Patents
Literature
1330 results about "Thermal effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The thermal effect refers to the thermal radiations emitted by the body. The thermal effect refers to the heat lost by the body or object. The removal of heat by cooling towers is an example of thermal effect as cooling tower is a body from which heat is being lost or removed due to thermal effect. 3.0.
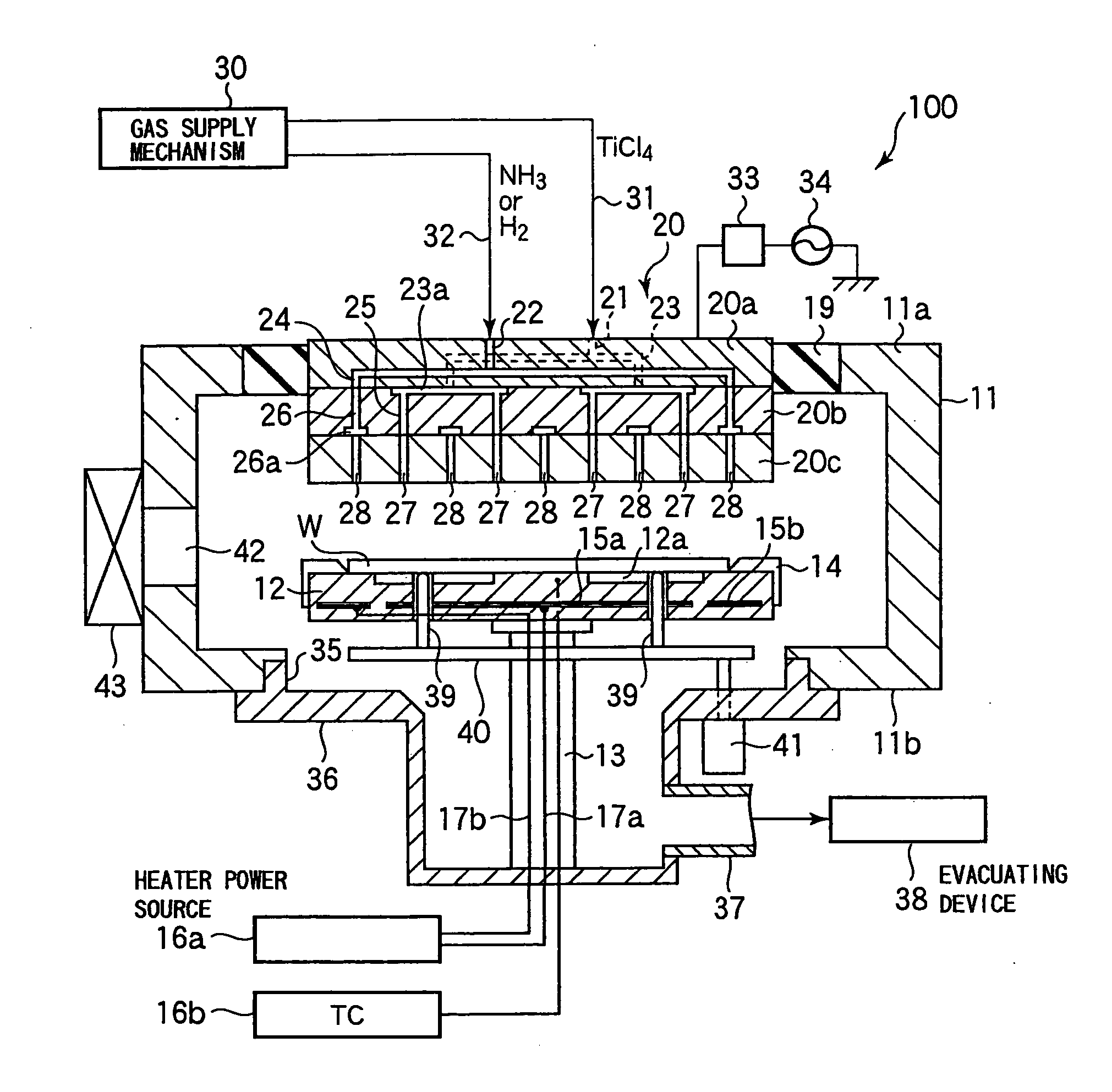
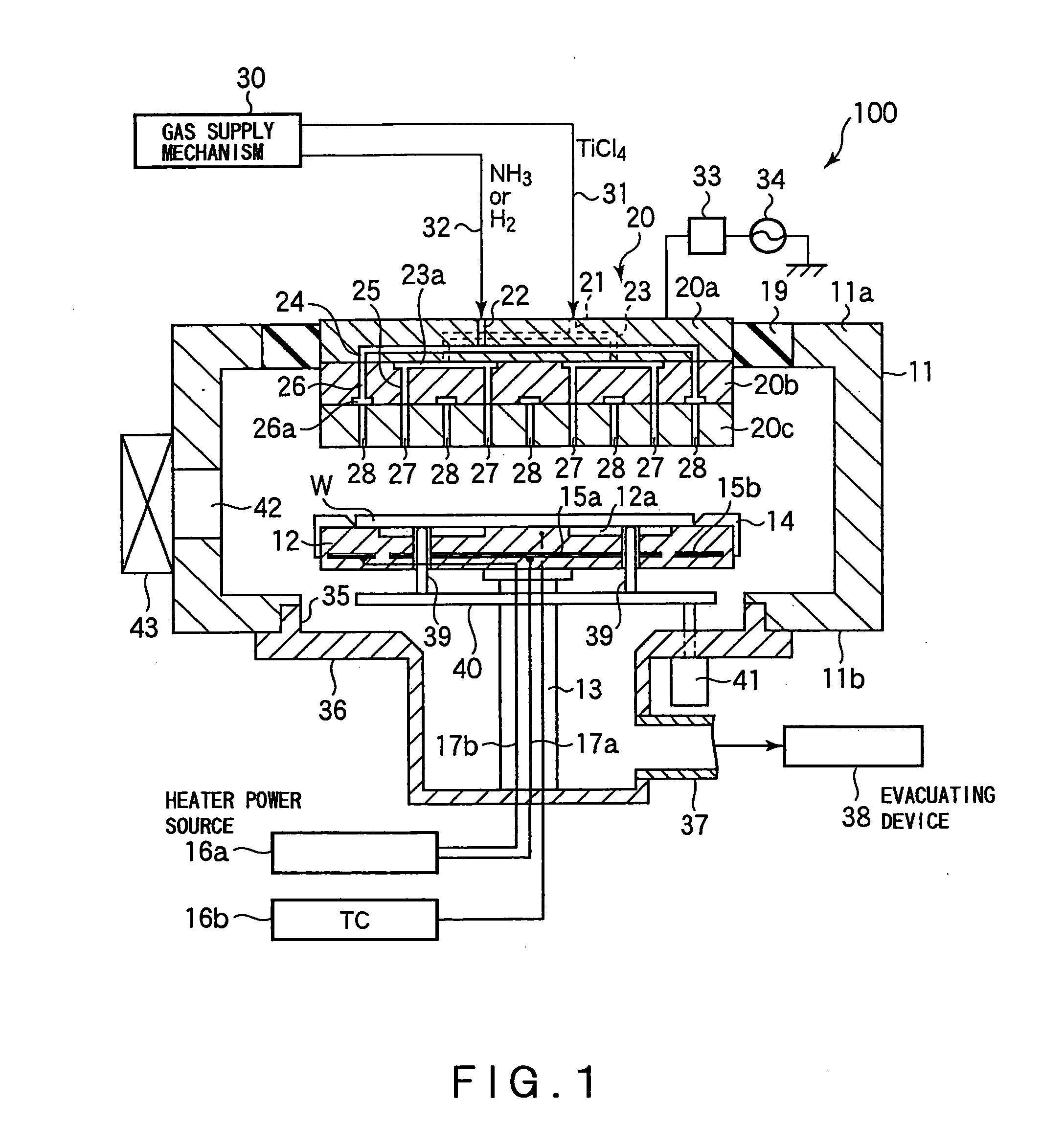
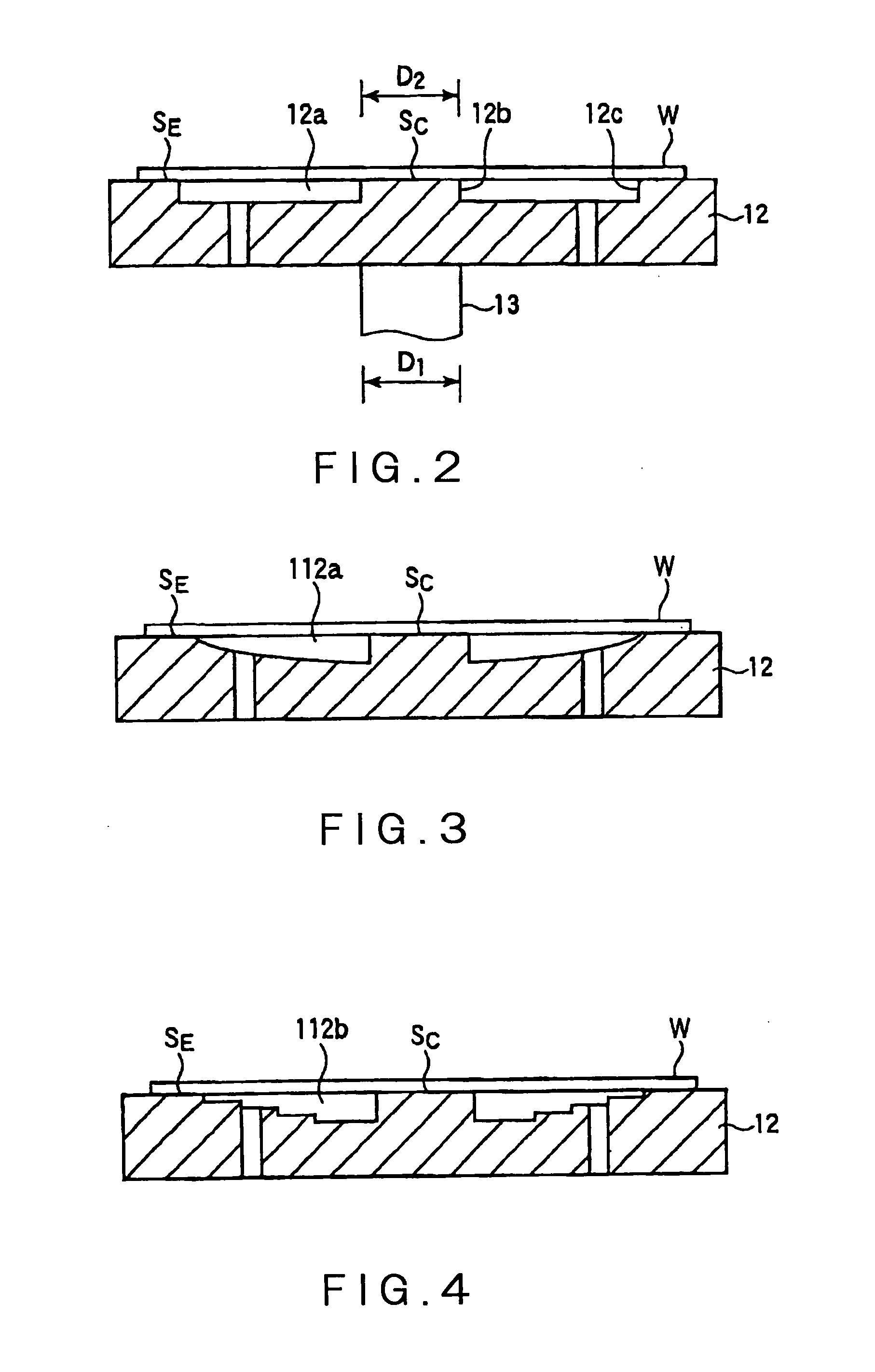
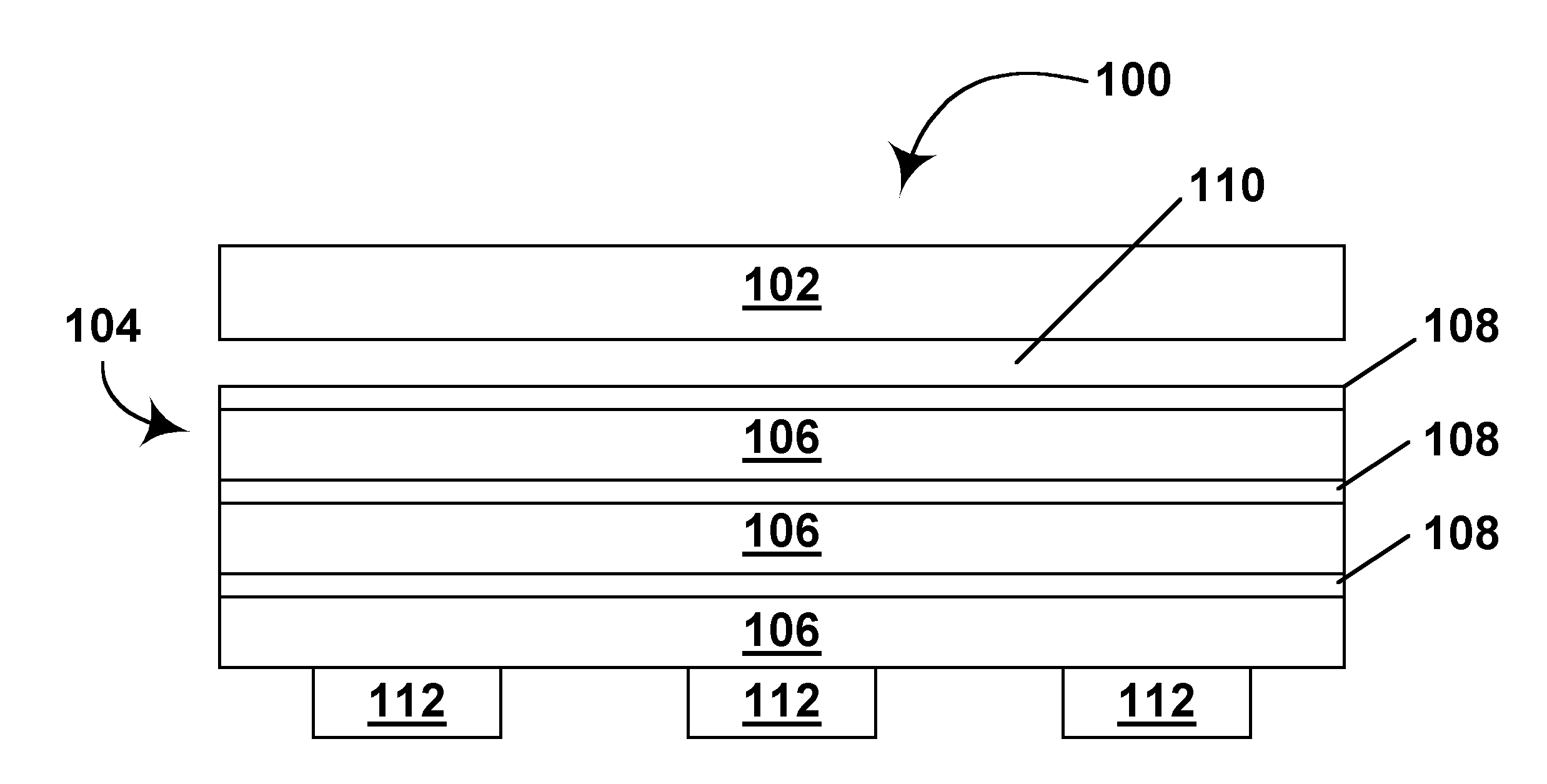
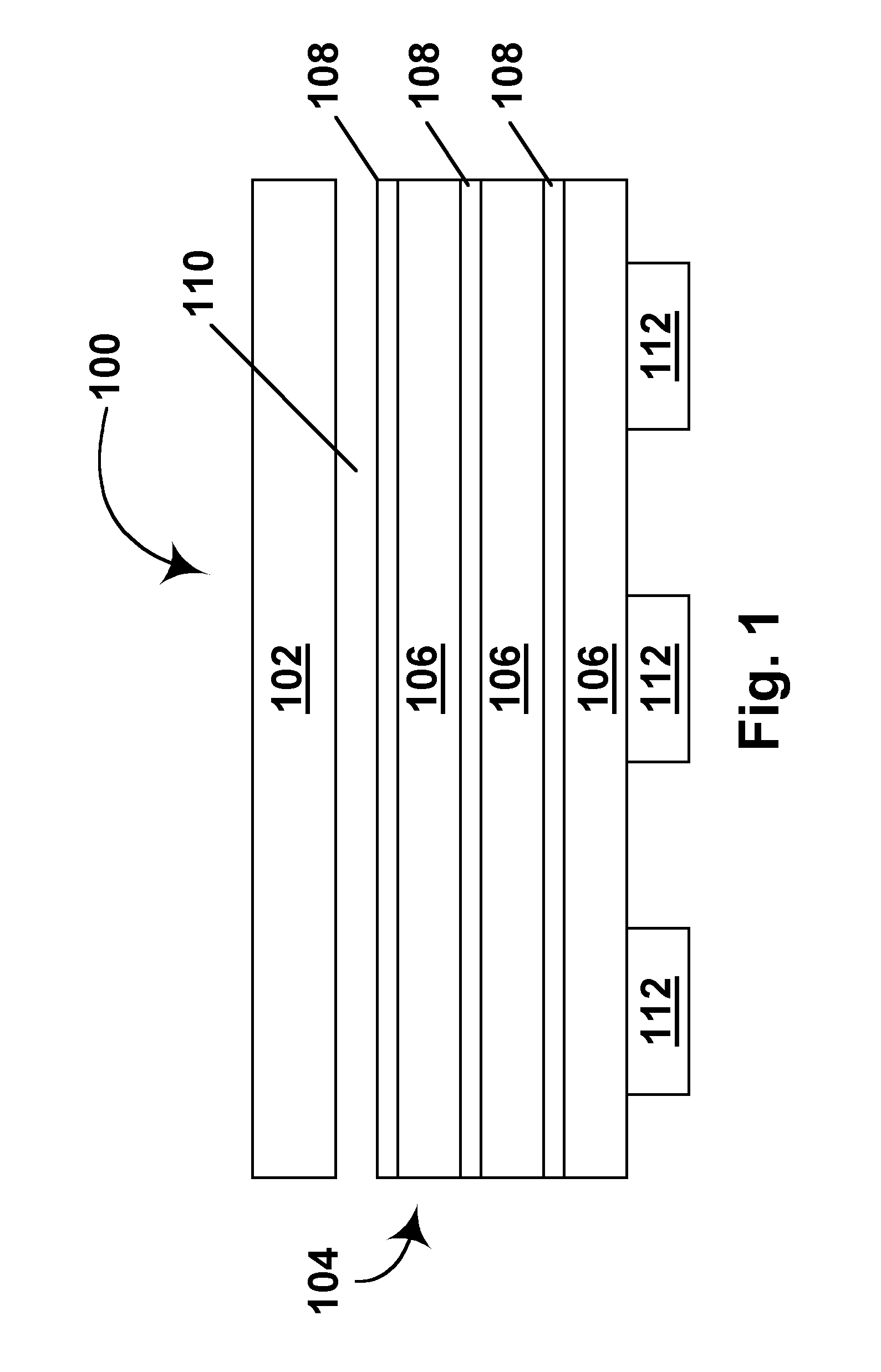
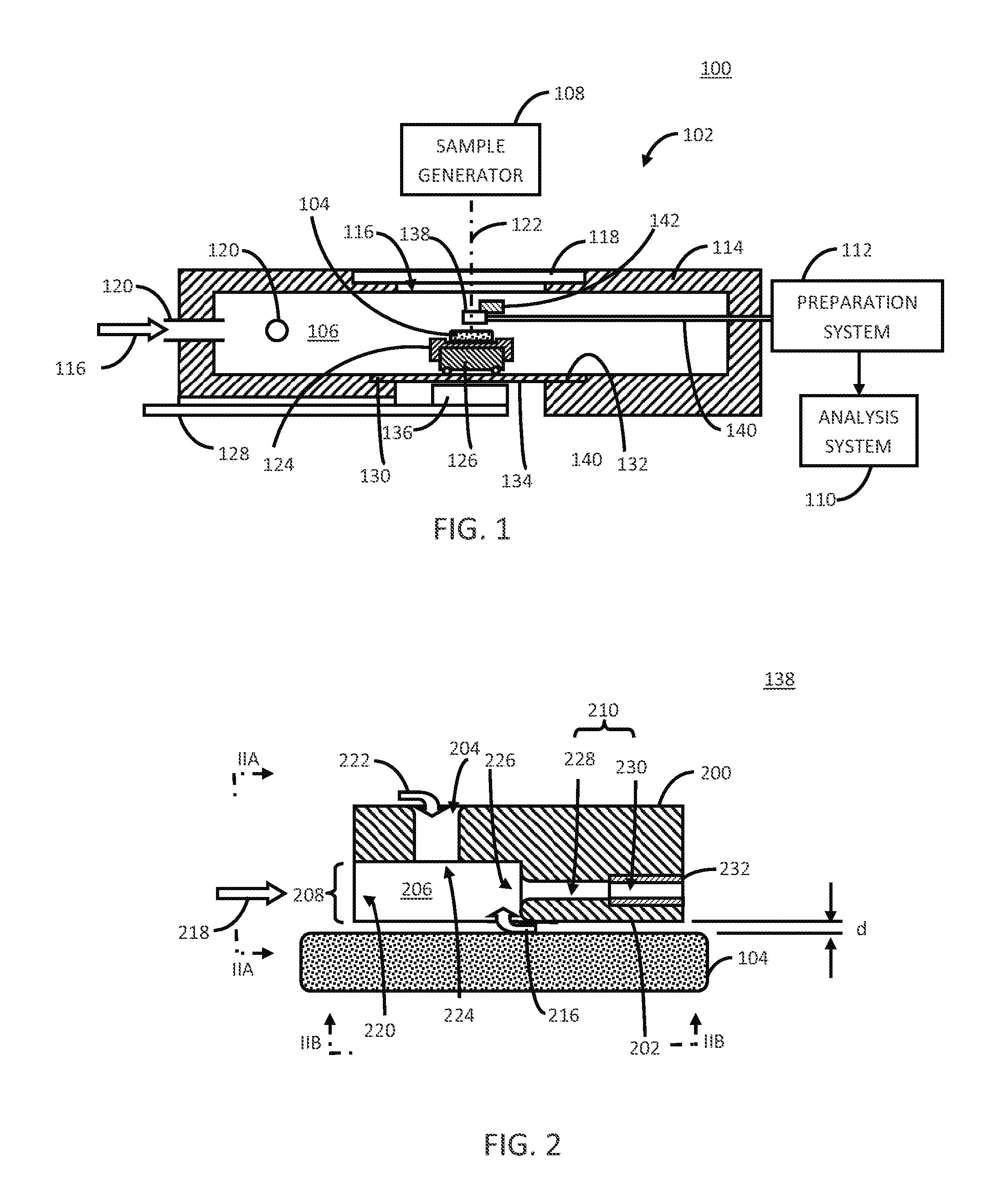
Substrate Processing Apparatus and Substrate Mount Table Used in the Apparatus
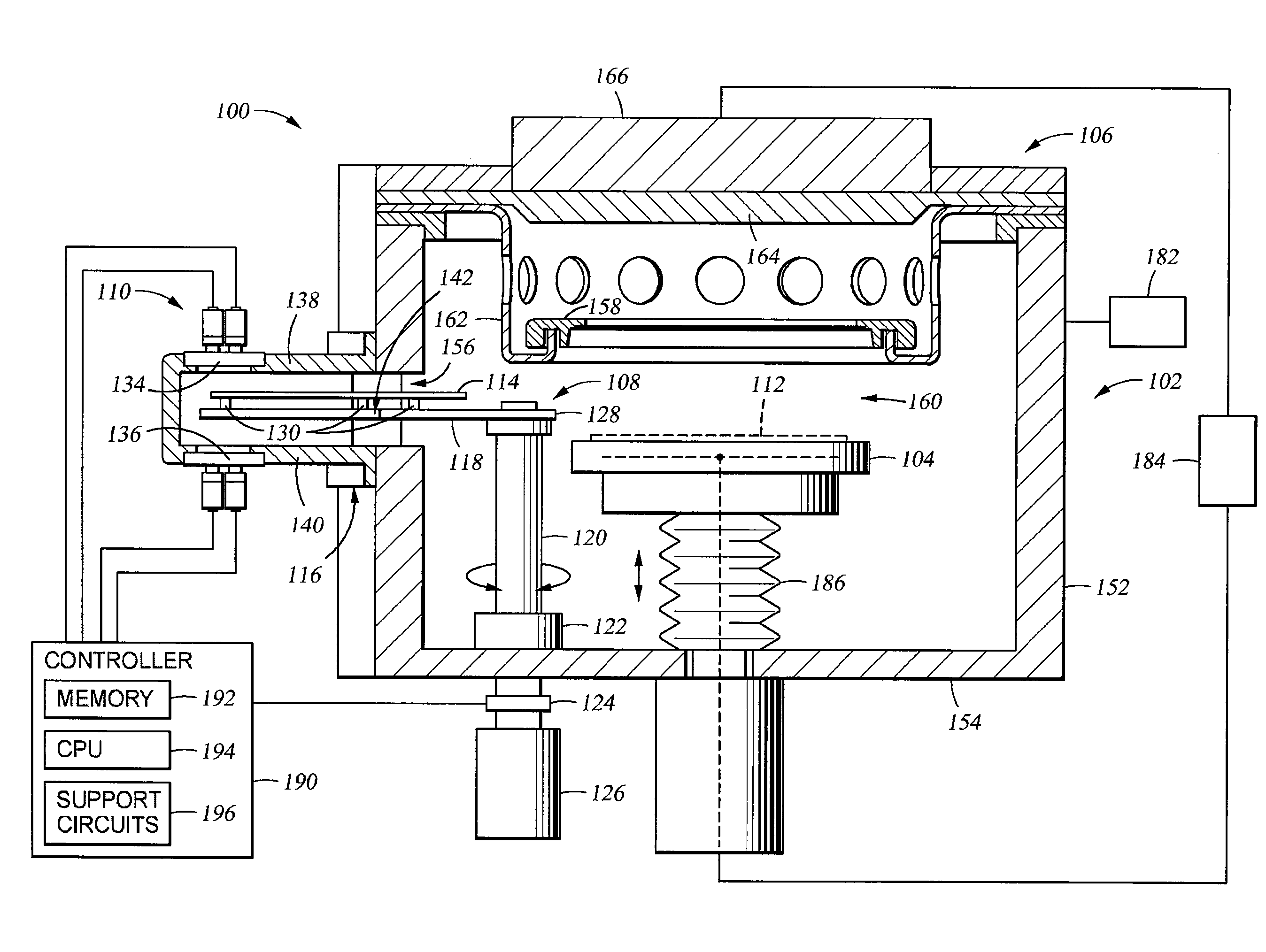
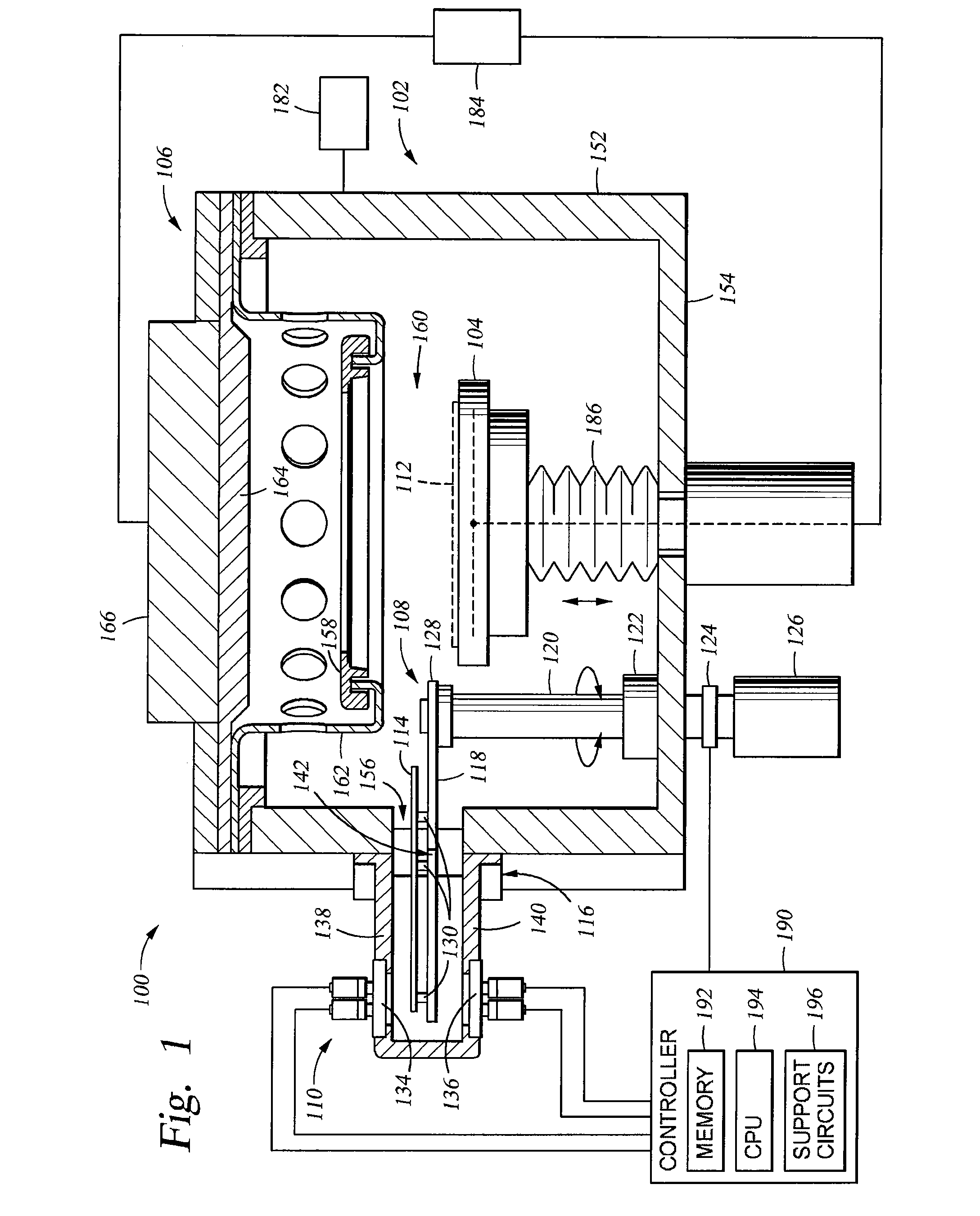
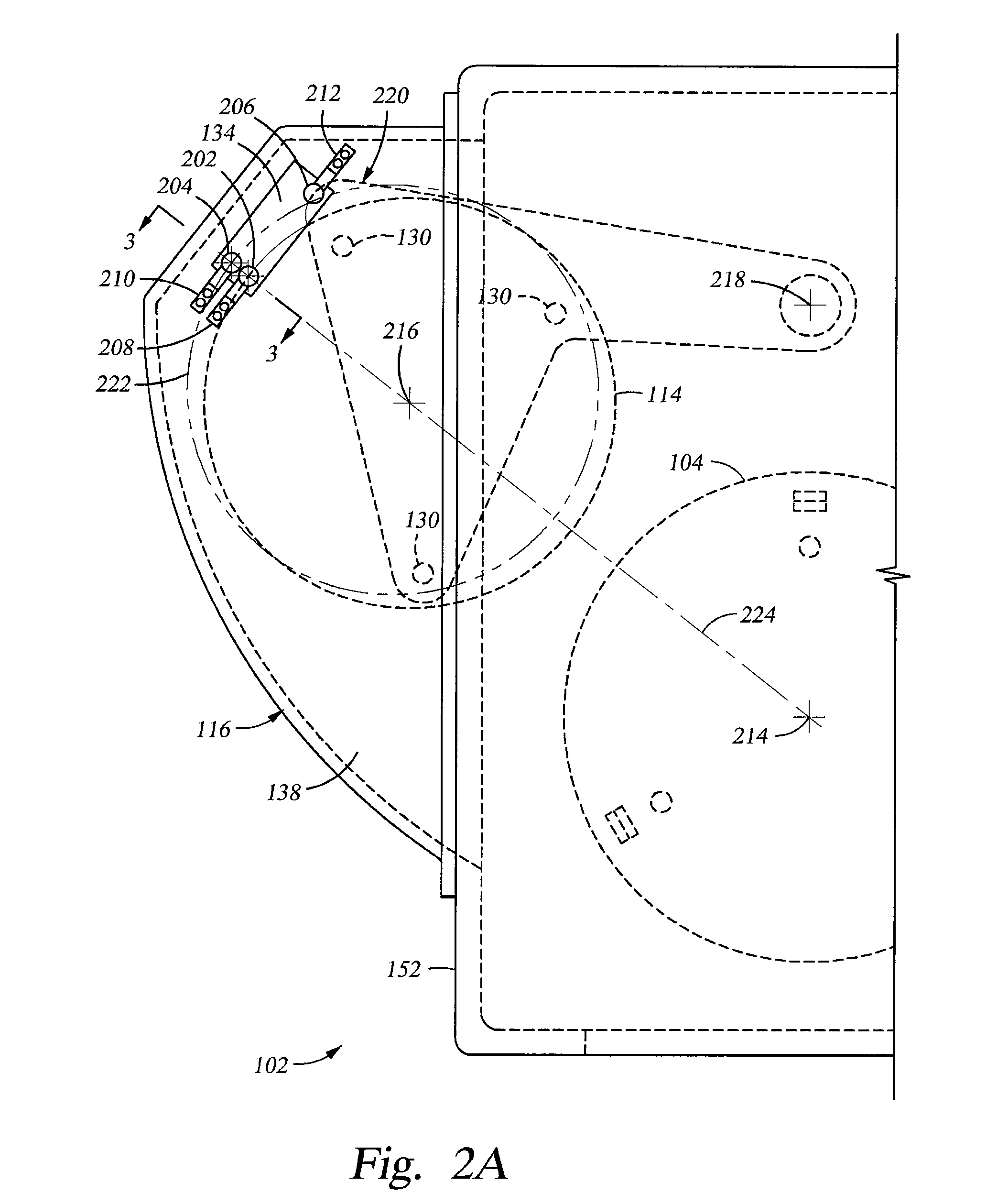
InactiveUS20100162956A1Achieving temperature uniformityEliminate the effects ofElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInternal pressureSusceptor
Disclosed is a susceptor which achieves uniform temperature distribution of a wafer placed on the susceptor, and also disclosed is a substrate processing apparatus provided with the susceptor. An annular recess 12a is formed in an intermediate portion between the central portion and the peripheral portion of a wafer support surface of the susceptor 12. Due to the provision of the recess, the substrate heating effect by thermal radiation from the susceptor is suppressed in the intermediate portion. The geometrical dimension of the recess is determined taking the chamber internal pressure into consideration.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
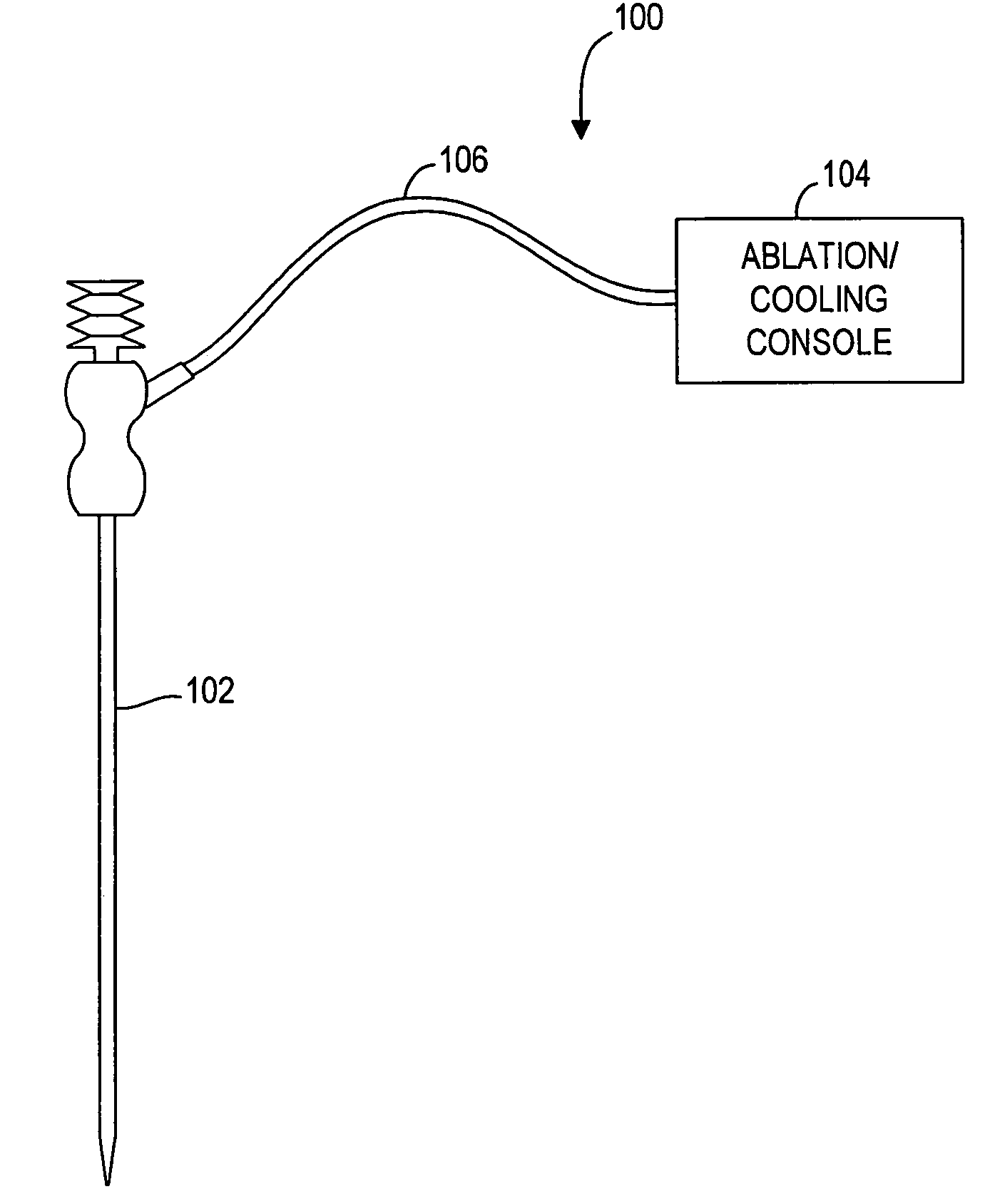
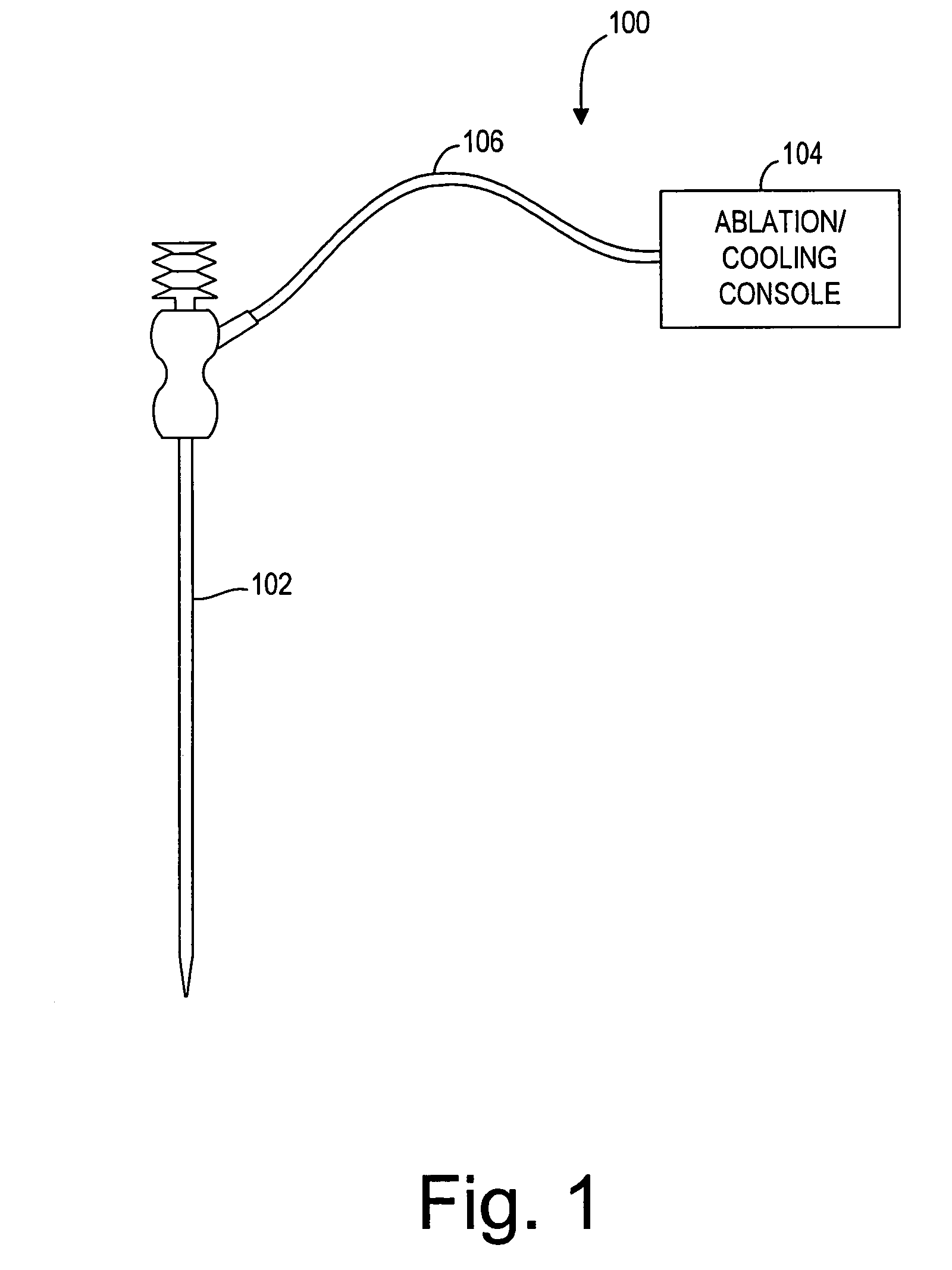
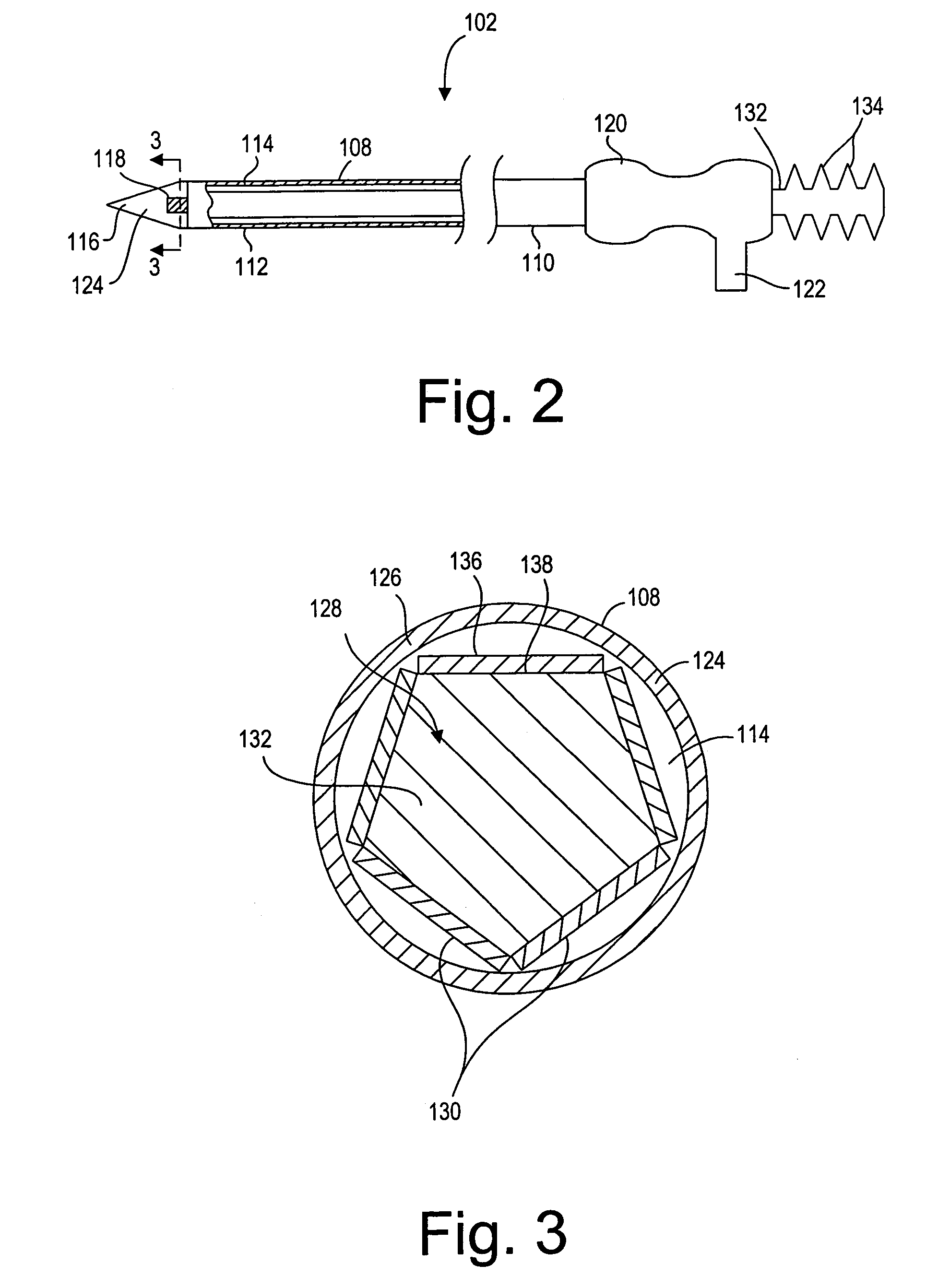
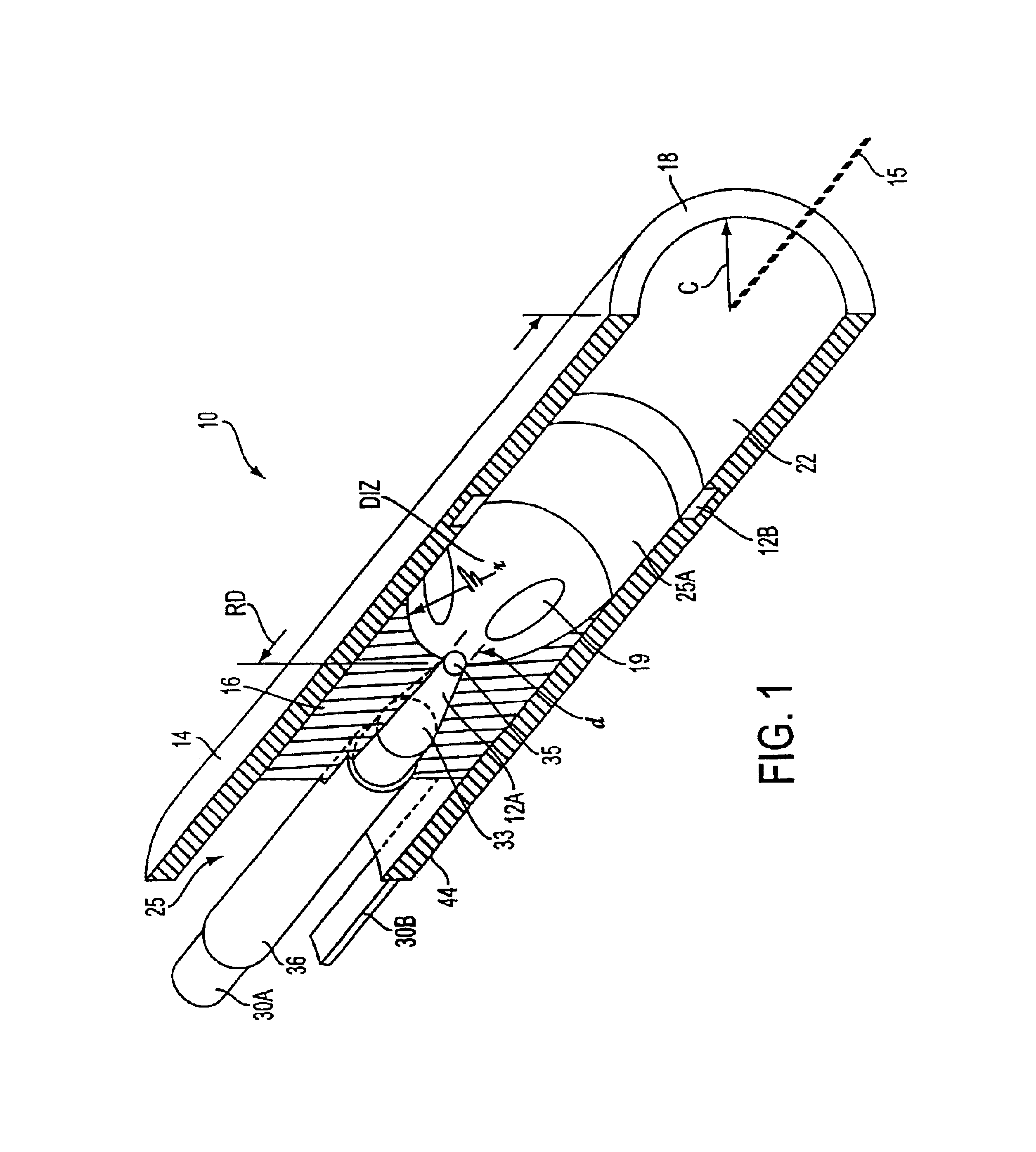
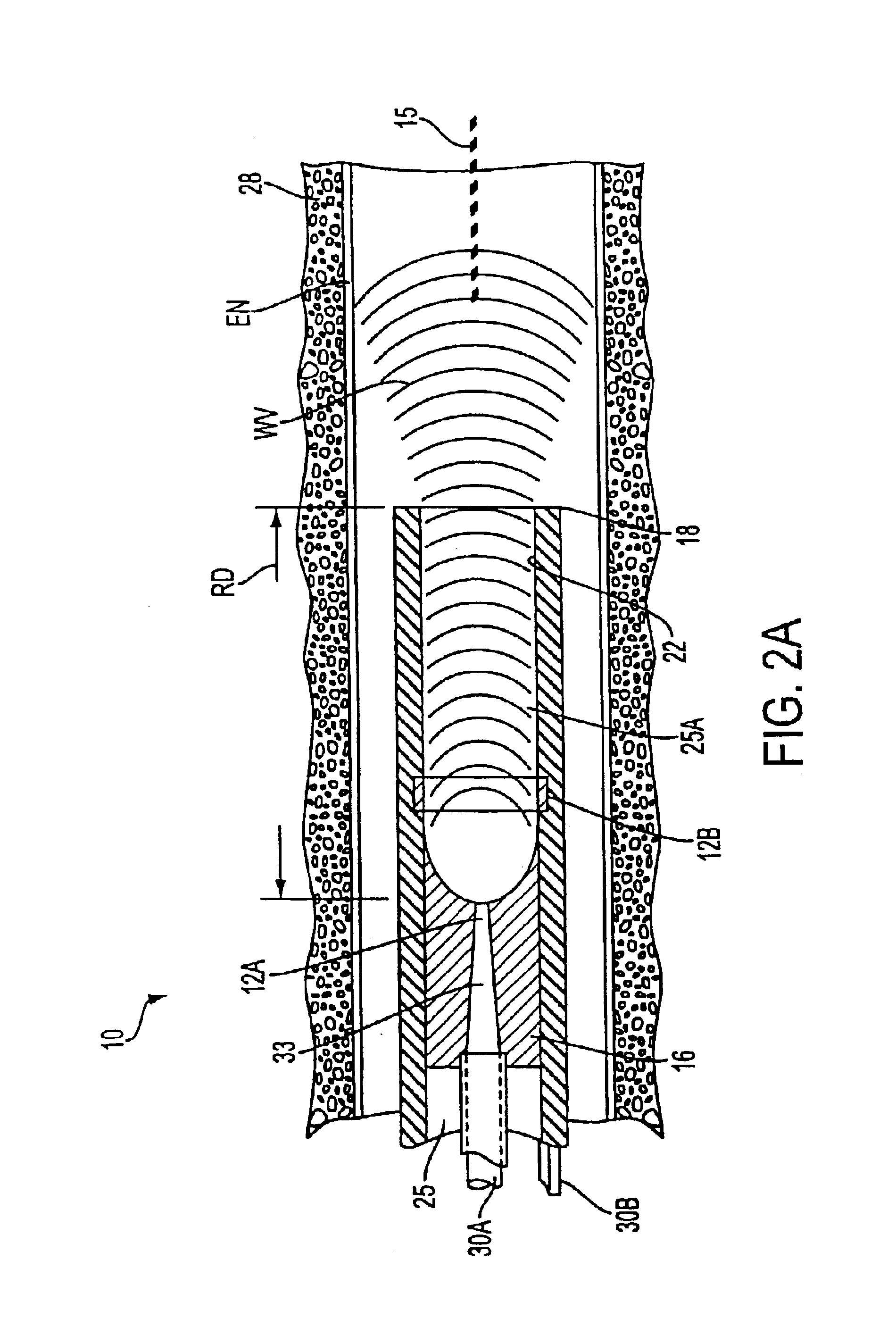
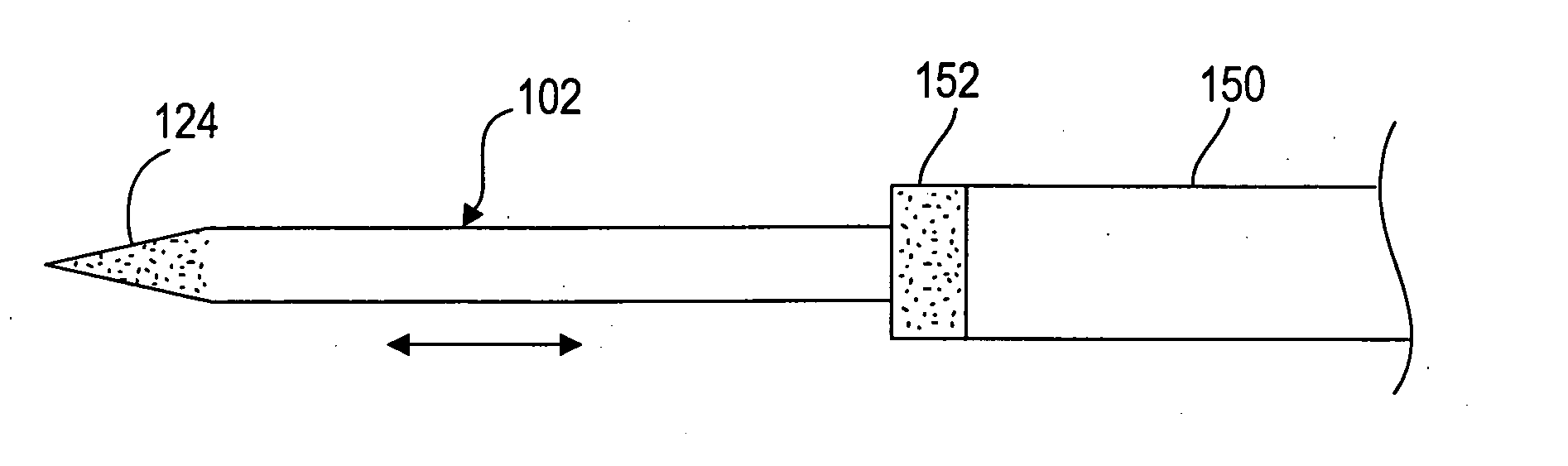
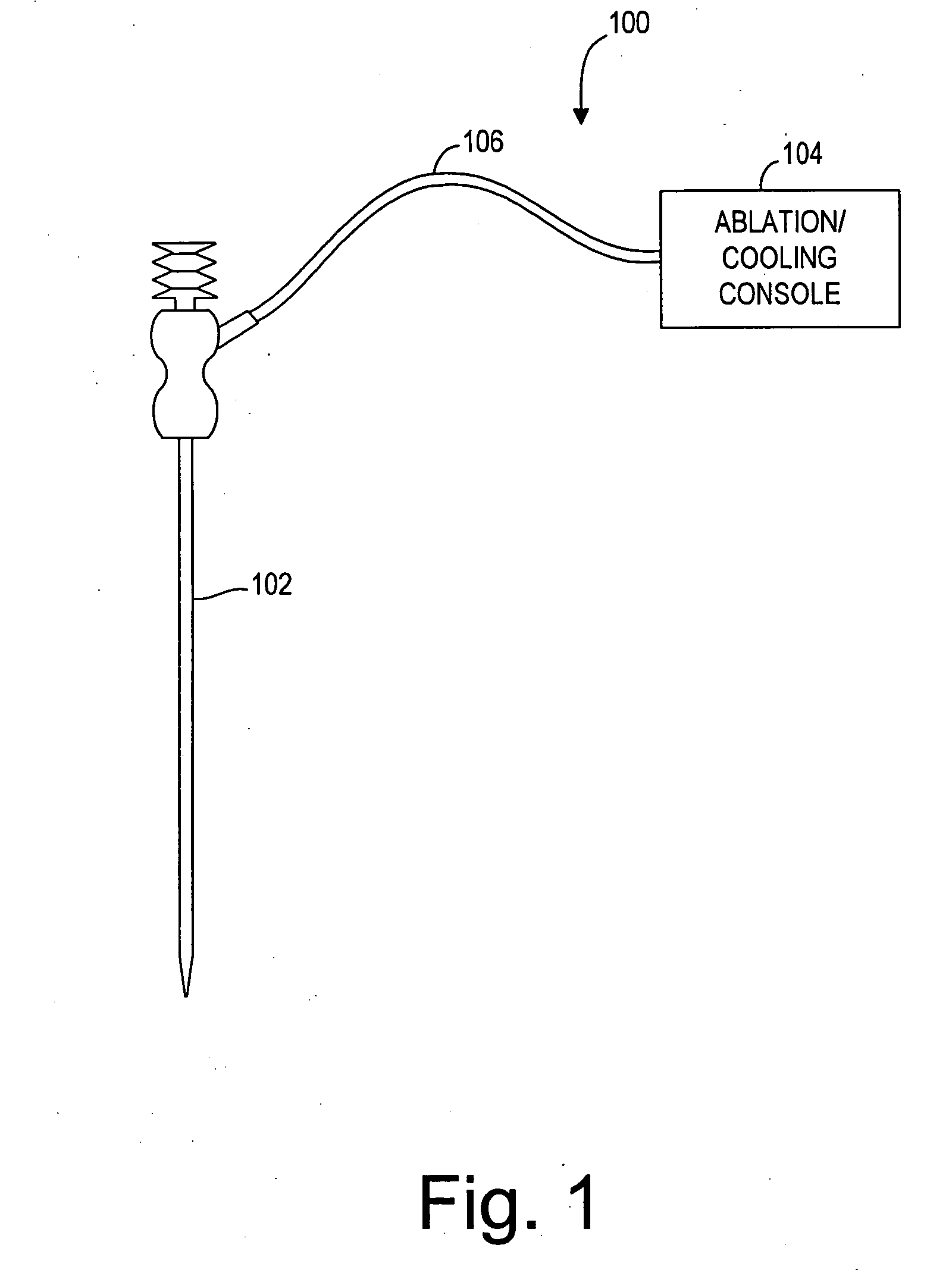
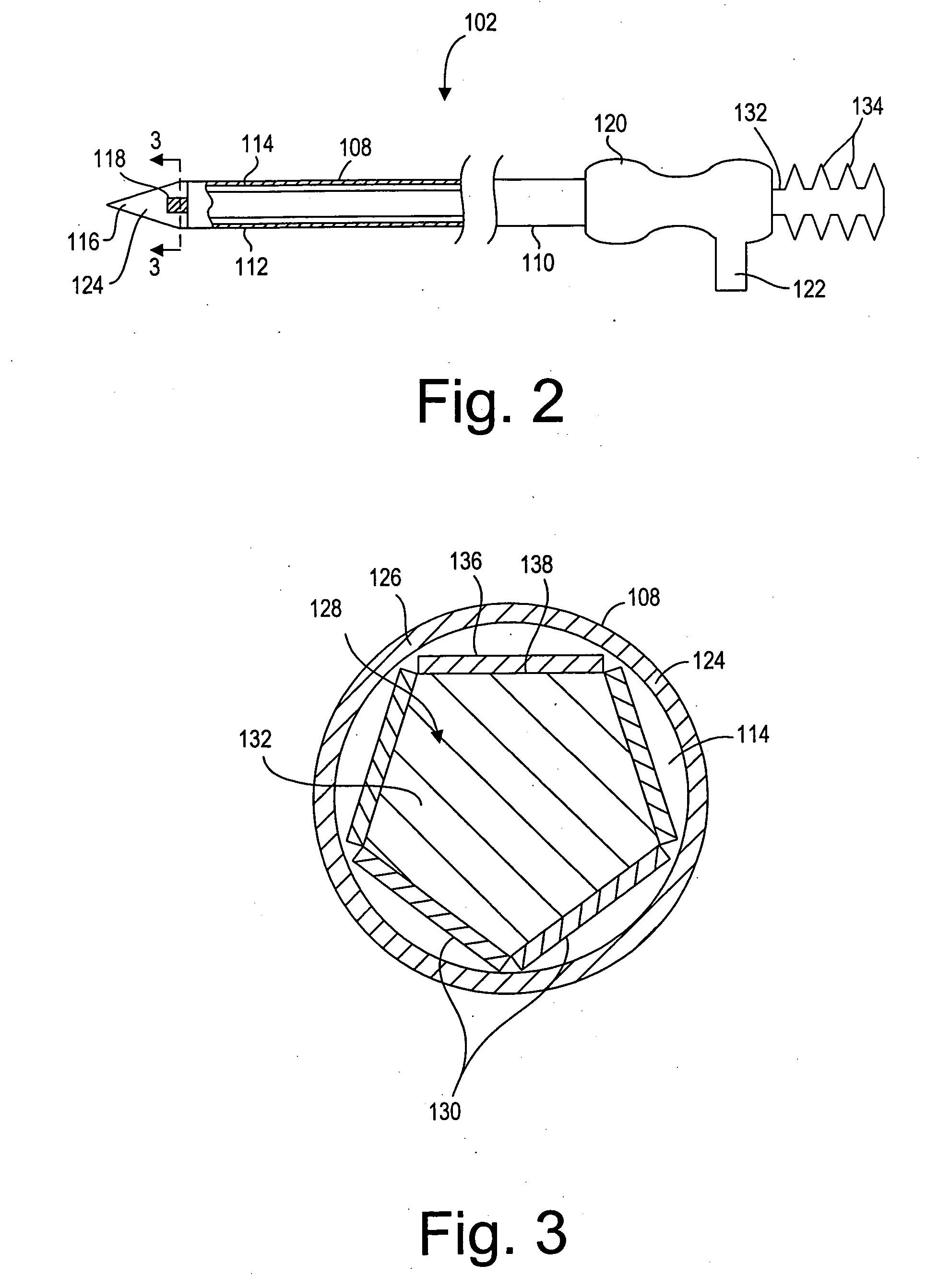
