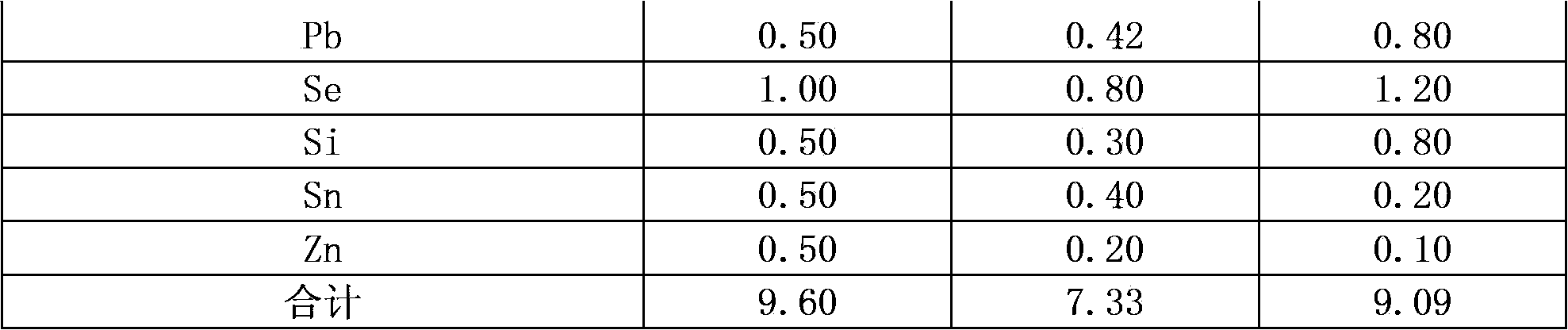
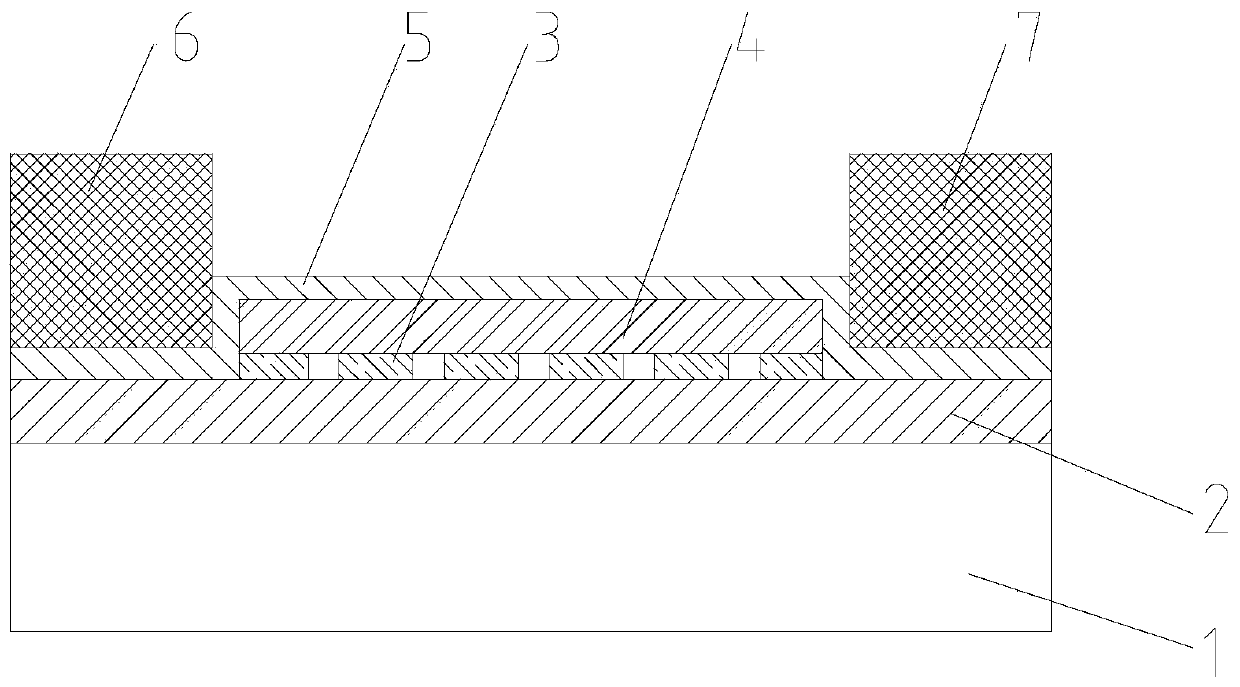
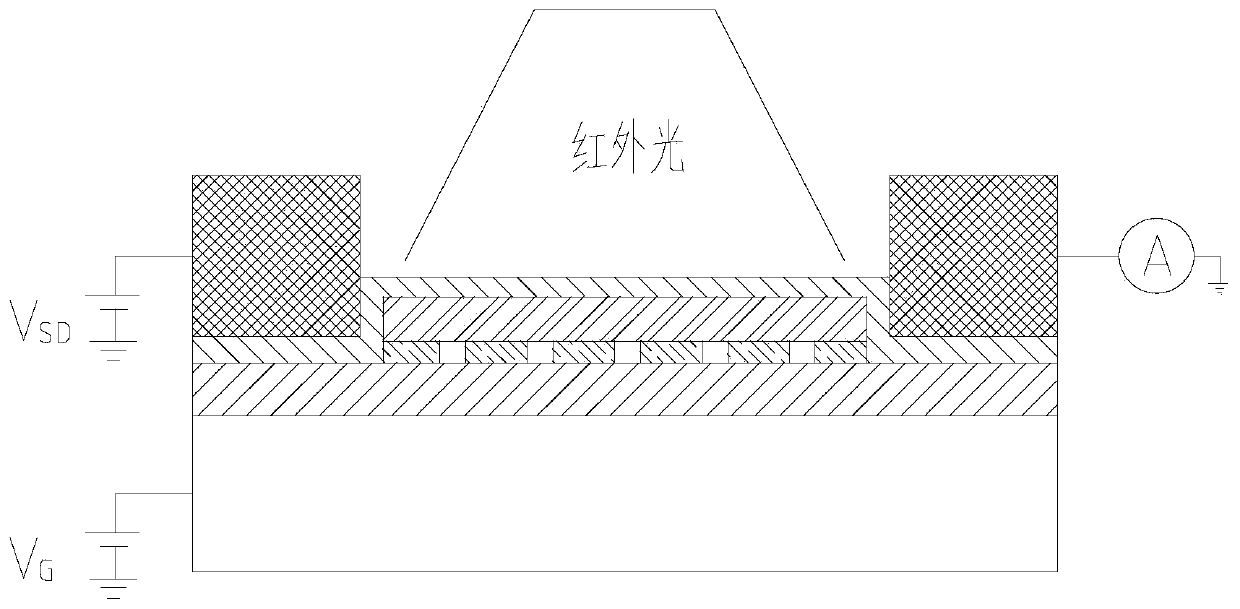
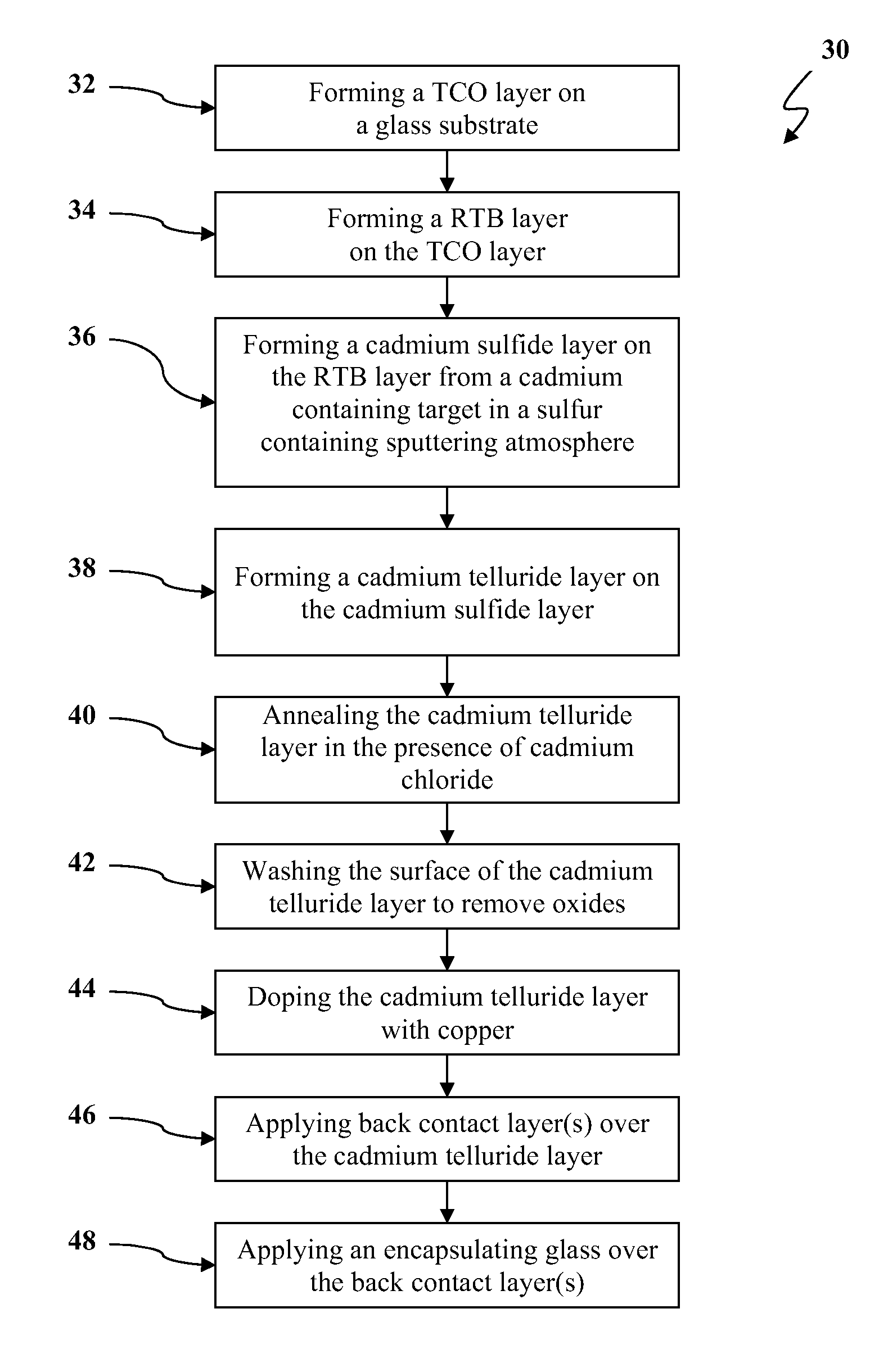
Patents
Literature
223 results about "Mercury cadmium telluride" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
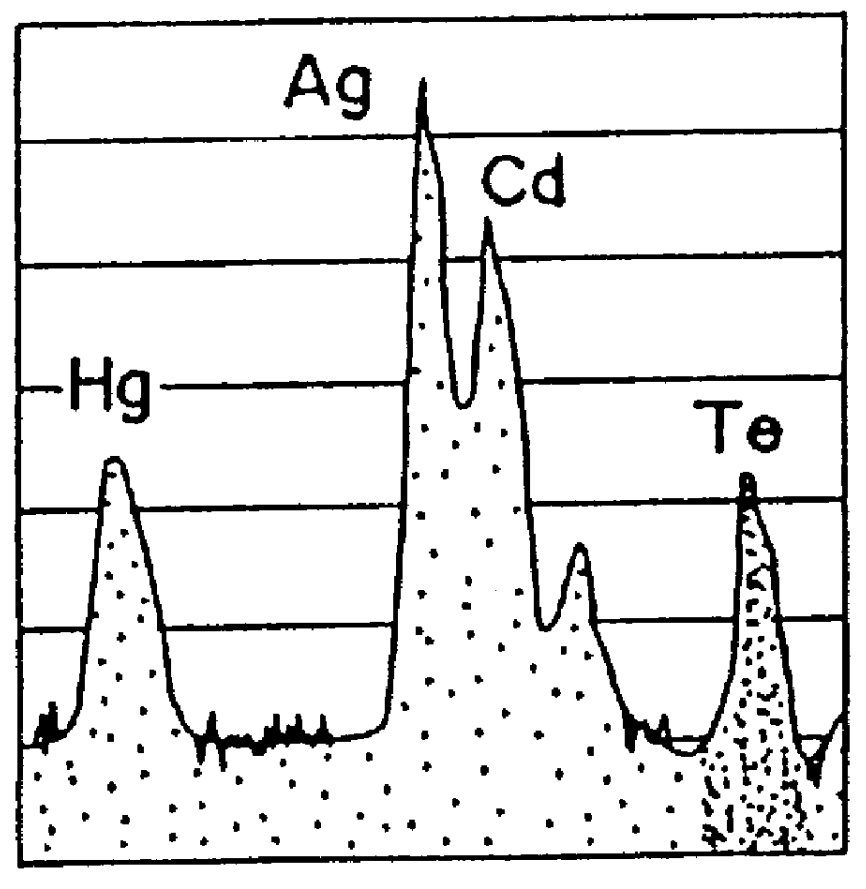
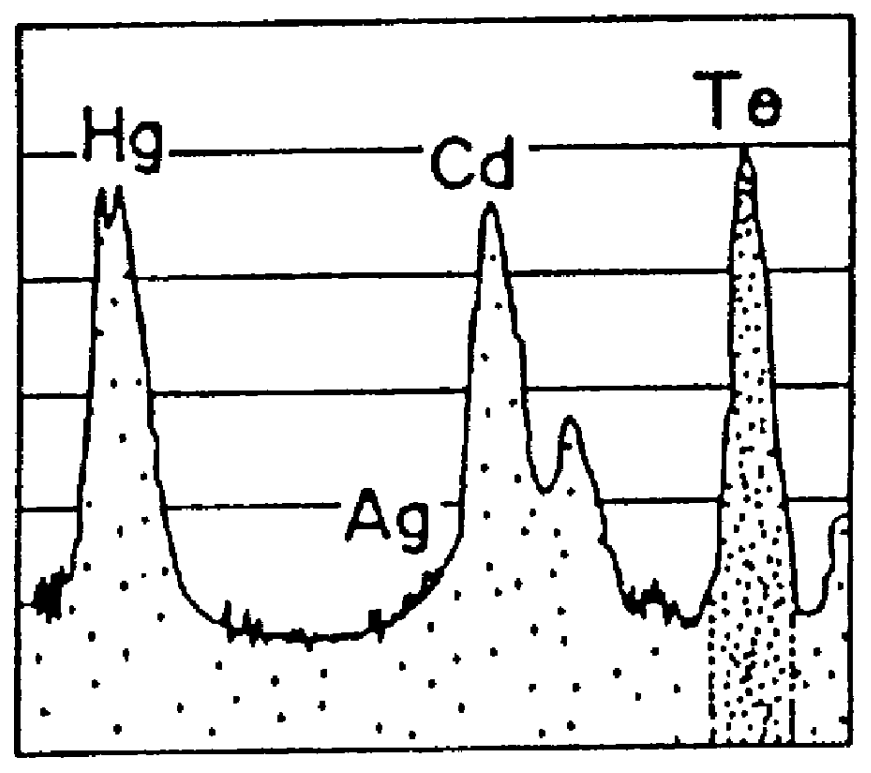
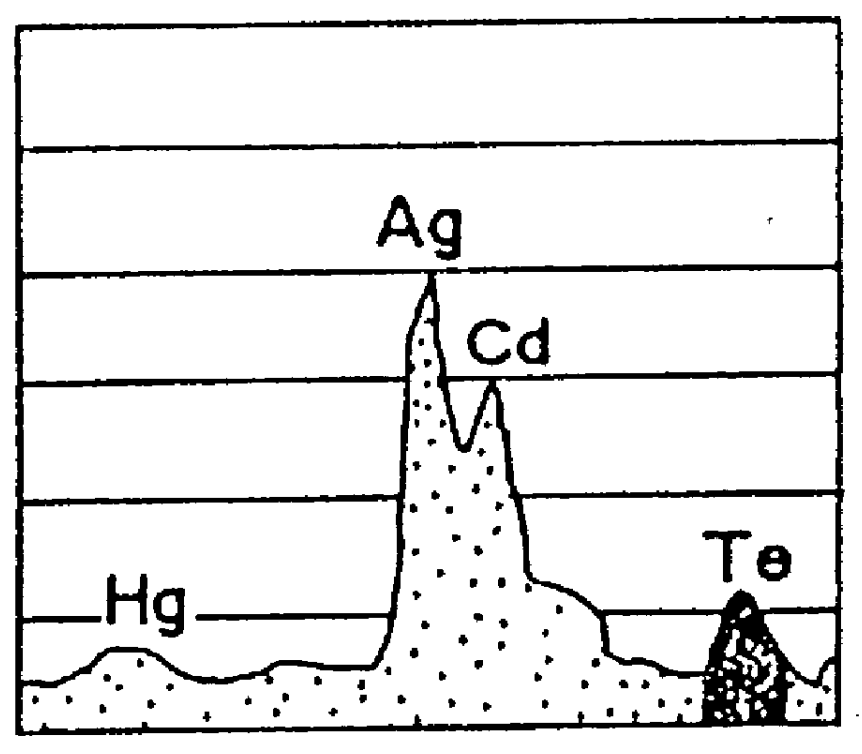
Hg₁₋ₓCdₓTe or mercury cadmium telluride (also cadmium mercury telluride, MCT, MerCad Telluride, MerCadTel, MerCaT or CMT) is an chemical compound of cadmium telluride (CdTe) and mercury telluride (HgTe) with a tunable bandgap spanning the shortwave infrared to the very long wave infrared regions. The amount of cadmium (Cd) in the alloy can be chosen so as to tune the optical absorption of the material to the desired infrared wavelength. CdTe is a semiconductor with a bandgap of approximately 1.5 electronvolts (eV) at room temperature. HgTe is a semimetal, which means that its bandgap energy is zero. Mixing these two substances allows one to obtain any bandgap between 0 and 1.5 eV.
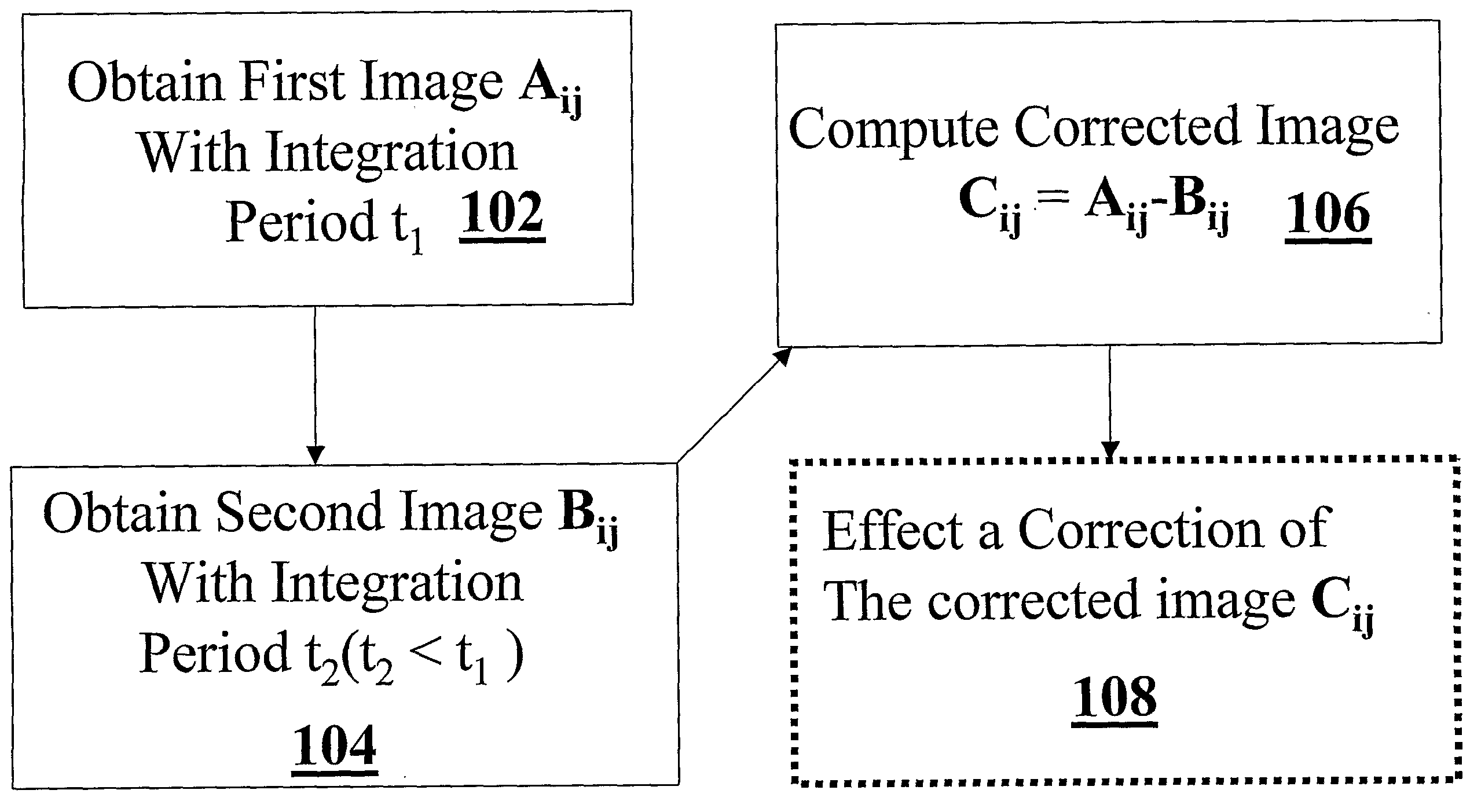
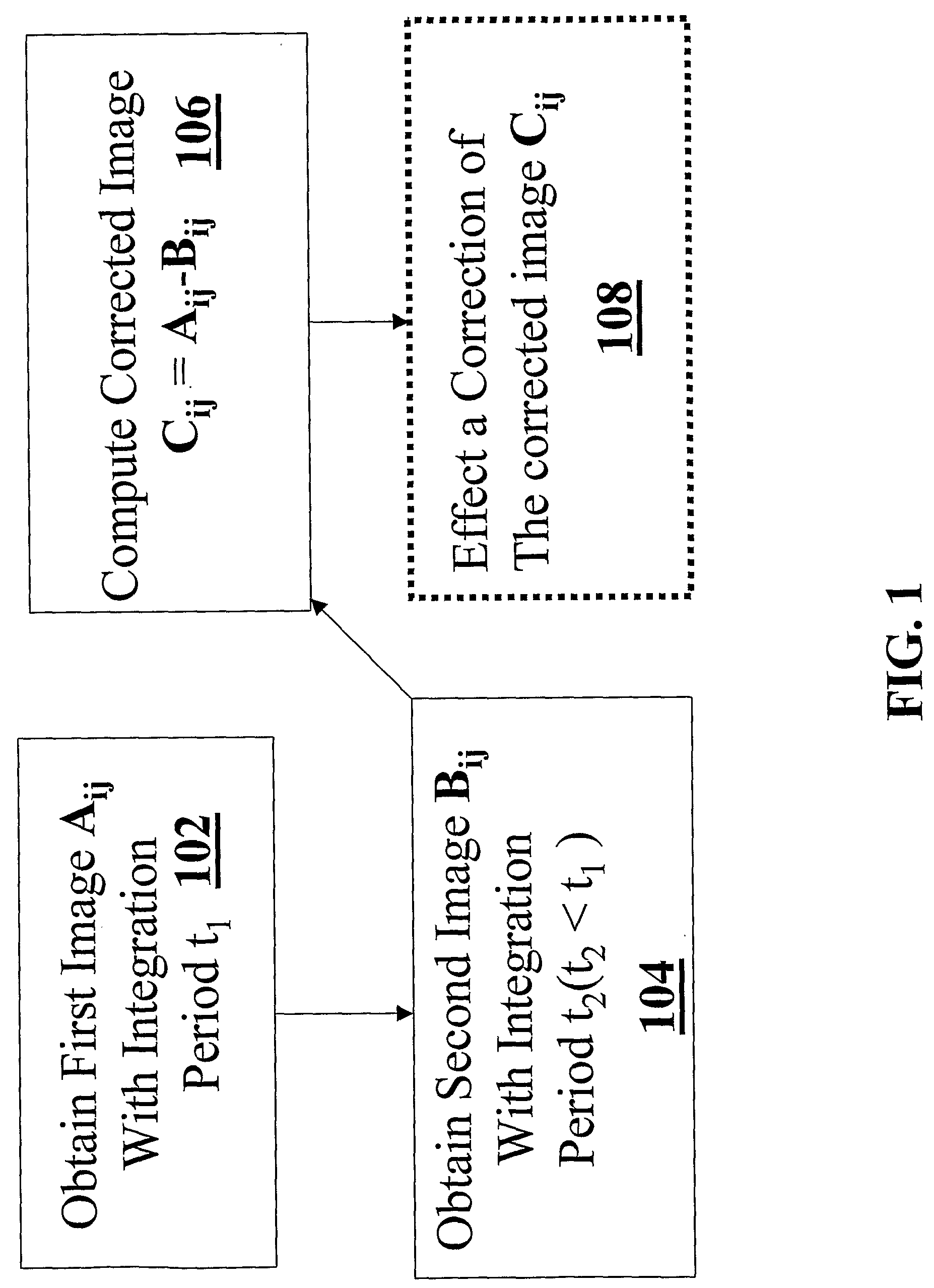
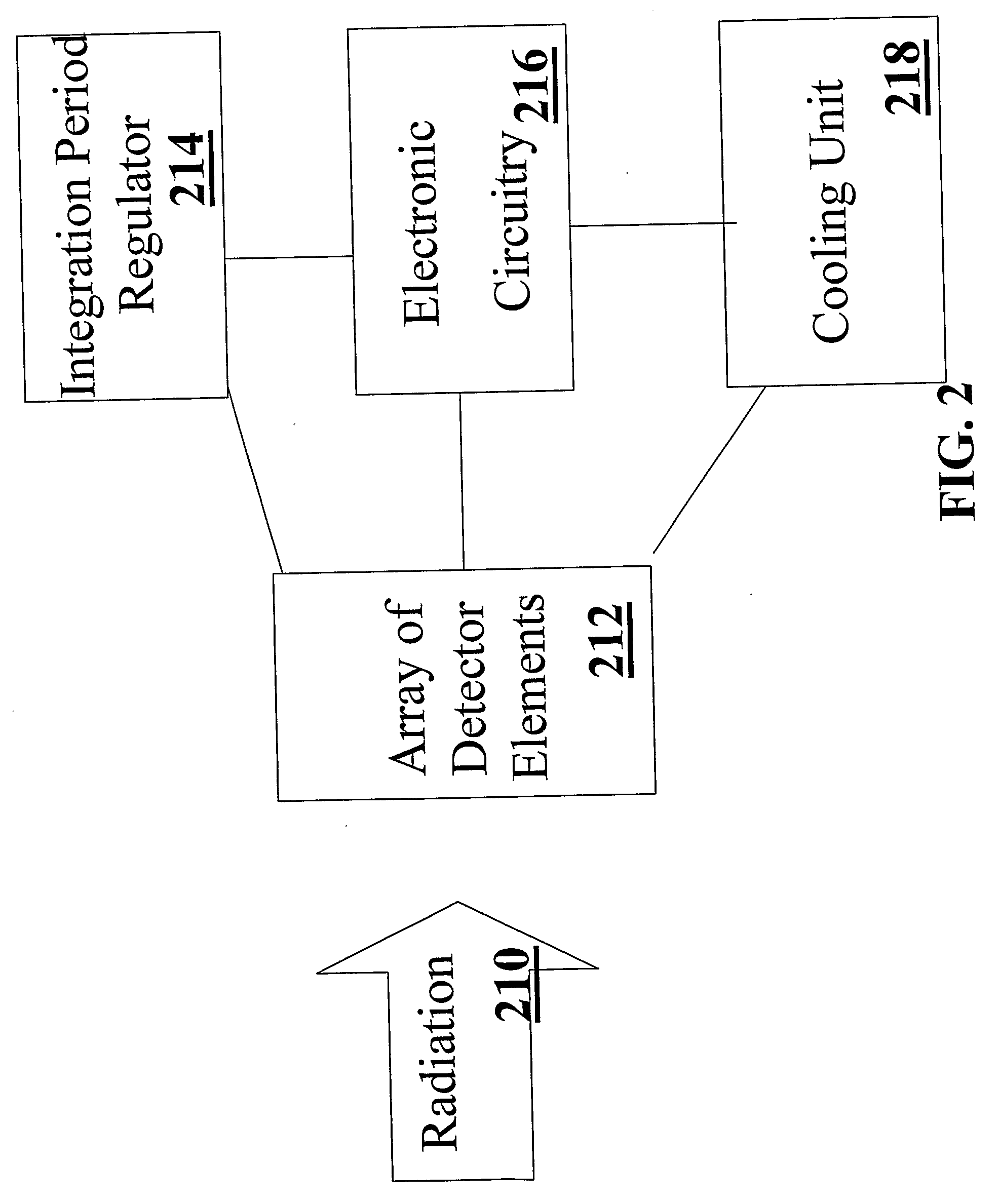
Non-uniformity correction of images generated by focal plane arrays of photodetectors
ActiveUS20090079854A1Reduce residual non-uniformityEliminate unevennessImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
Methods and apparatus for effecting a non-uniformity correction of images of a scene obtained with an array of detector elements are disclosed. A first image of the scene having a first integration period is acquired using the array of detector elements. A second image of the scene having a different integration period is acquired, and a corrected image of the scene is generated by computing a difference of the images. In some embodiments, the first and second images are images of substantially identical scenes. According to some embodiments, the images are infrared images. Optionally, the corrected image is subjected to further correction using pixel dependent correction coefficients, such as gain coefficients. Exemplary image detection elements include but are not limited to InSb detector elements and ternary detector elements, such as InAlSb, MCT (Mercury Cadmium Telluride), and QWIP technology (Quantum Well Infrared Photodiodes). In some embodiments, the detector elements are cooled to a temperature substantially equal to an atmospheric boiling point of liquid nitrogen. Alternatively, the detector elements are cooled to a temperature below an atmospheric boiling point of liquid nitrogen, or any other operating temperature.
