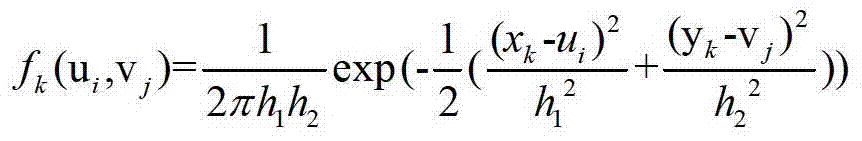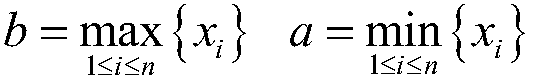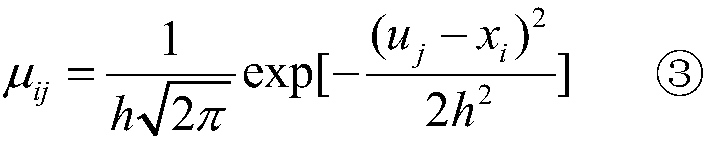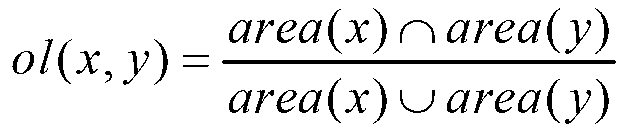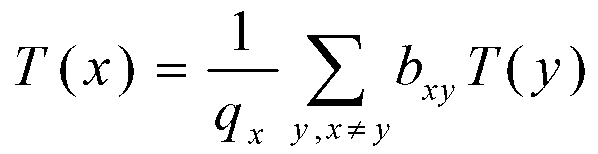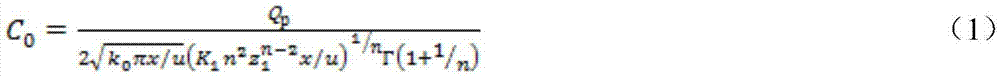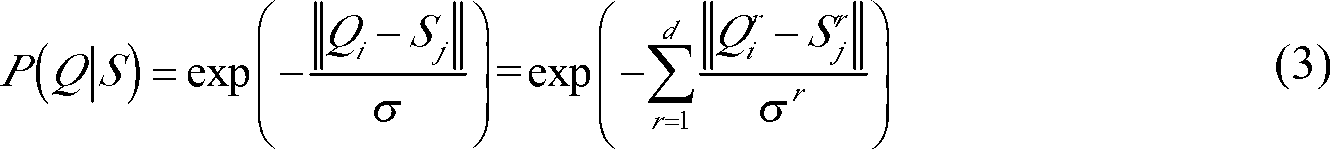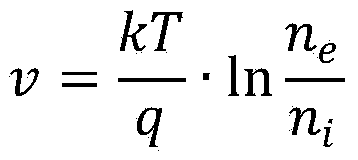Patents
Literature
40 results about "Diffusion theory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Diffusion theory. The theory that in semiconductors, where there is a variation of carrier concentration, a motion of the carriers is produced by diffusion in addition to the drift determined by the mobility and the electric field.
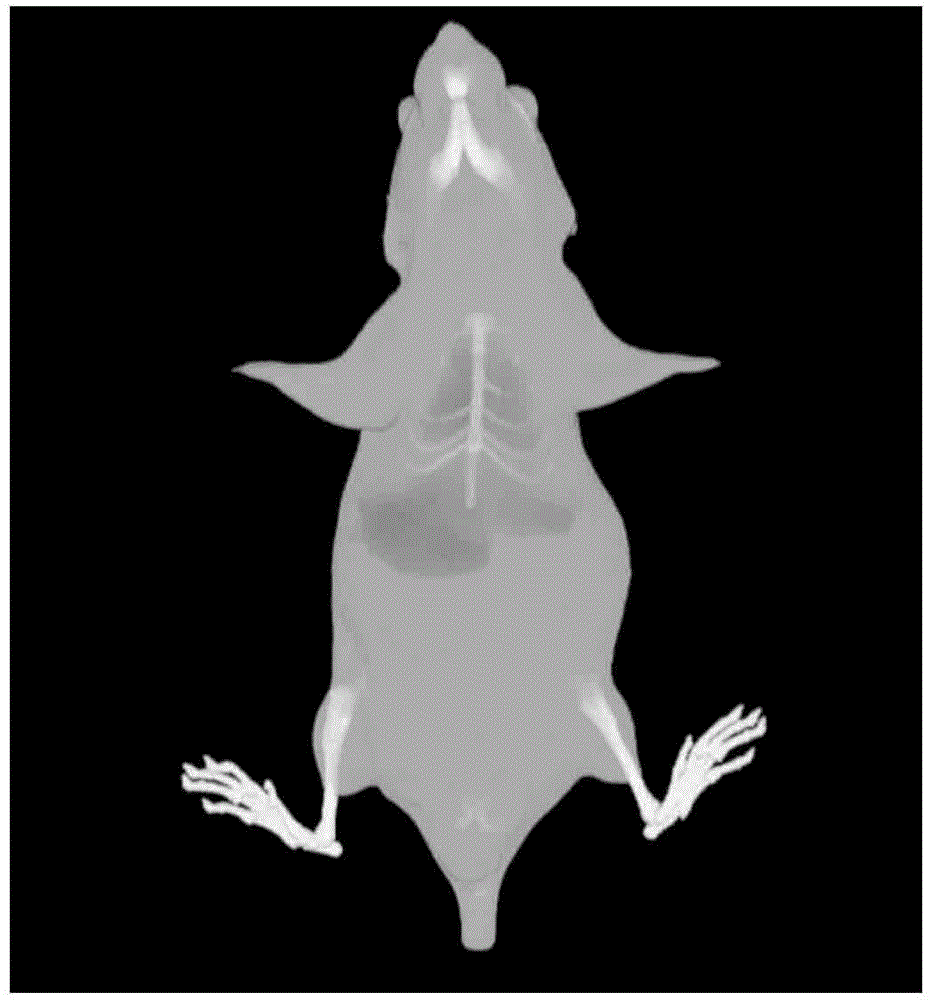
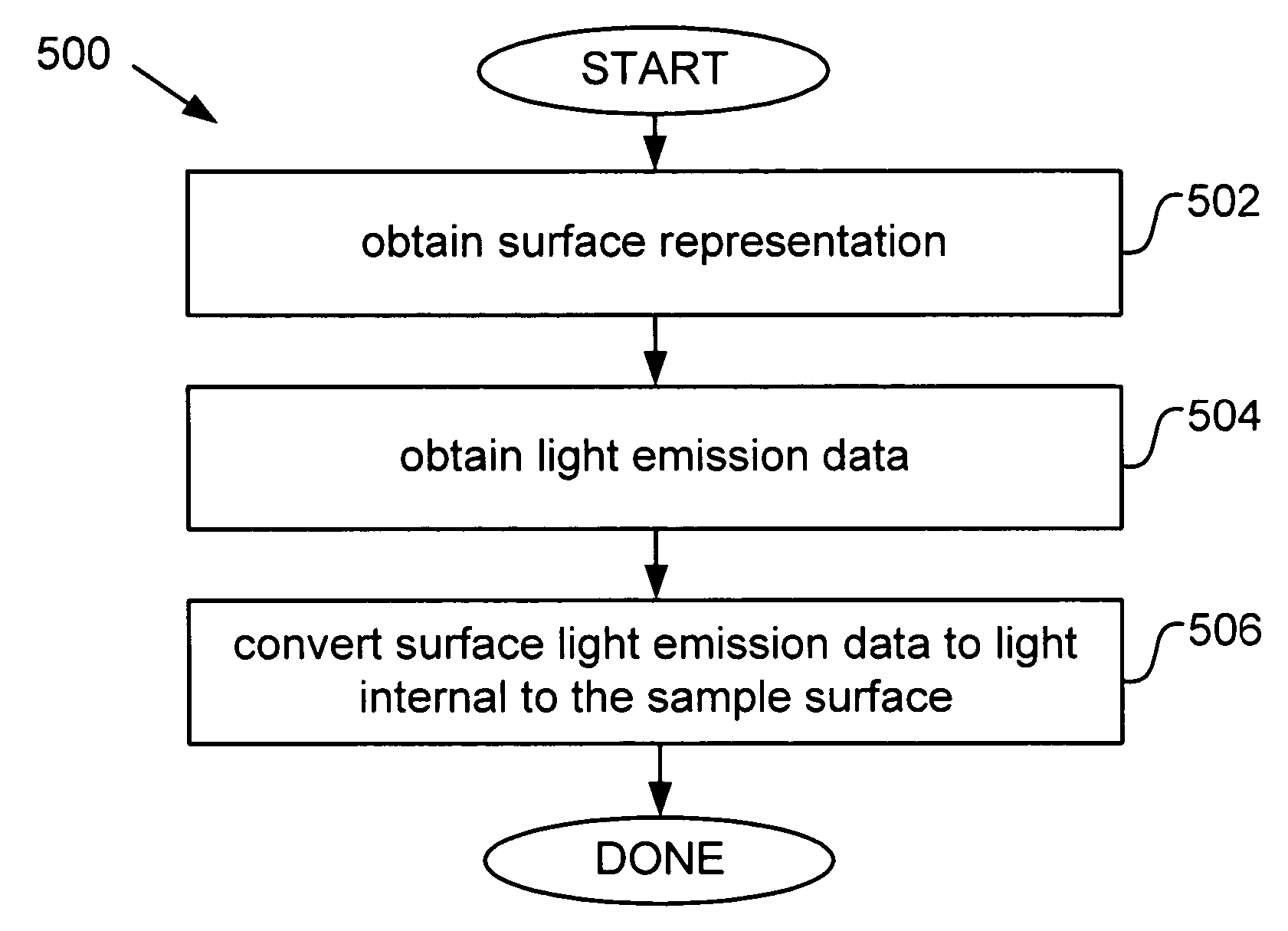
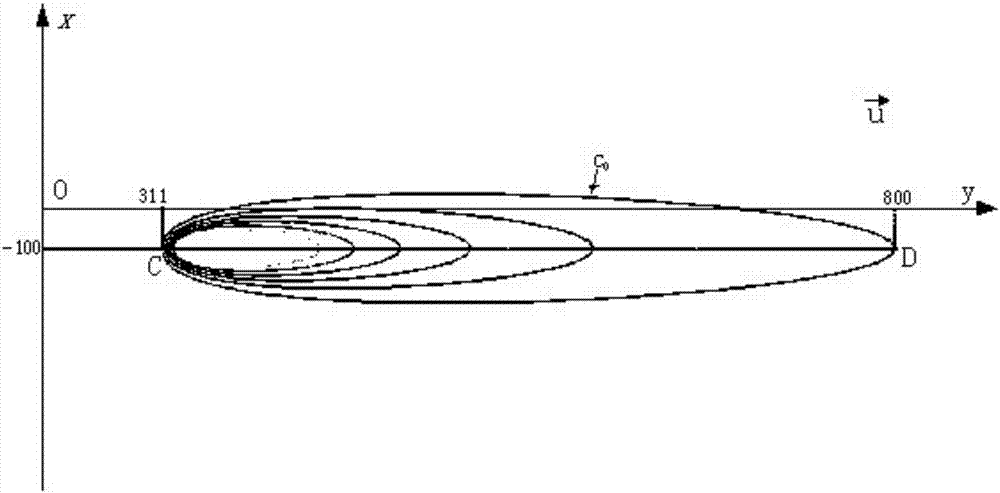
3-D in-vivo imaging and topography using structured light
InactiveUS20050201614A1X-ray/infra-red processesMaterial analysis by optical meansMammalian tissueDiffusion theory
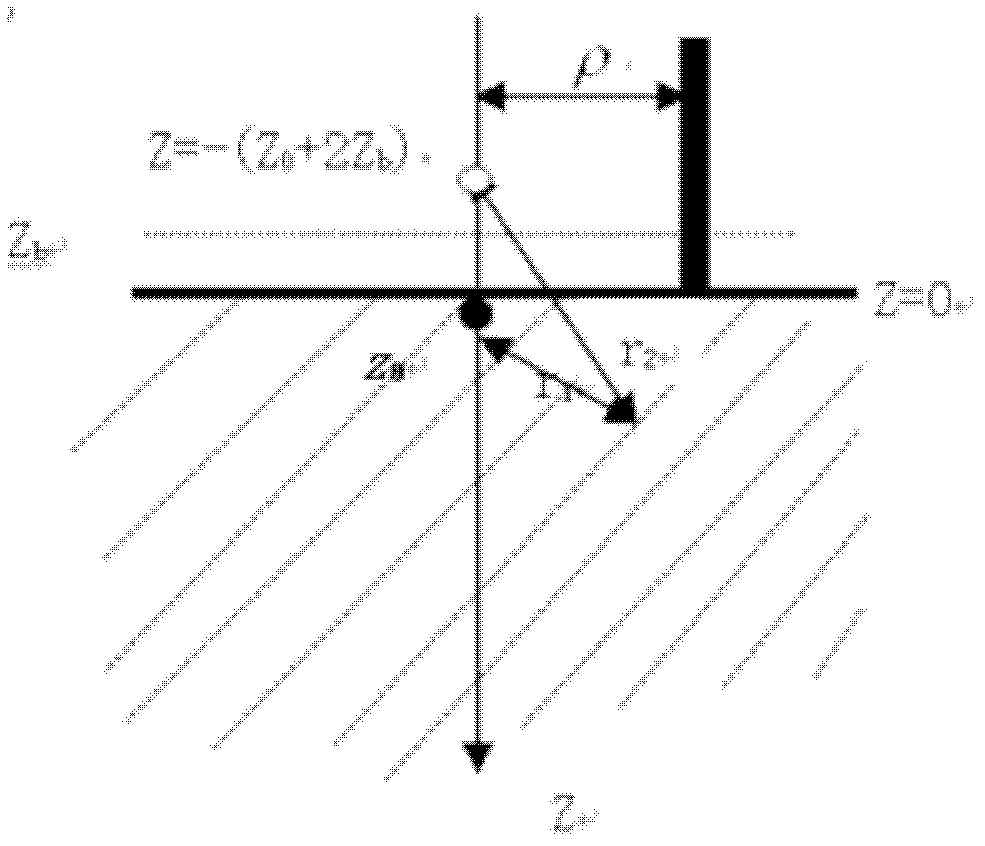
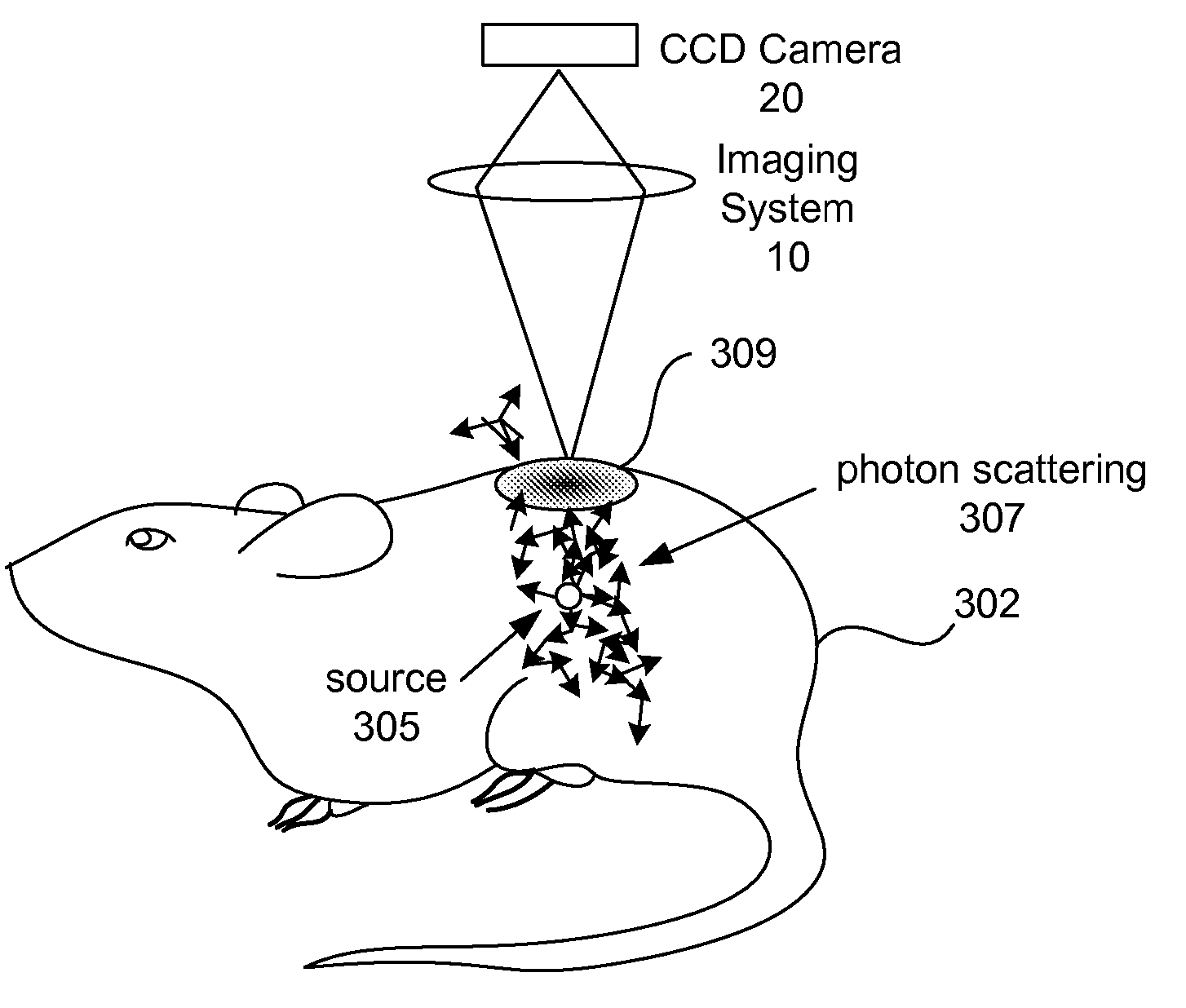
The present invention provides systems and methods for obtaining a three-dimensional (3D) representation of one or more light sources inside a sample, such as a mammal. Mammalian tissue is a turbid medium, meaning that photons are both absorbed and scattered as they propagate through tissue. In the case where scattering is large compared with absorption, such as red to near-infrared light passing through tissue, the transport of light within the sample is described by diffusion theory. Using imaging data and computer-implemented photon diffusion models, embodiments of the present invention produce a 3D representation of the light sources inside a sample, such as a 3D location, size, and brightness of such light sources.
