Patents
Literature
394results about "Cadmium compounds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
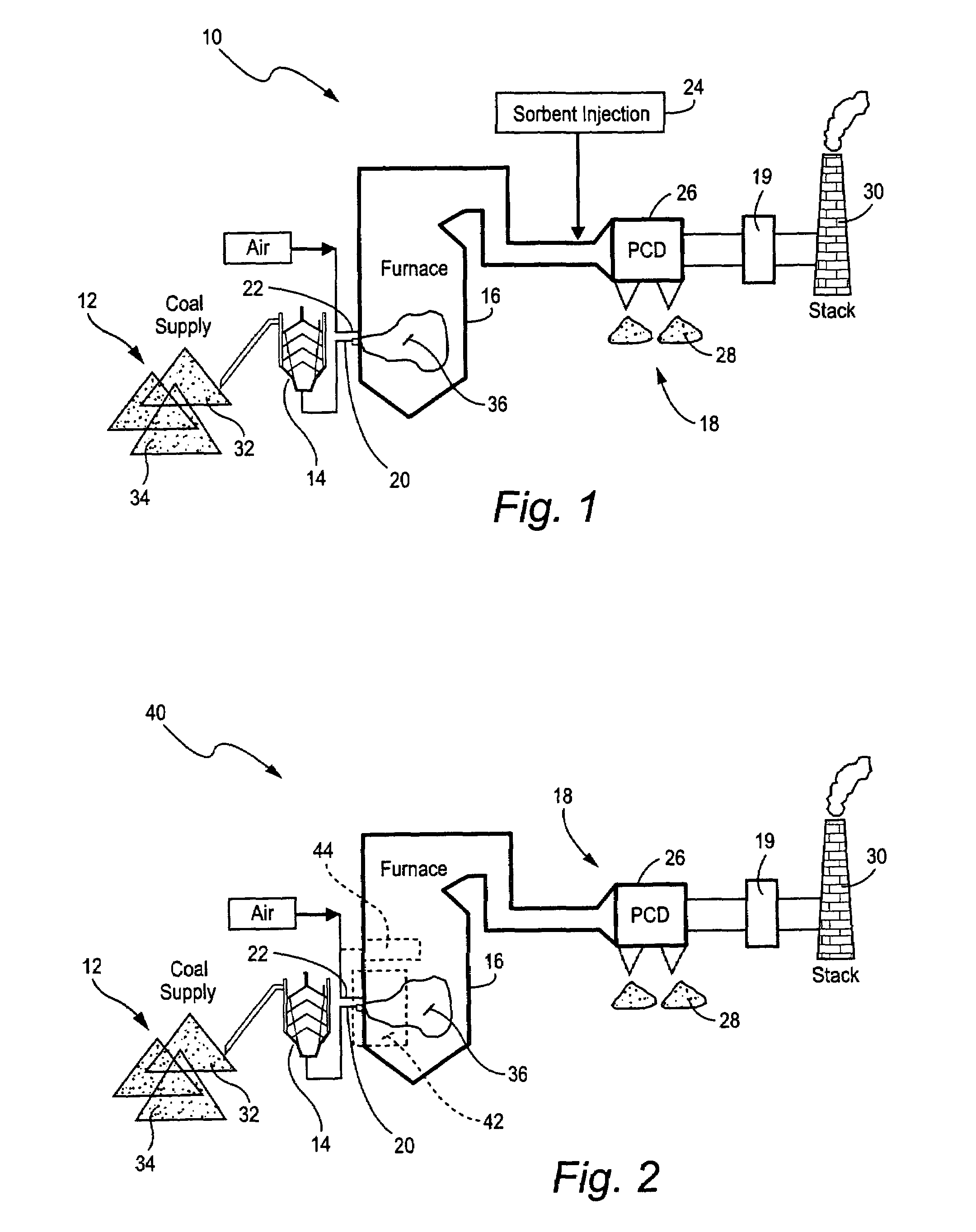
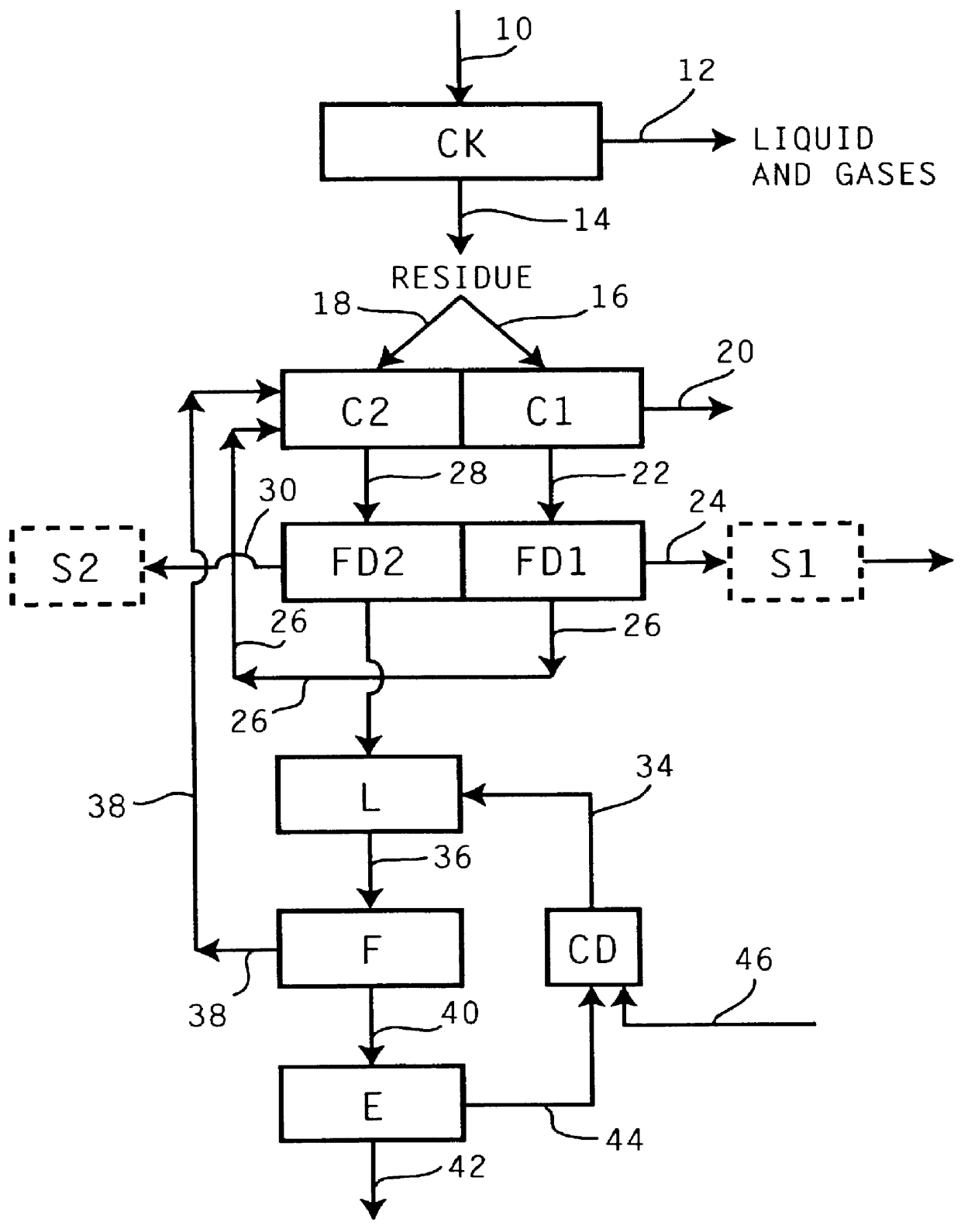
Method for removal and stabilization of mercury in mercury-containing gas streams
InactiveUS6942840B1Improve scalabilityCombination devicesDispersed particle filtrationOxygenVapor phase
The present invention is directed to a process and apparatus for removing and stabilizing mercury from mercury-containing gas streams. A gas stream containing vapor phase elemental and / or speciated mercury is contacted with reagent, such as an oxygen-containing oxidant, in a liquid environment to form a mercury-containing precipitate. The mercury-containing precipitate is kept or placed in solution and reacts with one or more additional reagents to form a solid, stable mercury-containing compound.
