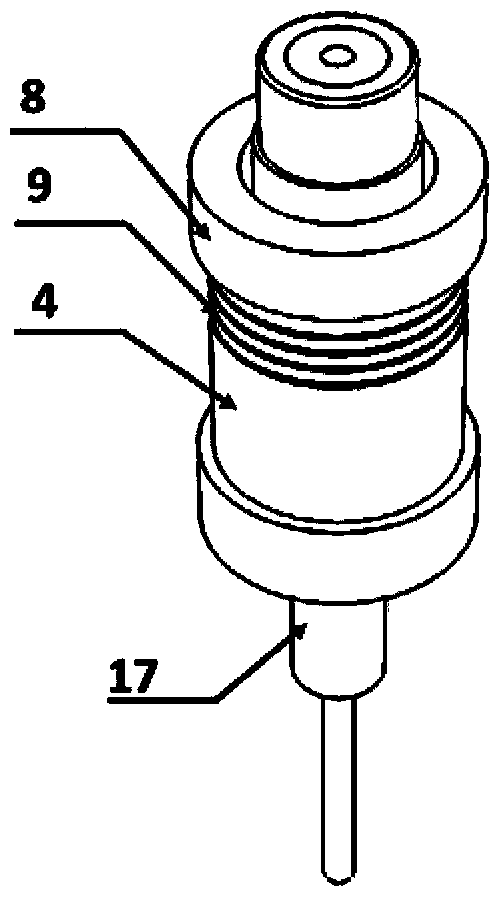
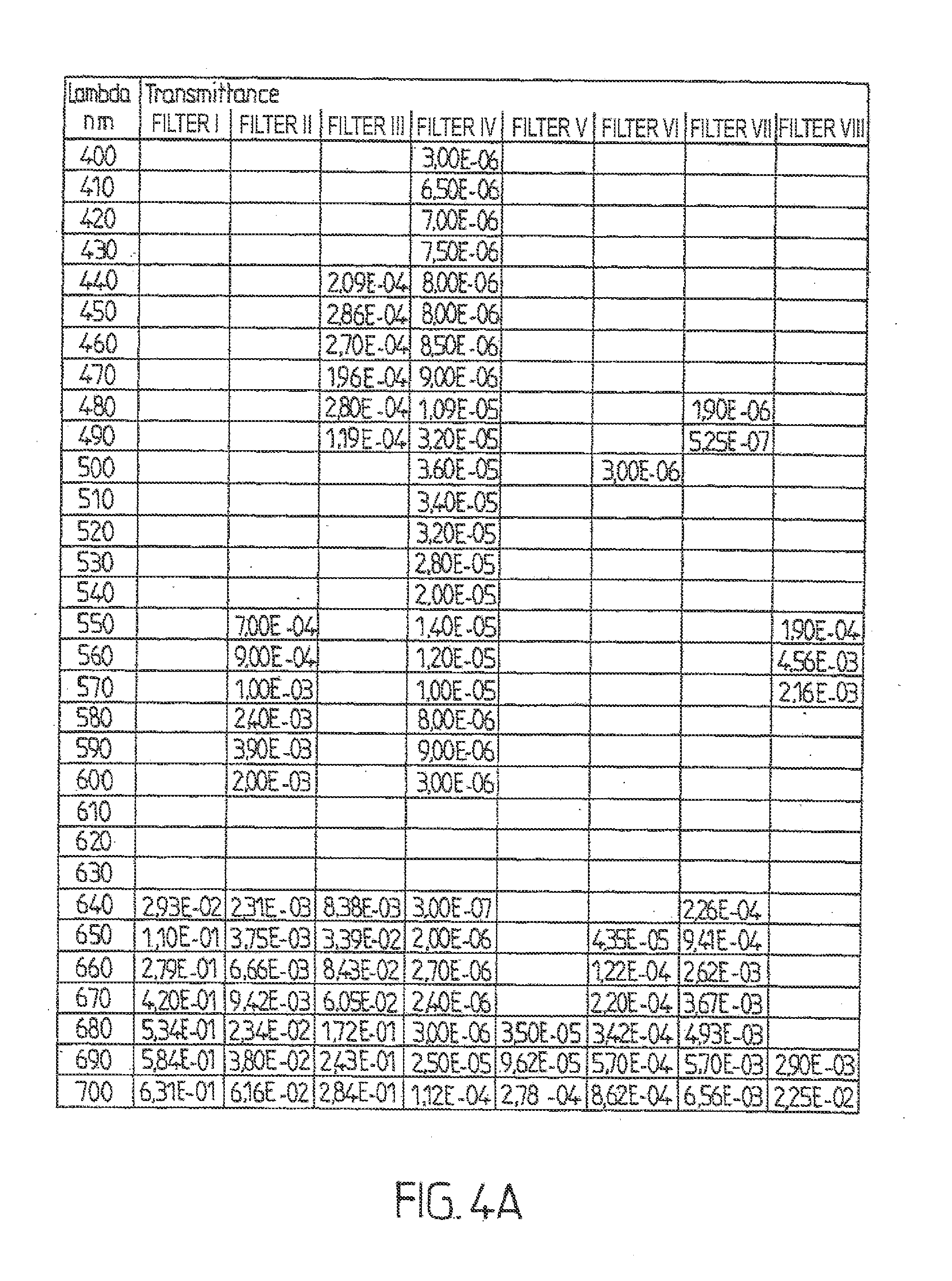
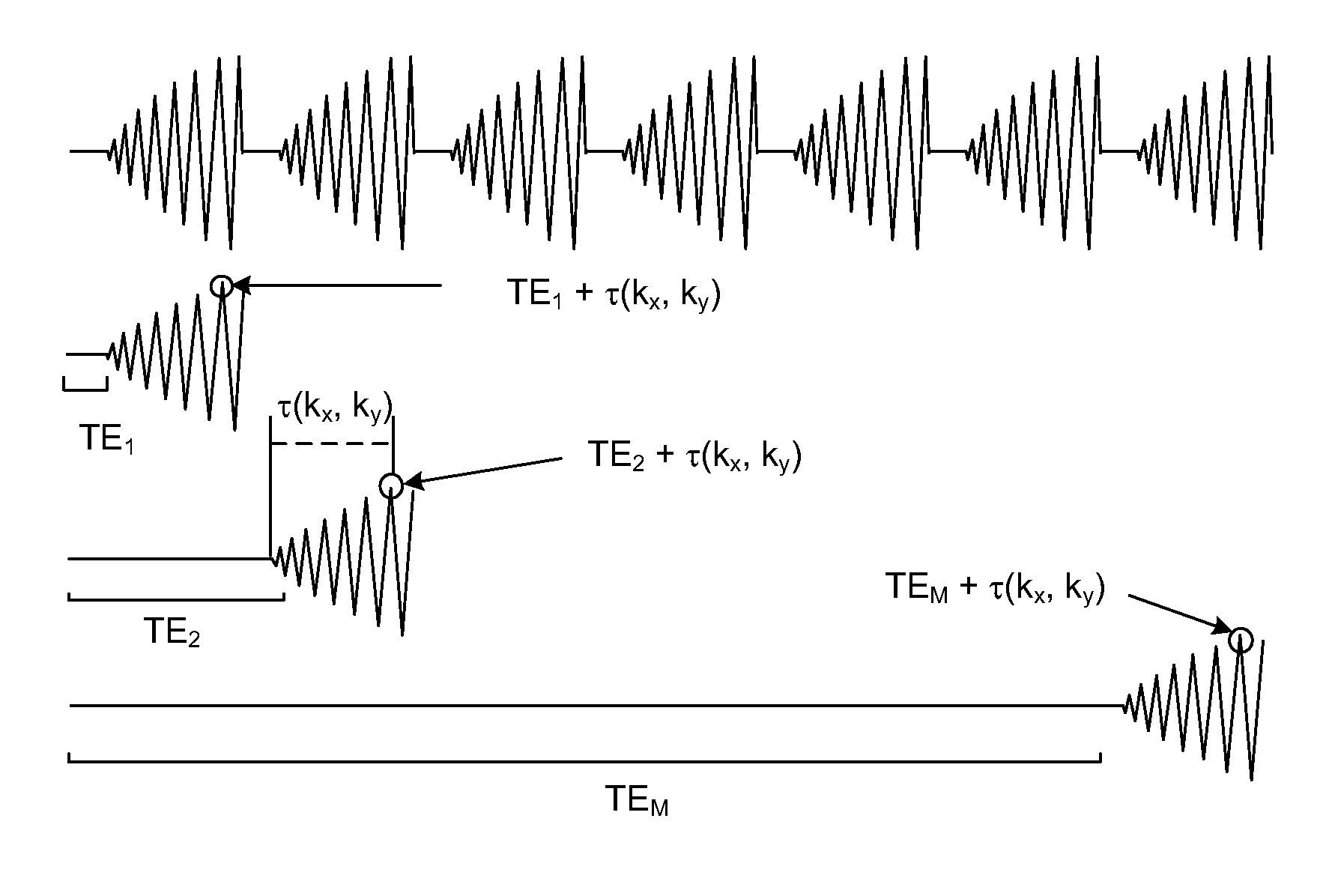
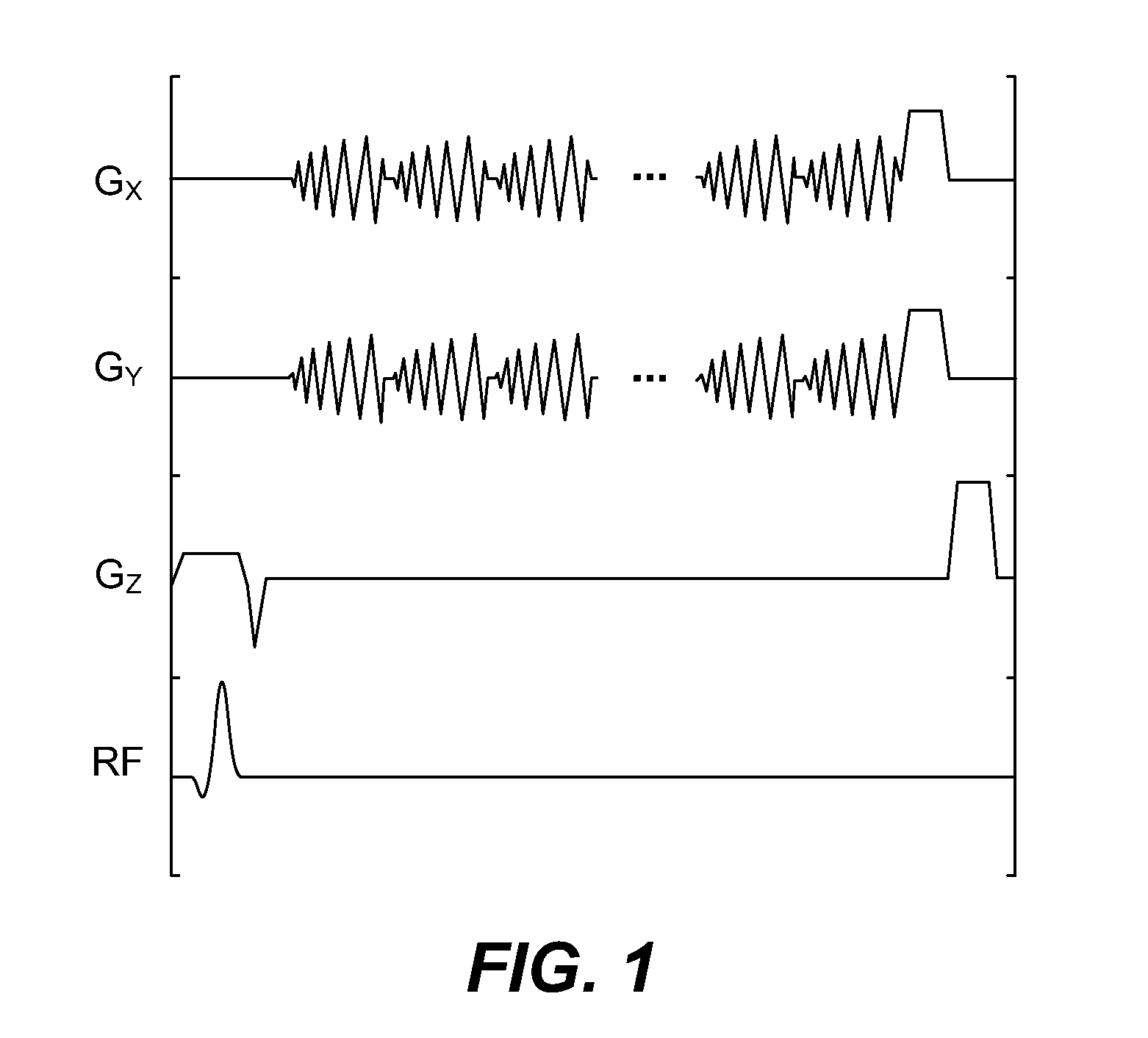
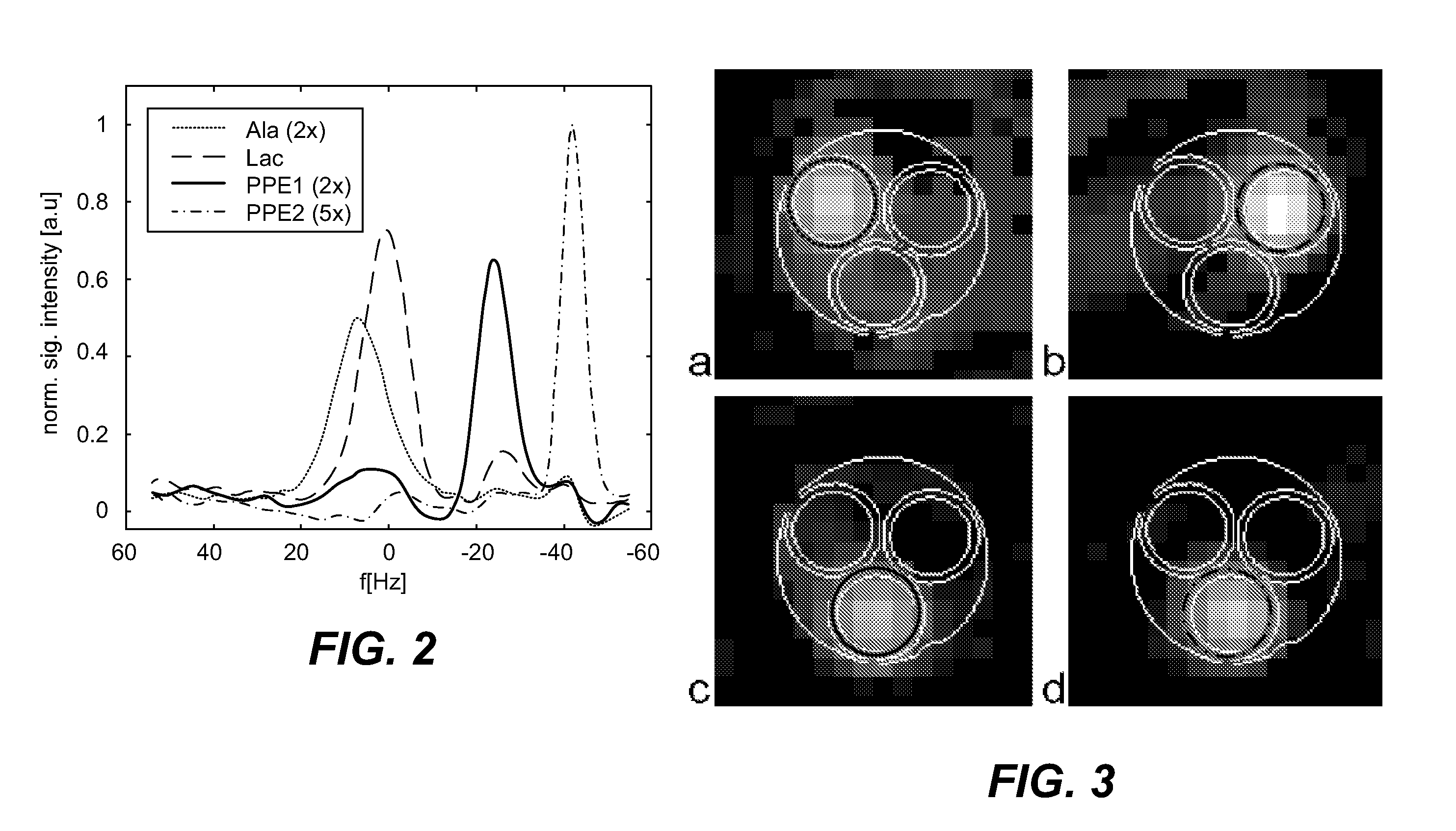
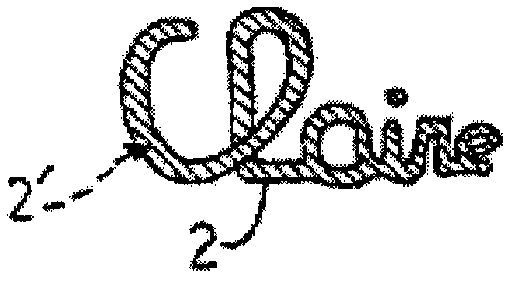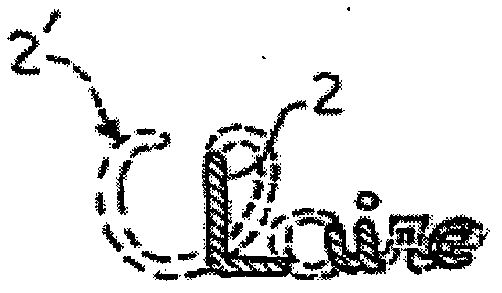Patents
Literature
45 results about "Spectral window" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Spectral window. A function of an angular frequency defining a weight function used in the non-parametric estimation of the spectral density of a stationary stochastic process by smoothing the periodogram constructed from the observed data of the process.
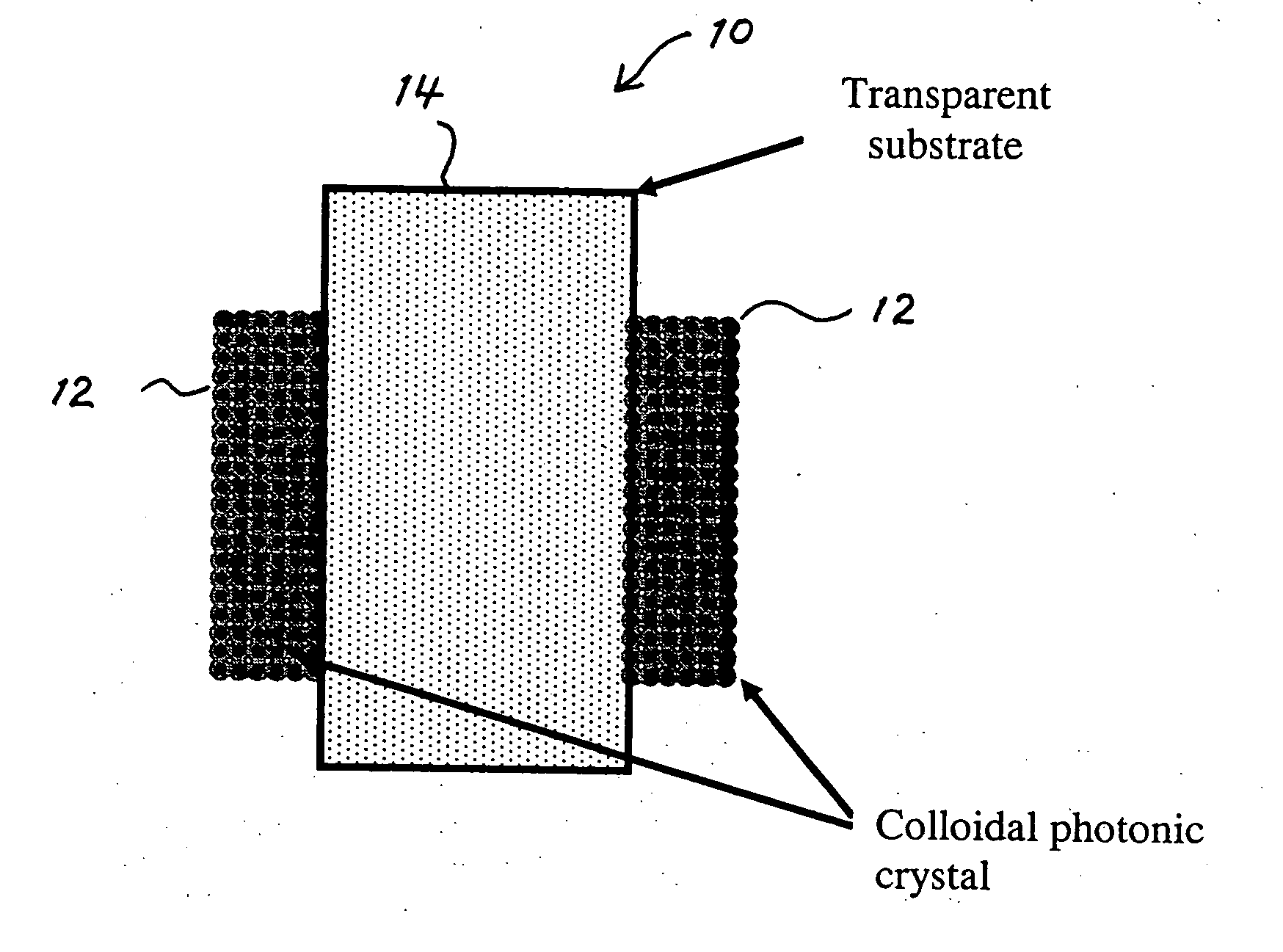
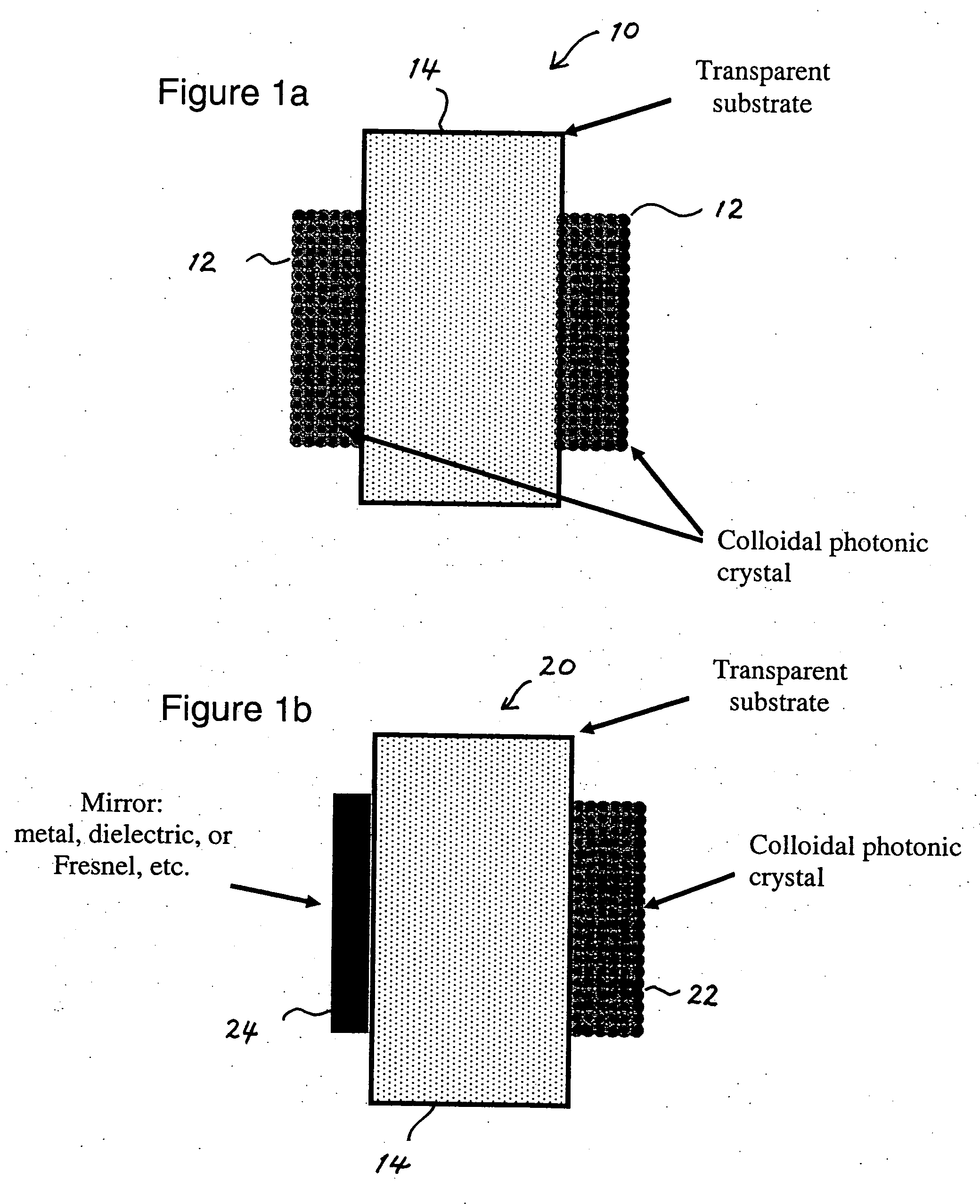
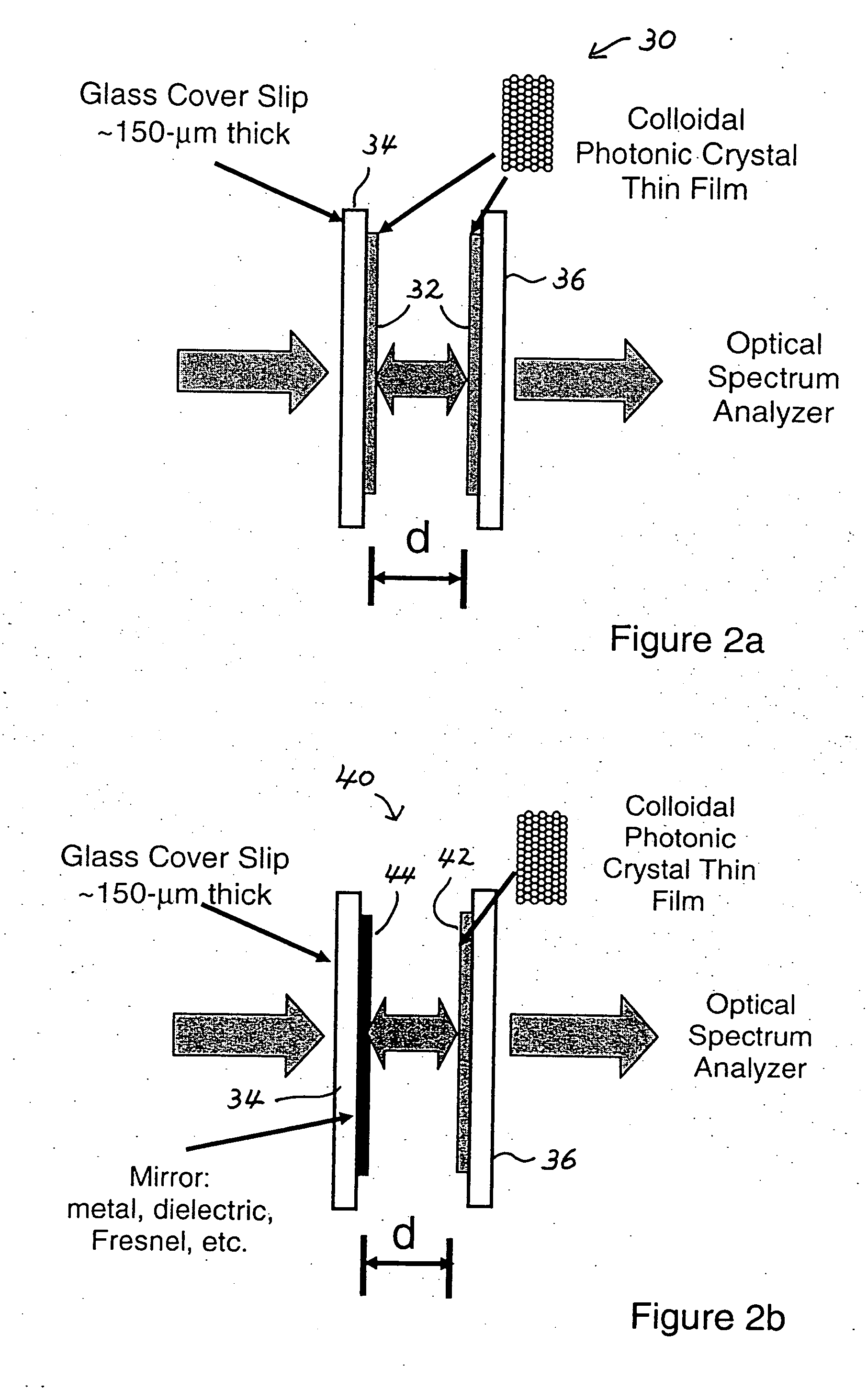
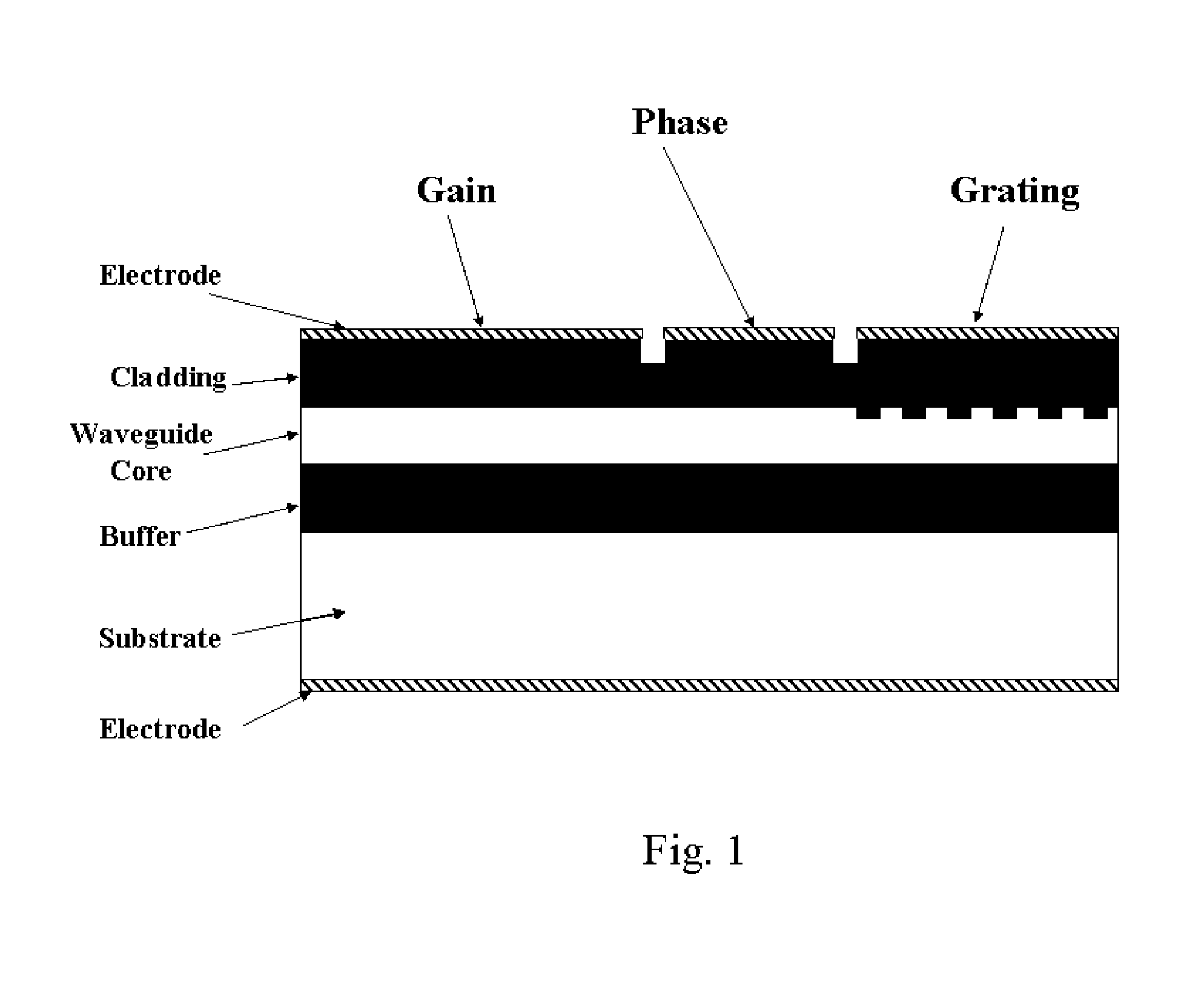
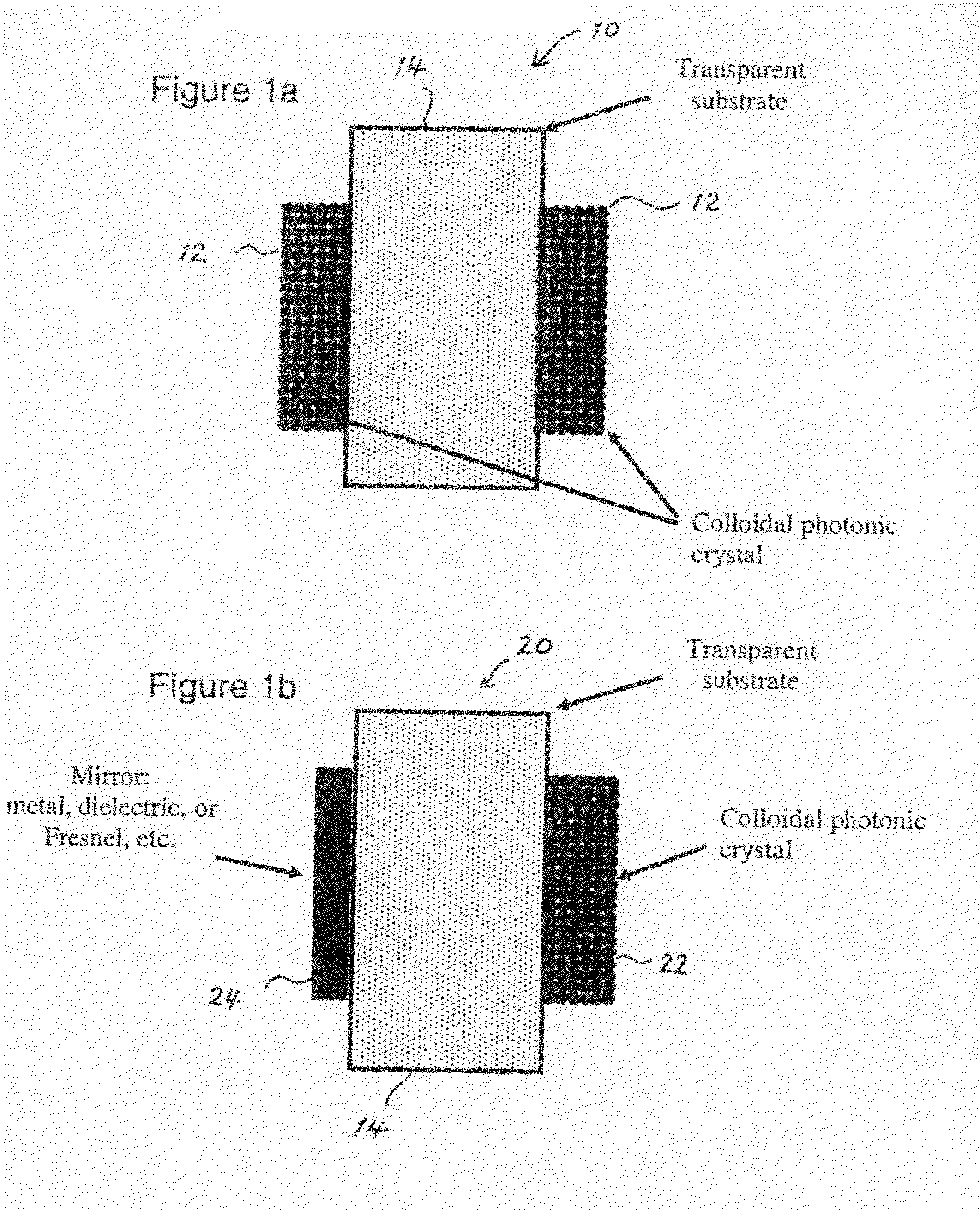
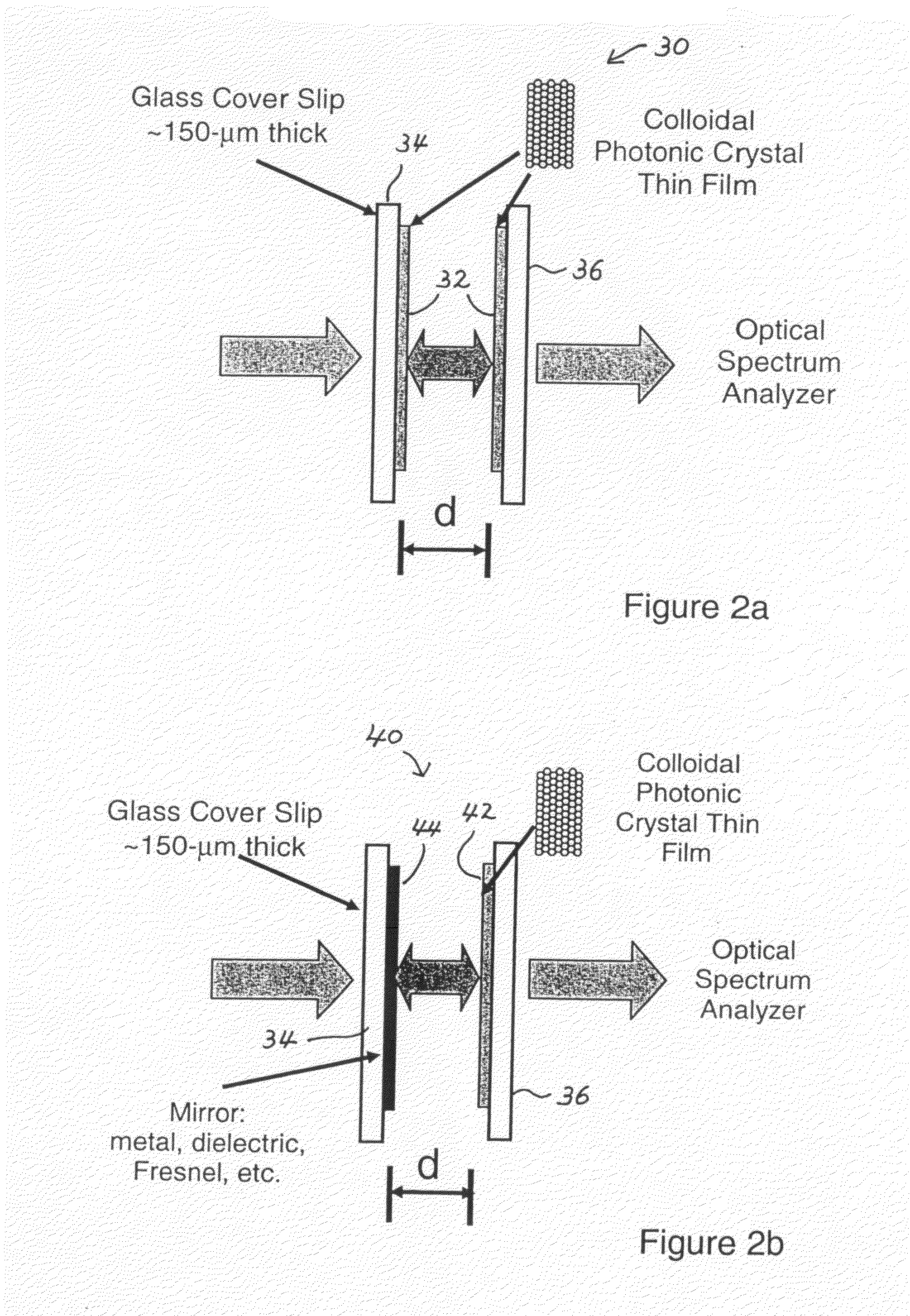
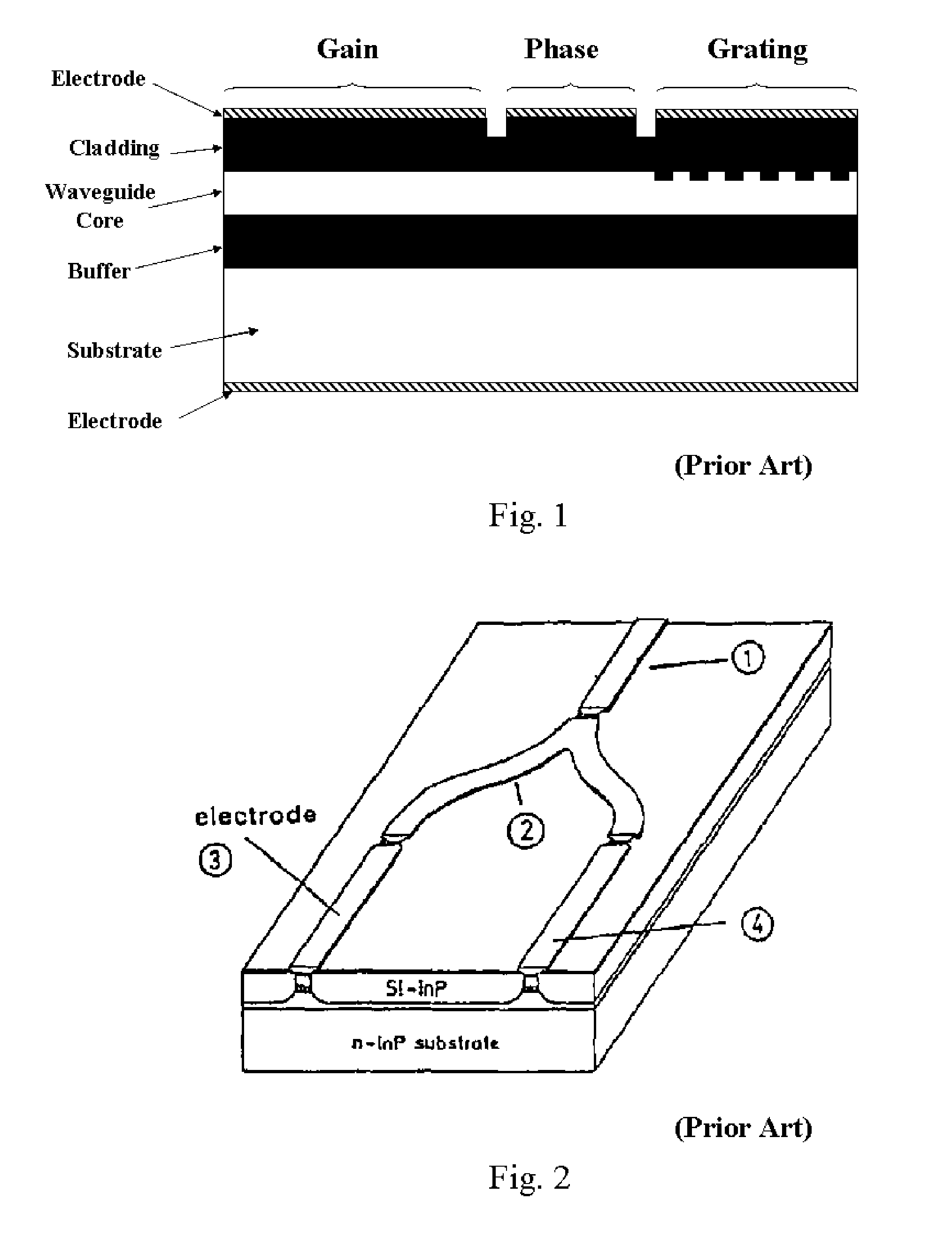
Photonic crystal mirrors for high-resolving power fabry perots
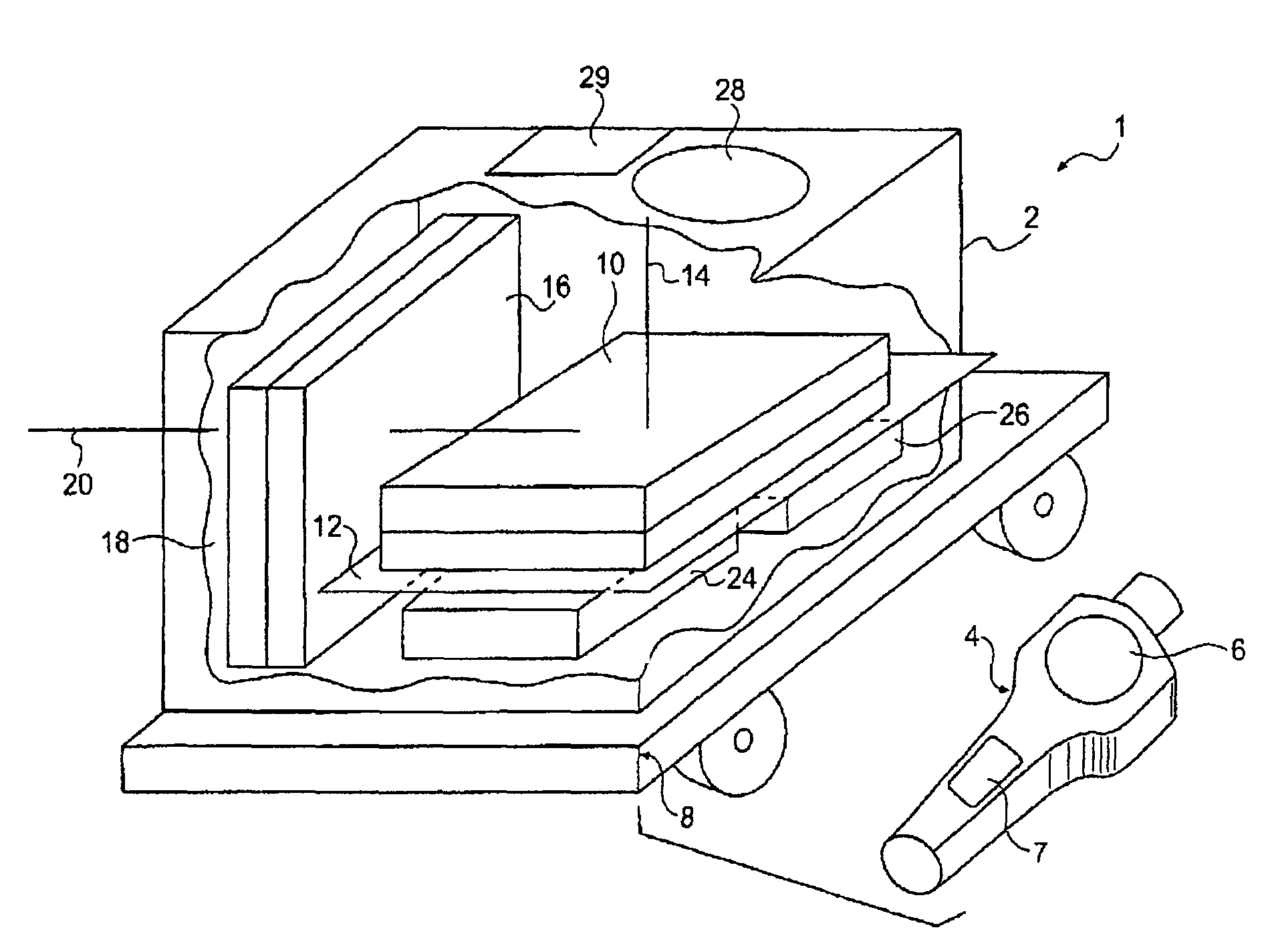
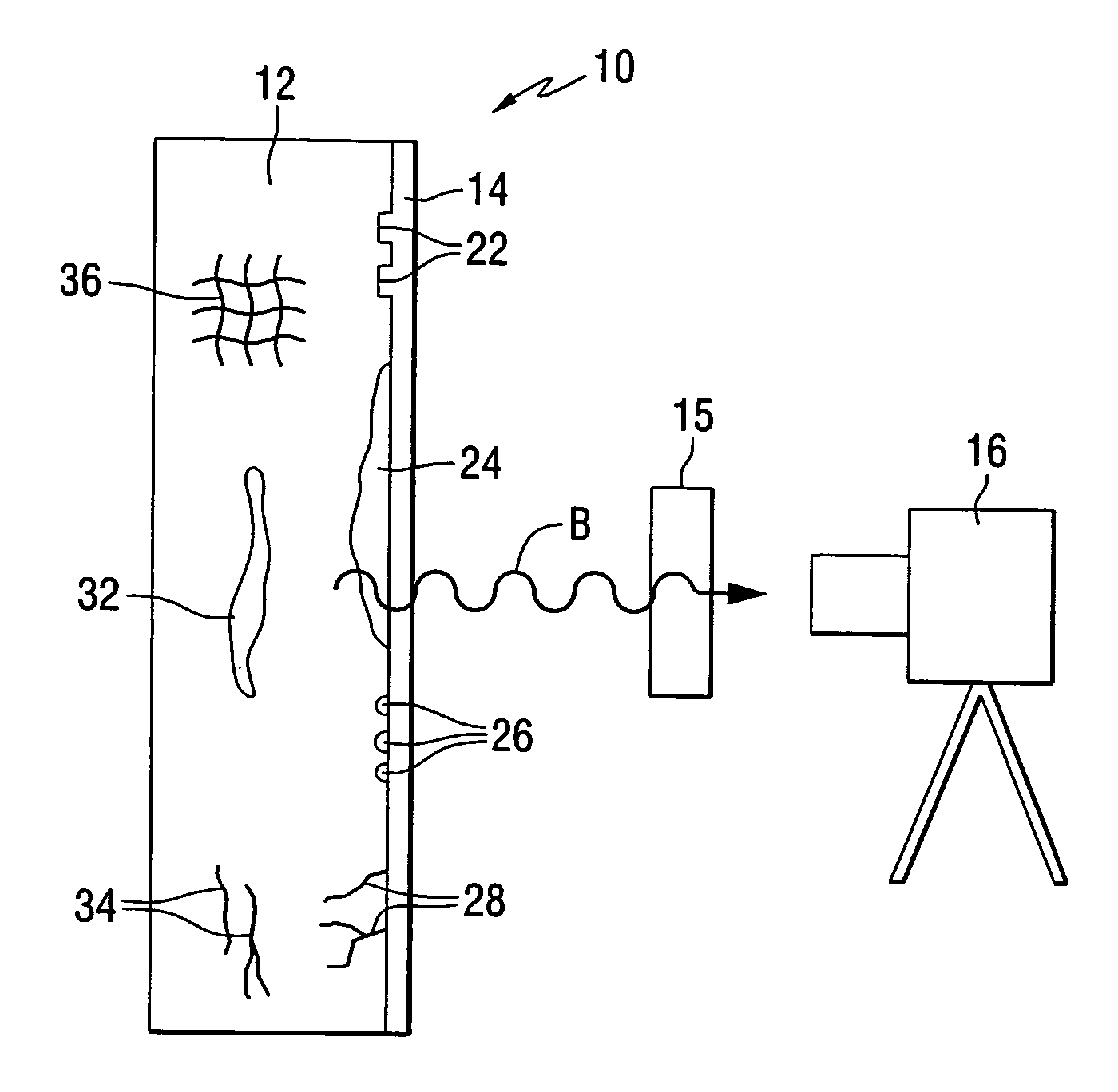
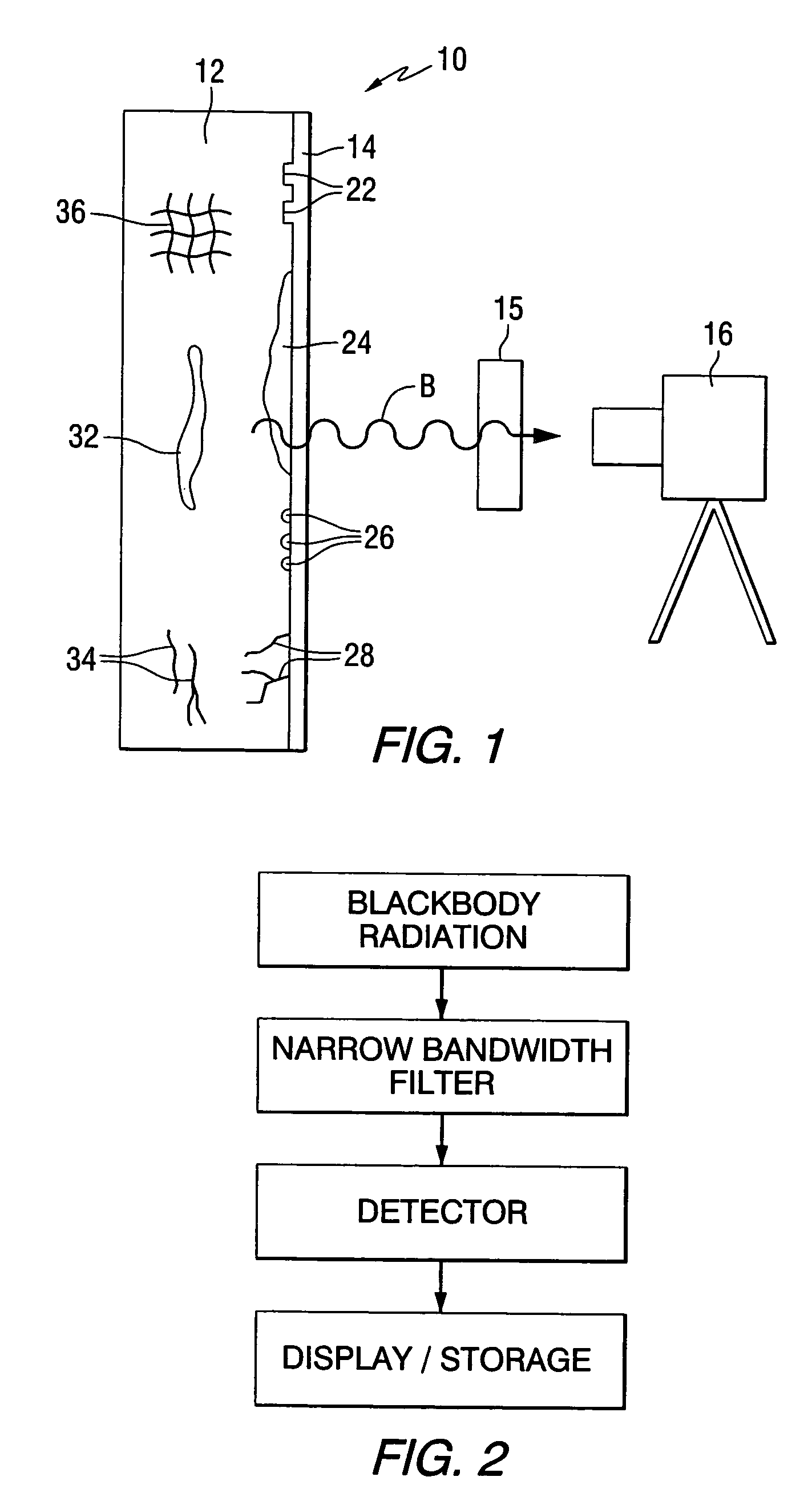
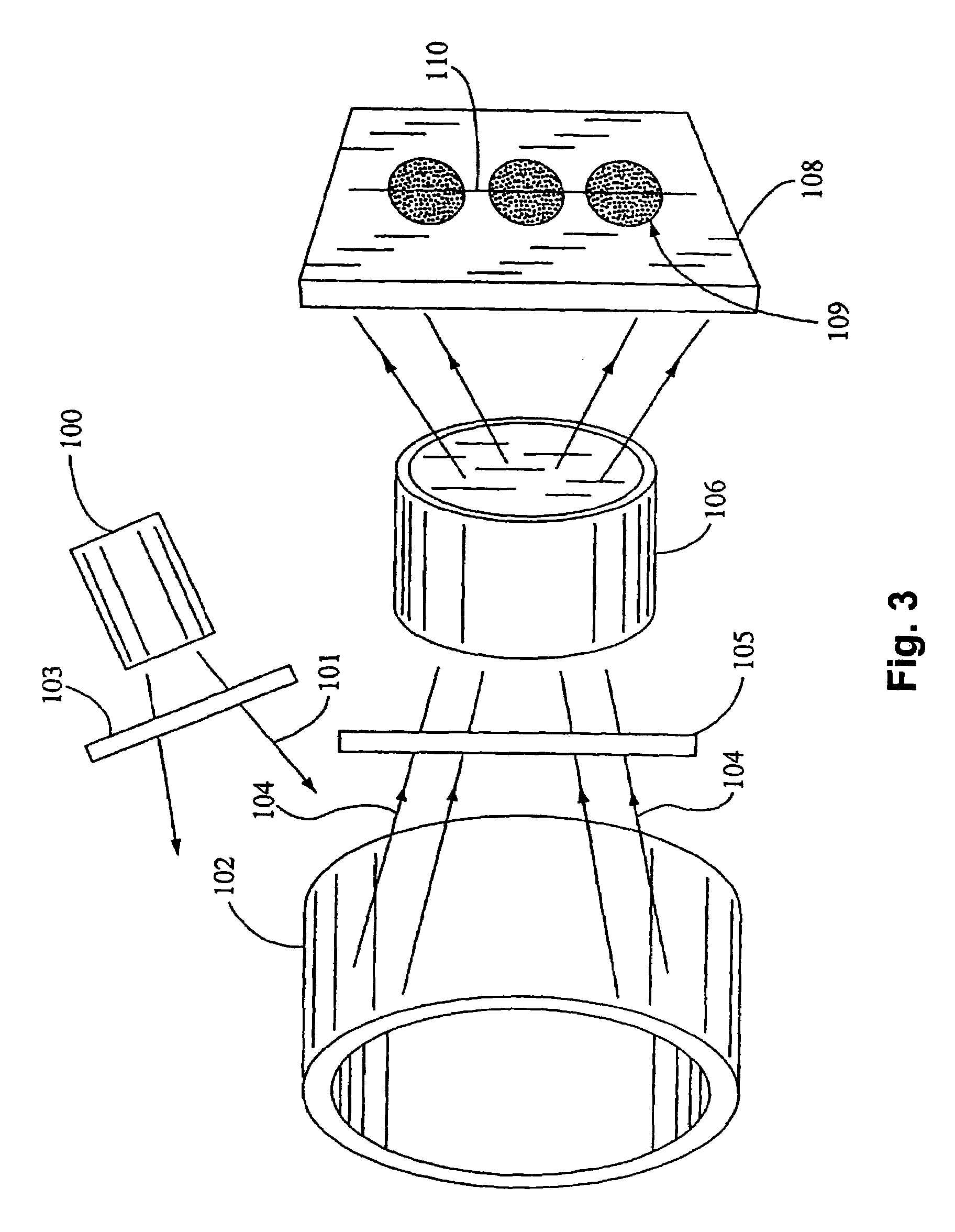
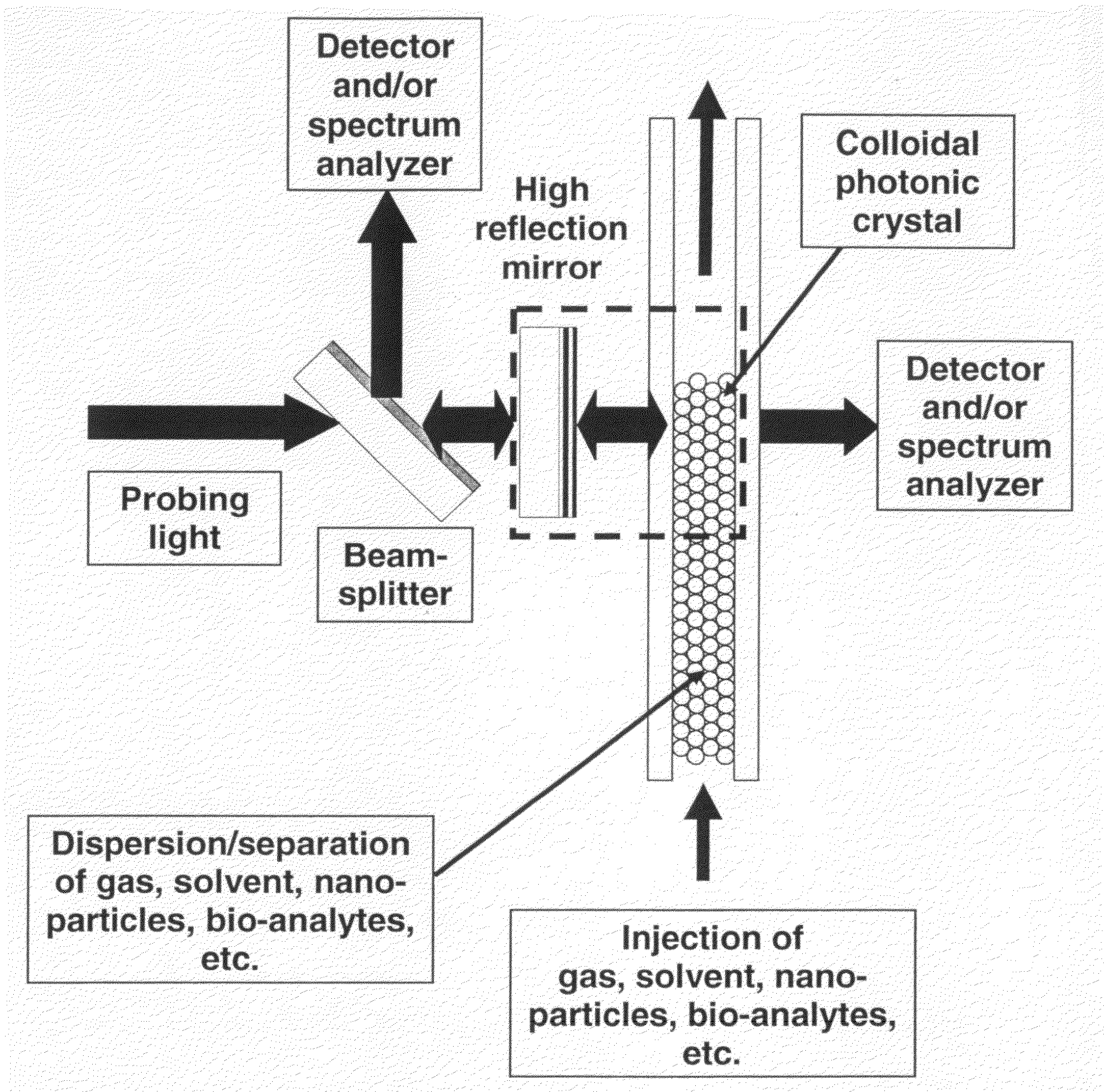
A Fabry-Perot cavity comprised of three-dimensional photonic crystal structures is disclosed. The self-assembly of purified and highly monodispersed microspheres is one approach to the successful operation of the device for creating highly ordered colloidal crystal coatings of high structural and optical quality. Such colloidal crystal film mirrors offer high reflection with low losses in the spectral window of the photonic band gap that permit Fabry-Perot resonators to be constructed with high resolving power, for example, greater than 1000 or sharp fringes that are spectrally narrower than 1.0 nm. The three-dimensional photonic crystals that constitute the Fabry-Perot invention are not restricted to any one fabrication method, and may include self-assembly of colloids, layer-by-layer lithographic construction, inversion, and laser holography. Such photonic crystal Fabry-Perot resonators offer the same benefits of high reflection and narrow spectral band responses available from the use of multi-layer dielectric coatings. However, the open structure of three-dimensional photonic crystal films affords the unique ability for external media to access the critical reflection layers and dramatically alter the Fabry-Perot spectrum, and provide means for crafting novel laser, sensor, and nonlinear optical devices. This open structure enables the penetration of gas and liquid substances, or entrainment of nano-particles or biological analytes in gases and liquids, to create subtle changes to the colloidal mirror responses that manifest in strong spectral responses in reflection and transmission of the collective Fabry Perot response.
