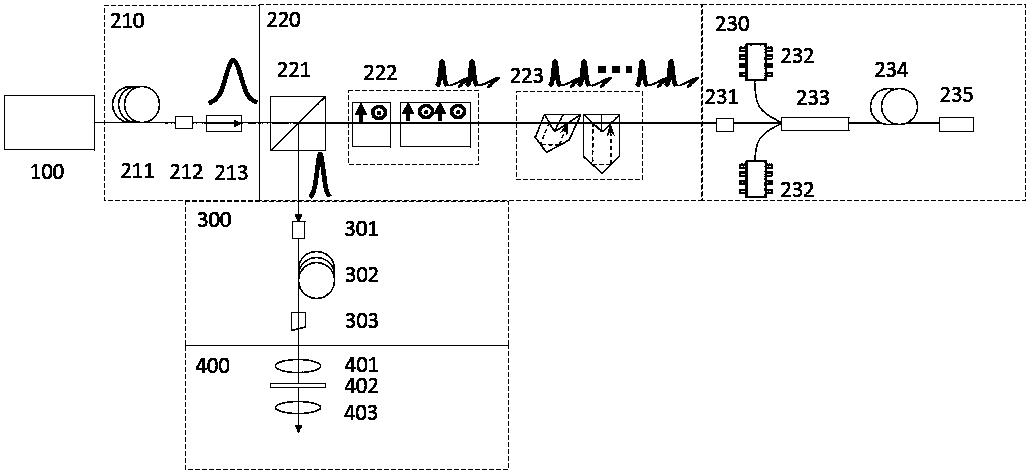
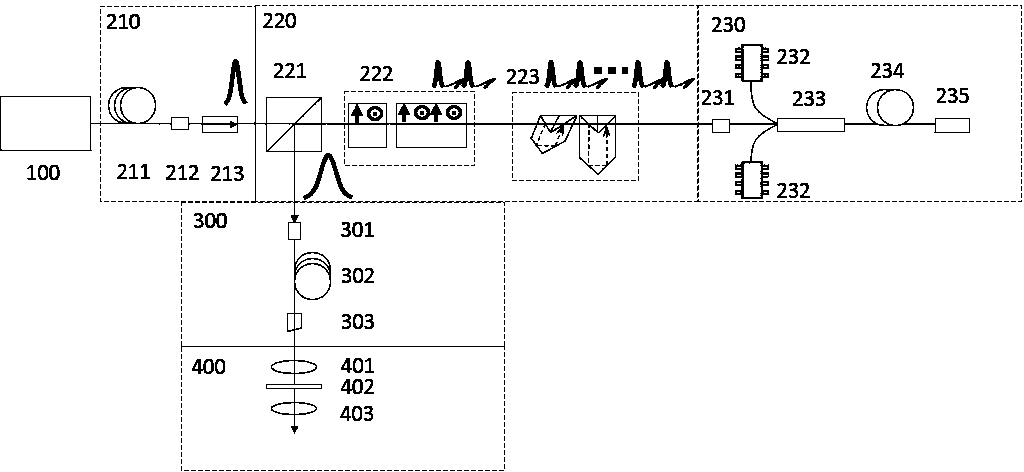
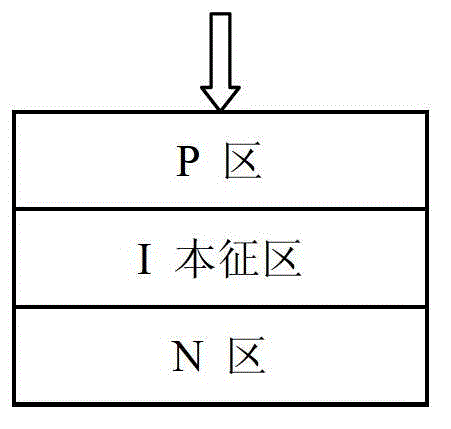
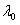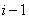Patents
Literature
251results about How to "Reduce coupling loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Integrated optics spot size converter and manufacturing method
ActiveUS20060204175A1Enhanced couplingReduce lossCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideCoupling lossOptical communication
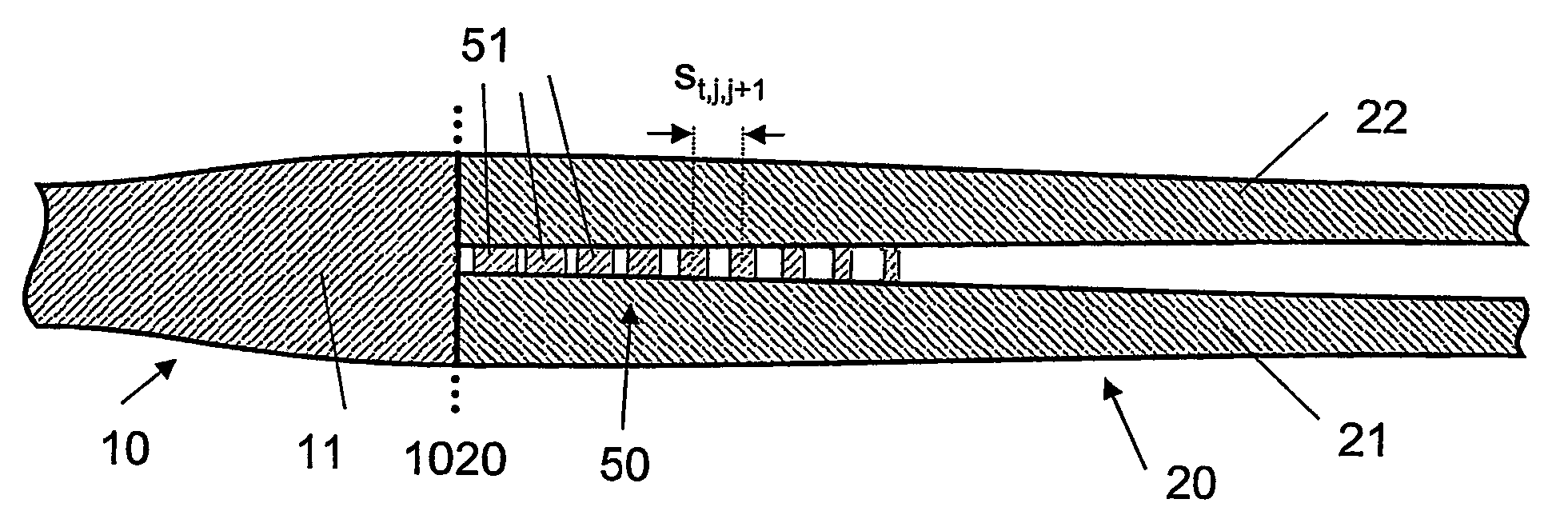
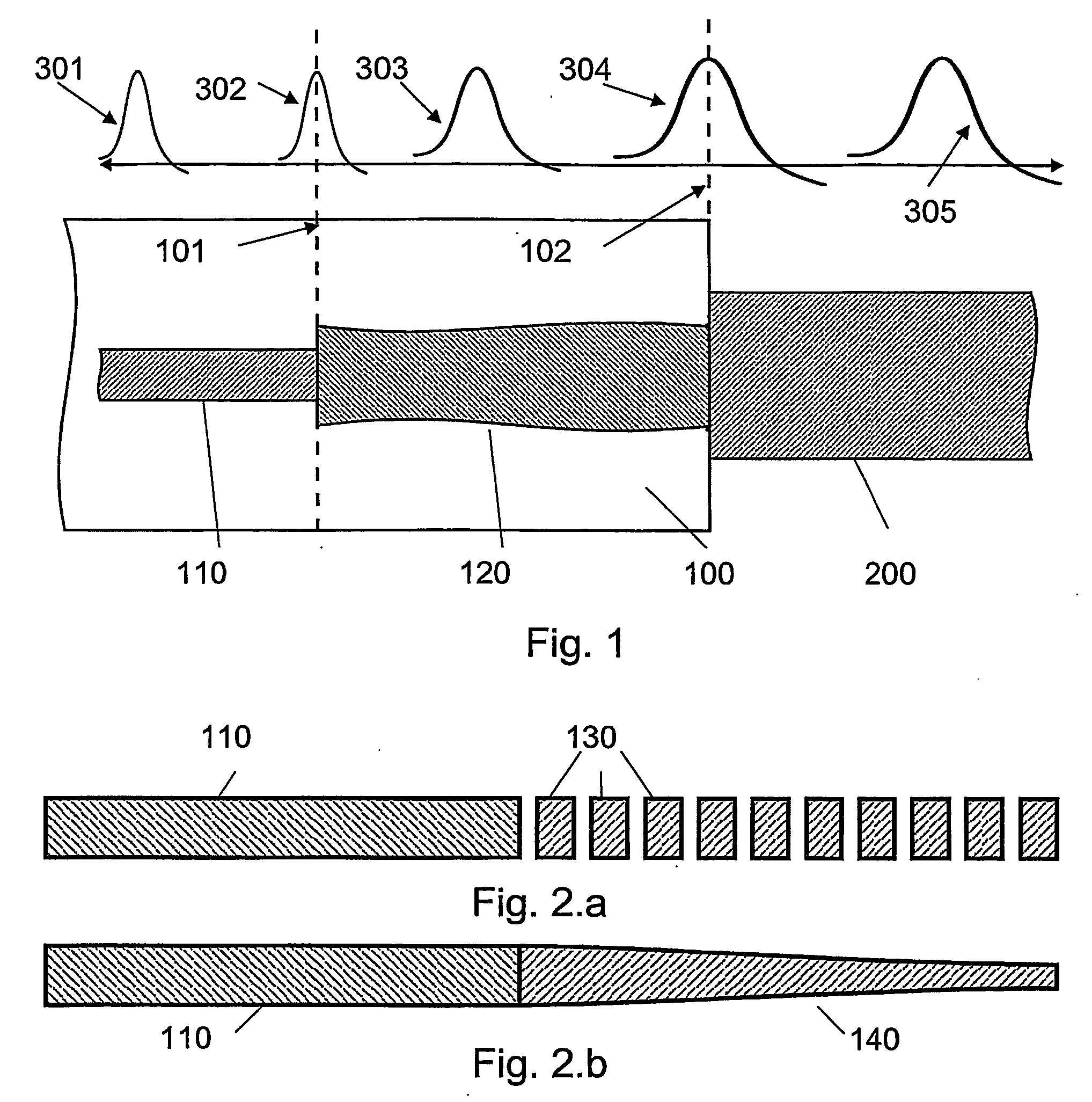
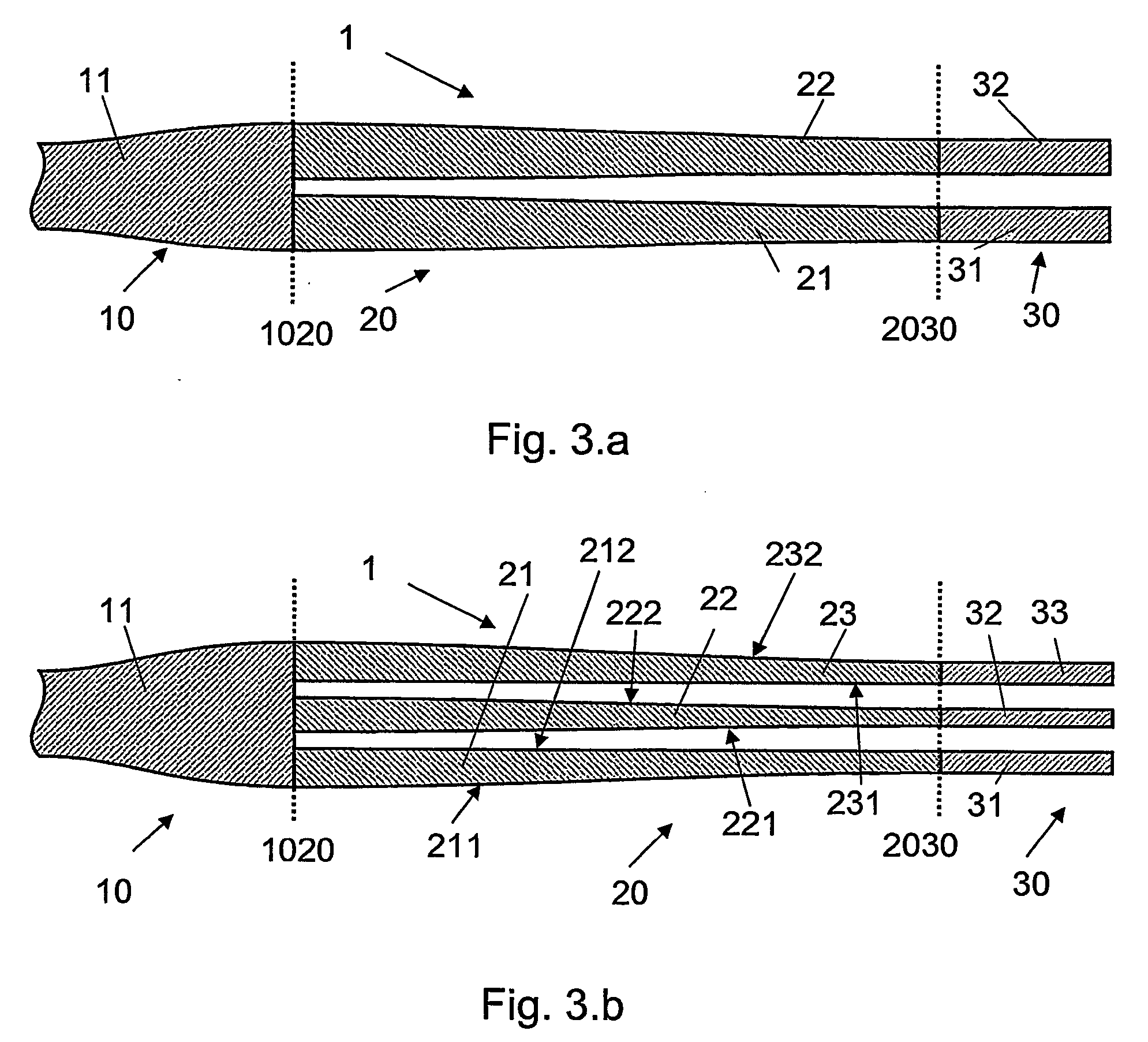
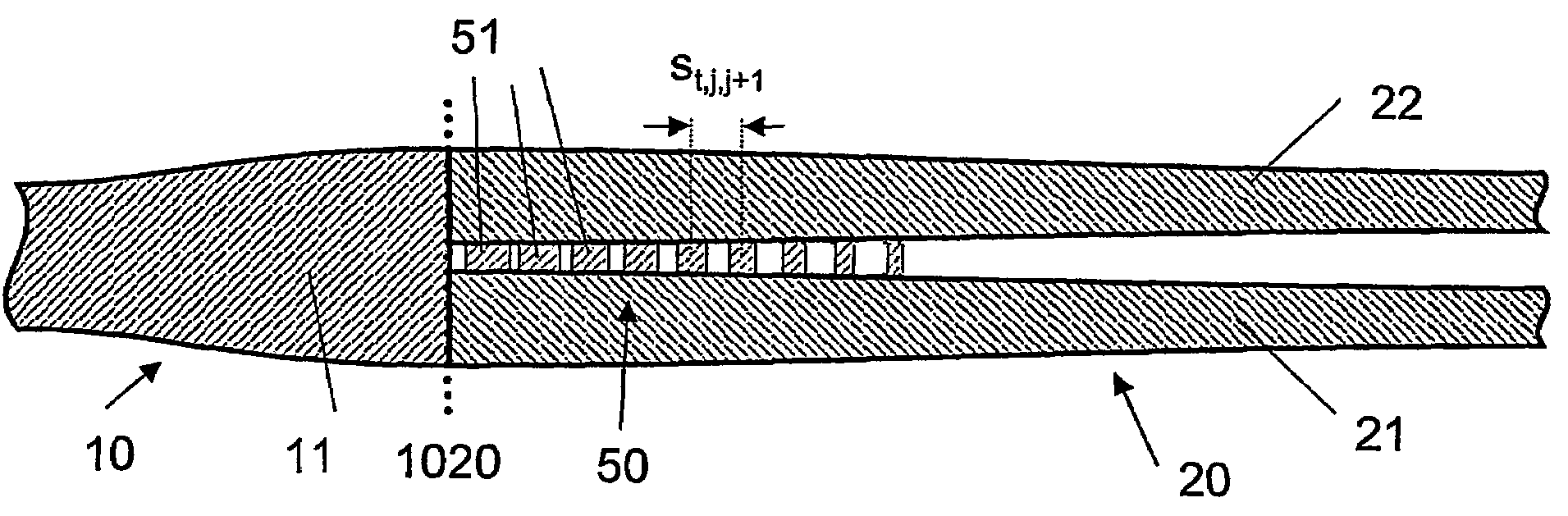
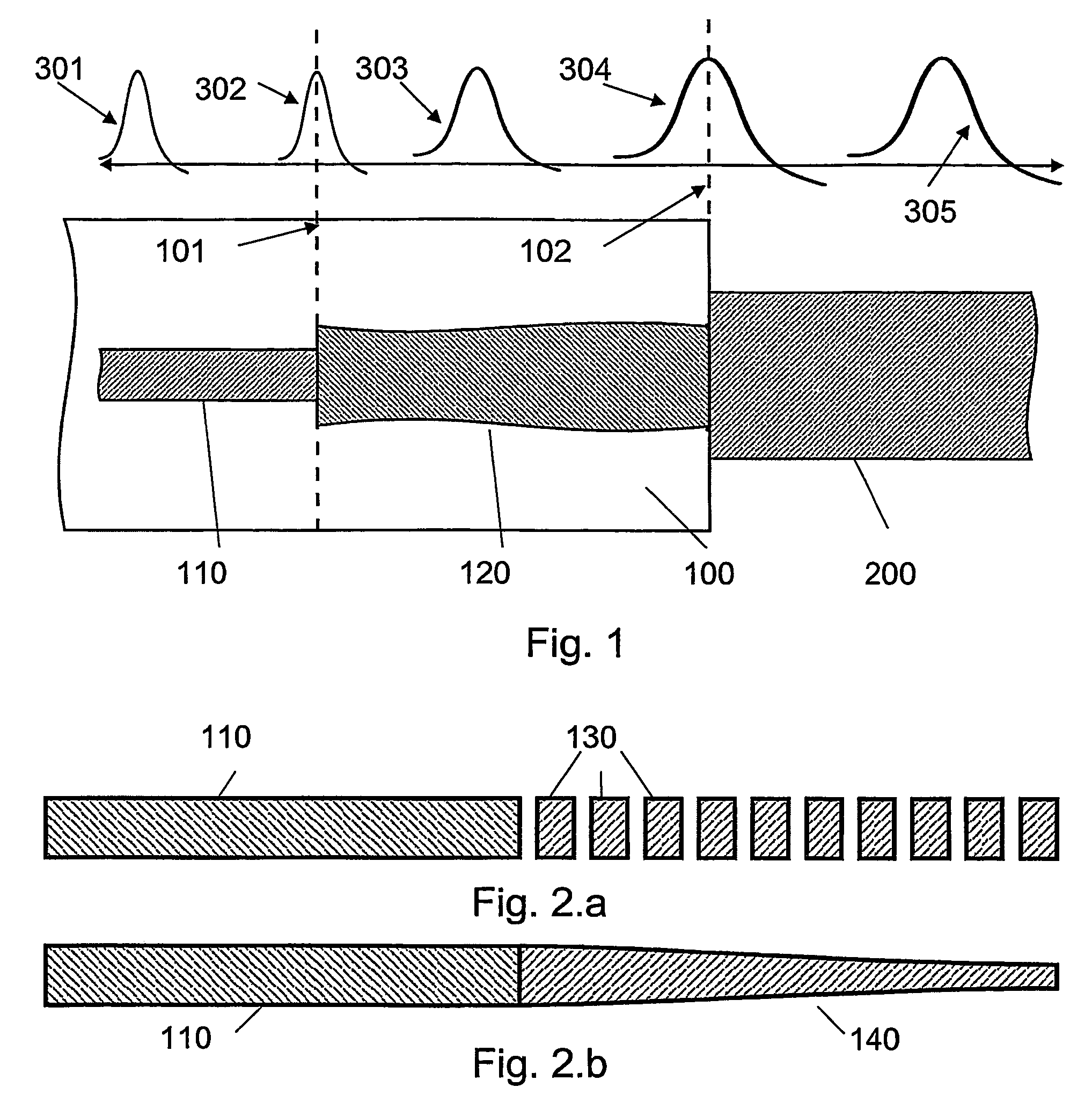
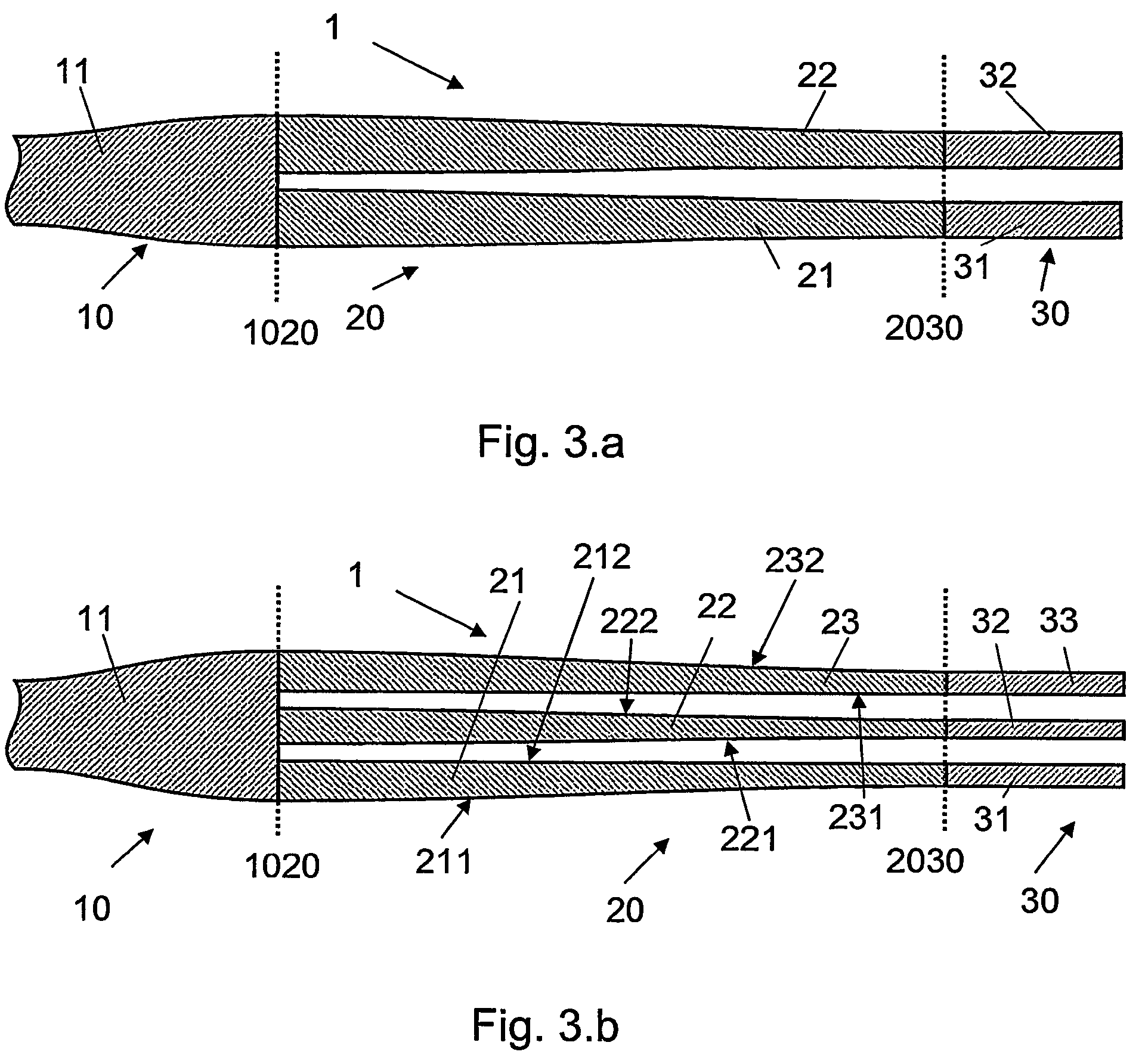
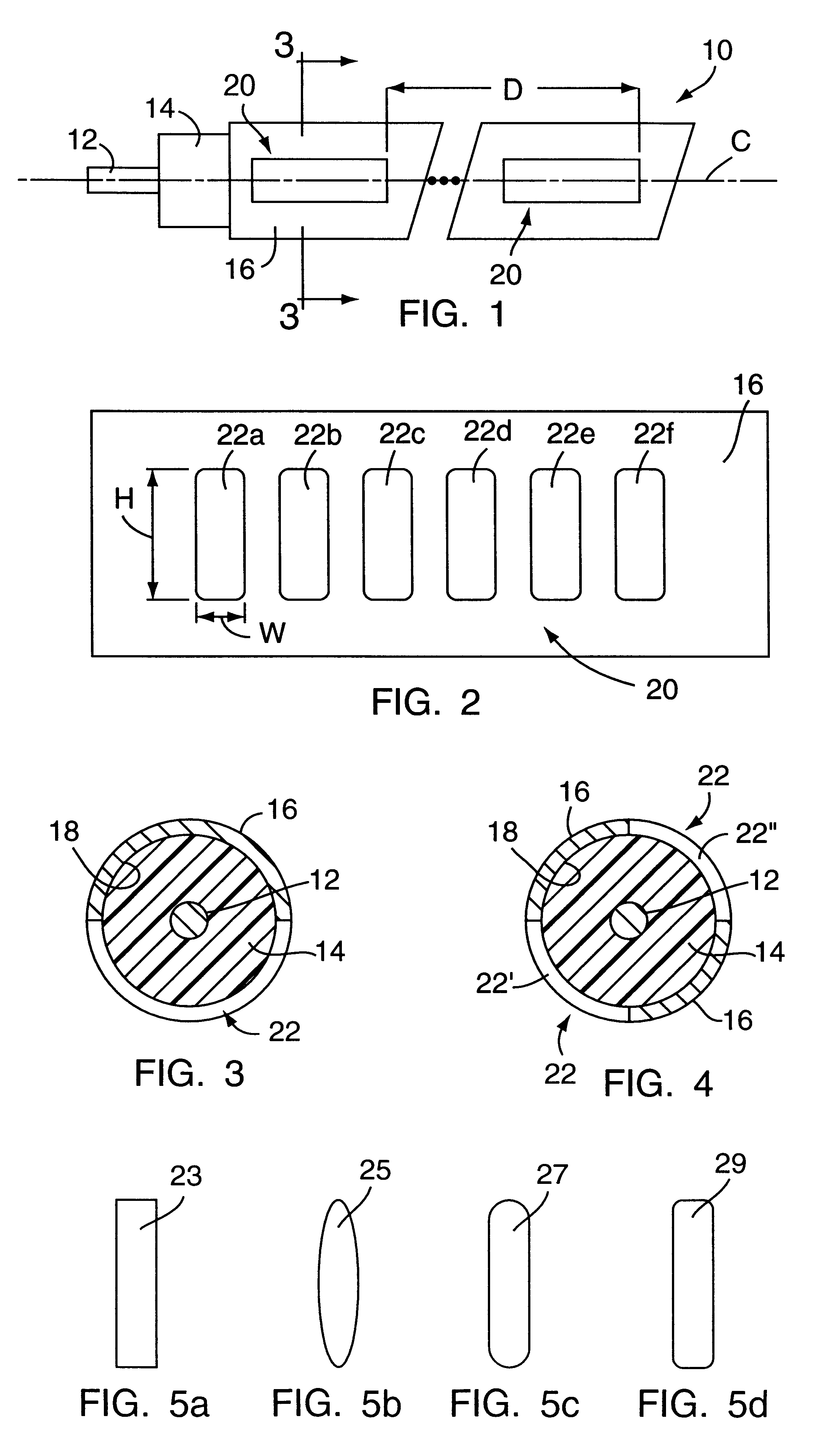
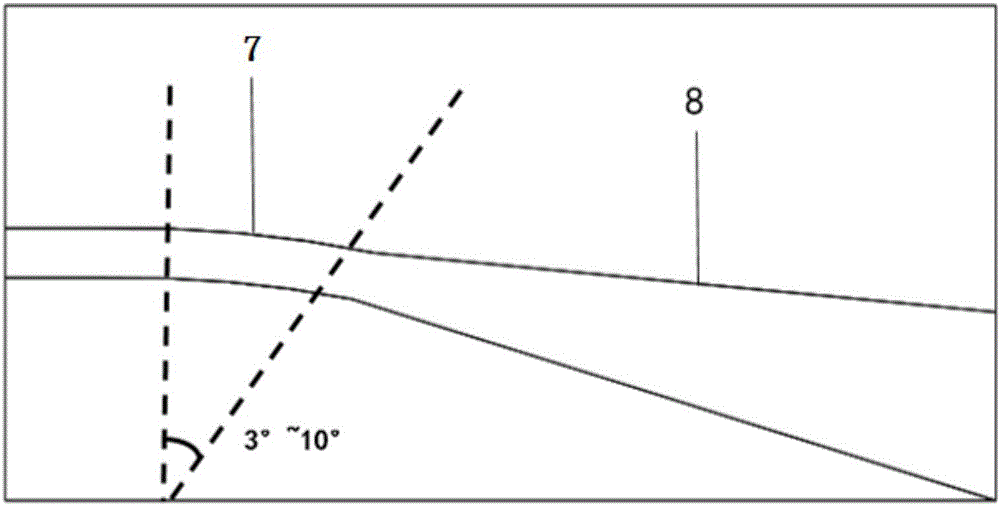
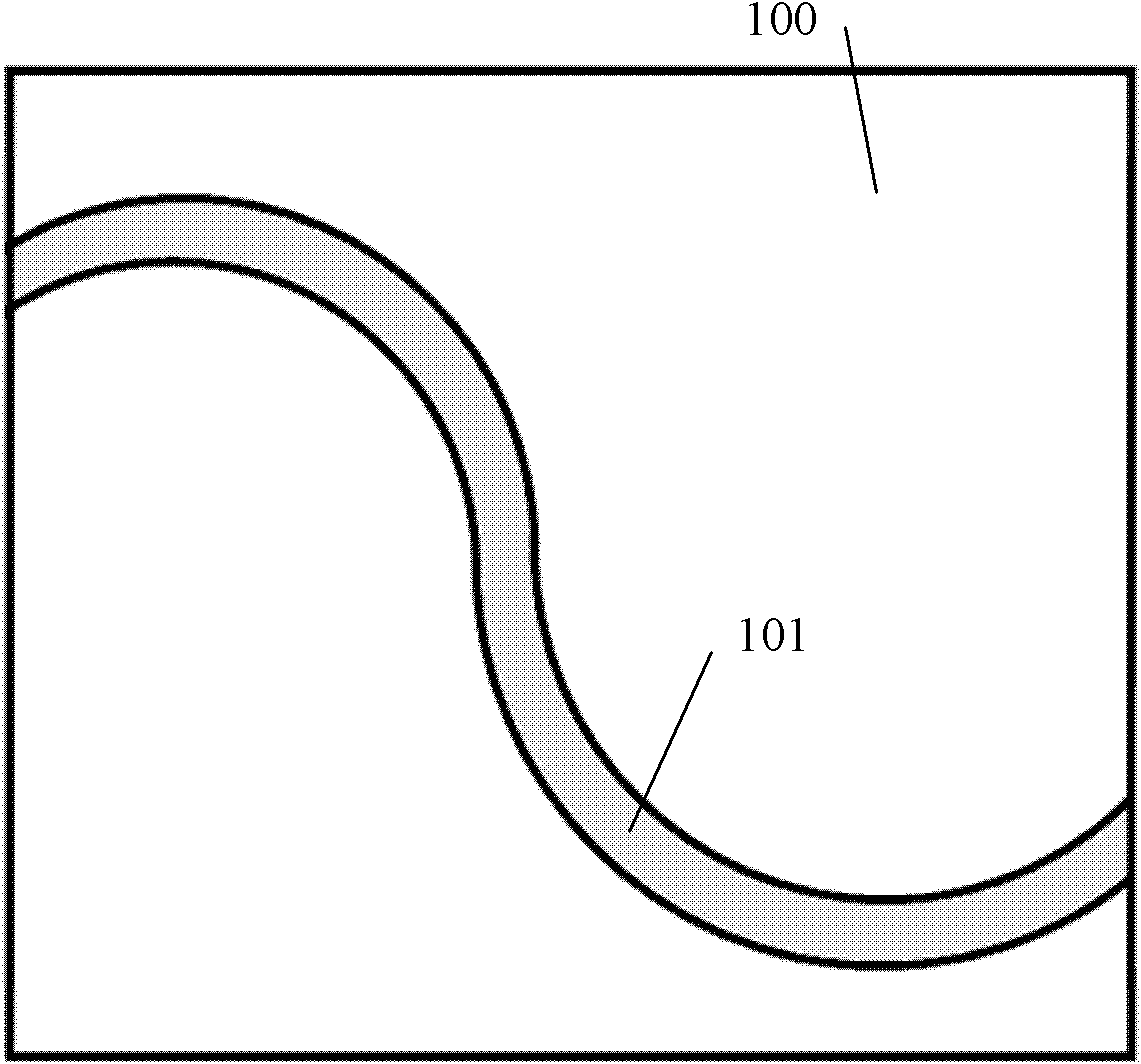
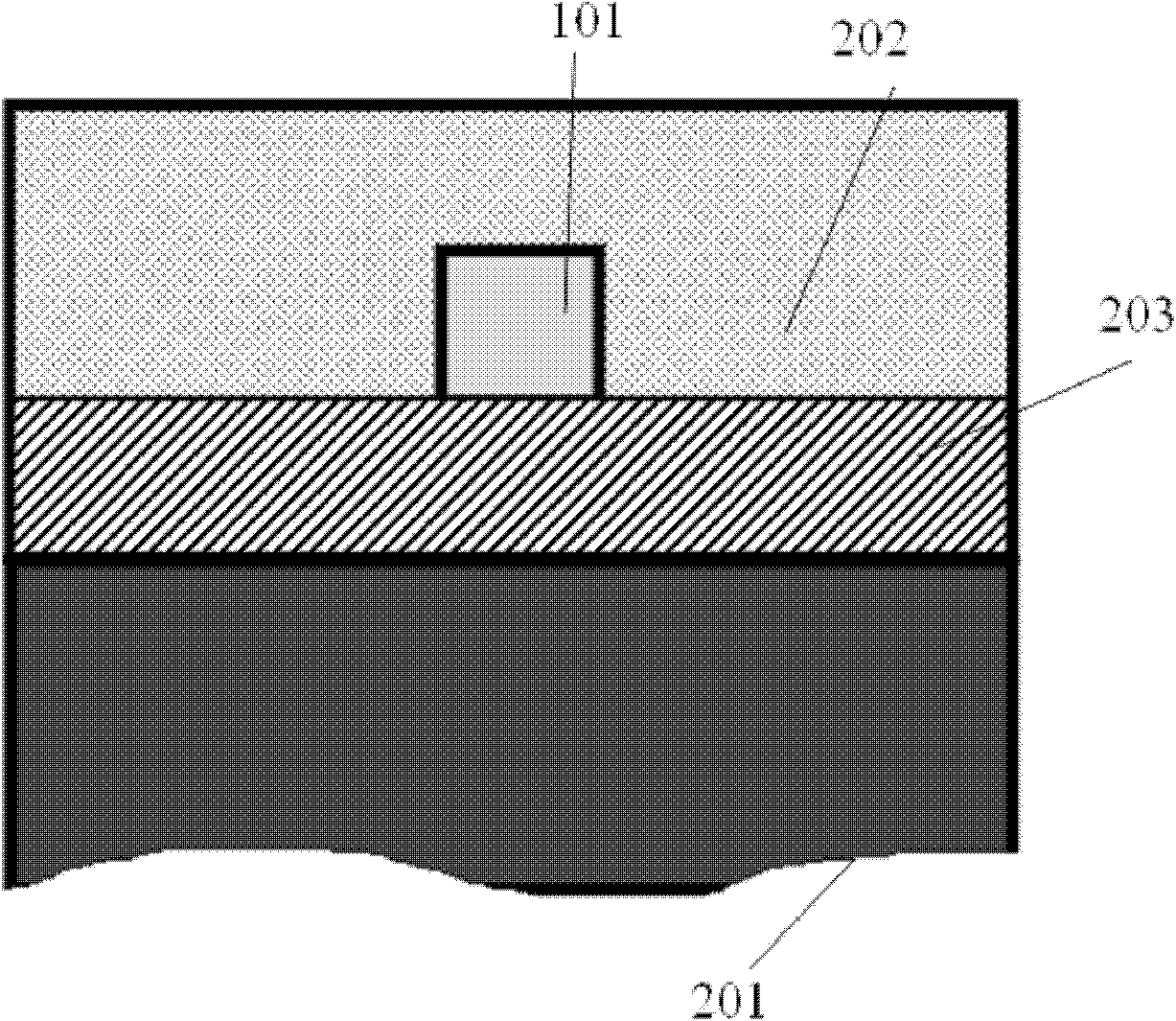
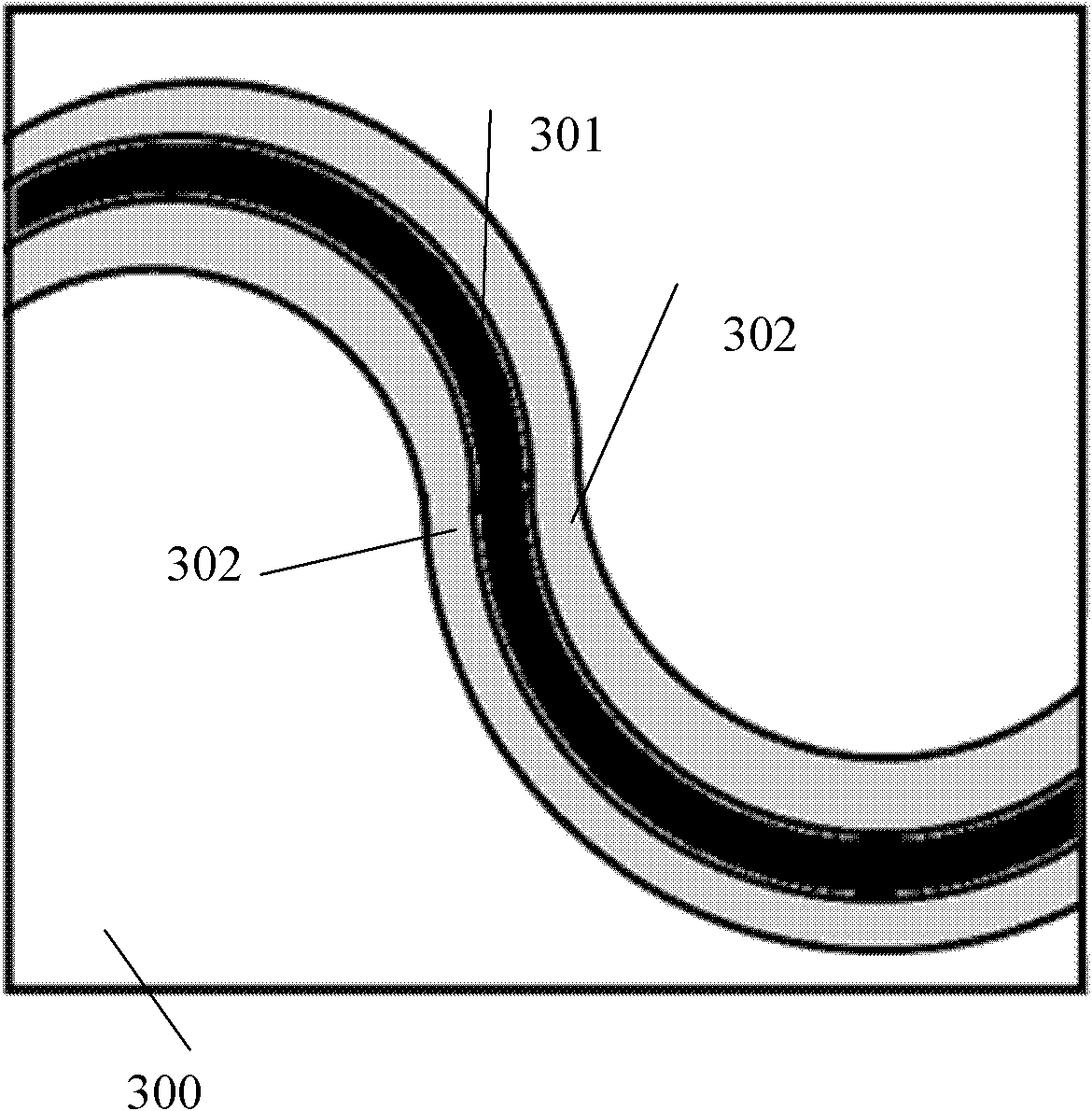
The invention relates to an optical component (1) comprising a combination of optical waveguide elements for modifying the spot size of a mode of an electromagnetic field propagated by an optical waveguide element, the optical waveguide elements being formed on a substrate. The object of the present invention is to provide a mode coupler with low coupling loss that is easy to manufacture and process tolerant. The problem is solved in that the optical component further comprises a) a first section (10), comprising a first optical waveguide element (11) adapted to sustain at least one mode of the electromagnetic field, b) a second section (20) comprising at least two cooperating optical waveguide elements (21, 22), each of said at least two cooperating optical waveguide elements comprising at least one waveguide segment, said at least two cooperating optical waveguide elements being optically connected to said first optical waveguide element of said first section; wherein said cooperating optical waveguide elements (21, 22) of said second section (20) are adapted to maintain optical coupling between said optical waveguide elements to ensure that said at least one mode of the electromagnetic