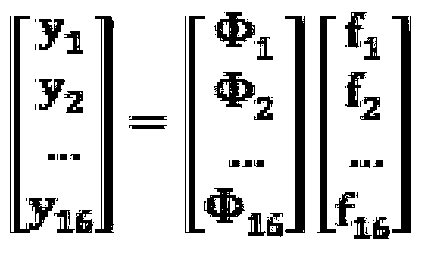Patents
Literature
512 results about "Medium wave" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Medium wave (MW) is the part of the medium frequency (MF) radio band used mainly for AM radio broadcasting. For Europe the MW band ranges from 526.5 kHz to 1606.5 kHz, using channels spaced every 9 kHz, and in North America an extended MW broadcast band ranges from 525 kHz to 1705 kHz, using 10 kHz spaced channels. The term is a historic one, dating from the early 20th century, when the radio spectrum was divided on the basis of the wavelength of the waves into long wave (LW), medium wave, and short wave (SW) radio bands.
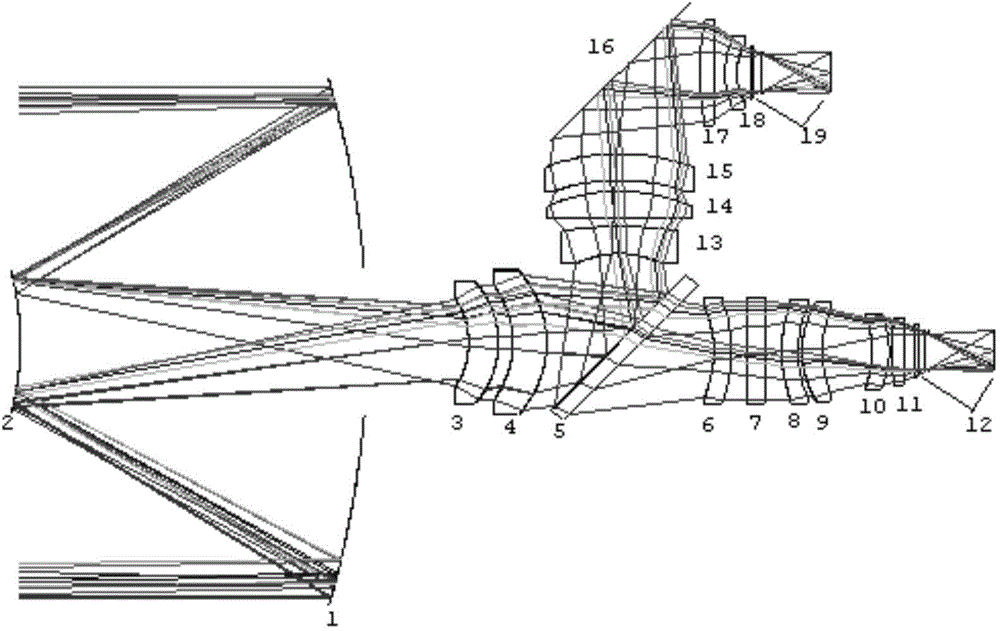
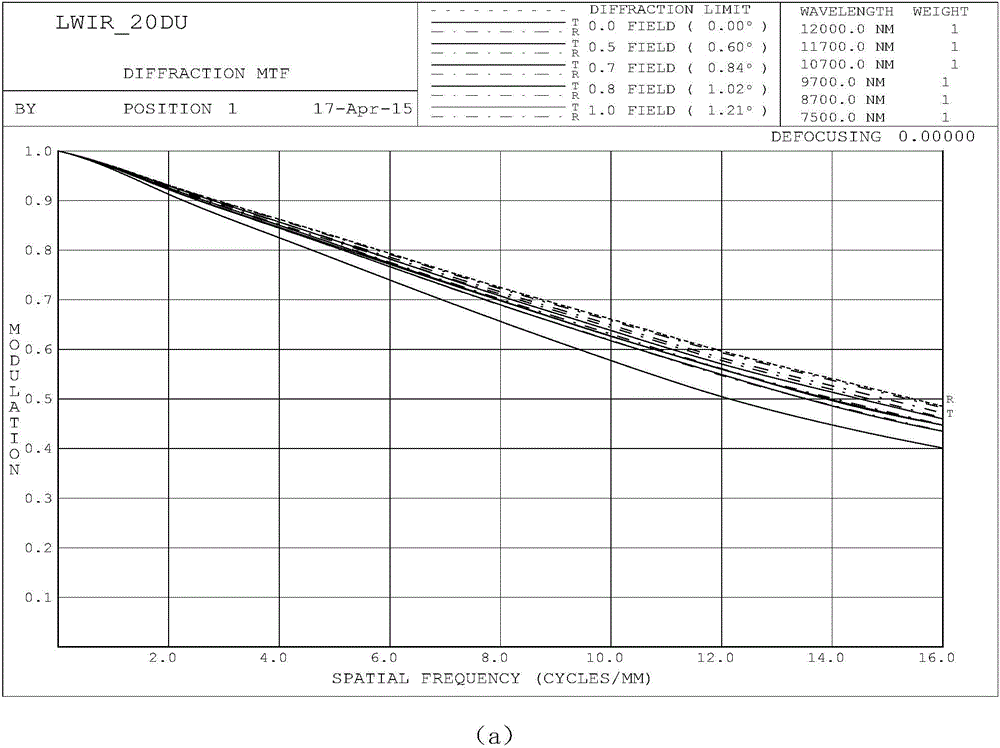
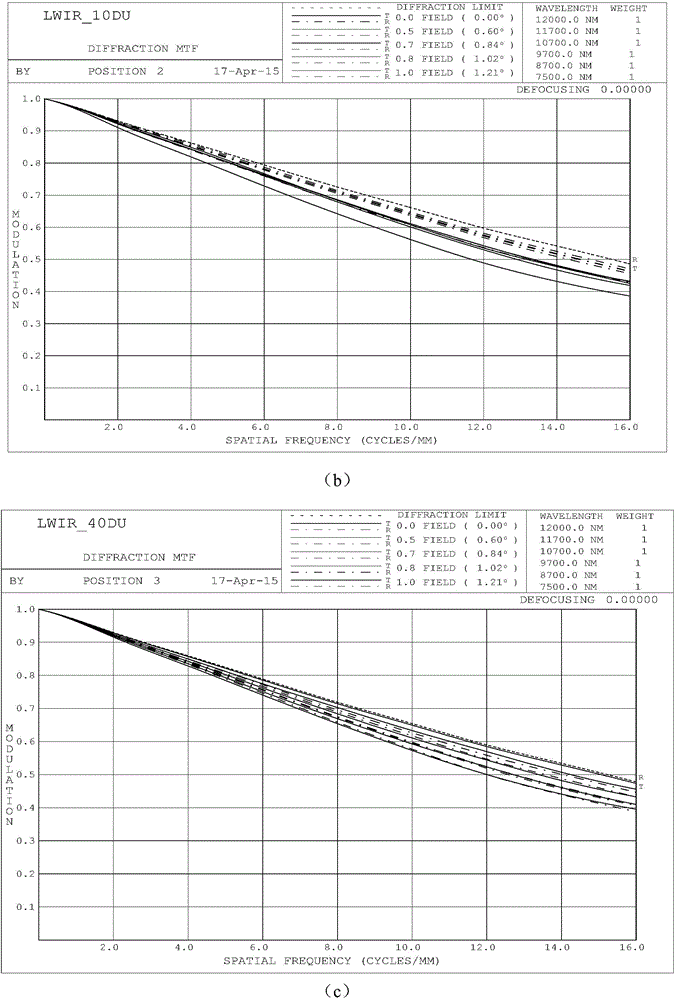
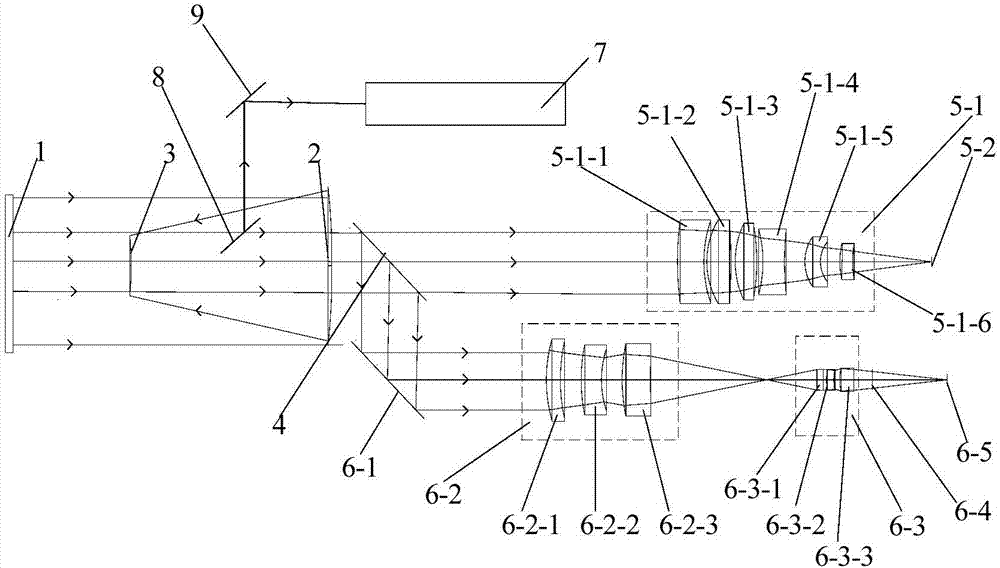
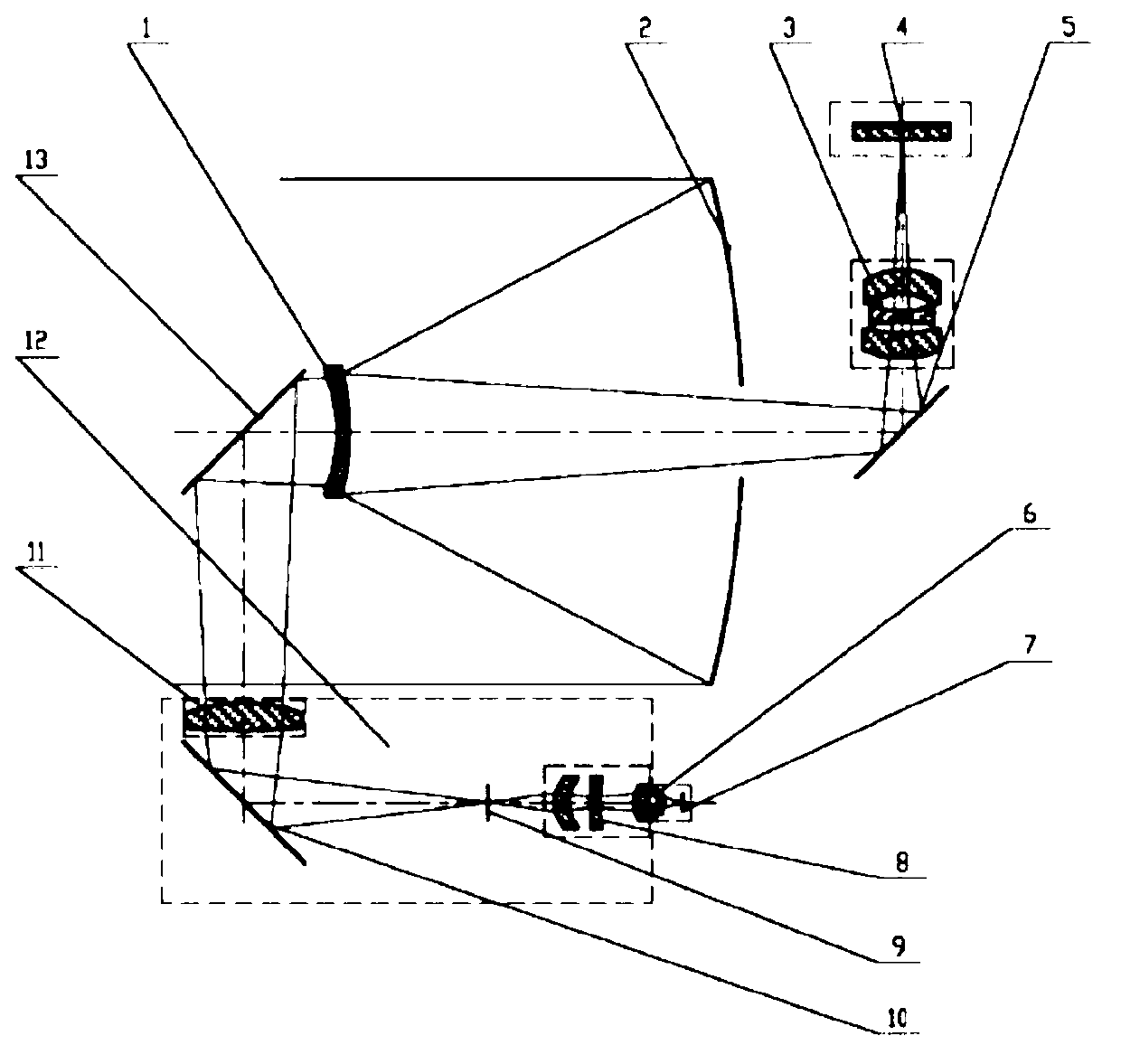
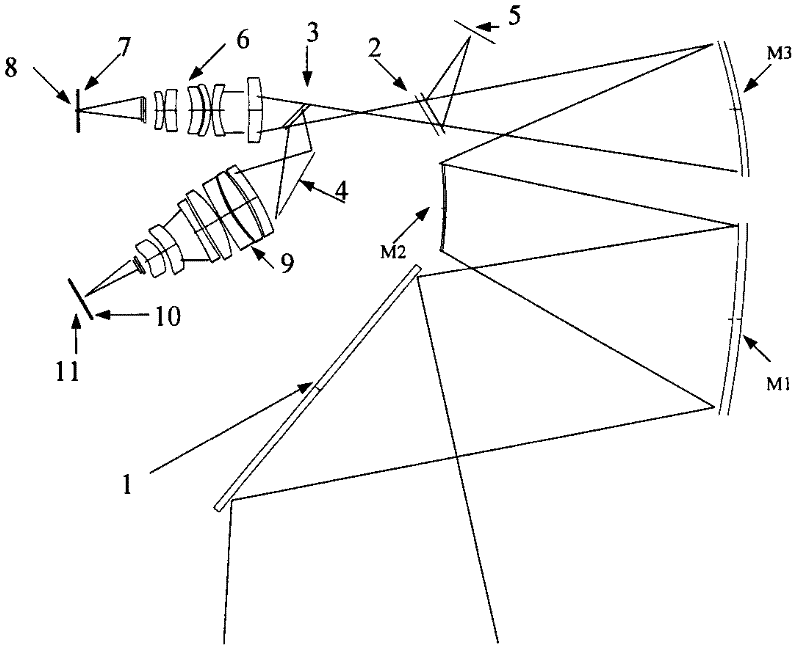
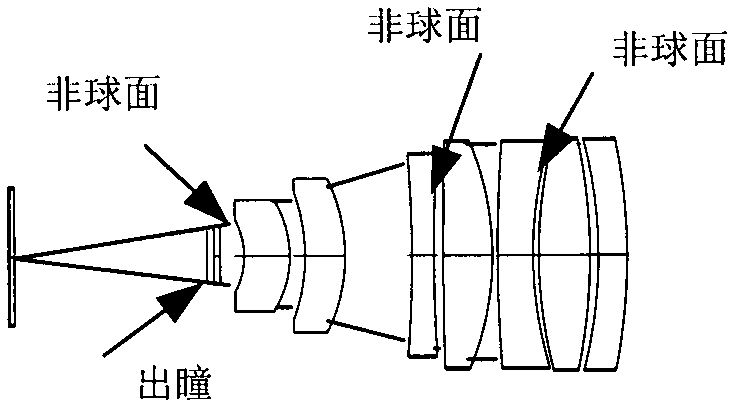
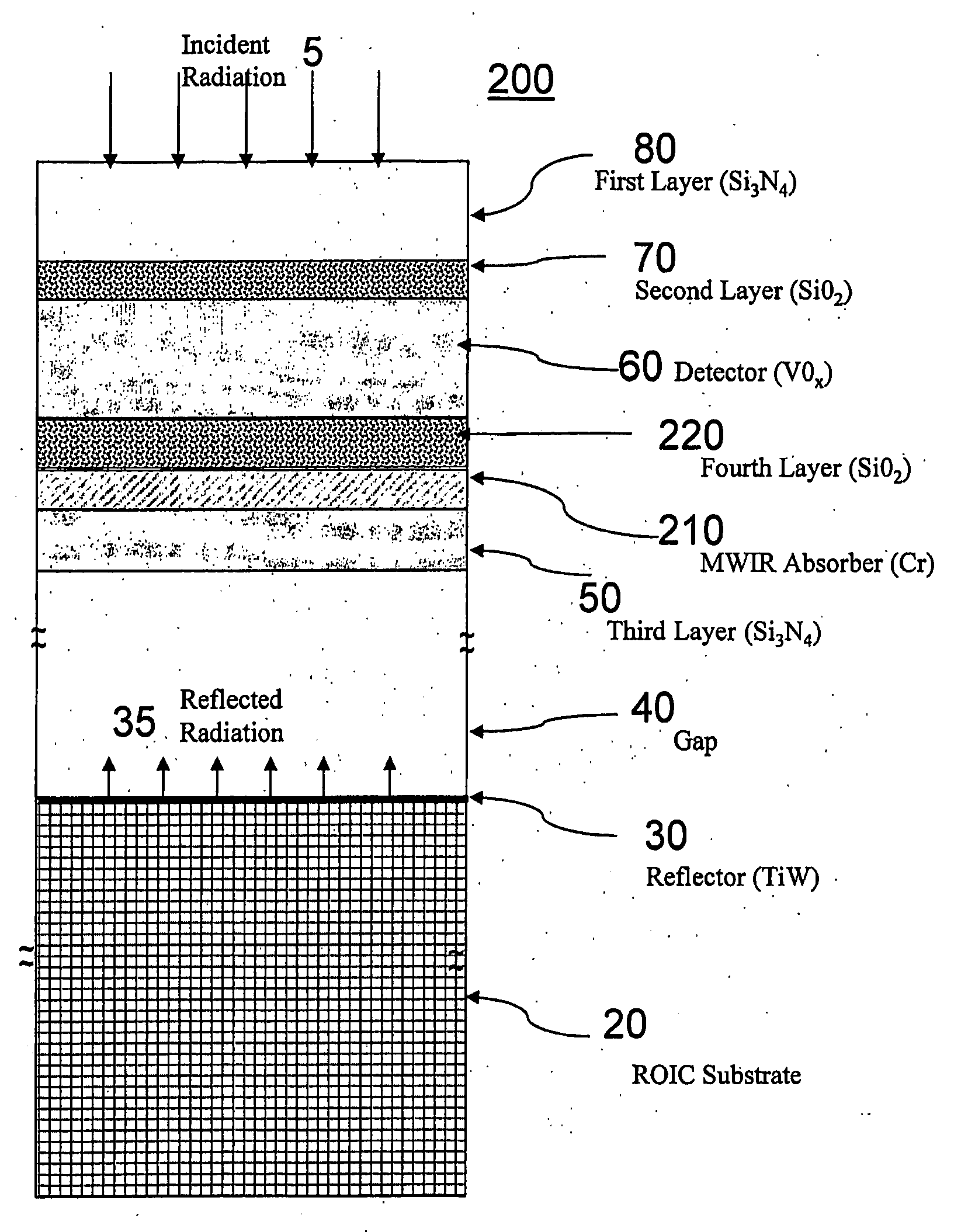
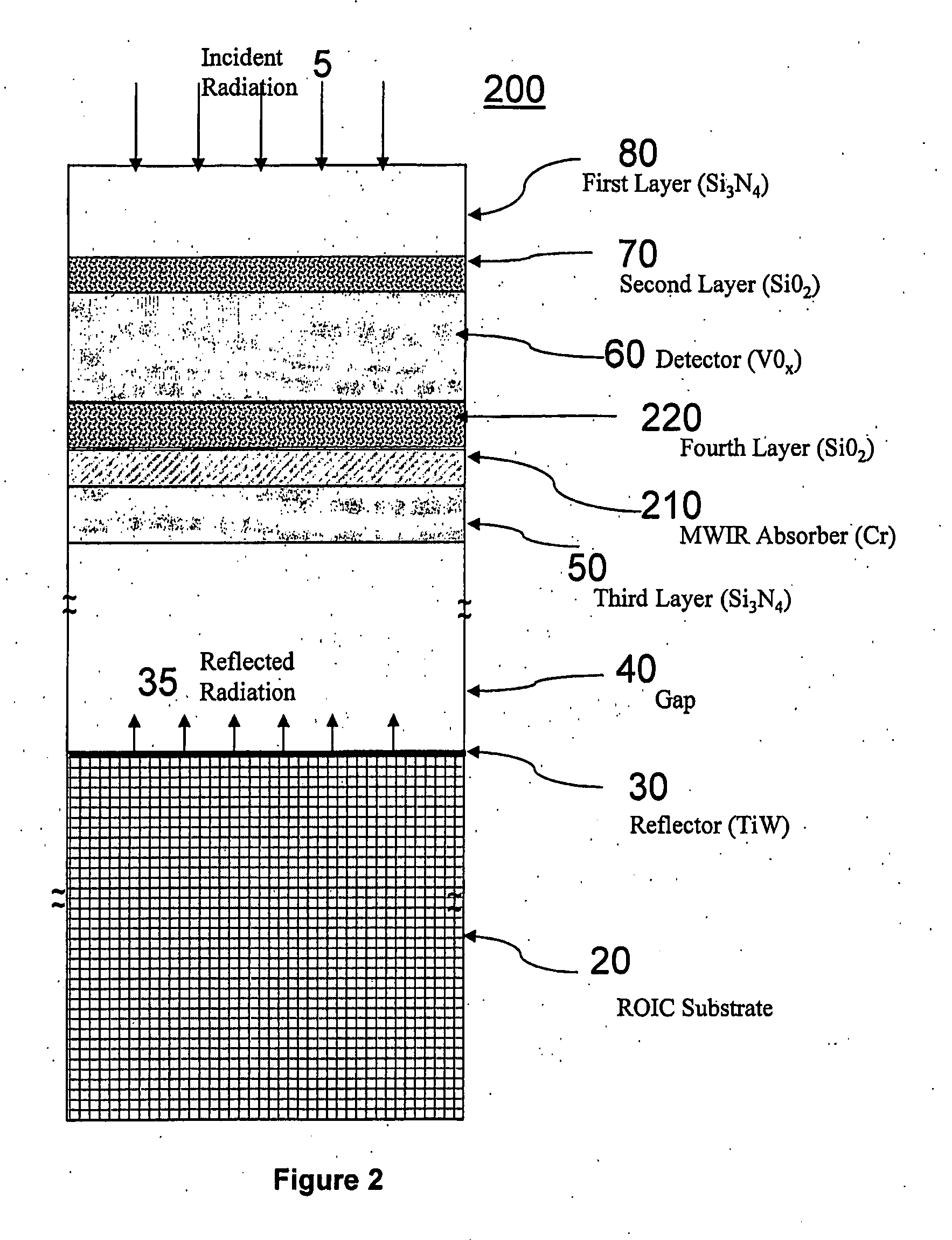
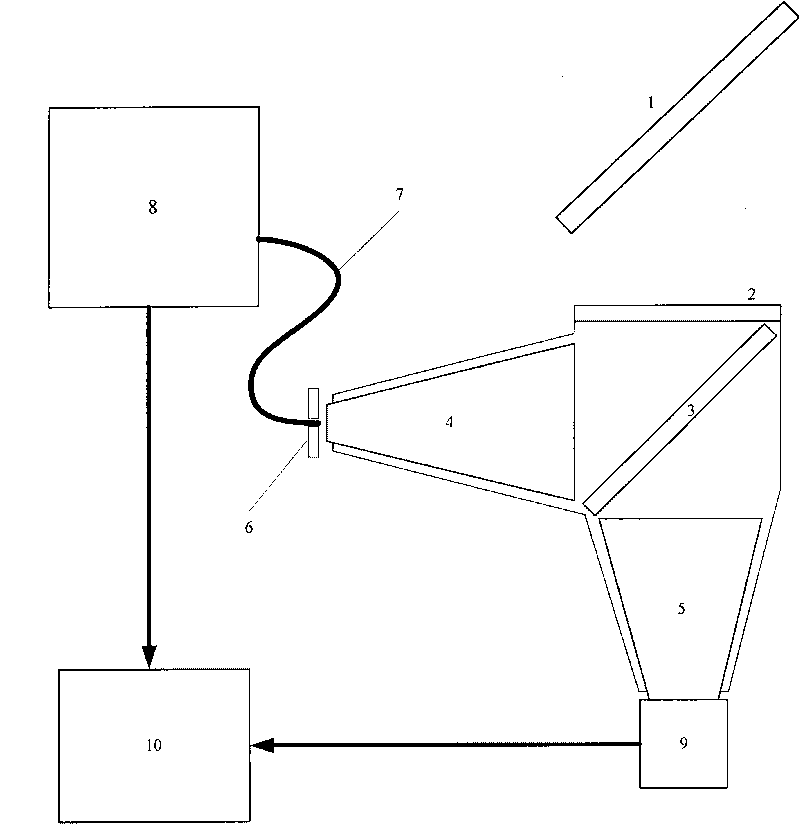
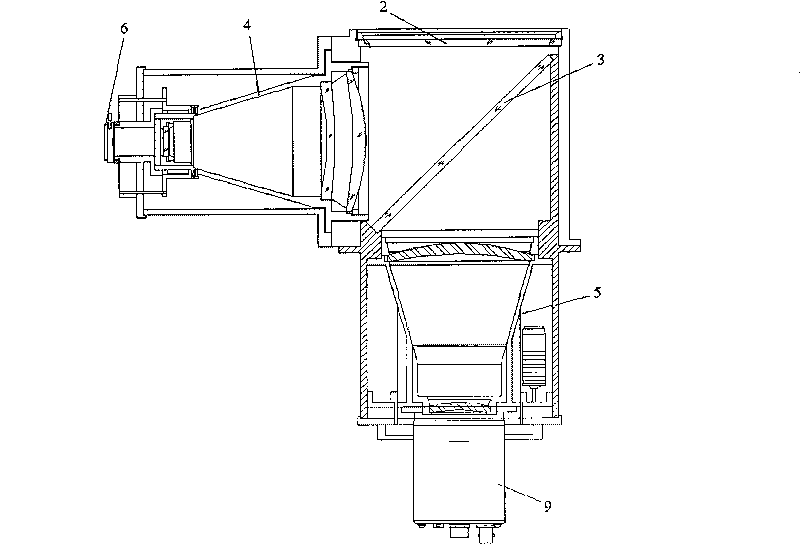
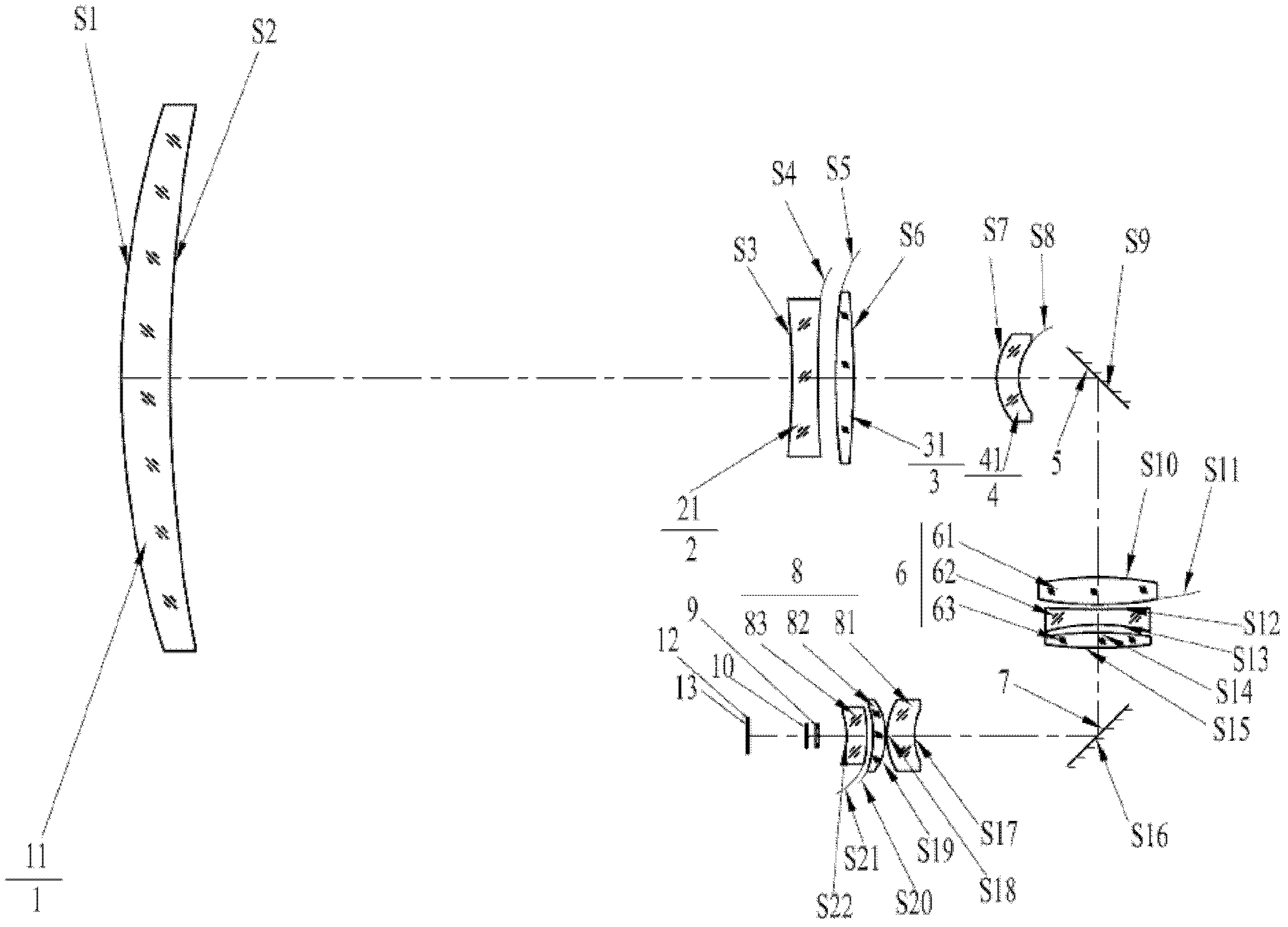
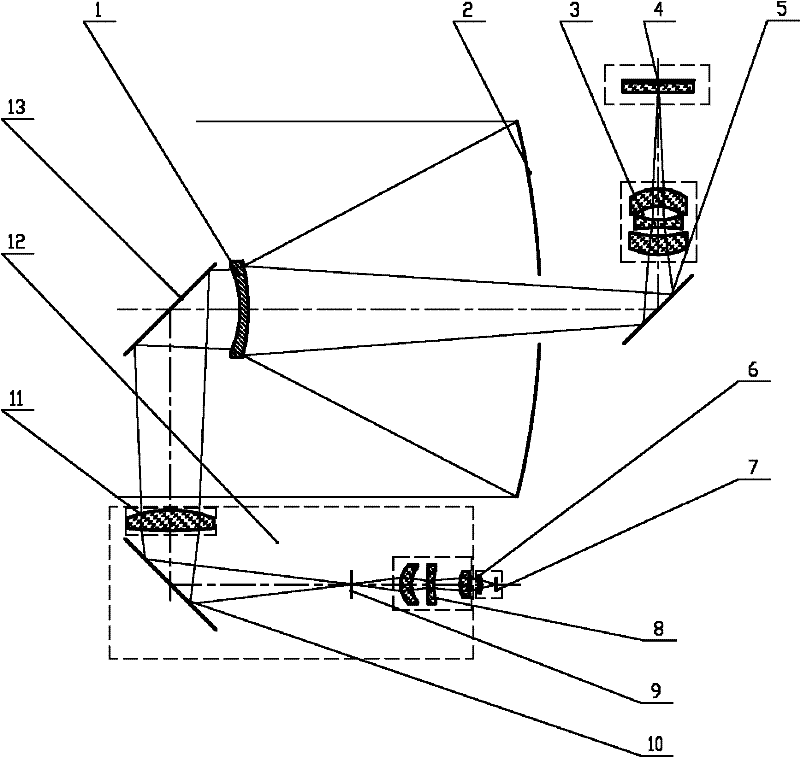
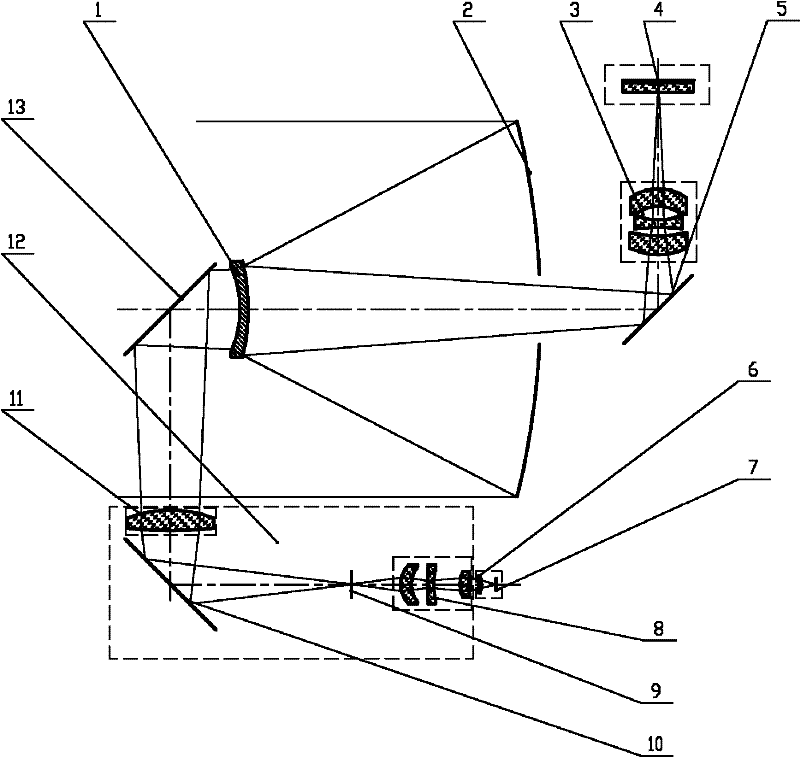
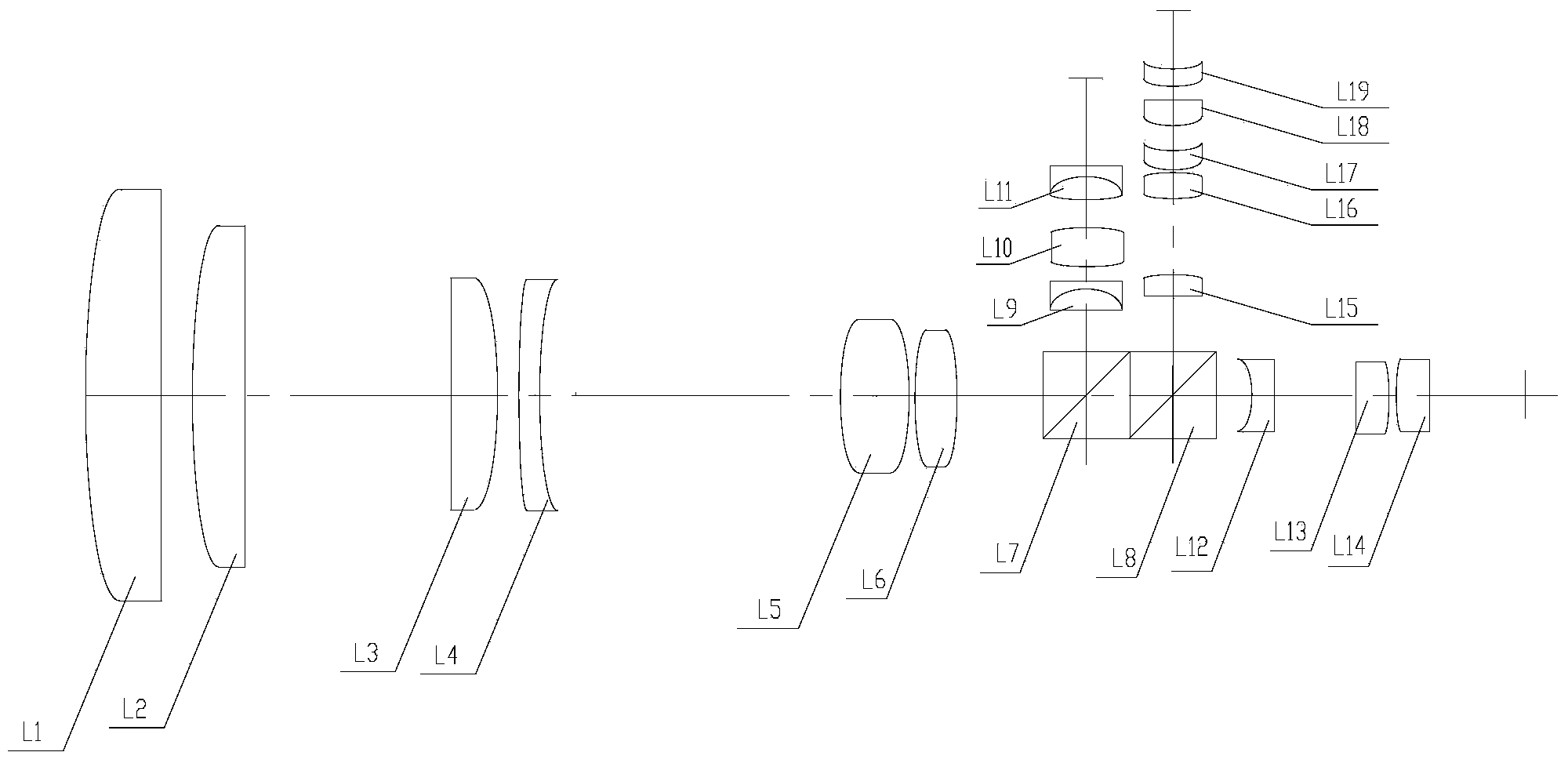
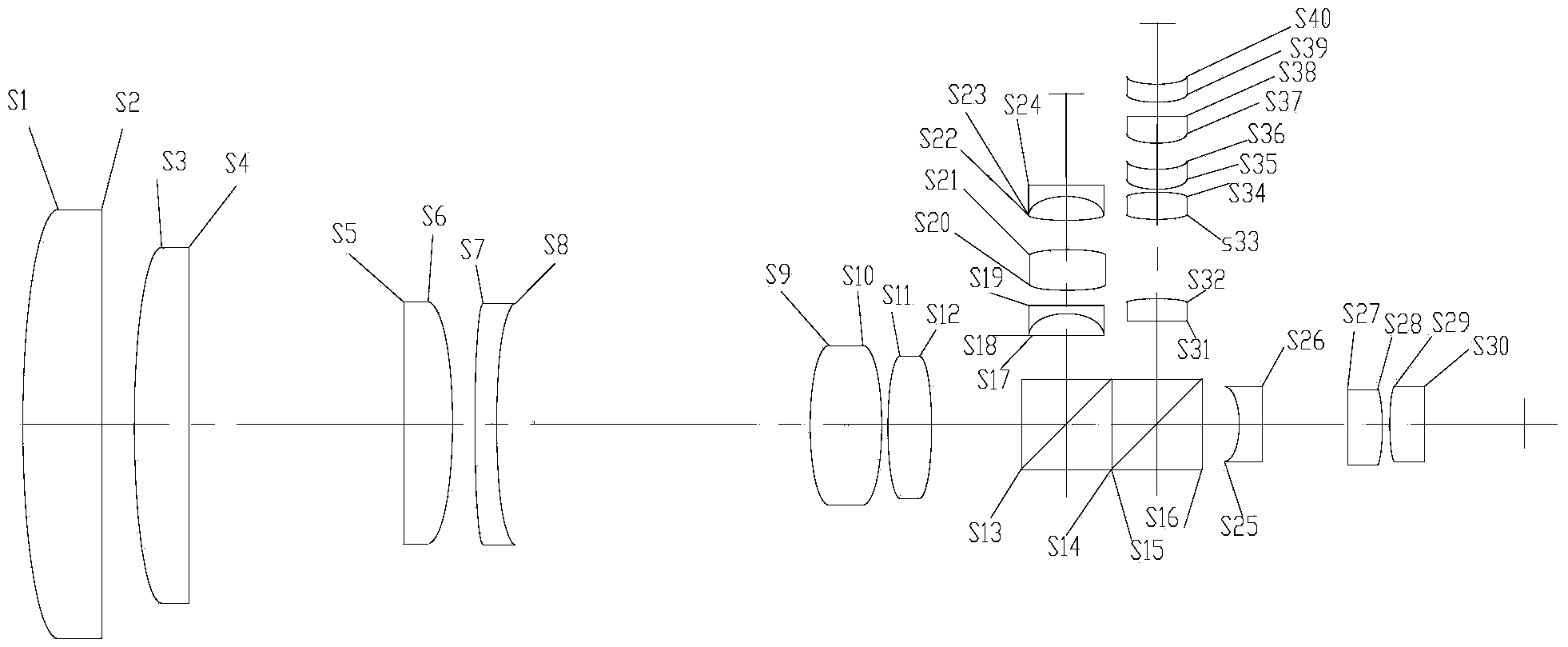
Laser and middle- and long-wavelength infrared common-aperture three-band imaging system
ActiveCN103278916AReduce volumeExcellent aberration correctionOptical elementsBeam splitterImaging quality
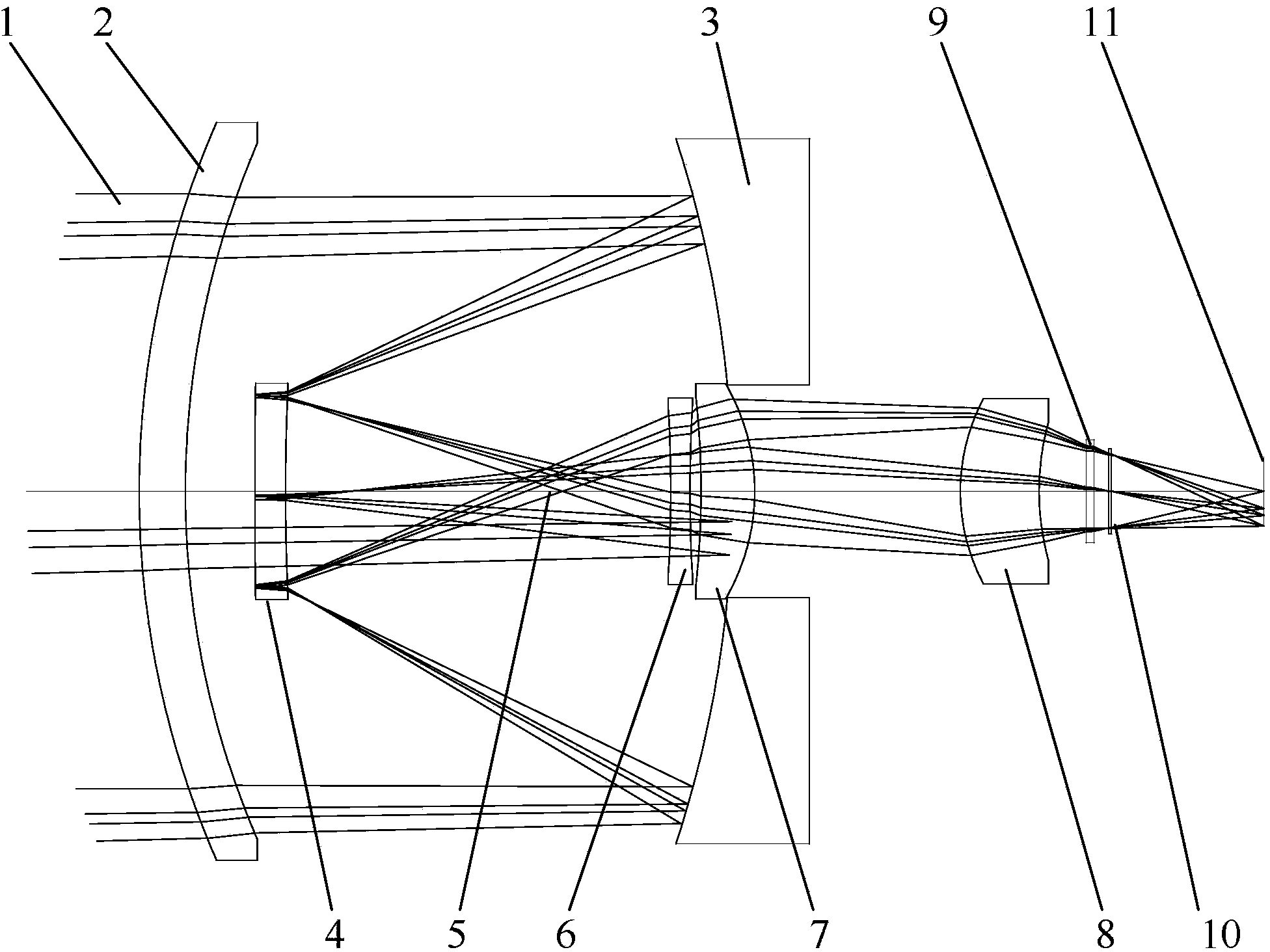
The invention relates to a laser and middle- and long-wavelength infrared common-aperture three-band imaging system, which comprises an entrance pupil shared by each band, a primary mirror, a secondary convex mirror, a middle / long-wavelength infrared optical path imaging lens group, a laser converging light spot receiving unit, a middle- and long-wavelength infrared band beam splitter, a middle- and long-wavelength infrared dual-band imaging lens group and a detection image surface, wherein the reflection surface of the primary mirror is a concave surface, and a hole is formed in the center of the primary mirror. The system can be used for realizing the common-aperture collection of scene infrared radiation energy of the same object and laser echo energy reflected by the object; and the entrance pupil is positioned in front of the primary mirror, the secondary mirror is used for the beam splitting of laser and middle- and long-wavelength infrared bands, and a dichroic mirror is inclined to split middle-wavelength infrared light and long-wavelength infrared light, so that the system is compact in structure, the utilization rates of optical energy and space of the system are increased, the aberration correction and beam focusing of middle- and long-wavelength infrared bands are facilitated respectively, and the imaging quality is remarkably improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
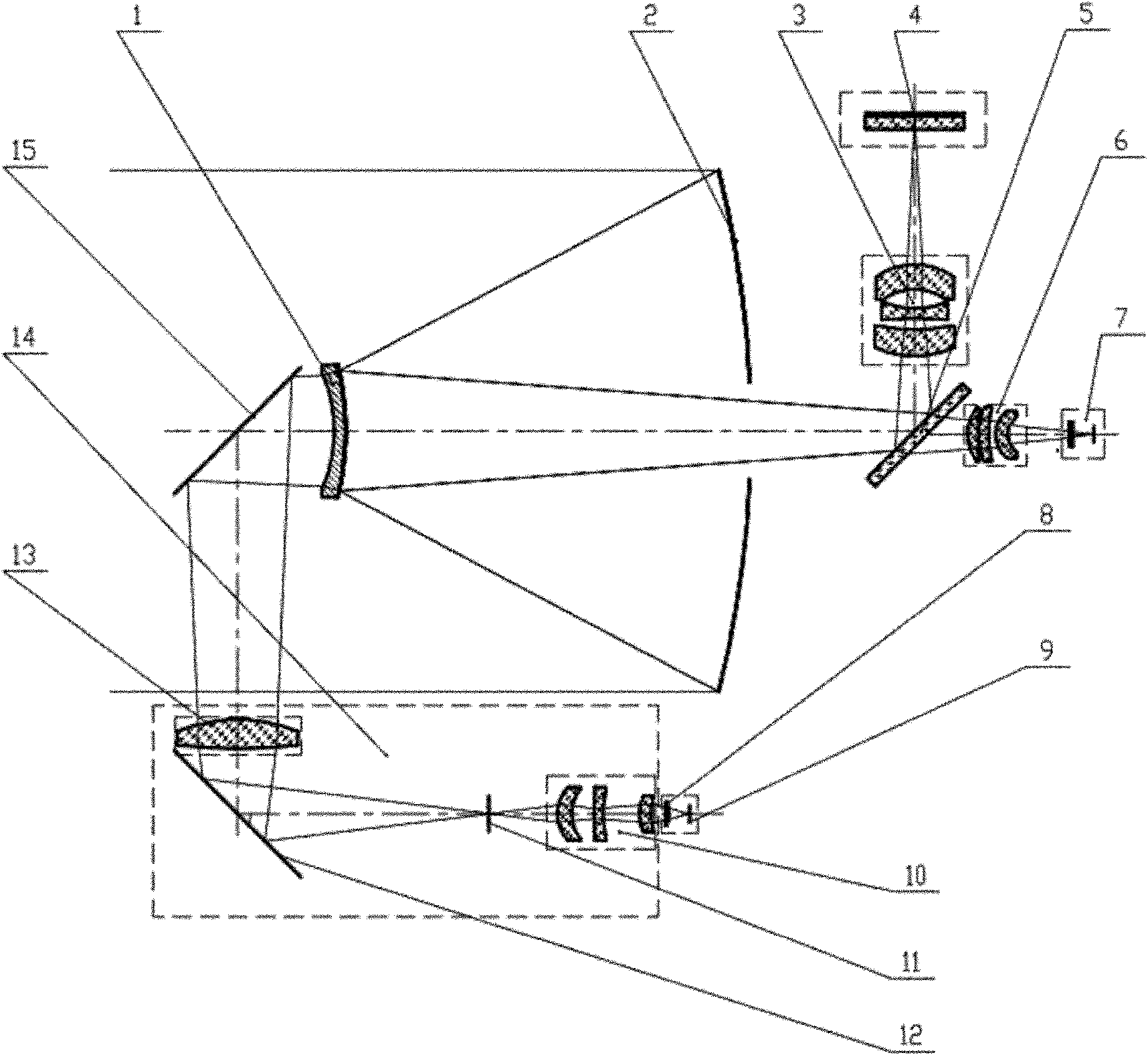
Spatial large view field, superwide spectral band and multispectral imaging optical system
InactiveCN102508361AReduce in quantityNo color differenceRadiation pyrometryCoatingsSpectral bandsLarge range
