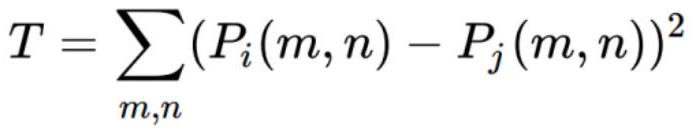Patents
Literature
36 results about "Narrow-band imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
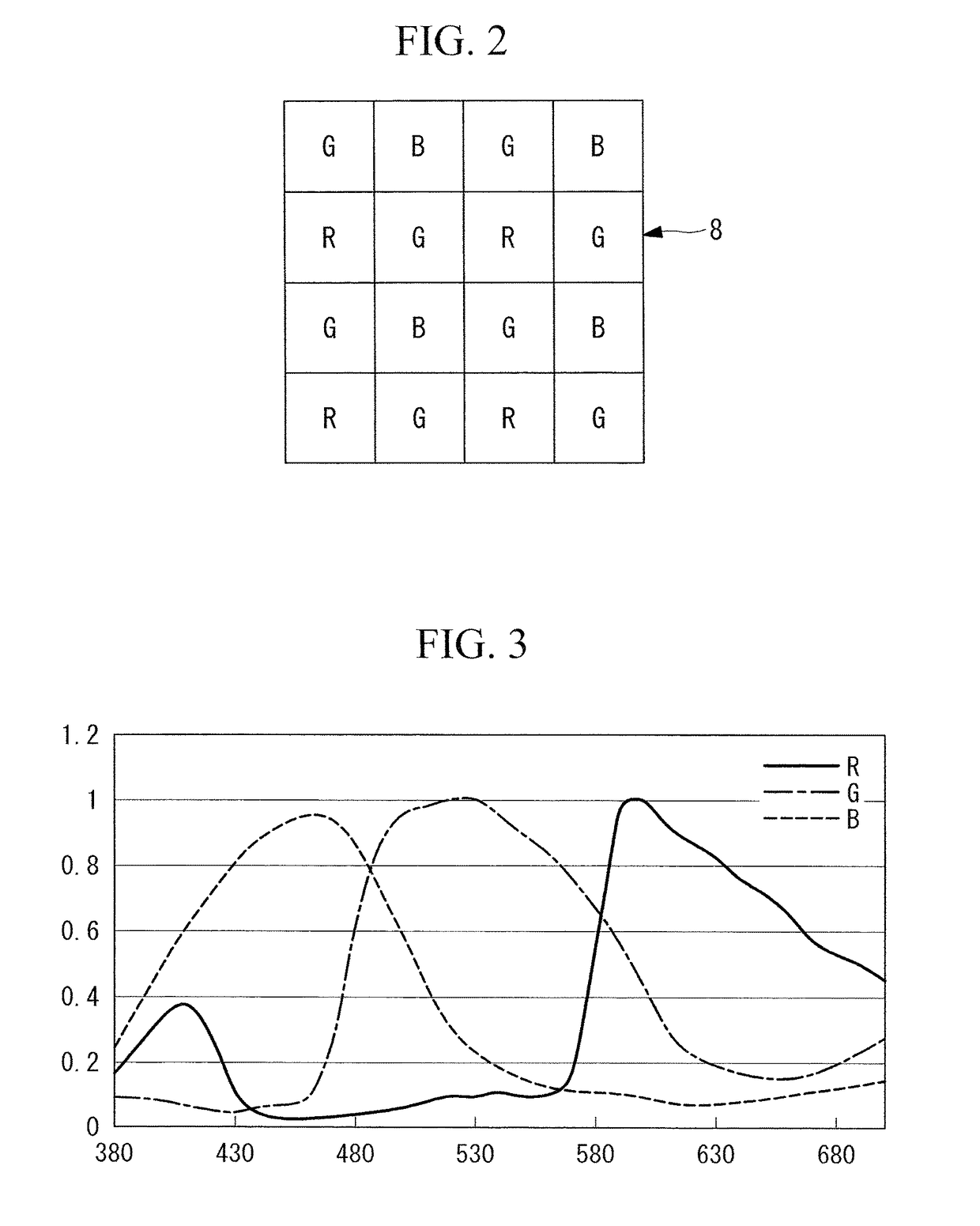
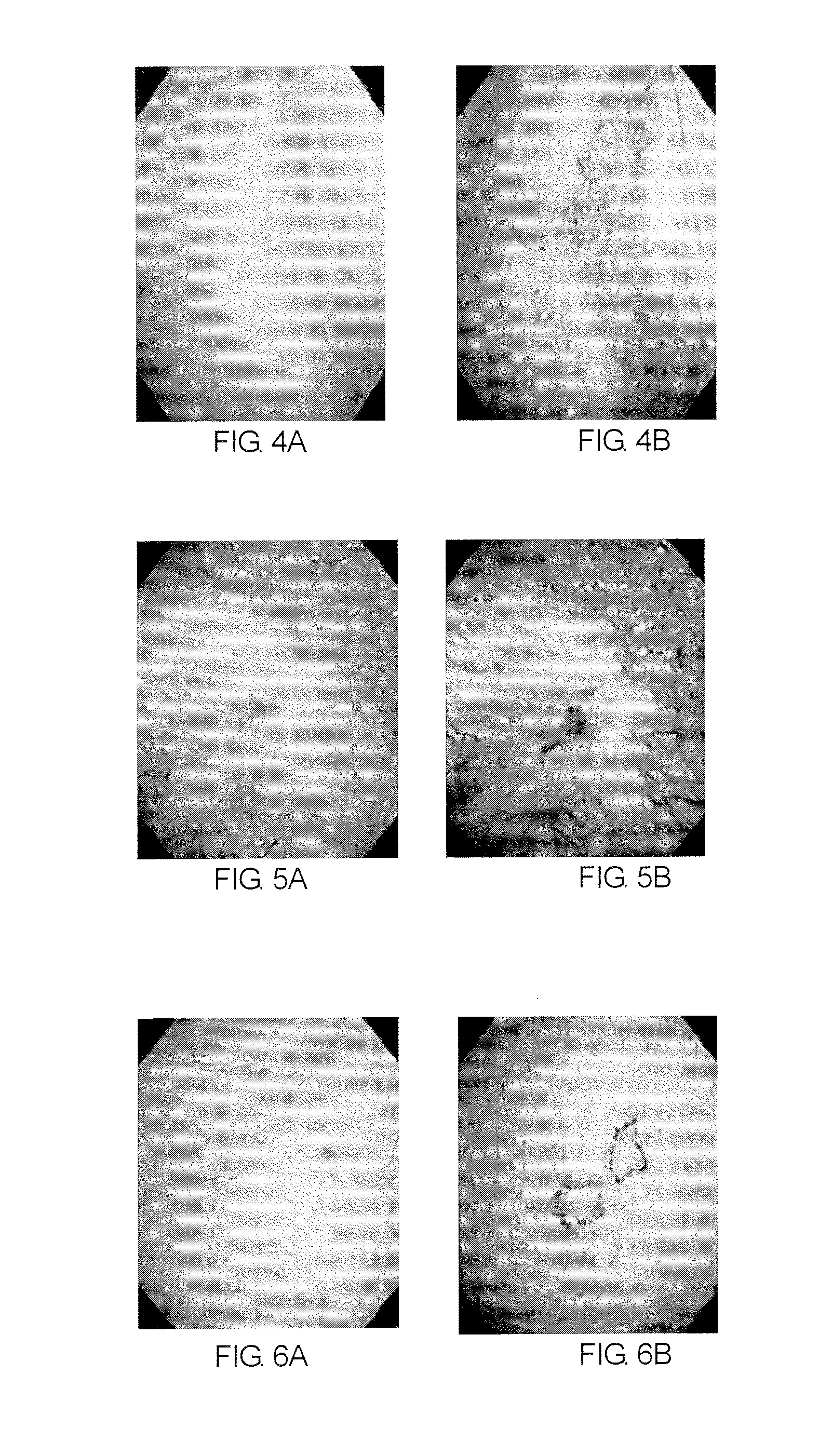
Narrow-band imaging is an imaging technique for endoscopic diagnostic medical tests, where light of specific blue and green wavelengths is used to enhance the detail of certain aspects of the surface of the mucosa. A special filter is electronically activated by a switch in the endoscope leading to the use of ambient light of wavelengths of 415 nm (blue) and 540 nm (green). Because the peak light absorption of hemoglobin occurs at these wavelengths, blood vessels will appear very dark, allowing for their improved visibility and in the improved identification of other surface structures.
Device and method for cooperatively detecting moving target by using all-optical-waveband map
ActiveCN105182436ASimple structureReduce dampingRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationVisible near infraredNarrow-band imaging
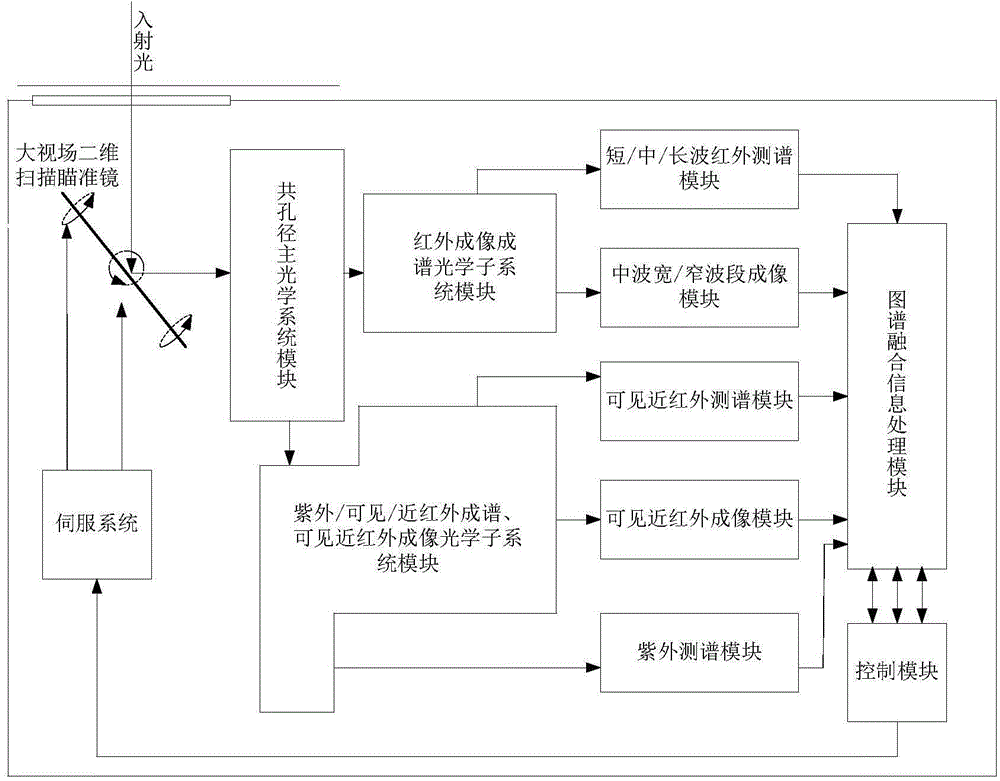
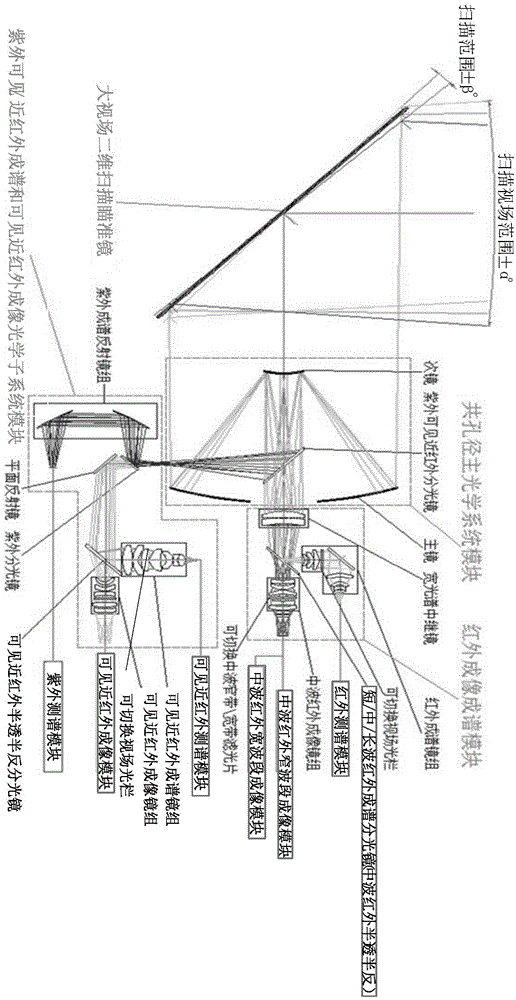
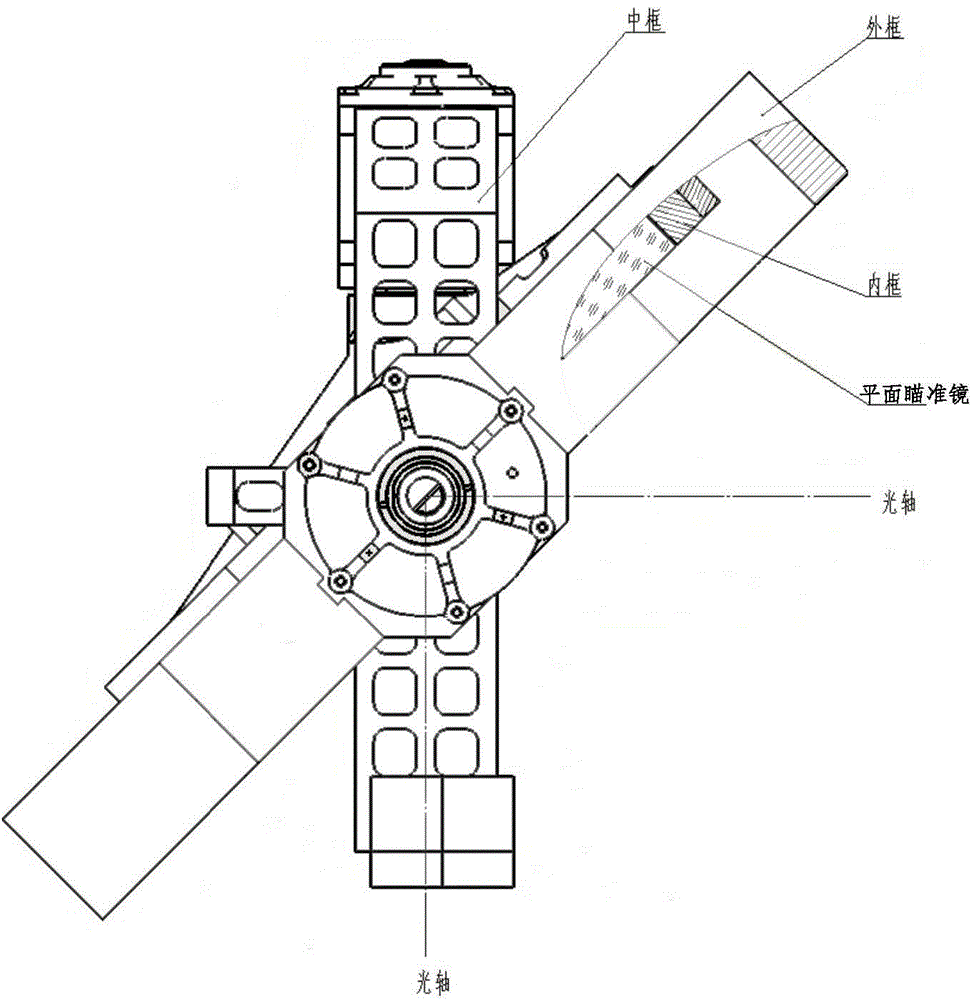
The invention discloses a device and a method for cooperatively detecting a moving target by using all-optical-waveband (including ultraviolet, visible, near-infrared, medium-wave infrared and long-wave infrared) maps. The device comprises a large field-of-view two-dimensional scanning sighting telescope, a common aperture primary optical system module, an infrared imaging and spectrum forming optical subsystem module, an ultraviolet / visible / near-infrared spectrum forming and visible near-infrared imaging optical subsystem module, a short / medium / long-wave infrared spectrum measuring module, a medium-wave wide / narrow band imaging module, a visible near-infrared spectrum measuring module, a visible near-infrared imaging module, an ultraviolet measuring module, a map fusion signal processing module, a control module and a servo system. The device and the method utilizes medium-wave infrared imaging and visible near-infrared imaging for recognizing a suspected moving target and guides spectrum measurement, completes the final recognition of the suspected target with cooperation of spectrum measurement data, and solves the difficulties of the existing detection device such as incomplete detection bands, limited optical path layout, large equipment size, few types of detected moving targets and dynamic changing objects, and poor detection capability.