Owner:XENOGEN CORP
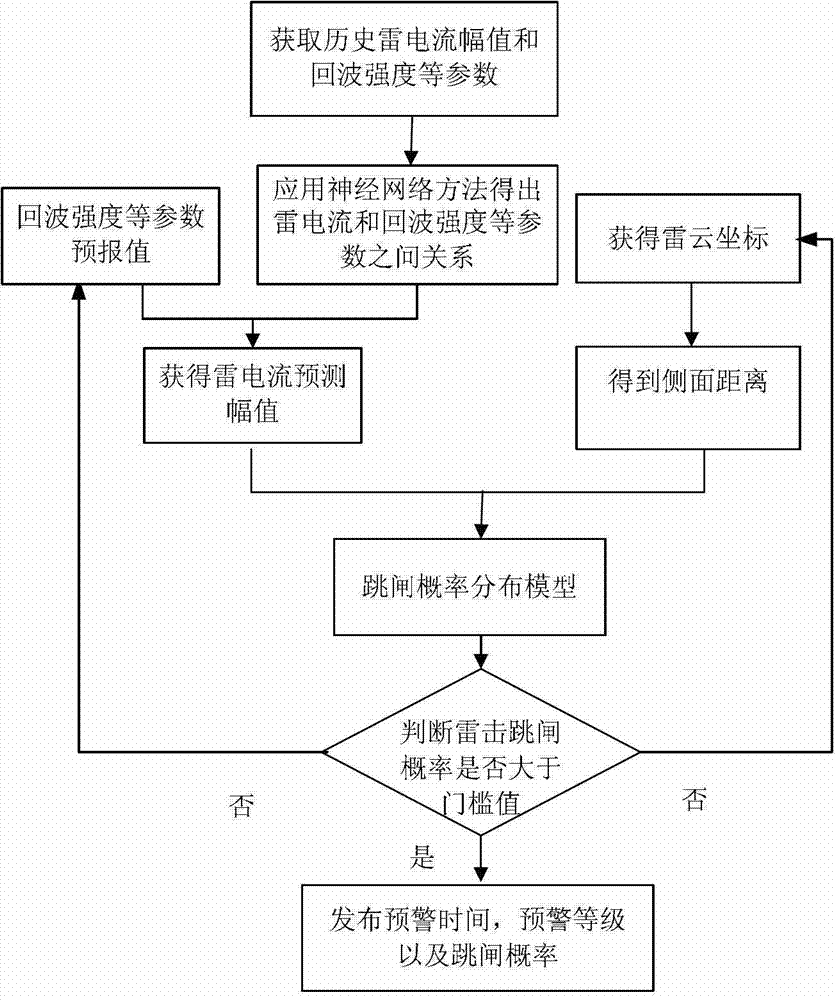
On-line transmission line lightning shielding failure trip early-warning method
ActiveCN103207340AReduce economic lossImprove reliable operationElectrical testingWeather radarBack propagation neural network
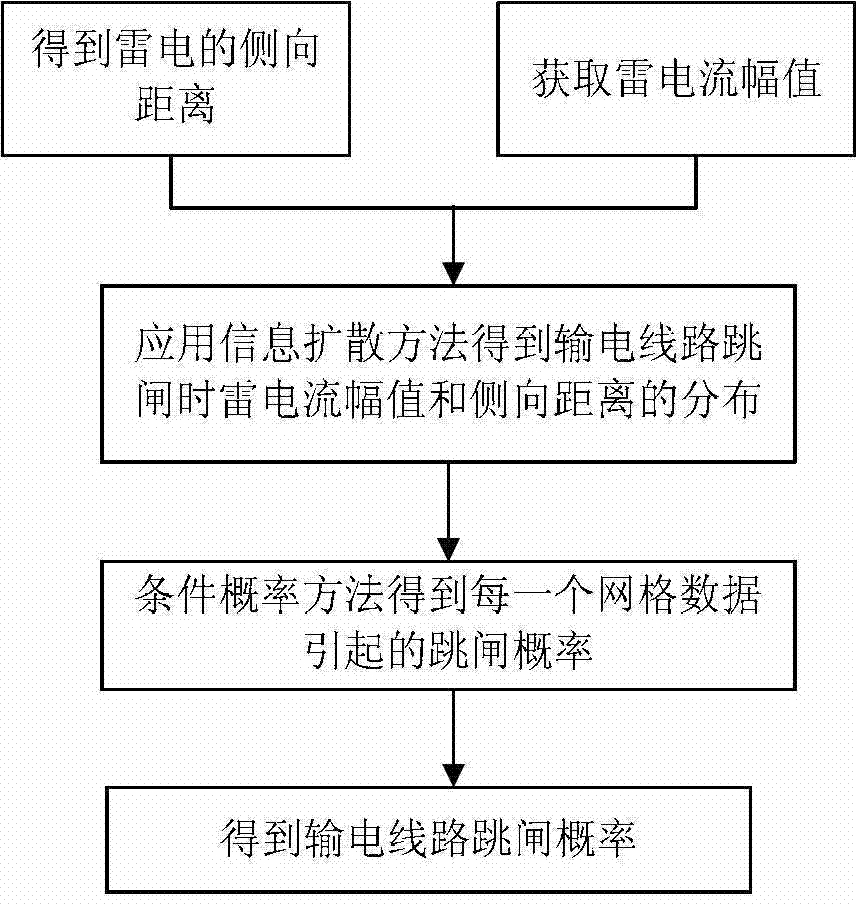
The invention discloses an on-line transmission line lightning shielding failure trip early-warning method. The method comprises the following steps of: performing statistics on historical lightning shielding failure trip information to obtain transmission line lightning shielding failure trip probability distribution by a two-dimensional information diffusion theory and a conditional probability method; selecting radar forecast data, such as echo intensity, echo tops and vertical accumulated liquid water content; establishing a lightning current magnitude prediction model based on a back propagation neural network; and sending real-time early warning and an early warning grade of transmission line lightning shielding failure trip probability according to the predicted lightning current magnitude and the side distance to lightning stroke and by virtue of the transmission line lightning shielding failure trip probability distribution model. According to the real-time forecast data of a meteorological radar, the method provided by the invention can predict the trip probability of a transmission line and send an early warning signal, thereby providing reference for decision-making analysis of grid dispatching operators, making a transmission line dispatching strategy in time, improving power supply reliability, lowering economic loss of a grid, and improving the reliable running ability of the grid.
Owner:SHENZHEN POWER SUPPLY BUREAU +1
River and lake bottom sludge pollutant flux test method and device based on diffusion theory
ActiveCN102590479AWide applicabilityThe concentration of pollutants does not need to be testedEarth material testingTesting waterSludgeSample water
The invention discloses a river and lake bottom sludge pollutant flux test method and a river and a device based on a diffusion theory. The method comprises the following steps of: A, acquiring a bottom sludge sample; B, putting the bottom sludge into a base of an experimental device, and enabling the sludge surface to be horizontal; C, slowly injecting water to a column port along a column wall; D, injecting running water into the experimental device without the bottom sludge; E, standing for a certain time; F, measuring the pollutant concentration of the taken water sample; G, calculating a degrading coefficient of the pollutant in the water; H, calculating an initial concentration value of the bottom sludge water; and I, calculating a pollutant exchange flux of a water-sludge interface. A base plate is fixed at the bottom of a constant-temperature water tank; a base wall is arranged on the base plate; a lower flange disk is arranged on the upper part of the base wall; an upper flange disk is arranged at one end of a column body; and an upper flange disk fixing bolt flange hole is formed in the upper flange disk. The method is feasible, and is convenient to operate; the experimental device has a rational and simple structure; operations of accommodating deposits, sampling water samples and the like are extremely convenient; and outstanding economic benefit is achieved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Quantitative broadband absorption and scattering spectroscopy in turbid media by combined frequency-domain and steady state methodologies
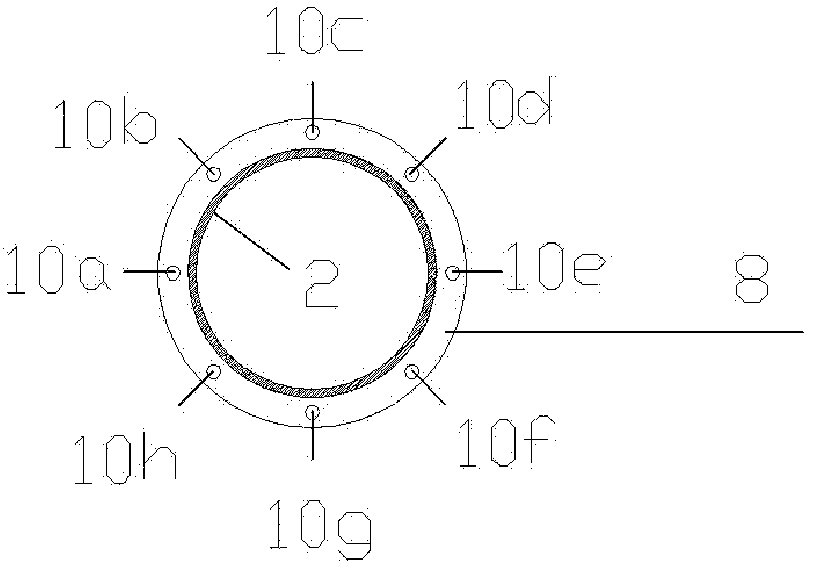
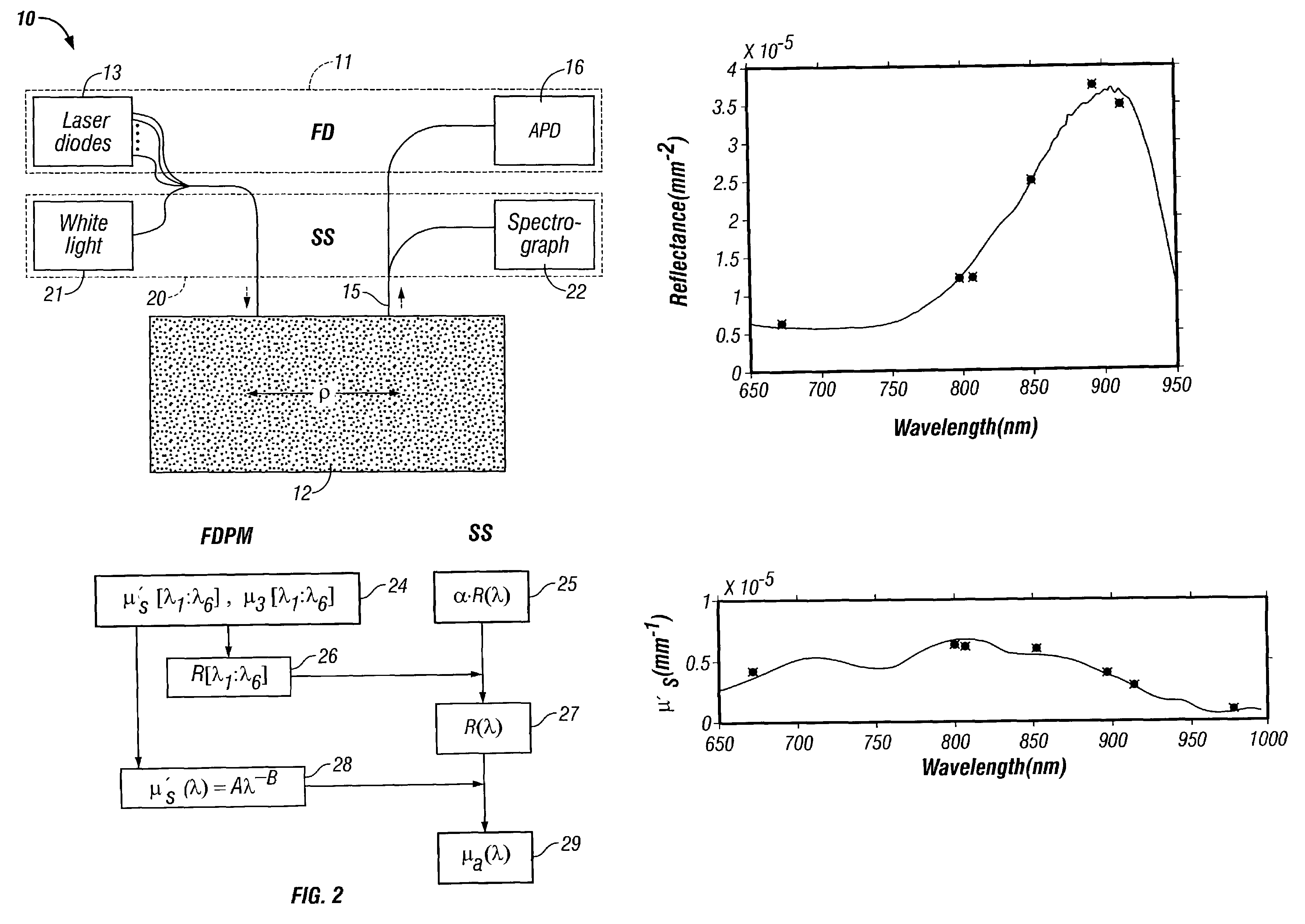
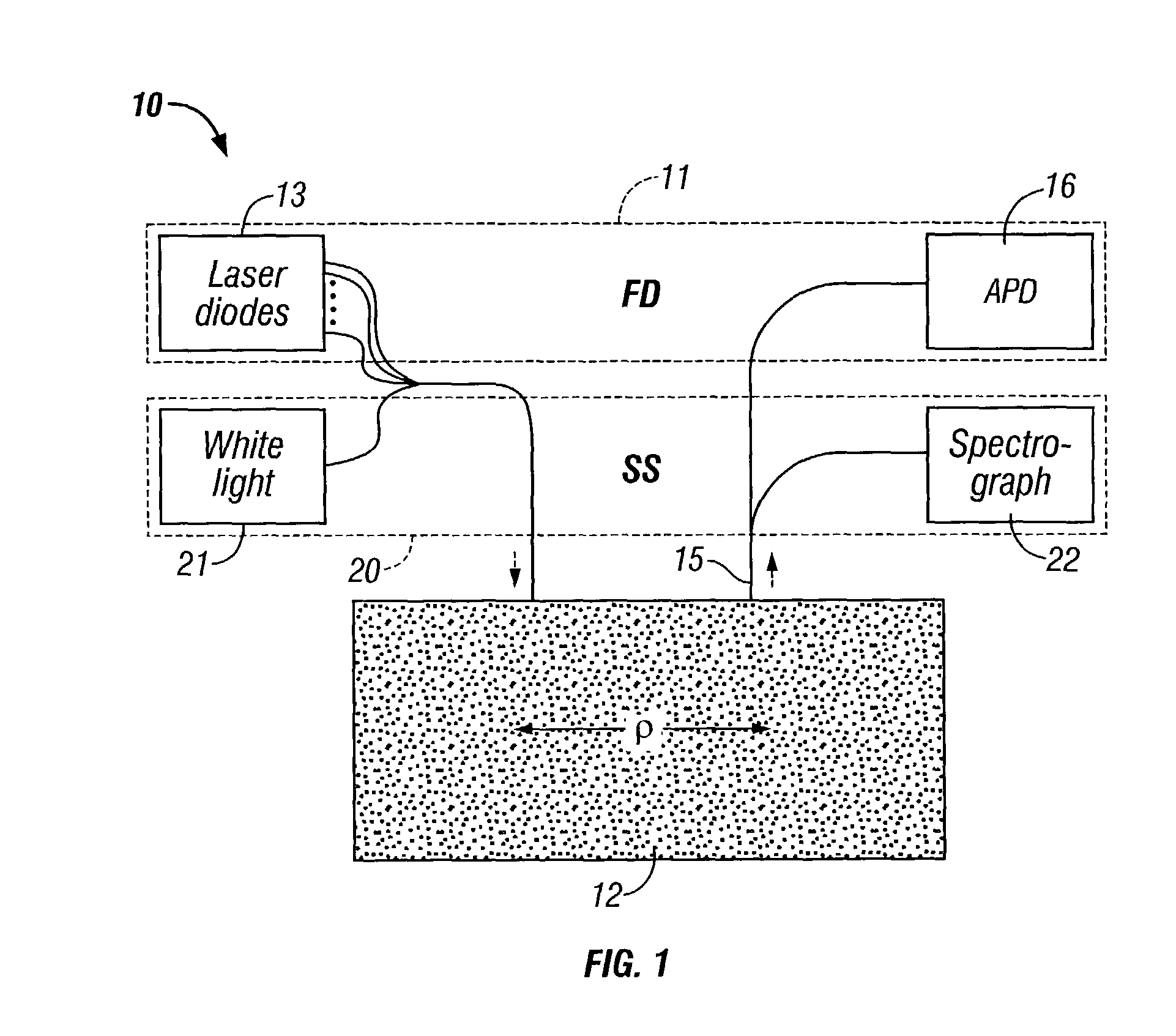
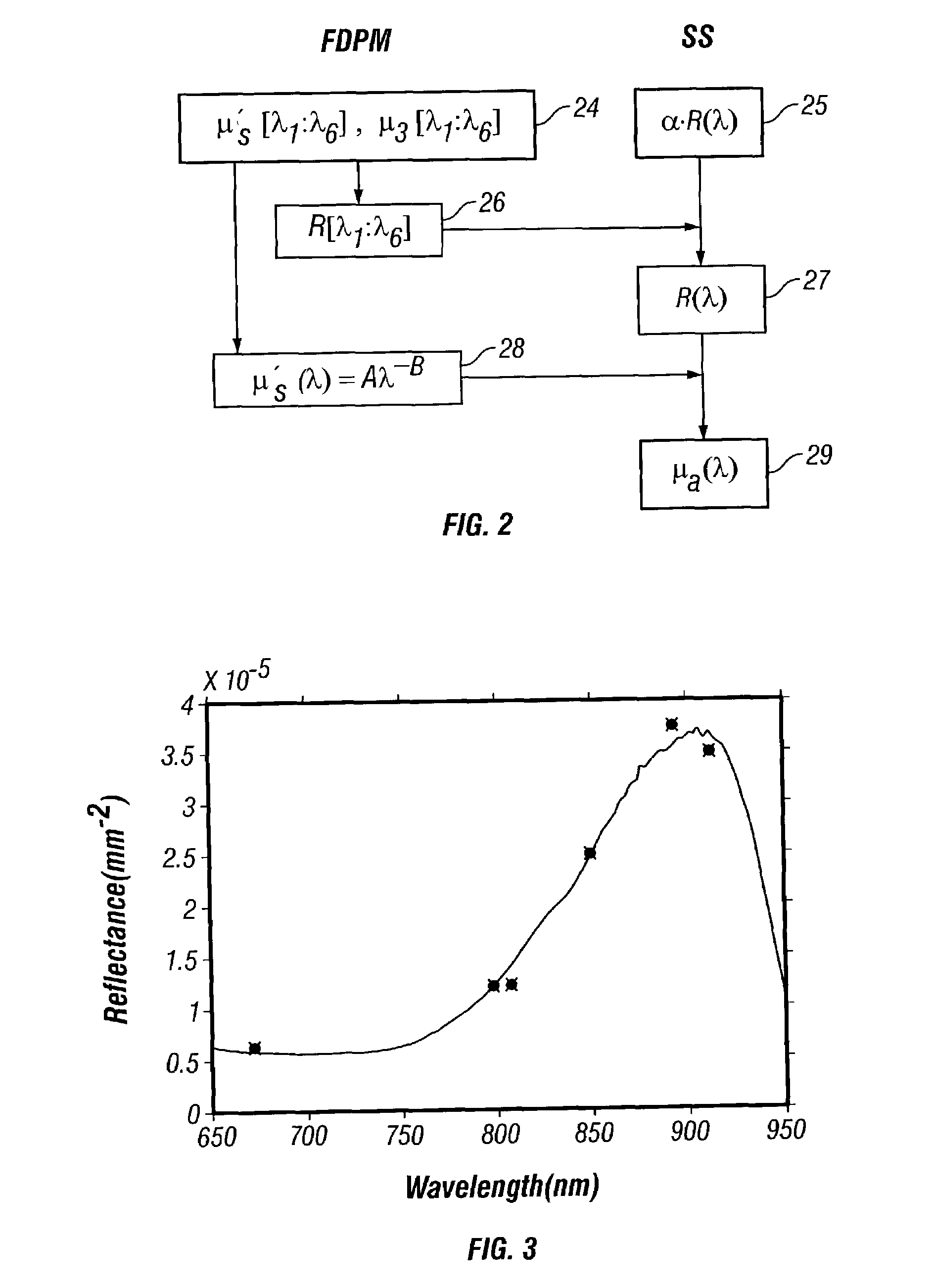
ActiveUS7428434B2Increase penetration depthWide wavelength coverageRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationBroadband absorptionDiffusion theory
