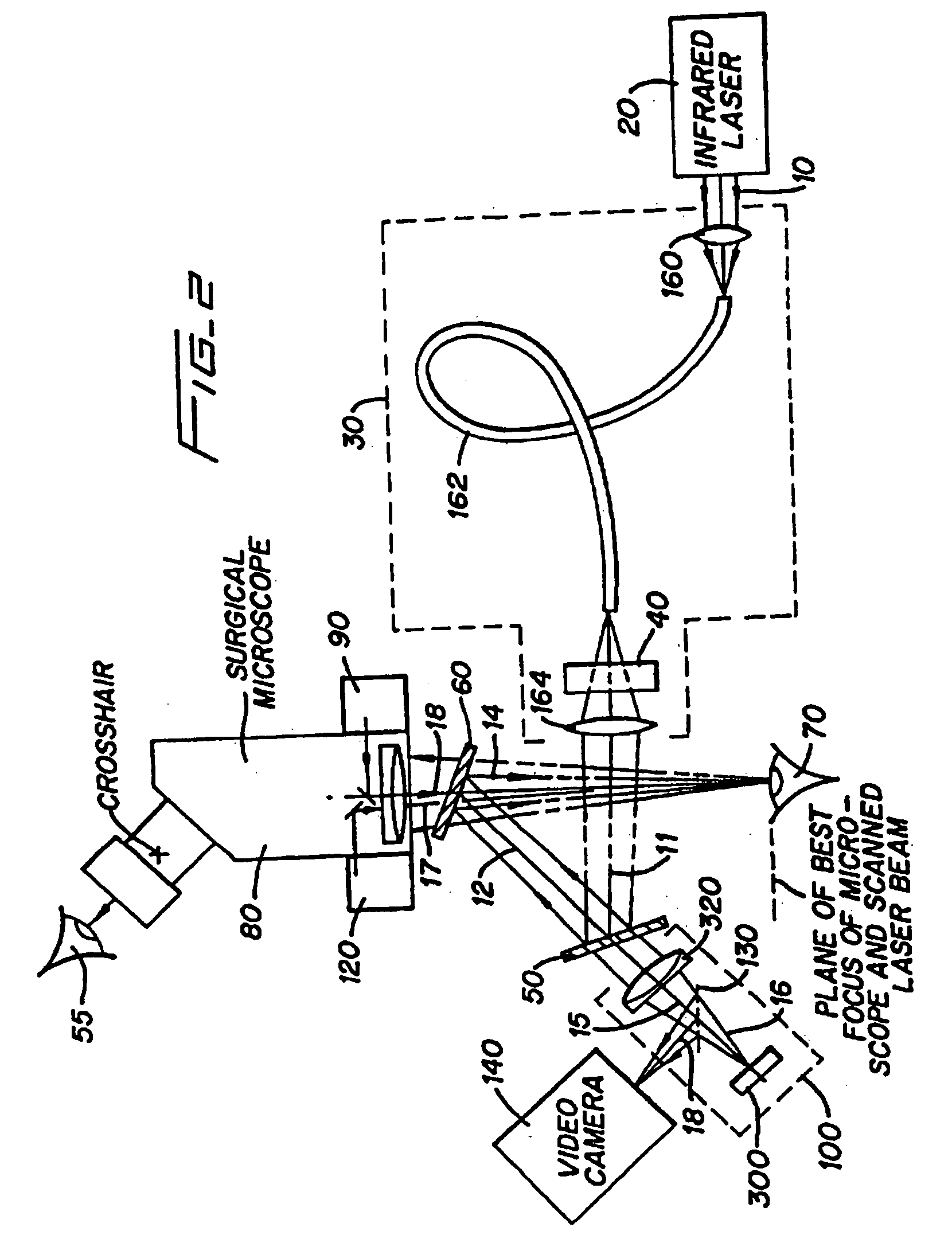
Method and apparatus for removing corneal tissue with infrared laser radiation and short pulse mid-infrared parametric generator for surgery
InactiveUS20050197655A1Reduce undesirable thermal damageMaximum flexibilityLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsLaser scalpelMid infrared laser
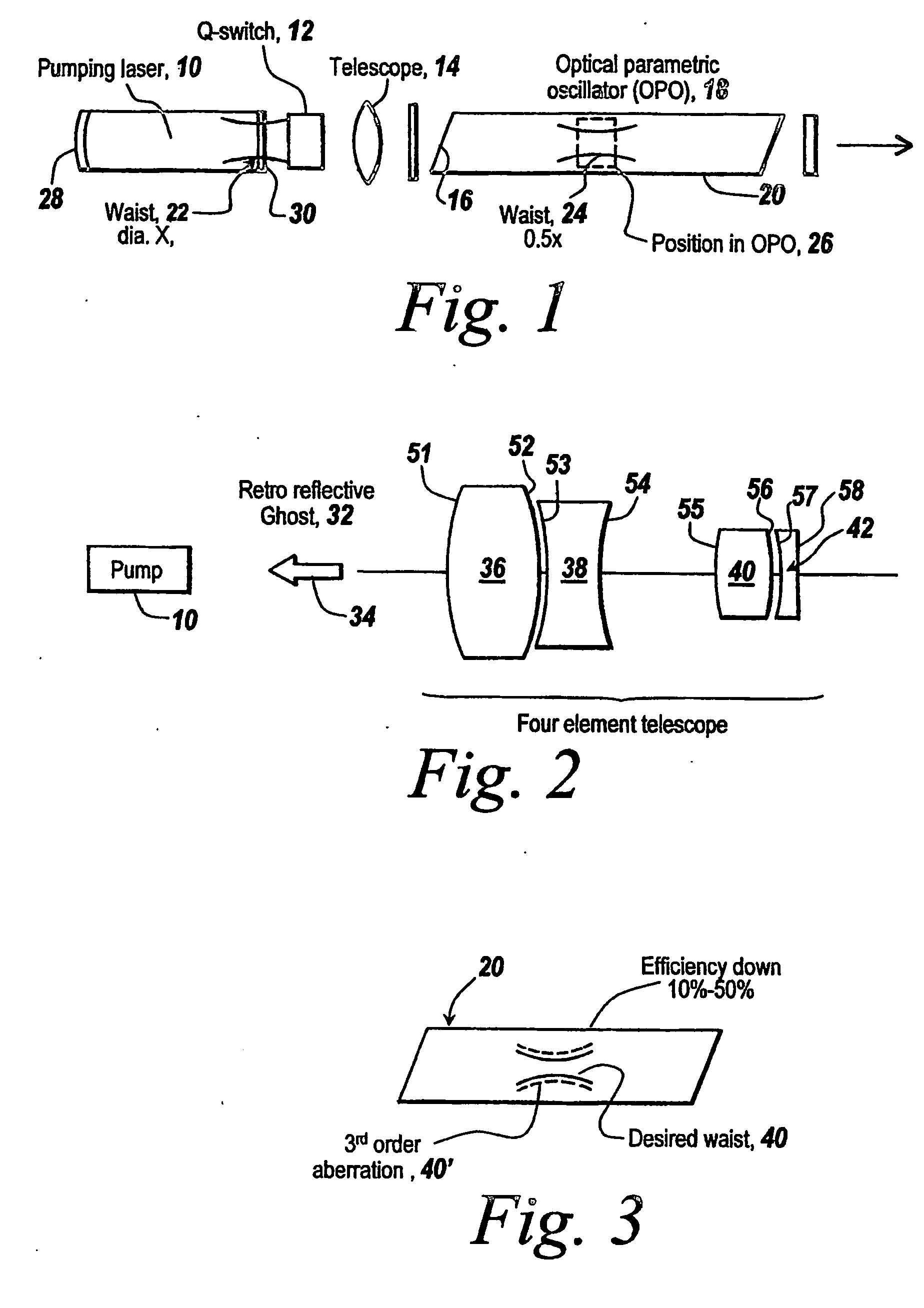
A surgical technique for removing corneal tissue with scanned infrared radiation is disclosed which utilizes short mid-infrared laser pulses to provide a tissue removal mechanism based on photospallation. Photospallation is a photomechanical ablation mechanism which results from the absorption of incident radiation by the corneal tissue. Since photospallation is a mechanical ablation process, very little heat is generated in the unablated adjacent tissue. The disclosed surgical system includes a scanning beam delivery system which allows uniform irradiation of the treatment region and utilizes low energy outputs to achieve controlled tissue removal. A real-time servo-controlled dynamic eye tracker, based on a multiple-detector arrangement, is also disclosed which senses the motion of the eye and provides signals that are proportional to the errors in the lateral alignment of the eye relative to the axis of the laser beam. Temporal and frequency discrimination are preferably utilized to distinguish the tracking illumination from the ambient illumination and the surgical laser beam. A laser parametric generator for surgical applications is disclosed which utilizes short-pulse, mid-infrared radiation. The mid-infrared radiation may be produced by a pump laser source, such as a neodymium-doped laser, which is parametrically down converted in a suitable nonlinear crystal to the desired mid-infrared range. The short pulses reduce unwanted thermal effects and changes in adjacent tissue to potentially submicron-levels. The parametrically converted radiation source preferably produces pulse durations shorter than 25 ns at or near 3.0 microns but preferably close to the water absorption maximum associated with the tissue. The down-conversion to the desired mid-infrared wavelength is preferably produced by a nonlinear crystal such as KTP or its isomorphs. In one embodiment, a non-critically phased-matched crystal is utilized to shift the wavelength from a near-infrared laser source emitting at or around 880 to 900 nm to the desired 2.9-3.0 microns wavelength range. A fiber, fiber bundle or another waveguide means utilized to separate the pump laser from the optical parametric oscillation (OPO) cavity is also included as part of the invention.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
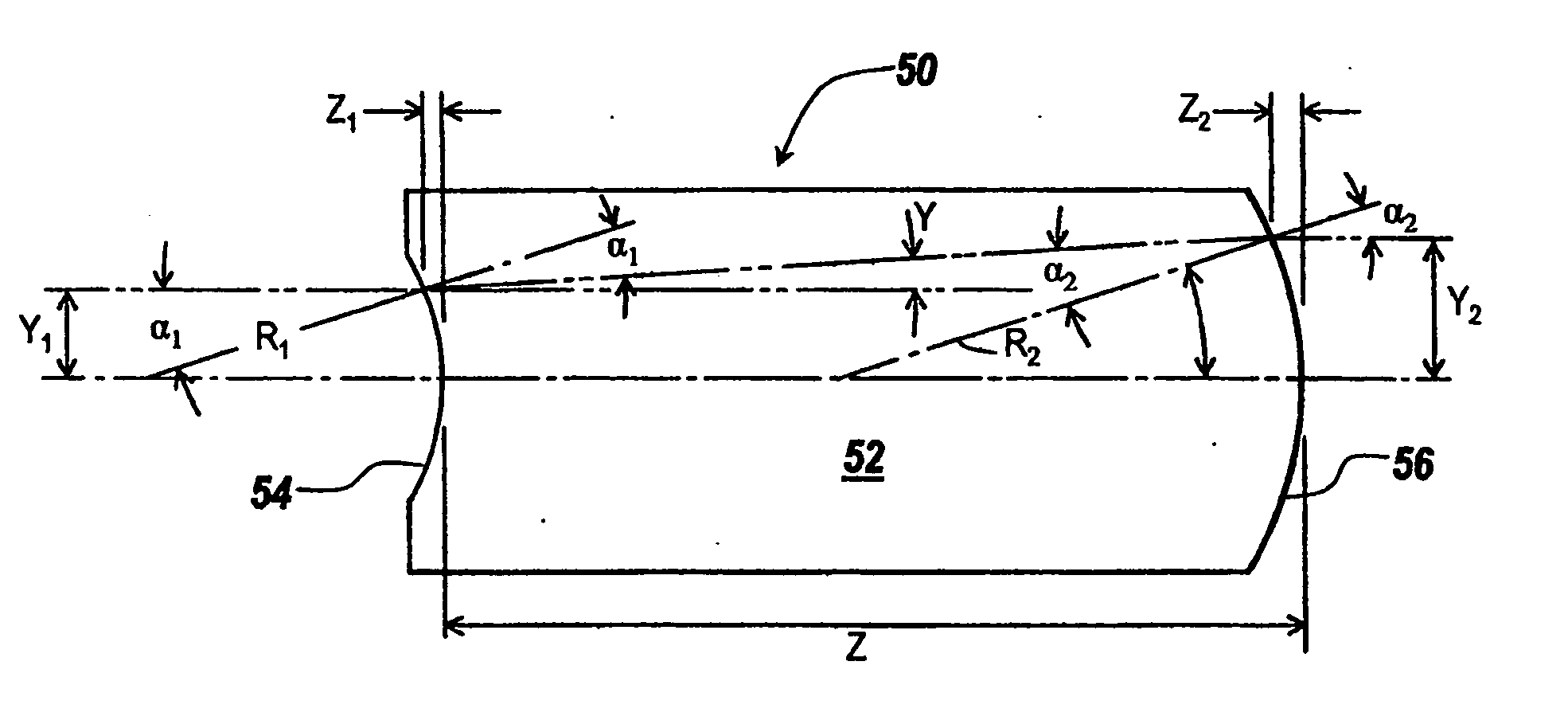
Singlet telescopes with controllable ghosts for laser beam forming
A singlet telescope is provided for reshaping the laser beam to a larger or smaller diameter while maintaining the inherent quality of the beam. Applications for the singlet telescope include intercavity expansion to accommodate the damage thresh-old of various components, expansion of beams to match the size of different wavelengths for final collimation, and shrinking of beams to provide high irradiance for nonlinear processes such as optical parametric oscillation and frequency doubling, with the above applications usually requiring low power magnification or demagnification. Problems involving the utilization of these telescopes over wide temperature ranges and ghost reflections in which a light is reflected back to a pumping laser are minimized with the singlet construction, with the ghost reflections potentially creating damage of components including self-damage or breakdown of air, as well as damage to a Q-switched resonator which causes pre-lasing.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Method and apparatus for optical frequency comb generation using a monolithic micro-resonator
ActiveUS7982944B2Low costReduce power consumptionLaser detailsElectromagnetic transmissionElectricityLaser light
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) arrays pumped solid-state lasers
ActiveUS7430231B2Efficient couplingCompact and robustOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserVertical-external-cavity surface-emitting-laser
Solid-state lasers pumped by incoherent or partially coherent, monochromatic light sources such as high power VCSEL arrays. Efficient and uniform injection of pumping energy into gain medium is achieved through spectral match of the pump source with the gain medium absorption and multi-bounce reflections of unabsorbed pump light in a diffusing pump chamber. One preferred embodiment of the diffusing pump chamber is a hollow cylinder coaxially surrounding the gain medium. One or more transparent windows, slit-shaped or otherwise, for transmission of pump light are evenly distributed around the perimeter of the chamber and are parallel to the axis. Another preferred embodiment of the diffusing pump chamber is a highly reflecting compound parabolic concentrator. A 2-D VCSEL array is employed as the pump source and the gain medium is located at the focusing point of the chamber. This invention demonstrates solid-state lasers that are compact, robust, low-cost, and able to produce high power output in CW or pulse modes for practical applications. An important application of the present invention is high-power solid-state lasers featuring wavelength conversion such as optical parametric oscillation and second-harmonic generation. Another important application of the present invention is injection seeding, especially for pulse mode with high repetition rates.