Owner:RAFAEL ADVANCED DEFENSE SYSTEMS
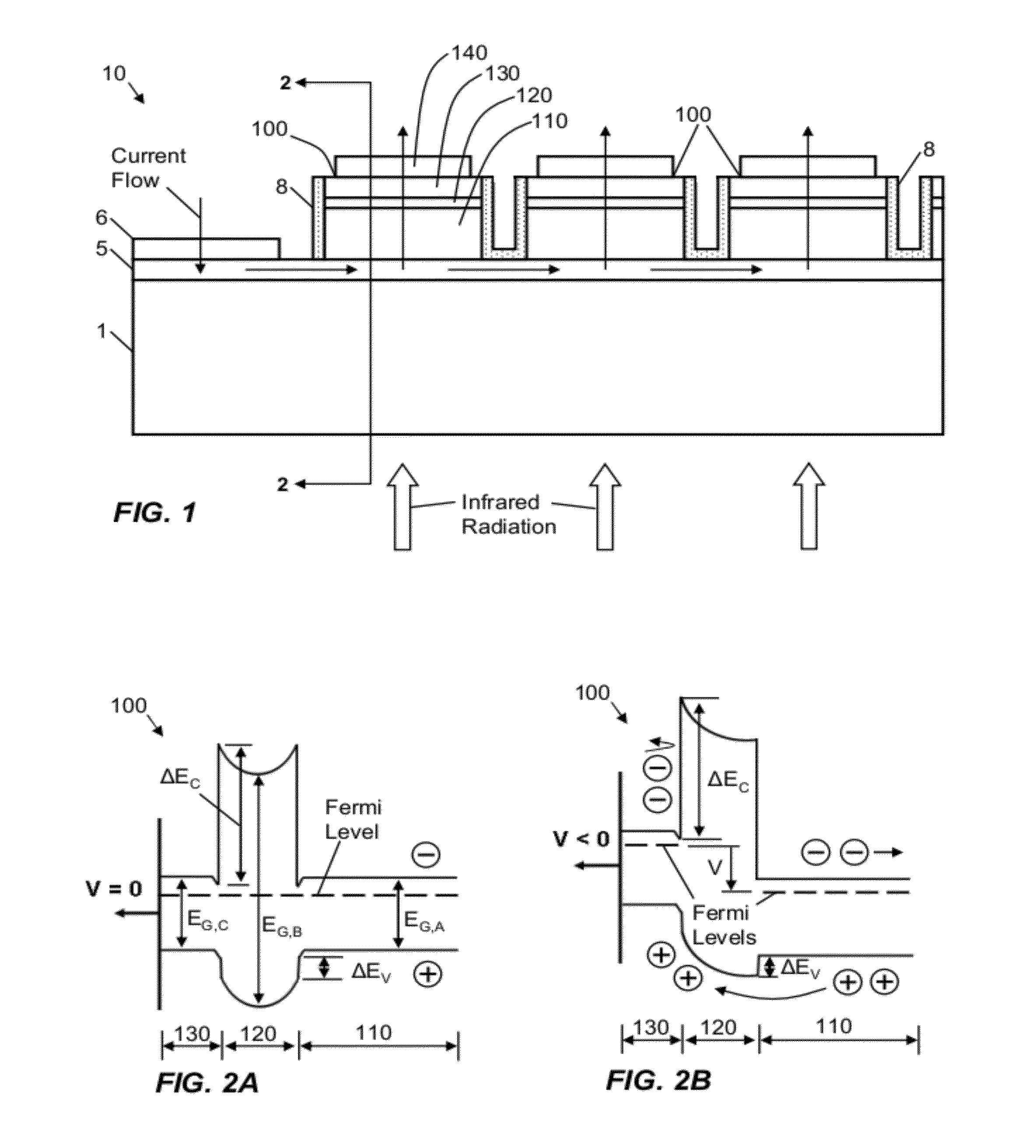
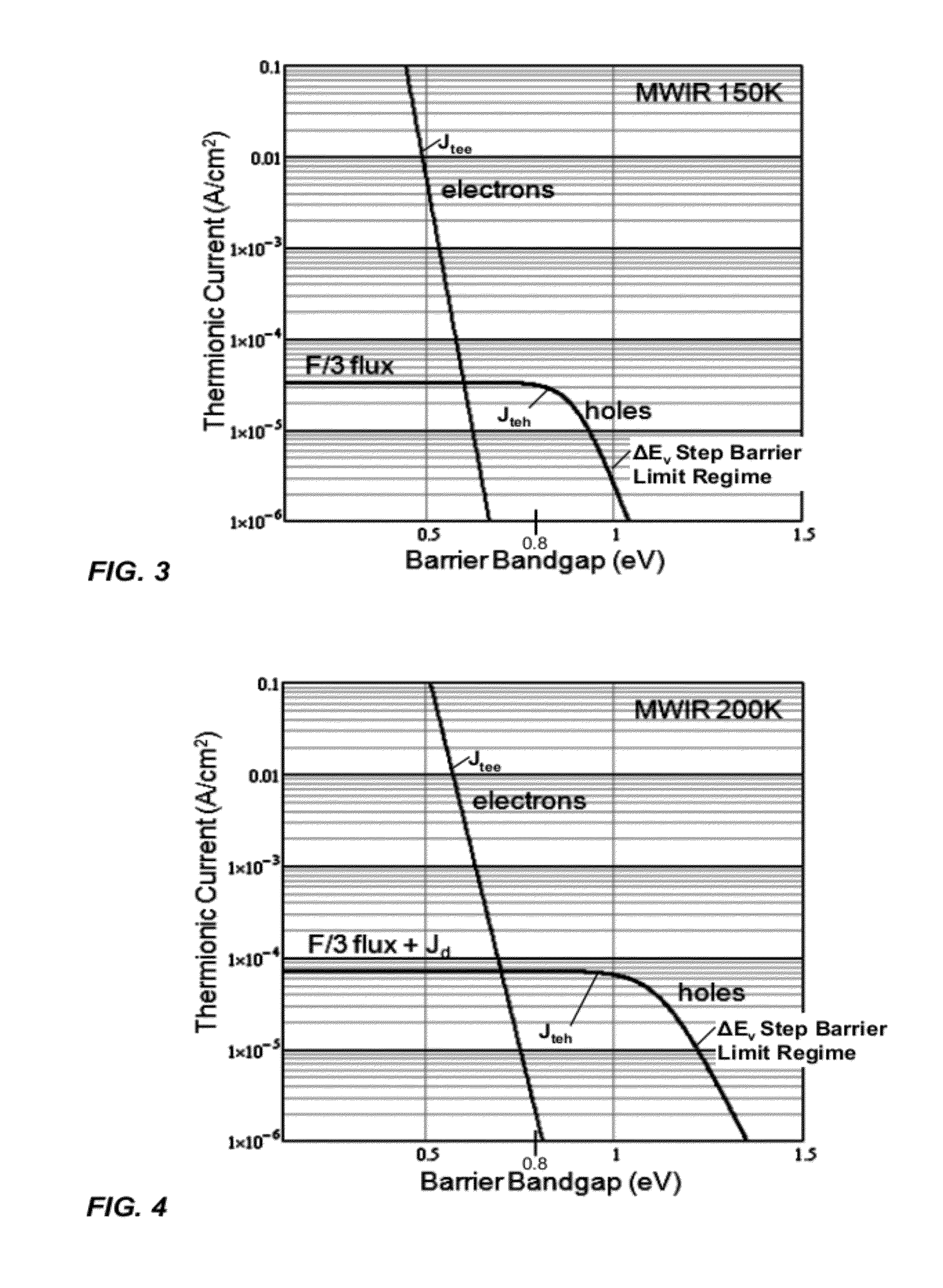
MINORITY CARRIER BASED HgCdTe INFRARED DETECTORS AND ARRAYS
ActiveUS20120273838A1Less expensiveReduce manufacturing costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantManufacturing cost reduction
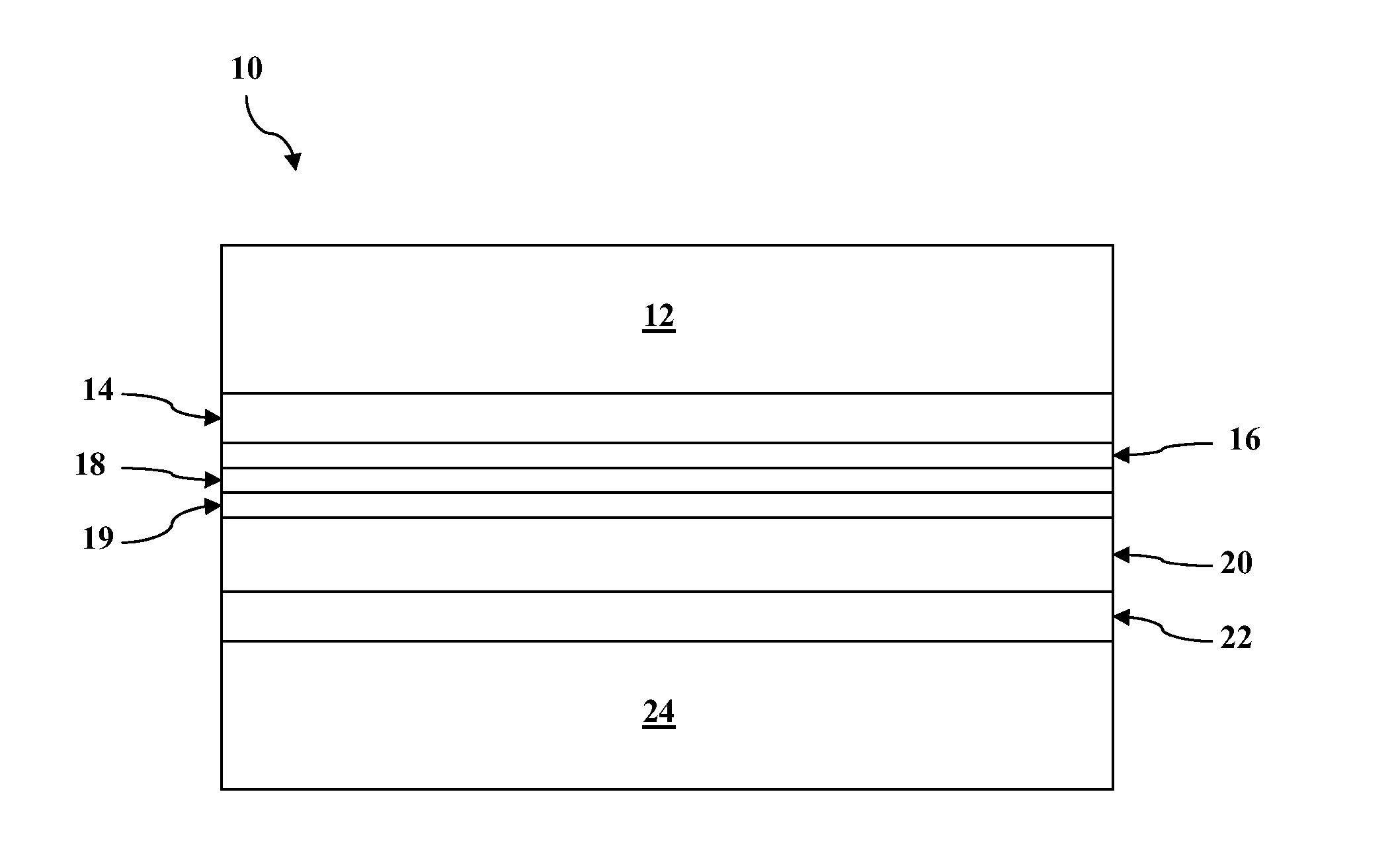
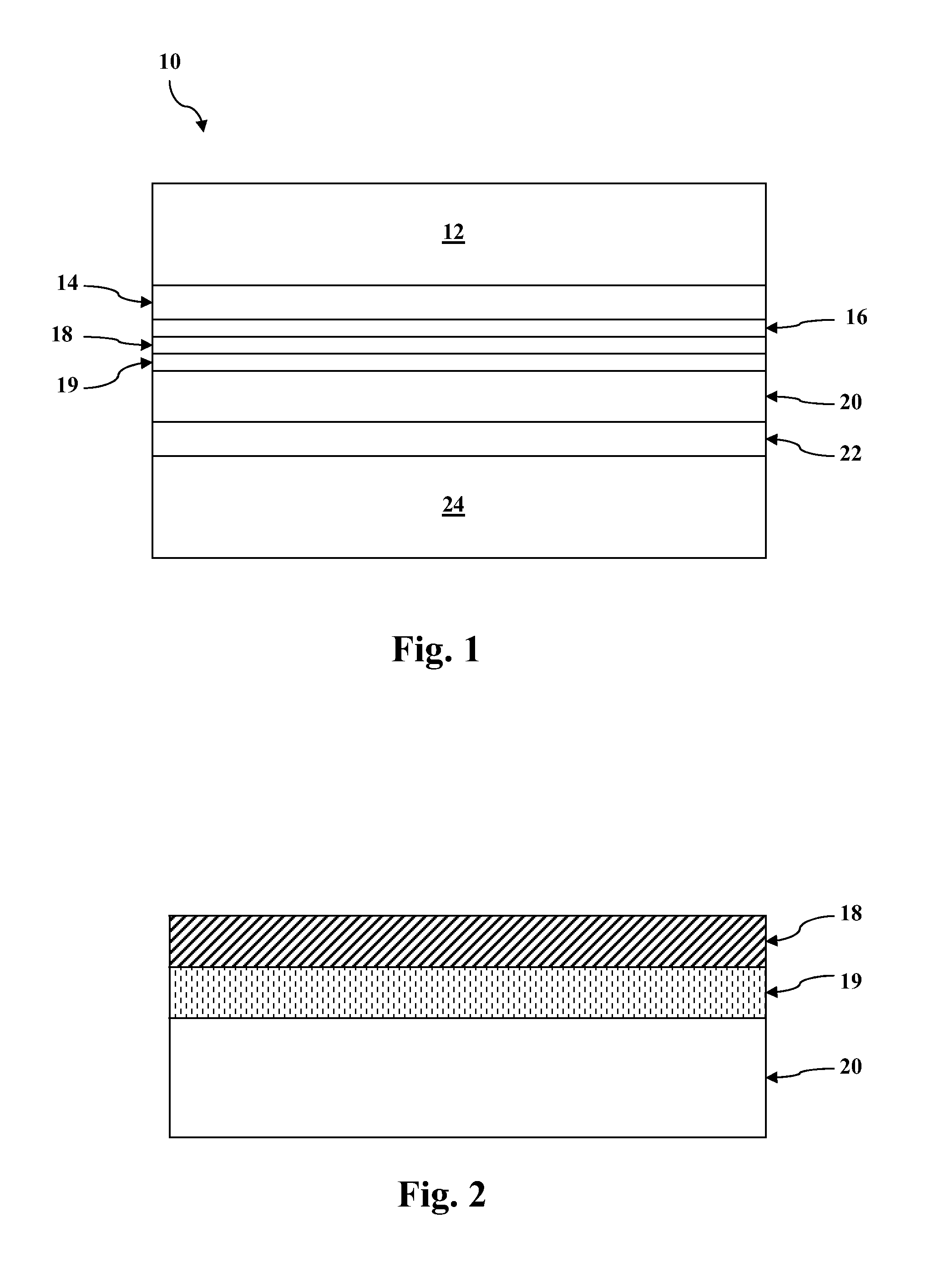
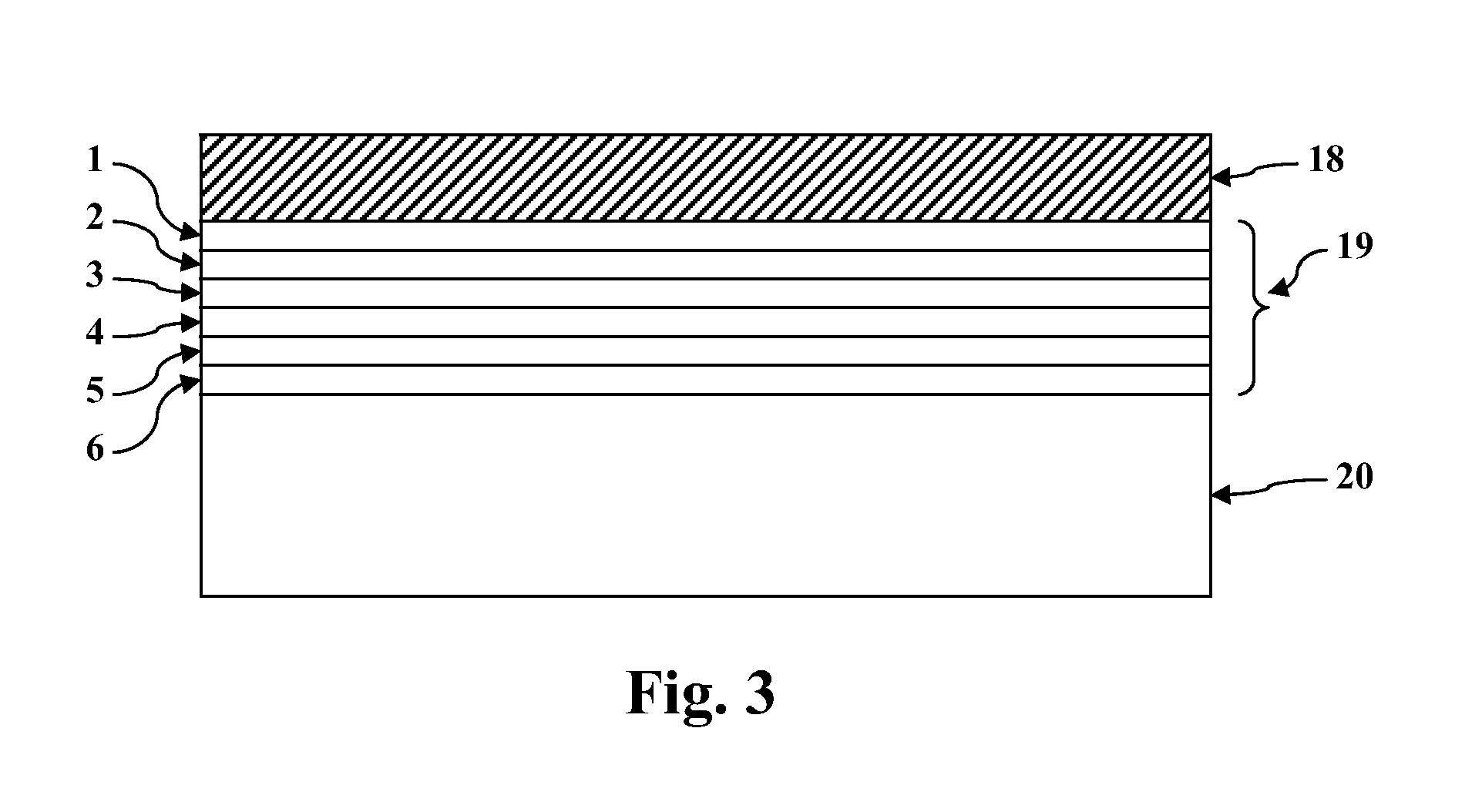
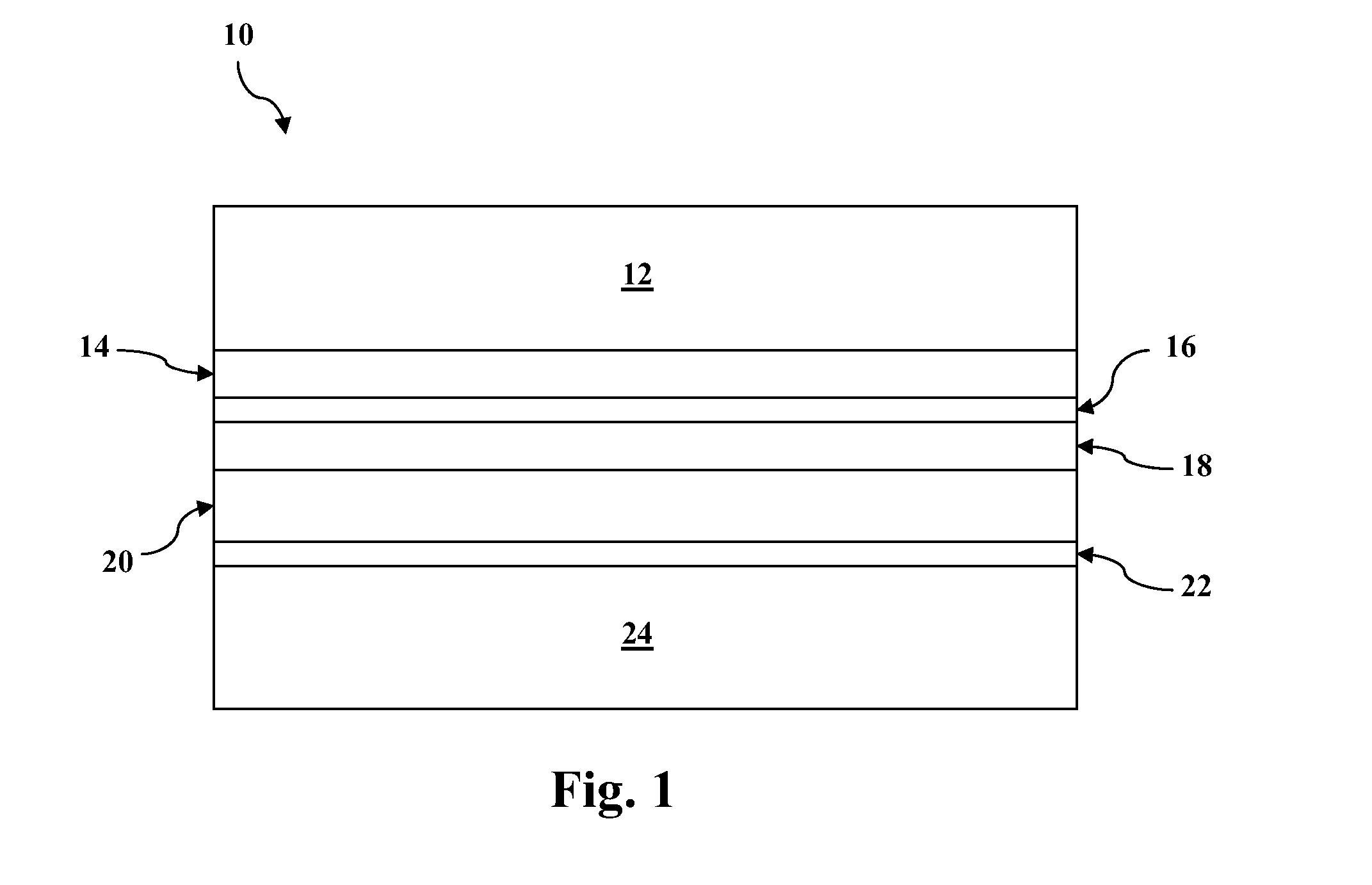
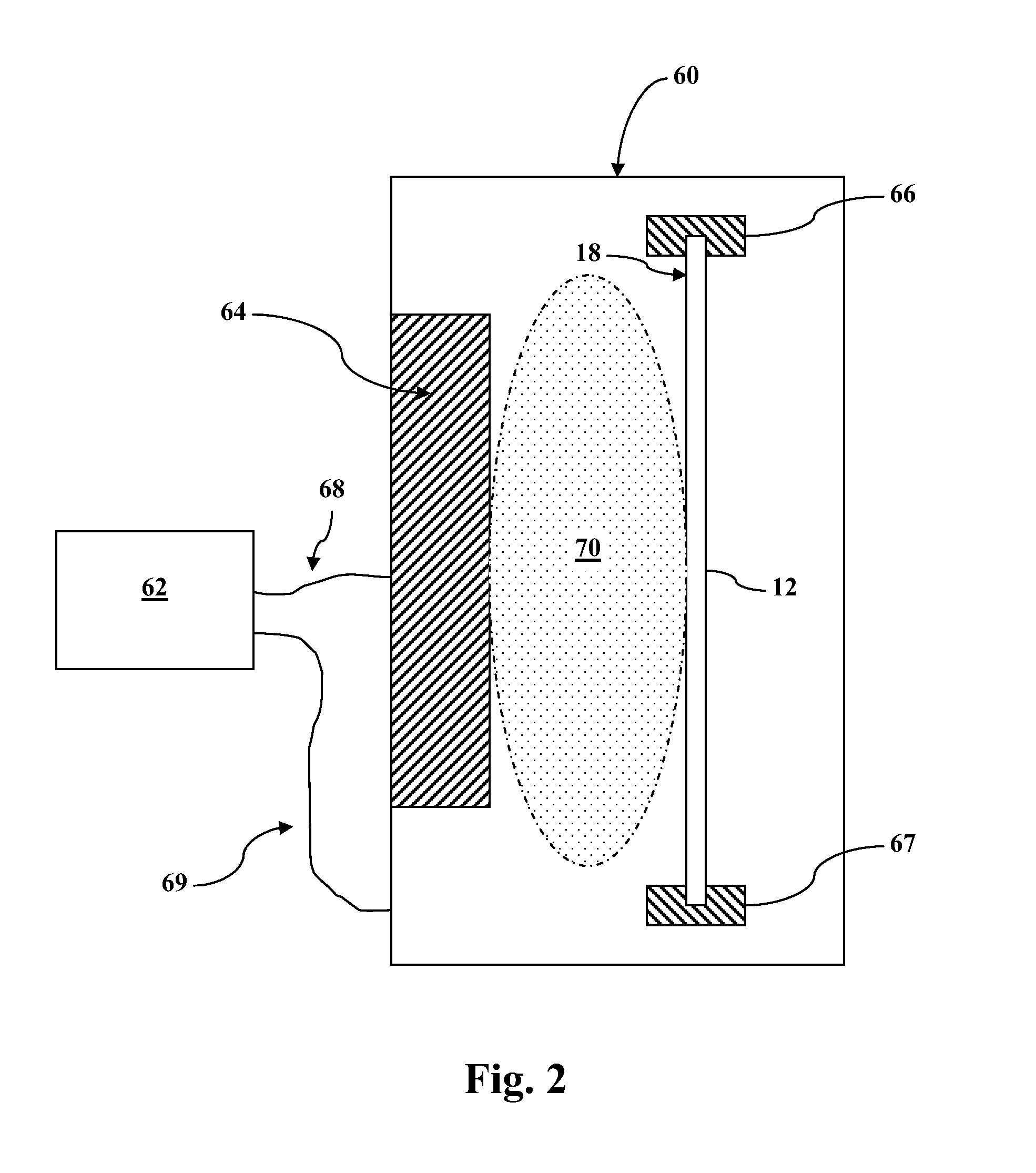
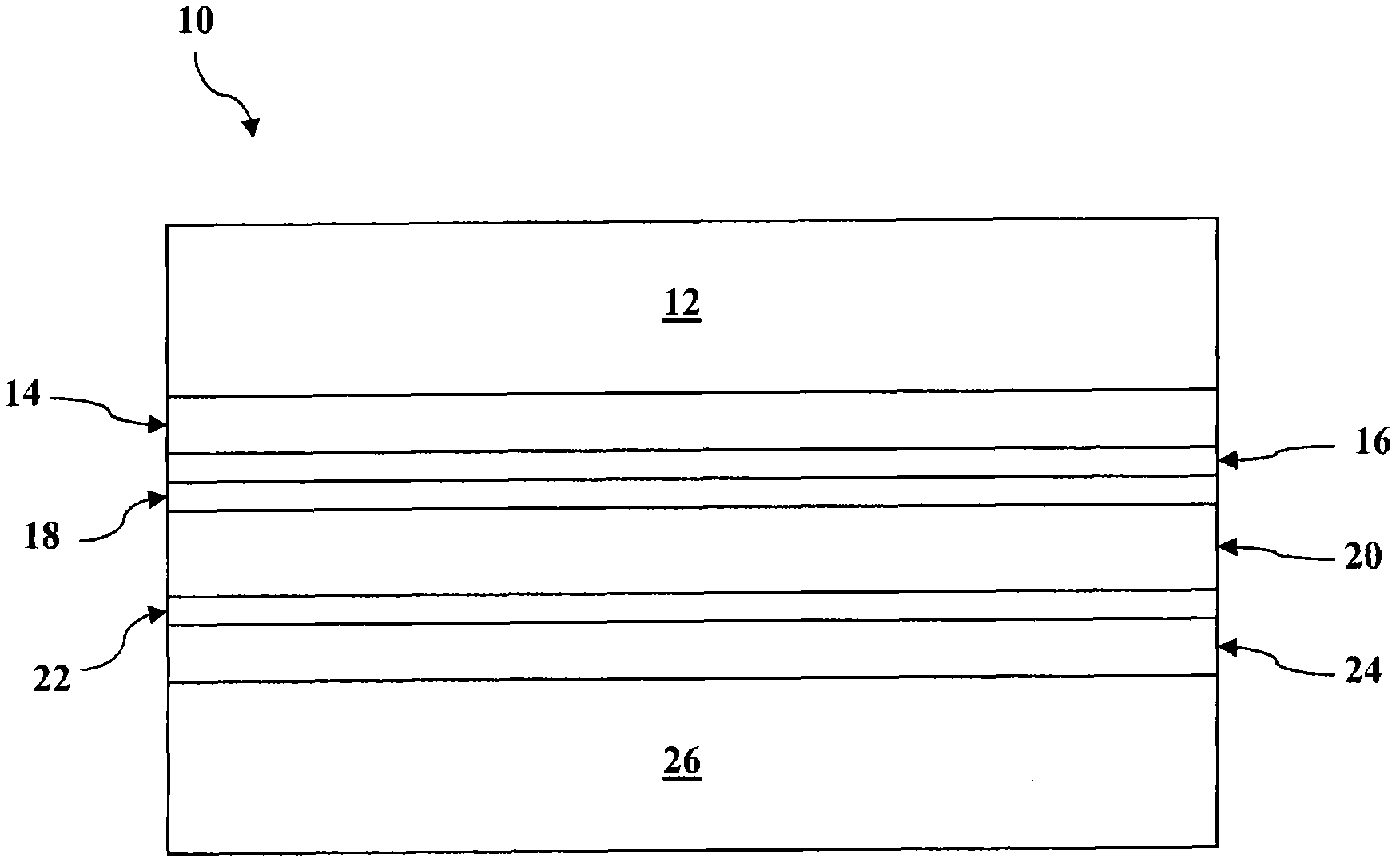
Disclosed are minority carrier based mercury-cadmium telluride (HgCdTe) infrared detectors and arrays, and methods of making, are disclosed. The constructions provided by the invention enable the detectors to be used at higher temperatures, and / or be implemented on less expensive semiconductor substrates to lower manufacturing costs. An exemplary embodiment a substrate, a bottom contact layer disposed on the substrate, a first mercury-cadmium telluride layer having a first bandgap energy value disposed on the bottom contact layer, a second mercury-cadmium telluride layer having a second bandgap energy value that is greater than the first bandgap energy value disposed on the first mercury-cadmium telluride layer, and a collector layer disposed on the second mercury-cadmium telluride layer, wherein the first and second mercury-cadmium telluride layers are each doped with an n-type dopant.
Owner:DRS NETWORK & IMAGING SYST
Synthesis method for cadmium selenide and cadmium telluride quantum dot
InactiveCN1631793ANarrow size distributionReduce consumptionCadmium compoundsBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsFluorescenceSynthesis methods
The invention belongs to the method for compounding cadmium selenide and quanta of cadmium telluride, which is: use cadmium oxide containing 2~18 carbon atom as cadmium source, selenium powder as selenium source and tellurium powder as tellurium source, and the mol ratio of cadmiumsource and selenium source or tellurium source is 5:1-1:5, dissolve the selenium and tellurium powder with tricapryl phosphine, make oleic acid, and tricapryl phosphine oxide as enveloping agent and the mol ratio of cadmium source and enveloping agent is 1:2-1:6, use benzene, toluene, cyclohexane, normal hexane and normal heptane as solvent, under the condition that the density of cadmium source is 0.001-0.015M, the temperature in autoclave is 140-180deg.C, heat them for 0.8-16 hours and obtain cadmium selenide and quanta of cadmium telluride with different sizes by changing the reaction time. The cadmium selenide and quanta of cadmium telluride has narrower size distribution which is shown as narrower shooting of fluorescence whose half-peak width of quanta of cadmium selenide is 22-33nm and that of quanta of cadmium telluride is 29-35nm.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
Mixed sputtering target of cadmium sulfide and cadmium telluride and methods of their use
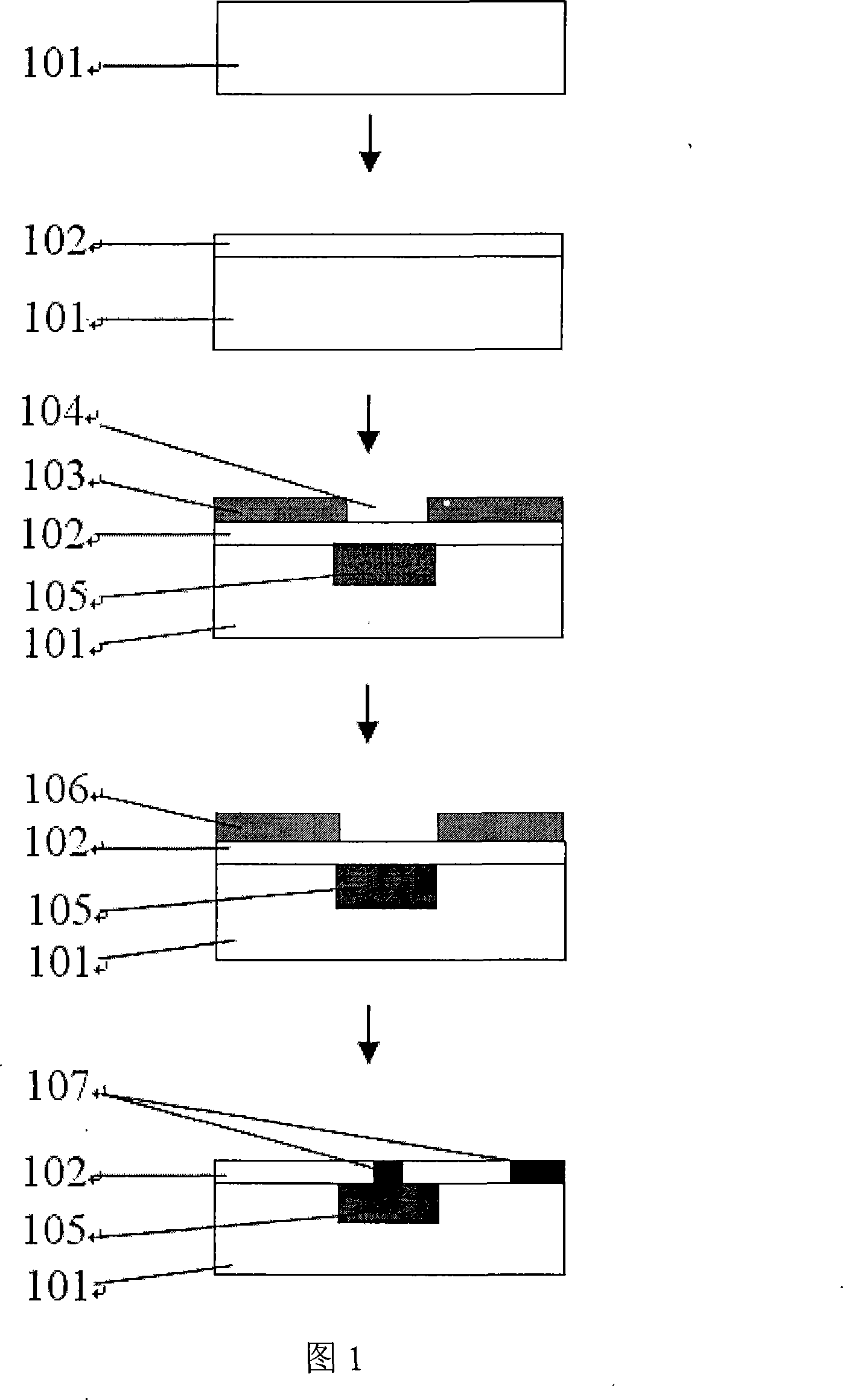
Mixed targets are generally disclosed for sputtering an intermixed layer of cadmium sulfide and cadmium telluride. The mixed target can include cadmium sulfide, and cadmium telluride. Methods of forming the mixed target are also provided. For example, a powdered blend can be formed from powdered cadmium sulfide and powdered cadmium telluride, and pressed into a mixed target Methods are also generally disclosed for manufacturing a cadmium telluride based thin film photovoltaic device having an intermixed layer. For example, a mixed target of cadmium sulfide and cadmium telluride can be sputtered directly on a cadmium sulfide layer to form an intermixed layer, and a cadmium telluride layer can be formed on the intermixed layer.
