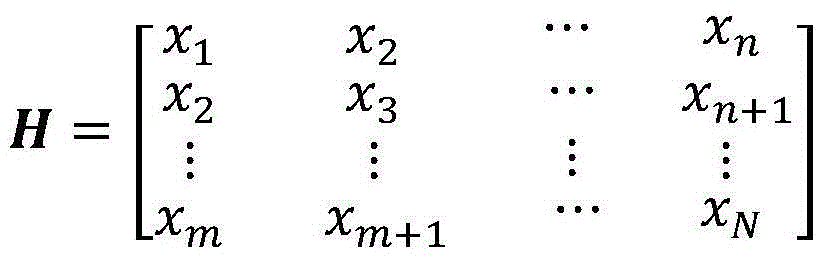Patents
Literature
140 results about "Faraday effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
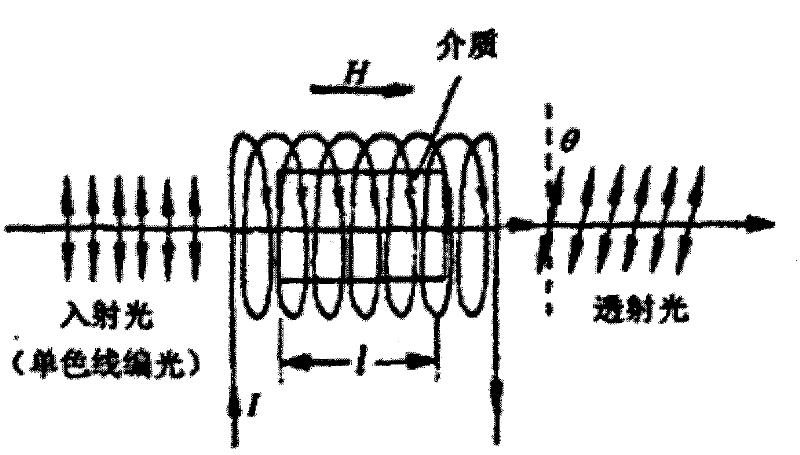
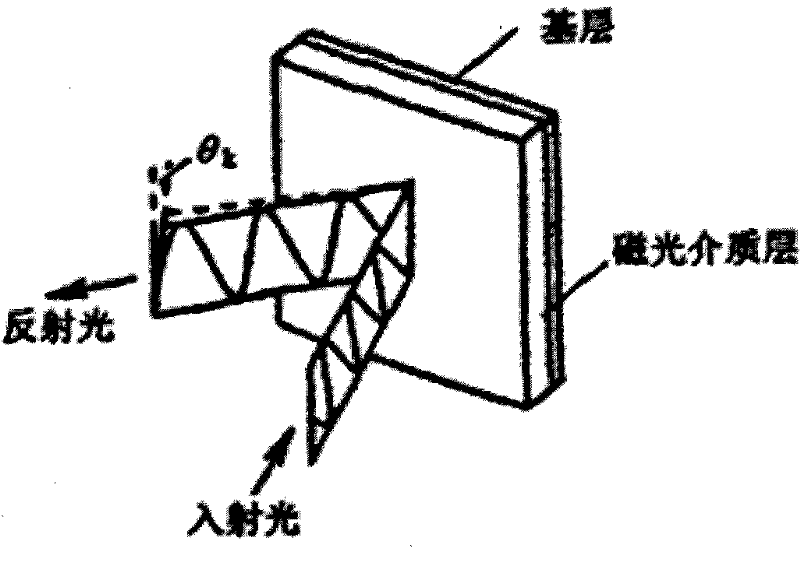
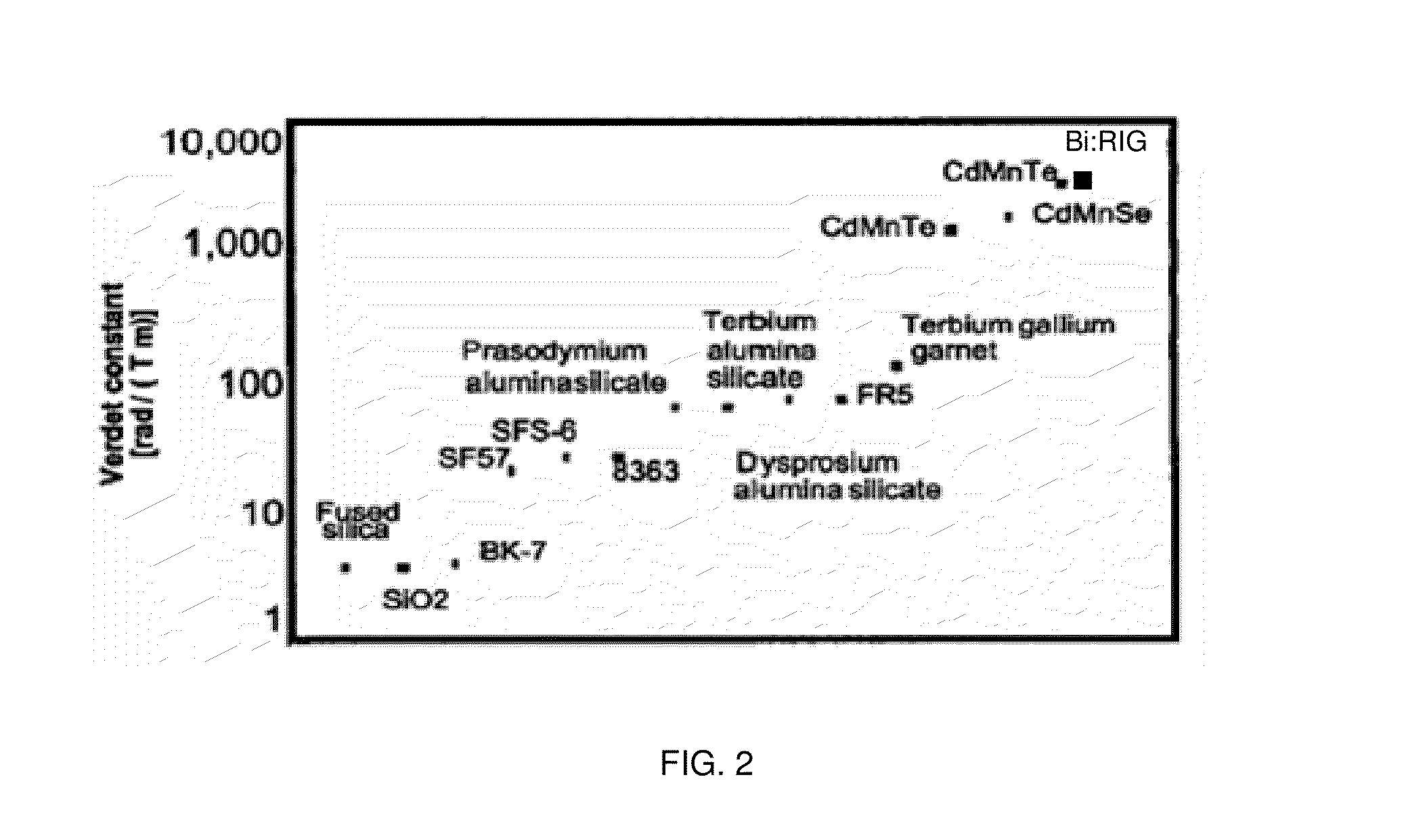
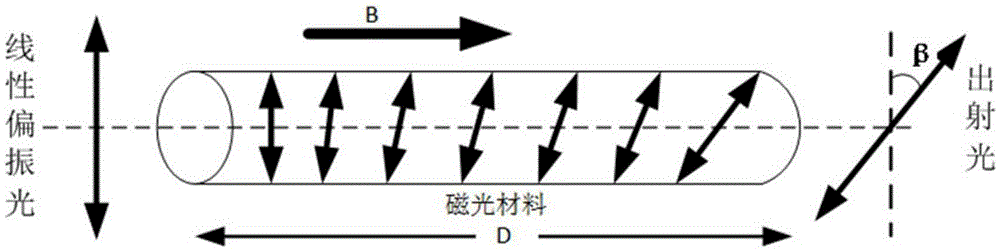
In physics, the Faraday effect or Faraday rotation is a magneto-optical phenomenon—that is, an interaction between light and a magnetic field in a medium. The Faraday effect causes a rotation of the plane of polarization which is linearly proportional to the component of the magnetic field in the direction of propagation. Formally, it is a special case of gyroelectromagnetism obtained when the dielectric permittivity tensor is diagonal.
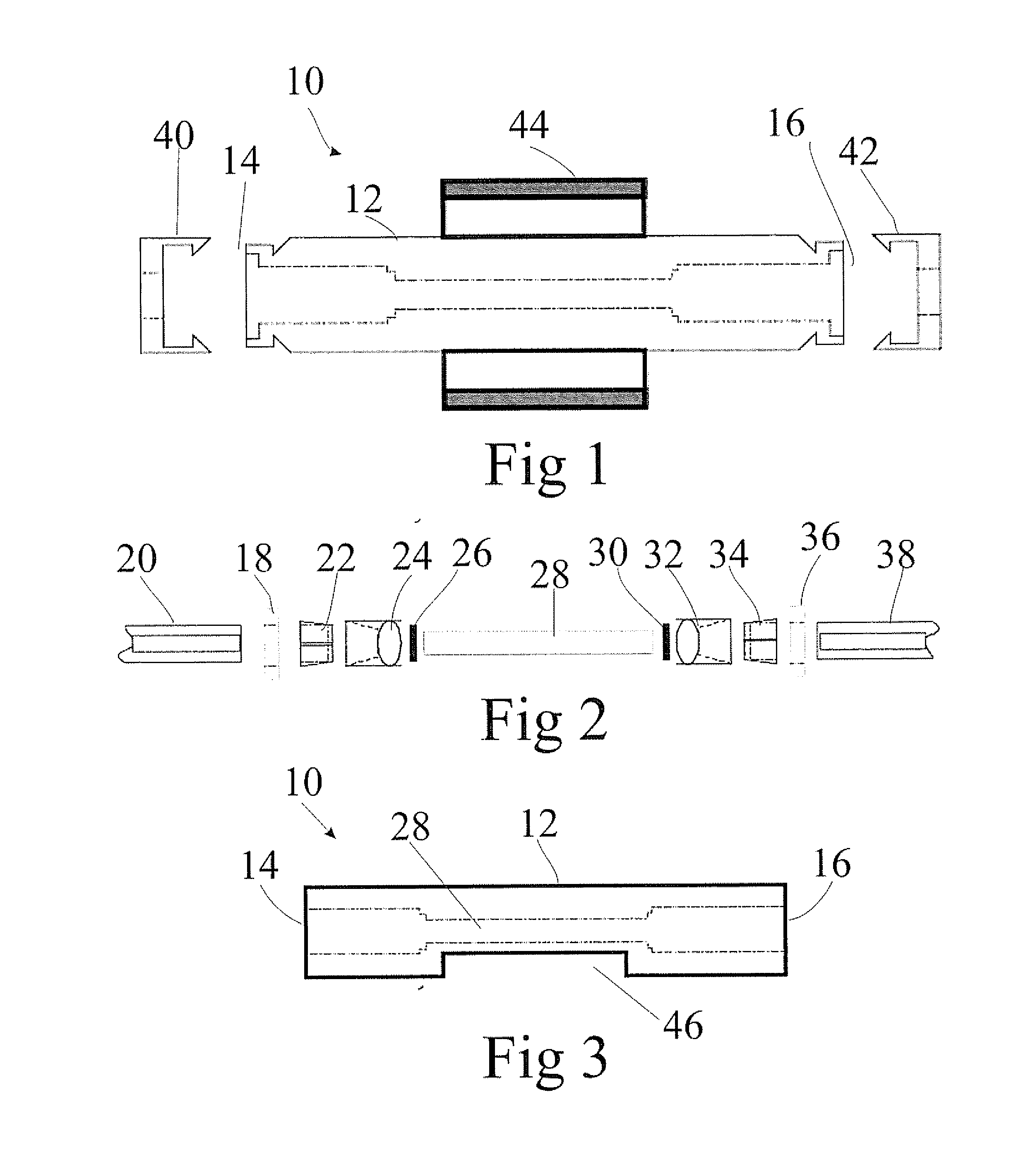
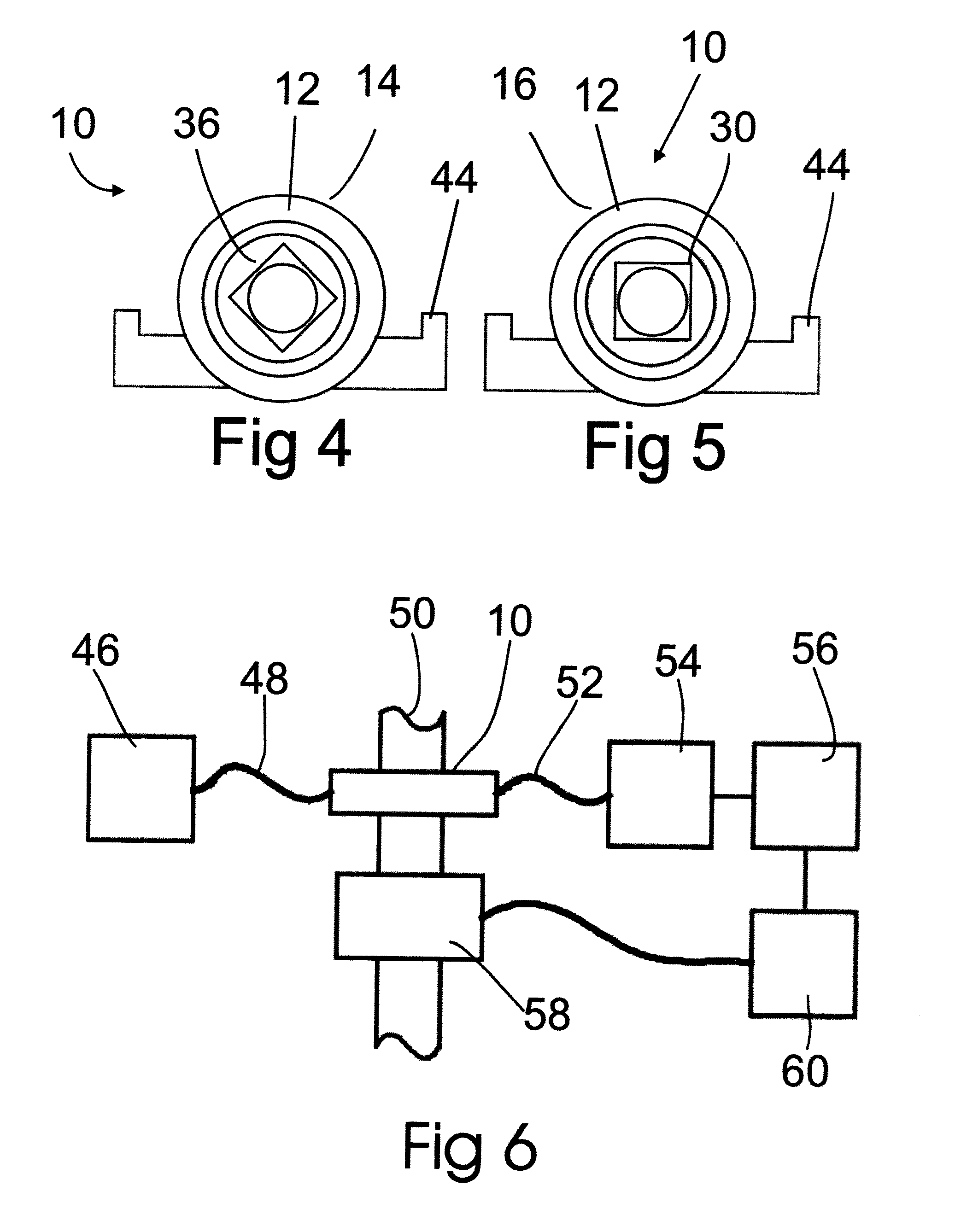
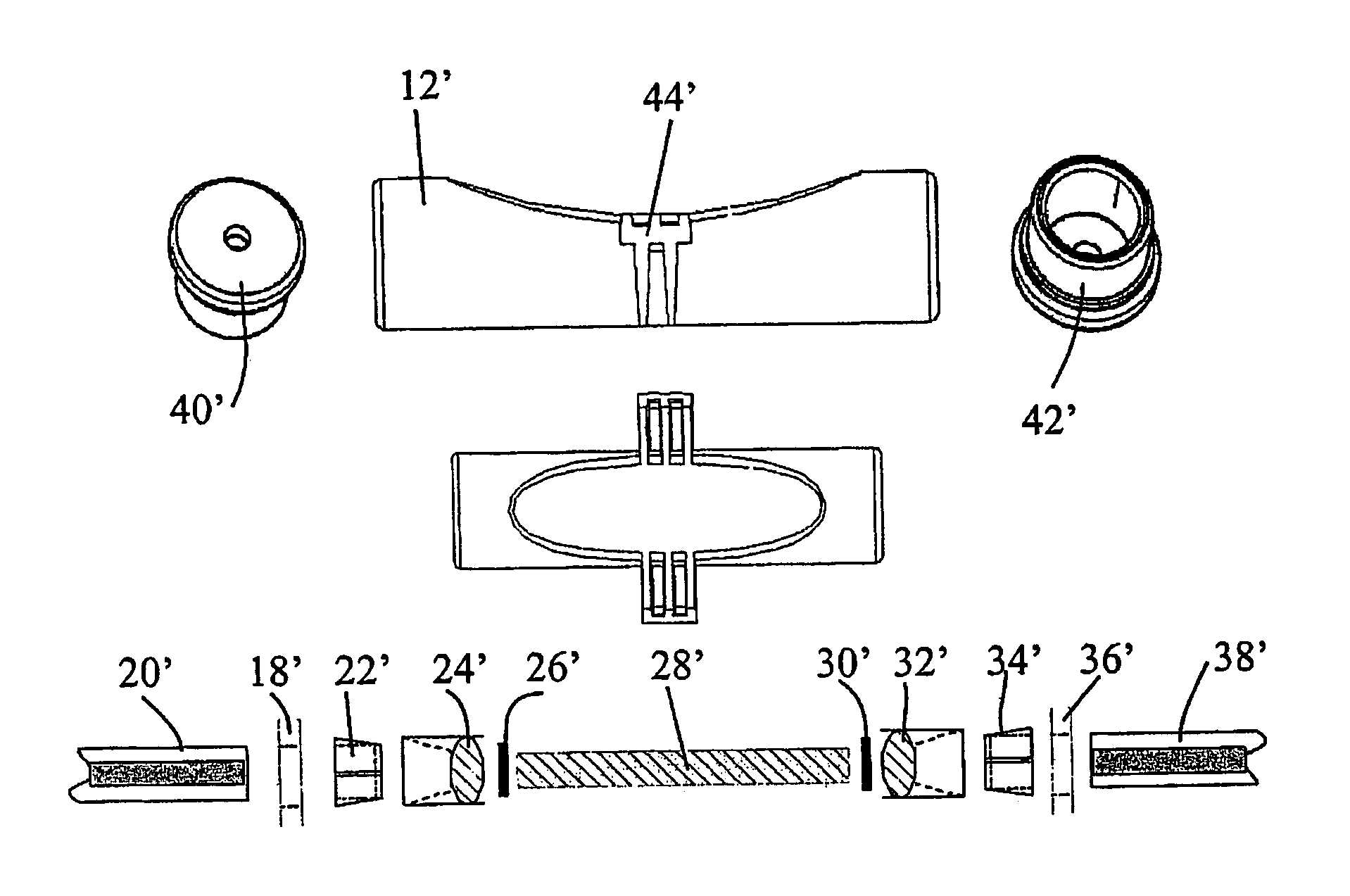
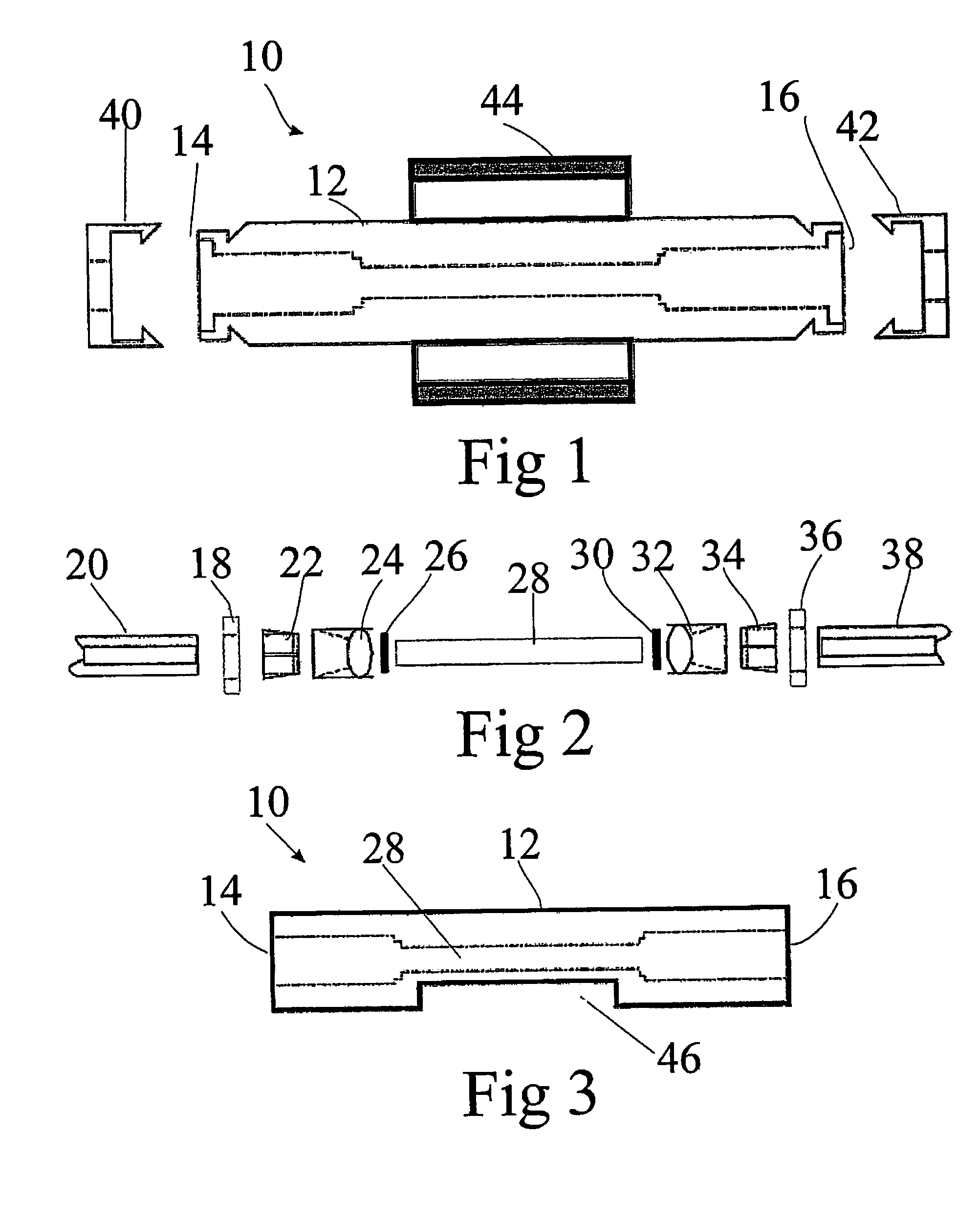
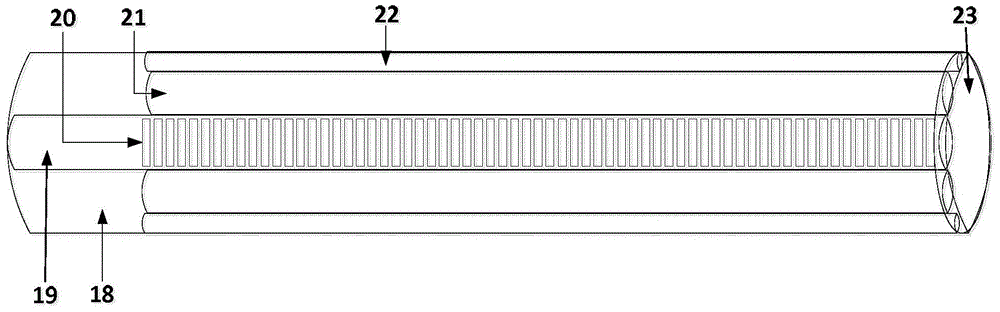
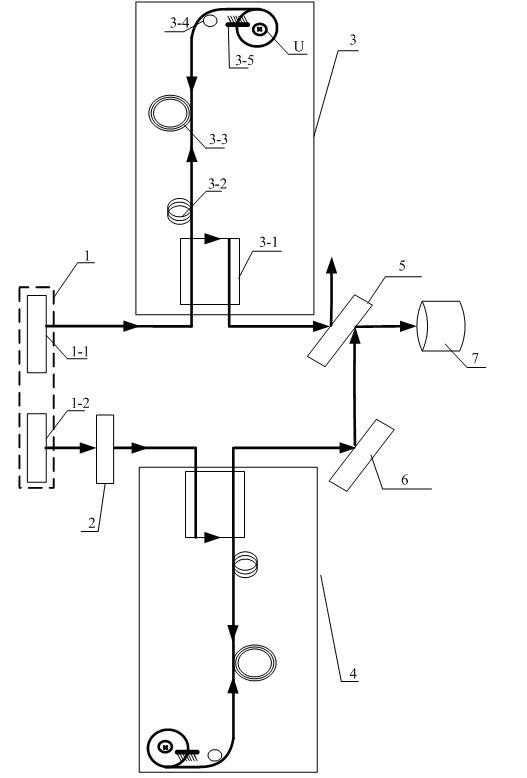
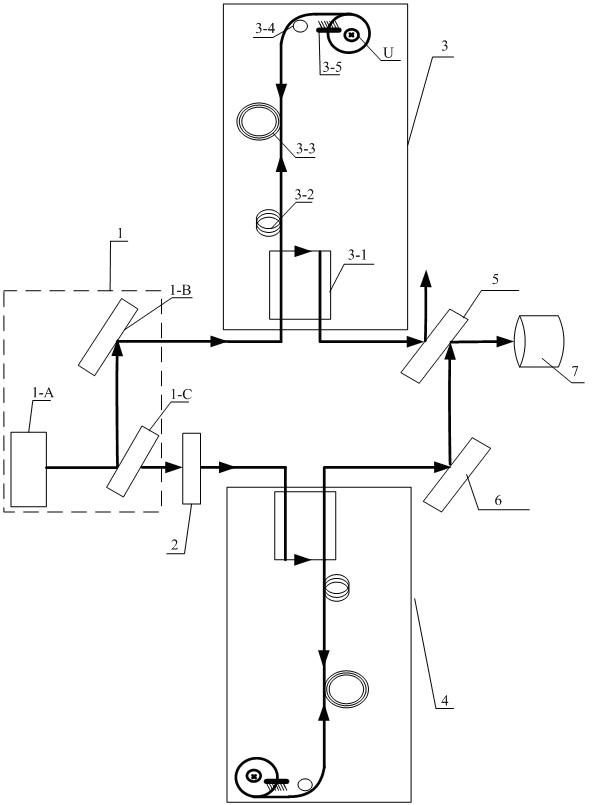
Optical fiber gyroscope frequency characteristic elevating method and device based on Faraday effect
InactiveCN102788595ASolve the problem of limited output frequencyHigh frequency outputMeasurement devicesDigital signal processingGyroscope
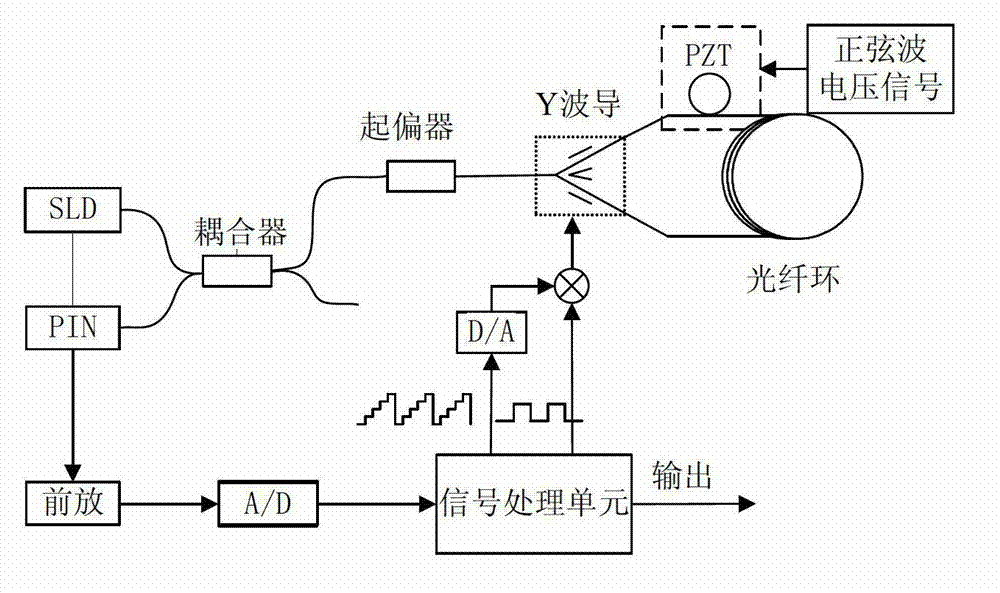
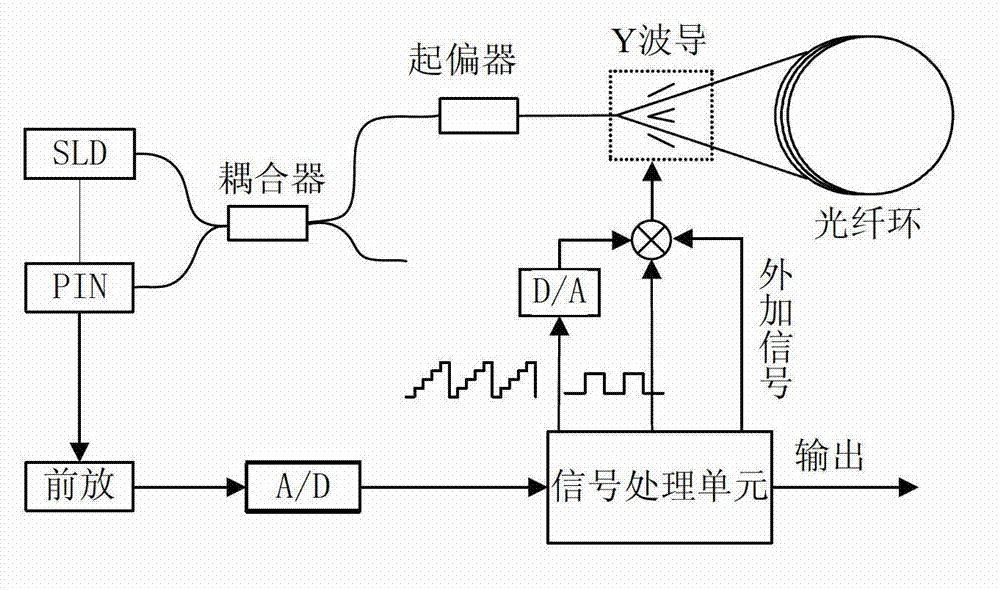
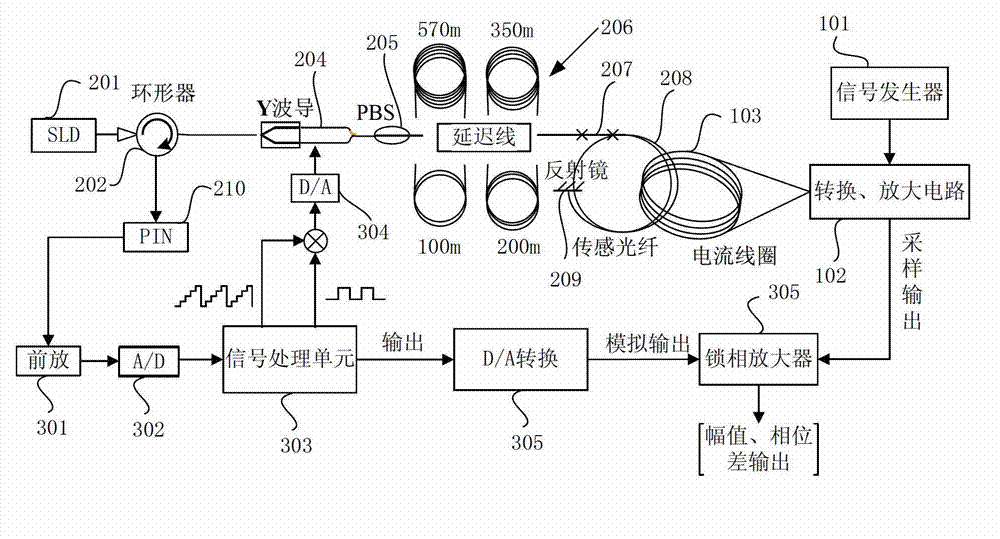
The invention discloses an optical fiber gyroscope frequency characteristic elevating device based on a Faraday effect. An excitation current source comprises a signal generator, a conversion amplifying circuit and a current coil, wherein a sensitive light path comprises a light source, a circulator, a Y waveguide phase regulator, a polarization beam splitter, a polarization-maintaining fiber coil, a gamma / 4 wave plate, a sensing optical fiber, a reflecting mirror and a detector; and an analog optical fiber gyroscope signal processing detection circuit comprises a front amplifying circuit, an A / D (Analog to Digital) converting circuit, a digital signal processing unit, a first D / A (Digital to Analog) converting unit, a second D / A converting circuit and a phase-locked amplifier. The Faraday effect applied in the invention is generated by exciting the sensitive light path with sinusoidal current, and a sinusoidal signal serving as an exciting signal can be output at a high frequency, so that the problem of limitation on the excitation signal output frequency during frequency characteristic test of an optical fiber gyroscope is solved, and evaluation of high bandwidth can be realized.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Compensation of simple fiber optic faraday effect sensors
ActiveUS20100295692A1Fast fault locationMagnetic measurementsCurrent/voltage measurementFiberGround failure
A monitoring system for detecting earth faults in an electrical power supply grid providing a power signal includes a plurality of monitoring devices, each of the monitoring devices including a detector for detecting the level of harmonics in the power signal, wherein the level of harmonics is detected in a specific frequency range. Each of the monitoring devices further includes a memory for storing a harmonics reference value, a processor for comparing the detected level of harmonics with the reference level, and a communication device for transmitting an alarm if the detected level of harmonics is above the reference level for a specific period of time. Each of the detectors includes an optical sensor for detecting the harmonics by use of the Faraday effect.
Owner:LANDIS & GYR OY
Compensation of simple fibre optic Faraday effect sensors