field is sustained by said at least two cooperating optical waveguide elements in cooperation. Preferably, the waveguides of the first and / or second sections are tapered according to a cosine function or to a 5th or 7th order polynomial. An advantage of an optical component according to the invention is that it provides a mode size converter that is relatively simple to manufacture in that it requires no extra process steps. A further advantage is that it is readily suitable for integration with other optical circuitry on a common substrate. The invention may be used in optical communication systems (e.g. systems employing WDM) where coupling of light between integrated optical circuits and optical fibres are needed.
Owner:IGNIS PHOTONYX AS
Integrated optics spot size converter and manufacturing method
ActiveUS7317853B2Reduce coupling lossEasy to manufactureCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideConvertersEngineering
An optical component having a combination of optical waveguide elements for modifying the spot size of a mode of an electromagnetic field propagated by an optical waveguide element, the optical waveguide elements being formed on a substrate. The optical component further includes a first section having a first optical waveguide element, and a second section having at least two cooperating optical waveguide elements. The cooperating optical waveguide elements of the second section are configured to maintain optical coupling between the optical waveguide elements to ensure that at least one mode of the electromagnetic field is sustained by the at least two cooperating optical waveguide elements in cooperation.
Owner:IGNIS PHOTONYX AS
Production technology of optical fiber combiner based on capillary tube
InactiveCN102841408ALayout rules and convenienceReduce complexityCoupling light guidesFiber bundleEngineering