Owner:PAVILION INTEGRATION
Vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) arrays pumped solid-state lasers
ActiveUS20060245460A1Efficient couplingCompact and robustOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserVertical-external-cavity surface-emitting-laser
Solid-state lasers pumped by incoherent or partially coherent, monochromatic light sources such as high power VCSEL arrays. Efficient and uniform injection of pumping energy into gain medium is achieved through spectral match of the pump source with the gain medium absorption and multi-bounce reflections of unabsorbed pump light in a diffusing pump chamber. One preferred embodiment of the diffusing pump chamber is a hollow cylinder coaxially surrounding the gain medium. One or more transparent windows, slit-shaped or otherwise, for transmission of pump light are evenly distributed around the perimeter of the chamber and are parallel to the axis. Another preferred embodiment of the diffusing pump chamber is a highly reflecting compound parabolic concentrator. A 2-D VCSEL array is employed as the pump source and the gain medium is located at the focusing point of the chamber. This invention demonstrates solid-state lasers that are compact, robust, low-cost, and able to produce high power output in CW or pulse modes for practical applications. An important application of the present invention is high-power solid-state lasers featuring wavelength conversion such as optical parametric oscillation and second-harmonic generation. Another important application of the present invention is injection seeding, especially for pulse mode with high repetition rates.
Owner:PAVILION INTEGRATION
Multi-wavelength terahertz wave parametric oscillator
InactiveCN102331649AAchieve continuous tuning outputTuning method is simpleNon-linear opticsResonancePrism
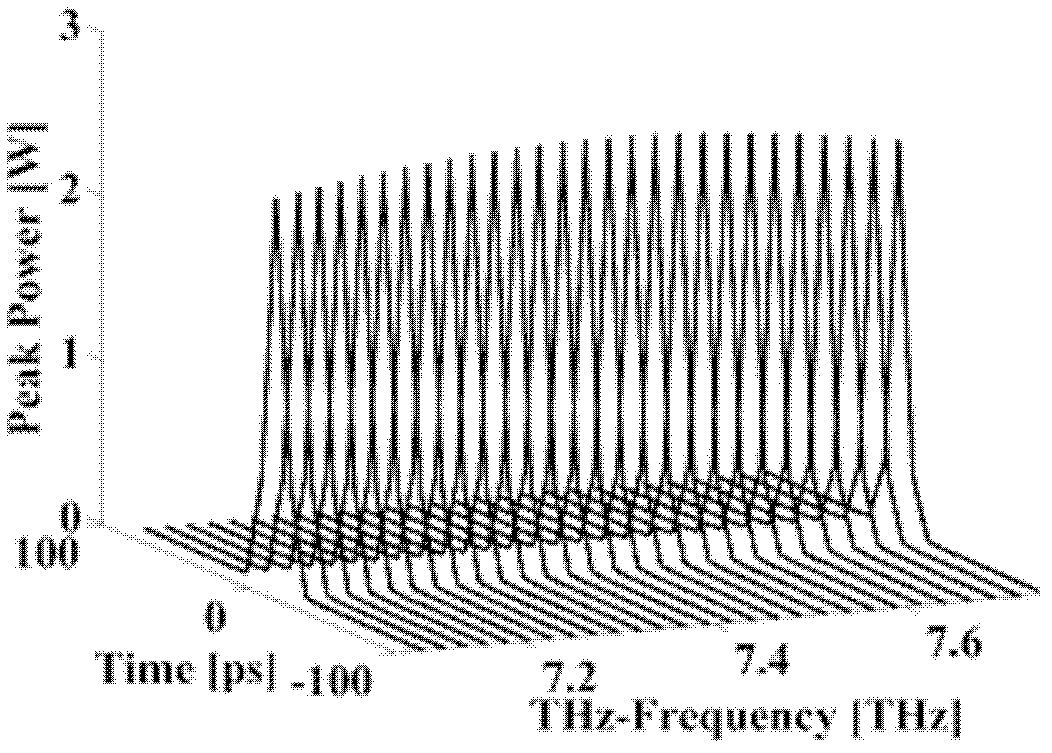
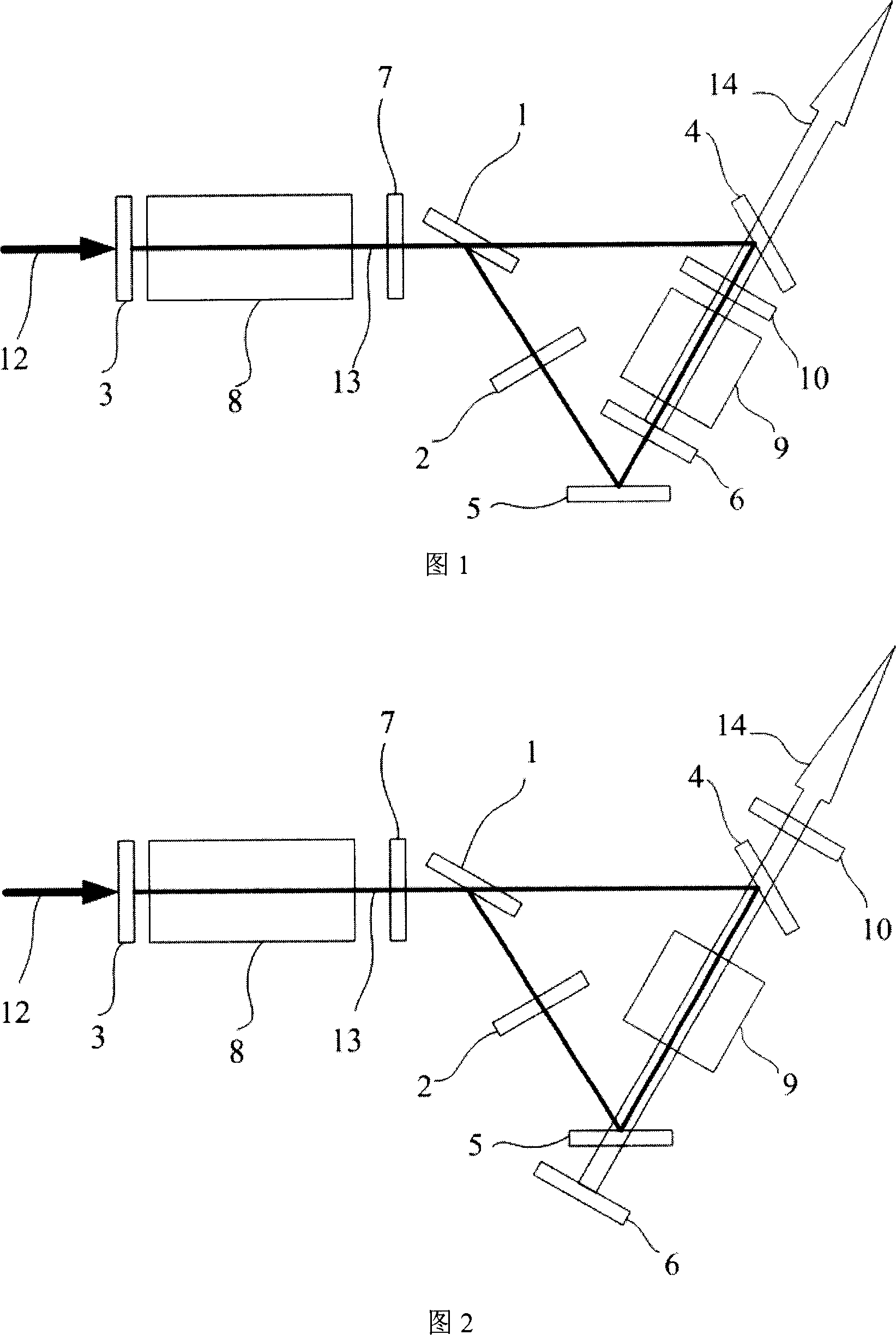
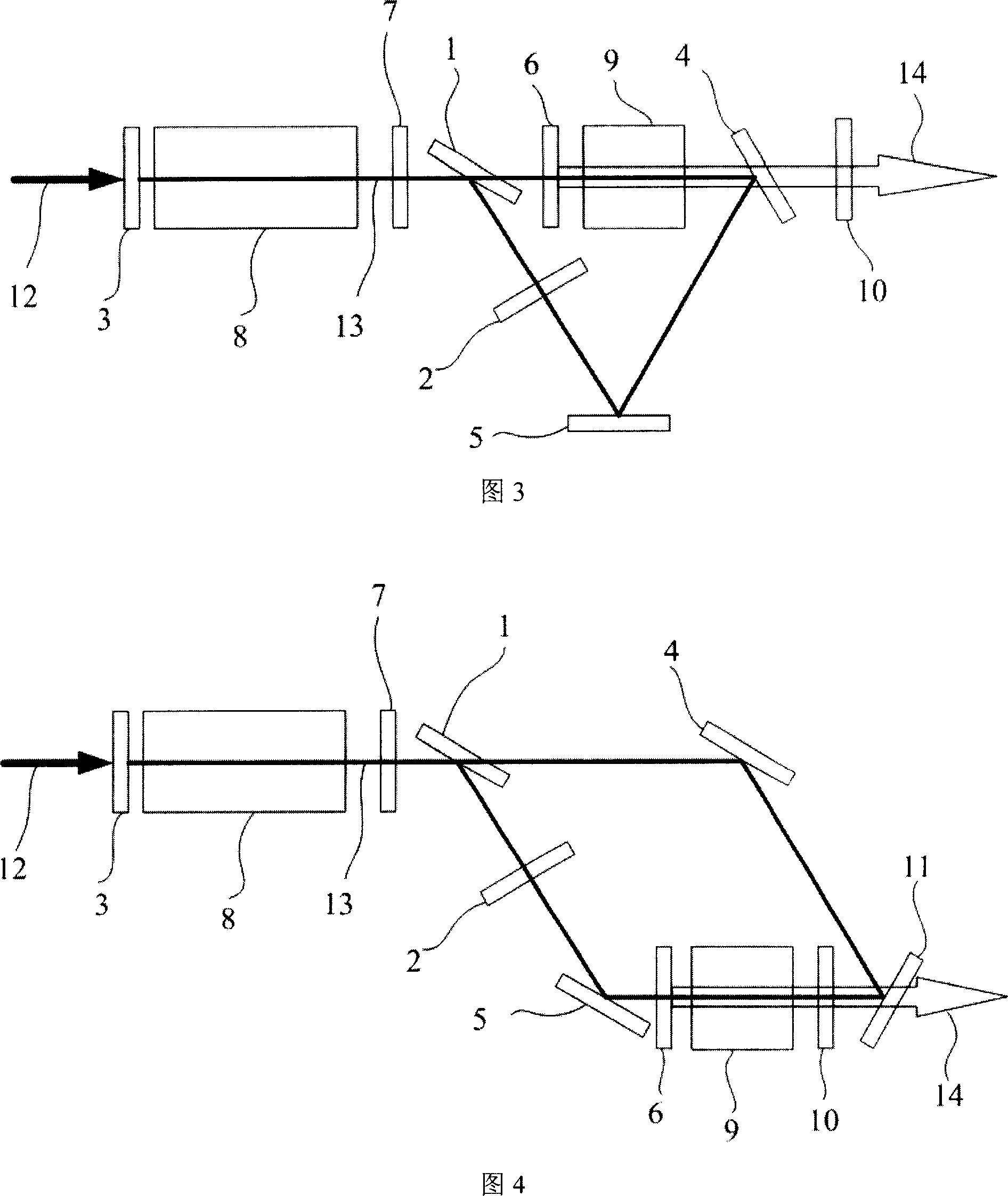
The invention discloses a multi-wavelength terahertz wave parametric oscillator, which comprises a laser pump cavity and a terahertz wave parametric oscillation cavity, wherein the laser pump cavity consists of a totally reflecting mirror, a one-fourth wave plate, an electro-optical Q-switch device, a polarizer, a pulse laser pump source module, a micropore diaphragm and a laser output mirror; the terahertz wave parametric oscillation cavity comprises two right-angle prism resonance cavities respectively consisting of a right-angle prism, a reflector, a MgO:LiNbO3 crystal arranged between themicropore diaphragm and the laser output mirror, and a plurality of semi-circular output mirrors; and two silicon prism arrays are arranged on the surface of the MgO:LiNbO3 crystal. Pump light oscillating back and forth in the laser pump cavity is vertically transmitted to the MgO:LiNbO3 crystal, and two beams of oscillating Stokes light and two groups of four-beam terahertz waves are generated through excitation in the two right-angle prism resonance cavities, and are transmitted out of the silicon prism arrays. The continuous tunable output of the two groups of four-beam terahertz waves canbe realized, and the output energy is basically equal.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Cascaded noncritical optical parametric oscillator
InactiveUS6785041B1Low pumping thresholdImprove efficiencyLight demodulationNon-linear opticsPath lengthMid infrared
Method and system for providing laser light that is tunable over a relatively wide mid-infrared wavelength range, such as 2-17 .mu.m. A first noncritically phase matched nonlinear crystal receives a laser light beam and converts the light to a first cavity beam having a first selected wavelength, using optical parametric oscillation techniques. A second noncritically phase matched nonlinear crystal receives the first cavity beam and converts the light to a second cavity beam having a second selected wavelength. Where the first wavelength is tuned (e.g., by temperature change or effective path length change) over a wavelength range of 2-5 .mu.m, the second wavelength can vary over a higher and broader wavelength range, such as 3-17 .mu.m.