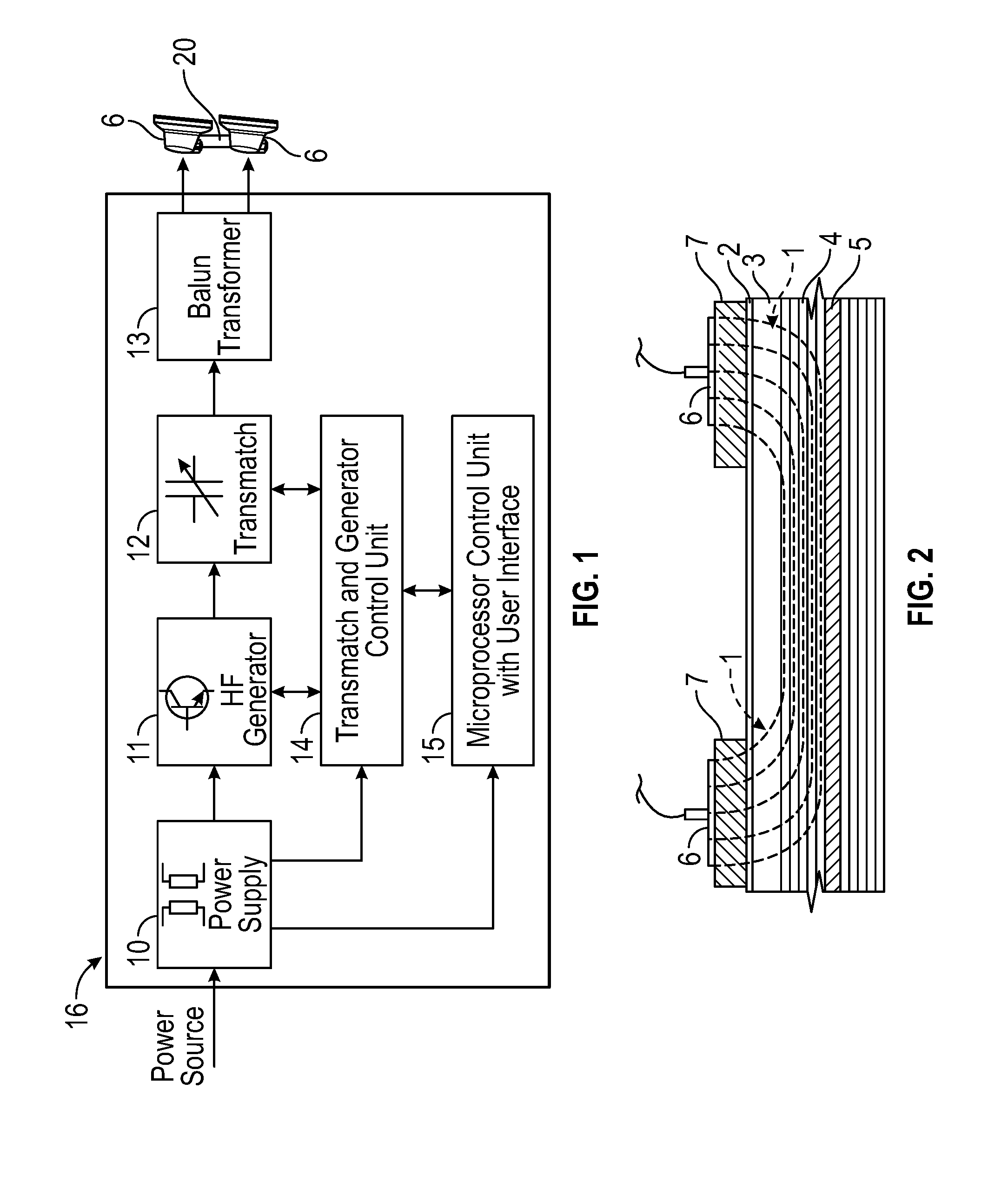
Ablation probe with peltier effect thermal control
ActiveUS7238184B2Easy to introduceSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingMedicineThermal effect
A tissue ablation probe, system, and method are provided. The ablation probe comprises an elongated member, an ablative element mounted on the distal end of the elongated member, and at least one thermoelectric device mounted to the member in thermal communication with the ablative element. The system may include the ablation probe, thermal control circuitry for controlling the thermal effect of the thermoelectric device, and an ablation source for suppying ablation energy to the ablative element. A plurality of circumferentially distributed thermoelectric devices can be provided, so that radial tissue sectors can be selectively affected by independently controlling the thermal effect of the thermoelectric devices. In one embodiment, the thermoelectric device(s) can be used to cool a heat ablative element. In another embodiment, the thermoelectric device(s) can be used to heat an ablative element, thereby forming a heat ablative element. In still another embodiment, the thermoelectric device(s) can be used to cryogenically cool an ablative element, thereby forming a cryogenic ablative element.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
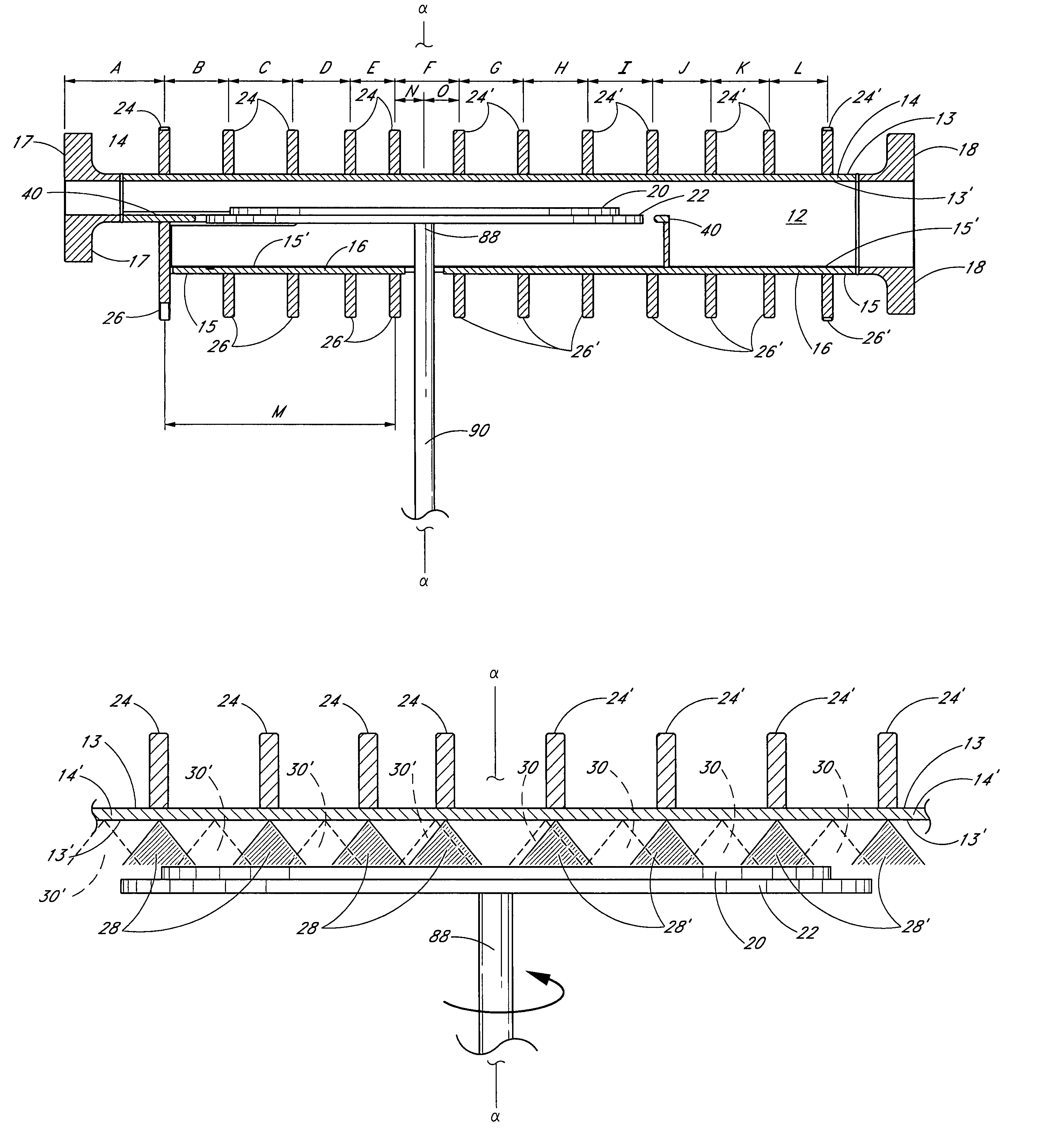
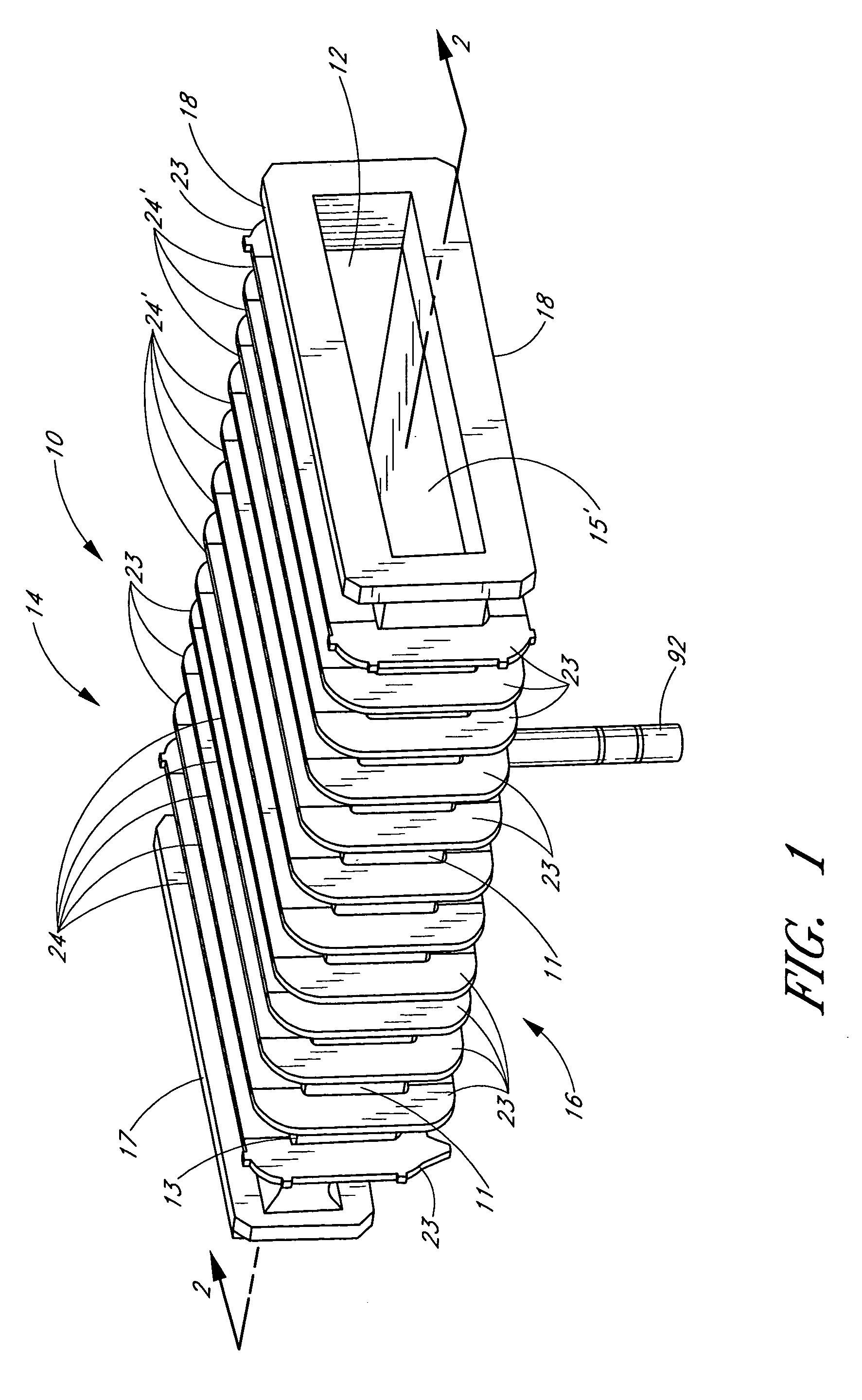
Staggered ribs on process chamber to reduce thermal effects
ActiveUS7108753B2Diffusion/dopingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringThermal effect
A semiconductor processing chamber having a plurality of ribs on an exterior surface of the chamber is provided. The ribs are positioned relative to the chamber such that shadows cast into the chamber by the ribs are offset from one another, thus more uniformly distributing radiant energy entering the chamber. In one embodiment, the ribs are positioned on the exterior surface