ActiveUS7068025B2Eliminate signal attenuationCompensate for interferenceMeasurement using dc-ac conversionElectrical testingMeasurement deviceEngineering
Owner:LANDIS & GYR OY
All-fiber current transformer and working method thereof
InactiveCN101915866AImprove the extraction effectAvoid influenceVoltage/current isolationFaraday effectOptical fiber coupler
Owner:SHANGHAI BOOM FIBER SENSING TECH
Implementation method for difference detection of coherent population trapping magnetometer
ActiveCN105699919ASuppression of AM noiseGood signal to noise ratioMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesTrappingFaraday effect
The present invention discloses an implementation method for difference detection of a coherent population trapping magnetometer. The method employs the linear polarization polychromatic light outputted by VCSEL and the atom effect in a magnetic field to extract CPT signals by means of an Faraday effect through a difference detection technology so as to effectively inhibit the AM and FM-AM noise generated by laser in signals, eliminate background noise generated by polychromatic light useless optical frequency components, improve the measurement precision of a CPT magnetometer, and extend the detection range of the magnetic field intensity through the difference.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Anti-counterfeiting component and anti-counterfeiting product
InactiveCN102446451AImprove anti-counterfeiting performanceImprove the efficiency of authenticity identificationStampsInorganic material magnetismInformation layerFaraday effect
The invention discloses an anti-counterfeiting component and an anti-counterfeiting product, wherein the anti-counterfeiting component comprises a base layer. A magneto-optical information layer is arranged on the base layer, machine-readable safety information based on a magneto-optical characteristic is loaded on the magneto-optical information layer. The magneto-optical characteristic comprises a magneto-optical faraday effect or a magneto-optical Kerr effect. The anti-counterfeiting product comprises an object which is provided with the anti-counterfeiting component. The anti-counterfeiting component is adhered to the object through a first adhesive layer and / or a second adhesive layer. An embodiment of the anti-counterfeiting component and the anti-counterfeiting product can improve anti-counterfeiting performance of the anti-counterfeiting component and safety of the anti-counterfeiting product.
Owner:SECURITY PRINTING INST OF PEOPLES BANK OF CHINA +1
Micro-ring cavity gyroscope with magnetic field lock-in minimization
InactiveUS20030020918A1Easy to analyzeSimple calculationSagnac effect gyrometersSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsOptical gyroscopeFaraday effect
The invention is a compact optical gyroscope based on the Sagnac effect that combines a micro-ring cavity laser comprising a magneto-optical material and a magnetic field to circumvent the lock-in phenomenon at low rates of rotation. The invention also embodies novel processes for breaking lock-in using a transverse Faraday effect.
Owner:DELAWARE UNIV OF A DE
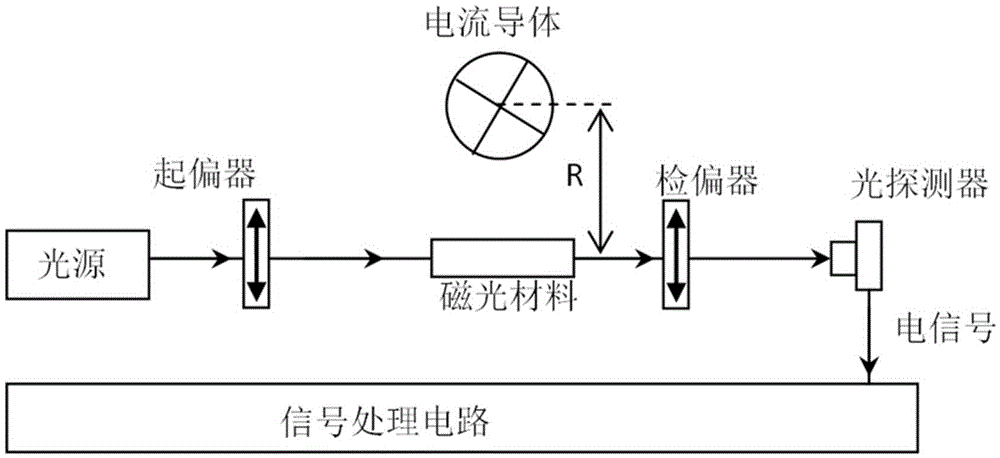
Current sensor
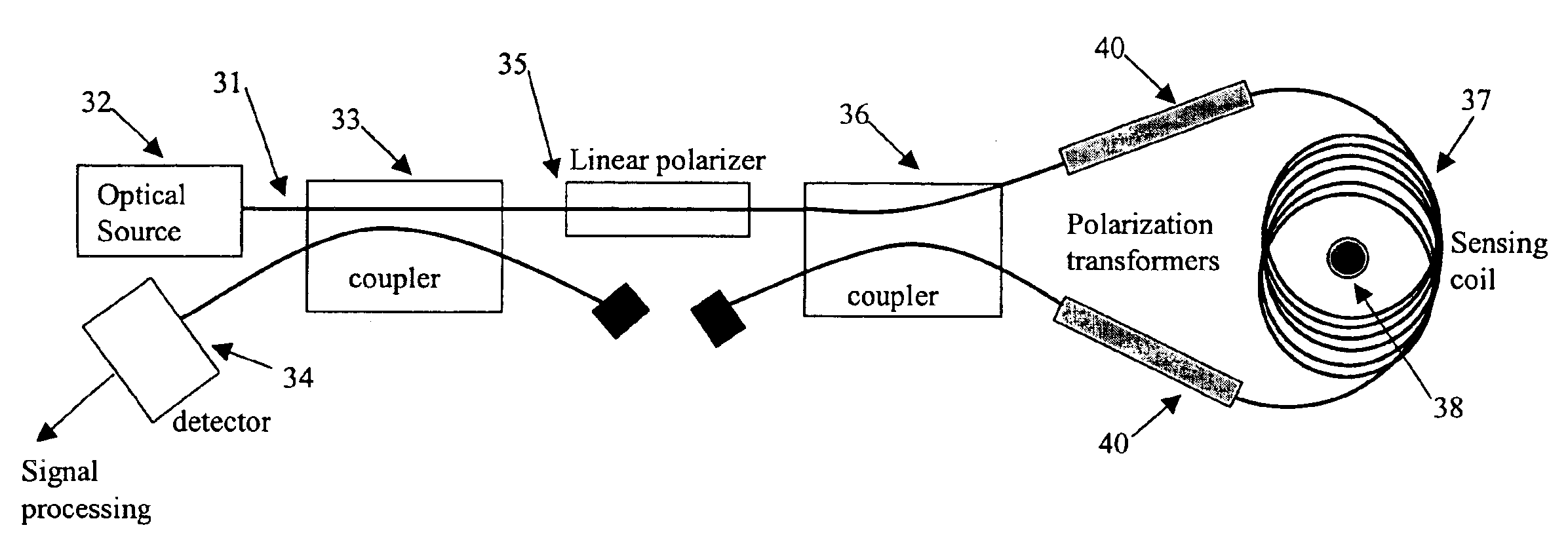
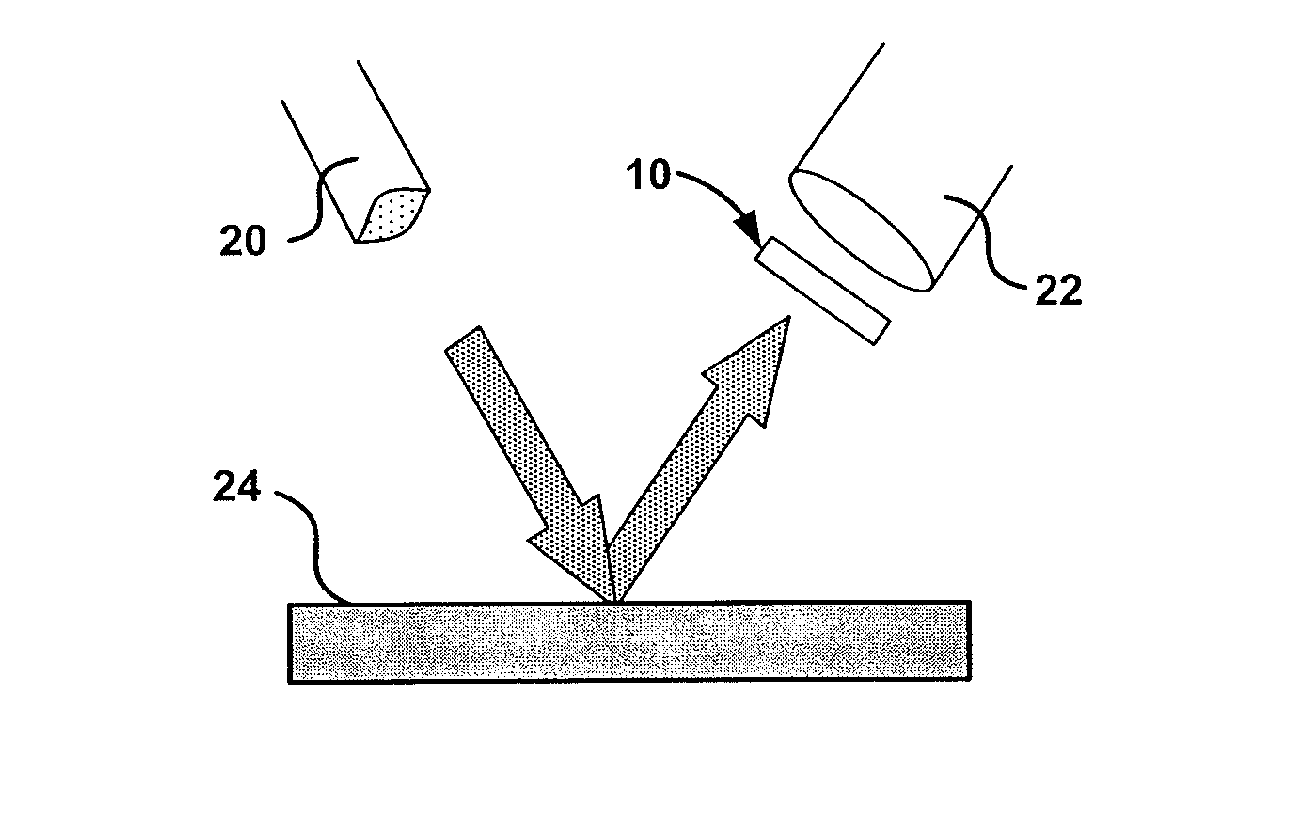
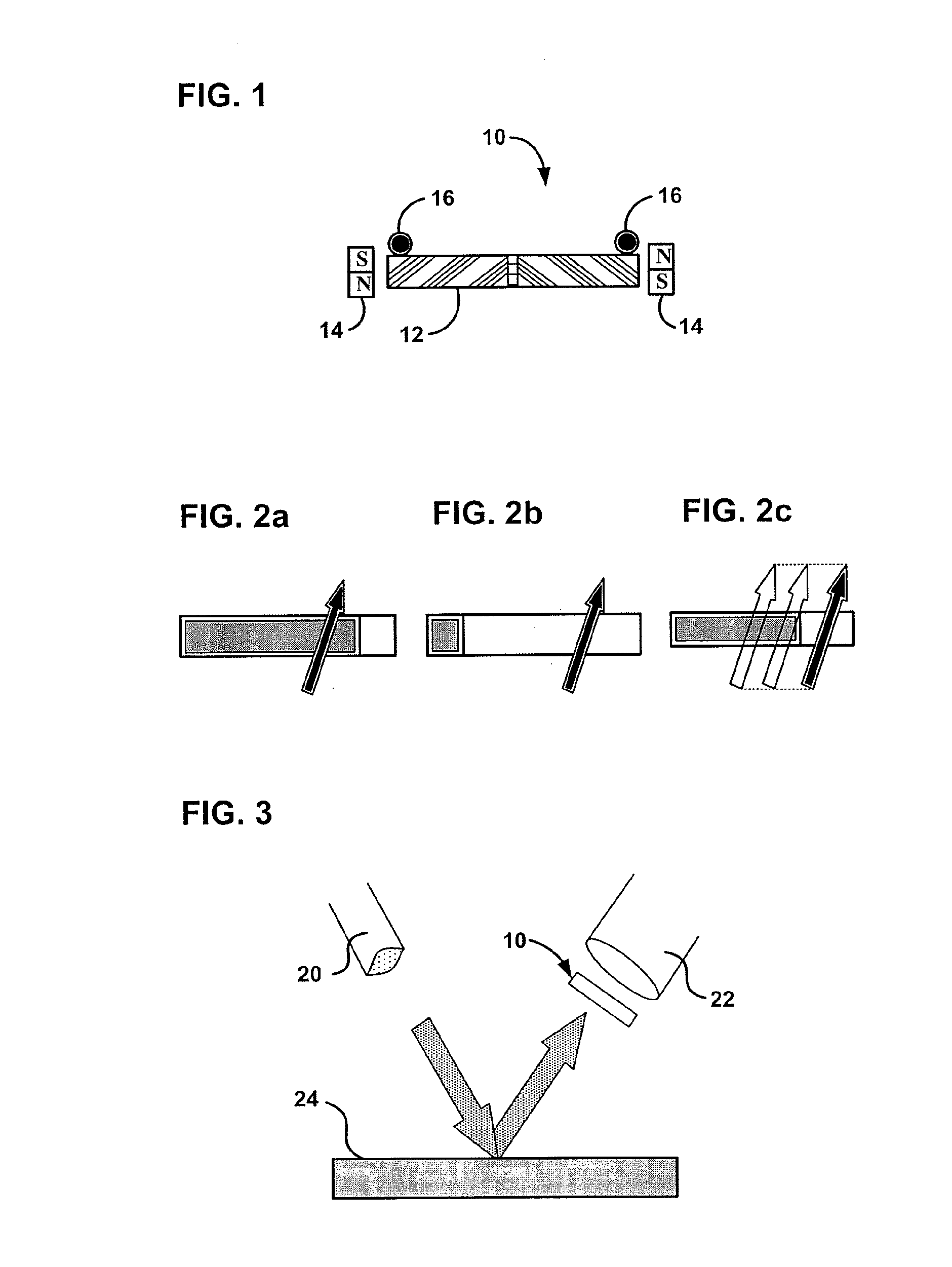
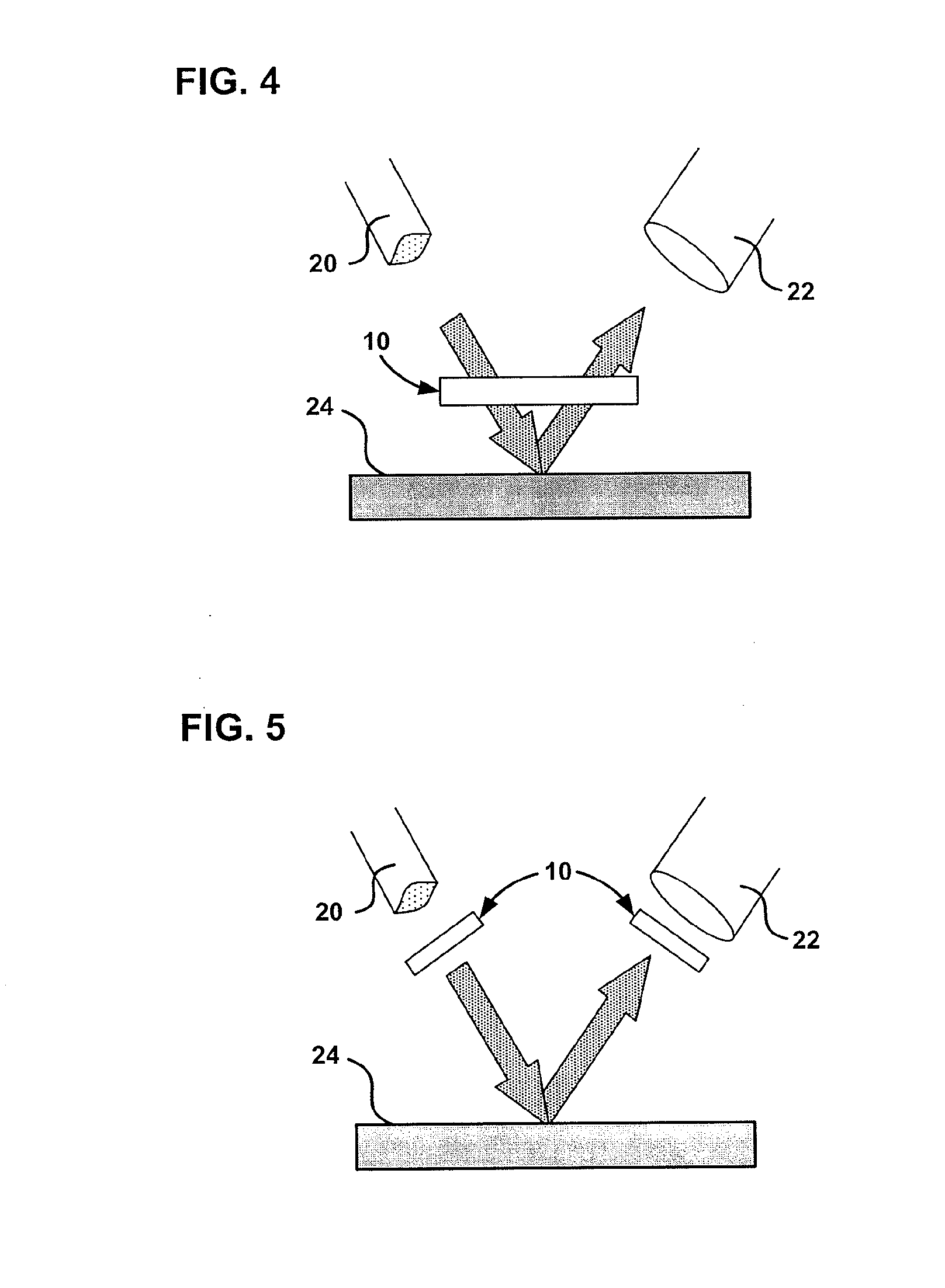
A method and device for measuring the current in a conductor are presented. They utilize the Faraday effect on counter-propagating circularly polarized beams of light in a fiber optic coil. The light beams are transformed to and from circular polarization by a polarization transformer comprised of a birefringent fiber with a twist through an appropriate angle at an appropriate distance from one end.