Owner:NANJING HUATU INFORMATION TECH
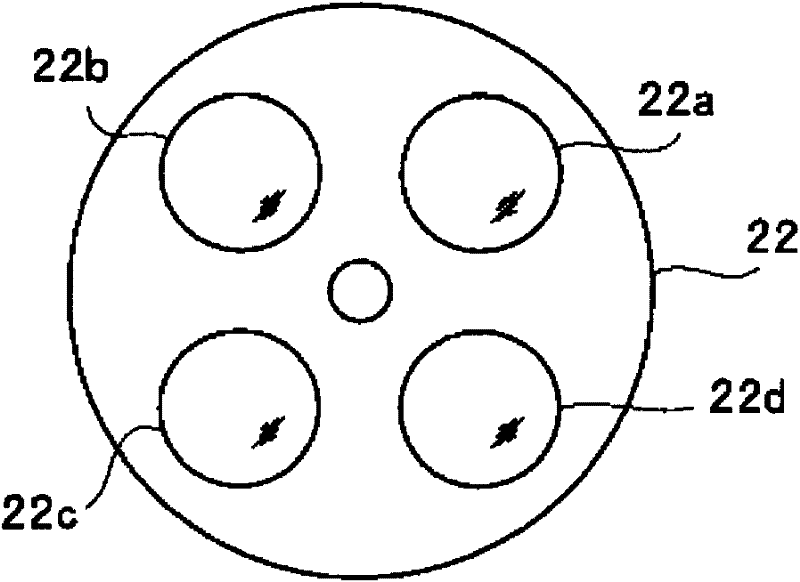
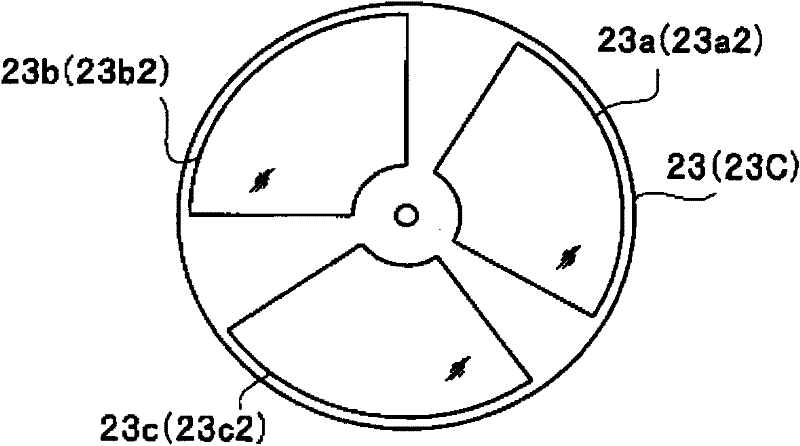
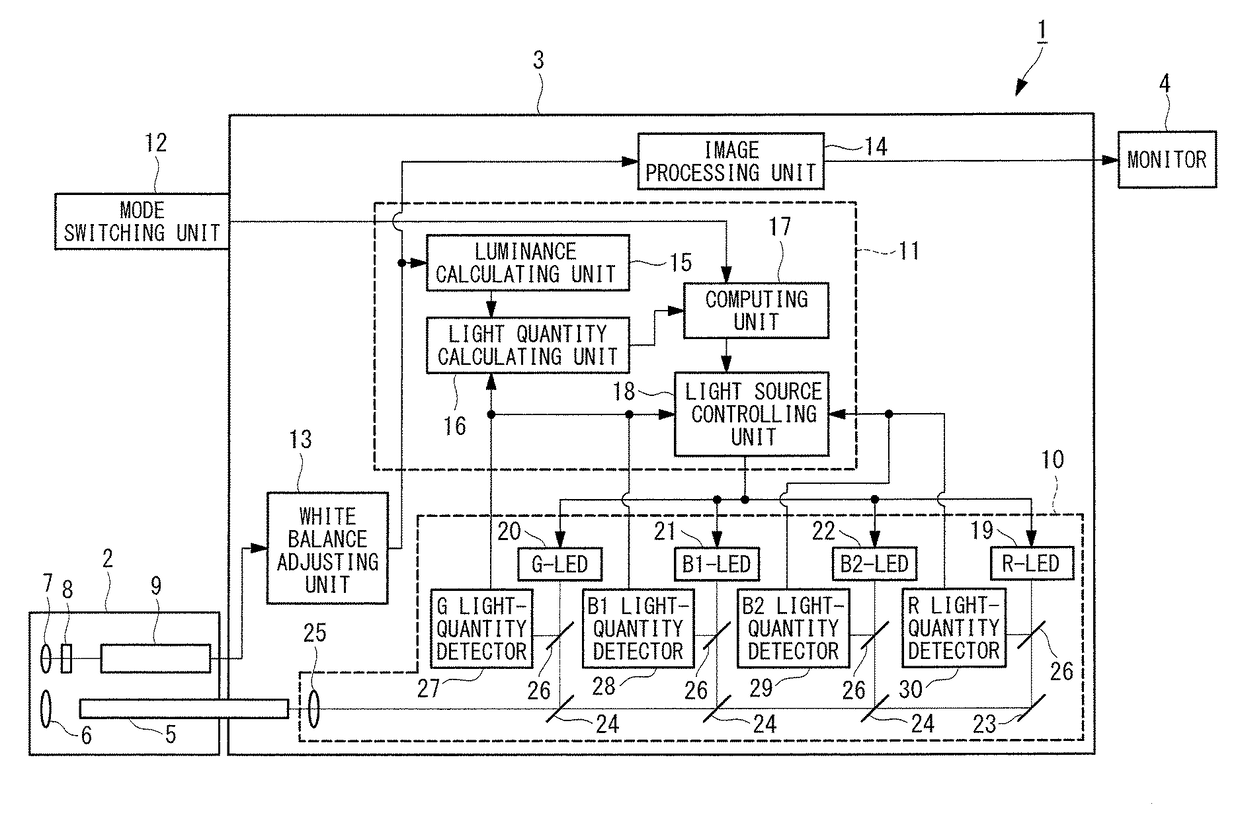
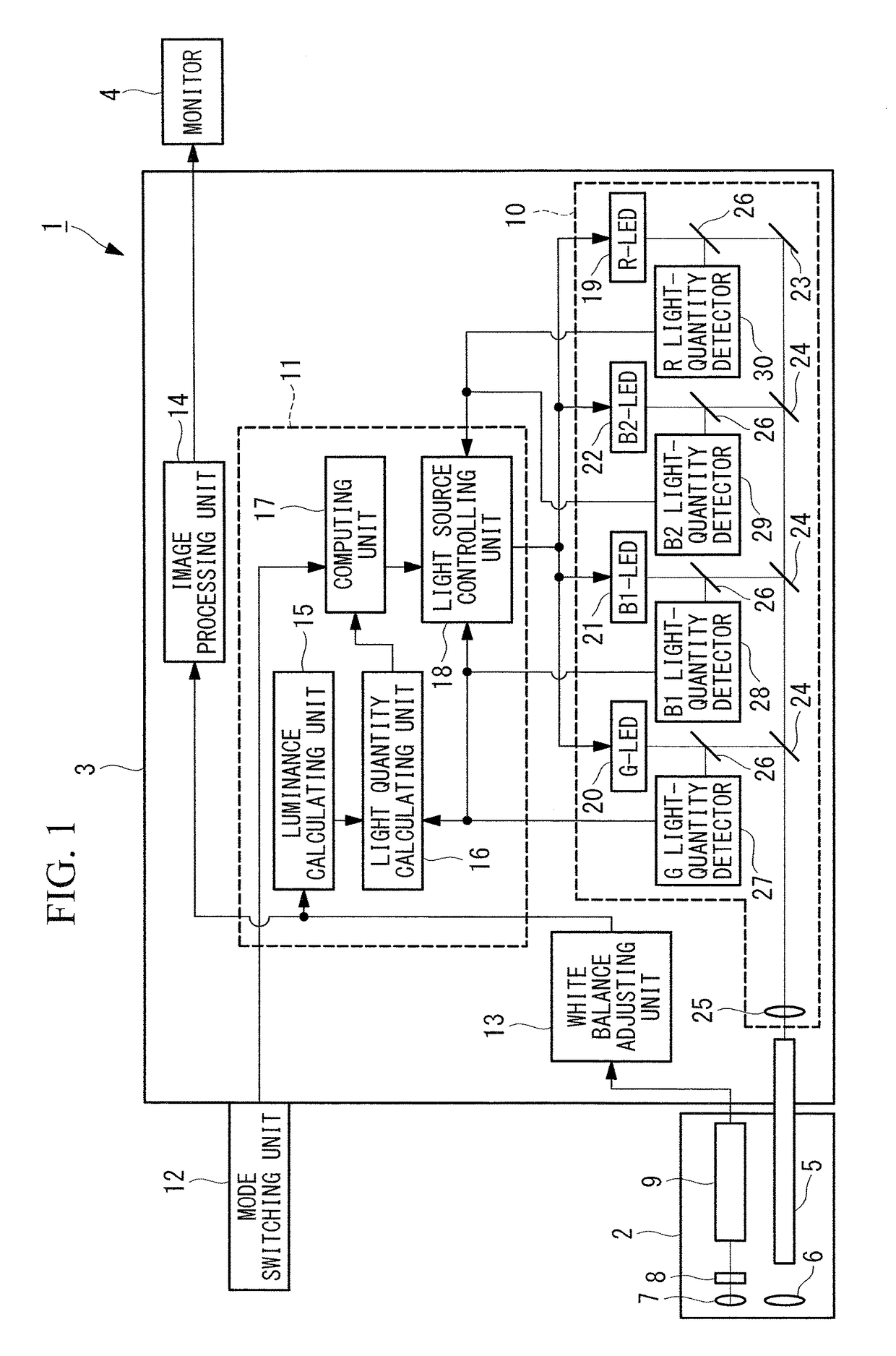
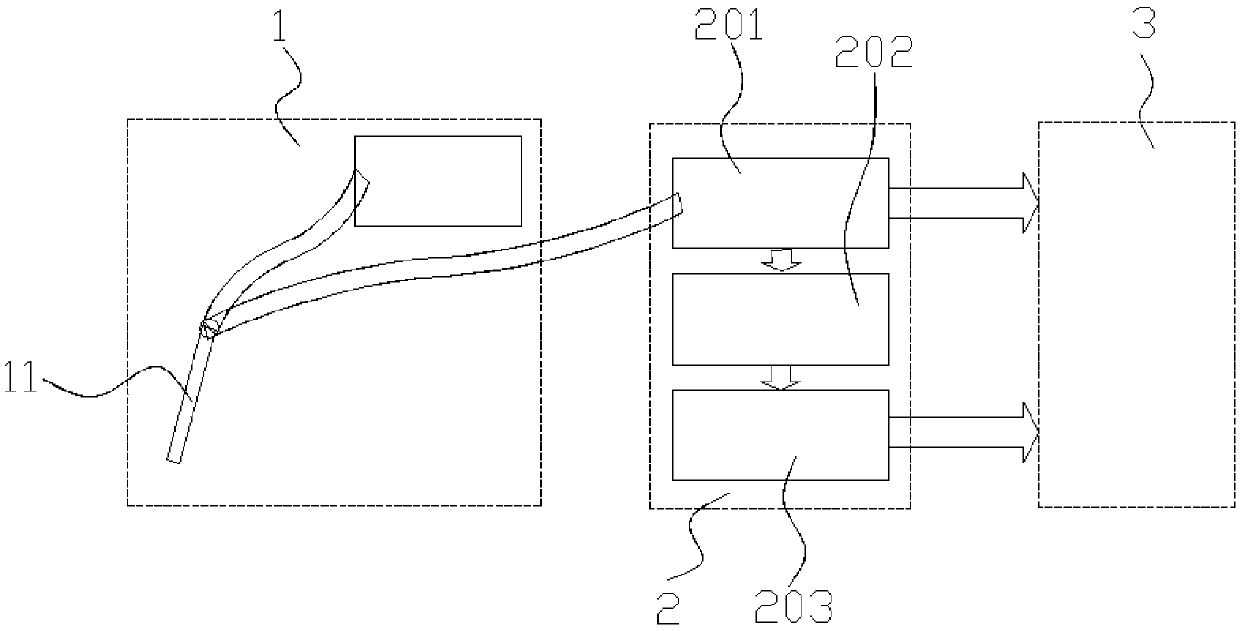
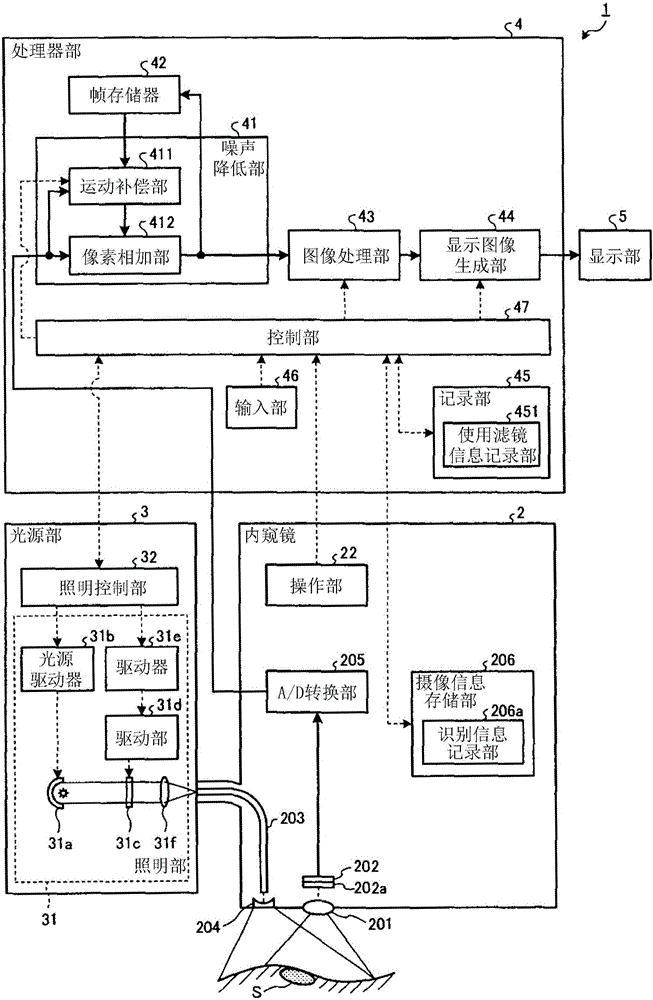
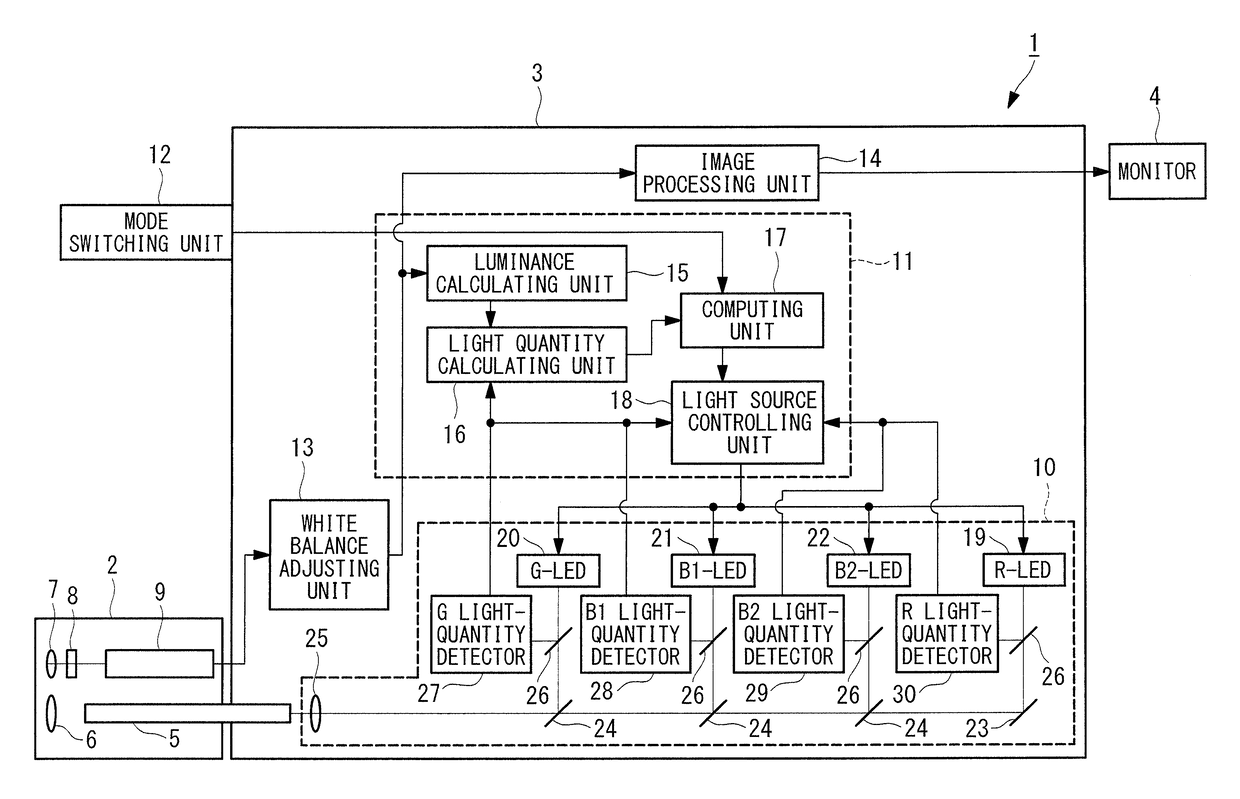
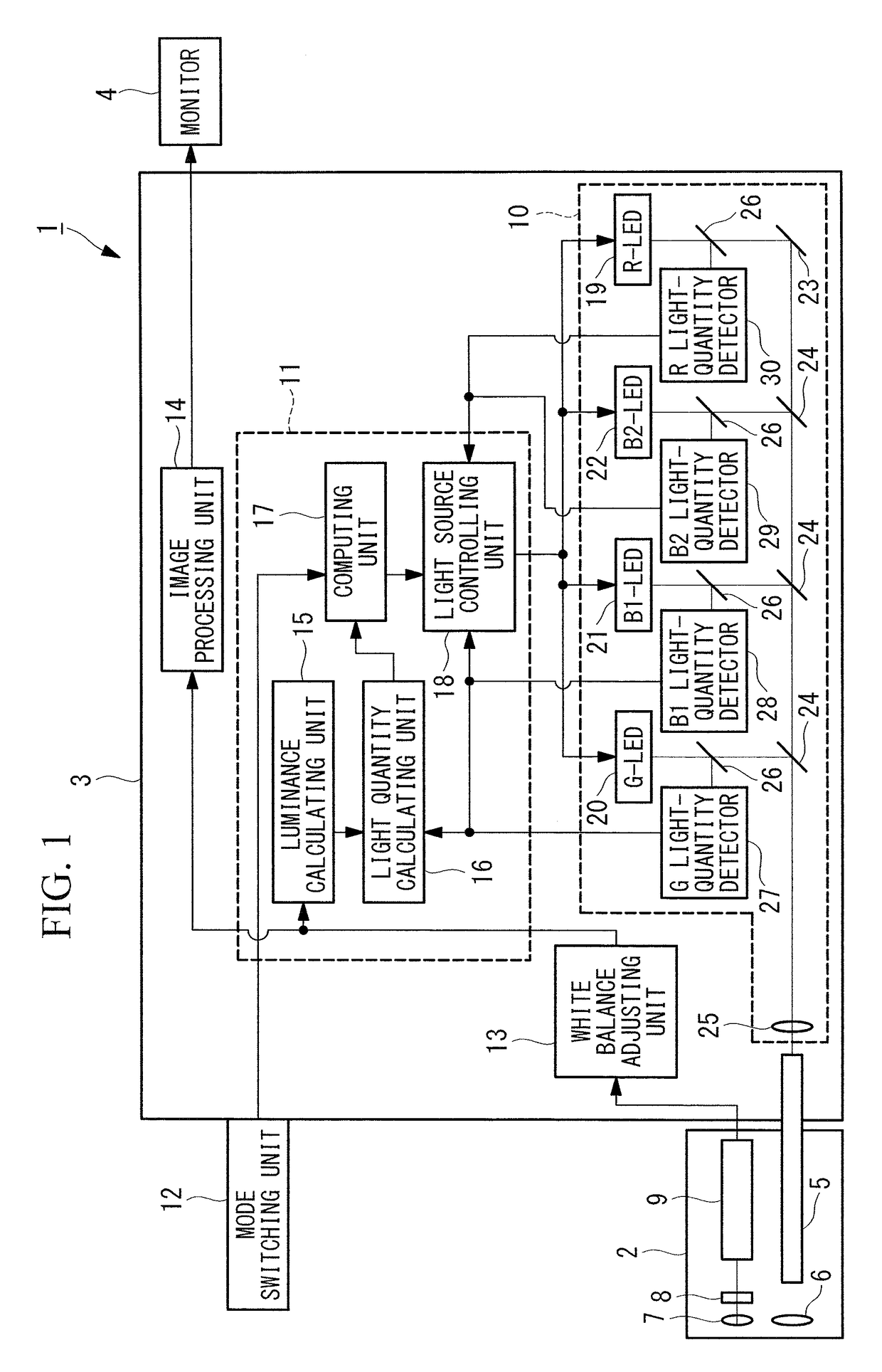
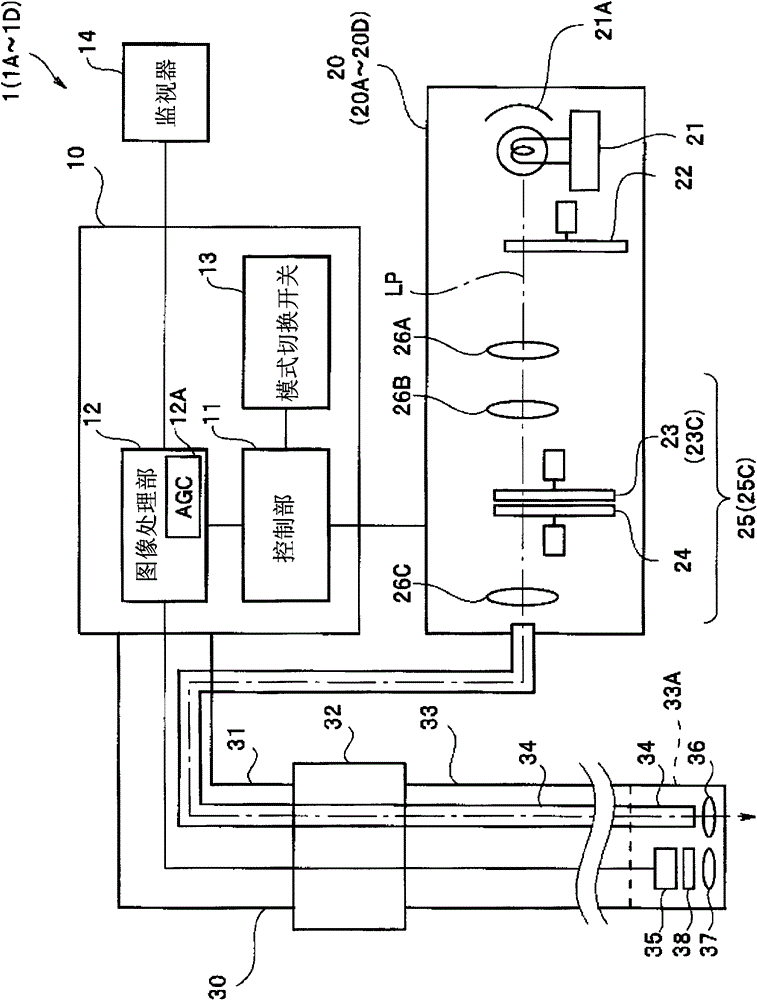
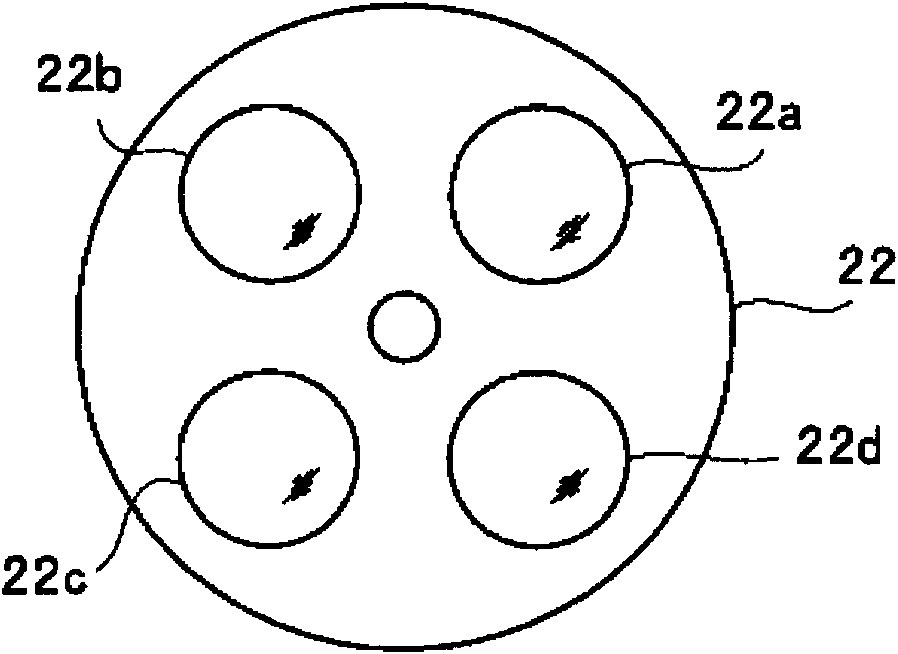
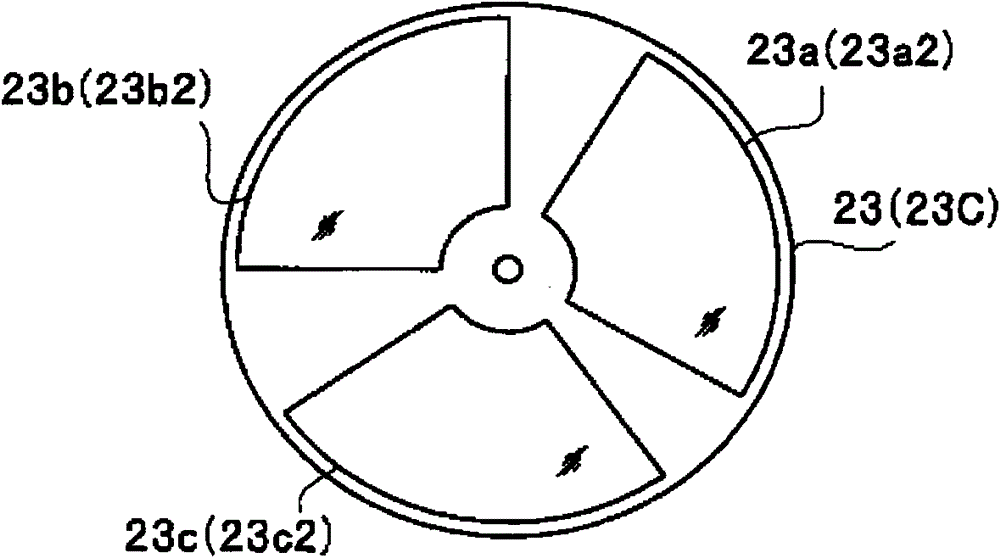
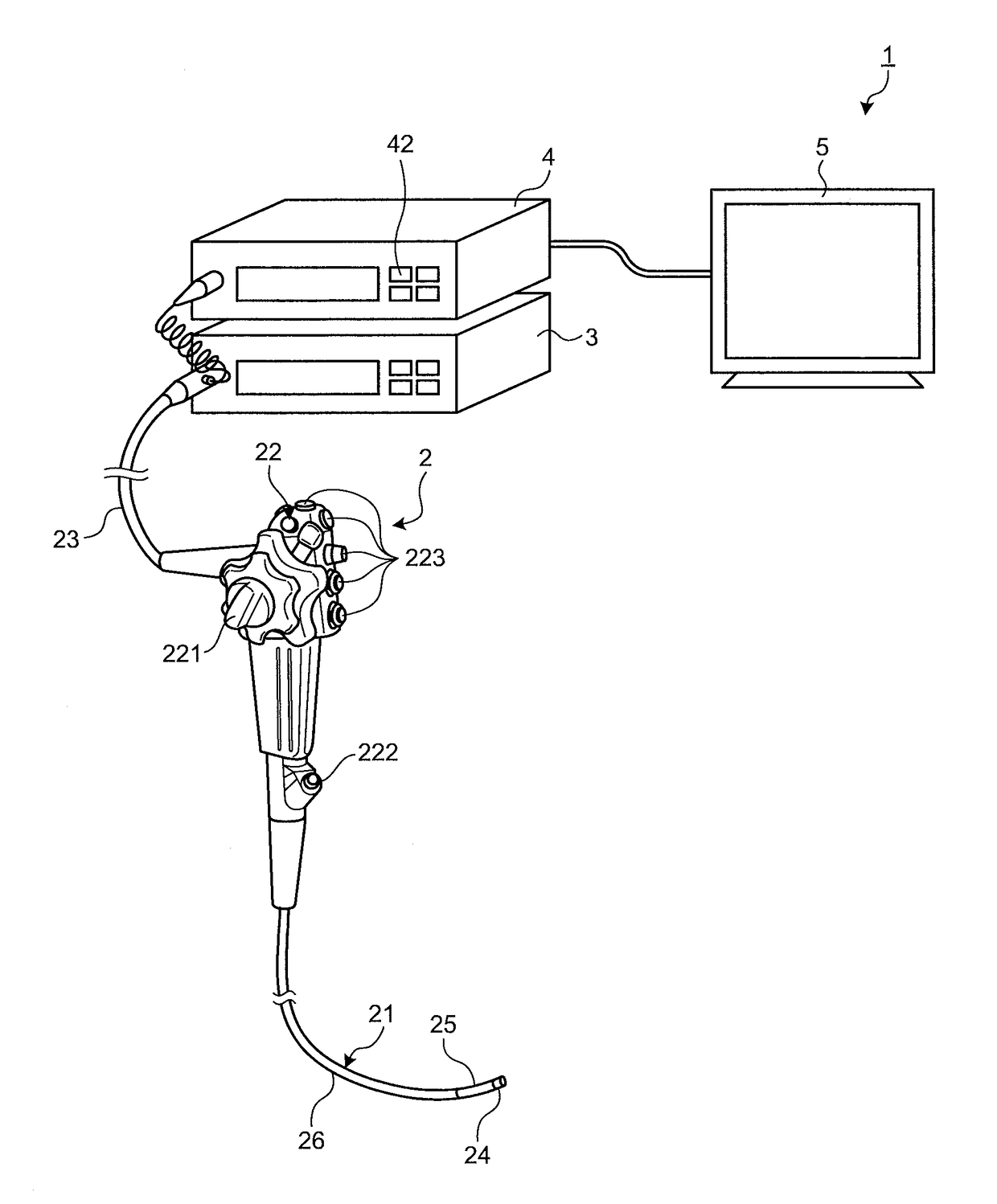
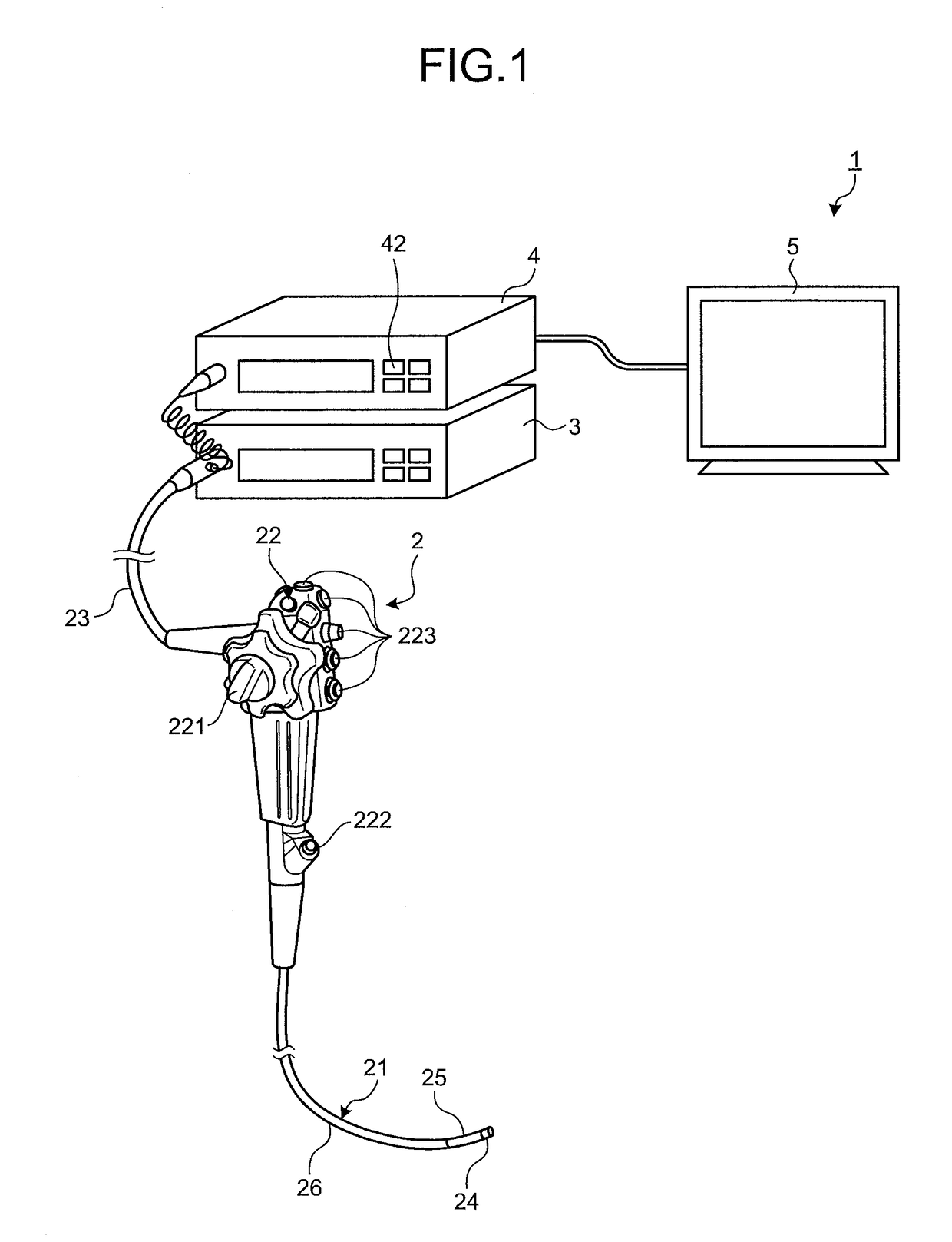
Light source device and endoscope system
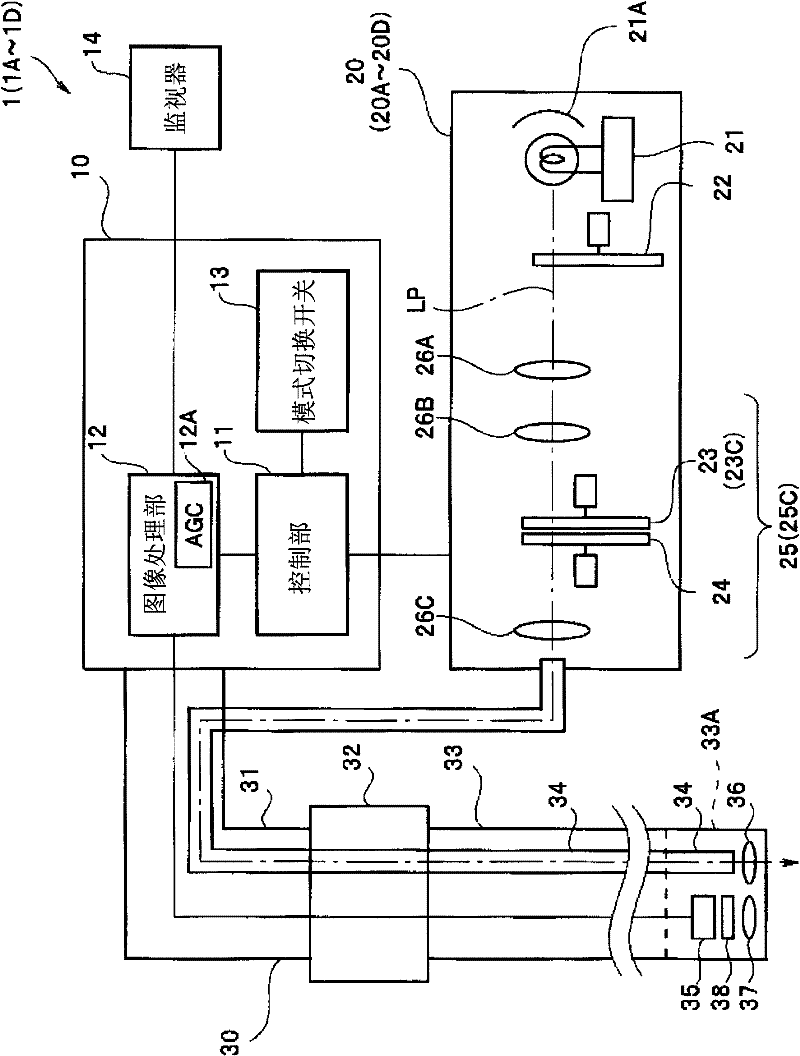
A light source device (20) comprises a first rotational filter part (23) in which a blue filter (23a), a green filter (23b), and a magenta filter (23c) can be disposed in a light path (LP), a second rotational filter part (24) in which an yellow filter (24a) can be disposed therein, and a band selection filter part (22) in which an NBI filter for limiting blue or green light to a narrow band can be disposed therein. The first and second rotational filter parts (23, 24) can be controlled so that in the case of normal light imaging, the yellow filter (24a) is disposed in the light path (LP) when the magenta filter (23c) is disposed in the light path (LP), and in the case of narrow band imaging, the NBI filter is disposed in the light path (LP), and the yellow filter (24a) is disposed in thelight path (LP) when the green filter (23b) is disposed in the light path (LP).
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
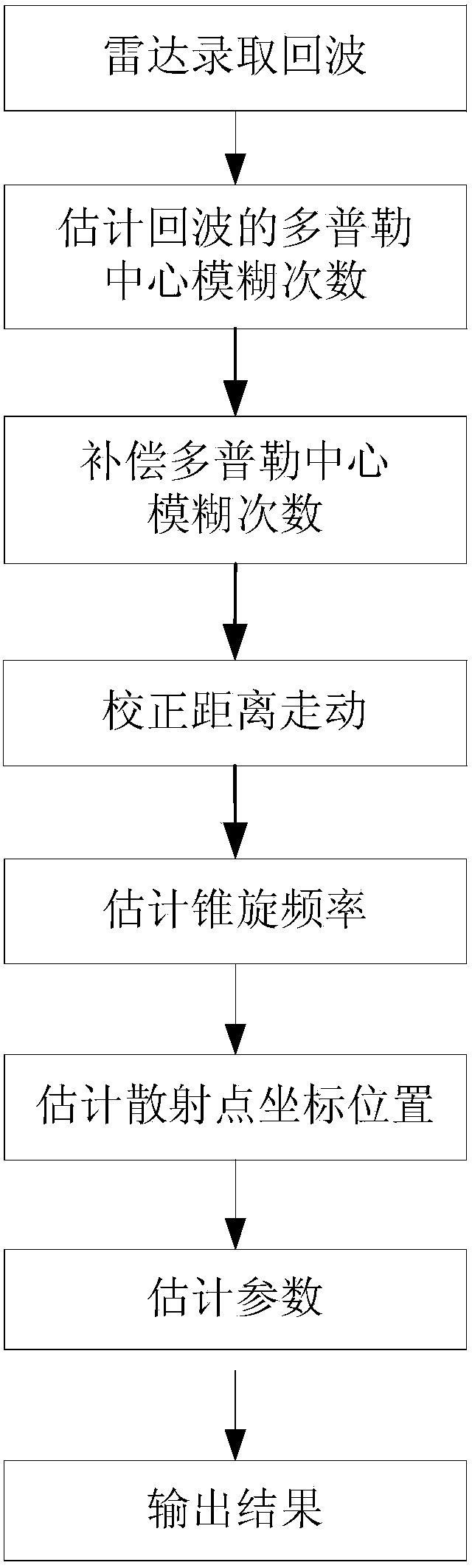
Smooth procession cone parameter estimation method based on high-resolution ISAR imaging
ActiveCN103424741ATo overcome the large amount of calculationTo overcome the lack of needing a lot of prior informationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTime domainRadar
A smooth procession cone parameter estimation method based on high-resolution ISAR imaging mainly solves the problems that joint estimation on cone geometrical parameters and motion parameters in the parameter estimation process of a smooth cone is difficult to carry out, and the calculated amount is large and the needed prior information amount is large in narrow-band imaging and parameter estimation. The method includes the steps of 1, obtaining frequency in ISAR recording, namely, a slowness-time domain echo, 2, estimating the number of Doppler ambiguity times of