of the chamber so that they have dissimilar radial distances from a center of the chamber. When a substrate rotates within the chamber, shadows produced by the ribs on a first side of the chamber fall substantially between secondary shadows produced by the ribs on a second side of the chamber. Likewise, shadows produced by the ribs on the second side of the chamber fall substantially between the secondary shadows produced by the ribs on the first side of the chamber.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
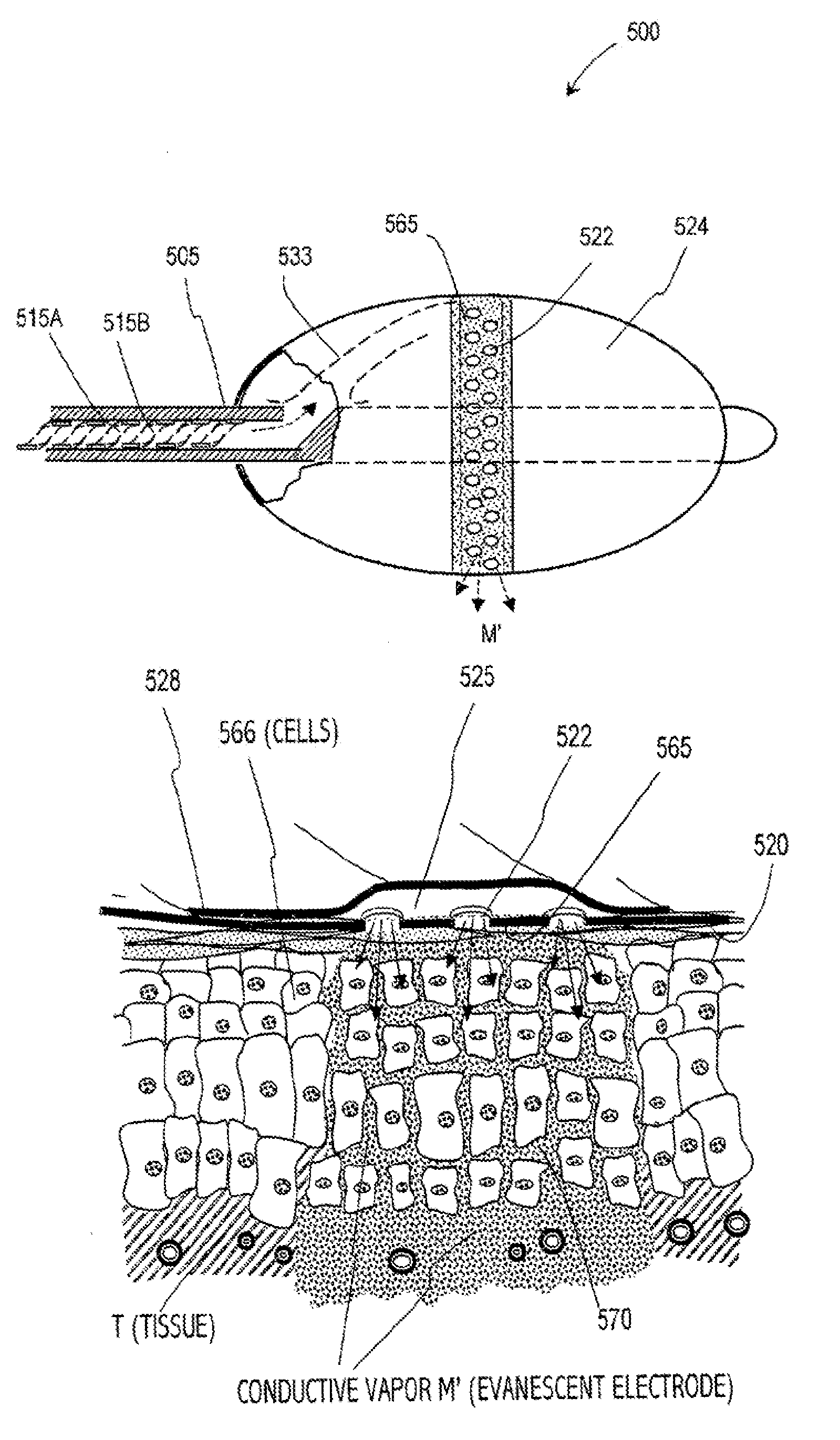
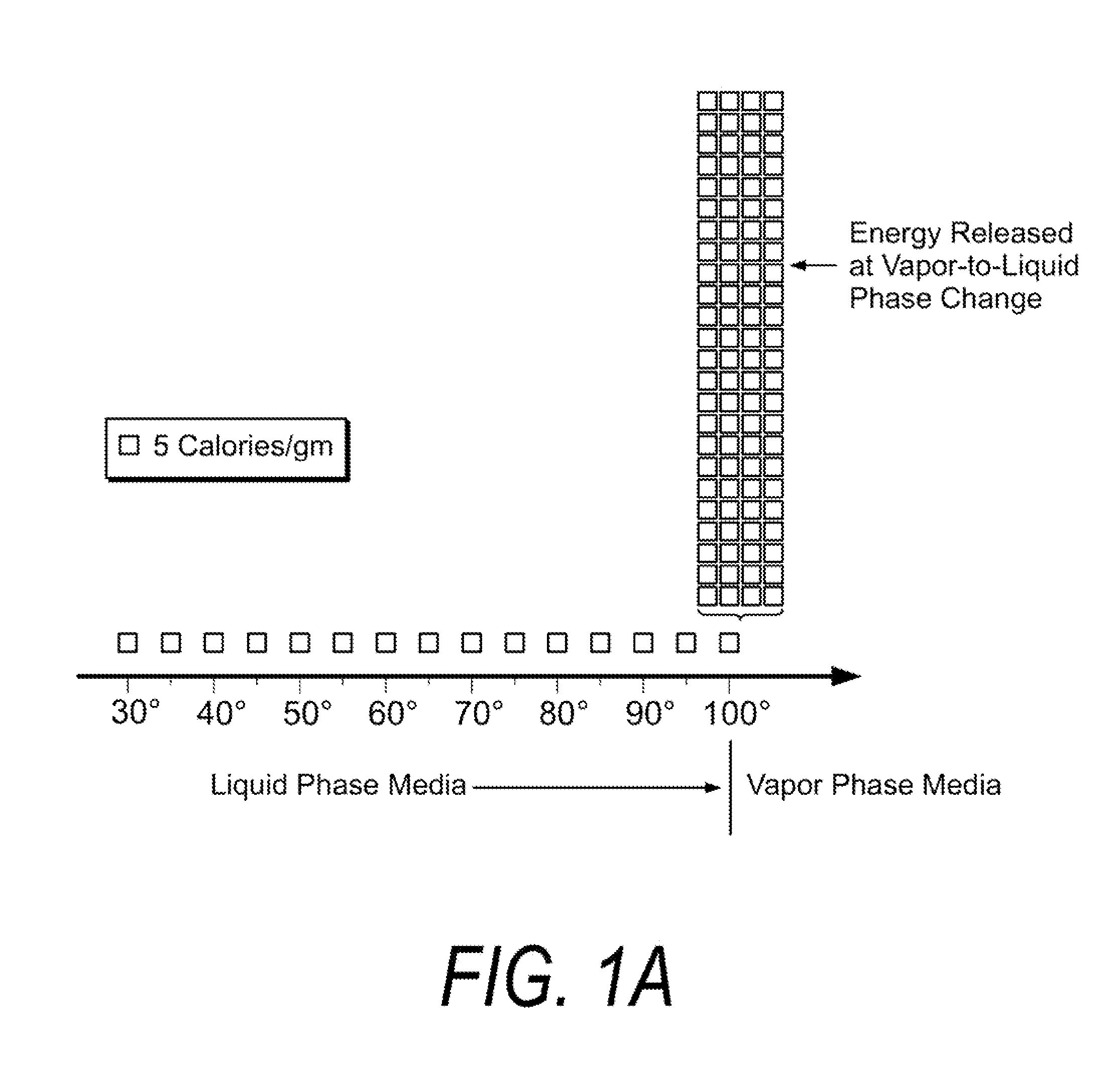
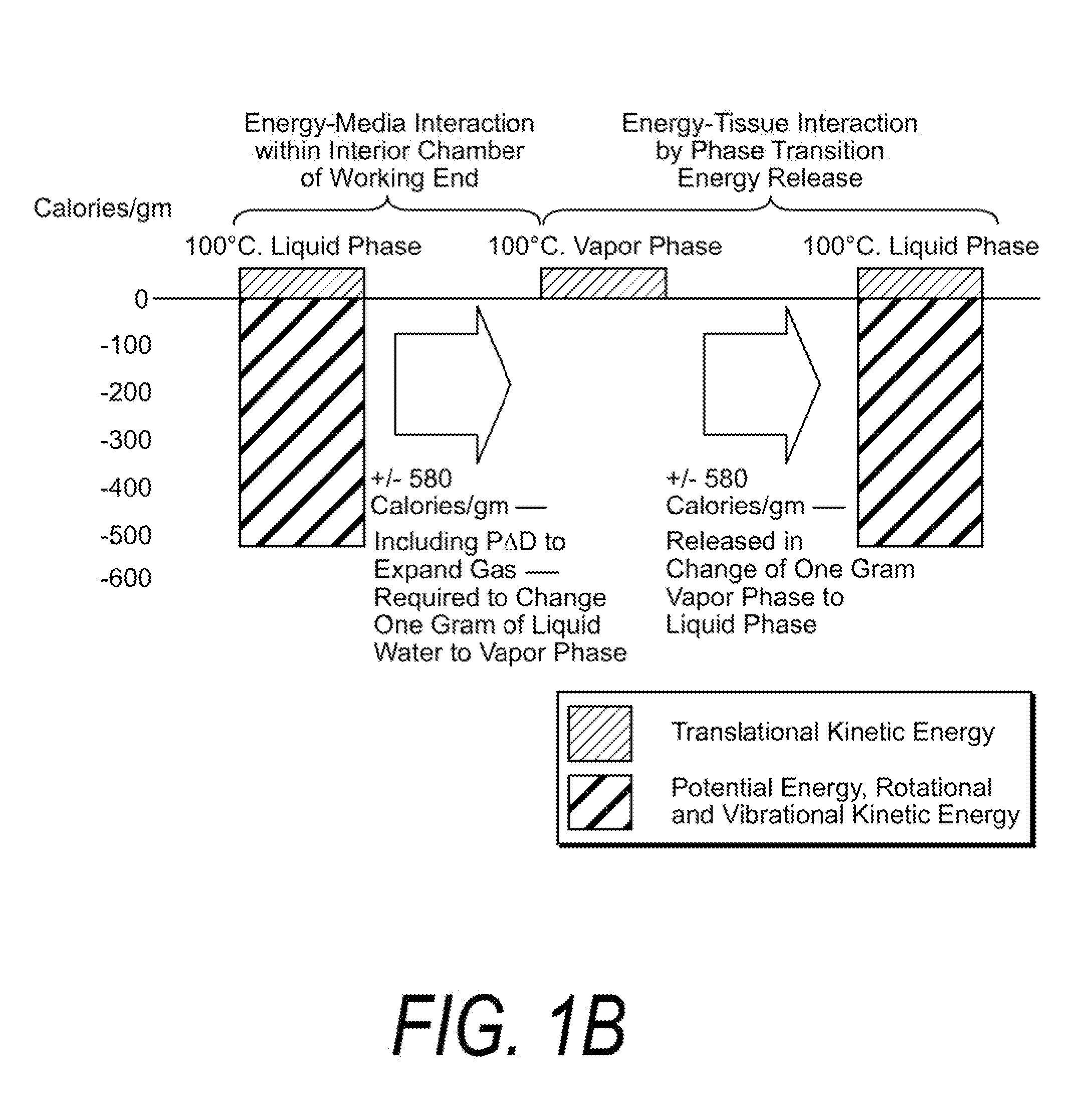
Medical instruments and techniques for thermally-mediated therapies
InactiveUS7674259B2Thermal ablation rapidly and efficientlyPrevents desiccationDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for heatingThermal energyGas phase
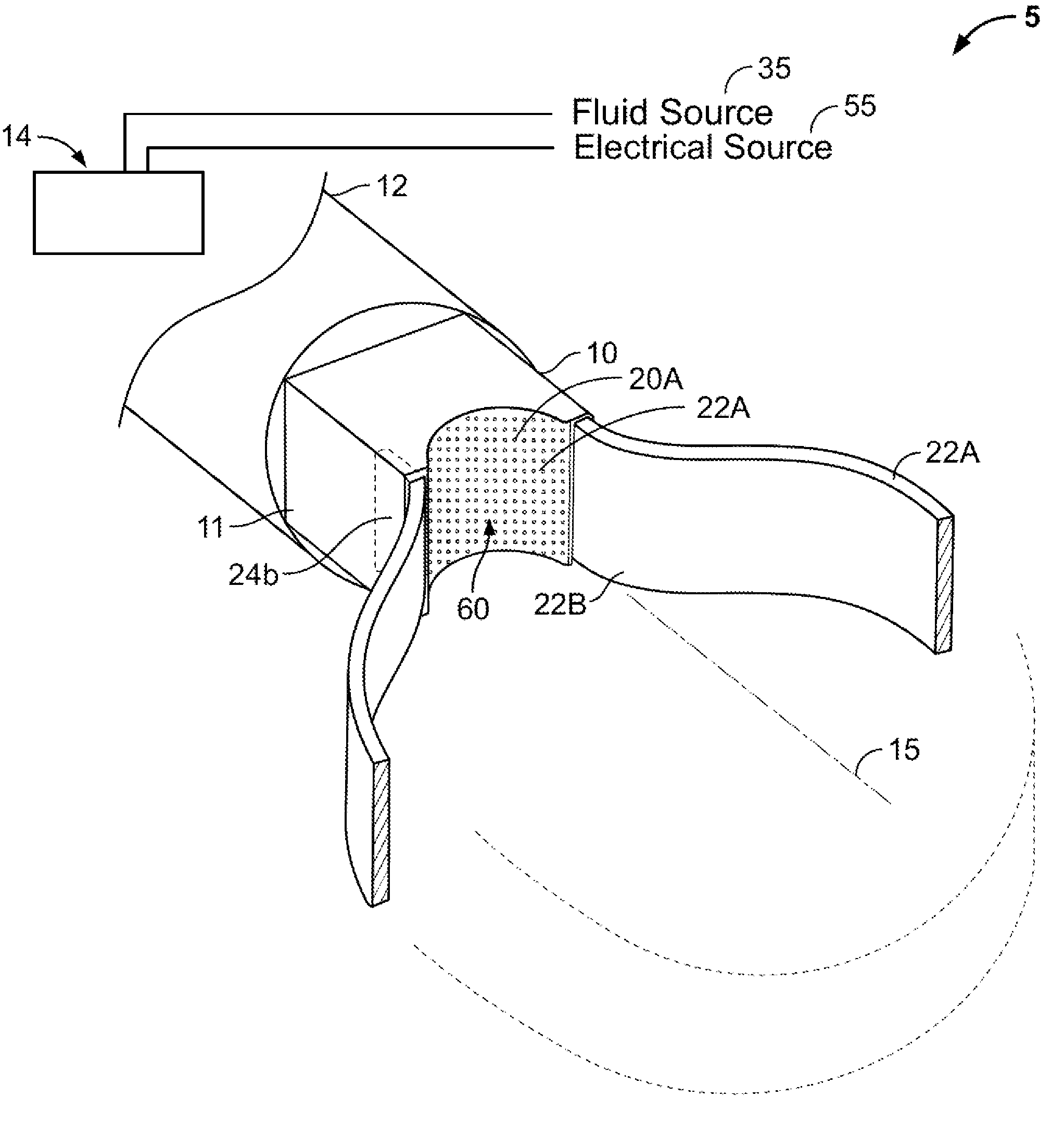
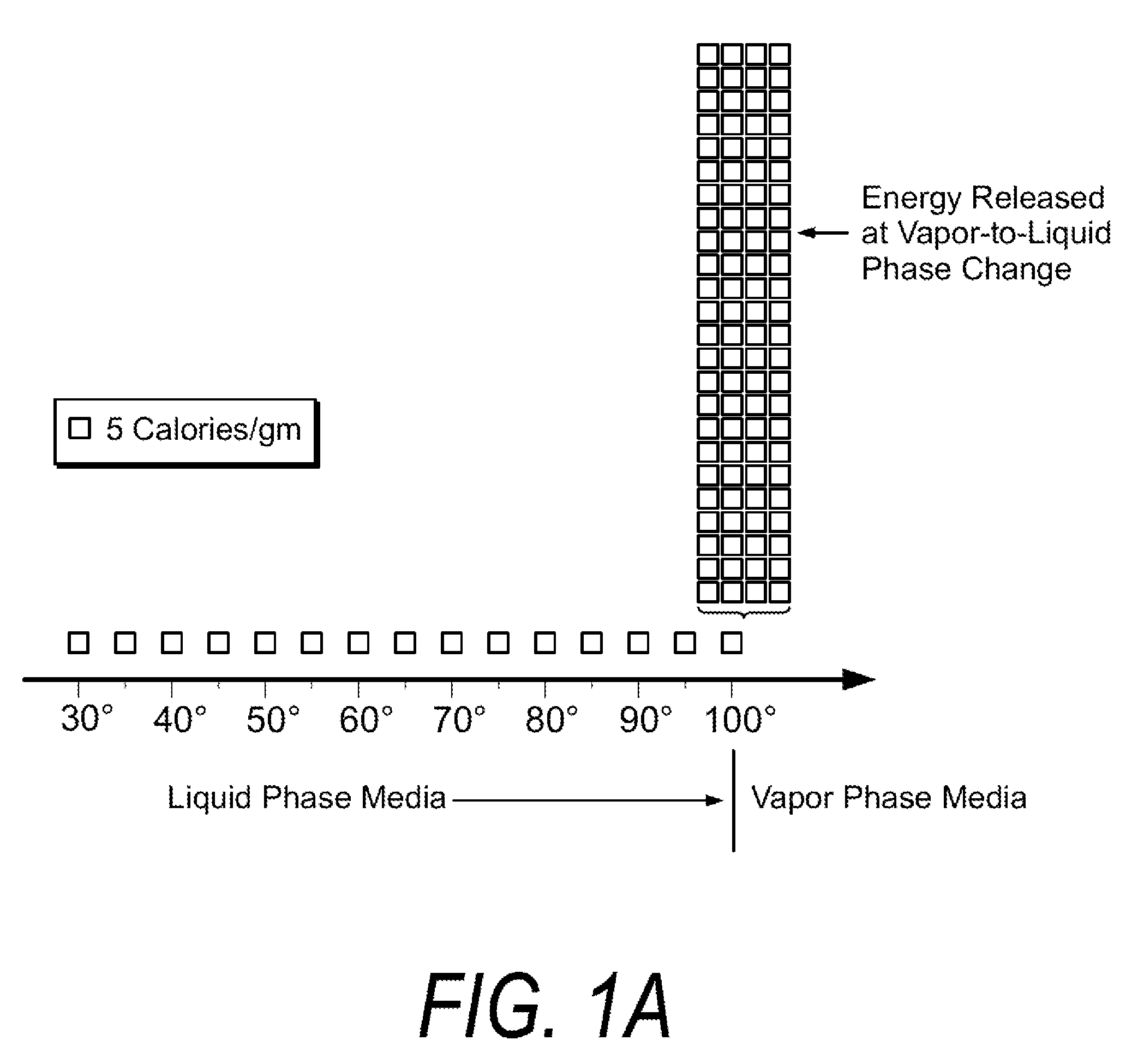
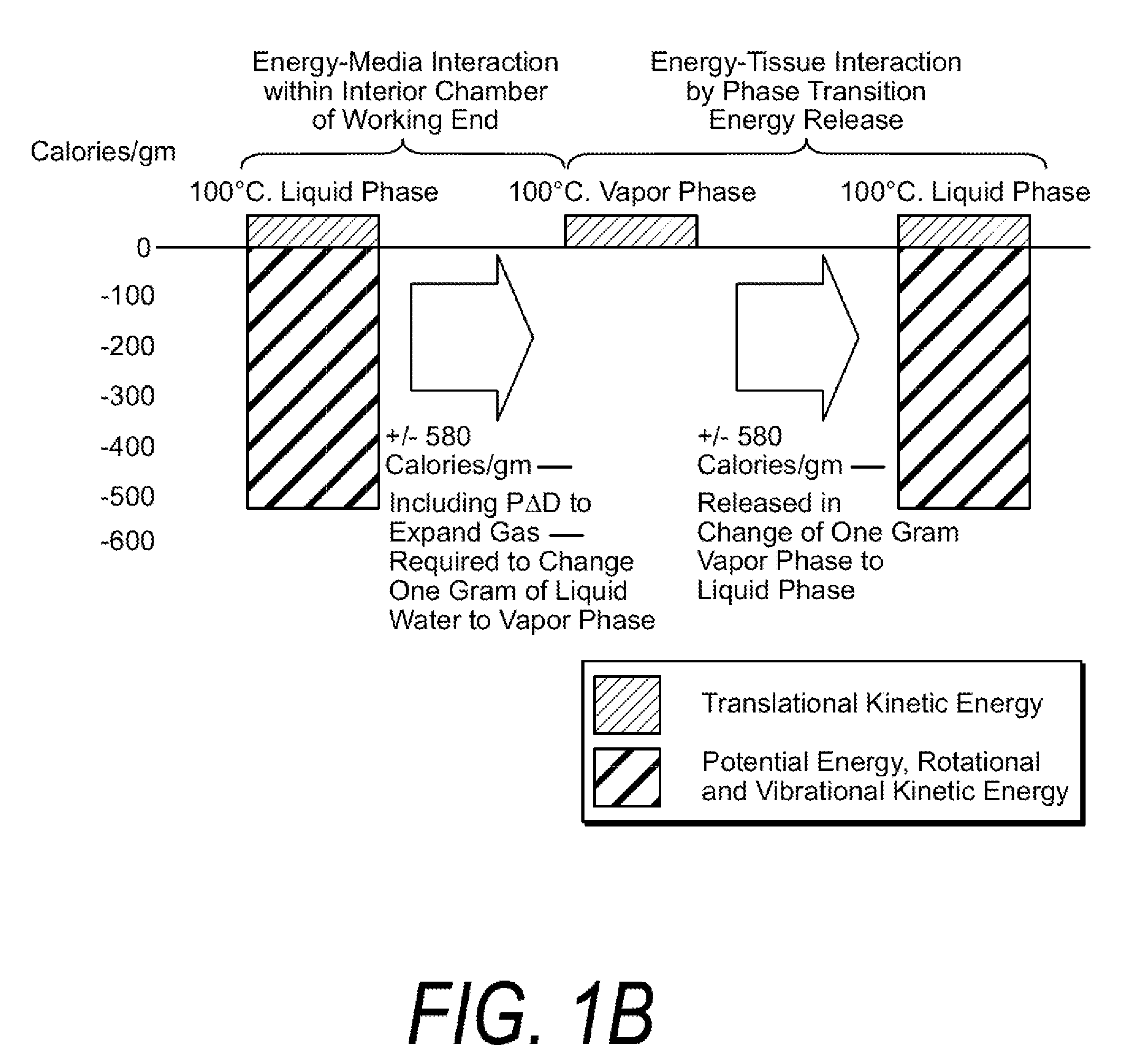
A surgical instrument for thermally-mediated therapies in targeted tissue volumes and for causing thermal effects in polymer tissue-contacting members. In one embodiment, the instrument has a working end with an interior chamber that is supplied with a biocompatible liquid. An energy source causes a liquid-to-vapor phase change within the interior of the instrument. The vapor phase media then is ejected from the working surface of the instrument, and a controlled vapor-to-liquid phase change in an interface with tissue applies thermal energy substantially equal to the heat of vaporization to ablate tissue. The vapor-to-liquid phase transitions, or internal energy releases, can be provided about thin-film flexible structures for engaging body lumens and cavities. An exemplary embodiment can be used for shrinking, sealing, welding or creating lesions in tissue—while causing limited collateral thermal damage and while totally eliminating electrical current flow in the engaged tissue.