Owner:KVH IND INC
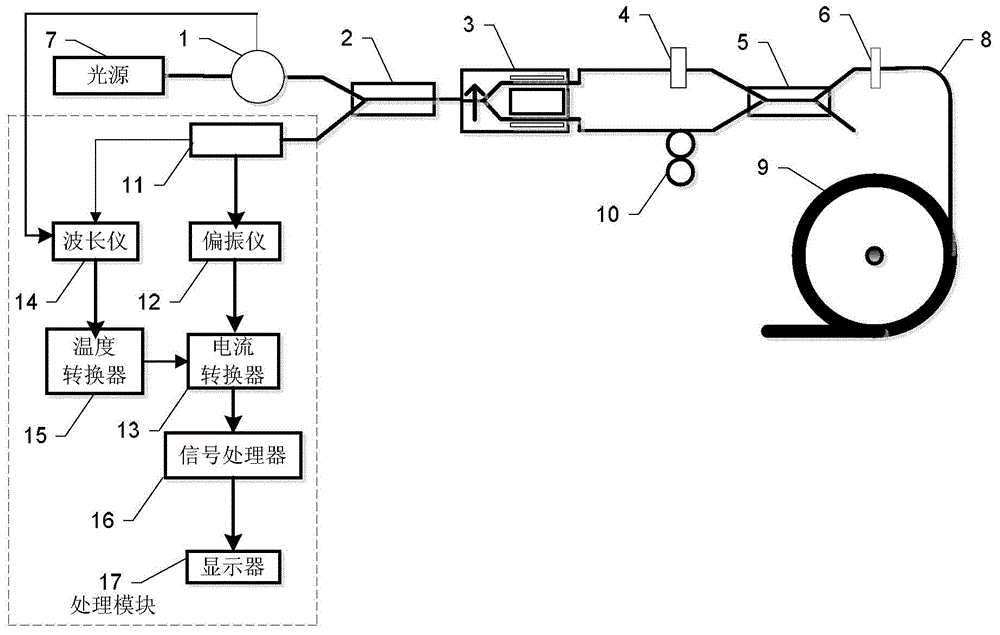
Stability control device for transmission spectrums of optical fiber current transducer
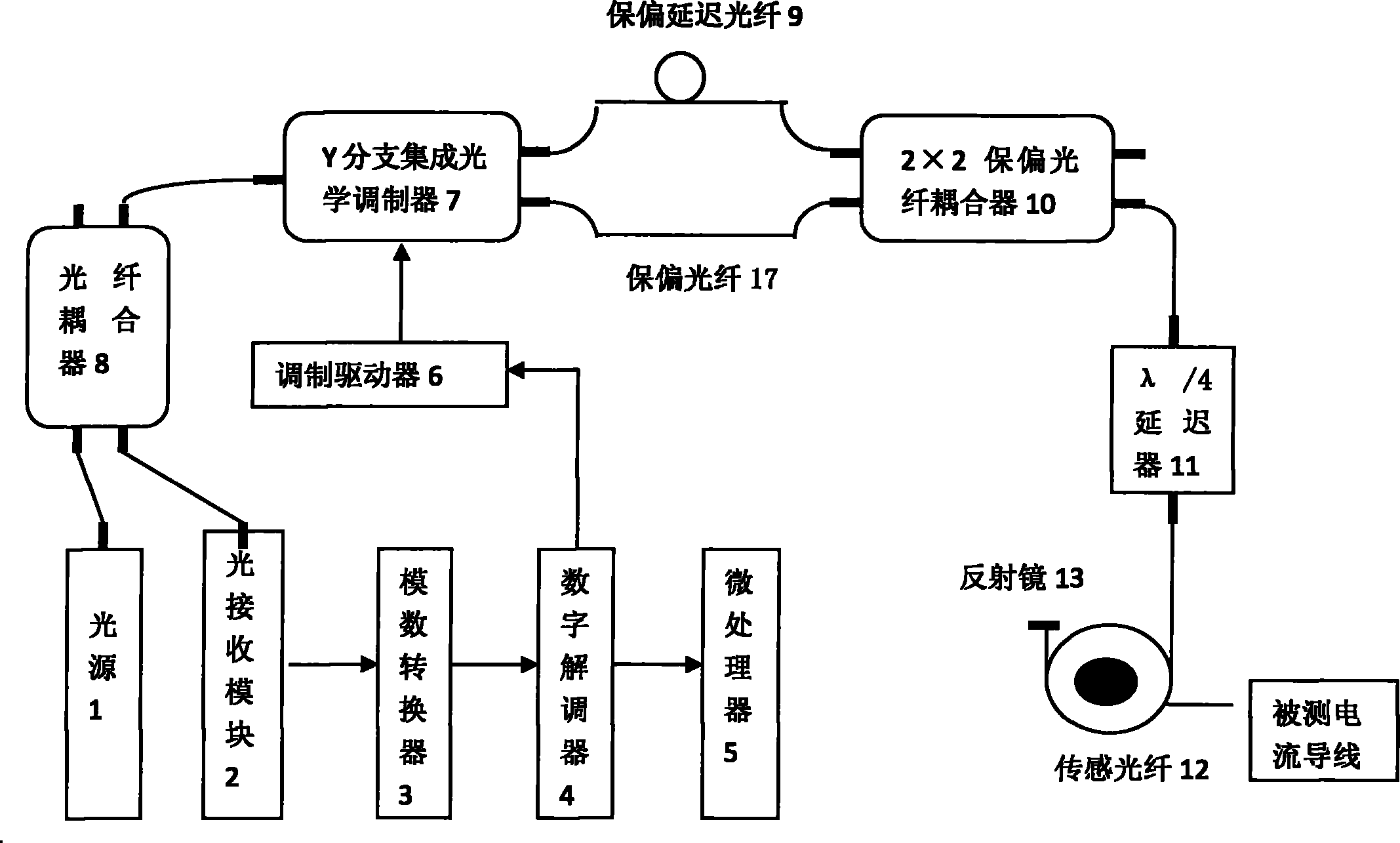
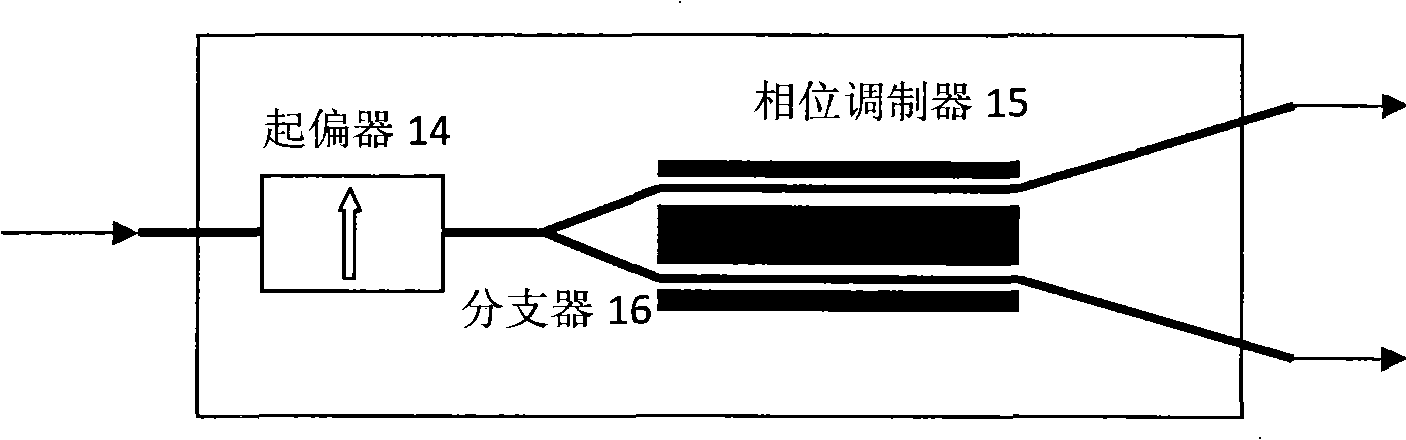
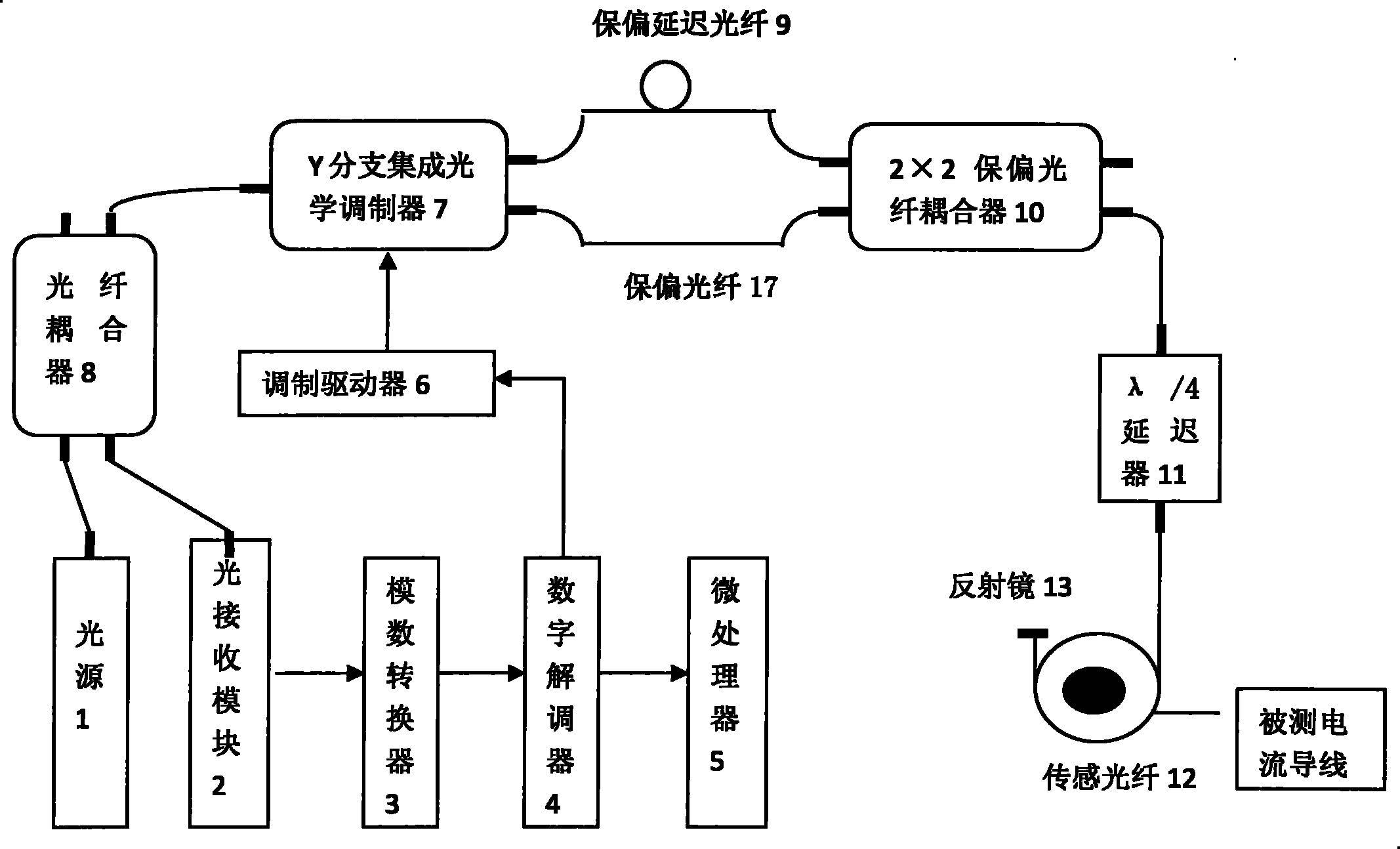
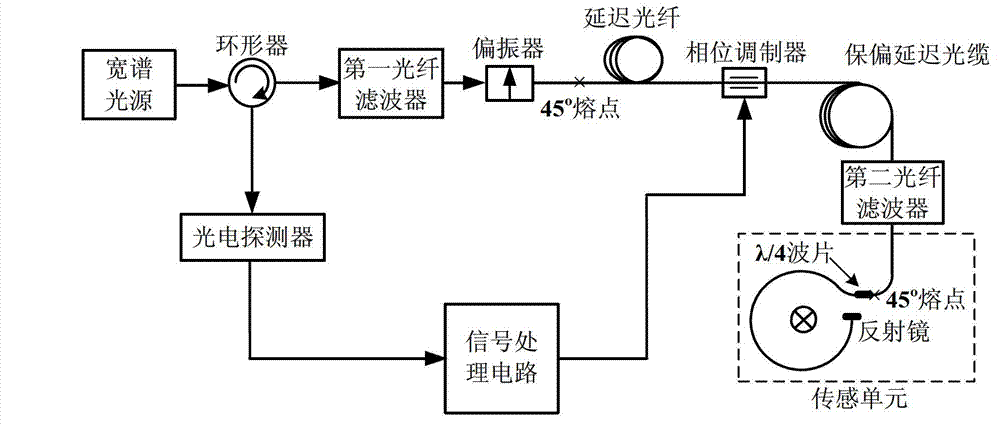
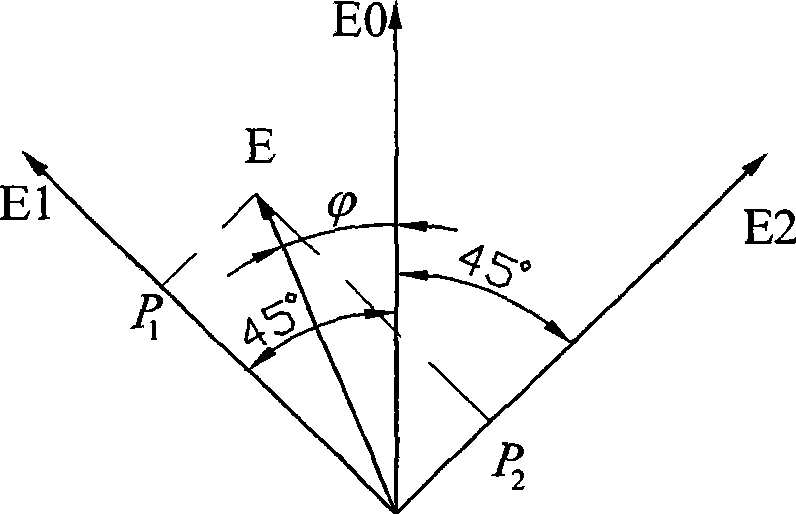
The invention discloses a stability control device for transmission spectrums of an optical fiber current transducer, and belongs to the technical field of optical fiber transmission. According to the stability control device, the front end of a polarizer is provided with a first optical fiber filter, and the front end of a sensing unit is provided with a second optical fiber filter. According to the invention, the changes in the spectral form and power of optical waves induced by the drifting of a spectral window of an optical device caused by shaft-aligning errors and temperature in the optical fiber current transducer are eliminated, so that the transmission spectrum in the optical fiber current transducer is stable, thereby eliminating integral optical phase shifting errors of a Faraday effect of the sensing unit. A new scheme for optical paths of all-optical-fiber current transducers based on an optical fiber filter provided by the invention solves the problem that in a traditional optical path, a spectral window of an optical device drifts due to temperature drift and difficulty in accurate shaft-aligning among optical fibers or between an optical fiber and a device, eliminates the influence of spectrum fluctuation on error signals, expands the range of a system for tracking direct-current random phase drift, and improves the anti-jamming capability and stability of the system.