The invention discloses a spatial large view field, superwide spectral band and multispectral imaging optical system, which comprises a switching reflector, a main optical off-axis three-reflector system, a medium- and short-wave focus-free relaying optical system and a long-wave focus-free relaying optical system, wherein a radiation light beam of an imaging target enters from the switching reflector, and is divided into light rays in three channels, namely a visible multispectral channel, a short-wave / medium-wave channel and a long-wave infrared channel, by color division sheets after passing through the main optical off-axis three-reflector system; the light ray in the visible multispectral channel is reflected by the first color division sheet, and then full-color multispectral imaging is realized through a five-color device; the light rays in the short-wave / medium-wave channel and the long-wave infrared channel are transmitted / reflected by the second color division sheet, respectively pass through the own focus-free relaying optical systems, and then are focused on a focal surface for imaging after being subdivided by filters. The spatial large view field, superwide spectral band and multispectral imaging optical system has the advantages of large view field, large relative aperture, wide spectral range, high subdivision degree, compact structure, small volume, light weight and the like; and large-range, all-day and high-resolution dynamic and stable detection can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH
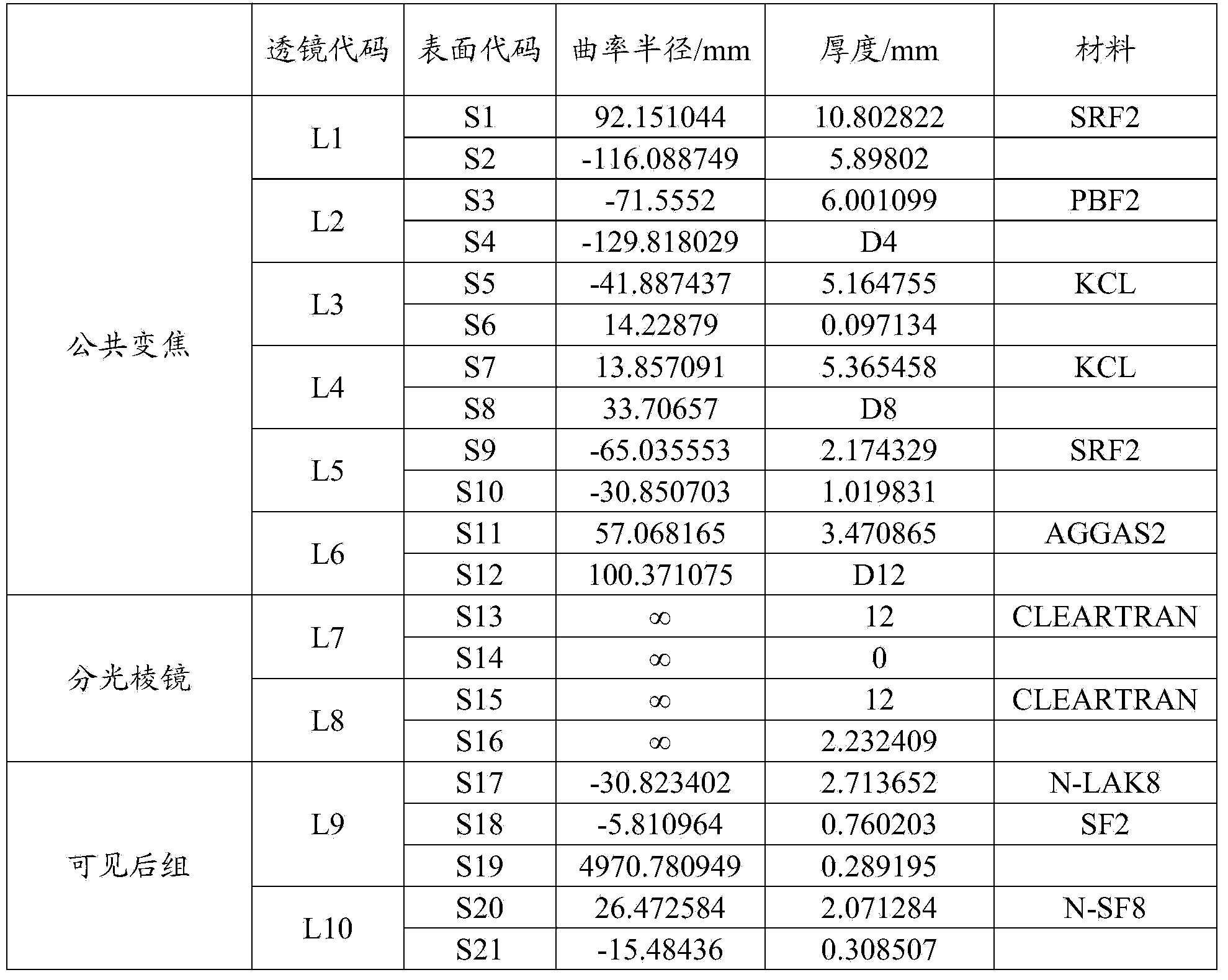
Medium wave infrared continuous zoom lens
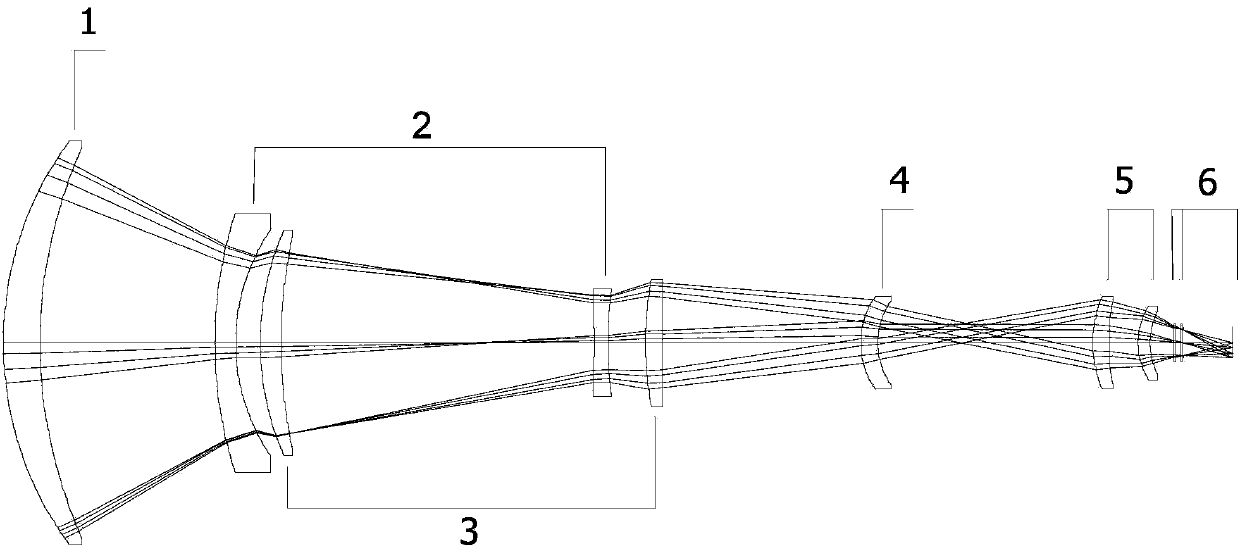
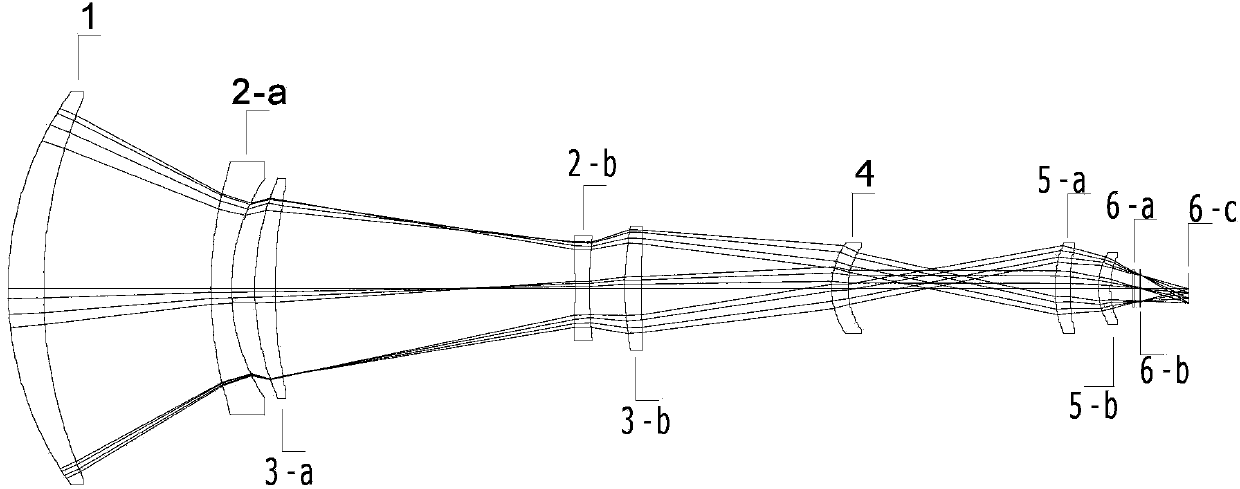
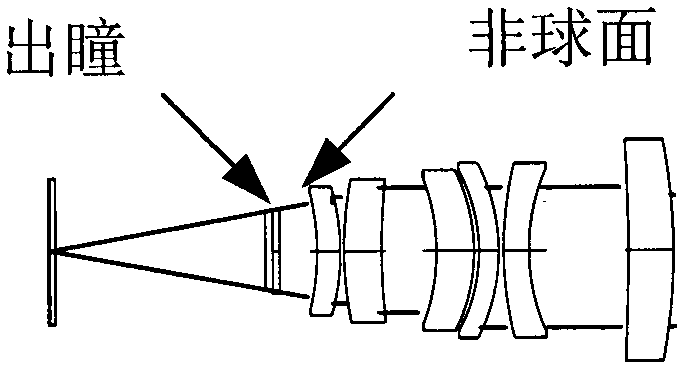
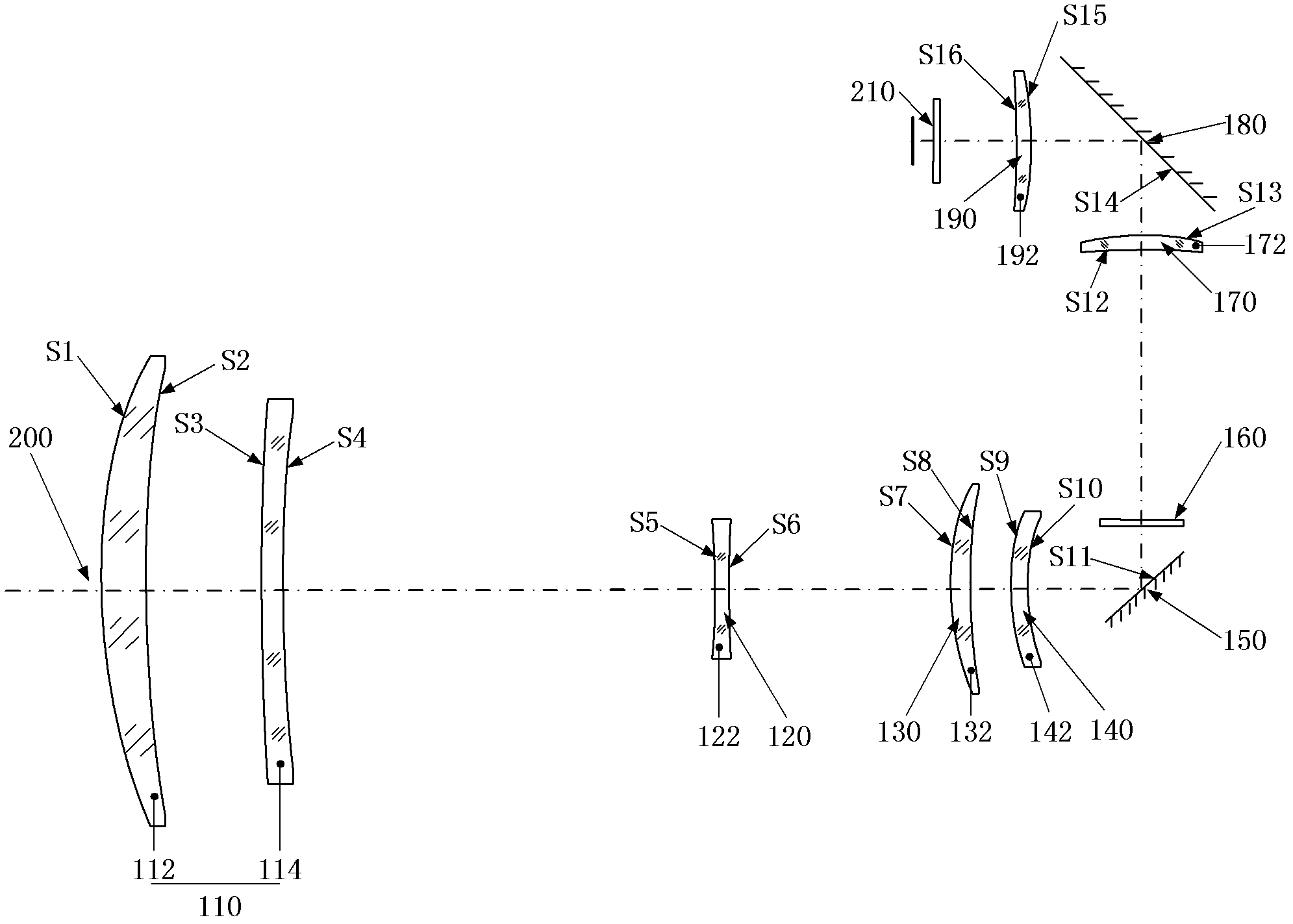
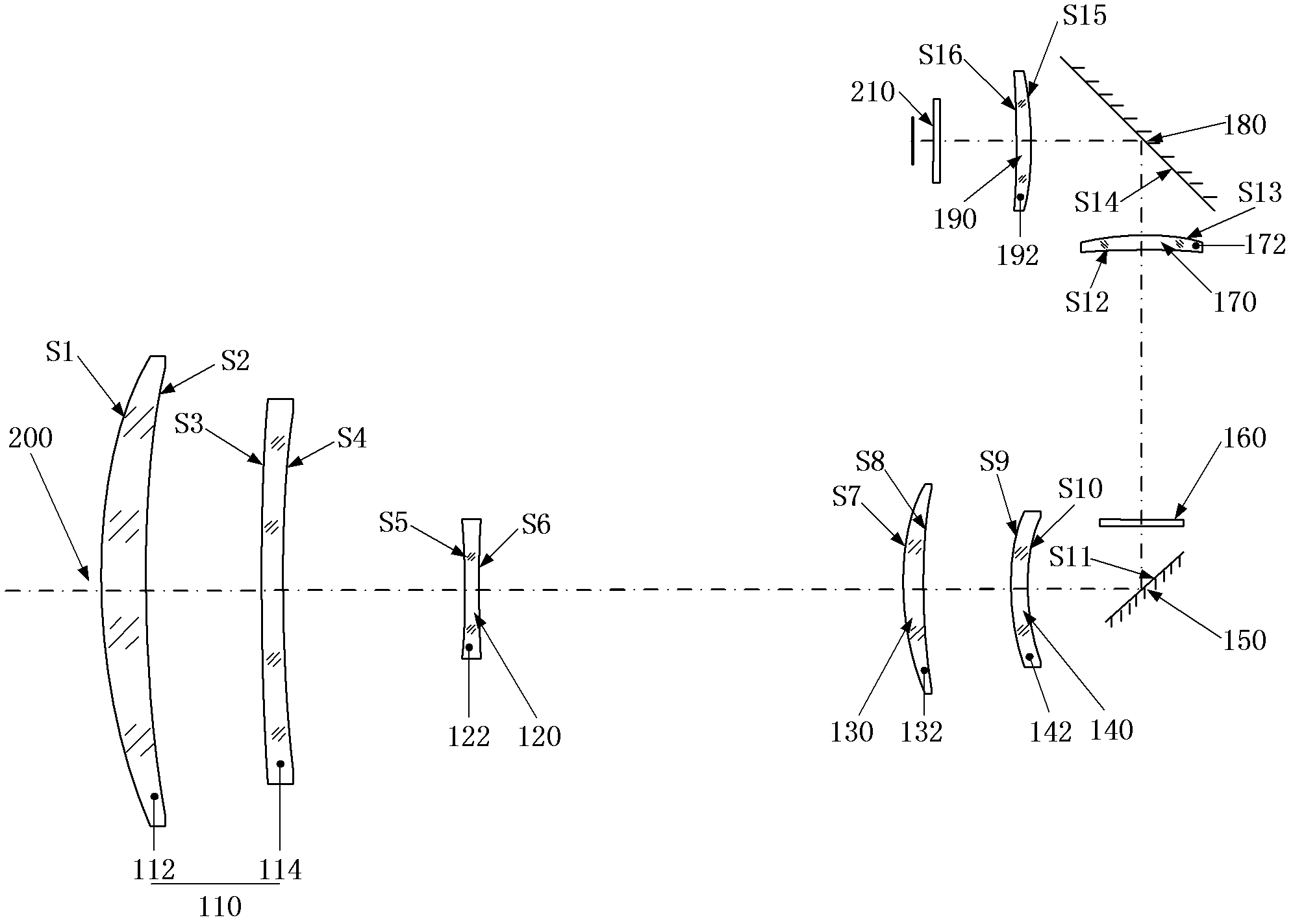
The invention discloses a medium wave infrared continuous zoom lens. The medium wave infrared continuous zoom lens comprises a first lens group with positive diopter, a second lens group with negative diopter, a third lens group with positive diopter, a fourth lens group with negative diopter, a first reflector for turning back a light path, a flat plate reference source for correcting a background, a fifth lens group with positive diopter and a sixth lens group with positive diopter from an object space to an image space, wherein the first lens group serving as a front fixing group comprisesa crescent silicon positive lens of which the convex surface faces the object side and a crescent germanium negative lens of which the convex surface faces the object side; the second lens group is used as a zoom group; the third lens group is used as a compensation group; the fourth lens group is used as a rear fixing group; the fifth lens group is used as a relaying group; and the sixth lens group is used as a focusing group. The medium wave infrared continuous zoom lens can be applied to 640*512-element or even larger surface array refrigeration medium wave detectors; and the medium wave infrared continuous zoom lens has a simple structure and low motion charge; and only two lenses move during zooming.
Owner:11TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
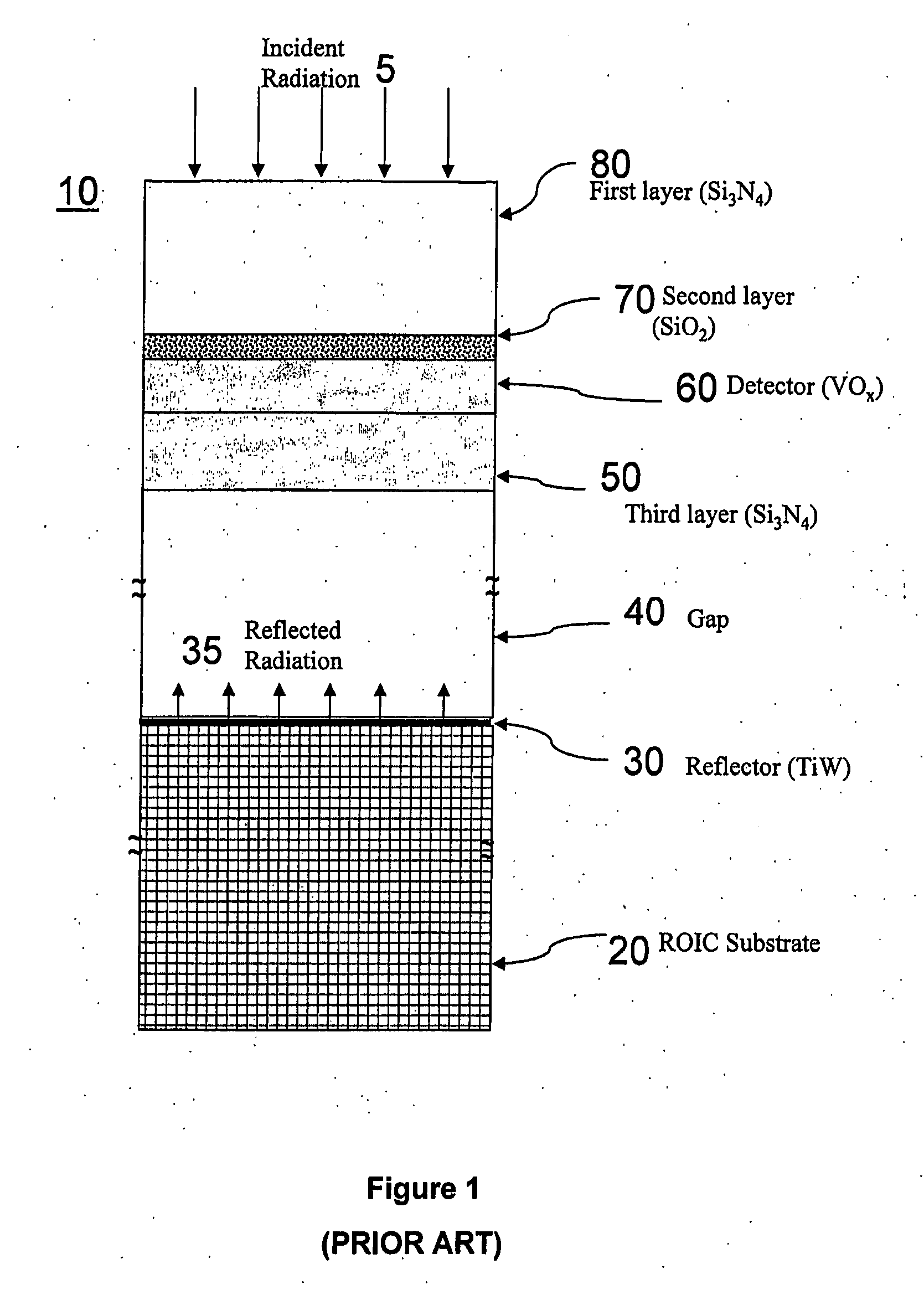
Multi-spectral uncooled microbolometer detectors
InactiveUS20070176104A1High sensitivitySpectrum investigationSolid-state devicesMicrobolometerWave band