Owner:TSUNAMI MEDTECH
Shutter blade and robot blade with cte compensation
Processing chamber shutter blade and robot blade assemblies are constructed to eliminate thermal effects on the placement of elements in processing chambers. Such blade assemblies may contain at least two parts, which may include a positioning member including a low CTE material and a thermal compensating member including a high CTE material. The positioning member includes a coupling point and a reference point on a reference axis separated by a first distance. The thermal compensating member includes a connection point and a controlled point separated by another distance that is less than the first distance. A distance ratio of the first distance to the other distance is substantially equal to a CTE ratio of the high CTE material to the low CTE material, and the positioning member is joined to the thermal compensating member through the coupling point and the connection point.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
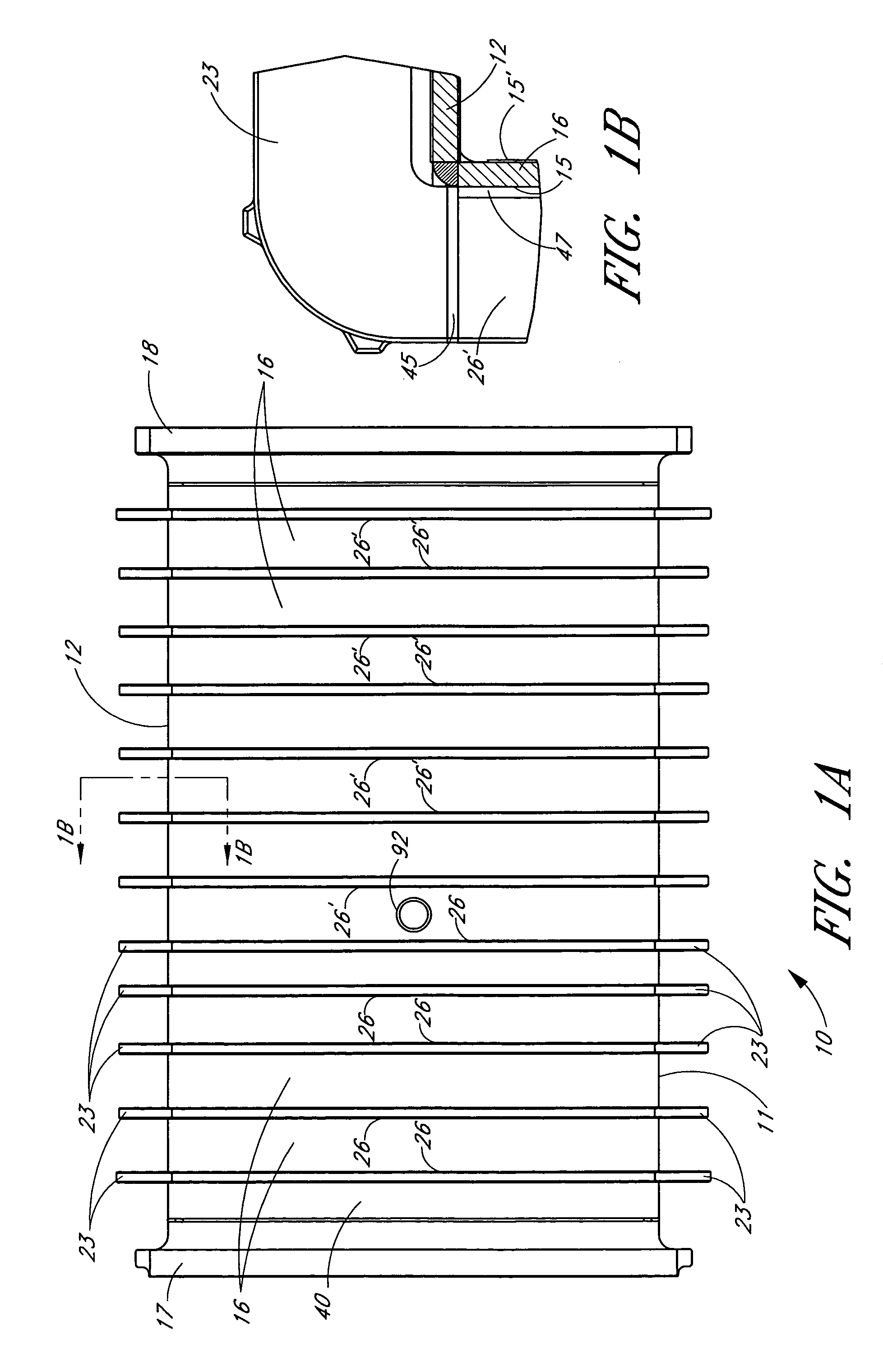
Medical instrument working end and method for endoluminal treatments
InactiveUS6911028B2Avoid damageEasily damagedSurgical instruments for heatingTherapeutic coolingVaporizationThermal effect
A medical instrument that utilizes electrical energy delivery between first and second opposing polarity electrodes in an interior bore of a working end to cause vaporization of an inflowing fluid media. The vaporization and expansion of the fluid media creates pressure gradients in the working end that causes heated vapor to propagate distally from the working end. The propagation or jetting of the vapor media is used to controllably cause thermal effects in endoluminal environments. The instrument and method can be used to shrink and occlude blood vessels in a treatment for varicose veins.
Owner:TSUNAMI MEDTECH
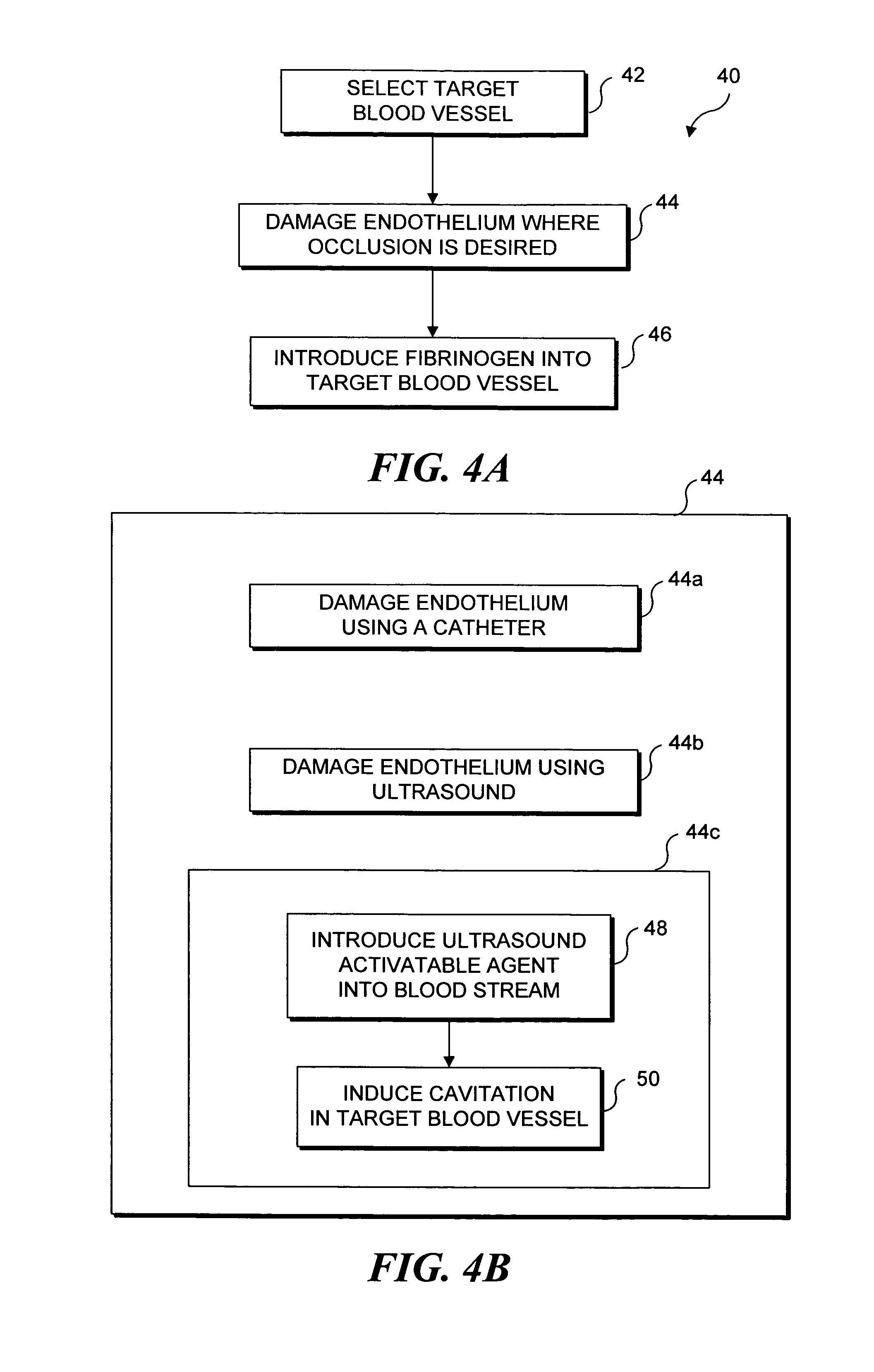
Ultrasound target vessel occlusion using microbubbles
InactiveUS7591996B2Eliminate heat damageFew techniqueUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyCavitationThrombus
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Exhaust tip
InactiveUS7007720B1Severe design restrictionOverall design flexibilityThermal insulationSilencing apparatusEngineeringThermal effect
An exhaust tip for attachment to a tailpipe that includes a thermoset heat shield at least partially surrounding and fastened to the tailpipe, and a thermoplastic decorative cover at least partially surrounding and fastened to the thermoset heat shield. The thermoset heat shield insulates the thermoplastic decorative cover from thermal effects of the tailpipe and spaces the thermoplastic decorative cover a predetermined distance away from the tailpipe.
Owner:LACKS INDUSTRIES INC
Ablation probe with peltier effect thermal control
ActiveUS20050203505A1Easy to introduceSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingThermal effectTissue ablation
A tissue ablation probe, system, and method are provided. The ablation probe comprises an elongated member, an ablative element mounted on the distal end of the elongated member, and at least one thermoelectric device mounted to the member in thermal communication with the ablative element. The system may include the ablation probe, thermal control circuitry for controlling the thermal effect of the thermoelectric device, and an ablation source for suppying ablation energy to the ablative element. A plurality of circumferentially distributed thermoelectric devices can be provided, so that radial tissue sectors can be selectively affected by independently controlling the thermal effect of the thermoelectric devices. In one embodiment, the thermoelectric device(s) can be used to cool a heat ablative element. In another embodiment, the thermoelectric device(s) can be used to heat an ablative element, thereby forming a heat ablative element. In still another embodiment, the thermoelectric device(s) can be used to cryogenically cool an ablative element, thereby forming a cryogenic ablative element.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
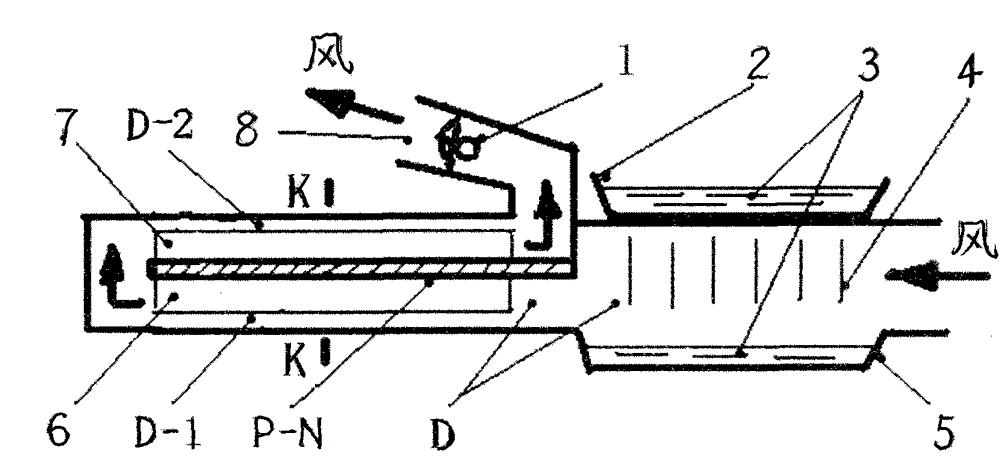
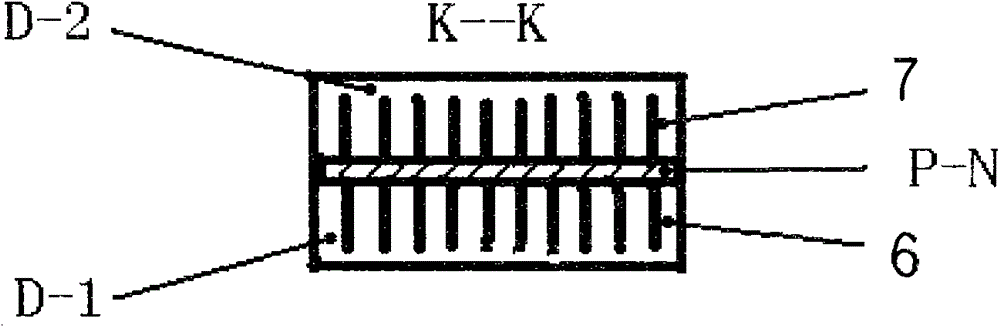
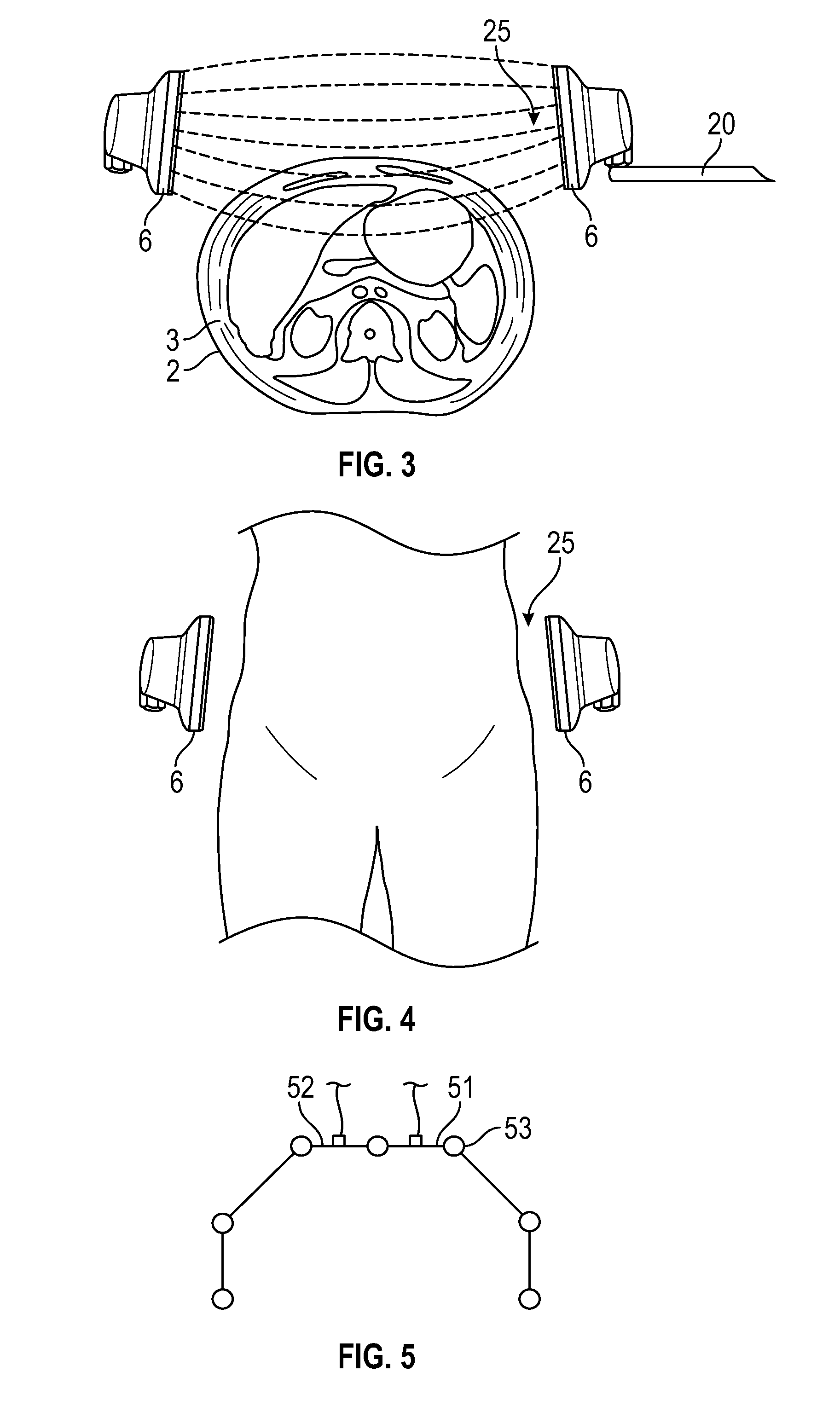
Air purification device with water spraying as main part and semiconductor refrigeration thermal effect as auxiliary part
InactiveCN104976714AReduce project sizeMechanical apparatusUsing liquid separation agentStructural cohesionWater storage
The invention discloses a method for using a semiconductor heating-cooling device in water-spraying air purification equipment. The semiconductor heating-cooling device is structurally formed by that heat exchange fins are arranged at the lower cold ends and upper hot ends of a same group of P-N-node semiconductor devices (p-n) to form the semiconductor heating-cooling device (W) with refrigerating fins (6) and heating fins (7). The key utilization method, namely structural cohesion requirements in utilization includes: enabling a refrigerating passage formed by a portion, with the refrigerating fins (6), of the semiconductor heating-cooling device (W) to join with a rain area air purification passage (D) formed by a water storage plate (2) and a water receiving plate (5); enabling a heating passage (D-2) formed by a portion, with the heating fins (7), of the semiconductor heating-cooling device (W) to join with an air purification passage (D) with a fan driver (1). By taking the advantage of double effects of the semiconductor devices (p-n) with one side for refrigerating and the other side for heating after electrification, conditions are created for both greatly simplifying heating-cooling facilities (size reduced) and greatly saving energy.