the echo by utilizing a curve fitting method, 3, compensating the number of Doppler ambiguity times of the echo, 4, correcting range walk of the echo, 5, carrying out the ISAR imaging on echo data by utilizing a matched filtering method, and accurately estimating position information of a scattering center, and 6, carrying out the joint estimation on cone sizes, radar sights and angles of precession by utilizing a least square fitting method. The smooth procession cone parameter estimation method has the advantages of being easy to operate, high in estimation accuracy, small in amount of needed prior information, and capable of carrying out the joint estimation on the cone geometrical parameters and the motion parameters.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
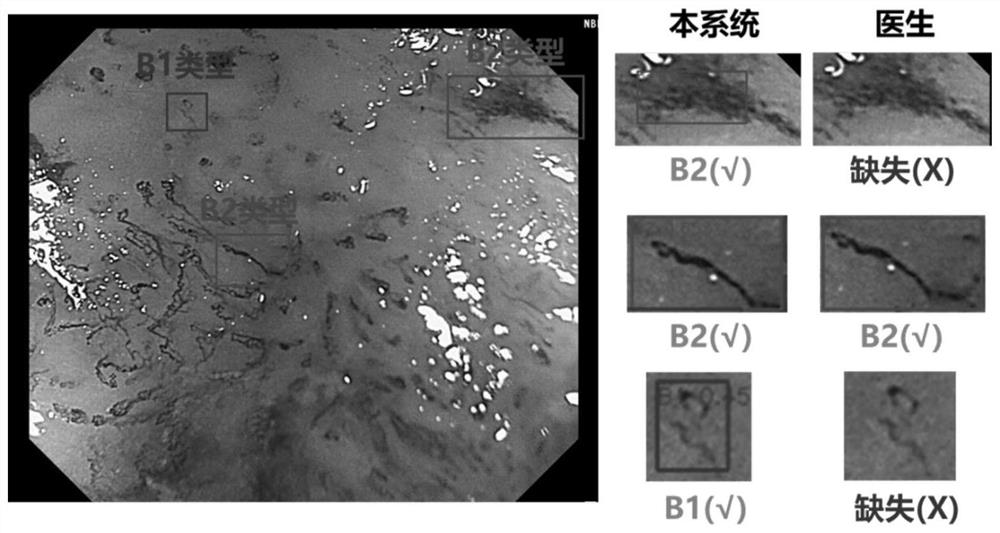
Artificial intelligence diagnosis method for gastric cancer under narrow-band imaging amplification gastroscope
PendingCN112435246AAuxiliary differential diagnosisImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionImage segmentation
The invention relates to the technical field of medical technology assistance, in particular to an artificial intelligence diagnosis method for gastric cancer under a narrow-band imaging amplificationgastroscope, which comprises the following steps: S1, constructing a mini-UNet neural network model; S2, constructing a UNet + + image segmentation neural network model, and obtaining an area ratio Rabnormal of an image feature difference region; S3, adopting a generative adversarial network (GAN) technology to obtain a microvascular morphological diagram and a microstructure morphological diagram of the feature abnormal region; S4, identifying the microvessel form dissimilarity degree and the microstructure form dissimilarity degree in the microvessel form diagram and the microstructure formdiagram by the neural network model ResNet50; and S5, carrying out identification and judgment by using the random forest model obtained by training to obtain final judgment of cancer or non-cancer,and identifying the canceration position range of the image, which is judged to be cancer, as the identified image feature difference region Pabnormal. The sensitivity and specificity of the kit to cancer and non-cancer recognition reach about 93.4% and 90.7% respectively, a clinician can be effectively assisted in discriminating and diagnosing cancer and non-cancer, and a canceration position range is given.