Owner:BLUELEAF LLC
Generation of frequency-pre-selectable radiation by using more than one cascaded frequency conversion processes of resonantly enhanced beams
InactiveUS20110150015A1Improve frequency efficiencyCheap can be madeLaser detailsResonant cavityFrequency conversion
The invention describes methods and apparatus for the generation of laser radiation with pre-selectable frequency, which could be bigger or smaller than its fundamental beam frequency, through a combination of two or more intracavity frequency conversion processes of two or more resonantly enhanced beams. These techniques are particularly useful for generating continuous wave tunable frequency radiation in uv, visible and infrared wavelength ranges. These processes can be a combination of an intracavity fundamental beam pumped optical parametric oscillation (OPO) and an intracavity sum- or difference-frequency-mixing of the fundamental laser beam with an OPO generated beam and an intracavity frequency doubling the optical parametrical generated signal or idler beam to desirable frequencies for continuous wave. These plural intracavity nonlinear processes can be a combination of an intracavity or resonantly cavity-build-up fundamental beam pumped OPO and another frequency conversion within this OPO and the fundamental cavity. These intracavity enhanced frequency conversion processes allow for minimizing the parent frequency beams' losses and increasing the final conversion and, particularly, highly efficient conversion for continuous waves.
Owner:ZHOU DR JIANPING
Certainty soliton mode locking method for Kerr optical frequency comb in optical microcavity
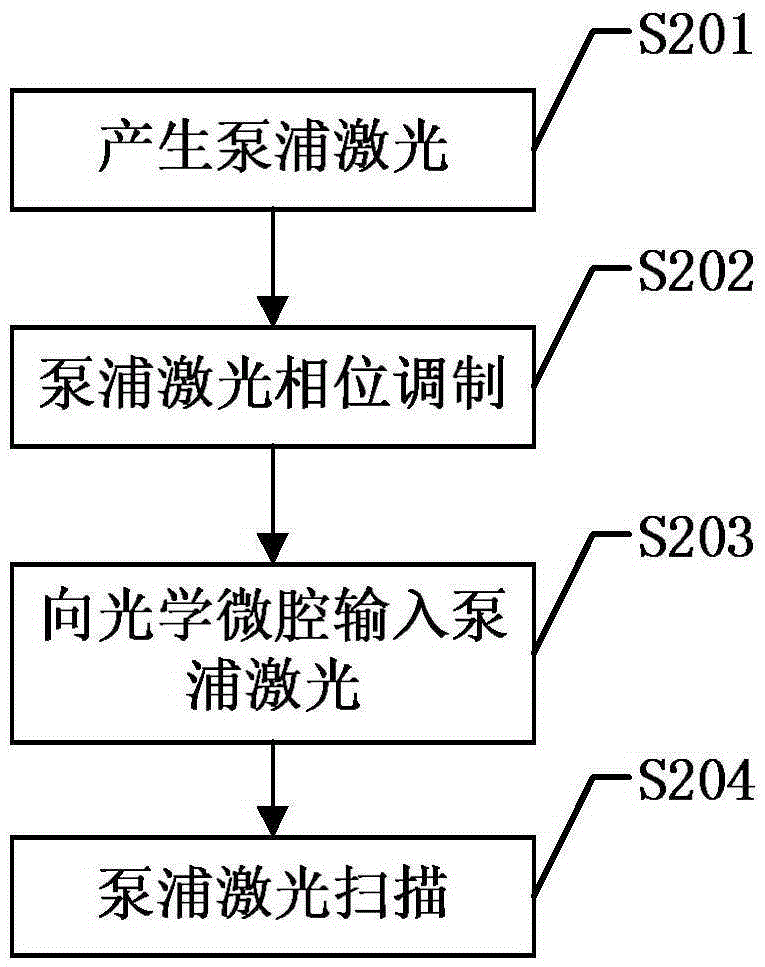
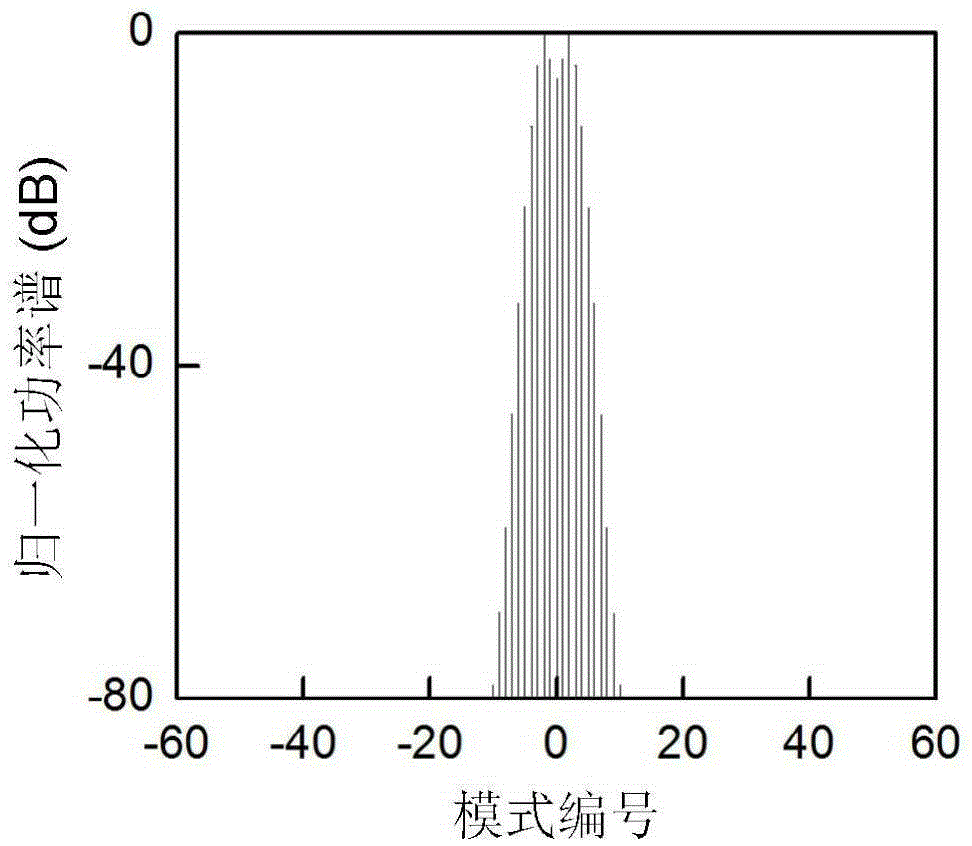
The invention discloses a certainty soliton mode locking method for a Kerr optical frequency comb in an optical microcavity. A pump laser power is set to be less than optical microcavity parametric oscillation threshold valve power; the generated pump laser is modulated; the frequency of a modulating signal is accordant with free frequency spectrum width of the optical microcavity; the amplitude of the modulating signal is obtained by calculating three-order dispersion value of the optical microcavity; the pump laser, after being subjected to phase modulation, enters the optical microcavity through a microcavity coupler in a coupling manner; the coupling coefficient is controlled to enable the optical microcavity to work in a critical coupling state; the pump laser is scanned from a long wavelength direction to a short wavelength direction in the optical microcavity; the spectrum of the output pump laser is collected at the output end of the optical microcavity; and in case that the current pump laser spectrum comprises a smooth envelope, the soliton mode locking is finished, and the scanning is stopped. According to the certainty soliton mode locking method for the Kerr optical frequency comb in the optical microcavity, the problems of high randomness, low reliability, high probability of disturbance and the like of the existing Kerr optical frequency comb mode locking scheme are overcame, so that the rapid and accurate soliton mode locking is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Generating device for continuous variable polychrome entangled optical field
InactiveCN103091933ACompact structureImprove performanceNon-linear opticsQuantum memoryOptical field
The invention provides a generating device for a continuous variable polychrome entangled optical field. The generating device for the continuous variable polychrome entangled optical field comprises a laser device, two non-degenerate optical parametric oscillation cavities and three to five unequal-arm Mach-Zehnder interference measuring systems. Due to the fact that the two cascading non-degenerate optical parametric oscillation cavities are utilized to generate the continuous variable polychrome entangled optical field, the generating device for the continuous variable polychrome entangled optical field has the advantages of being compact in structure, convenient to adjust, good in reliability and the like. The generated continuous variable polychrome entangled optical field can be applicable to both quantum memory and quantum communication and has important application values in quantum information networks.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Infrared laser in ultra quantum conversion limit based on optic superlattice and construction method thereof
The invention discloses a construction method of an infrared laser in ultra quantum conversion limit based on optic superlattice. By utilizing the optic superlattice of the structure, the structure of the optic superlattice provides two reciprocal lattice vectors simultaneously, wherein one reciprocal lattice vector is used for compensating phase mismatch in an OPO (optical parametric oscillation) process from near infrared to intermediate infrared, and the other reciprocal lattice vector is used for compensating phase mismatch in a signal light pump OPA (optical parametric amplification) from the OPO process, in the process, the intermediate infrared laser which is generated in the OPO process can be amplified further, thus more efficient intermediate infrared laser output of the ultra quantum conversion limit is obtained; and a commensurability ratio double periodic structure is adopted for the optic superlattice, thus the more efficient intermediate infrared laser of the ultra quantum conversion limit is obtained.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ADVANCED LASER TECH