Owner:开元锐德(北京)光电科技有限公司
Optical fiber current sensing device used for monitoring subway stray current
InactiveCN101446600ALight weightEasy to integrateCurrent/voltage measurementVoltage/current isolationFaraday effectOptical polarization
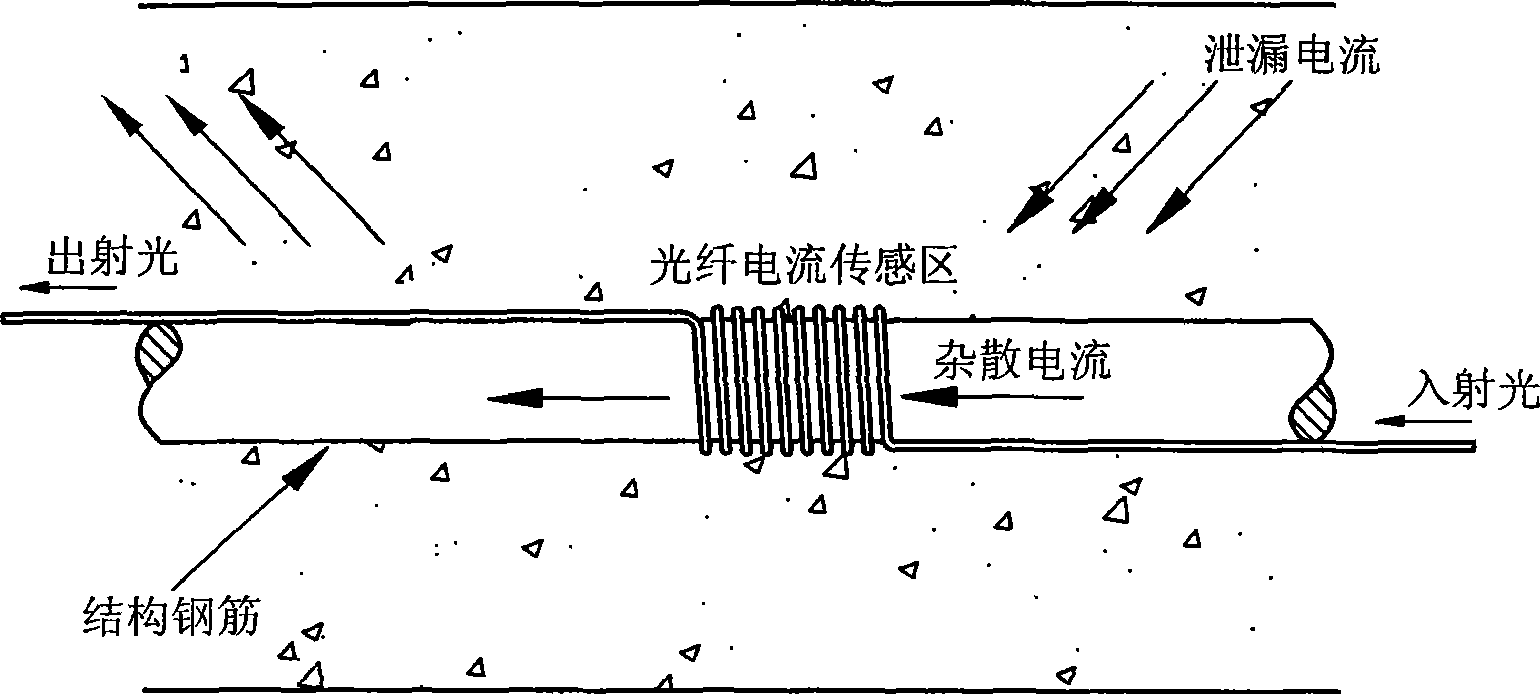
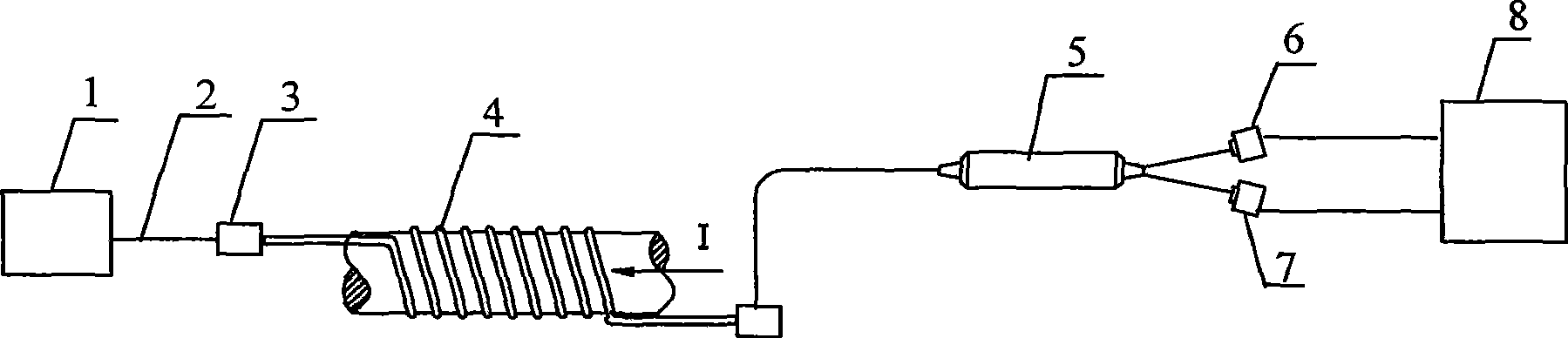
The invention discloses an optical fiber current sensing method used for monitoring subway stray current and a sensing device thereof. Light-transmitting parts and sensing parts in the optical fiber current sensing device adopted by the invention are connected by all-fiber. The measurement results of the existing subway stray current monitoring method which is based on polarization potential monitoring are affected by factors and evaluated in a non-directviewing way. The invention is based on faraday effect, utilizes polarization property of optical fiber and indirectly measures current by measuring faraday rotation angle in the optical fiber, thereby overcoming the disadvantages of the traditional stray current monitoring method. The method has the prominent advantages that system test sensitivity can be adjusted according to specific conditions so as to be suitable for measuring current with different ranges. In the invention, the all-fiber is used for transmitting, thereby ensuring simple light path and good insulating property; closed circuit integral of a magnetic filed generated by current is detected by the sensing device, so that the measurement results are difficult to be affected by a stray field; the measurement frequency band is wide, and the dynamic range is wide, therefore, the invention has good project application prospect.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Magnetic induction measurement method and apparatus
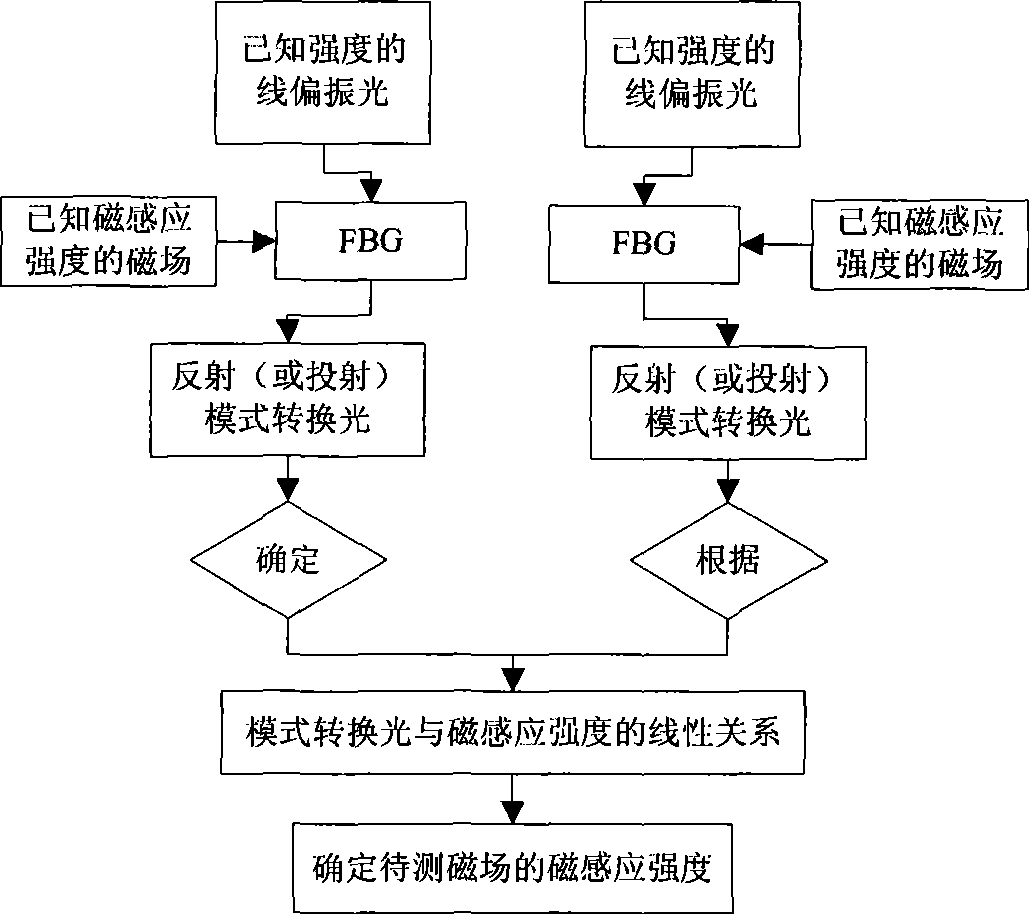
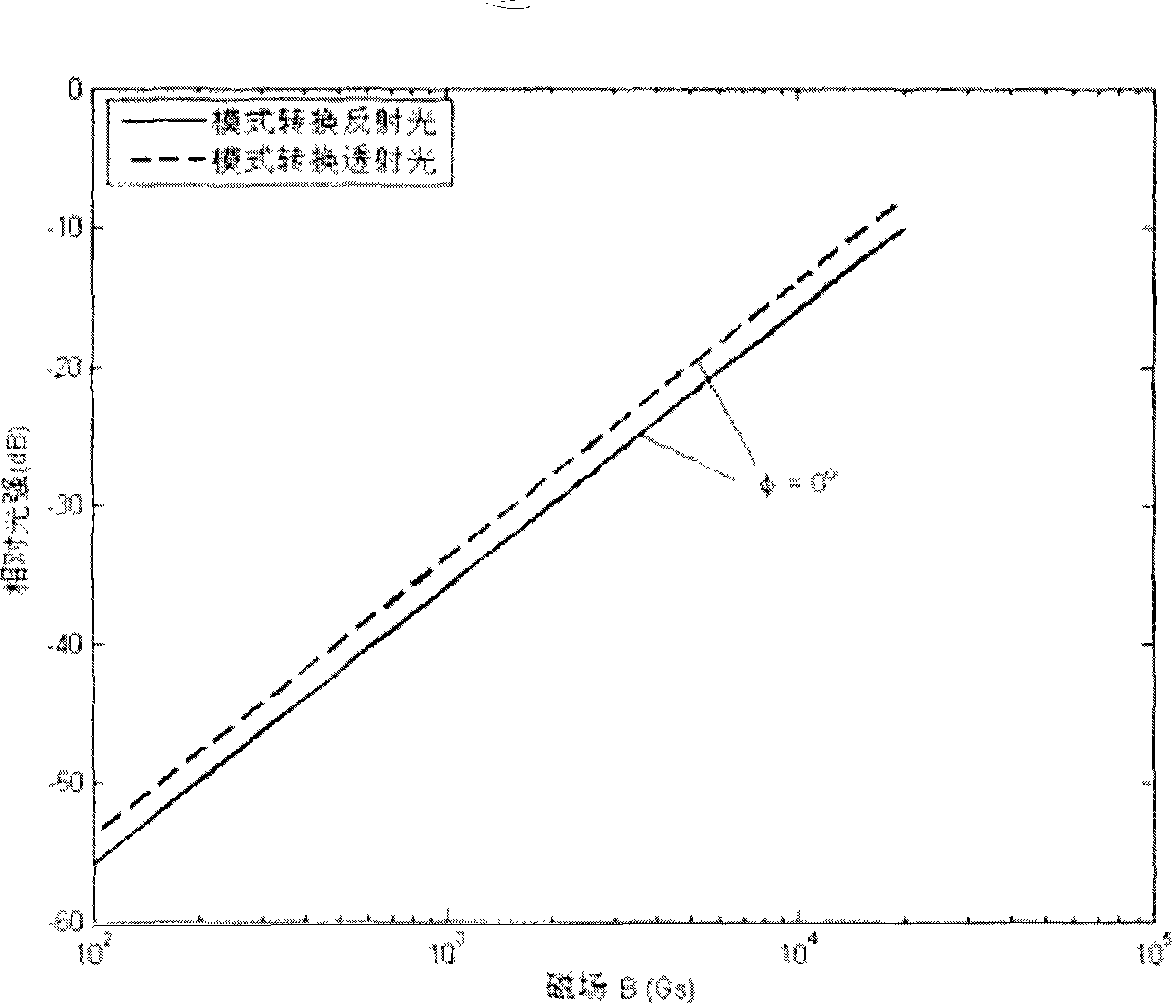
InactiveCN101509962AThe magnetic field measurement method is practicalMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesFiberLinear relationship
A method for measuring magnetic induction intensity and a device thereof belong to the technical field of fiber sensing in electronic information technology and relate to the method for measuring magnetic induction intensity and the device thereof. The invention is based on FBG structure and the magnetic-optic Faraday Effect, and the linear relationship between the relative intensity of FBG mode switching reflection light (or transmitted light) and the magnetic induction intensity B of an externally-applied magnetic field is obtained by measuring the relative intensity of a linearly polarized light with known light intensity and reflected to the mode switching reflection light (or transmitted light) by incidence after FBG under the action of a magnetic filed with known magnetic induction intensity B; and then according to the obtained linear relationship, the magnitude of the magnetic induction intensity B of the magnetic field to be measured can be determined by measuring the relative intensity of the linearly polarized light with known light intensity and reflected to the mode switching reflection light (or transmitted light) by incidence after FBG under the action of the magnetic filed with the magnetic induction intensity B to be measured. The invention has the advantages of high measuring precision, simple use and low cost, and the invention is especially suitable for measuring the size of the magnetic field in the magnetic pole of an electromagnet and for measuring the magnetic field which is generated by high-voltage current.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Micro-ring cavity gyroscope with magnetic field lock-in minimization
InactiveUS6603558B2Minimize lock-in phenomenonSmall sizeSagnac effect gyrometersSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsOptical gyroscopeFaraday effect
The invention is a compact optical gyroscope based on the Sagnac effect that combines a micro-ring cavity laser comprising a magneto-optical material and a magnetic field to circumvent the lock-in phenomenon at low rates of rotation. The invention also embodies novel processes for breaking lock-in using a transverse Faraday effect.
Owner:DELAWARE UNIV OF A DE
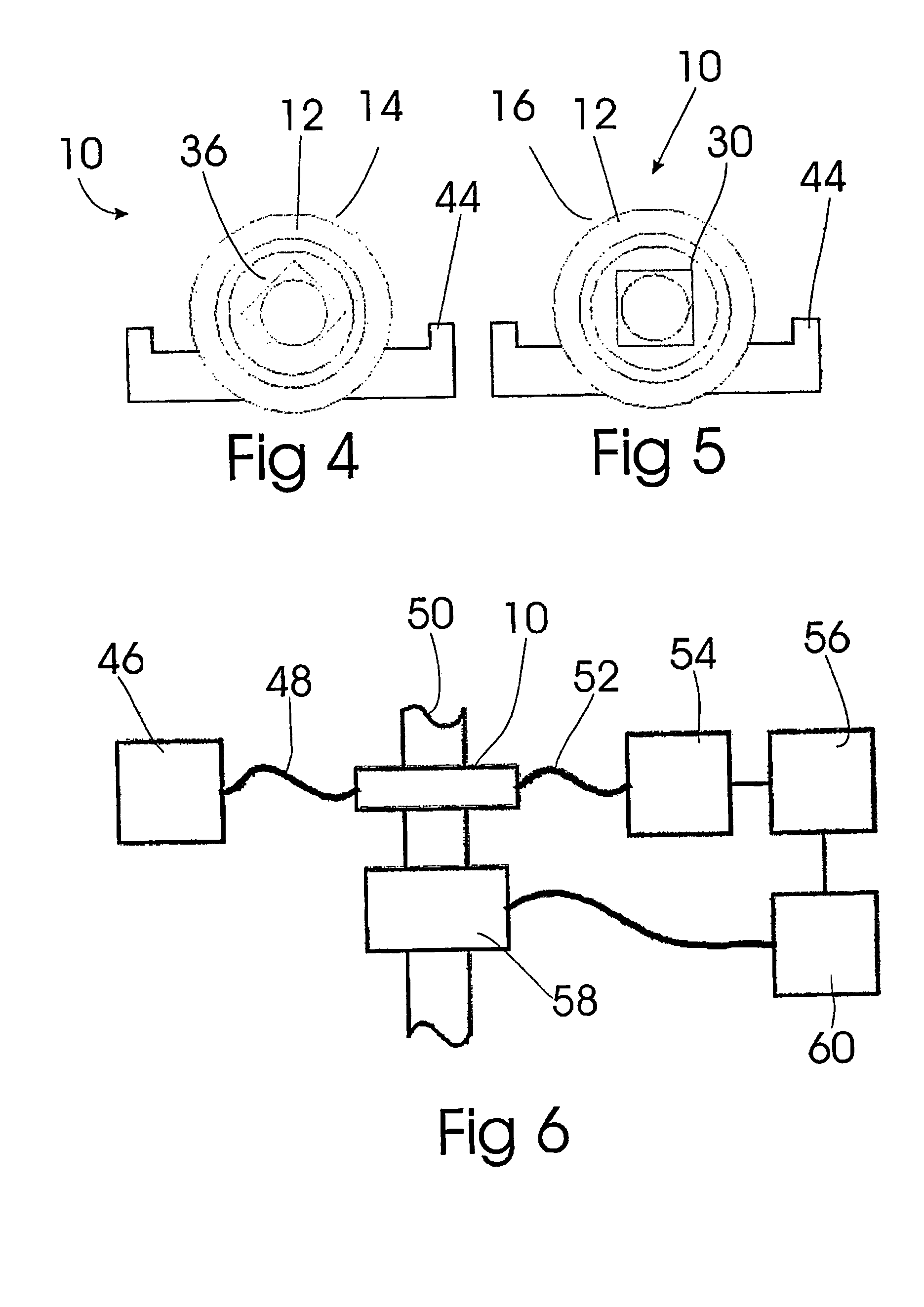
Polarization-maintaining retroreflector apparatus
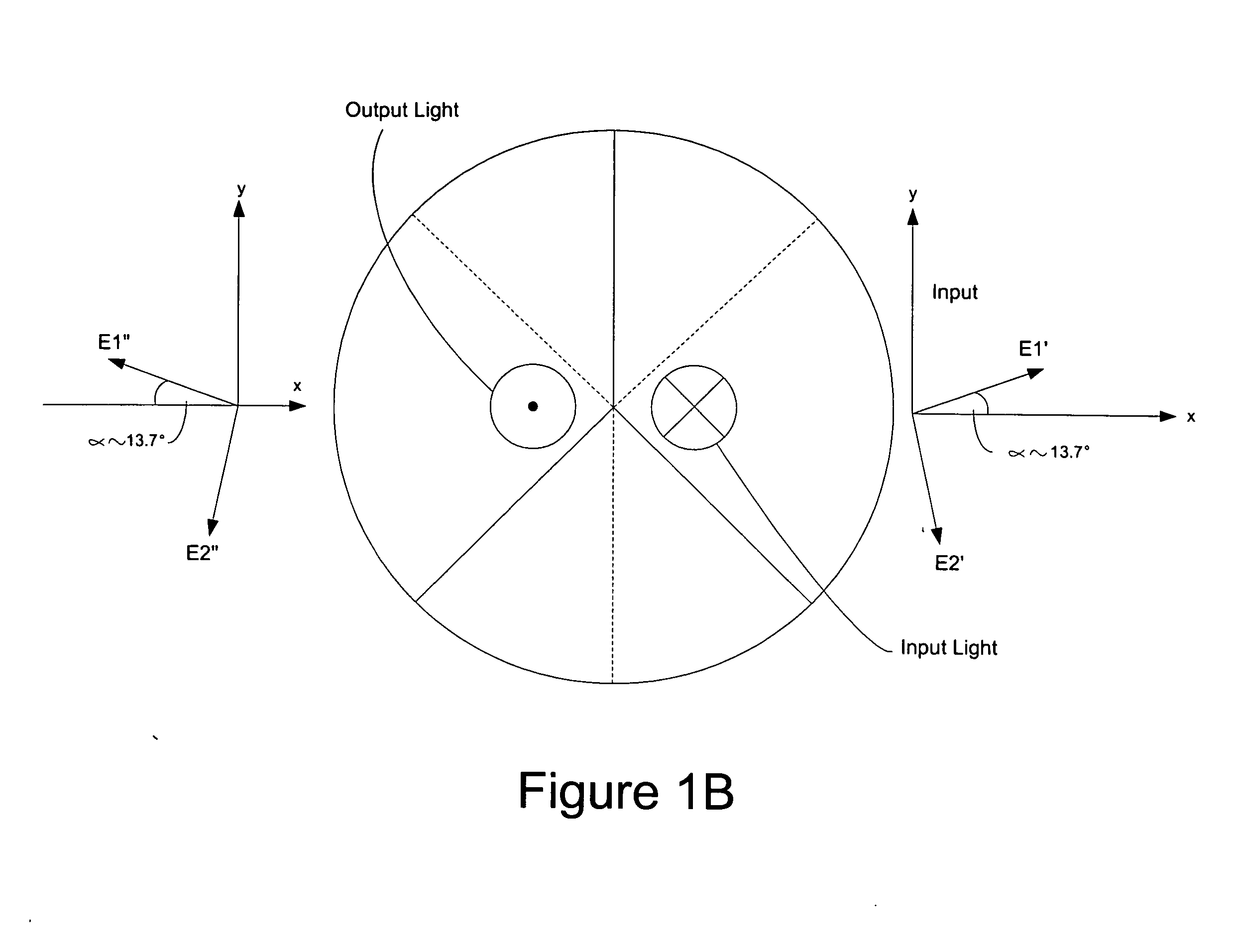
A polarization-maintaining cube corner retroreflector apparatus that provides output light having a desired polarization state. The apparatus has a cube corner retroreflector and a polarization-manipulating optical structure that provides output light having a desired polarization state. The polarization-manipulating optical structure can be one or more polarization-manipulating optical components such as a retarder, an optical rotator formed of a material having optical activity, an optical rotator formed of a material exhibiting the Faraday Effect, or some combination of these components.
Owner:AVAGO TECH ECBU IP (SINGAPORE) PTE LTD
Microporous glass waveguides doped with selected materials
The present invention concerns waveguides made from porous glass which have been doped with certain selected materials which exhibit optical properties. In the context of the invention, the selected materials are optical materials which exhibit optical activity or a Faraday effect, such as an electro-optic material, and more specifically a polymer. Devices made according to the present invention can be used as phase modulators.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
Novel power transmission line lightning stroke point locating method based on OPGW (optical fiber composite overhead ground wire) light polarization state
ActiveCN104655987AHigh positioning accuracyLow input costFault locationSingular value decompositionEngineering
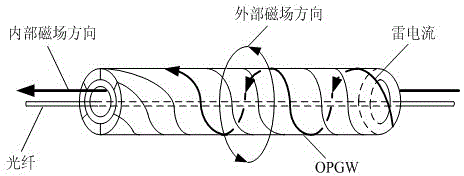
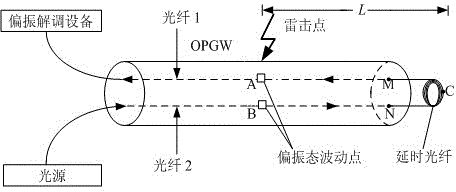
The invention relates to a power transmission line lightning stroke point fault locating method, in particular to a novel power transmission line lightning stroke point locating method based on the OPGW (optical fiber composite overhead ground wire) light polarization state. According to the method, fault points are located accurately by extracting the moment at which polarization state mutation information of transmission light in OPGWs at lightning stroke points is transmitted to polarization demodulation equipment with an iteration SVD (singular value decomposition) algorithm in combination with a generalized mathematical morphology method, a wavelet analysis method and the like through lightning stroke OPGW tests. According to the method, the Faraday effect is applied to power transmission line fault location, the effect that the location accuracy is interfered by factors such as transition resistance, line parameters, system running modes, traveling wave transmission dispersion, traveling wave speeds and the like in traditional fault location methods is avoided, and the location accuracy is very high. All that is required is to perform monitoring at two ends of a line during location, so that the input cost is reduced.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Compact narrow band imaging system
InactiveUS8314612B1Polarising elementsMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesThermal isolationPolarizer
A compact narrow band imaging system includes a vapor cell having a gas that receives and transmits light in accordance with the Faraday effect. A magnetic source is provided for applying a magnetic field to the vapor cell. Crossed polarizers are disposed before and after the vapor cell creating a Faraday optical filter. The only light that passes through the filter is light within a narrow band near the absorption peaks of the vapor. Other optical elements of the imaging system including filters, image detectors, electron multipliers, signal digitizers, and heat filters are co-located within the imaging system's common thermal isolation container to provide improved performance. The compact system is suitable for wide area surveillance, including daylight surveillance for combustion sources such as forest fires and missile exhaust.