Owner:梁嘉麟
Protection of electro-optic displays against thermal effects
InactiveUS20140078024A1Reduction factorHollow inflatable ballsStatic indicating devicesElectrophoresisHeat conducting
An electro-optic display comprises a layer of reflective electro-optic material capable of changing its optical state on application of an electric field, an electrode, a heat generating component in heat conducting relationship with the electro-optic material, and a heat shield disposed between the heat generating component and the electro-optic material, the heat shield comprising a layer of thermally insulating material and a layer of thermally conducting material, the thermally conducting material being disposed between the thermally insulating material and the electro-optic material. The invention also provides an electrophoretic medium comprising a suspending fluid and a plurality of electrically charged particles suspended in the suspending fluid and capable of moving therethrough upon application of an electrical field to the electrophoretic medium, the suspending fluid containing a compatibilizer to reduce its coefficient of thermal expansion.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
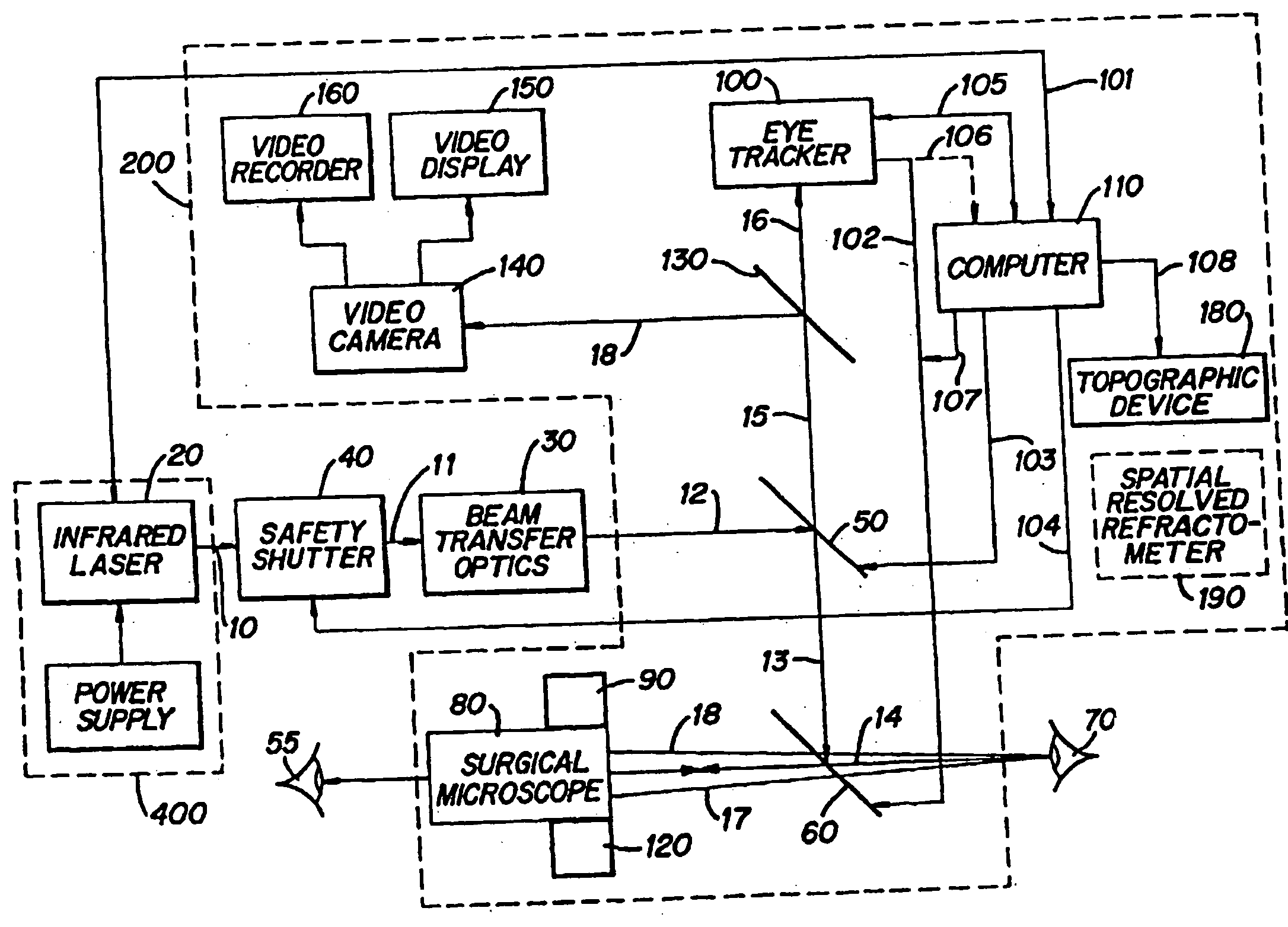
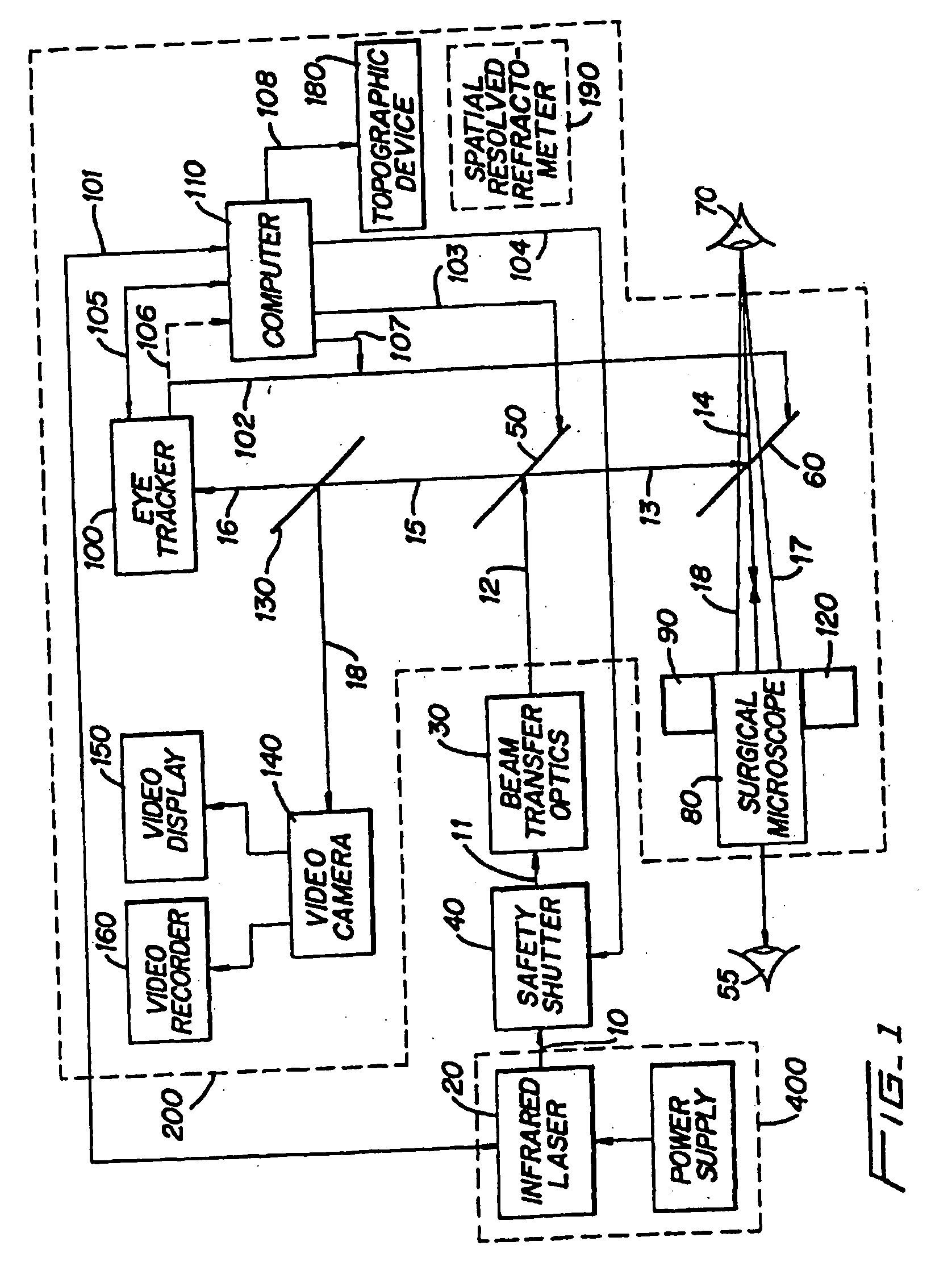
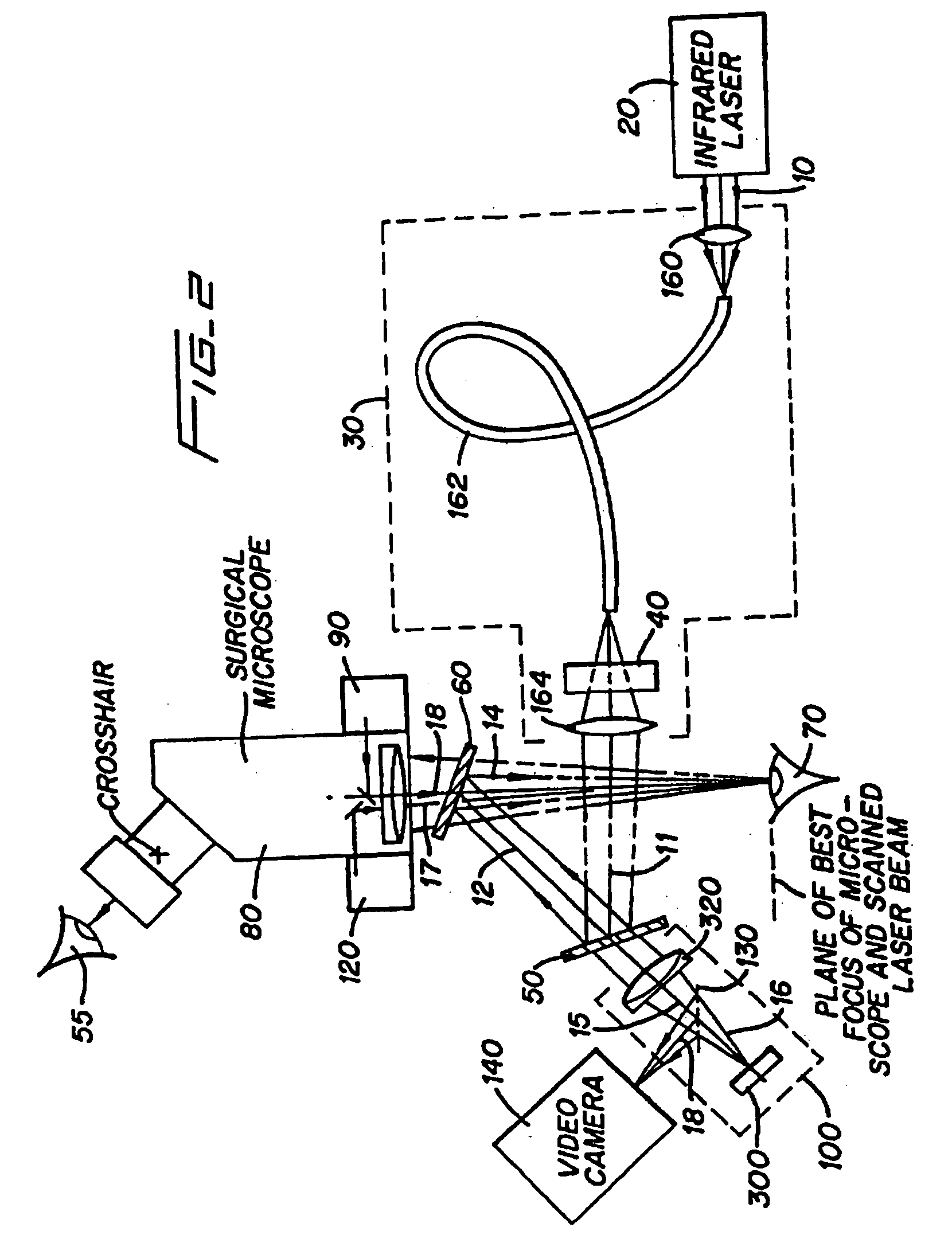
Method and apparatus for removing corneal tissue with infrared laser radiation and short pulse mid-infrared parametric generator for surgery
InactiveUS20050197655A1Reduce undesirable thermal damageMaximum flexibilityLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsLaser scalpelMid infrared laser
A surgical technique for removing corneal tissue with scanned infrared radiation is disclosed which utilizes short mid-infrared laser pulses to provide a tissue removal mechanism based on photospallation. Photospallation is a photomechanical ablation mechanism which results from the absorption of incident radiation by the corneal tissue. Since photospallation is a mechanical ablation process, very little heat is generated in the unablated adjacent tissue. The disclosed surgical system includes a scanning beam delivery system which allows uniform irradiation of the treatment region and utilizes low energy outputs to achieve controlled tissue removal. A real-time servo-controlled dynamic eye tracker, based on a multiple-detector arrangement, is also disclosed which senses the motion of the eye and provides signals that are proportional to the errors in the lateral alignment of the eye relative to the axis of the laser beam. Temporal and frequency discrimination are preferably utilized to distinguish the tracking illumination from the ambient illumination and the surgical laser beam. A laser parametric generator for surgical applications is disclosed which utilizes short-pulse, mid-infrared radiation. The mid-infrared radiation may be produced by a pump laser source, such as a neodymium-doped laser, which is parametrically down converted in a suitable nonlinear crystal to the desired mid-infrared range. The short pulses reduce unwanted thermal effects and changes in adjacent tissue to potentially submicron-levels. The parametrically converted radiation source preferably produces pulse durations shorter than 25 ns at or near 3.0 microns but preferably close to the water absorption maximum associated with the tissue. The down-conversion to the desired mid-infrared wavelength is preferably produced by a nonlinear crystal such as KTP or its isomorphs. In one embodiment, a non-critically phased-matched crystal is utilized to shift the wavelength from a near-infrared laser source emitting at or around 880 to 900 nm to the desired 2.9-3.0 microns wavelength range. A fiber, fiber bundle or another waveguide means utilized to separate the pump laser from the optical parametric oscillation (OPO) cavity is also included as part of the invention.
Owner:AMO MFG USA INC
Method and apparatus for treating a subterranean formation
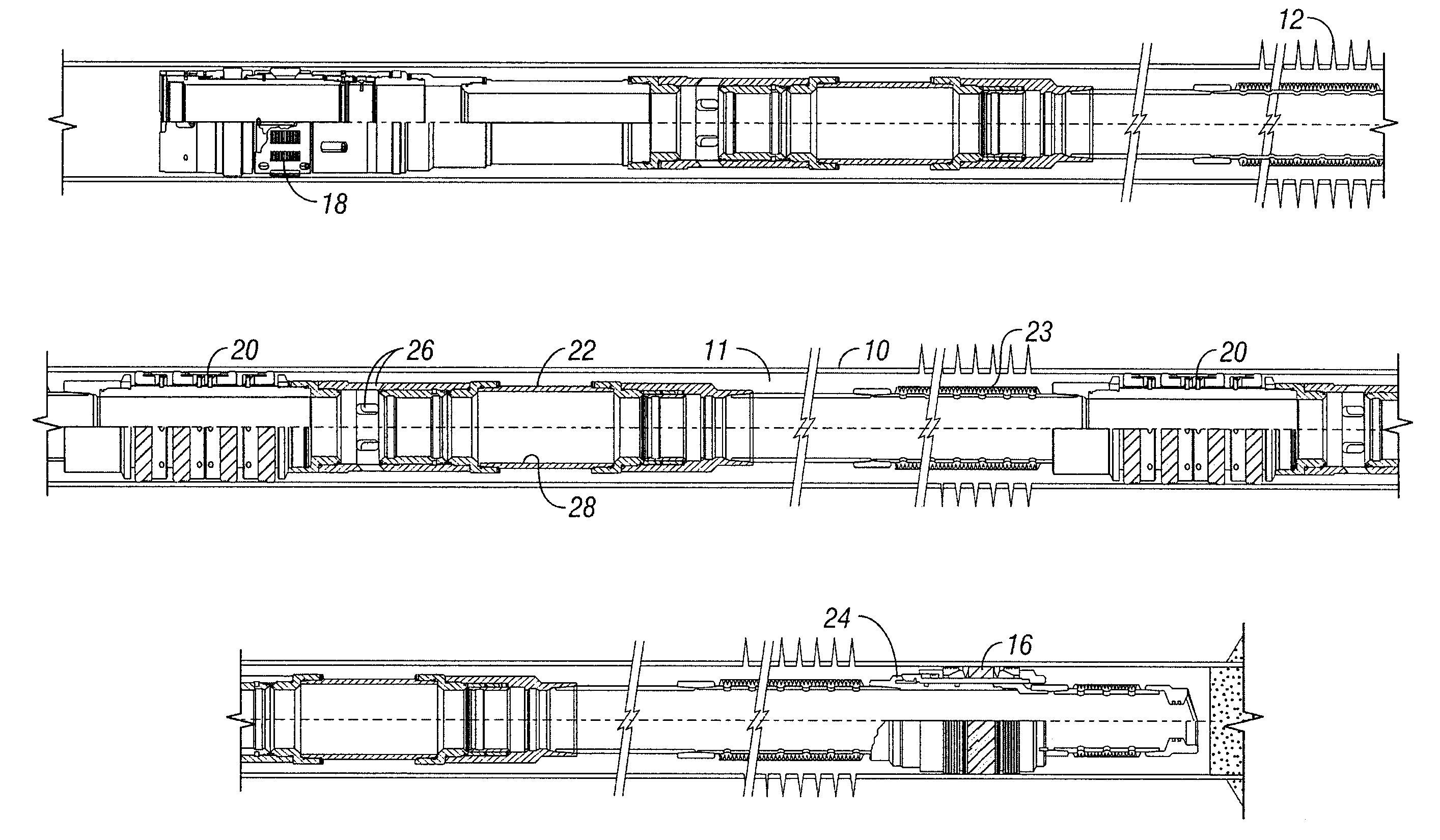
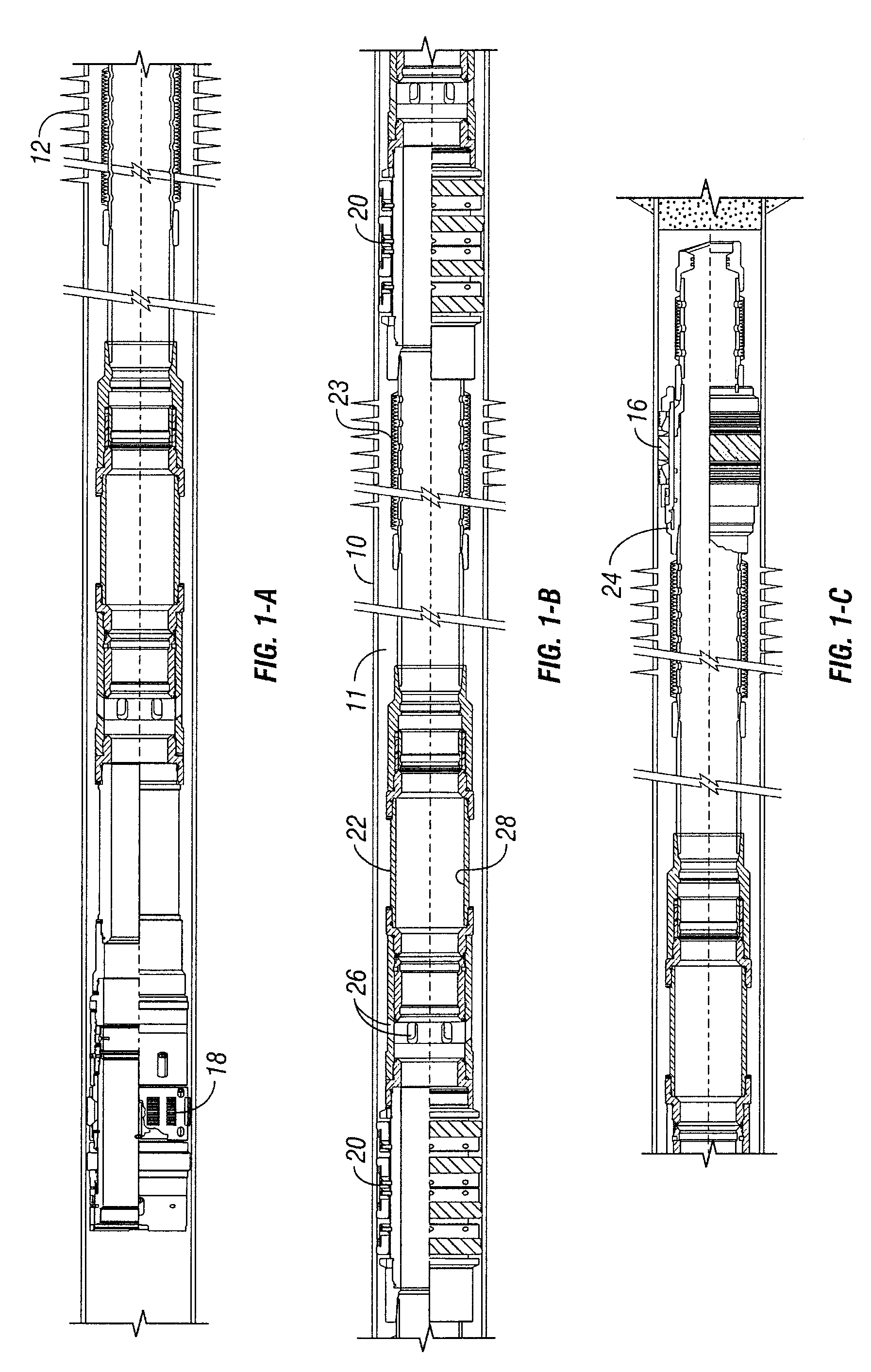
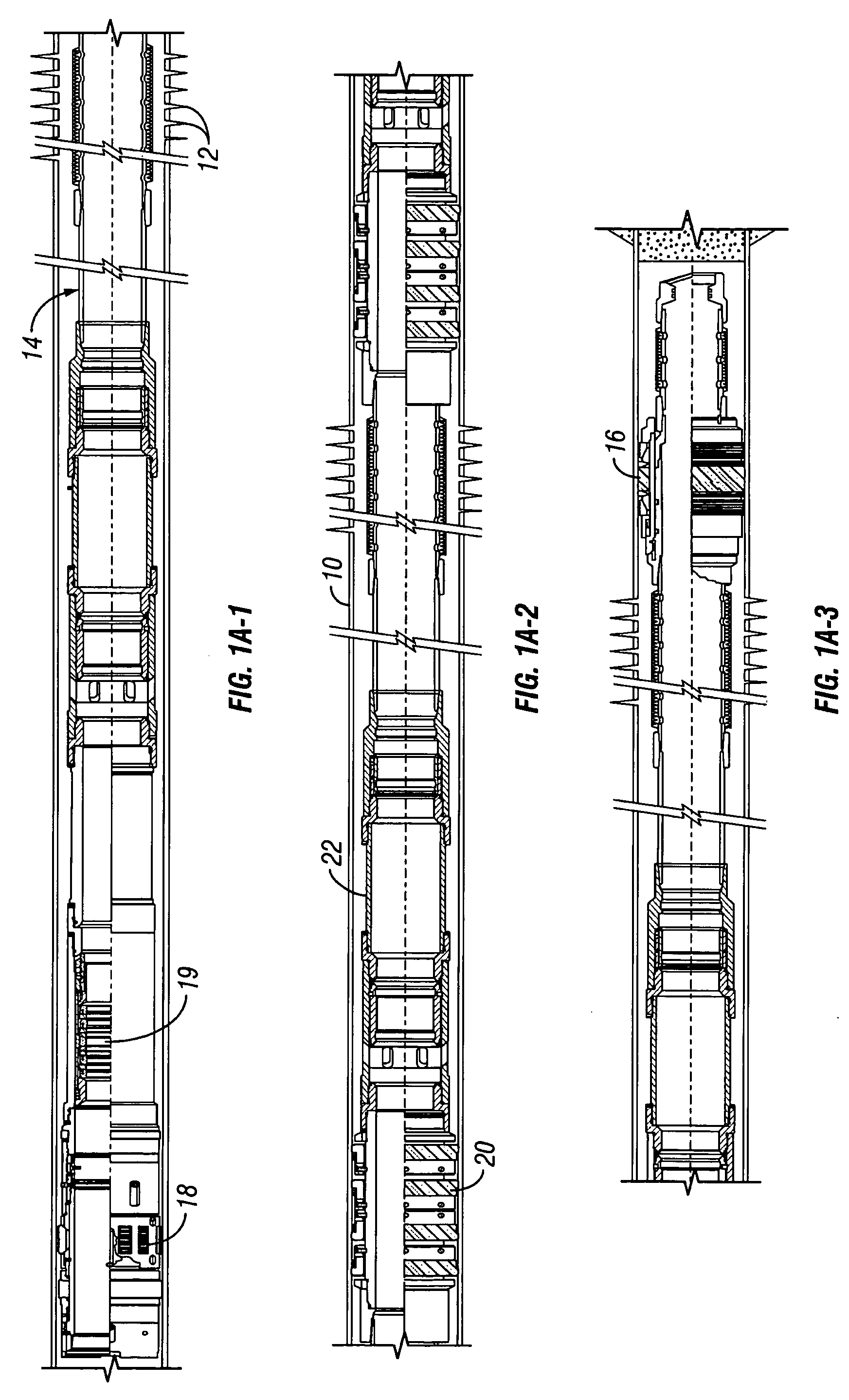
InactiveUS7066264B2Precise positioningMaintain positionFluid removalVibration devicesSleeve valveEngineering
A service / completion liner having a plurality of downhole selectable indicating tools and being used in sand control (gravel pack) placement systems in conjunction with a straddle packer service tools or with conventional crossover type service tools. Each indicating collar has a downhole selectable indicating collar providing a robust, landing profile for precisely locating and maintaining service tool position during well treatment operations. The landing collars accommodate hydraulic and / or thermal effects commonly referred to as tubing move effects which are the principle cause of tool position error and excessive seal wear. The landing collar is downhole convertible between a pass through (Go) and non pass through (No-go) condition by simple upward and downward cycling via the tool running and treatment fluid tubing and a shifting tool, which may also be referred to as a set down collet. The shifting / set down collet is also used to open and close a downhole sliding sleeve valve and may be an integral part of an injection tool or a tool for gravel or fracture packing. A sliding sleeve valve design and a straddle packer configuration that protects the primary PBRs in the gravel pack system and also protects the sliding sleeve while sand is placed in the screen casing annulus.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Optical accelerometer or displacement device using a flexure system
InactiveUS6955085B2Radiation pyrometryAcceleration measurement using interia forcesFiberAccelerometer
Disclosed herein is an accelerometer and / or displacement device that uses a mass coupled to a rhomboidal flexure to provide compression to an optical sensing element preferably having a fiber Bragg grating (FBG). The transducer includes a precompressed optical sensor disposed along a first axis between sides of the flexure. The top portion of the flexure connects to the mass which intersects the flexure along a second axis perpendicular to the first axis. When the mass experiences a force due to acceleration or displacement, the flexure will expand or contract along the second axis, which respectively compresses or relieves the compression of the FBG in the optical sensing element along the first axis. Perturbing the force presented to the FBG changes its Bragg reflection wavelength, which is interrogated to quantify the dynamic or constant force. A temperature compensation scheme, including the use of additional fiber Bragg gratings and thermal compensators axially positioned to counteract thermal effects of the optical sensing element, is also disclosed.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Method and device for excavating submerged stratum
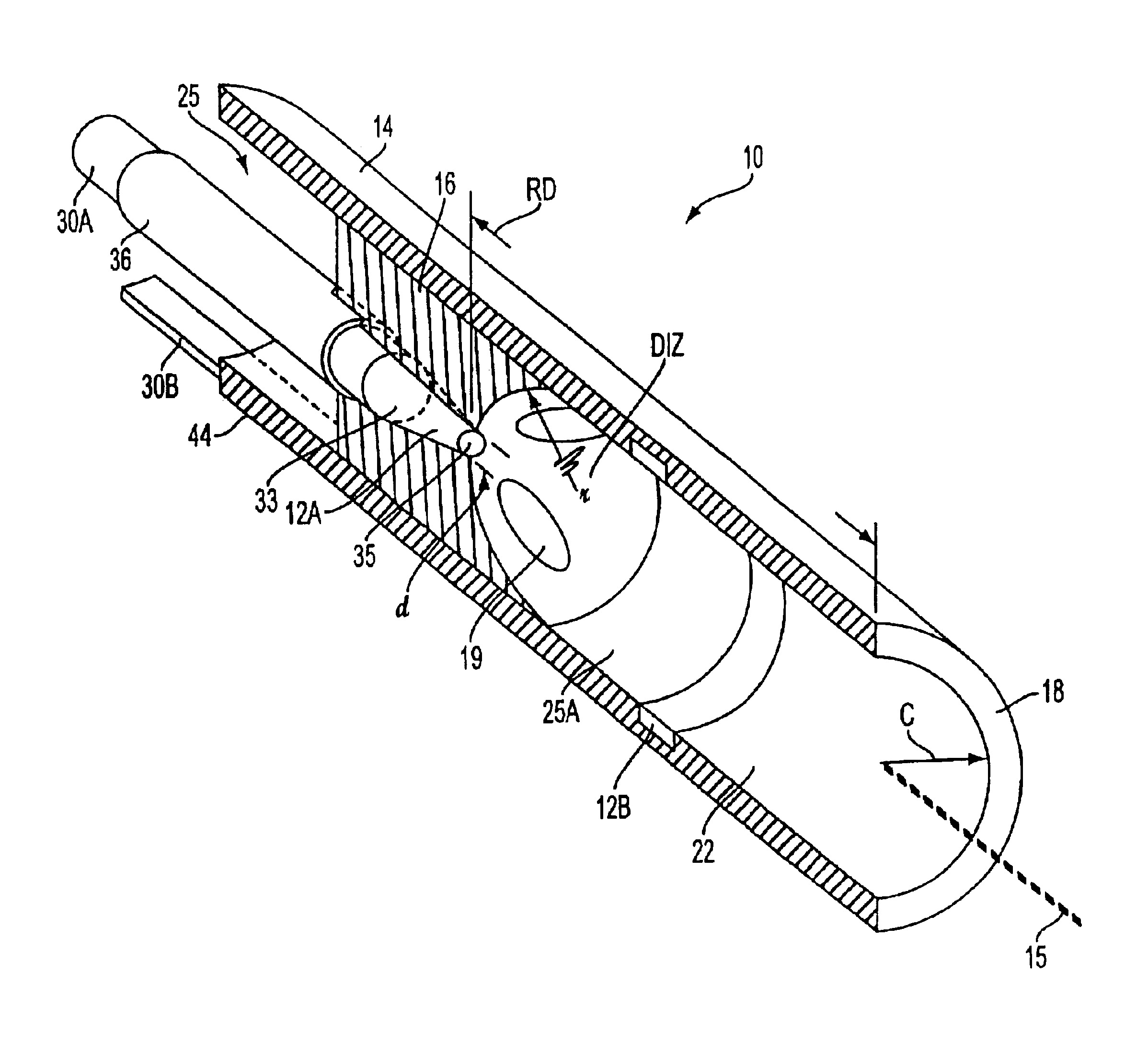
InactiveUS20090126235A1Reduce energy transferReduce loadMachines/dredgers working methodsMechanical machines/dredgersAbsorptanceLaser induced bubble
An excavation technique for a stratum capable of excavating a submerged stratum such as a layer containing an underground resource by using laser irradiation in liquid is provided. In this technique, a laser beam transmitted through laser transmission means 20 is irradiated in liquid 90 in form of a laser beam having a wavelength with high absorptance of the liquid 90 by laser-induced bubble generation means 35, generating a bubble flow 36, thus excavation of a submerged stratum may be carried out by using a laser-induced destruction effect. Moreover, a laser beam 41 having low absorptance of the liquid 90 is irradiated by laser irradiation means 39 and passed through the bubble flow 36, thereby applying a thermal effect to a stratum to destroy rock and excavate the stratum. The destruction effect and the thermal effect also may be cooperatively worked.