Owner:HERMAN PETER +2
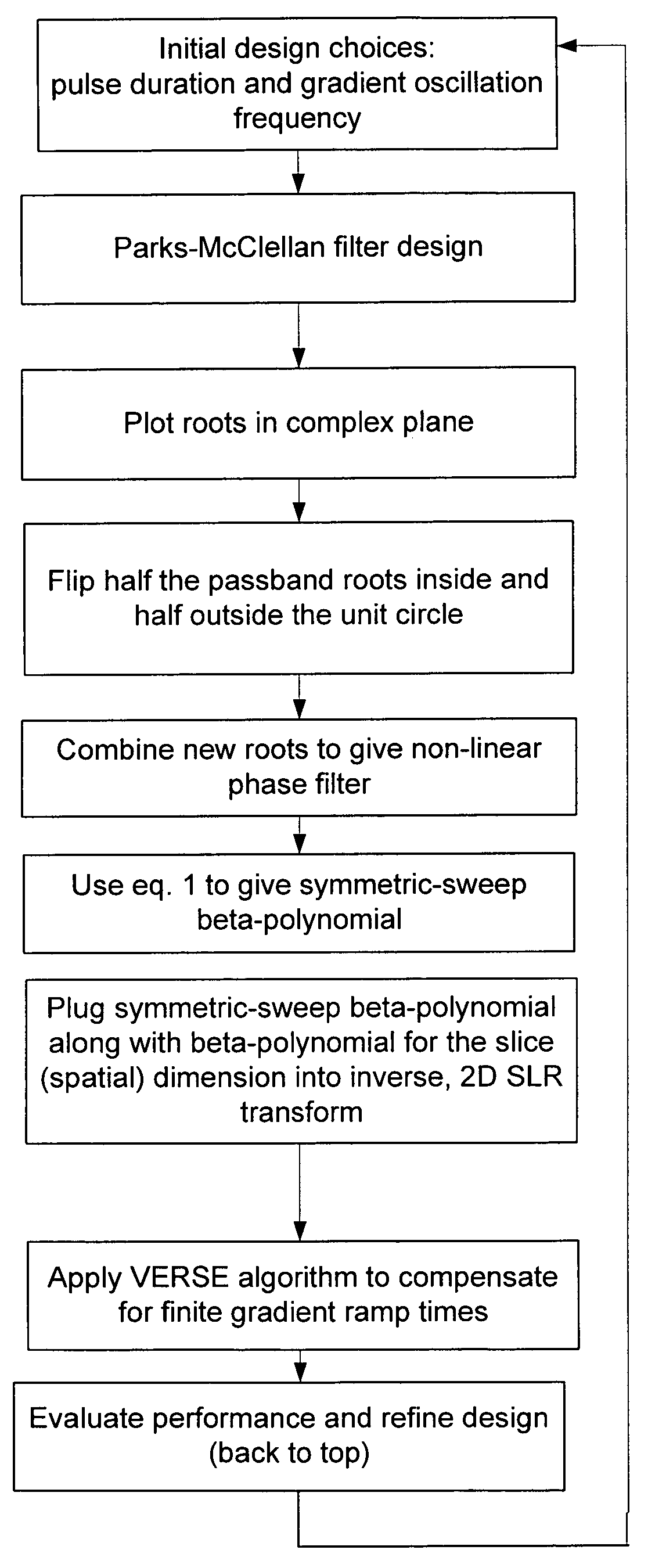
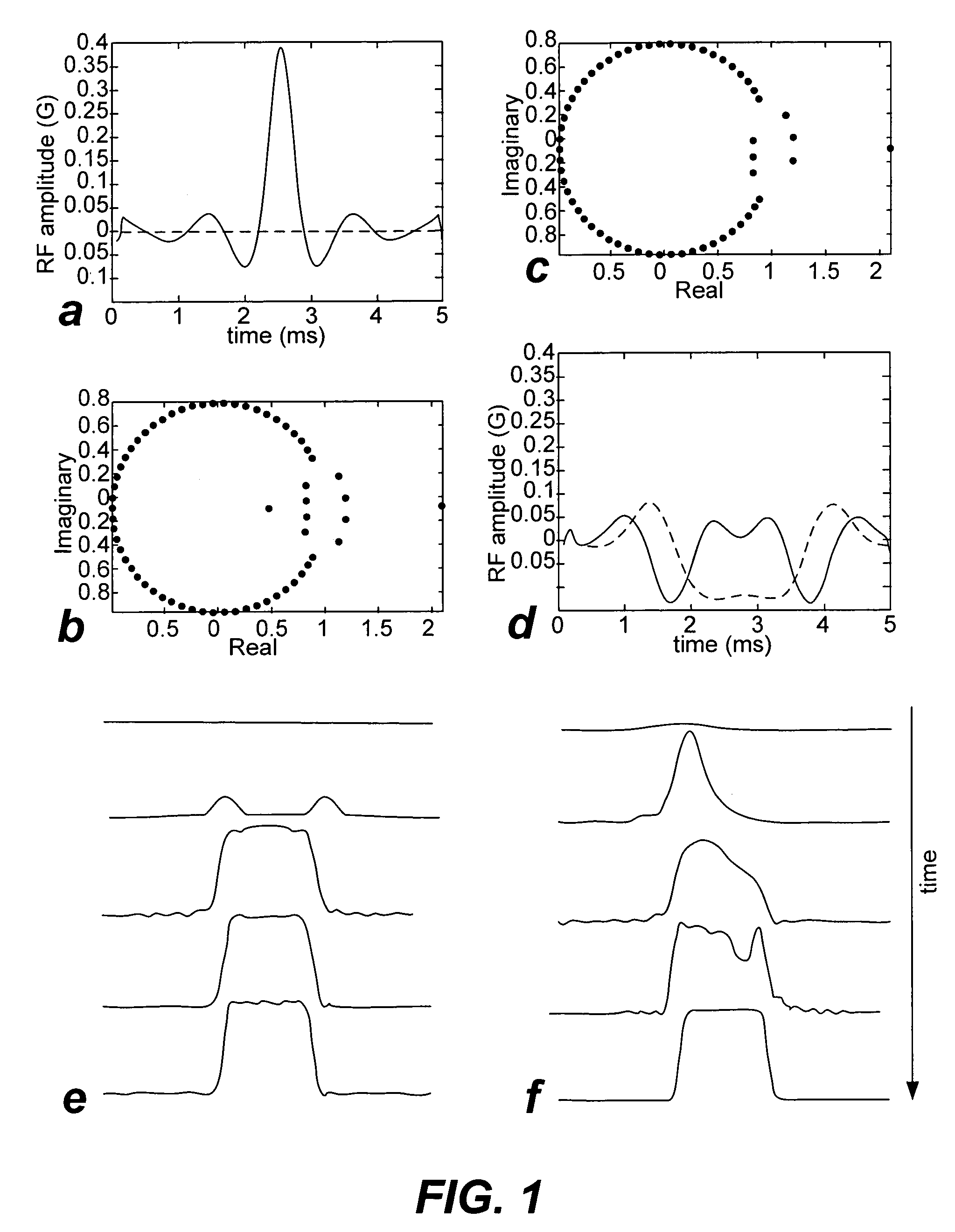
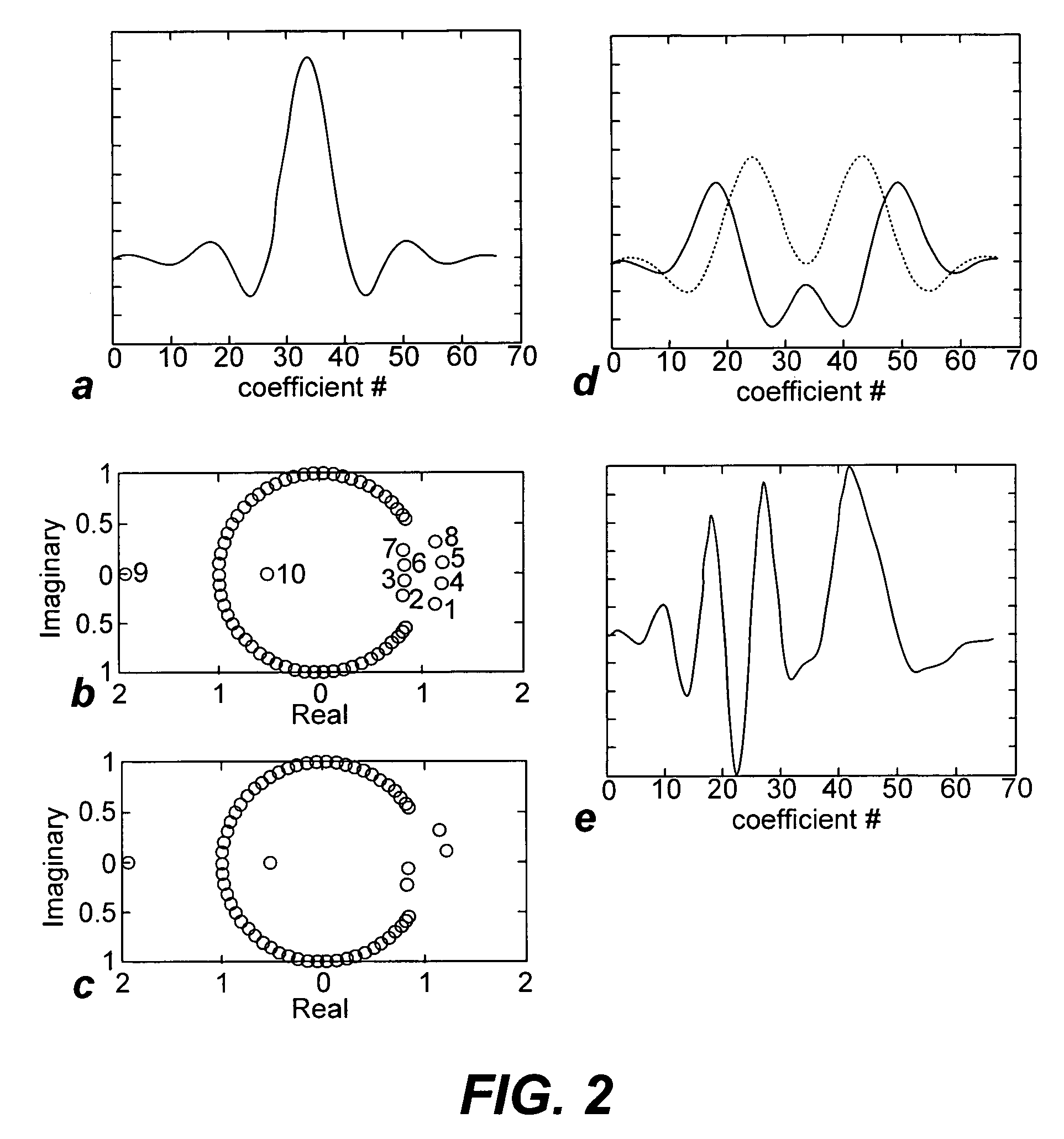
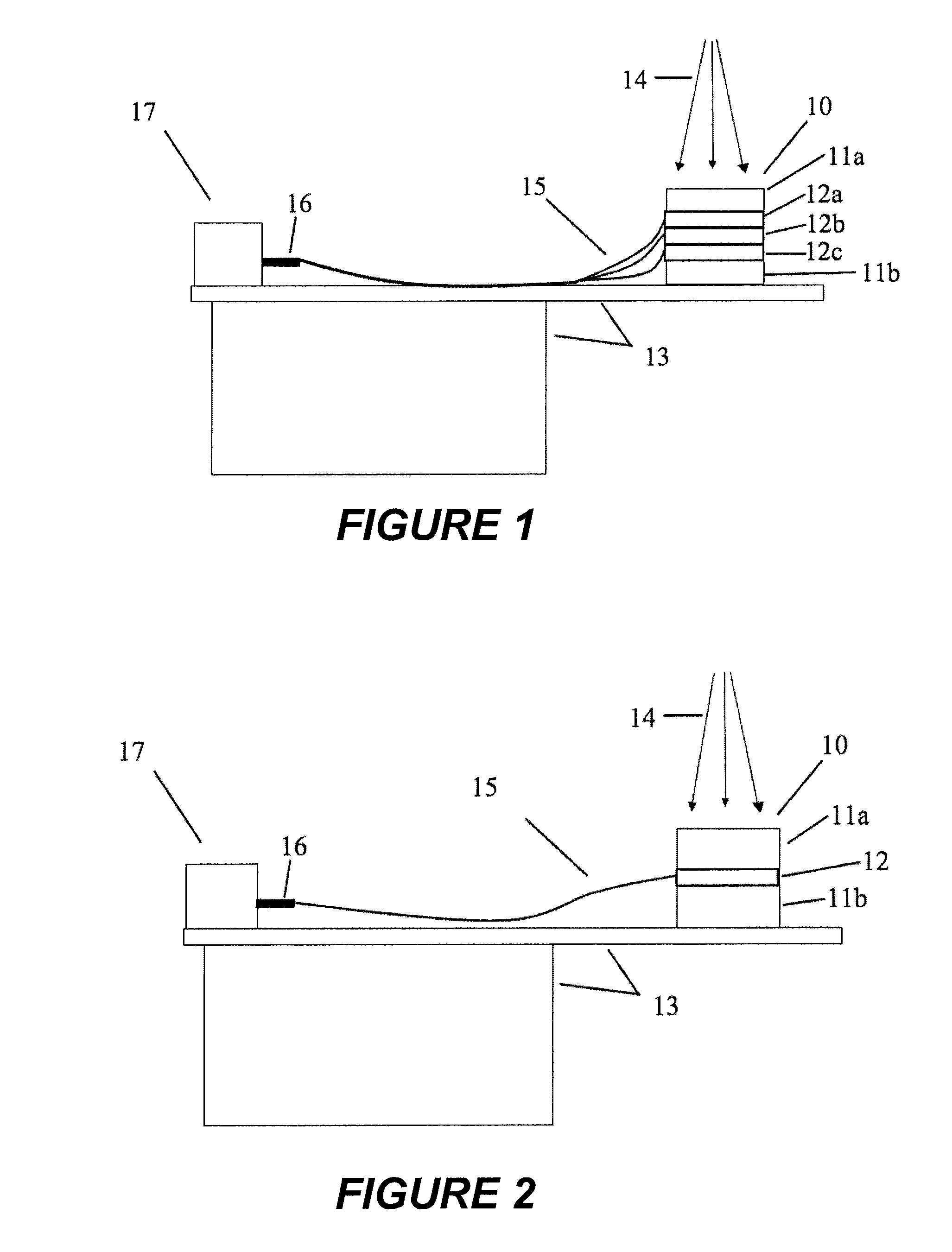
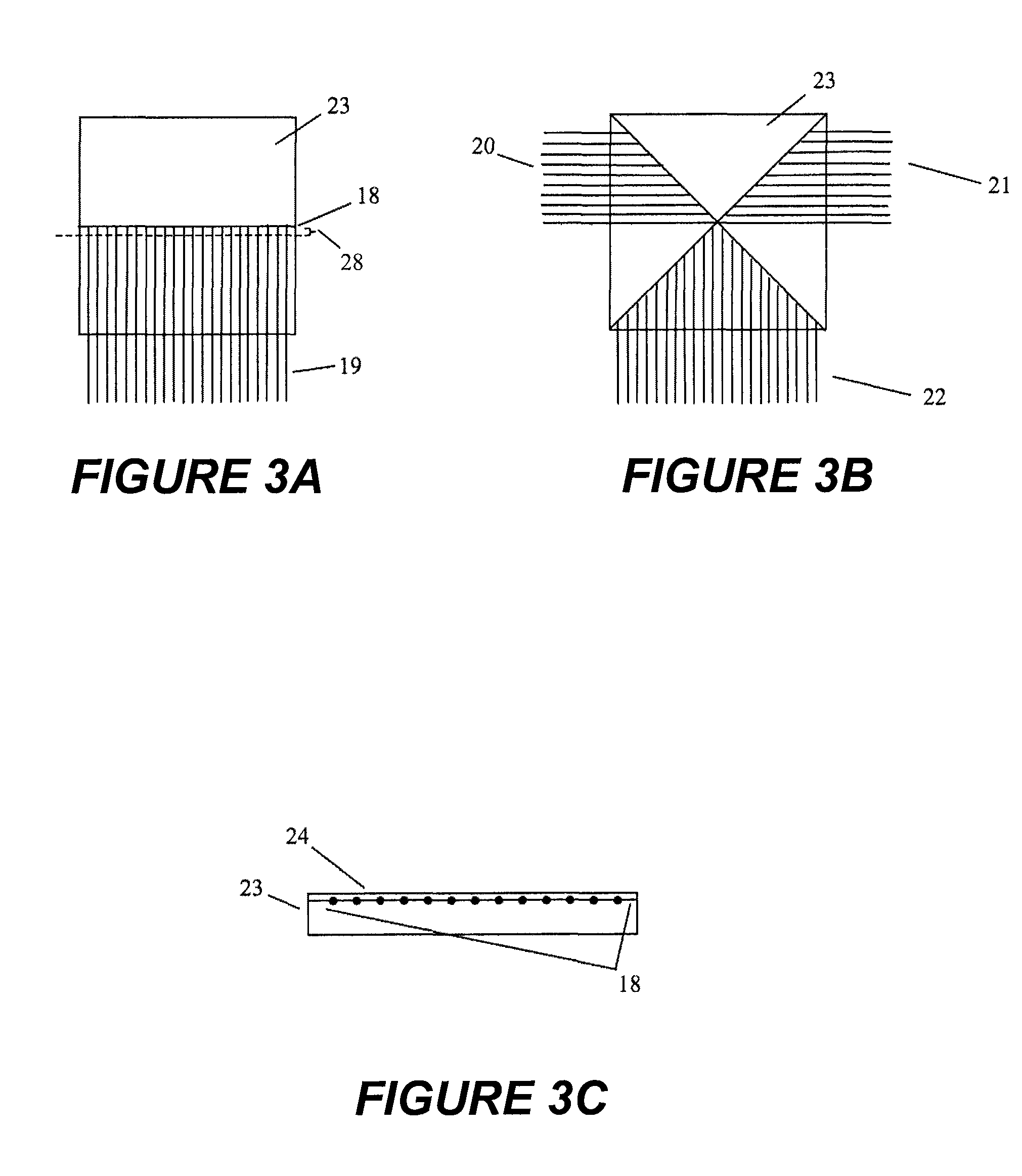
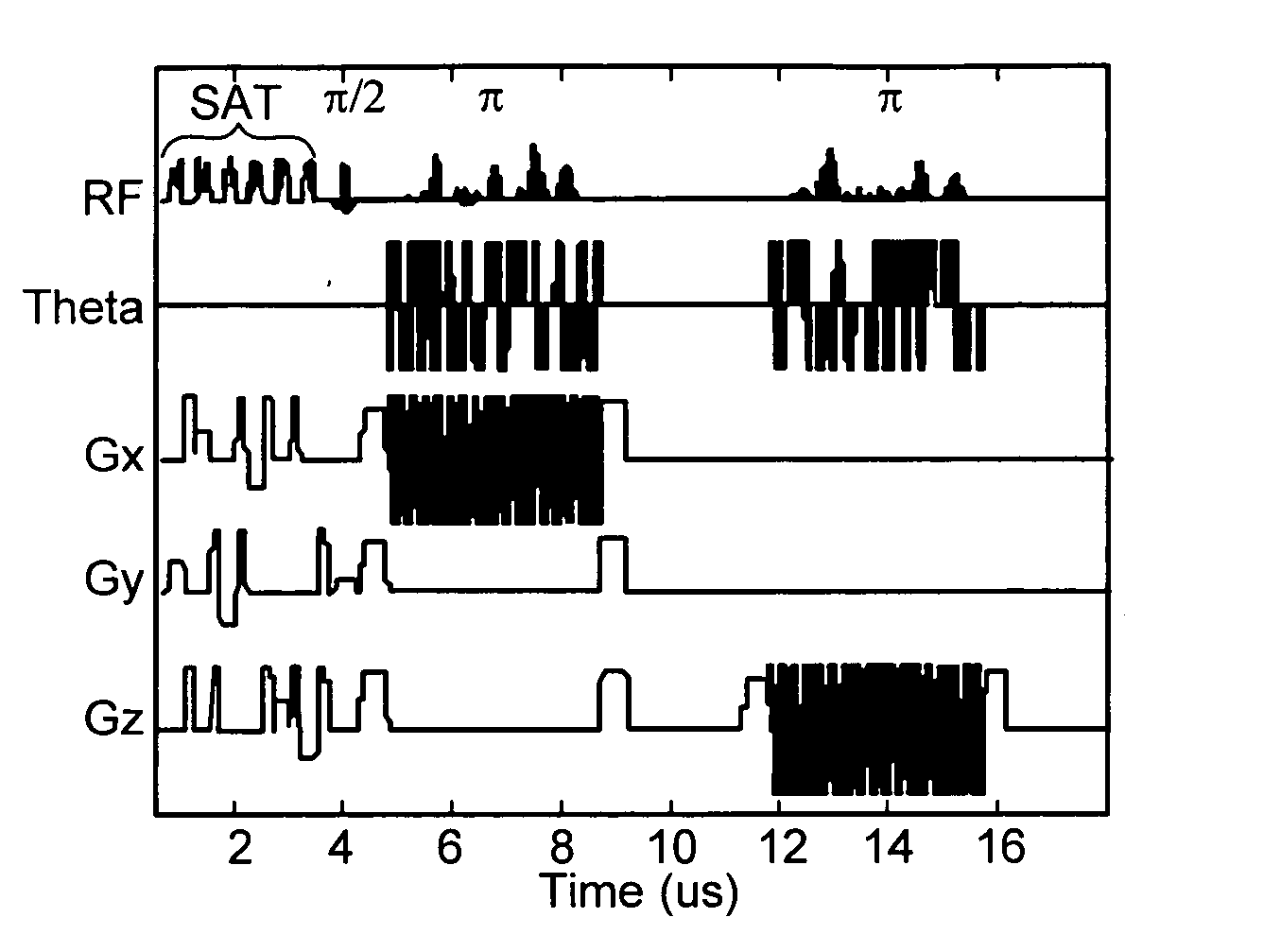
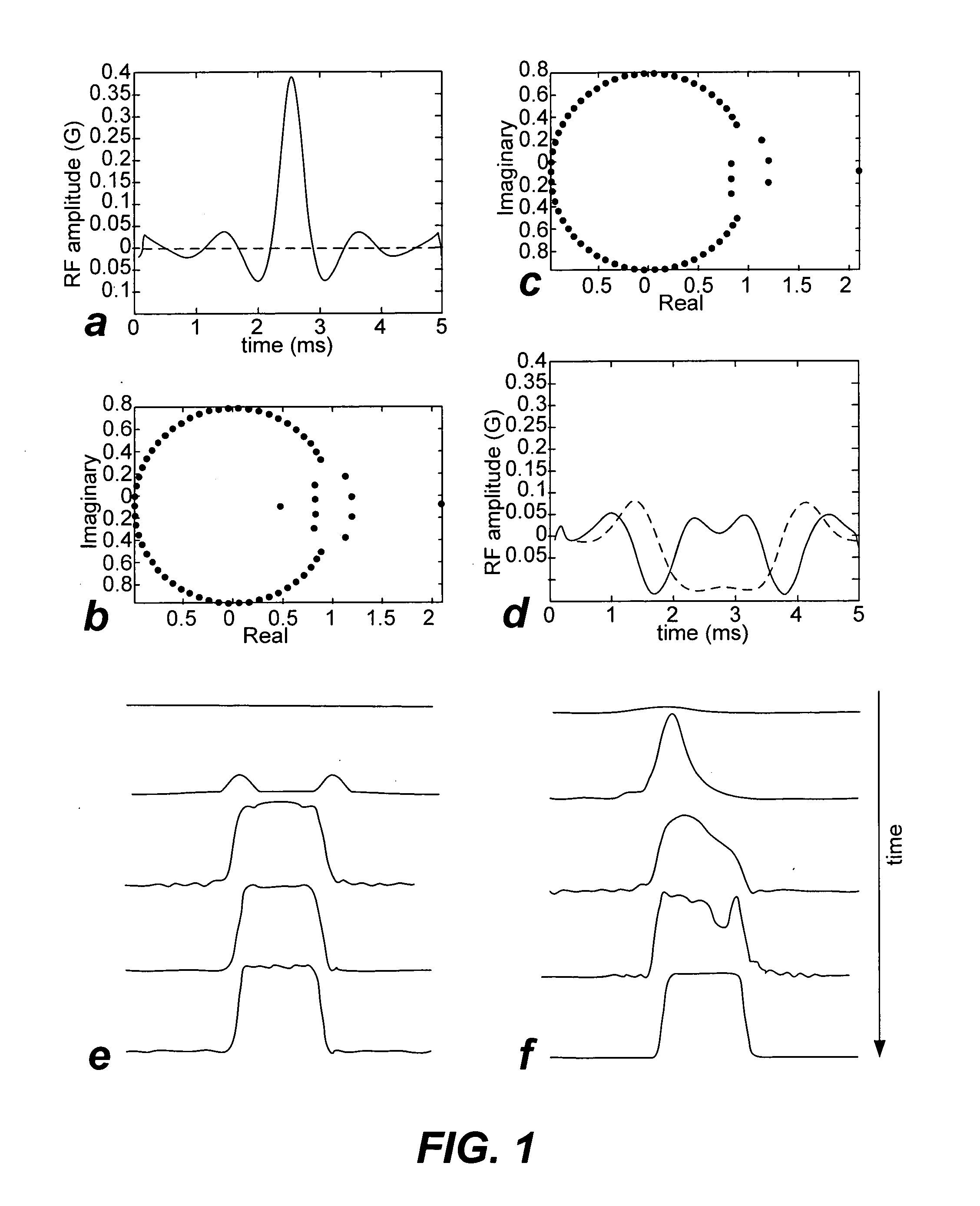
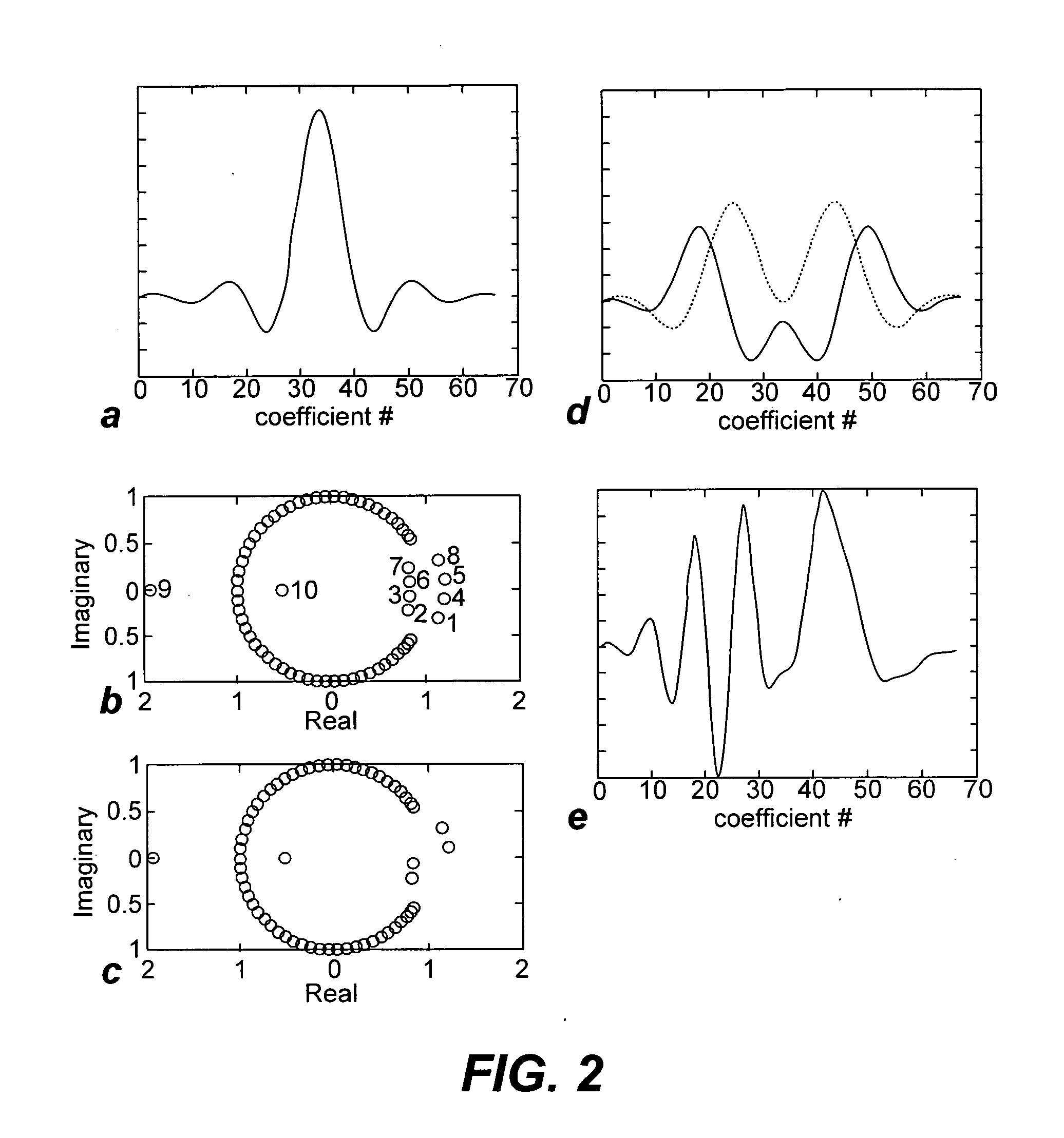
Non-linear symmetric sweep spectral-spatial RF pulses for MR spectroscopy
ActiveUS7042214B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionSpectroscopyRadio frequency
A method for designing non-linear phase 180° spectral-spatial radio frequency pulses that can be used for spectral editing in magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. A novel feature of the pulse is a symmetric sweep developed by the spectral profile from the outside edges of the spectral window towards the middle whereby coupled components are tipped simultaneously and over a short interval. Pulses have been designed for lactate editing at 1.5T and 3T. The spectral and spatial spin-echo profiles of the RF pulses can be measured experimentally and altered in an iterative manner. Spectral-spatial radio frequency (SSRF) pulses allow simultaneous selection in both frequency and spatial domains. These pulses are particularly important for clinical and research magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) applications for suppression of large water and lipid resonances.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
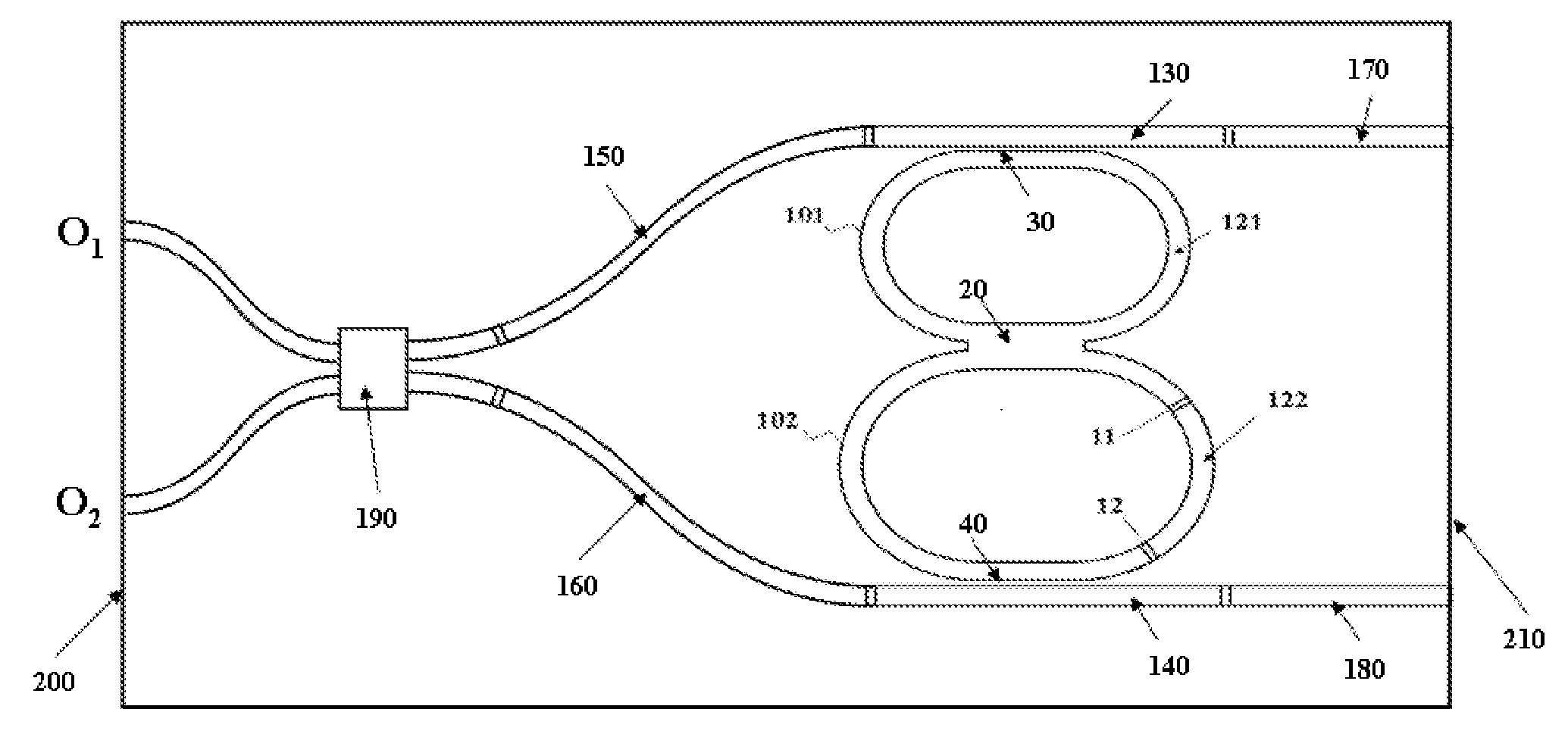
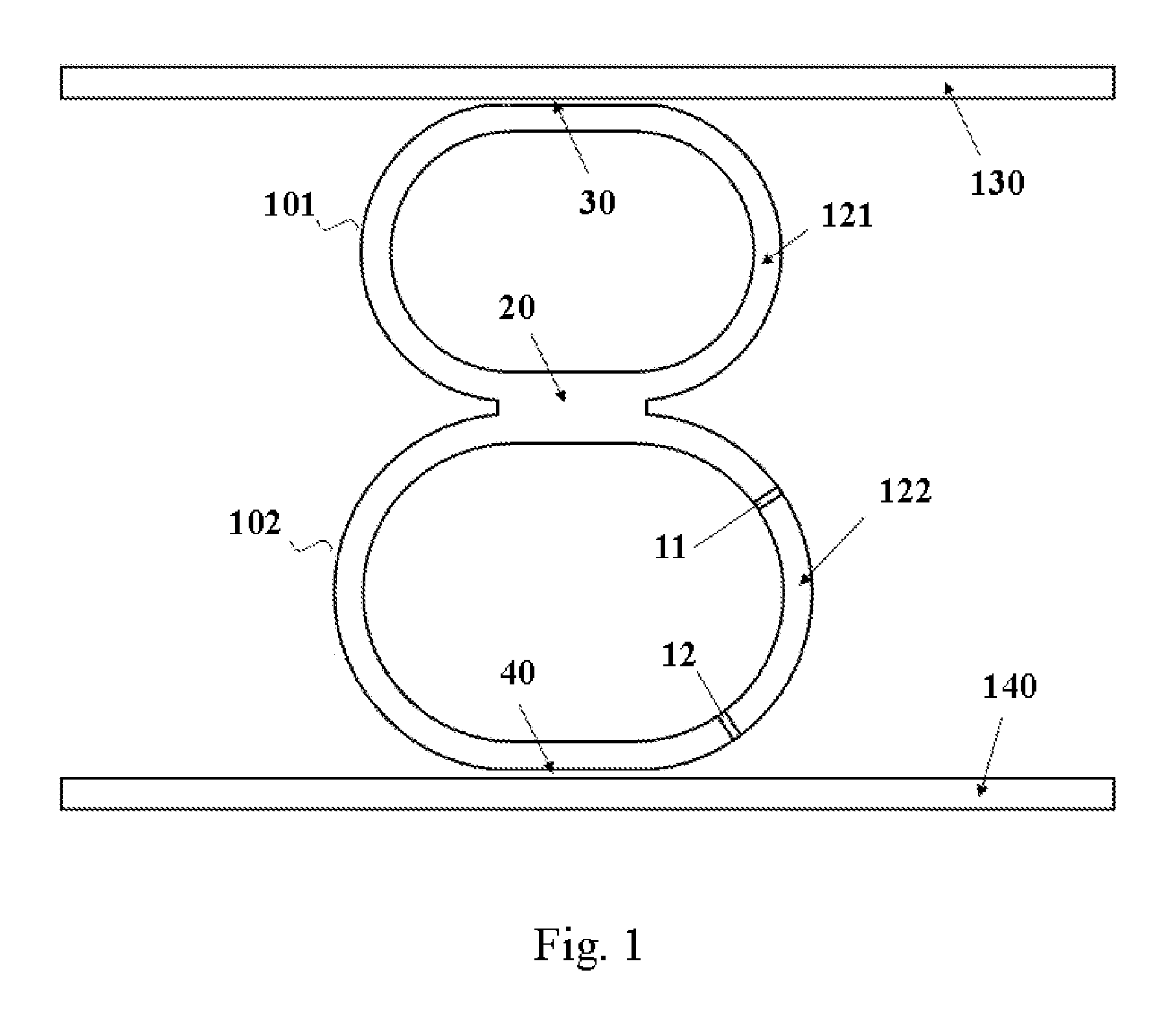
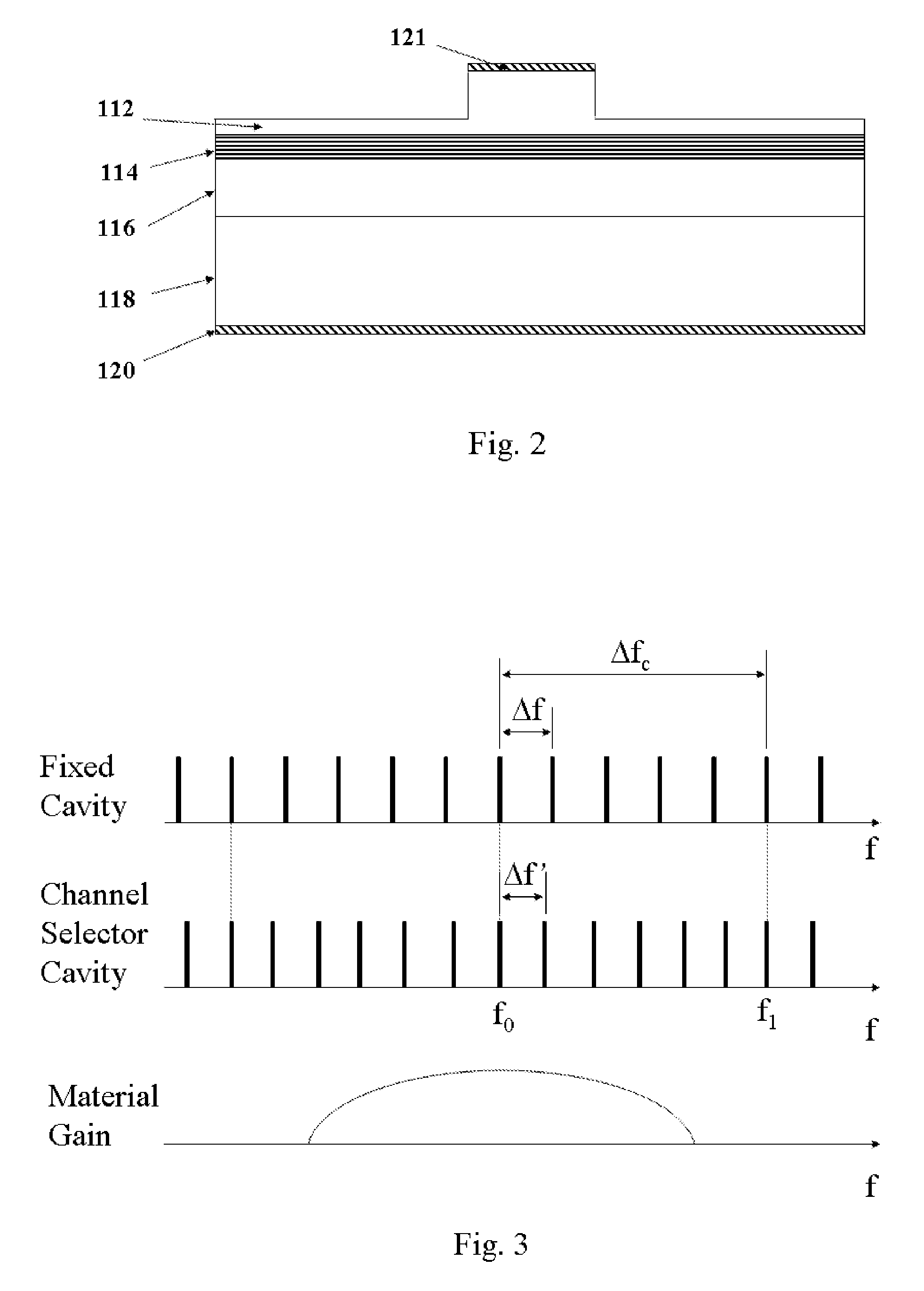
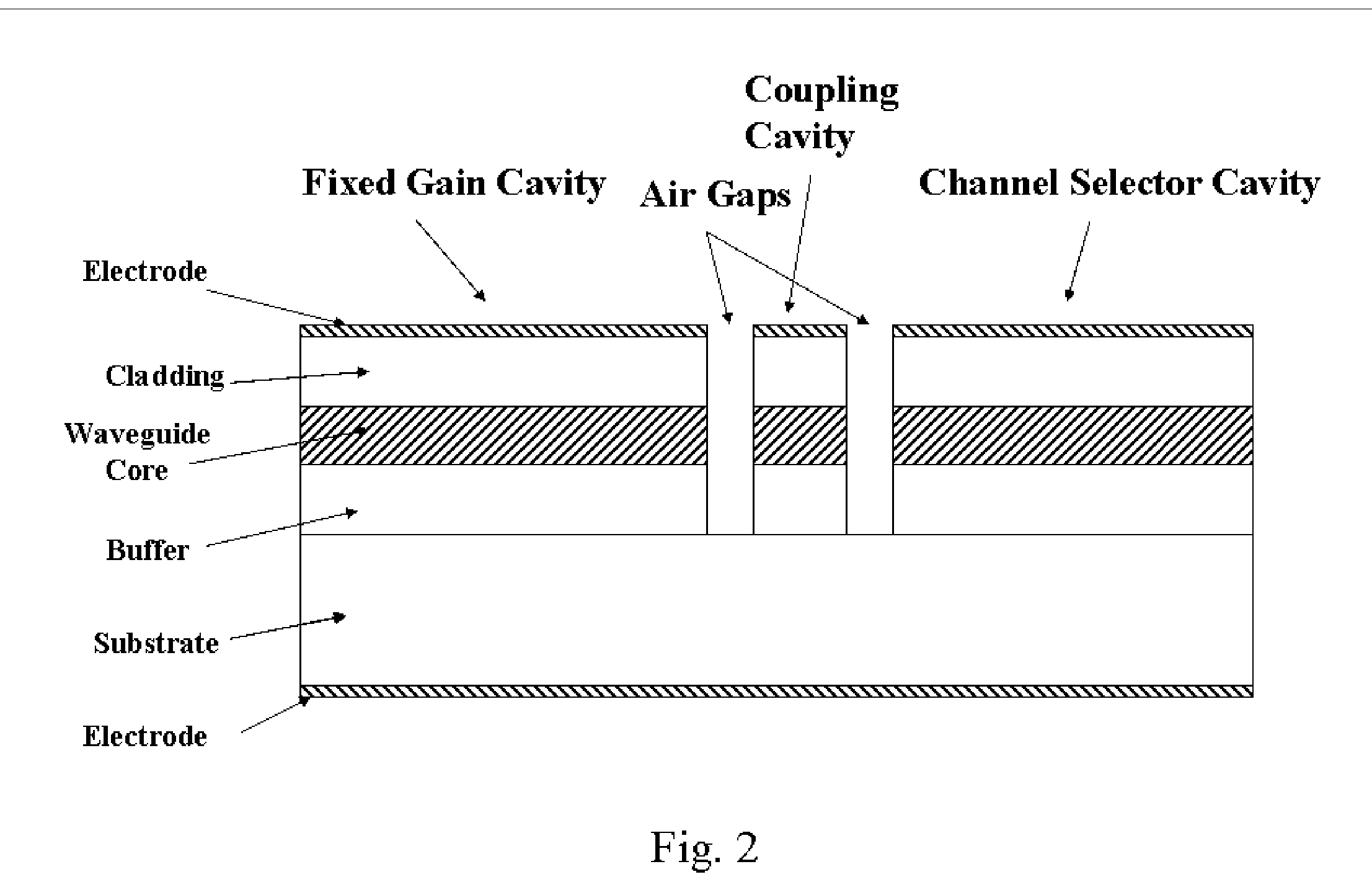
Wavelength switchable semiconductor laser using half-wave coupled active double-ring resonator
ActiveUS20080123701A1Optimal single-mode selectivityOptical resonator shape and constructionCoupling light guidesOptical pathlengthOptical coupler
A semiconductor laser comprises two optical ring resonators, each comprising an optical waveguide electrically pumped to provide optical gain. The two ring resonators have different round-trip optical path lengths, and are coupled to each other through a half-wave optical coupler. The half-wave optical coupler has a predetermined cross-coupling coefficient and a 180-degree cross-coupling phase. The cross-coupling coefficient is substantially less than the self-coupling coefficients in order to achieve an optimal single-mode selectivity of the laser. The first ring resonator has an optical path length such that its resonant wavelengths correspond to a set of discrete operating channels. The second ring resonator has a slightly different length so that only one resonant wavelength coincides with one of the resonant wavelengths of the first ring resonator over the operating spectral window. The lasing action occurs at the common resonant wavelength. In operation, at least a portion of the optical waveguide in each of the first and the second ring resonators are forward biased to provide substantially equal round-trip optical gains. The second ring resonator is tuned by varying the effective refractive index of a portion of the waveguide through an electrical means, resulting in wavelength switching among the set of discrete operating wavelengths as determined by the first ring resonator.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Scintillating fiber dosimeter array
ActiveUS20090236510A1Accurate measurementMinimizes optical crosstalkDosimetersMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberDosimeter
A radiation dosimetry apparatus and method use a scintillating optical fiber array for detecting dose levels. The scintillating optical fiber detectors generate optical energy in response to a predetermined type of radiation, and are coupled to collection optical fibers that transmit the optical energy to a photo-detector for conversion to an electrical signal. The detectors may be embedded in one or more modular, water-equivalent phantom slabs. A repeatable connector couples the collection fibers to the photo-detector, maintaining the fiber ends in a predetermined spatial relationship. The detector fibers may be distributed as desired in a three-dimensional detection space, and may be oriented with their longitudinal axes at different orientations relative to a transmission axis of an incident radiation beam. A calibration method uses two measurements in two spectral windows, one with irradiation of the scintillator at a known dose and one with only irradiation of the collection fiber.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Wavelength switchable semiconductor laser using half-wave coupled active double-ring resonator
ActiveUS7738527B2Optical resonator shape and constructionCoupling light guidesOptical pathlengthOptical coupler