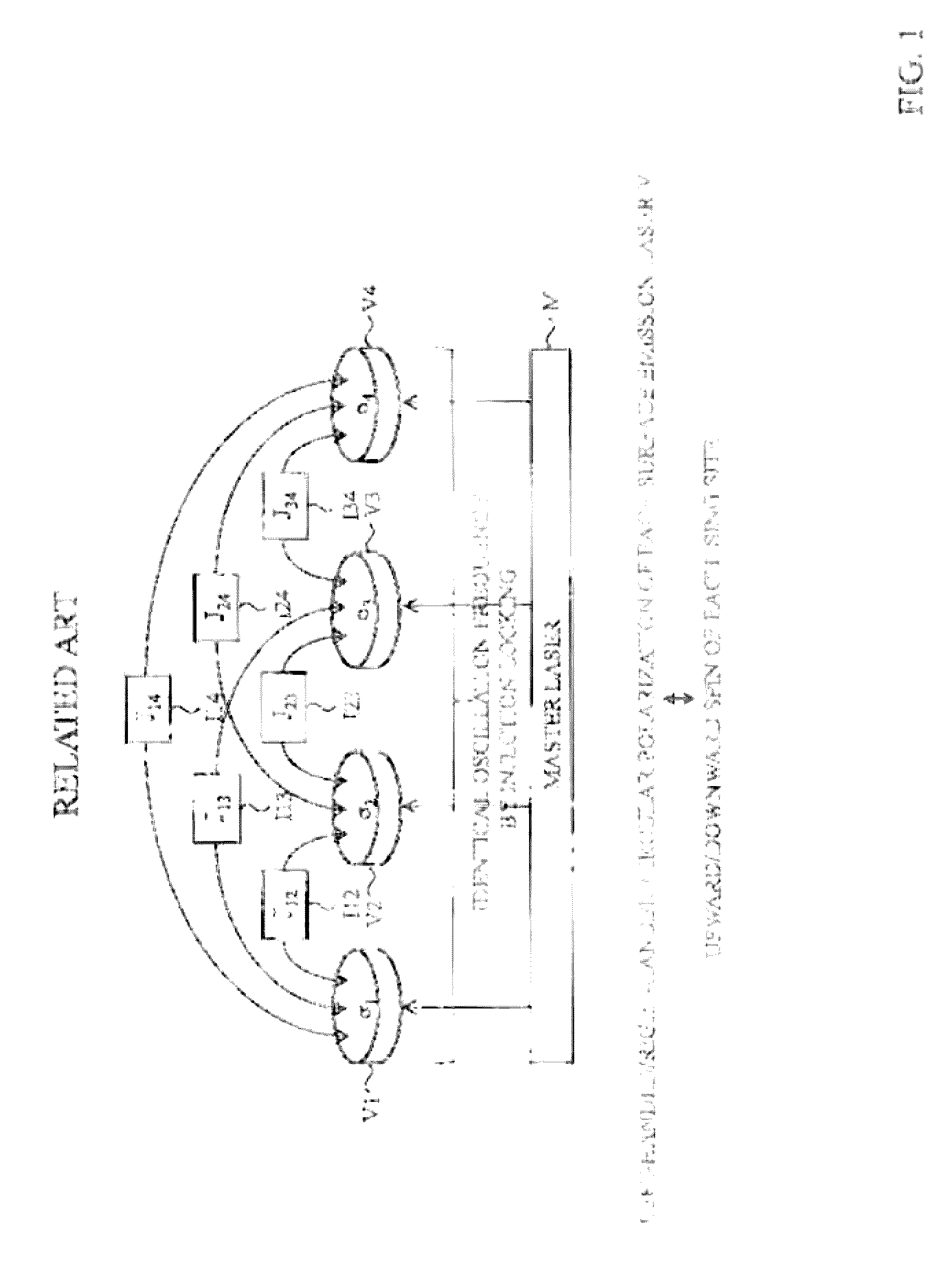
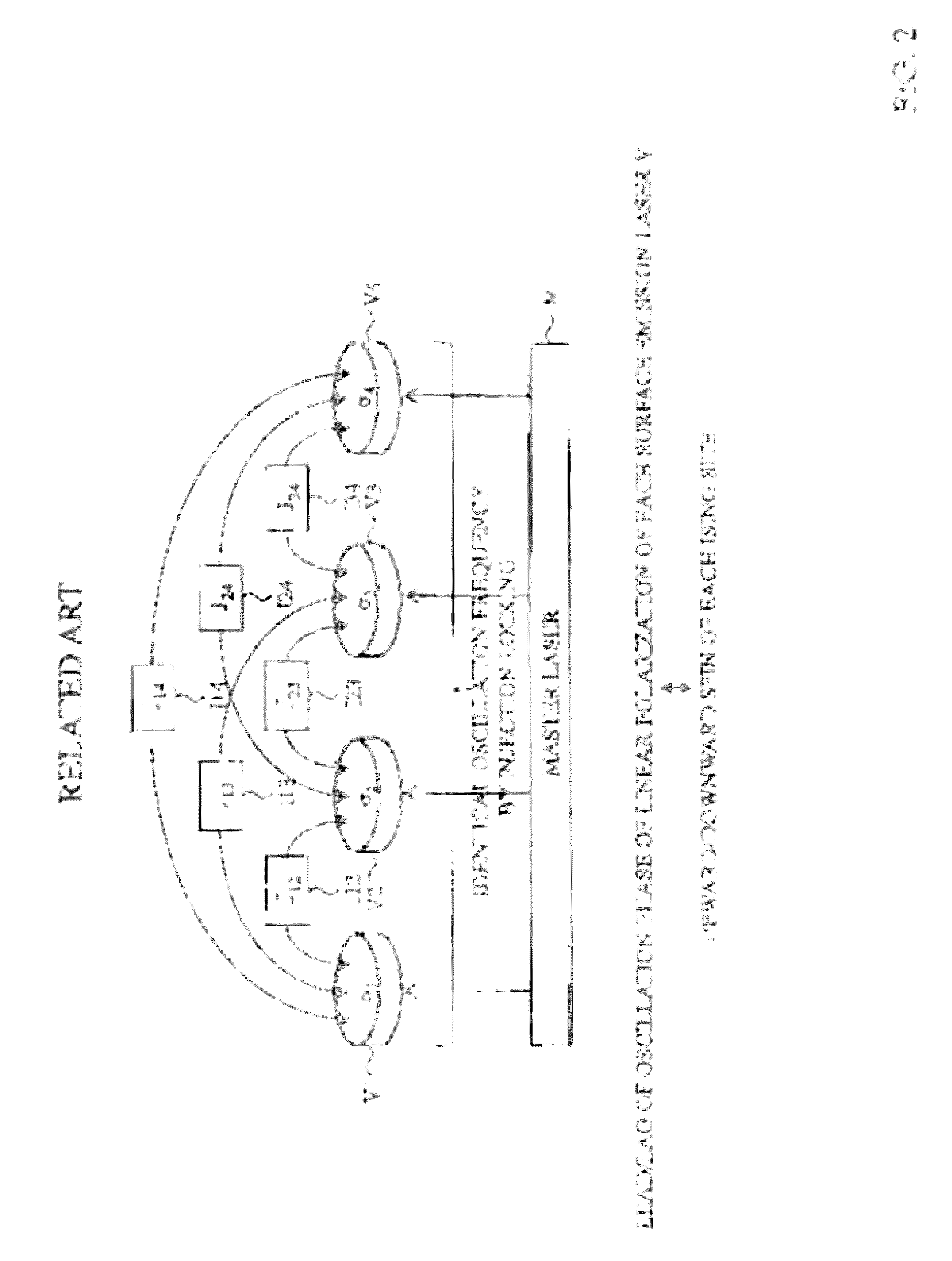
Quantum computing device for ising model, quantum parallel computing device for ising model, and quantum computing method for ising model
ActiveUS20170024658A1Simple circuit configurationAvoid mistakesQuantum computersMagnetic measurementsIsing modelParametric oscillator
A parametric oscillator oscillates a plurality of pseudo spin pulses SPi having mutually an identical oscillation frequency by using parametric oscillation, an interaction implementing unit performs feedback implementation of a magnitude and a sign of interaction related to each pseudo spin pulse SPi (the proportionality coefficient λi+ΣJijσj+ΣKijkσjσk with respect to σi) by using a tentative measurement result of oscillation phases φi(tentative) of the plurality of pseudo spin pulses SPi, and a pseudo spin measuring unit measures the pseudo spins σi of the plurality of pseudo spin pulses SPi, based on a final measurement result of oscillation phases φi(steady) of the plurality of pseudo spin pulses SPi.
Owner:INTER UNIV RES INST RES ORG OF INFORMATION & SYST +1
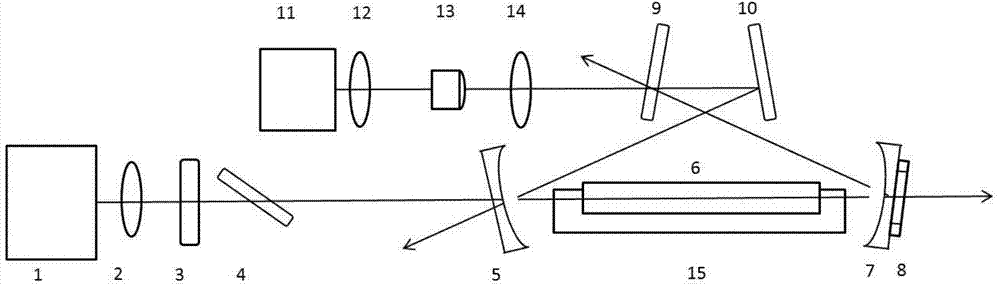
Intermediate infrared single-frequency optical parametric oscillator
The invention discloses an intermediate infrared single-frequency optical parametric oscillator. The intermediate infrared single-frequency optical parametric oscillator comprises a pumping laser, a focusing lens, a half-wave plate, a polarizer, a plano-concave partial reflection mirror, a PPLN crystal, a plano-concave total reflection mirror, a piezoelectric ceramic, a planar coupling mirror, a planar reflecting mirror, a DFB seed laser, an collimation lens, an isolator, a focusing lens and a crystal temperature controlling furnace. According to the intermediate infrared single-frequency optical parametric oscillator, through the addition of a seed laser of 1.57 micrometers, optical parametric oscillation of 3.3 micrometers is realized; the intermediate infrared single-frequency optical parametric oscillator can be applied to the fields of medical diagnosis, light spectrum resolution, military detection, and the like, and has the characteristics of being high in conversion efficiency, high in single-frequency performance, and tunable.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optically parametric oscillator
ActiveCN101499608ASatisfy Phase Matching RequirementsAchieving tuned outputActive medium materialNon-linear opticsZero-dispersion wavelengthLine width
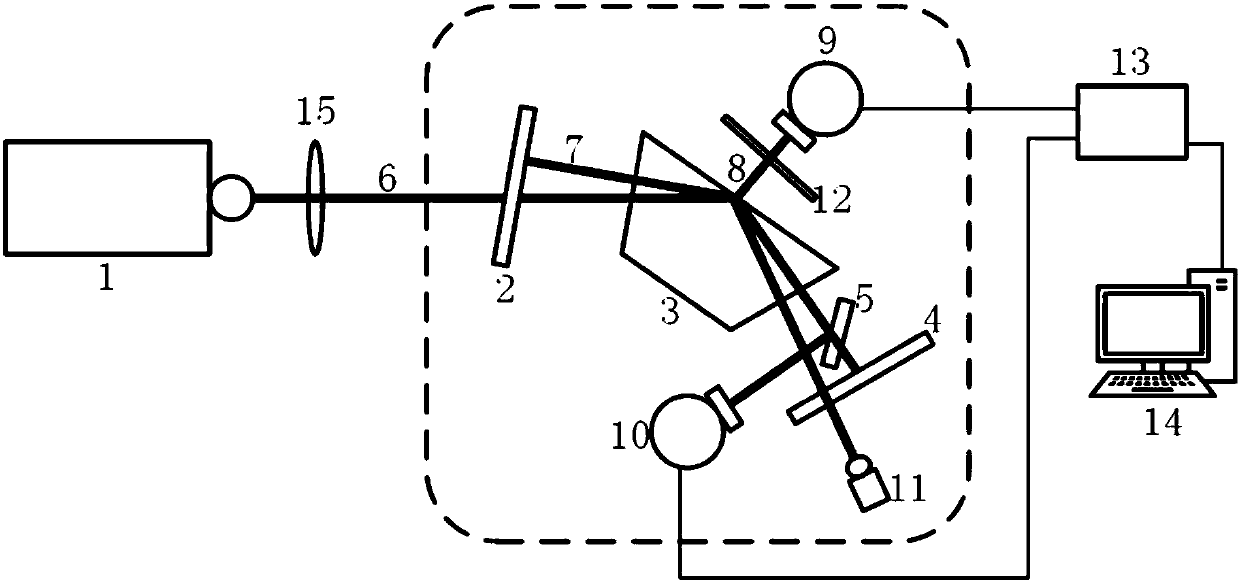
The invention relates to an optical parametric oscillator, which comprises a nonlinear optical material (1) with the double-zero dispersion wavelength, a high reflector (2), an output mirror (3), a parametric oscillation optical beam collimator (4), a parametric optical line width compressor (5), a pumped optical coupler (6), a lambda / 2 phase retarder (7), a laser power controller (8) and an optical isolator (9). The nonlinear optical material (1) has a double-zero dispersion wavelength and is arranged in a resonant cavity formed by the high reflector and the output mirror. The pumped optical wavelength is in the anomalous dispersion regime of the photonic crystal fiber, thereby ensuring the phase matching conditions and generating the highly efficient four-wave mixing effect. For the parametric oscillation formed by simplifying the four-wave mixing, the wavelengths of the two parametric lights are respectively arranged at the double-zero dispersion wavelength of the photonic crystal optical fiber, thereby realizing the group velocity dispersion compensation of the parametric light, solving the problem of the ultra-short pulse dispersion compensation, and greatly reducing the pumping threshold.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Solid state terahertz radiation frequency multiplier
InactiveUS20100073110A1Improve efficiencyMultiple-port networksNanoopticsTerahertz radiationDistributed structure
A nonlinear solid-state device useful for frequency conversion of electromagnetic radiation and in particular for harmonic generation, comprising a waveguiding electromagnetically distributed structure (WEDS) which includes monolithically a synthetic nonlinear material (SNM). Input radiation coupled into the WEDS is converted into a higher frequency output radiation through a constricted oscillatory motion of charge carriers and phase matched harmonic frequency generation of radiation which builds up coherently over an interaction length many time larger than the radiation wavelengths. In one embodiment, microwave radiation is converted into terahertz radiation. In other embodiments, SNM based WEDS devices are adapted for frequency mixing and parametric oscillation.