A technique for measuring broadband near-infrared absorption spectra of turbid media that uses a combination of frequency-domain and steady-state reflectance methods. Most of the wavelength coverage is provided by a white-light steady-state measurement, whereas the frequency-domain data are acquired at a few selected wavelengths. Coefficients of absorption and reduced scattering derived from the frequency-domain data are used to calibrate the intensity of the steady-state measurements and to determine the reduced scattering coefficient at all wavelengths in the spectral window of interest. The absorption coefficient spectrum is determined by comparing the steady-state reflectance values with the predictions of diffusion theory, wavelength by wavelength. Absorption spectra of a turbid phantom and of human breast tissue in vivo, derived with the combined frequency-domain and steady-state technique, agree well with expected reference values.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
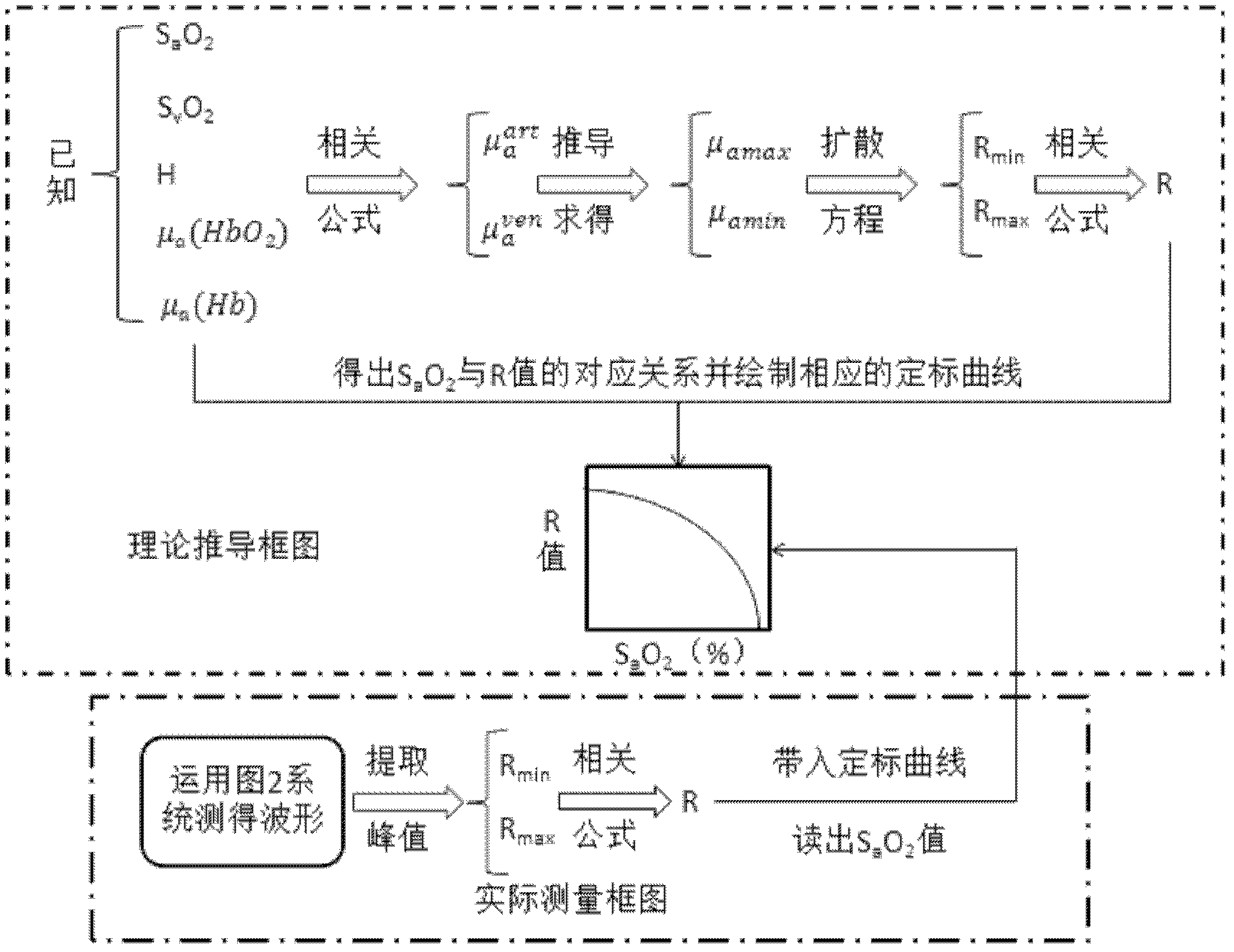
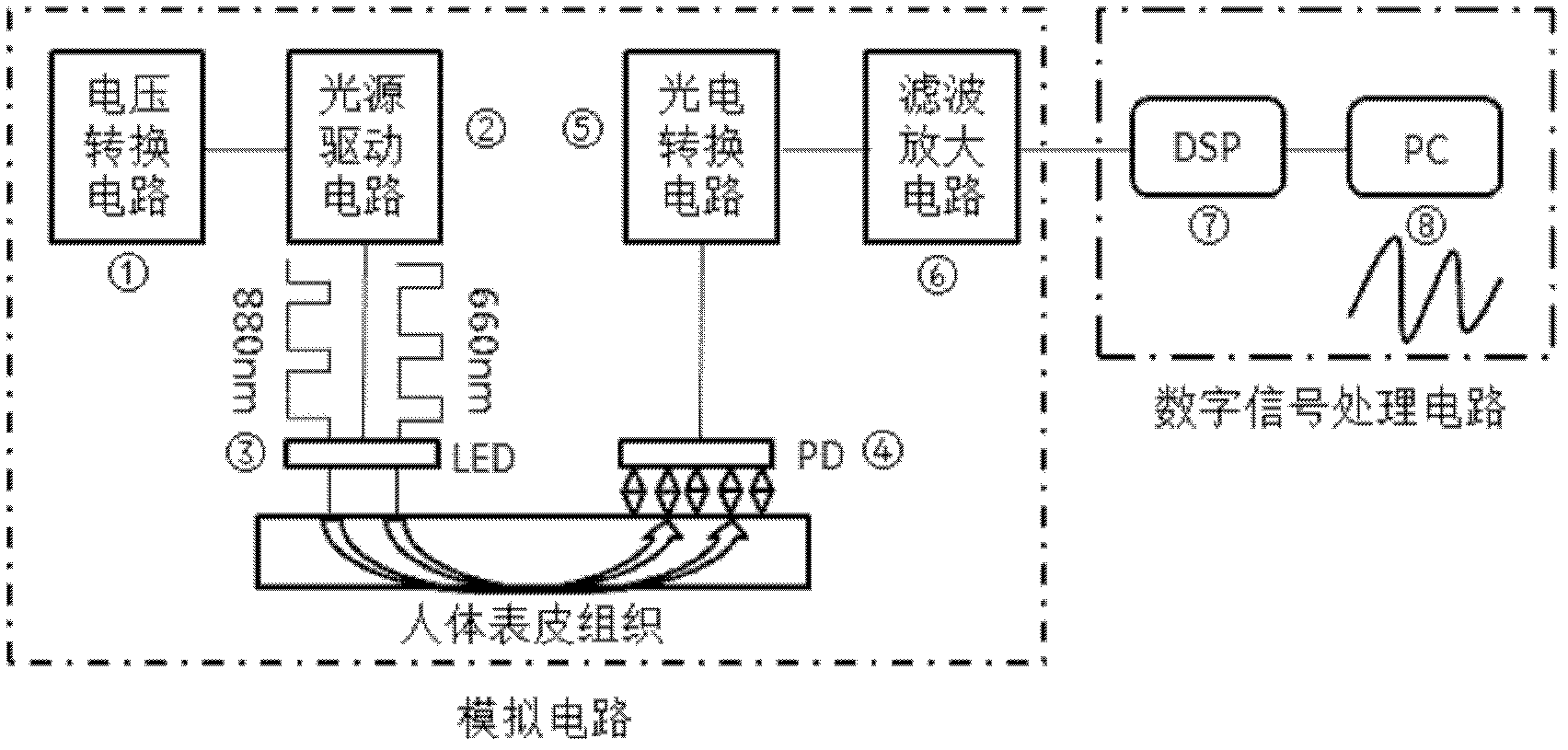
Reflective pulse blood oxygen detecting method based on diffusion theory
InactiveCN102579053AGuaranteed real-timeGuaranteed validityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDiffusion theoryPeak value
The invention belongs to the technical field of human body physiological parameter measurement, and relates to a reflective pulse blood oxygen detecting method based on diffusion theory, which includes the steps: (1) establishing the relationship between organizer absorption coefficient and SaO2 (oxygen saturation); (2) establishing the relationship between reflection light intensity and organizer absorption coefficient; (3) establishing the relationship between an R value and the reflection light intensity; (4) acquiring pulse wave signals of a red light wavelength and a near-infrared light wavelength; (5) detecting features of pulse wave signals of the infrared light wavelength to extract peak values which are the maximum value and the minimal value of the reflection light intensity; (6) calculating blood oxygen saturation coefficient R; and (7) plugging the R value into a calibration curve to obtain needed blood oxygen saturation coefficient in real time. The reflective pulse blood oxygen detecting method based on the diffusion theory can be used for realizing non-invasive real-time measurement, and is higher in precision and wider in application range.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
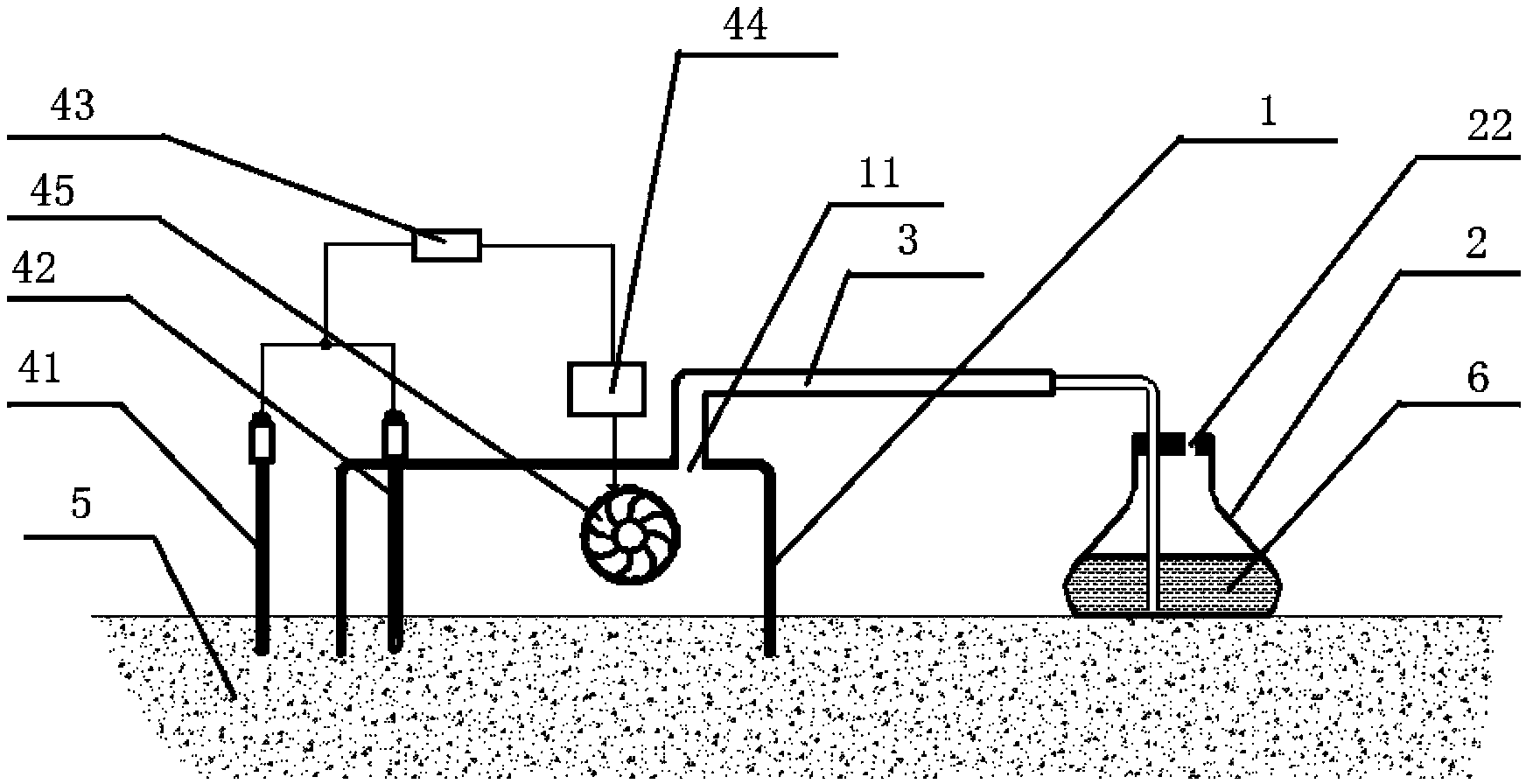
Collection device for ammonia gas in soil and method for determining loss amount of nitrogen in soil by using same
InactiveCN103364232AReduce mistakesAccurate reflection of lossesProgramme controlComputer controlTemperature controlDiffusion theory
The invention relates to a continuous collection device for volatile ammonia gas in field soil and a method for determining the loss amount of nitrogen in the soil by using the same. The device comprises an ammonia gas collector, an ammonia gas recycling device, a connection pipeline for connecting the ammonia gas collector and the ammonia gas recycling device, and an automatic temperature control device for regulating an internal temperature and an external temperature of the ammonia gas collector. Through measurement, collection and comparison of the internal soil temperature and the external soil temperature of the device, the internal soil temperature of the device can be automatically regulated, so the internal soil temperature and the external soil temperature of the device are kept consistent, and the effect of too large temperature difference on result authenticity is avoided. At the same time, with the use of a reaction principle of NH3 and sulfuric acid, a gas diffusion theory and an excess collection liquid, the soil volatile ammonia gas can be ensured to be continuously and completely collected. The device not only can be used for long-term continuous collection of the volatile ammonia gas in the field soil, can relatively accurately reflect the effect of the soil ammonia gas volatilization on the loss of nitrogen in the soil, but also has the characteristics of simple structure, easy operation and relatively low labor cost.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
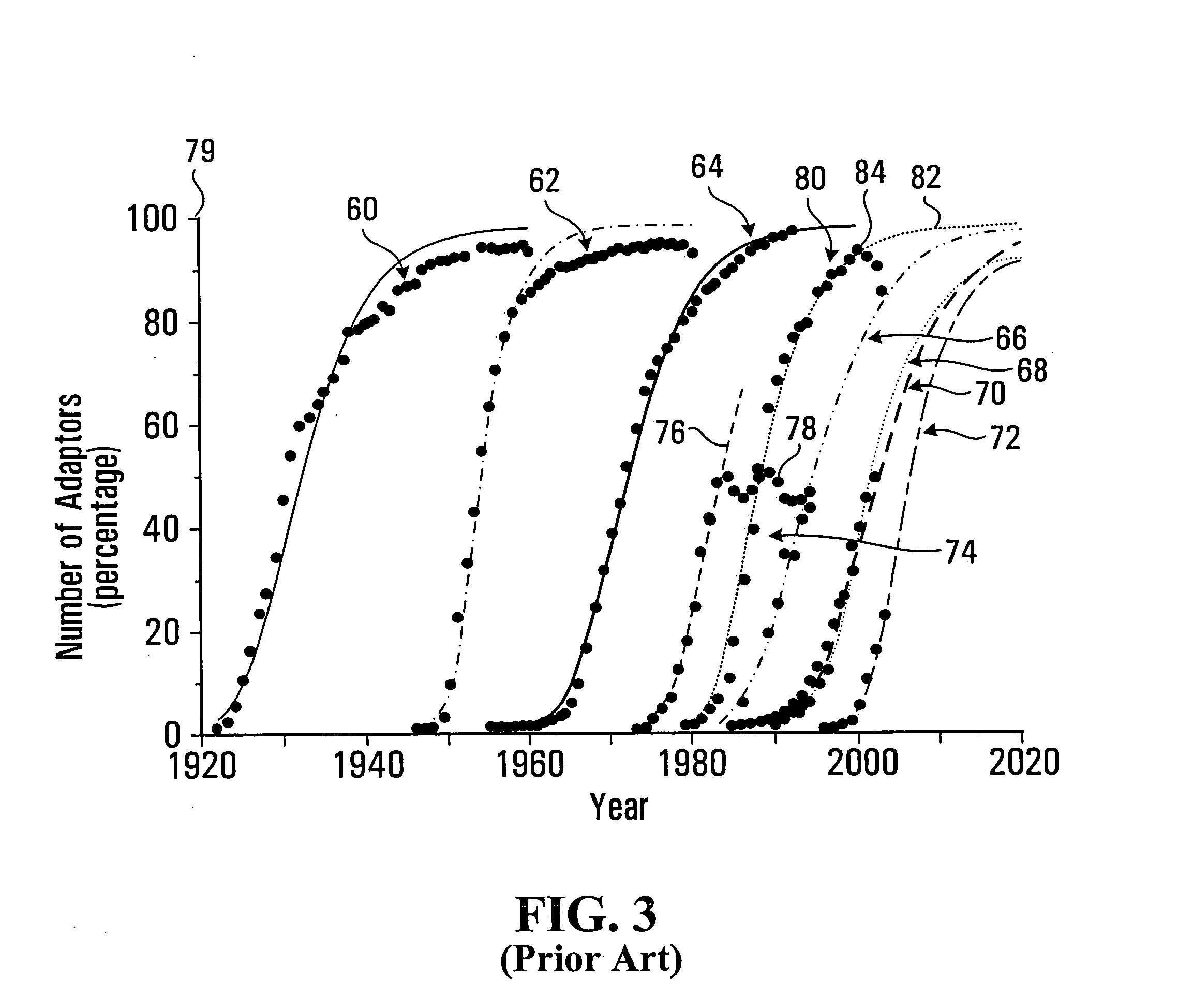
Method and system for predicting the adoption of services, such as telecommunication services
InactiveUS20080091483A1Enhanced diffusion modelFacilitated DiffusionForecastingTransmissionDiffusionDiffusion theory