A semiconductor laser comprises two optical ring resonators, each comprising an optical waveguide electrically pumped to provide optical gain. The two ring resonators have different round-trip optical path lengths, and are coupled to each other through a half-wave optical coupler. The half-wave optical coupler has a predetermined cross-coupling coefficient and a 180-degree cross-coupling phase. The cross-coupling coefficient is substantially less than the self-coupling coefficients in order to achieve an optimal single-mode selectivity of the laser. The first ring resonator has an optical path length such that its resonant wavelengths correspond to a set of discrete operating channels. The second ring resonator has a slightly different length so that only one resonant wavelength coincides with one of the resonant wavelengths of the first ring resonator over the operating spectral window. The lasing action occurs at the common resonant wavelength. In operation, at least a portion of the optical waveguide in each of the first and the second ring resonators are forward biased to provide substantially equal round-trip optical gains. The second ring resonator is tuned by varying the effective refractive index of a portion of the waveguide through an electrical means, resulting in wavelength switching among the set of discrete operating wavelengths as determined by the first ring resonator.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Apparatus for imaging hydrogen sulfide plume and method of the same
ActiveUS20160097714A1Gain in hMaterial analysis by optical meansBandpass filteringOil and natural gas
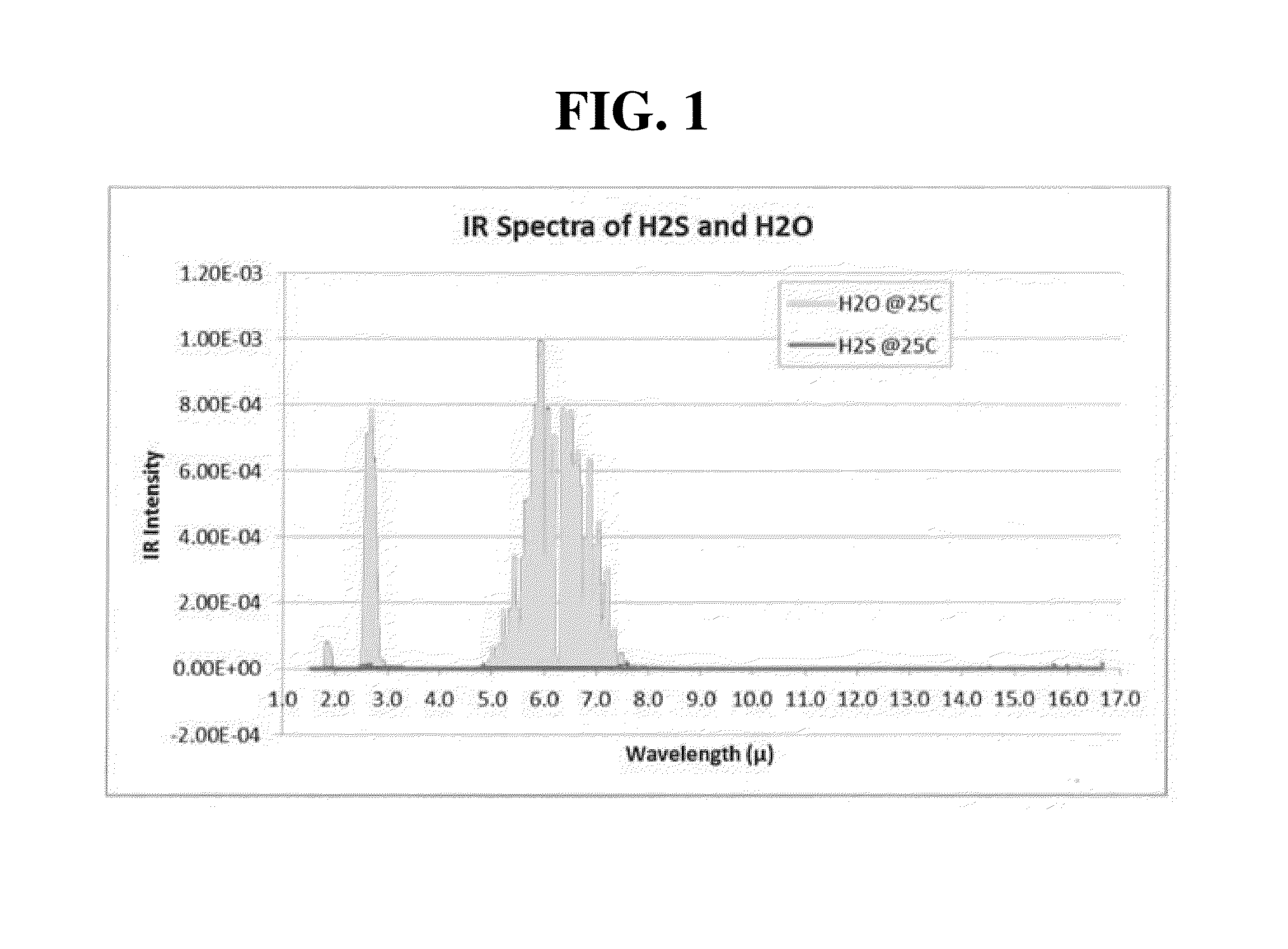
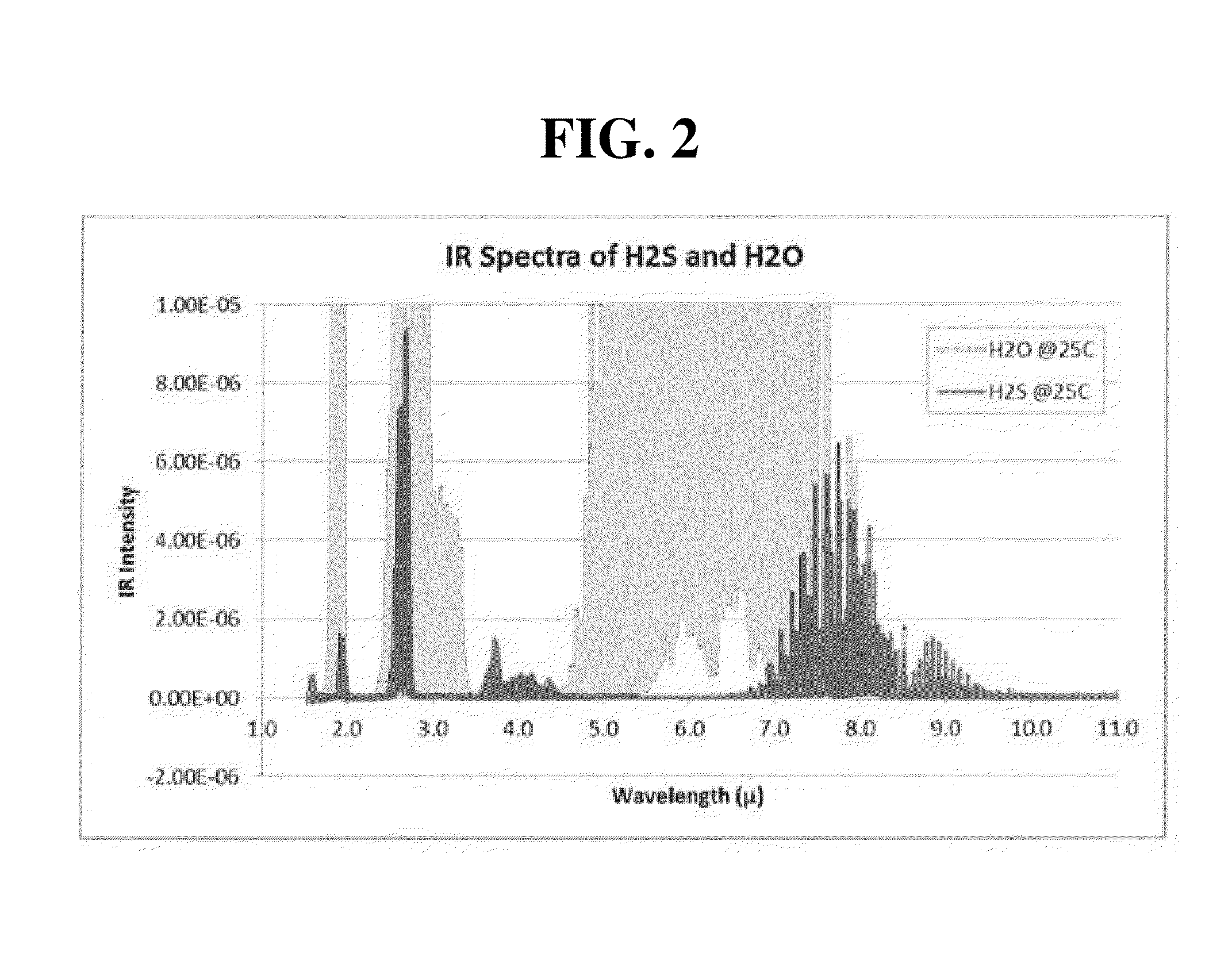
As hydrogen sulfide is toxic and widely present in many oil and gas facilities, it is highly desirable to use an infrared camera to detect the presence of a hydrogen sulfide (H2S) plume from a safe distance. The proposed are an imaging system and method for detecting hydrogen sulfide (H2S) in a safe distance. The imaging system includes an infrared (IR) imager capable of capturing an image of a scene that includes a gas plume, and a narrow bandpass filter installed in the infrared imager. The narrow bandpass filter has a spectral window. A width of the spectral window is in the range of 100 nm to 300 nm. The spectral window is included in a wavelength range between 2.5 μm and 2.8 μm, a wavelength range between 1.5 μm and 2.0 μm, or a wavelength range between 7.0 μm and 10.0 μm.
Owner:PROVIDENCE PHOTONICS
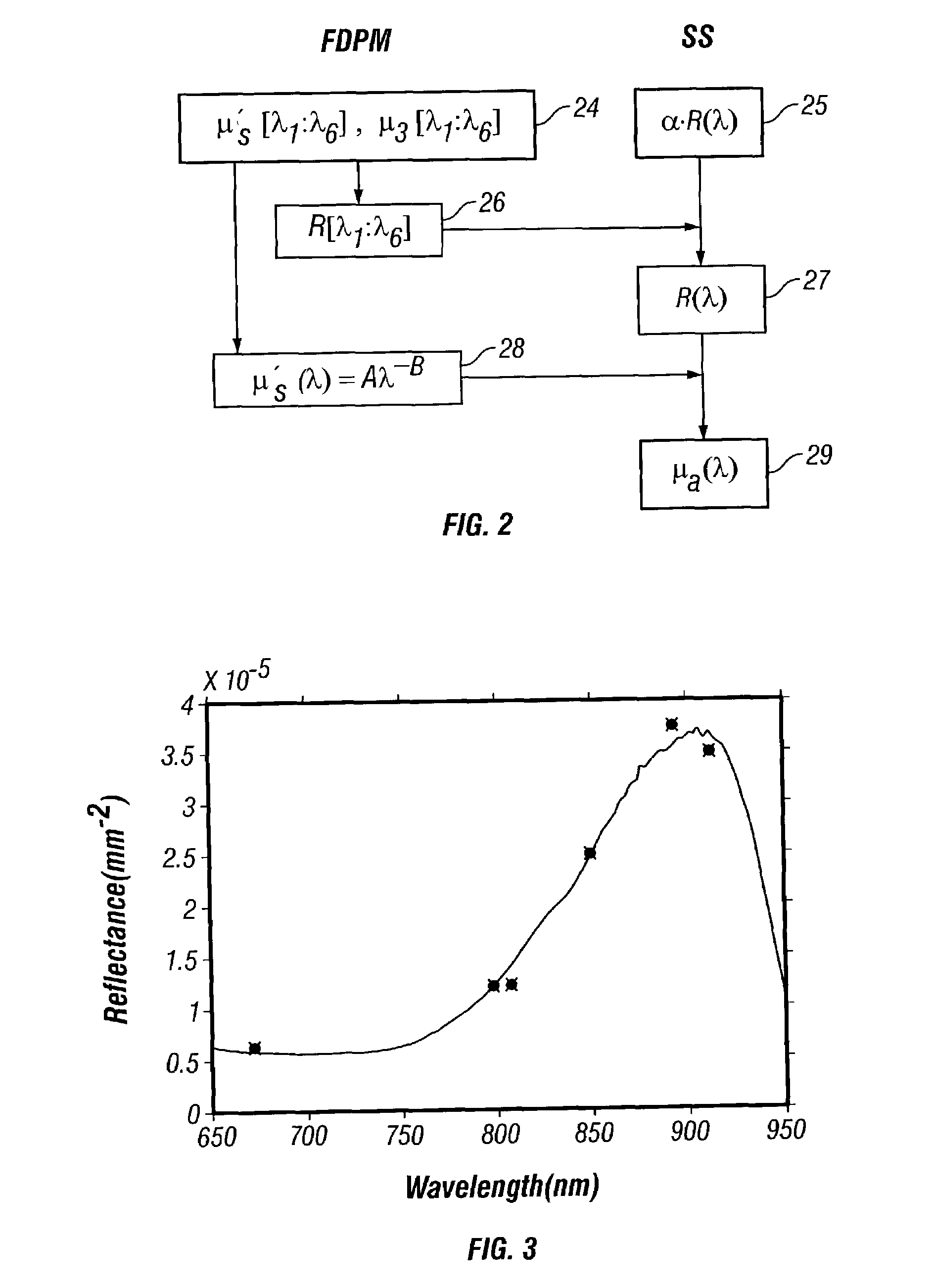
Quantitative broadband absorption and scattering spectroscopy in turbid media by combined frequency-domain and steady state methodologies
ActiveUS7428434B2Increase penetration depthWide wavelength coverageRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationBroadband absorptionDiffusion theory
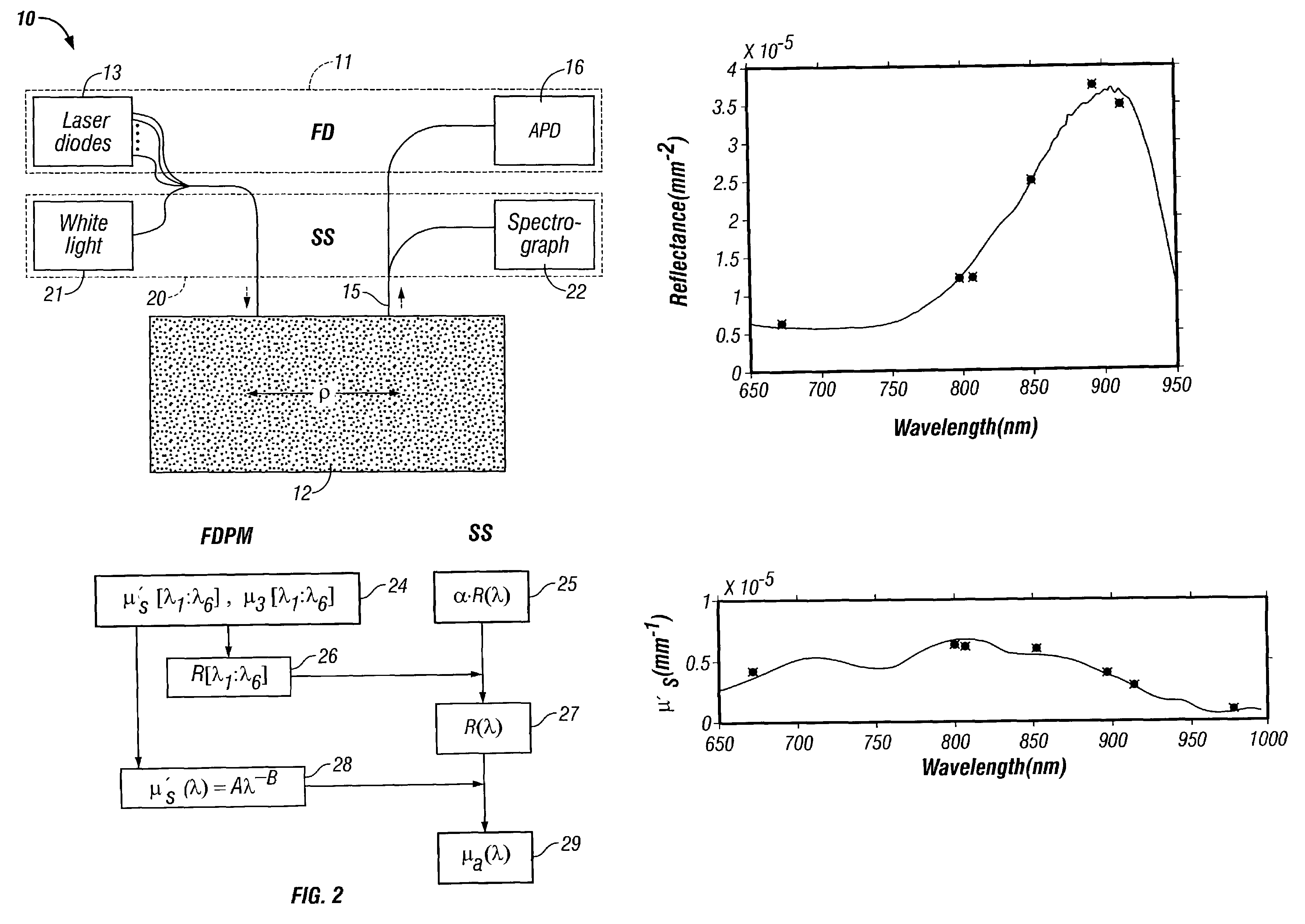
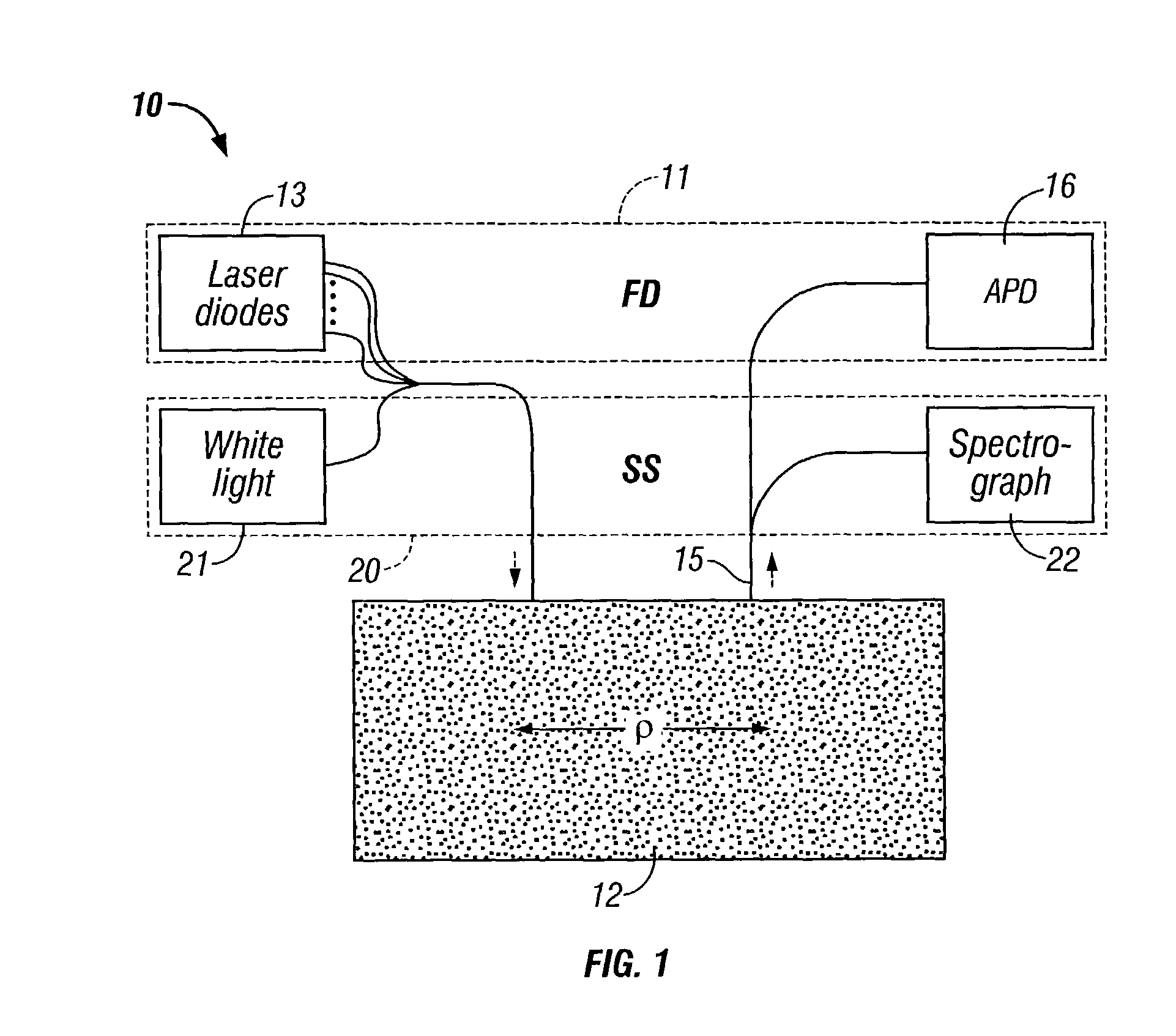
A technique for measuring broadband near-infrared absorption spectra of turbid media that uses a combination of frequency-domain and steady-state reflectance methods. Most of the wavelength coverage is provided by a white-light steady-state measurement, whereas the frequency-domain data are acquired at a few selected wavelengths. Coefficients of absorption and reduced scattering derived from the frequency-domain data are used to calibrate the intensity of the steady-state measurements and to determine the reduced scattering coefficient at all wavelengths in the spectral window of interest. The absorption coefficient spectrum is determined by comparing the steady-state reflectance values with the predictions of diffusion theory, wavelength by wavelength. Absorption spectra of a turbid phantom and of human breast tissue in vivo, derived with the combined frequency-domain and steady-state technique, agree well with expected reference values.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Spectral filter system for infrared imaging of substrates through coatings
ActiveUS20060289766A1Improve viewing clarityRadiation pyrometryInvestigating composite materialsBandpass filteringPolymer
An improved system for visual inspection of substrates coated with paints and polymers is disclosed. Painted substrates can be inspected for environmental and physical damage such as corrosion and cracks without removing the paint. The present invention provides the ability to maximize paint thickness penetration. This is accomplished with a spectral bandpass filter that rejects reflected light from the coating opaque bands, while allowing light in the paint window to pass to an IR detector such as an IR camera focal plane. The narrow bandpass range enhances the ability for IR imaging to see through thicker paint layers and improves the contrast over standard commercial IR mid-wave cameras. The bandpass may be adjusted to coincide with the full spectral window of the paint, consistent with the ability of the imaging focal plane to detect light in the spectral region.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Apparatus and method for detection, location, and identification of gamma sources
InactiveUS8067742B2Improve responseIncrease pointsMaterial analysis by optical meansHandling using diaphragms/collimetersPhotodetectorScintillation crystals
An apparatus for detecting and determining a source azimuth for gamma radiation includes at least two scintillation crystals at angular offsets and directed toward a common plane of detection, photodetectors adjacent to each of the scintillation crystals for converting the light response of the scintillation crystals into distinct electrical signals, and a digital processing system configured to analyze spectral data from each electrical signal produced for each crystal. The digital processing system monitors a finite number of spectral windows corresponding to a selected set of radioisotopes, and uses one or more of the electrical signals to determine a signal intensity and a likely source azimuth for a detected radioisotope in the plane of detection. Another scintillation crystal directed outside of the common plane of detection may be used for three-dimensional detection. Related methods for detection and location of gamma ray sources are discussed.