Owner:FIRST SOLAR INC (US)
Preparation method for cadmium telluride
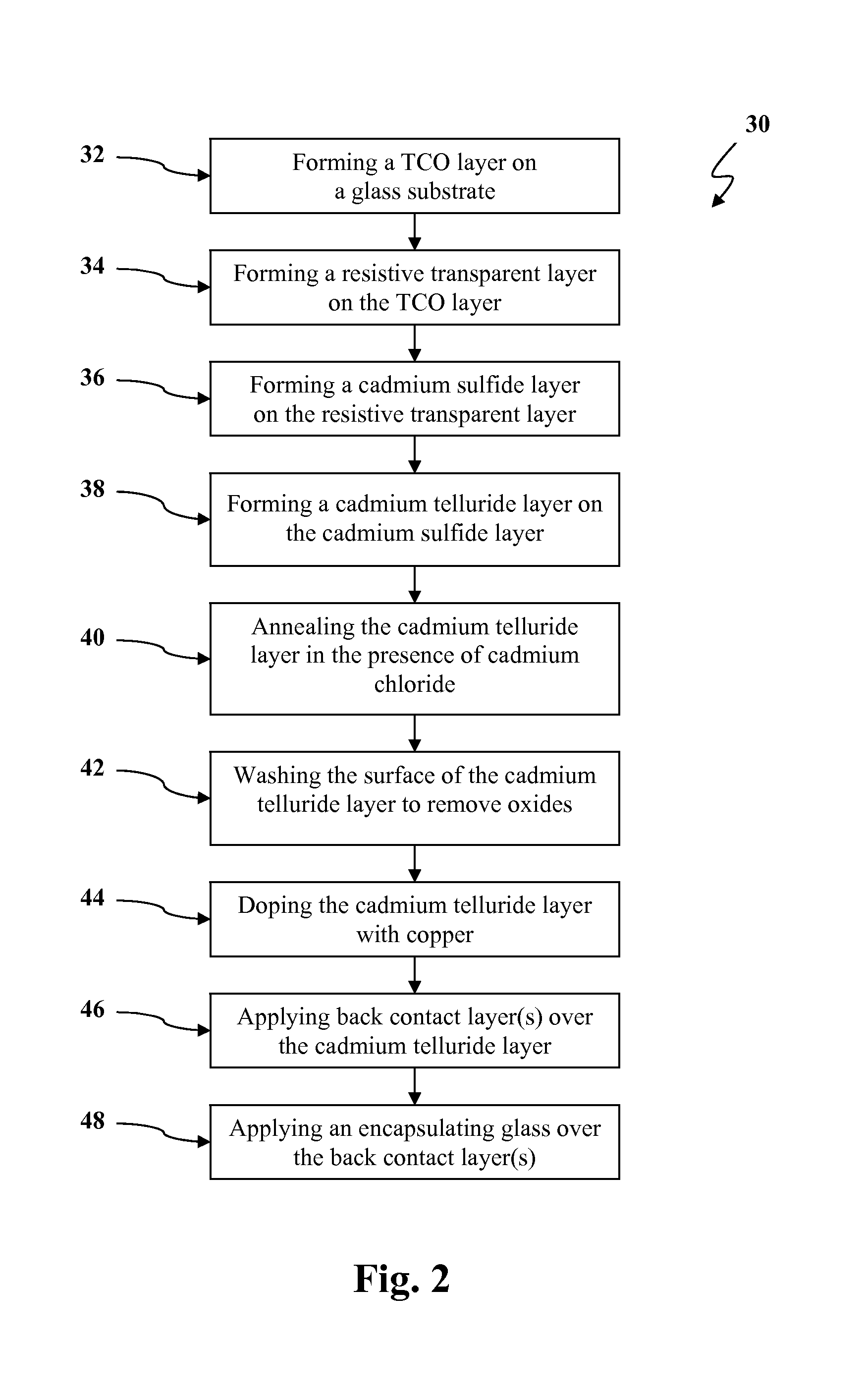
ActiveCN103420346AFully synthesizedSynthetic heating evenlyCadmium compoundsMetal selenides/telluridesMercury cadmium tellurideRoom temperature
The invention provides a preparation method for cadmium telluride. The method comprises a first synthesis and a second synthesis. The first synthesis comprises steps: tellurium and cadmium are mixed and placed in a first graphite boat; the first graphite boat is then placed in a first quartz tube; the first quartz tube is then placed in a first synthetic furnace; a first inert gas is introduced to empty air in the first quartz tube; a first multi-section heating and heat preservation process is carried out, the first inert gas is introduced in the front section and a first reducing gas is introduced in the back section; after the synthetic reaction, the first synthetic furnace is cooled to room temperature in sections, the first reducing gas is introduced in the front section and the first inert gas is introduced in the back section; first synthetics are obtained. The second synthesis comprises steps: the first synthetics are placed in a second graphite boat; the second graphite boat is then placed in a second quartz tube; the second quartz tube is then placed in a second synthetic furnace; a second inert gas is introduced to empty air in second first quartz tube; a second multi-section heating and heat preservation process is carried out, a second inert gas is introduced in the front section and a second reducing gas is introduced in the back section; after the synthetic reaction, heating is stopped, the second synthetic furnace is cooled to room temperature in sections, the second reducing gas is introduced in the front section and the second inert gas is introduced in the back section; second synthetics are obtained.
Owner:XIANDAO THIN FILM MATERIALS GUANGDONG CO LTD
Graphene mid-infrared light detector based on plasmon enhancement and preparation method
InactiveCN111554757APromote absorptionHigh resonance factorFinal product manufactureNanotechnologyHigh energyMaterials science
The invention discloses a graphene mid-infrared light detector based on plasmon enhancement, and belongs to the technical field of mid-infrared light detection. The graphene mid-infrared light detector comprises a silicon substrate, a silicon dioxide layer, a graphene micro-nano array and a dielectric layer which are sequentially stacked from bottom to top, wherein the graphene micro-nano array and the dielectric layer are positioned in the middle of the silicon dioxide layer; the surfaces of the silicon dioxide layer and the dielectric layer are covered with a graphene layer; and a first electrode and a second electrode are arranged on the two sides of the graphene layer respectively. According to the infrared detector manufactured by using the structure, the photoelectric conversion efficiency is greatly improved, the preparation method is simple, the infrared detector is compatible with the existing silicon process, the problems of continuous low-temperature refrigeration, high energy consumption, weak signal and the like of the traditional infrared detector using mercury cadmium telluride, indium antimonide and the like are solved, and the operation cost performance is greatlyimproved.