Owner:WUHAN ENDOANGEL MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
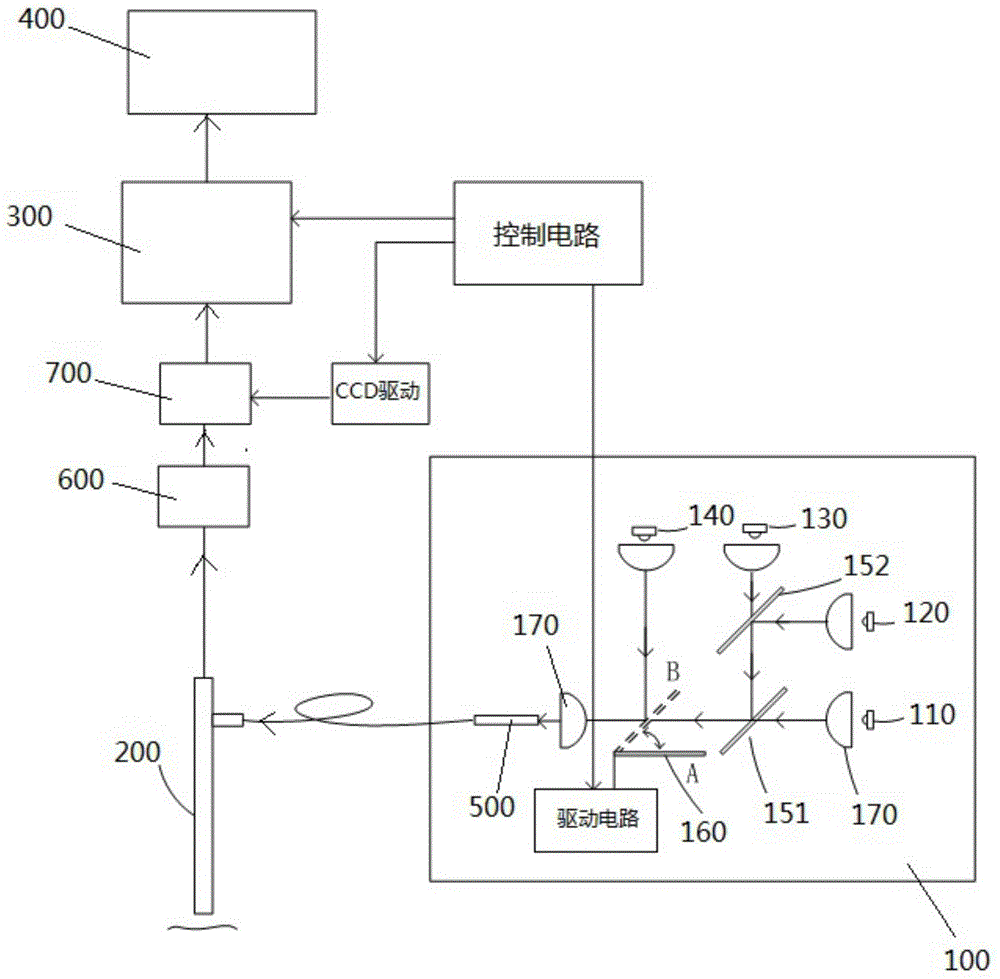
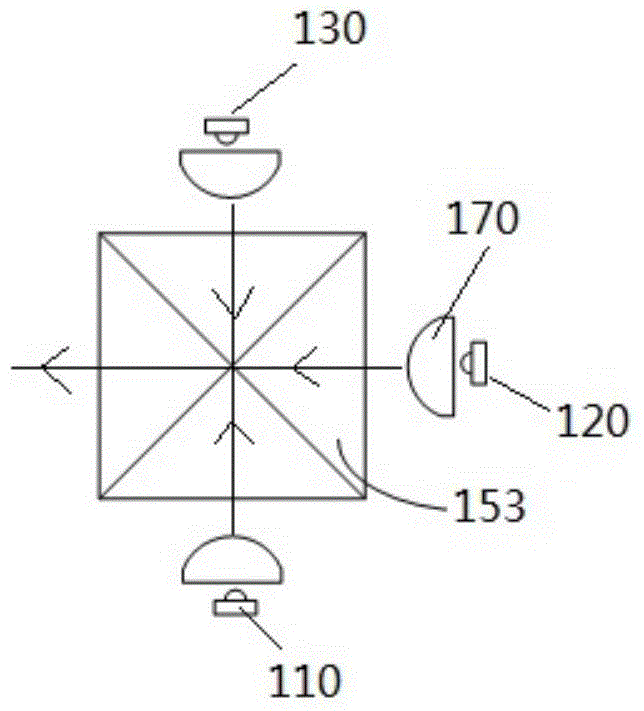
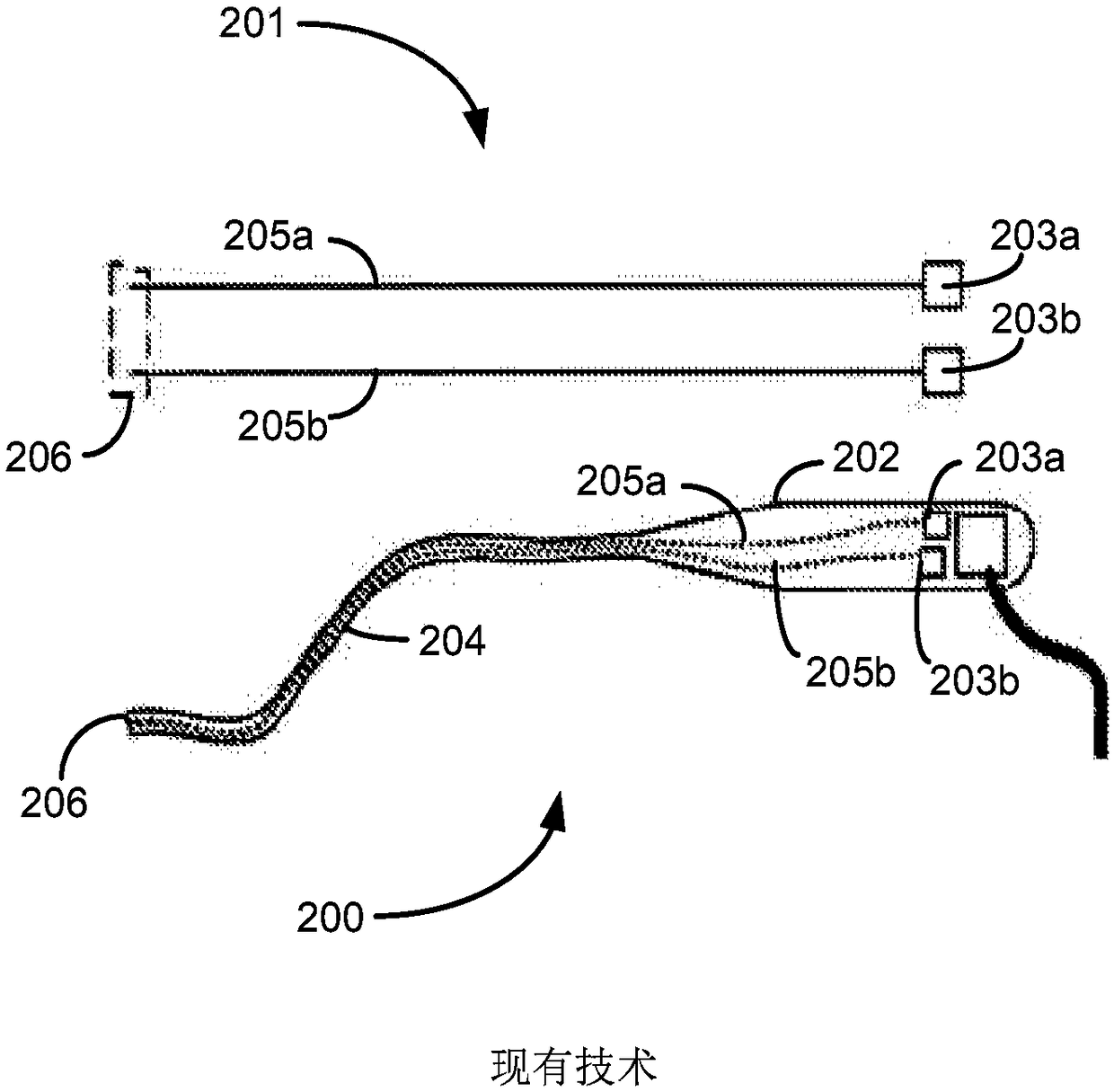
Narrow-band imaging endoscope device
InactiveCN104523214AResolve distortionSimple structureSurgeryEndoscopesNarrow-band imagingFrequency band
The invention discloses a narrow-band imaging endoscope device which comprises a light source structure, an endoscope structure, an image processing module, a synchronous irradiating assembly and a spectrum light splitting assembly. The light source structure irradiates at least one beam of illuminating light provided with regulated wavelength frequency bands on detected tissue. The endoscope structure photographs an image of the detected tissue irradiated by the illuminating light provided with the regulated wavelength frequency bands. The image processing module processes the image photographed by the endoscope structure. The synchronous irradiating assembly irradiates the illuminating light emitted by the light source structure on the surface of the detected tissue synchronously. The spectrum light splitting assembly splits the light reflected back by the detected tissue and then inputs the light into the image processing module. The narrow-band imaging endoscope device effectively solves the problem that due to motion of the detected tissue, a narrow-band image is distorted, the structure of the endoscope device is simplified, the reliability of the endoscope device is improved, and consumed energy is reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPTO MEDIC TECH CO LTD
Compact narrow band imaging system
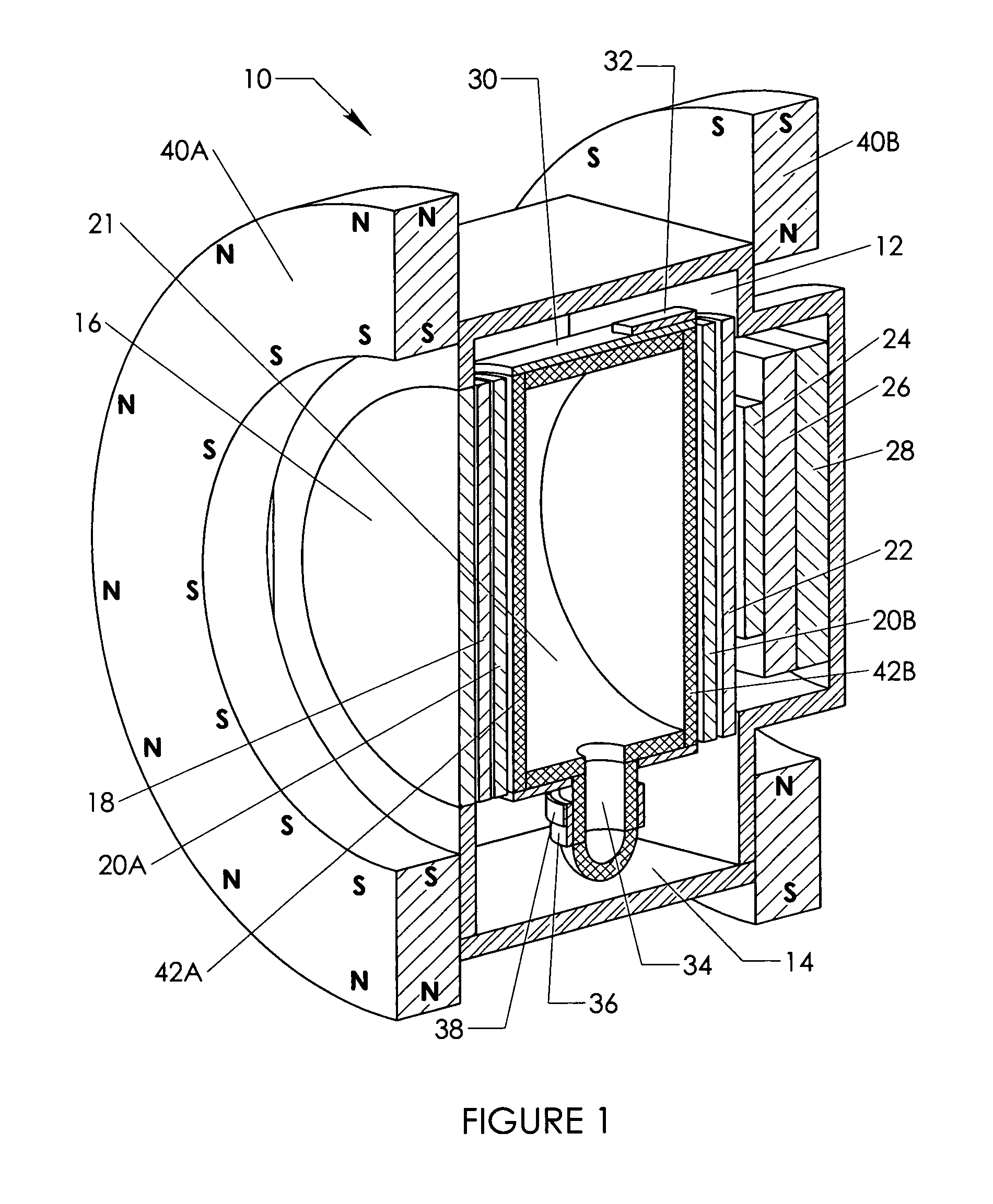
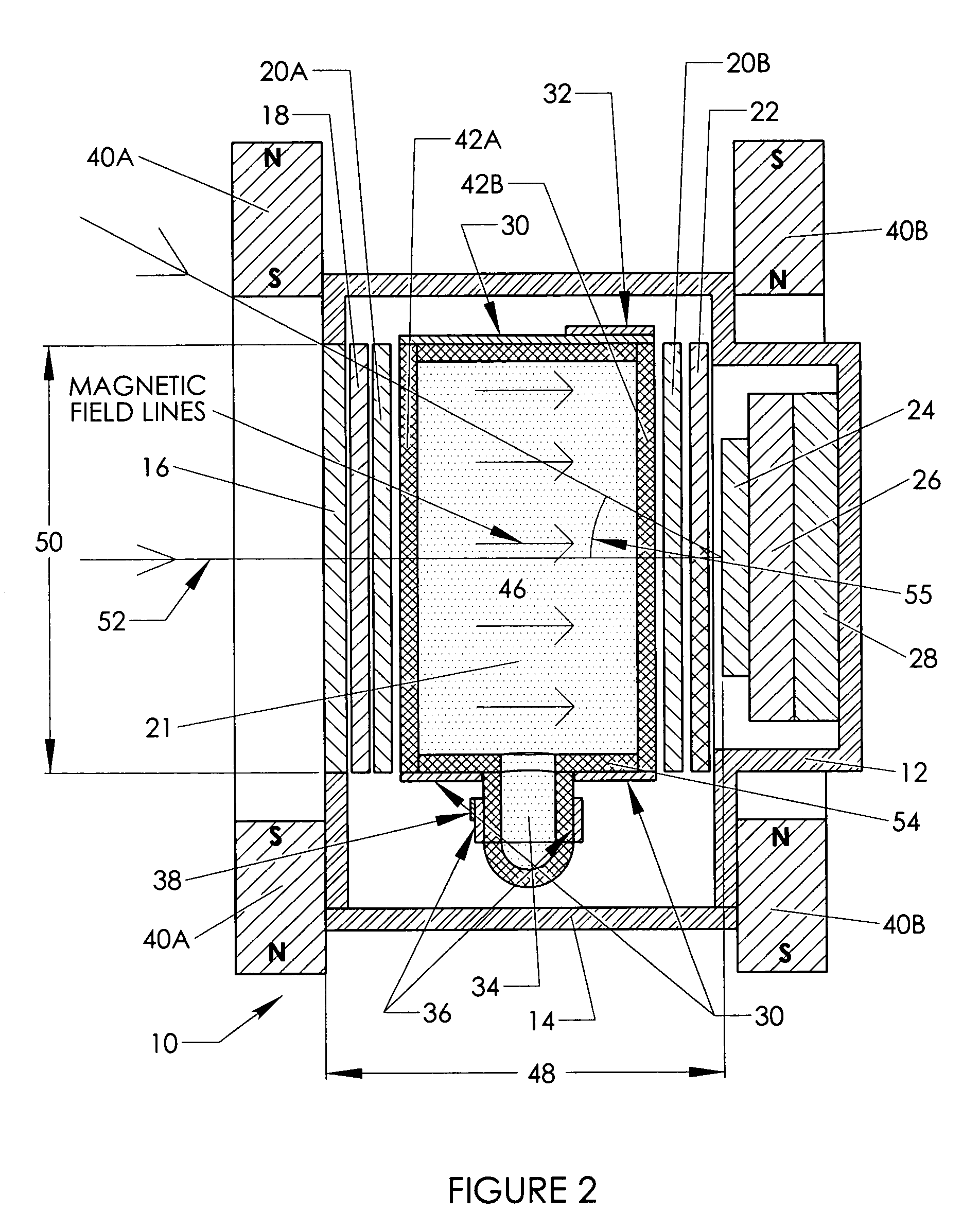
InactiveUS8314612B1Polarising elementsMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesThermal isolationPolarizer
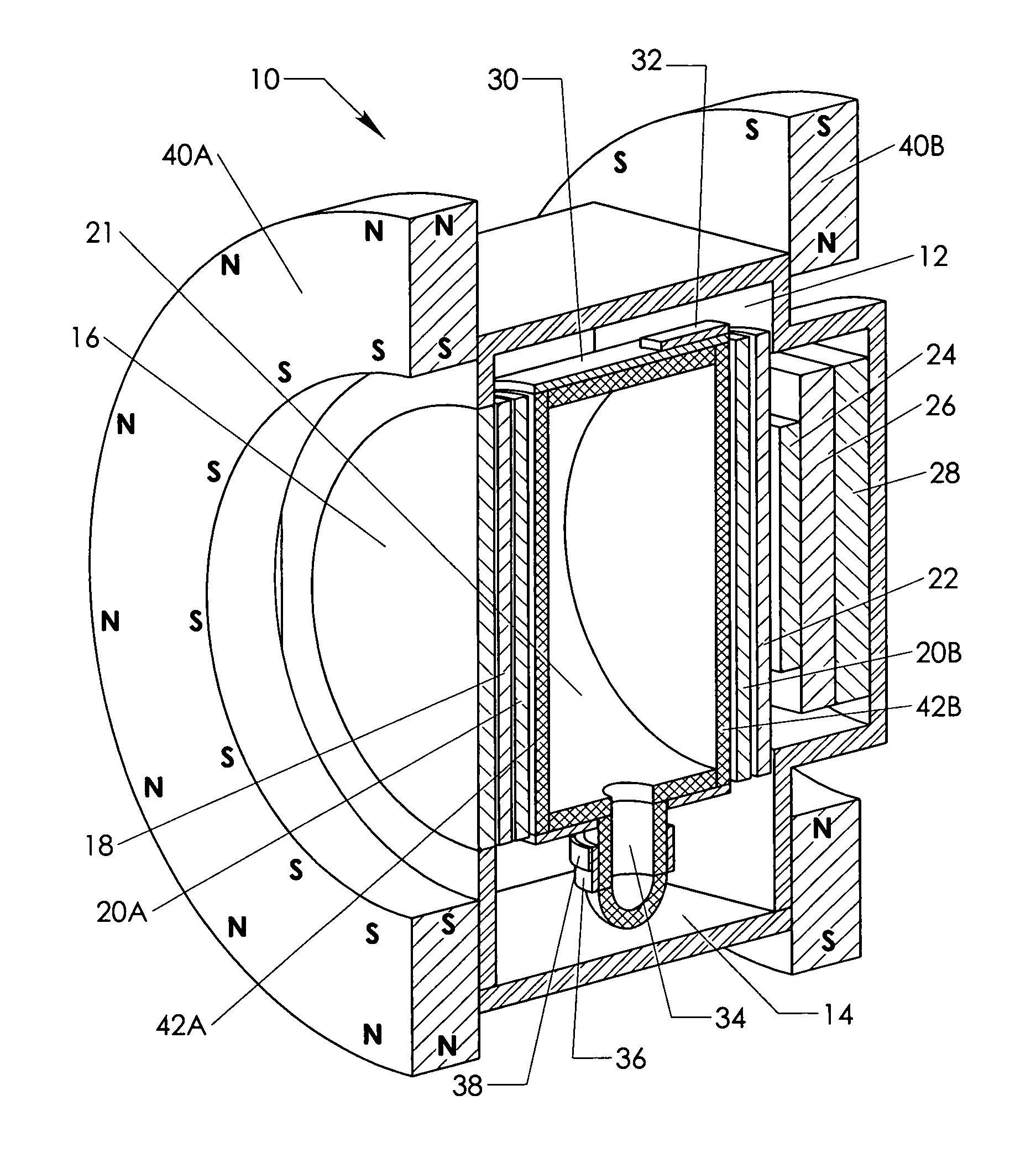
A compact narrow band imaging system includes a vapor cell having a gas that receives and transmits light in accordance with the Faraday effect. A magnetic source is provided for applying a magnetic field to the vapor cell. Crossed polarizers are disposed before and after the vapor cell creating a Faraday optical filter. The only light that passes through the filter is light within a narrow band near the absorption peaks of the vapor. Other optical elements of the imaging system including filters, image detectors, electron multipliers, signal digitizers, and heat filters are co-located within the imaging system's common thermal isolation container to provide improved performance. The compact system is suitable for wide area surveillance, including daylight surveillance for combustion sources such as forest fires and missile exhaust.