Owner:SPACE MICRO A CORP OF DELAWARE
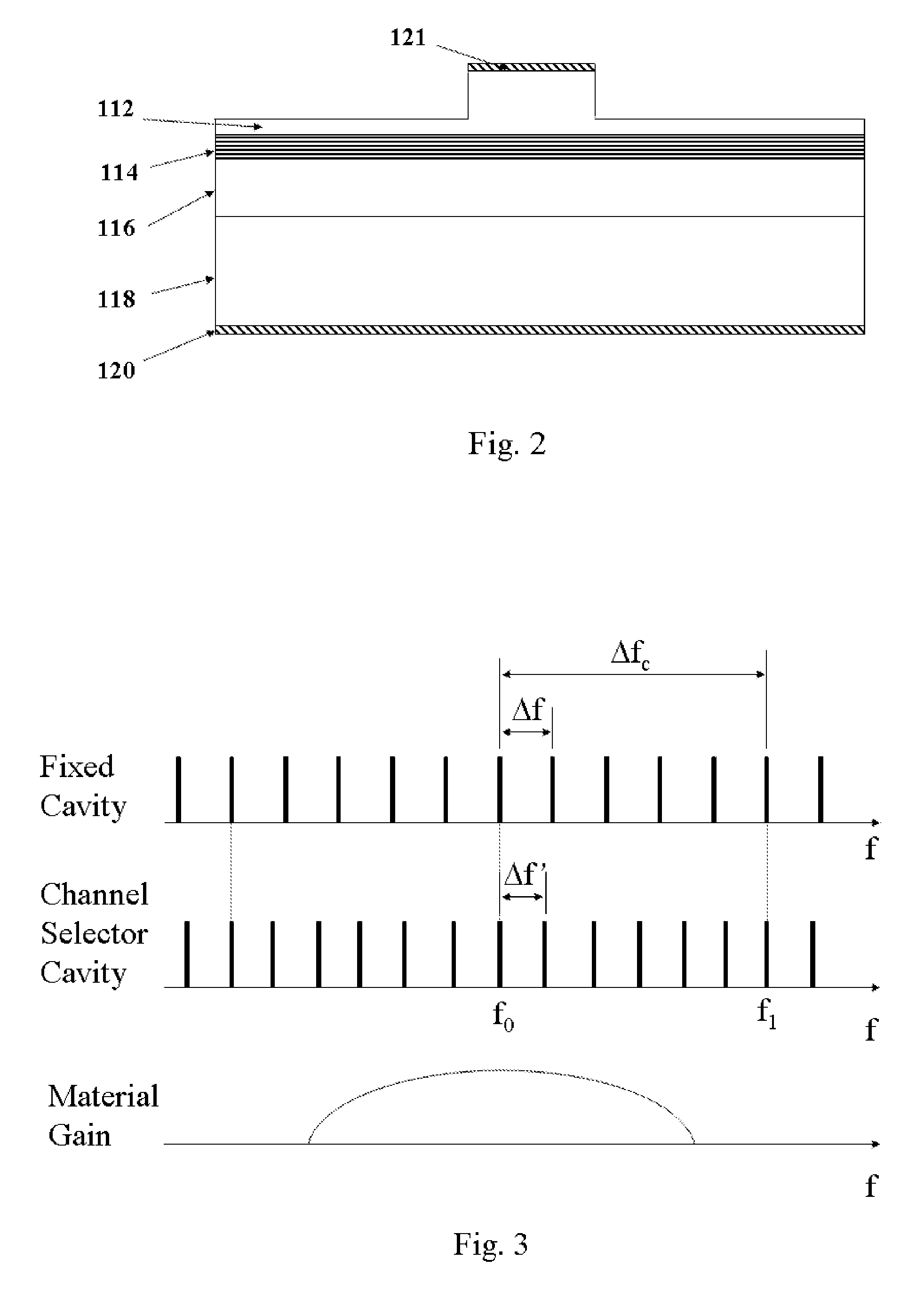
Wavelength switchable semiconductor laser
A monolithically integrated wavelength switchable laser comprises three coupled Fabry-Perot cavities. The length and consequently the free spectral range of the first cavity are designed such that the resonant peaks correspond substantially to a set of discrete operating wavelengths separated by a constant channel spacing. The second cavity has a slightly different length so that only one resonant peak coincides with one of the resonant peaks of the first cavity over the spectral window of the material gain. The lasing action occurs at the common resonant wavelength. The two cavities are coupled through a third short cavity that produces a certain coupling loss and phase relationship between the first and the second cavities in order to achieve an optimal mode selectivity of the combined cavity laser. In operation, both the first and the second cavities are forward biased to provide optical gains for the laser action. The second cavity is tuned by varying the refractive index of at least a portion of the waveguide within the cavity through an electrical means, resulting in wavelength switching of the laser among the set of discrete operating wavelengths as determined by the first cavity.
Owner:LIGHTIP TECH
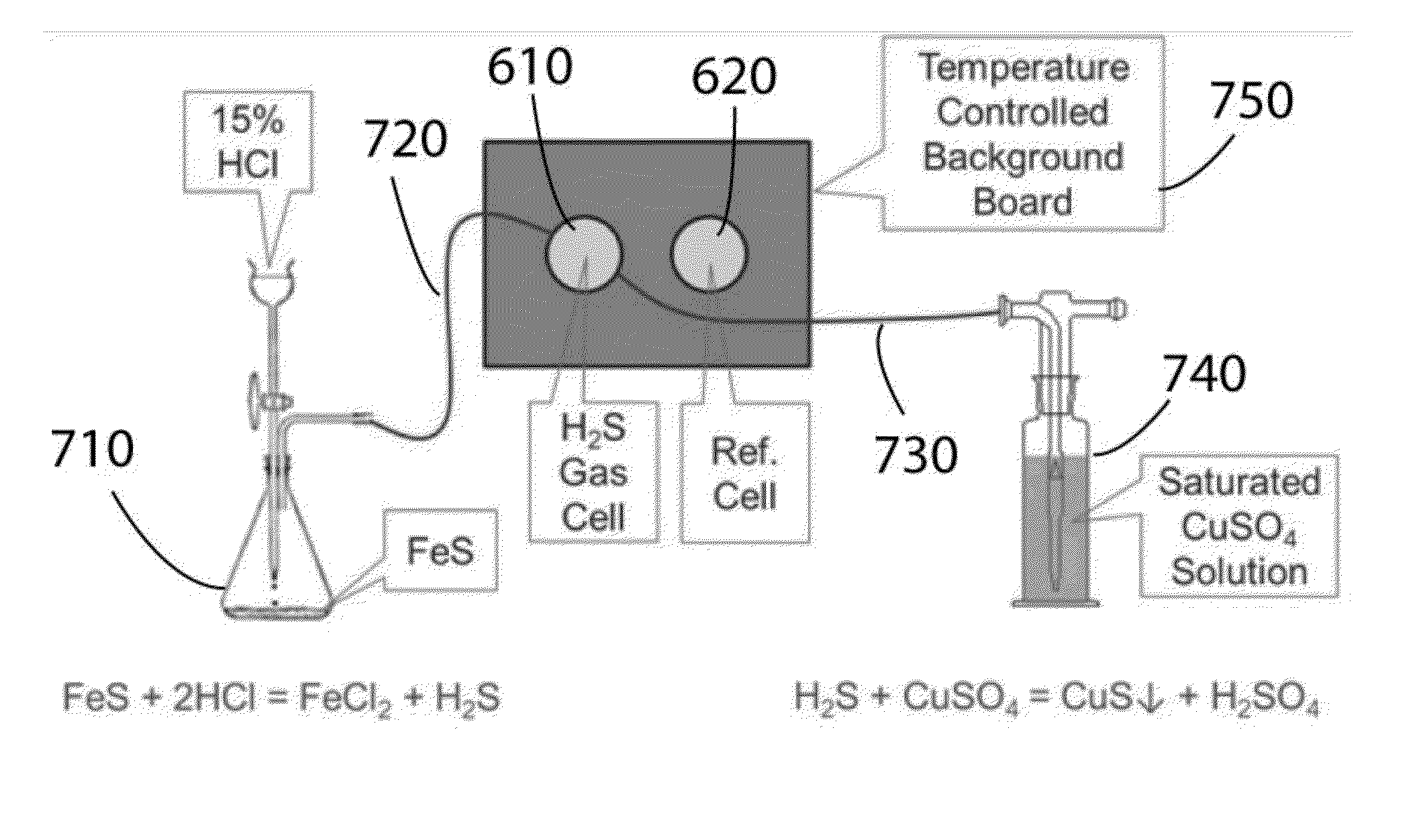
Spectral electrolytic cell suitable for in-situ characterization of Raman spectrum
InactiveCN103399000AImprove sealingWill not introduce pollutionRaman scatteringMaterial electrochemical variablesTop capSmall hole
The invention discloses a spectral electrolytic cell suitable for in-situ characterization of a Raman spectrum and relates to a spectral electrolytic cell. The spectral electrolytic cell is provided with a spectral electrolytic cell body, a top cover, an electrode sleeve, a reference electrode connection end, a spectral window sheet, limiting rings, limiting adjustment gaskets, reference electrode sealing covers, a counter electrode and a working electrode, wherein the cell body is connected with the top cover; window sheet sealing rings are fixed on the top cover; a first hole is formed in the middle of the cell body; the electrode sleeve is arranged in the first hole; a second hole is formed in the bottom in the cell body and is connected with the reference electrode connection end; a through hole is formed in the electrode sleeve; the upper end of the reference electrode connection end is connected with the reference electrode sealing covers; the spectral window sheet is arranged at the bottom in the top cover; small holes are formed in the middles of the reference electrode sealing covers; a third hole is formed in the side edge of the cell body; the counter electrode is arranged in the third hole; the limiting rings and the limiting adjustment gaskets are arranged at the periphery of the electrode sleeve; one end of the counter electrode is a sphere; a trench is formed in the bottom of the top cover; a gas storage tank is arranged beside the trench; a gas exhaust hole is formed in the upper end of the gas storage tank.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
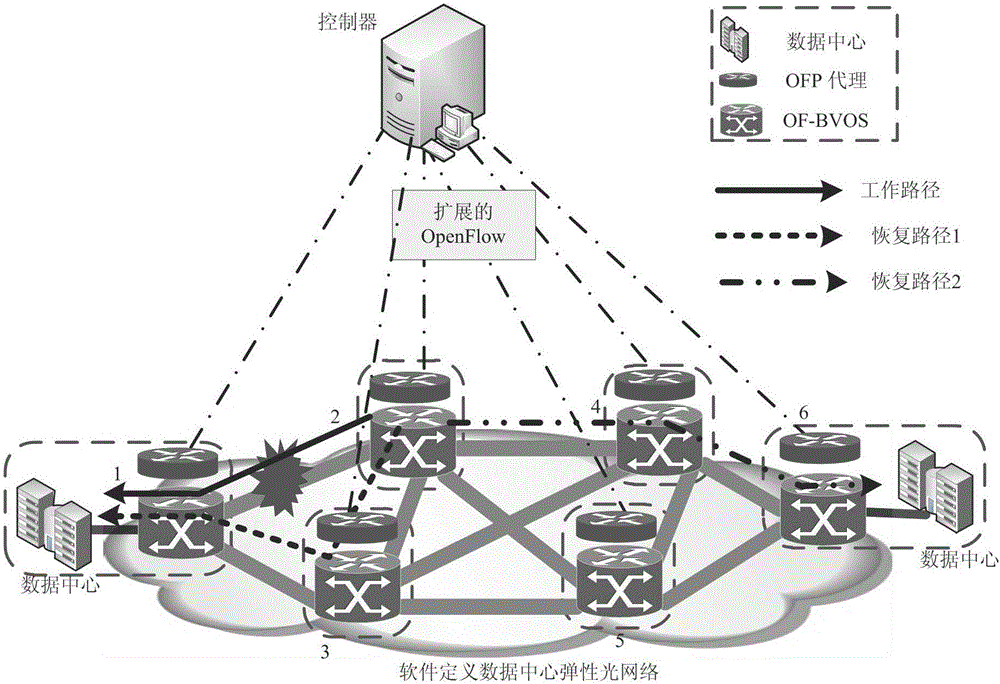
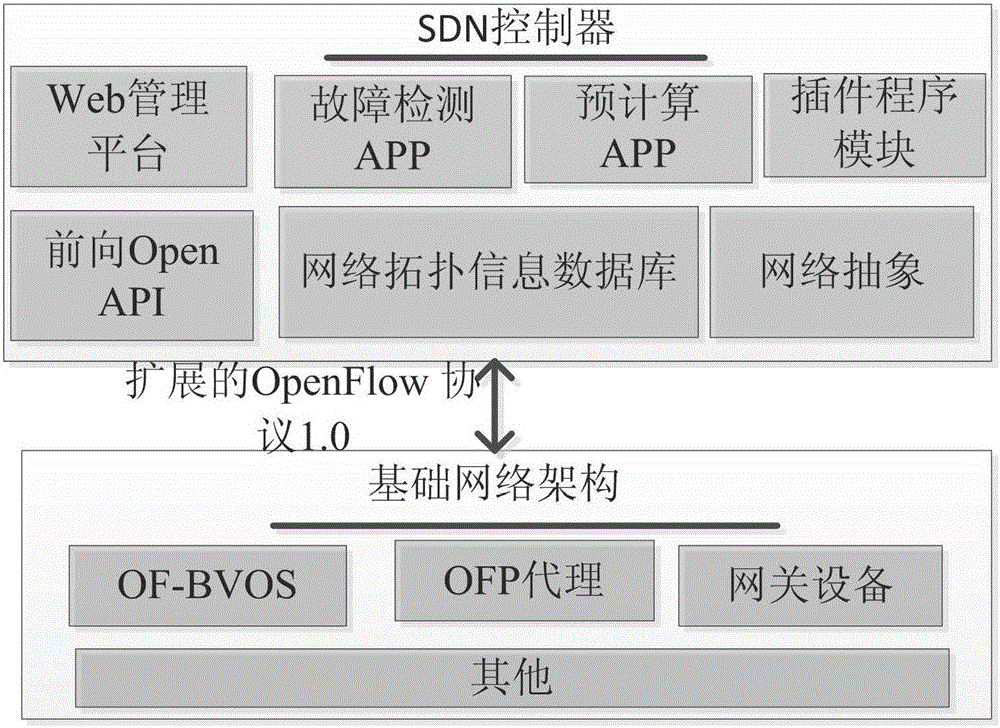
Pre-calculating recovery method based on distance self-adaptive route and spectrum distribution
ActiveCN105933174AFlexible definitionFlexible controlMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching networksRecovery methodFrequency spectrum
The invention relates to a pre-calculating recovery method based on distance self-adaptive route and spectrum distribution. The method includes that an elastic optical interconnection data center network configuration is defined by means of design software, a network control plane and a data forwarding plane are separated, a controller function module and an OpenFlow protocol are expanded to realize the function of rapid and flexible customization of network; according to the number of spectral gaps on the link, the network topology is divided into layers and a spectral window layered auxiliary graph model is constructed, a proper modulation format is selected based on distance self-adaption, the business route and spectrum distribution is carried out based on the spectral window layered auxiliary graph model; and when the fault business is recovered, a recovered route is calculated for the business in advance by means of pre-calculating recovery technology, and when the business has faults, network resources are opened for the interrupted business by means of a pre-calculating recovery scheme and the recovered route can be rapidly established. According to the method, the dual restraint of spectrum adjacency and continuity can be met, obstruction can be prevented, and meanwhile, the fault business can be rapidly recovered, and the integral performance of the network can be improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
System and method for modulating frequency domain of block transmission system based on filter set
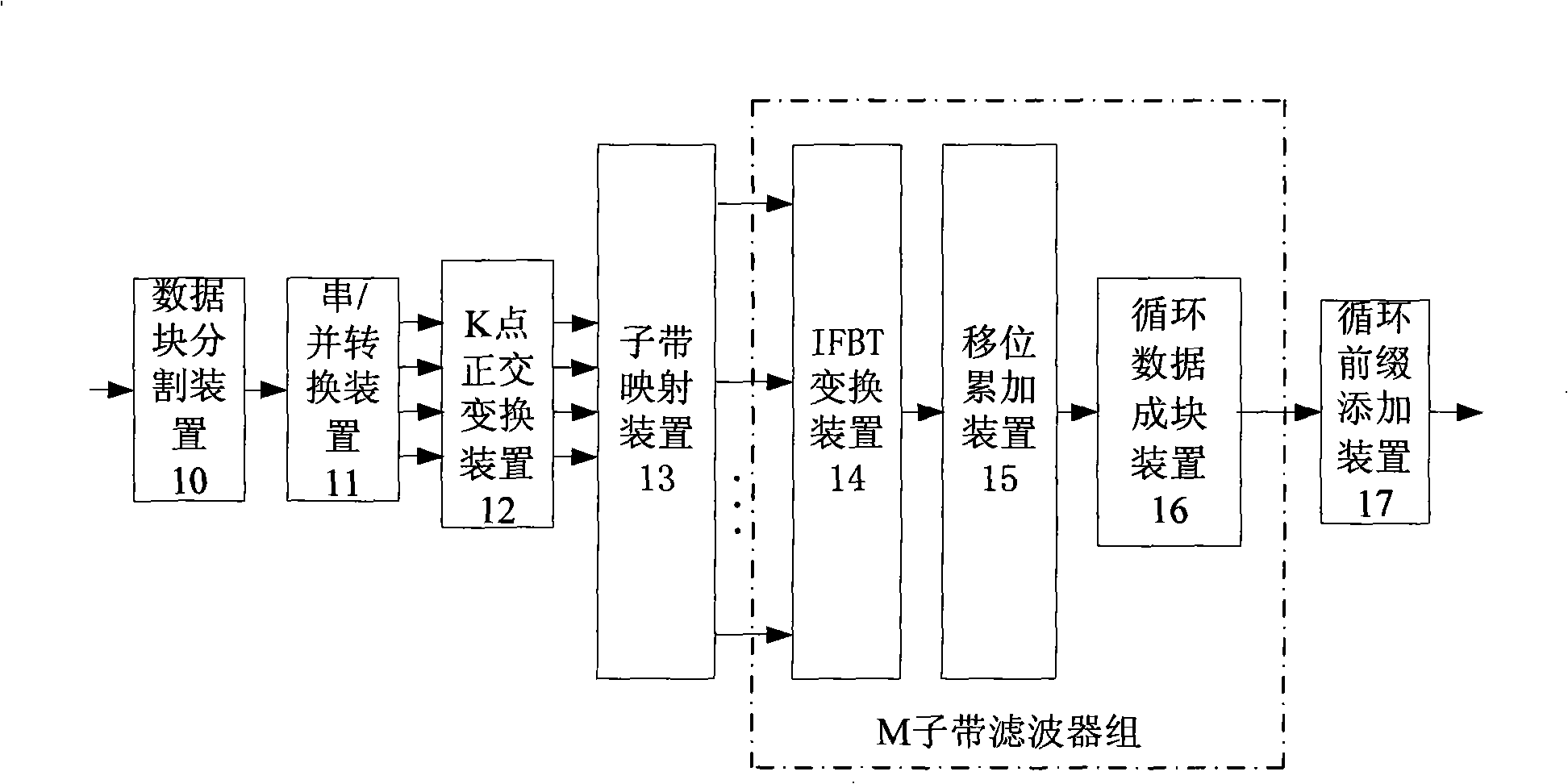
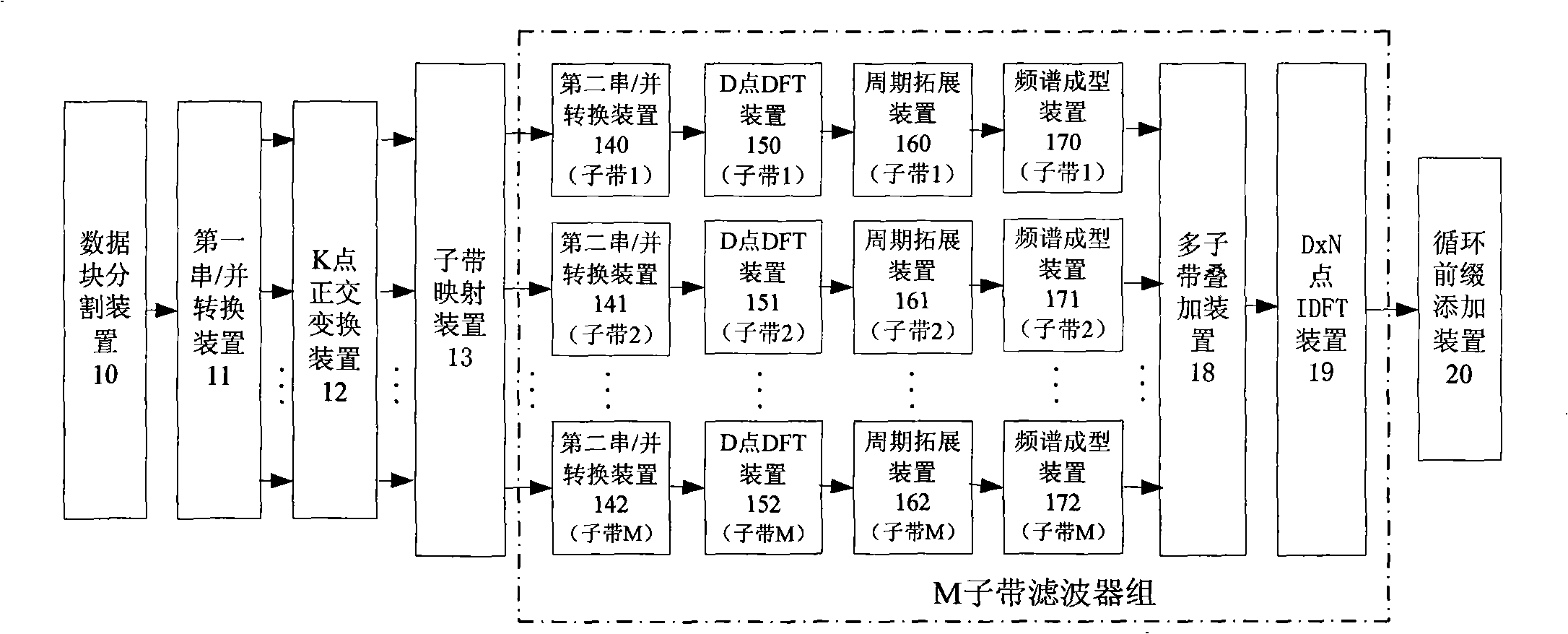
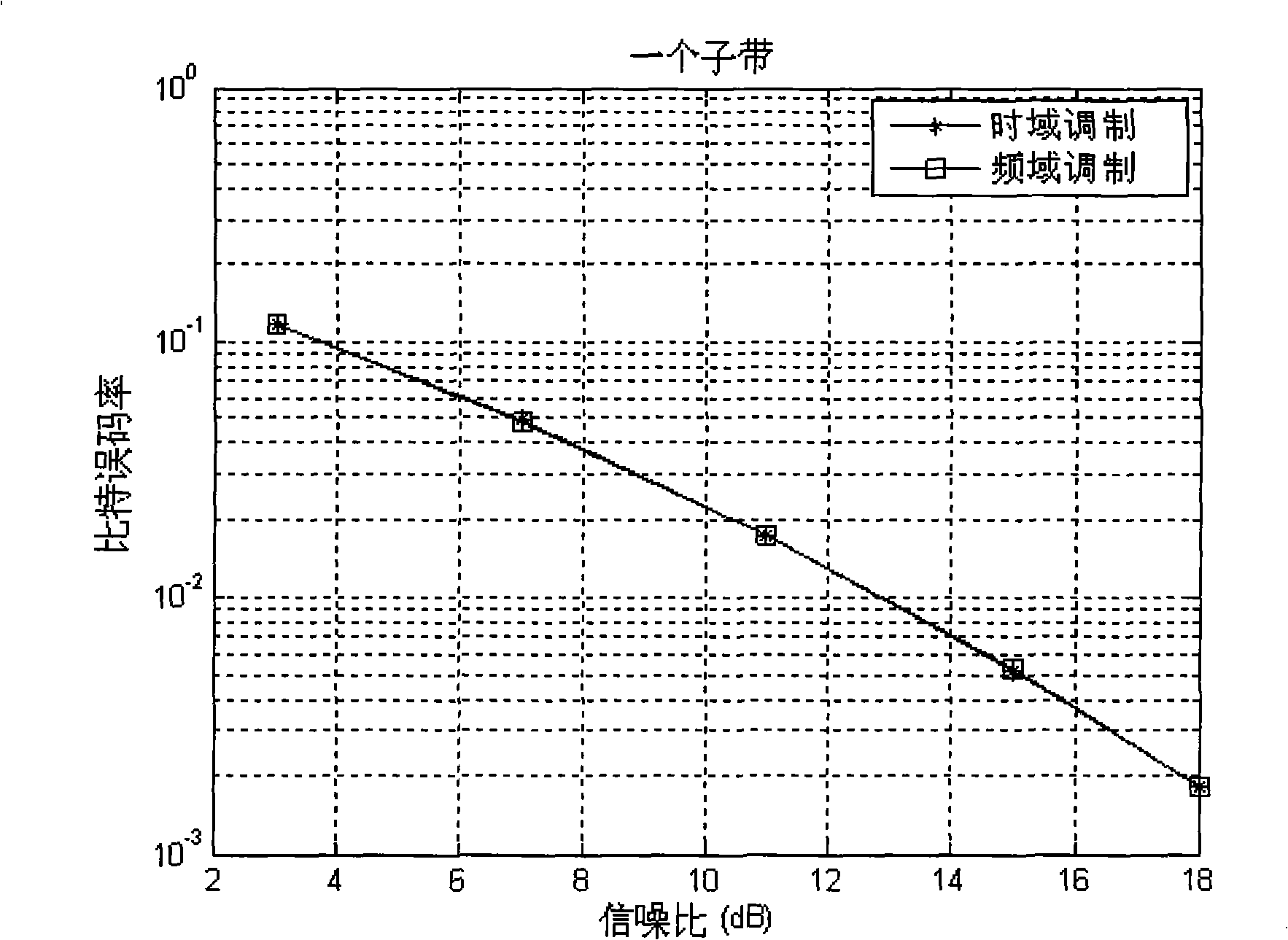
The invention provides a system and a method for modulating frequency domain of a block transmission system based on a wave filter set. The method comprises the following: firstly, an inputted serial modulating symbol sequence is divided into D data block sequences, with a length of K for each, the K point orthogonal transformation is performed; secondly, K elements outputted by each orthogonal transformation are respectively mapped to the K subbelts distributed by the system to transmit by the subbelt mapping; thirdly, the D point DFT transformation is performed on the data block with a length of D transmitted on each subbelt, the data block with a length of D*N is expanded in cycle; fourthly, the K data blocks with a length of D*N are respectively multiplied by corresponding spectral window functions on eachbelt to perform the frequency spectrum forming and the data block accumulation so as to form a data block with a length of D*N; and finally, the D*N point inverse Fourier transform to the data block is performed and the cyclic prefix is added to transmit the processed data block, thereby reducing the complexity on the condition of keeping the performance, particularly on the condition that the number of the distributed sub belts is small such as an upstream link circuit.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Stability control device for transmission spectrums of optical fiber current transducer
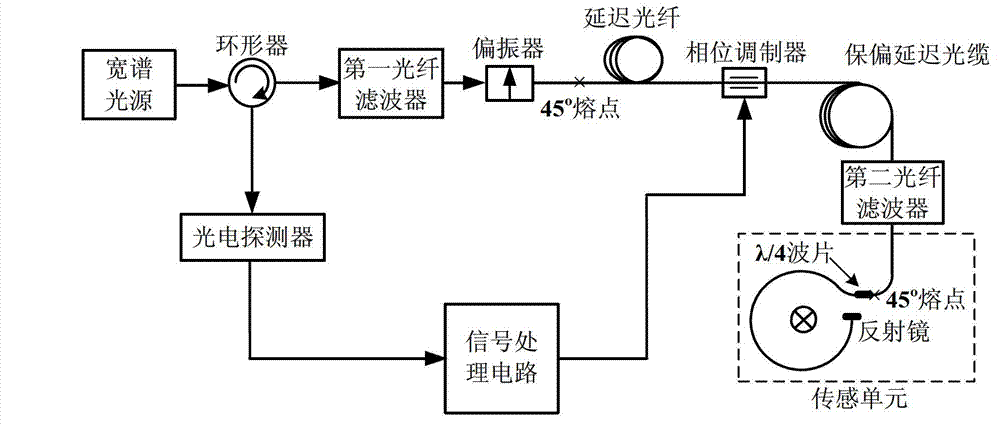
The invention discloses a stability control device for transmission spectrums of an optical fiber current transducer, and belongs to the technical field of optical fiber transmission. According to the stability control device, the front end of a polarizer is provided with a first optical fiber filter, and the front end of a sensing unit is provided with a second optical fiber filter. According to the invention, the changes in the spectral form and power of optical waves induced by the drifting of a spectral window of an optical device caused by shaft-aligning errors and temperature in the optical fiber current transducer are eliminated, so that the transmission spectrum in the optical fiber current transducer is stable, thereby eliminating integral optical phase shifting errors of a Faraday effect of the sensing unit. A new scheme for optical paths of all-optical-fiber current transducers based on an optical fiber filter provided by the invention solves the problem that in a traditional optical path, a spectral window of an optical device drifts due to temperature drift and difficulty in accurate shaft-aligning among optical fibers or between an optical fiber and a device, eliminates the influence of spectrum fluctuation on error signals, expands the range of a system for tracking direct-current random phase drift, and improves the anti-jamming capability and stability of the system.