Owner:RODGERS WAYNE EUGENE +1
Thin film type all-fiber current transformer with temperature compensation
InactiveCN104459267AEliminate errorsHigh measurement accuracyCurrent/voltage measurementVoltage/current isolationFiberFiber coupler
The invention discloses a thin film type all-fiber current transformer with temperature compensation, and belongs to the technical field of optical current sensors. The problem that a fiber current transformer is likely to be influenced by temperature and vibration, and measurement accuracy is low is solved. According to the thin film type all-fiber current transformer, light emitted by a light source passes through a circulator, a first polarization-maintaining fiber coupler and a Y-waveguide in sequence, the Y-waveguide outputs two paths of light, one path of light passes through a welding branch, rotates by 90 degrees and enters a second polarization-maintaining fiber coupler, the other path of light passes through a compensating coil and enters the second polarization-maintaining fiber coupler, the two paths of light are coupled into one path to be input into a 1 / 4 wave plate by the second polarization-maintaining fiber coupler, the 1 / 4 wave plate outputs left rotating light and right rotating light, a Faraday effect happens in a sensor fiber, and then the left rotating light and the right rotating light return to the first polarization-maintaining fiber coupler. In the return process, the original light returned through the welding branch is input into the compensating coil, the other path of light is input into a processing module through the welding branch and the first polarization-maintaining fiber coupler, and the processing module processes the input light to obtain a current value to be measured. The thin film type all-fiber current transformer is used for measuring the current value.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Fiber-optic sensor and method
InactiveUS20160377660A1Reduce impactAccurate measurementCurrent/voltage measurementElectrical testingEngineeringFaraday effect
A fiber optic sensor and related method are described, with the sensor including a cross-coupling element in the optical path between a polarizing element and a sensing element, but separated from the sensing element itself; with the cross-coupling element generating a defined cross-coupling between the two orthogonal polarization states of the fundamental mode of a polarization maintaining fiber guiding light from the light source to the sensing element thus introducing a wavelength-dependent or temperature-dependent sensor signal shift to balance wavelength-dependent or temperature-dependent signal shifts due to other elements of the sensor, particularly signal shifts due to the wavelength dependence of the Faraday effect or the electro-optic effect constant.
Owner:HITACHI ENERGY SWITZERLAND AG
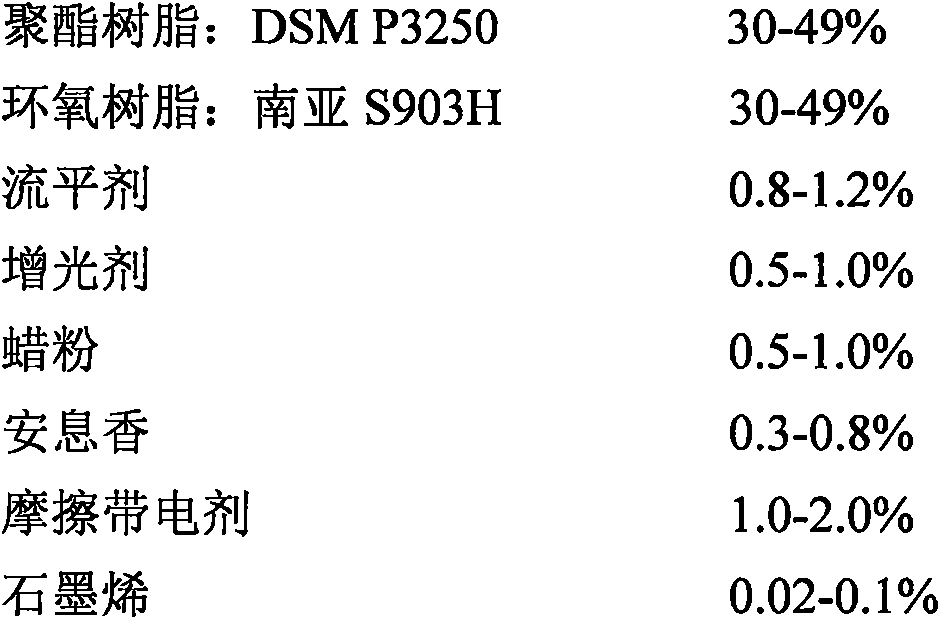
Graphene transparent powder coating for tribo gun to spray MDF plate
InactiveCN106634468AUniform thicknessNo powder accumulationPretreated surfacesPowdery paintsEpoxyWax
The invention relates to a transparent powder coating, specifically to a graphene transparent powder coating for tribo gun to spray an MDF plate. The graphene transparent powder coating is prepared from the following raw materials in percentages: 30 to 60% of polyester resin, 24 to 48% of epoxy resin, 0.8 to 1.2% of a leveling agent, 0.5 to 1.0% of a gloss enhancer, 0.5 to 1.0% of wax powder, 0.3 to 0.8% of benzoin, 1.0 to 2.0% of a triboelectric charging additive and 0.02 to 0.1% of graphene. According to the invention, powder coating is realized by using a tribo gun through addition of the triboelectric charging additive; by adopting a method of spraying a powder coating with the tribo gun, no Faraday effect is generated; meanwhile, no free ions are generated; charged powder ions may not mutually exclude; a formed coatingn film has good leveling properties; and through addition of graphene, the transparent powder coating can be improved in glossiness, adhesive force, water resistance, conductivity, flexibility, etc.
Owner:燕园众欣纳米科技(北京)有限公司
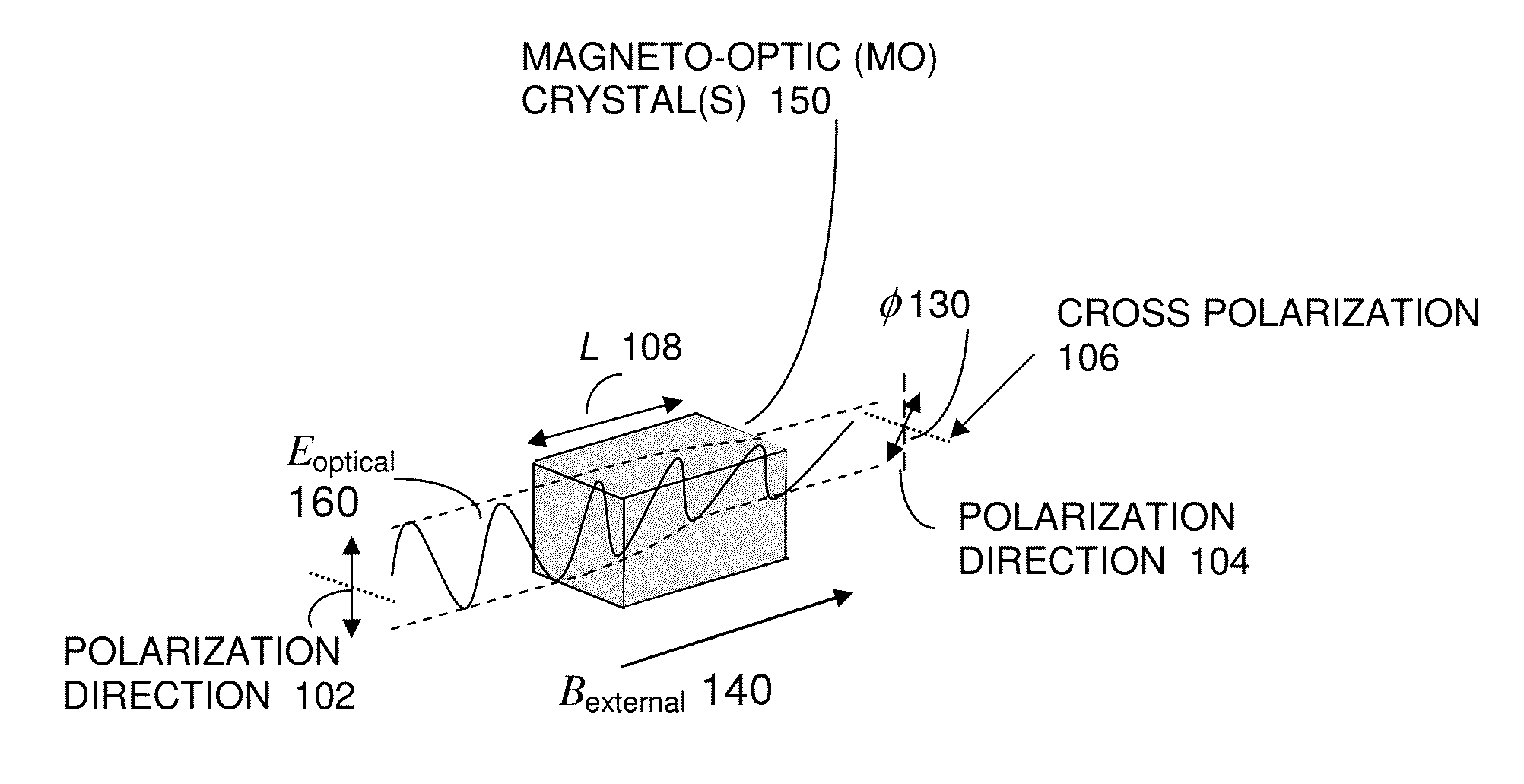
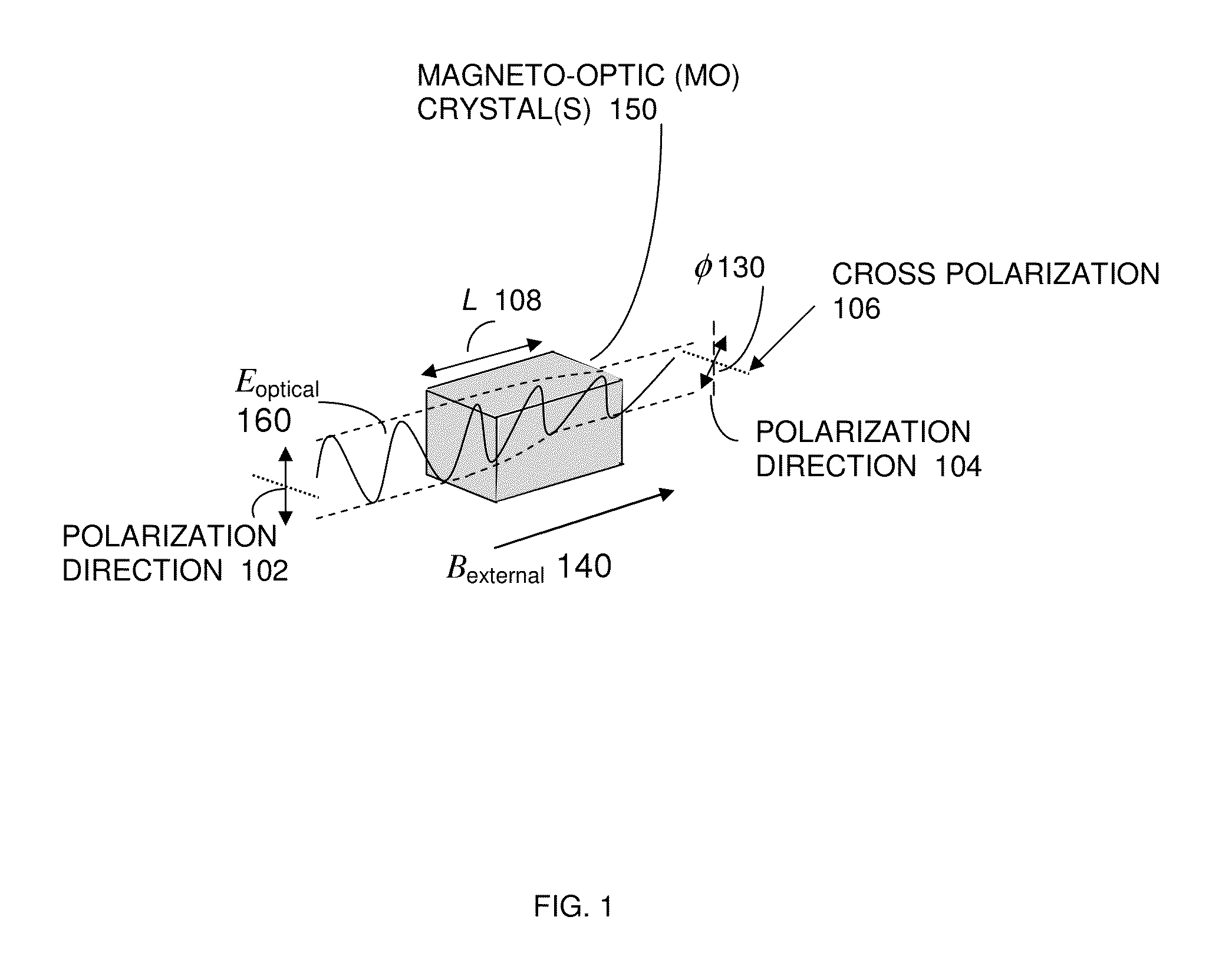
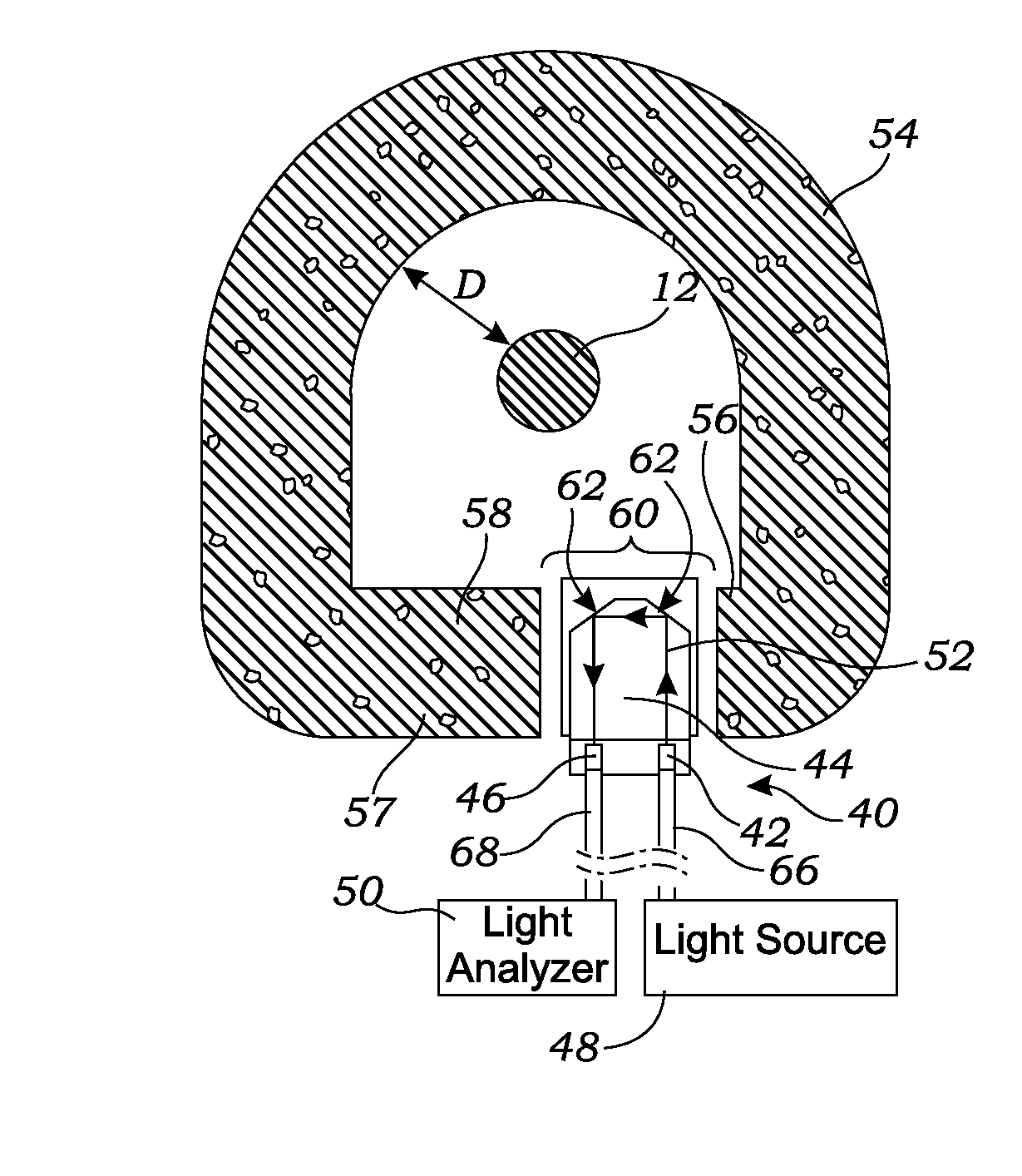
Apparatus method and system of an ultra sensitivity optical fiber magneto optic field sensor
InactiveUS20130038324A1Magnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesFaraday effectUltra sensitive
An apparatus and system, capable of measuring the magnitude and direction of magnetic fields including an ultra-sensitive, wideband magneto optic (MO) sensor having magneto-optic crystals is disclosed herein. The sensor exploits the Faraday Effect and is based on a polarimetric technique. An ultra sensitivity optical-fiber magneto-optic field sensor measures a magnetic field with minimal perturbation to the field, and the sensor can be used for High-power microwave (HPM) test and evaluation; Diagnosis of radar and RF / microwave devices; Detection / measurement of weak magnetic fields (e.g., magnetic resonance imaging); Characterization of very intense magnetic fields (>100 Tesla, for example rail gun characterization); Detection of very low-frequency magnetic fields; Characterization of a magnetic field over an ultra broad frequency band (DC—2 GHz); Submarine detection; and Submarine underwater communication.
