Multifunctional coherent raman scattering biological imaging light source
A technology of Raman scattering and biological imaging, which is applied in the direction of laser scattering effect, laser, laser parts, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient detection sensitivity, low pump light utilization rate, and inaccurate information, etc., to reduce costs, The effect of improving parameter conversion efficiency and improving resolution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
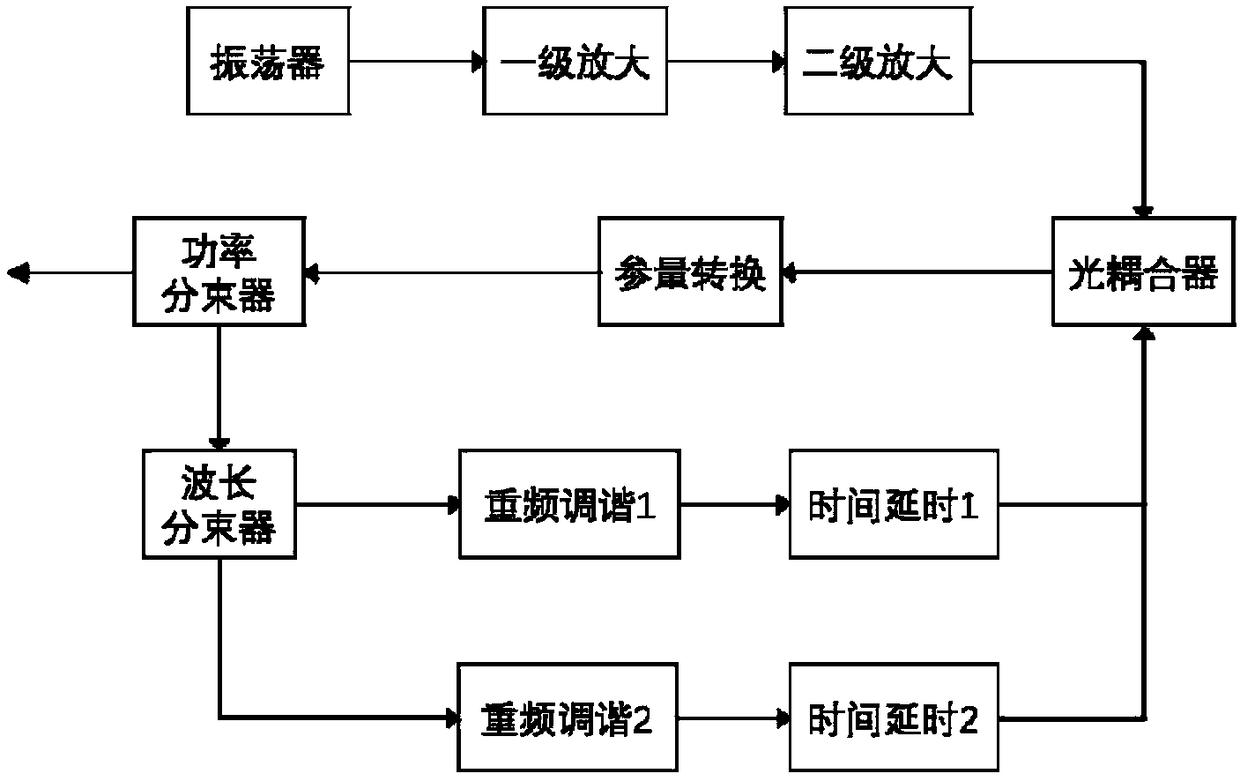
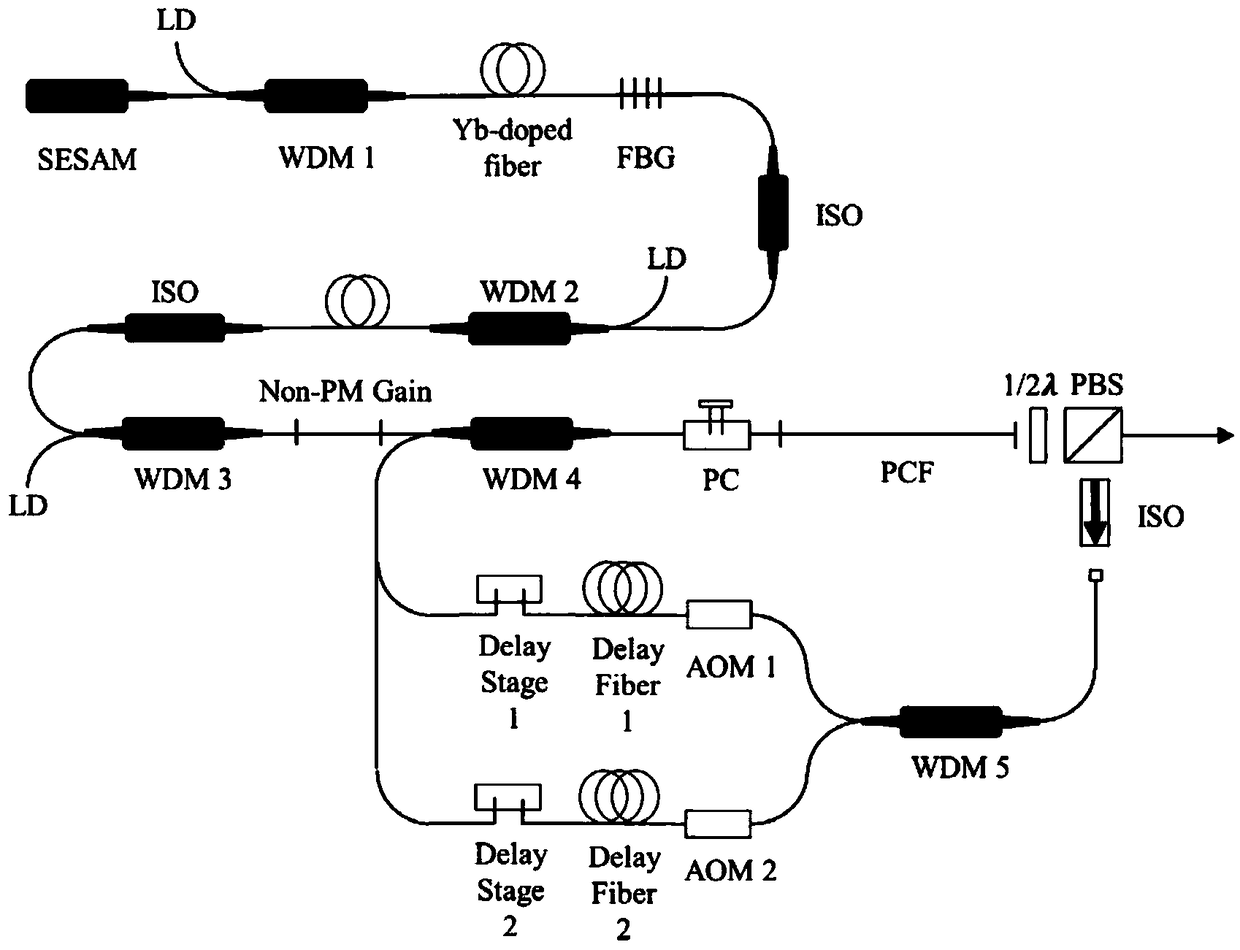
[0022] Embodiment one, figure 2 It is a structural diagram of the present embodiment, and its specific implementation process is as follows:
[0023] The oscillator of the biological imaging light source of the invention adopts the semiconductor saturable absorbing mirror SESAM passive mode-locking mode, and the cavity components include sequentially connected SESAM, wavelength division multiplexer WDM 1, ytterbium-doped Yb-doped gain fiber, and fiber Bragg grating FBG. The pulse seed light output by the oscillator is coupled to the Yb-doped gain fiber through the wavelength division multiplexer WDM 2 to amplify the average power of the seed light, and the isolator ISO is used to separate the two-stage amplification modules to prevent the return light from damaging the cavity Component; after that, the seed light is coupled to the secondary amplification module composed of non-polarization-maintaining Non-PM gain fiber through the wavelength division multiplexer WDM3 to reali...