The invention relates to a production technology of an optical fiber combiner based on a capillary tube. The technology comprises the following steps of: 1) obtaining bundle fiber bundles; 2) bundling and arranging the bundle fiber bundles obtained from the step 1) by the capillary tube and forming the capillary tube which is internally embedded with the bundle fiber bundles; 3) carrying out beam combining treatment on the capillary tube internally embedded with the bundle fiber bundles obtained from the step 2) and forming a cone-shape optical waveguide. According to the invention, the production technology of the optical fiber combiner based on the capillary tube, which is convenient to fix and easy to taper, can greatly reduce energy loss in a laser combining process, and can improve a power bearing level of a beam combiner, is provided.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Laser and grating coupler packaging structure and method
ActiveCN105259623AGuaranteed placement accuracyEfficient couplingLaser detailsSemiconductor laser optical deviceGratingEngineering
The invention provides a laser and grating coupler packaging structure and method. The packaging structure comprises a laser unit, a collimating lens, an isolator and a reflection prism, wherein the laser unit, the collimating lens, the isolator and the reflection prism are mounted on a silicon-based photoelectric chip. The silicon-based photoelectric chip comprises a first electrode, first and second marks, a grating coupler and a waveguide layer which are all arranged at the surface; the laser unit comprises a transitional substrate and a laser; the collimating lens comprises a first lens and a second lens, the first lens is vertical to the surface, the second lens is arranged at the surface at the position of the second mark, and thus, the grating coupler is placed in the central area of the main axis of the optical path of the second lens; and the isolator is mounted at the surface between the first lens and the second lens, so that diverging light output by the laser is collimated by the first lens, then reflected to the reflection prism through the isolator, deflected by the reflection prism for certain angle, and gathered by the second lens, and the gathering point is placed at the surface of the grating coupler. Thus, technical problems in accurate in-place packaging are solved, convenience is provided for preparation, and the yield rate is improved.