Owner:GOVT OF UNITED STATES OF AMERICA REPRESENTED BY SEC OF THE NAVY CHIEF OF NAVAL RES ONR NRL
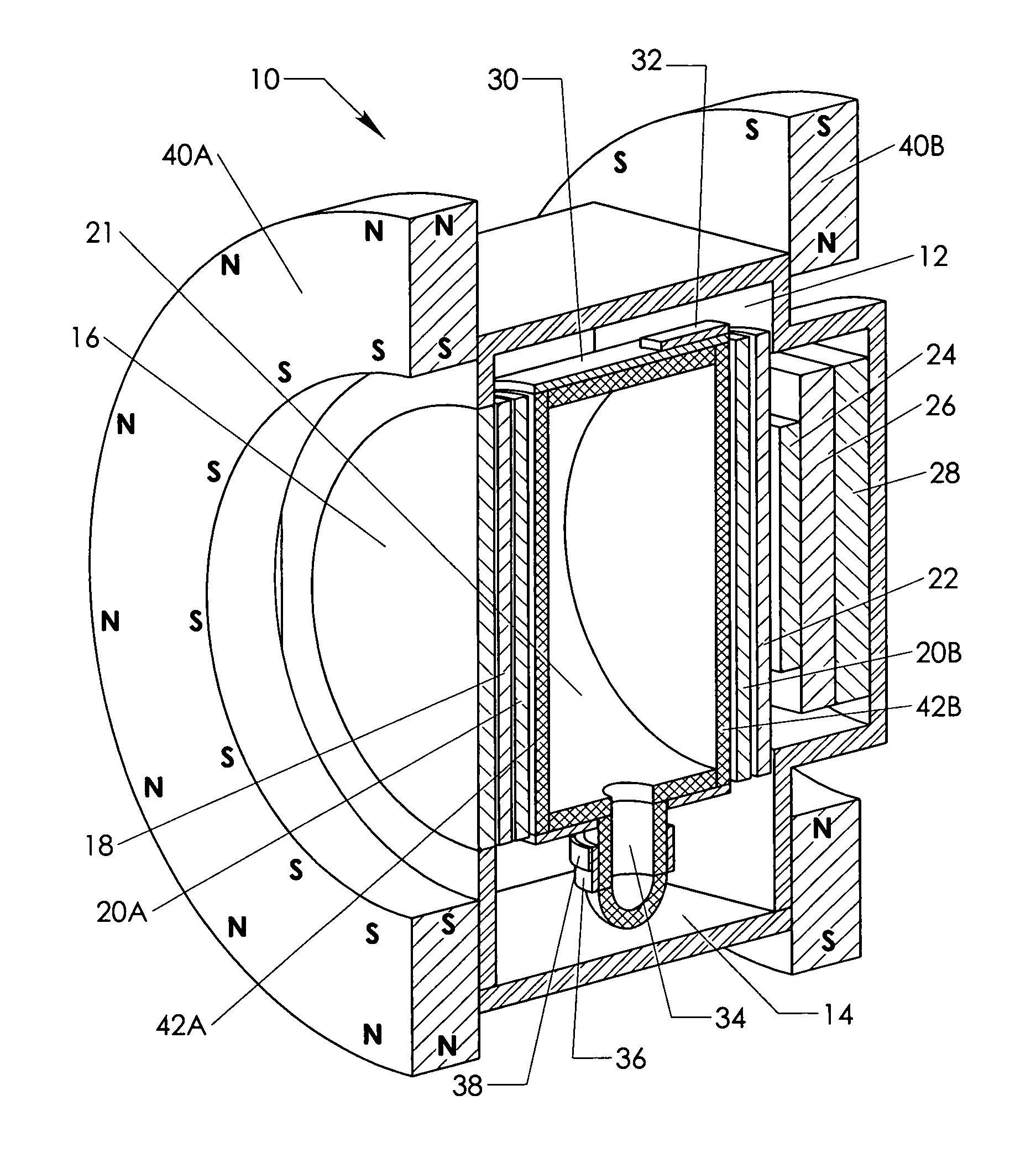
Magneto-Optic Remote Sensor For Angular Rotation, Linear Displacements, And Evaluation Of Surface Deformations
InactiveUS20070057668A1Enhance aircraft safetyImprove securityPolarisation-affecting propertiesMagnetic property measurementsTemporal changeAngular rotation
A system and method to detect angular rotation, linear displacement and / or surface deformations is presented. The method is based on the ability of a linear polarized light to interact with magnetic materials and to change its polarization angle due to Faraday effect. A basic structure of the system consists of a magneto-optic (MO) film with a two-domain structure and a single domain wall which are generated by gradient magnetic field produced by opposite polarity permanent magnets placed near the film. An AC magnetic field applied perpendicular to the MO film surface causes the magnetic domain wall in the MO film to oscillate at the same frequency. This leads to a detected output AC modulated signal. By measuring the temporal changes in this signal, information on angular rotation, linear displacement and / or surface deformation can be obtained.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Ultra narrowband atomic filter and filtering method realization method
ActiveCN108539569AEliminate the effects ofActive medium materialNon-linear opticsFrequency stabilizationOscillator strength
The invention discloses an ultra narrowband atomic filter and a filtering method realization method. In the technical scheme, the velocity transfer effect of atoms is used to transfer an atomic highly-excited state transition spectrum line with weak oscillator strength to an atomic lowly-excited state transition spectrum line with strong oscillator strength, Faraday effects are combined, magneto-optic rotation happens to detection light through the atomic filter, and target light signals corresponding to pump laser are outputted. The pump light uses a saturated absorption spectrum for frequency stabilization, and the size of a magnetic field can be strictly controlled by changing the magnitude of current. Rubidium bubbles are placed in a magnetic shielding box to eliminate influences of the magnetic field. Compared with the traditional atomic filter, the atomic filter is narrower in passband bandwidth and better in filtering effects.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SPACE TECH
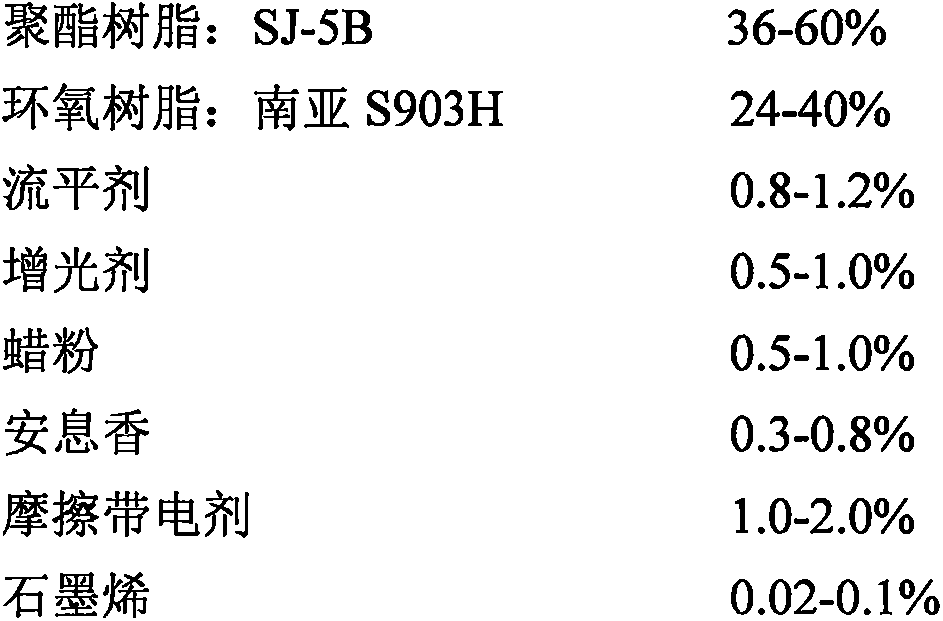
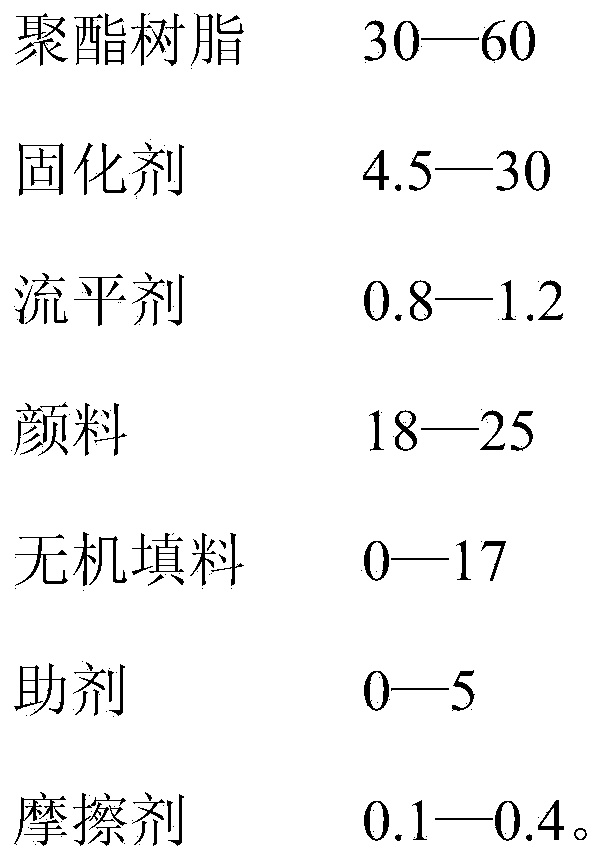
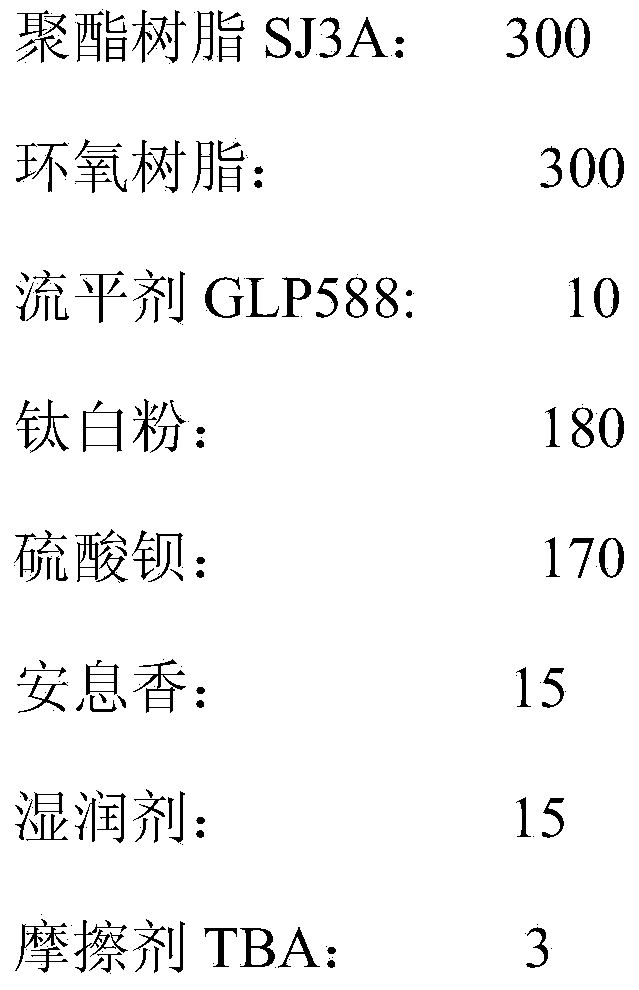
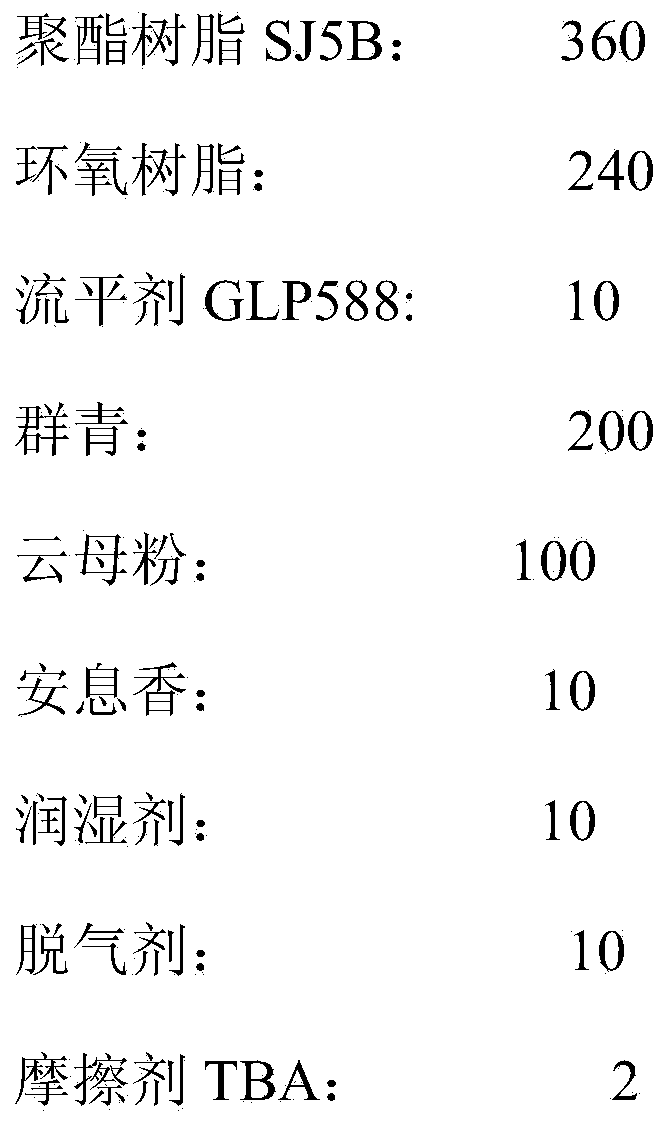
Powder coating
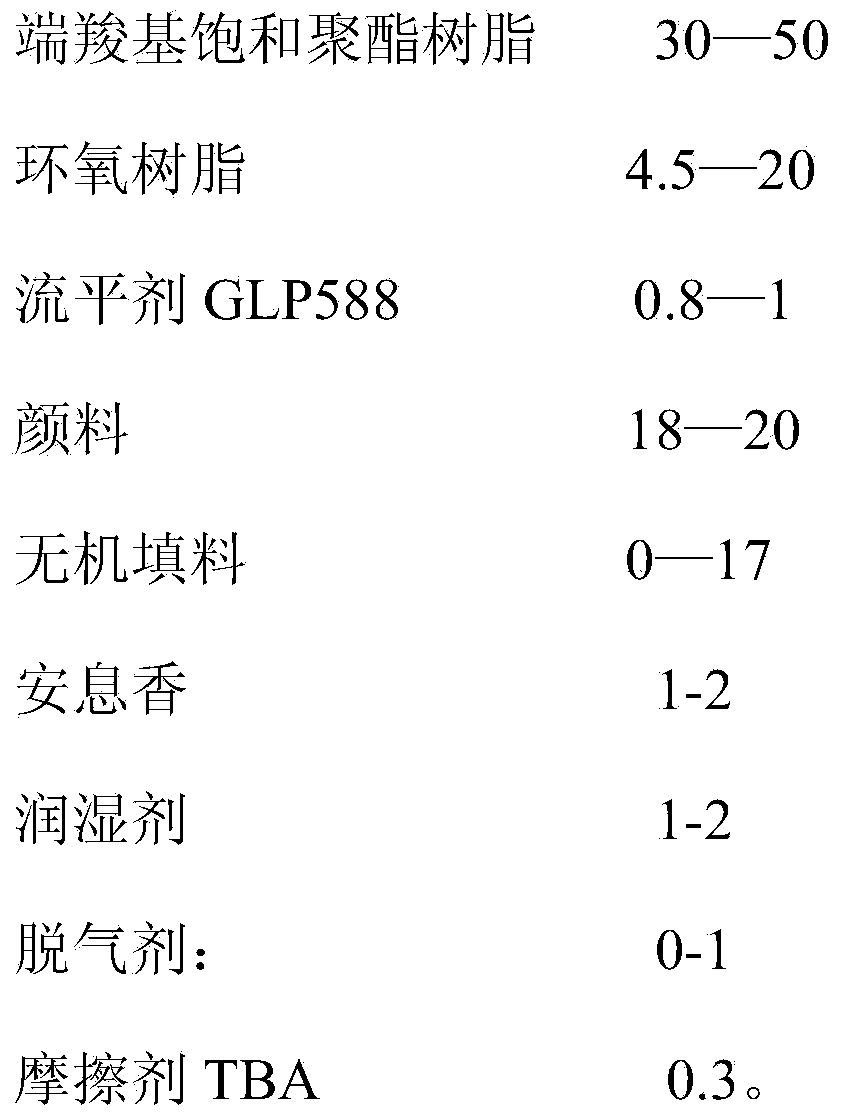
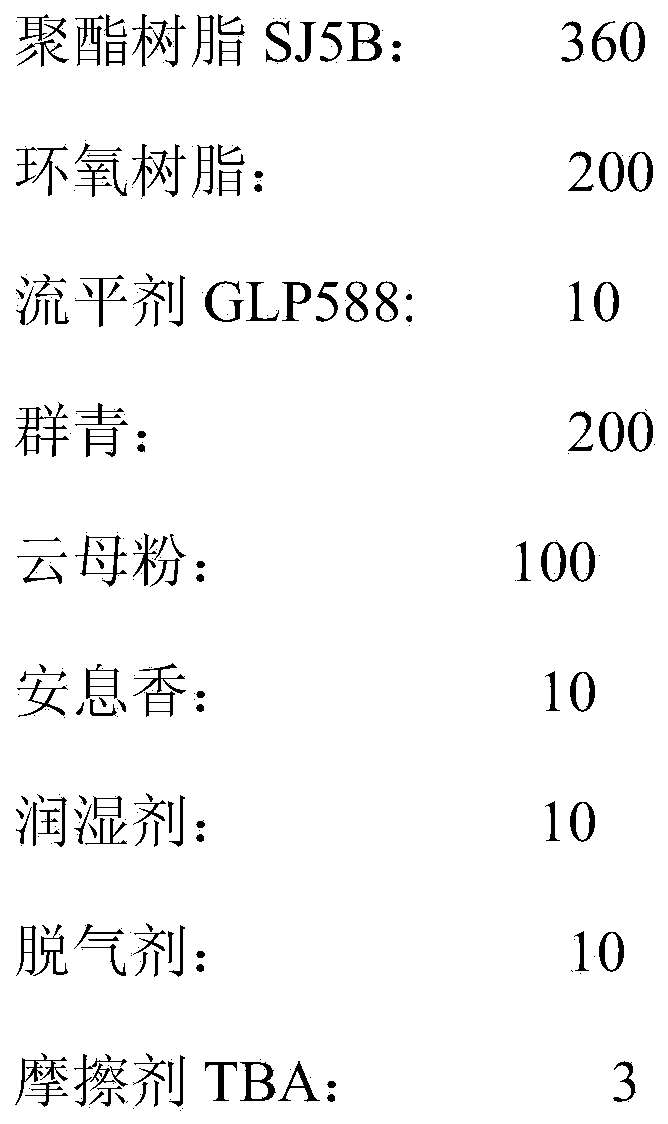
InactiveCN104341982AImprove the powder rateAvoid the Faraday EffectPowdery paintsEpoxy resin coatingsEpoxyDielectric
The invention discloses a powder coating, comprising the following substances in parts by weight: 30-50 parts of end carboxyl saturated polyester resin, 4.5-20 parts of epoxy resin, 0.8-1 part of a flatting agent GLP588, 18-20 parts of a pigment, 0-17 parts of an inorganic filler, 1-2 parts of benzoin, 1-2 parts of a wetting agent, 0-1 part of a degassing agent and 0.3 part of an abrasive TBA. Through introduction of the abrasive, a large gap is formed between the powder coating and a fabrication material (high-polymer PTFE material) of a pipe wall of a friction gun and a friction rod in dielectric constant in the friction spraying process; the powder coating is prompted to be perfectly adsorbed on a work-piece after rubbing with the material in the friction gun to be electrified under the power of dry airflow; through a frictional electrification manner, the Faraday effect generated by a corona field is avoided; every corner of the work-piece can be completely covered by the powder coating; meanwhile, relatively to electrostatic spraying, the powdering rate of the work-piece is relatively high; the solidified film is relatively excellent in flatting.
Owner:ANHUI SHENJIAN NEW MATERIALS
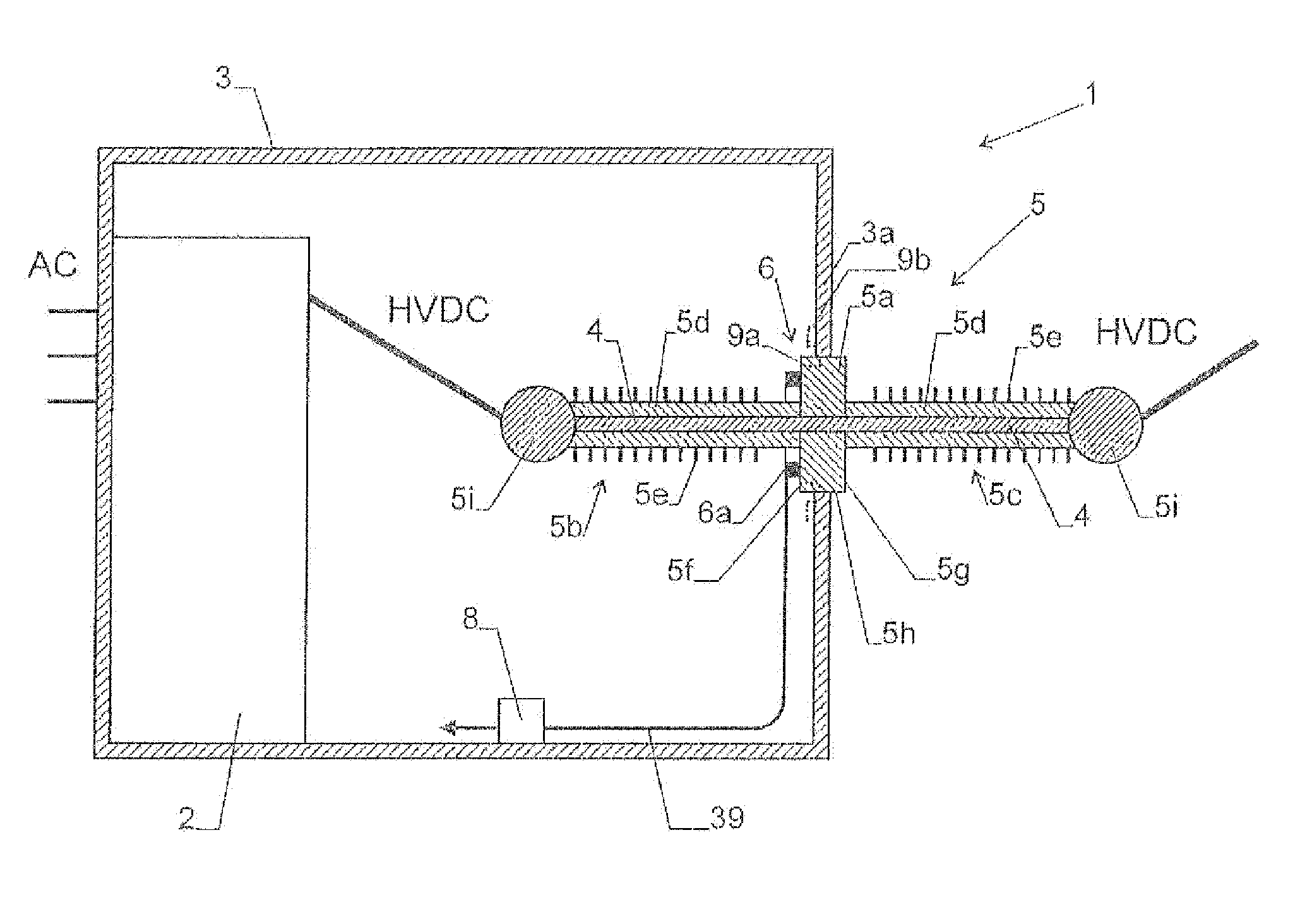
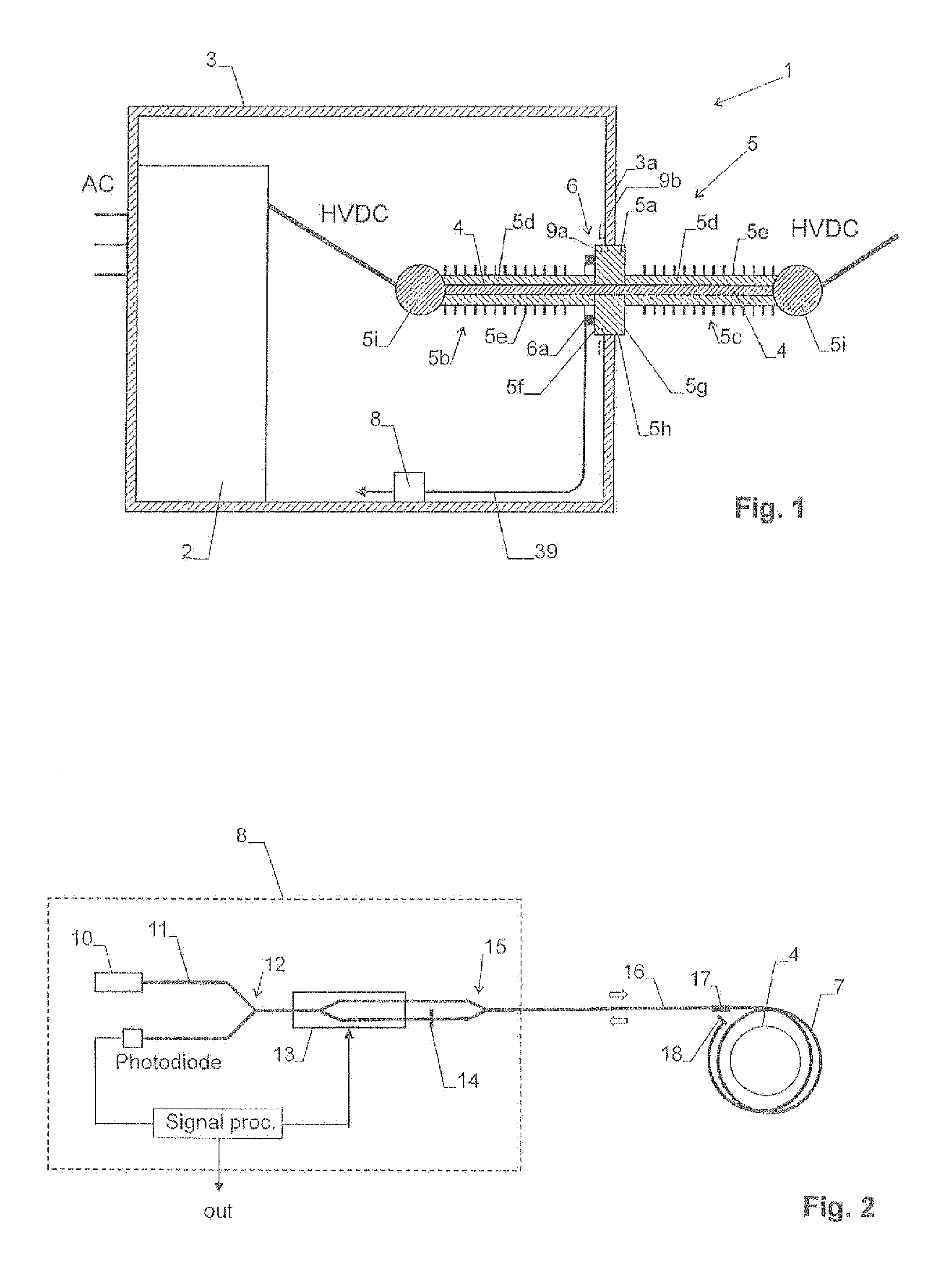
High voltage ac/dc or dc/ac converter station with fiber-optic current sensor
InactiveUS20110122654A1Easy to reachSwitchgear arrangementsBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsFiberDc current
DC current in a high voltage AC / DC or DC / AC converter station can be measured via the Faraday effect in one or more loops of an optical sensing fiber located at the base of a bushing extending through a wall of the hall. This arrangement can exploit the base of the bushing being at ground potential, which can simplify mounting work and maintenance.