Owner:JAPAN DRILLING CO LTD +2
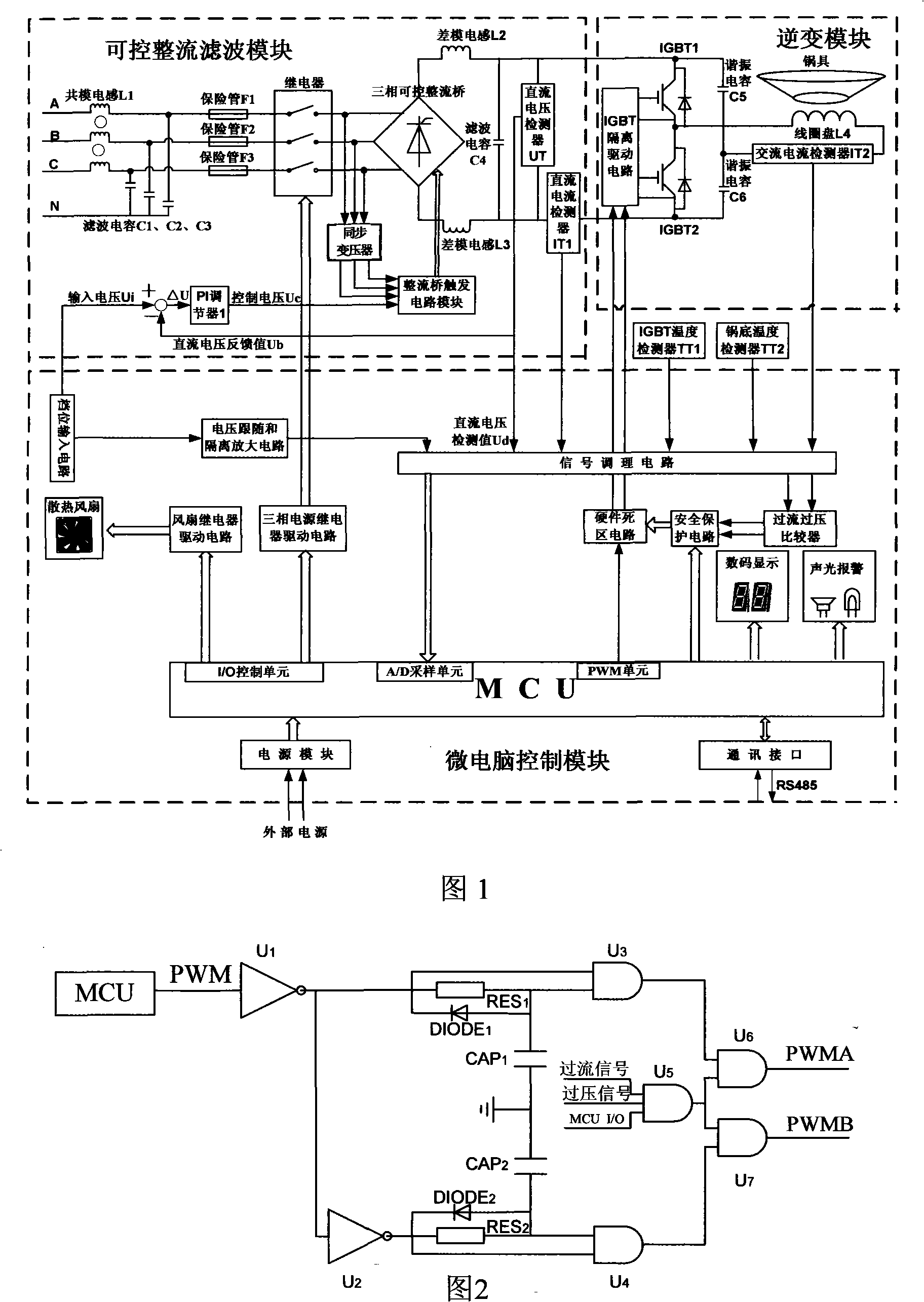
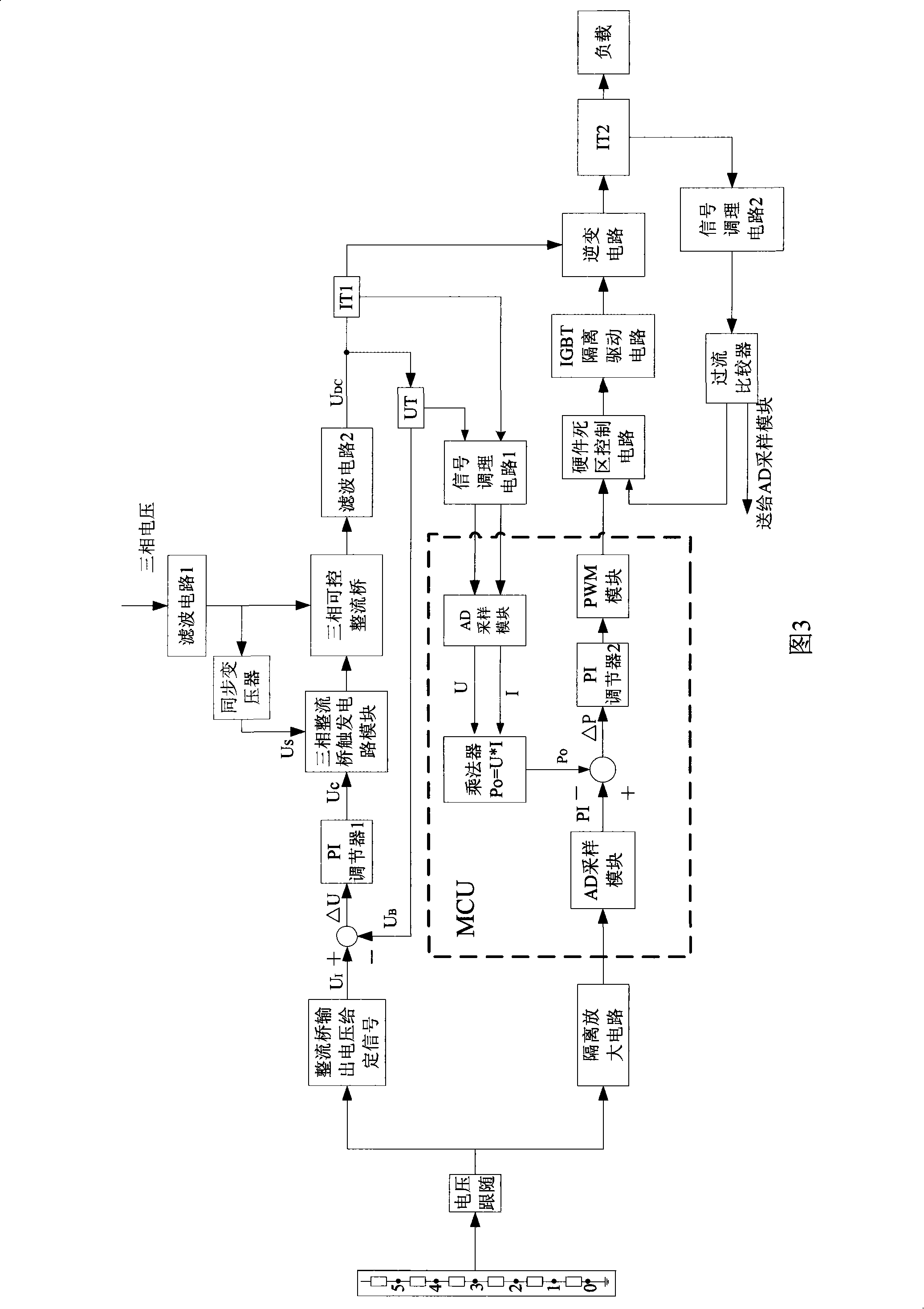
Intelligent control apparatus and method for high-power energy saving electromagnetic stove
InactiveCN101309529ASuppressor mutationProtection securityAc-dc conversionInduction heating controlConstant powerElectric network
The invention relates to an intelligent control device of a high power energy saving electromagnetic stove, and the method thereof, The intelligent control device comprises a controllable rectifying and filtering module, a contravariant module and a microcomputer controlling module, which is characterized in that a three-phase alternating current power supply is rectified into an adjustable direct current power supply through the controllable rectifying and filtering module ; the direct current power supply is inverted into a high frequency alternating current power supply through the contravariant module, and then the electric energy is converted into electromagnetic energy to be radiated to the bottom of a cookware, and vortex flow is generated, and the cookware can be heated because of the thermal effect of the vortex flow; the microcomputer controlling module is the core of the entire system, which is used for collecting data and transmitting control information to each module; the device adopts a series of advanced control policies, such as the trigger control of the rectifier bridge of an PI regulator, the intelligent self-adaptive constant power control, the intelligent soft-start control, the intelligent cookware detection control, etc., and thereby the working stability and the security of the electromagnetic stove are enhanced. The harmonic pollution of the equipment to the electric network can be reduced to the utmost extent when the electric energy of the electromagnetic stove is saved, and the electromagnetic stove is suitable for various kitchens and dining rooms.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Ultrasound target vessel occlusion using microbubbles
InactiveUS20070041961A1Less invasive techniqueSimple technologyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyCavitationThrombus
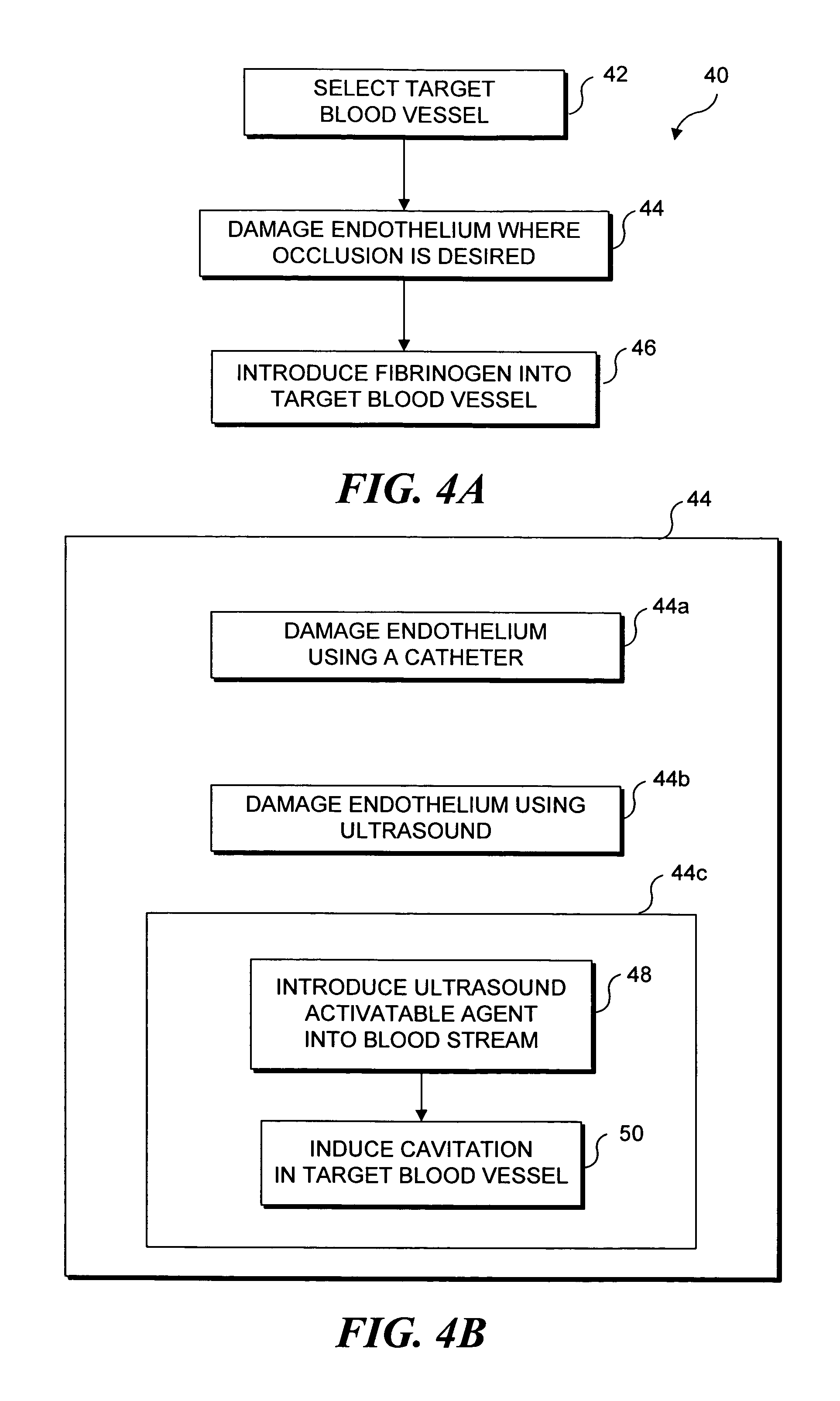
Selective occlusion of a blood vessel is achieved by selectively damaging endothelial cells at a target location in the blood vessel, resulting in the formation of a fibrin clot proximate to the damaged endothelial cells. Additional fibrinogen can then be introduced into the blood vessel if occlusion is not achieved, as the fibrinogen is converted to fibrin by enzymes released by the exposed thrombogenic tissue and activated platelets. Endothelial cells are selectively damaged using thermal effects induced by ultrasound, by mechanical effects induced by ultrasound, or by mechanical effects produced by a tool introduced into the blood vessel (such as a catheter-based tool). A particularly preferred technique for selectively damaging endothelial cells involves introducing an ultrasound activatable agent into the blood vessel, and causing cavitation in that agent using pulses of high-intensity focused ultrasound having a duration insufficient to induce thermal damage in adjacent perivascular tissue.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
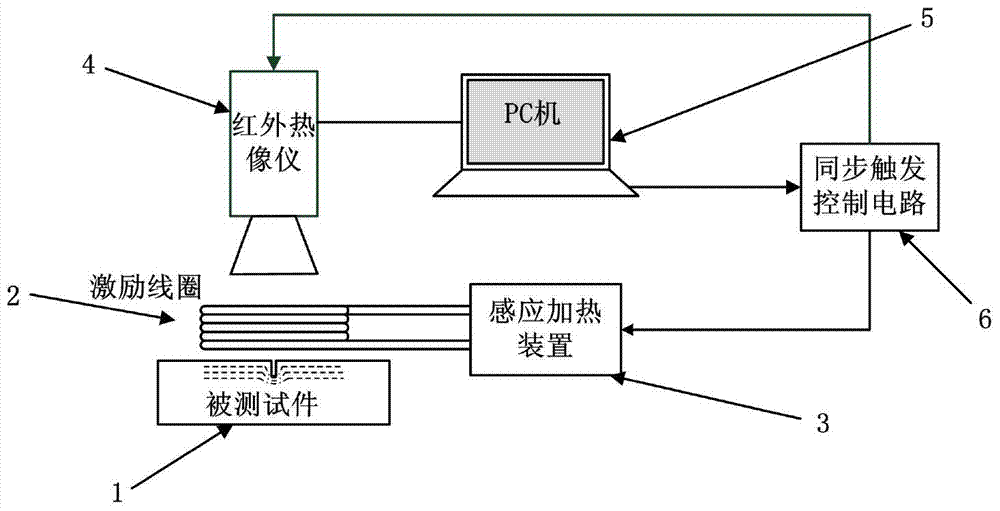
Pulsed eddy current infrared thermal imaging detection system and method for steel rail cracks
InactiveCN104764770AConvenient and intuitive detection meansThe energy of the pulse signal is largeMaterial flaws investigationThermodynamicsImage resolution
The invention discloses a pulsed eddy current infrared thermal imaging detection system and method for steel rail cracks. The system comprises an excitation device, an induction heating device, an infrared thermal imager and a PC, wherein the induction heating device is used for generating a pulse current signal; the pulse current signal is exerted to a tested part through the excitation device; eddy current is induced from the surface of the tested part and a thermal effect is generated, so that the surface temperature distribution changes; the infrared thermal imager is used for recording the surface temperature change process of the tested part and transmitting to the PC to process and analyze. The pulsed eddy current infrared thermal imaging detection system is characterized by also comprising a synchronous trigger control circuit, which is used for synchronously controlling the excitation and recording time of the induction heating device and the infrared thermal imager, so that the heating and cooling processes after complete induction of the tested part are accurately recorded; and the condition that the PC obtains accurate data to analyze and treat is ensured. The pulsed eddy current infrared thermal imaging detection system is high in detection efficiency and high in image resolution ratio; excitation of an excitation source and the infrared thermal imager can be synchronously carried out; and the detection result is not affected by human factors.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
High temperature treated media
ActiveUS20120234748A1Reduce and eliminate in filtrationImprove filtering effectNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperParticulatesFiber
A thermally bonded filtration media that can be used in high temperature conditions in the absence of any loss of fiber through thermal effects or mechanical impact on the fiber components is disclosed. The filter media can be manufactured and used in a filter unit or structure, can be placed in a stream of removable fluid, and can remove a particulate load from the mobile stream at an increased temperature range. The combination of bi-component fiber, other filter media fiber, and other filtration additives provides an improved filtration media having unique properties in high temperature, high performance applications.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
Medical instruments and techniques for thermally-mediated therapies
InactiveUS20100160905A1Thermal ablation rapidly and efficientlyPrevents desiccationBalloon catheterDiagnosticsThermal energyGas phase
A surgical instrument for thermally-mediated therapies in targeted tissue volumes and for causing thermal effects in polymer tissue-contacting members. In one embodiment, the instrument has a working end with an interior chamber that is supplied with a biocompatible liquid. An energy source causes a liquid-to-vapor phase change within the interior of the instrument. The vapor phase media then is ejected from the working surface of the instrument, and a controlled vapor-to-liquid phase change in an interface with tissue applies thermal energy substantially equal to the heat of vaporization to ablate tissue. The vapor-to-liquid phase transitions, or internal energy releases, can be provided about thin-film flexible structures for engaging body lumens and cavities. An exemplary embodiment can be used for shrinking, sealing, welding or creating lesions in tissue—while causing limited collateral thermal damage and while totally eliminating electrical current flow in the engaged tissue.
Owner:TSUNAMI MEDTECH
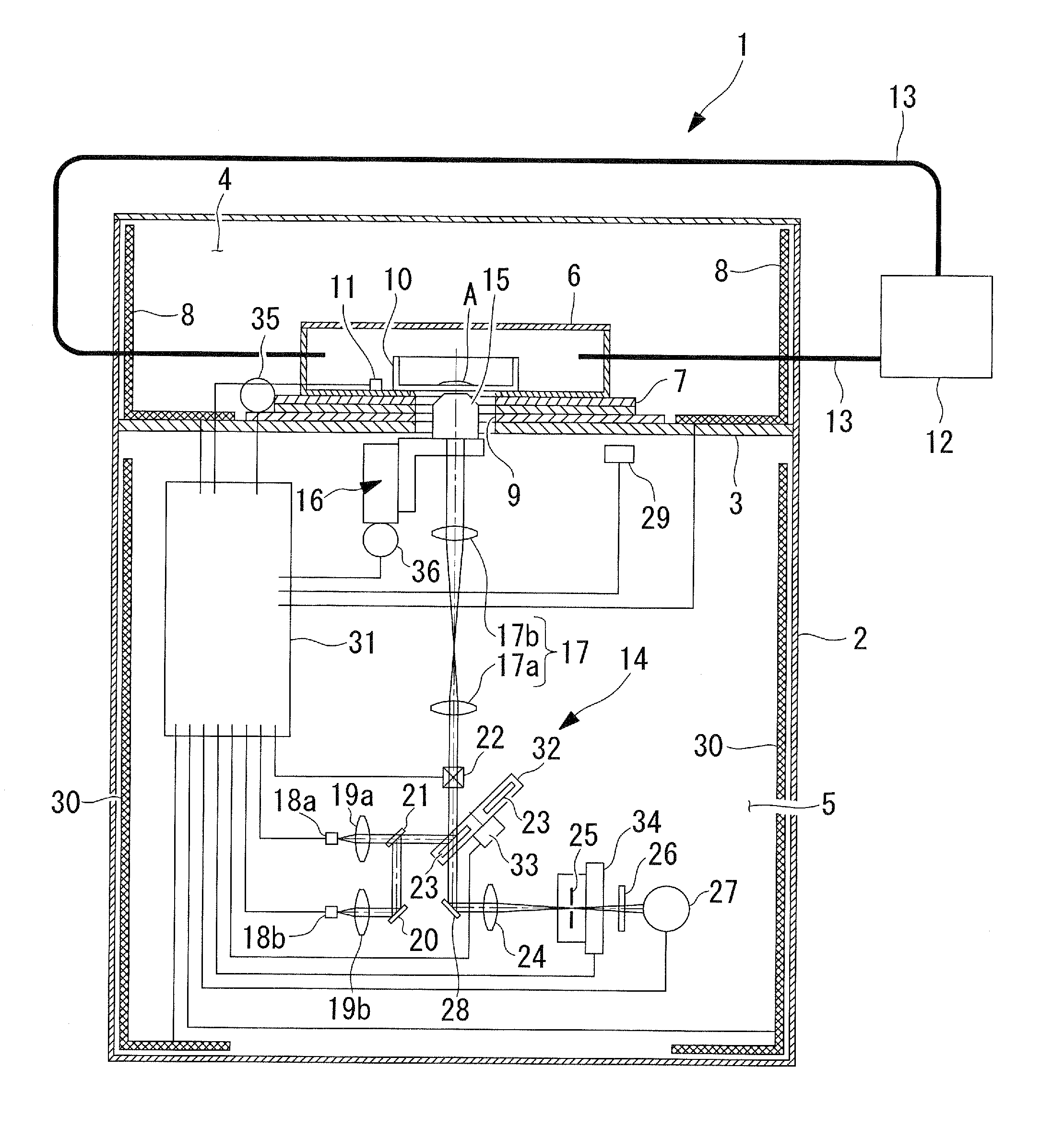
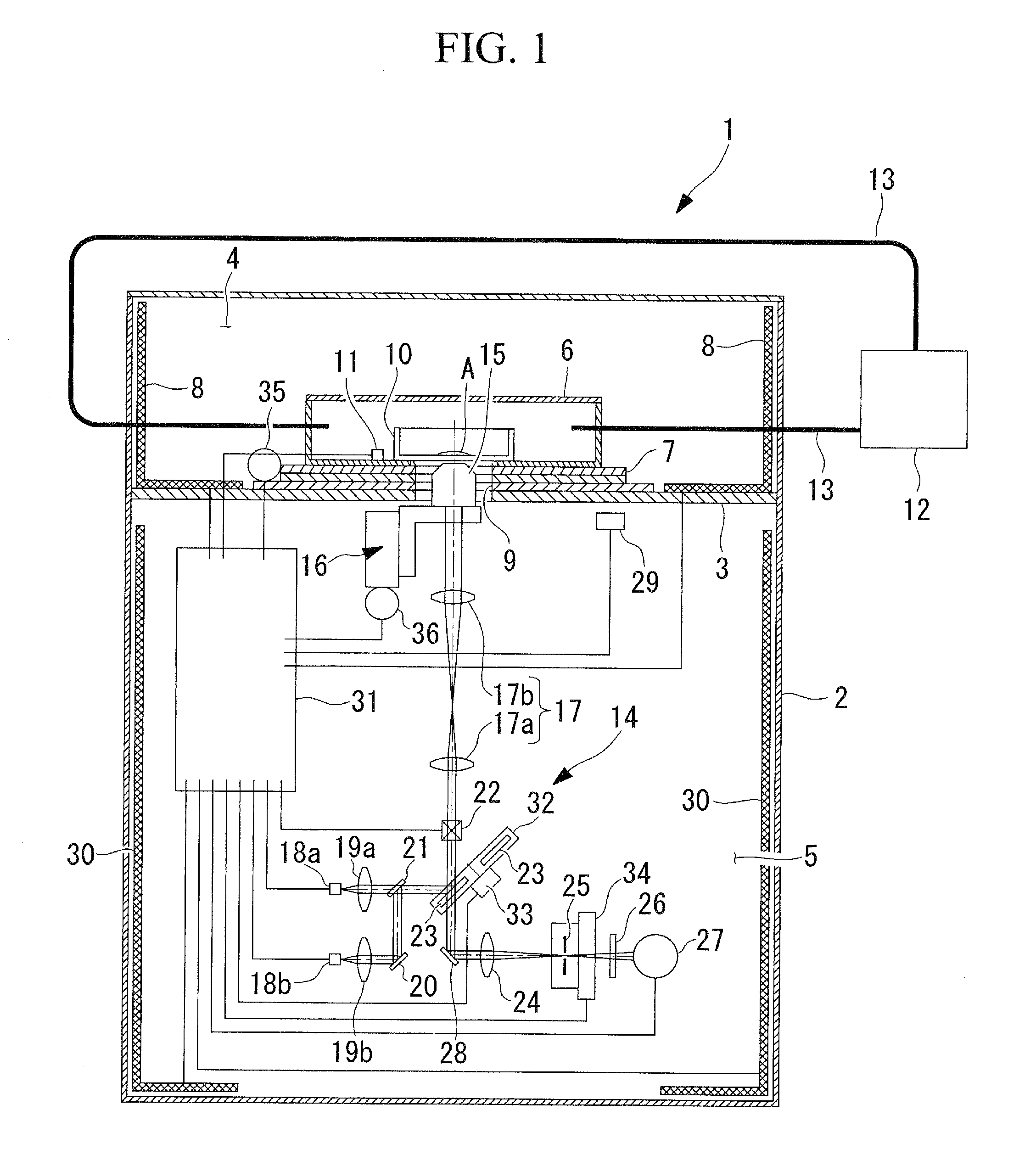
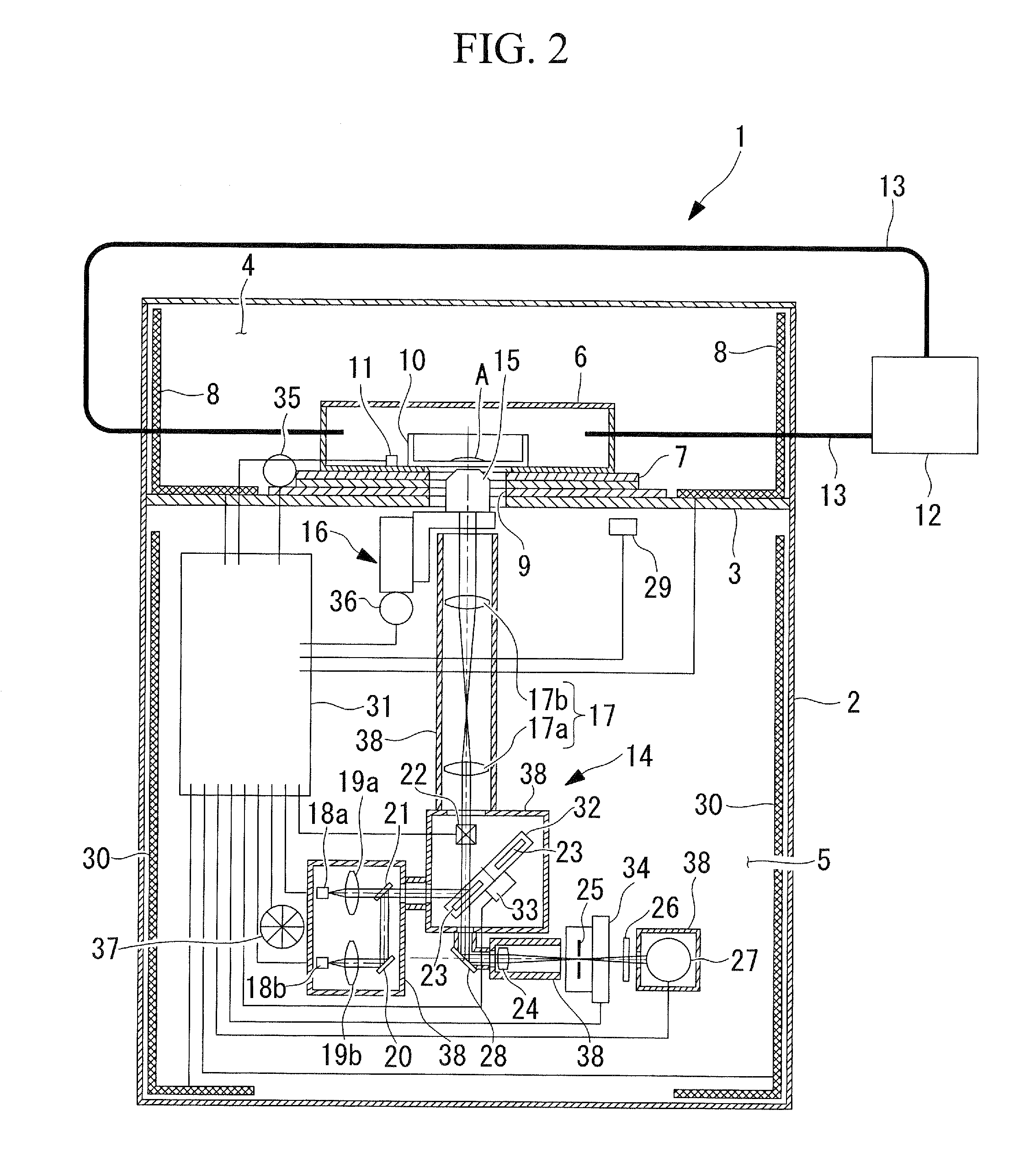
Scanning confocal microscope
A scanning confocal microscope can provide an image while preventing a decrease in brightness and blurring due to strain caused in optical and mechanical systems by thermal effects in a high-temperature, high-humidity incubation container. This scanning confocal microscope includes an incubation container that has a space in which a specimen is disposed and that can maintain an internal environment thereof at a predetermined temperature and high humidity and an optical system space adjacent to the incubation container and separated therefrom based on humidity. The optical system space accommodates a light-scanning unit and a scanner optical system, an objective lens, a confocal pinhole, and a focus adjustment mechanism. The optical system space further accommodates a temperature-maintaining unit for the optical system space to maintain the optical system space at a temperature substantially equal to the temperature in the incubation container.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Method and system for skin treatment
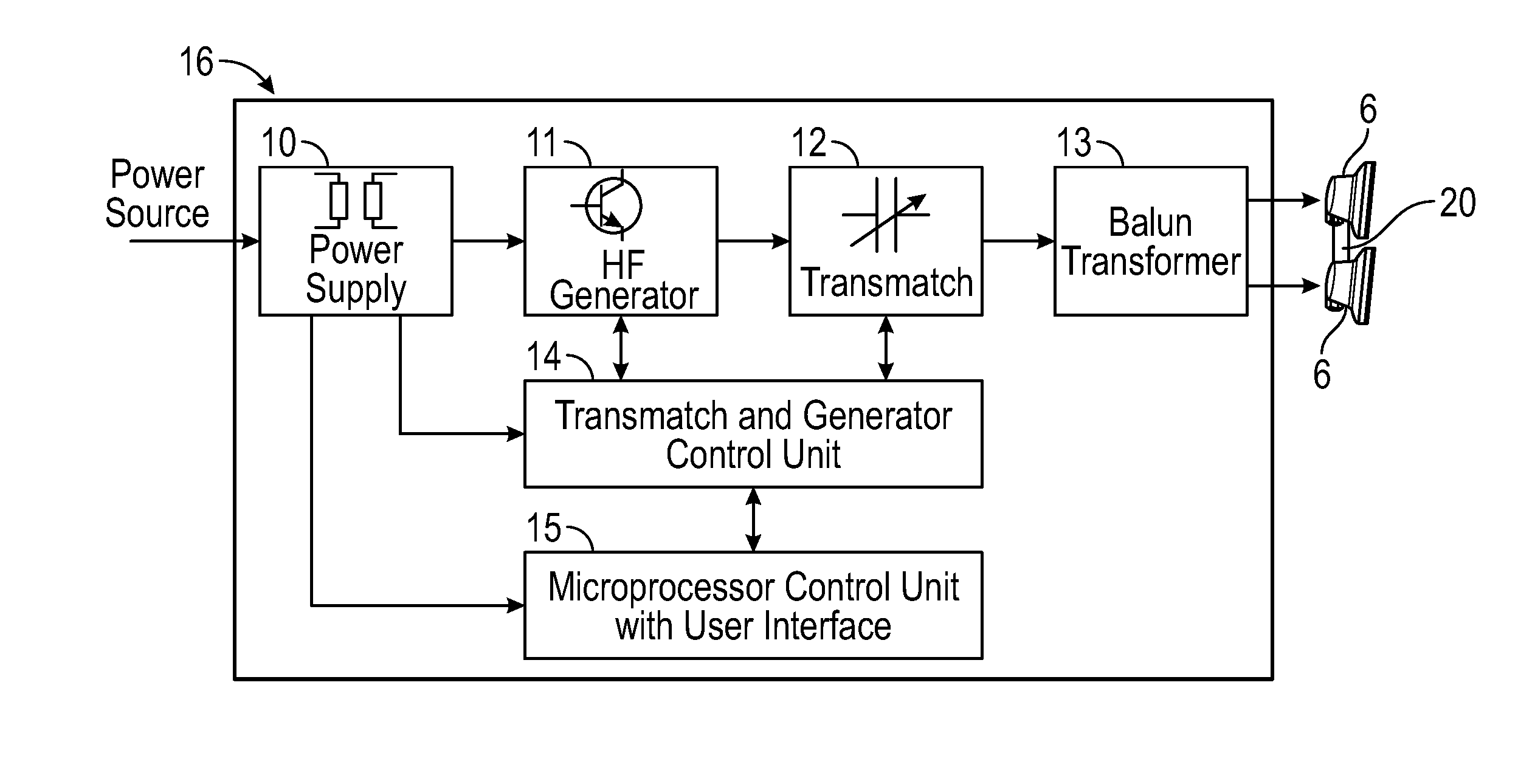
InactiveUS20160220834A1Reduce the numberReduce volumeElectrotherapyLight therapySkin treatmentsThermal effect
Methods are provided for remodeling and / or reducing target tissue, body contouring, tightening skin tissue and many other skin rejuvenation processes and treatments, as well as for pain relief, applying electromagnetic waves to the targeted areas of the body. The electromagnetic waves cause thermal and non-thermal effects and their parameters may be finely adjusted to achieve more indications and / or higher efficiency treatment in one session. The electromagnetic energy may be applied via one or more applicators without touching the skin.