Owner:WUHAN TELECOMM DEVICES
Grating anchor rod force-measuring device and method for monitoring anchor rod stress variation
InactiveCN101358886ASmall sizeReduce weightForce measurement by measuring optical property variationFiberGrating
The invention discloses an optical fiber raster anchor rod dynamometry device and an application method thereof, wherein, a manometer is connected with an oil pipe; a horizontal pipe is connected with a hydraulic cylinder; an anchor rod is inserted in the inner hole of the hydraulic cylinder; an vertical pipe is connected with an optical fiber raster sensor; the inside of the shell of the optical fiber raster sensor is connected with a cladding and a fiber core which is connected with a raster; the two ends of the fiber core are connected with an optical fiber raster sensing network analyzer and a computer. In the dynamometry device and the application method, an optical fiber raster demodulator detects the variation of the wavelength and converts the variation of the wavelength into an electrical signal; the optical fiber raster sensing network analyzer calculates the stress and strain of a point to be tested and a distribution state in the whole point to be tested; an optical fiber raster wavelength demodulation analyzing soft reads a testing data; a unitary linear regression model is established for getting the stress and strain value of the point to be tested under the action of external force, the invention has a simple structure, low cost and good anti-interference performance. Multi-parameter sensing measurement has a measurement with high precision and stable performance, which can be largely applied to the field of mine, tunnel or side slope, etc., and the signal can be transmitted far.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Millimetre wave planar antenna and array thereof
InactiveCN101982898ASmall dielectric lossUniform radiation patternAntenna arraysRadiating elements structural formsPhysicsRadiation
The invention discloses a millimetre wave planar antenna and an array thereof, wherein the millimetre wave planar antenna includes a metal patch, a medium substrate, a metal floor board and ground poles, the metal patch is placed on an upper surface of the medium substrate, and a lower surface of the medium substrate is fixed with an upper surface of the metal floor board; the metal patch is parallel to the upper surface of the metal floor board; the metal patch is provided with at least one pair of same first bar-shaped channels, each pair of first bar-shaped channels are distributed in bilateral symmetry form, symmetrical centre lines of each pair of bar-shaped channels are superposed, a centre line in a length direction of each first bar-shaped channel is parallel to each other, and length of each first bar-shaped channel is 1 / 2 of an operating wavelength; the ground poles vertically penetrate through the medium substrate, the ground poles are circularly distributed at intervals at the periphery of a region where the first bar-shaped channels are distributed, and two ends of each ground pole are respectively contacted with the metal patch and the metal floor board. The invention can reduce loss of a millimetre wave antenna, improve radiation efficiency of the millimetre wave antenna, simultaneously, guarantee work bandwidth of the antenna, and improve antenna gain.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Optical device
ActiveCN103608708AImprove practicalityReduce coupling lossCoupling light guidesMulticore optical fibreCoupling lossOptical axis
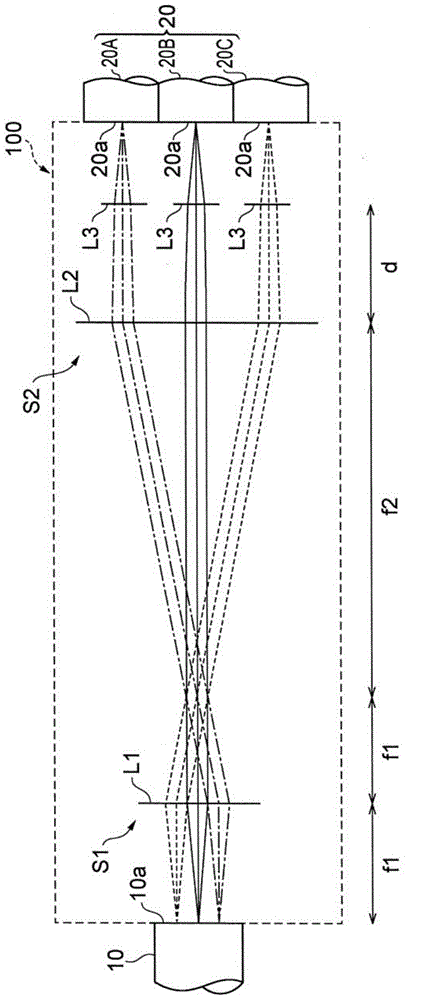
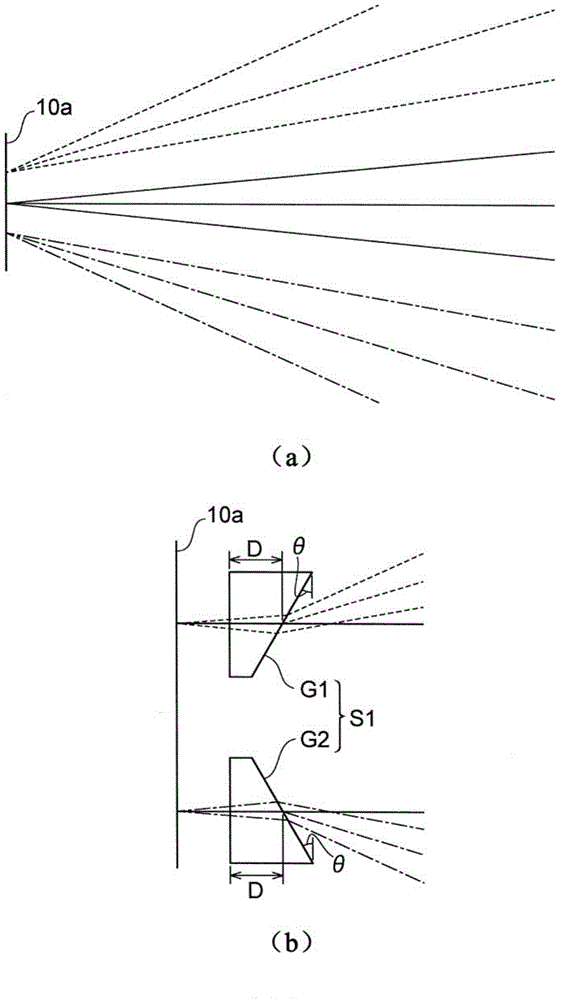
Provided is an optical device in which connection loss is reduced while practicality is enhanced. A multi-core fiber connection device (100) is an optical device for connecting a multi-core fiber (10) to a single-core fiber (20), and comprises a first optical system (S1) positioned on the optical axes of a plurality of beams emitted from a multi-core fiber (10), the first optical system for separating the optical axes of the beams from each other by making the optical axes non-parallel to each other, and a second optical system (S2) for making the optical axes of the plurality of beams substantially parallel to each other, the optical axes having been non-parallel to each other at the first optical system (S1).
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Wireless device having antenna
InactiveCN1661855AReduce coupling lossEasy to adjustSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsGround planeAntenna element
A wireless device includes a first antenna element resonating with a first frequency, a first feeding point coupled to the first antenna element and disposed on a ground plane in the wireless device, a first matching circuit of which first end is coupled to the first feeding point, a second antenna element resonating a second frequency higher than the first frequency, a second feeding point coupled to the second antenna element and disposed on the ground plane, a second matching circuit of which one end is coupled to the second feeding point, and a radio circuit coupled via a transmission line to a common connection point (18) shared by respective second ends of the first and second matching circuits.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Optical waveguide element, manufacturing method for optical waveguide element, optical deflecting element, and optical switching element
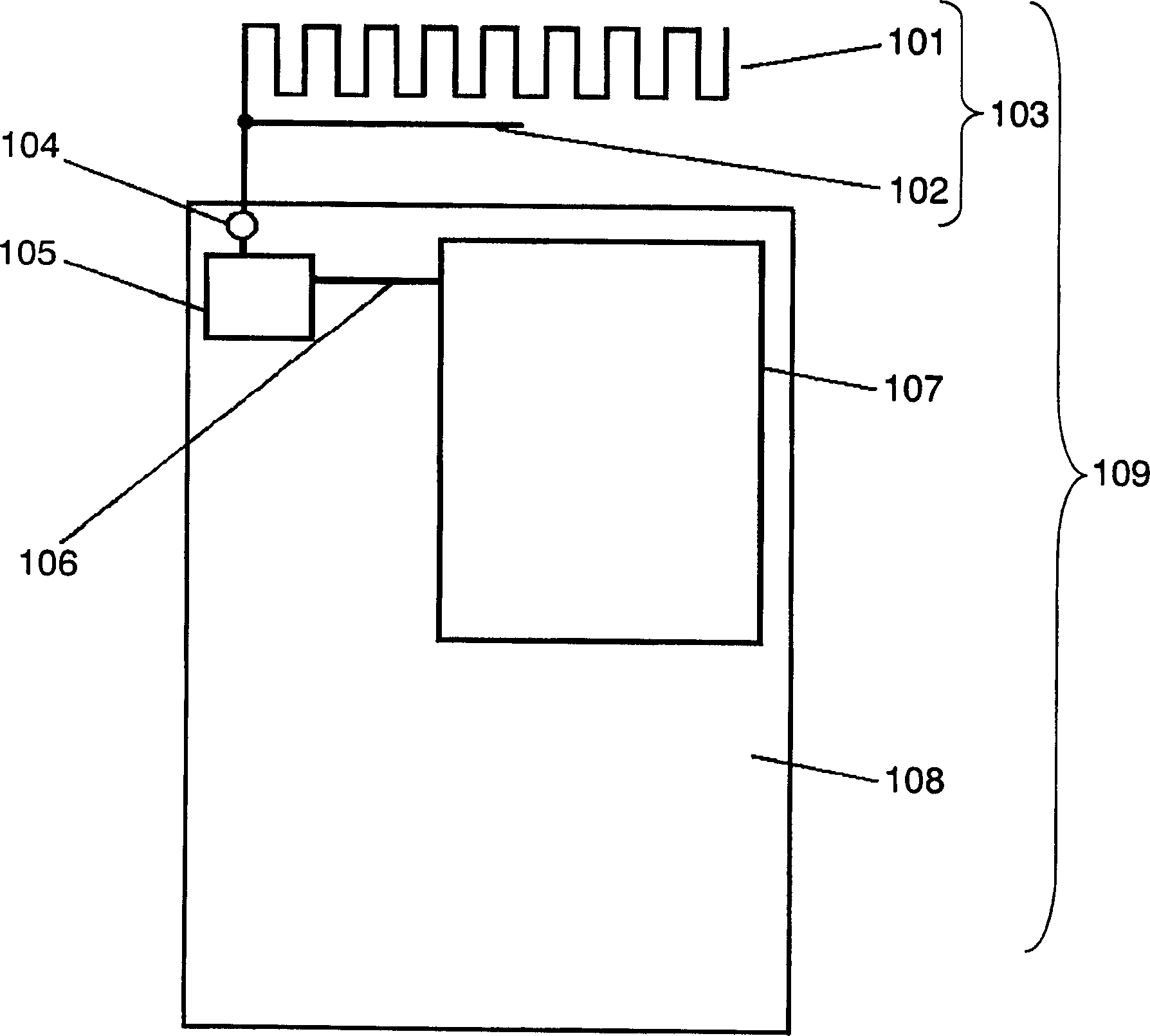
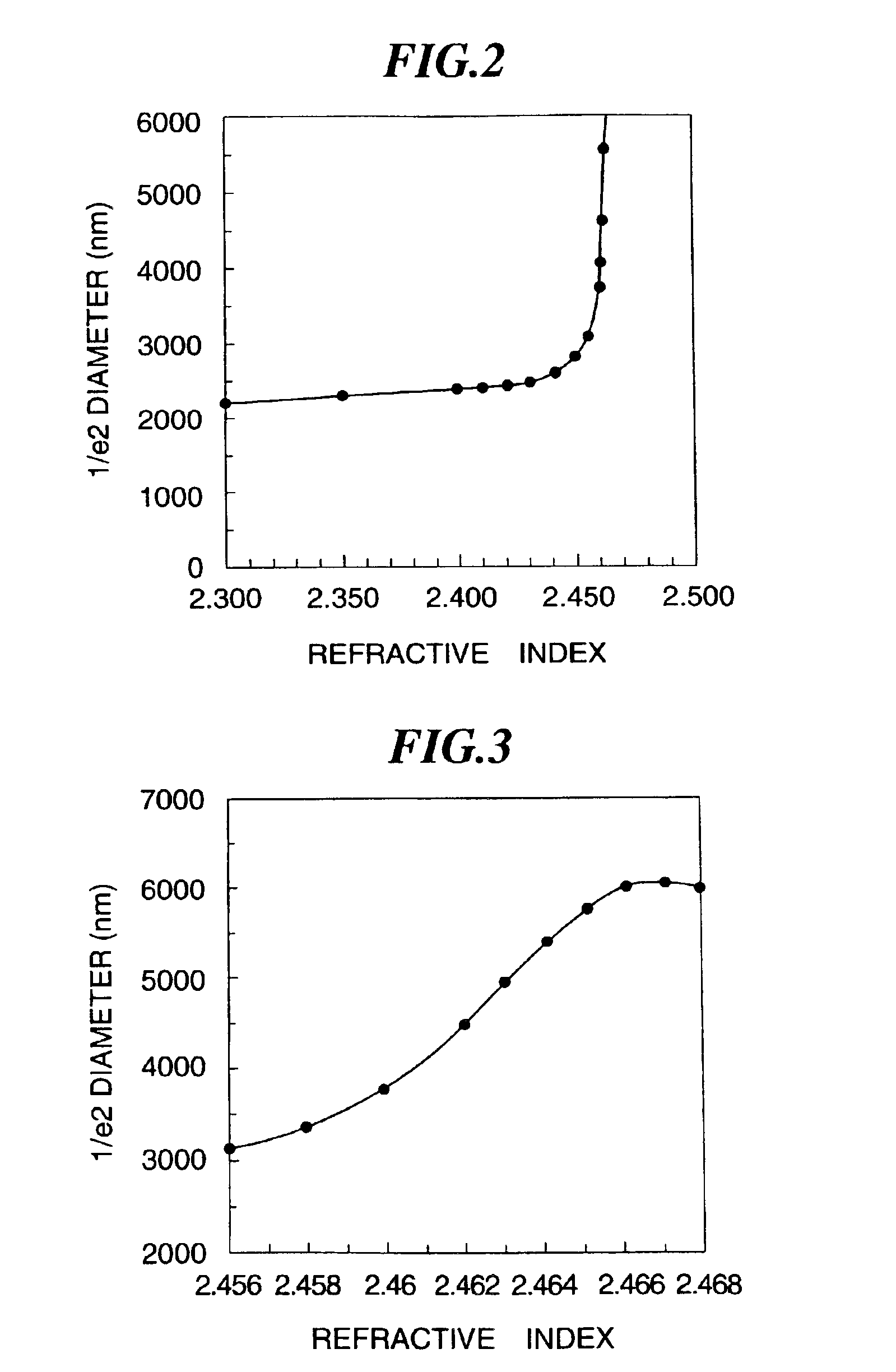
InactiveUS6862393B2Reduce coupling lossIncrease the diameterCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideOptical propagationCoupling loss
An optical waveguide element capable of being coupled with optical fibers at high coupling efficiency is to be provided. Also an optical waveguide element manufacturing method permitting accurate production of such optical waveguide elements is to be provided. The optical waveguide element is provided with a buffer layer formed over a monocrystalline substrate and an optical waveguide layer formed over the buffer layer, and a recess is formed in the buffer layer along the lengthwise direction of the monocrystalline substrate. The optical waveguide layer is provided to fit into this recess to form a channel optical waveguide. Over the upper face of the optical waveguide layer on the light incidence side and the light emission side, a cladding layer whose refractive index is smaller than that of the optical waveguide layer and whose thickness increases towards the end face(s) in a flared shape is provided in the same width as that of the monocrystalline substrate. By providing the cladding layer whose refractive index is smaller than that of the optical waveguide layer, it is made possible to expand the mode field diameter and substantially reduce the coupling loss between the optical fiber and the optical waveguide element. Further by increasing the thickness of the cladding layer in a flared shape toward the end face(s), it is made possible to gradually compress the mode field diameter and to reduce the optical propagation loss within the optical waveguide.