Owner:GOVER AVRAHAM +2
Multifunctional coherent raman scattering biological imaging light source
ActiveCN108963748AHigh-resolutionIncrease profitLaser using scattering effectsBeam splitterTime delays
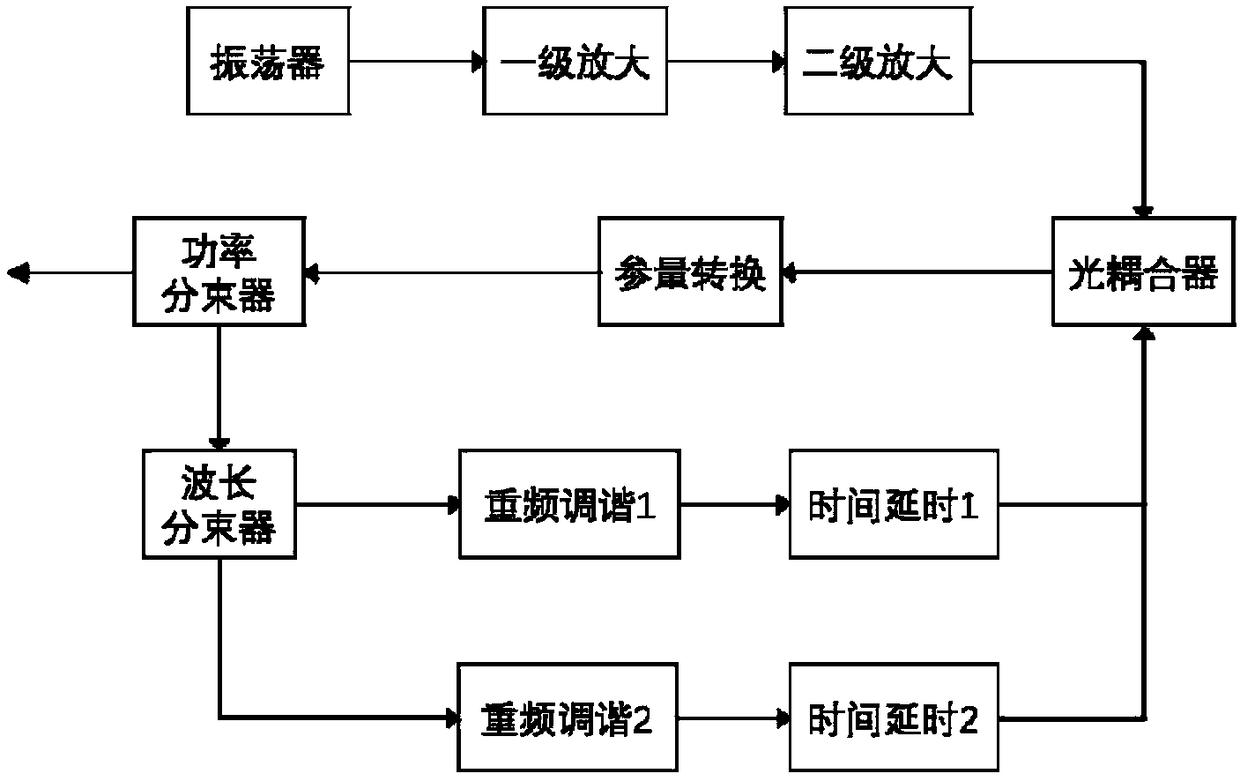
The invention relates to a multifunctional coherent raman scattering biological imaging light source. Seed light output by a laser oscillator passes through primary and secondary amplification modules, so average power is improved, and a threshold value condition of parametric conversion is met. Amplified light enters a parametric conversion module through an optical coupler, so stokes light is generated and then is subjected to beam splitting through a power beam splitter. One part of the light is used as an imaging light source to be output and the other part enters a wavelength beam splitter, so separation of the stokes light and pump light is achieved. Separated light enters two repeated-frequency tuning modules which are capable of mutually independently controlling repeated frequencyof the stokes light and the pump light and are connected with a first-time time delay module and a second-time time delay module. Chromatic dispersion is adjusted, so two beams of feedback light passes the optical coupler and then is coupled to the parametric conversion module. Pump light and stokes light fed back to the optical coupler synchronize in time and coincide in space, so double parametric oscillation feedback is achieved. Thus, the high-efficiency multifunctional coherent raman scattering biological imaging light source is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Polarization-independent quasi-phase-matching frequency multiplier and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102338966AConsistent strengthAvoid dependenceLaser detailsNon-linear opticsFrequency multiplierFundamental frequency
The invention discloses an implementing scheme of a polarization-independent quasi-phase-matching frequency multiplier. The implementing scheme comprises the following steps of: according to quasi-phase-matching conditions at room temperature, calculating a period; according to the period, selecting two same crystals to carry out room temperature polarization; pumping a fundamental frequency light source to select an optical fiber laser of which emergent light is randomly polarized; in an optical path, ensuring a c-axis of a first crystal along a z-direction, ensuring a c-axis of a second crystal along a y-direction and placing a depolarizer in front of the first crystal; and after the light passes through the frequency multiplier, measuring the light intensity of the frequency multiplier by a power meter, so that the polarization-independent quasi-phase-matching frequency multiplier can be implemented. The polarization-independent quasi-phase-matching frequency multiplier is simple and practicable. The defect of dependence of the frequency multiplying process on the polarization direction of the fundamental frequency light can be overcome. Meanwhile, the polarization-independent quasi-phase-matching frequency multiplier can be suitable for other nonlinear processes such as sum frequency, difference frequency, parametric oscillation, cascading and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Infrared laser in self-optical parametric oscillation of double-cavity composite unsteady cavity mode selection pump
ActiveCN107528197AGuaranteed non-interferenceImprove output efficiencyActive medium materialActive medium shape and constructionFiberBeam splitter
An infrared laser in a self-optical parametric oscillation of double-cavity composite unsteady cavity mode selection pump relates to the laser field. A problem that the infrared laser in a self-optical parameter based on an Nd: MgO: PPLN crystal considers matching of high power and high beam quality base frequency light self-pump and a focusing parameter during a self-optical parameter oscillation process is solved. The laser comprises two laser diode pump sources, two energy transfer fibers, four focusing lenses, two 45 degree beam splitter mirrors, a parameter-oscillation-cavity totally-reflective mirror, a parameter oscillation cavity output mirror, the Nd: MgO: PPLN crystal, a temperature controller and an acousto-optic Q switch. Through adopting a double-cavity composite structure of a base-frequency optical resonant cavity and a parametric optical oscillation cavity, integration compactness is considered and simultaneously the two cavities completely work separately so that cavity-type structure parameter designs of the two cavities do not interfere with each other. Large base mode high beam quality base frequency optical pump can be realized, oscillation parameter light and base frequency light focusing parameters are highly matched, and energy conversion efficiency is high.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Nonlinear optical crystal material, preparation method and application thereof