Owner:RODGERS WAYNE EUGENE +1
Cancer lesion detection and diagnosis system for early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma of narrow-band endoscopic image
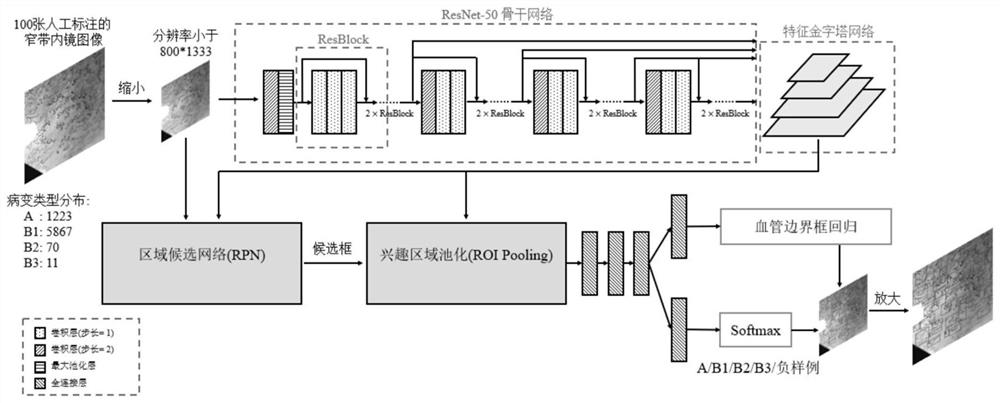
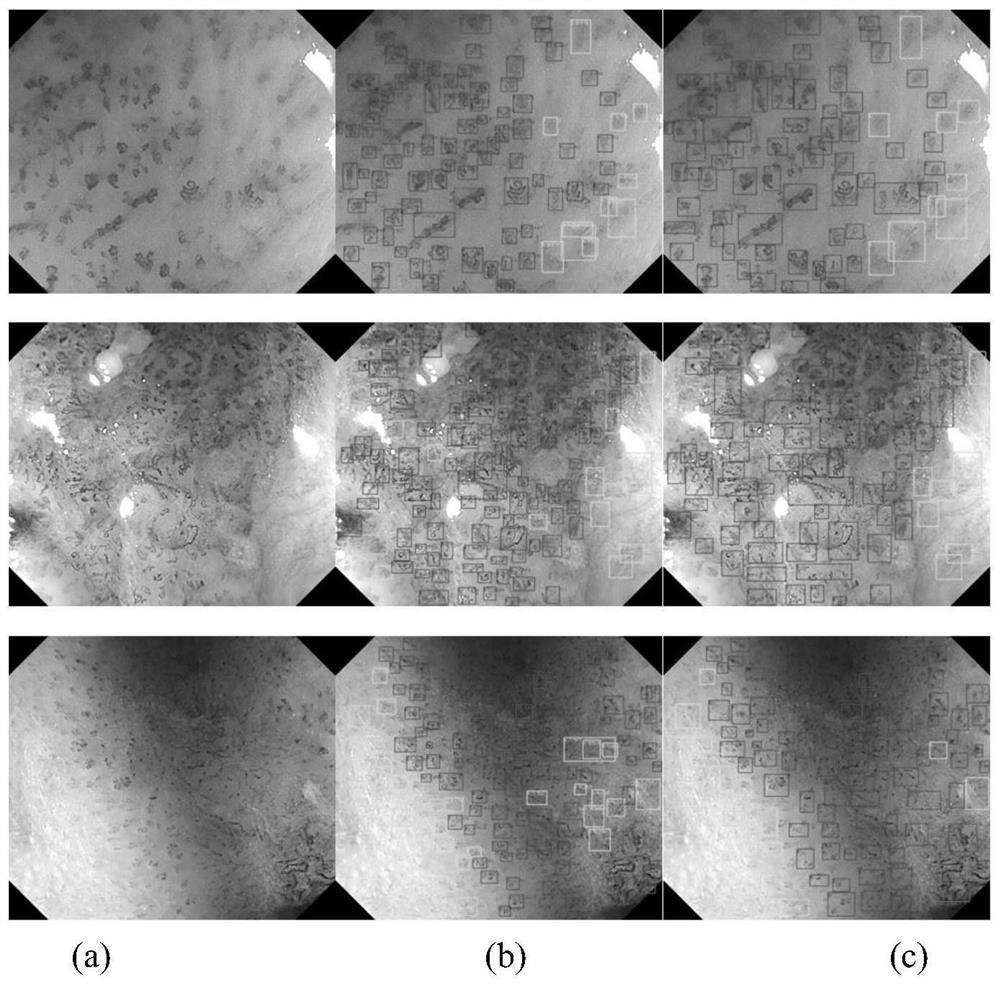
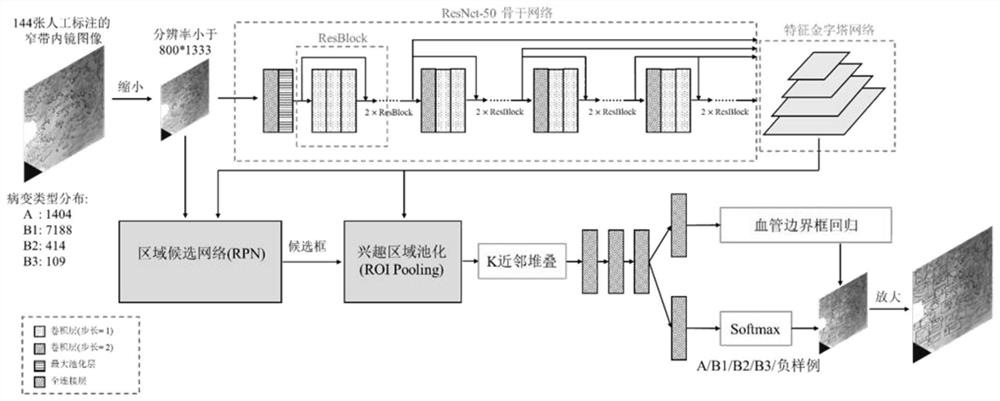
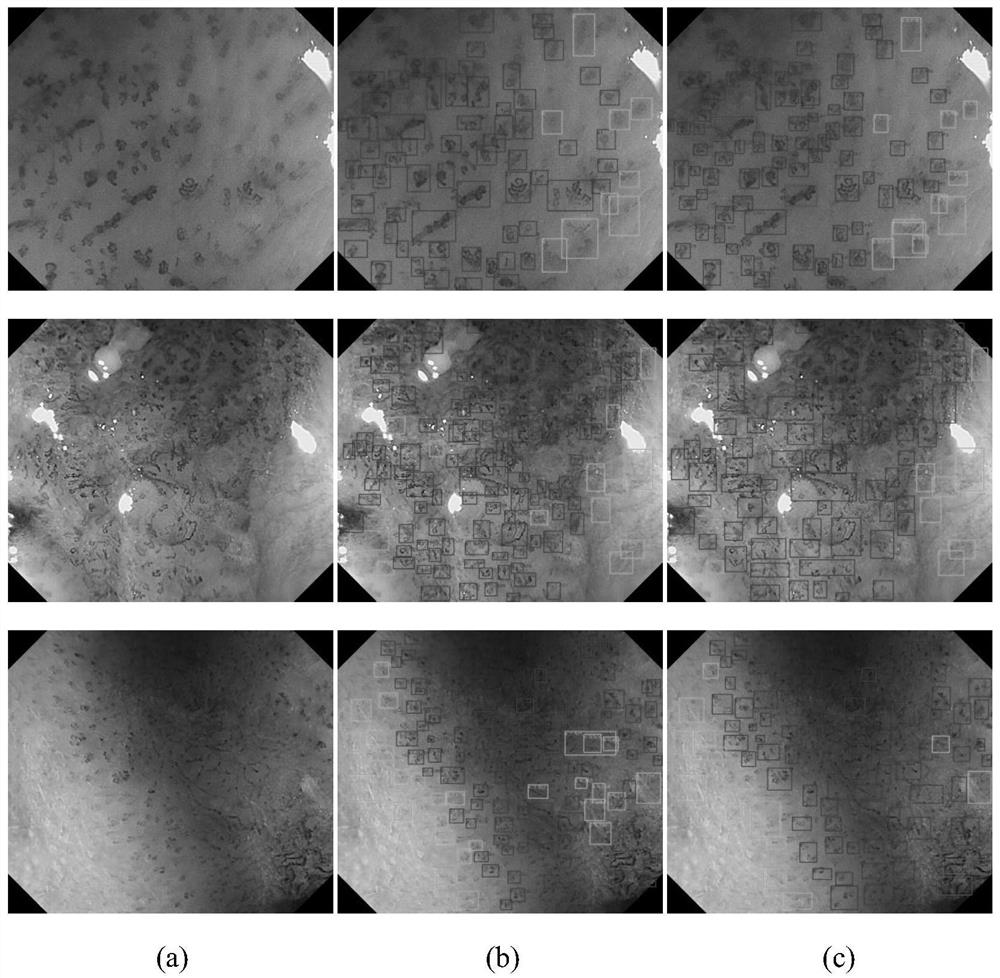
ActiveCN112102256AAccurate detectionAccurate diagnosisImage enhancementImage analysisDiagnostic systemEndoscopic image
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical image processing, and particularly relates to a cancer lesion detection and diagnosis system for early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma of a narrow-band endoscopic image. The system comprises a feature extraction backbone network, a feature pyramid, a region candidate network, a region of interest pooling unit and a cancer focus classification network, and a system for visualization on a narrow-band imaging endoscope image. The backbone network is used for extracting a feature map of an input image; the feature pyramid is used for fusing features of different scales; the region candidate network proposes a possible lesion region; the region of interest pooling unit pools the features to a suspected lesion area; the cancer lesion classification network classifies the cancer lesions; and finally, a narrow-band imaging endoscopic image is visualised, and frame selection marking is carried out on the cancer lesions by using different colors. The image of the narrow-band imaging endoscope is input into the network model, the cancer focus of the early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma existing in the image is detected and diagnosed, the diagnosis efficiency can be effectively improved, and a doctor is assisted in obtaining higher diagnosis precision.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
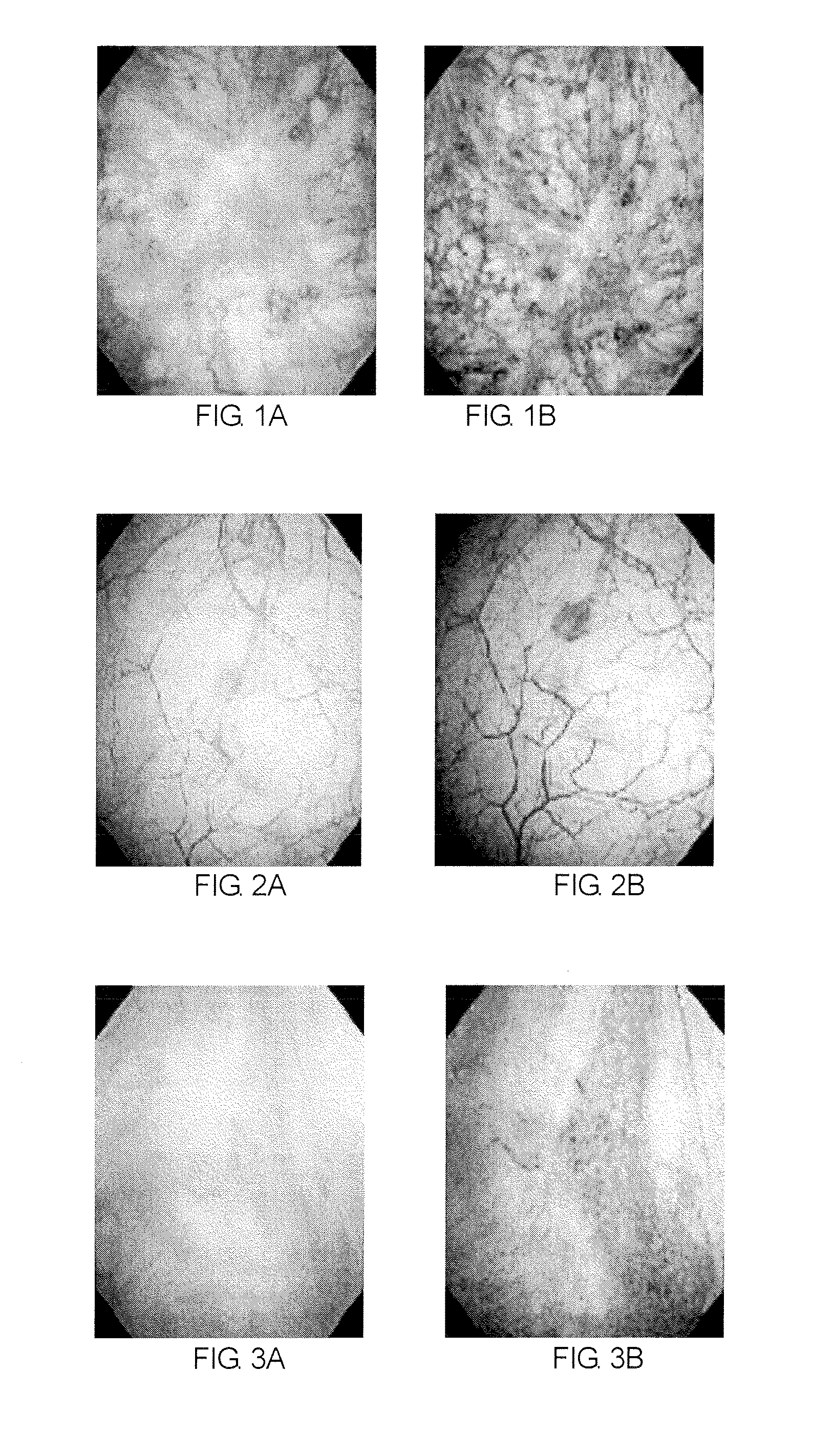
Method of diagnosing a lower urinary tract disorder
A method for sensitively diagnosing lower urinary tract disorders, particularly interstitial cystitis, is provided. The method can visually, simply, and clearly diagnose bladder ulcer without requirement of bladder hydrodistention under anesthesia. In the method, lower urinary tract disorders are diagnosed by observing an abnormality of a blood vessel and / or a newly formed blood vessel in a surface of bladder mucous membrane among abnormalities in blood vessels and / or newly formed blood vessels by visually comparing an image of the surface of the bladder mucous membrane and an image of a deep portion of the bladder mucous membrane obtained using a bladder endoscope system having a narrow band imaging device.
Owner:N M A
Optical system for infrared medium and long wave spectrum imaging
InactiveCN102980657ALarge apertureSimple structureRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationCamera lensParallel plate
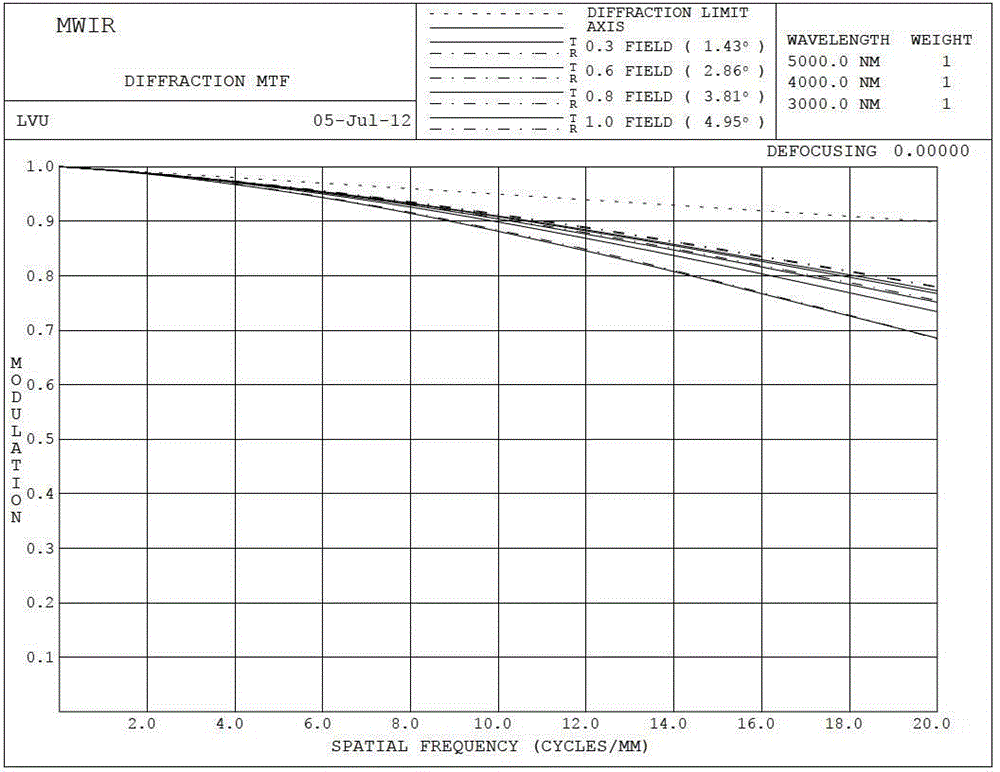
The invention discloses an optical system for infrared medium and long wave spectrum imaging. The optical system comprises a board band lens assembly and a multi-spectral filter assembly. The board band lens assembly is arranged in front of the multi-spectral filter assembly and used for optical wave focus imaging. The multi-spectral filter assembly is used for conducting filtering and cofocal plane compensation on optical wave used for focusing the broad band lens assembly. The optical system for imaging is large in hole diameter which can reach 0.9-1.1, and imaging quality approaches diffraction limit. The optical system adopts the broad band lens assembly and the multi-spectral filter assembly to achieve the multi-spectral imaging system. The system is simple in structure and easy to achieve. Cofocal plane compensation in narrow band imaging is well achieved by thickness change of a band-pass parallel plate filter, and complexity of broad band lens design is reduced. The optical system is used for non-refrigeration broadband infrared multi-spectral imaging and has wide application prospect in the fields of military industry and civil use.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Multifunctional medical LED (Light Emitting Diode) lighting system
A multifunctional medical LED lighting system provided by the invention comprises four groups of LED modules which are exactly the same in sizes and provided with an R chip, a G chip, a B chip and a UW chip respectively; optical collimators with identical in structures are mounted at the front parts of the light-emitting surfaces of the LED chips respectively to collimate emergent light of the LEDs; three ways of emergent light of three LEDs of R / G / B are mixed into a one-way emergent light via an X-ray plate; two ways of emergent light of two LEDs of R / UW are mixed into a one-way emergent light via a dichroic mirror; the dichroic mirror is controlled by a motor to rotate for 45 degrees; when white light is chosen for lighting, the LEDs of G / B do not emit light, the LEDs of R / UW emit light, and at the moment, a UW (cold white) light and an R (red) light are mixed to generate a white light source via the dichroic mirror; when a RGB narrow-band light source is chosen, the UW LED does not emit light, and at the moment, the LEDs of R / G / B emit light at different time; when the UW LED goes wrong, the LEDs of R / G / B emit light at the same time and can be used as the spare white light source; and a condensing lens is mounted at the front of the dichroic mirror, so that the emergent light of the light source is enabled to be coupled in light fiber optic arrays conveniently. The multifunctional medical LED lighting system is compact in structure, low in cost, high in reliability, high color rendering white light and narrow-band images.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Light source device
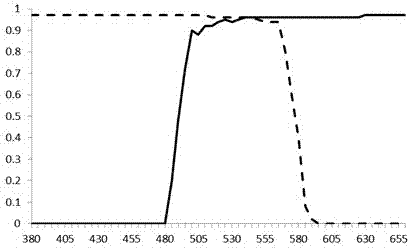
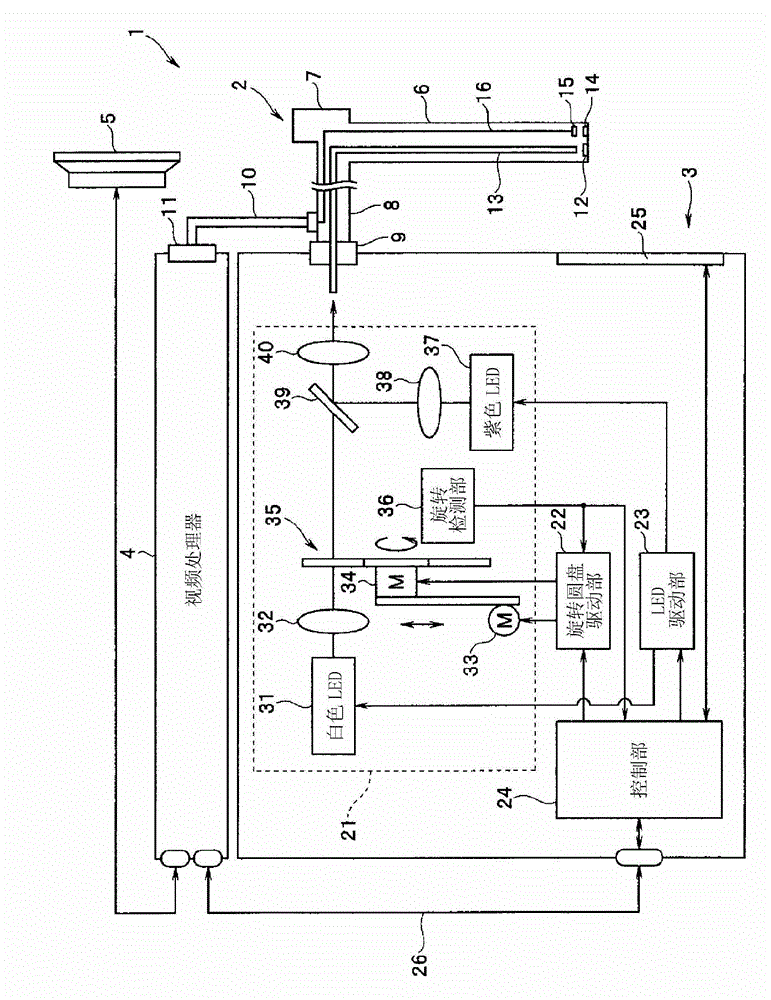
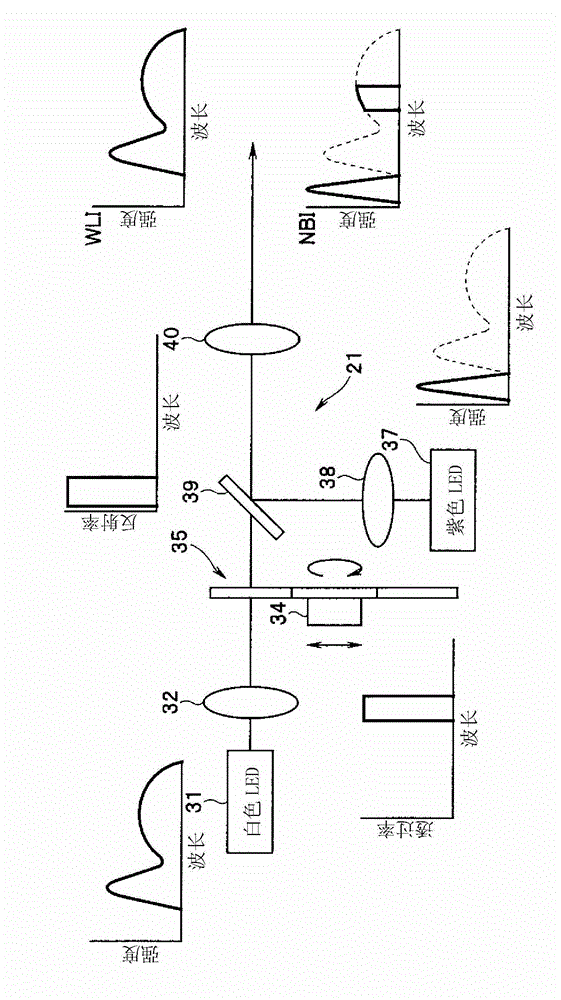
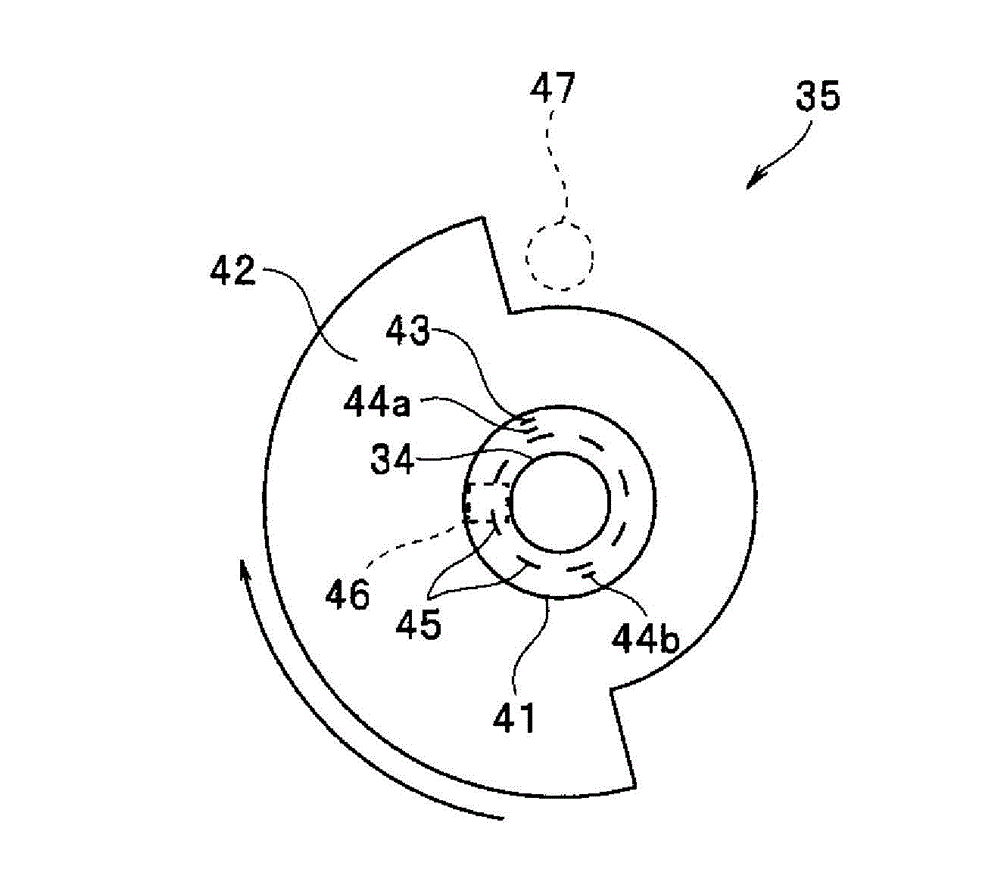
A light source device (3) has a white LED (31) that emits light comprising a first wavelength band and a second wavelength band, a violet LED (37) that emits light of a third wavelength band, and a rotating disc (35) that has a filter (42) which passes light of the first wavelength band when inserted in the light path of the white LED (31). The light source device (3) also has a rotating disc-driver (22) that changes the position of the rotating disc (35), so that the filter (42) is withdrawn from the light path of the light emitted from the white LED (31) when the white-light imaging mode is selected; the filter (42) is inserted continuously in the light path of the light emitted from the white LED (31) when the narrow-band imaging mode is selected; and the filter (42) is inserted intermittently in the light path of the light emitted from the white LED (31) when the twin mode are selected.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Observation device