Owner:深圳激子科技有限公司
Methods of sputtering cadmium sulfide layers for use in cadmium telluride based thin film photovoltaic devices
InactiveUS7943415B1Final product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingSputteringMercury cadmium telluride
Methods are generally provided of sputtering a cadmium sulfide layer on a substrate. The cadmium sulfide layer can be sputtered on a substrate from a target in a sputtering atmosphere, wherein the target comprises about 75% to about 100% by weight cadmium, and wherein the sputtering atmosphere comprises a sulfur-containing source gas. The cadmium sulfide layer can be used in methods of forming cadmium telluride thin film photovoltaic devices.
Owner:FIRST SOLAR INC (US)
Substrate material for mercury cadmium telluride material growth by liquid phase epitaxy method and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101348941AImprove lattice qualityQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthMaterial growthProcess equipment
The invention relates to a substrate material used for the growth of a mercury cadmium telluride material by a liquid phase epitaxy method. On the basis of the prior substrate material, a layer of cadmium zinc telluride single-crystal film completely matched with the lattice constant of mercury cadmium telluride is grown. The substrate material of the invention has the advantages that an epitaxial film has high lattice quality, and compositions can be flexibly adjusted according to the lattice constants of short wave, medium wave and long wave mercury cadmium telluride materials; meanwhile, the cadmium zinc telluride film has even compositions; the method adopts mature process, and has the advantages of simpler process equipment, short process cycle and low cost; and the substrate material with large area, high quality and high composition evenness can be provided for an infrared focal plane detector.
Owner:11TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
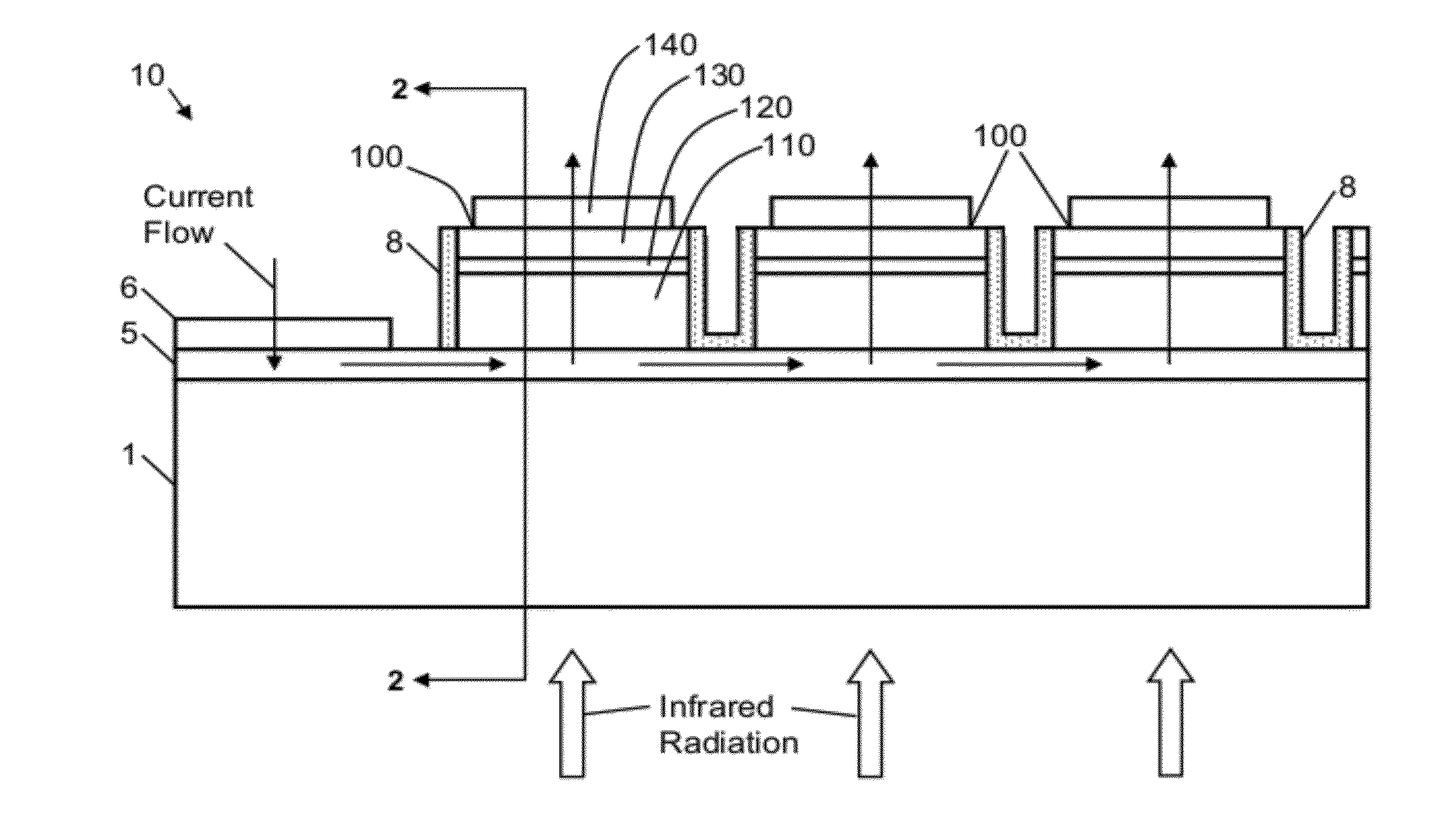
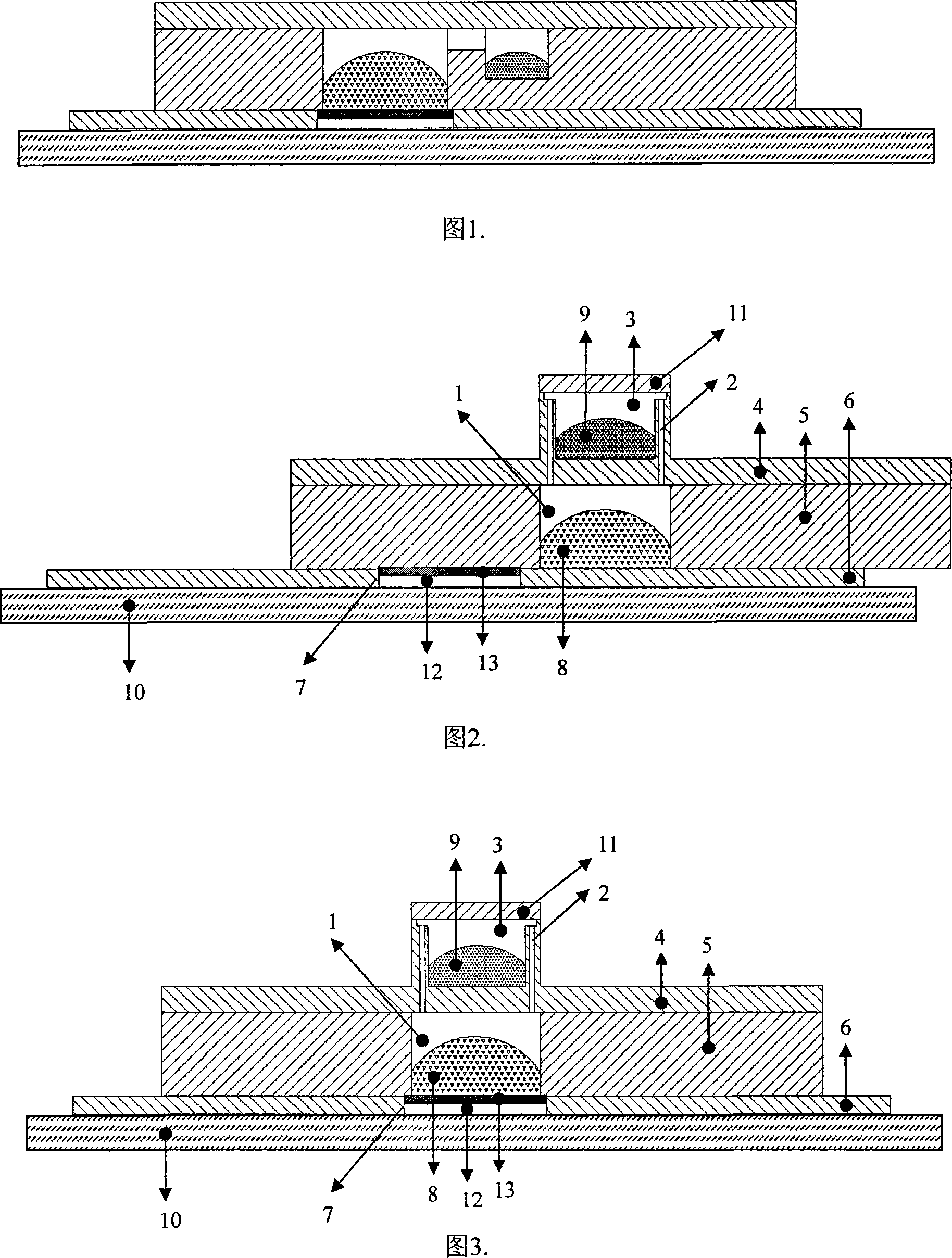
Back-illuminated mercury cadmium telluride long-wave light-guide type infrared flat-panel detector
ActiveCN101728403AReduce intervalImprove accuracySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPhotometryEpoxyZinc selenide
The invention discloses a back-illuminated mercury cadmium telluride long-wave light-guide type infrared flat-panel detector. The detector is characterized by comprising a zinc selenide substrate and a mercury cadmium telluride sheet fixed on the substrate by epoxy glue, wherein one face of the mercury cadmium telluride sheet, which is in contact with the substrate, is provided with an anodized layer and a ZnS anti-reflection layer, and the double-layer passivation surface on the surface of the mercury cadmium telluride sheet forms an a photosensitive element area array and a signal extraction electrode area and a common electrode area which are respectively positioned at both ends of a photosensitive element by photoengraving. The signal extraction electrode area and the common electrode area are both extracted from the back side of a light collection surface, an indium bump grows in a specified area, another indium bump grows on a signal reading circuit board, and the indium bumps are interconnected. An indium bump of a chip electrode and an indium bump of an electrode plate are connected together. An indium layer, an aurum layer and indium bumps are orderly grow on the signal electrode area and the common electrode area, thereby forming the back-illuminated mercury cadmium telluride long-wave light-guide type infrared flat-panel detector.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of p-type doping of cadmium telluride
InactiveUS8748214B2Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantHalogen
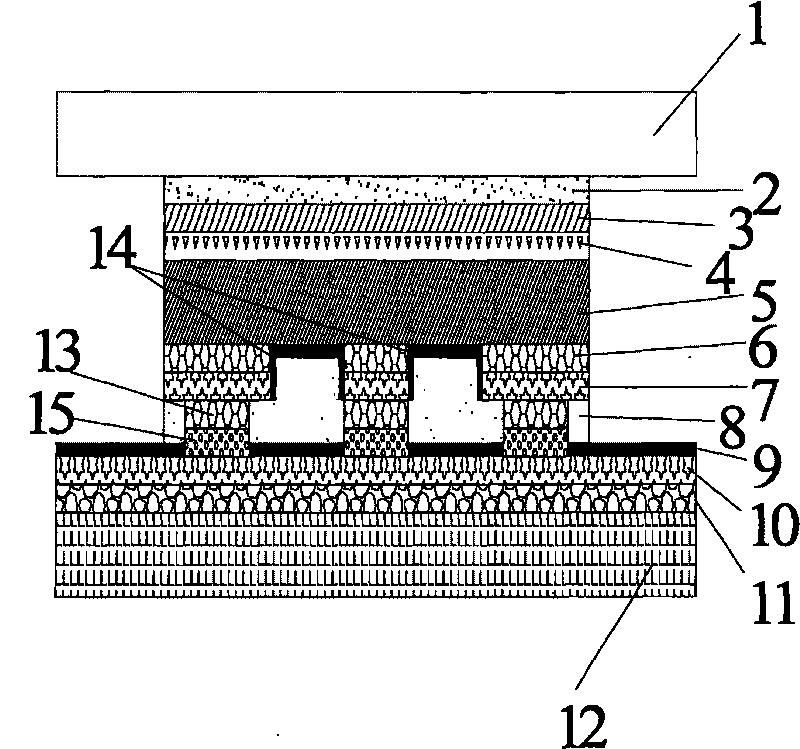
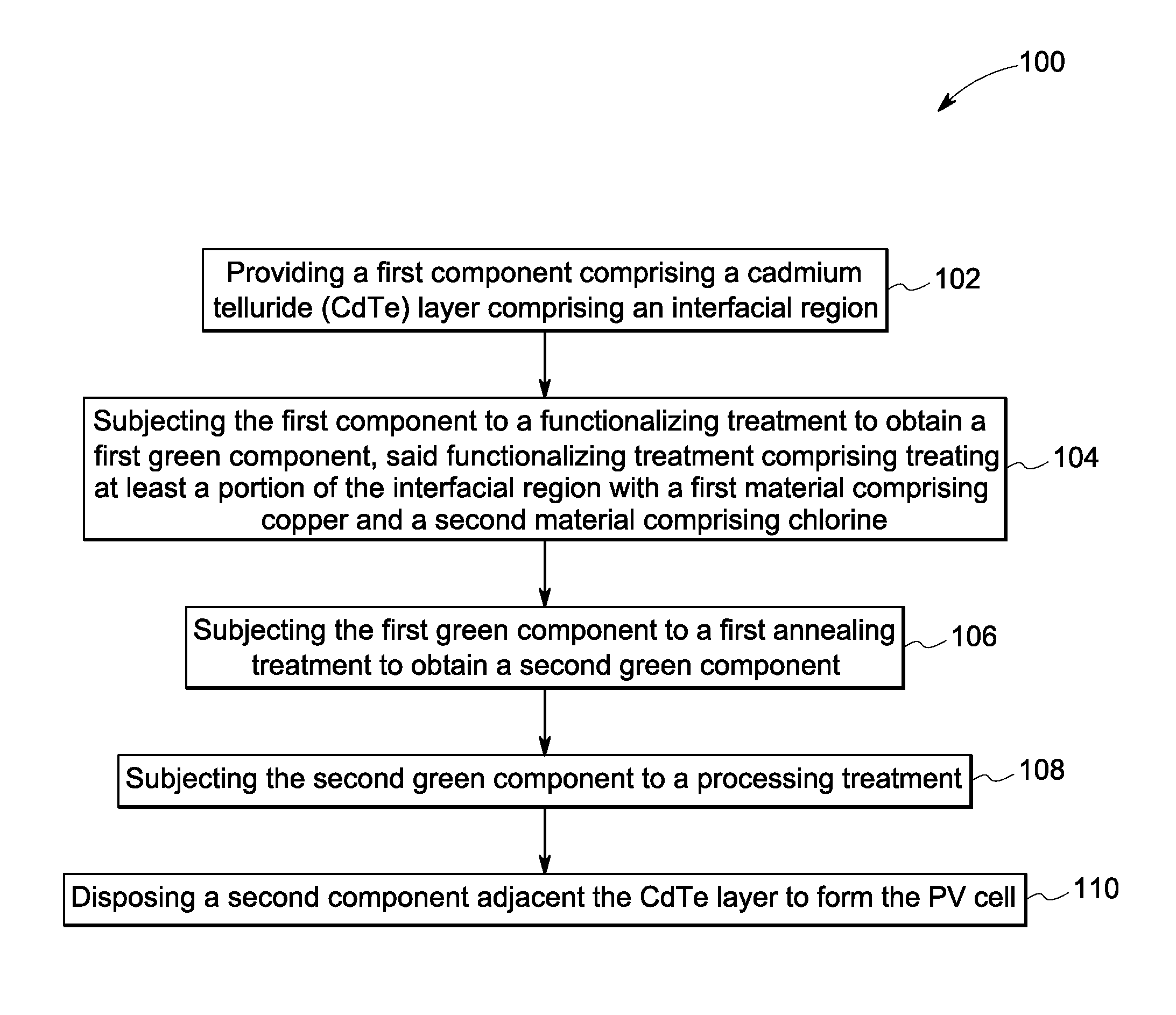
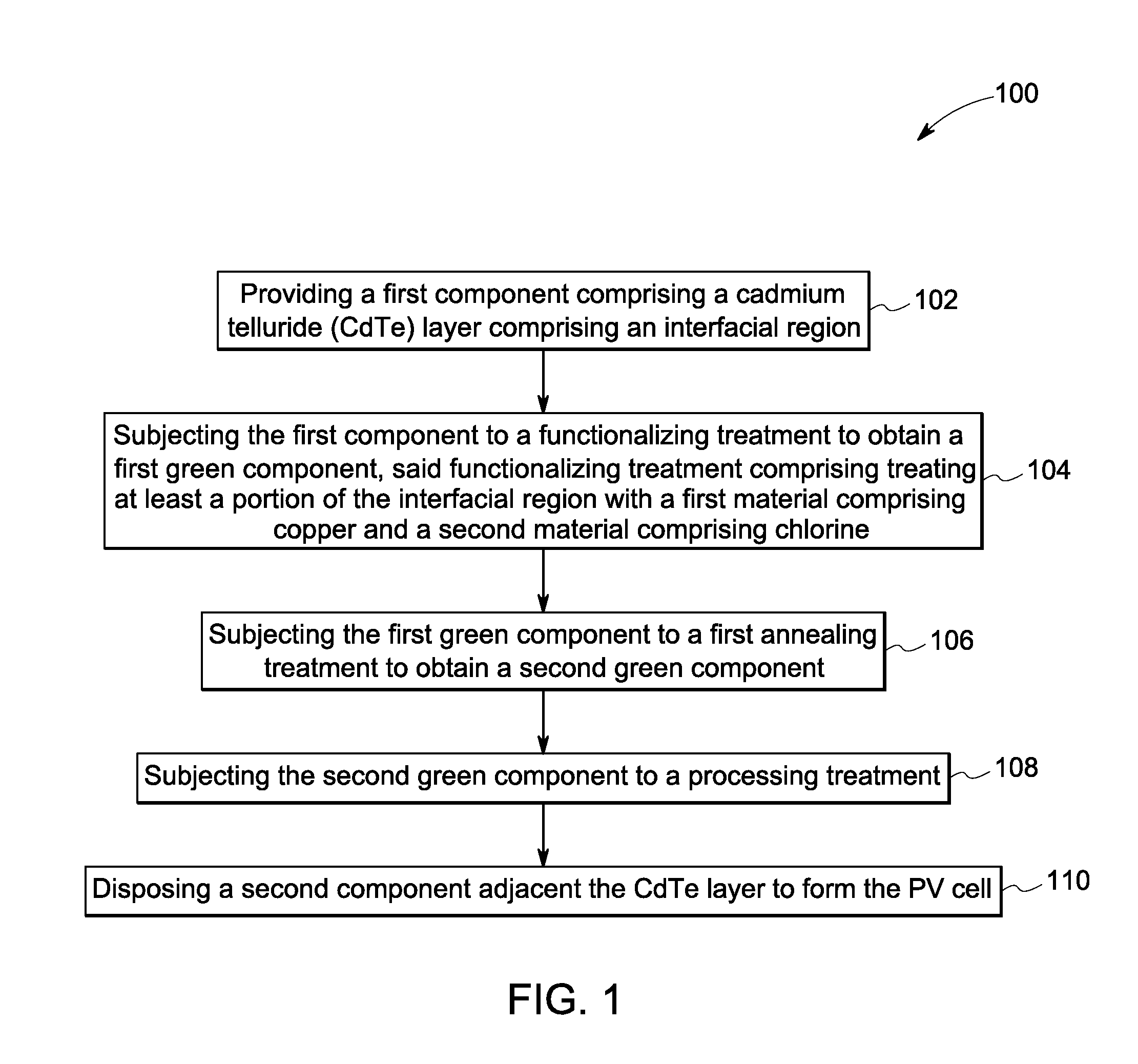
A method of p-type doping cadmium telluride (CdTe) is disclosed. The method comprising the steps of, (a) providing a first component comprising cadmium telluride (CdTe) comprising an interfacial region, and (b) subjecting the CdTe to a functionalizing treatment to obtain p-type doped CdTe, said functionalizing treatment comprising a thermal treatment of at least a portion of the interfacial region in the presence of a first material comprising a p-type dopant, and of a second material comprising a halogen. A method of making a photovoltaic cell is also disclosed.