A process and system for a medium wave infrared (MWIR) uncooled microbolometer focal plane array (FPA). One embodiment is for a single MWIR band uncooled IR detector, wherein the design and fabrication utilizes standard silicon processing techniques reducing manufacturing costs and preserving existing manufacturing capabilities. Another embodiment is a two color uncooled microbolometer IR detector providing broadband detection.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Multiband infrared radiation automatic measuring system
ActiveCN101793563AEliminate inconsistenciesTo achieve the purpose of real-time correctionRadiation pyrometryBlack-body radiationControl system
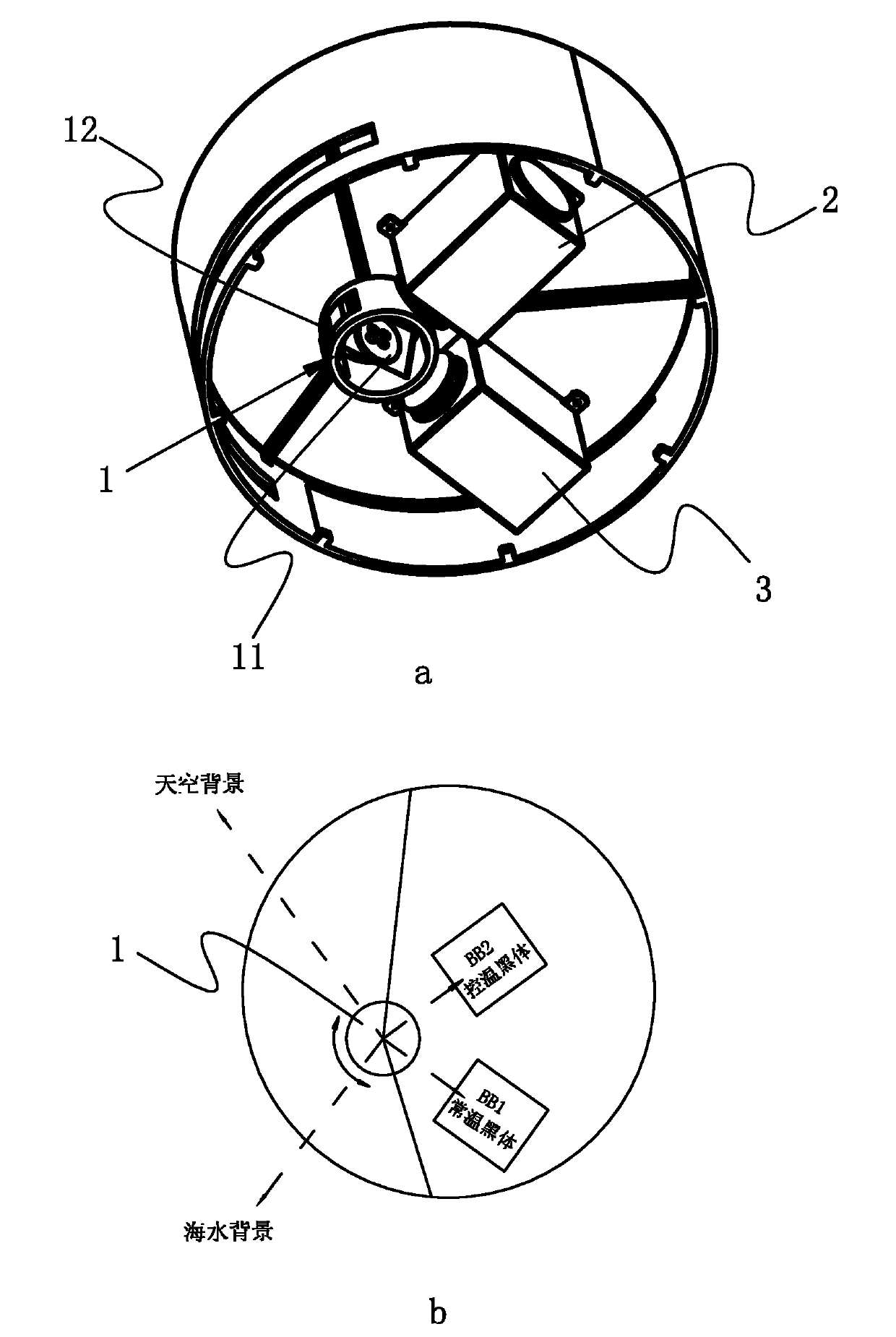
The invention provides a multiband infrared radiation automatic measuring system which can timely and automatically measure the infrared radiation characteristics of a measured object within different bands under complicated backgrounds and completely meets the requirements of long-term fault-free automatic observation radiation calibration measurement. The multiband infrared radiation automatic measuring system comprises a scanning device, a light splitting device, an infrared detection device and a control system / circuit, wherein the scanning device, the light splitting device and the infrared detection device are sequentially arranged on a light path in a radiation incident direction; and the scanning device comprises a protection window capable of rotating, a rotary reflecting mirror and a fixed double-blackbody correction assembly. In the invention, light spectrum light splitting and band modulating and canning technologies are used, and two medium and long wave detectors are selected to match with the technologies, thereby increasing measurable optical channels to effectively form the radiation calibration measurement to more long-wave and medium wave bands. Moreover, the radiation size required by a blackbody radiation cavity is compressed, the design and manufacture difficulties of the blackbodies are reduced, and the controllable precision is improved.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
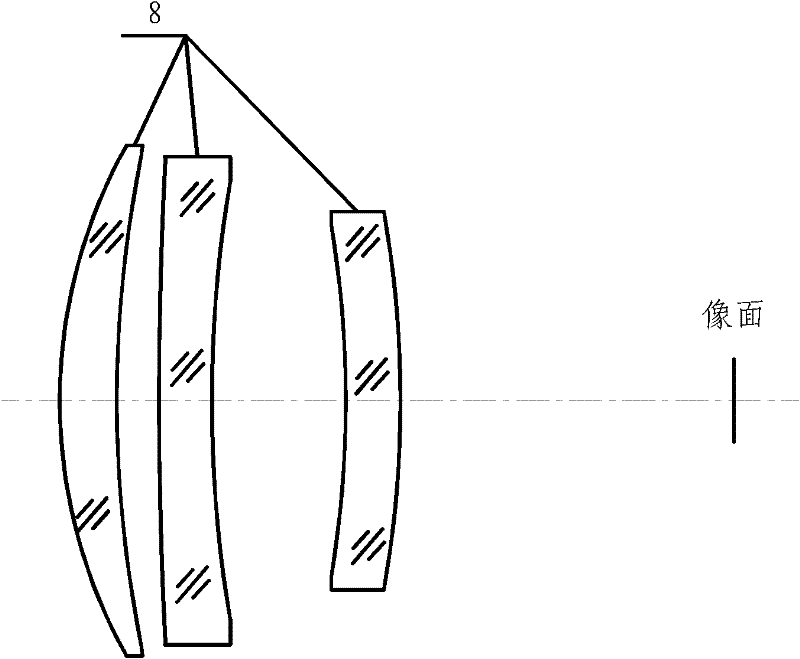
Low-cost refracting-reflecting athermalizing medium wave infrared lens
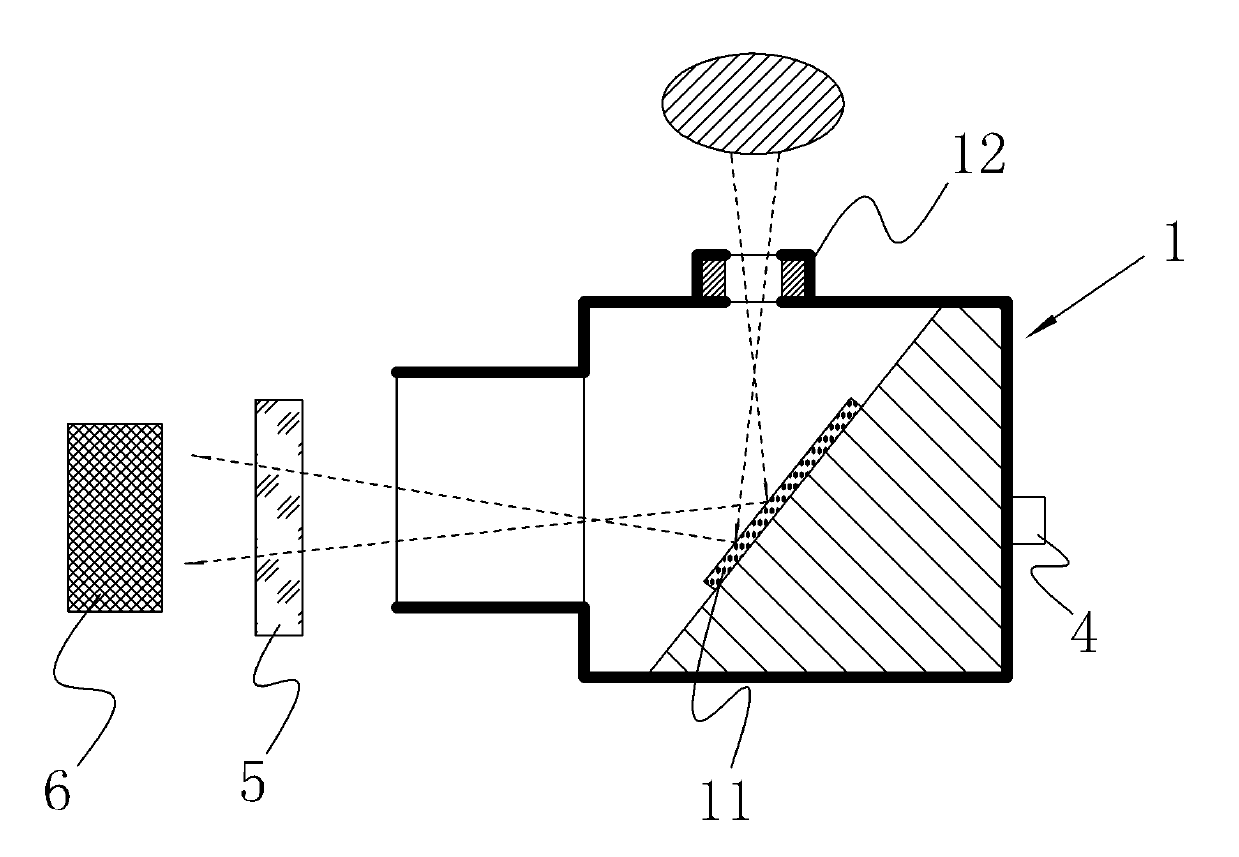
The invention provides a low-cost refracting-reflecting athermalizing medium wave infrared lens and aims at providing a low-cost refracting-reflecting optical lens which is small in aspherical mirror number, low in cost, made of a small amount of aspherical lenses and conventional silicon and germanium optical materials at a 3.7-4.8 [mu]m medium-wave infrared band and having the optical passive athermalizing performance. The technical scheme is that parallel light enters a main reflection spherical mirror (3) to form a converged light beam through a spherical cover (2) in an incidence mode, a convergence angle is decreased through a Mangin refracting-reflecting mirror (4), a primary mirror face (5) is formed by decreasing a part of aberration and increasing a part of balanced aberration and negative thermal difference of a lens to be arranged behind, the light beam is changed into divergent light, the divergent light enters a negative lens (6) made of an aspherical germanium material and a positive meniscus lens (7) made of a silicon material so as to reduce chromatic aberration and aberration, then converges through a positive convex lens (8) made of the silicon material, enters a detector window (9) and finally forms an image on a detector focal plane (11) through a cold light diaphragm (10), and the whole imaging process is finished.