Owner:EPIPHOTONICS CORP
Ultrasonic transducer used in fluid medium
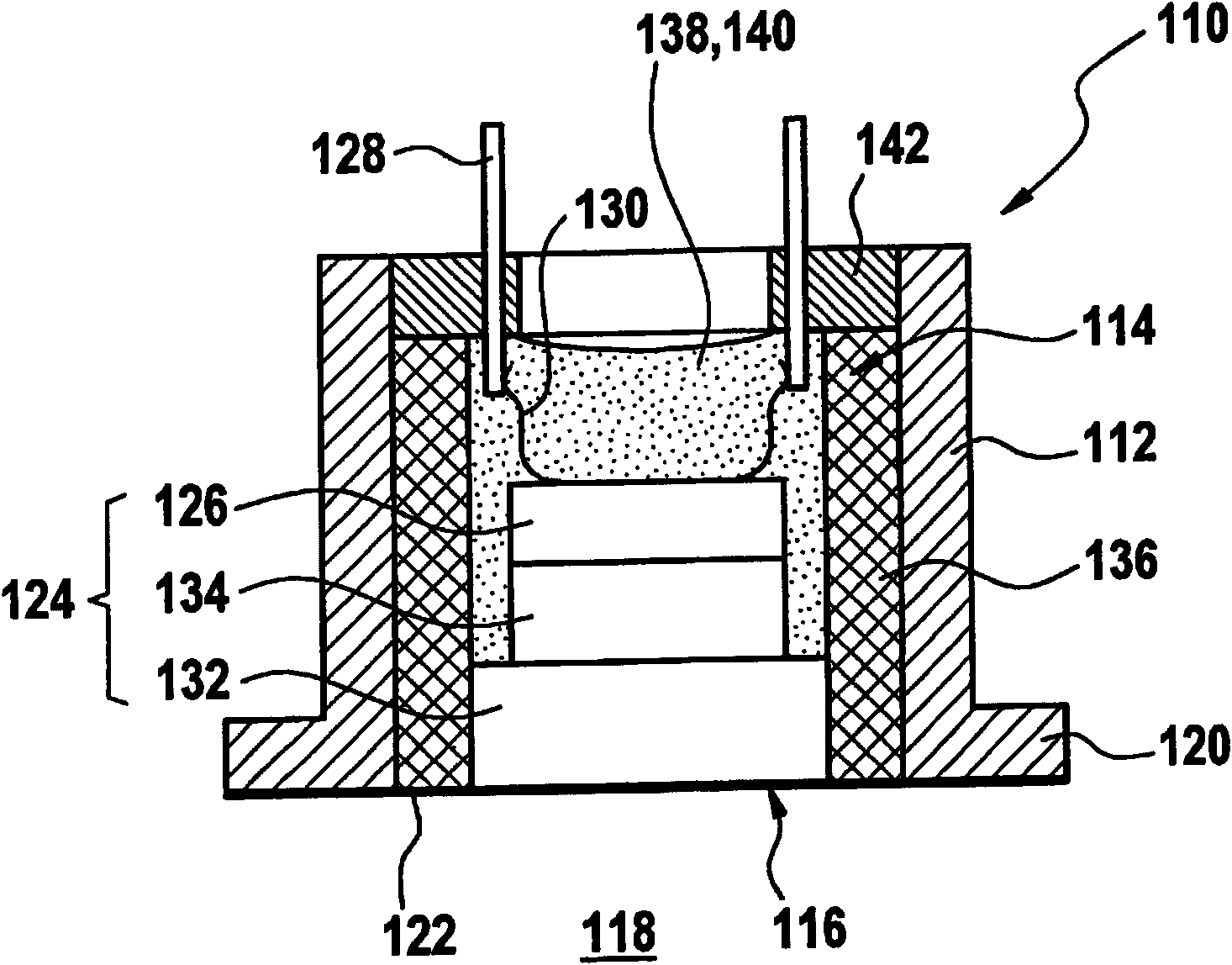
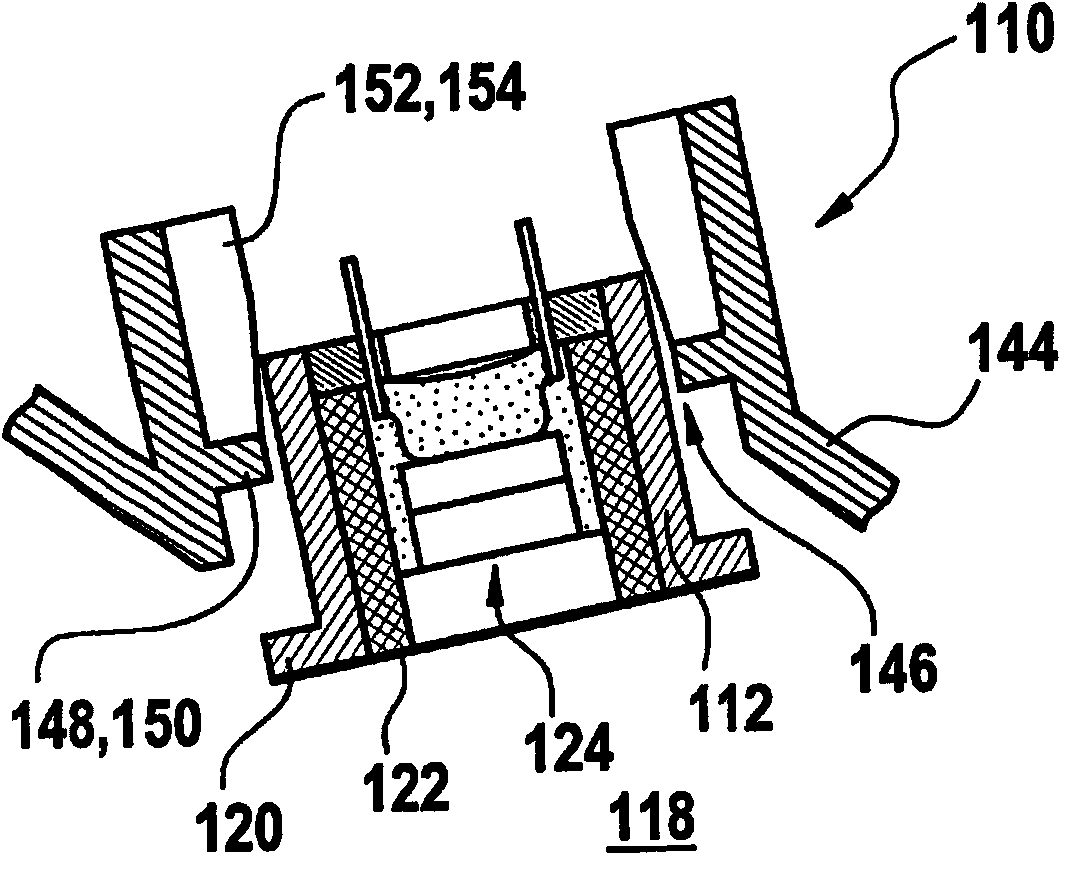
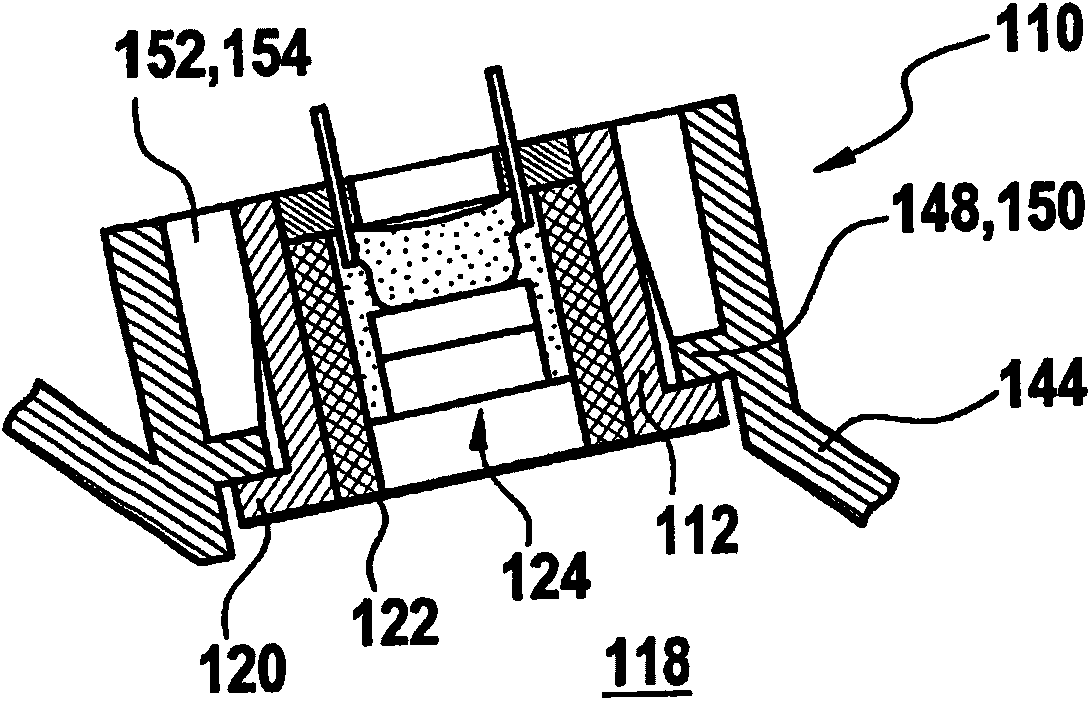
InactiveCN102065361AReduce coupling lossPlay a bridging roleVolume/mass flow measurementPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersUltrasonic sensorTransducer
The invention presents an ultrasonic transducer (110) used in fluid medium (118). The ultrasonic transducer (110) comprises at least one casing cover (112) with at least one casing cavity (114), in which at least one transducer core (124) is installed. The transducer core (124) comprises at least one acoustic-electro transducer element (126). At least one damping element (156) is in contact with the casing cover (112), and is equipped at an outer side of the casing cavity (114) for damping solid state sound.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Radiating coaxial cable having groups of spaced apertures for generating a surface wave at a low frequencies and a combination of surface and radiated waves at higher frequencies
InactiveUS6292072B1Reduce coupling lossMinimize the numberWaveguidesSlot antennasElectrical conductorCoaxial cable
A radiating coaxial cable includes an inner conductor, an electrical insulator located about a periphery of the inner conductor, and an outer conductor located about a periphery of the electrical insulator. The outer conductor defines groups of apertures spaced from each other a predetermined distance in the range of from about twice the longest operational wavelength of the cable to less than ten meters. The aperture groups are designed in such a way to excite a surface wave at low operating frequencies and a combination of surface and radiating waves at high operational frequencies.
Owner:TIMES MICROWAVE SYST DIV OF SMITHS AEROSPACE
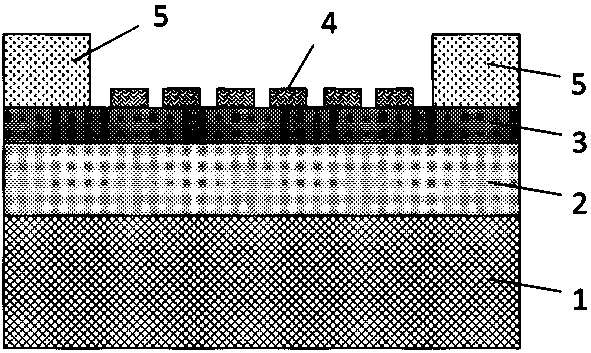
Graphene mid-infrared light detector based on plasmon enhancement and preparation method
InactiveCN111554757APromote absorptionHigh resonance factorFinal product manufactureNanotechnologyHigh energyMaterials science
The invention discloses a graphene mid-infrared light detector based on plasmon enhancement, and belongs to the technical field of mid-infrared light detection. The graphene mid-infrared light detector comprises a silicon substrate, a silicon dioxide layer, a graphene micro-nano array and a dielectric layer which are sequentially stacked from bottom to top, wherein the graphene micro-nano array and the dielectric layer are positioned in the middle of the silicon dioxide layer; the surfaces of the silicon dioxide layer and the dielectric layer are covered with a graphene layer; and a first electrode and a second electrode are arranged on the two sides of the graphene layer respectively. According to the infrared detector manufactured by using the structure, the photoelectric conversion efficiency is greatly improved, the preparation method is simple, the infrared detector is compatible with the existing silicon process, the problems of continuous low-temperature refrigeration, high energy consumption, weak signal and the like of the traditional infrared detector using mercury cadmium telluride, indium antimonide and the like are solved, and the operation cost performance is greatlyimproved.