An innovative service modeling framework is provided that can be used to analyze and assess the business opportunities of existing and emerging telecommunication services. This forecasting model / tool provides an approach to assess current and future markets—thus lowering investment risks, ensuring better decisions and subsequently having a greater impact. The core of the framework relies on a novel forecasting model (based on the theory of diffusion or S-curves) that departs from typical models used by popular research firms. The enhanced diffusion model relies on multi-dimensional input parameters and can take into account the impact of disruptions, regulations, network readiness, user utility and other dynamics. The input parameters are modeled as a series of vectors and are used to represent perturbations to the model. These influence the behavior of the adoption rate process in more realistic way.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
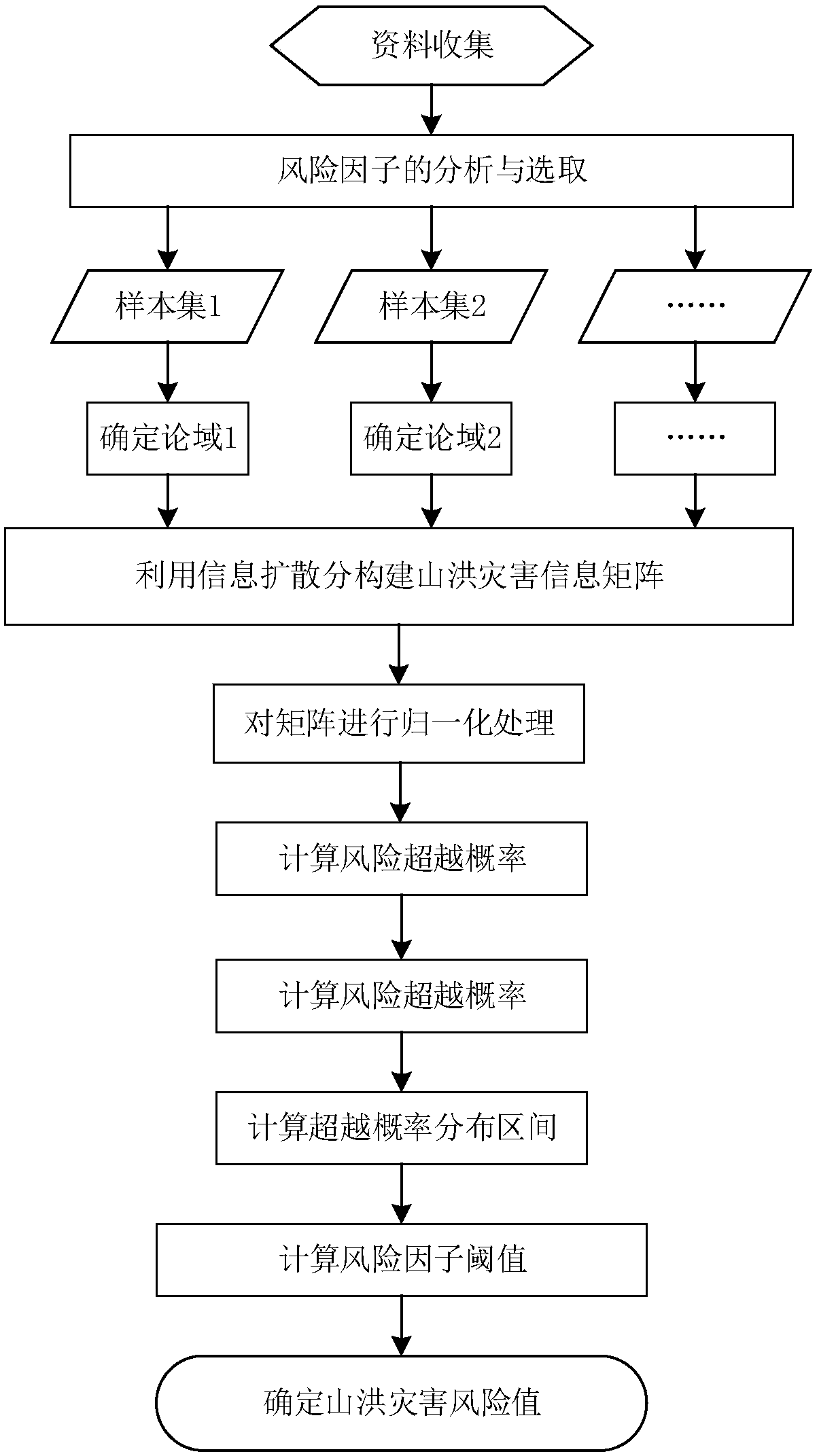
Information diffusion-based small watershed mountain torrent disaster risk analysis method
ActiveCN108269016AEasy to operateTake advantage ofClimate change adaptationResourcesDiffusionRisk profiling
The invention relates to an information diffusion-based small watershed mountain torrent disaster risk analysis method. According to the method, an information diffusion theory is introduced; based onlimited historical mountain torrent data, set-valued processing is performed on samples with monodromy observation values under incomplete information conditions, so that the samples can be transformed into fuzzy set-valued samples with fuzzy uncertainties; a mountain torrent disaster information matrix is established; the calculation of Pearson's III type curve, exceedance probability and confidence is introduced; and therefore, the quantitative assessment of a mountain torrent disaster risk can be carried out rapidly, and a result is closer to actual situations. With the method of the invention adopted, the objectivity and scientificity of the analysis result of the mountain torrent disaster risk can be improved.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
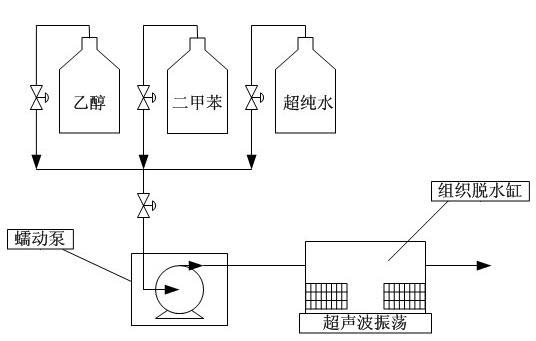
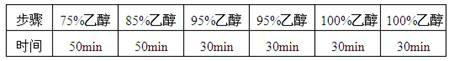
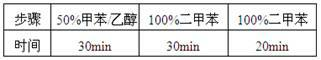
Biological tissue dehydrator and application thereof
InactiveCN101923018AEfficient dehydrationAvoid damagePreparing sample for investigationDiffusion theoryUltrasonic vibration
The invention relates to a dehydrated method using a biological tissue dehydrator, belonging to the field of biological pathology detection. The biological tissue dehydrator is a continuous feeding and discharging airtight sample slot. In the dehydrating mode of the dehydrator, a biological pathology tissue is fixed in the sample slot, and dehydrating agents the concentrations of which are from low to high are continuously introduced to carry out dehydration. In the process of tissue dehydration or transparency, the speed of molecular diffusion is increased, the tissue dehydration and transparency speed is accelerated and the high-efficiency dehydration and transparency of the pathology tissue are realized according to a diffusion theory through stirring or supersonic vibration in the sample slot. The invention has important facilitation on promoting the speed and the efficiency of biological pathology tissue detection.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
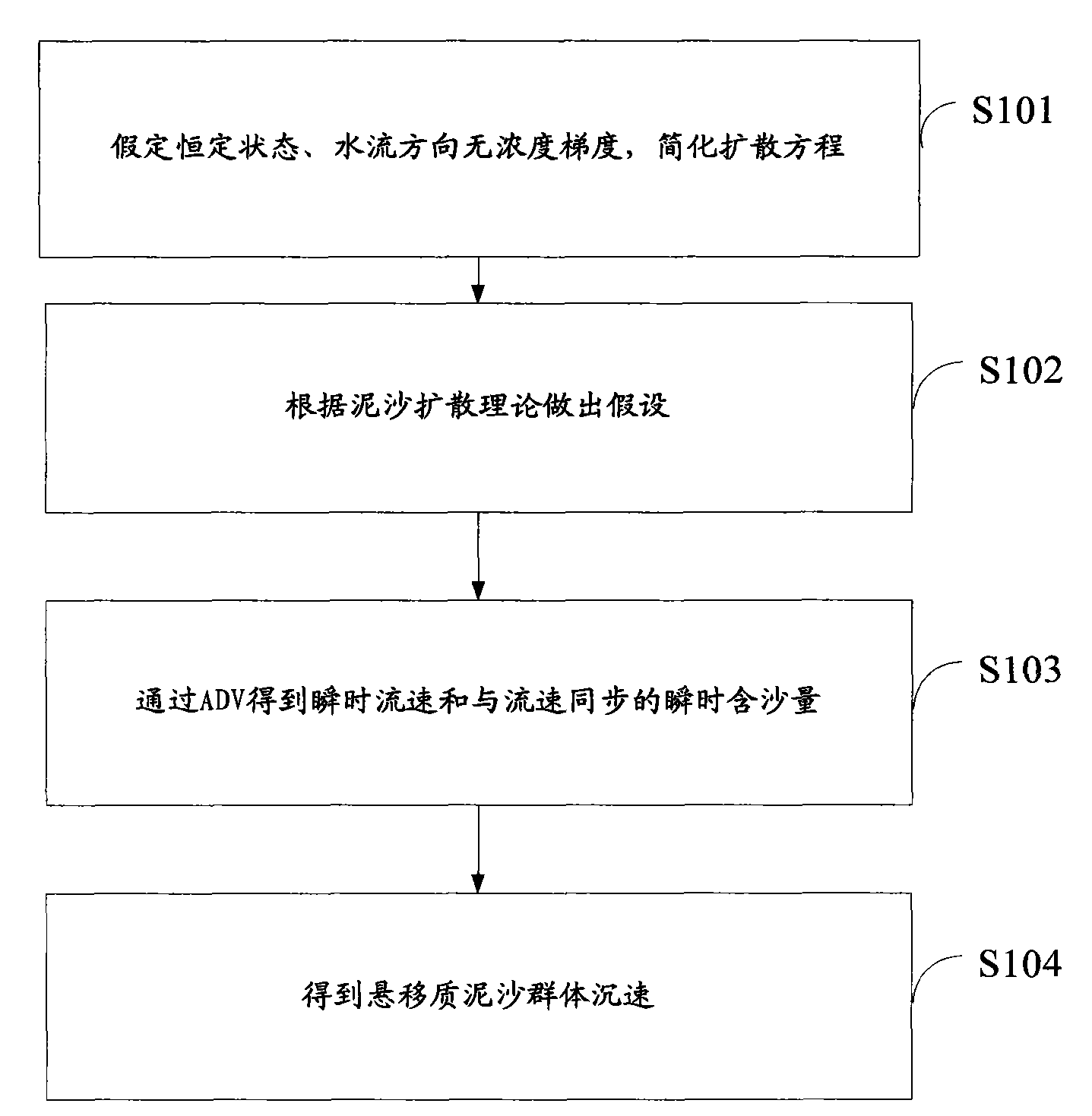
Method for detecting settling velocities of suspended sediment groups
The invention discloses a method for detecting settling velocities of suspended sediment groups. The method includes reducing a diffusion equation under hypothetic conditions of constant states and zero concentration gradients of water flow directions; performing hypothesis according to a sediment diffusion theory; acquiring instantaneous velocities and instantaneous sediment concentration synchronous with the velocities by the aid of an ADV (acoustic Doppler velocimeter); finally acquiring the settling velocities of the suspended sediment groups. The method has the advantages that the method is applicable to laboratories and fields, and can be applied to fine-grained suspended loads no matter whether flocculation actually occurs or not, distribution of the settling velocities along the depth of water and change of the settling velocities along with the sediment concentration can be measured by the method, and an effect of the method is superior to an effect of the traditional measuring method.