Owner:SOUTH WEST INST OF TECHN PHYSICS
Device and method for cooperatively detecting moving target by using all-optical-waveband map
ActiveCN105182436ASimple structureReduce dampingRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationVisible near infraredNarrow-band imaging
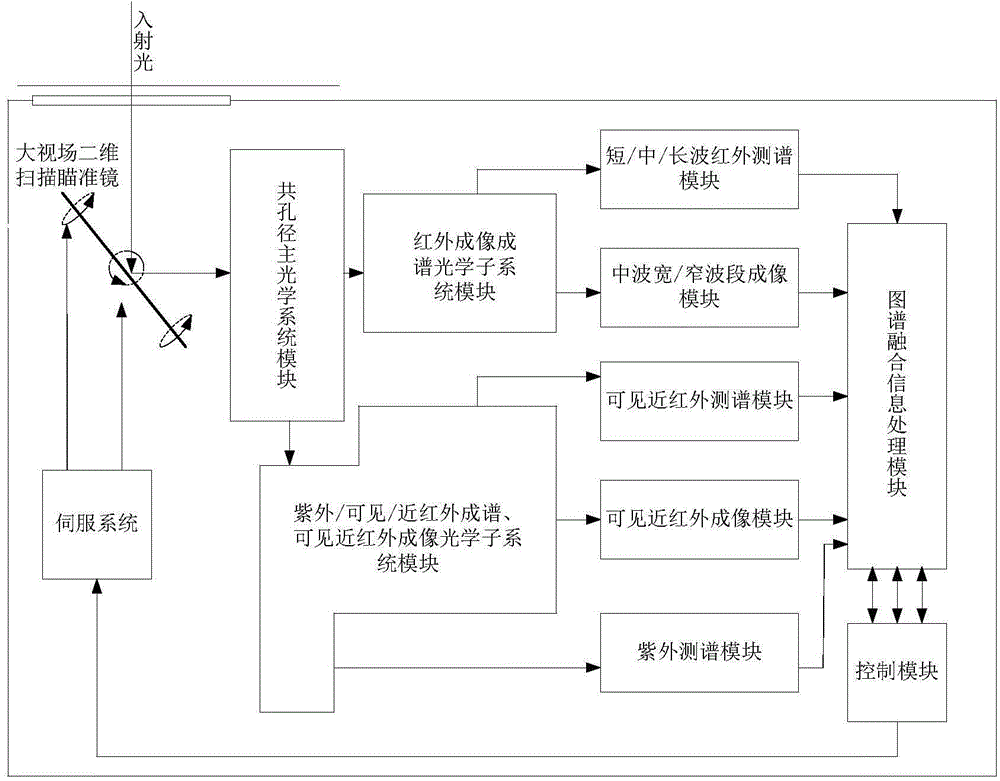
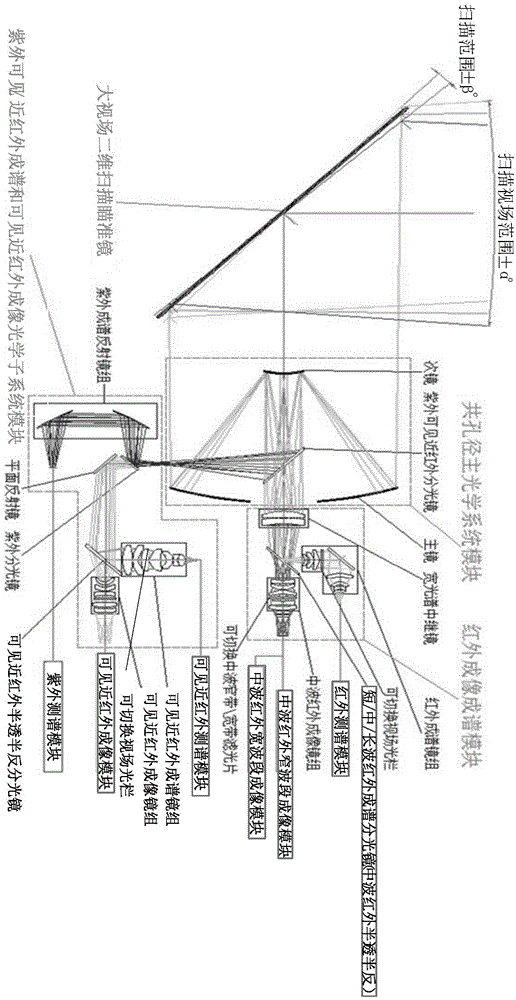
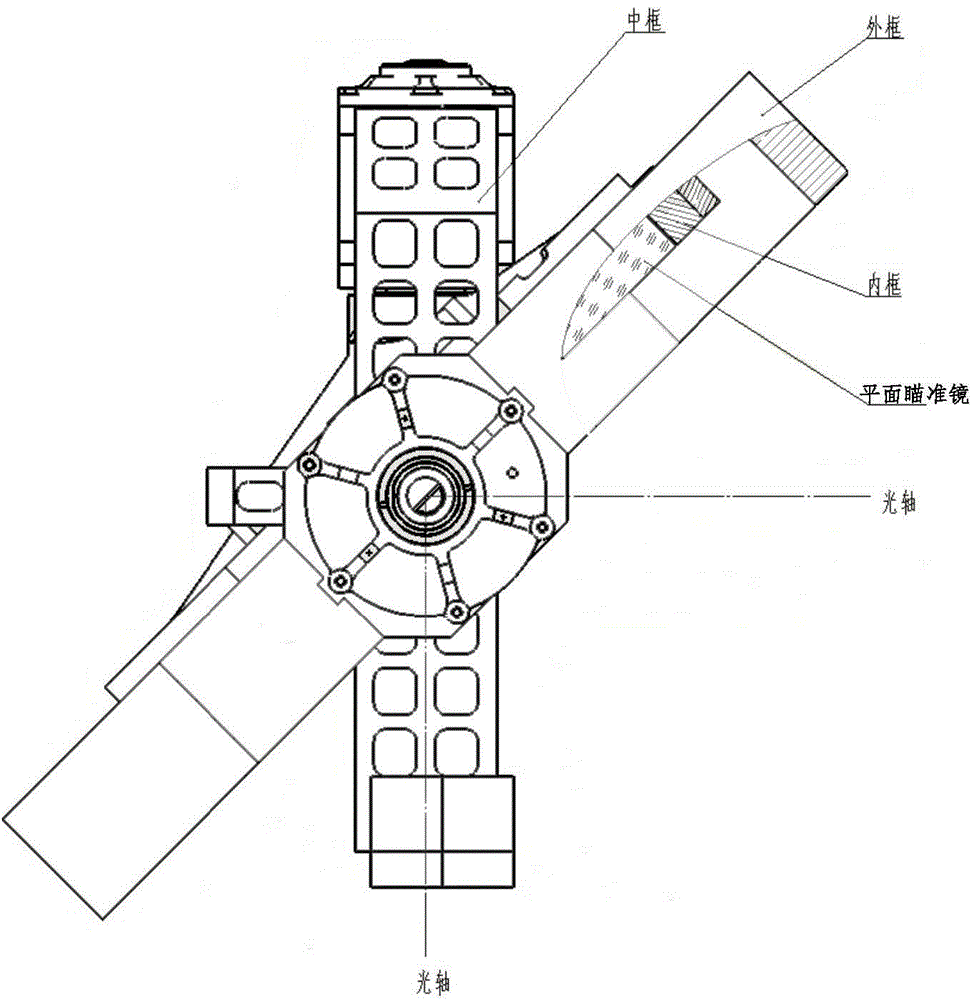
The invention discloses a device and a method for cooperatively detecting a moving target by using all-optical-waveband (including ultraviolet, visible, near-infrared, medium-wave infrared and long-wave infrared) maps. The device comprises a large field-of-view two-dimensional scanning sighting telescope, a common aperture primary optical system module, an infrared imaging and spectrum forming optical subsystem module, an ultraviolet / visible / near-infrared spectrum forming and visible near-infrared imaging optical subsystem module, a short / medium / long-wave infrared spectrum measuring module, a medium-wave wide / narrow band imaging module, a visible near-infrared spectrum measuring module, a visible near-infrared imaging module, an ultraviolet measuring module, a map fusion signal processing module, a control module and a servo system. The device and the method utilizes medium-wave infrared imaging and visible near-infrared imaging for recognizing a suspected moving target and guides spectrum measurement, completes the final recognition of the suspected target with cooperation of spectrum measurement data, and solves the difficulties of the existing detection device such as incomplete detection bands, limited optical path layout, large equipment size, few types of detected moving targets and dynamic changing objects, and poor detection capability.
Owner:NANJING HUATU INFORMATION TECH
Short wave/medium wave/long wave infrared detector based on InAs/GaSb class II-type superlattice materials
ActiveCN104576805AImprove performanceSuppress crosstalkSemiconductor devicesContact layerMetal electrodes
The invention discloses a short wave / medium wave / long wave infrared detector based on InAs / GaSb class II-type superlattice materials. The detector comprises a GaSb substrate, an epitaxial structure deposited on the GaSb substrate, a passivation layer and a metal electrode, wherein the epitaxial structure sequentially comprises a GaSb buffering layer, an n-type InAs / GaSb superlattice contact layer, a first M-type InAs / GaSb / AlSb / GaSb / InAs superlattice hole blocking layer, a p-type InAs / GaSb superlattice long wave infrared absorbing layer, a first p-type InAs / GaSb superlattice contact layer, a p-type InAs / GaSb superlattice medium wave infrared absorbing layer, a second M-type InAs / GaSb / AlSb / GaSb / InAs superlattice hole blocking layer, a p-type InAs / GaSb superlattice short wave infrared absorbing layer, a second p-type InAs / GaSb superlattice contact layer and a cover layer. The detector is of a pMp-p-pi-M-n heterostructure and has the advantages of being low in crosstalk, low in dark current and high in detection rate.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Two-waveband infrared optical system
InactiveCN101738619AAdjustable focal lengthOptimize space layoutPhase-affecting property measurementsElectromagnetic wave reradiationCamera lensBeam splitter
The invention provides a two-waveband infrared optical system, belongs to an infrared remote sensing optical system, and solves the problems of limited optical path layout of the conventional map-integrated device and large volume of the entire device. The system comprises a scanning rotating mirror, a two-waveband infrared optical lens, a spectrometer, an infrared focal plane detector and a signal processor, wherein the two-waveband infrared optical lens consists of an infrared window, a beam splitter, a medium wave lens and a long wave lens; the scanning rotating mirror is positioned above the infrared window; an infrared optical fiber transmits infrared light output by the medium wave lens to the spectrometer; the infrared focal plane detector is positioned on an output optical axis of the long wave lens; and output signals of the spectrometer and the infrared focal plane detector are transmitted to the signal processor through a transmission cable. The system has small volume, high integration level, and convenient and flexible use, can realize automatic scanning, identification and track of a target by observing two wavebands of external scenery, and can be effectively applied to military or civil fields of missile infrared guidance, atmospheric pollution, remote measurement of poisonous gas and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
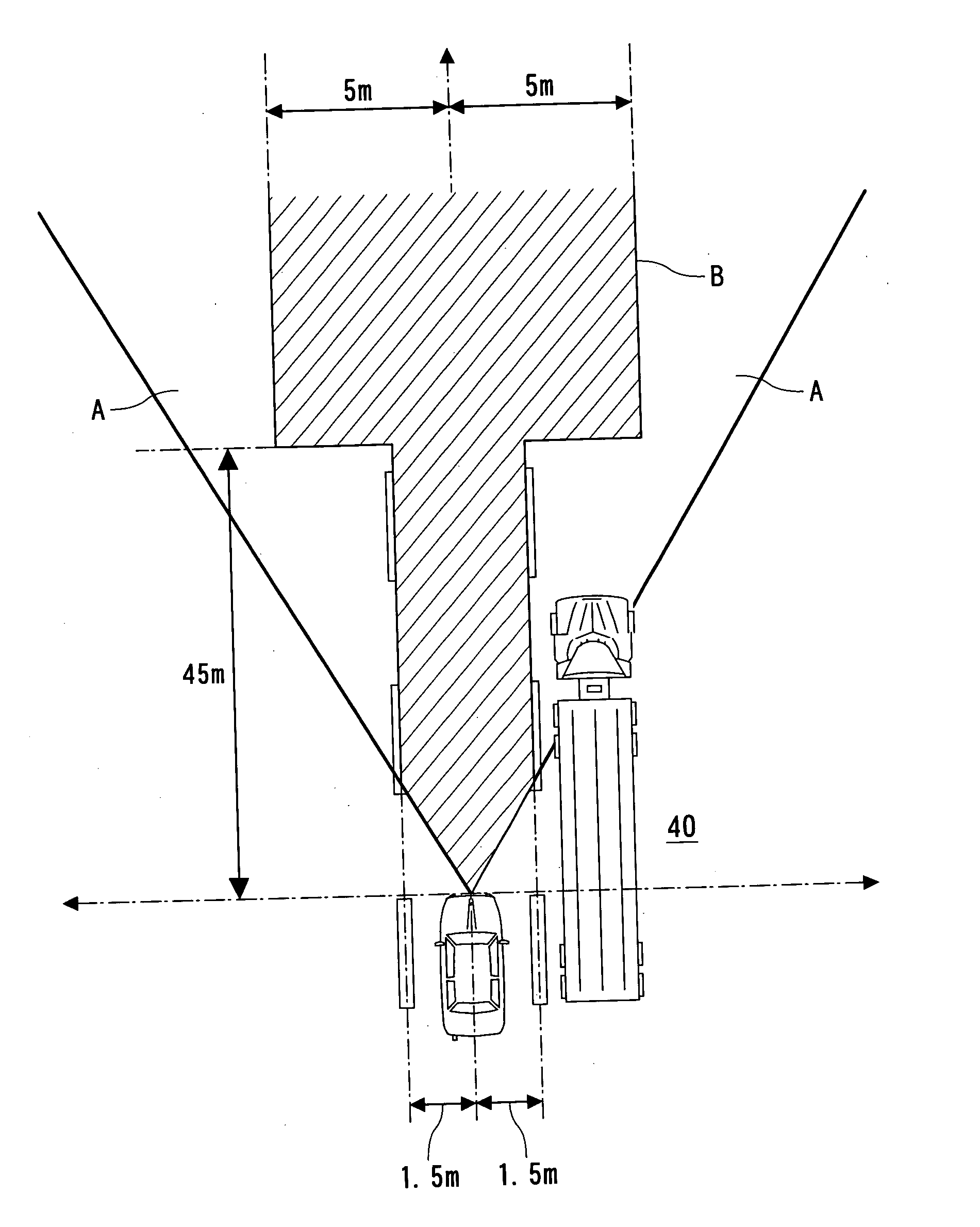
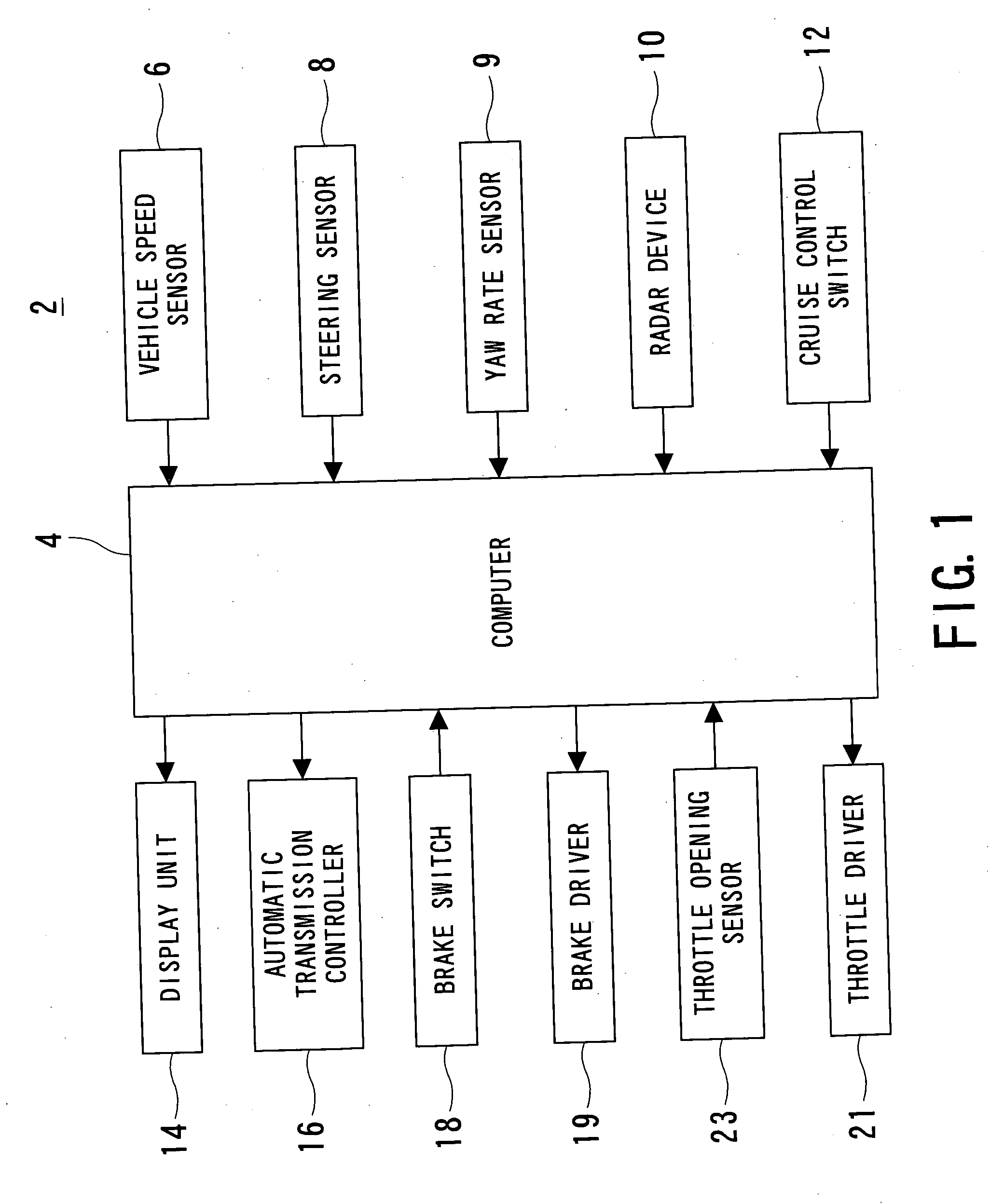
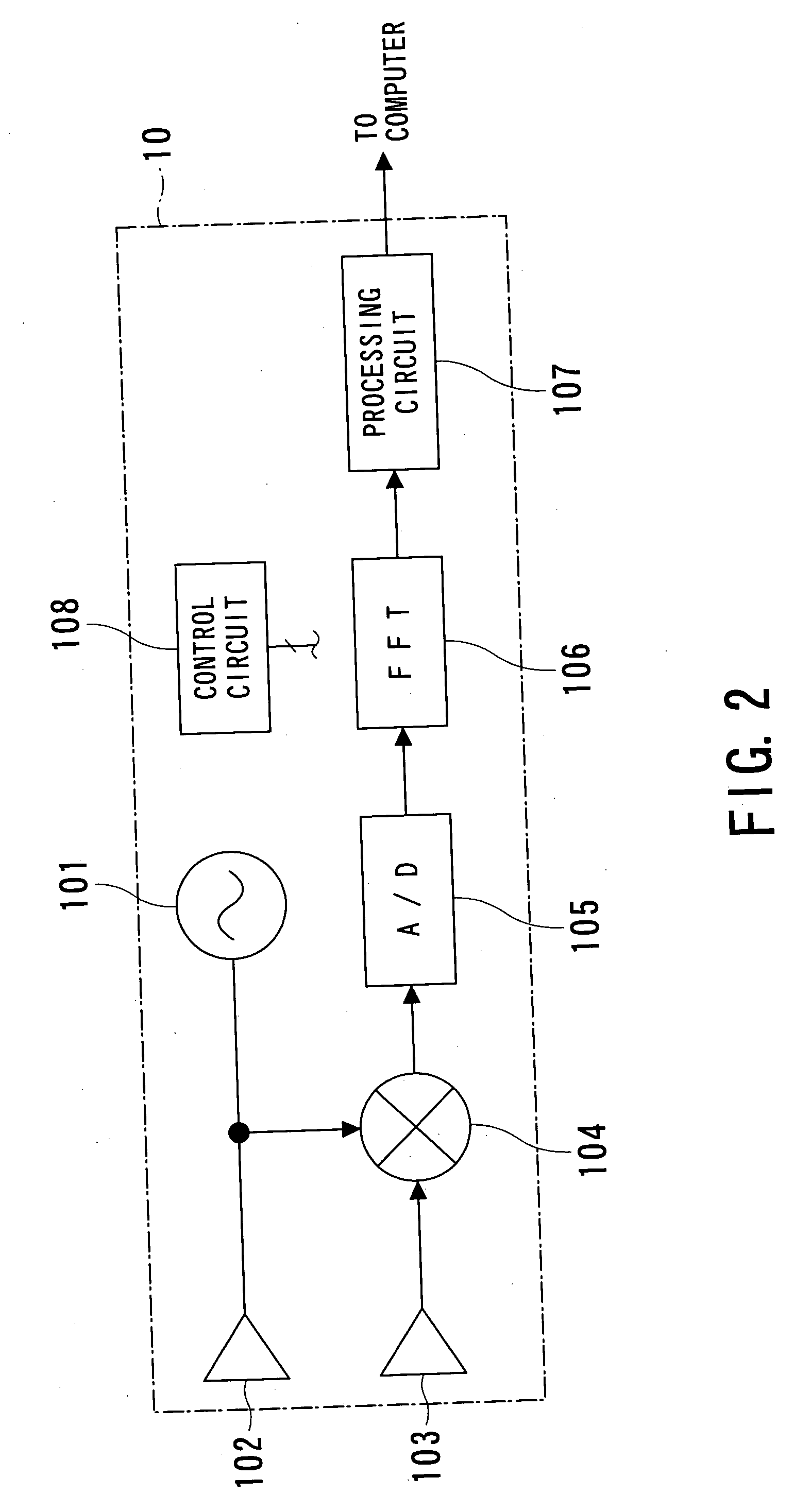
Method and apparatus for recognizing predetermined particular part of vehicle
InactiveUS20050024258A1Raise the possibilityImprove accuracyAnti-collision systemsImage data processing detailsReflected wavesDevice Sensor
An on-vehicle apparatus for recognizing objects is provided. The apparatus comprises a transmission / reception unit, detection unit, estimation unit, and specification unit. The transmission / reception unit transmits a medium wave toward a desired directional range from the vehicle and receives reflected waves of the medium wave and the detection unit detects objects existing in the desired directional range on the basis of the reflected wave. The estimation unit estimates a possibility that each detected object has been detected based on a reflected wave from a first part (e.g., cabin) of a further vehicle other than a second part (e.g., rear part) of the further vehicle, the first part being other than the second part that is the closest in distance to the apparatus-mounted vehicle. The specification unit specifies the second part as an object to finally be recognized of the apparatus-mounted vehicle depending on an estimated result by the estimation unit.