Owner:深圳激子科技有限公司
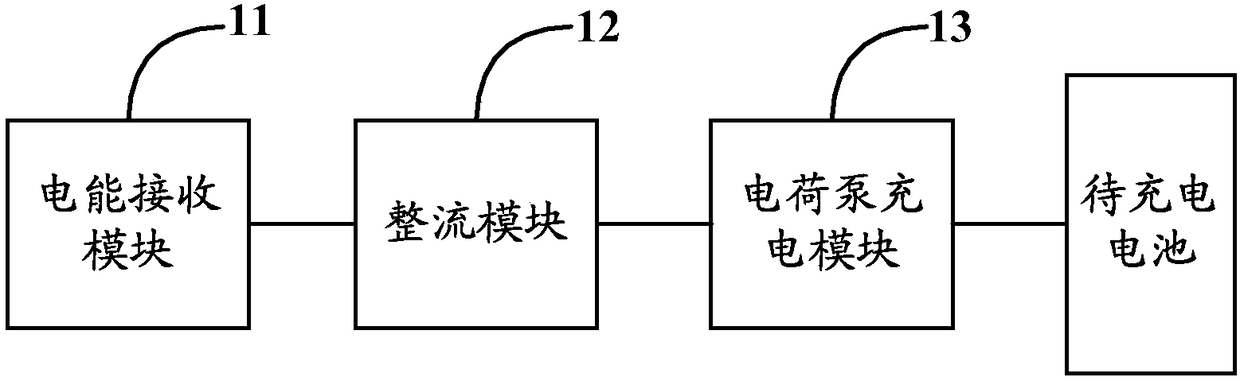
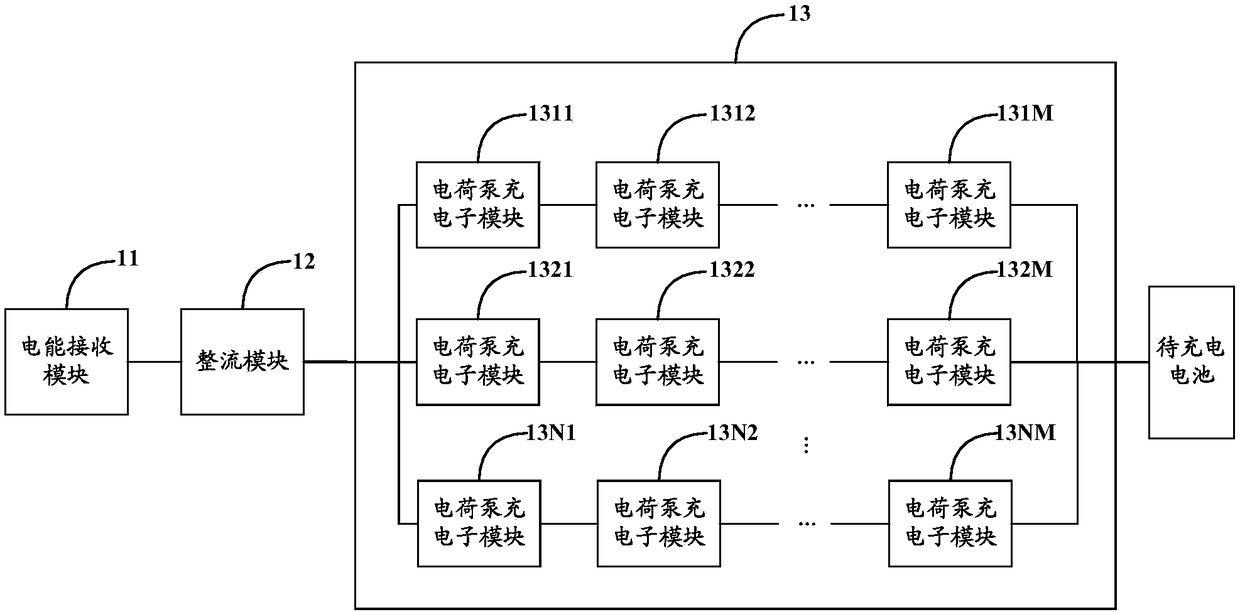
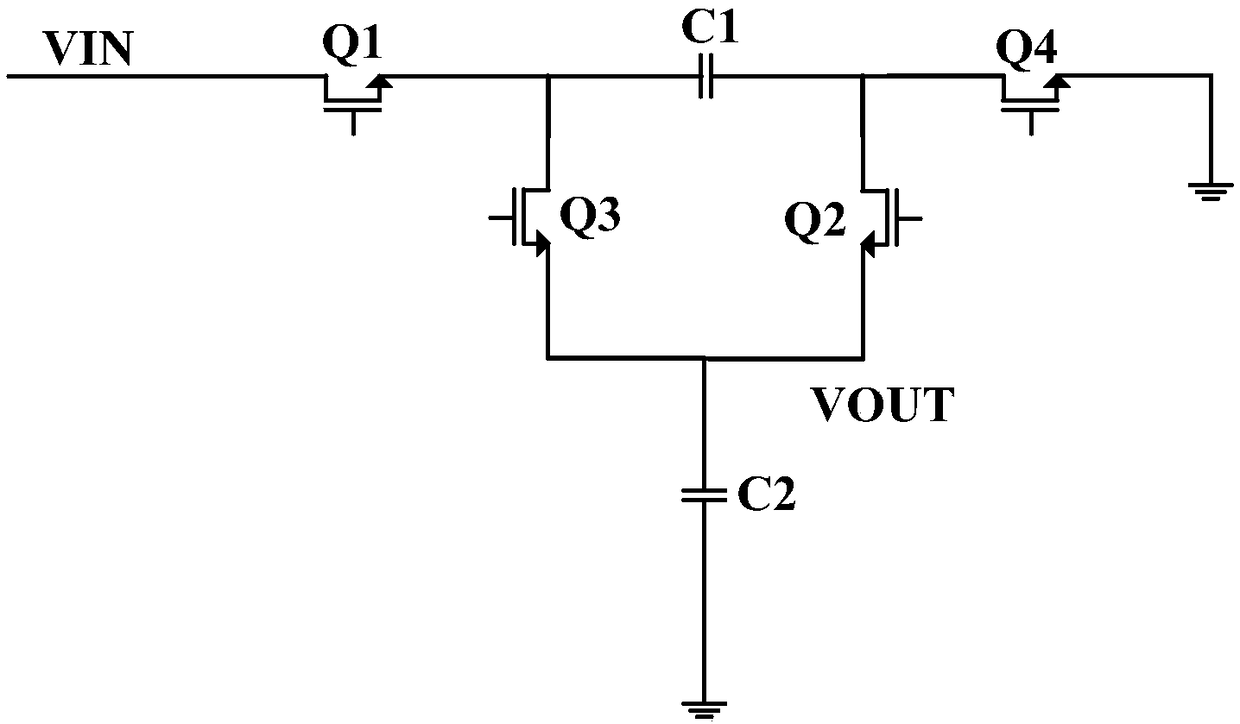
Wireless charging circuit, system and method and electronic equipment
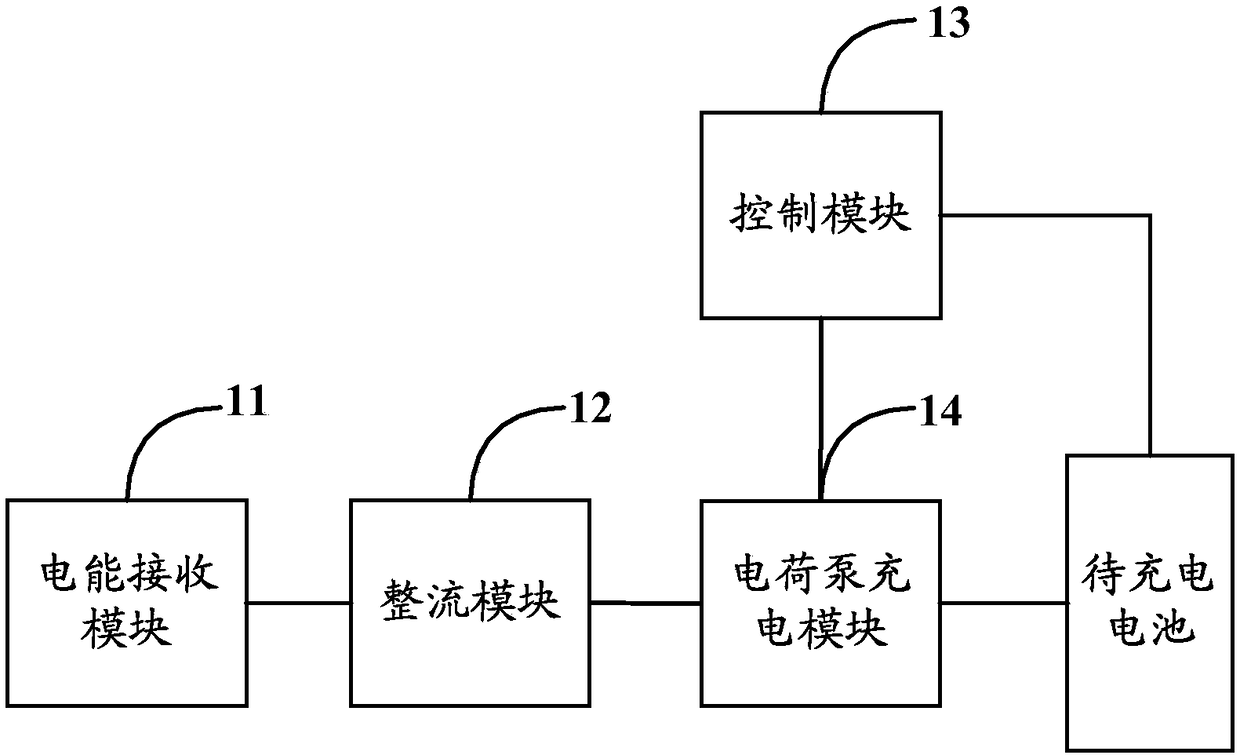
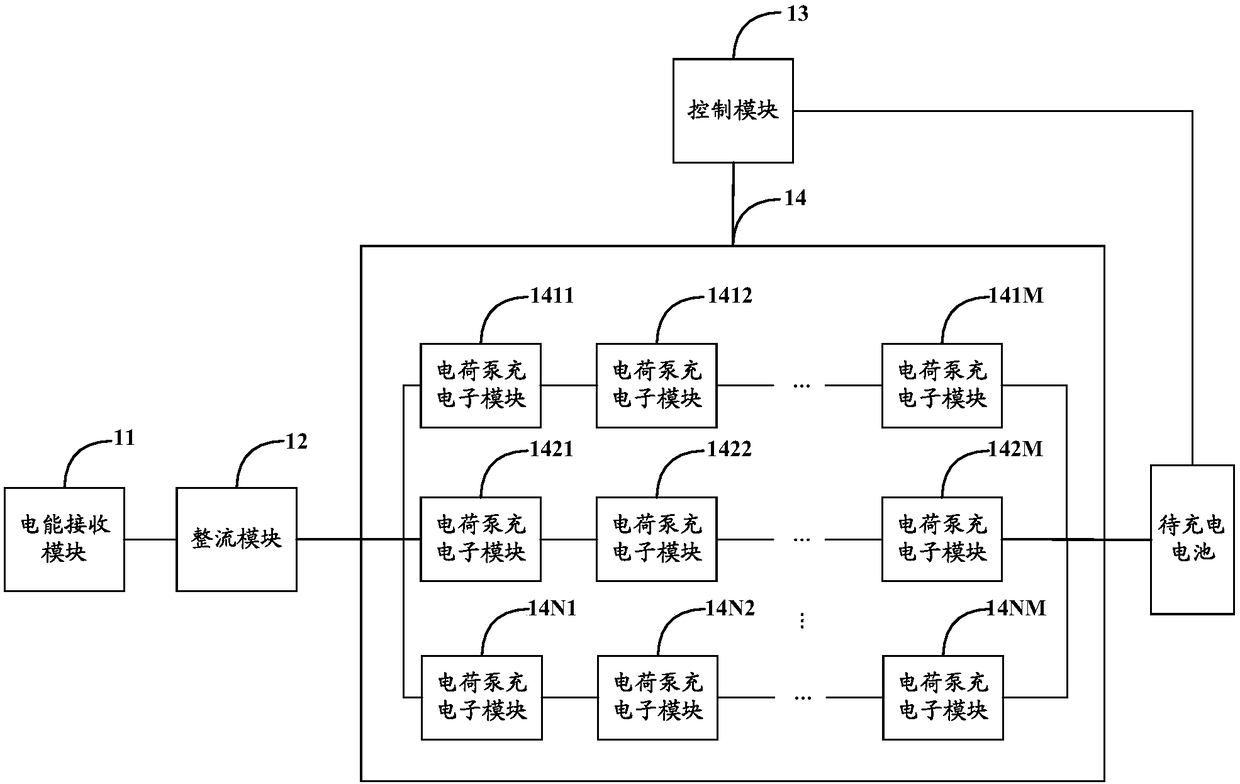
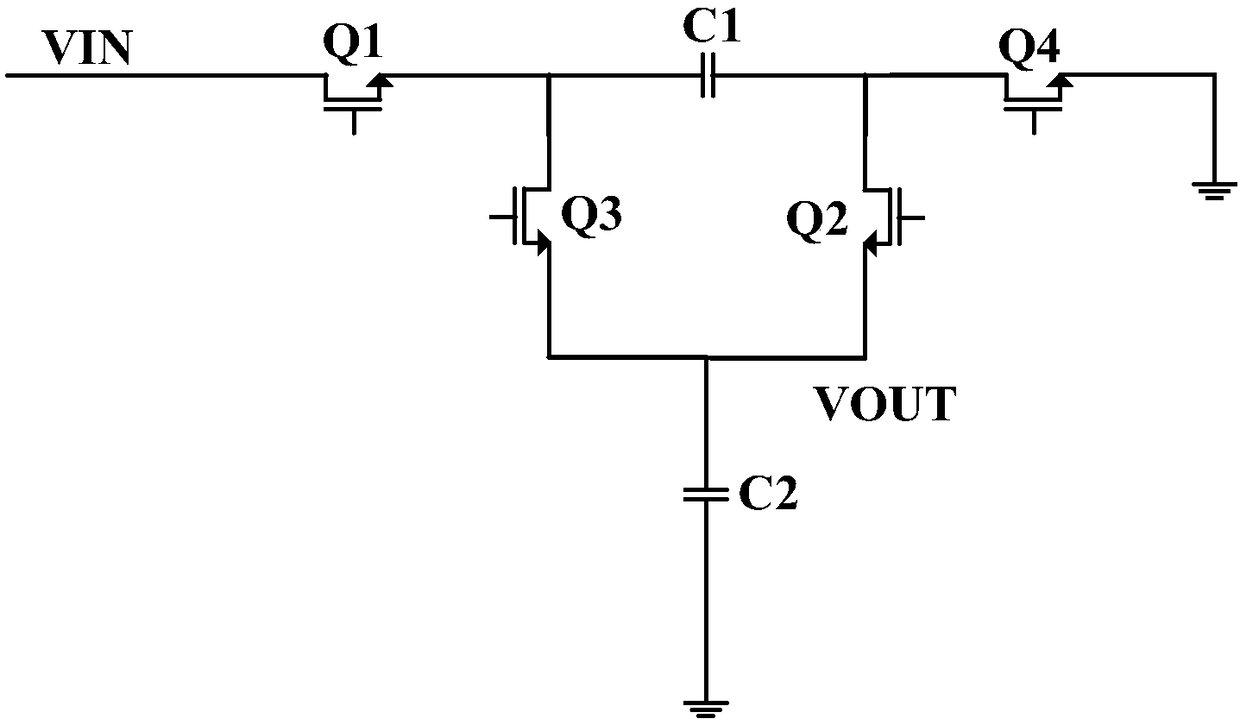
InactiveCN108233454AImprove Buck Conversion EfficiencyReduced Buck Conversion EfficiencyBatteries circuit arrangementsSecondary cells charging/dischargingCoupling lossControl signal
The invention discloses a wireless charging circuit, system and method and electronic equipment. The wireless charging circuit can comprise an electric energy receiving module, a rectifying module, acontrol module and a charge pump charging module. The electric energy receiving module is used for receiving the alternating current transmitted by the electric energy transmitting module of a wireless adapter. The rectifying module is used for converting the alternating current into direct current. The control module is used for generating a first control signal in the constant current stage. Thecharge pump charging module is used for performing voltage reduction and current enhancement on the direct current when receiving the first control signal and transmitting the direct current after voltage reduction and current enhancement to a battery to be charged. Compared with the circuits in the prior art, the wireless charging circuit has no step-down conversion module; the charge pump charging module having no inductance component is used in the constant current stage; and the current of the pre-circuit of the charge pump charging module is low and the coupling loss is low in the constant current stage so that the problems of low charging efficiency and low safety in the prior art can be solved.
Owner:MEIZU TECH CO LTD
Wavelength division multiplexer capable of being integrated in CFP and CFP2 standard high-speed transceivers
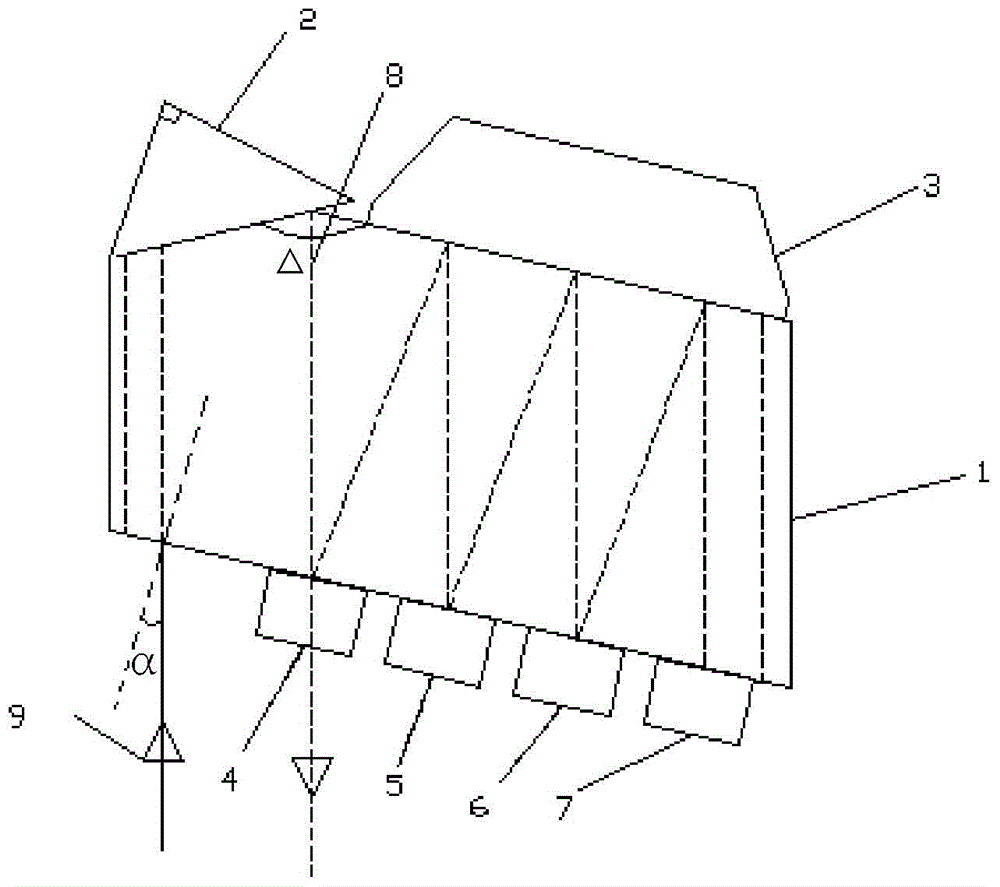
The invention discloses a wavelength division multiplexer which can be integrated into CFP and CFP2 standard high-speed transceivers, which comprises a filter holder and a plurality of filters, and the plurality of filters sequentially transmit light of a set wavelength and reflect the rest of the light to the bottom A filter, the filter holder is provided with an incident light inlet, and also includes a right-angle prism and a plane mirror, all filters and the incident light inlet are installed on the same side of the filter holder, and the right-angle prism and the plane mirror are installed on the filter The other side of the sheet holder is arranged opposite to all the filters. The oblique surface of the rectangular prism refracts the incident light to the nearest filter, and each filter transmits the light of the set wavelength and reflects the light of the remaining wavelengths to the flat mirror behind the flat mirror. Reflected to the next filter; the invention can greatly compress the size of the device, not only can be applied to high-speed transceivers, but also can save production costs, reduce product footprint, and have higher stability than traditional coarse wavelength division multiplexing , with a wide range of applications.