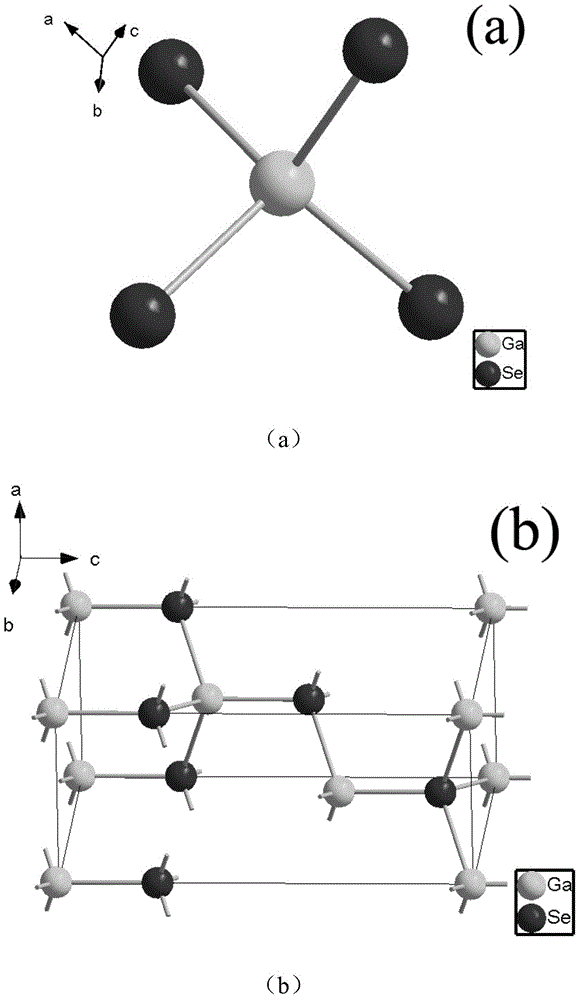
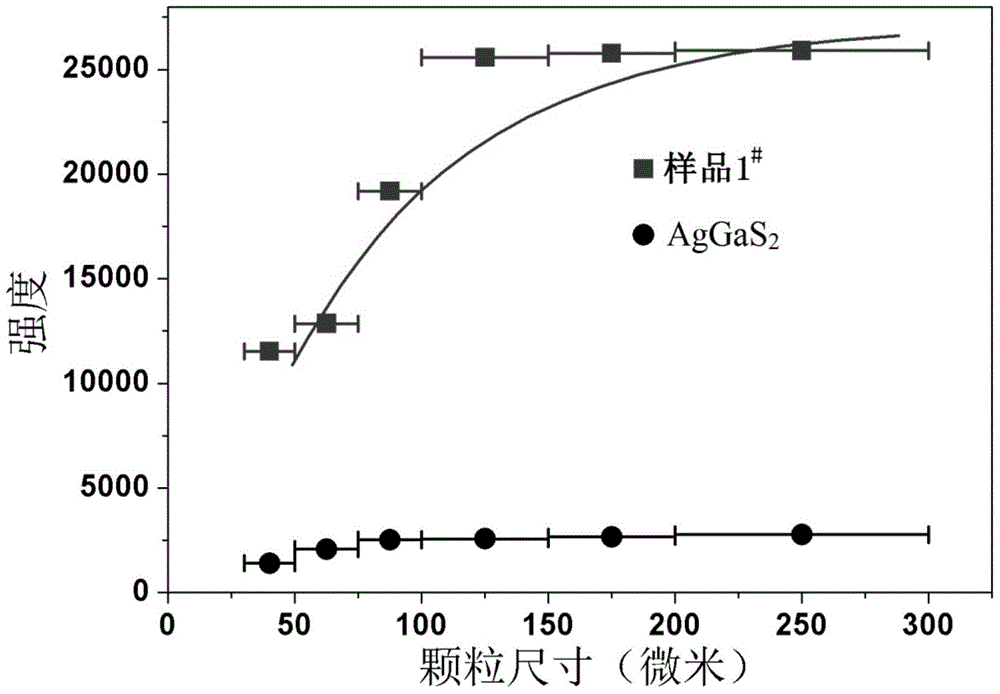
ActiveCN104532352AExcellent infrared nonlinear optical performanceHigh purityPolycrystalline material growthFrom solid stateNonlinear optical crystalLaser damage
The invention discloses a nonlinear optical crystal material, a preparation method and application thereof. The material has excellent infrared nonlinear optical properties, frequency multiplication intensity that reaches 9.3 times that of the same particle size AgGaS2, and satisfies type I phase matching. The powder laser-damaged threshold of the material can be 7.5 times that of the same particle size AgGaS2. The material provided by the invention has important application value in middle and far infrared wave band laser multiplication, sum frequency, difference frequency, optical parametric oscillation and other frequency-converters.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
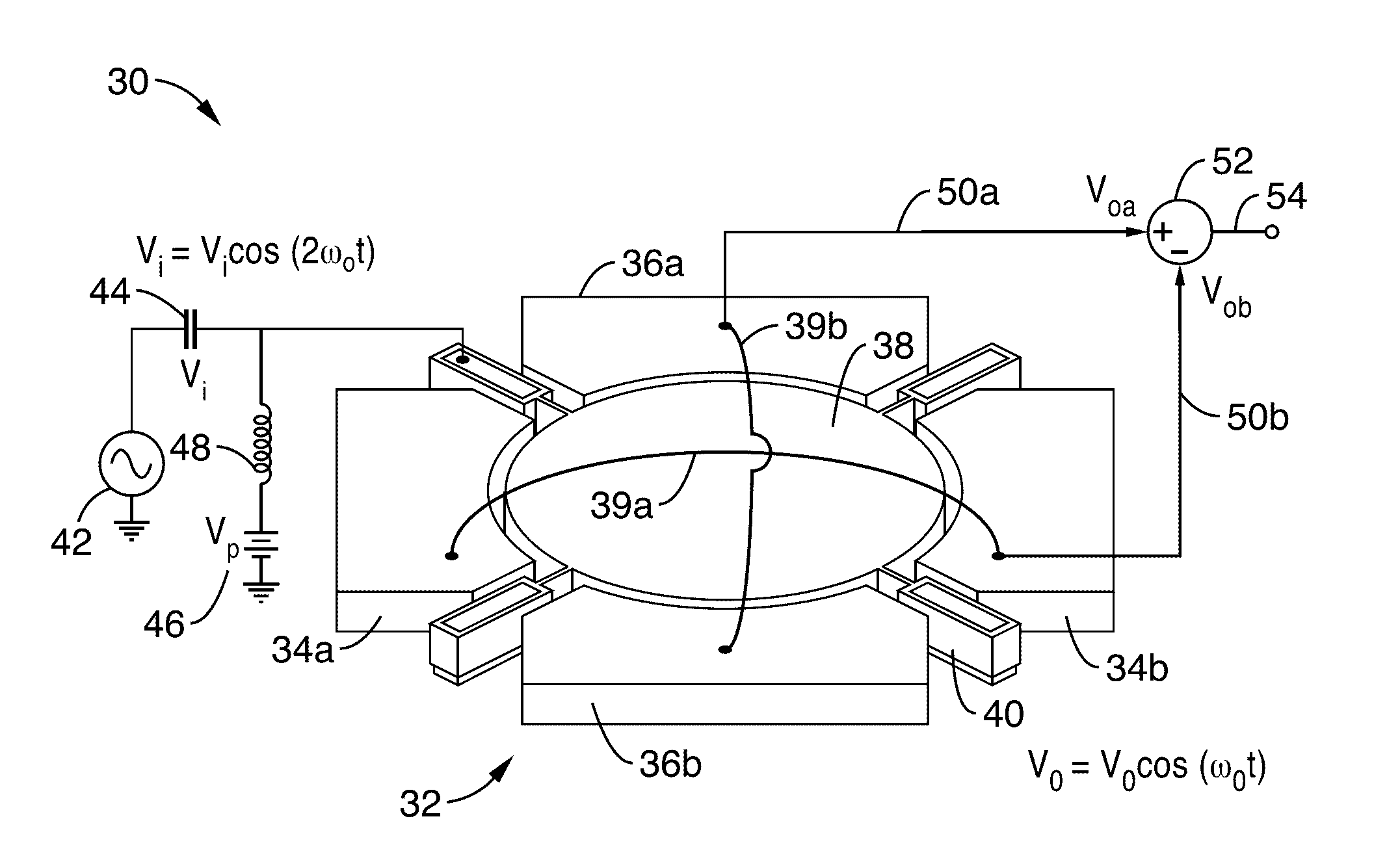
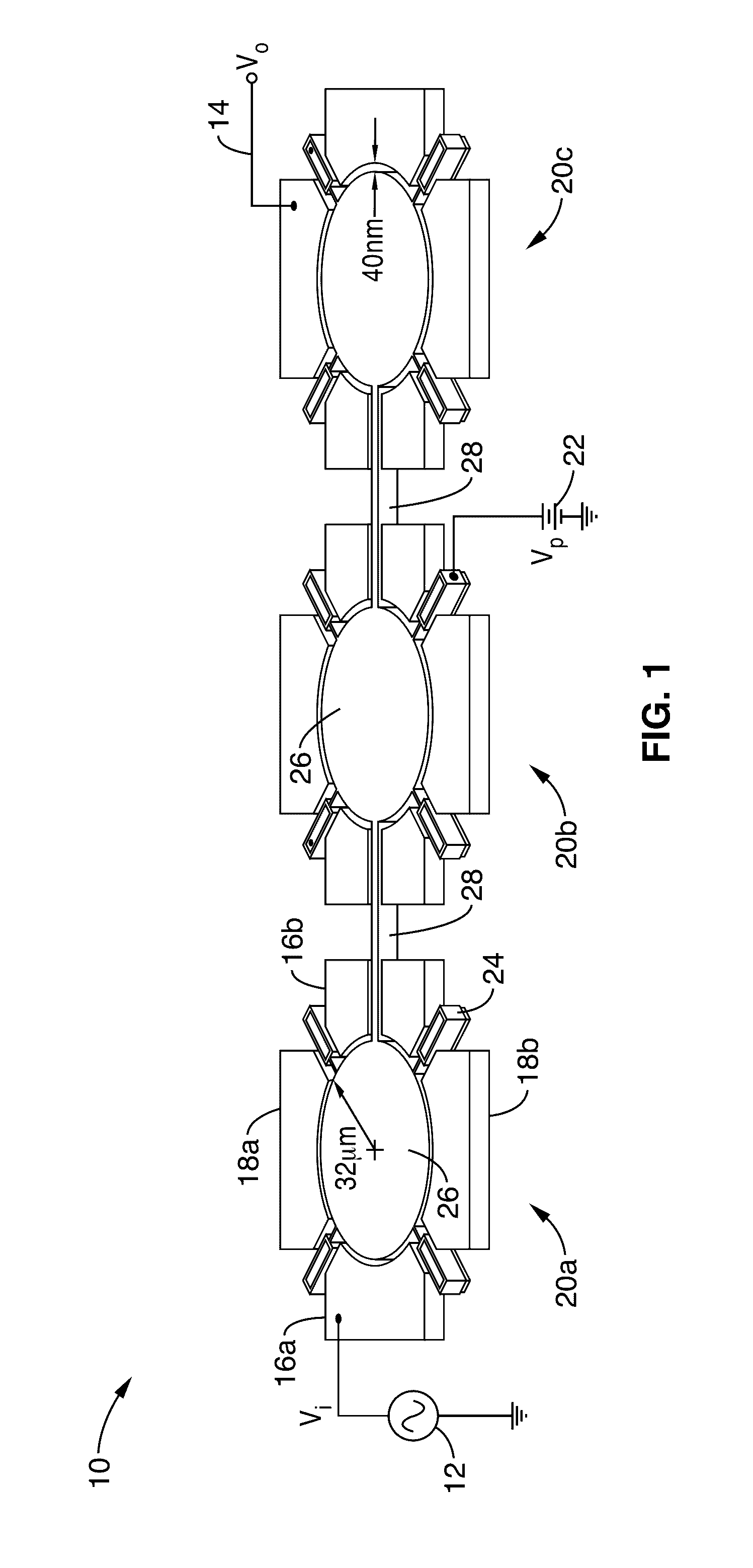
Micromechanical frequency divider
ActiveUS20170047893A1Minimal noiseHigh-frequency operationPulse automatic controlImpedence networksCapacitanceCapacitive coupling
A micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) frequency divider apparatus having one or more MEMS resonators on a substrate is presented. A first oscillator frequency, as an approximate multiple of the parametric oscillation frequency, is capacitively coupled from a very closely-spaced electrode (e.g., 40 nm) to a resonant structure of the first oscillator, thus inducing mechanical oscillation. This mechanical oscillation can be coupled through additional MEMS resonators on the substrate. The mechanical resonance is then converted, in at least one of the MEMS resonators, by capacitive coupling back to an electrical signal which is a division of the first oscillation frequency. Output may be generated as a single ended output, or in response to a differential signal between two output electrodes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
3-5-micron waveband intermediate infrared solid laser
ActiveCN103236633AAvoid badInhibitionActive medium materialNon-linear opticsResonant cavityPlane mirror
The invention discloses a 3-5-micron waveband intermediate infrared solid laser, which belongs to the optical field and aims to solve the problems of low output power and poor luminance of the traditional intermediate infrared solid laser. The 3-5-micron waveband intermediate infrared solid laser comprises a No.1 plano-convex lens, a No.2 plano-convex lens, a No.3 plano-convex lens, a No.4 plano-convex lens, a No.1 input mirror, a No.1 plane mirror, a No.2 input mirror, an OPO (optical parametric oscillator) output mirror, a lens, a No.1 optical parametric oscillation crystal and a No.2 optical parametric oscillation crystal, wherein the No.1 plano-convex lens and the No.2 plano-convex lens form a No.1 coupled system; the No.3 plano-convex lens and the No.4 plano-convex lens form a No.2 coupled system; the No.1 input mirror, the No.1 plane mirror, the No.2 input mirror and the OPO output mirror form an optical parametric oscillation resonant cavity; pumped laser light emitting laser light enters the optical parametric oscillation resonant cavity respectively by two coupled systems; and the two optical parametric oscillation crystals are used for converting the wavelength of the laser light for generating 3-5-micron waveband intermediate infrared solid laser light.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
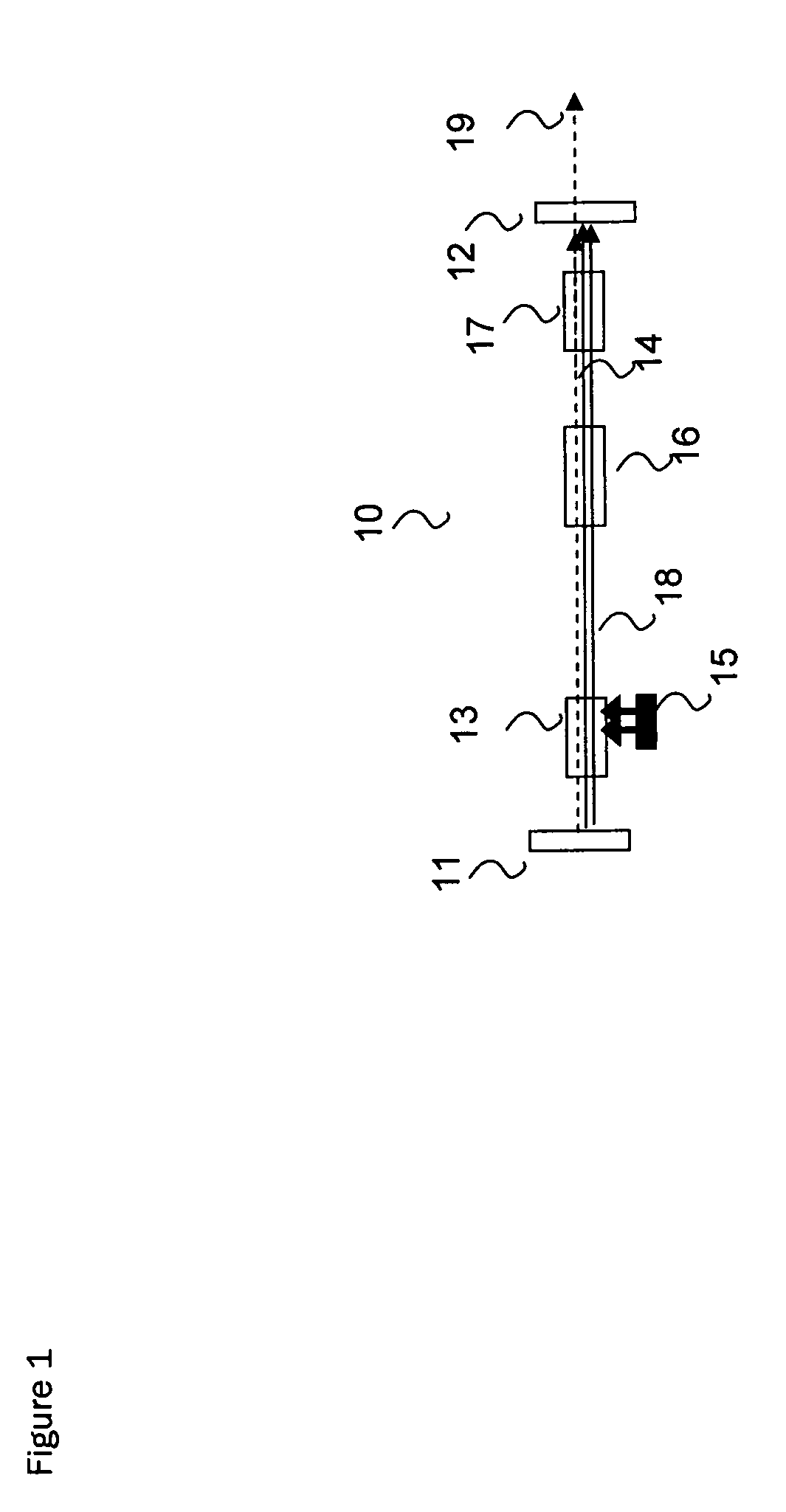
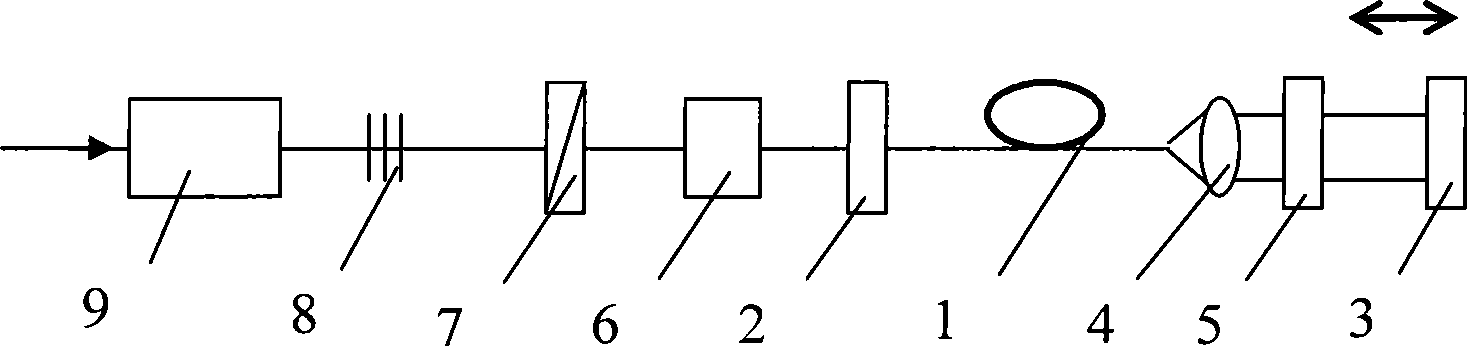
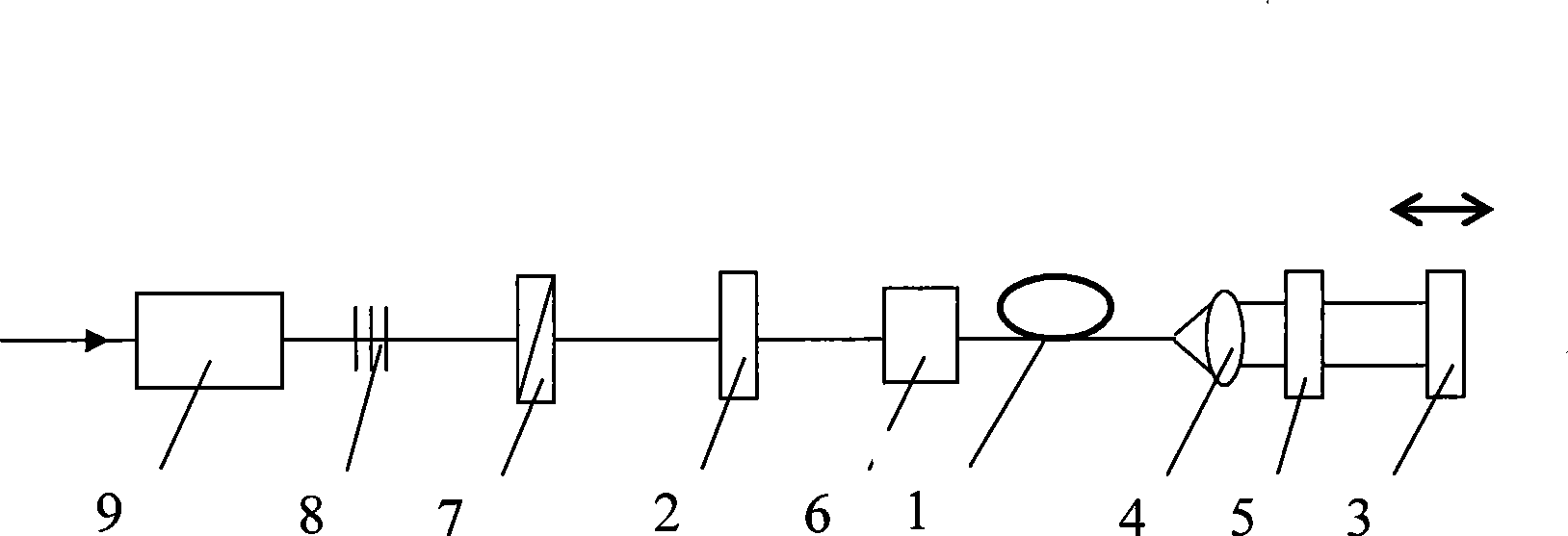
Optical parametric oscillator capable of generating 2 microns wave band laser
InactiveCN101676785AHigh effective nonlinear coefficientIncrease effective lengthLaser detailsNon-linear opticsNonlinear optical crystalResonant cavity
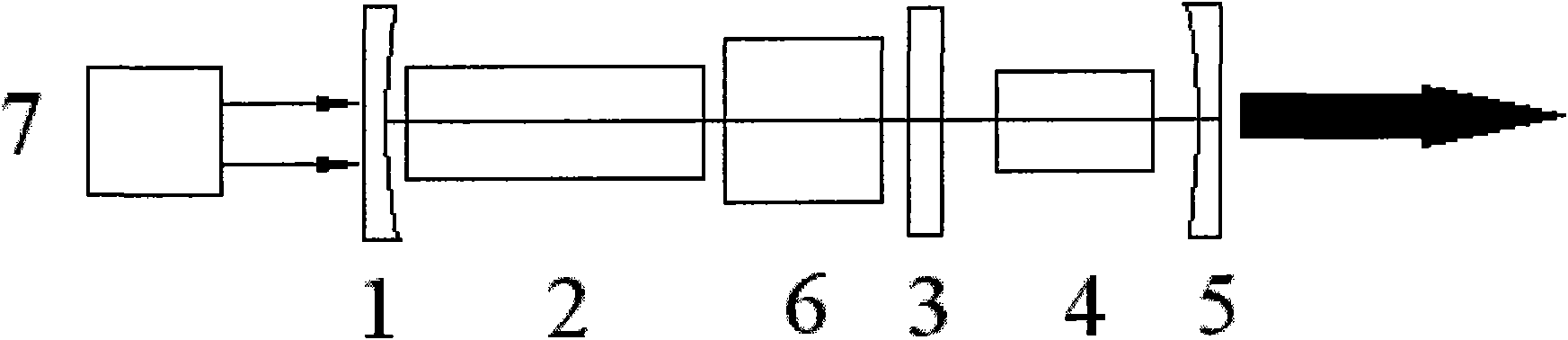