Owner:DENSO CORP
U-shaped folded medium wave infrared 30-times continuous zooming optical system
ActiveCN102590991AAchieve continuous zoomOptical total lengthOptical elementsImaging qualityImaging technology
The invention discloses a U-shaped folded medium wave infrared 30-times continuous zooming optical system, which sequentially consists of a front fixed set, a zooming set, a compensation set, a rear fixed set, a first reflector, a secondary imaging set, a second reflector and a ternary imaging set from an object side to an image side. The system has a structure of which focal power distribution is sequentially positive, negative, positive, negative, positive and positive. The two-component zooming principle and the ternary imaging technology are adopted in the system, the focal length is continuously variable in a range of 23 to 701 millimeters, the travel of the zooming set is 194 millimeters, the travel of the compensation set is 39 millimeters, 30-times continuous zooming is realized, the optical total length of the system is only 559 millimeters, the ratio of the total length to the focal length is 0.79, the overall shape size of the system is 345mm*176mm*224mm (length*width*height), the F value of the optical system is 4 and constant, and the system has the advantages of large zooming ratio, low optical total length, smooth overall zooming locus and excellent imaging quality in the whole focal length range.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PHYSICS
Catadioptric hybrid multispectral imaging system
InactiveCN102116673AImprove transmittanceSave spaceRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationBeam splitterImaging quality
The invention discloses a catadioptric hybrid multispectral imaging system, which comprises a primary mirror, a catadioptric dual-purpose secondary mirror, a wedge-shaped dichroic beam splitter, a medium wave or long wave infrared or medium-long wave infrared dual-waveband imaging mirror assembly, a medium wave or long wave infrared or medium-long wave infrared dichroic detector unit, a visible to near infrared waveband imaging mirror assembly, a visible to near infrared waveband beam splitting device and a detection unit thereof, a short wave infrared waveband imaging mirror assembly, and a short wave infrared waveband beam splitting device and a detection unit thereof, wherein a hole is formed at the center of the primary mirror, and the reflecting surface of the primary mirror is a concave surface; and the incident surface of the catadioptric dual-purpose secondary mirror is a convex surface. The system can realize imaging with common field of view and common aperture of a same object, improve the utilization rate of light energy, save space for the beam splitter and the system, prevent parasitic light from directly leaking into the imaging mirror assembly from the hole formed on the primary mirror, correct asymmetric aberration, be more conductive to realizing large aperture and the larger field of view and significantly improve the imaging quality. The imaging with the same optical axis and the common field of view can enable an image to be easy to register.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF SPATIAL MECHANICAL & ELECTRICAL TECH +1
Mutually-visual-field common-aperture multi-spectral imaging system with Cassegrain front end
InactiveCN102175318AConvenient registrationImprove light energy utilizationRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationImaging qualityImaging lens
The invention discloses a mutually-visual-field common-aperture multi-spectral imaging system with a Cassegrain front end. The system comprises a main lens, a refracting-reflecting dual-purpose secondary lens, a medium wave or long wave infrared or medium-long wave infrared dual-waveband imaging lens group, a medium wave or long wave infrared or medium-long infrared double-color detector unit, a visible to near infrared band imaging lens group, a visible to near infrared band color analyzer and a detection unit, wherein the main lens is provided with a central opening; the reflecting surface of the main lens is a concave surface; and the incident surface of the refracting-reflecting dual-purpose secondary lens is a convex surface. In the system, the main lens is taken as a public entrance pupil of each waveband and primary light splitting is realized by using the secondary lens, so that the luminous energy utilization ratio is increased, the spaces of a spectroscope and the system are saved, the realization of a long aperture and a large visual field is facilitated, and the imaging quality is improved remarkably. Due to the adoption of co-optical-axis mutually-visual-field imaging, images are easy to register.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Integrated multi-waveband common-path synchronous continuous variable-focus optical system
The invention discloses an integrated multi-waveband common-path synchronous continuous variable-focus optical system. The optical system comprises a public front fixed group, a public zooming group and a public compensation group which are arranged in sequence along an optical axis, as well as a first group of beam splitter prisms for reflecting visible light and transmitting medium-wave infrared light and long-wave infrared light, and a second group of beam splitter prisms for reflecting long-wave infrared light and transmitting medium-wave infrared light. A common-caliber, common-path and common-variable-focus form is adopted, a visible waveband, a medium-wave waveband and a long-wave infrared waveband are zoomed synchronously and continuously along with the movement of the public zooming group in a zooming process, and the three wavebands are of the same focal lengths, zooming ratios and visual fields, thereby realizing synchronous observation, synchronous tracking and synchronous measurement of a target in the visible waveband, the medium-wave waveband and the long-wave infrared waveband. When different wavebands are needed for observing, path switching and new search of the target are unnecessary, thereby increasing the reaction speed of the optical system and preventing loss of a target moving at a high speed during path switching.
Owner:XIAN TECH UNIV
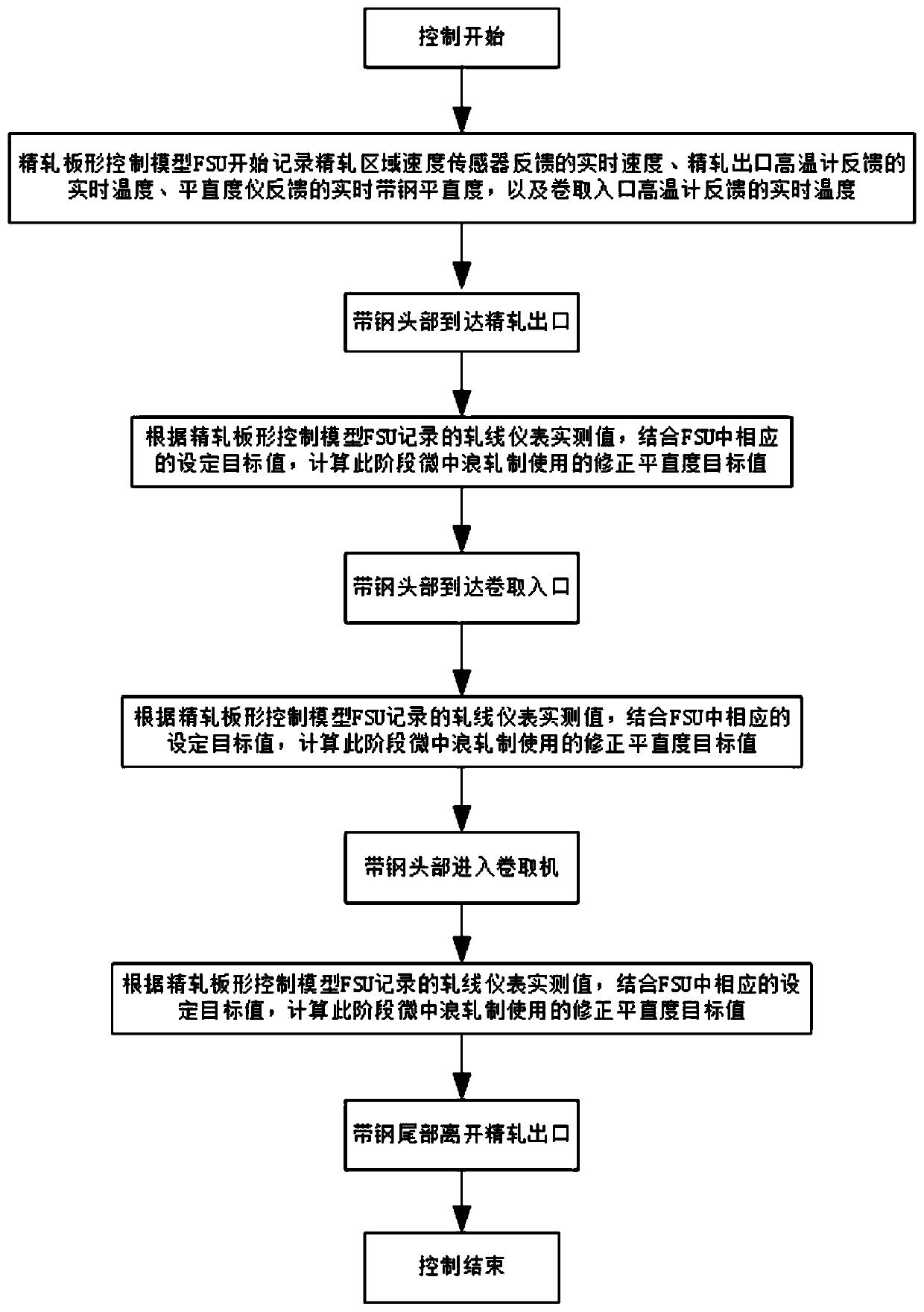
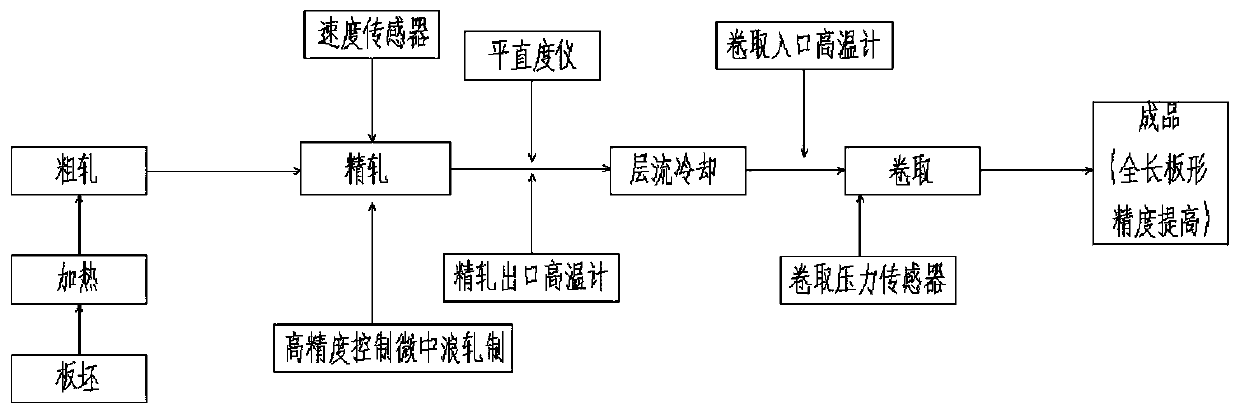
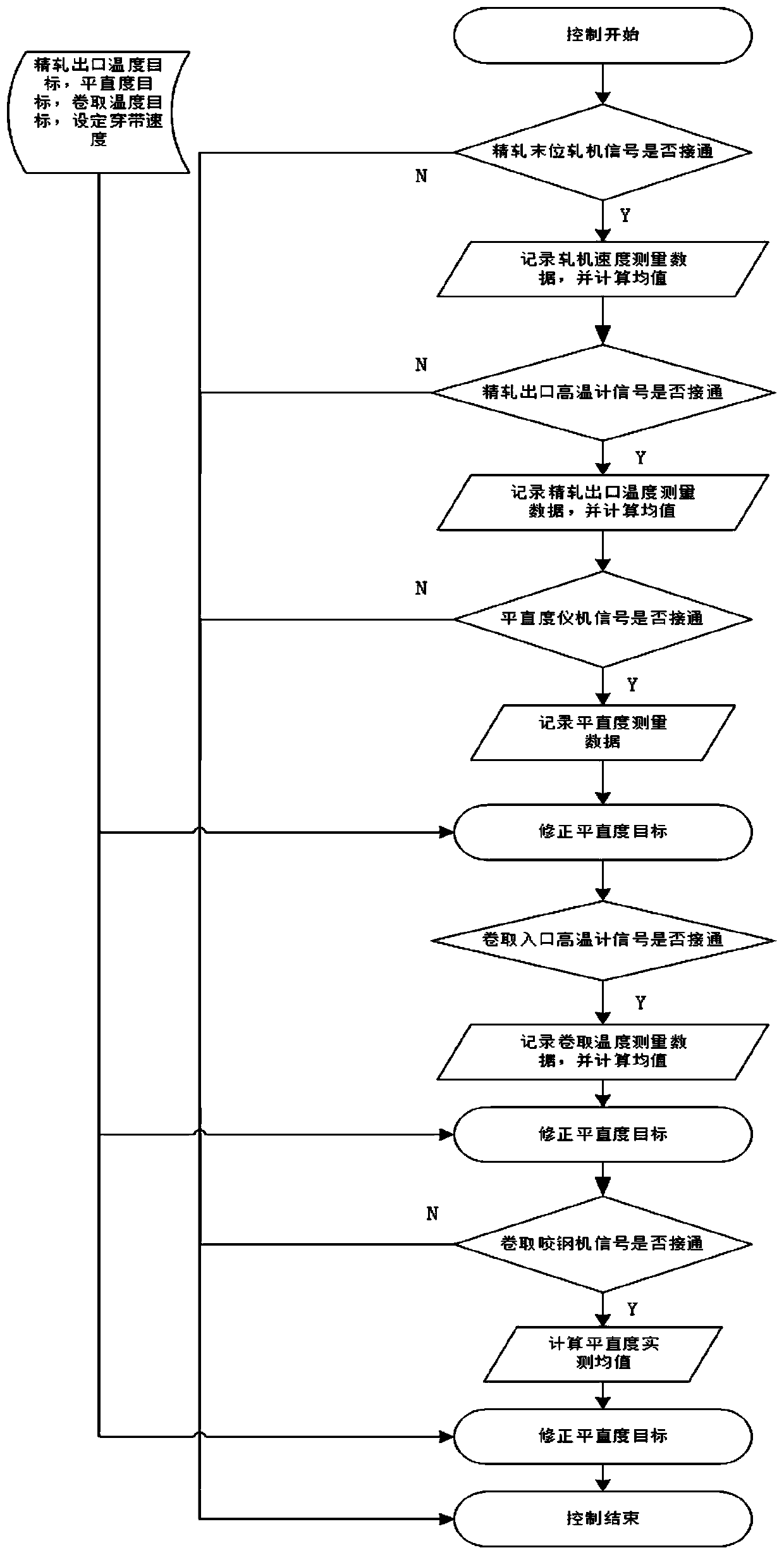
Method for controlling micro-medium wave rolling of hot-rolled strip steel at high precision
ActiveCN110404978AHigh shape accuracyReduce manufacturing costProgramme controlComputer controlChange factorStrip steel