Owner:杭州埃戈光电科技有限公司
Coupling structure and coupling method of semiconductor laser chip and silicon optical chip
InactiveCN110401101AReduce lossReduce light field scattering lossLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersCoupling lossScattering loss
The present invention provides a coupling structure and a coupling method of a semiconductor laser chip and a silicon optical chip. The coupling structure comprises: a laser unit comprising a laser chip; a silicon optical chip provided with a waveguide; and an etching groove arranged at the coupling end of the silicon optical chip and used for connecting with the laser unit and the silicon opticalchip. The coupling structure and the coupling method of the semiconductor laser chip and the silicon optical chip can achieve high-efficiency coupling of the semiconductor laser chip and the siliconoptical chip and facilitates providing of a high-quality light source for the silicon optical hybrid integration, an antireflection film is plated at the coupling end face of the silicon optical chip,the coupling loss and the RIN noise of the laser are reduced, the refractive index matching rubber fills the gap of the laser chip and the silicon optical chip, the scattering loss of the optical field is reduced, and the coupling loss is further reduced.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Wireless charging circuit, method and system and electronic equipment
InactiveCN108233455AImprove Buck Conversion EfficiencyBuck Conversion Efficiency GuaranteedBatteries circuit arrangementsApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCoupling lossCapacitance
The invention discloses a wireless charging circuit, method and system and electronic equipment. The wireless charging circuit comprises an electric energy receiving module, a rectifying module and acharge pump charging module. The electric energy receiving module is used for receiving the alternating current transmitted by the electric energy transmitting module of a wireless adapter and transmitting the alternating current to the rectifying module. The rectifying module is used for converting the alternating current into direct current and transmitting the direct current to the charge pumpcharging module. The charge pump charging module is used for performing voltage reduction and current enhancement on the direct current and transmitting the direct current after voltage reduction andcurrent enhancement to a battery to be charged. Compared with the circuits in the prior art, the charge pump charging module is used as the charging module of the wireless charging circuit, and the internal charge and discharge element is the capacitor rather than the inductor; besides, the current of the pre-circuit is enabled to be low and the coupling loss is enabled to be low by the charge pump charging module so that the problems of low charging efficiency and low charging safety can be solved.
Owner:MEIZU TECH CO LTD
High-power, tunable and narrow linewidth external cavity semiconductor laser
InactiveCN105680320AImprove quality factor Q valueNarrow line widthLaser optical resonator constructionLaser output parameters controlLine widthRefractive index
A high-power, tunable and narrow linewidth external cavity semiconductor laser belongs to the technical field of a semiconductor laser and aims to solve the problem that the comprehensive requirements such as mode characteristic, beam quality, linewidth, coherence and tunability of a single laser are difficult to be met. The high-power, tunable and narrow linewidth external cavity semiconductor laser is formed by directly coupling a gain chip, a tunable external cavity and an inclined power amplifier with a curved waveguide through an end surface, wherein the gain chip is used for achieving laser output of single-mode wide spectrum; the tunable external cavity adopts a silicon on insulator (SOI) material; the linewidth is narrowed by increasing cavity length and a quality factor Q of a laser resonant cavity; the tunability is achieved by the adoption of refractive index of a thermal modulation material; and by the arrangement of the inclined power amplifier with curved waveguide, laser output with high power and high beam quality is achieved under ensuring the stability of the gain chip and the tunable external cavity. By the high-power, tunable and narrow linewidth external cavity semiconductor laser, a novel semiconductor laser integrating a single mode, high power, high beam quality, narrow linewidth, high coherence, tunable wavelength and the like is achieved, and the high-power, tunable and narrow linewidth external cavity semiconductor laser has important application prospect in the fields such as space laser communication and laser radar.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Arrayed waveguide grating wavelength division multiplexer
InactiveCN102183821AMiniaturization reducesReduce coupling lossOptical waveguide light guideRefractive indexCoupling loss
The invention relates to wavelength division multiplexing technology in the field of light transmission, in particular to an AWG (arrayed waveguide grating) wavelength division multiplexer, which comprises an input waveguide, an input planar waveguide, an arrayed waveguide and an output slab waveguide, and an output waveguide which are connected in sequence, wherein the sections of the input waveguide and the output waveguide respectively comprise a core layer and a covering layer covering the core layer, and the refractive index of the core layer is larger than that of the covering layer. The differences are that one end of the output waveguide, which is connected with the output slab waveguide, is provided with the output waveguide with an air slot; and the output waveguide with the air slot is a high-refractive index difference waveguide, wherein two sides of the core layer of high-refractive index difference are respectively etched with an air slot. The AWG wavelength division multiplexer has the advantages that the volume is small, the coupling loss between optical fibers is little, the wave length amplitude correlation of AWG is good, and the anti-crosstalk property between channels is excellent.
Owner:GUANGXUN SCI & TECH WUHAN
780 nm high-power optical-fiber femtosecond laser device
InactiveCN104283097ANot affected by dispersionReduce nonlinear effectsActive medium shape and constructionNon-linear opticsSeeds sourceComputer module
The invention discloses a 780 nm high-power optical-fiber femtosecond laser device. The laser device comprises a laser device seed source, a laser spreading and amplifying module, a laser compression module and a laser frequency doubling module, the laser device seed source and the preceding modules are sequentially connected, the laser spreading and amplifying module is composed of a chirped pulse spreading sub module, a pulse separation sub module and an optical fiber amplifying sub module, and the laser device seed source and the modules all work at the waveband of 1560 nm. A mixed pulse spreading mode is adopted, pulses are spread from 100 fs to 1ns in a small work space, the amplified pulses are compressed to below 100 fs through non-linear compression of a single-mode fiber, and ultimately the pulses reach 780 nm after frequency doubling of non-linear crystals. The laser device has the advantages of being high in stability, simple in structure, small and ingenious in size, low in cost and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI LANGYAN OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
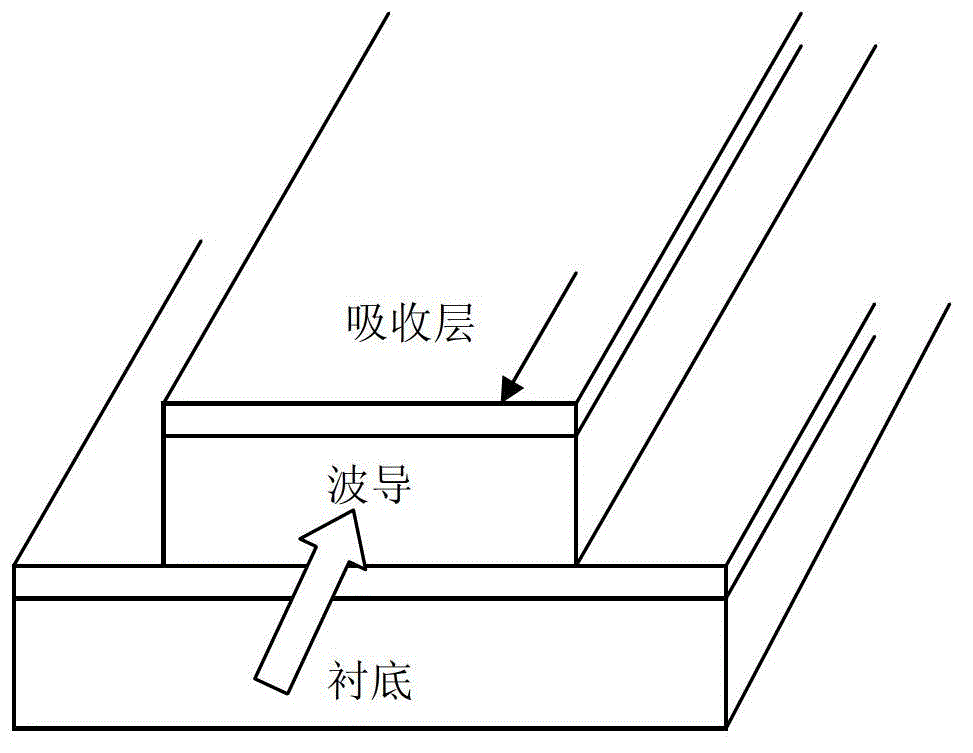
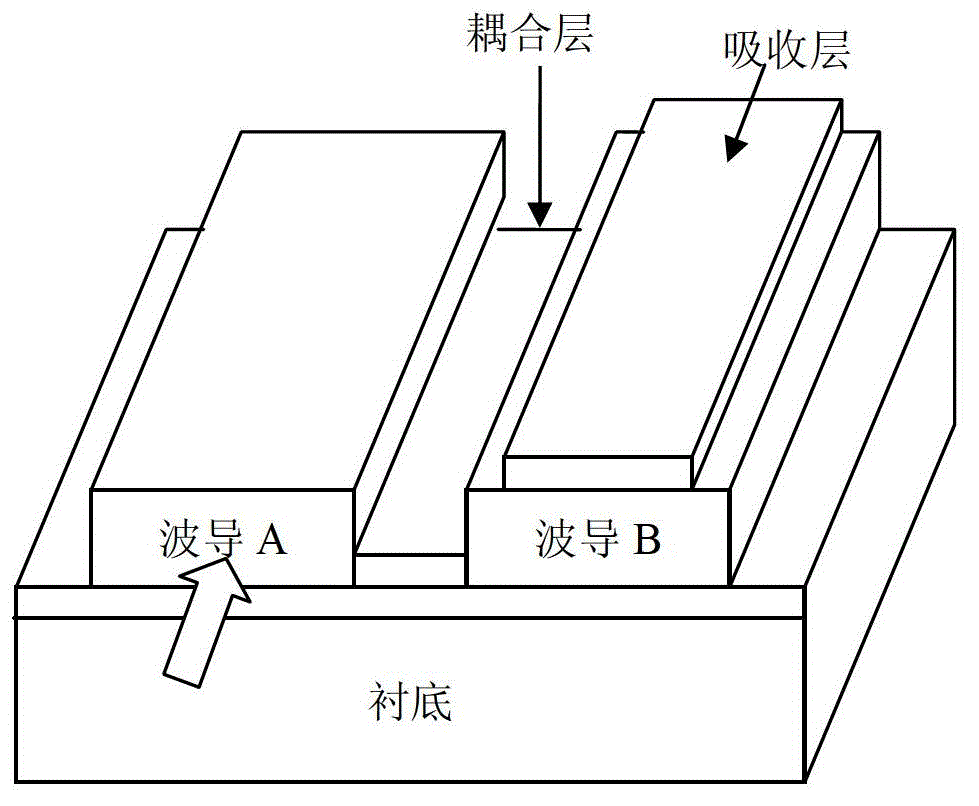
Optical waveguide structure of photoelectric detector for vertical coupling
InactiveCN102723383AEvenly distributedIncrease powerOptical light guidesSemiconductor devicesPhotovoltaic detectorsCoupling
The invention relates to an optical waveguide structure of a photoelectric detector for vertical coupling. The structure comprises an intrinsic layer, an absorption layer, an upper waveguide layer, a clearance layer, a lower waveguide layer, a cover layer and a substrate which are sequentially stacked from top to bottom, wherein the clearance layer is used as a low-refractive index coupling layer between the upper waveguide layer and the lower waveguide layer; and a vertical coupler (equivalent to a vertically-coupled photoelectric diode) composed of the upper waveguide layer and the lower waveguide layer is used for realizing that the light enters from the lower waveguide layer and is gradually coupled to the upper waveguide layer and transmitted in the upper waveguide layer and the lower waveguide layer while being absorbed by the absorption layer. The structure provided by the invention has the beneficial effect of overcoming the defects that the coupling length and the absorption length are changed when the air clearance in the horizontally-coupled photoelectric diode structure changes and the photoetching corrosion processing technology is difficult.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Graphene mid-infrared detector based on phonon exciton enhancement and preparation method thereof
PendingCN110098267APromote absorptionOvercoming the difficulty of enhancing the photoresponse in the mid-infrared bandFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesMid infraredSilicon dioxide
The invention relates to a graphene mid-infrared detector based on phonon exciton enhancement and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of mid-infrared detection. The graphene mid-infrared detector comprises a silicon substrate, a silicon dioxide layer, a graphene layer and a molybdenum trioxide micro-nanostructure array covering the graphene layer which are laminated inturn from bottom to top, wherein the molybdenum trioxide micro-nanostructure array and the graphene layer form a phonon exciton enhanced heterostructure; and the edge of the graphene layer is provided with an electrode above, and the electrode extends an overlapping region of the molybdenum trioxide micro-nanostructure array and the graphene layer. In order to solve the technical problems, the graphene mid-infrared detector achieves the purposes of greatly improving the photoelectric conversion efficiency in the mid-infrared band and being simple in preparation method and low in cost.
Owner:深圳激子科技有限公司
Serially connected optical switch based photon delay structure and numerical-control integrated photon delay device
InactiveCN103529521ARF broadband transparentFast tuningCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideCMOSSingle mode waveguides
A serially connected optical switch based photon delay structure comprises a plurality of optical switches and multiple sections of single mode waveguides, wherein one input end of a first optical switch is connected with an input optical fiber, and the other input end of the first optical switch is idle; two output end of the first optical switch are connected with two input ends of a second optical switch respectively through two sections of single mode waveguides; other optical switches are sequentially connected in series according to the connection mode of the first optical switch and the second optical switch; one output end of an Nth optical switch is connected with an output optical fiber, and the other output end of the Nth optical switch is idle; and every two optical switches are connected through a first single mode waveguide and a second single mode waveguide, and the first single mode waveguide is longer than the second single mode waveguide. The serially connected optical switch based photon delay structure has the benefits as follows: the serially connected optical switch based photon delay structure has the advantages of high tuning speed, working stabilization and controllability and realizes mass production by virtue of a mature CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) technology; and besides, a numerical-control integrated photon delay device is integrated on an SOI (silicon on insulator) silicon chip, the size is small, and the integration level is high.