The invention relates to a novel optical parametric oscillator capable of generating 2 microns wave band laser. A pump light source (7) is used for pumping fluorescence generated by a pump laser crystal (2); 1.3 microns wave band oscillation laser can be formed inside a laser resonant cavity formed by a total reflection cavity mirror (1) and an output cavity mirror (5); a Q switch (6) is used formodulating, and the 2 microns wave band laser can be generated by parametric oscillation of a non-linear optical crystal (4); the 2 microns wave band laser is strengthened by oscillation in an opticalparametric oscillation cavity formed by a compound cavity mirror (3) and the output cavity mirror (5); and finally, the 2 microns wave band laser can be output.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Angle tuning-free THz collinear difference frequency radiation system based on cadmium telluride
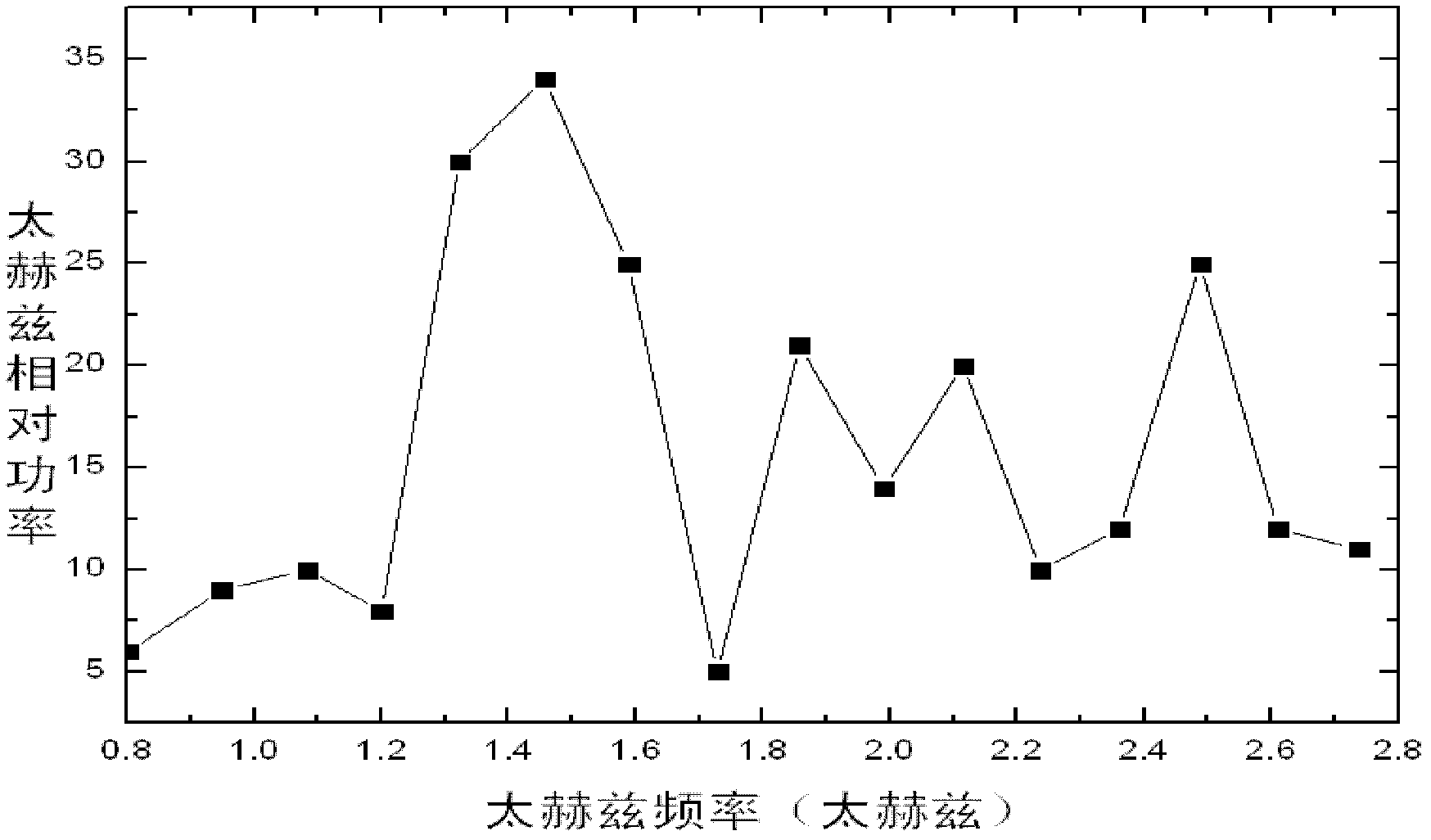
InactiveCN102570247AReduce the difficulty of operationImprove stabilitySolid masersNon-linear opticsBirefringent crystalLine width
The invention discloses an angle tuning-free nanosecond laser collinear difference frequency THz radiation system based on cadmium telluride crystals. The system can achieve THz light radiation without angle tuning by particularly using the principle of nonlinear optical collinear difference frequency and quasi-phase matching technology, and the wavelength tuning range of the system is 0.80THz to 2.74THz. The system not only has the characteristics of high power, quasi-continuity, narrow line width, room temperature operation and so on, but also has the advantages of convenient wavelength tuning by only tuning the output wavelength of a tunable laser, high easiness in adding an external infrared resonant cavity, compact structure, easy construction, high system stability, high convenience for actual large-scale application and so on in comparison with a radiation system using birefringent crystals as THz crystals and a parametric oscillation source based on lithium niobate crystals.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Near infrared twin photon source
Optical parametric oscillator including a semiconductor microcavity being configured to spatially localize polaritons of at least three quantized polariton energy levels to effect an optical parametric oscillation.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
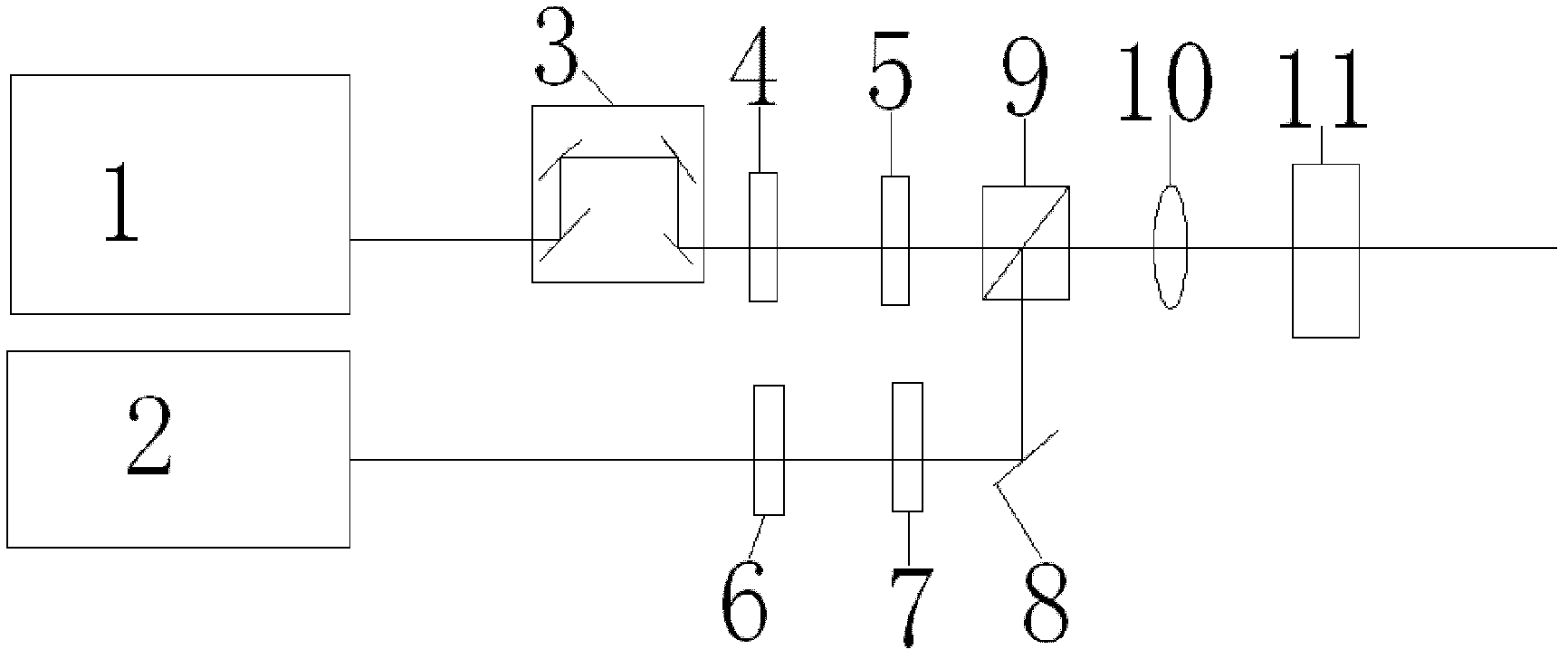
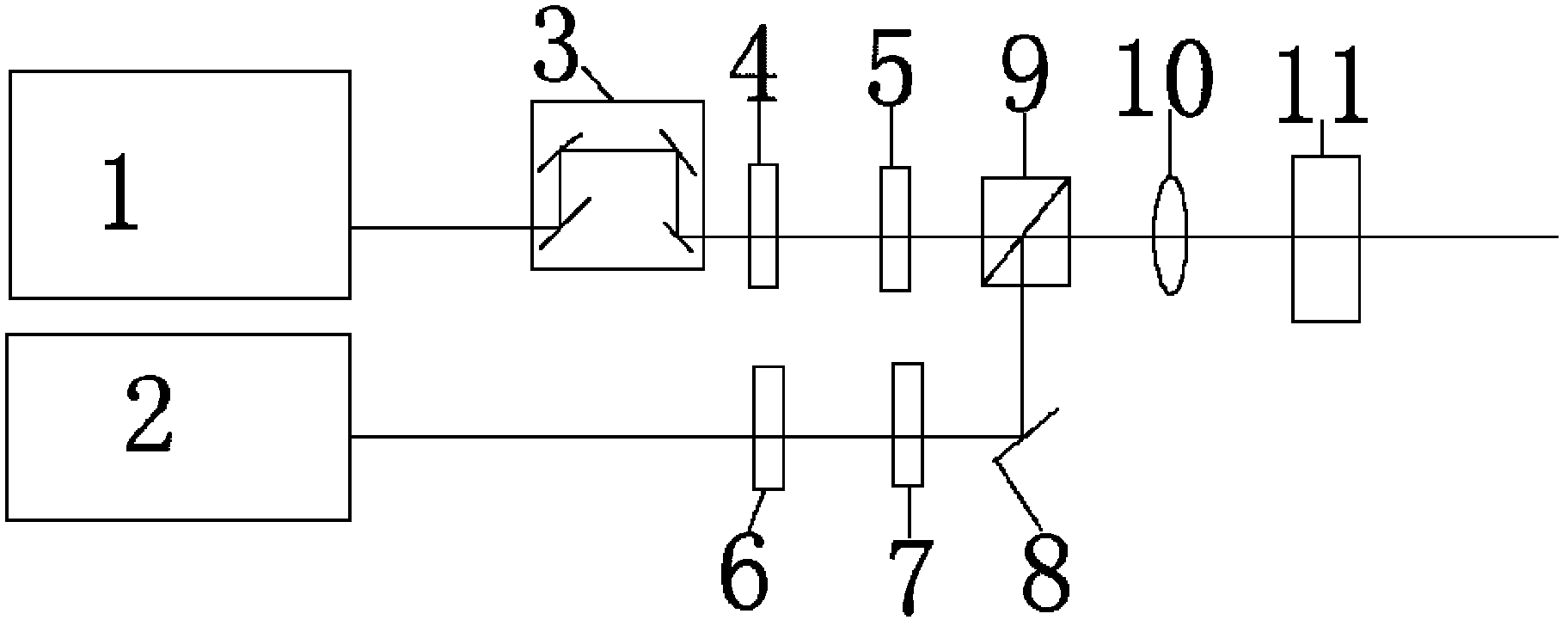
Device and method for improving measurement stability of Terahertz parametric oscillation source
PendingCN108489931AEliminate measurement errorsAvoid splittingColor/spectral properties measurementsObservational errorData acquisition
The invention discloses a device and method for improving the measurement stability of a Terahertz parametric oscillation source. The device comprises a laser, a Terahertz parametric oscillator, a Terahertz detector, a Stokes light detector, a light-beam collector, a sample, a data acquisition card, a computer and a refractive-index gradient mirror, wherein the Terahertz parametric oscillator comprises a nonlinear crystal and a Stokes light resonance cavity; the laser generates pump light which is incident to the Terahertz parametric oscillator through the refractive-index gradient mirror, onepart of the pump light is collected by the light-beam collector, and the other part of the pump light generates Stokes light and Terahertz wave on the basis of the action of stimulated polariton scattering. The device and method disclosed by the invention have the beneficial effects that by utilization of the characteristic that the stability of the Stokes light is in direct proportion to the stability of the Terahertz in the Terahertz parametric process, and the Stokes light is used as reference light of the Terahertz wave, so that the measurement error caused by instability of the Terahertzparametric source can be eliminated.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Photonic crystal fiber, THz wave parametric oscillation generating system and method
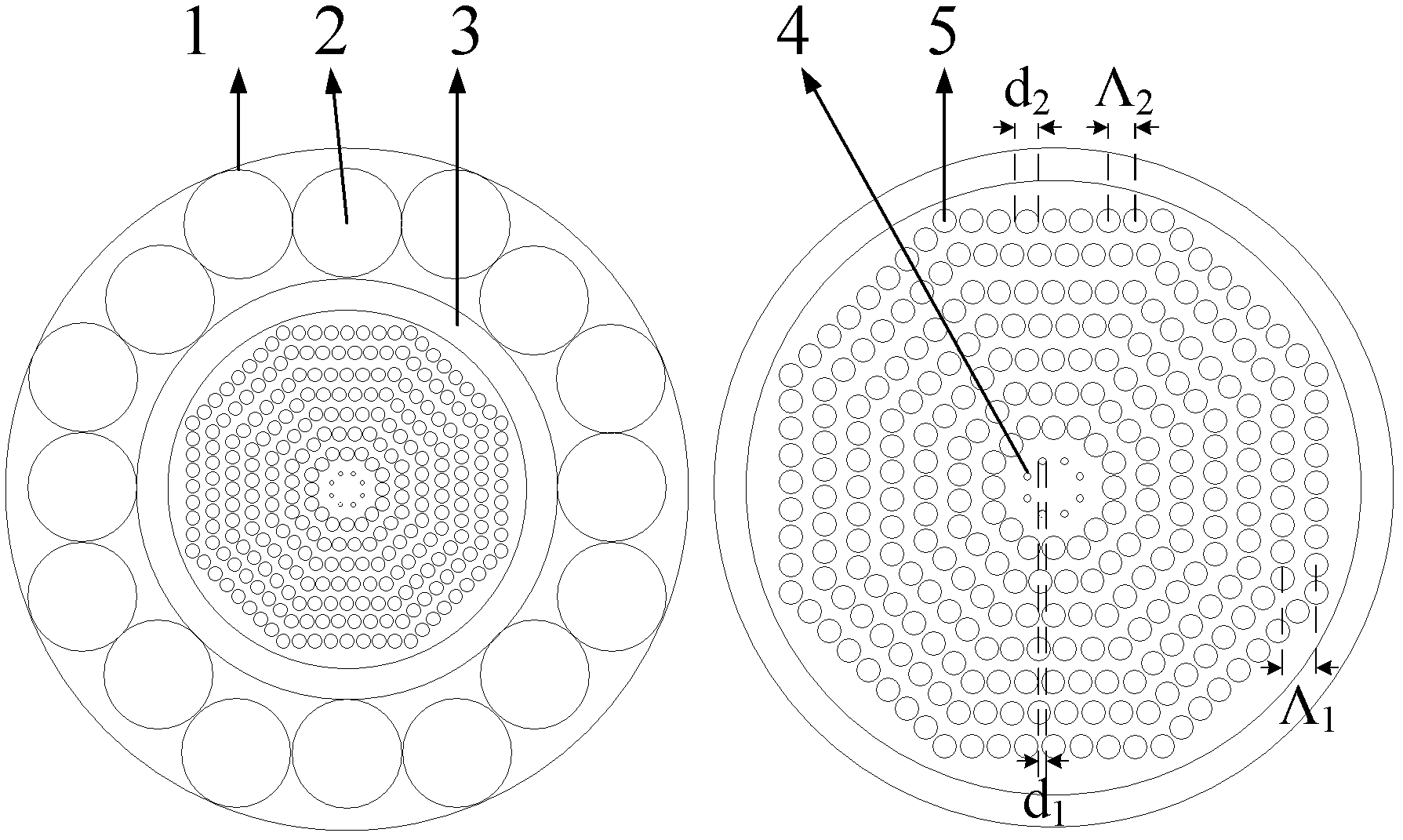
InactiveCN102540328AAdd nonlinearityIncrease powerOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingNon-linear opticsPhotonic crystalRoom temperature
