Serially connected optical switch based photon delay structure and numerical-control integrated photon delay device
A technology of delay device and integrated photonics, applied in the direction of optical waveguide light guide, optical waveguide coupling, etc., can solve the problems of inability to achieve large delay tuning, limited operating bandwidth, large energy consumption, etc., to achieve fast delay switching capability, RF broadband transparency , the effect of fast tuning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
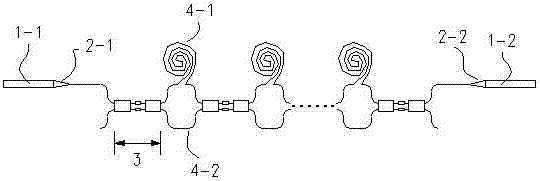
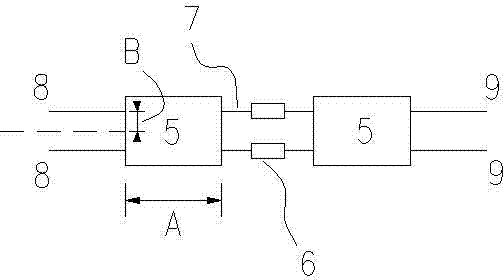
[0031] A digitally controlled integrated photon delay device based on a series optical switch, the digitally controlled integrated photon delay device is composed of two sections of coupling fibers, two mode-spot converters, a plurality of optical switches 3 and multiple sections of single-mode waveguides; the two sections of coupling fibers are respectively Recorded as input coupling fiber 1-1 and output coupling fiber 1-2; the mode spot converter is a waveguide shaped as an isosceles trapezoid, and the long base of the isosceles trapezoid forms the input end of the mode spot converter, and the isosceles trapezoid The narrow bottom edge of the optical switch 3 forms the output end of the speckle converter, and the two speckle converters are respectively recorded as the input speckle converter 2-1 and the output speckle converter 2-2; the optical switch 3 is an SOI-MMI optical switch, the optical switch 3 adopts a dual-input dual-output mode;
[0032] The output end of the inp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com