Owner:THE 44TH INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
Manufacturing method for optical waveguide module
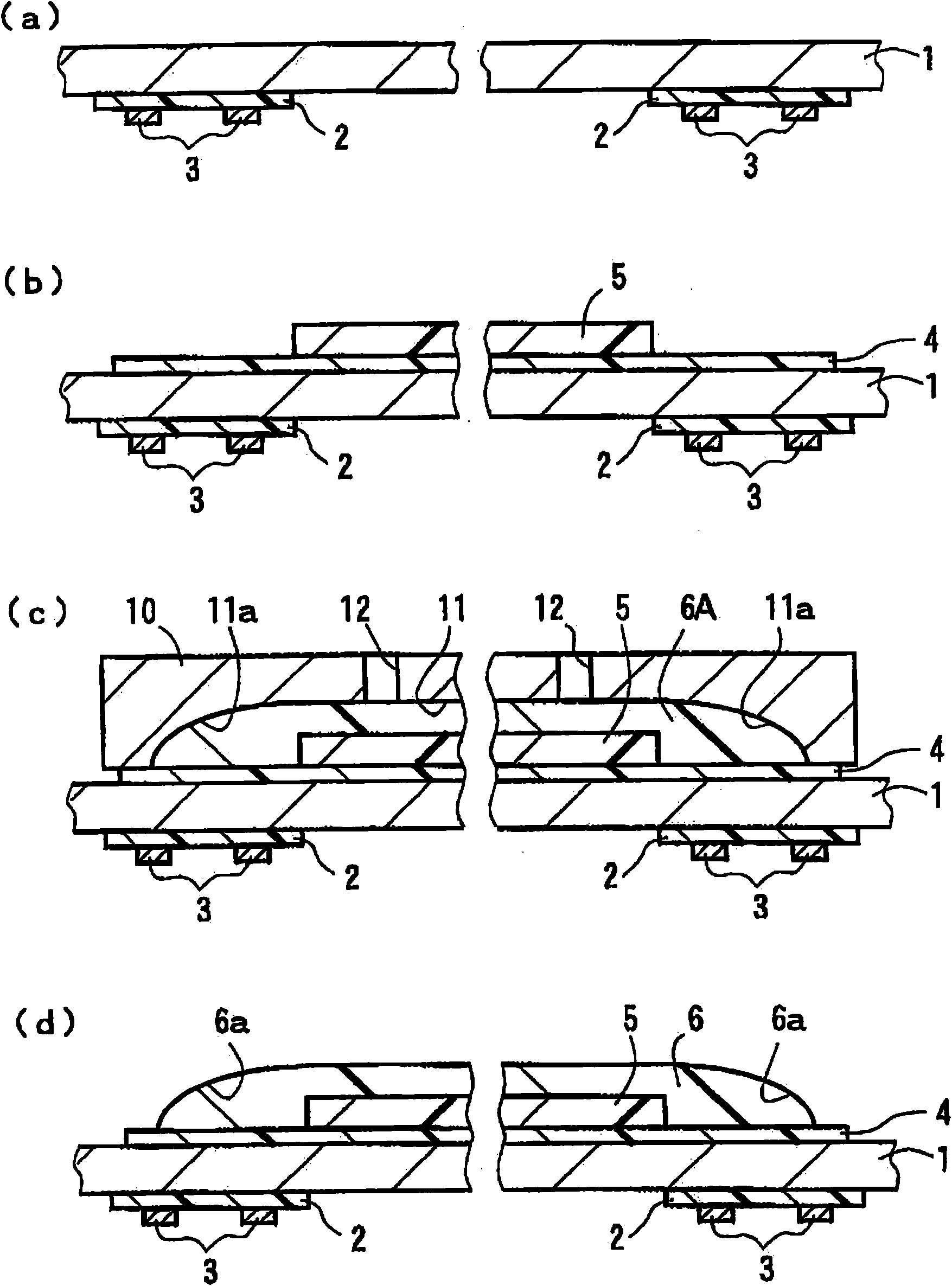
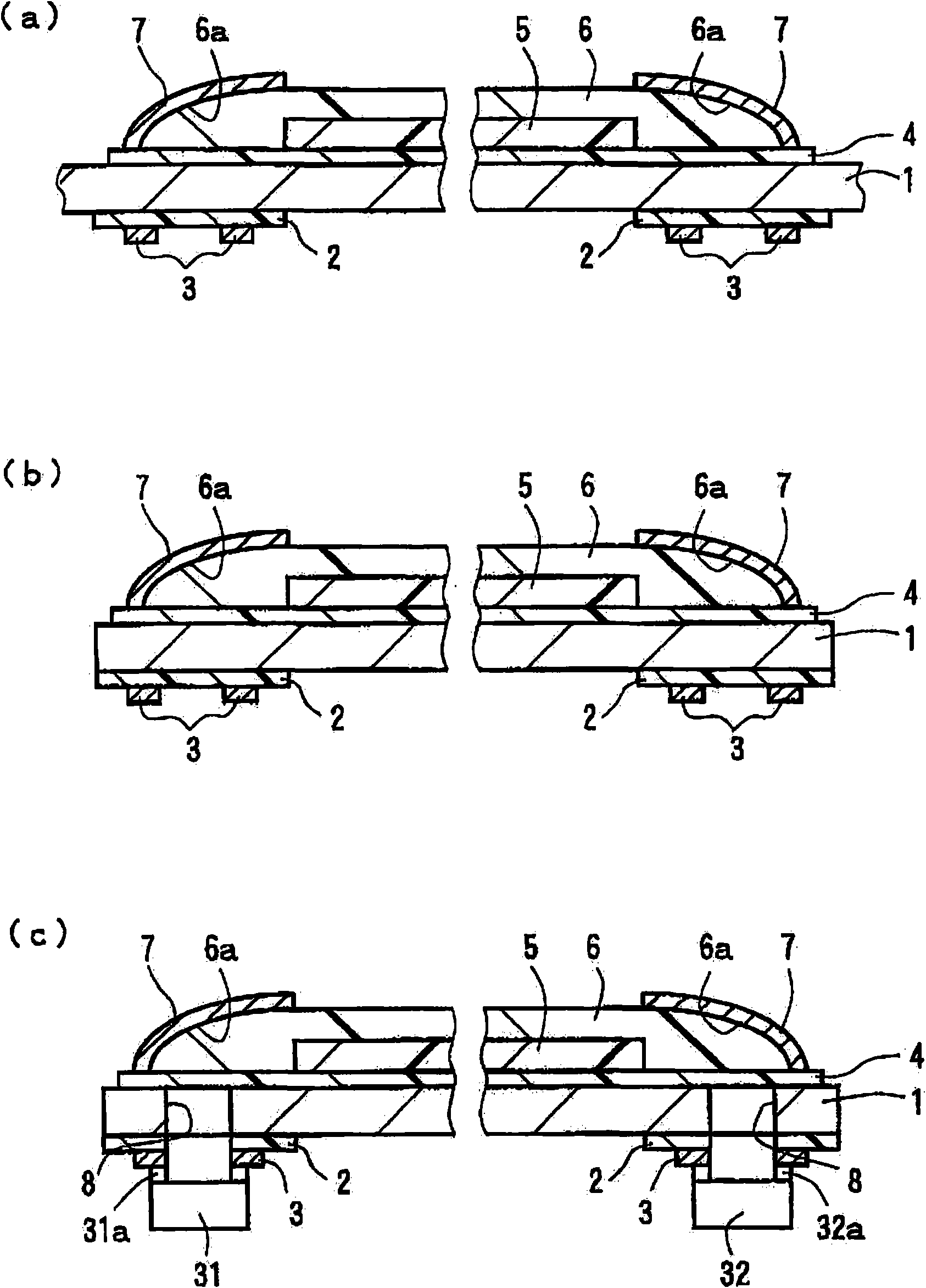
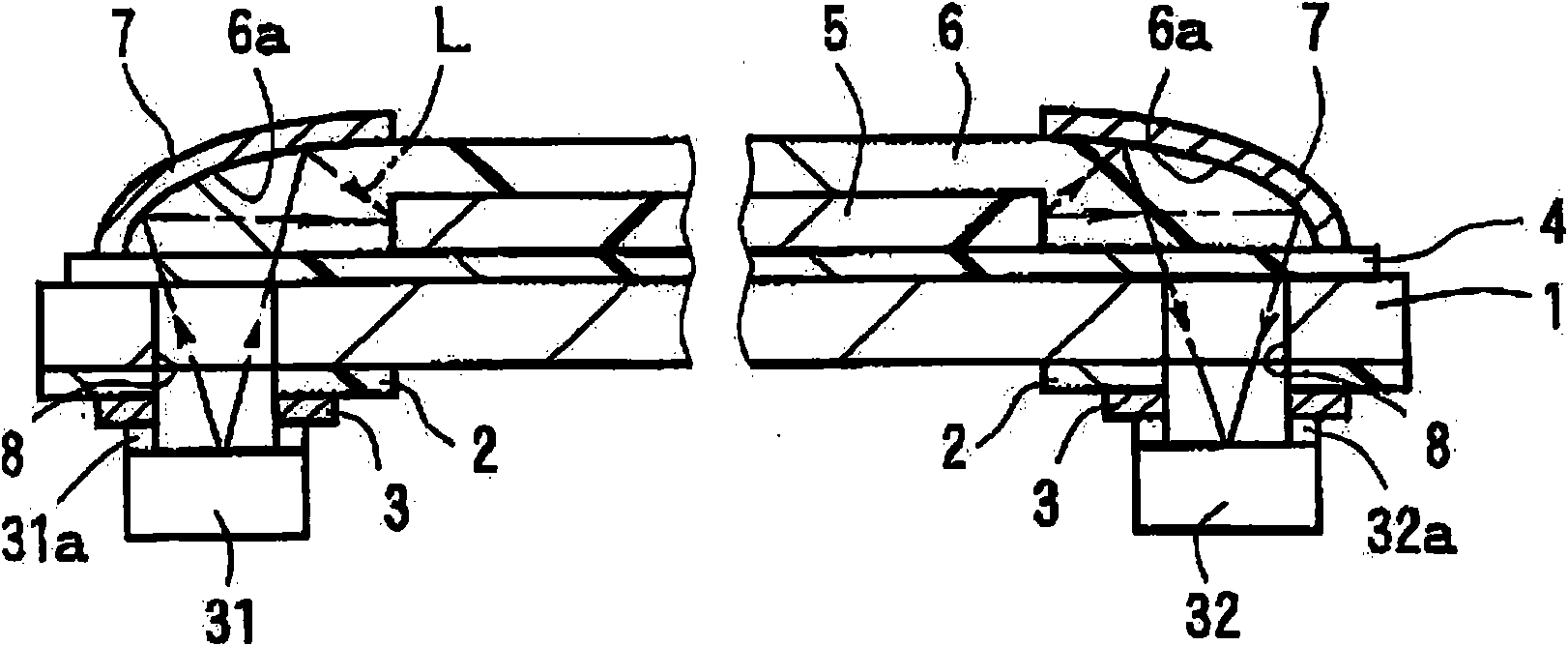
InactiveCN101561532AIncrease productivityReduce coupling lossCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideWaveguideLight wave
A manufacturing method for an optical waveguide module which is capable of forming a light reflecting portion with stabilized accuracy and which is good in production efficiency. The manufacturing method for an optical waveguide module in which an optical element is mounted on the back side of end portions of an optical waveguide is provided. For the production of the above-mentioned optical waveguide, end portions of an over cladding layer (6) corresponding to the end portions of the optical waveguide are formed so as to serve as reflective portions (6a) at the same time that the over cladding layer (6) is formed on the front side by a die-molding process using a molding die (10) so as to cover a core (5).
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Electroluminescence device and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103094488AReduce coupling lossReduce reflectionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGratingOrganic layer
The invention discloses an electroluminescence device and an electroluminescence display device, and belongs to the display field. Total reflection and waveguide effect of light in an organic layer and an anode interface can be reduced, the number of emergent photon is increased, light-taking-out efficiency of the device is improved, and therefore lighting effect is improved and power consumption is reduced. The electroluminescence device comprises a substrate, a first electrode, a second electrode, electroluminescence layer and a grating structure, wherein the first electrode and the second electrode are arranged on the substrate, the electroluminescence layer is arranged between the first electrode and the second electrode in a clamping mode, the first electrode close to the substrate is designed to be the grating structure.
Owner:HEFEI BOE OPTOELECTRONIC TECH CO LTD +1
Integrated wavelength selective grating-based filter
A wavelength selective grating-based filter includes a planar waveguide which includes a core surrounded by a cladding, the cladding including a lower cladding, the core being placed above the lower cladding, a lateral cladding adjacent to a first and a second opposite lateral sides of the core, and an upper cladding, said upper cladding being positioned above said core and lateral cladding. The waveguide also includes a grating structure, including a first and a second plurality of grating trenches formed in the lateral cladding in proximity of the first and second opposite lateral sides of the core, respectively. The first and second plurality of grating trenches are covered by the upper cladding.
Owner:PIRELLI & C
Silicon-based integrated optical isolation device based on topology protection mechanism
ActiveCN110941109ASmall sizeSmall group velocityNon-linear opticsOptical elementsCoupling lossPhotonic crystal
The invention belongs to the field of integrated optics, and particularly relates to a silicon-based integrated optical isolation device based on a topology protection mechanism. By adjusting the boundary states of the linear defect photonic crystal module and the topological non-uniform low group velocity photonic crystal module, the excitation and coupling regulation and control of the low groupvelocity boundary state are realized. According to the invention, the line defect photonic crystal waveguide with low group velocity is used as a transition coupling structure, so that the group velocity is matched while the coupling loss is reduced. The boundary state propagated in the photonic crystal has low group velocity and good locality, so that the size of the device is greatly reduced, and the loss is low; an isolator of TE polarization can be conveniently obtained; and in addition, steep bending transmission can be obtained through design. The invention provides a new mechanism of the optical isolation device; the processing tolerance can be obviously improved, and the stability and the expansibility are good; the design may be on-chip integrated using a semiconductor process.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Deep-etched SiO2 ridge waveguide and its preparing process
InactiveCN1743880AStrengthen restrictionsSmall bending radiusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingWaveguideSilicon dioxide
This invention discloses deep etched silicon dioxide rib waveguides and preparation thereof, which contains in turn depositing lower cladding, core cladding and upper cladding on substrate by silicon dioxide film deposition technology, etching penetrating upper cladding and core cladding by deep etching technology, etching part or all lower cladding, In said invention, the light field limitation is increased with reduced curve semidiameter and raised light integrity.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
All-fiber high-power middle- and far-infrared super-continuum spectrum light source
InactiveCN107046220AIncrease output powerEasy to integrateActive medium shape and constructionMode locked fiber laserPicosecond
The invention discloses an all-fiber high-power middle- and far-infrared super-continuum spectrum light source. The all-fiber high-power middle- and far-infrared super-continuum spectrum light source is characterized by comprising a thulium doped mode-locking fiber laser module, a thulium doped fiber amplification module, a first super-continuum (SC) spectrum generation module and a second SC spectrum generation module which are sequentially arranged, wherein the thulium doped mode-locking fiber laser module is used for generating a high-repeated frequency ultrashot pulse picoseconds or femtosecond, the thulium doped fiber amplification module is used for generating a high-power and high-order soliton pulse, the first SC spectrum generation module is used for generating high-power SC spectrum laser of 2-5 micrometers, the second SC spectrum generation module is used for generating high-power SC spectrum laser of 2-14 micrometers, and the thulium doped mode-locking fiber laser module, the thulium doped fiber amplification module, the first SC spectrum generation module and the second SC spectrum generation module all employ single-mode fibers. The all-fiber high-power middle- and far-infrared super-continuum spectrum light source has the advantages of low cost, high conversion efficiency, good output beam quality, wide bandwidth, simple and compact structure and high adaptive capacity to an environment.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
All-fiber pulsed fiber laser with composite chamber
ActiveCN102170082AImprove output efficiencyImproved output light pattern characteristicsOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionPhotoswitchEngineering
An all-fiber pulsed fiber laser device with a composite chamber comprises a semiconductor laser pumping source driven by a semiconductor laser pumping source driving module, a fiber wavelength division multiplexer, a gain medium fiber, a first optoisolator, a photo-coupler, a pigtailed photoswitch driven by a photoswitch driving module, and a second optoisolator, wherein an output terminal of the semiconductor laser pumping source is connected with a short wavelength input terminal of the fiber wavelength division multiplexer, an output terminal of the fiber wavelength division multiplexer is connected with an input terminal of the photo-coupler by successively passing through the gain medium fiber and the first optoisolator, an output terminal of the photo-coupler serves as an output terminal of the laser, one end of the pigtailed photoswitch is connected with a long wavelength input terminal of the fiber wavelength division multiplexer via the second optoisolator, a cascading interference chamber is arranged between the photo-coupler and the pigtailed photoswitch, an input terminal of the cascading interference chamber is connected with a feedback output terminal of the photo-coupler, and an output terminal of the cascading interference chamber is connected with the other end of the pigtailed photoswitch.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Silicon-based light transmitting-receiving component with parallel optical fiber transmission
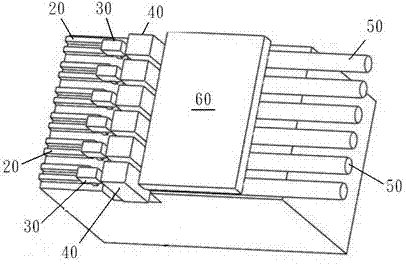
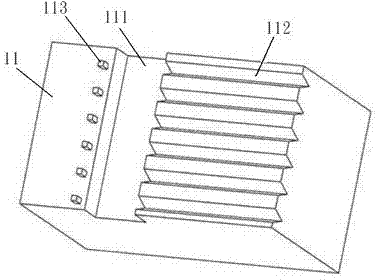
InactiveCN103676037AMeet the requirements of coupling toleranceImprove coupling efficiencyCoupling light guidesLaserFiber optic transmission
The invention provides a silicon-based light transmitting-receiving component with parallel optical fiber transmission. The silicon-based light transmitting-receiving component with parallel optical fiber transmission comprises a silicon substrate, multiple electrodes, multiple lasers / detectors, multiple lenses, multiple optical fiber heads and an optical fiber cover plate, wherein the silicon substrate comprises a surface plane which is provided with recess parts, multiple wire slots and positioning parts; the positioning parts and the front ports of the wire slots are spaced by the recess parts; the electrodes are arranged in parallel and are arranged on the front section of the surface plane in a convex manner; the lasers / detectors are connected to the electrodes and are mounted on the surface plane through the positioning parts; the lenses are mounted in the recess parts to correspond to the lasers / detectors; the optical fiber heads are arranged in the wire slots; one ends of the optical fiber heads close to the lenses are covered with the optical fiber cover plate. Through the structure or the combination thereof, the silicon-based light transmitting-receiving component is realized, and accordingly the good effects of reducing the volume, bringing convenience to the manufacturing and lowering the cost are achieved.
Owner:WUHAN TELECOMM DEVICES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com