Owner:FIRST SOLAR INC (US)
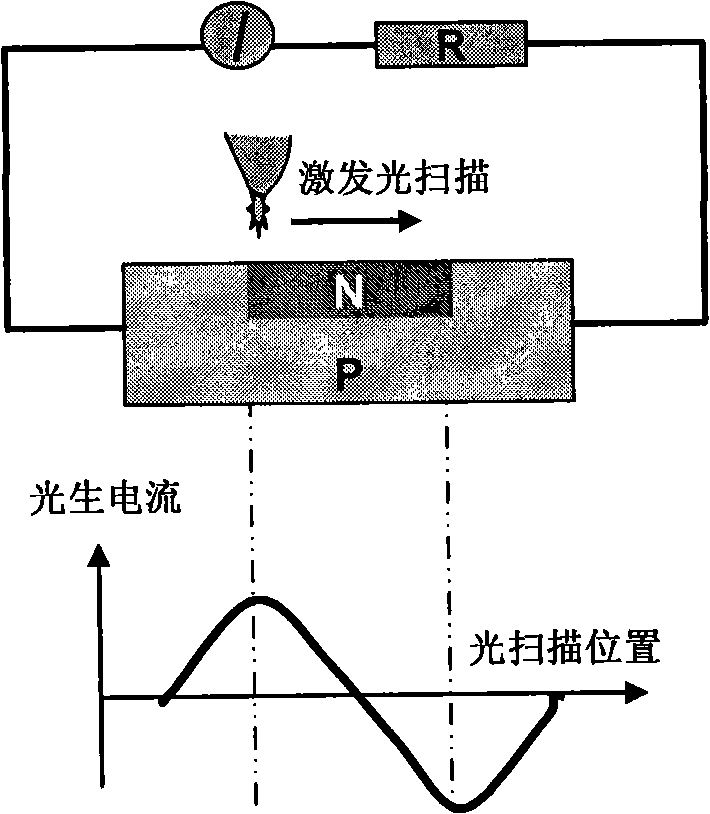
Method for measuring mercury cadmium telluride material pn junction depth
InactiveCN101383306ASimple test methodThe test result is accurateSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectrical testingMercury cadmium tellurideLaser beams
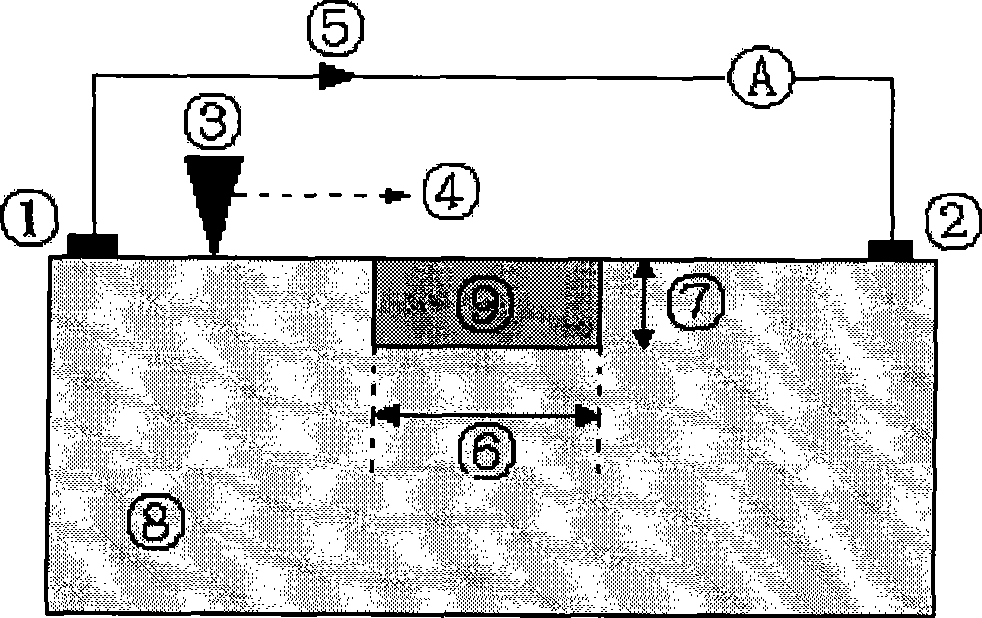
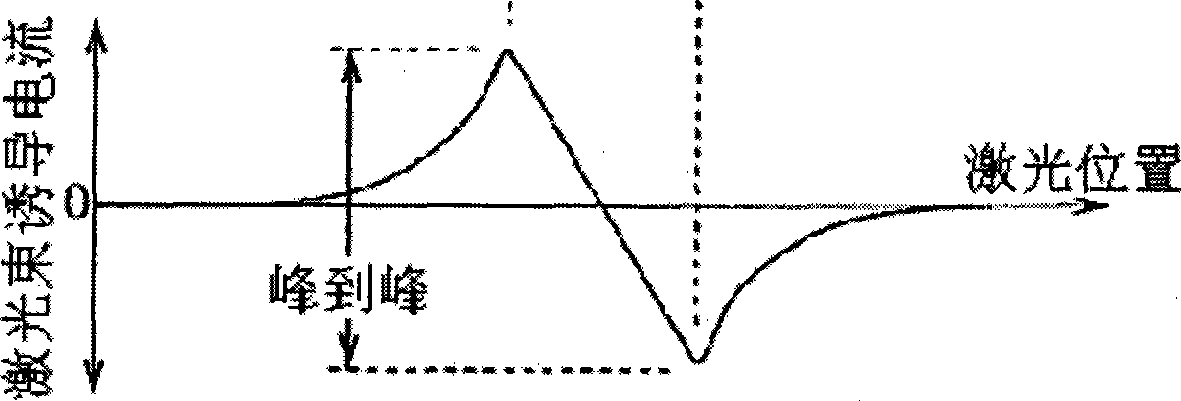
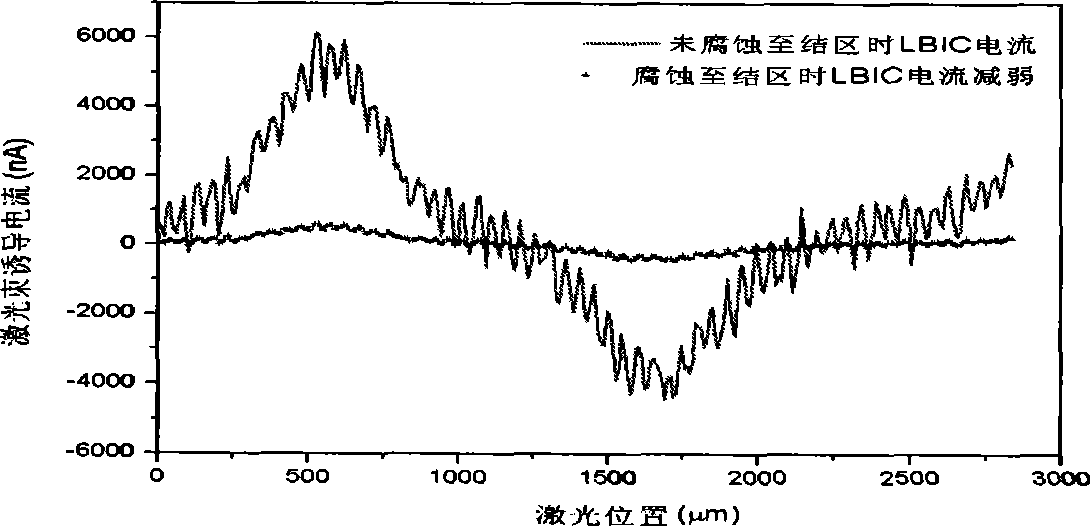
The invention discloses a method for measuring the pn junction depth of a mercury cadmium telluride material. The invention adopts a laser beam inducing current method to measure the pn junction depth of the mercury cadmium telluride material. When a laser beam irradiates a measured pn junction area, LBIC current has to be generated; when the mercury cadmium telluride material is eroded layer by layer, a built-in electric field gradually weakens until disappears, and the eroding depth of the mercury cadmium telluride material is the pn junction depth at the moment. The measuring method of the invention has no need to prepare electrodes for a plurality of times, the measuring method is simple, and the measuring result is accurate.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Graphene oxide-cadmium telluride/cadmium sulfide nano composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104212438AImprove performanceStable structure and performanceFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsCross-linkSolubility
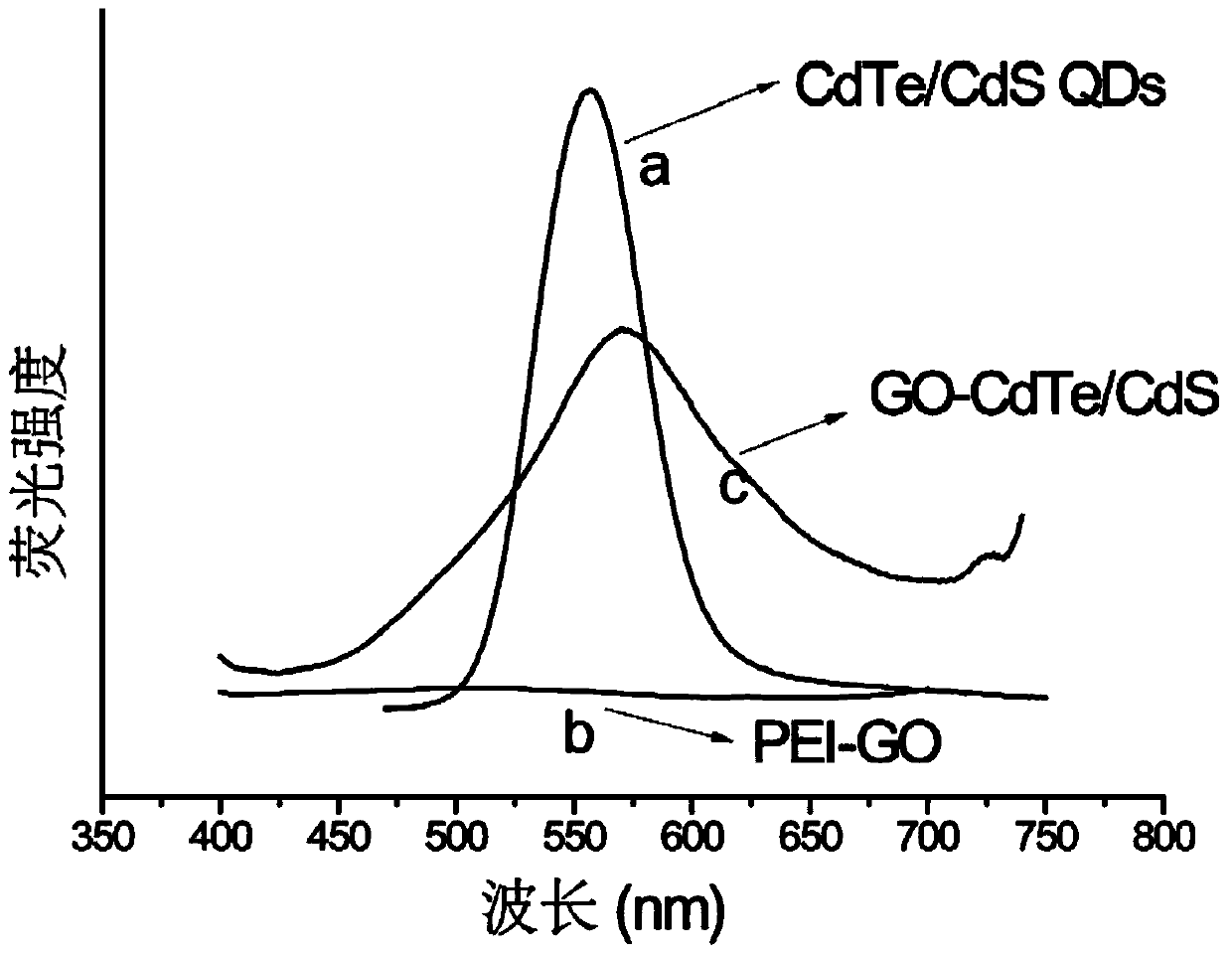
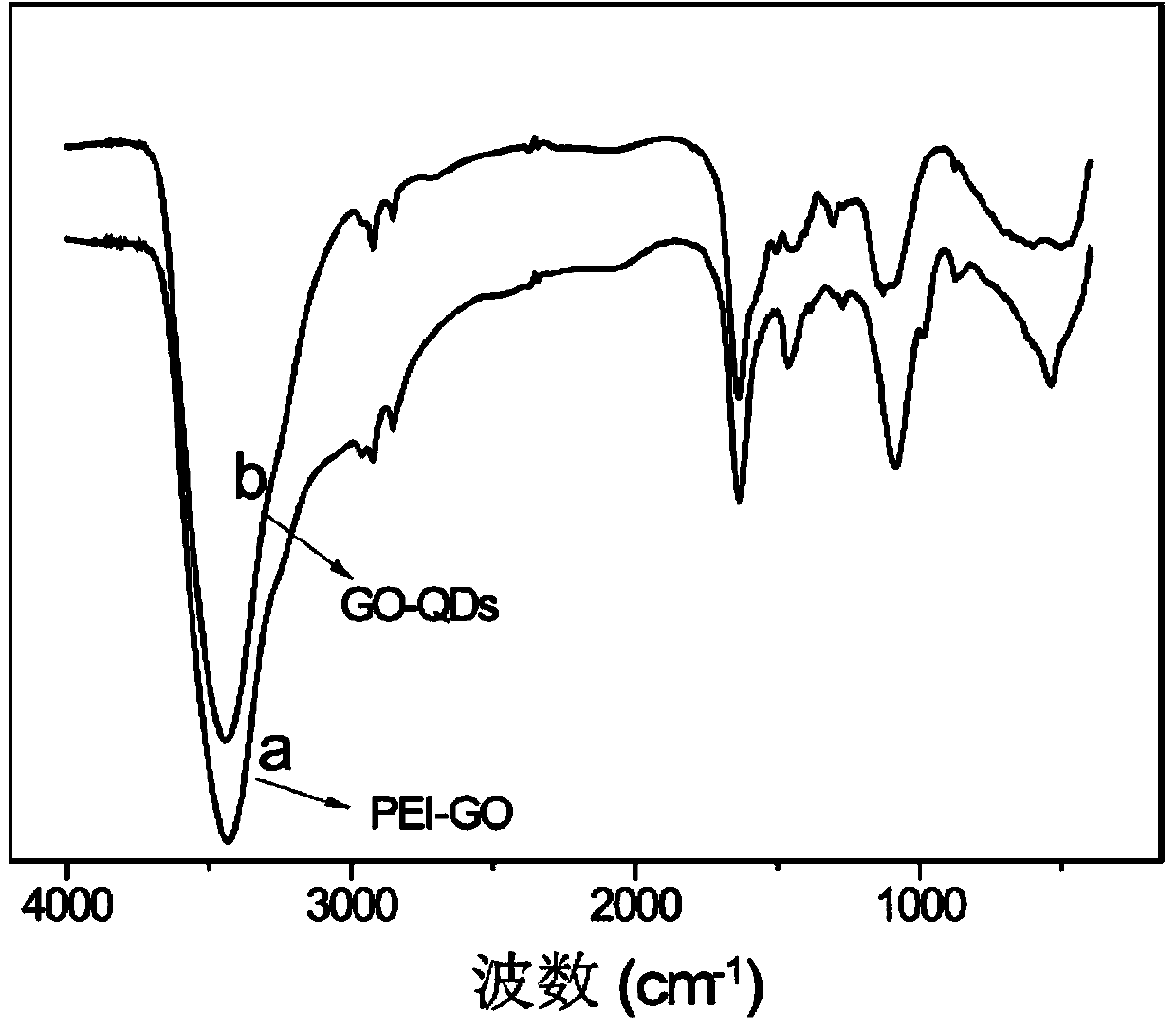
The invention relates to a graphene oxide-cadmium telluride / cadmium sulfide nano composite material and a preparation method thereof. The composite material is prepared by loading CdTe / CdS nuclear-shell quantum dot to the surface of PEI-GO by using covalent bonds. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding the CdTe / CdS nuclear-shell quantum dot and a cross-linking agent into double distilled water, providing ultrasonic wave for 3 hours, further adding PEI-GO, performing ultrasonic reaction for 24 hours, and dialyzing, thereby obtaining the graphene oxide-cadmium telluride / cadmium sulfide nano composite material GO-CdTe / CdS. The GO-CdTe / CdS nano composite material prepared by using the method is relatively large in specific surface area, relatively good in water solubility, relatively high in fluorescence intensity and fluorescence stability, and can be used as a novel nano fluorescence probe which is applied to the fields such as photoelectricity, biosensors and biomedicine.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
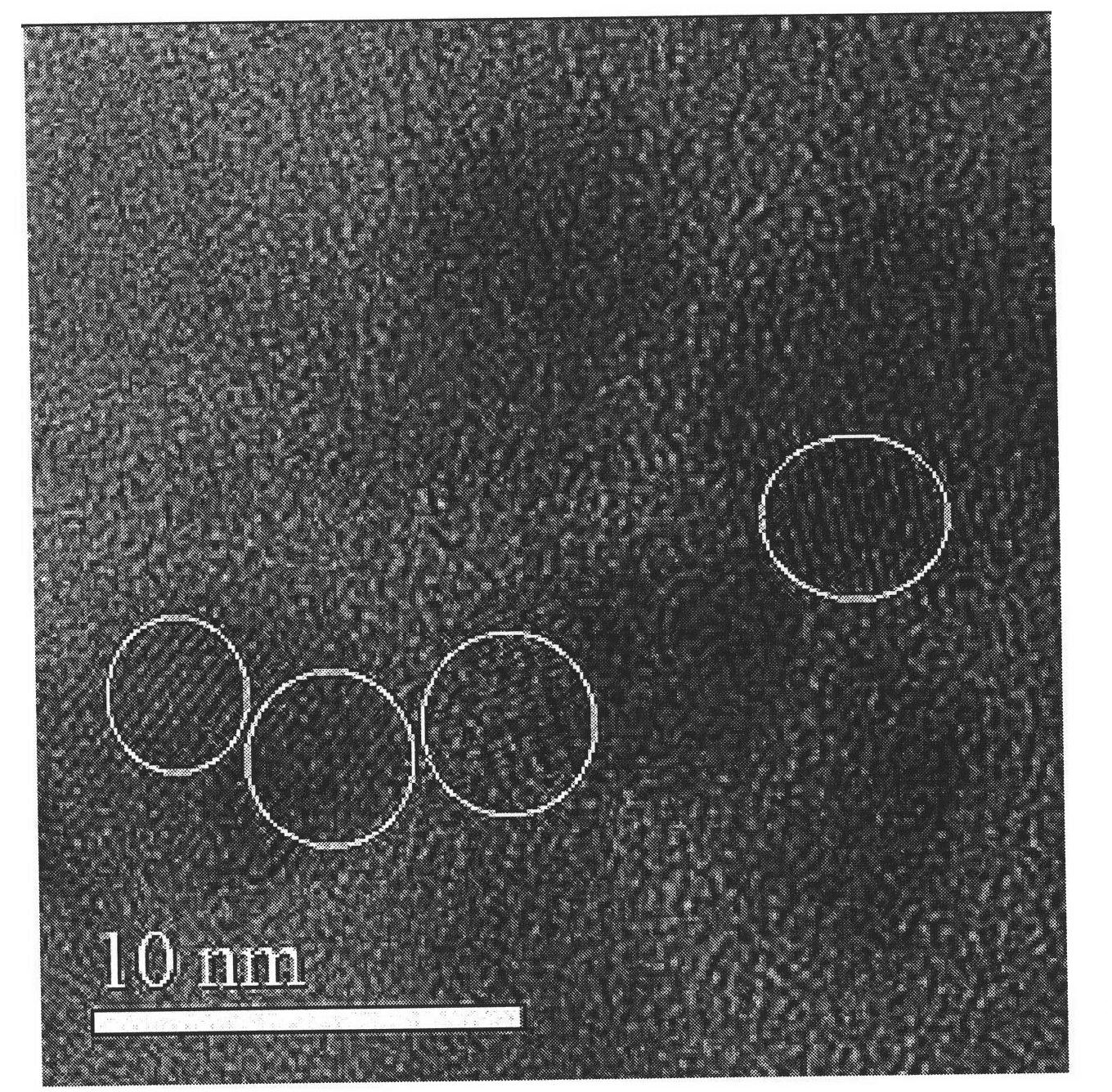
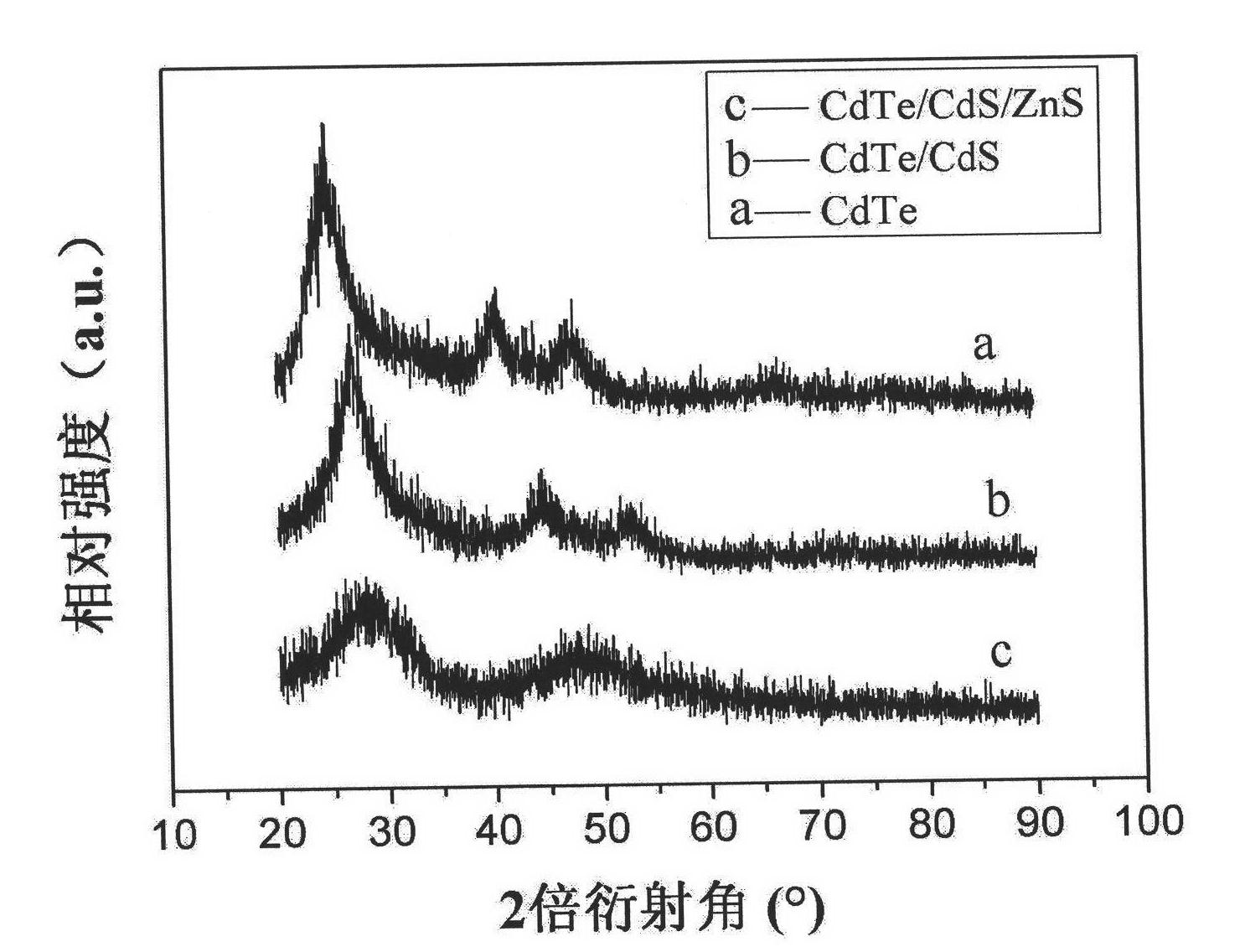
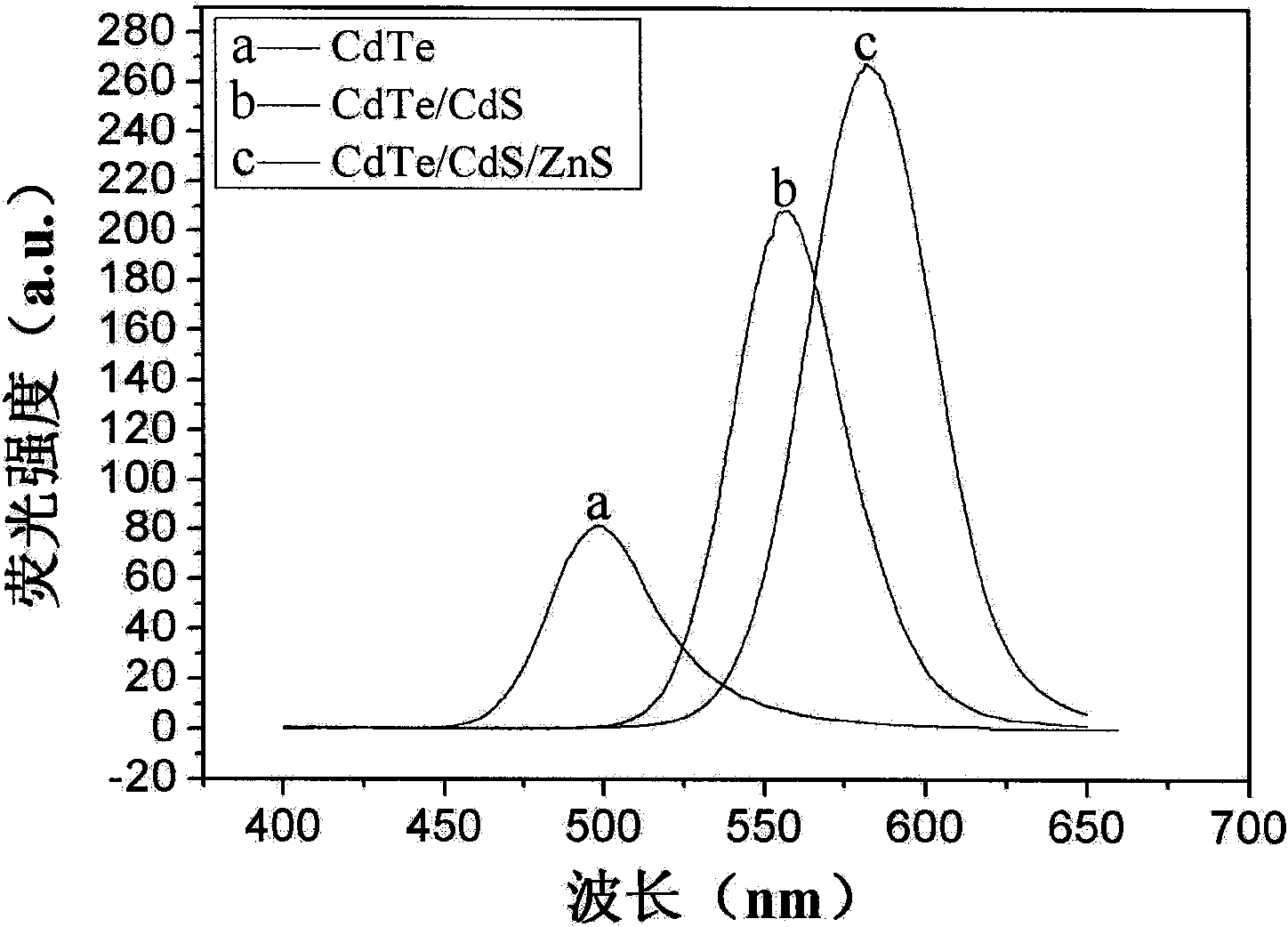
Synthetic method of cadmium telluride/cadmium sulfide/zinc sulfide quantum dots
InactiveCN101851511AHigh fluorescence intensityImprove stabilityLuminescent compositionsQuantum yieldOrganic dye
The invention relates to a synthetic method of admium telluride / cadmium sulfide / zinc sulfide quantum dots. An inner core is an admium telluride quantum dot and is coated by cadmium sulfide and zinc sulfide in sequence. The synthetic method for the quantum dots comprises the following steps of: firstly, preparing an admium telluride quantum dot with excellent fluorescent characteristic by hydrolyzing a sulfhydryl group; secondly, adding thiourea with a certain concentration into the reacted admium telluride solution, forming free suplfur ions released by slowly hydrolyzing and photolyzing thiourea and cadmium ion dangling bonds existing on the surface of the admium telluride quantum dot into bonds; generating a thin cadmium sulfide casing layer on the surface of the cadmium sulfide quantum dot; and finally adding a zinc acetate solution and a sodium sulfide solution into the admium telluride / cadmium sulfide quantum dots with nuclear shell structures and carrying out hydro-thermal growth in a polytetrafluoroethylene digestion tank to form the admium telluride / cadmium sulfide / zinc sulfide quantum dots. The quantum dots have the characteristics of high fluorescent strength, favorable stability, high quantum yield and low biotoxicity and are hopeful to be applied to the field of biomarkers instead of the traditional organic dye. The synthetic method has the advantages of simple process, convenience, low cost and strong operability.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
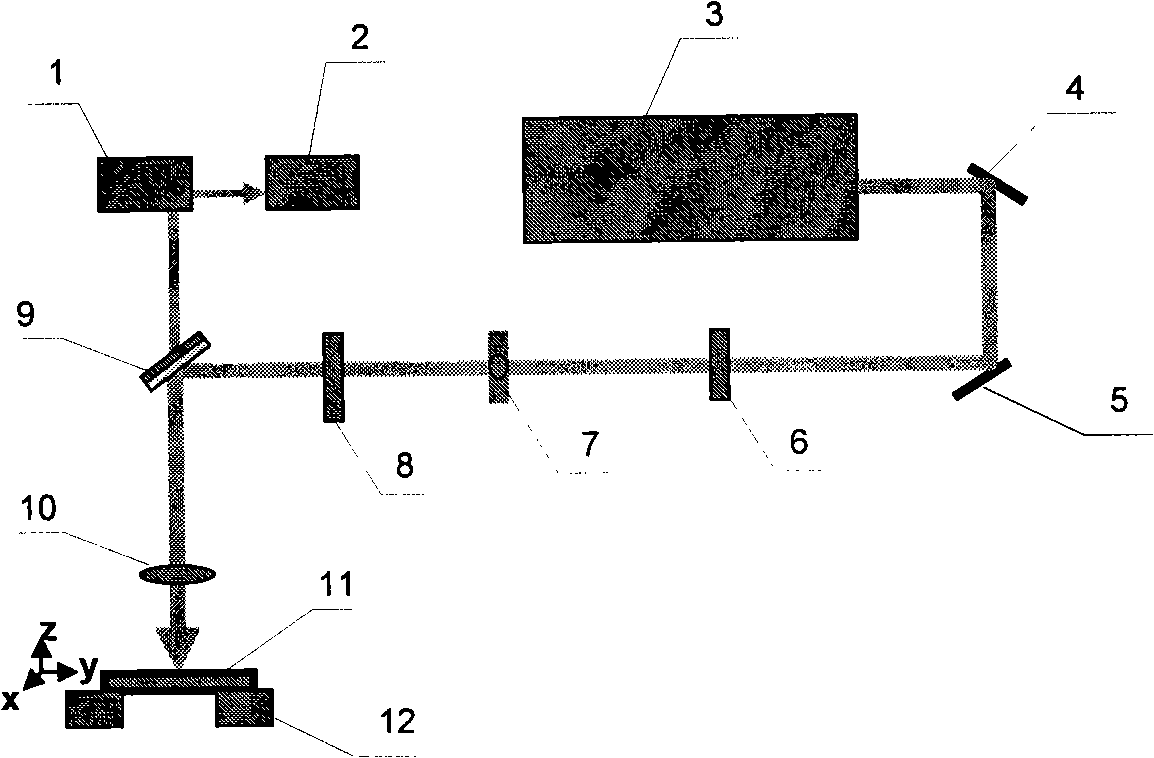
Method and device for forming PN junction on P type mercury cadmium telluride by laser process
InactiveCN101315957AReduce photolithography process stepsThe knotting process is simpleLaser beam welding apparatusSemiconductor devicesFemto second laserDisplay device
The invention relates to a laser processing method for forming a PN-junction on a P-typed Hg-Cd-Te material and a device thereof. The method comprises the following steps that: a pulse laser is focused on the surface of the P-typed Hg-Cd-Te material and the P-typed Hg-Cd-Te material is radiated in short time, thus forming a porous area melted and corroded on the material by the laser; the diameter of the pore is within a range from several micrometers to ten micrometers or so; an inversion area, namely an N-typed area is formed in the several micrometer area around the pore; the inversion area and the P-typed area at the periphery of the pore form a PN-junction area. The device of the invention consists of a femto-second laser, a deflecting mirror, a neutral density filter, a pupil, an aperture, a dichroic mirror, a lens, a CCD camera, a display and a workpiece platform. As the method of the invention has the advantages of laser direct writing, saves the lithography process step in the traditional junction-forming technique, leads the junction-forming process to be simplified and is beneficial to reducing the dead pixel caused by the process complexity. The method of the invention is completely compatible with other techniques of the prior art in the field such as read-out circuit technique and has direct and practical value.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Semiconductor device with stabilized junction
Self stabilizing concentration profiles are achieved in solids. More particularly, semiconductor devices are made from n- or p-type mercury cadmium telluride (MCT) of the general formula HgxCd1-xTe where x=0.2 to 0.5 and n- or p-type zinc mercury telluride (ZMT) of the general formula ZnxHg1-xTe where x=0.4 to 0.6. Silver, incorporated as a doping impurity or applied as an evaporated spot electromigrated within the MCT or ZMT to create one or more p-n junctions, usually under the influence of a pulsed positive bias. The resulting concentration profiles of silver and opposing internal electric fields of the p-n junctions achieve a balancing equilibrium that preserves and maintains the stability of the concentration profiles. For a specific telluride composition, Hg0.3Cd0.7Te, indium is the n-type dopant of choice.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
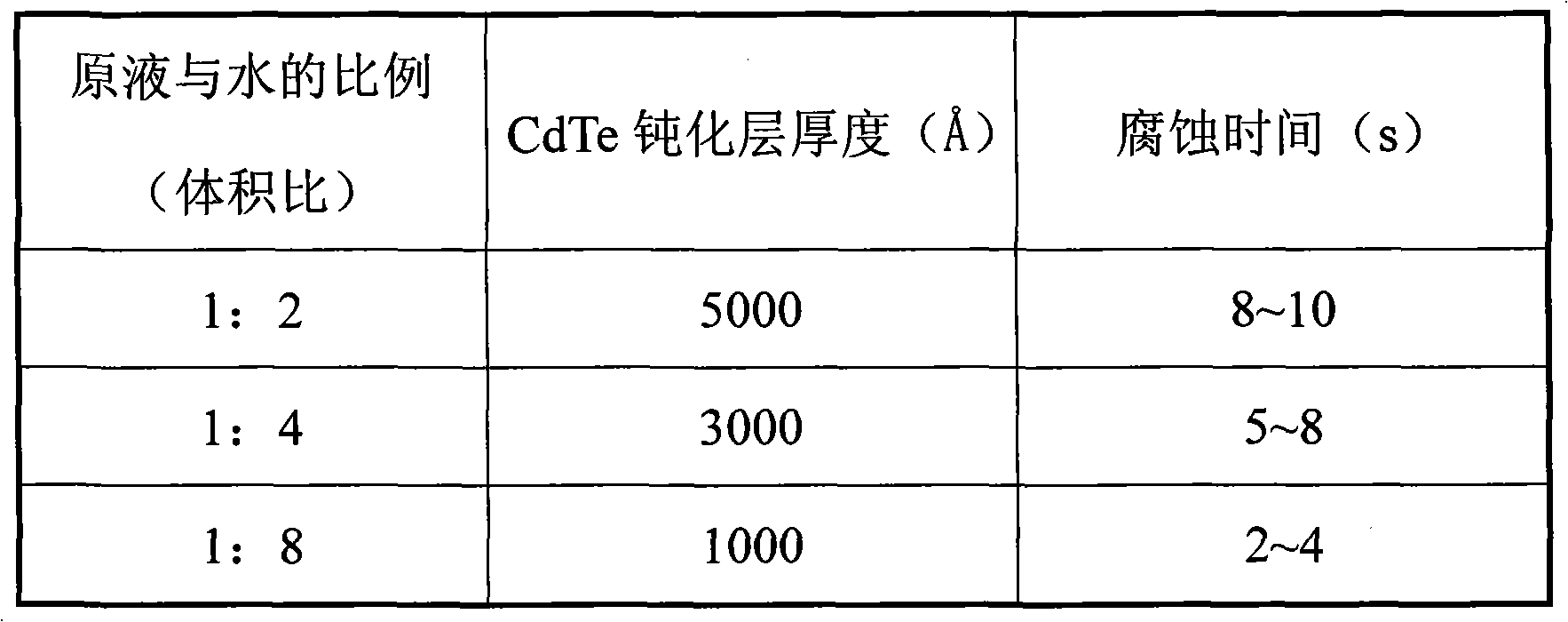
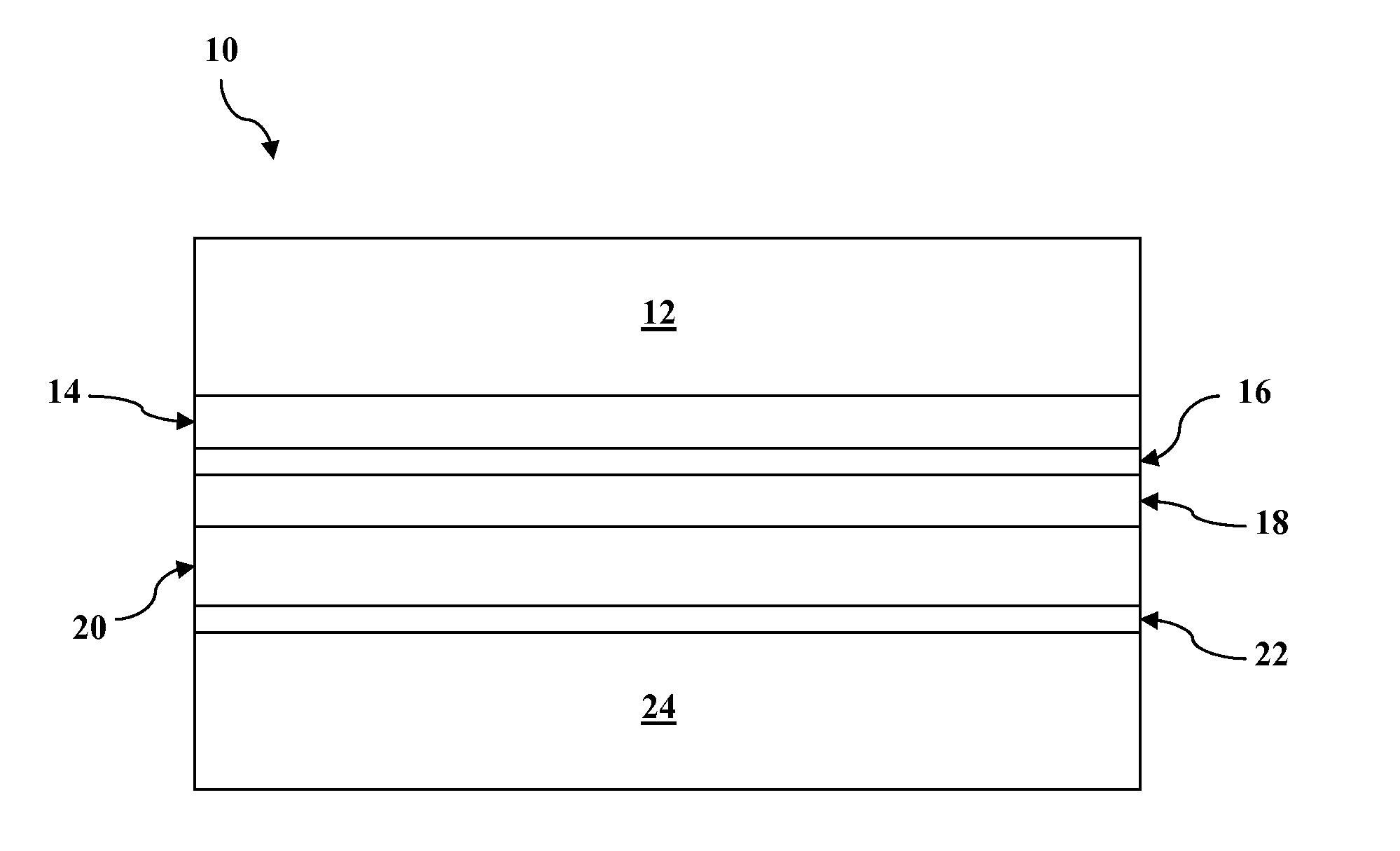