Owner:重庆交大国科航科技有限公司
Infrared detection method for break point of mold electric heating wire
The invention discloses an infrared detection method for a break point of a mold electric heating wire, and belongs to an active infrared detection technology, in particular to a method for realizing break point detection of the mold electric heating wire by exciting with a high-voltage discharge circuit. The method is characterized in that the high-voltage discharge circuit is designed firstly, high-voltage discharge spark is generated at the break point when the high-voltage discharge circuit is communicated with the electric heating wire with the break point, and energy is released. Heat is conducted onto the surface of a corresponding mold through an electric heating wire insulating layer, the surface temperature or the change of the surface temperature field of the mold is recorded through a thermal infrared imager, and automatic identification of the break point of the electric heating wire is realized by using a thermal diffusion theory.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY +3
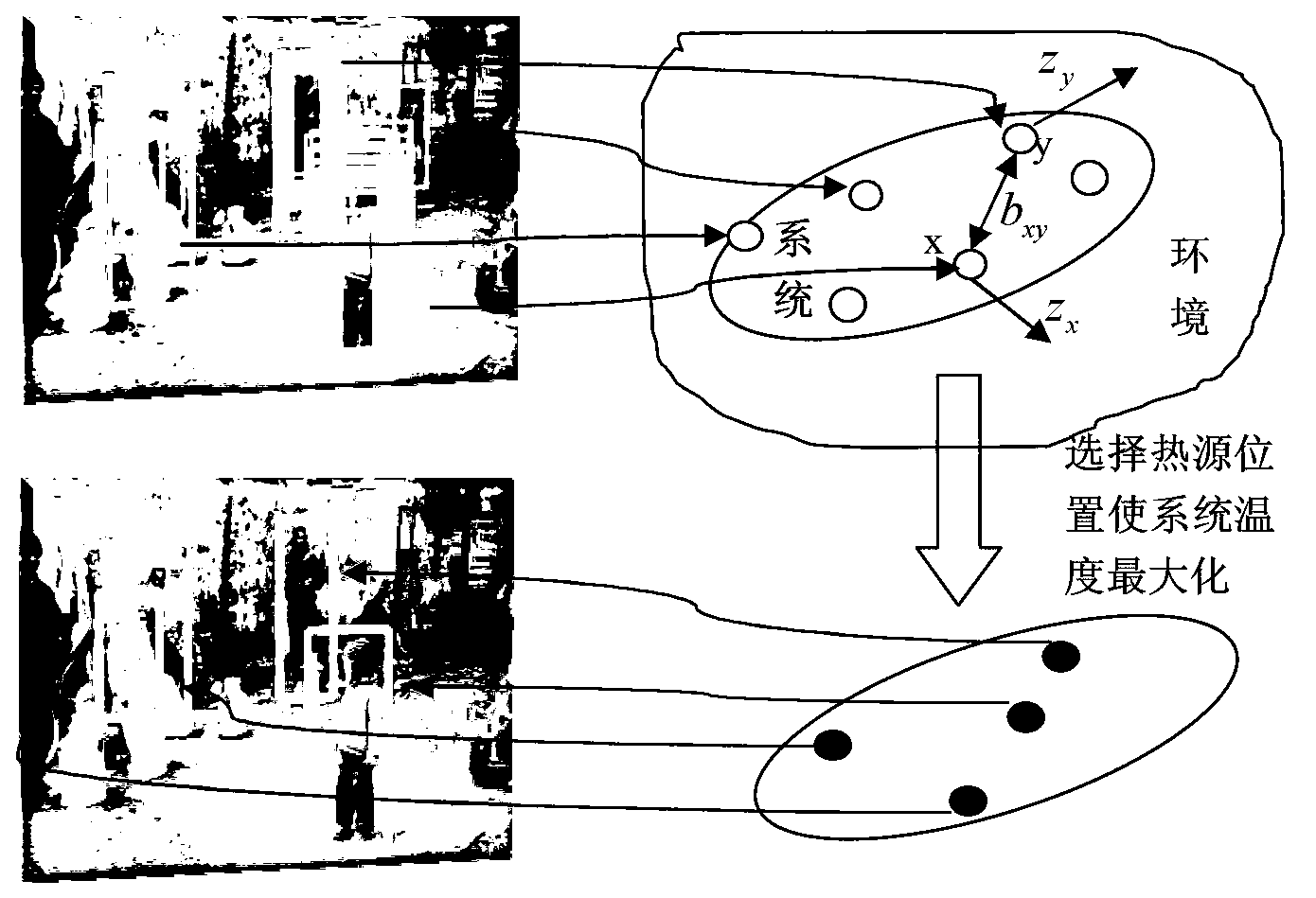
Window fusion method based on heat diffusion theory
ActiveCN103268586AExclude false positivesPrevent target interferenceImage analysisImage data processing detailsDiffusion theoryEngineering
Owner:厚普清洁能源(集团)股份有限公司
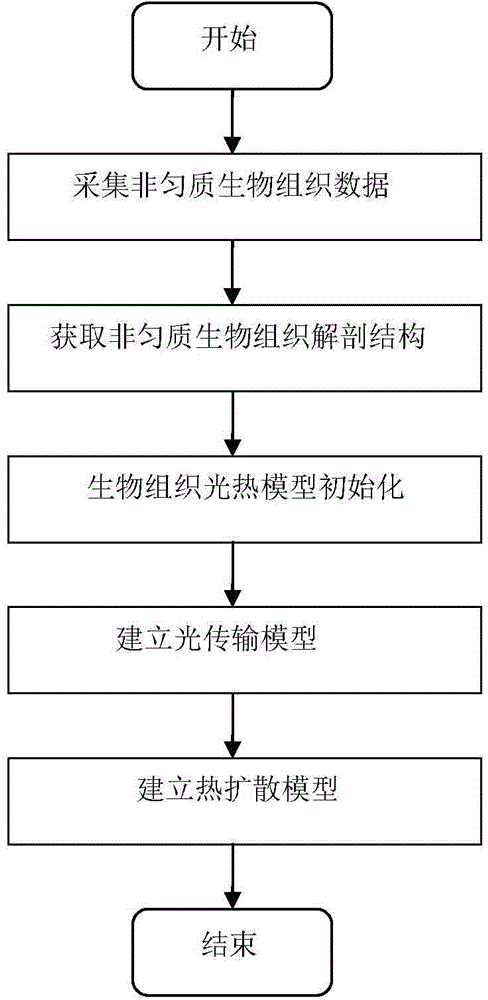
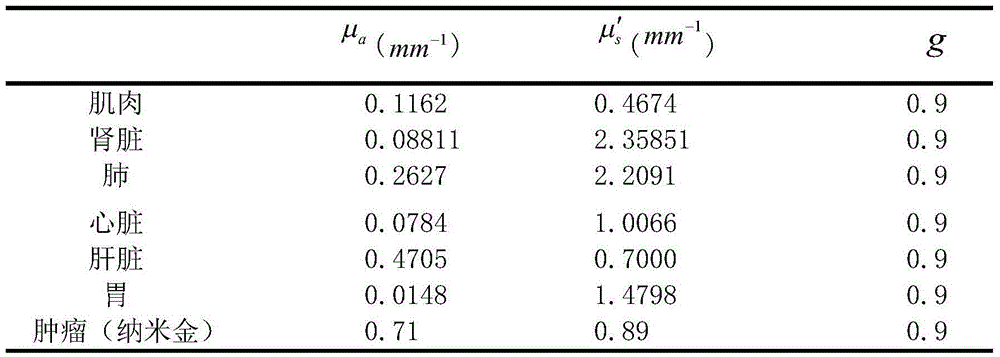
Nano-gold-based targeted non-homogeneous biological tissue photo-thermal therapy modeling method
The invention discloses a nano-gold-based targeted non-homogeneous biological tissue photo-thermal therapy modeling method and solves the problem that heat absorbed by a lesion part cannot be analyzed quantitatively when nano-gold photo-thermal therapy is carried out on the biological tissue in the prior art. The method describes an optical transmission process in the biological tissue according to the Boltzmann radiation transmission equation diffusion theory, and establishes a photo-thermal model of the nano-gold-based targeted non-homogeneous biological tissue according to a Pennes biological heat transfer equation and based on a thermal diffusion theory with heat conduction being a main approach. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a nano-gold-based targeted non-homogeneous biological tissue model; obtaining nano-gold-based targeted non-homogeneous biological tissue model data; establishing a light source model; establishing an optical transmission model; and establishing a heat transmission model. Under the condition of knowing the laser radiation power value and nanogold concentration value, light and heat absorbed by the lesion part after being injected with nanogold can be calculated, thereby optimizing treatment parameter so as to enhance photothermal conversion capability of the target area, and improving photo-thermal treatment efficiency of a living body.
Owner:屈晓超
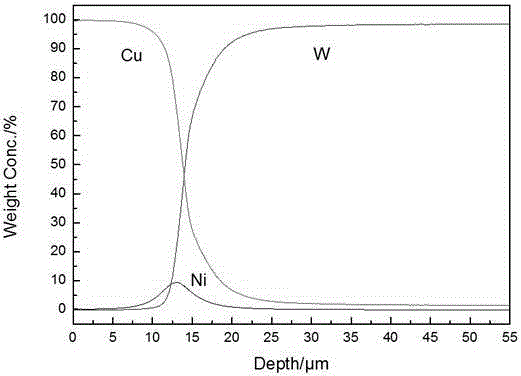
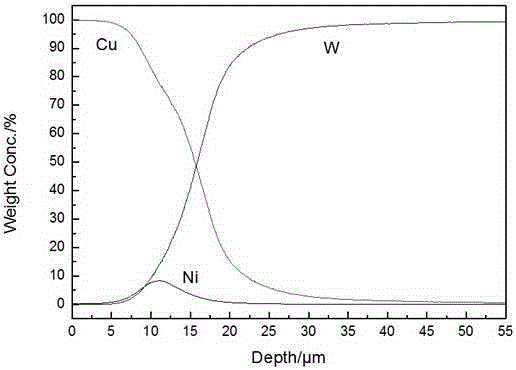
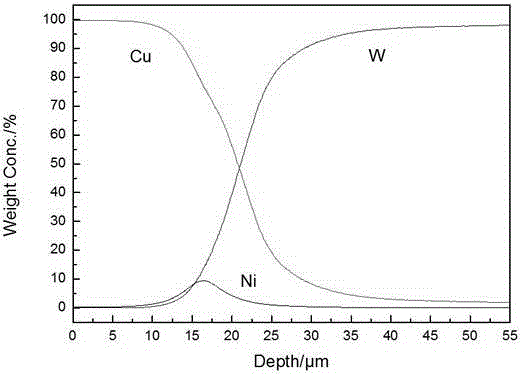
W-Ni-Cu gradient material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105177633AImprove impact performanceImprove heat resistanceCopper platingGradient material
The invention discloses a W-Ni-Cu gradient material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: taking a molten salt system of NaCl-KCl-NaF-NiO as an Ni leakage source and taking a copper-plating aqueous solution as a Cu leakage source; electrically depositing and leaking nickel on a pure W plate through molten salt, electrically depositing and leaking Cu through an aqueous solution; and finally diffusing and annealing to obtain the W-Ni-Cu gradient material. The material is high in thermal shock resistance and thermal fatigue resistance; all the components of the material are combined closely; the material surface structure is compact and smooth; the material has high electrical conductivity, high thermal conductivity and high mechanical performance. The method is capable of simultaneously carrying out mutual diffusion between W and Ni and carrying out mutual diffusion between Ni and Cu under the action of an electric field and a temperature field by using an electric deposition method according to the basic diffusion theory (the electric field can accelerate the diffusion of solid metals, and the diffusion speed of the opposite party can also be mutually improved when carrying out multi-element diffusion in the solid diffusion); the thickening of gradient layers can be accelerated; the W-Ni-Cu gradient material has the characteristics of rapid forming speed of the gradient layers, short preparation time, randomly controllable thickness of the gradient layers, compact surface structure of the material, high thermal conductivity and simple process.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method and apparatus for 3-d imaging of internal light sources
ActiveUS20080018899A1Material analysis by optical meansComputation using non-denominational number representationMammalMammalian tissue
The present invention provides systems and methods for obtaining a three-dimensional (3D) representation of one or more light sources inside a sample, such as a mammal. Mammalian tissue is a turbid medium, meaning that photons are both absorbed and scattered as they propagate through tissue. In the case where scattering is large compared with absorption, such as red to near-infrared light passing through tissue, the transport of light within the sample is described by diffusion theory. Using imaging data and computer-implemented photon diffusion models, embodiments of the present invention produce a 3D representation of the light sources inside a sample, such as a 3D location, size, and brightness of such light sources.
Owner:XENOGEN CORP
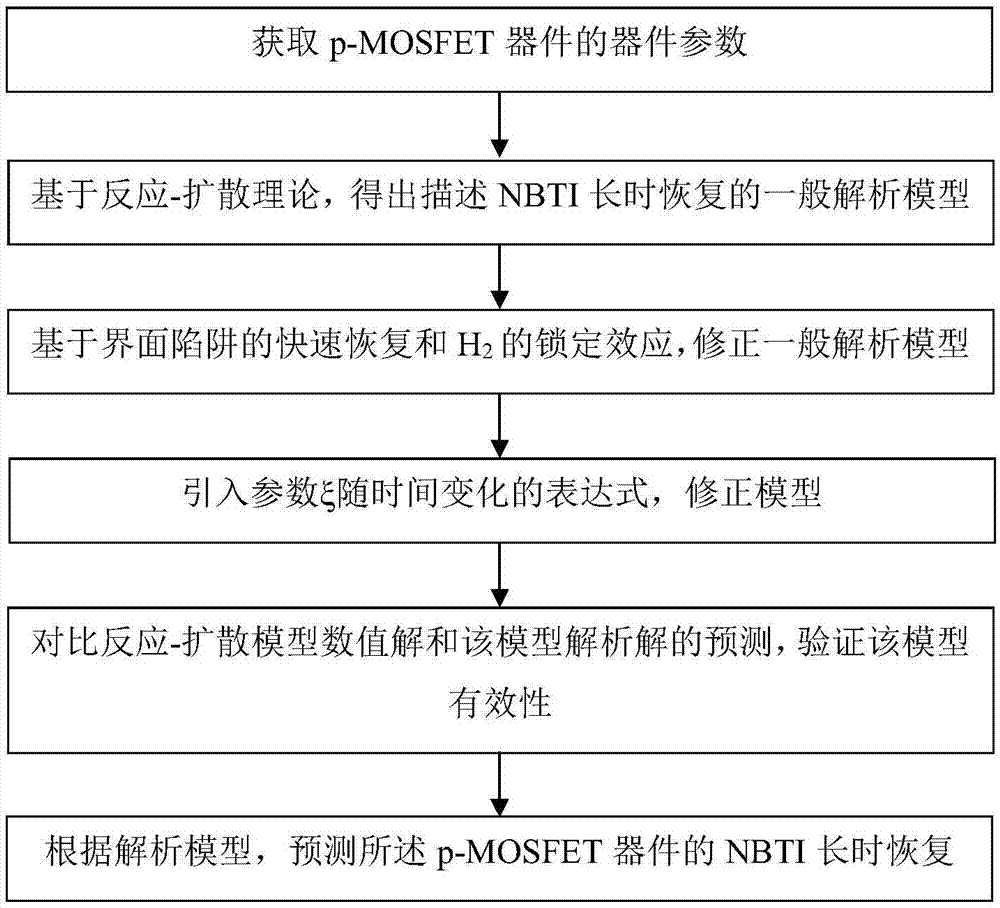
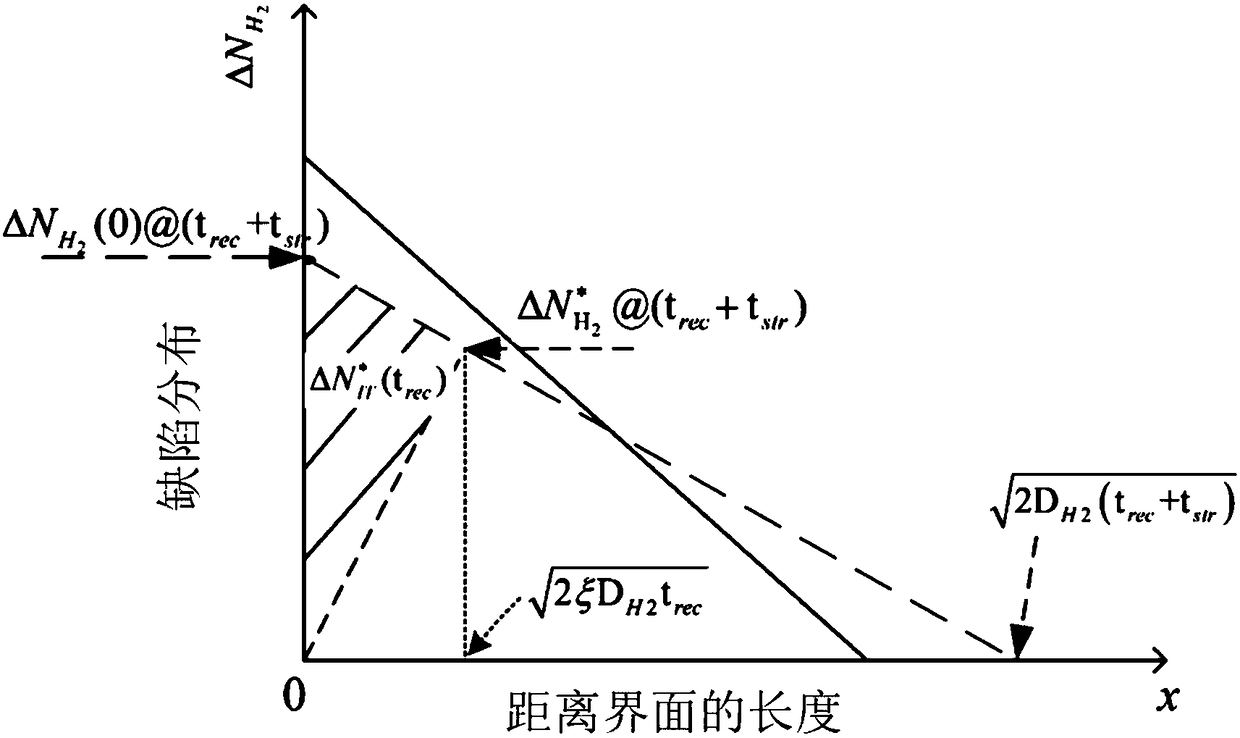
Analytical method for predicting NBTI long time recovery based on reaction-diffusion theory
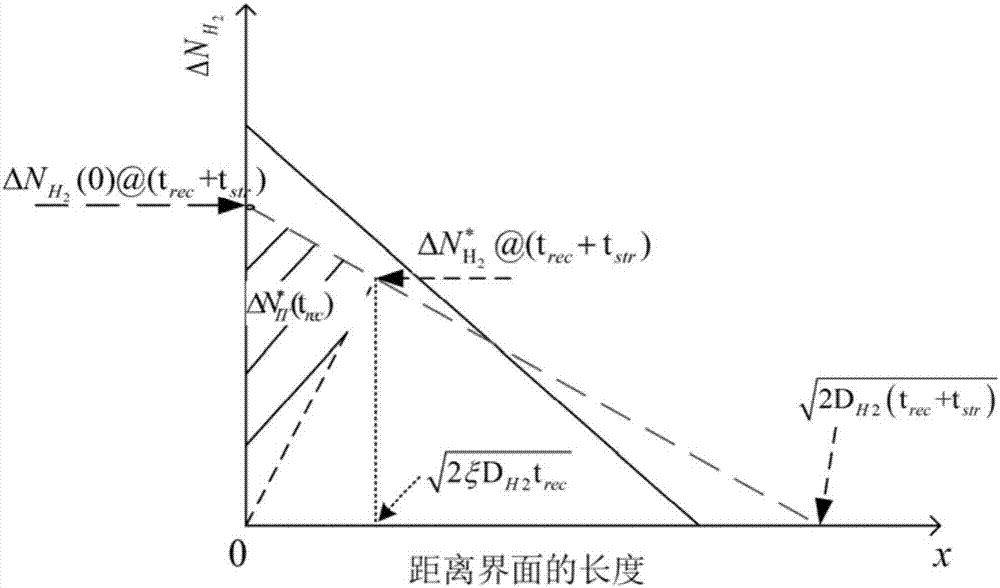
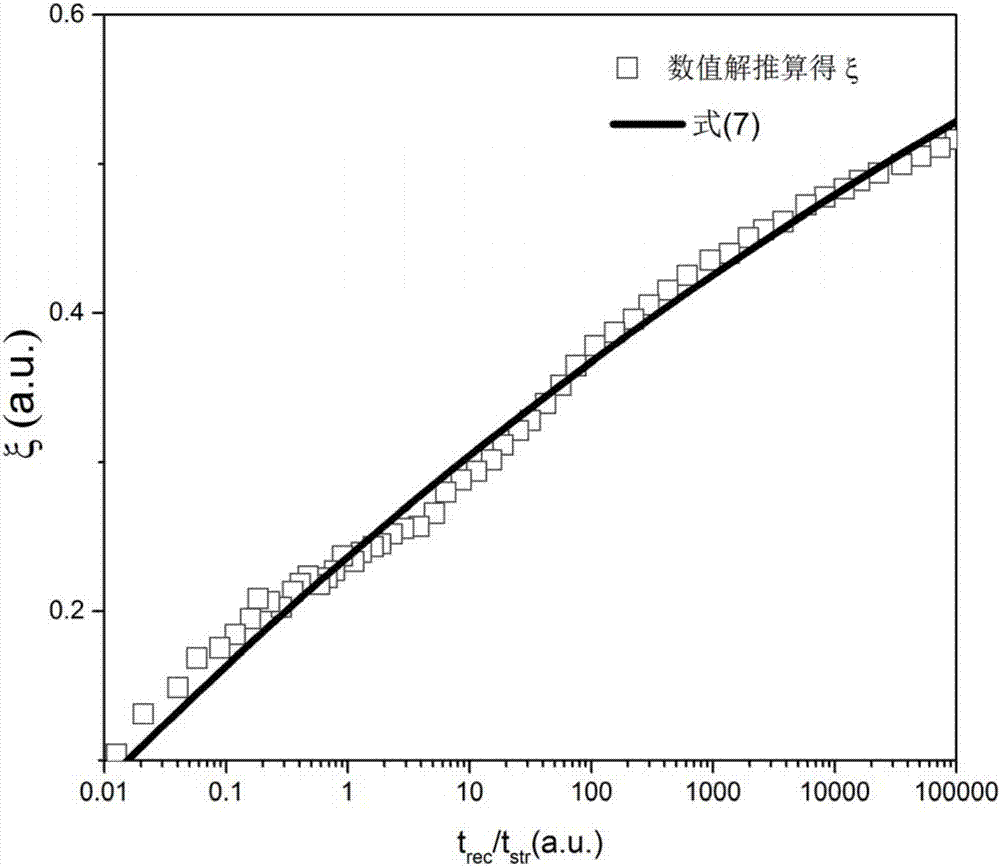
ActiveCN107203691AFew parametersWide applicabilityInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsUltrasound attenuationMOSFET