The invention discloses a method for controlling micro-medium wave rolling of hot-rolled strip steel at high precision. Under the condition that the change factor of the coiling tension and the cooling rate is considered, according to different rolling process states where the strip steel is located, in combination with the real-time speed and the real-time temperature, the full-length flatness target value of the strip steel is subjected to real-time dynamic compensation control, the micro-medium wave control precision of the full-length strip steel is improved, and micro-medium wave rollingof the strip steel is controlled at high precision. According to a finish-rolled plate shape control model established with the method, under the condition that the change factor of the coiling tension and the cooling rate is considered, according to the different rolling process states where the strip steel is located, in combination with the real-time speed and the real-time temperature, the full-length target flatness of the strip steel is subjected to dynamic compensation correction, the full-length plate type of the strip steel is dynamically controlled, the full-length plate shape precision of the strip steel is greatly improved, and micro-medium wave rolling of the strip steel is controlled at high precision. The method is high in precision, free of cost and suitable for rolling control of the strip steel of various specifications and varieties.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
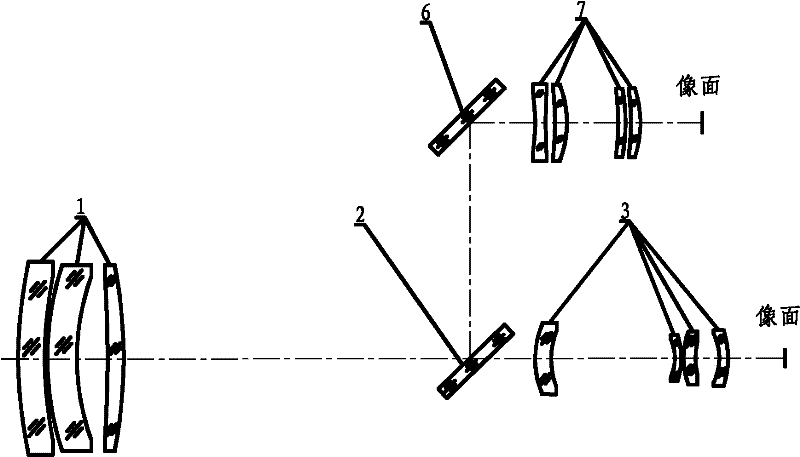
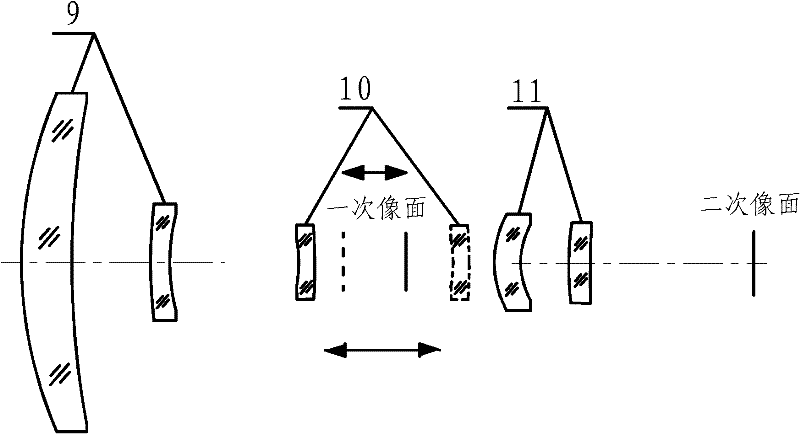
Two-color two-field infrared imaging optical system
ActiveCN102269871AMiniaturizationTake into account the requirementsRadiation pyrometryOptical elementsSystems designMiniaturization
The invention discloses a bicolor dual-view field infrared imaging optical system. The bicolor dual-view field infrared imaging optical system is characterized by consisting of five lenses including a front fixing lens set (9), a multifocal lens set (10) and a rear fixing lens set (11), wherein the front fixing lens set consists of two lenses, the multifocal lens set consists of one lens, and therear fixing lens set consists of two lenses. The multifocal lens set can axially move in front of or behind a primary image surface to realize switching between a wide view field and a narrow view field; in the five lenses, lenses with a binary diffraction surface is used as a second surface of a second lens and a second surface of a fourth lens. The bicolor dual-view field infrared imaging optical system has the advantages of simple and compact structure, small system size and less lenses, can simultaneously performing imaging at a medium wave infrared wave band with wavelength of 4-5 microns and a long wave infrared wave band with wavelength of 8-9 microns while implementing functions of searching (a wide view field of 9 degrees* 6.75 degrees) and aiming (a narrow view field of 3 degrees*2.25 degrees). The system design takes account of miniaturization and lightweight requirement of the infrared system and meets the use technology requirement of the infrared system.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PHYSICS
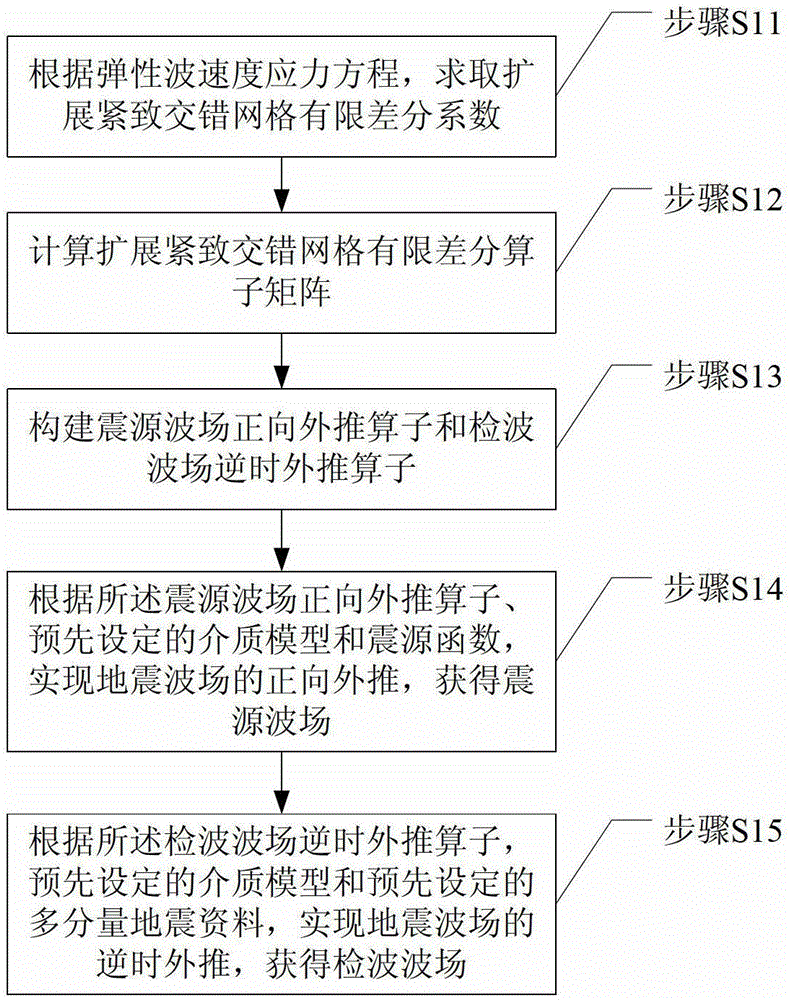
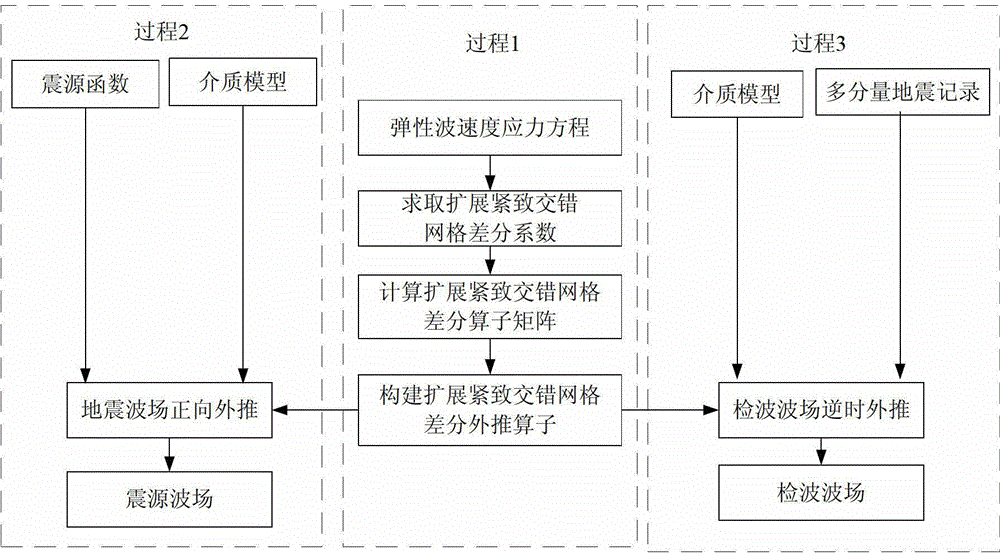
Elastic migration seismic wave field construction method and elastic migration seismic wave field construction device
ActiveCN103149585AFew grid pointsImprove build precisionSeismic signal processingReverse timeSource function
The invention provides an elastic migration seismic wave field construction method and an elastic migration seismic wave field construction device. The method includes computing a finite difference coefficient of extended compact staggered grids according to an elastic wave velocity stress equation; computing a finite difference operator matrix of the extended compact staggered grids; constructing forward direction extrapolation operator of a seismic source wave field, and a reverse-time extrapolation operator of a detection wave field; achieving forward direction extrapolation of a seismic wave field to obtain the seismic source wave field according to the forward direction extrapolation operator of the seismic source wave field, a preset medium model and a preset seismic source function; and achieving reverse-time extrapolation of the seismic wave field to obtain the detection wave field according to the reverse-time extrapolation operator of the detection wave field, a preset medium model and preset multi-component seismic data. Compared with an existing method for constructing an elastic deflection seismic wave field by utilization of a conventional finite difference method and a compact difference method, the number of difference base frame grid points is reduced under the condition of same difference orders, the construction precision of a complex medium wave field can be effectively improved, and therefore the imaging precision of reverse-time migration is improved.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
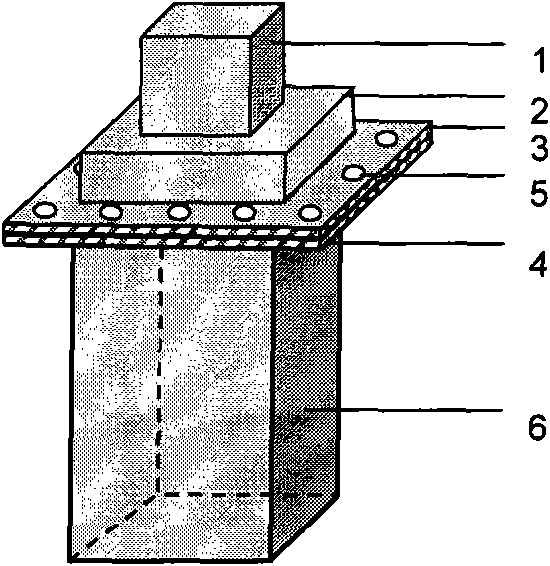
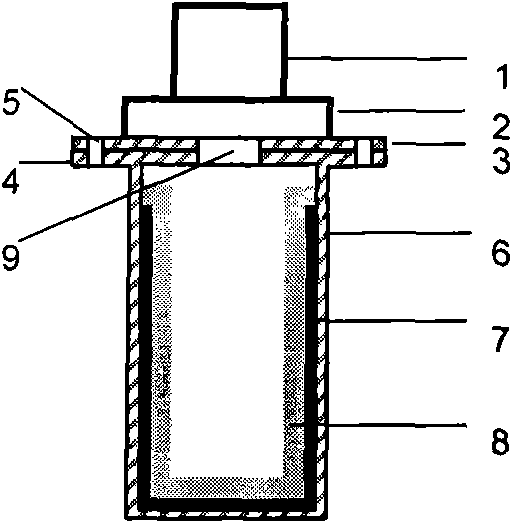
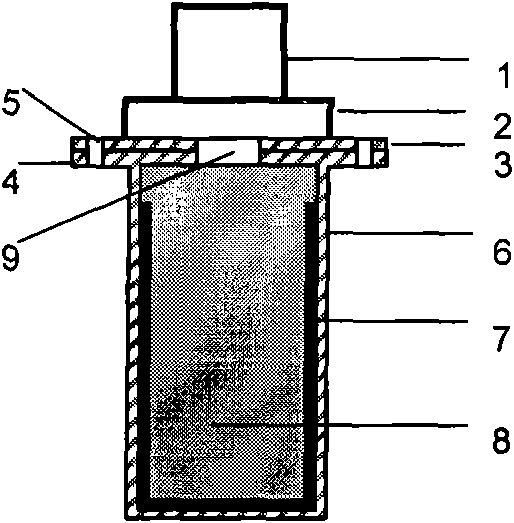
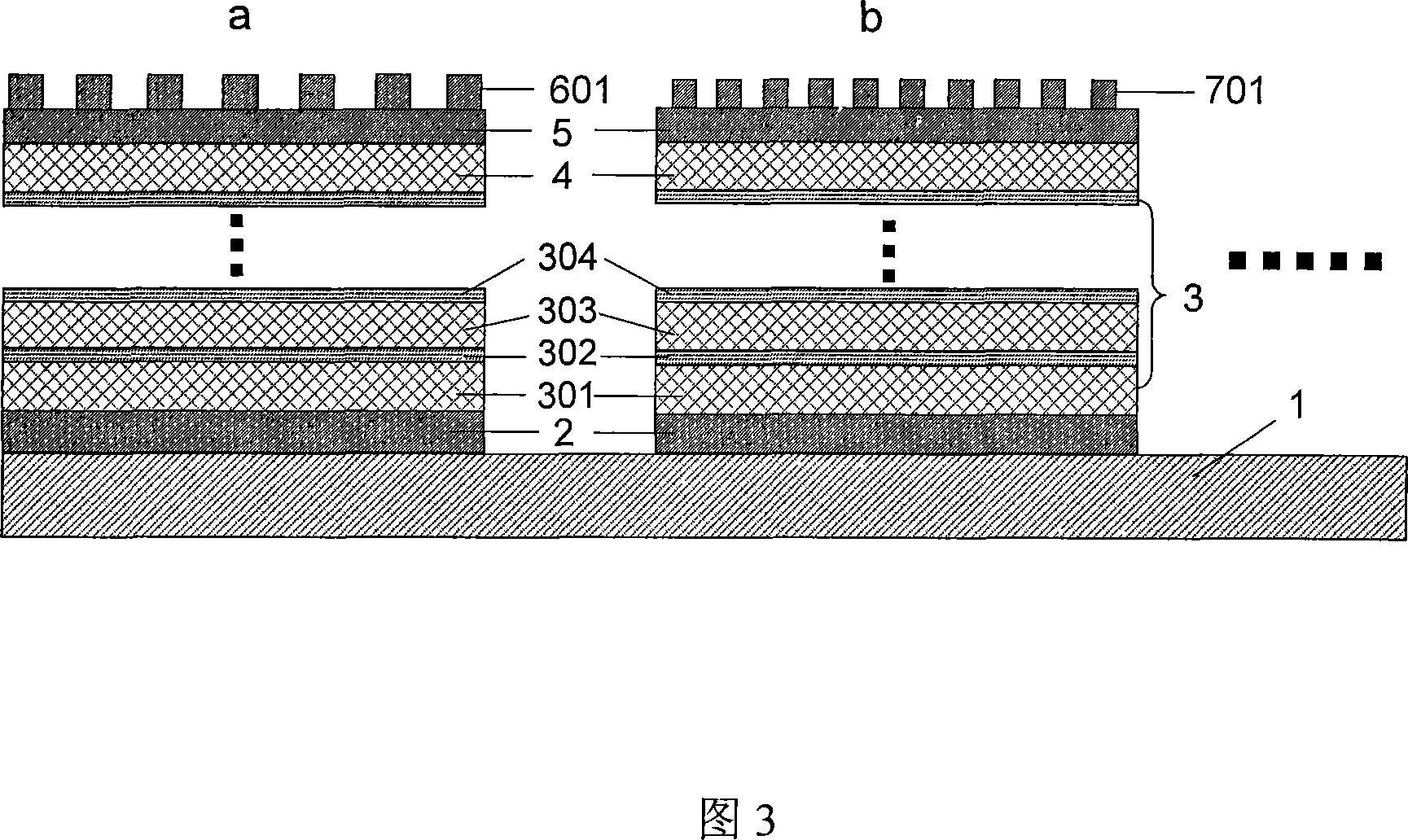
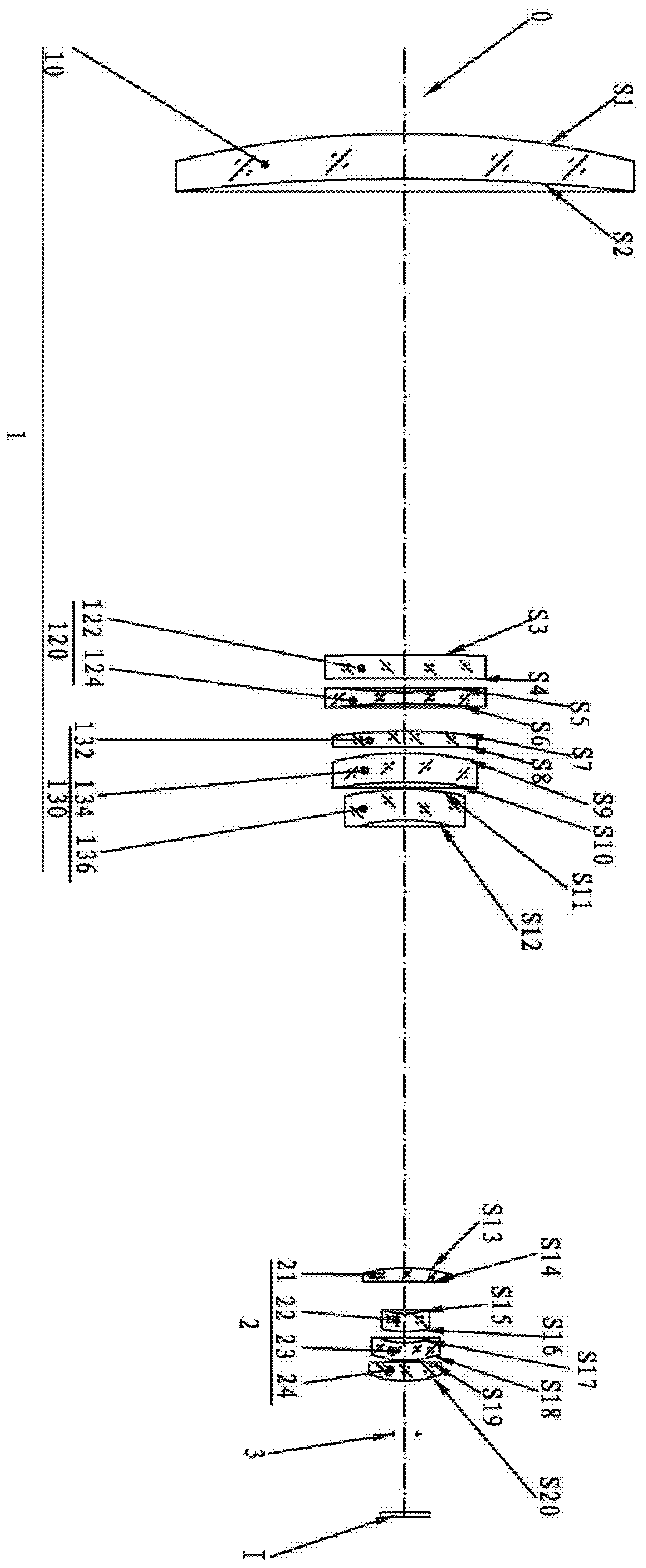
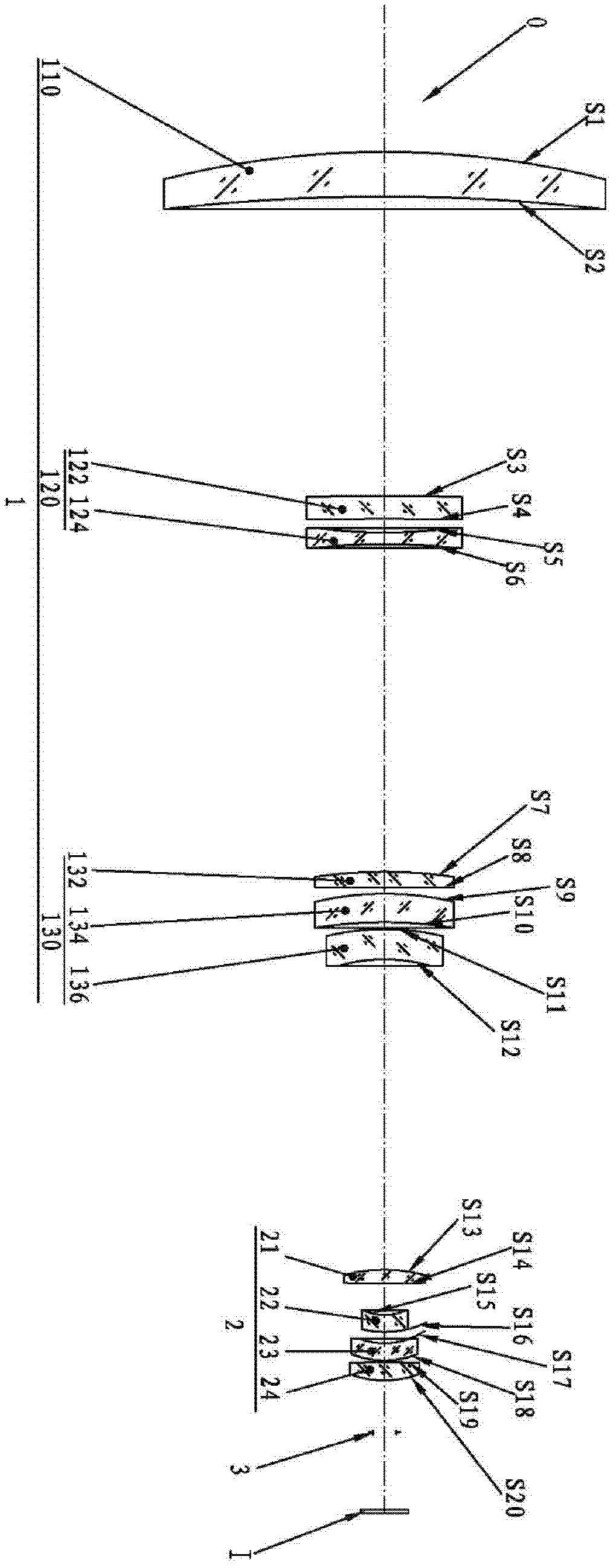
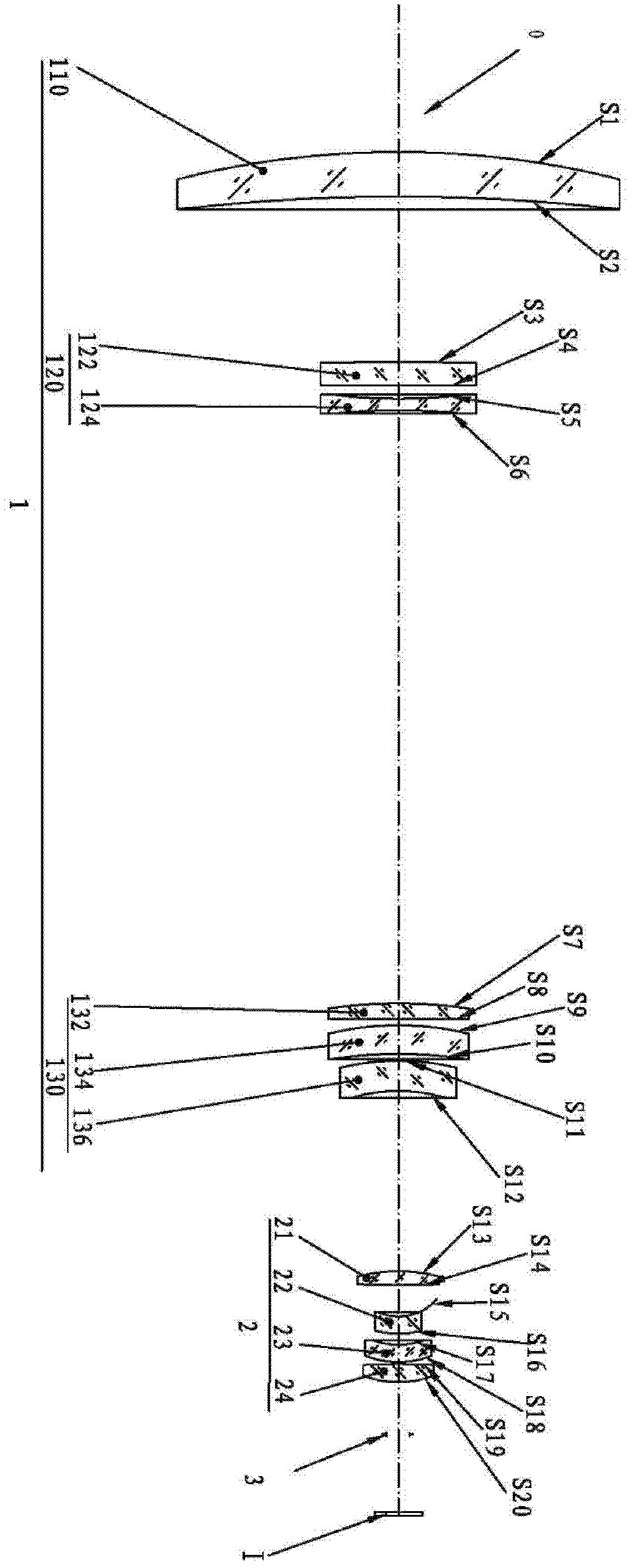
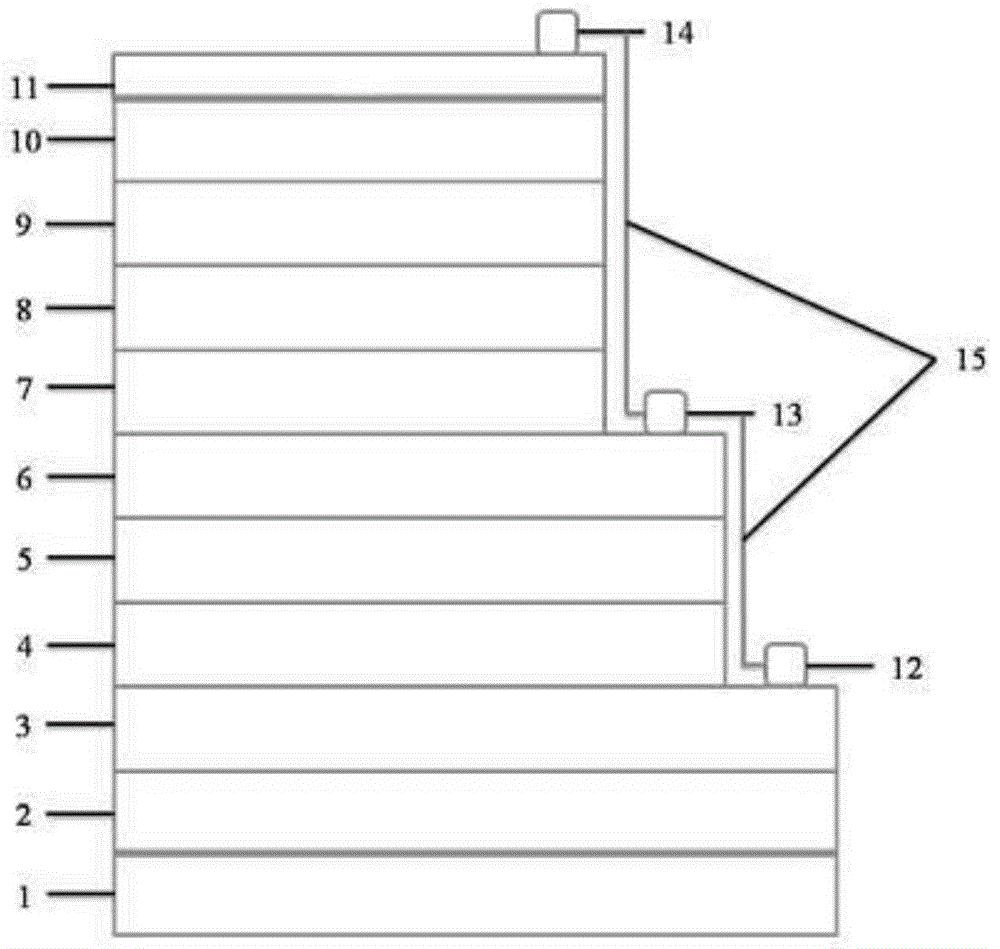
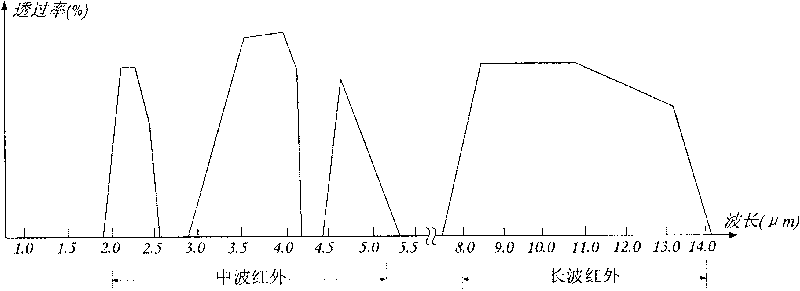
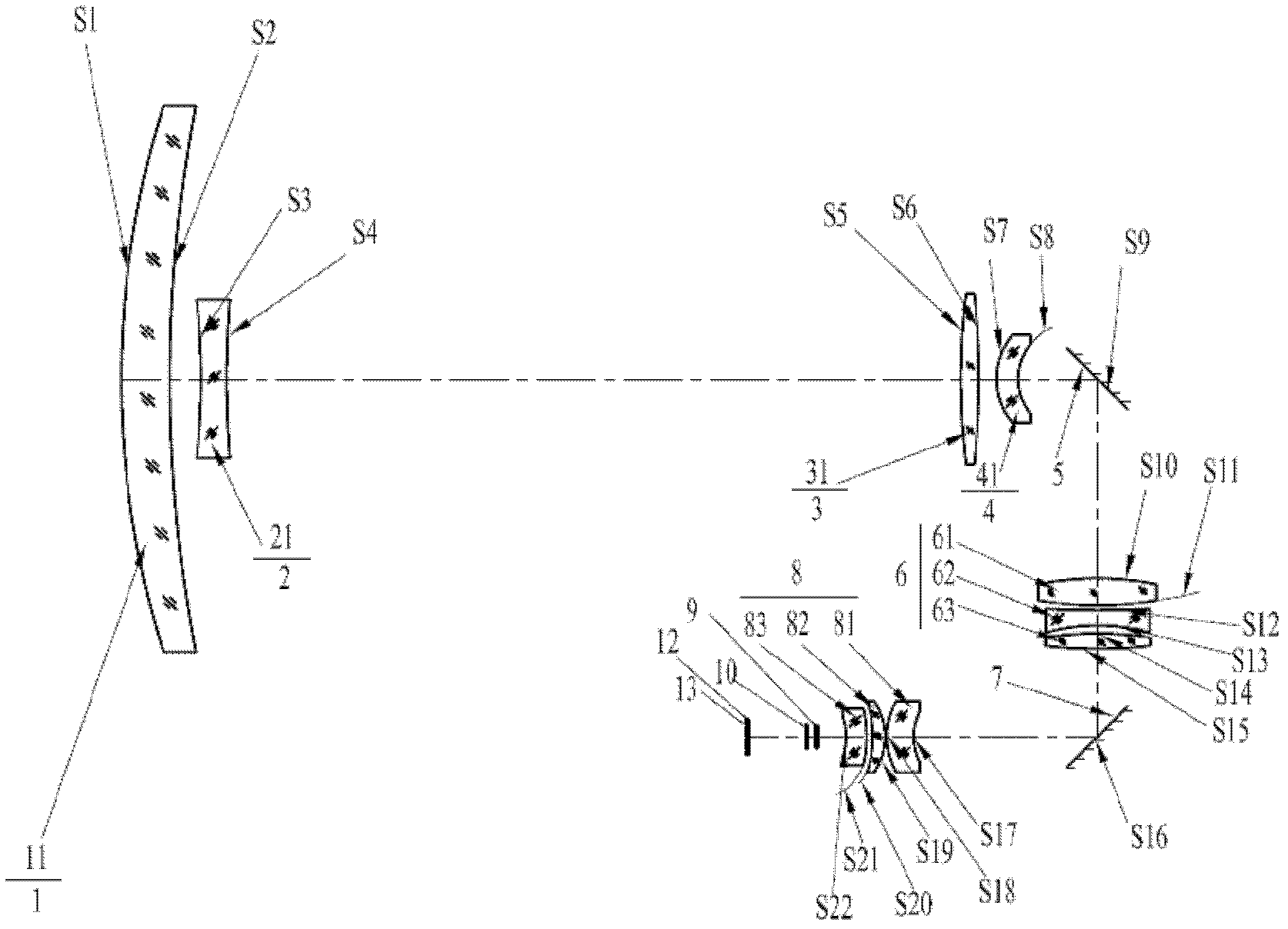
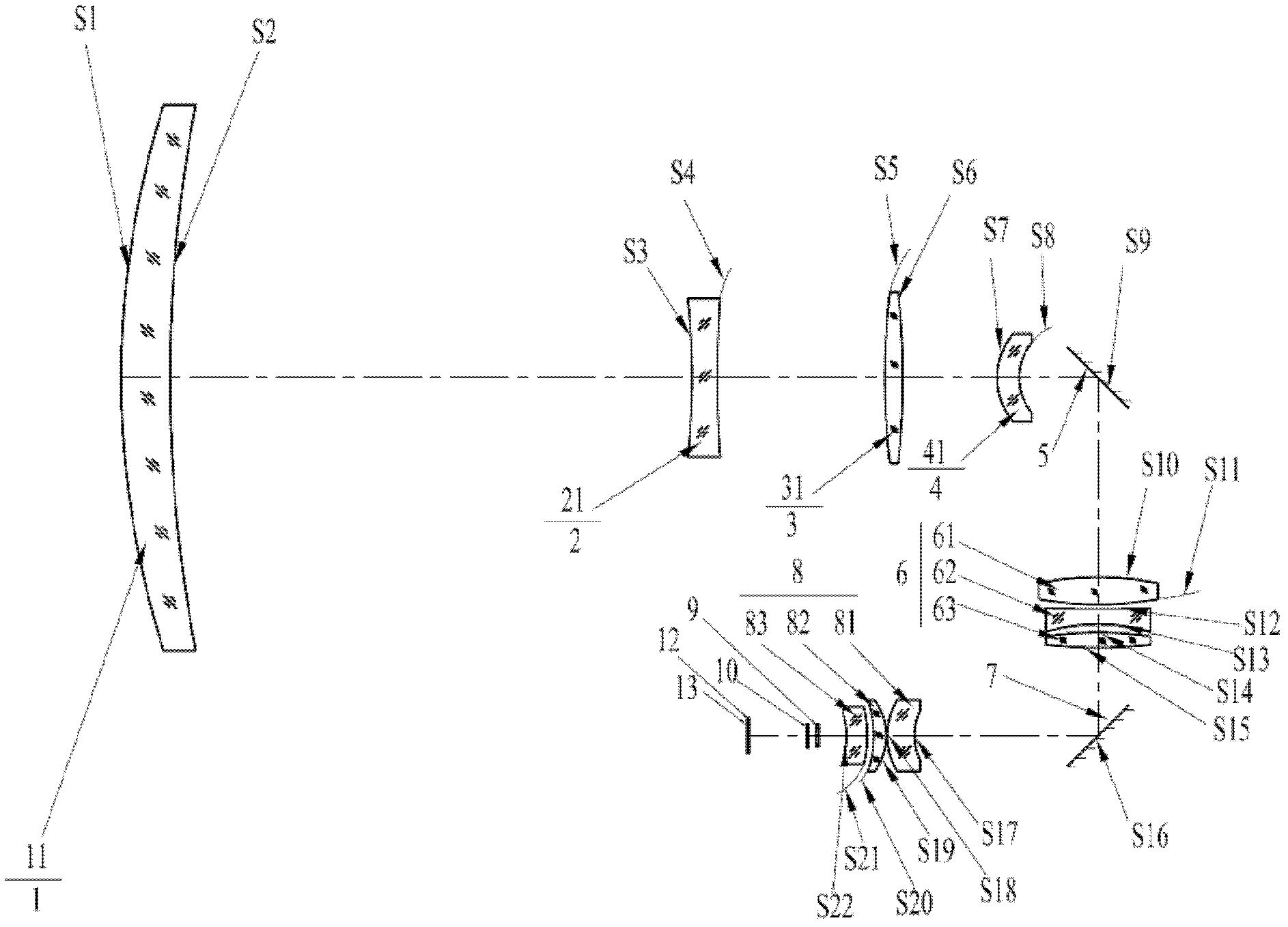
Film system structure of ZnS substrate with inverse 0.5-0.8[Mu]m visible light, laser with 1.064[Mu]m and transparent medium wave infrared colour separation with 3.7-4.8[Mu]m
The present invention provides a film system structure of ZnS substrate with inverse 0.5-0.8[Mu]m visible light, laser with 1.064[Mu]m and transparent medium wave infrared colour separation with 3.7-4.8[Mu]m. The film system structure comprises a ZnS substrate and a color separation film system, and the color separation film system is made of three film materials; the number of the film layers is 51, wherein the first layer and the 51th layer are oxidation zirconium film layer, the even layers from the second layer to the 50th layer are ytterbium fluoride film layers and the odd layers from the second layer to the 50th layer are zinc sulfide film layers. The transmittance is smaller than 2% with the waveband from 0.5 to 0.8 [Mu]m; the transmittance is smaller than 1% with the laser waveband of 1.064 [Mu]m; and the transmittance is larger than 95% with the medium wave infrared band from 3.7 to 4.8 [Mu]m. The film system structure is small in the number of layers, small in thickness, low in plating difficulty, good in technology repeatability, high in obtained film firmness and good in spectral property, is able to satisfy the use requirement of multi-waveband co-window optoelectronic system and the work requirement in the condition of the inclination with 45 degrees, and stand against the environment tests such as high and low temperature storage, temperature impact and the like, the adhesion test and the moderate friction test.