Owner:开元锐德(北京)光电科技有限公司
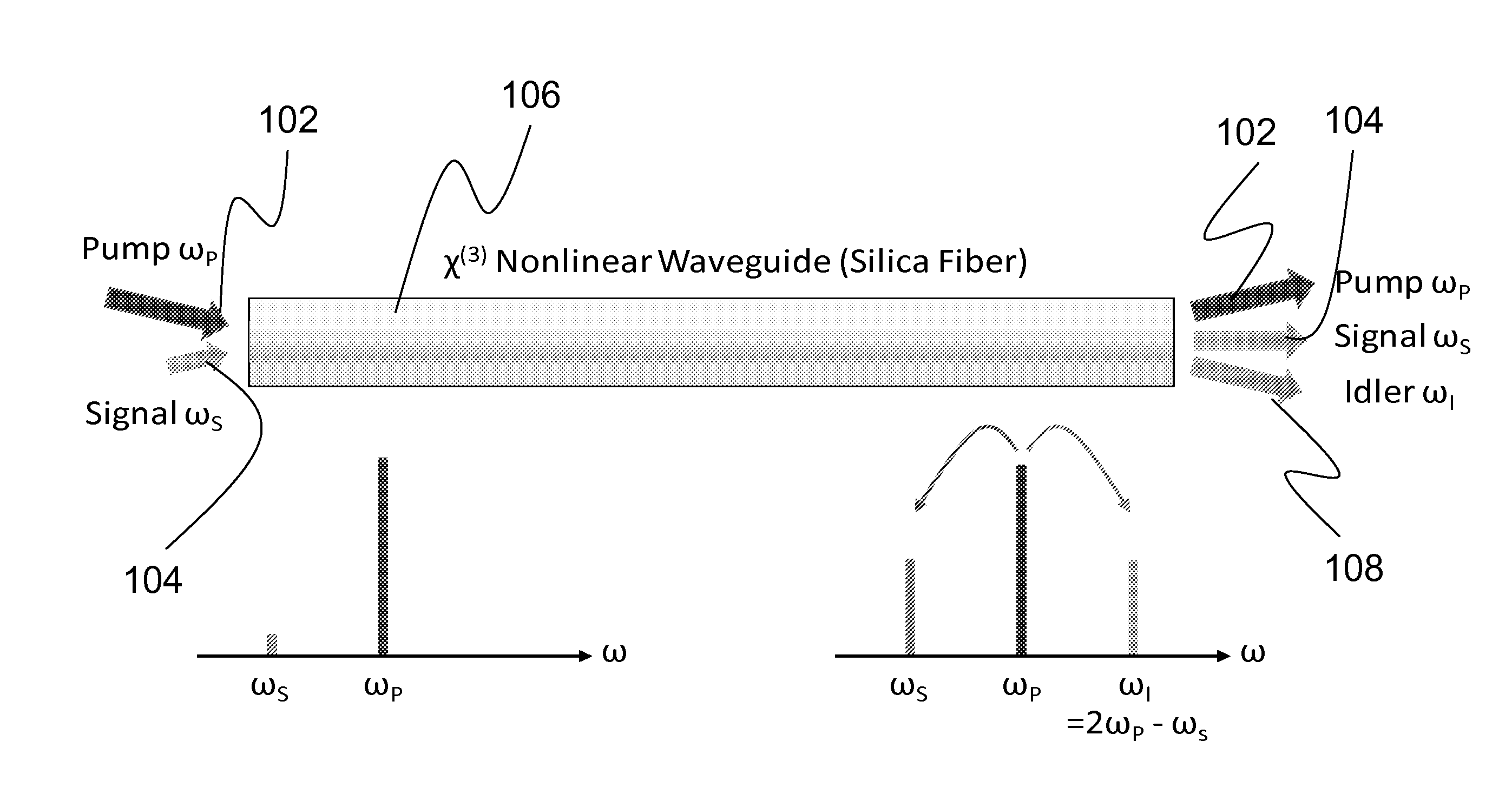
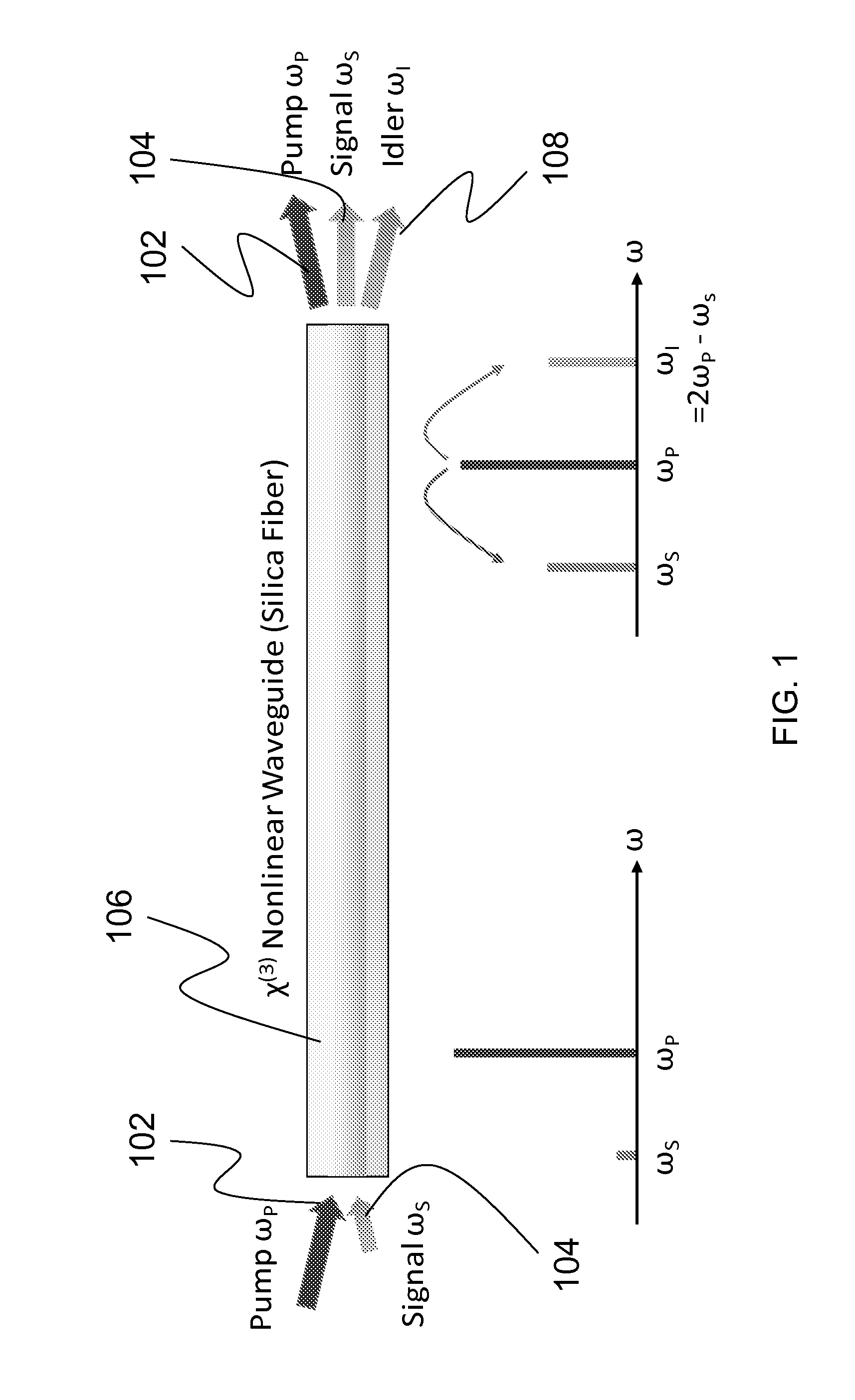
Systems and methods for fiber optic parametric amplification and nonlinear optical fiber for use therein
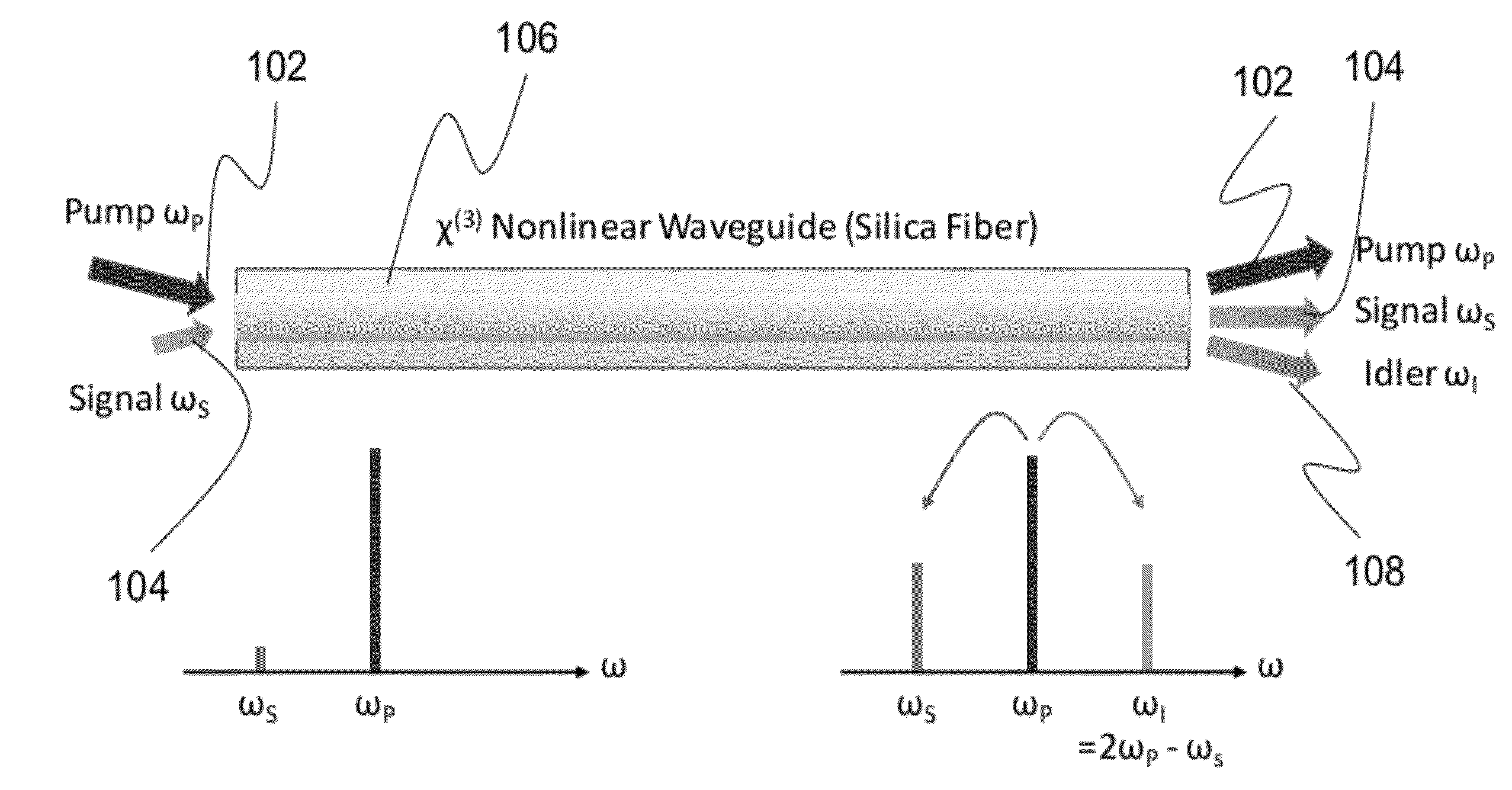
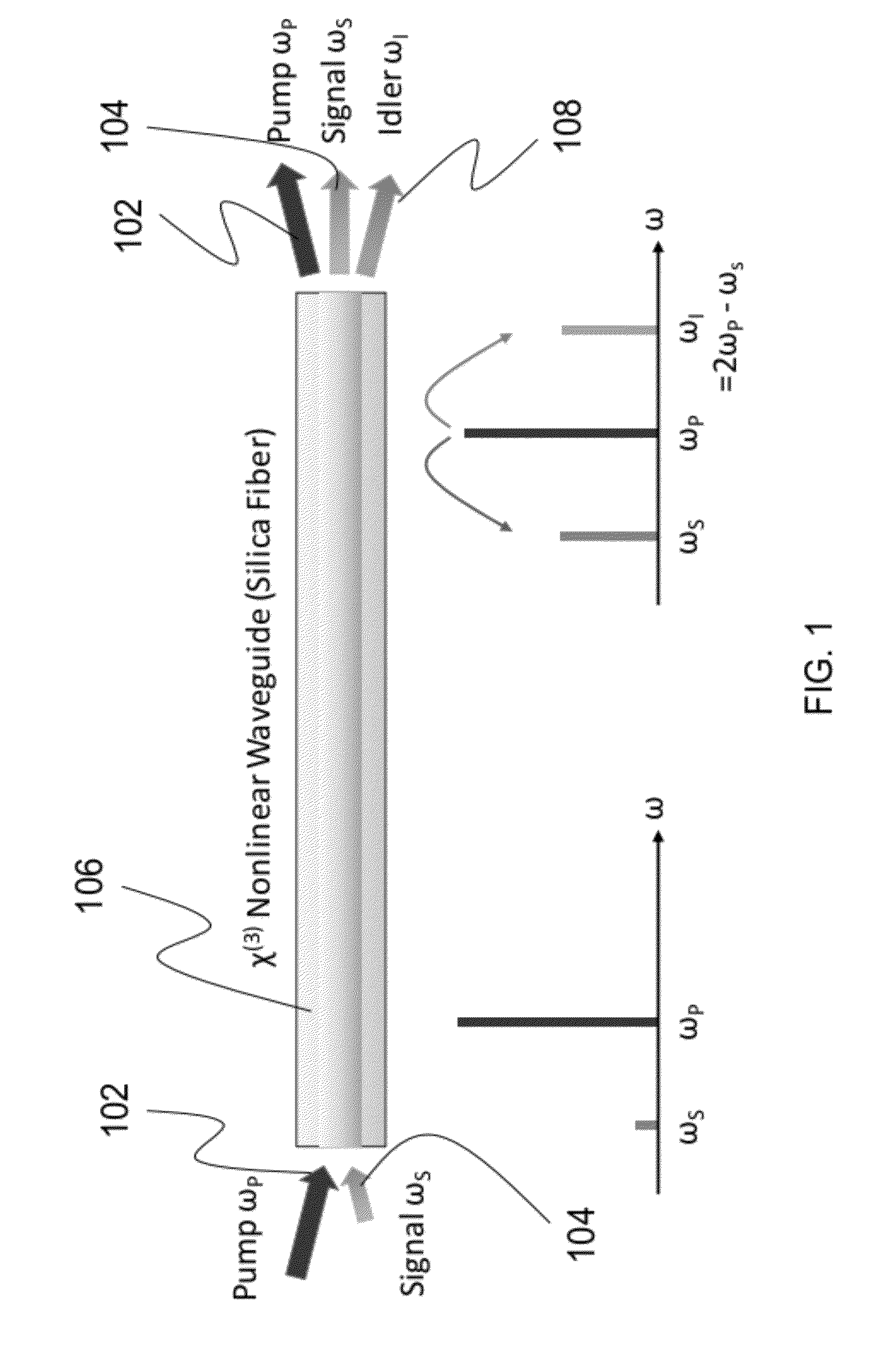
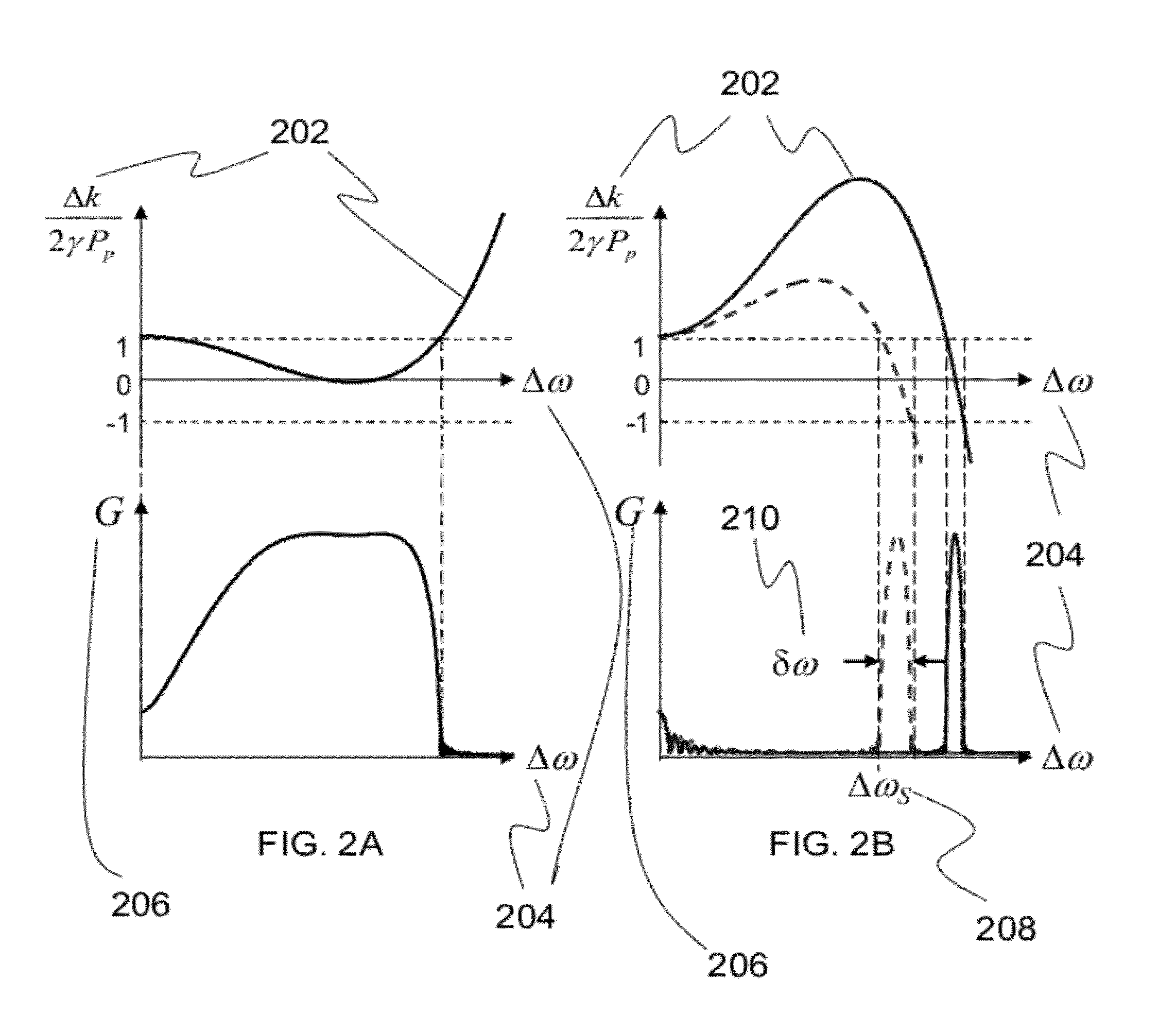
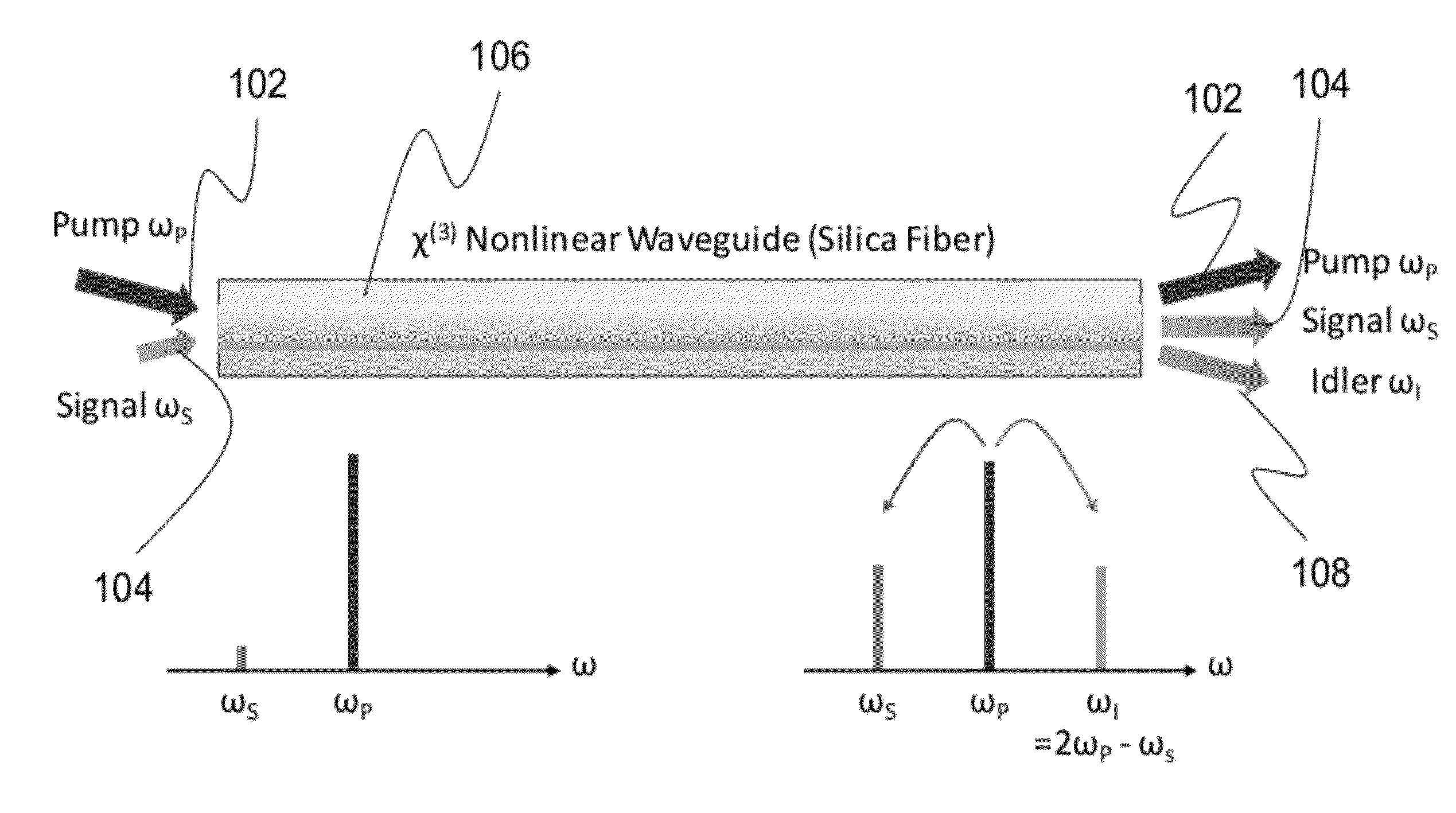
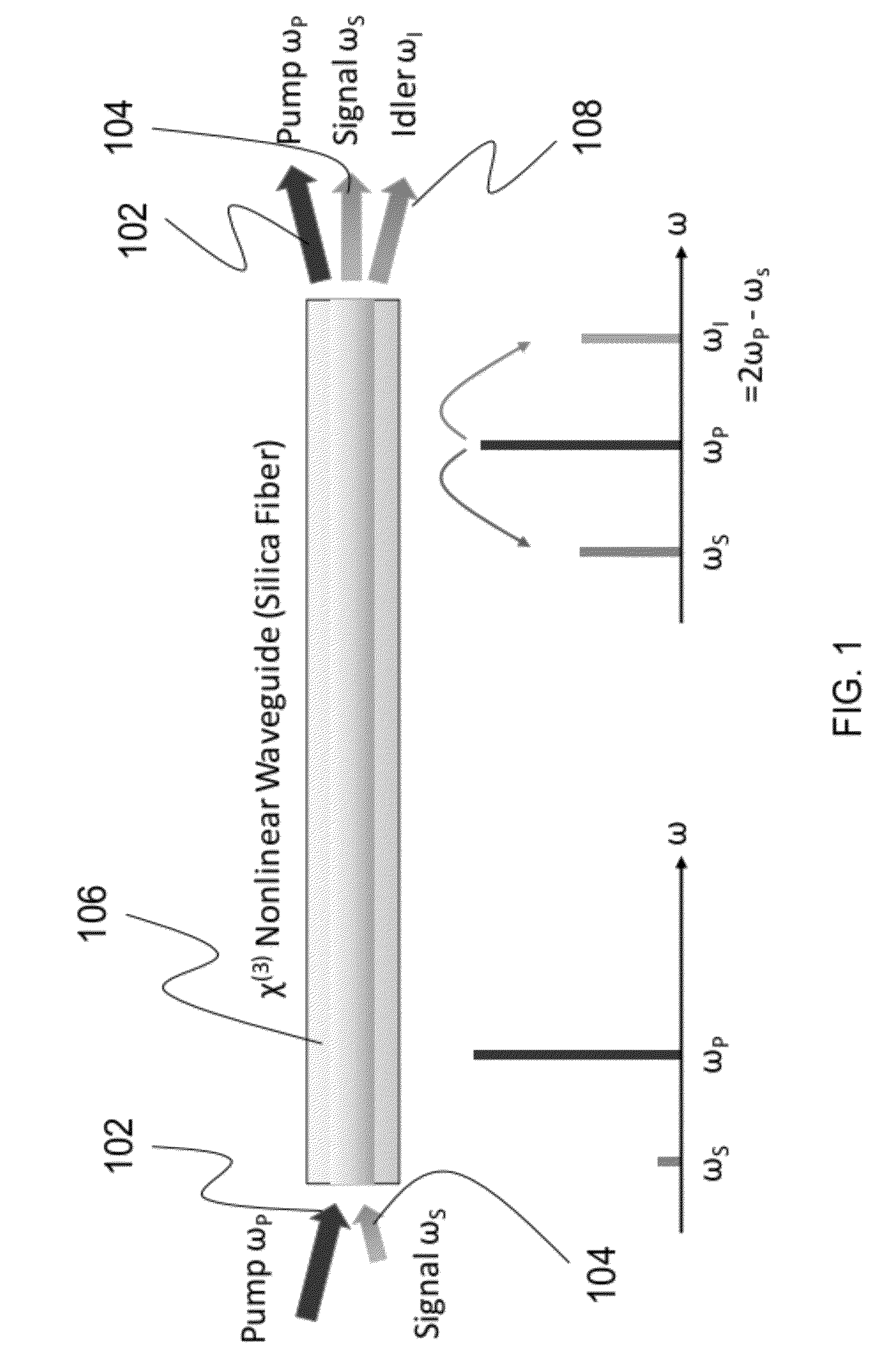
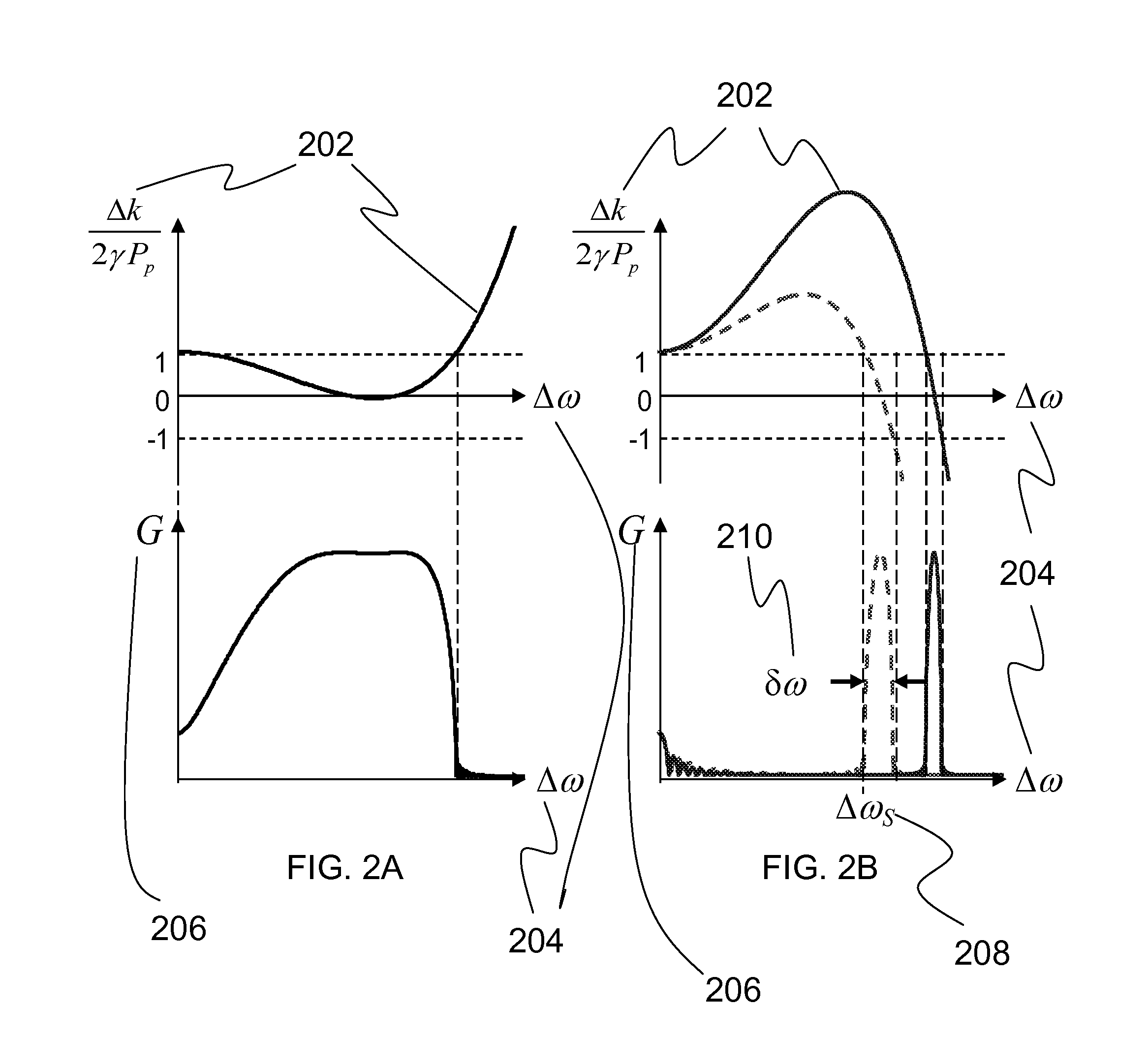
ActiveUS20120257270A1Precise physical propertySlow changeLaser detailsSpectrum investigationFiber optical parametric amplifierPhase matching
A high confinement nonlinear optical fiber is provided along with methods of parametric amplification for use thereof. The nonlinear optical fiber may include a plurality of concentric layers which are configured to provide different guiding regimes to low-frequency and high-frequency components through transverse geometry and refractive index profiling, thus reducing waveguide dispersion. The resulting optical fiber provides a parametric device with phase-matching in any spectral region of interest, such that a fiber optic parametric amplifier (FOPA) implementing the optical fiber can amplify in any spectral window of interest. A narrow-band FOPA configured to minimize phase mismatching is also provided for use with the optical fiber, and may be implemented as a light source or a monochromator.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Scintillating fiber dosimeter array
ActiveUS8183534B2Minimizes optical crosstalkAccurate locationDosimetersSolid-state devicesDosimeterRadiation measuring device
A radiation dosimetry apparatus and method use a scintillating optical fiber array for detecting dose levels. The scintillating optical fiber detectors generate optical energy in response to a predetermined type of radiation, and are coupled to collection optical fibers that transmit the optical energy to a photo-detector for conversion to an electrical signal. The detectors may be embedded in one or more modular, water-equivalent phantom slabs. A repeatable connector couples the collection fibers to the photo-detector, maintaining the fiber ends in a predetermined spatial relationship. The detector fibers may be distributed as desired in a three-dimensional detection space, and may be oriented with their longitudinal axes at different orientations relative to a transmission axis of an incident radiation beam. A calibration method uses two measurements in two spectral windows, one with irradiation of the scintillator at a known dose and one with only irradiation of the collection fiber.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
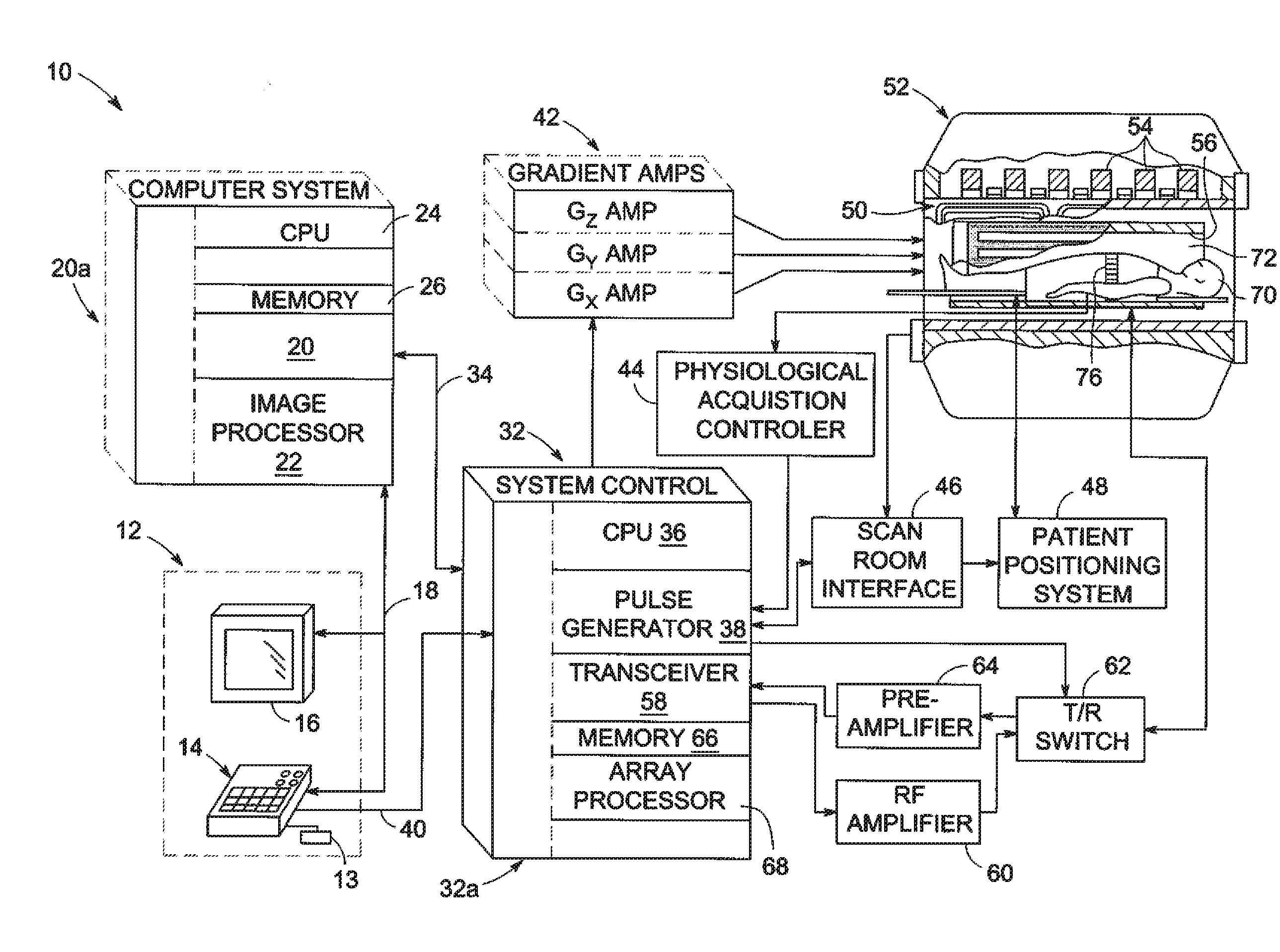
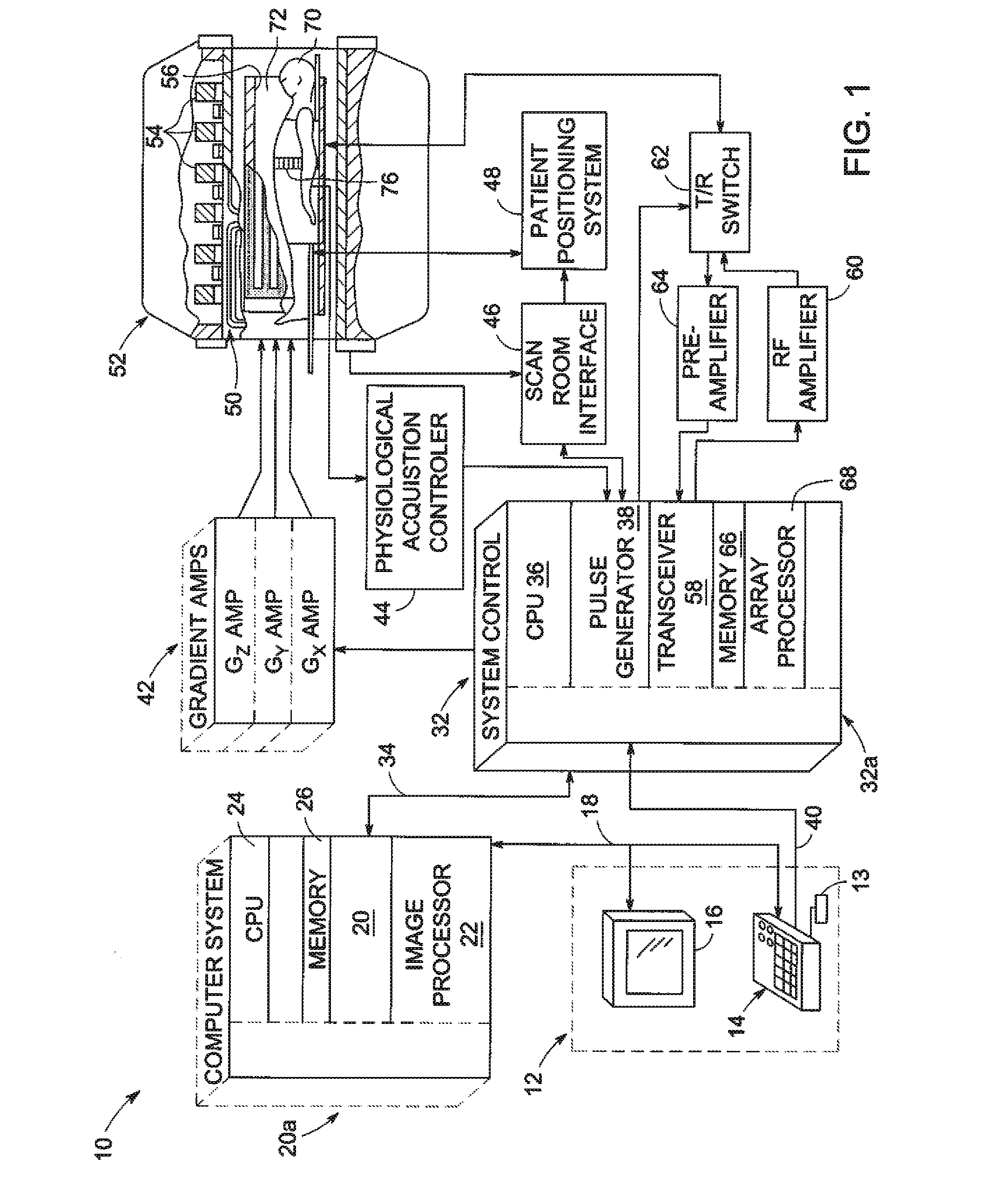
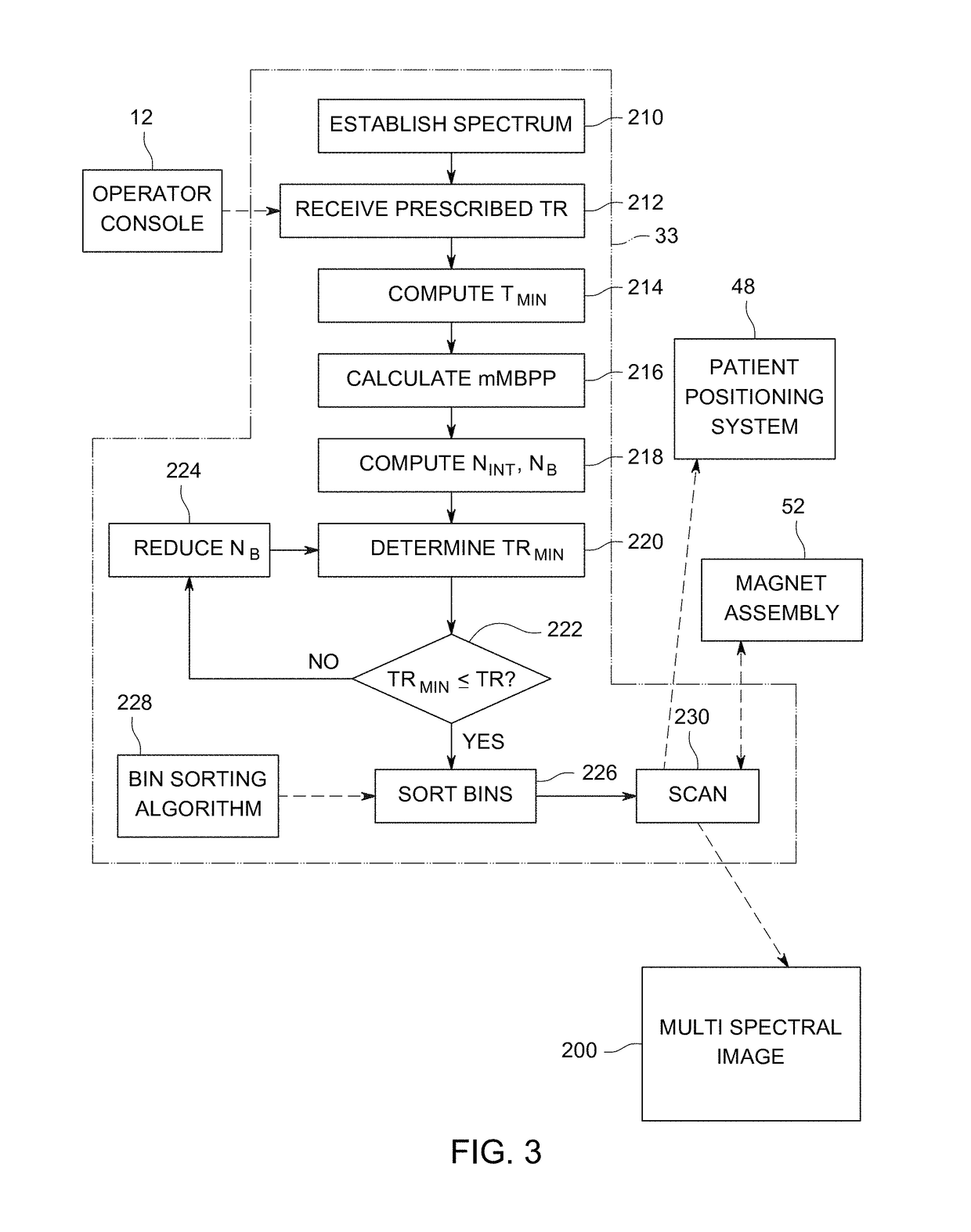
Accelerated multispectral data magnetic resonance imaging system and method
ActiveUS20120262167A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionFrequency spectrumMissing data
A method for processing magnetic resonance imaging data includes accessing the magnetic resonance imaging data, the data including a plurality of magnetic resonance data sets each collected at different excitation frequencies and defining reconstructable images representative of sections of a single image of a subject. Each magnetic resonance data set includes sampled data for sampled phase encoding points but is missing data for unsampled phase encoding points. The method further includes determining the missing data of at least one of the magnetic resonance data sets using a correlation between the sampled data for the respective magnetic resonance data set and sampled data from at least one other magnetic resonance data set within a spectral window encompassing at least the respective magnetic resonance data set and the at least one other magnetic resonance data set.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Systems and methods for fiber optic parametric amplification and nonlinear optical fiber for use therein
ActiveUS8482847B2Precise physical propertySlow changeLaser detailsSpectrum investigationFiber optical parametric amplifierLight source
A high confinement nonlinear optical fiber is provided along with methods of parametric amplification for use thereof. The nonlinear optical fiber may include a plurality of concentric layers which are configured to provide different guiding regimes to low-frequency and high-frequency components through transverse geometry and refractive index profiling, thus reducing waveguide dispersion. The resulting optical fiber provides a parametric device with phase-matching in any spectral region of interest, such that a fiber optic parametric amplifier (FOPA) implementing the optical fiber can amplify in any spectral window of interest. A narrow-band FOPA configured to minimize phase mismatching is also provided for use with the optical fiber, and may be implemented as a light source or a monochromator.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Spectral filter system for infrared imaging of substrates through coatings
ActiveUS7462809B2Improve viewing clarityRadiation pyrometryInvestigating composite materialsBandpass filteringPolymer
An improved system for visual inspection of substrates coated with paints and polymers is disclosed. Painted substrates can be inspected for environmental and physical damage such as corrosion and cracks without removing the paint. The present invention provides the ability to maximize paint thickness penetration. This is accomplished with a spectral bandpass filter that rejects reflected light from the coating opaque bands, while allowing light in the paint window to pass to an IR detector such as an IR camera focal plane. The narrow bandpass range enhances the ability for IR imaging to see through thicker paint layers and improves the contrast over standard commercial IR mid-wave cameras. The bandpass may be adjusted to coincide with the full spectral window of the paint, consistent with the ability of the imaging focal plane to detect light in the spectral region.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Photonic crystal mirrors for high-resolving-power fabry perots