The invention discloses an analytical method for predicting NBTI long time recovery based on a reaction-diffusion theory. The method includes the steps of 1, obtaining the device parameters of P-MOSFET devices; 2, based on the basic reaction-diffusion theory, obtaining a general analytical model for describing NBTI long time recovery; 3, based on the fast recovery of an interface trap and the locking effect of H2, modifying the general analytical model; 4, based on DH2 as a physical quantity which changes with time, introducing and modifying the expression that a parameter xi changes with time, and obtaining the whole analytical model for describing the NBTI long time recovery; 5, predicting of the NBTI long time recovery of the P-MOSFET devices based on the analytical model. The analytical model integrates the two H2 factors of attenuation with recovery time of the diffusion coefficient and the locking effect, and the validity of the analytical method for predicting NBTI long time recovery based on the reaction-diffusion theory is verified by being compared with the numerical solution of an R-D model.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
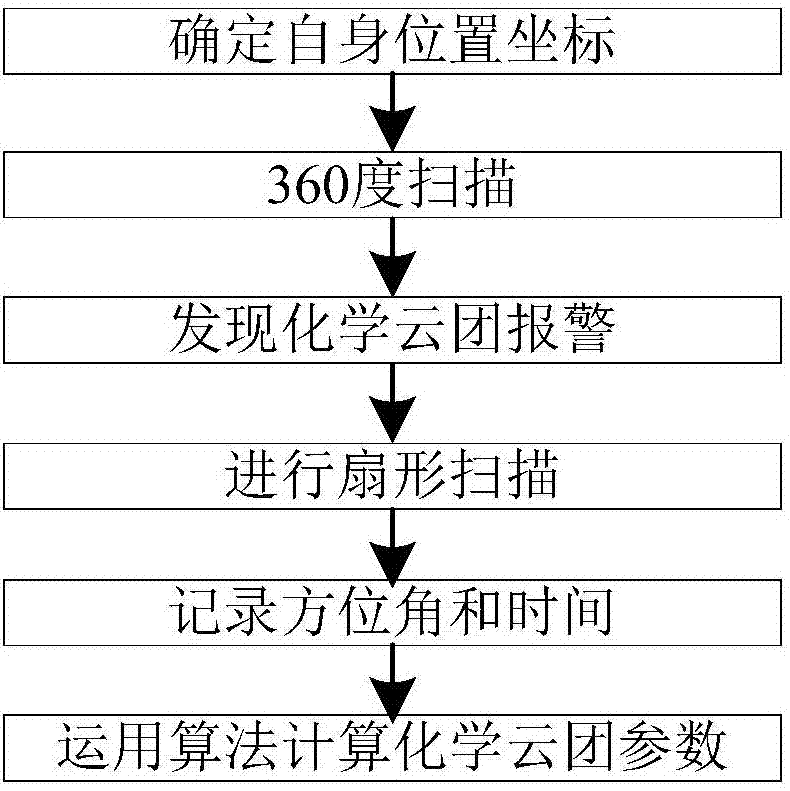
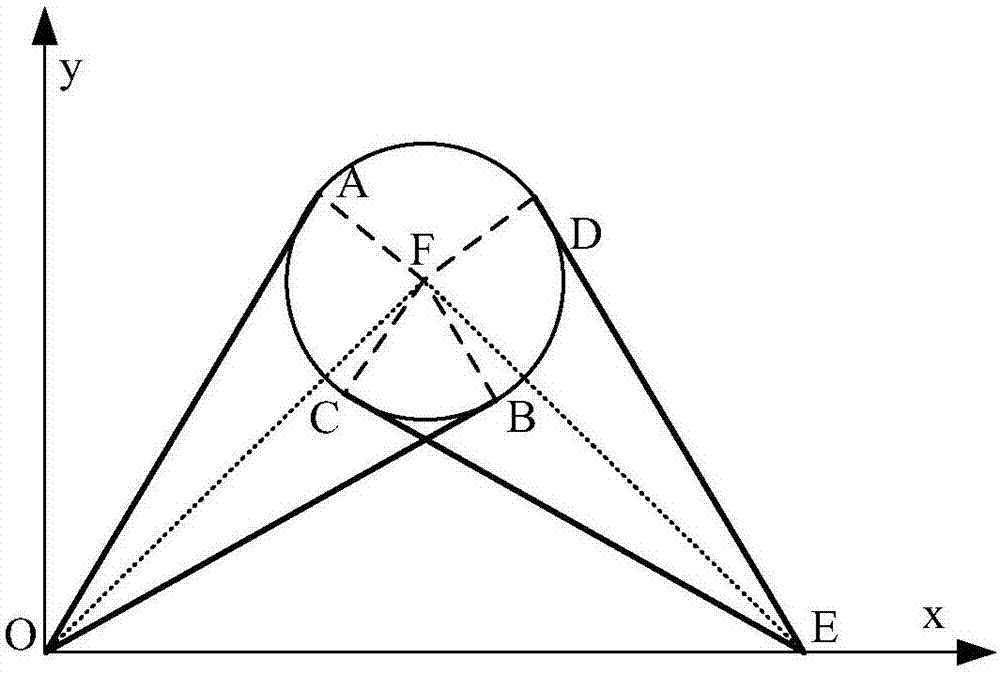
Land-based telemetric localization method of continuous point source based chemical cloud cluster
ActiveCN107290282ACalculation speedCalculation results are accurate and reliableMaterial analysis by optical meansDiffusionLand based
The invention relates to a land-based telemetric localization method of a continuous point source based chemical cloud cluster. End point position coordinates of the continuous point source based chemical cloud cluster are calculated based on angle parameters obtained by fixed-point scanning of two infrared telemetering devices according to a triangular relation formed by maneuvering, then, damage depth of the continuous point source based chemical cloud cluster is calculated, and the application amount and damage boundary of the continuous point source are calculated inversely through combination with the continuous point source diffusion principle. According to the method, the location problem of the cloud cluster by infrared spectra is solved with comprehensive application of principles of a diffusion theory, the novel maneuvering telemetric localization method of the continuous point source based chemical cloud cluster is provided, and technical support is provided for the application of the infrared telemetering devices.
Owner:中国人民解放军防化学院
River and lake bottom sludge pollutant flux test method and device based on diffusion theory
ActiveCN102590479BWide applicabilityThe concentration of pollutants does not need to be testedEarth material testingTesting waterSample waterSludge
The invention discloses a river and lake bottom sludge pollutant flux test method and a river and a device based on a diffusion theory. The method comprises the following steps of: A, acquiring a bottom sludge sample; B, putting the bottom sludge into a base of an experimental device, and enabling the sludge surface to be horizontal; C, slowly injecting water to a column port along a column wall; D, injecting running water into the experimental device without the bottom sludge; E, standing for a certain time; F, measuring the pollutant concentration of the taken water sample; G, calculating a degrading coefficient of the pollutant in the water; H, calculating an initial concentration value of the bottom sludge water; and I, calculating a pollutant exchange flux of a water-sludge interface. A base plate is fixed at the bottom of a constant-temperature water tank; a base wall is arranged on the base plate; a lower flange disk is arranged on the upper part of the base wall; an upper flange disk is arranged at one end of a column body; and an upper flange disk fixing bolt flange hole is formed in the upper flange disk. The method is feasible, and is convenient to operate; the experimental device has a rational and simple structure; operations of accommodating deposits, sampling water samples and the like are extremely convenient; and outstanding economic benefit is achieved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
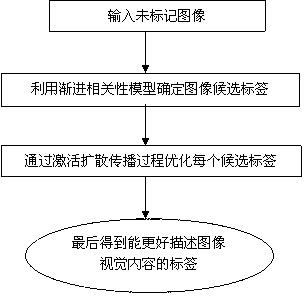
Image labeling method based on activation diffusion theory
InactiveCN103065157ACharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsDiffusion theoryBiological activation
The invention discloses an image labeling method based on an activation diffusion theory. Firstly, an image label is regarded as a node of semantic network, a progressive correlation model is utilized to obtain a joint probability among multiple image labels, candidate image labels are generated, then the activation diffusion theory is utilized to compute correlation value of each candidate image label, effective transmissibility of each candidate image label is refined, and corresponding numerical value is given on each candidate image label. The size of the numerical value depends on the relation between the each candidate image labels and other candidate image labels, and a final label of each image is the candidate image label of the highest correlation value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
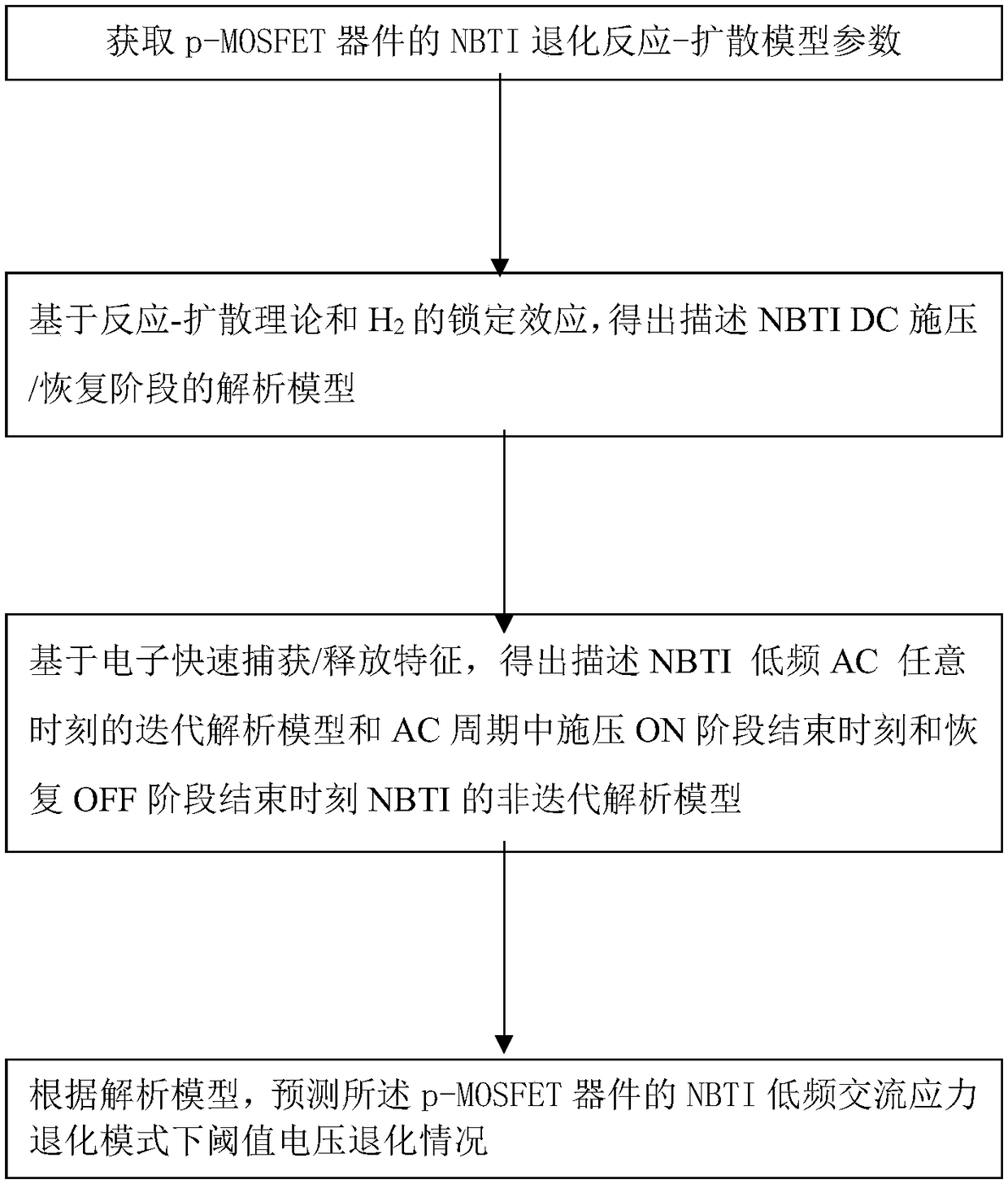
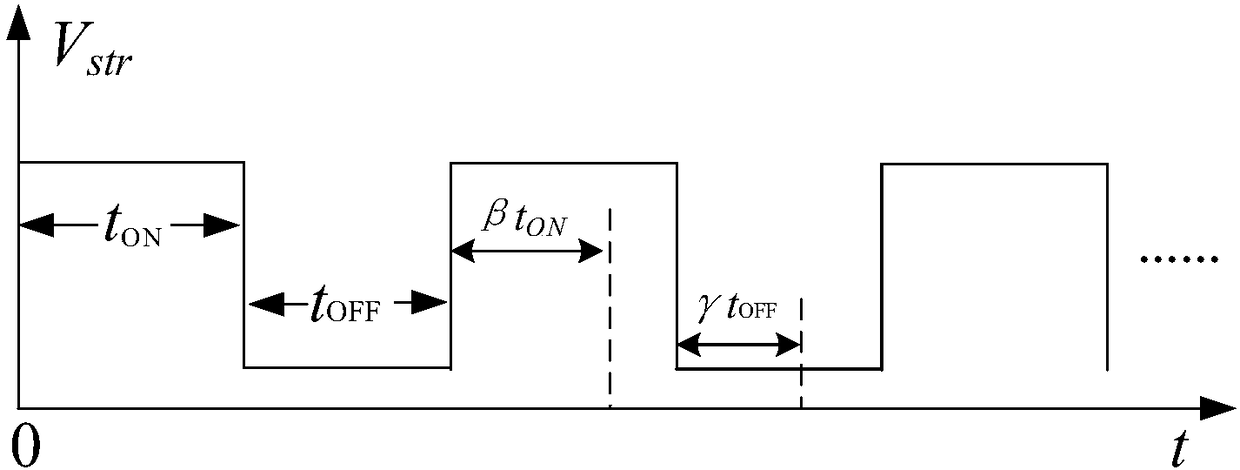
Analysis method and system for NBTI (Negative Bias Temperature Instability) degradation prediction under low-frequency alternating current stress mode
ActiveCN108363861AFew parametersWide applicabilityForecastingComputer aided designLockin effectDiffusion theory
The invention puts forward an analysis method and system for NBTI (Negative Bias Temperature Instability) degradation prediction under a low-frequency alternating current stress mode. The method comprises the following steps that: S1: obtaining the NBTI degradation reaction-diffusion model parameter of a p-MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor) device; S2: on the basis of a basic reaction-diffusion theory and an H2 lock-in effect, obtaining an analysis model for describing an NBTI direct-current pressurization / recovery stage; S3: on the basis of the quick capture / releaseof electrons, obtaining an iterative analysis model of any moment under a described NBTI low-frequency alternating current stress mode, and the non-iterative analysis model of the NBTI of a pressurized ON stage end moment and a recovery OFF stage end moment in an alternating current period; and S4: according to the analysis model, predicting a threshold value voltage degradation situation under the NBTI low-frequency alternating current stress degradation mode of the p-MOSFET device.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