Metalization hatch method for cadmium telluride passivating film of mercury cadmium telluride infrared detecting chip
InactiveCN101494254AWill not affect other surface treatment processesImprove corrosion selectivityFinal product manufactureMetallic material coating processesSelective leachingMercury cadmium telluride
The invention discloses a metalized opening method of a mercury cadmium telluride passive film in a mercury cadmium telluride infrared detection chip. The method relates to a preparation technology of an HgCdTe infrared focal plane detector, in particular comprising the preparation of a selective etching solution of a CdTe passive film of the HgCdTe detection chip and a method for using the etching solution to carry out the metalized opening of the detector chip. The result shows that the etching solution has a high etching selective ration on CdTe and HgCdTe materials, and is stable with controllable etching speed. The opening method is a stable and convenient technology, has no effect on other surface treatment technologies, facilitates the improvement of surface properties of a device, improves technological stability and is vital to realize the application of CdTe passivation to a focal plane device.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cadmium sulfide layers for use in cadmium telluride based thin film photovoltaic devices and methods of their manufacture
InactiveUS20110265874A1Final product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingMercury cadmium tellurideOptoelectronics
Methods are generally provided for forming a cadmium sulfide layer on a substrate. In one particular embodiment, the method can include sputtering a cadmium sulfide layer on a substrate in a sputtering atmosphere comprising an inorganic fluorine source gas. Methods are also generally provided for manufacturing a cadmium telluride based thin film photovoltaic device.Cadmium telluride based thin film photovoltaic devices are also generally provided. The device can include a substrate; a transparent conductive oxide layer on the substrate; a cadmium sulfide layer on the transparent conductive oxide layer; and, a cadmium telluride layer on the cadmium sulfide layer. The cadmium sulfide layer includes fluorine.
Owner:FIRST SOLAR INC (US)
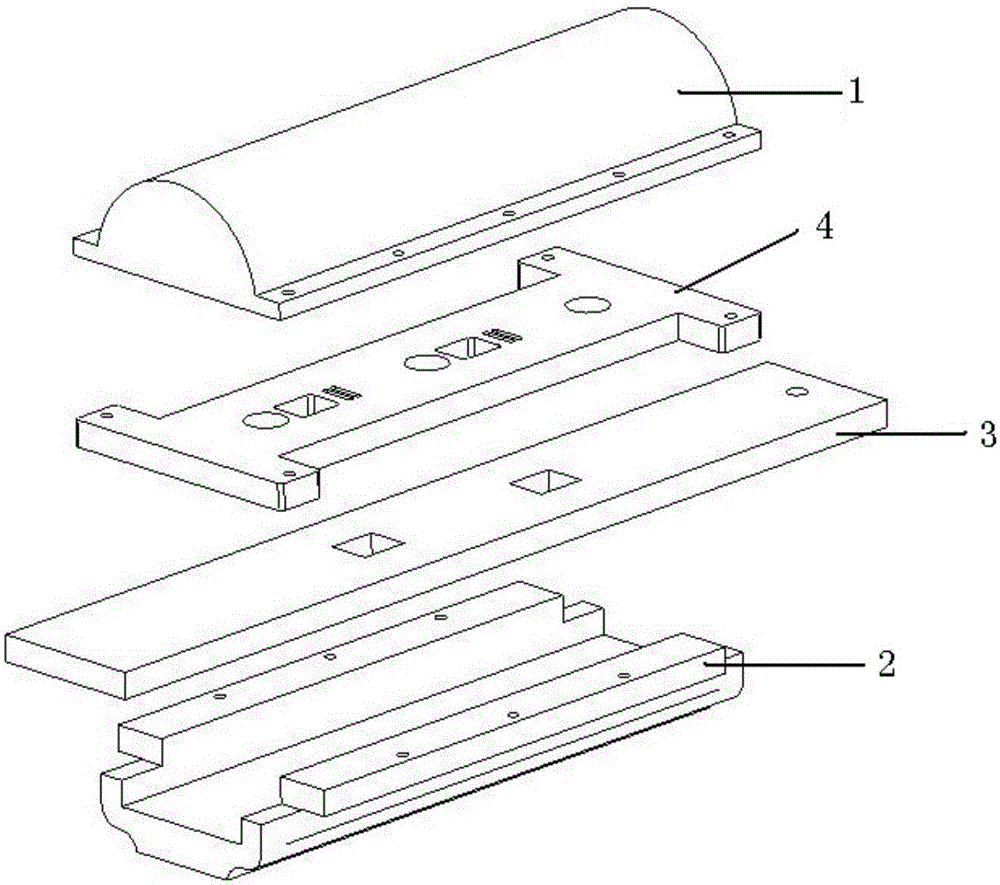
Graphite boat for improving mercury cadmium telluride rheotaxy membrane surface shape
ActiveCN101109105AReduce convectionSmall ripplePolycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthMercury cadmium tellurideMembrane surface
The invention discloses a graphite boat for improving the surface shape of the extended liquid-phase film of merury cadmium telluride, which is characterized in that the mercury supply tank formerly placed at front or rear of the mother liquid tank is changed to be placed right above the mother liquid tank, a channel is provided between the two tanks for communicating; the mercury steam generated by the mercury supply tank supplements mercury into the mother liquid from the top of the mother liquid tank, so that the supplementing of the mercury steam generated by the mercury supply tank becomes more even, hence the pressure above the mother liquid is more even; in addition, as the front and the rear strcuture of the mother liquid tank are similar, the temperature field surrounding the mother liquid tank becomes more even. The advantages with the invention is that the uneveness of pressure and temperature field can be removed to the max. extent, convection of mother liquid is slowed, hence the corrugation on the surface of the extended material is reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Graphite boat for epitaxial growth of horizontal liquid phase of mercury cadmium telluride thin film
InactiveCN106637390AImprove surface topographyImprove thickness uniformityPolycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthSolid structureGas phase
The invention discloses a graphite boat for epitaxial growth of a horizontal liquid phase of a mercury cadmium telluride thin film. The graphite boat comprises an upper cover, a bottom support, a sliding strip and a mother solution tank, wherein the bottom support comprises a groove with one bottom edge and two side edges; the sliding strip and the mother solution tank are arranged in the groove; the mother solution tank is fixed at the upper end of the groove; the upper surface of the mother solution tank is leveled with the upper surfaces of the two side edges; the sliding strip is located between the mother solution tank and the bottom edge of the bottom support, and can do movement relative to the mother solution tank along the bottom edge; the upper cover is of a solid structure and covers the side edges of the bottom support and the mother solution tank; a drainage channel is arranged in the upper cover; a starting point and a finishing point of the drainage channel are located on a contact surface of the upper cover and the mother solution tank. According to the graphite boat disclosed by the embodiment of the invention, a drainage groove is formed in the upper cover, and a temperature field, gas flow, gas-phase distribution and mercury pressure in an epitaxial growth process of the horizontal liquid phase can be improved to a certain extent, so that the problems about surface appearance and thickness uniformity of the mercury cadmium telluride thin film are solved.
Owner:11TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
Method for preparing high performance mercury cadmium telluride p-n junction by ion injection
InactiveCN101425552AReduce testing costsShorten the timeFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEvaporationP–n junction
The invention relates to a method for preparing a high-performance mercury cadmium telluride p-n junction through ion injection. The method comprises the following steps: adopting an identical mercury cadmium telluride film as a substrate; manufacturing a plurality of mask plates; evaporating a ZnS film as blocking layers for ion injection; photo etching a corresponding ion injection region on the blocking layers to inject; and then finishing the junction process of the p-n junction. The blocking layers for the ion injection are ZnS film blocking layers with different thickness obtained through a plurality of superposition and evaporation; the ion injection dosage is the dosage of an identical ion and identical injection energy value after being optimized. The invention obtains a serial testing unit for superposing and evaporating the blocking layers with different thickness obtained on identical backing material; the process improvement of the ion injection is conducted to a photo etching entrance and exit area according to the ion injection dosage after being optimized at a time, so as to prepare the high-performance mercury cadmium telluride p-n junction and provide more convenient and quicker experimental investigation on optimizing process parameters for a solar infrared detector. The invention has the advantages of low testing cost, and time and energy conservation; and the method can be popularized and applied to the optimization study on the thickness of the ion injection blocking layer in other backing material system.