Owner:MERCURY CONTROL TECH
Nitride semiconductor crystal and its production method
InactiveUS20110129669A1Easy to produceEfficient productionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGlass/slag layered productsCrystal growthSeed crystal
A method for efficiently producing a plate-like nitride semiconductor crystal having the desired principal plane in a simple method is provided. A raw material gas is fed to a seed crystal in which a ratio (L / W) of length L in a longitudinal direction and maximum width W, of a plane of projection obtained by projecting a crystal growth face on the seed crystal in a growth direction is from 2 to 400, and the maximum width W is 5 mm or less, thereby growing a plate-like semiconductor crystal on the seed crystal.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Process for the recovery of value metals from base metal sulfide ores
InactiveUS20050118081A1Simple gas/liquidReduce the amount requiredSulfur compoundsSolid sorbent liquid separationSulfideDissolution
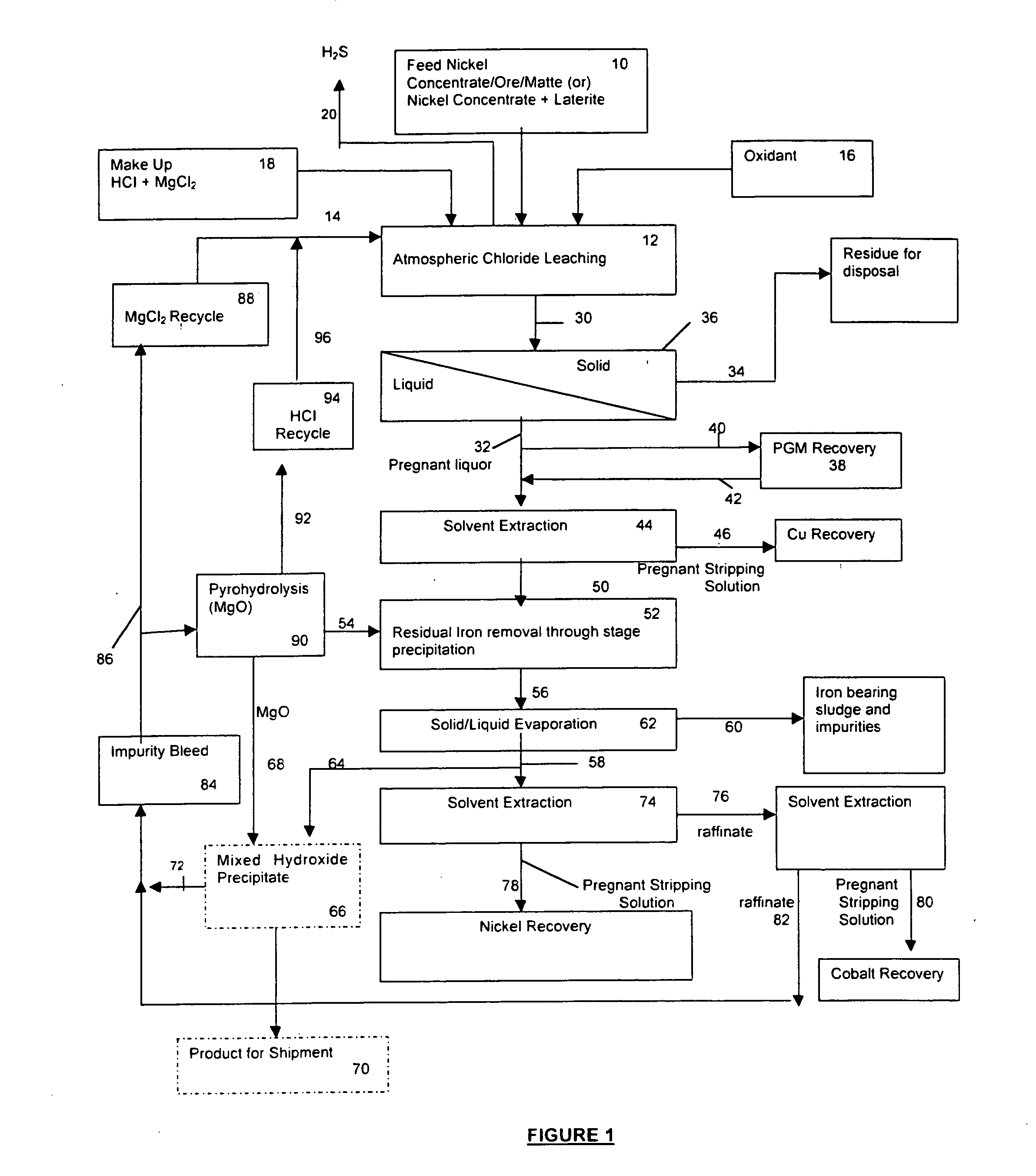
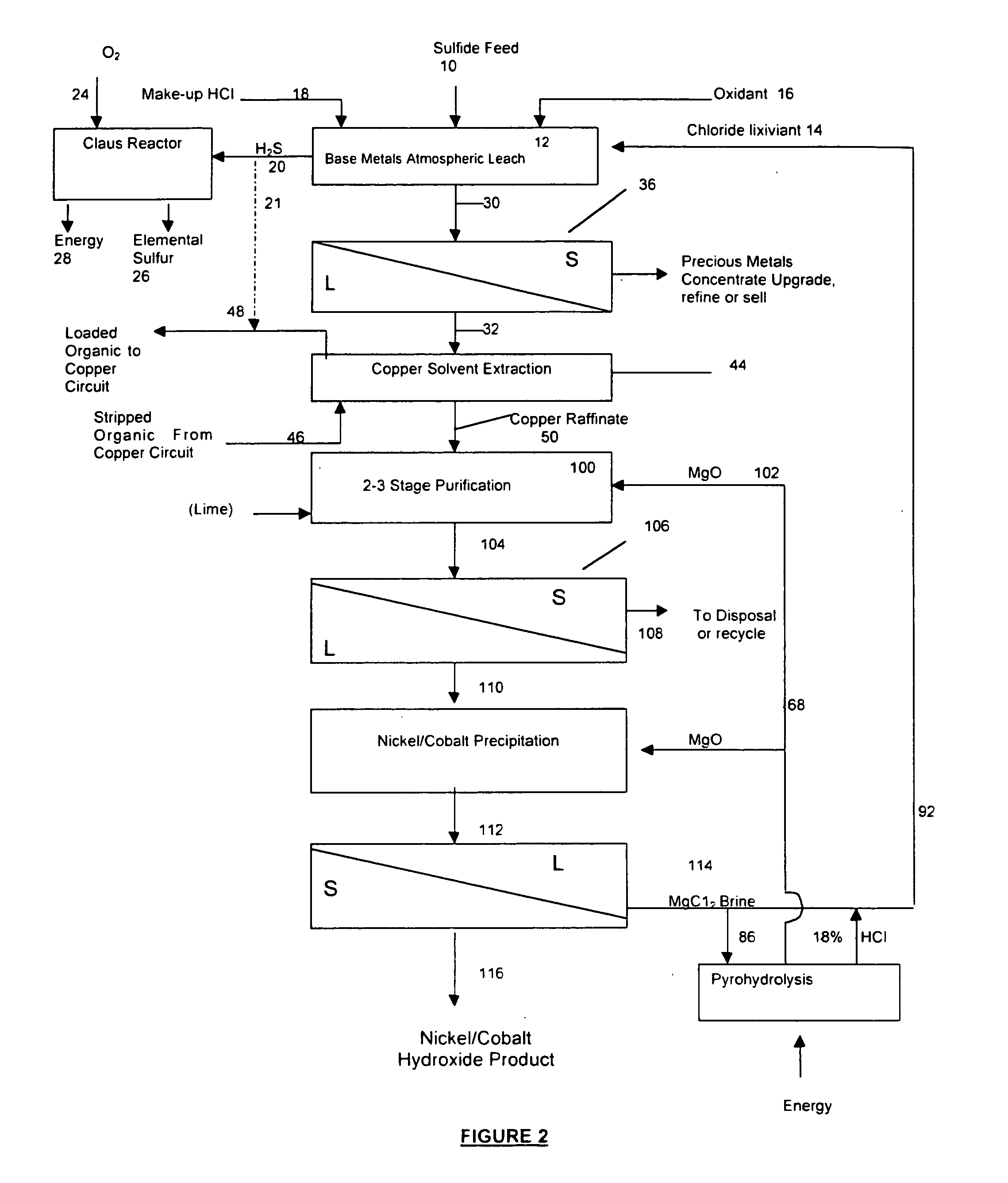
A process for leaching a value metal from a base metal sulfide ore, comprising the step of leaching the ore with a lixiviant comprising a chloride, an oxidant and hydrochloric acid is disclosed. The leaching is controlled, by use of low concentrations of hydrochloric acid and a redox potential, to effect formation of hydrogen sulfide from the base metal sulfide ore. The hydrogen sulfide is stripped from the leach solution, thereby reducing the amount of sulfate generated in the leach to very low levels. The leaching may also be conducted to limit the co-dissolution of platinum group metals and gold with the base value metals. The leach forms a value metal-rich leachate and a solids residue. The solids residue may be subsequently leached to recover the platinum group metals and gold. The value metal-rich leachate can be is oxidized and neutralized to recover the value base metals. In an embodiment, the chloride is magnesium chloride and lixiviant solution is regenerated.
