Method for regulating surface coarsening rate of film in in-situ large range
A surface roughening, large-scale technology, applied in metal material coating process, vacuum evaporation coating, coating, etc. simple craftsmanship
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
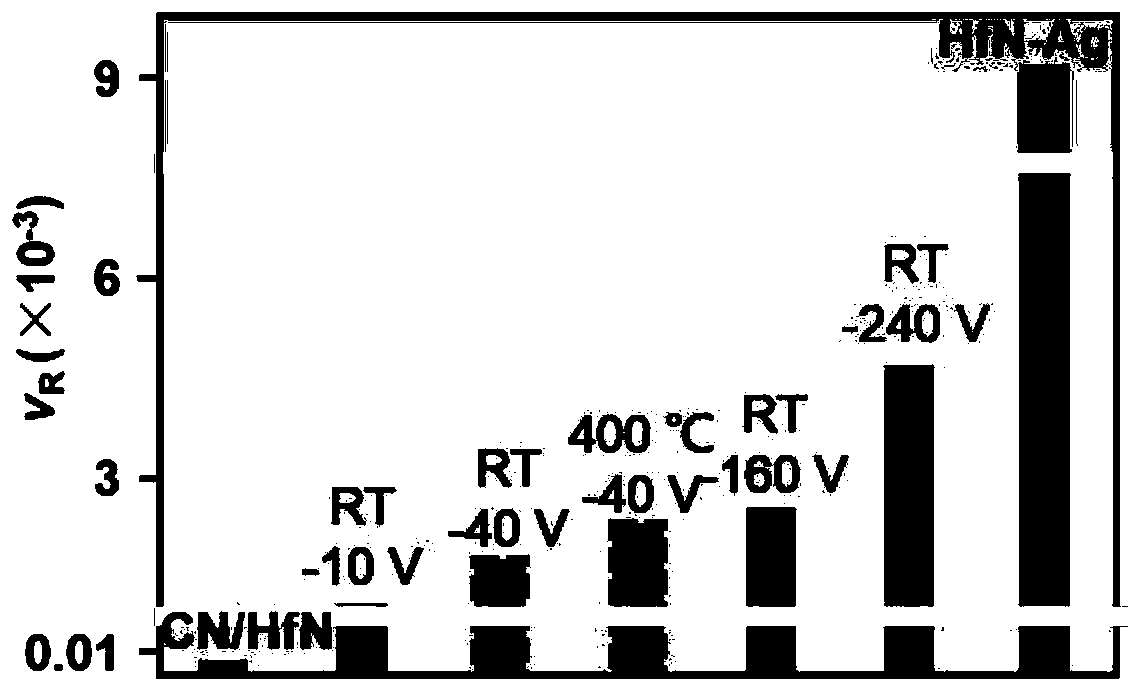
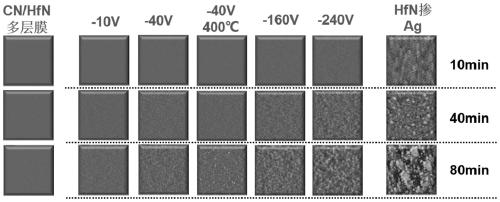
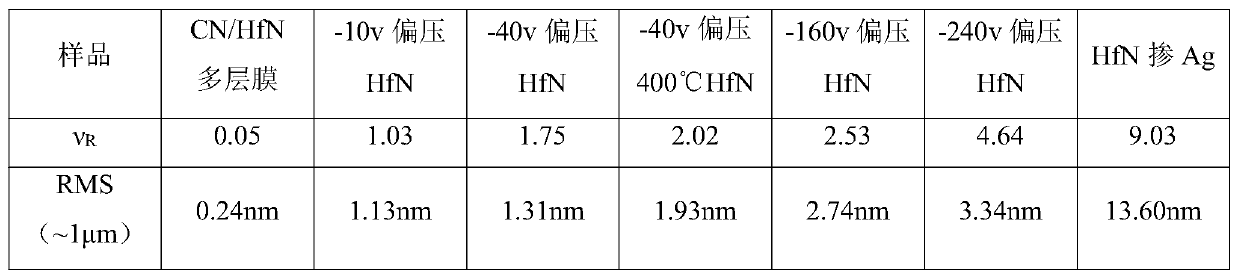
[0022] A method for in-situ large-scale regulation and control of the surface roughening rate of thin films, including a parent material, hafnium nitride is selected as the parent material. Amorphous encapsulation hinders uphill diffusion to obtain a low coarsening rate; by doping silver elements that are non-wetting with the parent material, the non-wetting property is used to hinder downhill diffusion and a high coarsening rate is obtained.
[0023] Specifically, the following steps are included:
[0024] a. Select the silicon wafer substrate as the substrate, ultrasonically clean the silicon wafer substrate with acetone, absolute ethanol, and distilled water in sequence, and dry it after cleaning to obtain the target material for use;
[0025] b. Use discharge gas during the deposition process, adjust the working pressure, control the sputtering power of the pure hafnium target and the required target, and perform sputtering according to the required conditions. After the s...
Embodiment 2
[0030] A method for in-situ large-scale regulation and control of the surface roughening rate of thin films, including a parent material, hafnium nitride is selected as the parent material. Amorphous encapsulation hinders uphill diffusion to obtain a low coarsening rate; by doping gold elements that are non-wetting with the parent material, the non-wetting property is used to hinder downhill diffusion and a high coarsening rate is obtained.
[0031] Specifically, the following steps are included:
[0032] a. Select the silicon wafer substrate as the substrate, ultrasonically clean the silicon wafer substrate with acetone, absolute ethanol, and distilled water in sequence, and dry it after cleaning to obtain the target material for use;
[0033] b. Use discharge gas during the deposition process, adjust the working pressure, control the sputtering power of the pure hafnium target and the required target, and perform sputtering according to the required conditions. After the spu...
Embodiment 3
[0036] A method for in-situ large-scale control of the roughening rate of the film surface, including the parent material, the sample material is hafnium oxide, in the preparation process, the tungsten oxide amorphous layer is introduced by using the method of magnetron co-sputtering The encapsulation hinders the uphill diffusion to obtain a low coarsening rate; by doping the gold element which is non-wettable with the parent material, the non-wetting property is used to hinder the downhill diffusion to obtain a high coarsening rate.
[0037] Specifically, the following steps are included:
[0038] a. Select the silicon wafer substrate as the substrate, ultrasonically clean the silicon wafer substrate with acetone, absolute ethanol, and distilled water in sequence, and dry it after cleaning to obtain the target material for use;
[0039] b. Use discharge gas during the deposition process, adjust the working pressure, control the sputtering power of the pure hafnium target and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com