Owner:ABB POWER GRIDS SWITZERLAND AG
All optical fiber nonreciprocal device and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an all optical fiber nonreciprocal device which comprises an optical fiber used for transmitting light and a reflecting film layer used for reflecting light, wherein the reflecting film layer is coated on the optical fiber and is located at a first light emitting window of the optical fiber, and an inclined fiber bragg grating is engraved on the core of the optical fiber; when incident light enters from one end of the optical fiber and passes through the fiber bragg grating, one part is emitted by the transmission of the fiber bragg grating, the other part is diffractedby the fiber bragg grating and then is reflected after being emitted by a first light outlet hole, and further is emitted after interfering with light transmitting the fiber bragg grating along an incidence direction; the incident light enters from the other end of the optical fiber and pass through the fiber bragg grating, one part is emitted by the transmission of the fiber bragg grating, and the other part is diffracted by the fiber bragg grating and then is emitted from a second light outlet hole; and transmission nonreciprocity of two directions is realized. The nonreciprocal device provided by the invention is simple and firm in structure, easy to produce, convenient for being integrated with other photoelectric devices, and capable of effectively solving the problem that a conventional optical fiber nonreciprocal device is limited by a magnetic field in a Faraday effect.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
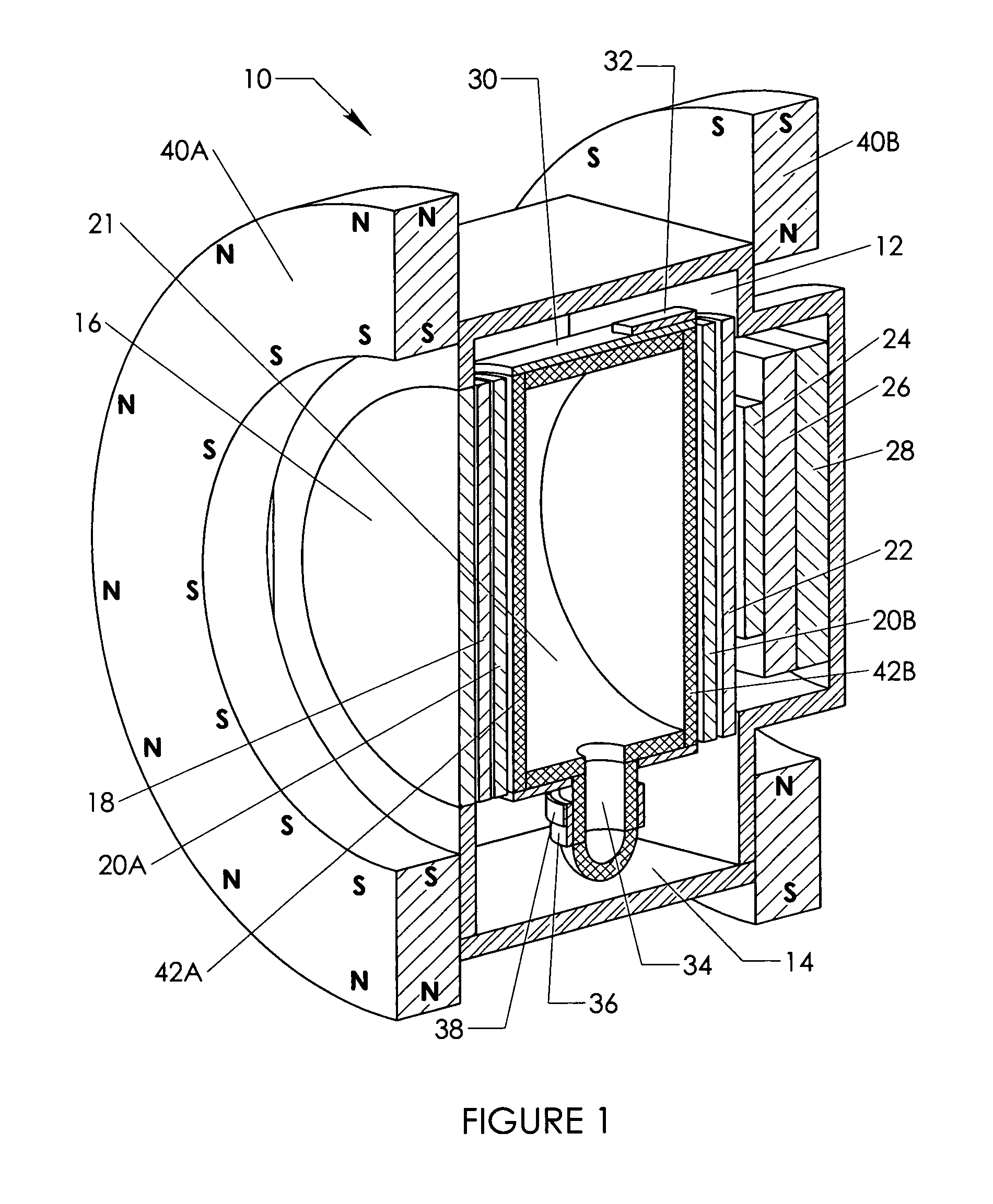
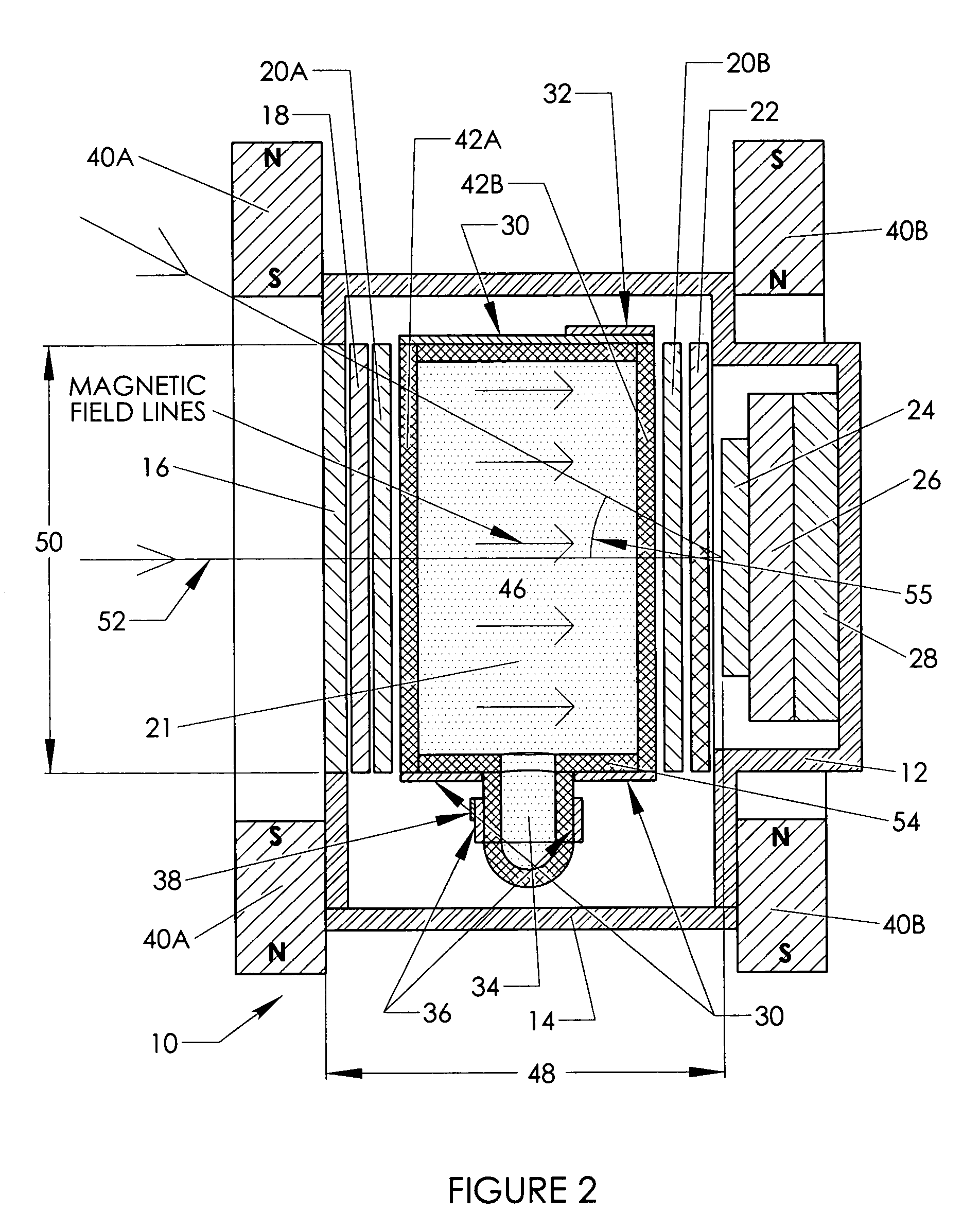
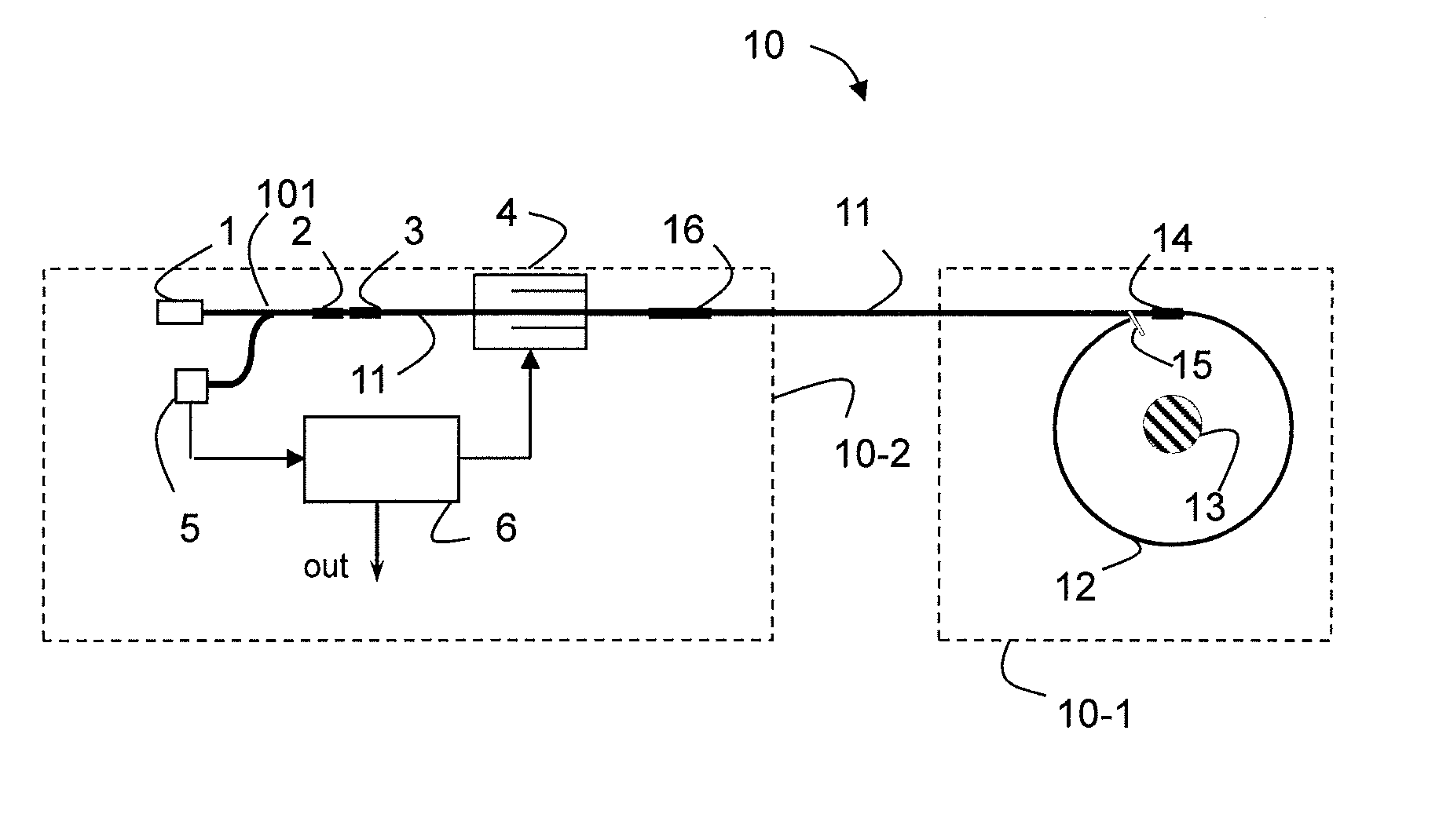
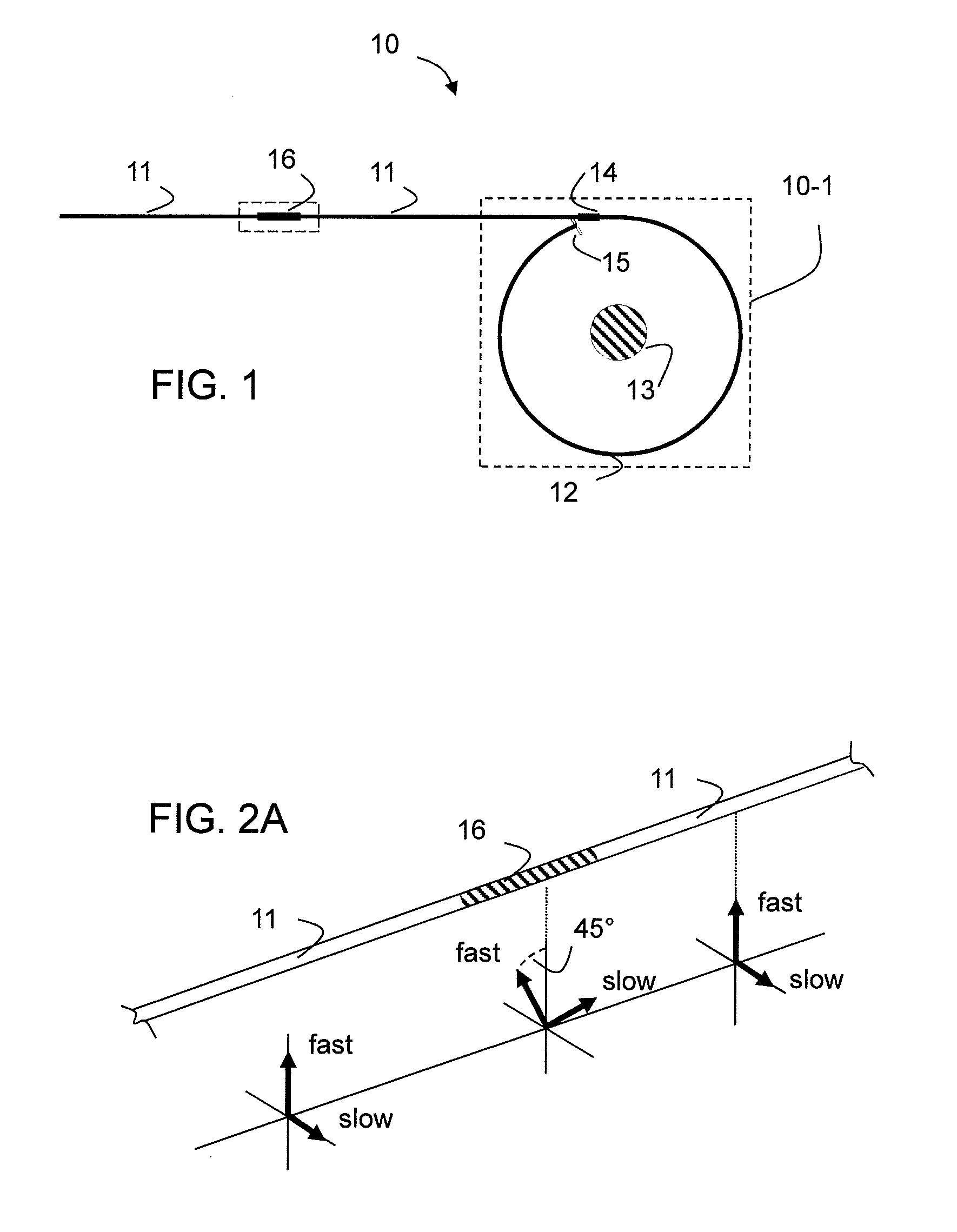
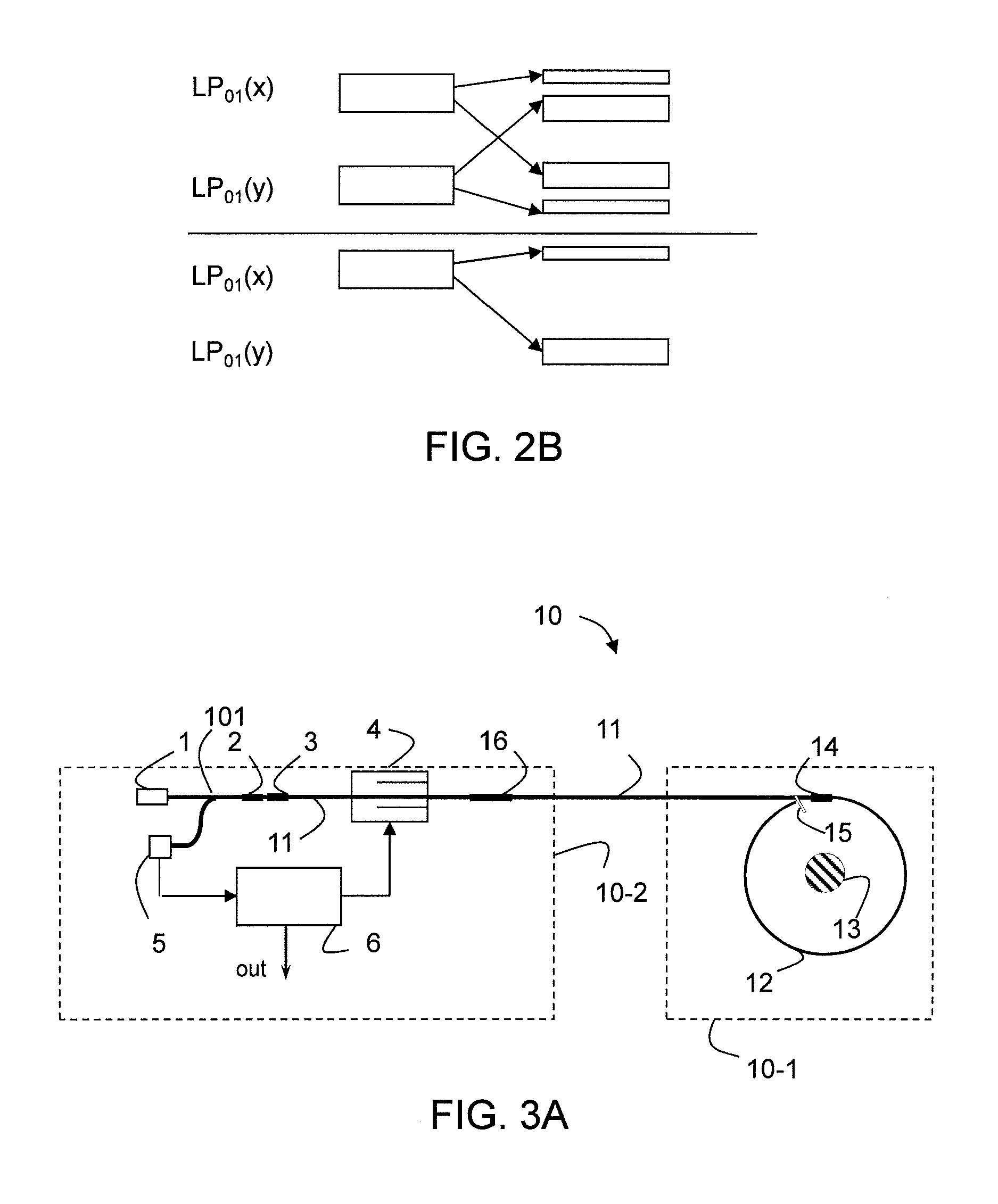
Faraday effect current sensor
ActiveUS20100271004A1Exclude influenceMagnetic measurementsCurrent/voltage measurementLight guideCurrent sensor
The present invention relates to a Faraday sensor assembly comprising a first light guiding element adapted to guide electromagnetic radiation along a first propagation direction, and a second light guiding element adapted to guide electromagnetic radiation along a second propagation direction, the second propagation direction being essentially oppositely arranged relative to the first propagation direction. The Faraday sensor assembly further comprises a measurement region arranged between the first and second light guiding elements, the measurement region being adapted to receive an electrically conducting element having, in the measurement region, its primary extension direction in a direction being essentially perpendicular to the first and second propagation directions. The present invention further relates to methods and systems for stabilizing output signal from the sensors, and to methods and systems for processing signals from the sensor assembly.