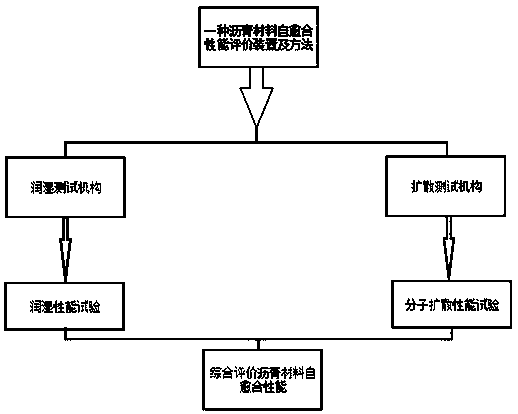
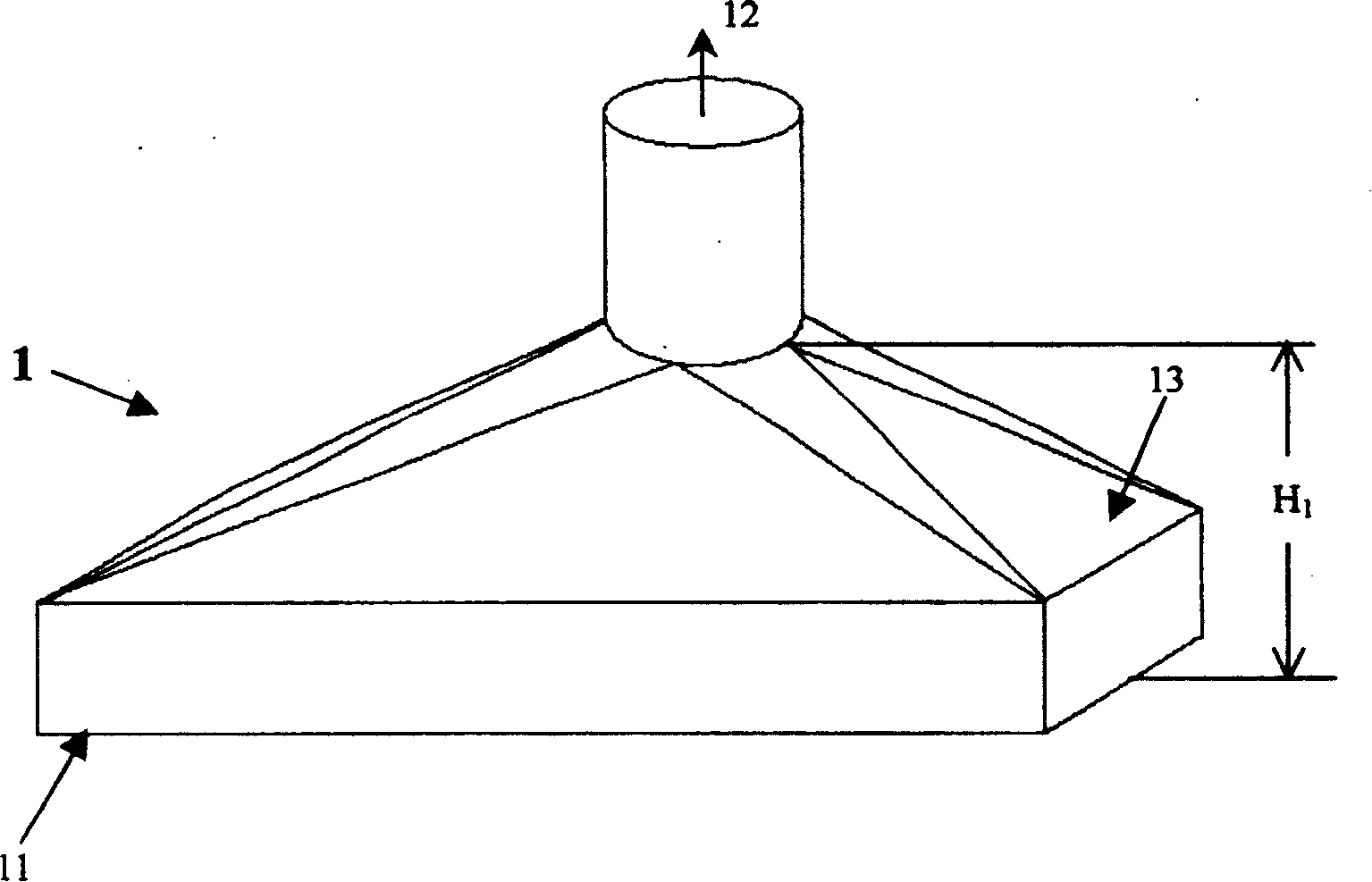
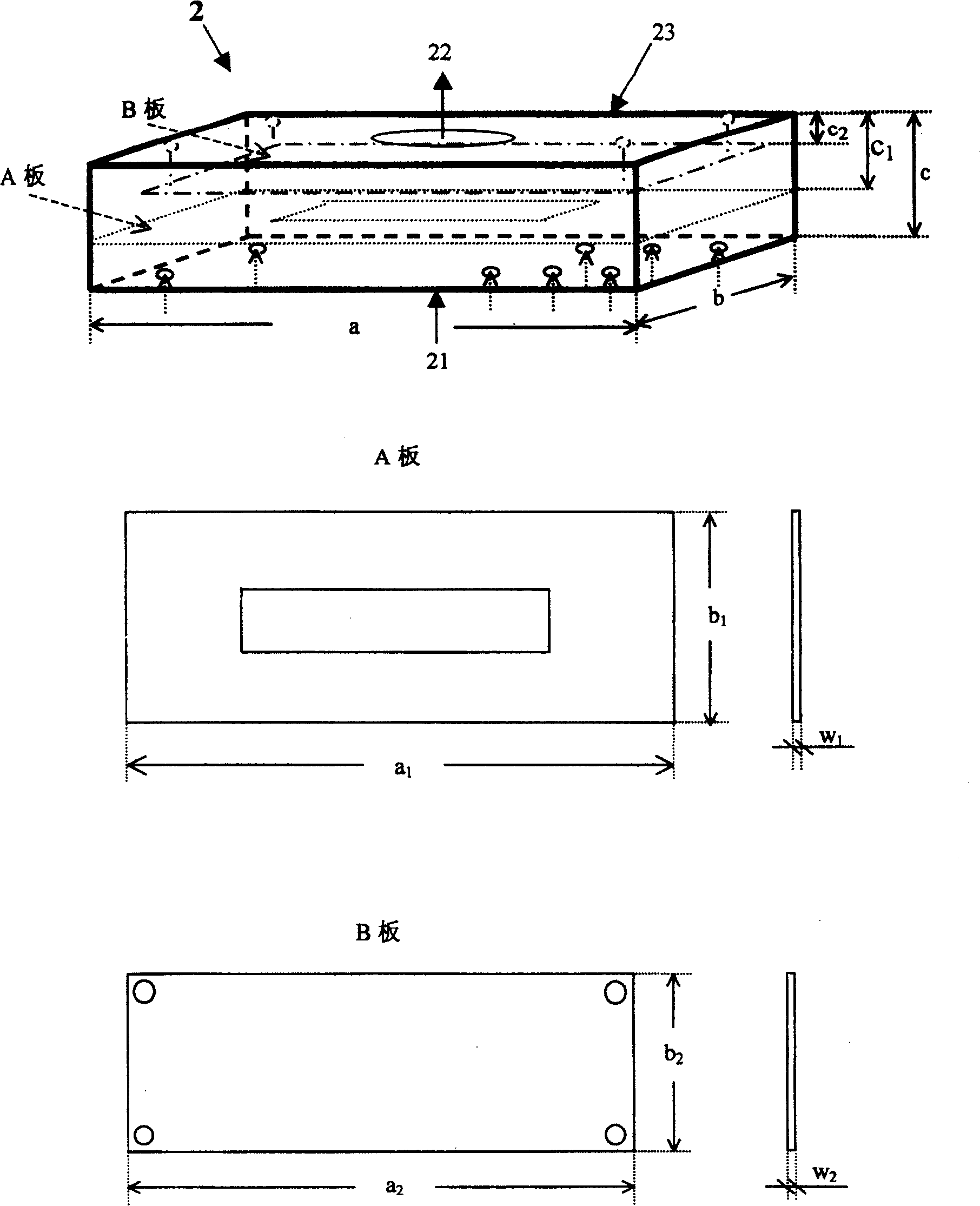
Asphalt material self-healing performance evaluation device and method
ActiveCN110297079AEasy to getEasy to operateClimate change adaptationMaterial testing goodsSelf-healingDiffusion
The invention provides an asphalt material self-healing performance evaluation device and method based on a capillary diffusion theory, which is used for solving the problems that an existing asphaltmaterial self-healing performance evaluation device and method is relatively complicated, relatively high in cost and relatively long in test time. The evaluation device comprises an environment box;a wetting testing mechanism and a diffusion testing mechanism are arranged in the environment box; the wetting testing mechanism comprises a culture dish; a support for placing an asphalt test block is arranged in the culture dish; a glass tube used for containing test asphalt is fixed on one side of the support; an open groove which is larger than the side surface of the asphalt test block is formed in one side of the glass tube; a baffle is arranged on the open groove; a handle is arranged at the upper part of the baffle; the diffusion testing mechanism comprises two opposite fixed ends; andthe two fixed ends are fixed on the two sides of the environment box through telescopic rods respectively. The device is simple in structure, low in cost, short in test duration and relatively accurate in test result, can be well used for evaluating the self-healing behavior of the asphalt material and is suitable for various practical materials in road engineering.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
New type uniform diffuser for flow field
InactiveCN100395389CEven fluid distributionSmall footprintDrafting machinesContinuous wound-up machinesDiffusion theoryEngineering
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
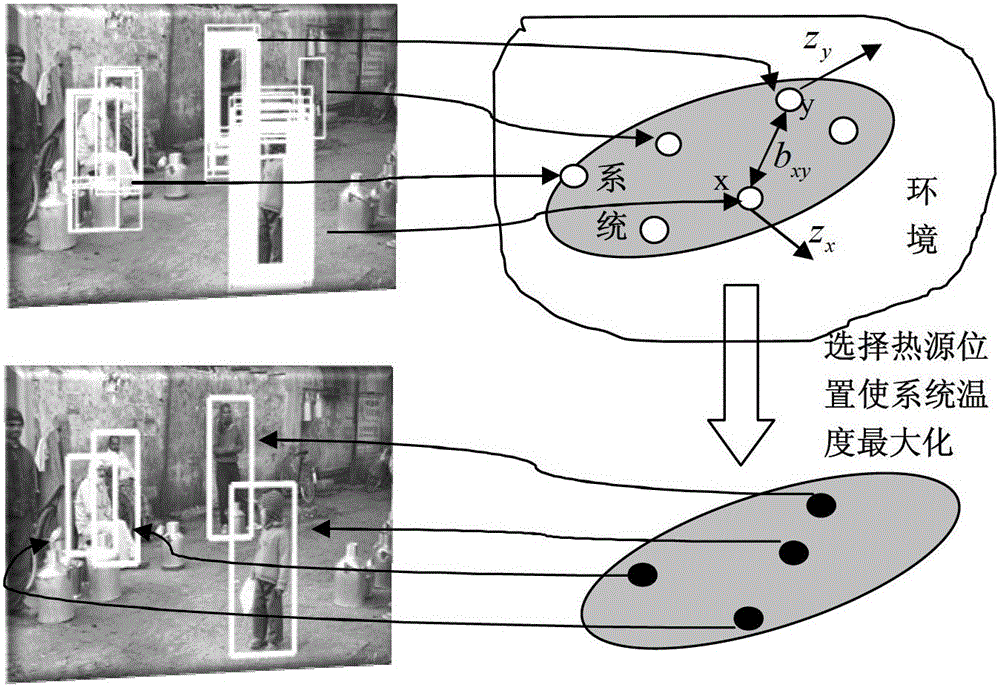
A Window Fusion Method Based on Thermal Diffusion Theory
ActiveCN103268586BExclude false positivesPrevent target interferenceImage analysisImage data processing detailsDiffusion theoryEngineering
The invention provides a window fusion method based on the heat diffusion theory. The method includes the steps that each initial detection window corresponds to one position in a thermodynamic system; a heat conduction coefficient between positions, corresponding to any two initial detection windows, in the thermodynamic system is calculated; a linear anisotropy heat diffusion equation which is in a discrete version under a steady state is established by using of the heat conduction coefficient between any two positions; K positions are selected in the system as heat sources to enable the temperature sum of the whole system to reach the maximum under the condition of heat diffusion; the repeated initial detection windows are eliminated through a non-maxima suppression method because duplicate detection of the corresponding K detection windows still possibly exists after the K positions of the heat resources are determined. According to the window fusion method based on the heat diffusion theory, the method of maximizing the temperature sum of the system under the condition of linear anisotropy heat diffusion is utilized for simulating an objective law of the initial detection windows, and therefore precision of target detection can be greatly improved.
Owner:HOPE CLEAN ENERGY (GRP) CO LTD
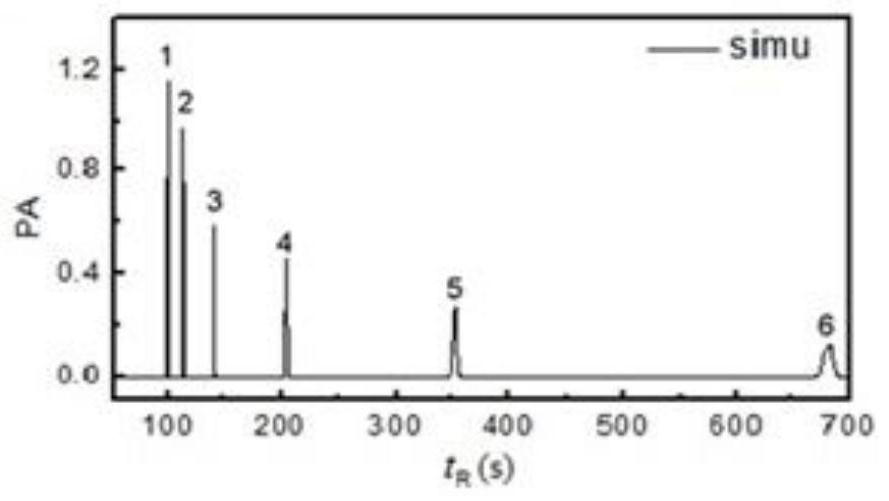
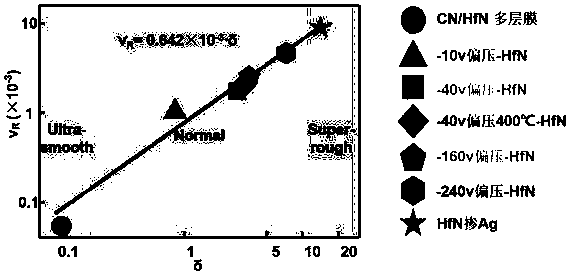
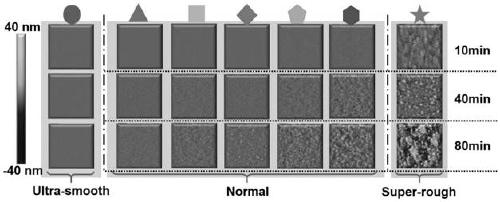
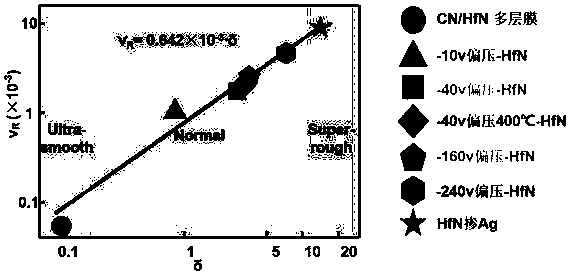
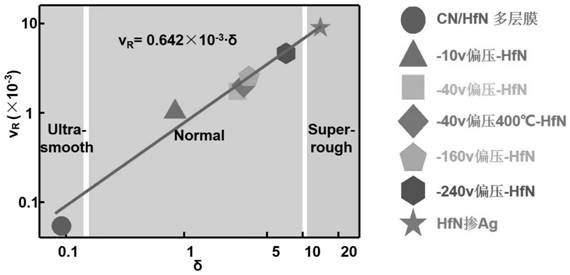
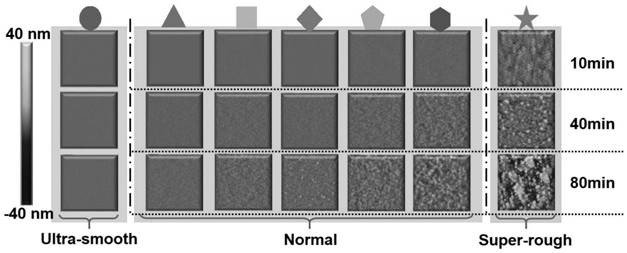
Method for regulating surface coarsening rate of film in in-situ large range
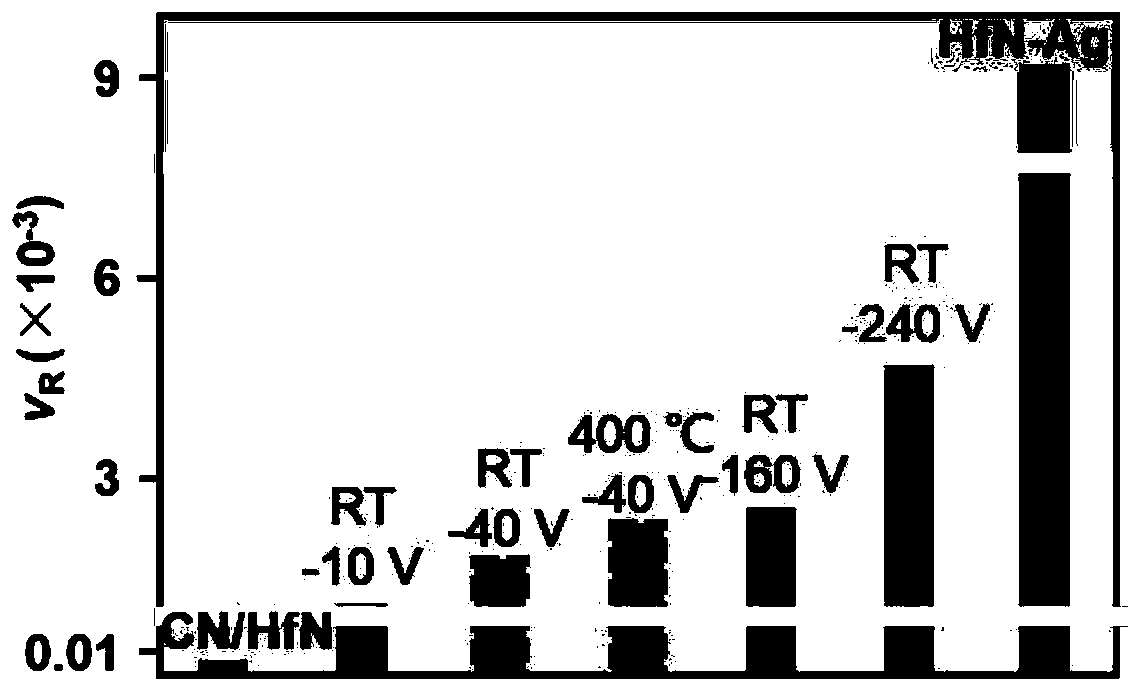
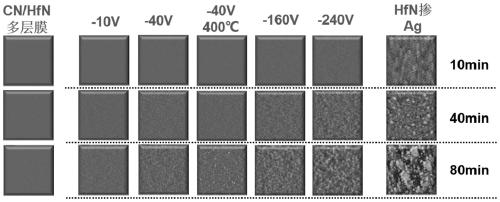
ActiveCN110016650ASimple processImprove efficiencyVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingDiffusionDiffusion theory
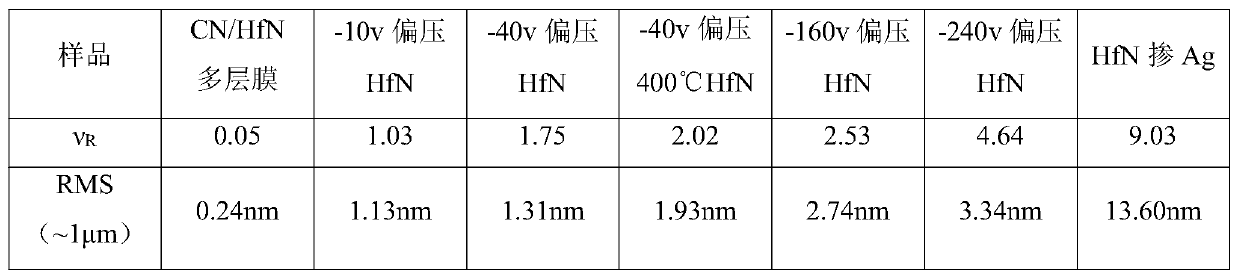
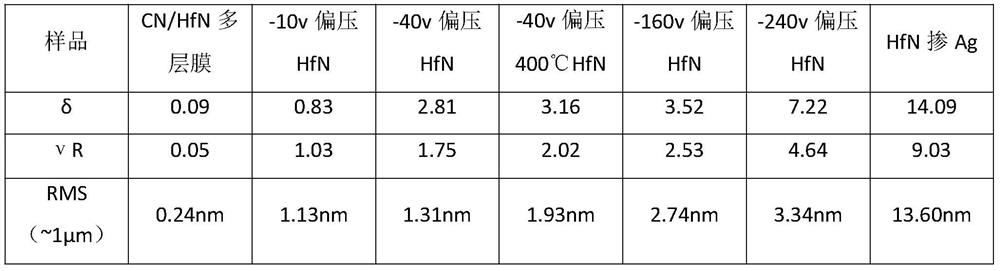
The invention relates to the field of film surface coarsening rate, in particular to a method for regulating the surface coarsening rate of a film in an in-situ large range. The method comprises a sample material, wherein the sample material is hafnium nitride; in the preparation process, an amorphous layer is introduced by adopting a magnetron co-sputtering method, and an amorphous coating effectis utilized to prevent uphill diffusion so as to obtain a low coarsening rate. According to the method, an atom-increasing diffusion theory is guided to practice, the complex diffusion is simplified,only uphill and downhill diffusion affecting the surface coarsening rate is considered, and a novel method for controlling the surface growth by the atomic level is provided. By introducing the amorphous layer, the uphill and downhill diffusion probability ratio is greatly reduced through preventing the uphill diffusion, so that the very low coarsening rate is obtained, and the ultra-smooth filmis prepared; and due to the fact that elements which are not wetted with a parent material are introduced, the uphill and downhill diffusion probability ratio is greatly reduced through preventing thedownhill diffusion, so that a very high coarsening rate is obtained, and a super-rough film is prepared.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
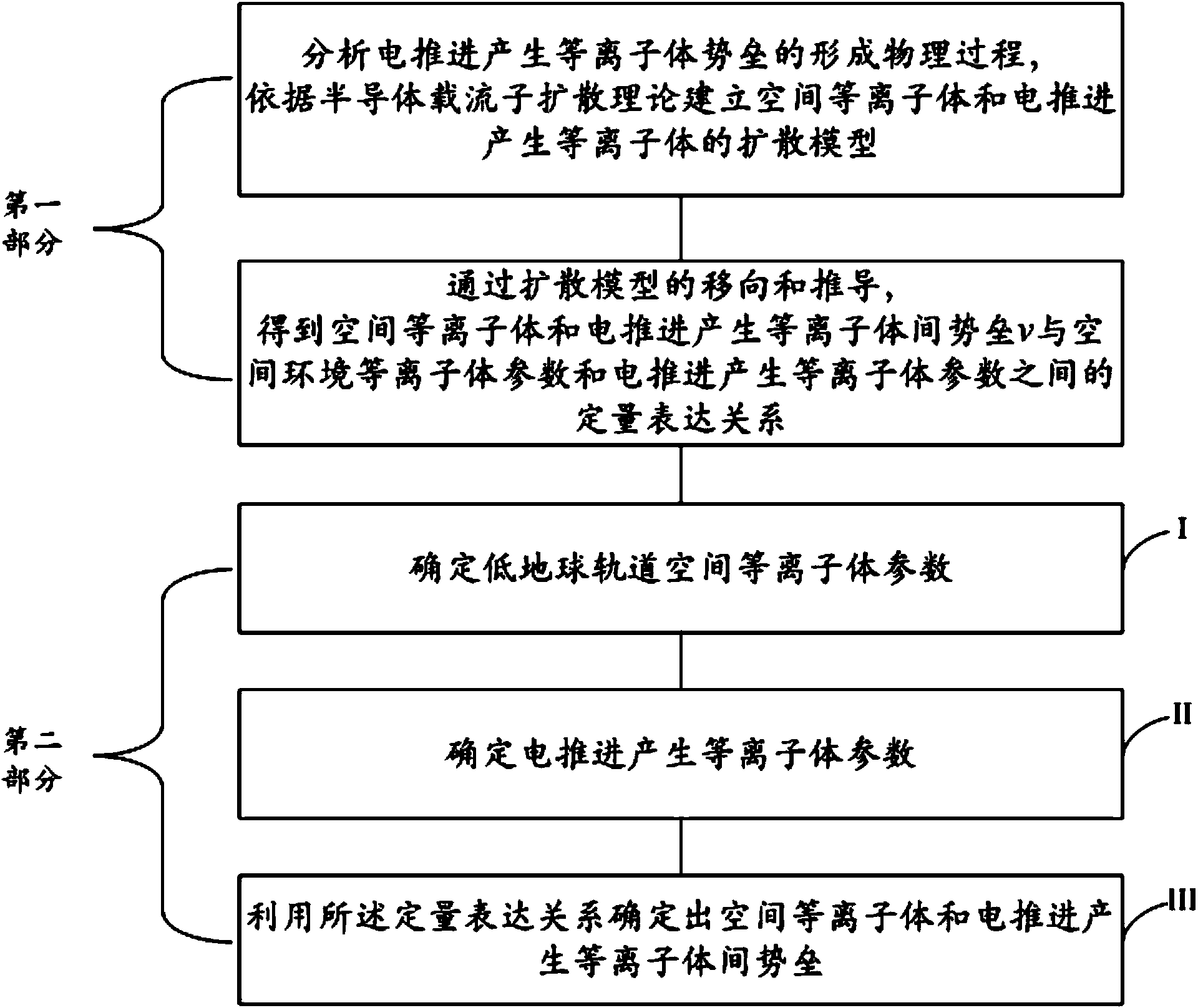
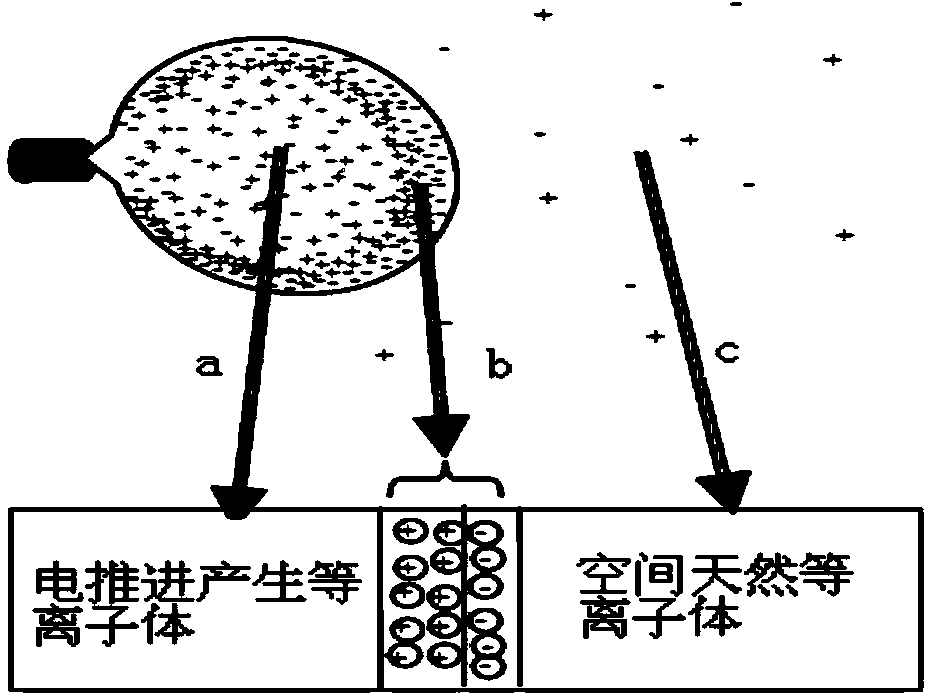
Quantitative analysis method for potential barrier between space plasma bodies and plasma bodies generated through electric propulsion