Owner:HERMAN PETER +2
Systems and methods for fiber optic parametric amplification and nonlinear optical fiber for use therein
ActiveUS20130314767A1Precise physical propertySlow changeLaser detailsSpectrum investigationRefractive indexFiber optical parametric amplifier
A high confinement nonlinear optical fiber is provided along with methods of parametric amplification for use thereof The nonlinear optical fiber may include a plurality of concentric layers which are configured to provide different guiding regimes to low-frequency and high-frequency components through transverse geometry and refractive index profiling, thus reducing waveguide dispersion. The resulting optical fiber provides a parametric device with phase-matching in any spectral region of interest, such that a fiber optic parametric amplifier (FOPA) implementing the optical fiber can amplify in any spectral window of interest. A narrow-band FOPA configured to minimize phase mismatching is also provided for use with the optical fiber, and may be implemented as a light source or a monochromator.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Non-linear symmetric sweep spectral-spatial RF pulses for mr spectroscopy
ActiveUS20050225323A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionLipid formationFrequency spectrum
A method for designing non-linear phase 180° spectral-spatial radio frequency pulses that can be used for spectral editing in magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. A novel feature of the pulse is a symmetric sweep developed by the spectral profile from the outside edges of the spectral window towards the middle whereby coupled components are tipped simultaneously and over a short interval. Pulses have been designed for lactate editing at 1.5 T and 3 T. The spectral and spatial spin-echo profiles of the RF pulses can be measured experimentally and altered in an iterative manner. Spectral-spatial radio frequency (SSRF) pulses allow simultaneous selection in both frequency and spatial domains. These pulses are particularly important for clinical and research magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) applications for suppression of large water and lipid resonances.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
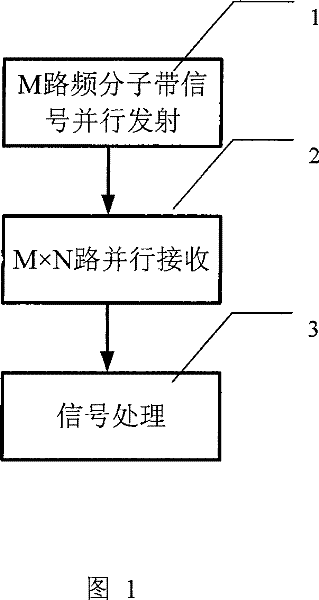
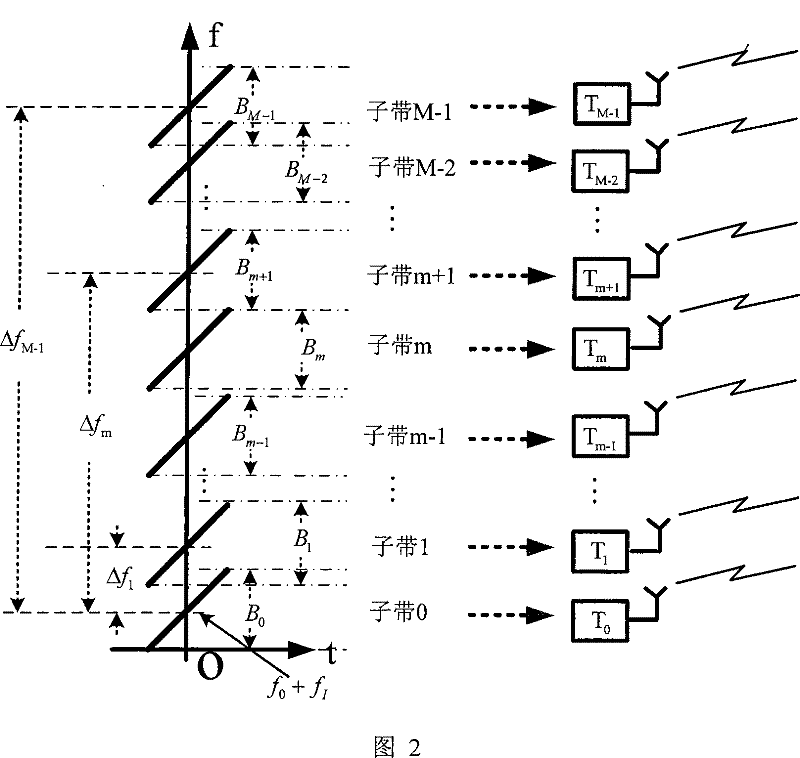
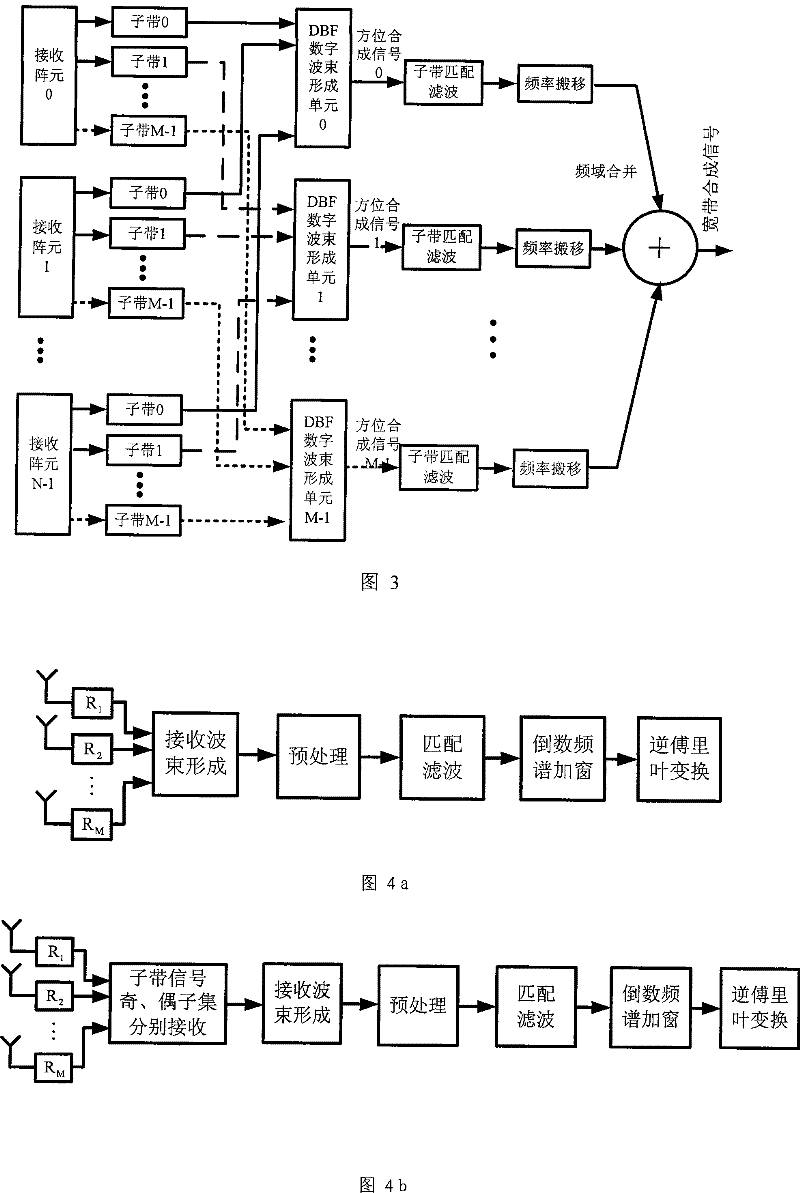
Wideband Signal Synthesis Method Based on Multiple Transmit Multiple Receive Frequency Division Radar
InactiveCN101452073BLower performance requirementsSuppress interferenceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumRadar imaging
The present invention provides a broadband signal synthesis method based on multi-transmission and multi-reception frequency division radar, comprising the following steps: 1) at the transmission end of the multi-transmission and multi-reception radar, synchronously transmit M subband signals from M transmitting array elements of the transmitting array; 2) At the receiving end of the multi-transmit and multi-receive radar, N receiving array elements in the receiving array receive echo signals, and each receiving array element is provided with M receiving channels to obtain N×M receiving signals corresponding to different frequency bands and different array elements; 3) Perform beamforming processing and matched filtering processing to obtain M narrowband signals, and then add the spectra of the M narrowband signals to obtain a composite broadband signal, and multiply the composite broadband signal by the reciprocal spectral window to obtain the final broadband signal. The present invention effectively overcomes the problem of side lobes generated when a plurality of narrowbands are synthesized into wideband signals. Therefore, the present invention can use a plurality of narrowband transceiving channels to realize high-resolution range images, thereby greatly reducing the performance requirements of imaging radars for wideband devices.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
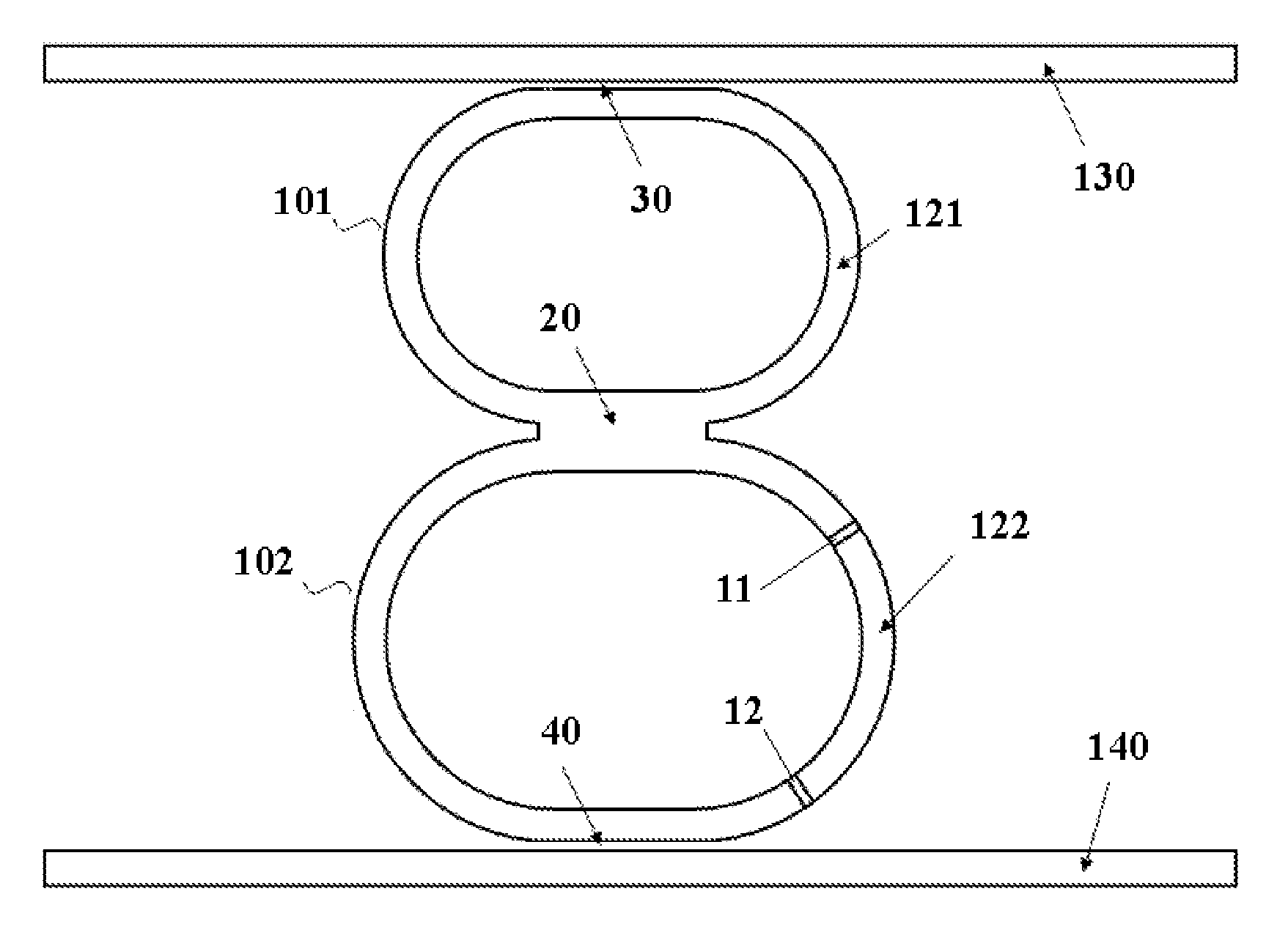
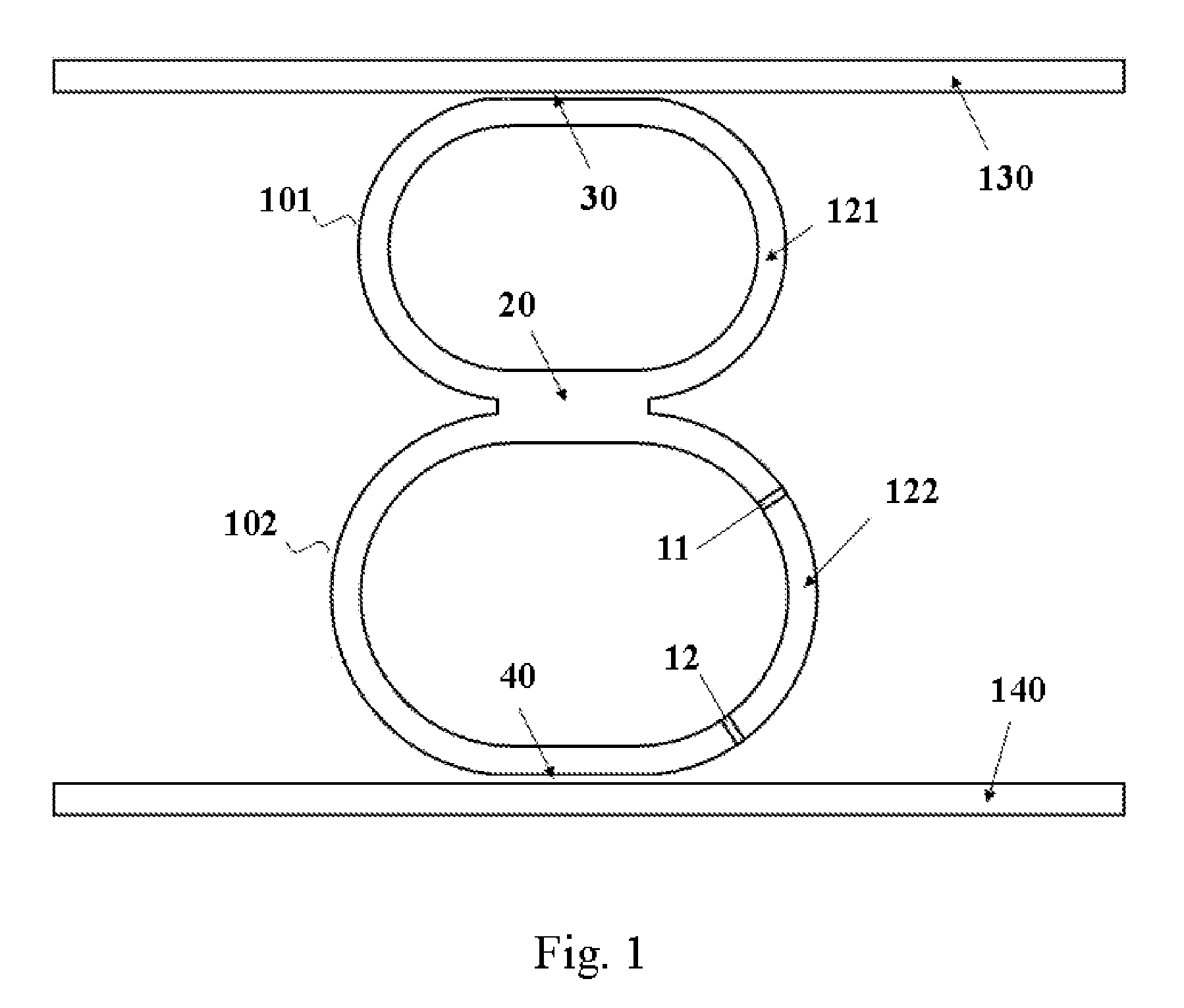
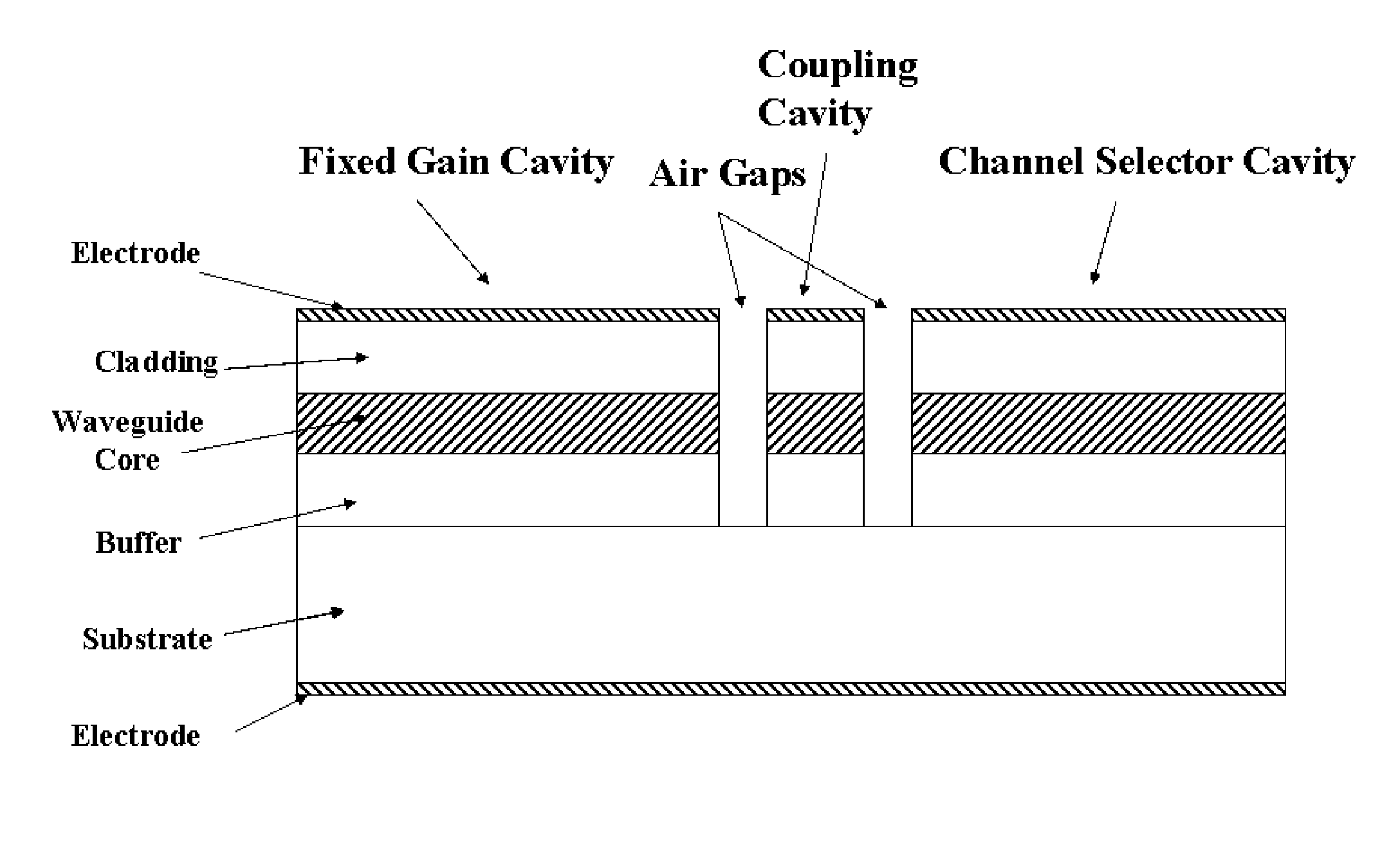
V-coupled-cavity semiconductor laser
A semiconductor laser comprises two optical cavities, each comprising an optical waveguide bounded by two partially reflecting elements. The two optical waveguides are disposed on a substrate to form a substantially V-shaped geometry with substantially no cross-coupling at the open end and a predetermined cross-coupling at the closed end for achieving an optimal single-mode selectivity of the laser. The first cavity has a length such that its resonant wavelengths correspond to a set of discrete operating channels. The second cavity has a slightly different length so that only one resonant wavelength coincides with one of the resonant wavelengths of the first cavity over the operating spectral window. The lasing action occurs at the common resonant wavelength. In operation, at least a portion of the optical waveguide in each of the first and the second cavities are forward biased to provide substantially equal round-trip optical gains. The second cavity is tuned by varying the effective refractive index of a portion of the waveguide through an electrical means, resulting in wavelength switching among the set of discrete operating wavelengths as determined by the first cavity.