The invention discloses a photonic crystal fiber, a THz wave parametric oscillation generating system and a THz wave parametric oscillation generating method. The photonic crystal fiber comprises an outer cladding, an inner cladding arranged in the outer cladding, an interlayer arranged in the inner cladding and a fiber core arranged in the interlayer, wherein the inner cladding comprises a plurality of polytetrafluoroethylene tubes uniformly distributed on the circumference, the interlayer is a polyethylene tube, and the fiber core has an octagonal structure. The technical problems of poor beam quality, low power, low efficiency and incapability of realizing operation at room temperature in the conventional method for optically generating THz wave are solved; and the THz wave parametric oscillation generating method and the THz wave parametric oscillation generating device based on the octagonal photonic crystal fiber solve the technical problems of low radiant power, complex equipment structure, high cost and poor stability in conventional photo-produced THz wave.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cascade optical parameter oscillating laser
InactiveCN1937334ASimple structureLow costOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser arrangementsResonant cavityBeam splitter
In order to overcome disadvantages of high cost and complex structure existed in laser device in high power and long wavelength, the invention discloses new type structured cascading optical parametric oscillation laser device (OPOLD) in high average power. Using polarized beam splitter component couples a sect of resonant cavity to annular cavity. 90 degrees polarization rotator is placed in the annular cavity to constitute circulated resonant cavity of polarized light. Laser in cavity can realize polarization state circulated resonant of polarized light in two frequencies or near degeneracy. First stage OPOLD and second stage OPOLD are placed at suitable positions in optical path of the resonant cavity. First stage OPOLD outputs degenerate or near degenerate laser pumps second stage OPOLD to output laser in long wavelength. Features are: simple structure, low cost, and high utilization efficiency.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Cavity mirror-free optical parametric oscillator, manufacturing method thereof, and medium-far infrared laser
ActiveCN108711728AReduce volumeReduce the difficulty of adjustmentOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionGratingFar infrared
The invention discloses a Cavity mirror-free optical parametric oscillator, a manufacturing method thereof, and a medium-far infrared laser. The oscillator comprises a crystal polarization region anddistributed feedback curved face optical grating regions. The distributed feedback curved face optical grating regions are symmetrically arranged on the outer side of the crystal polarization region by taking the crystal polarization region as the center and are connected with optical paths of the crystal polarization region. By writing the distributed feedback curved face optical gratings (c-DBR)on two ends of the crystal polarization region to replace a traditional cavity mirror in an optical parametric oscillation system, the size of the obtained optical parametric oscillator is effectively reduced. Elements of the middle-far infrared laser in the optical parametric oscillator are reduced. Difficulty level in adjustment is reduced and use stability is improved. The invention also provides a making method of the cavity mirror-free optical parametric oscillator and a middle-far infrared laser including the cavity mirror-free optical parametric oscillator. A pump light laser is used for directly pumping the device, so a portable small-size middle-far infrared laser can be obtained.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Intermediate infrared laser
InactiveCN102570268AImprove conversion efficiencyWavelength adjustmentLaser detailsAcousto-opticsMid infrared laser
The invention discloses an intermediate infrared laser. The intermediate infrared laser is characterized in that: a semiconductor laser with the wavelength of 790nm is used for pumping a thulium doped lithium yttrium fluoride (Tm:YLF) crystal to obtain 1.9 mu m laser; and 1.9 mu m pulsed laser is generated in an acousto-optical Q-switching way. Two quartz etalons unplated with a dielectric film are arranged in a Tm:YLF laser, so that the spectrum width of the output 1.9 mu m laser is decreased to less than 1nm, and the output laser is stabilized at the central wavelength of 1,907.5nm, and can be prevented from being absorbed by water molecules in the atmosphere; and the laser is used as a pump source for pumping a magnesium oxide (MgO) doped periodically poled lithium niobate (MgO:PPLN) crystal, and stable intermediate infrared laser output with the wavelengths of 3 to 5 mu m is obtained in an optical parametric oscillation way. The intermediate infrared laser has the characteristics of simple structure, high conversion efficiency, high tunability and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com