The invention discloses a quantitative analysis method for potential barrier between space plasma bodies and plasma bodies generated through electric propulsion. The quantitative analysis method is applicable to the analysis of the action process of the space plasma bodies and the plasma bodies generated through the GEO orbit satellite electric propulsion. The diffusion process of the plasma bodies generated through the electric propulsion is compared with the diffusion process of current carriers in a semiconductor, and a diffusion model for the space plasma bodies and the plasma bodies generated through the electric propulsion is built according to the semiconductor current carrier diffusion theory; the quantitative expression relationship between the potential barrier intensity v between the space plasma bodies and the plasma bodies generated through the electric propulsion, and the parameters of space environment plasma bodies and the parameters of the plasma bodies generated through the electric propulsion is deduced by using the diffusion model; during the analysis, the parameters of the space plasma bodies of a GEO rail and the parameters of the plasma bodies generated through the electric propulsion are determined; according to the two kinds of determined plasma body parameters, the parameters are substituted into the quantitative expression relationship to determine the potential barrier intensity between the space plasma bodies and the plasma bodies generated through the electric propulsion.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SPACE TECH
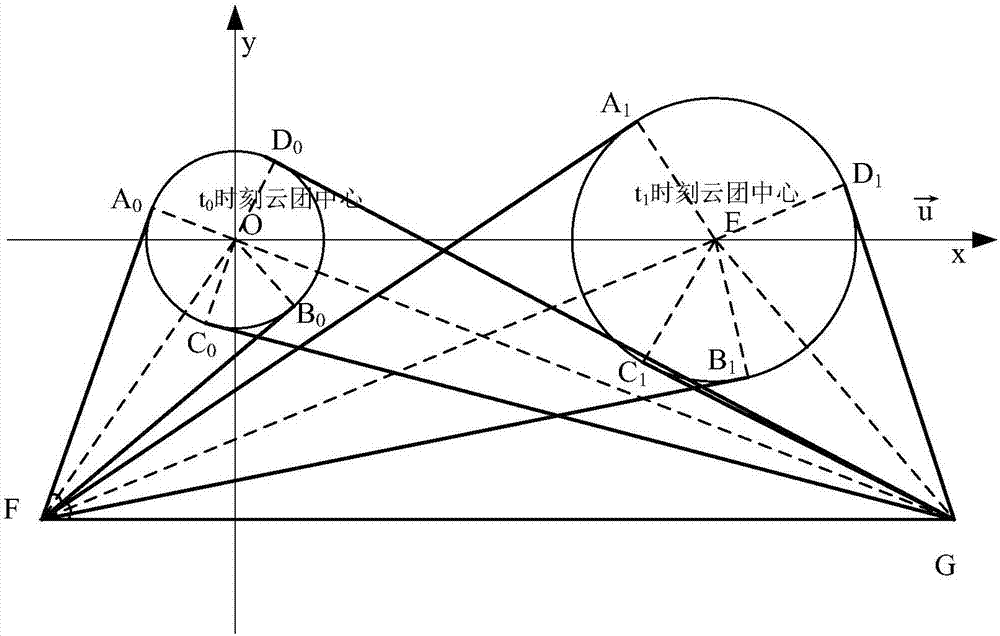
Continental rise remote measurement positioning method based on instantaneous point source chemical cloud cluster
InactiveCN107356948ACalculation speedCalculation results are accurate and reliableMaterial analysis by optical meansSatellite radio beaconingDiffusionMeasurement device
The invention relates to a continental rise remote measurement positioning method based on an instantaneous point source chemical cloud cluster. Two sets of infrared remote measurement devices are utilized to carry out fixed point scanning to acquire angle parameters, a forward intersection method is utilized to determine the center point position of the chemical cloud cluster, observation data at two different moments are utilized, in combination with the instantaneous point source diffusion principle, source intensity of the instantaneous point source and the generation time, the relative distance and the cloud cluster radius of the chemical cloud cluster are acquired through inverse computation. The method is advantaged in that the diffusion theory and the forward intersection principle are comprehensively utilized, a problem of cloud cluster positioning difficulty of infrared light spectrum is solved, the new instantaneous point source chemical cloud cluster fixed point remote measurement positioning method is realized, and technical support is provided for application of infrared remote measurement devices.
Owner:中国人民解放军防化学院
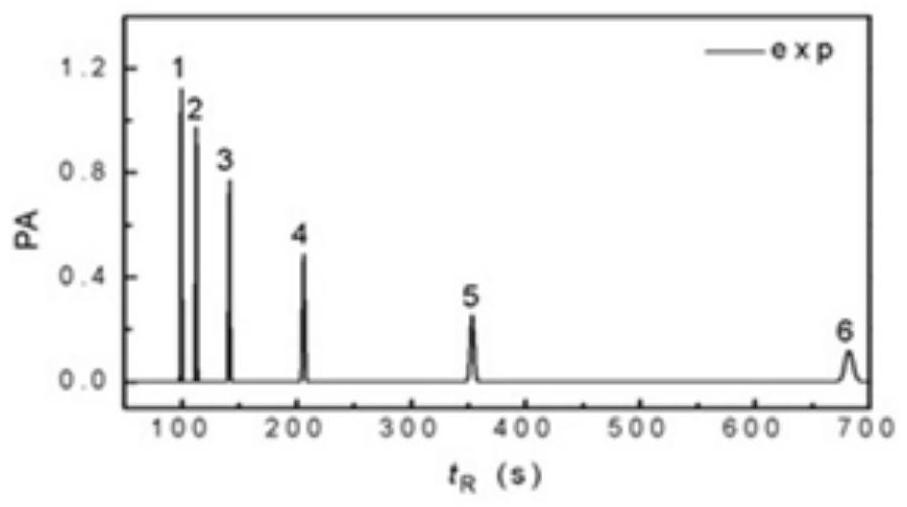
A Gas Chromatographic Separation Simulation Method Based on Stochastic Diffusion Theory
ActiveCN108875284BReduce dosageShorten test timeDesign optimisation/simulationComputational theoretical chemistryChromatographic separationGas liquid chromatographic
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
Adatom diffusion model for adjusting and controlling coarsening rate
ActiveCN109913834AForecast of changeAchieve ultra-smoothVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingDiffusionSurface roughness
The invention relates to the technical field of films, in particular to an adatom diffusion model for adjusting and controlling the coarsening rate. An adatom diffusion theory is used for guiding practice, complex diffusion is simplified, uphill diffusion and downhill diffusion which influence the surface coarsening rate are only considered, the 'adatom diffusion' model is established, and the relationship between microcosmic adatom diffusion and macroscopic surface coarsening is quantitatively revealed; and according to the adatom diffusion model for controlling the coarsening rate, experiments can be guided to prepare films with various surface roughness in situ, the changing degree of the surface roughness of the films can further be predicted, and the adatom diffusion model is widely applied to various sedimentation preparation methods.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
A method for detecting charging power of an electric vehicle
ActiveCN103513098BAchieve a win-win situationAccurately predict macroscopic response propertiesElectric devicesElectric power measurementDiffusionStaring
The invention relates to a charging power detection method for an electric car. The charging power detection method for the electric car comprises the following steps that (1) a charging battery of the electric car is analyzed; (2) a model is built based on the diffusion theory according to the analysis result; (3) a diffusion equation is obtained according to the diffusion model; (4) the total charging power of the electric car is obtained according to the diffusion equation. The charging power detection method for the electric car takes the key factors, affecting the total charging load, such as charging power, the number of electric cars, a staring SOC, the starting charging time and the capacity of the battery all into account, and can predict the SOC state of the battery at a certain time.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
An Atomized Diffusion Model with Controlled Coarsening Rate
ActiveCN109913834BForecast of changeAchieve ultra-smoothVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingChemical physicsMacroscopic scale
The invention relates to the technical field of films, in particular to an adatom diffusion model for adjusting and controlling the coarsening rate. An adatom diffusion theory is used for guiding practice, complex diffusion is simplified, uphill diffusion and downhill diffusion which influence the surface coarsening rate are only considered, the 'adatom diffusion' model is established, and the relationship between microcosmic adatom diffusion and macroscopic surface coarsening is quantitatively revealed; and according to the adatom diffusion model for controlling the coarsening rate, experiments can be guided to prepare films with various surface roughness in situ, the changing degree of the surface roughness of the films can further be predicted, and the adatom diffusion model is widely applied to various sedimentation preparation methods.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com