Owner:西安应用光学研究所
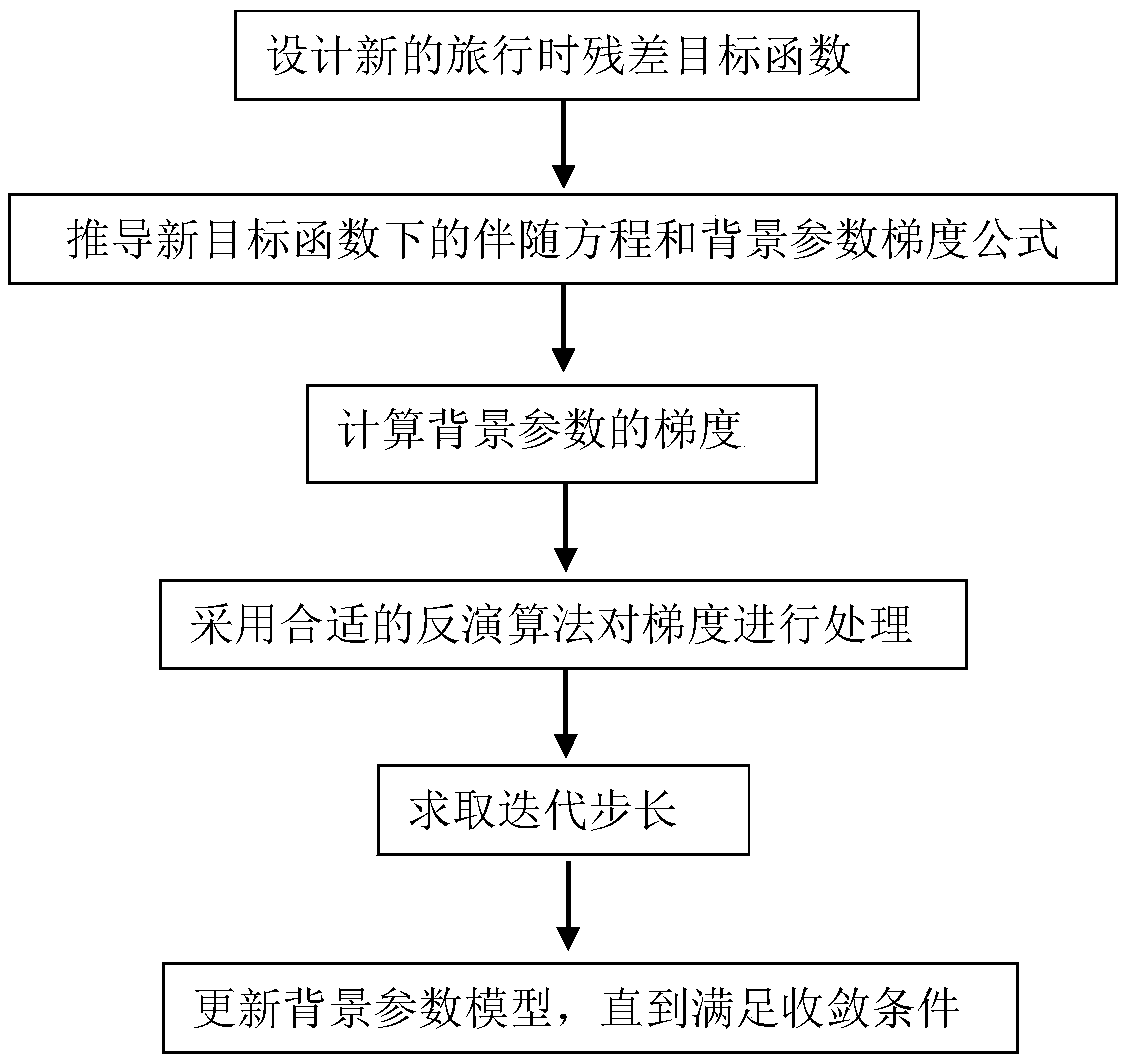
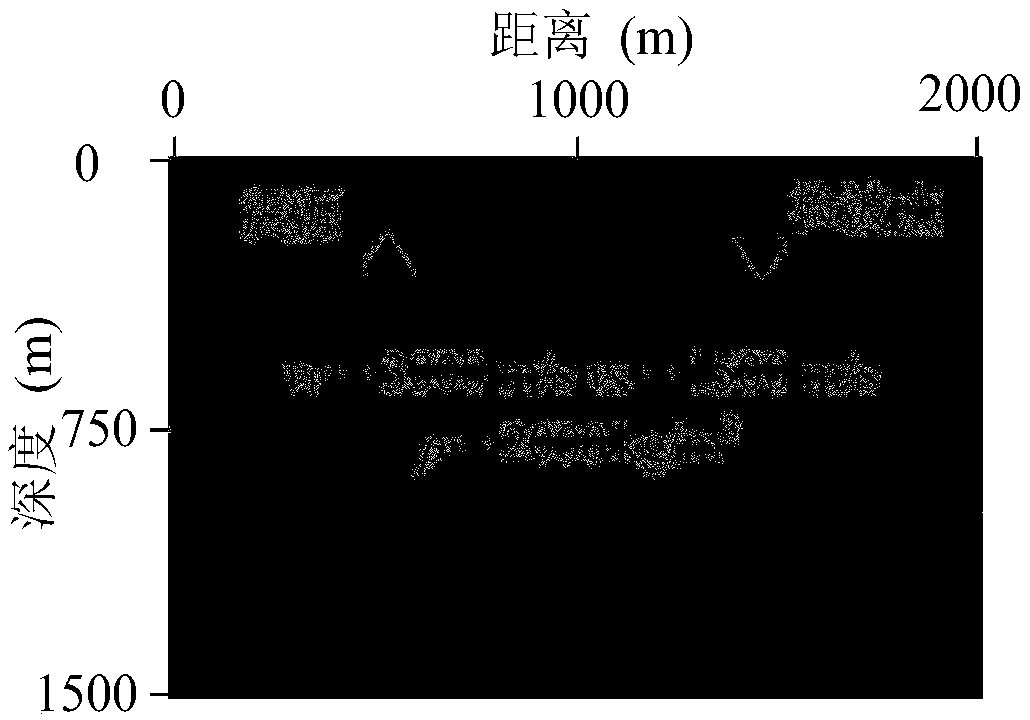
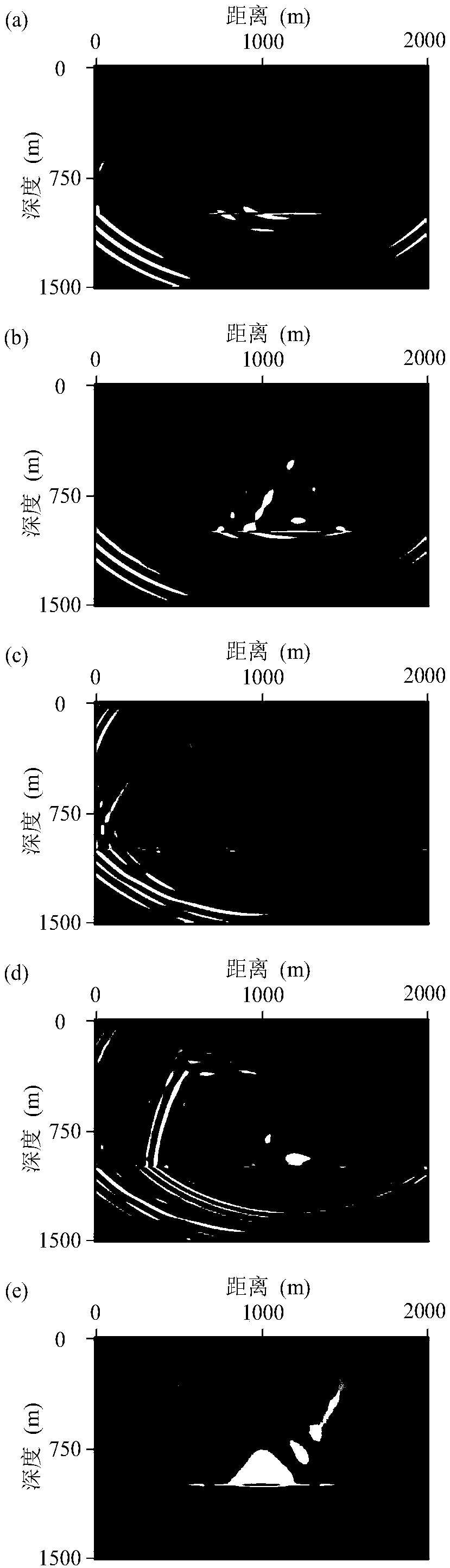
Elastic medium wave equation return wave travel time retrieval method
The invention provides an elastic medium wave equation return wave travel time retrieval method. The method comprises the steps of designing a new travel time residual target function; deducing an adjoint equation and a background parameter gradient formula under the new target function; calculating the gradient of background parameters; processing the gradient by using the quasi-Newton method retrieval algorithm; calculating the iteration step size by using the parabola fitting method; updating a background parameter model until the convergence condition is met. The method has the advantage that the precision of elastic medium return waveform retrieval is improved by using the new travel-time target function, so that reliable longitudinal wave velocity and transverse wave velocity initialmodels can be obtained.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Microwave heater for heating liquid and/or gases
InactiveCN101568209AAchieve heatingEasy to connect in seriesFluid heatersMicrowave heatingMicrowaveThermal insulation
The invention relates to a microwave heater for heating liquid and / or gases, which consists of a heating chamber, a microwave generator and a temperature measurement and control system, wherein the heating chamber consists of three functional layers, namely an external wave-reflecting heat-conducting metal shell, a medium wave absorbing and heating layer and an internal wave-transmitting thermal insulation layer. The microwave heater is characterized in that: after passing through the thermal insulation layer, microwaves emitted by the microwave generator are absorbed by the wave absorbing and heating layer for heating; and heat is transmitted outward to the metal shell which transmits the heat to surrounding liquid and / or gases to realize the heating of flowing or static liquid and / or gases at last. The microwave heater unit with the structure can be used singly or a plurality of microwave heater units are used in serial and / or parallel connection. The microwave heater has the advantages of simple structure, low manufacturing cost, high thermal efficiency, easy replacement, maintenance and carrying and high safety due to non-contact heating, and can be used as a heat source in various fields such as large and small shower water heaters, hydrothermal heating, hot air heating and industrial production.
Owner:徐艳姬
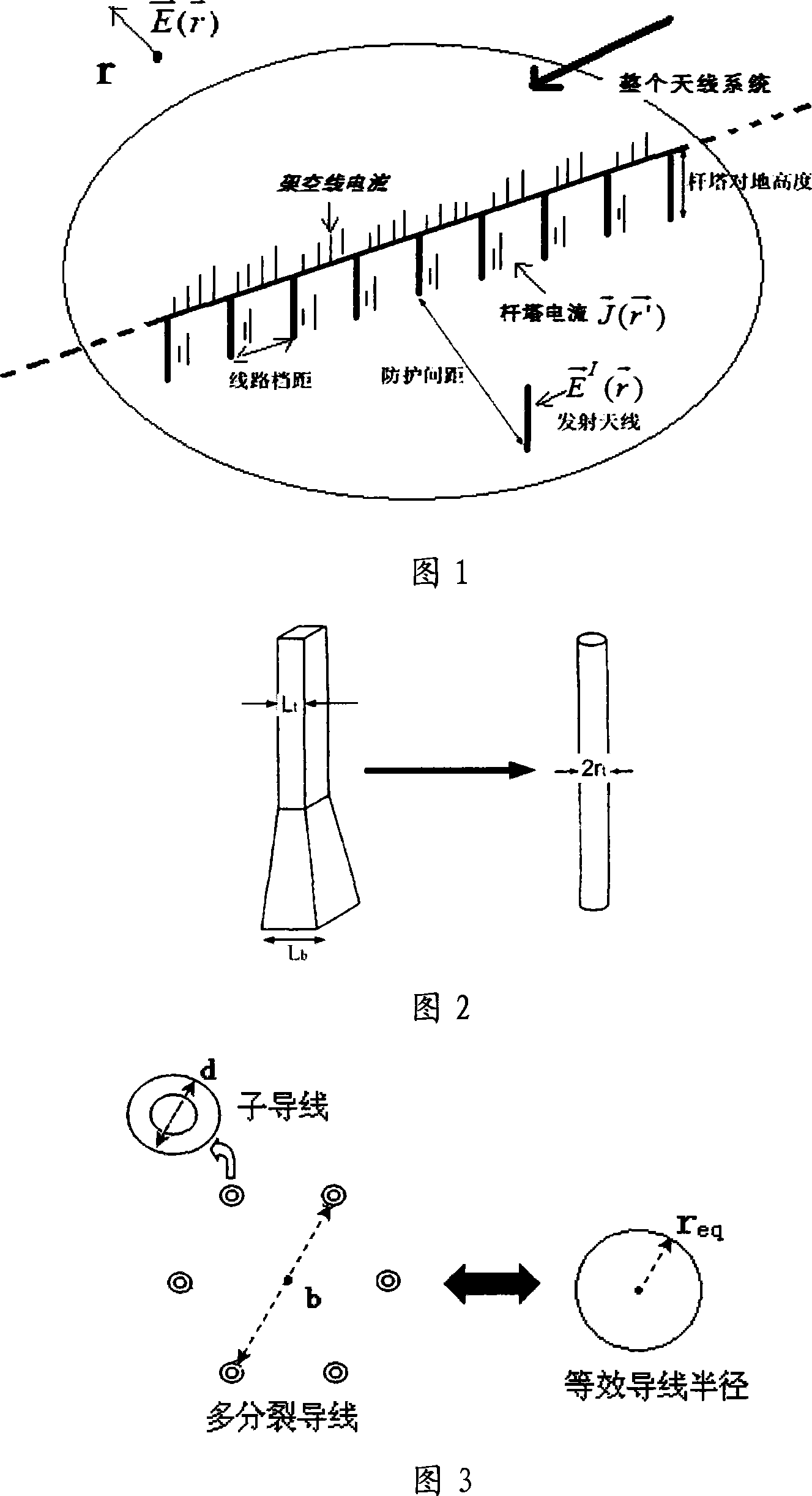
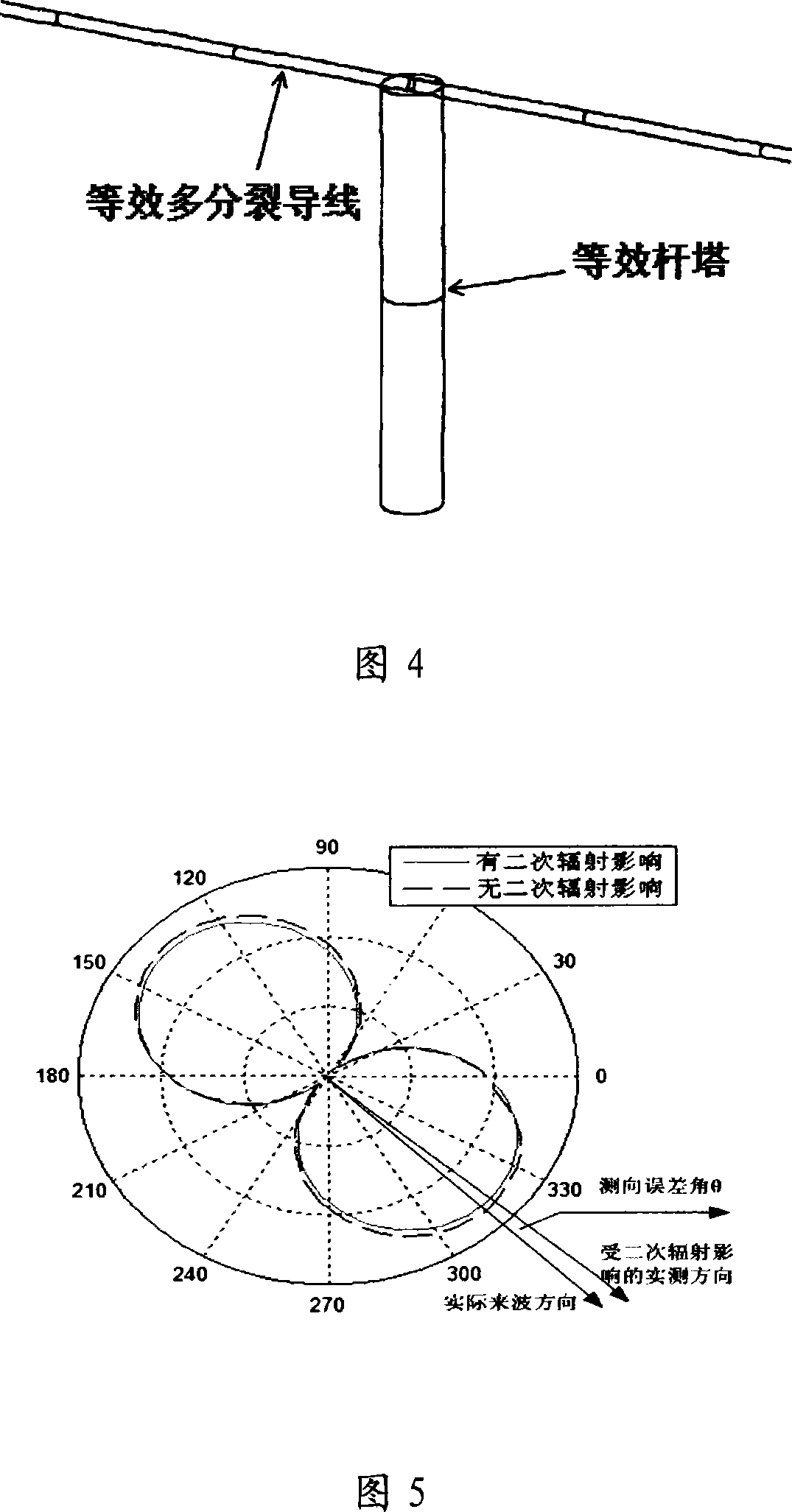
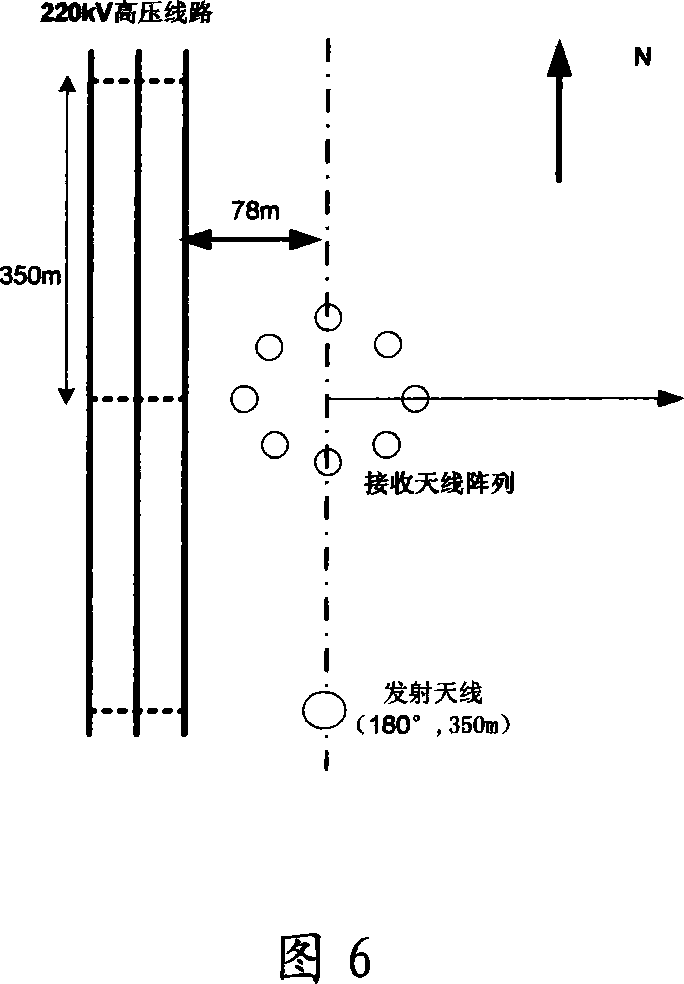
Method for confirming protection distance between extra-high voltage alternating current line and medium wave navigation station
ActiveCN101221204AImprove accuracyElectrical testingElectromagentic field characteristicsReduced modelHigh pressure
The invention relates to a method for determining the protective distance between an AC line with extra-high voltage and a medium wave navigation station, which adopts the method of moments for computing the electric current distribution on the AC transmission line with extra-high voltage and a simplified model of the AC transmission line with extra-high voltage; furthermore, the method comprises the following steps: firstly the method adopts the method of moments and the simplified model of the AC transmission line with extra-high voltage for computing the electric current distribution on the AC transmission line with extra-high voltage, computes a secondary radiation intensity vector which is generated by the induction current according to the acquired induction current distribution on the electric current transmission line, implements the superimposing of the secondary radiation intensity vector and a source radio wave, and computes the interference influence intensity of the AC transmission line with the extra-high voltage of 1000 kilovolts on a medium wave navigation station, thus acquiring the protective distance for the passive jamming between the AC transmission line with extra-high voltage and the medium wave navigation station. The test data comparison acquired from a test proves that the method for determining the protective distance between the AC line with extra-high voltage and the medium wave navigation station has higher accuracy and is applicable for the precise computation of the electromagnetic protective distance between an electric current transmission line with high voltage and an adjacent radio station in the future.
Owner:STATE GRID ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Medium wave infrared continuous zooming optical system with high zoom ratio
ActiveCN103389570ACompact structureImprove detection distanceOptical elementsOphthalmologyImaging quality
The invention relates to a medium wave infrared continuous zooming optical system with high zoom ratio, belongs to the technical field of optic lens, and aims to solve the existent problems of long zooming stroke, large F value and more lens in the prior art. The system comprises a front fixing group, a lens A of a time changing group, a lens C of a compensation group, a lens B of the time changing group, a lens D of the compensation group, a back fixing group, a secondary image formation group and a probe, coaxially arranged from left to right in sequence, wherein the continuous zooming of the system is realized through the axial movement of the time changing group and the compensation group. Through adopting the structure that the lens A and the lens B of the time changing group and the lens C and the lens D of the compensation group are arranged in a crossing manner to move, the continuous zooming is realized, the zooming stroke is short, the curve is smooth, 100% cold light stop efficiency is satisfied, the F value is constant to be 2, the continuous zooming can be carried out within the range of 10 mm to 300 mm of focal distance, and the image formation quality is sound in the whole focal distance range.