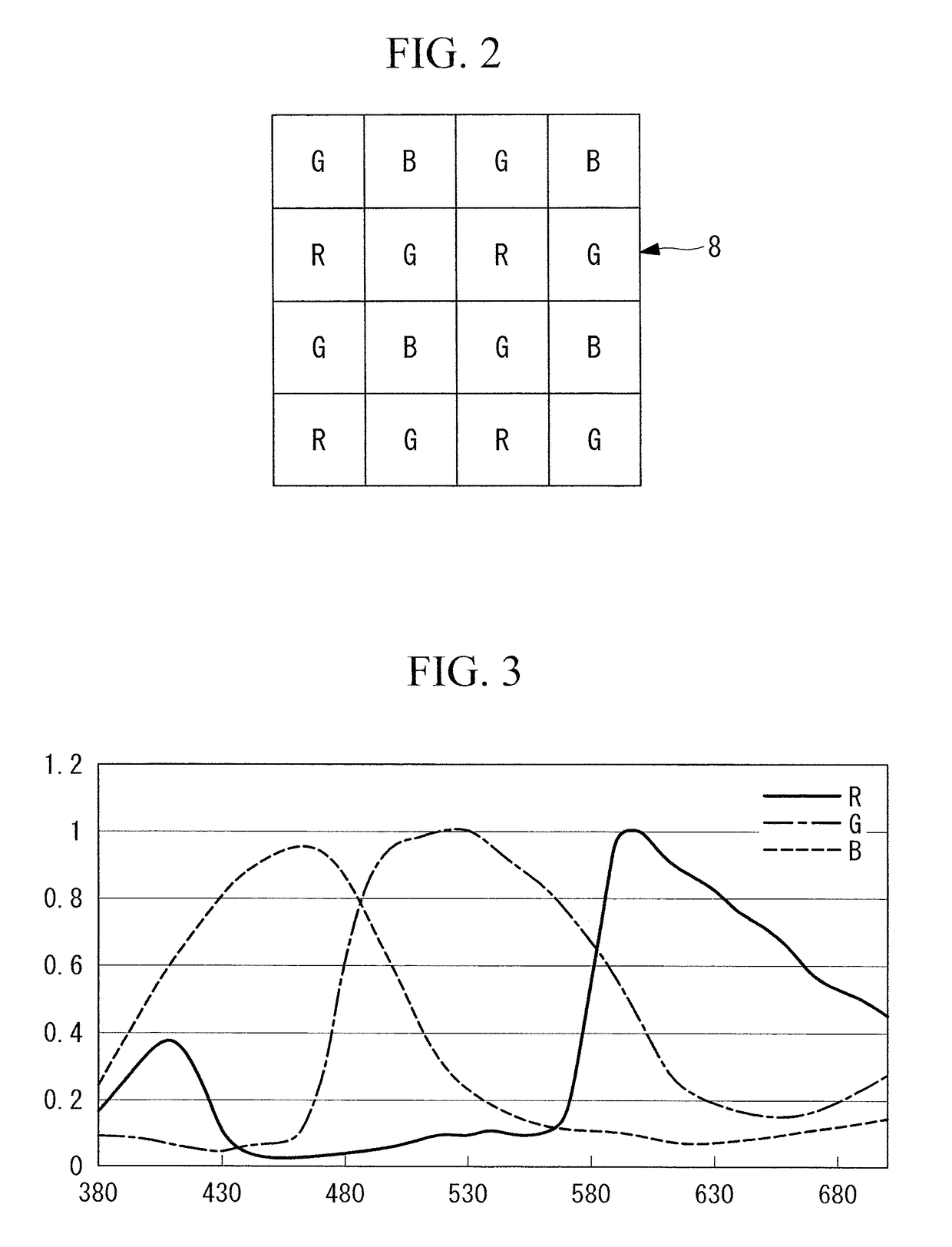
ActiveUS20170231502A1Easy to detectHigh color reproductionTelevision system detailsMechanical apparatusLength waveNarrow-band imaging
An observation device includes a light source unit capable of adjusting a quantity of 390-490 nm illuminating light according to a B1 range and a B2 range having a longer wavelength than the B1 range, and an imaging element that images reflected light from a subject irradiated with illuminating light. The light source unit changes the light quantity ratio of the B1 range to the B2 range depending on whether white light imaging is conducted or narrow band imaging is conducted. The imaging element includes RGB color filters arranged according to pixels and the R color filter transmits more light in an R range and the B1 range than light in the second B range and has a spectral characteristic that satisfies a predetermined conditional formulae.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
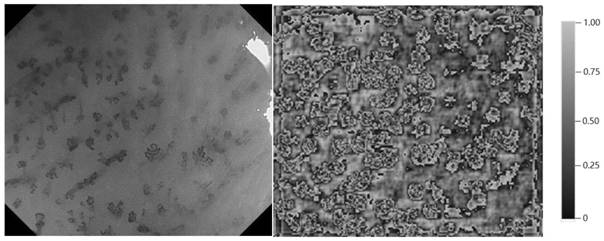
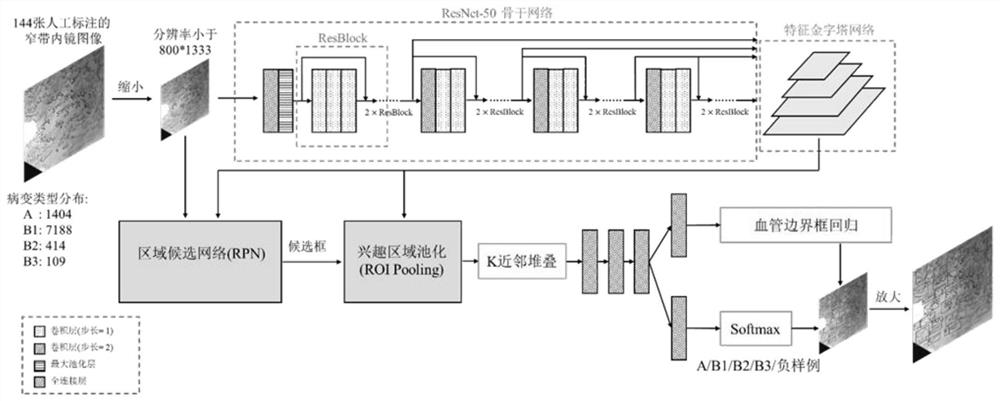
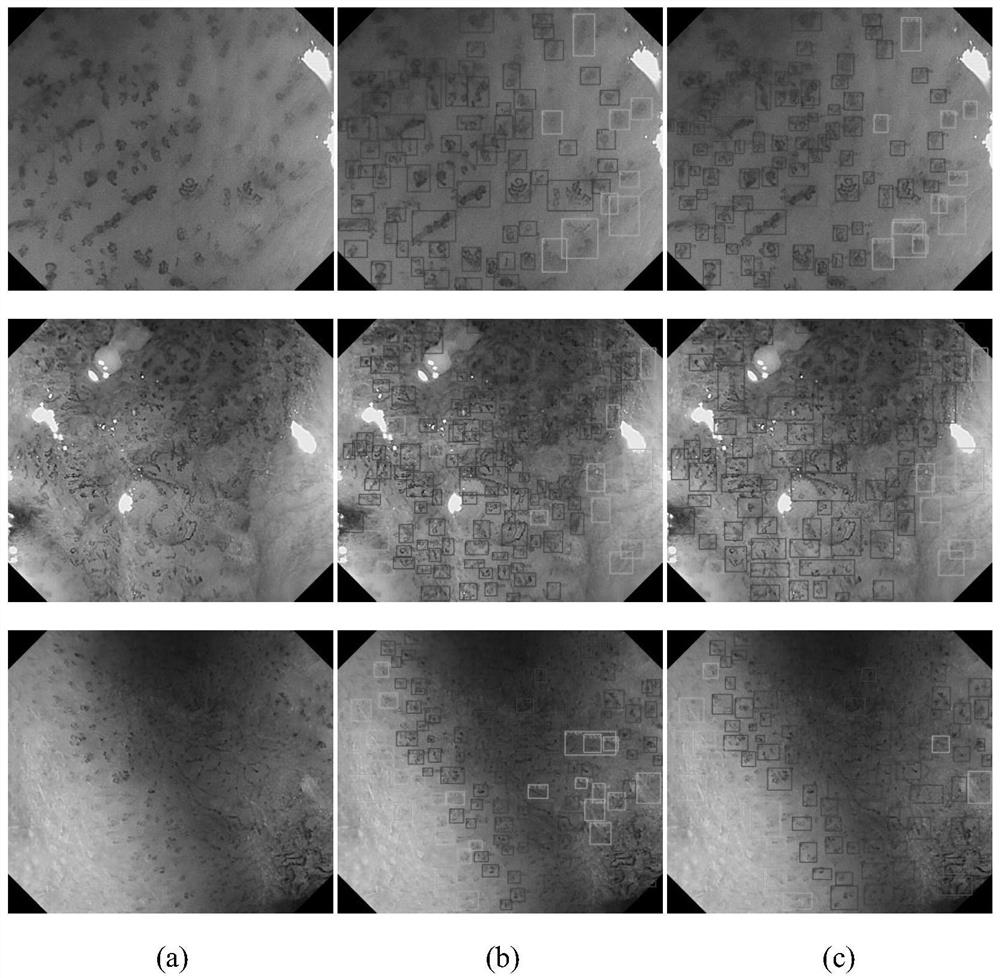
Deep detection network for quantifying esophageal mucosa IPCLs vascular morphological distribution
ActiveCN112419246AEasy to detectImplement diagnosticsImage enhancementImage analysisBlood vesselEndoscopic image
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical image processing, and particularly relates to a deep detection network for quantifying esophageal mucosa IPCLs vascular morphological distribution. The deep detection network comprises a feature extraction network, a feature pyramid, a region candidate network, an interest region pooling and clustering distribution priori self-embedded cancerlesion classification network and a system for visualization on a narrow-band imaging endoscope image. The feature extraction network extracts a feature map of the input image; the feature pyramid fuses the features of different scales; the region candidate network proposes a possible lesion region; the region of interest is pooled, and the features are pooled to a suspicious lesion region; the cancer lesions are classified by a clustering distribution priori self-embedded cancer lesion classification network; and finally, visualizing is carried out on a narrow-band imaging endoscopic image,and frame selection marking is carried out on the cancer lesion by using different colors. The cancer focus of the early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma existing in the image is detected and diagnosed, the diagnosis efficiency can be effectively improved, and a doctor is assisted in obtaining higher diagnosis precision.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
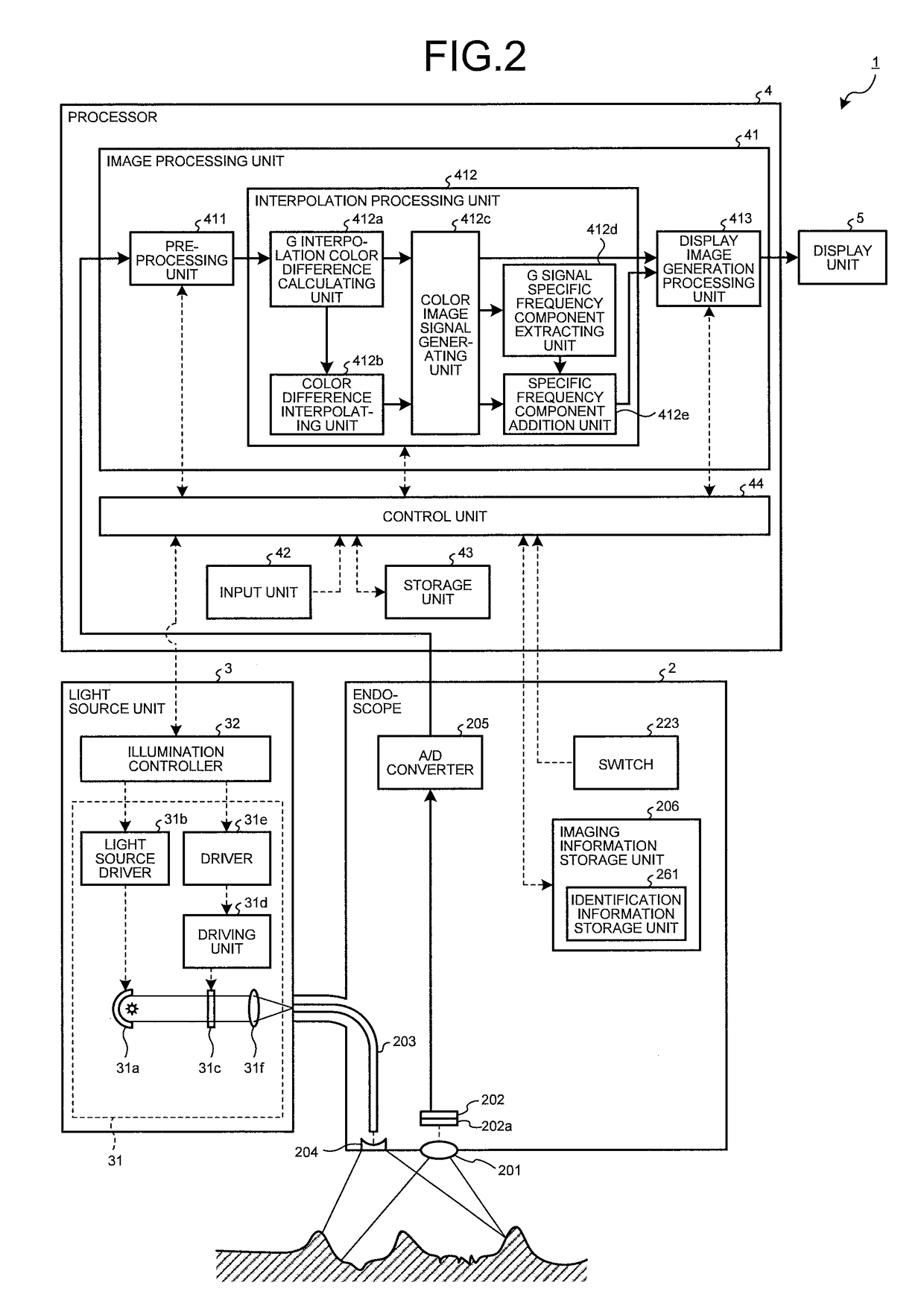
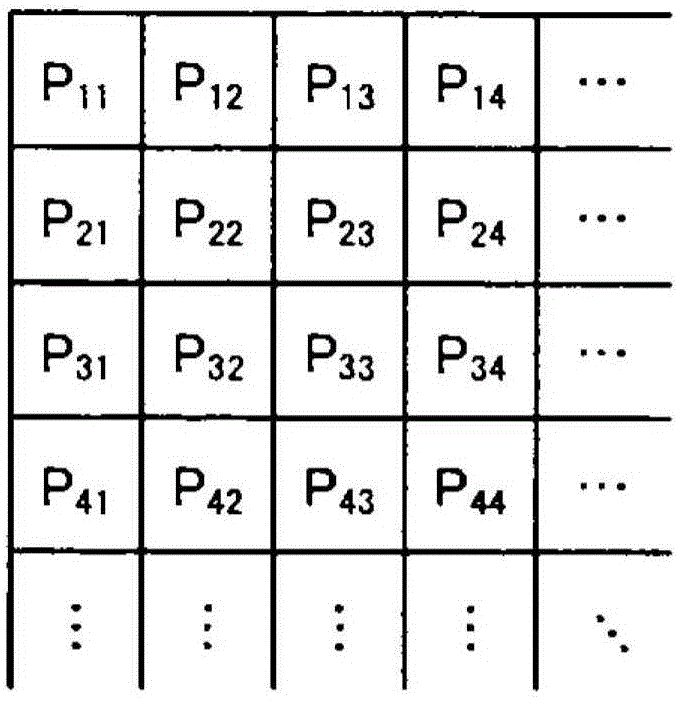
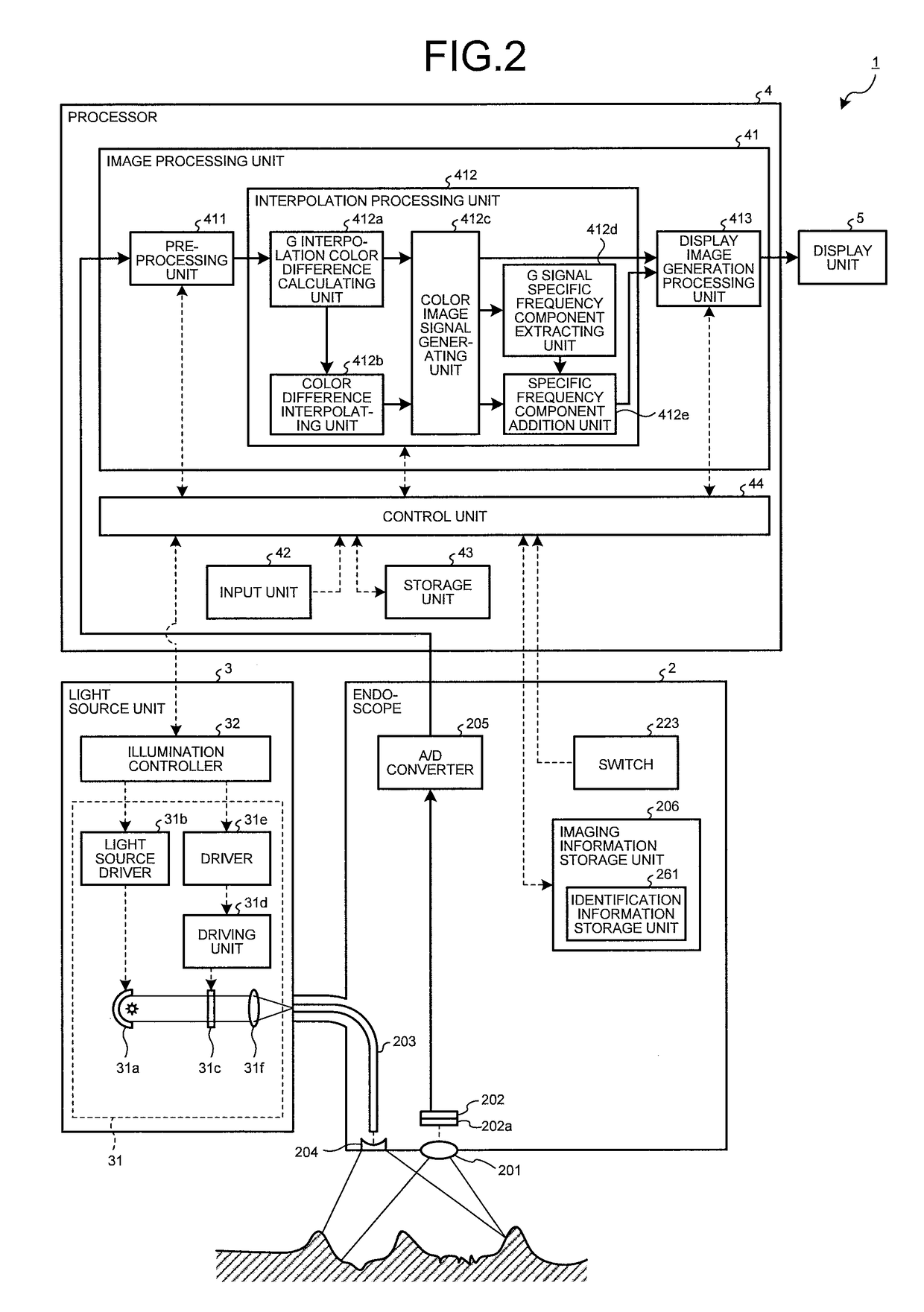
Image processing apparatus, method for operating image processing apparatus, computer-readable recording medium, and endoscope device
ActiveUS20170296034A1Accurate detectionImprove the display effectImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingNarrow-band imaging
An image processing apparatus interpolates a signal of a missing color component based on first, second, and third color signals respectively generated by first, second, and third pixels of an image sensor, to generate color signals. These pixels are arranged in a matrix. The first pixels generate the first color signal of a first luminance component of white light. The second pixels generate the second color signal of a second luminance component of narrow band light. Density of the first pixels being higher than density of the second pixels and density of the third pixels. The apparatus extracts a specific frequency component signal from a color signal of the first luminance component among the color signals generated by interpolation, and adds the specific frequency component signal to a color signal of a color component different from the first luminance component depending on white light imaging or narrow band imaging.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Enhanced display narrow band imaging endoscopy system and imaging method thereof
ActiveCN107625513AEnhance location information imageImprove convenienceImage enhancementImage analysisFlexible endoscopeImaging processing
The invention provides an enhanced display narrow band imaging endoscopy system. The system comprises an image collection device, an image processing device and an image display device. The image collection device comprises multiple cameras, and the image processing device comprises an image collection module and a narrow band image processing module. According to the enhanced display narrow bandimaging endoscopy system, the cameras are used for collecting narrow band images and white light images, the white light images pass through the image collection module and then are directly output tothe image display device to be displayed in a normal mode, and the narrow band images are processed by the narrow band processing module and displayed in a narrow band mode through the image displaydevice. The narrow band mode display can improve the image quality of narrow band imaging and enhance the blood vessel image information. The invention further provides an imaging method of the enhanced display narrow band imaging endoscopy system.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
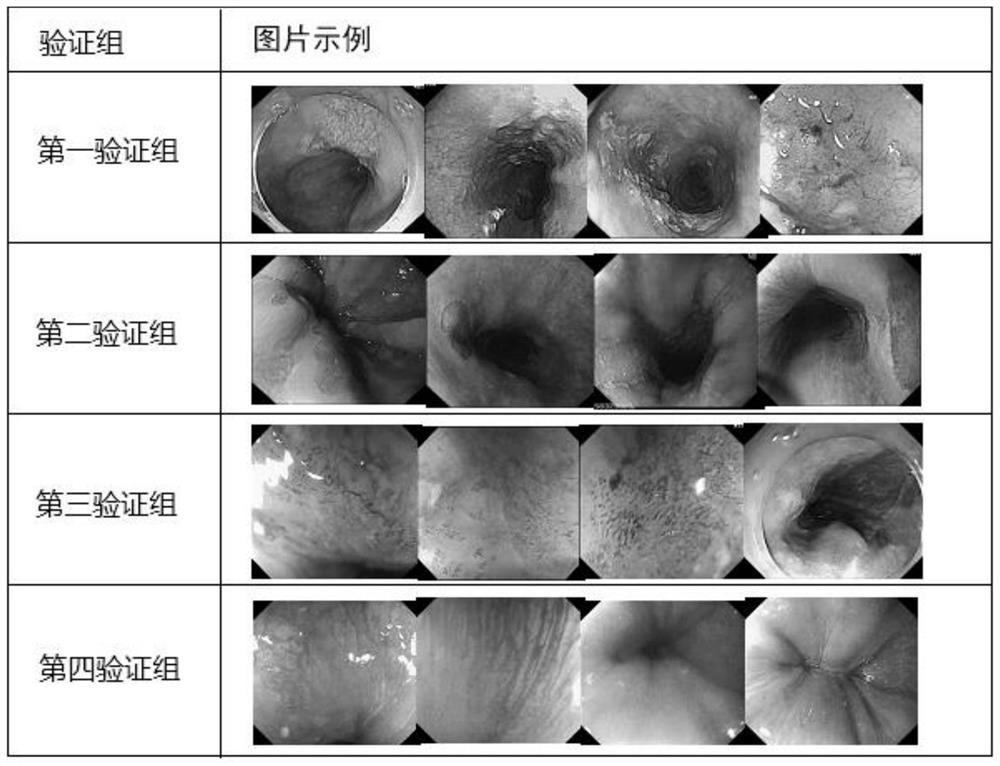
Picture screening method and system for esophageal cancer model training and storage medium
PendingCN112950601AImprove generalization abilityImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionNarrow-band imagingNarrow band
The invention discloses a picture screening method and system for esophageal cancer model training, and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: inputting a to-be-screened static picture; clustering the static pictures by adopting a clustering algorithm according to the characteristics of the static pictures to obtain a plurality of types of static pictures; and screening the static pictures in each cluster by adopting a distance function to obtain static pictures with low similarity as training samples for establishing an esophageal cancer recognition model. According to the method, when the static pictures are input, a larger sample size can be allowed to be adopted to solve the problem of poor model generalization ability, meanwhile, the static pictures with large samples are clustered through a clustering algorithm, then the static pictures with low similarity in each cluster are screened through a distance function, and the static pictures with high similarity are obtained. And finally, on the premise that the sample coverage rate is not obviously influenced, the transformation from a large sample to a small sample is realized, and an esophageal squamous carcinoma lesion picture suitable for training and identifying narrow-band imaging is obtained.
