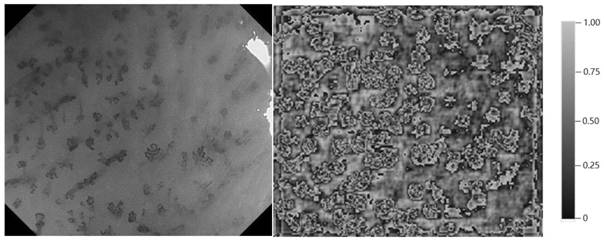
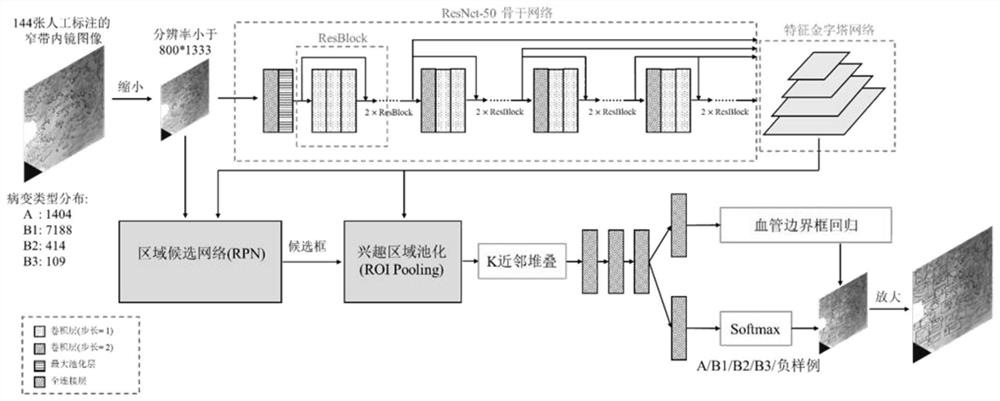
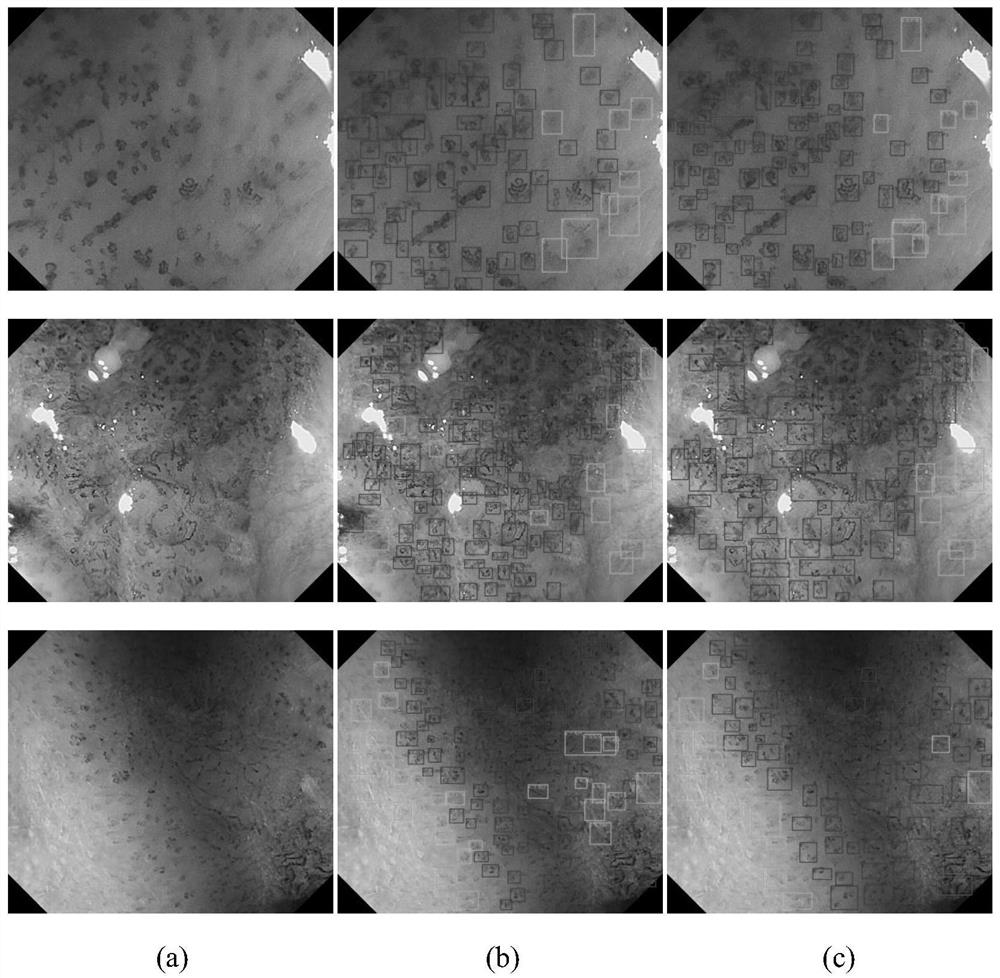
Deep detection network for quantifying esophageal mucosa IPCLs vascular morphological distribution
A technology for esophageal mucosa and depth detection, applied in the field of medical image processing, can solve the problems of lack of quantifiable concepts, medical decision-making errors, visual fatigue, etc., and achieve the effect of improving diagnostic efficiency, improving efficiency and accuracy, and reducing the amount of calculation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] The embodiments of the present invention will be described in detail below, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to the examples.
[0030] The present invention adopts figure 1 The network framework shown was trained using 144 narrow-band imaging endoscopic images that were annotated by multiple experienced doctors, so as to obtain a model that can automatically detect and diagnose esophageal squamous cell carcinoma foci on narrow-band imaging endoscopic images. The specific process is:
[0031] (1) Before training, the network parameters of the ResNet-50 model are randomly initialized, and the images in the training set are scaled so that their resolution does not exceed 800×1333, and the corresponding bounding boxes are also scaled at the same time. .
[0032] (2) During training, first the image is normalized to the three channels (R, G, B) of the image according to the mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406] and standard deviation=[0.229, 0.224, 0.2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com