Owner:长春长光睿视光电技术有限责任公司
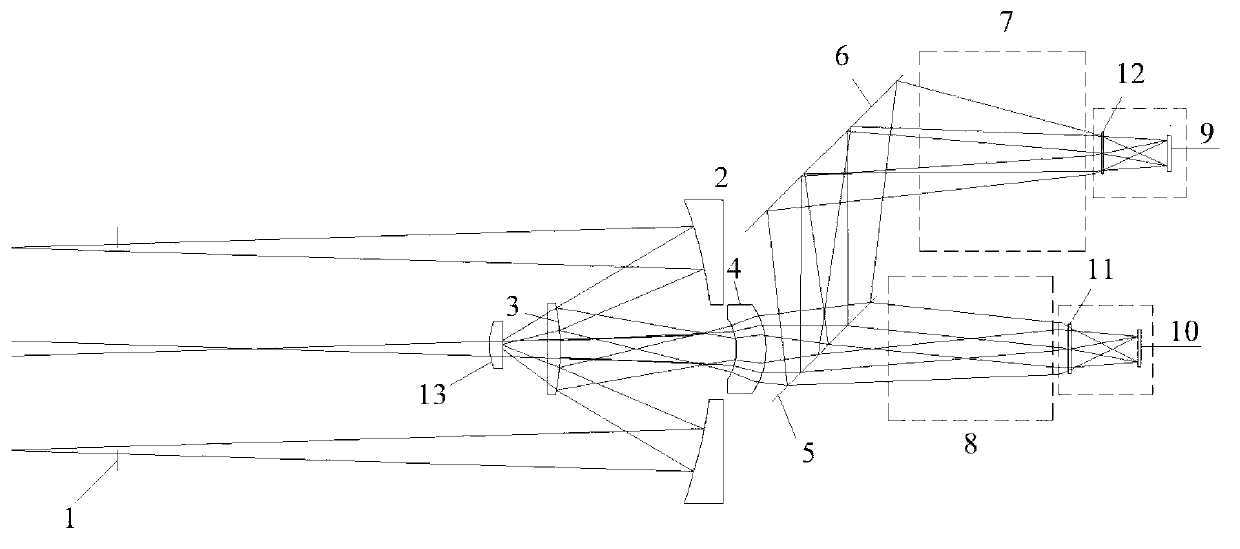
Infrared dual-waveband common-aperture refraction and reflection imaging system
The invention discloses an infrared dual-waveband common-aperture refraction and reflection imaging system which is used for imaging target radiation of medium-wave spectral wavebands and long-wave spectral wavebands at infinite positions on a long-wave infrared detector and a medium-wave infrared detector. The infrared dual-waveband common-aperture refraction and reflection imaging system is characterized in that a main optical path is a long-wave infrared optical path, a reflex optical path is a medium-wave infrared optical path, the main optical path comprises a primary mirror, a secondary mirror, a first collimating mirror, a second collimating mirror, a beam splitter mirror, a first long-wave correcting mirror, an optical filter, a second long-wave correcting mirror, a third long-wave correcting mirror, a fourth long-wave correcting mirror, a fifth long-wave correcting mirror and a long-wave detector assembly which are sequentially arranged from a beam incidence direction, and the reflex optical path comprises the primary mirror, the secondary mirror, the first collimating mirror, the second collimating mirror, the beam splitter mirror, a first medium-wave correcting mirror, a second medium-wave correcting mirror, a third medium-wave correcting mirror, a medium-wave turning reflecting mirror, a fourth medium-wave correcting mirror, a fifth medium-wave correcting mirror and a medium-wave detector assembly. The infrared dual-waveband common-aperture refraction and reflection imaging system has the advantages of relatively compact structure, light weight, good imaging quality, capability of working in wide temperature ranges, and the like.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
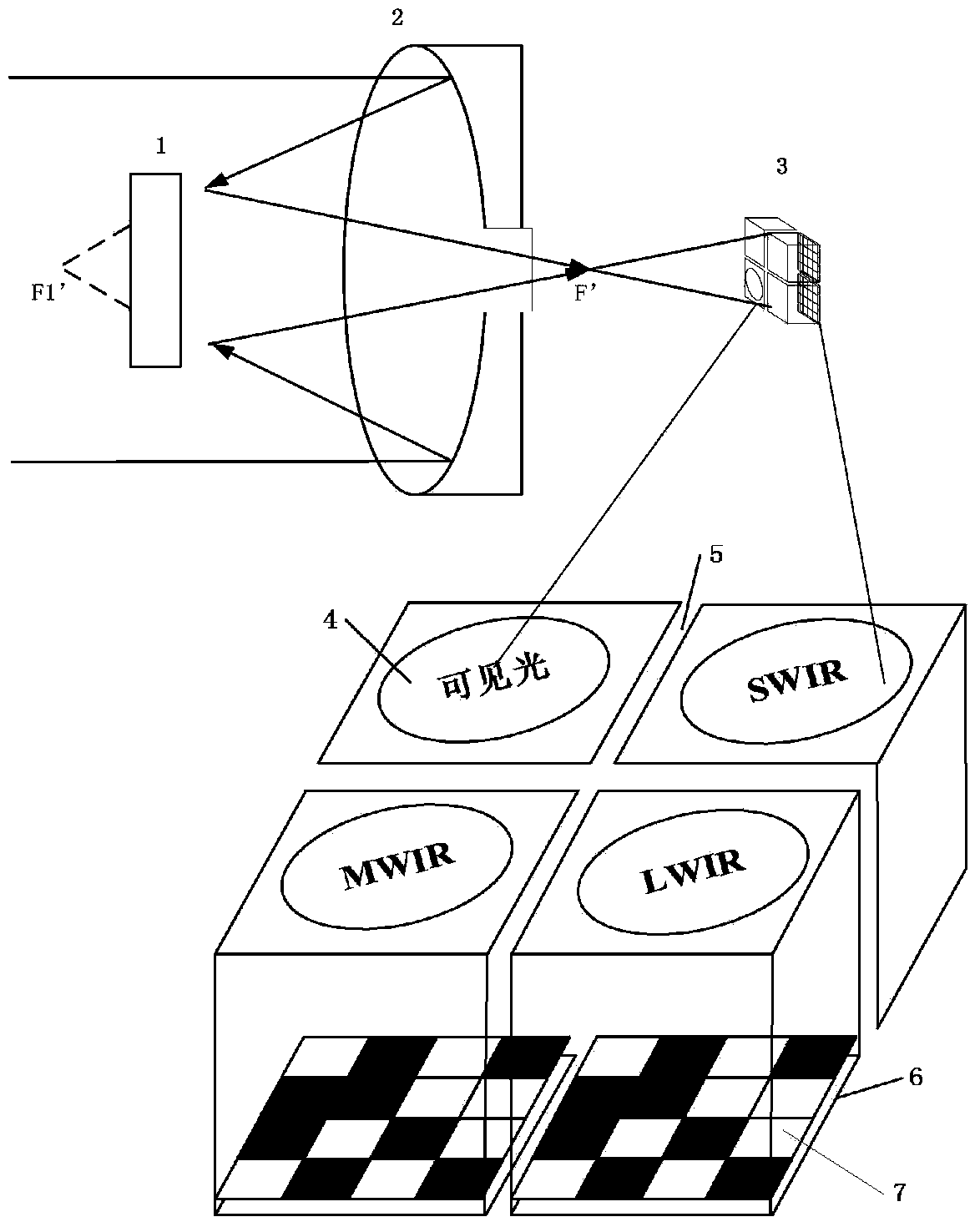
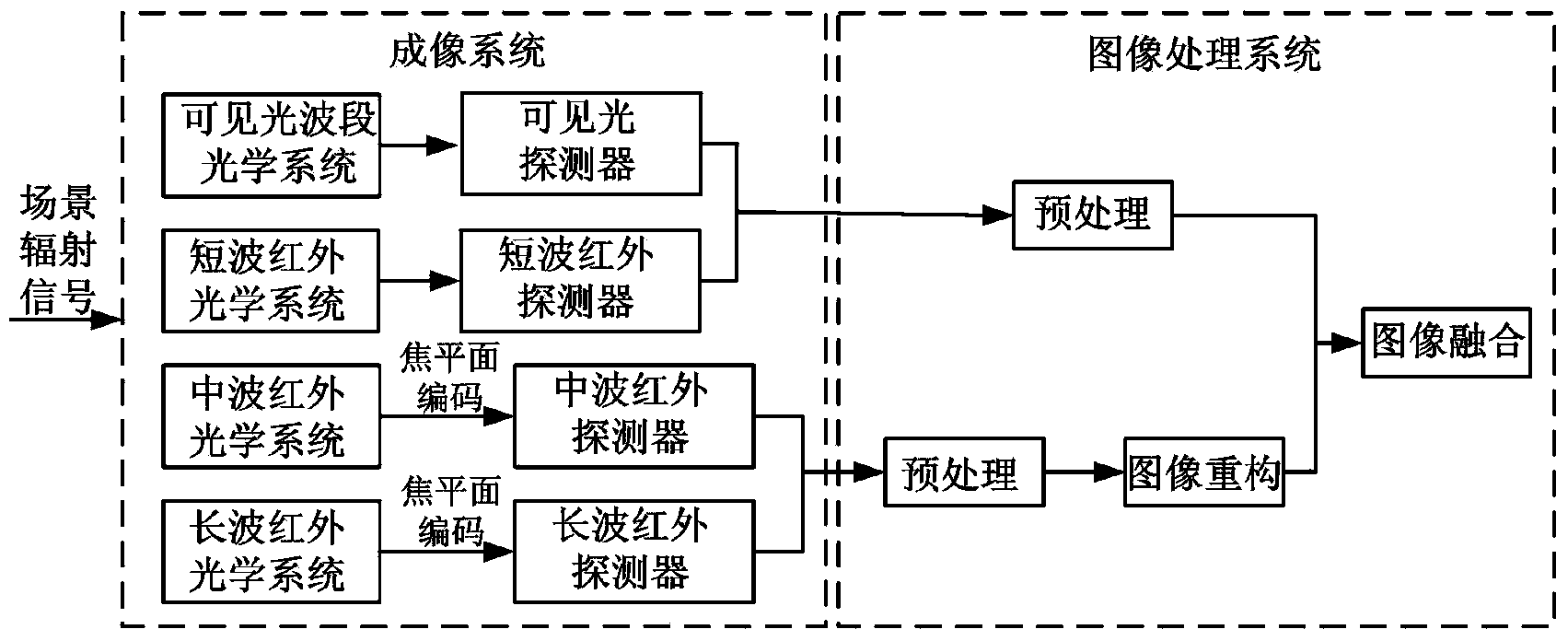
Multi-aperture multi-band high-resolution-ratio imaging device and method
ActiveCN104168429AAvoid difficultiesOvercome the defect of small field of viewTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMulti bandFalse alarm
The invention discloses a multi-aperture multi-band high-resolution-ratio imaging device and method. The device comprises a Cassegrain optical system and a multi-aperture multi-band imaging device. The Cassegrain optical system is composed of a primary mirror of a Cassegrain telescope and a secondary mirror of the Cassegrain telescope. The multi-aperture multi-band imaging device comprise a square visible light CCD detector array, a square short wave infrared CCD detector array, a square medium wave infrared CCD detector array, a square long wave infrared CCD detector array, four lenses corresponding to visible lights, short wave infrared rays, medium wave infrared rays and long wave infrared rays, a focal plane coding module and a light insulation baffle, wherein the four CCD detector arrays are equal in size. The multi-aperture multi-band high-resolution-ratio imaging device and method overcome the difficulties encountered when a single-band infrared image is used for detecting a small target in the prior art, and reduce the false alarm probability in small target detection. The multi-aperture multi-band high-resolution-ratio imaging device and method have the advantages of having ultrahigh-resolution-ratio imaging capacity and saving imaging pixels and effectively overcome the common defect that the field of view is small.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
GaAs/AlGaAs/InGaAs dual color focal plane detector
InactiveCN101055882ASimple structurePhotocoupling efficiency dropsRadiation controlled devicesSemiconductor devicesWave detectionQuantum well
The invention discloses a GaAs / AlGaAs / InGaAs two color quantum trap infrared focal plane detector, which adopts a GaAs-base material, to alternately grow up AlGaAs potential barrier, GaAs quantum trap, AlGaAs potential barrier, InGaAs quantum trap, and AlGaAs potential barrier, using the intersubband transition in GaAs quantum trap to form a survey of long wave band, and using the intersubband transition in InGaAs quantum trap to form a survey of medium wave band. According to the GaAs quantum trap of long wave detection, the AlGaAs / InGaAs / AlGaAs layer forms a potential barrier of GaAs quantum trap; and to the InGaAs quantum trap of medium wave band, the AlGaAs / GaAs / AlGaAs layer has also comprised the potential barrier of InGaAs quantum trap; and the total thickness of the AlGaAs / GaAs / AlGaAs layer and the total thickness of the AlGaAs / InGaAs / AlGaAs layer is made to be a potential barrier thickness in the conventional quantum grap infrared detector, wherein the factor of the decrease of optical coupling efficiency of devices because of the increase of thickness is eliminated. In optical coupling manner, the two-dimension diffraction grating of binary cycle is adopted, and a shallow depth etching method with minor difficulty is adopted in grating etching technics.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Substrate material for mercury cadmium telluride material growth by liquid phase epitaxy method and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101348941AImprove lattice qualityQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthMaterial growthProcess equipment
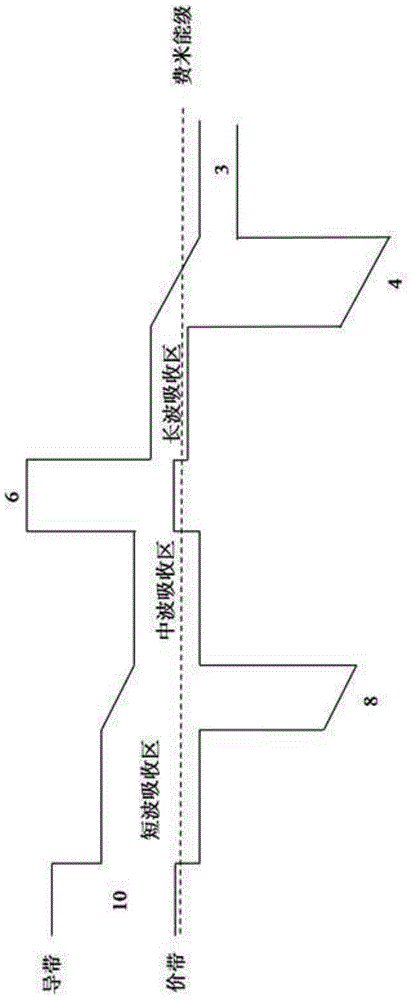
The invention relates to a substrate material used for the growth of a mercury cadmium telluride material by a liquid phase epitaxy method. On the basis of the prior substrate material, a layer of cadmium zinc telluride single-crystal film completely matched with the lattice constant of mercury cadmium telluride is grown. The substrate material of the invention has the advantages that an epitaxial film has high lattice quality, and compositions can be flexibly adjusted according to the lattice constants of short wave, medium wave and long wave mercury cadmium telluride materials; meanwhile, the cadmium zinc telluride film has even compositions; the method adopts mature process, and has the advantages of simpler process equipment, short process cycle and low cost; and the substrate material with large area, high quality and high composition evenness can be provided for an infrared focal plane detector.
Owner:11TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
Tilted layered viscoelasticity dielectric medium wave field forward modelling method
The invention discloses a tilted layered viscoelasticity dielectric medium wave field forward modelling method. The method aims at viscoelasticity layered medium, wherein a geologic model of the viscoelasticity layered medium is provided with a tilted interface, a spherical wave stimulated by a point source is decomposed into a plane wave, a character that vector wave equation does not rely on a coordinate system is utilized, under a fixed coordinate system and a moving coordinate system which changes along with the tilted interface, spreading of waves is alternately discussed, firstly, reflection and transmission coefficients of the plane wave of a single tilted interface are deduced through traditional reflection and transmission coefficients, reflection and transmission waves of the interface are obtained, then the reflection and transmission coefficients of the plane wave when passing through multiple tilted interfaces are obtained by recurrence, and finally plane waves after transmitted are combined to obtain a point source excitation wave field. In the process of combination, a rapid oscillatory integral calculation method and an integral path which is suitable for viscoelasticity medium are adopted.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
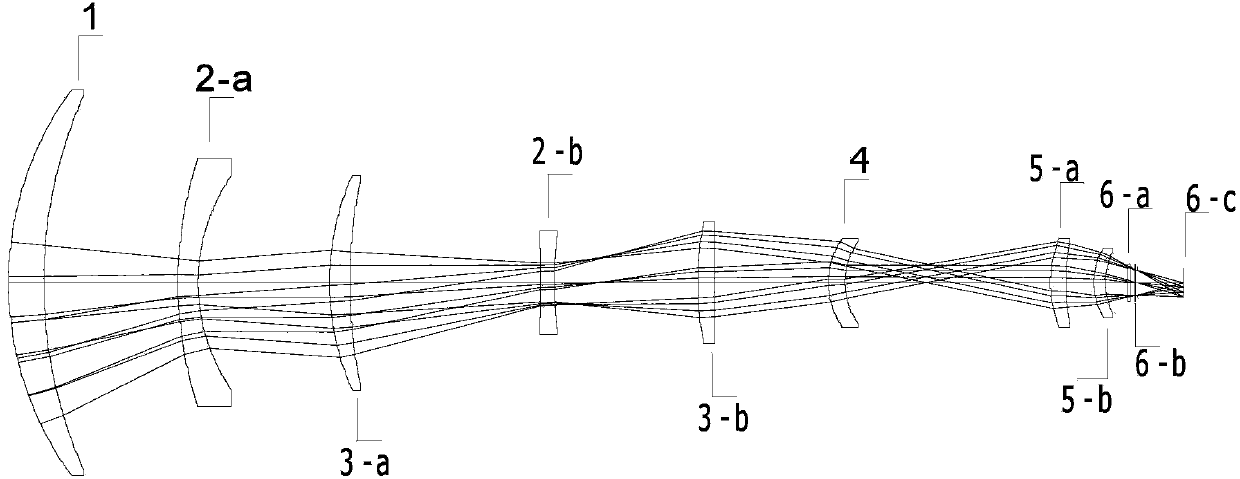
Medium wave infrared 30 times continuous zooming optical system without rear fixed group
The invention relates to a medium wave infrared 30 times continuous zooming optical system without a rear fixed group. The optical system consists of a vari-focal objective lens and a repeater group from an object side to an image side; the vari-focal objective lens consists of a front fixed group lens, a variable time group and a compensating group, the focal powers of the three groups of lenses are distributed into a positive structure, a negative structure and a positive structure in sequence, and the zoom function is realized by the axial movement of the variable time group and the compensating group; the repeater group consists of four lenses, the first lens is a double-convex silicon positive lens, the second lens and the third lens are falcate germanium negative lens facing to the image side, and the fourth lens is a zinc selenide positive lens with the convex surface facing to the image side and is used for repeating an image and stabilizing an image surface in a zooming process. According to the optical system, the double-component mechanical compensation zooming without the rear fixed group and the secondary imaging technology are adopted, the 30 times of large zooming ratio is realized, the focal distance can be changed continuously in a range from 17.5mm to 525mm, the maximum stroke of the zooming group is 106mm, the maximum stroke of the compensating group is 50mm, the total optical length of the system is 350mm, and 100% of cold stop efficiency is realized.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PHYSICS
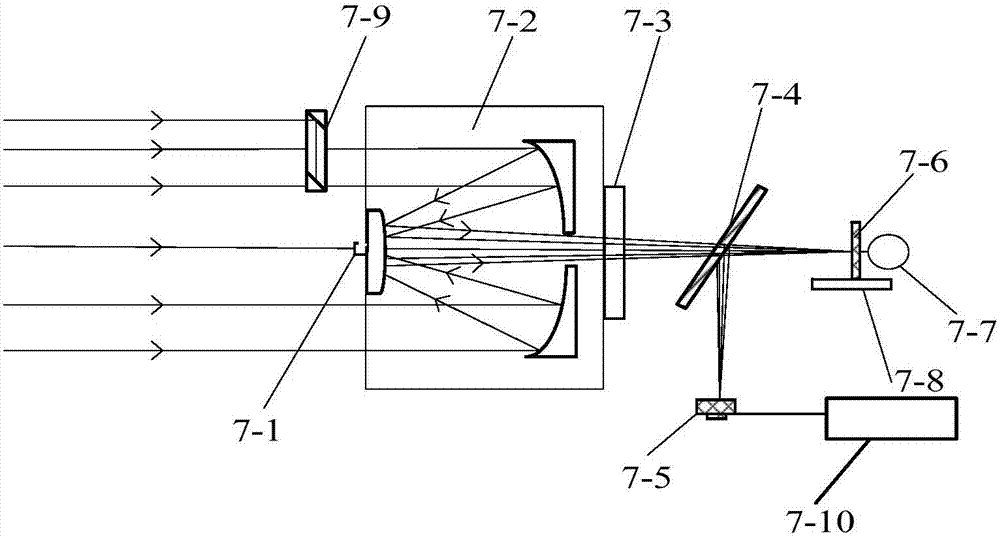
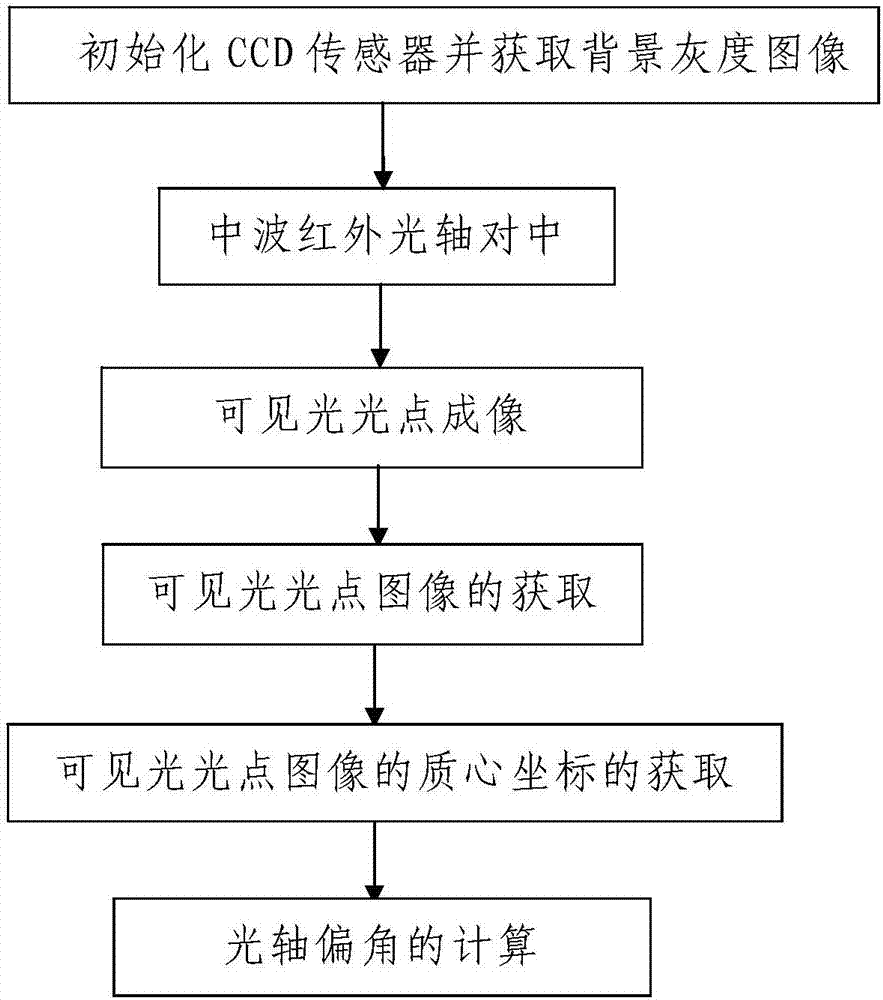
Infrared-visible light dual-band photoelectric detection system and axis angle error measuring method
InactiveCN107991686AAccurately identify the targetHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsBeam splitterImaging quality
The invention discloses an infrared-visible light dual-band photoelectric detection system and an axis angle error measuring method. The Infrared-visible light dual-band photoelectric detection systemand axis angle error measuring method comprises a reflecting system, a beam splitter, a visible light imaging unit on a reflecting path of the beam splitter, a medium-wave infrared imaging unit on atransmitting path, and an axis angle error measuring unit. The axis angle error measuring method comprises: I, initializing a CCD (charge coupled device) sensor, and acquiring a background gray image;II, centering a medium-wave infrared axis; III, performing visible light spot imaging; IV, acquiring a visible light spot image; V, acquiring coordinates of a center of mass of the visible light spotimage; VI, calculating axis angle error. The infrared-visible light dual-band photoelectric detection system and the axis angle error measuring method have the advantages that the advantages of a visible light band optical system and those of a medium-wave infrared band optical system are combined, observing efficiency and inspecting efficiency are improved, remote high-definition all-weather imaging is achieved, imaging quality is effectively improved, the axis angle error measuring unit can measure angle errors for visible light axis and medium-wave infrared axis, and stability of the photoelectric detection system can be measured.
Owner:XIAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIV
Technology for enriching soybean sprout isoflavone
The invention relates to a technology for enriching soybean sprout isoflavone. The technology adopting physiologically active soybean grains as a raw material comprises the following steps: disinfecting the raw materials in an aqueous sodium hypochlorite solution through a known method, placing the disinfected raw material in purified water with according to a ratio of 3-5:1 (v / w), immersing the raw material at 30 DEG C for 5 h, placing the immersed raw material in a germinator, and germinating the raw material at 30 DEG C; and continuously radiating medium wave ultraviolet lights (UV-B) (with the wavelength of 280-320 nm, the radiation distance of 30-50 cm and the radiation distance of 20-50 [mu]W.cm<-2>) on the germinated soybeans for 2-4 d in the germination period, and carrying out spray germination with a 0-15 [mu]M abscisic acid (ABA) and 0-3 mM sodium nitroprusside (SNP) mixed aqueous solution for 1-3 min every 1-4 h, wherein the flow amount of the above spraying liquid is 50-200 mL / min. The technology is simple to operate, and allows the content of isoflavone in the soybean sprouts to reach 4000-5500 [mu]g / g DW.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
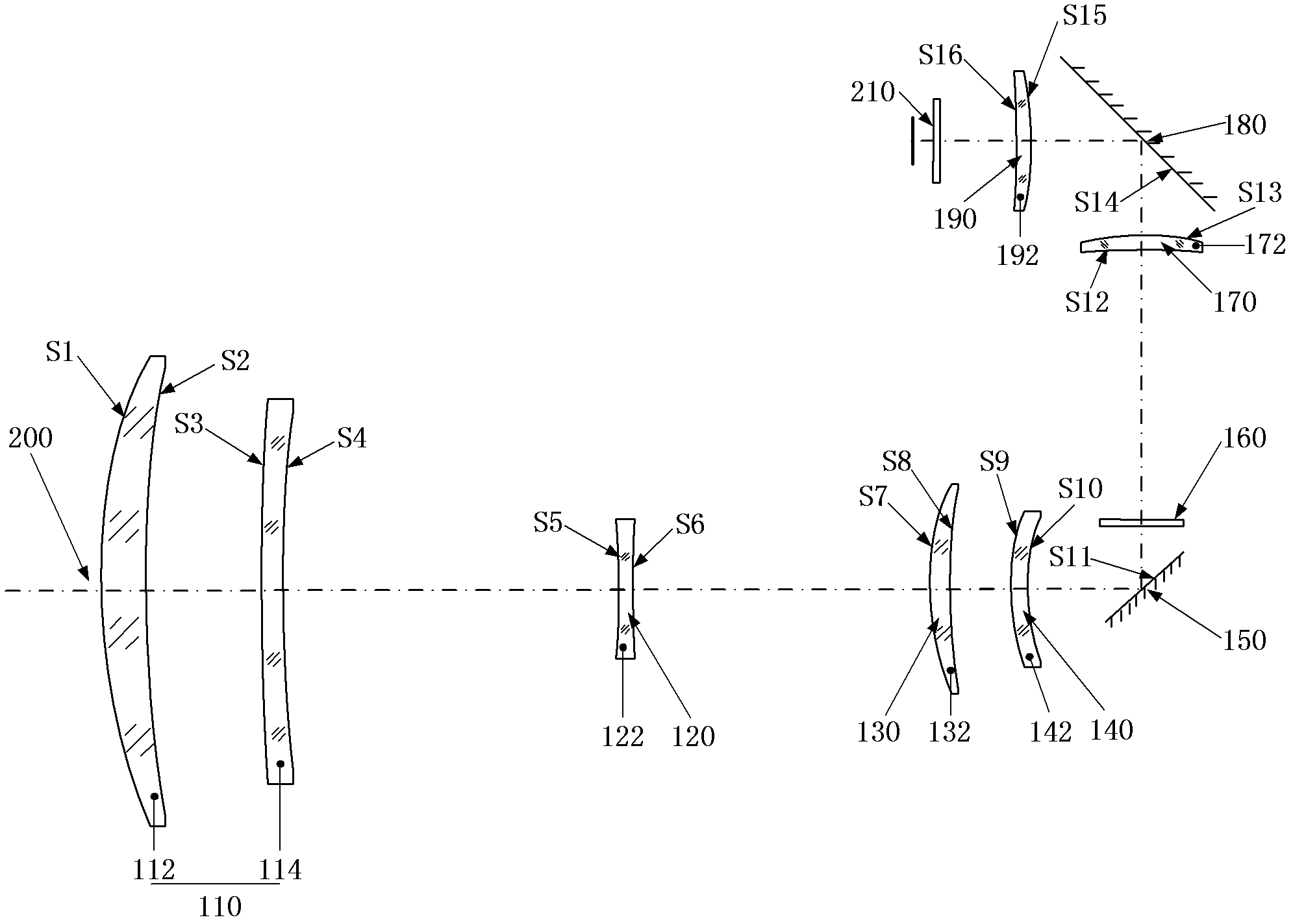
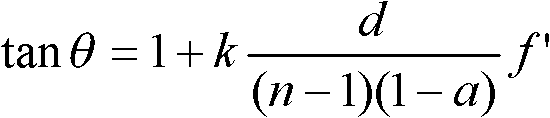
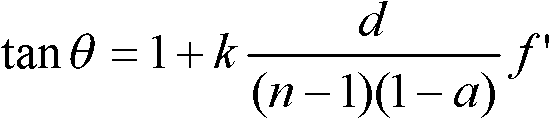
![Film system structure of ZnS substrate with inverse 0.5-0.8[Mu]m visible light, laser with 1.064[Mu]m and transparent medium wave infrared colour separation with 3.7-4.8[Mu]m Film system structure of ZnS substrate with inverse 0.5-0.8[Mu]m visible light, laser with 1.064[Mu]m and transparent medium wave infrared colour separation with 3.7-4.8[Mu]m](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/ccf59059-14df-43e5-8333-0f40ea1f7297/HDA0000976674960000011.PNG)
![Film system structure of ZnS substrate with inverse 0.5-0.8[Mu]m visible light, laser with 1.064[Mu]m and transparent medium wave infrared colour separation with 3.7-4.8[Mu]m Film system structure of ZnS substrate with inverse 0.5-0.8[Mu]m visible light, laser with 1.064[Mu]m and transparent medium wave infrared colour separation with 3.7-4.8[Mu]m](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/ccf59059-14df-43e5-8333-0f40ea1f7297/HDA0000976674960000012.PNG)
![Film system structure of ZnS substrate with inverse 0.5-0.8[Mu]m visible light, laser with 1.064[Mu]m and transparent medium wave infrared colour separation with 3.7-4.8[Mu]m Film system structure of ZnS substrate with inverse 0.5-0.8[Mu]m visible light, laser with 1.064[Mu]m and transparent medium wave infrared colour separation with 3.7-4.8[Mu]m](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/ccf59059-14df-43e5-8333-0f40ea1f7297/HDA0000976674960000021.PNG)