Owner:BTL MEDICAL SOLUTIONS AS +1
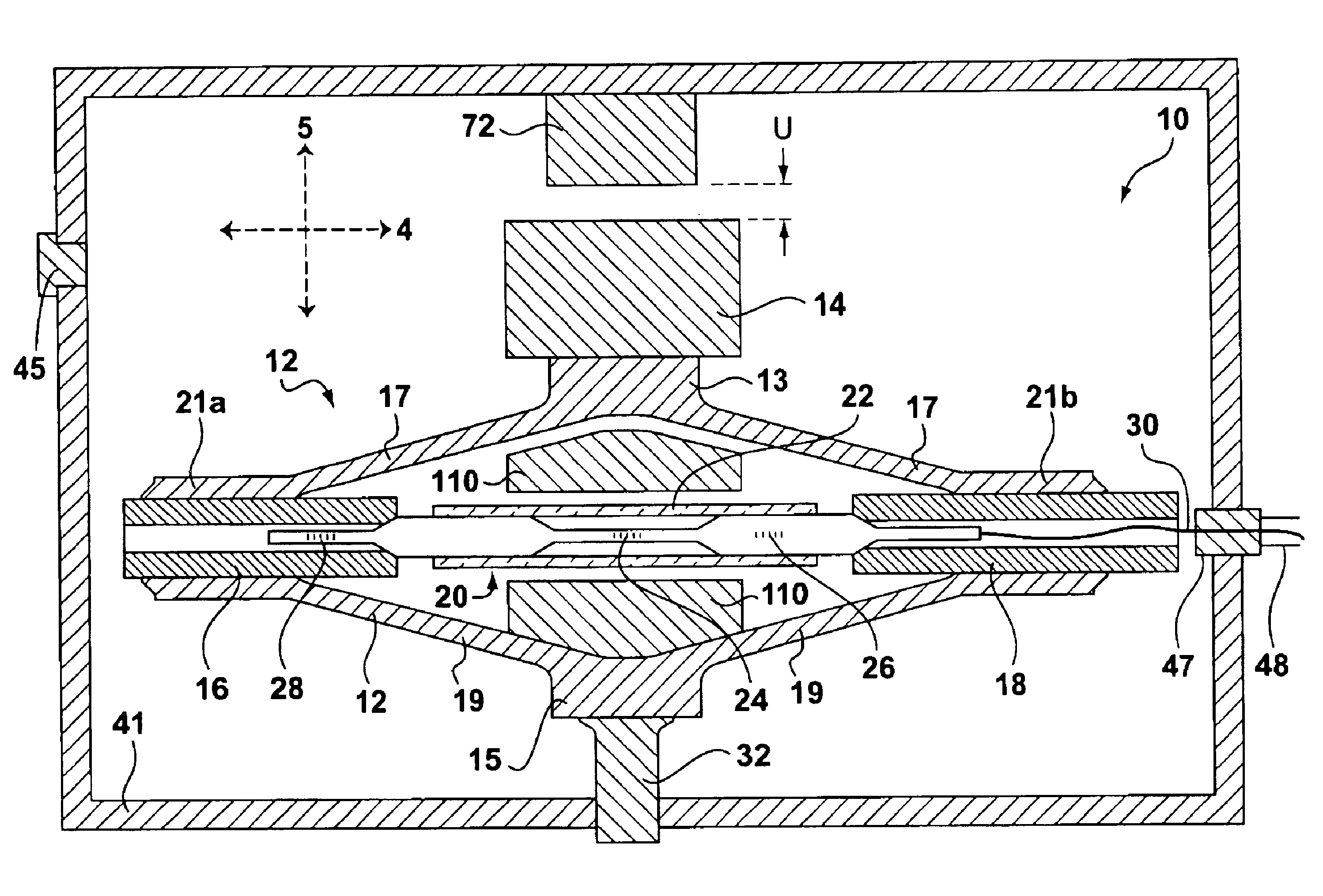
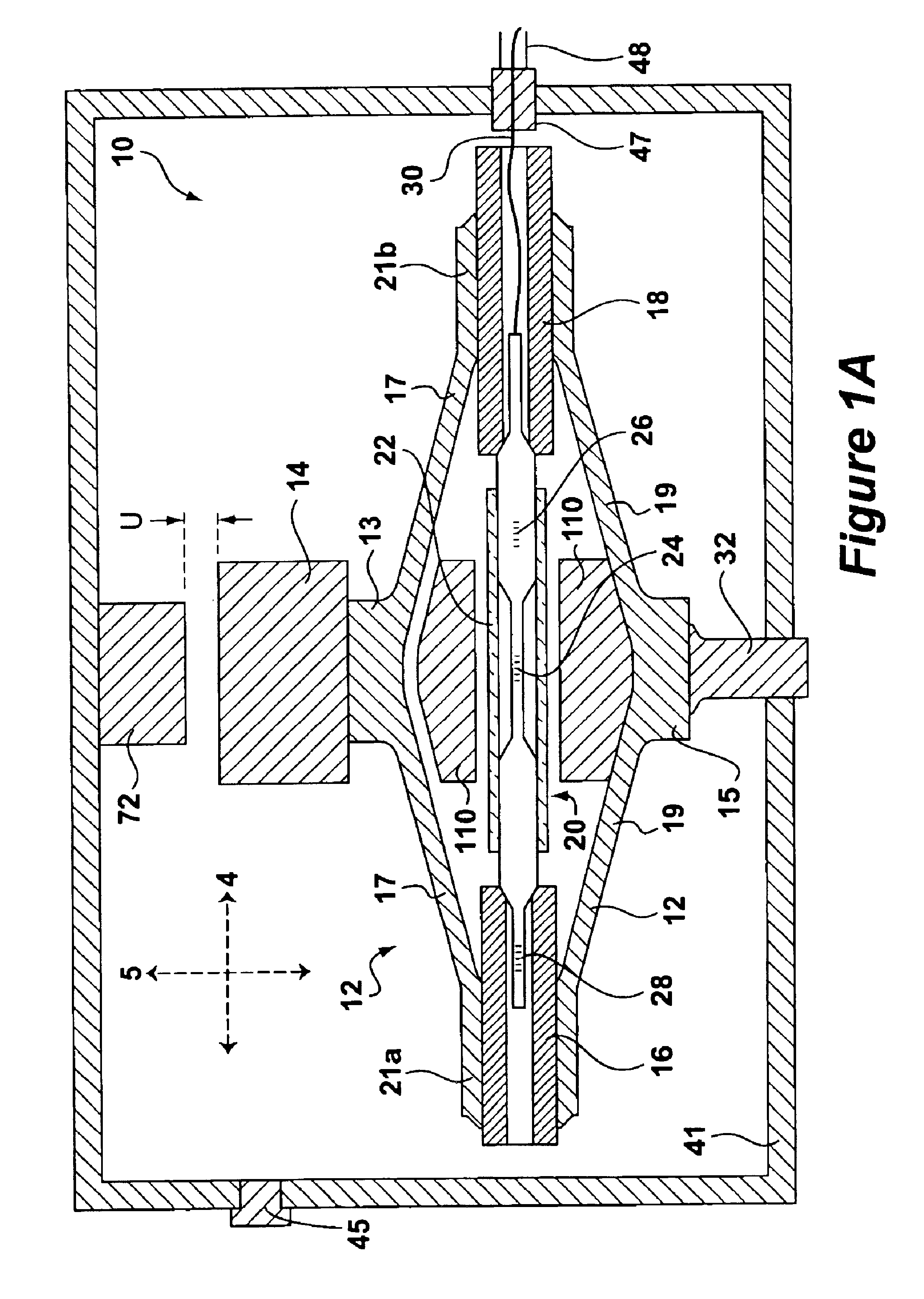
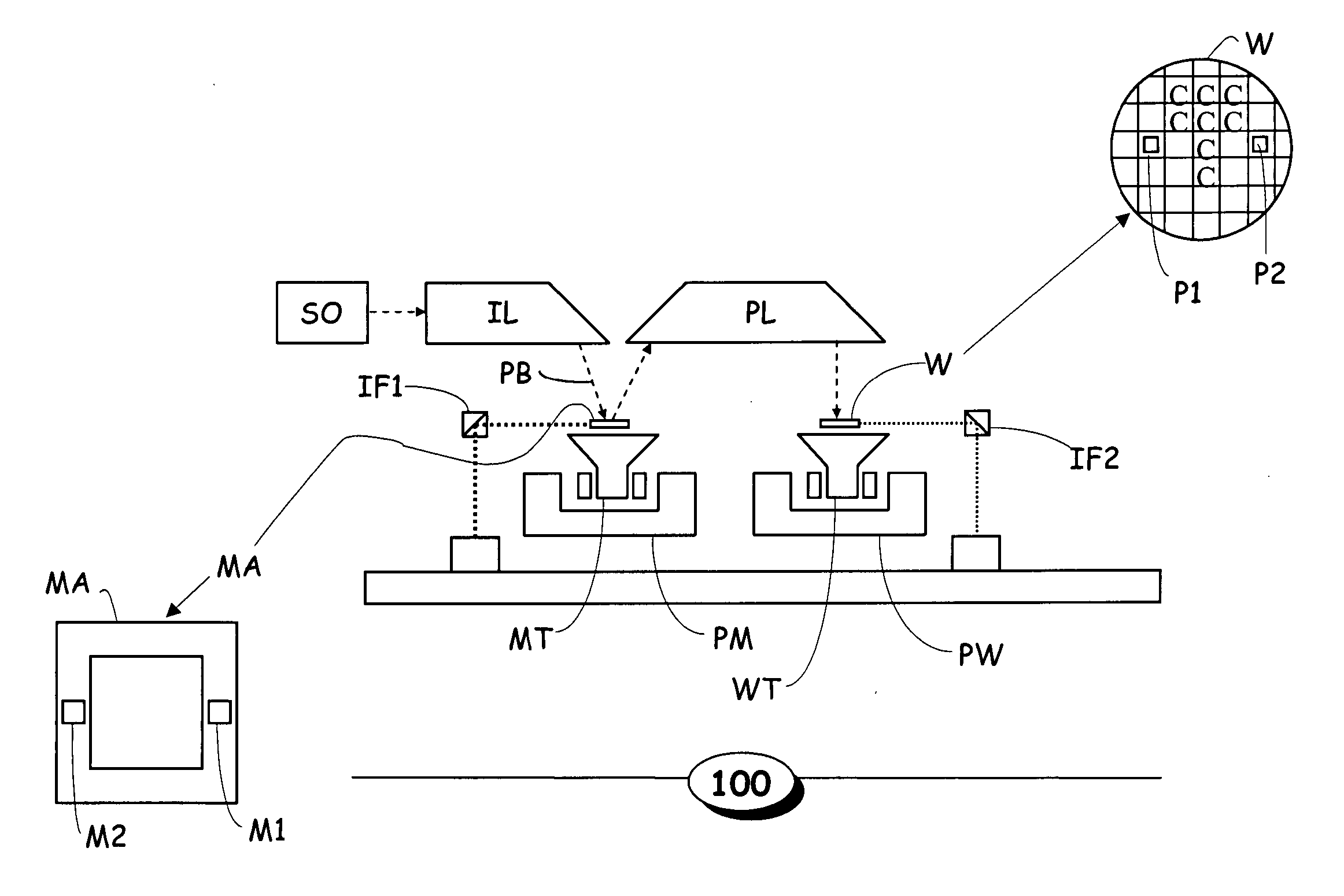
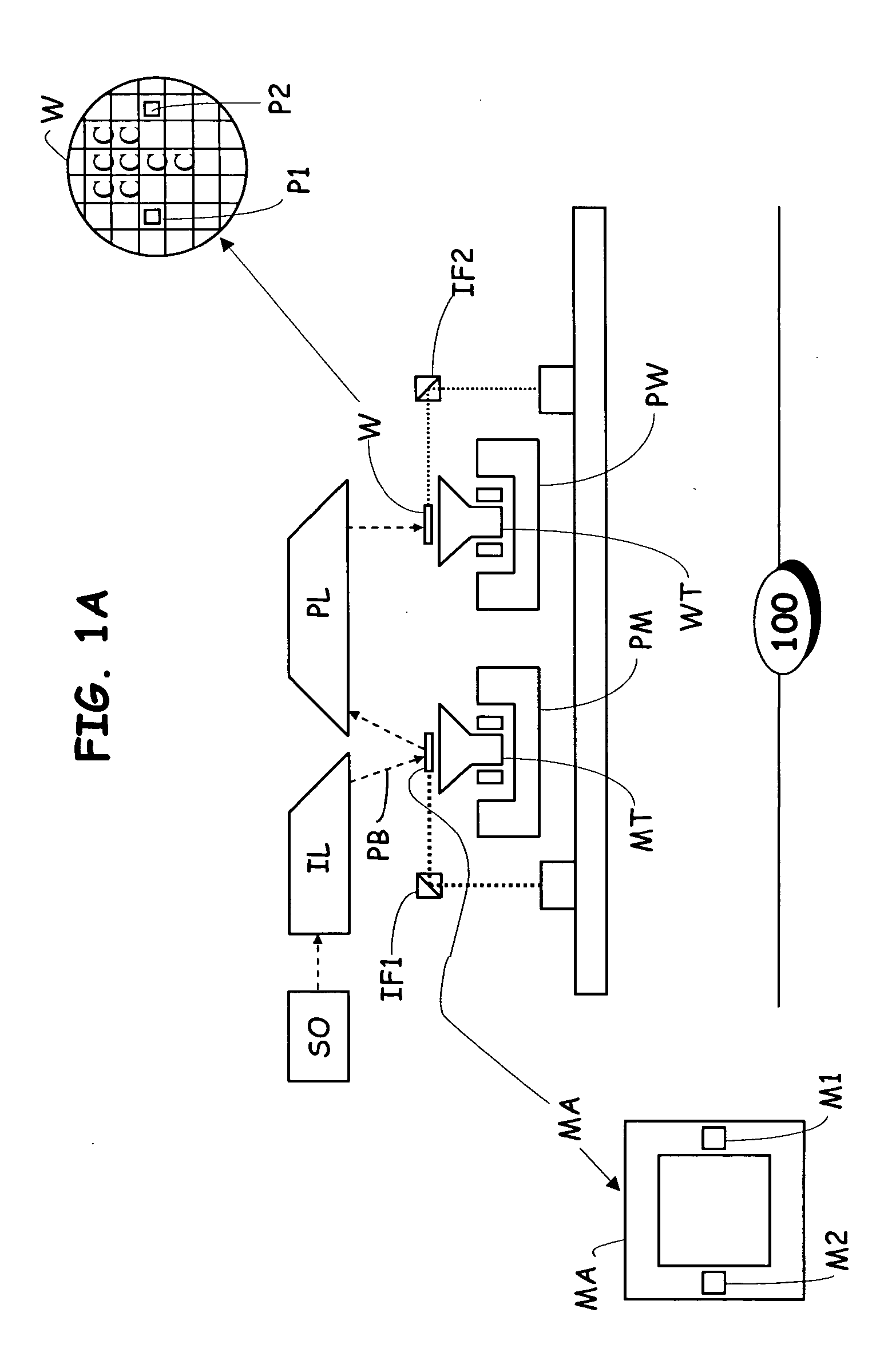
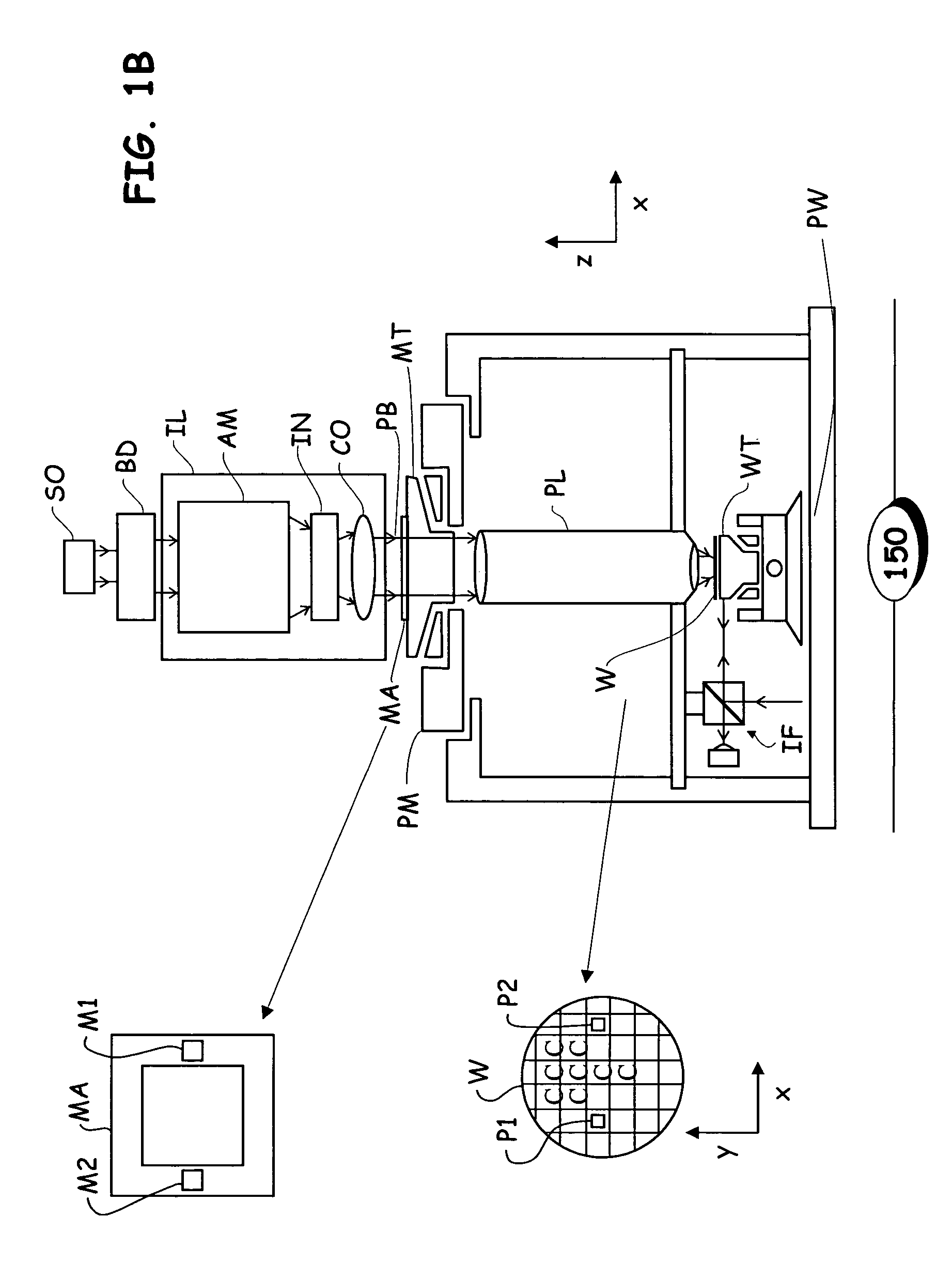
Optimized correction of wafer thermal deformations in a lithographic process
InactiveUS20050136346A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusThermal deformationThermal effect
A method and apparatus of correcting thermally-induced field deformations of a lithographically exposed substrate, is presented herein. In one embodiment, the method includes exposing a pattern onto a plurality of fields of a substrate in accordance with pre-specified exposure information and measuring attributes of the fields to assess deformation of the fields induced by thermal effects of the exposing process. The method further includes determining corrective information based on the measured attributes, and adjusting the pre-specified exposure information, based on the corrective information, to compensate for the thermally-induced field deformations. Other embodiments include the use of predictive models to predict thermally-induced effects on the fields and thermographic imaging to determine temperature variations across a substrate.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
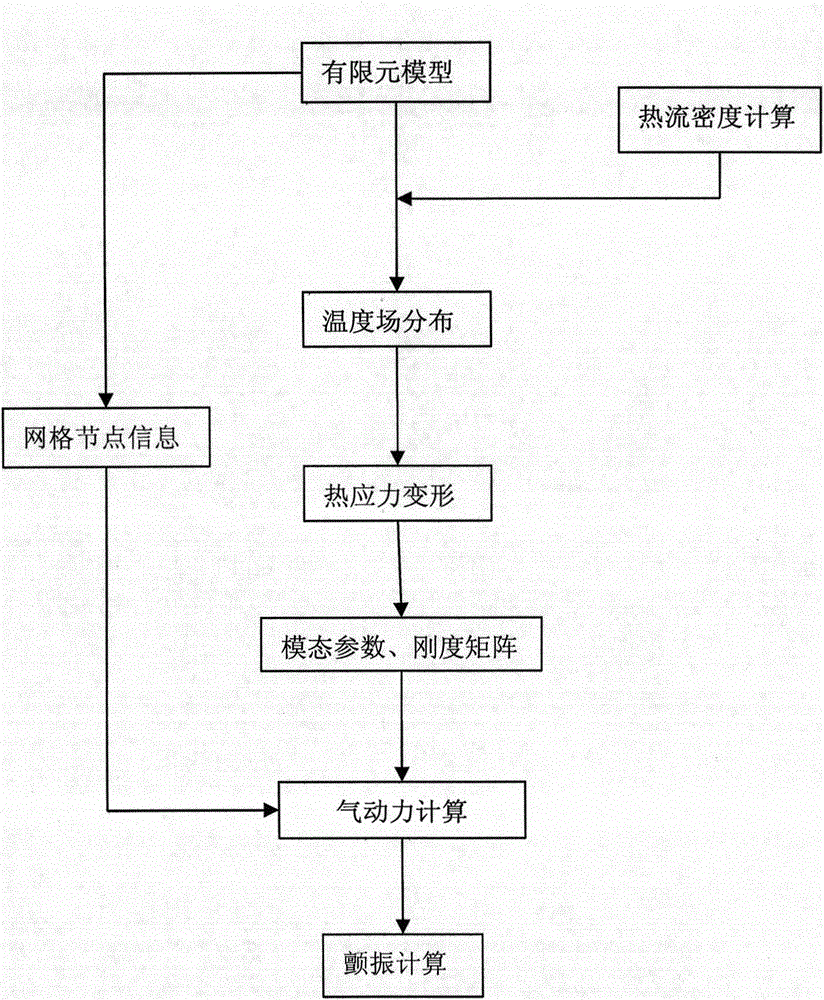
Pneumatic elastic mechanical characteristic analytical method of hypersonic speed aircraft in thermal environment
ActiveCN104133933AGuaranteed continuitySustainable transportationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelEngineering
The invention relates to a pneumatic elastic analytical method, and provides a pneumatic elastic mechanical characteristic analytical method of a hypersonic speed aircraft in thermal environment. According to the method, the piston theory is used for carrying out frequency domain nonsteady aerodynamic calculation on a full-aircraft finite element model of the hypersonic speed aircraft; on the basis, the pneumatic thermal effect on the model in the hypersonic speed thermal environment is considered; the weak coupling effect of pneumatic thermal input in aerodynamic input and elastic force input is ignored; only the structure temperature steady-state characteristics under the pneumatic thermal load effect are considered; after the steady aerodynamic calculation, the thermal flux density on the surface of the aircraft is obtained by adopting a reference enthalpy method; further, the steady temperature distribution on the surface of the aircraft is calculated; the practical equivalent rigidity matrix of the structure at the moment is obtained; and the critical flutter speed is calculated by an engineering method. The pneumatic elastic mechanical characteristic analytical method has the advantages that the pneumatic elastic analytical problem of the hypersonic speed aircraft in the pneumatic thermal environment is solved, and the pneumatic elastic performance of the hypersonic speed aircraft is improved through flutter speed analysis.
Owner:ANHUI JINSANHUAN METAL SCI & TECH
Micropulse grid pattern laser treatment and methods
ActiveUS20140228824A1Short durationLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsDiabetic retinopathyMedicine
Owner:IRIDEX CORP
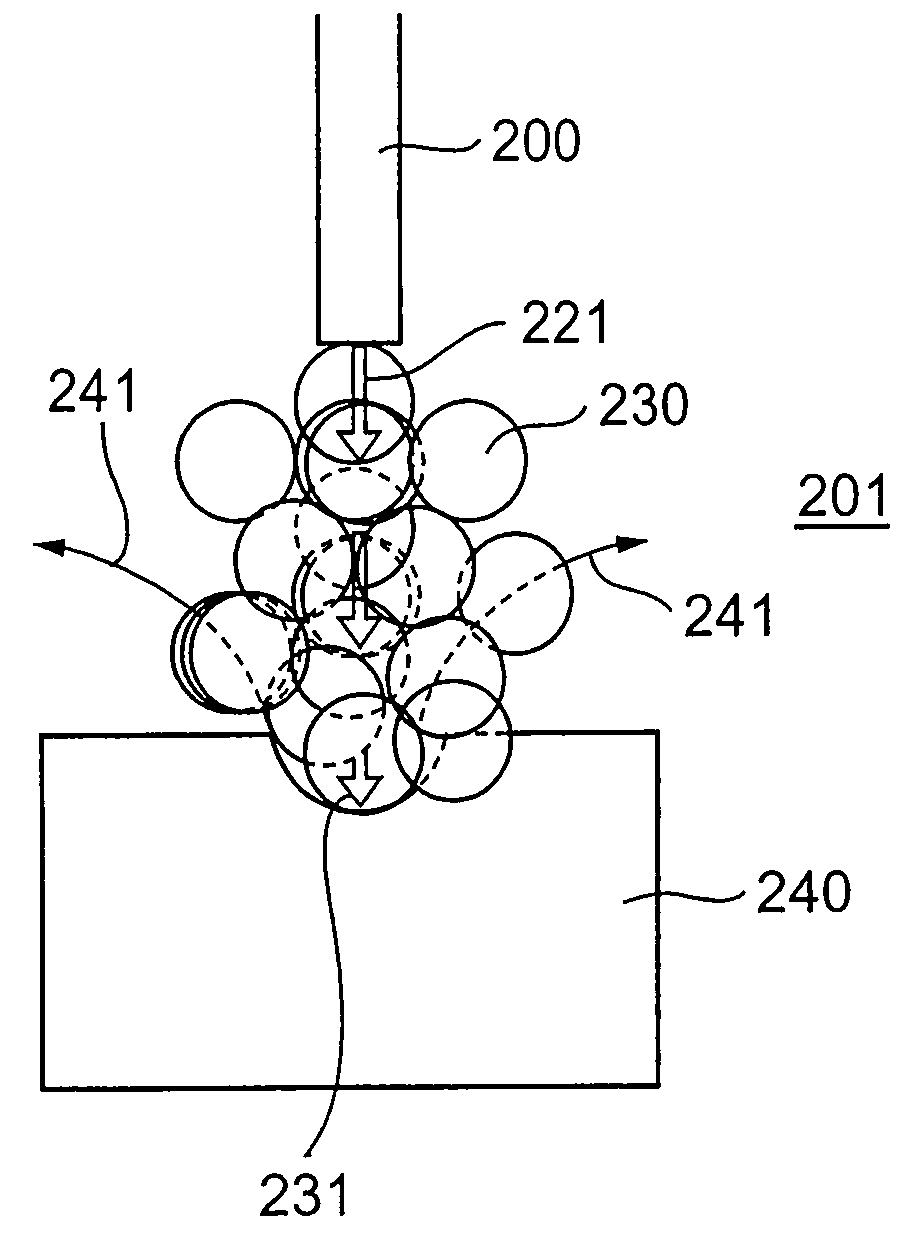
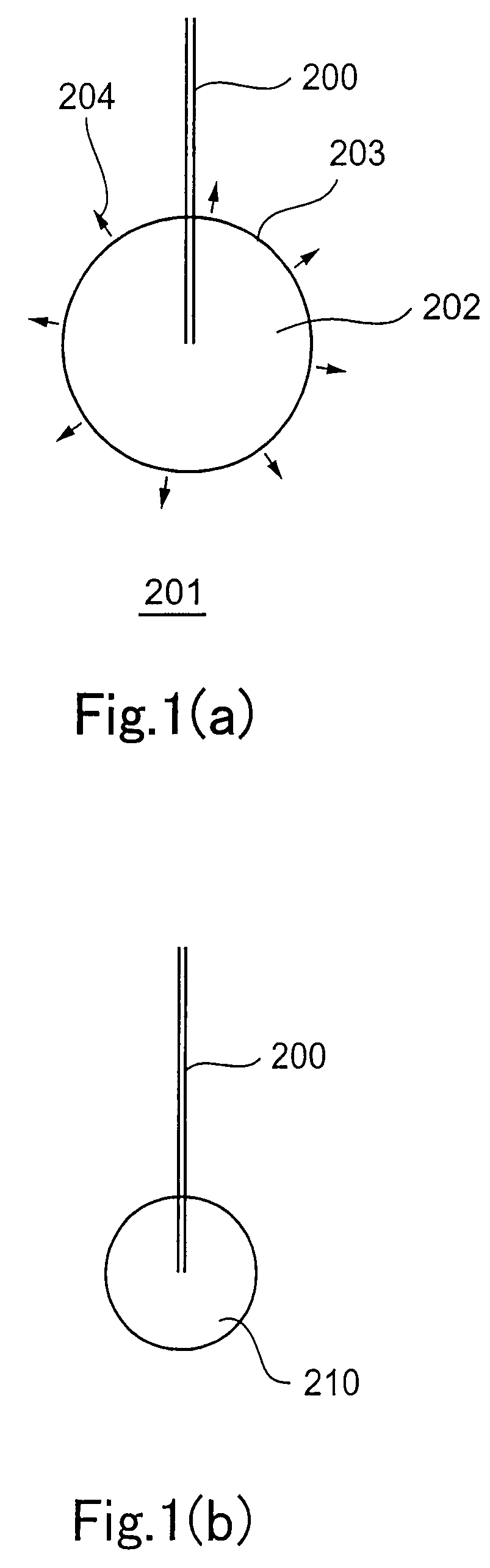
Laser sampling methods for reducing thermal effects
InactiveUS20140268134A1Reduce thermal effectsEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryTarget surfaceOptical emission spectrometry
A method for reducing thermal effects in laser ablation optical emission spectrometry includes creating discrete ablation spots along an analysis line on a target surface. At least one of the following is also carried out. First, the ablation spots are positioned so that a pair of successive ablation spots are spaced apart from one another along the analysis line and are separated from one another by another ablation spot. Second, when the analysis line comprises generally parallel, adjacent analysis line segments, the ablation spots are positioned so that (A) a pair of successive ablation spots are on different analysis line segments, and (B) the successive ablation spots are positioned to be at different longitudinal positions along the analysis line segments when the different analysis line segments are adjacent to one another. As a result, a linear scan of isolated ablation spots can be generated.