Owner:成都微识医疗设备有限公司
Methods and apparatus for image processing in wireless capsule endoscopy
ActiveUS20130271585A1Television system detailsColor television detailsImaging processingWireless capsule endoscope
Methods and apparatus for image processing suitable for use in wireless capsule endoscopy are provided. The image processing techniques exploit characteristic features of endoscopic images to enable low complexity compression. A color space conversion, coupled with lossless predictive coding and variable length coding are employed. Sub-sampling and clipping may also be used. The described image processing can be used both with both white-band imaging and narrow-band-imaging.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN
Optical system for infrared medium and long wave spectrum imaging
InactiveCN102980657BLarge apertureSimple structureRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationParallel plateBroadband
The invention discloses an optical system for infrared medium and long wave spectrum imaging. The optical system comprises a board band lens assembly and a multi-spectral filter assembly. The board band lens assembly is arranged in front of the multi-spectral filter assembly and used for optical wave focus imaging. The multi-spectral filter assembly is used for conducting filtering and cofocal plane compensation on optical wave used for focusing the broad band lens assembly. The optical system for imaging is large in hole diameter which can reach 0.9-1.1, and imaging quality approaches diffraction limit. The optical system adopts the broad band lens assembly and the multi-spectral filter assembly to achieve the multi-spectral imaging system. The system is simple in structure and easy to achieve. Cofocal plane compensation in narrow band imaging is well achieved by thickness change of a band-pass parallel plate filter, and complexity of broad band lens design is reduced. The optical system is used for non-refrigeration broadband infrared multi-spectral imaging and has wide application prospect in the fields of military industry and civil use.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Endoscopic device
ActiveCN105828692AReduce noise componentsColor televisionGeometric image transformationNarrow-band imagingNoise reduction
Provided are an endoscopic device which is capable of carrying out appropriate NR processes in both a white light imaging method and a narrow band imaging method, and a noise reduction processing method. An endoscopic device (1) comprises a noise reduction unit which selects a pixel of interest on the basis of information on filter to be used determined in accordance with light emitted from a light source unit (3) and properties of each filter that constitutes a color filter (202a), and by detecting the movement in images imaged at different times using an electrical signal outputted by the pixel of interest, reduces noise components included in the image signal.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
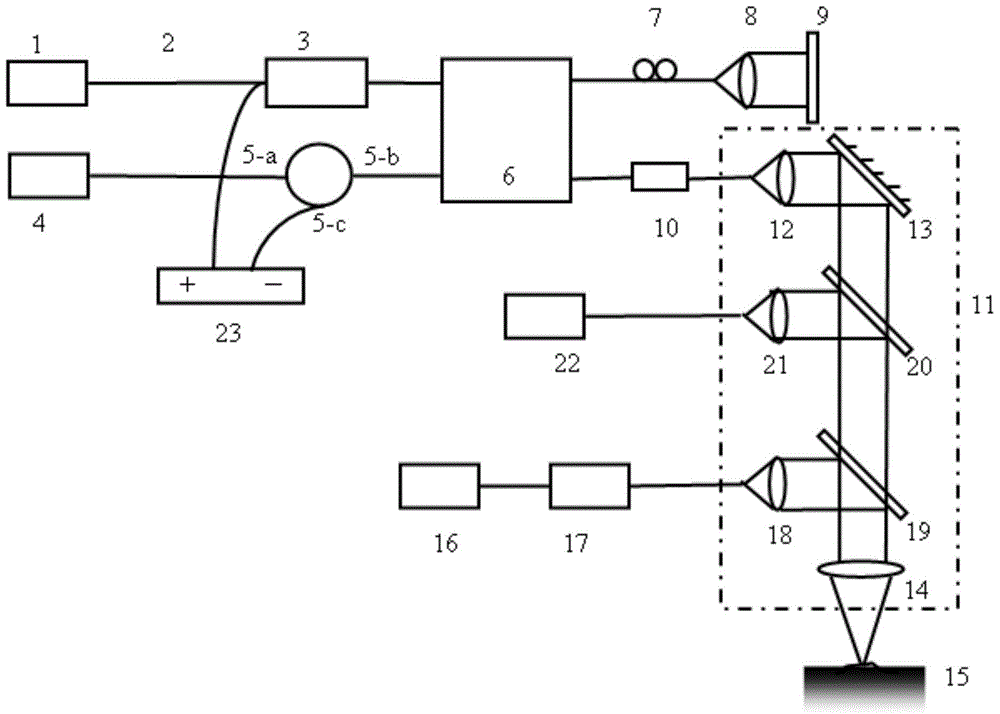
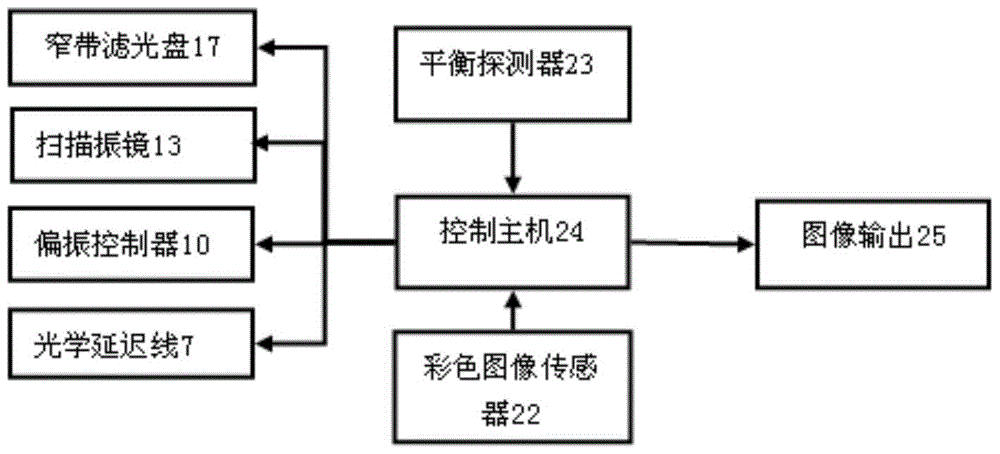
A composite narrow-band imaging endoscopic imaging system
The invention discloses a composite narrowband imaging endoscope imaging system, which comprises a narrowband imaging module used for micro imaging, wherein the narrowband imaging module consists of a white light source, a narrowband filtering disc, a third collimating lens, a wideband beam splitting flat plate, a dichroscope, a fourth collimating lens and a color image sensing device, the composite narrowband imaging endoscope imaging system is also provided with an optical coherence tomography module used for microscopic imaging, the optical coherence tomography module and the narrowband imaging module share the same optical path system, a control host respectively controls a color image sensing device of the narrowband imaging module and a balance detector of the optical coherence tomography module for carrying out data collection, through the processing on the collected data, two groups of mutually verified diagnosis images are output, and through combining the optical coherence tomography imaging and narrowband imaging, the microcosmic imaging and micro imaging functions are combined, so that the composite narrowband imaging endoscope imaging system belongs to a medical diagnosis tool with high sensitivity and specificity.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPTO MEDIC TECH CO LTD
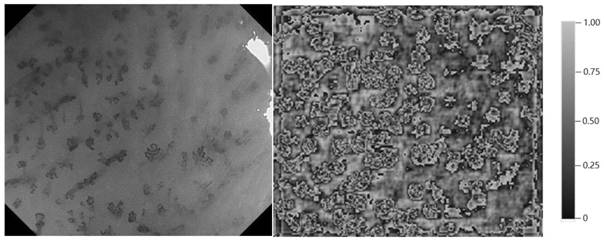
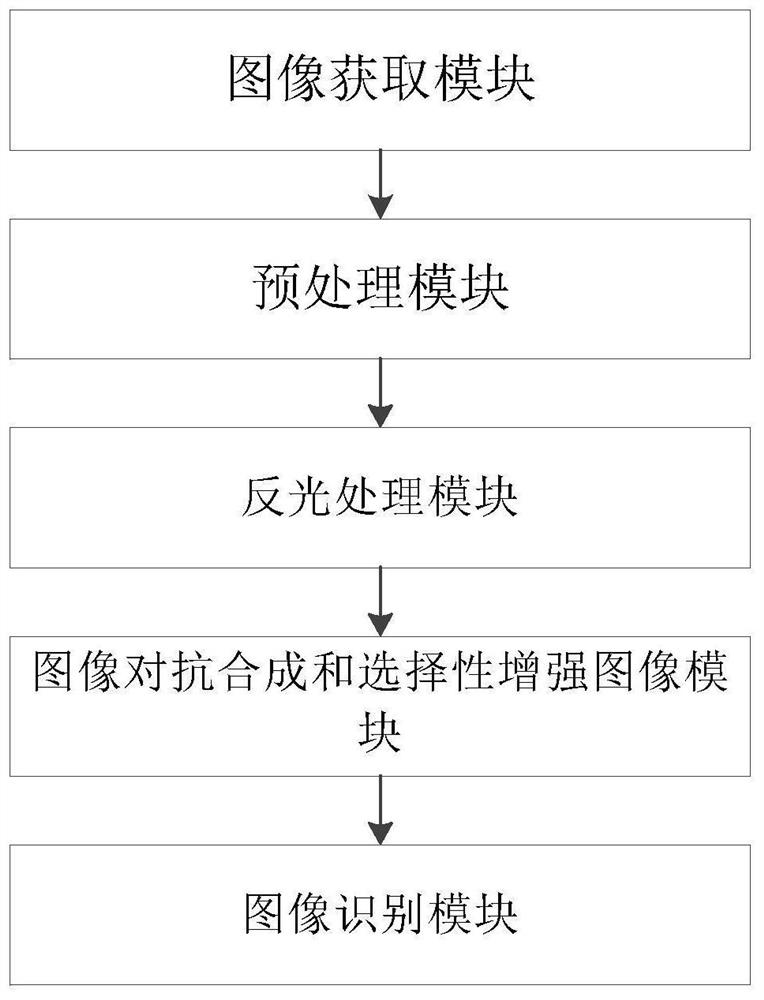
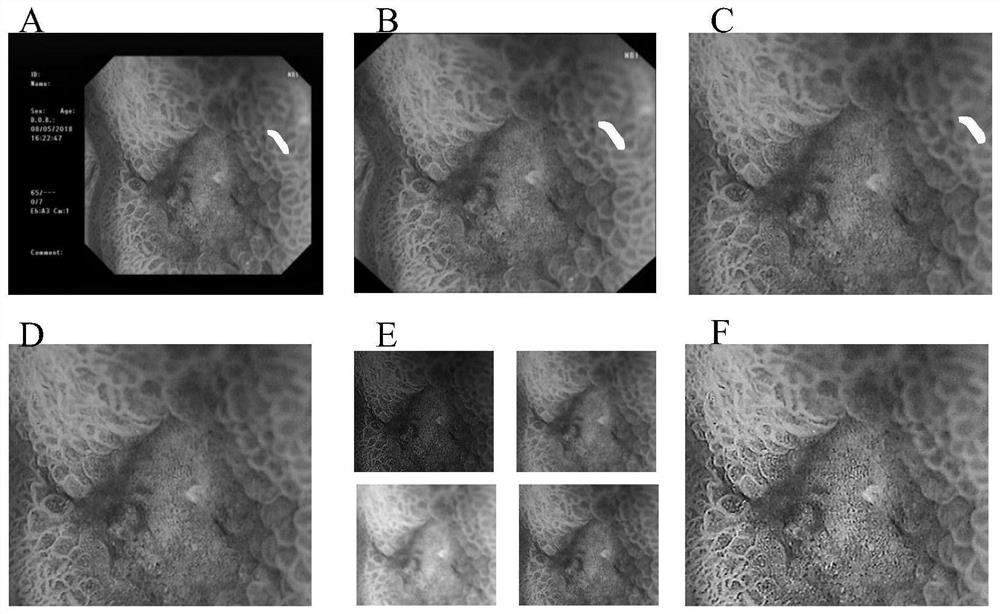
Gastroscope image analysis system and method based on repair and selective enhancement, and equipment
ActiveCN113256572AImprove accuracyHigh selectivityImage enhancementImage analysisImaging analysisRadiology
The invention belongs to the field of image recognition, particularly relates to a gastroscope image analysis system and method based on restoration and selective enhancement, and equipment, and aims to solve the problem that an existing gastroscope image recognition system cannot accurately recognize an early gastric cancer image. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a narrow-band imaged gastroscope image as a to-be-detected image; performing preprocessing to obtain a to-be-detected image only containing gastric mucosa; obtaining a to-be-detected image without reflection through the reflection processing module; generating a composite image through the trained generative adversarial network, and automatically selecting a more vivid image; and enabling the trained gastroscope image recognition network to obtain the early gastric cancer probability of the image to be detected and obtain a region image of suspected early gastric cancer through a gradient weighted class activation mapping method. According to the method, selective enhancement of data features is carried out through the generative adversarial network, feature information most related to the classification task is automatically learned through the recognition model, and the accuracy of gastroscope image analysis is improved.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Observation device
ActiveUS9820654B2Easy to detectHigh color reproductionTelevision system detailsMechanical apparatusLength waveNarrow-band imaging
An observation device includes a light source unit capable of adjusting a quantity of 390-490 nm illuminating light according to a B1 range and a B2 range having a longer wavelength than the B1 range, and an imaging element that images reflected light from a subject irradiated with illuminating light. The light source unit changes the light quantity ratio of the B1 range to the B2 range depending on whether white light imaging is conducted or narrow band imaging is conducted. The imaging element includes RGB color filters arranged according to pixels and the R color filter transmits more light in an R range and the B1 range than light in the second B range and has a spectral characteristic that satisfies a predetermined conditional formulae.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Illumination Balance in Endoscopes and Solid-State Narrowband Imaging and Assembly Using Fiber Bundle Design
Semiconductor-based light source arrangement for endoscopes for power and / or color distribution of light. A semiconductor-based light source arrangement comprising a plurality of semiconductor light sources and a plurality of fiber bundles, wherein each fiber bundle is separated into a plurality of fiber sub-bundles for directing substantially the same amount of illumination from each semiconductor light source to the arrangement Each of a respective plurality of illumination windows at the distal end of the endoscope. By providing such a semiconductor-based light source in which each semiconductor light source is operated to adjust the brightness and / or color or wavelength of light emitted by each semiconductor light source, it is possible to obtain an and / or desired color temperature and / or color balance for lighting of other substances.