Embodiment 2
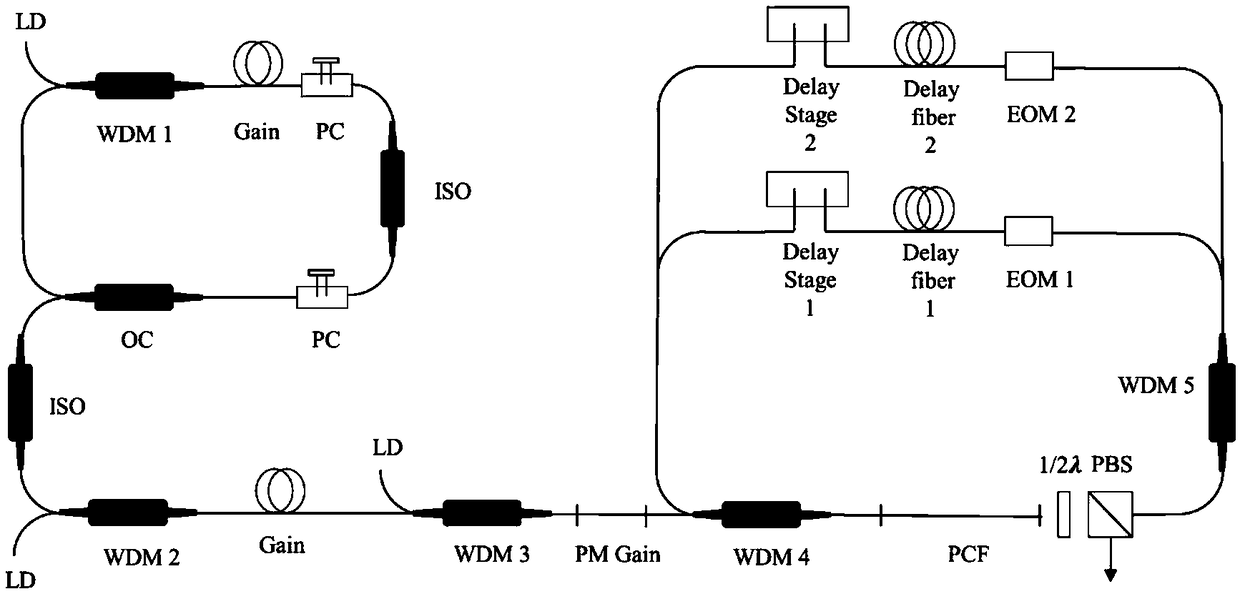
[0024] Embodiment two, image 3 It is the second structure diagram of this embodiment, and its specific implementation process is as follows:
[0025] The oscillator of the bio-imaging light source of the invention adopts nonlinear polarization rotation (NPR) passive mode-locking mode, and the cavity components include wavelength division multiplexer WDM 1, gain Gain fiber, polarization controller PC, isolator ISO, output Coupler OC. The oscillator outputs the pulsed seed light from the output coupler OC to increase the average power of the first-stage amplifier module, and the ISO separates the two-stage amplifier modules to prevent the returning light from damaging the cavity components; the output light of the first-stage large module enters the polarization-maintaining PM The secondary amplification module composed of gain fiber realizes the re-amplification of the seed light power to meet the threshold condition of parameter conversion; after that, through WDM 4, the coupl...
Embodiment 3
[0026] Embodiment three, Figure 4 It is the structure diagram of the third embodiment, and its specific implementation process is as follows:
[0027] The nonlinear biological imaging light source oscillator of the invention adopts the passive mode-locking mode of the nonlinear magnifying loop mirror (NALM). The cavity components include: WDM, band-pass filter BP, output coupler OC, isolator ISO, Gain, dispersion compensation fiber ( DCF). The pulsed seed light output by the oscillator enters the primary amplification module, and the average power of the seed light is increased. After that, the seed light enters the secondary amplification module composed of double-clad polarization-maintaining gain fiber (20 / 130) through the focusing lens. After the gain fiber Place a dichroic mirror DM1 with high transparency of 980 nm and high reflection pump light, and the continuous light of 980 nm is input from the reverse direction to realize the re-amplification of the seed light pow...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com