Owner:HUAIYIN TEACHERS COLLEGE +1
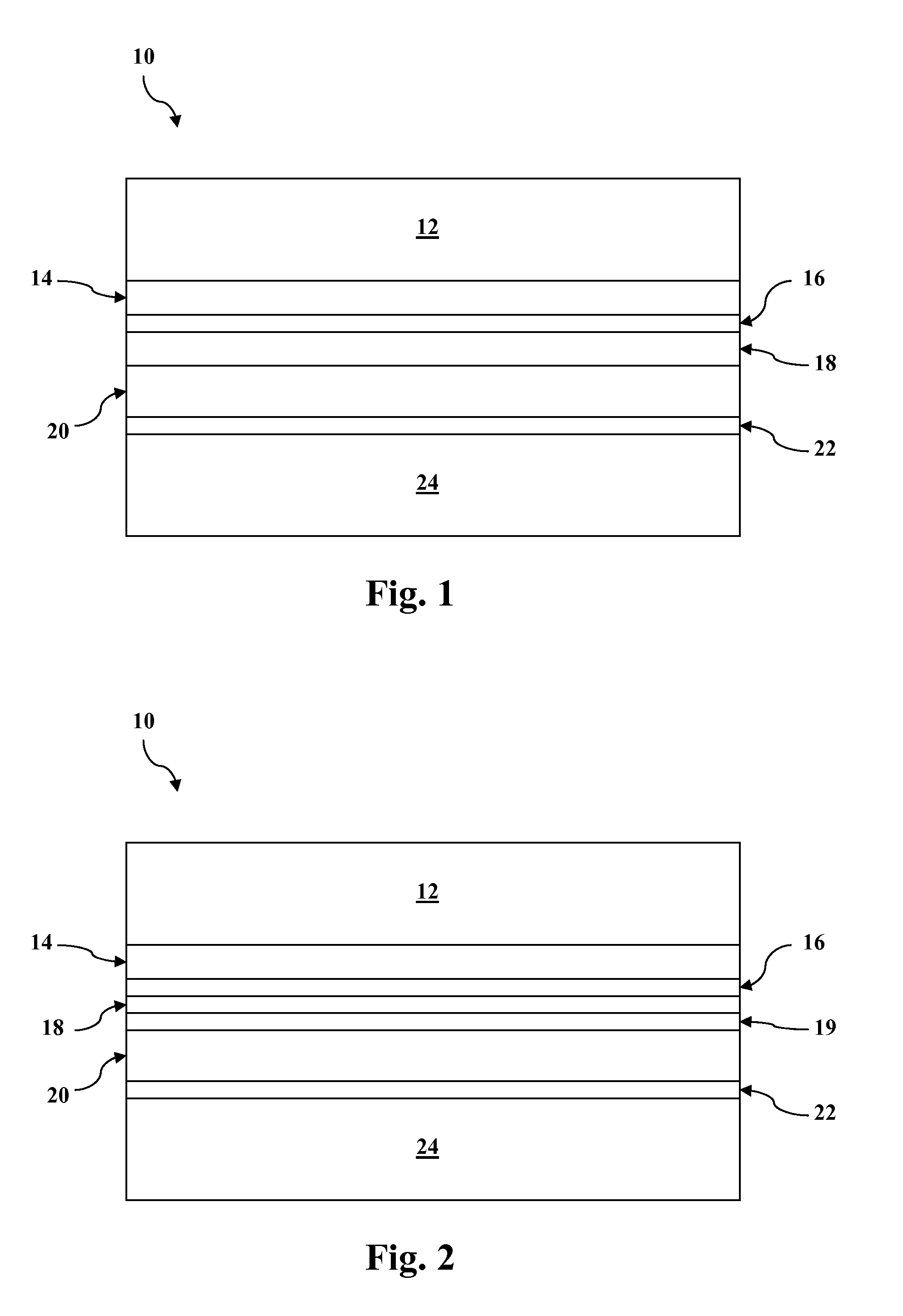
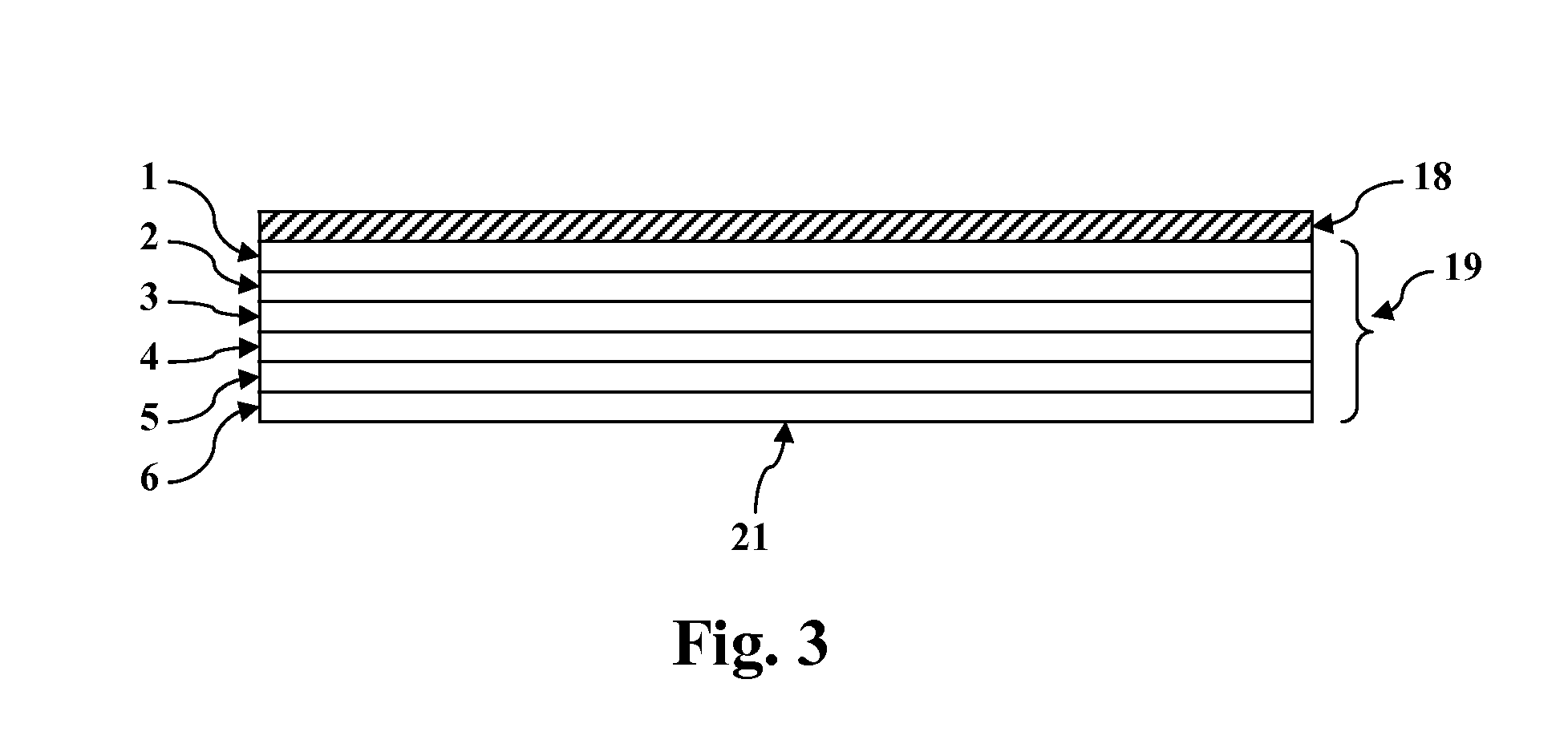
Graded alloy telluride layer in cadmium telluride thin film photovoltaic devices and methods of manufacturing the same
InactiveCN102142475AFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingMercury cadmium tellurideAlloy
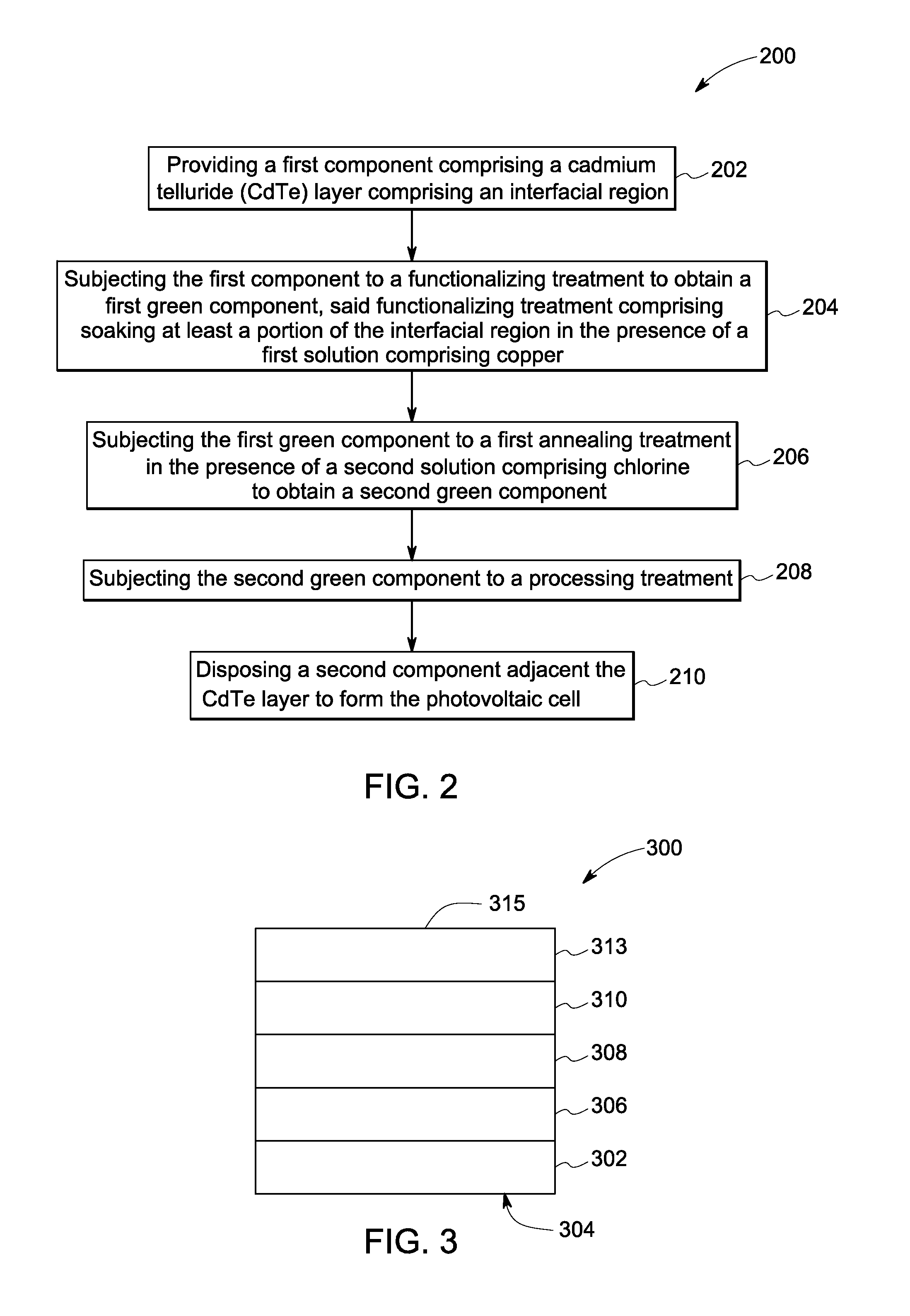
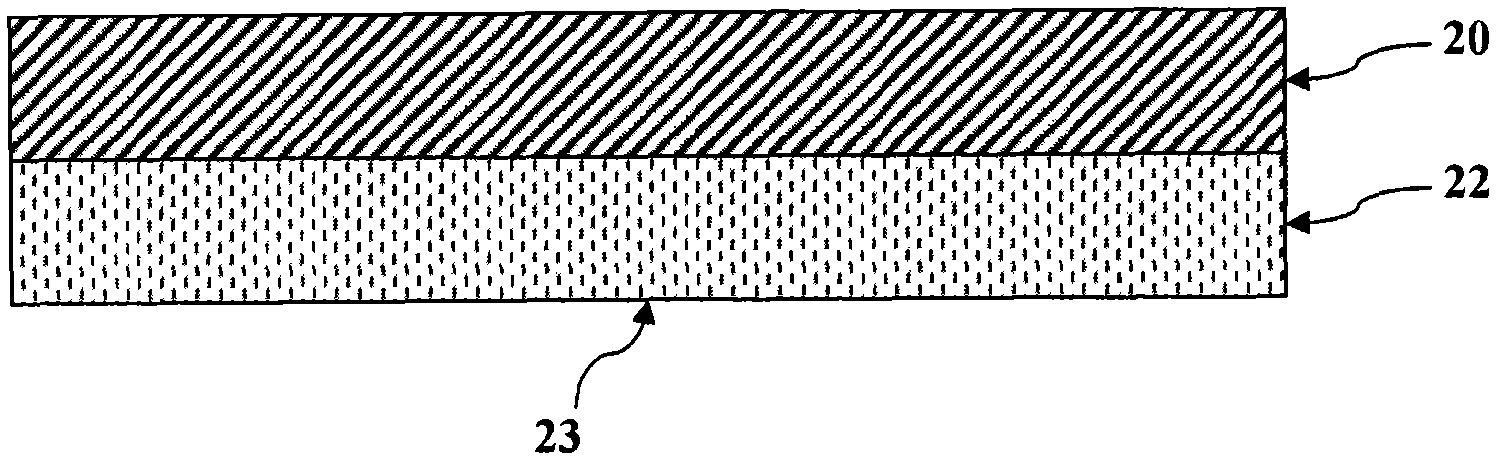
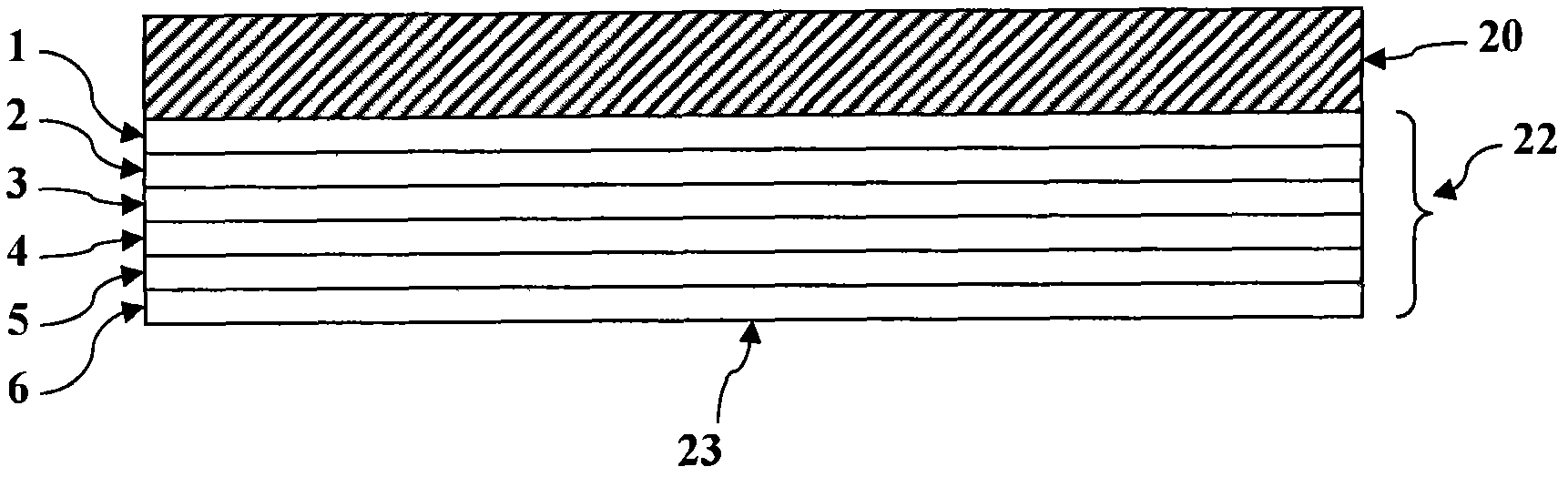
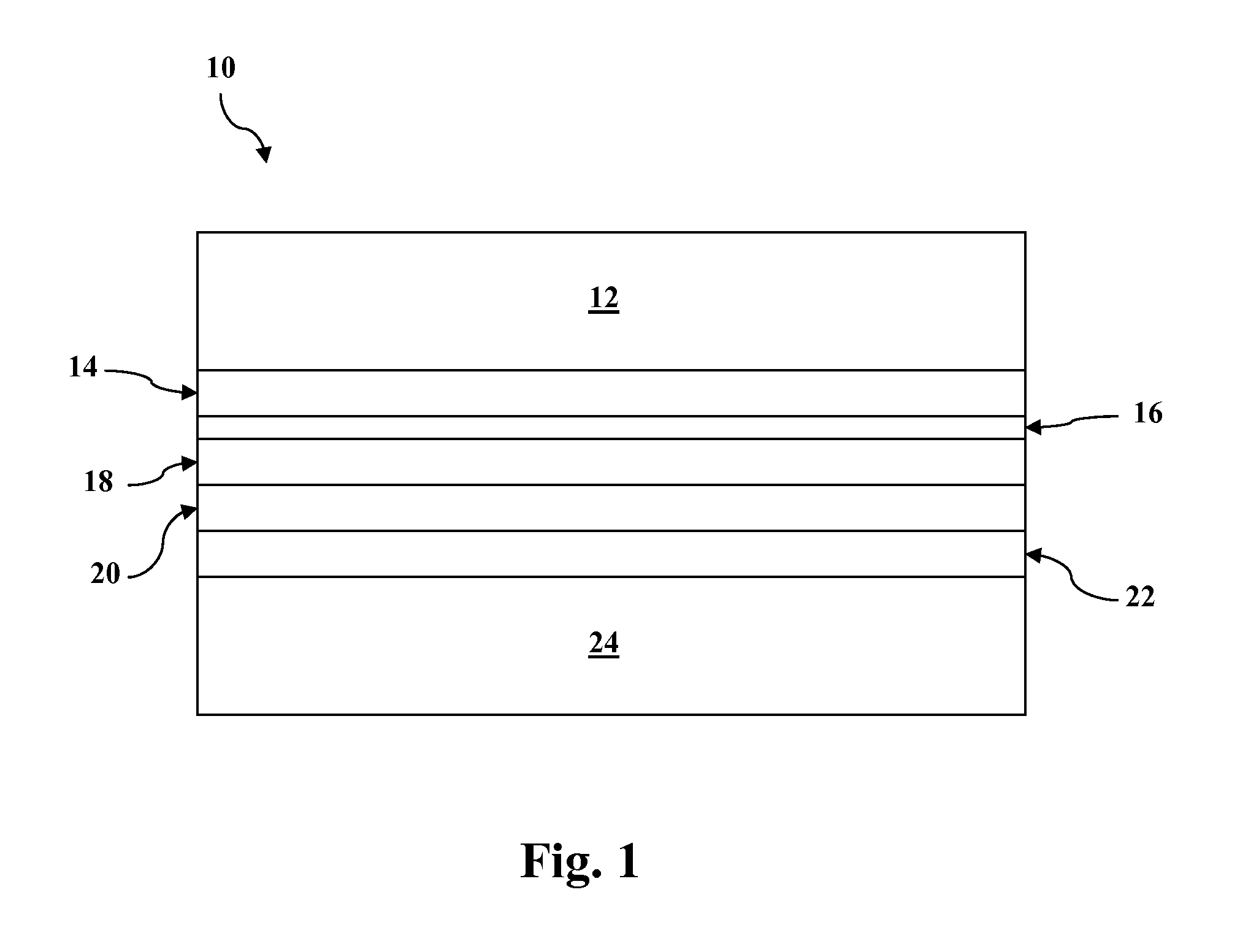
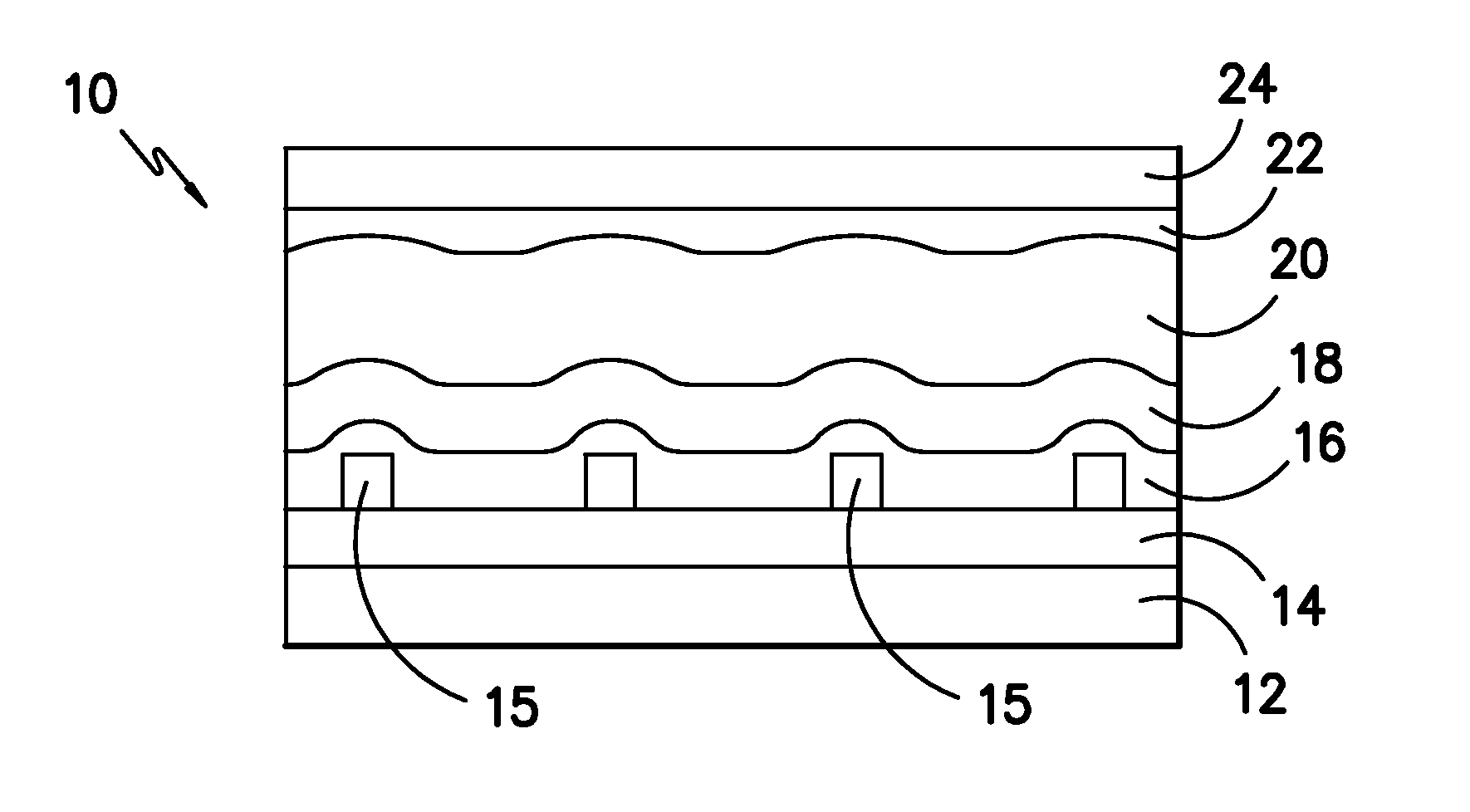
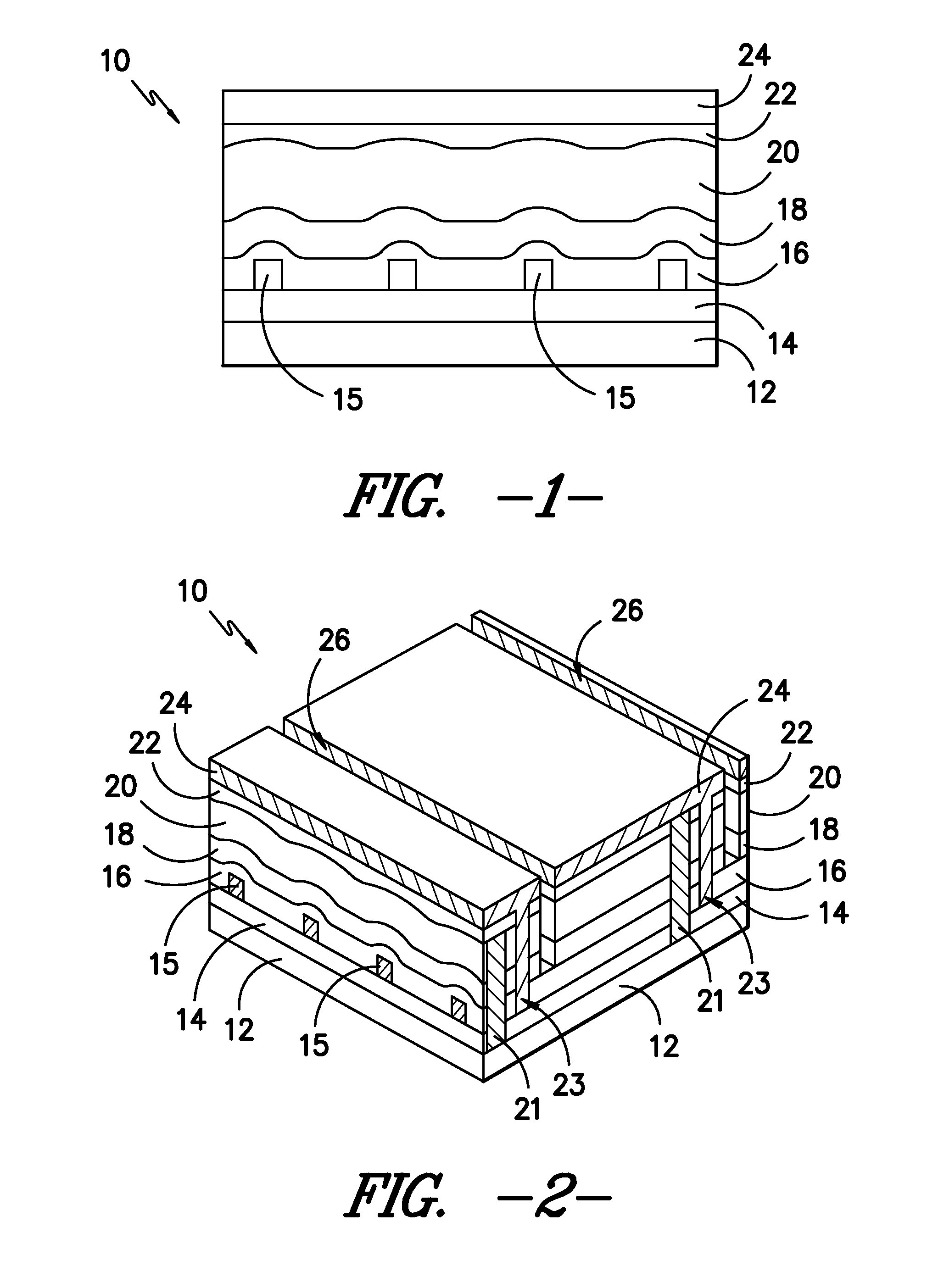
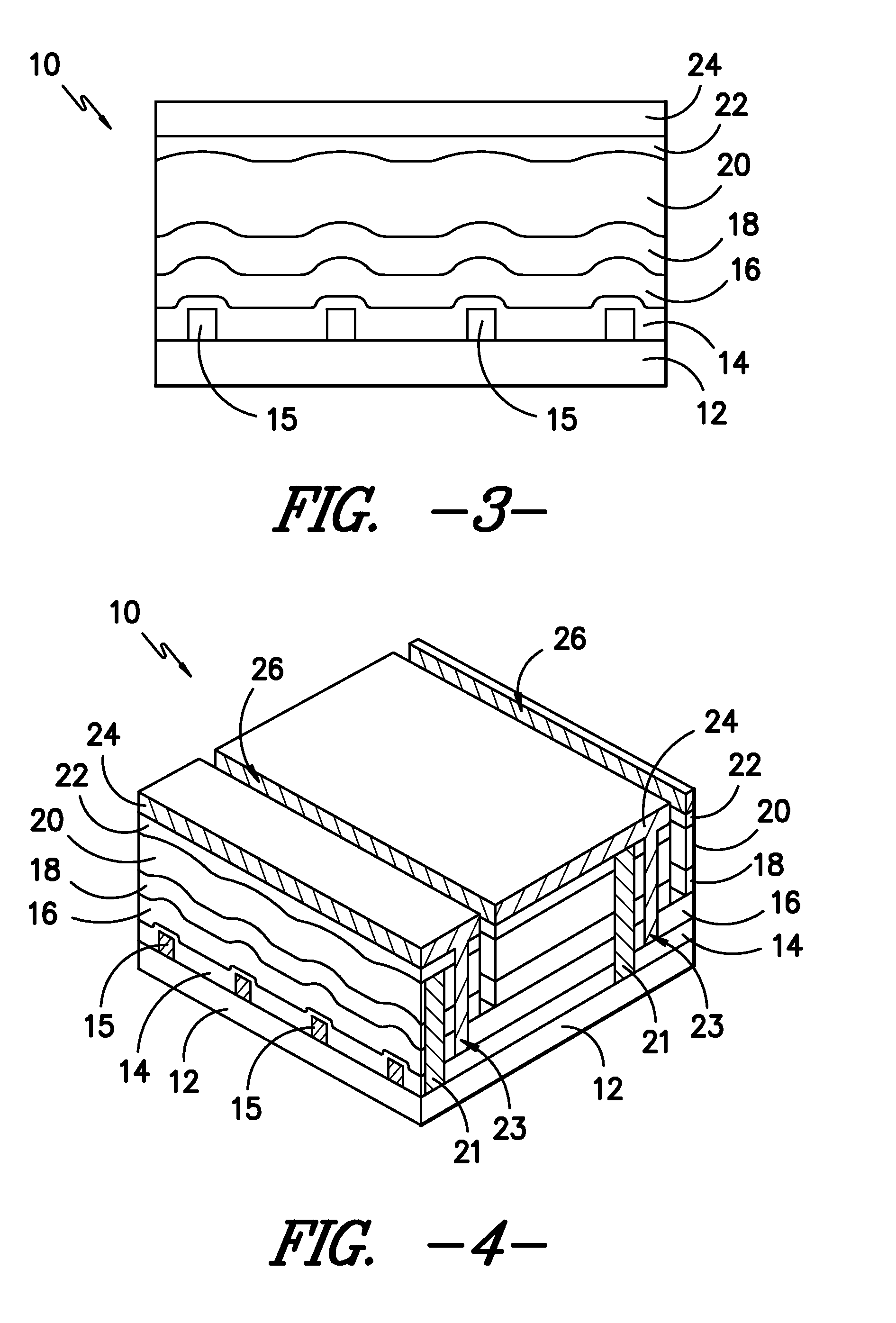
Cadmium telluride thin film photovoltaic devices (10) are generally disclosed including a graded alloy telluride layer (22). The device can include a cadmium sulfide layer (18), a graded alloy telluride layer (22) on the cadmium sulfide layer (18), and a back contact (24) on the graded alloy telluride layer (22). The graded alloy telluride layer (22) generally has an increasing alloy concentration and decreasing cadmium concentration extending in a direction from the cadmium sulfide layer (18) towards the back contact layer (24). The device (10) may also include a cadmium telluride layer (20) between the cadmium sulfide layer (18) and the graded alloy telluride layer (22). Methods are also generally disclosed for manufacturing a cadmium telluride based thin film photovoltaic device having a graded cadmium telluride structure.