Owner:ELEMENTAL SCI LASERS LLC
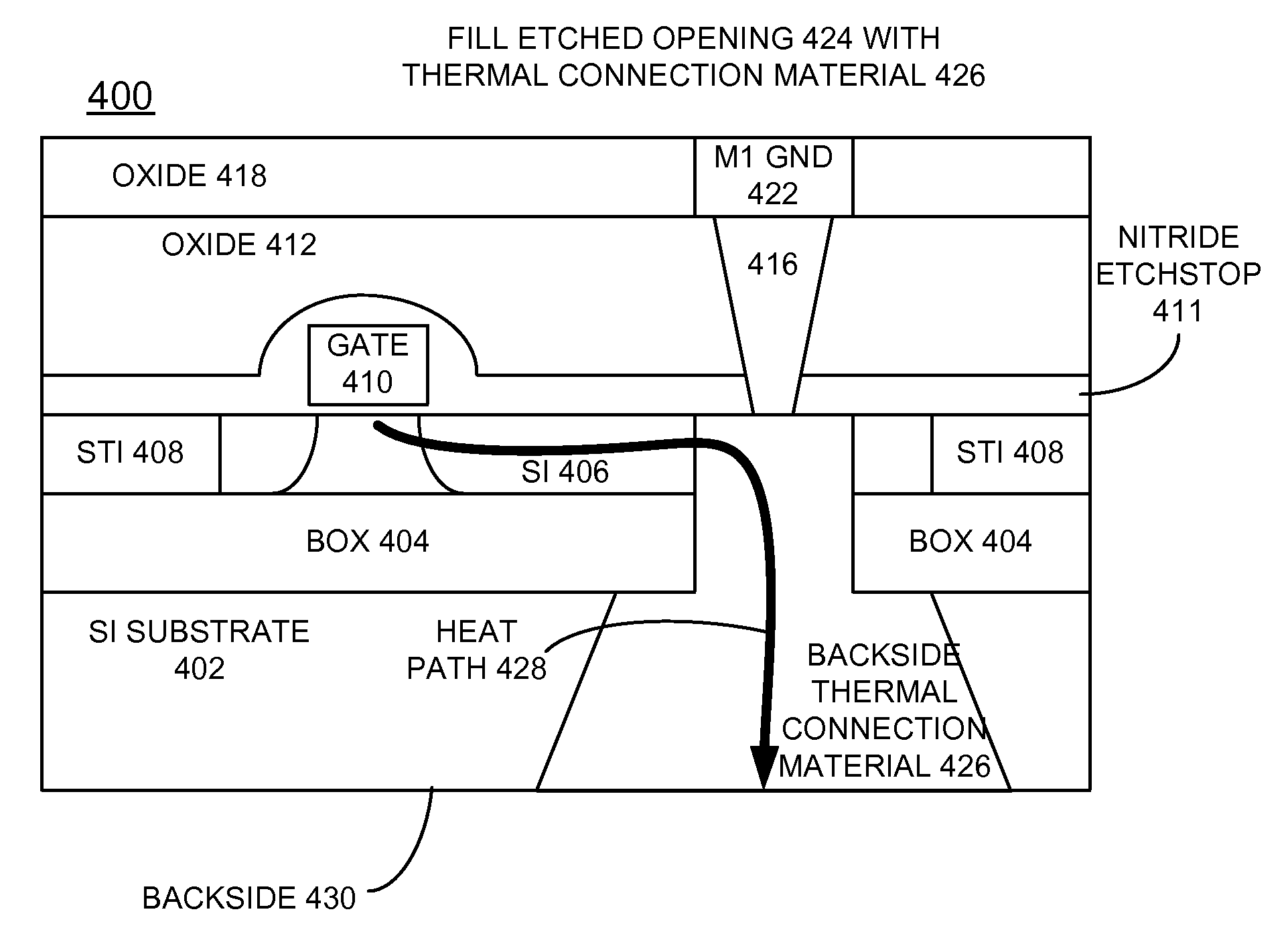
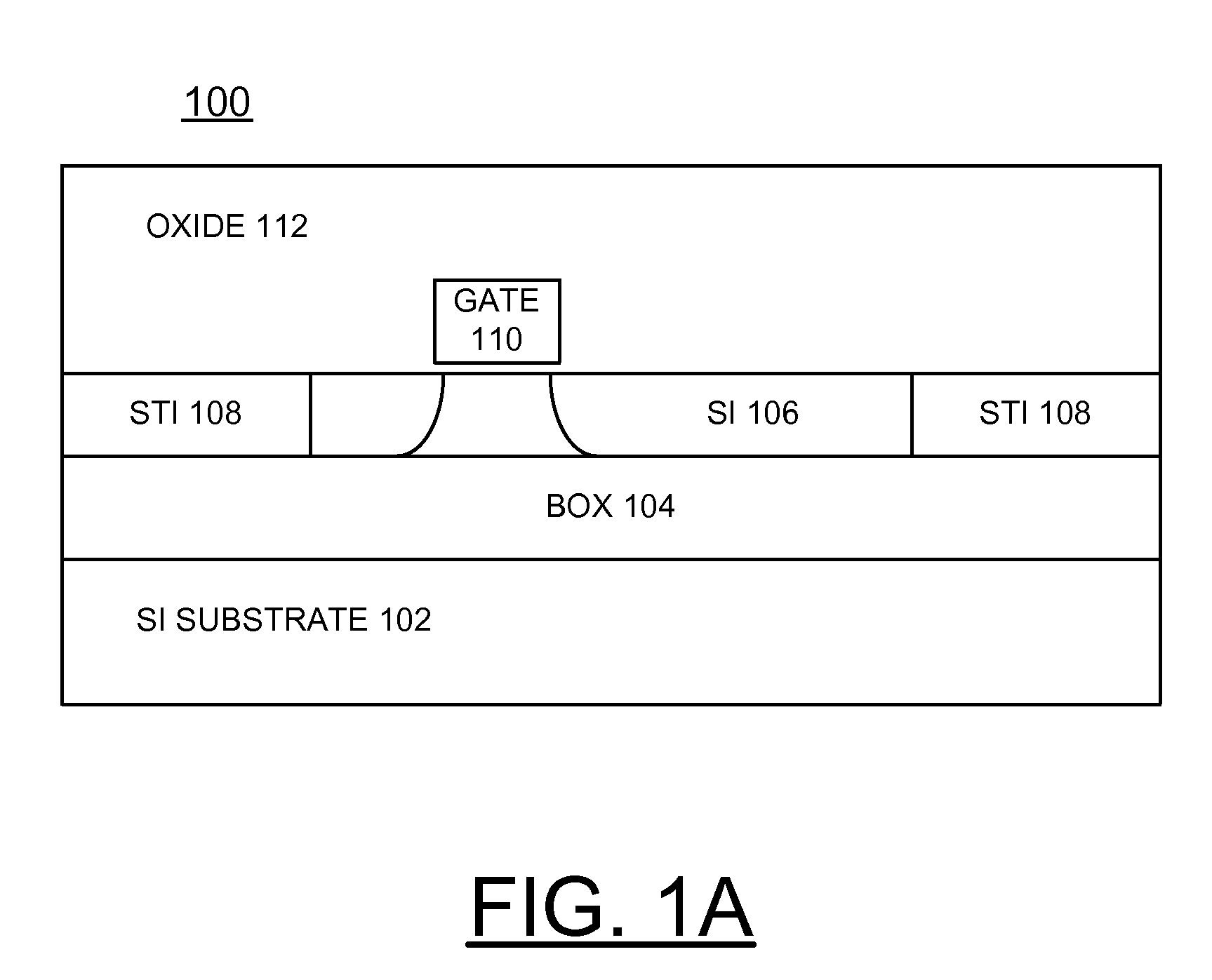
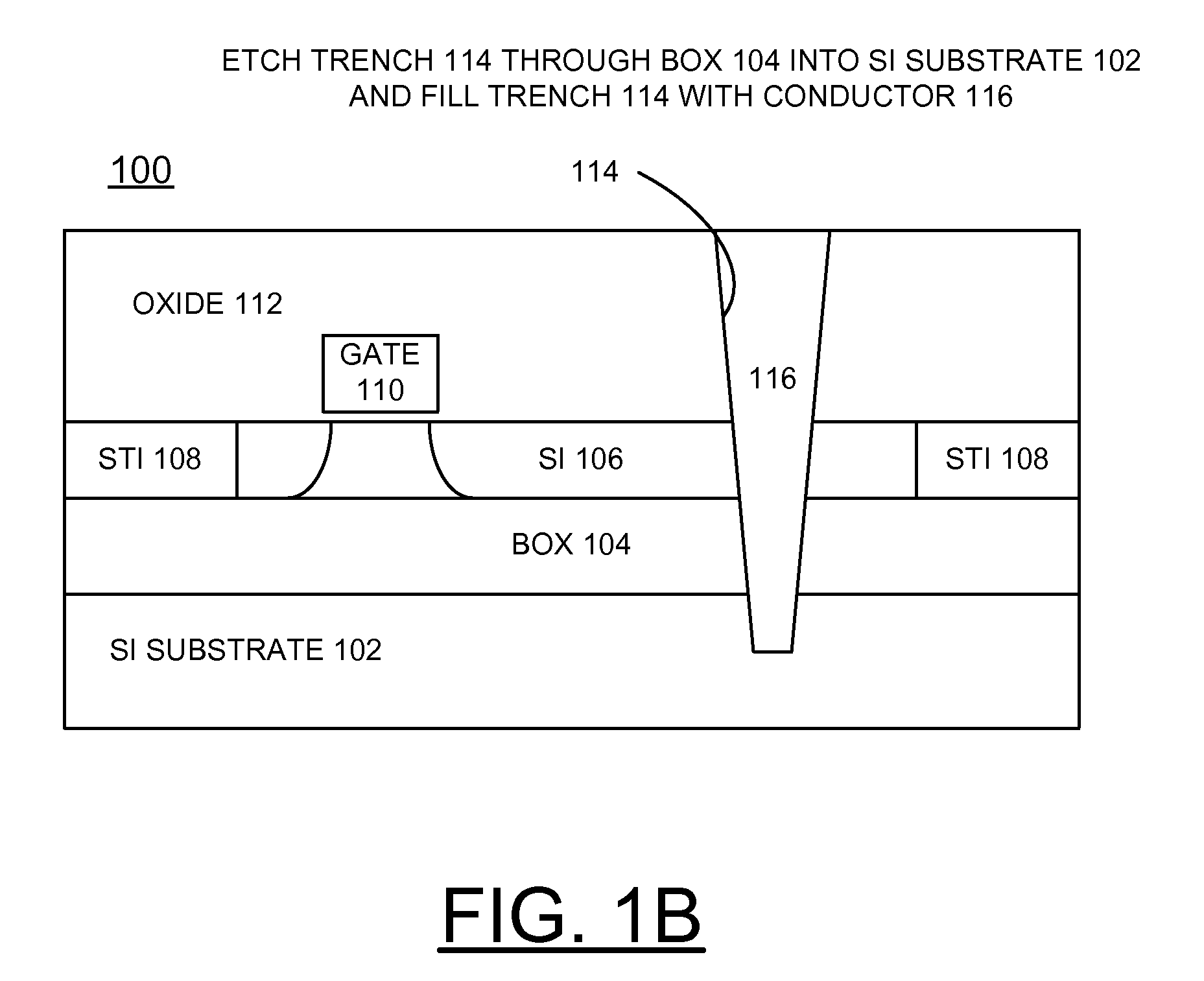
Implementing Reduced Hot-Spot Thermal Effects for SOI Circuits
InactiveUS20100019385A1Reduce thermal effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesThermal effectActive layer
Methods and structures are provided for implementing reduced hot spot thermal effects for silicon-on-insulator (SOI) circuits. A silicon-on-insulator (SOI) structure includes a silicon substrate layer, a thin buried oxide (BOX) layer carried by the silicon substrate layer, an active layer carried by the thin BOX layer, and a pad oxide layer carried by the active layer. A thermal conductive path is built to reduce thermal effects of a hotspot area in the active layer and extends from the active layer to the backside of the SOI structure. A trench etched from the topside to the active layer, and is filled with a thermal connection material. A thermal connection from a backside of the SOI structure includes an opening etched into the silicon substrate layer from the backside and filled with a thermal connection material.
Owner:IBM CORP
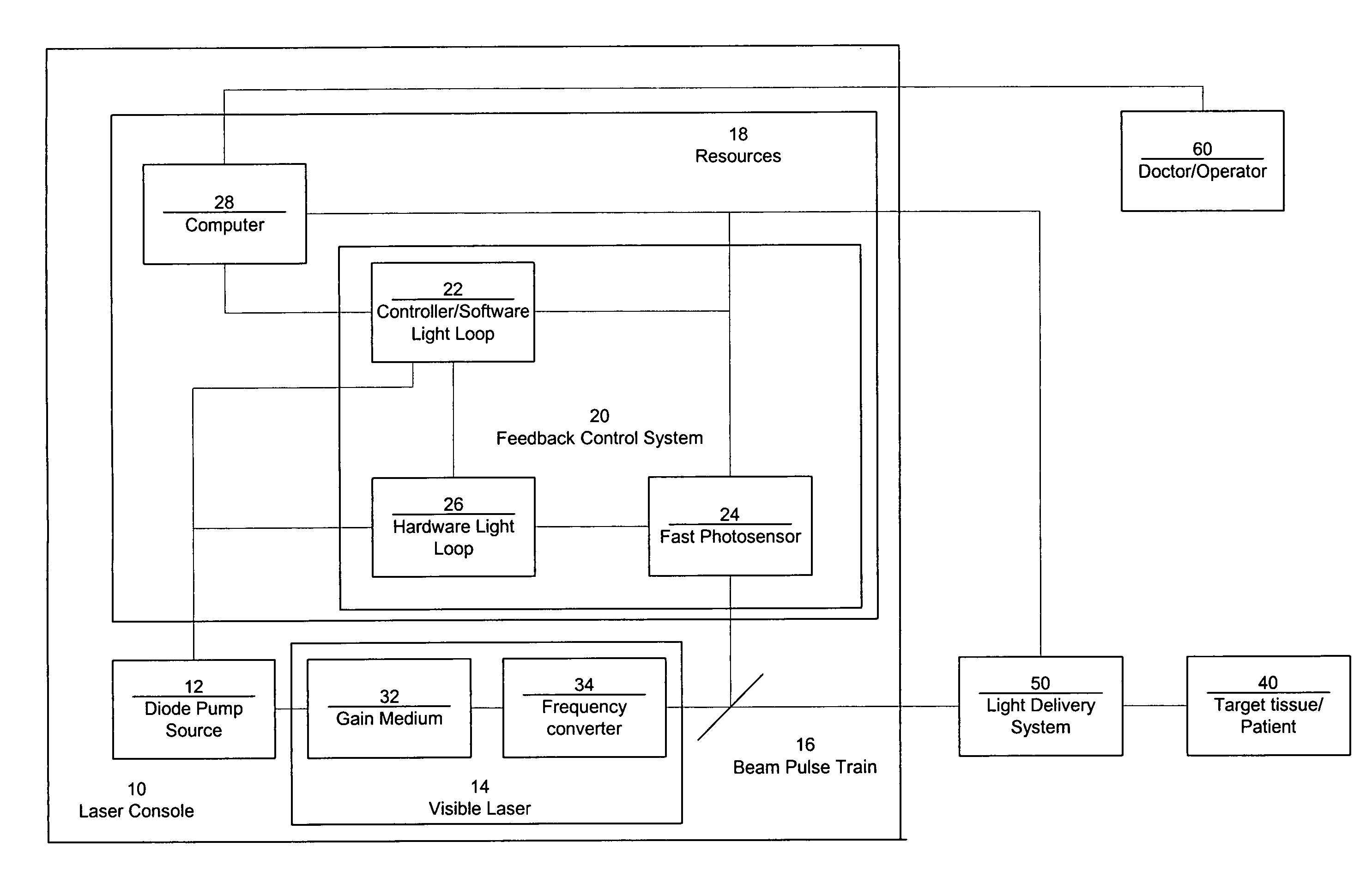
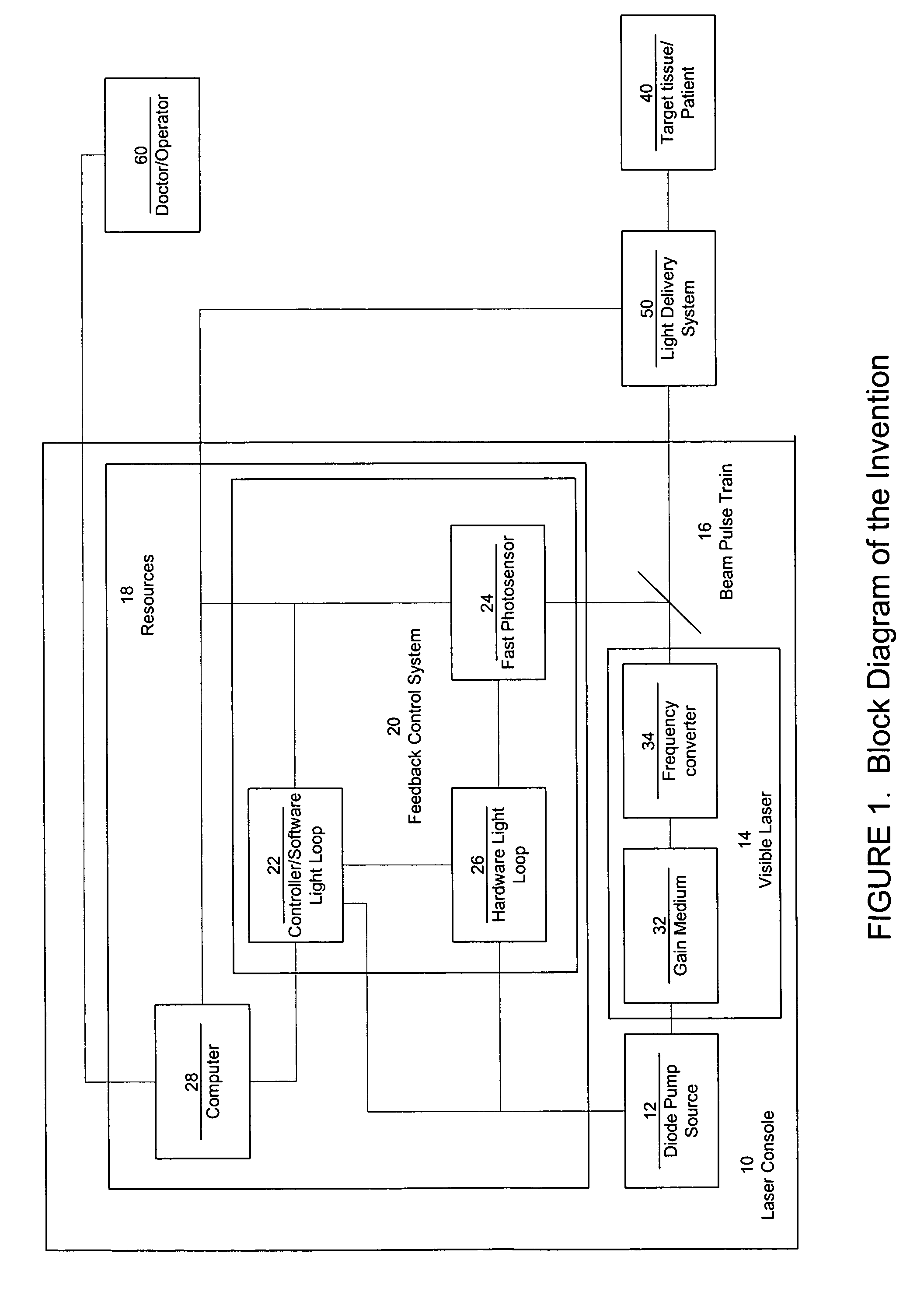
Laser system with short pulse characteristics and its methods of use
ActiveUS7771417B2Short and controlled pulse width trainsReduce power fluctuationsLaser surgeryLaser detailsPulse characteristicsRetinal damage
A laser system that includes a diode pump source. A frequency doubled solid state visible laser is pumped by the diode pump source and produces a pulsed laser output with a train of pulses. Resources provide instructions for the creation of the pulsed output, with on and off times that provide for substantial confinement of thermal effects at a target site. This laser system results in tissue specific photoactivation (or TSP) without photocoagulation damage to any of the adjacent tissues and without causing full thickness retinal damage and the associated vision loss.
Owner:IRIDEX CORP
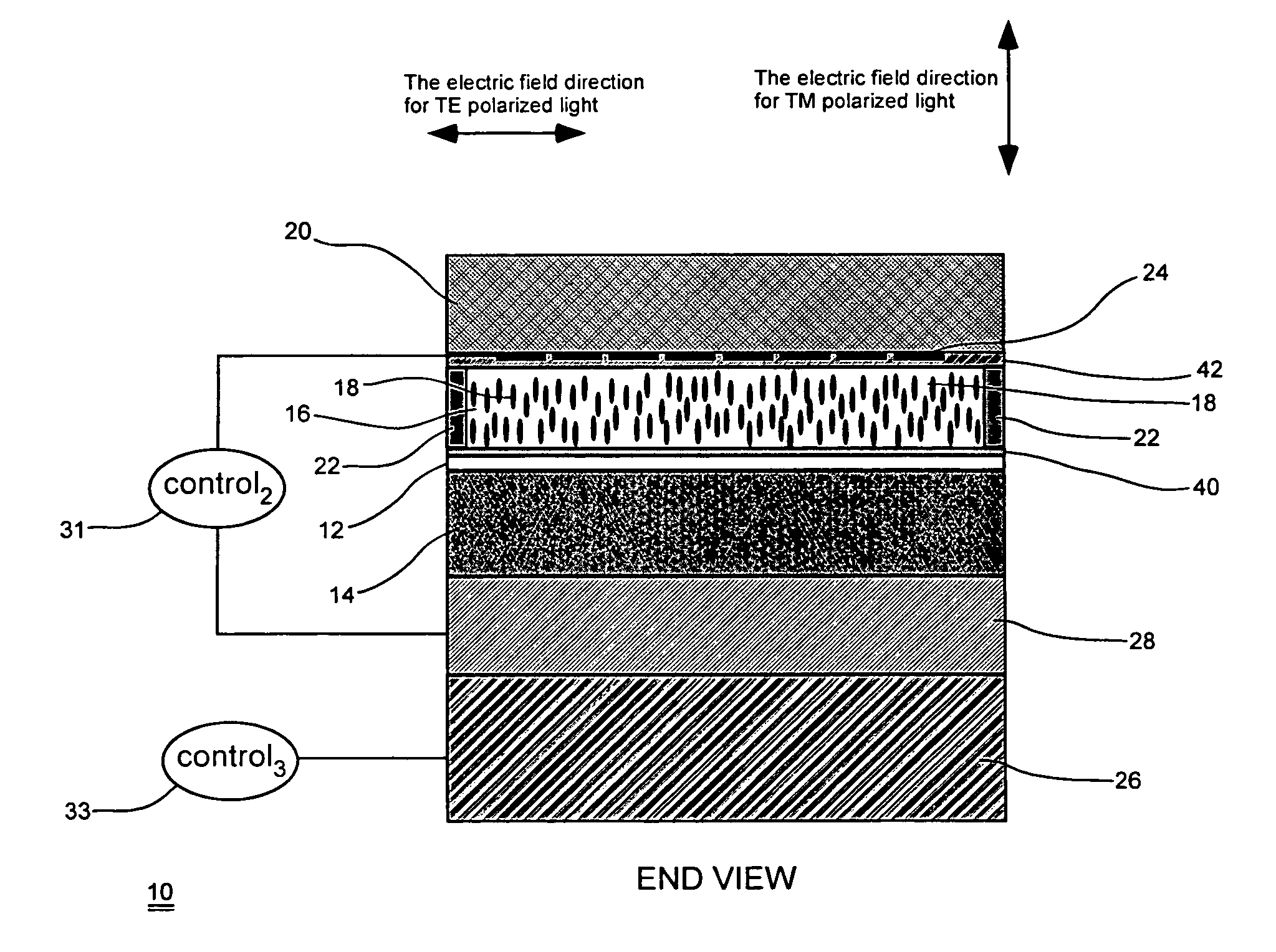
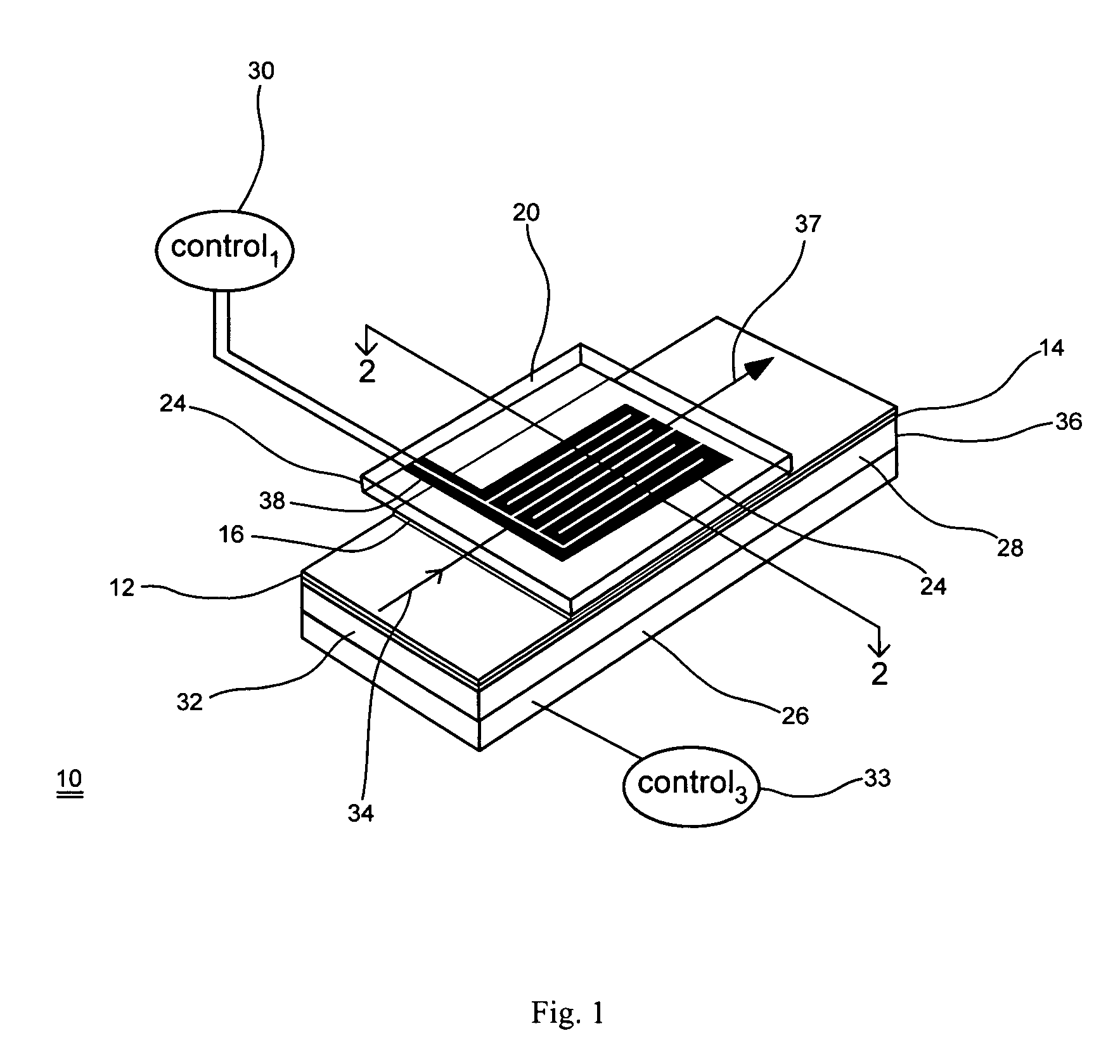
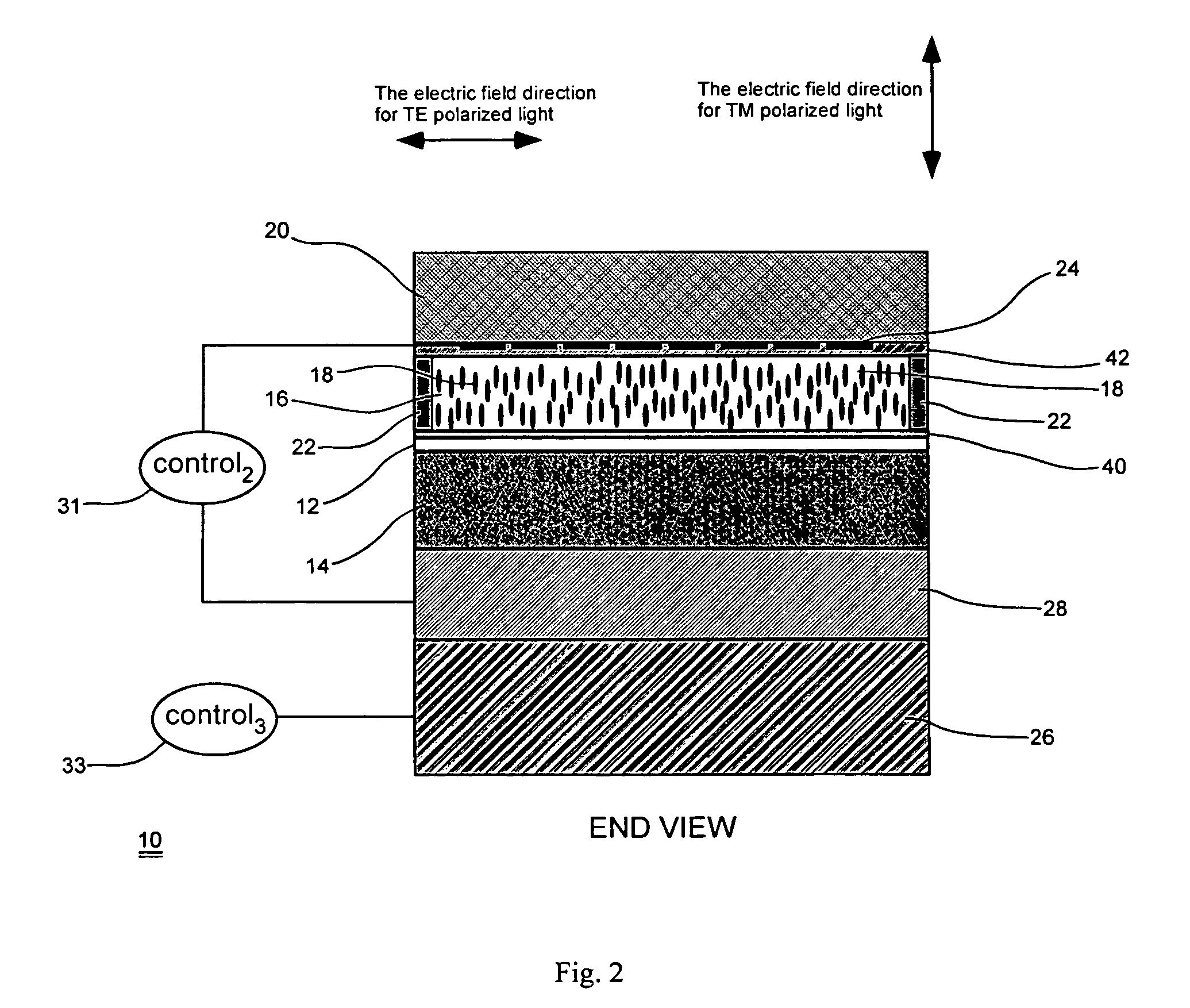
Thermo-optic liquid crystal waveguides
ActiveUS7570320B1Static indicating devicesNon-linear opticsTemperature controlElectrical resistance and conductance
A waveguide having an adjustable index of refraction (or an adjustable optical path length, or for providing an adjustable optical phase delay) based in part on thermal effects in the waveguide. In one example, the waveguide may include a core for guiding a light beam through the waveguide; at least one cladding; liquid crystal material disposed within the waveguide; and at least one temperature control element, such as resistive heater, for receiving at least one control signal to control a temperature of at least a portion of the liquid crystal material; wherein the index of refraction (or the optical path length, or the optical phase delay of the light beam) of the waveguide is altered by an amount that is controlled by the control signal.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Method and device for excavating submerged stratum
InactiveUS7802384B2Machines/dredgers working methodsMechanical machines/dredgersAbsorptanceLaser induced bubble
An excavation technique for a stratum capable of excavating a submerged stratum such as a layer containing an underground resource by using laser irradiation in liquid is provided. In this technique, a laser beam transmitted through laser transmission means 20 is irradiated in liquid 90 in form of a laser beam having a wavelength with high absorptance of the liquid 90 by laser-induced bubble generation means 35, generating a bubble flow 36, thus excavation of a submerged stratum may be carried out by using a laser-induced destruction effect. Moreover, a laser beam 41 having low absorptance of the liquid 90 is irradiated by laser irradiation means 39 and passed through the bubble flow 36, thereby applying a thermal effect to a stratum to destroy rock and excavate the stratum. The destruction effect and the thermal effect also may be cooperatively worked.
Owner:JAPAN DRILLING CO LTD +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com