Owner:GYRUS ACMI INC (D B A OLYMPUS SURGICAL TECH AMERICA)
Light source device and endoscope system
A light source apparatus 20 includes a first rotational filter section 23 that can place a blue filter 23a, a green filter 23b and a magenta filter 23c in a light path LP, a second rotational filter section 24 that can place a yellow filter 24a in the light path and a band selection filter section 22 that can place an NBI filter that limits blue and green light to a narrow band, wherein the first and the second rotational filter sections 23, 24 are controllable so that in the case of normal light imaging, the yellow filter 24a is placed in the light path LP when the magenta filter 23c is placed in the light path LP and in the case of narrow band imaging, the NBI filter is placed in the light path LP and the yellow filter 24a is placed in the light path LP when the green filter 23b is placed in the light path LP.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Image processing apparatus, method for operating image processing apparatus, computer-readable recording medium, and endoscope device
ActiveUS10070771B2Accurate detectionImprove the display effectImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging processingNarrow-band imaging
An image processing apparatus interpolates a signal of a missing color component based on first, second, and third color signals respectively generated by first, second, and third pixels of an image sensor, to generate color signals. These pixels are arranged in a matrix. The first pixels generate the first color signal of a first luminance component of white light. The second pixels generate the second color signal of a second luminance component of narrow band light. Density of the first pixels being higher than density of the second pixels and density of the third pixels. The apparatus extracts a specific frequency component signal from a color signal of the first luminance component among the color signals generated by interpolation, and adds the specific frequency component signal to a color signal of a color component different from the first luminance component depending on white light imaging or narrow band imaging.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Method of diagnosing a lower urinary tract disorder
A method for sensitively diagnosing lower urinary tract disorders, particularly interstitial cystitis, is provided. The method can visually, simply, and clearly diagnose bladder ulcer without requirement of bladder hydrodistention under anesthesia. In the method, lower urinary tract disorders are diagnosed by observing an abnormality of a blood vessel and / or a newly formed blood vessel in a surface of bladder mucous membrane among abnormalities in blood vessels and / or newly formed blood vessels by visually comparing an image of the surface of the bladder mucous membrane and an image of a deep portion of the bladder mucous membrane obtained using a bladder endoscope system having a narrow band imaging device.
Owner:N M A
A deep detection network to quantify the vascular morphological distribution of esophageal mucosal IPCLs
ActiveCN112419246BEasy to detectImplement diagnosticsImage enhancementImage analysisBlood vesselEndoscopic image
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical image processing, in particular to a depth detection network for quantifying the morphological distribution of esophageal mucosal IPCLs blood vessels. The present invention includes feature extraction network and feature pyramid, region candidate network, interest region pooling and cluster distribution prior self-embedded cancer focus classification network, and visualization system on narrow-band imaging endoscopic images. The feature extraction network extracts the feature map of the input image; the feature pyramid fuses the features of different scales; the region candidate network proposes possible lesion regions; the pooling of the interest region pools the features to the suspicious lesion region; the cluster distribution prior self-embedding The cancer foci classification network of the system classifies the cancer foci; finally, it is visualized on the narrow-band imaging endoscopic image, and the cancer foci are box-marked with different colors. The present invention detects and diagnoses the cancer foci of early esophageal squamous cell carcinoma existing in the image, which can effectively improve the diagnosis efficiency and assist the doctor to obtain higher diagnosis accuracy.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Illumination balancing and solid state narrow band imaging utilizing fiber bundle design and assembly techniques in endoscopes
ActiveCN106572784APower balanceUniform and/or color distributionBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesFiber bundleWavelength
A semiconductor-based light source device for an endoscope that provides for a even power distribution and / or color distribution of light. The semiconductor-based light source device includes a plurality of semiconductor light sources and a plurality of fiber bundles, in which the respective fiber bundles are each segregated into a plurality of fiber sub-bundles for directing substantially the same amount of illumination from a respective semiconductor light source to each of a corresponding plurality of illumination windows disposed at a distal end of the endoscope. By providing such a semiconductor-based light source device, in which the respective semiconductor light sources are operative to adjust the intensity and / or color or wavelength of the light emitted by the respective semiconductor light sources, a desired color temperature and / or color balance for illumination of tissue and / or other matter under examination by the endoscope can be achieved.
Owner:GYRUS ACMI INC (D B A OLYMPUS SURGICAL TECH AMERICA)
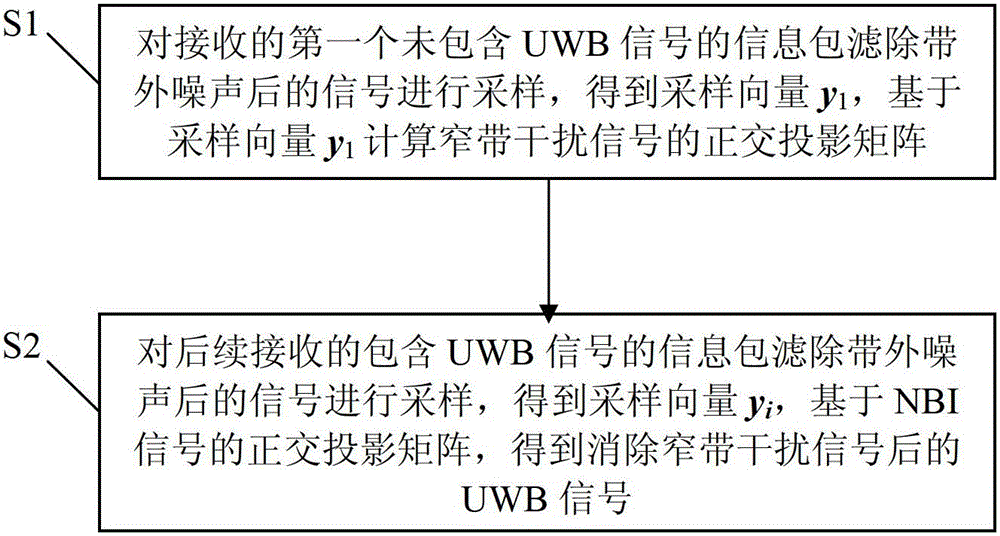
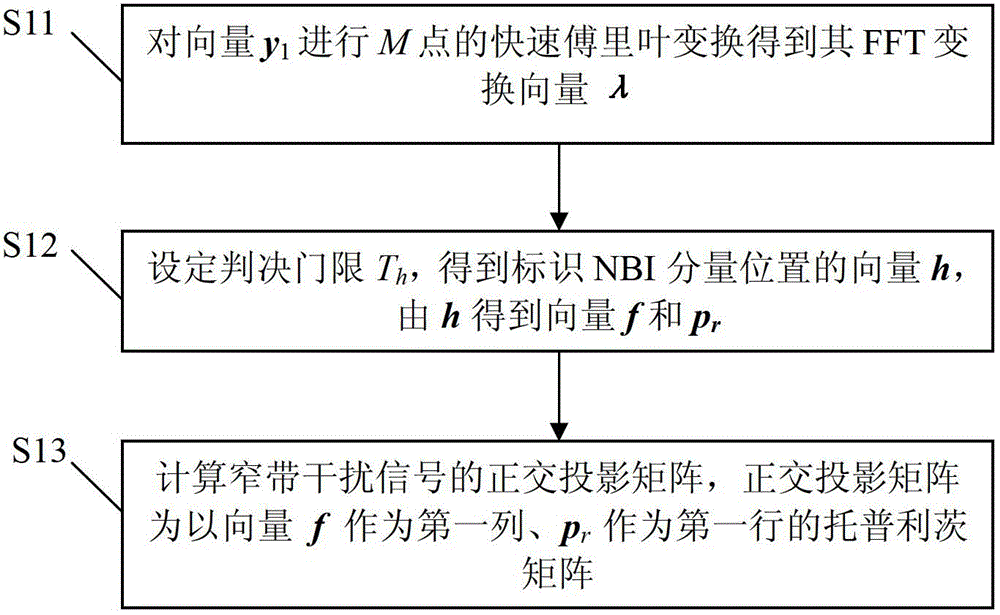
Method for eliminating narrow-band interference in under-sampling rate pulse UWB (Ultra Wide Band) communication system
InactiveCN102710290BReduce the difficulty of implementationReduce power consumptionTransmissionHat matrixCommunications system
The invention relates to a method and a device for eliminating the narrow-band interference in an under-sampling rate pulse UWB (Ultra Wide Band) communication system. The method comprises the following steps of: S1, sampling the received signal in which out-of-band noise in an information packet which does not contain a UWB signal is filtered to obtain a sampling vector y1 and calculating an orthogonal projection matrix of a narrow-band interference signal; and S2, sampling a subsequently received signal in which out-of-band noise in an information packet which contains a UWB signal is filtered to obtain a sampling vector yi and obtaining the UWB signal in which the narrow-band interference signal is eliminated based on the orthogonal projection matrix of an NBI (Narrow Band Imaging) signal. According to the method and the device disclosed by the invention, the NBI signal can be effectively eliminated, the signal-noise ratio is increased and the system sampling rate is far lower than the Nyquist sampling rate; and in addition, the estimation and elimination of the NBI are completely carried out in a digital domain without a parallel system structure or generation of a simulation projection signal, and thus the complexity and the realization difficulty of the system are greatly reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
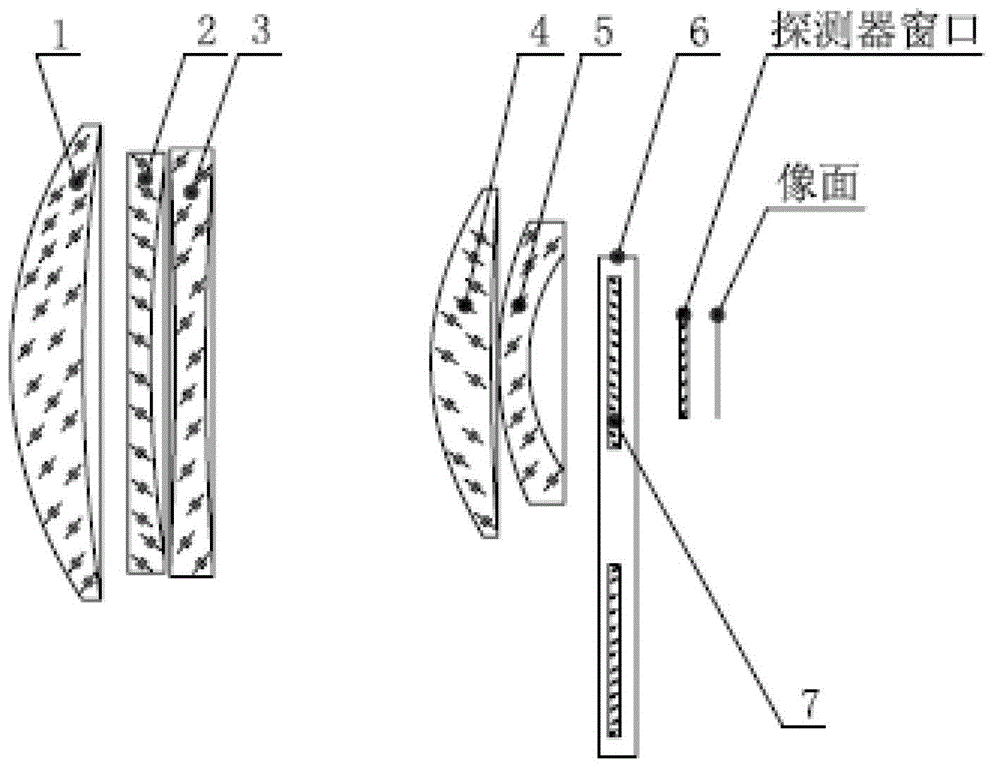
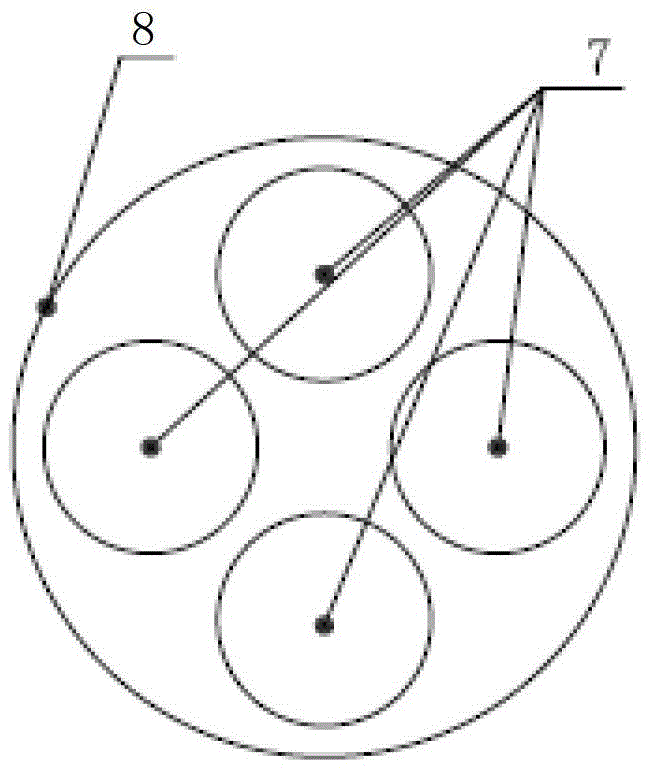
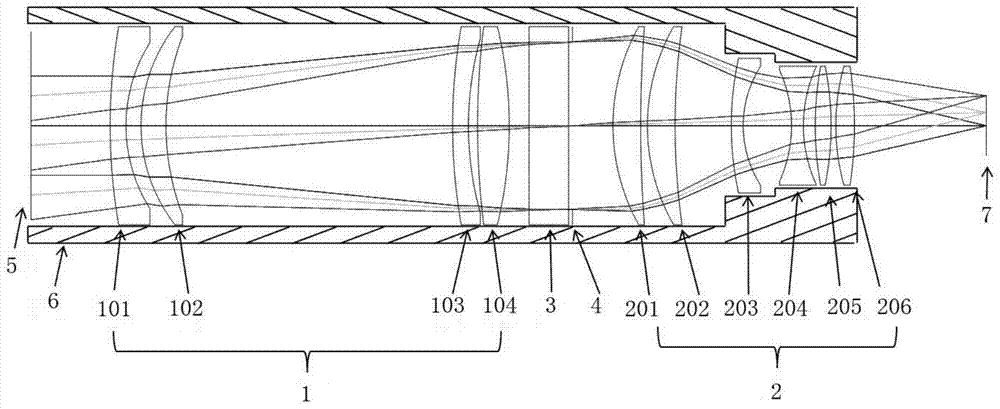
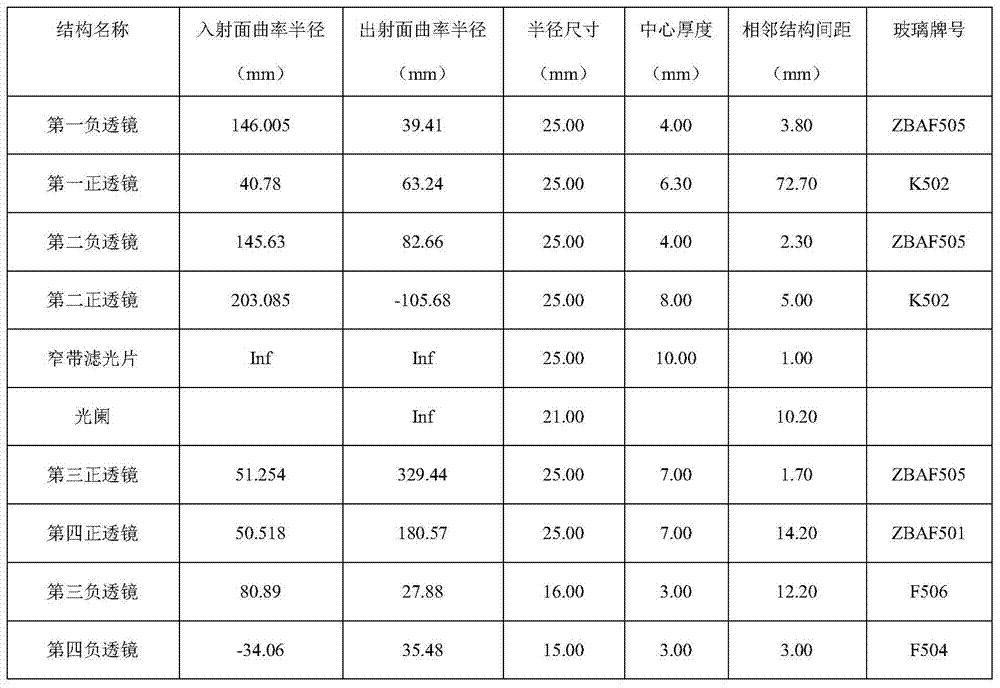
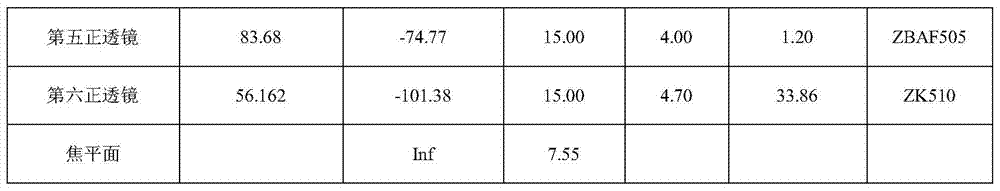
A Lens for Narrowband Imaging Observation of Space Environment
ActiveCN104635321BRealize the angle adjustment functionEasy to adjustOptical elementsComing outCamera lens
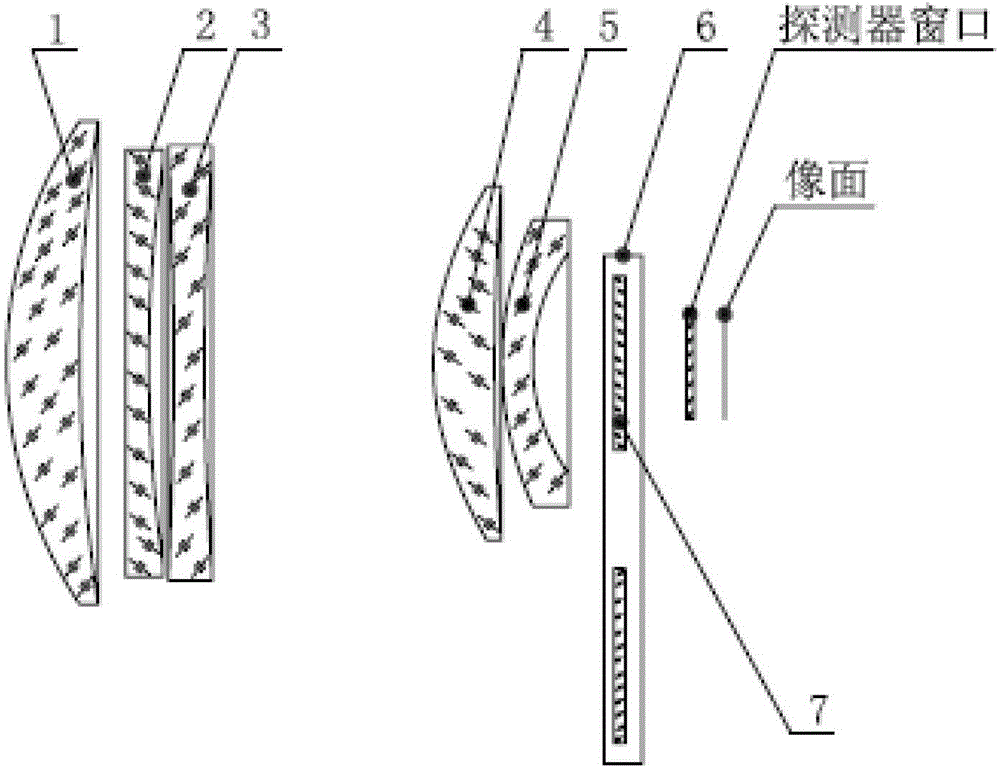
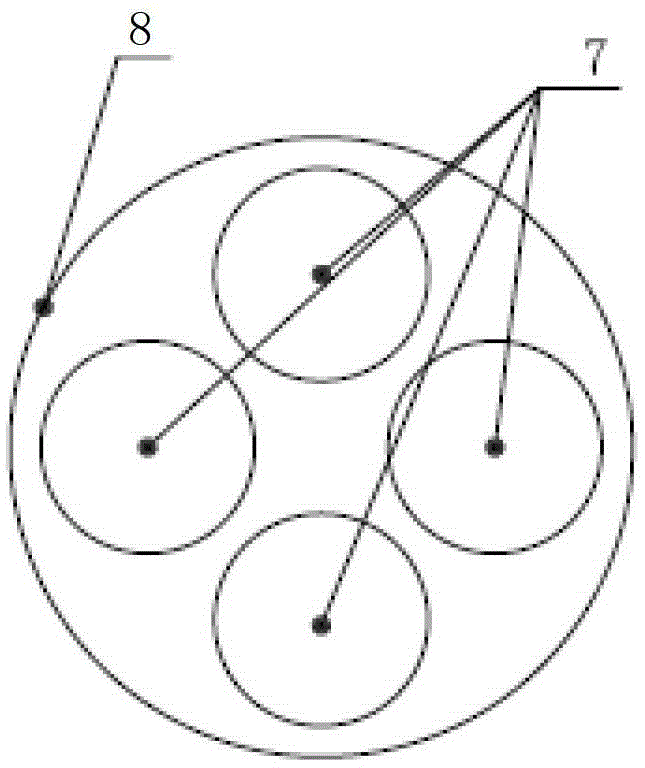
The invention provides a camera lens for space environment narrow-band imaging observation. The camera lens comprises a lens cone (6), a first lens set (1), a second lens set (2), a narrow-band filer plate (3) and a diaphragm (4), wherein the first lens set (1), the narrow-band filter plate (3), the diaphragm (4) and the second lens set (2) are successively arranged in the lens cone (6) in parallel in an incidence direction of a light path; the first lens set (1) is used for regulating an angle of light which comes into the space environment, so that the light is adaptive to an incidence angle requirements while coming into the narrow-band filer plate (3), and is matched with the narrow-band filer plate (3) to realize narrow-band filtering; the second lens set (2) is used for performing re-imaging processing on light which comes out of the narrow-band filter plate (3) to correct lens aberration errors to obtain low distortion imaging effects. The camera lens is suitable for performing TDI (Time Delay and Integration) imaging on a faint light source with bandwidth of several nanometers in the space environment.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com