Owner:JAGUAR NICKEL INC
Method of coating nanoparticles
Disclosed herein is a method of coating nanoparticles with a metal oxide. The method includes substituting surfaces of hydrophobic nanoparticles with an organic substance having a hydrophilic group effective to render the nanoparticles hydrophilic; and injecting the hydrophilic nanoparticles and a precursor of the metal oxide into an organic solvent including an amphiphilic surfactant to coat the nanoparticles with a metal oxide.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
GRADED CORE/SHELL SEMICONDUCTOR NANORODS and NANOROD BARCODES
InactiveUS20080188063A1Improve quantum efficiencyIncrease in photoluminescence QYMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAnalyteBarcode
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
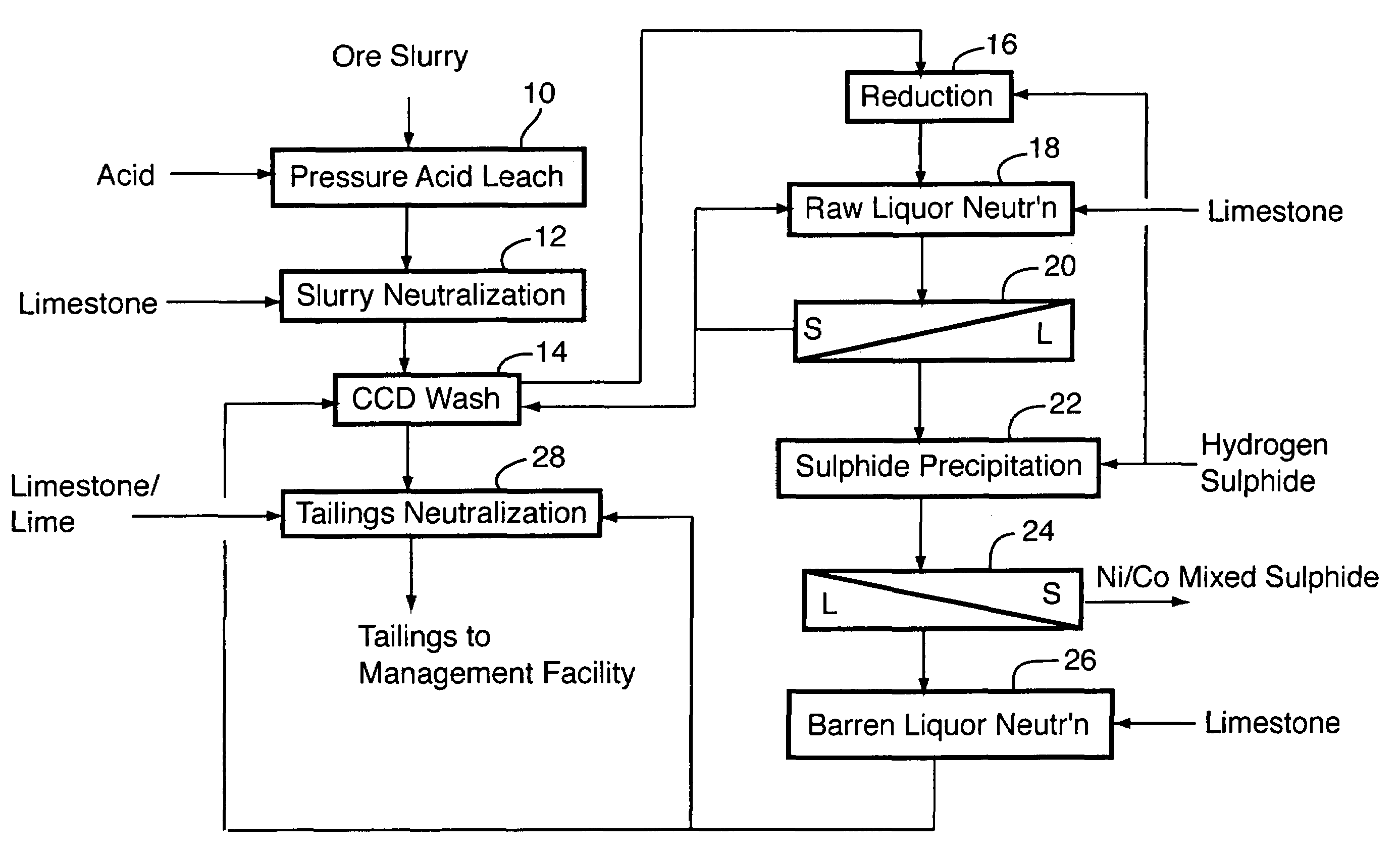
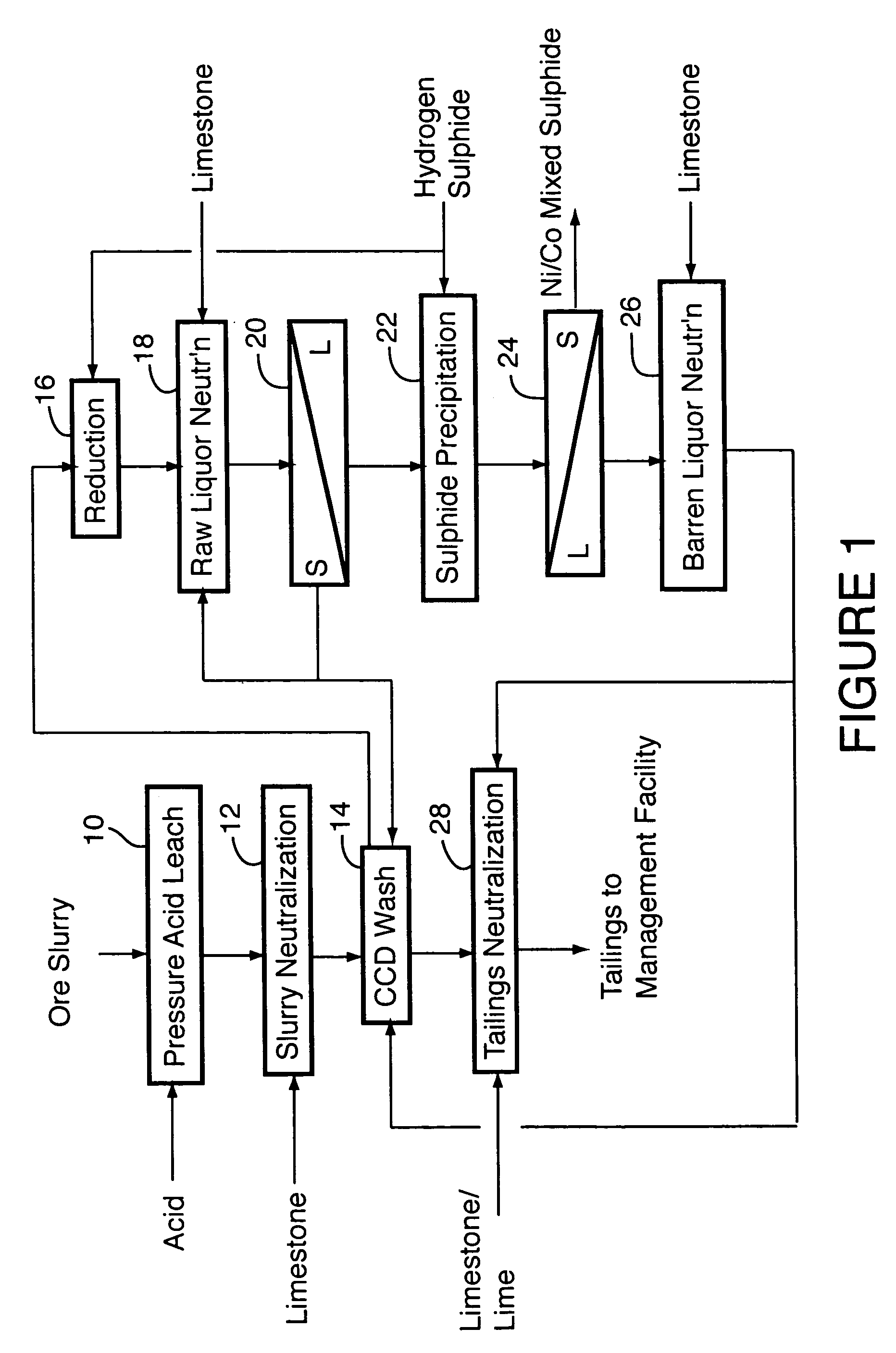
Process for recovery of nickel and cobalt from laterite ore
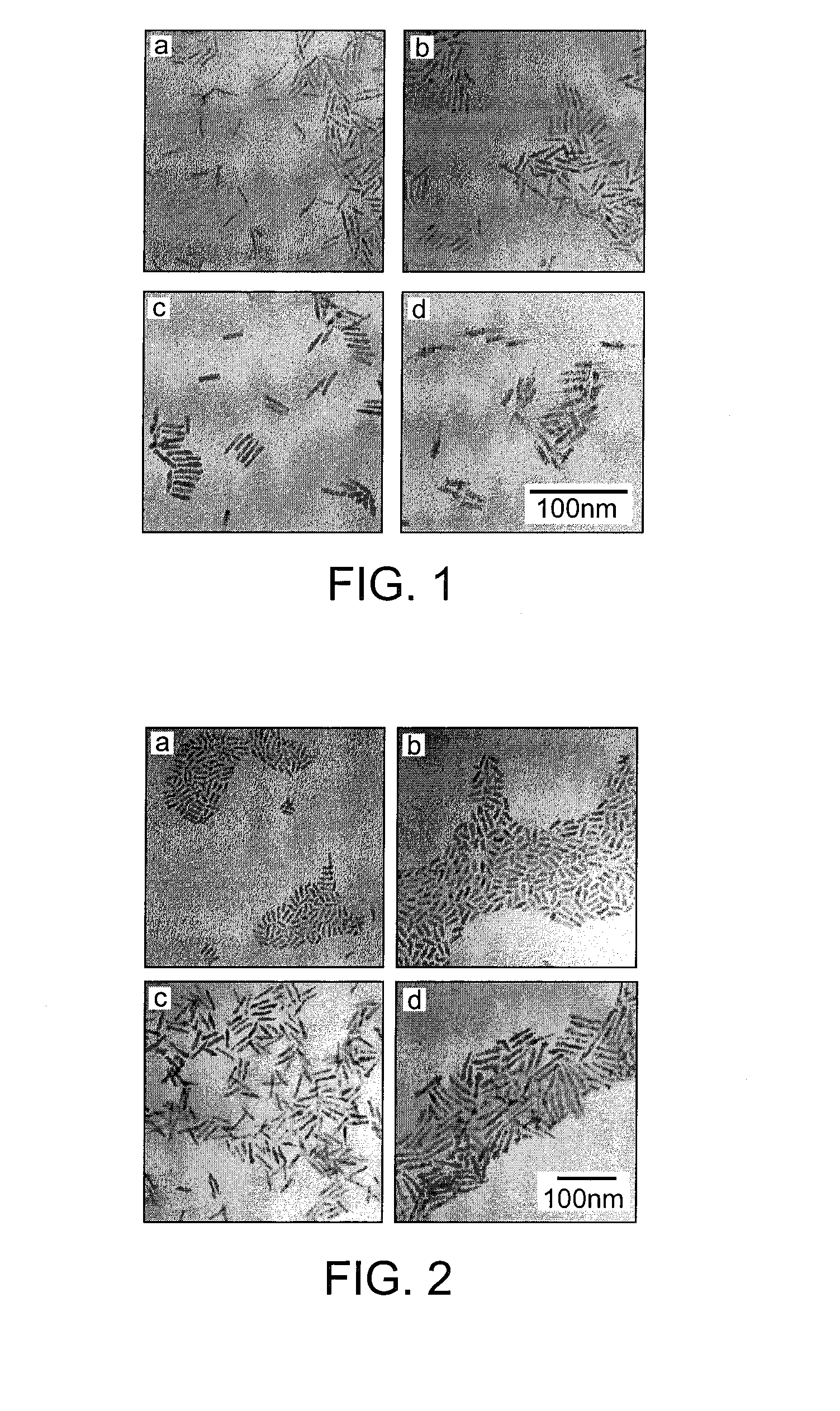
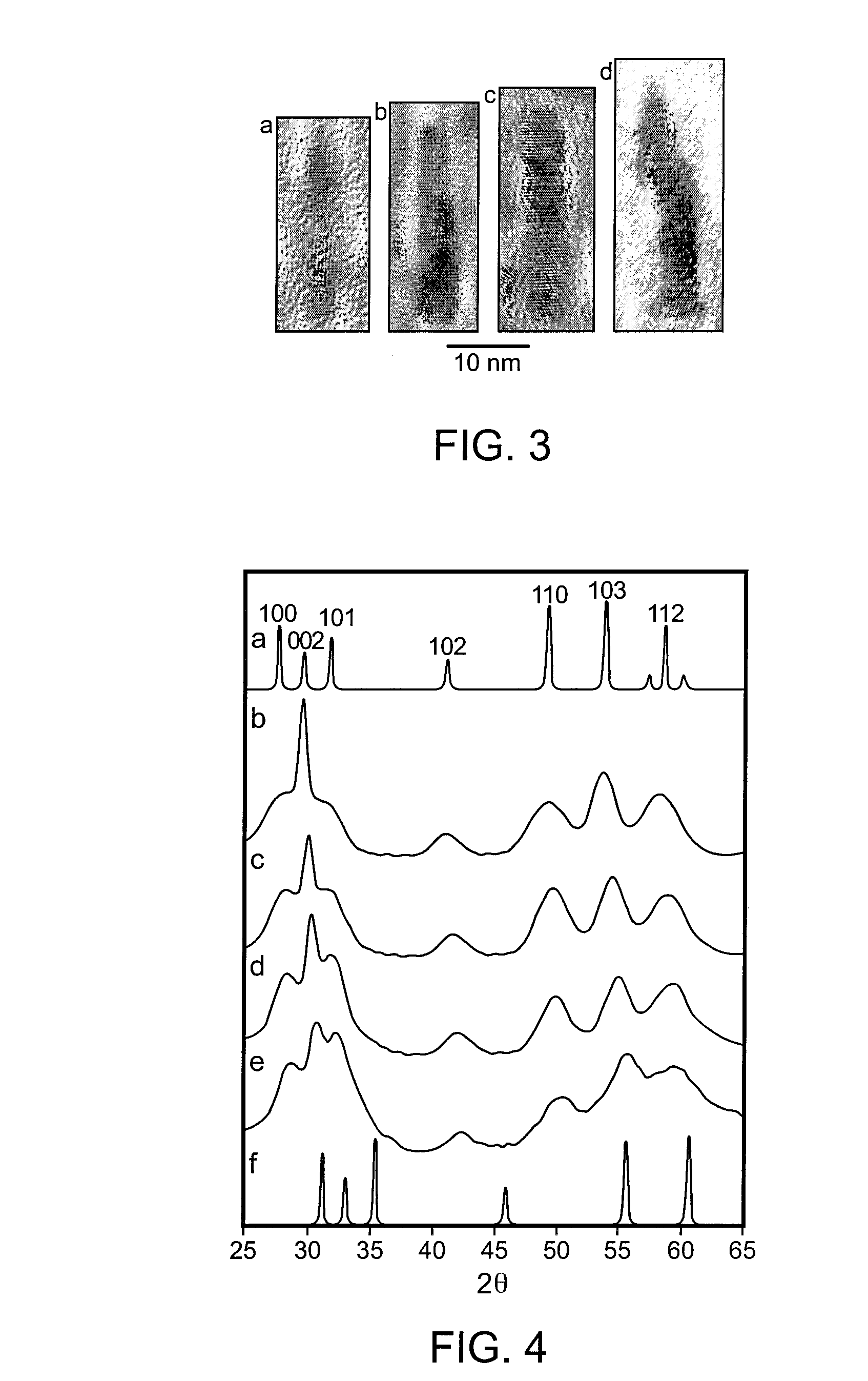
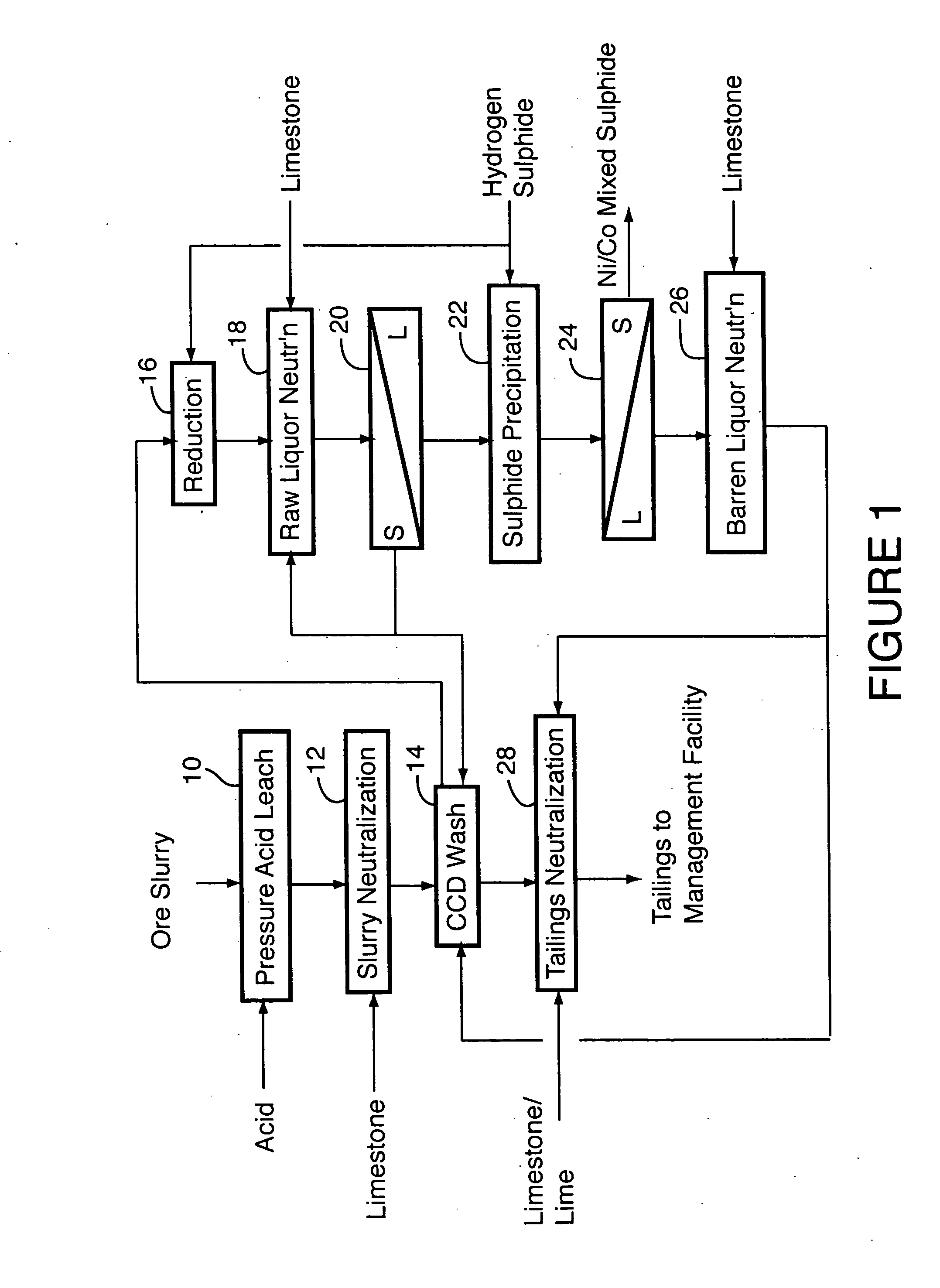
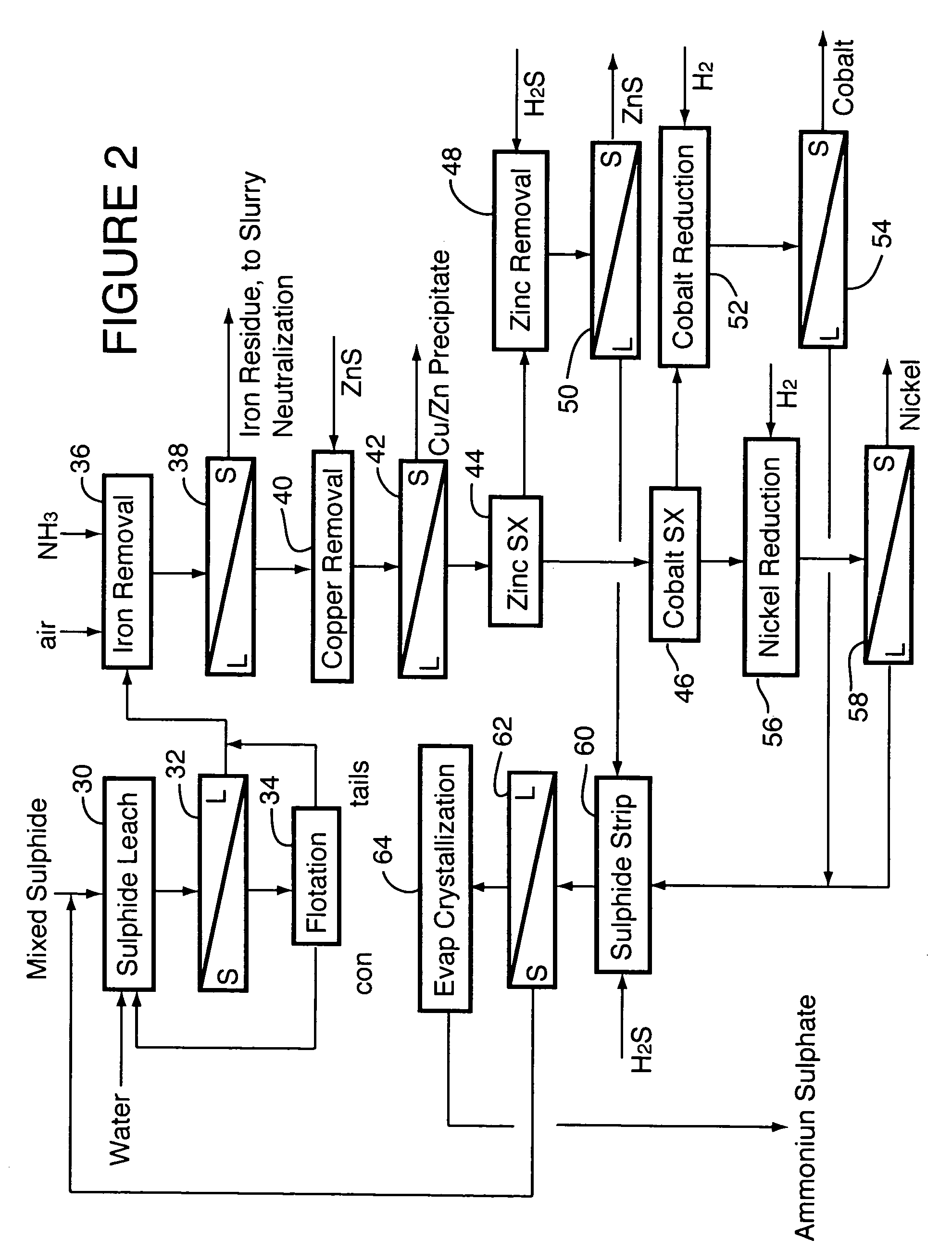
ActiveUS20060228279A1Efficient separation and recoveryHigh purityCobalt sulfidesSolvent extractionFree solutionSlurry