Owner:PRIMESTAR
Preparation method for cadmium telluride
InactiveCN103818886AOvercome the defect of being easily oxidizedWell mixedBinary selenium/tellurium compoundsHydrogenMercury cadmium telluride
The invention discloses a preparation method for cadmium telluride. The preparation method sequentially comprises the following steps: qualified tellurium powder and cadmium powder are taken according to the molar ratio of 1:1 and then subjected to homogeneous mixing, the mixed raw materials subjected to homogenizing are loaded into a graphite boat, and the graphite boat is placed into a synthesis furnace for first synthesis; the material obtained after first synthesis is taken out of the graphite boat and crushed; the crushed material is loaded into the graphite boat, and the graphite boat is placed into the synthesis furnace for second synthesis; screening and ball milling are performed, wherein in the processes of the first synthesis and the second synthesis, multistage temperature rising and temperature dropping are performed under the protection of nitrogen and hydrogen. According to the invention, homogeneous treatment is performed on the tellurium powder and cadmium powder firstly so as to enable the two raw materials to be mixed fully and uniformly, meanwhile, the defect that the cadmium powder is easy to oxidize is overcome, the two raw materials can be synthesized preliminarily under relatively low temperature, purity of a synthesized product is improved, and the utilization ratios of raw materials are increased; synthesis is performed for two times, so that the raw materials react fully, thereby improving the purity and yield of the product finally.
Owner:张家港绿能新材料科技有限公司
Biodiesel detector
ActiveUS20160139040A1Short amount of timeColor/spectral properties measurementsSpectral responseAbsorbance
A device and method of use are provided for measuring the concentration of fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) in jet fuel to a limit of detection of 1 ppm. The device measures concentration of FAME in jet fuel via Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) with a spectral resolution of 1 cm−1. The device can use an infrared light emitting diode (IR LED) and mercury cadmium telluride (MCT) detector in which the spectral output of the IR LED and the spectral response of the MCT detector is centered on the spectral absorbance of an ester bond, a defining spectral characteristic of FAME. Other IR LEDs with differing spectral outputs can be used to measure the presence and / or concentration of different analytes in different fluids.
Owner:EMCEE ELECTRONICS
Cadmium telluride/bismuth telluride integrated nano structure material with photo-thermal synergic electric generation and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103451599ARealize the effect of synergistic utilization and conversion of light and heatThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentFinal product manufactureNano structuringMercury cadmium telluride
The invention relates to a cadmium telluride / bismuth telluride integrated nano structure material with photo-thermal synergic electric generation. The preparation method comprises the following: depositing a cadmium telluride nanorod layer on a conducting surface of a conducting glass substrate, and depositing a tellurium-doped bismuth telluride layer on the surface of the cadmium telluride nanorod layer to constitute the cadmium telluride / bismuth telluride integrated nano structure material. The material can simultaneously convert light and heat in the solar spectrum into electric power, thereby implementing the effect of photo-thermal synergic utilization. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the cadmium telluride / bismuth telluride integrated nano structure material.
Owner:杭州知创新材料技术有限公司
Cadmium telluride in-situ passivation method of mercury cadmium telluride infrared focal plane chip
ActiveCN101740662ASimple processEasy to operateFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesMercury cadmium tellurideTe element
The invention discloses a cadmium telluride in-situ passivation method of a mercury cadmium telluride (HgCdTe) infrared focal plane chip, which relates to a manufacturing process technology of a photoelectric detector. The invention adopts the technical scheme that the cadmium telluride in-situ passivation method comprises the following steps of: at the end point of a mercury cadmium telluride infrared detection material grown by molecular beam epitaxy, firstly in situ growing a layer of cadmium telluride film on the surface of an HgCdTe film and carrying out nondestructive cadmium telluride in-situ passivation for the cadmium telluride film at a region to be passivated in the preparation process of an HgCdTe infrared detection chip, thereby effectively solving the problems of detection performance loss and low process stability of a mercury cadmium telluride (HgCdTe) infrared focal plane detection chip caused by a conventional cadmium telluride passivation method. The method has the characteristics of simple process, convenient operation, high stability and good passivation effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for reducing ion implantation damage influence of mercury cadmium telluride photovoltaic device
InactiveCN101226971APrevent inversionImprove performanceFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesIon implantationHydrogen ion
The invention discloses a method for reducing the effects of ion radiation damage of a mercury cadmium telluride photovoltaic device. The method is that a mercury cadmium telluride sample after being injected with ions are defined into a hydrogen ion treatment region through lithography, and then the sample is put in an atmosphere of hydrogen ion to treat. The hydrogen ion treatment region is determined through a method of changing the area, form the size of an initial defined ion implanted region, the hydrogen ion treatment region is gradually enlarged, the current-voltage curve of the mercury cadmium telluride sample which is treated through the hydrogen in different regions is tested, and the size of the hydrogen ion treatment region is determined through observing the increasing phenomenon of a dark current under a reverse bias.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods of forming a conductive transparent oxide film layer for use in a cadmium telluride based thin film photovoltaic device
Methods are generally provided for forming a conductive oxide layer on a substrate. In one particular embodiment, the method can include sputtering a transparent conductive oxide layer (e.g., including cadmium stannate) on a substrate from a target in a sputtering atmosphere comprising cadmium. The transparent conductive oxide layer can be sputtered at a sputtering temperature greater of about 100° C. to about 600° C. Methods are also generally provided for manufacturing a cadmium telluride based thin film photovoltaic device.
Owner:FIRST SOLAR INC (US)
High-pixel infrared focal plane array detector and preparation method thereof
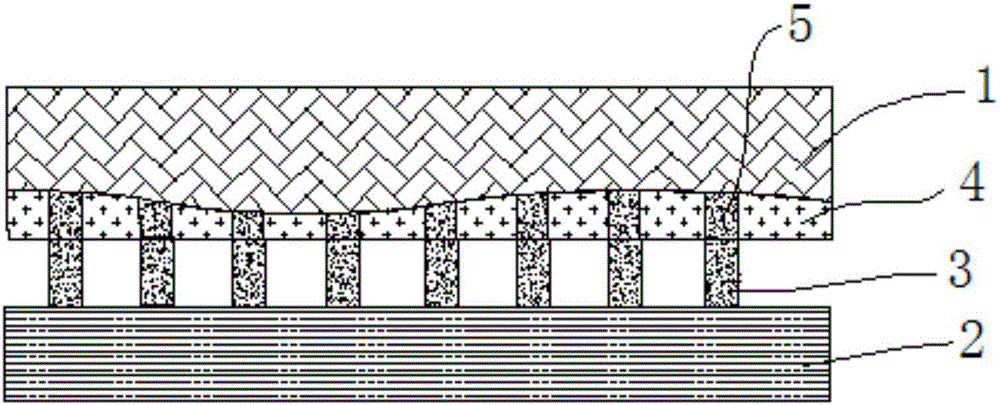
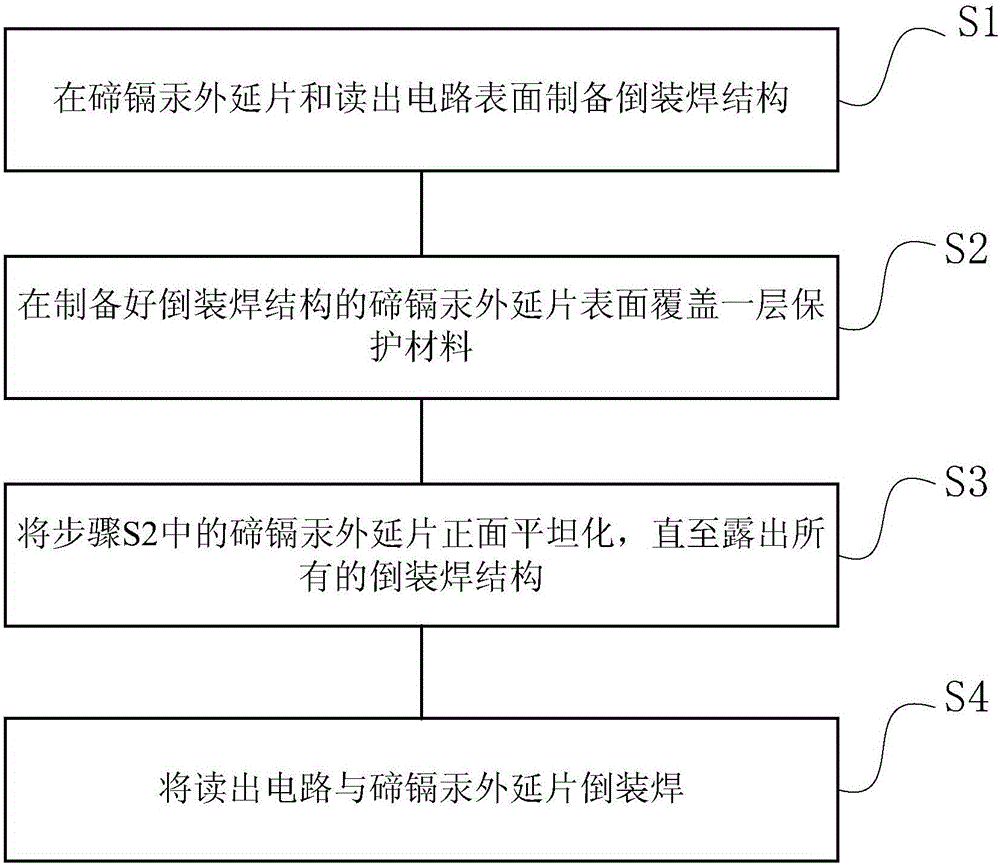
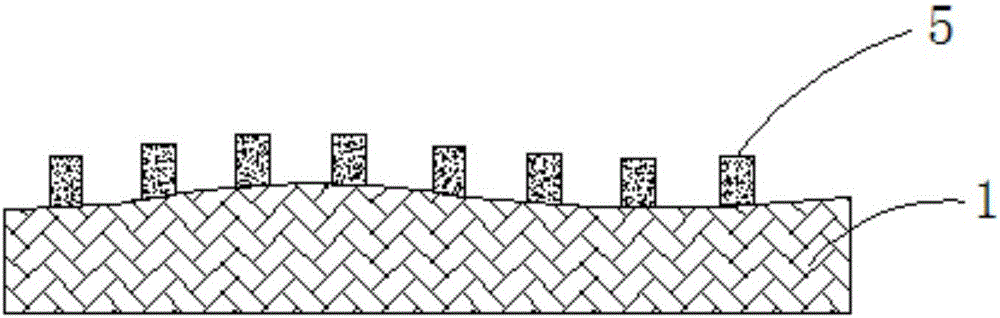
ActiveCN105870097ASolve the problem of flip chip failureEven by forceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAdhesiveMercury cadmium telluride
The invention relates to a high-pixel infrared focal plane array detector and a preparation method thereof. The detector comprises a mercury cadmium telluride epitaxial wafer and a read-out circuit, which are connected with each other, wherein a flip-chip bonding structure is prepared on the surfaces of the read-out circuit and the mercury cadmium telluride epitaxial wafer; a protective material layer also covers the surface of the mercury cadmium telluride epitaxial wafer; a filling adhesive or ZnS and the like can be selected as the protective material; the flip-chip bonding structure exposed outside the surface of the mercury cadmium telluride epitaxial wafer covers the mercury cadmium telluride epitaxial wafer; and the read-out circuit is connected with the mercury cadmium telluride epitaxial wafer through the flip-chip bonding structure. The problem of surface roughness of the mercury cadmium telluride epitaxial wafer is solved through planarization; the flip-chip bonding yield is improved; and meanwhile, the material stress caused by roughness in the flip-chip bonding process is avoided.
Owner:WUHAN GAOXIN TECH
Metallic gridlines as front contacts of a cadmium telluride based thin film photovoltaic device
InactiveUS20110315185A1PV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationMercury cadmium tellurideOptoelectronics
Cadmium telluride based thin film photovoltaic devices are generally described. The device can include a transparent conductive oxide layer on a substrate. A plurality of metal gridlines can directly contact the transparent conductive oxide layer, and can be oriented in a first direction. A cadmium sulfide layer can be included on the transparent conductive oxide layer, and a cadmium telluride layer can be included on the cadmium sulfide layer. A plurality of scribe lines can be defined through the thickness of the cadmium sulfide layer and the cadmium telluride layer to define a plurality of photovoltaic cells such that the plurality of scribe lines are oriented in a second direction that intersects with the first direction.
Owner:FIRST SOLAR INC (US)
Method for producing cadmium telluride or cadmium zinc telluride single crystal
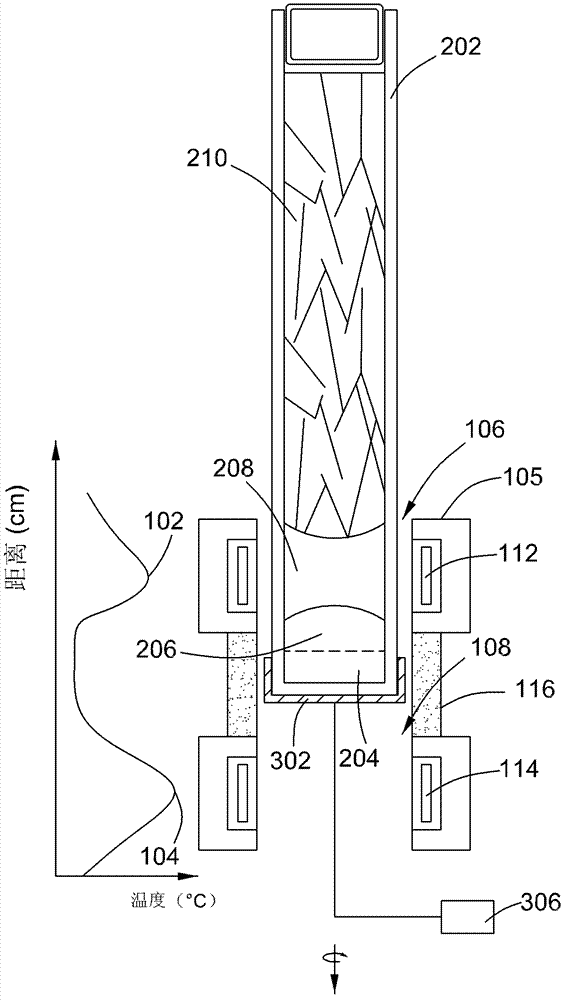
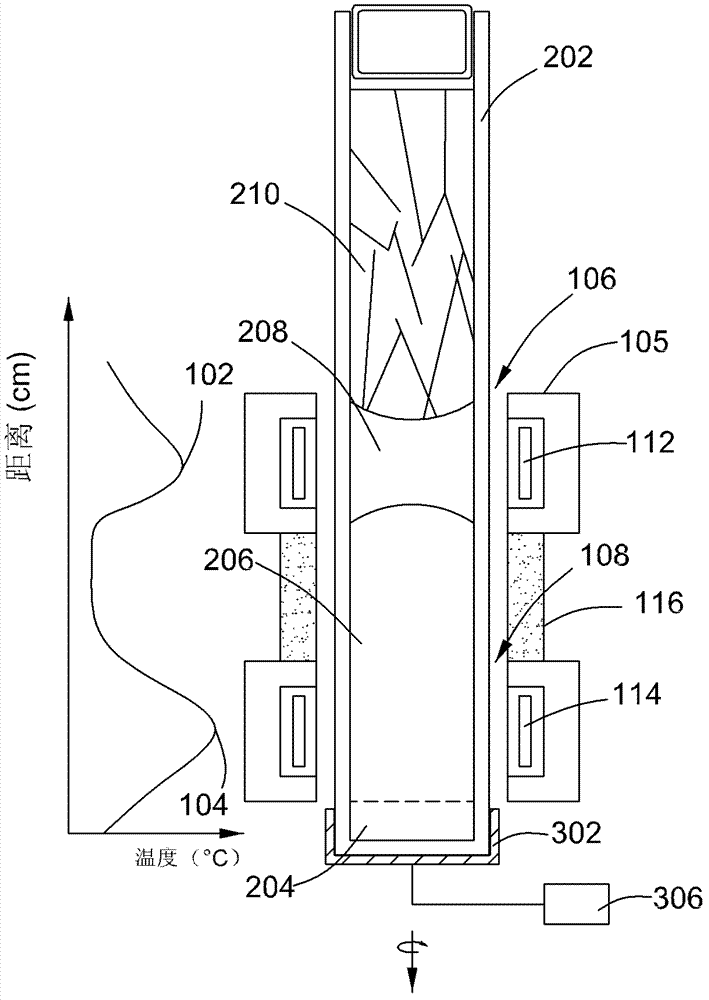
ActiveCN103114335AReduced tellurium inclusion contentPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsMercury cadmium tellurideCrucible
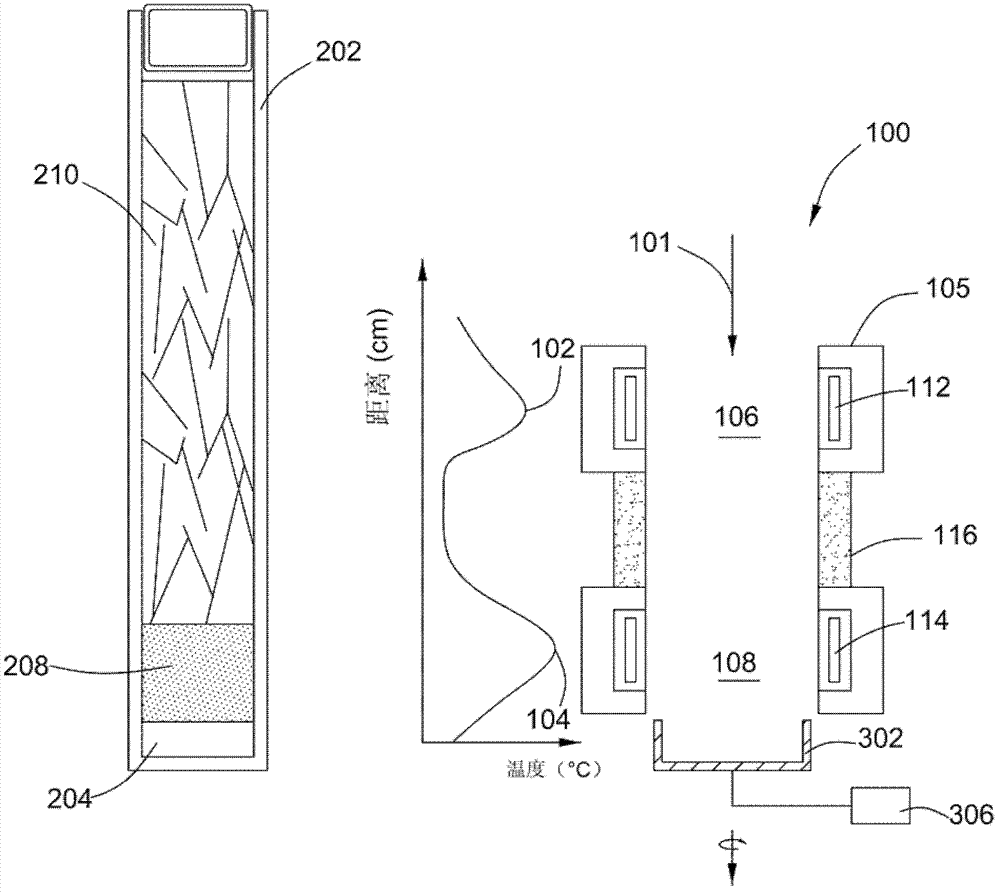
The invention relates to a method for producing a cadmium telluride or cadmium zinc telluride single crystal. The method comprises the following steps of: forming an overall temperature field including a crystal growing zone and an in-situ annealing zone; passing a crucible with a rich-tellurium material and a cadmium telluride or cadmium zinc telluride polycrystalline material through the crystal growing zone, wherein the rich-tellurium material in the crucible is molten to form a melting zone in the process, the cadmium telluride or cadmium zinc telluride polycrystalline material is gradually molten into the melting zone and cooled down and the cadmium telluride or cadmium zinc telluride single crystal is separated out; and passing the crucible through the in-situ annealing zone, wherein the cadmium telluride or cadmium zinc telluride single crystal generated in the crystal growing zone is annealed in the process so as to reduce the tellurium conclusion content of the single crystal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com