Owner:LANDIS & GYR OY
All-fiber current monitoring device based on Faraday effect
InactiveCN101793916ALess susceptible to electromagnetic interferenceSmall electromagnetic interferenceCurrent/voltage measurementVoltage/current isolationFiberPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention discloses an all-fiber current monitoring device based on a Faraday effect, which relates to the field of current monitoring and solves the problems of inaccurate current monitoring results because of low accuracy rate of light beam deflection judged by traditional current monitoring equipment by using a digital signal and high economic cost by using two photo detectors. The device comprises a light source system, a half-wave plate, a first fiber mutual inductor, a second fiber mutual inductor, a first semi-reflecting semi-transmitting mirror, a second total reflection mirror and a photo detector, wherein the light source system emits a first light beam to the first fiber mutual inductor and a first polarized light output by the first fiber mutual inductor is input to the photo detector through the first semi-reflecting semi-transmitting mirror; the light source system further emits a second light beam, the second light beam is emitted to the second fiber mutual inductor after being transmitted through the half-wave plate, a second polarized light output by the second fiber mutual inductor is input to the first semi-reflecting semi-transmitting mirror through the second total reflection mirror and the first semi-reflecting semi-transmitting mirror outputs reflected lights to the photo detector. The invention is applied to current monitoring.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
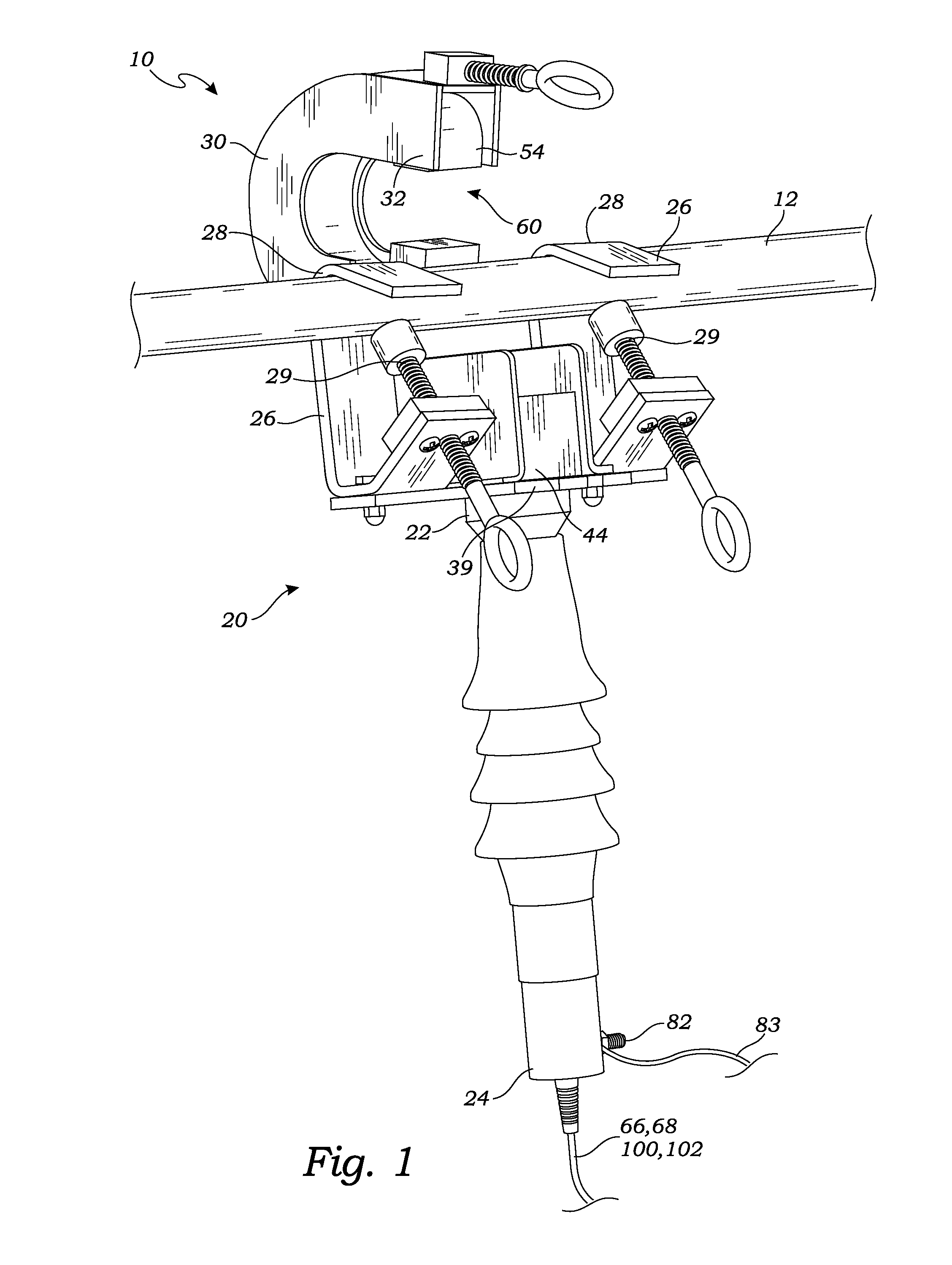
Optical sensor assembly for installation on a current carrying cable
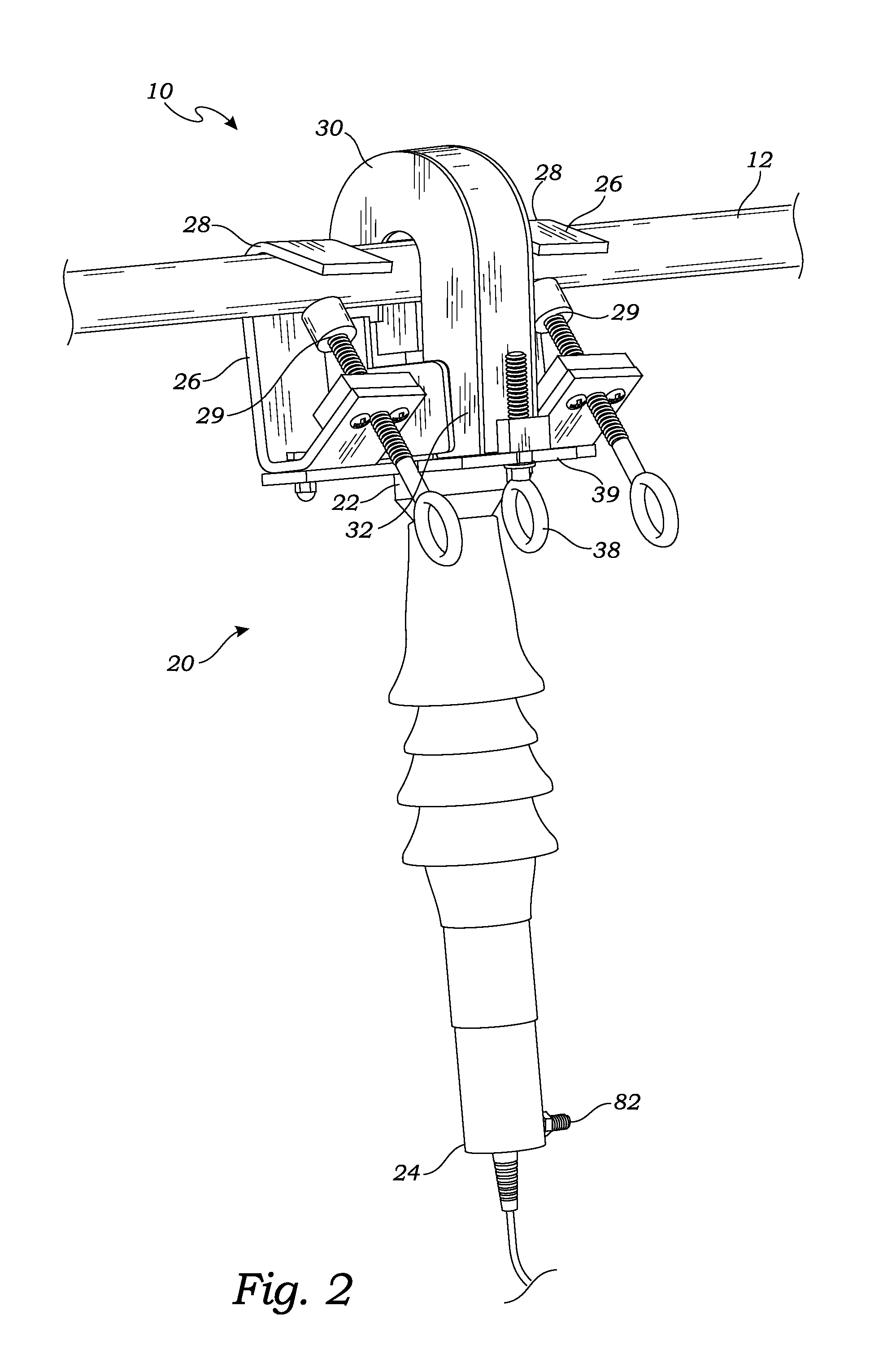
ActiveUS20130033267A1Electrical measurement instrument detailsDigital variable/waveform displayElectricityCurrent sensor
An optical sensor assembly, for installation on a current carrying cable, senses the current in the cable and provides an electrical output indicating the current. To sense the current, a magnetic concentrator is placed in close proximity to the cable and creates a magnetic field representing current in the cable. An optical current sensor, within the created magnetic field, exposes a beam of polarized light to the magnetic field. The beam of polarized light is rotated thereby, by Faraday effect, according to the current in the cable. The amount of rotation is analyzed and converted to electrical signals to portray the current in the cable. The electrical signals may be processed, evaluated and analyzed to provide one or more of several elements of quality of the current in the cable.
Owner:MICATU
Powder coating sprayed through friction gun
InactiveCN104277683AImprove the powder rateAvoid the Faraday EffectPowdery paintsPolyester coatingsAdjuvantMetallurgy
The invention discloses a powder coating sprayed through a friction gun. The powder coating comprises the following substances in parts by weight: 30-60 parts of polyester resin, 4.5-30 parts of curing agent, 0.8-1.2 parts of flatting agent, 18-25 parts of pigment, 0-17 parts of inorganic filler, 0-5 parts of adjuvant and 0.1-0.4 part of friction agent. Due to the introduction of the friction agent, a great difference between dielectric constants of the powder coating and a material (polymer PTFE material) for preparing the pipe wall and a friction rod of the friction gun is generated in the frictional spraying process, so that the powder coating can be perfectly adsorbed on a workpiece after being electrified by virtue of friction with the material in the friction gun under the drive of dry airflow; in addition, the frictional electrification way is adopted, so that the Faraday effect generated by a corona field is avoided, and all corners of the workpiece can be completely coated by the powder coating. Meanwhile, compared with an electrostatic spraying way, the powder coating has the advantages that the powdering rate of the workpiece is higher, and a cured coating film is more excellent in flatting effect.
Owner:ANHUI SHENJIAN NEW MATERIALS
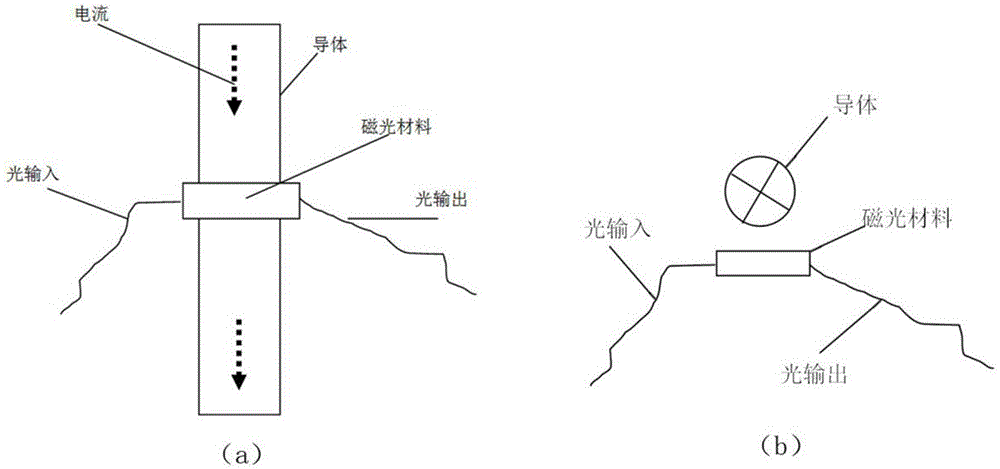
Device and method for measuring conductor current through employing magneto-optic materials
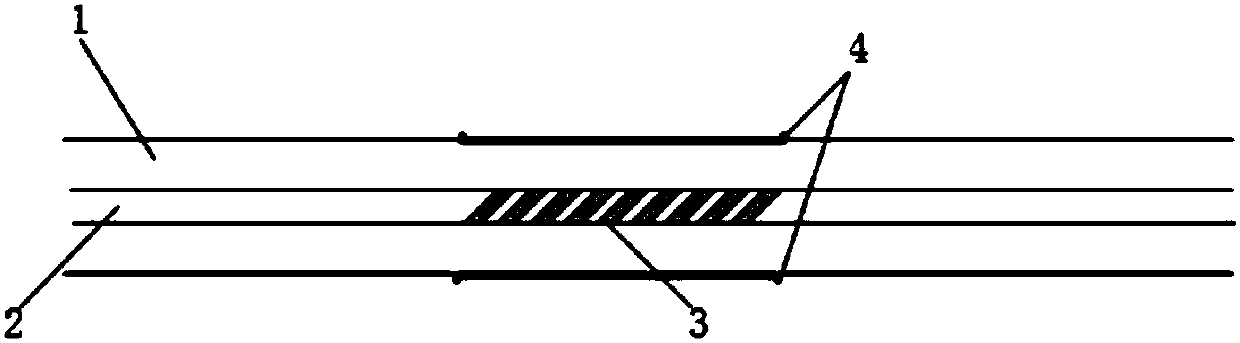
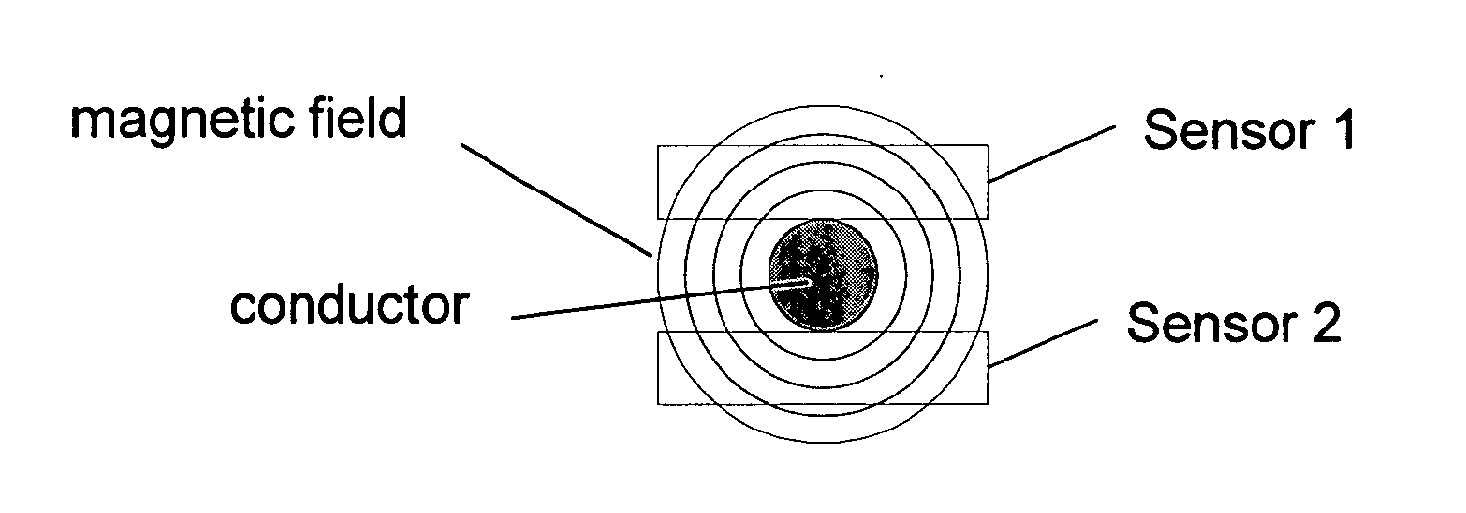
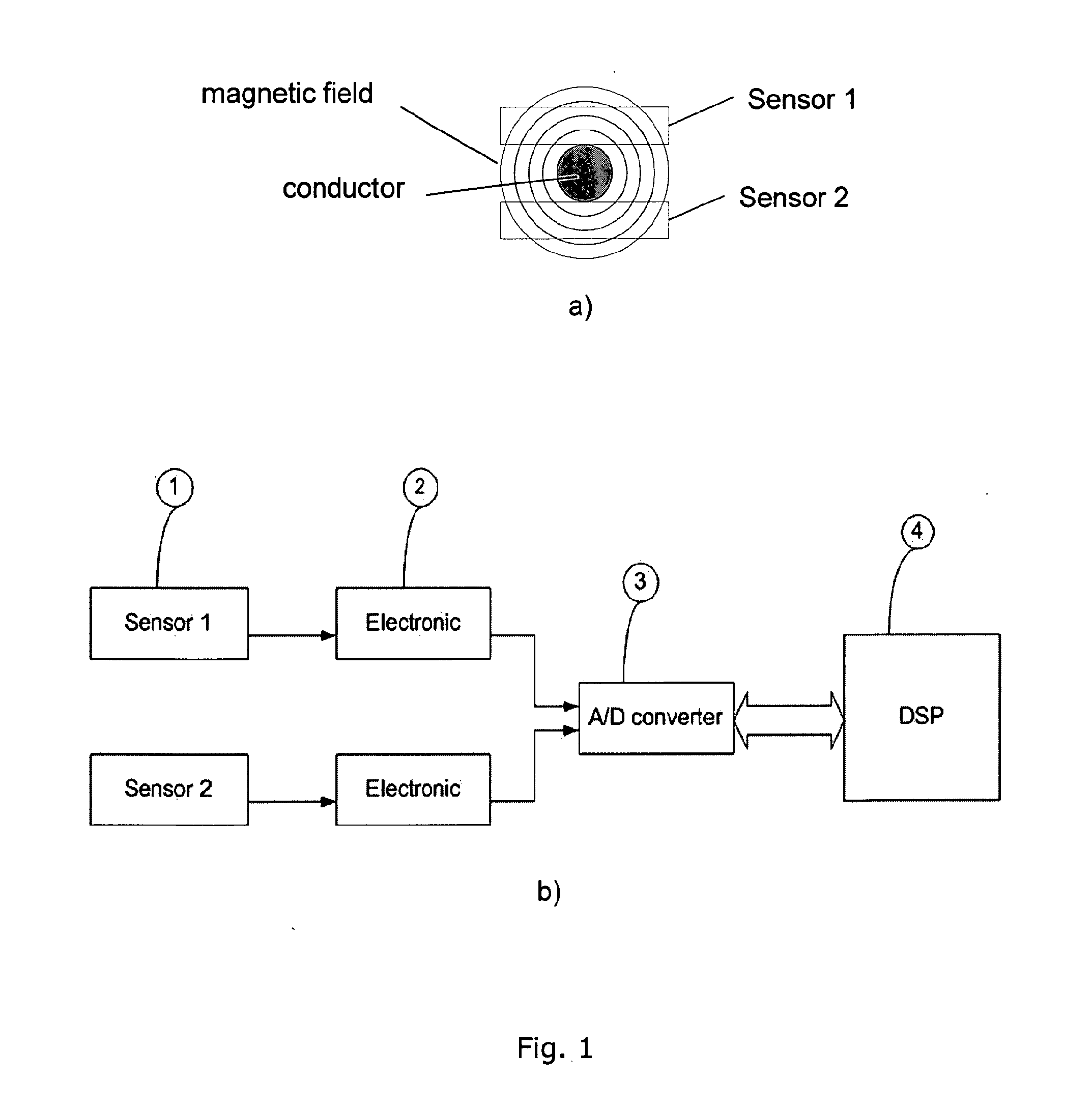
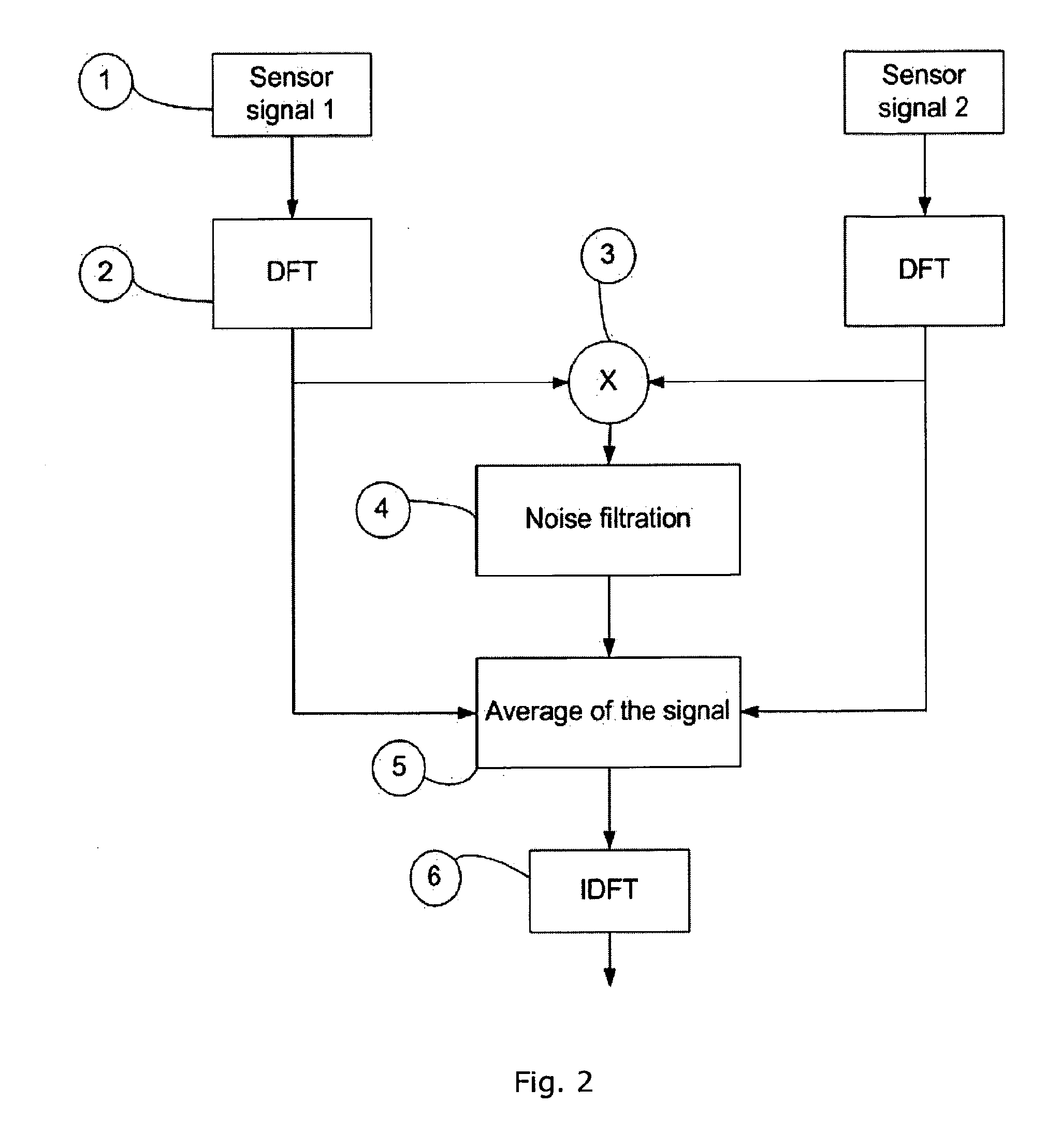
The invention provides a device and method for measuring a conductor current through employing magneto-optic materials. The two magneto-optic materials are arranged to be opposite to each other, and serve as current sensing devices at the same time. The device and method guarantee that the relative position of the two magneto-optic materials is not changed in a measurement process of the conductor current. When the two magneto-optic materials are located in a magnetic field formed by an electrified conductor, the polarization directions of polarized light passing through the magneto-optic materials will be changed because of the Faraday effect. Through the measurement of the deflection angles of two polarized light beams after the polarized light beams pass through the two magneto-optic materials, the device and method can calculate the current in a conductor through the difference between the distances from optical paths in the two magneto-optic materials to the center of the conductor. When the device and method are used for measuring the conductor current, the installation distances of the two magneto-optic materials to the conductor are not sensitive, and a measurement error caused by the nondeterminacy of the position between the magneto-optic materials and the conductor in the prior art can be eliminated.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com