Owner:LIGHTIP TECH
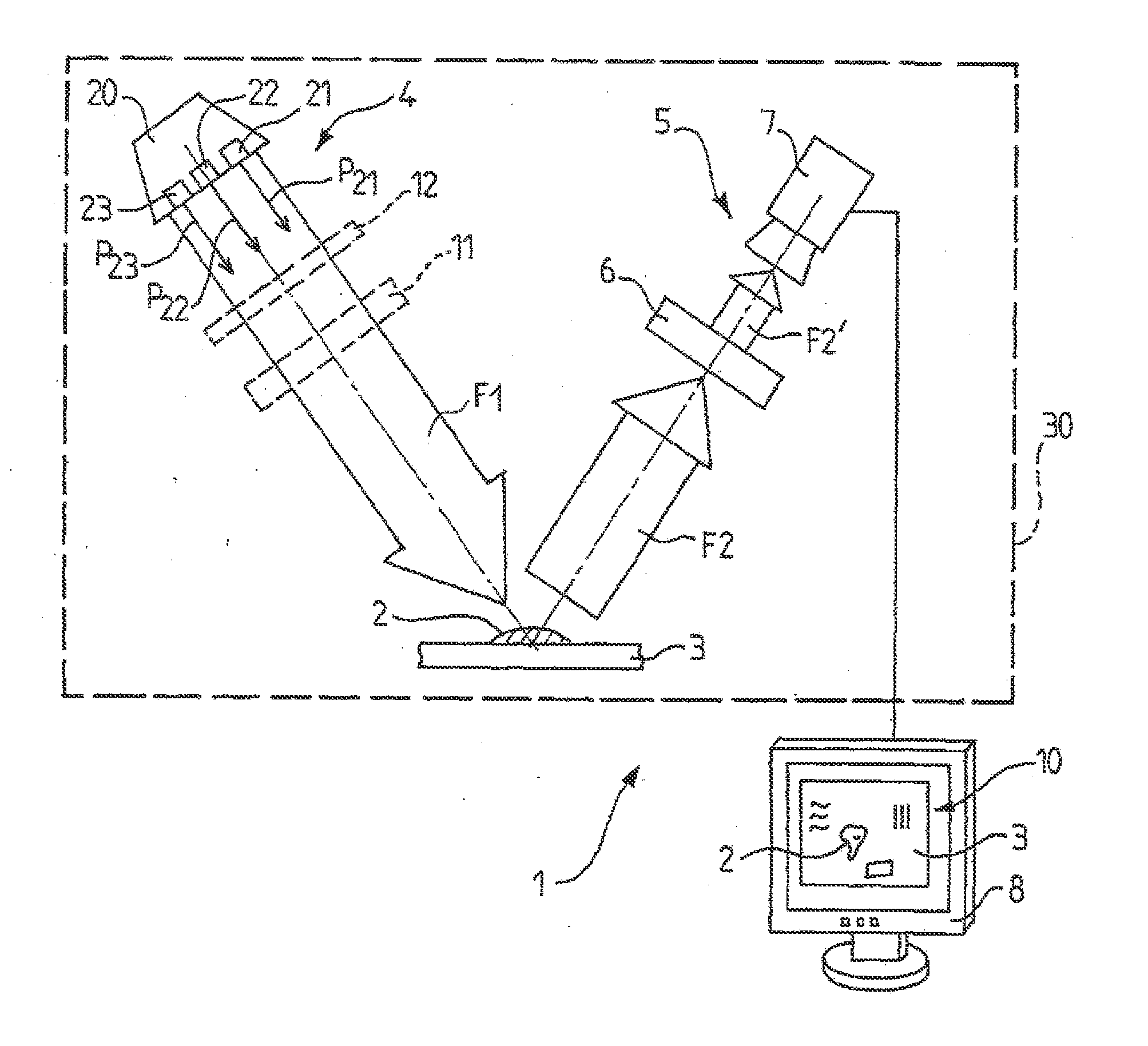
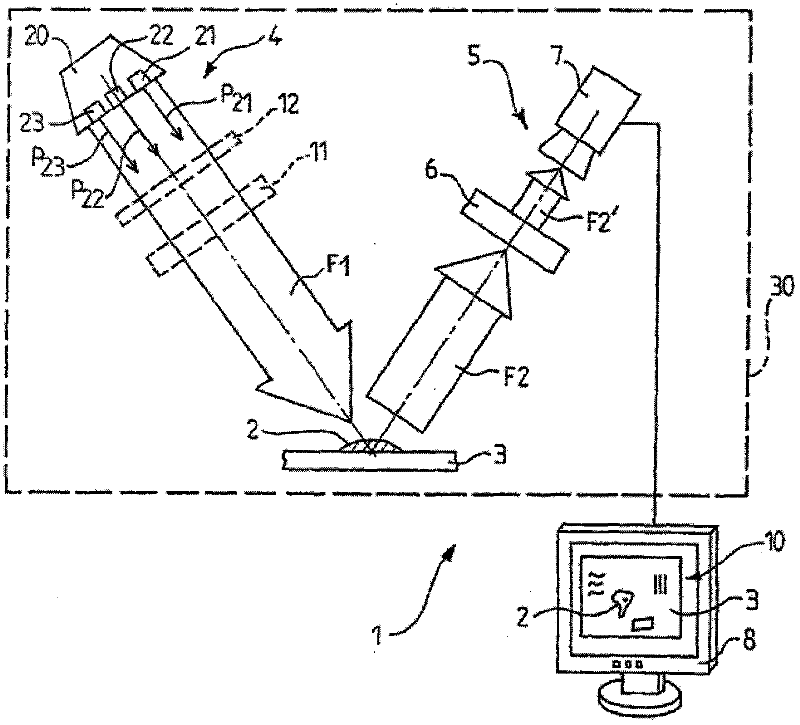
Device and method for the optical analysis of documents
InactiveUS20120038905A1Simple and intuitive to implementSimple and compact and cheap structurePaper-money testing devicesPhotometryLight beamMaterials science
The invention relates to an optical analysis method for distinguishing a substance (2) present on a substrate such as an object or a document, wherein said method includes the step (a) of illuminating said substrate with a primary light beam selected in order to interact with the substance (2) so that the latter transmits, within a secondary light beam in the visible spectrum, a characteristic chromatic radiation that is not directly detectable in the secondary light beam, and a detection step (b) that comprises a selective filtration sub-step (b1) during which the secondary light beam is filtered through a spectral window of the visible spectrum adapted to said characteristic chromatic radiation in order to detect the substance (2) from the environment thereof. The invention can be used for the optical analysis of documents.
Owner:BALBUENA JOSE
Fast metabolic imaging of systems with sparse spectra using spiral CSI
ActiveUS7709266B2Reduced measurement timeImprove acquisitionMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringMetaboliteChemical shift imaging
A method of imaging the individual components of systems with sparse spectra using magnetic resonance imaging including the steps of a) exciting nuclei of labeled components using a MRI pulse sequence, b) selecting a proper spectral window to avoid / minimize signal overlap of aliased frequency components. In step a) preferably a spiral chemical shift imaging (spCSI) sequence is employed. In a preferred embodiment, hyperpolarized nuclei of 13C are used for labeling in a pyruvate substrate with metabolites of lacatate, alanine, and bicarbonate.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
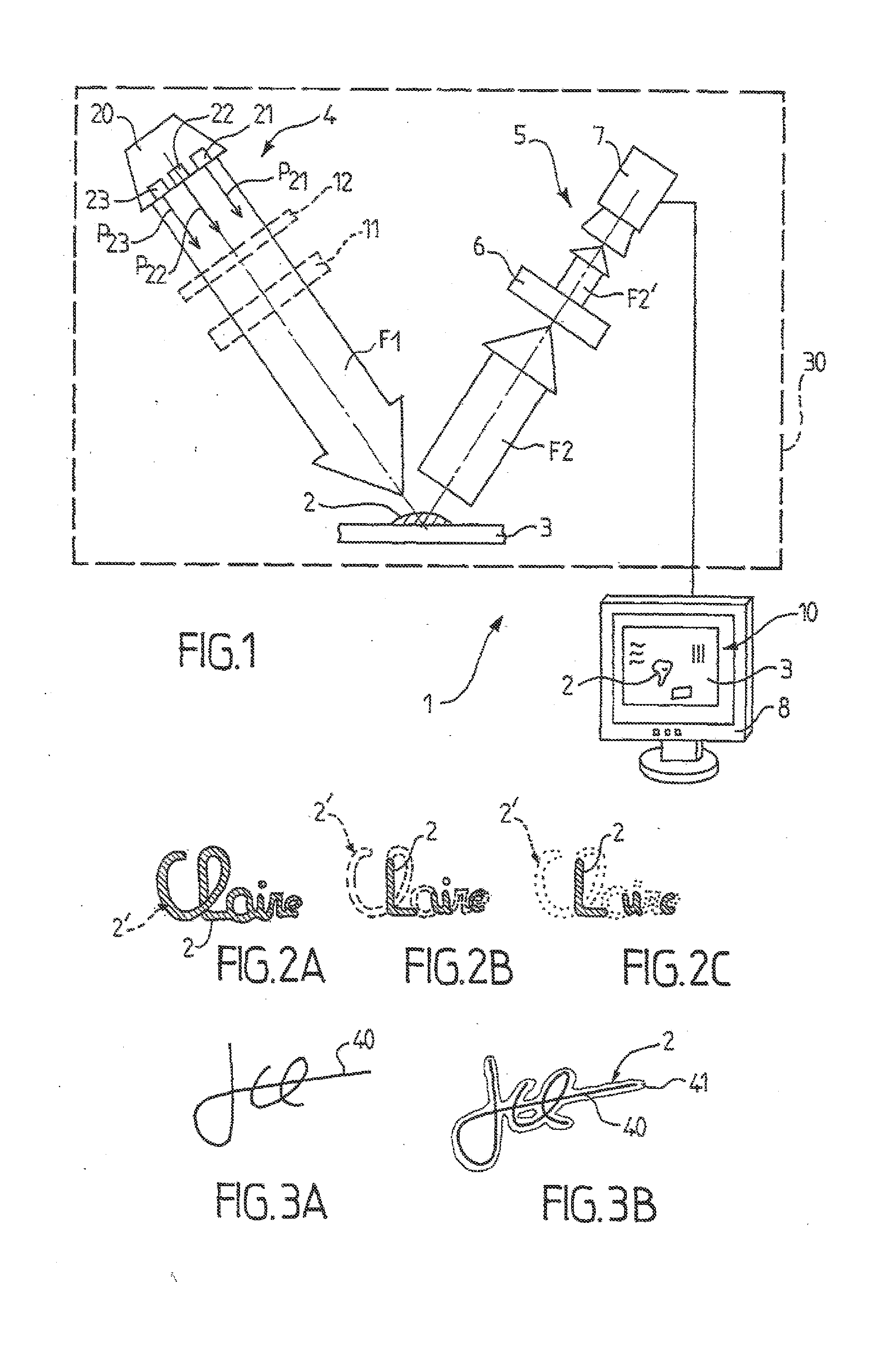
Device and method for optical analysis of documents
InactiveCN102483867AStrong discriminationEasy to implementPaper-money testing devicesFiltrationLight beam
The invention relates to an optical analysis method for distinguishing a substance present on a substrate such as an object or a document, wherein said method includes the step (a) of illuminating said substrate with a primary light beam (F1) selected in order to interact with the substance (2) so that the latter transmits, within a secondary light beam (F2) in the visible spectrum, a characteristic chromatic radiation that is not directly detectable in the secondary light beam, and a detection step (b) that comprises a selective filtration sub-step (b1) during which the secondary light beam is filtered through a spectral window of the visible spectrum adapted to said characteristic chromatic radiation in order to detect the substance (2) from the environment thereof.
Owner:若泽・巴尔武埃纳
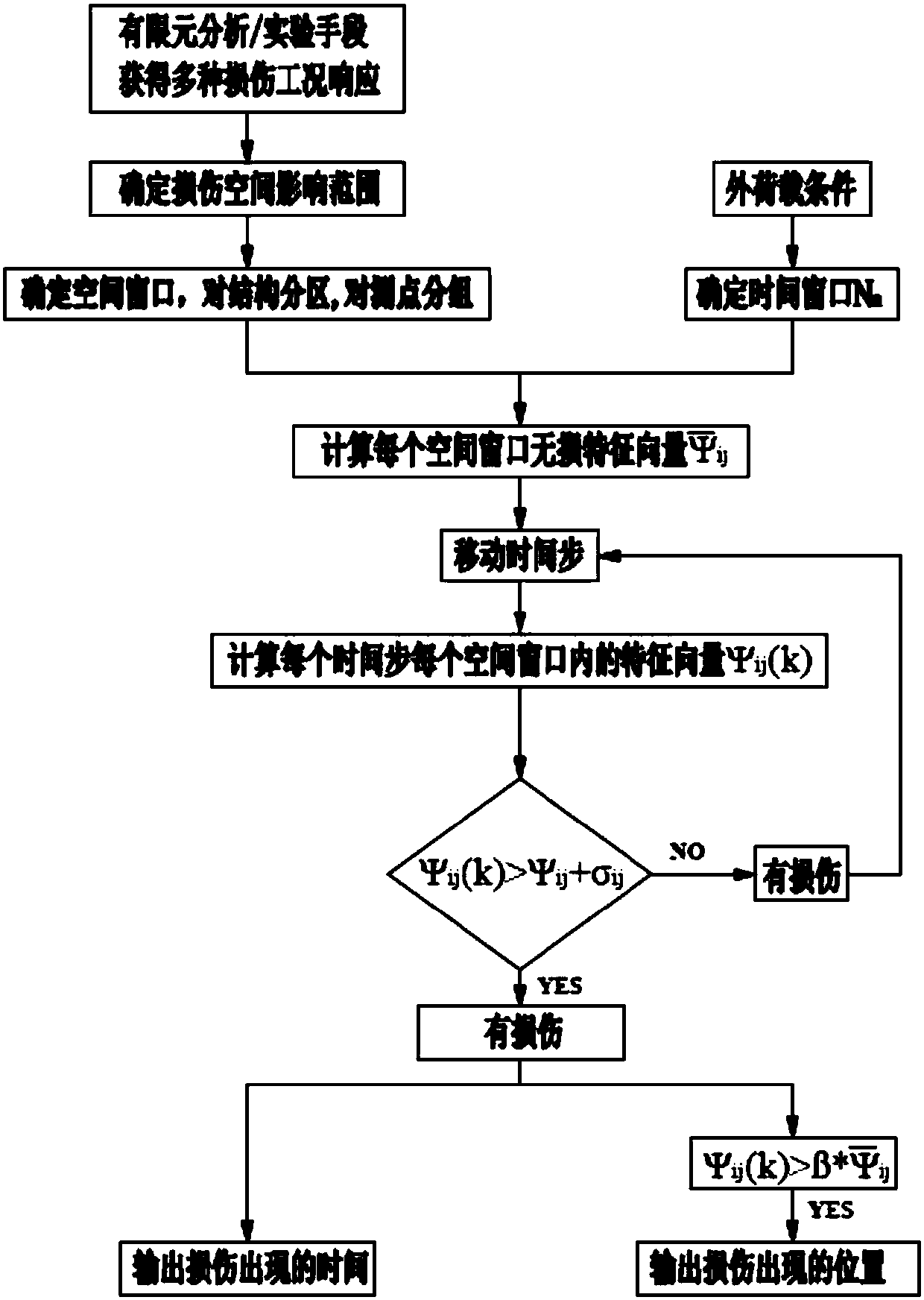
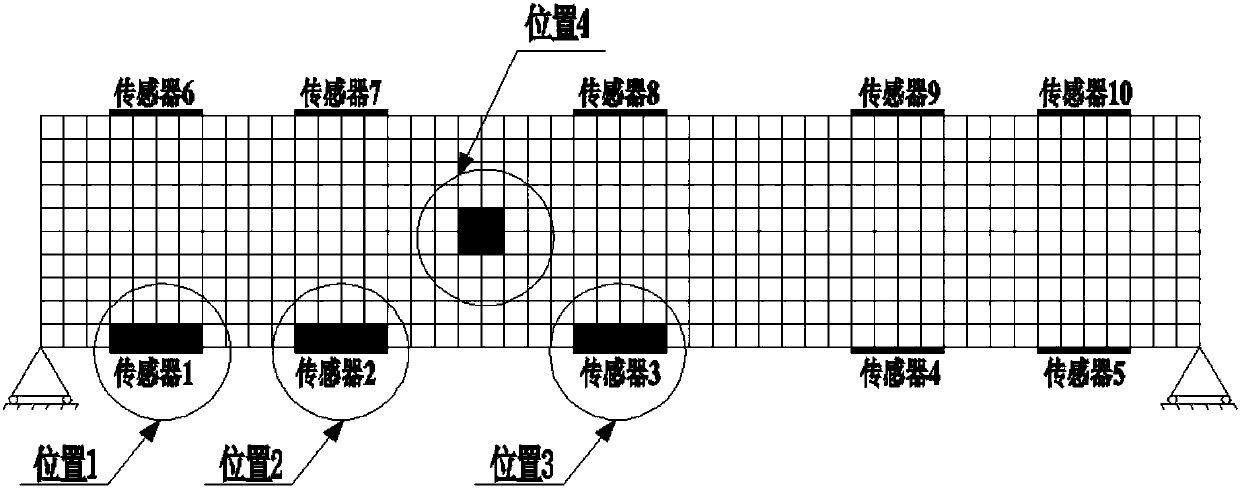
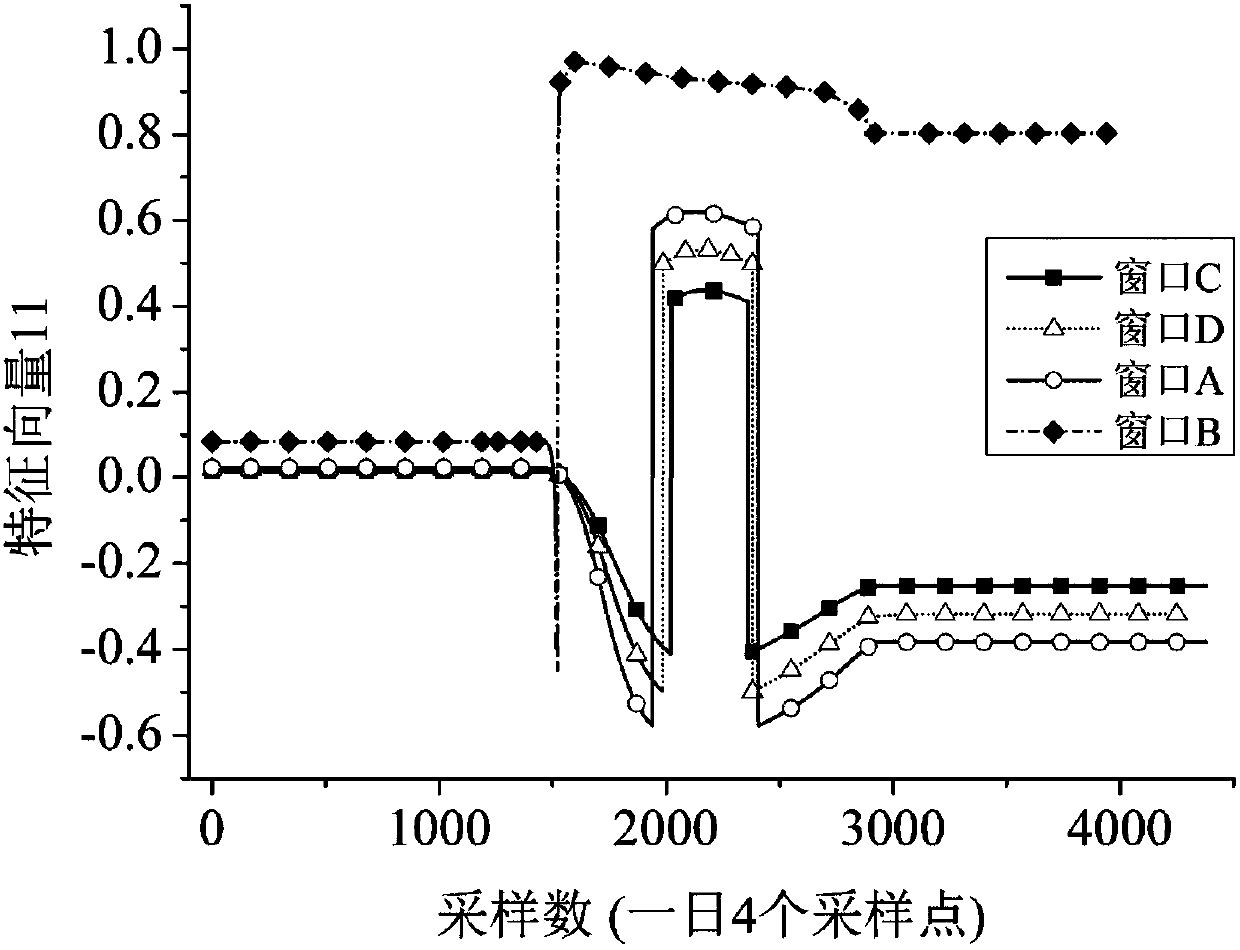
Improved PCA damage detection method under spatiotemporal window
ActiveCN108009566AHigh accuracy of damage measurementQuickly determine the timeCharacter and pattern recognitionDesign optimisation/simulationFeature vectorStructural monitoring
The invention discloses an improved PCA damage detection method under a spatiotemporal window. Firstly, a numerical simulation or experiment means is used to determine a spatial influence range corresponding to damages at different positions under multiple working conditions with damages at different spatial positions, a structural space area sensitive to the damages is further determined, and that is, a spatial window is determined; then, according to a PCA principle, a temporal window related to an external load cycle is determined; and finally, after the temporal window and the spatial window are determined, a PCA method is used for all measurement point data in the spatial window, a feature vector is used as a monitoring index, a damage can be monitored in real time, and the damage positioning is realized. The method carries out PCA analysis on a structural response in limited temporal and spatial windows, the damage recognition precision and the sensitivity are thus improved, andlong-term structure monitoring data can be used to carry out damage recognition on a long-span solid bridge or other structures.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method, apparatus, and article for frequency-overlapped 3-D multispectral magnetic resonance images
ActiveUS10061007B2Increase contrastMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceNear neighbor
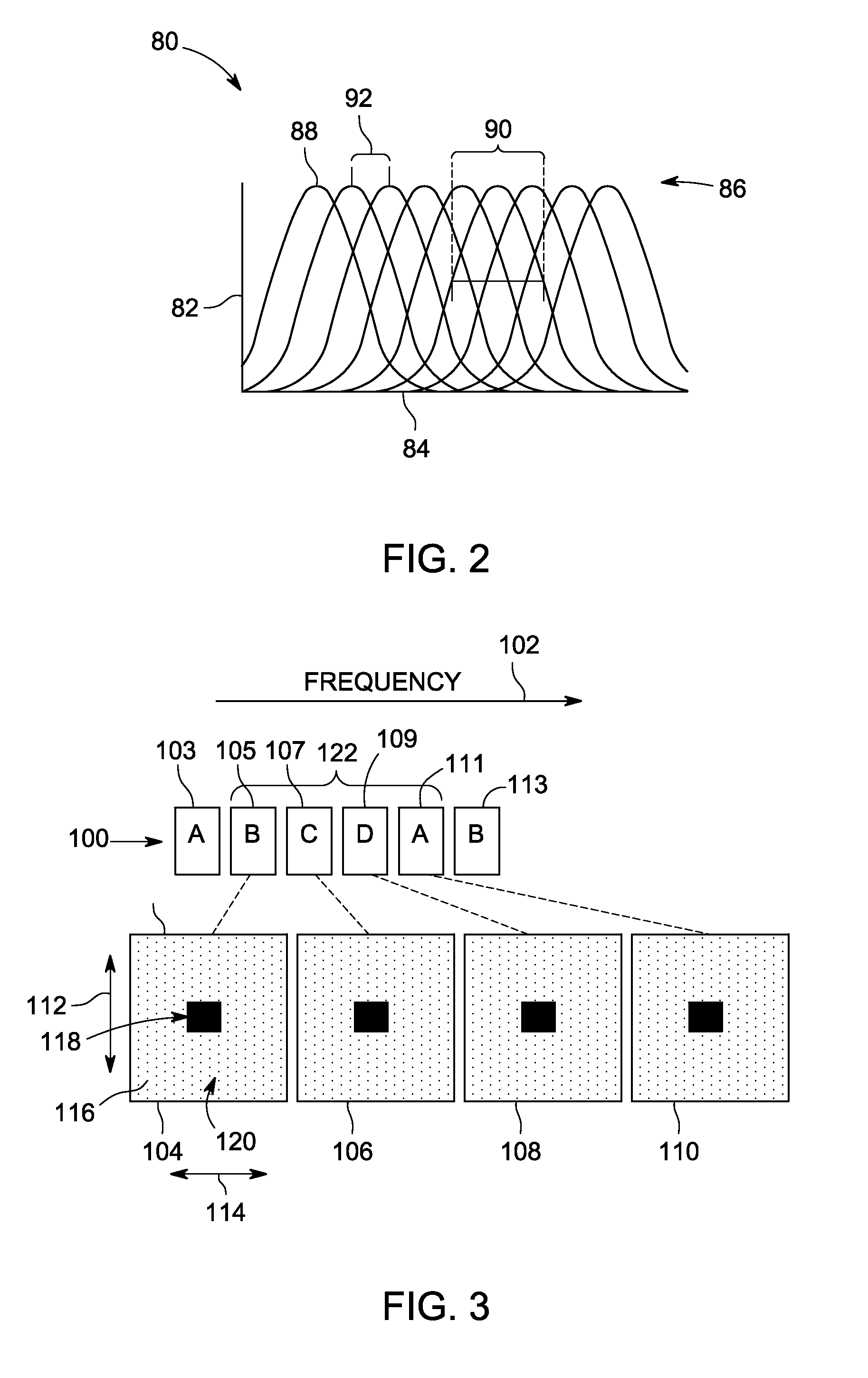
A method for acquiring 3D multispectral MRI of a target includes scanning a spectrum of spectral windows with an MRI scanner, wherein each spectral window of the spectrum defines a continuously-differentiable distribution of frequencies around a scan frequency and adjacent scan frequencies are spaced apart by substantially uniform frequency offsets such that adjacent spectral windows substantially uniformly overlap, wherein selected adjacent spectral windows are scanned in consecutive passes, and nearest neighbor spectral windows within each pass are scanned at a maximum temporal spacing within the pass.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
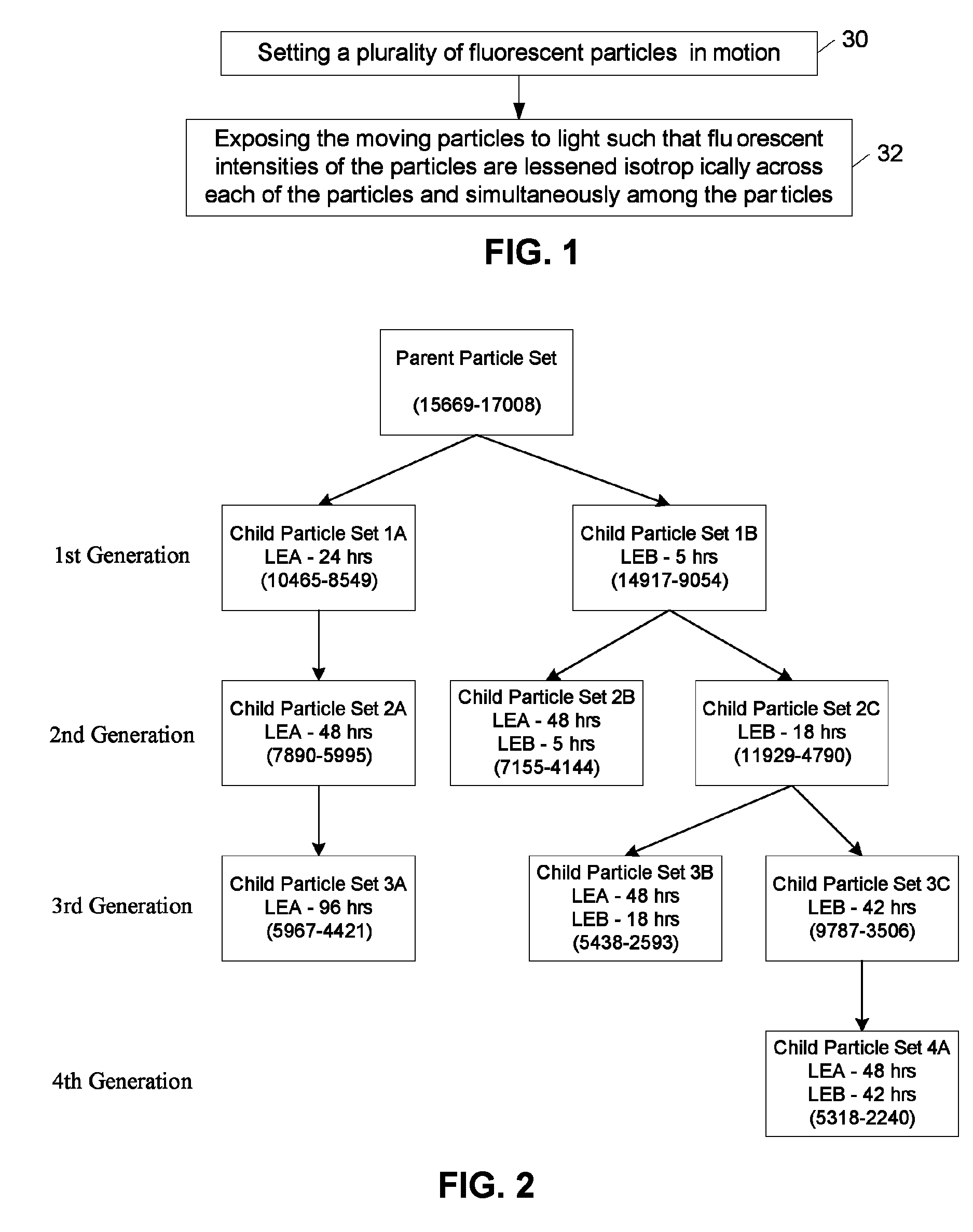
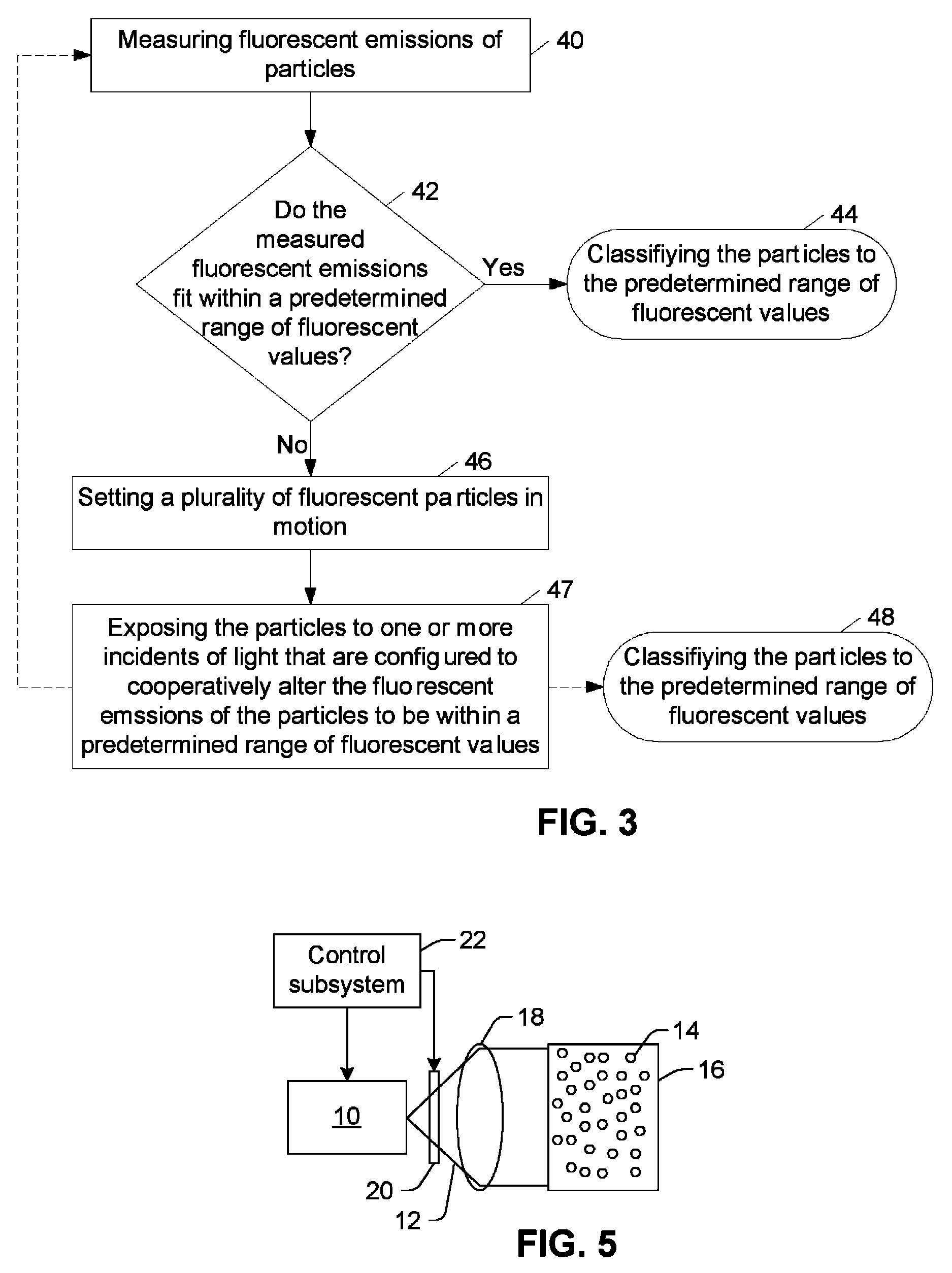
Methods and systems for altering fluorescent intensities of a plurality of particles
ActiveUS8124943B1Decrease of fluorescence emissionPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersLength wavePhysics
A method for altering fluorescent emissions of particles includes setting the particles in motion and exposing the moving particles to light such that fluorescent intensities of the particles are lessened isotropically and substantially simultaneously. Another method includes measuring fluorescent emissions of particles, determining the measured fluorescent emissions do not collectively fit within a first predetermined range of fluorescent values, and exposing the particles to one or more incidents of light that are configured to cooperatively alter the fluorescent emissions of the particles to be within a second predetermined range of fluorescent values. An embodiment of an apparatus includes a vessel configured to contain a plurality of particles and a means for setting the particles in motion. The apparatus further includes an illumination subsystem configured to direct light toward the vessel and at a spectral window (i.e., wavelength or band of wavelengths) which is configured to isotropically and substantially simultaneously lessen the fluorescent emissions of each of the particles.
Owner:LUMINEX
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com