A process for recovering nickel and cobalt values from nickel- and cobalt-containing laterite ores as an enriched mixed nickel and cobalt sulphide intermediate and for producing nickel and cobalt metal from the nickel and cobalt sulphide intermediate. The laterite ore is leached as a slurry in a pressure acid leach containing an excess of aqueous sulphuric acid at high pressure and temperature, excess free acid in the leach slurry is partially neutralized to a range of 5 to 10 g / L residual free H2SO4 and washed to yield a nickel- and cobalt-containing product liquor, the product liquor is subjected to a reductant to reduce any Cr(VI) in solution to Cr(III), the reduced product liquor is neutralized to precipitate ferric iron and silicon at a pH of about 3.5 to 4.0, and the neutralized and reduced product liquor is contacted with hydrogen sulphide gas to precipitate nickel and cobalt sulphides. The precipitated nickel and cobalt sulphides can be leached in a water slurry in a pressure oxidation leach, the leach solution subjected to iron hydrolysis and precipitation, the iron-free solution contacted with zinc sulphide to precipitate copper, the iron- and copper-free solution subjected to zinc and cobalt extraction by solvent extraction to produce a nickel raffinate, the nickel raffinate contacted with hydrogen gas to produce nickel powder and the cobalt strip solution from the solvent extraction step contacted with hydrogen gas to produce cobalt powder.
Owner:SHERRITT INTERNATIONAL
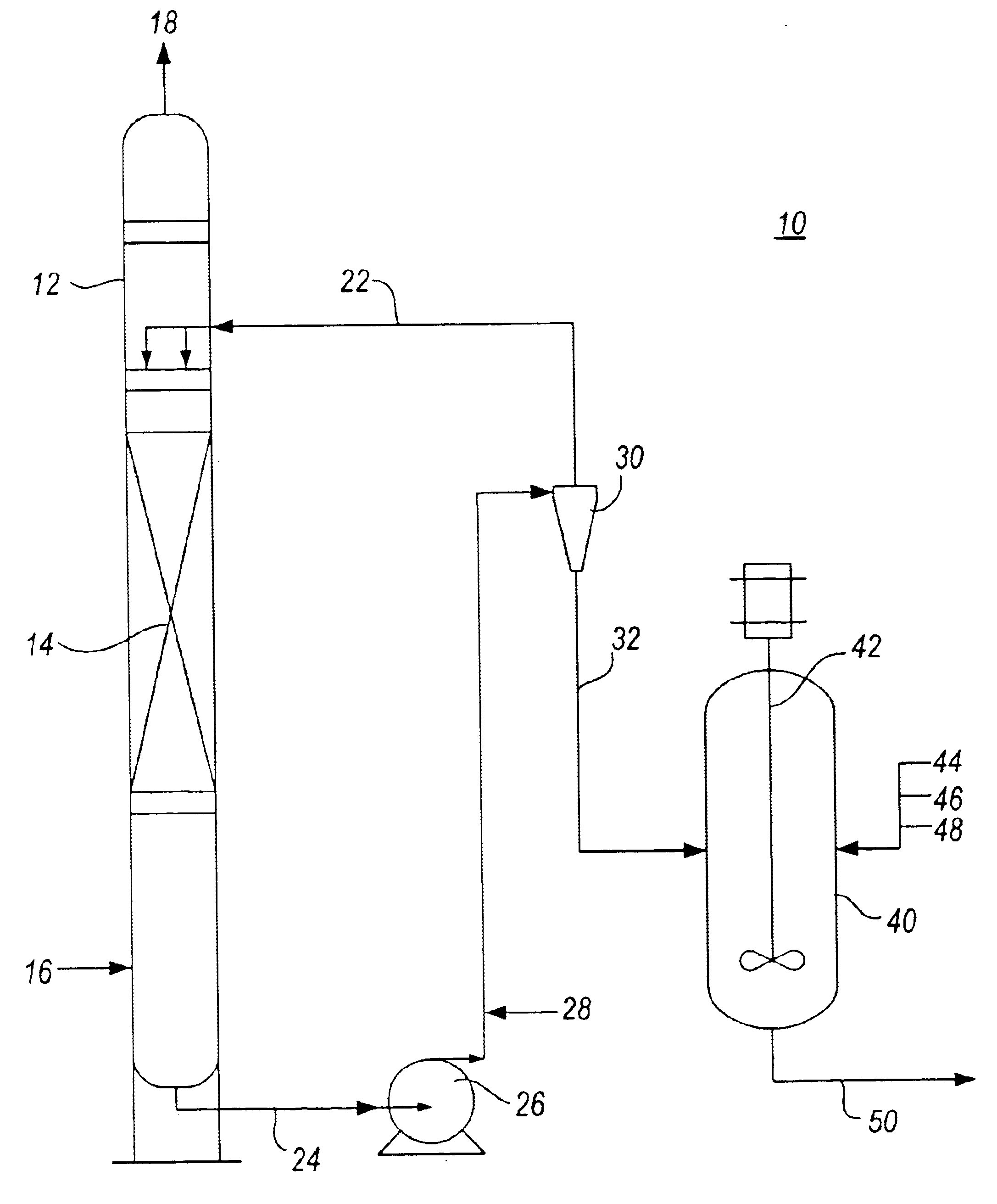
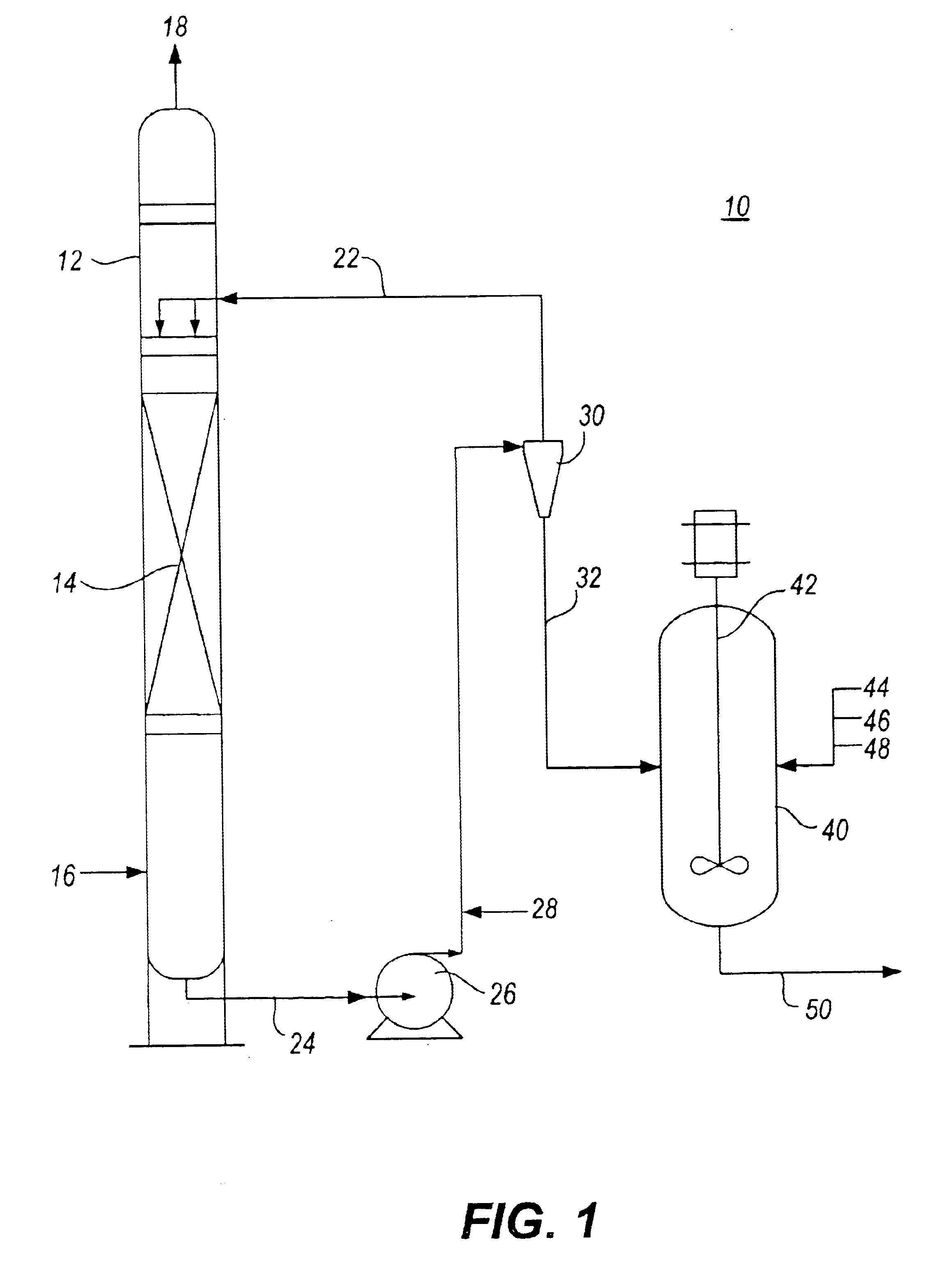
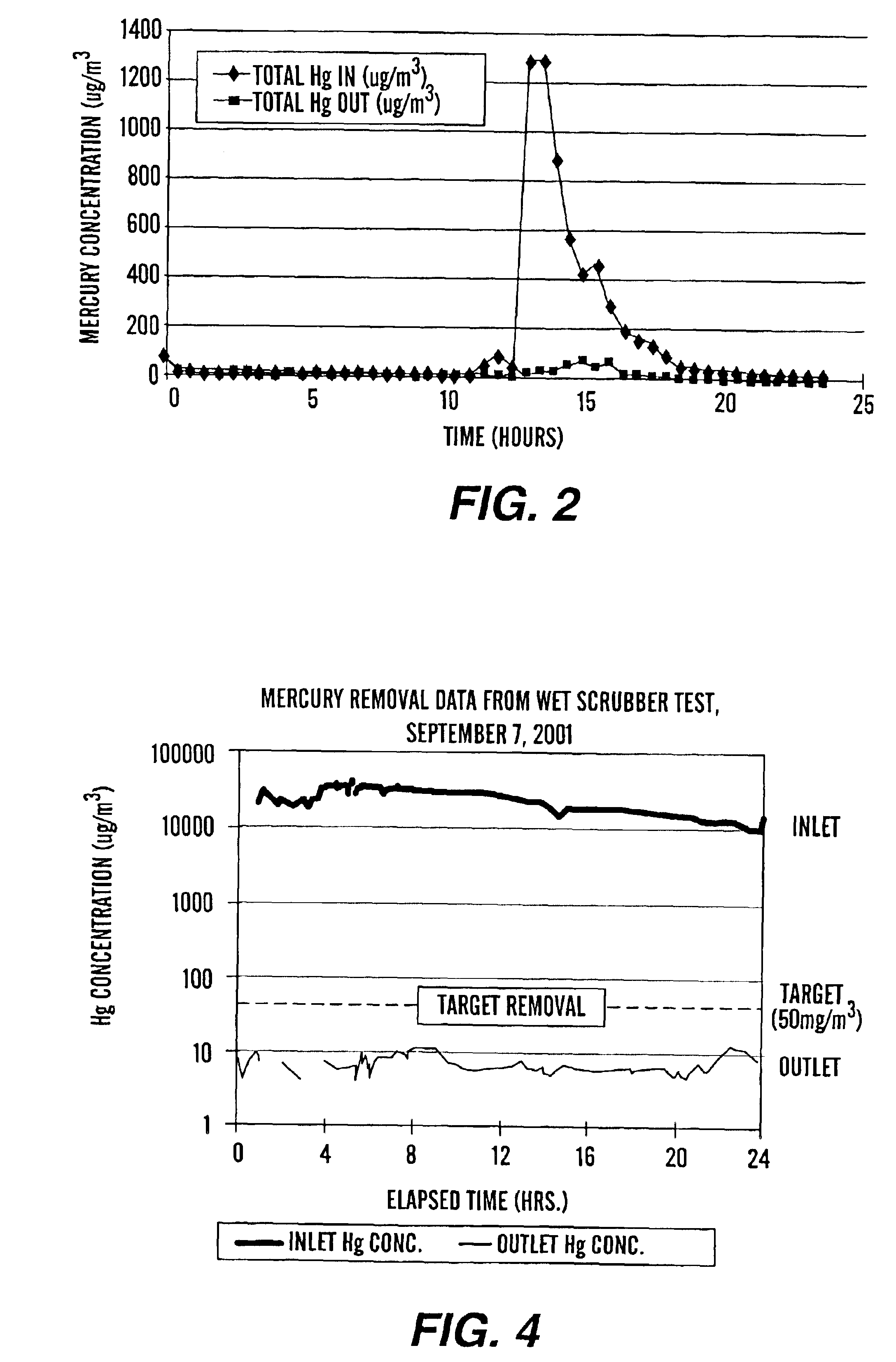
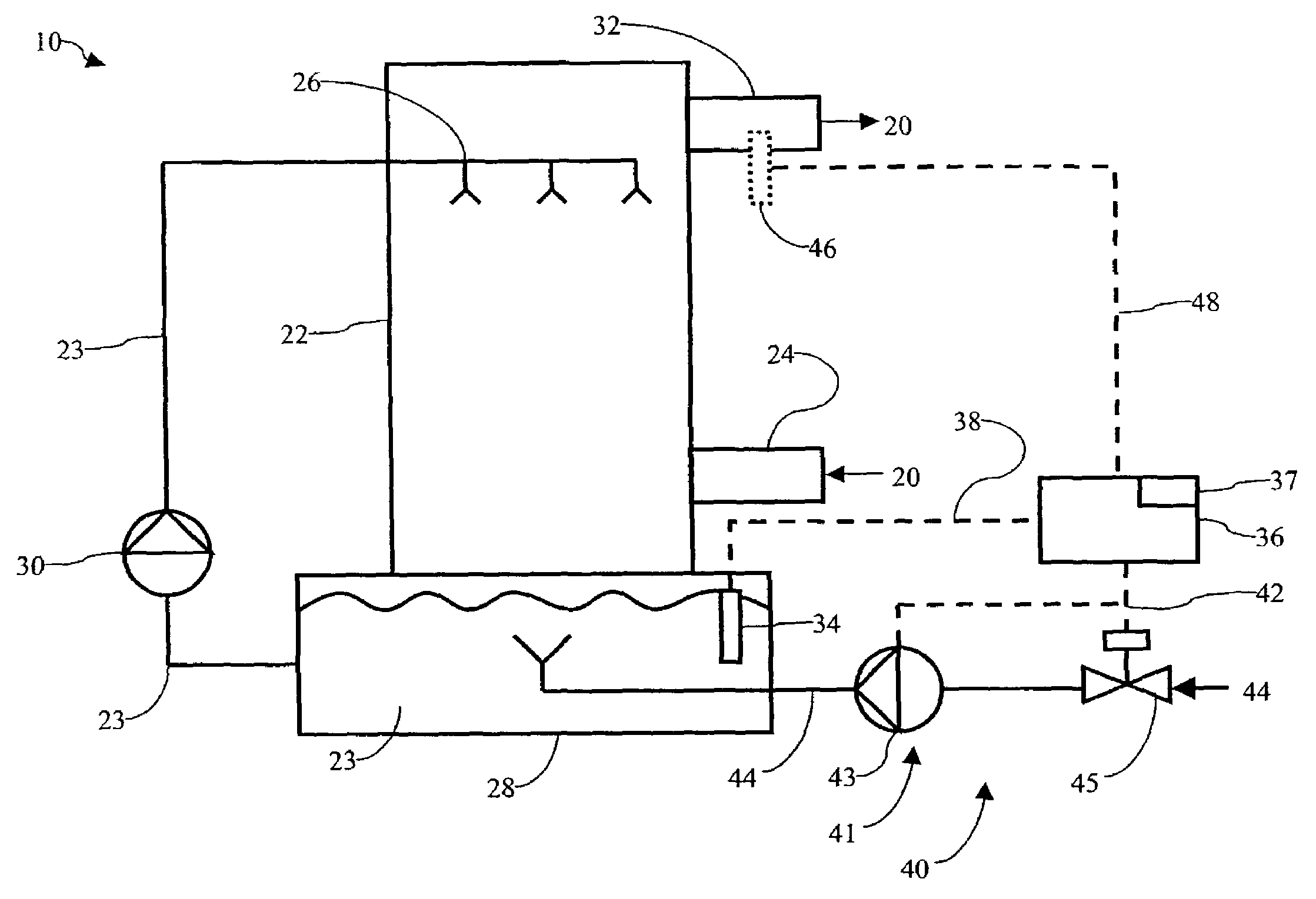
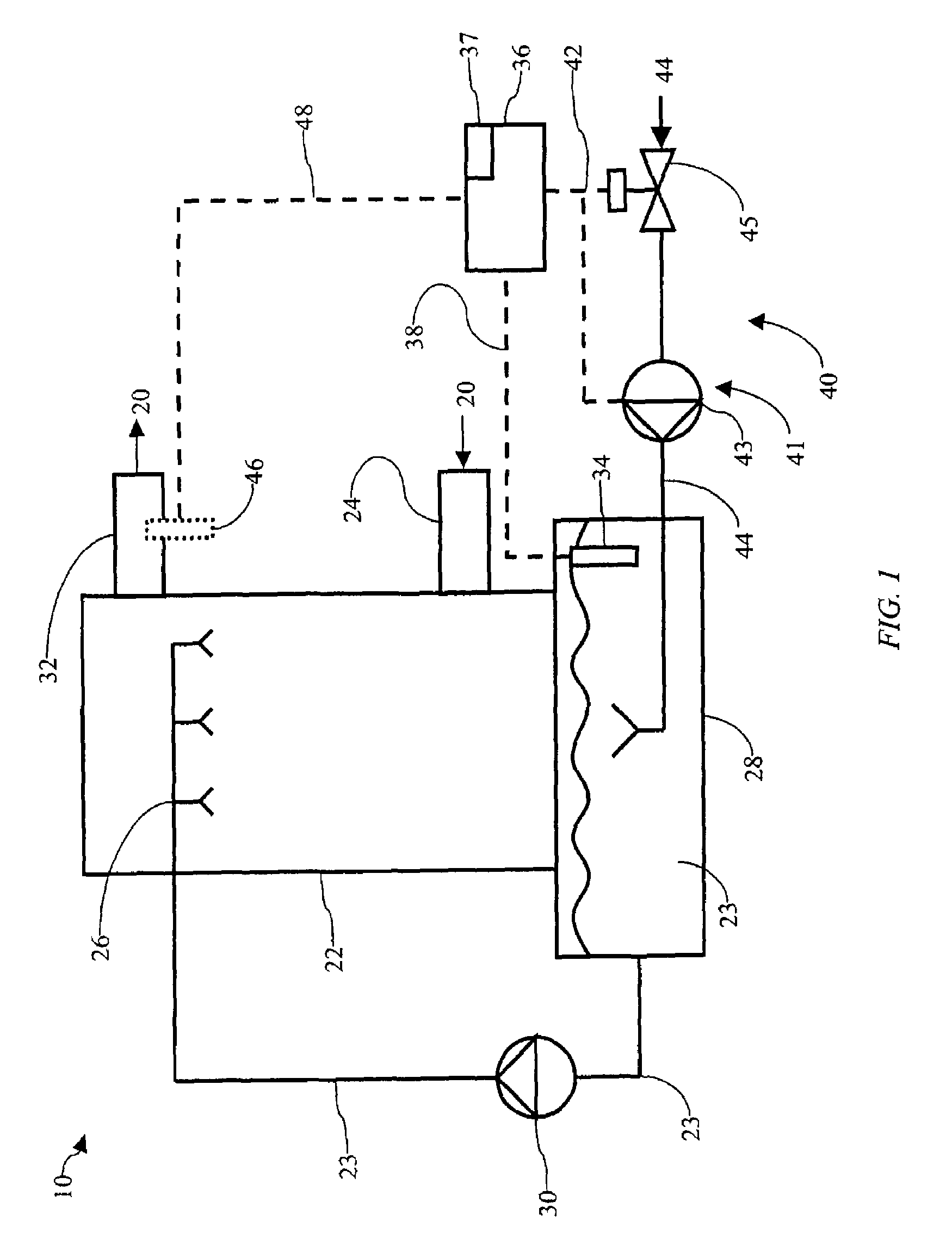
Method of mercury removal in a wet flue gas desulfurization system
Controlling the reductive capacity of an aqueous alkaline slurry (23) in a wet scrubber makes it possible to accurately control the mercury emission from the scrubber to a desired value. One method of controlling the reductive capacity of the slurry is to measure the reduction-oxidation potential (“redox potential”) of the aqueous alkaline slurry (23) and to add or remove substances that affect the redox potential and thus the reductive capacity of the slurry. In wet scrubbers in which limestone is used for absorption of acid gases and where a gypsum slurry is circulated, it has been found to be an attractive solution to control the amount of oxidation air blown into the scrubber in order to control the redox potential and thereby the mercury emissions.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
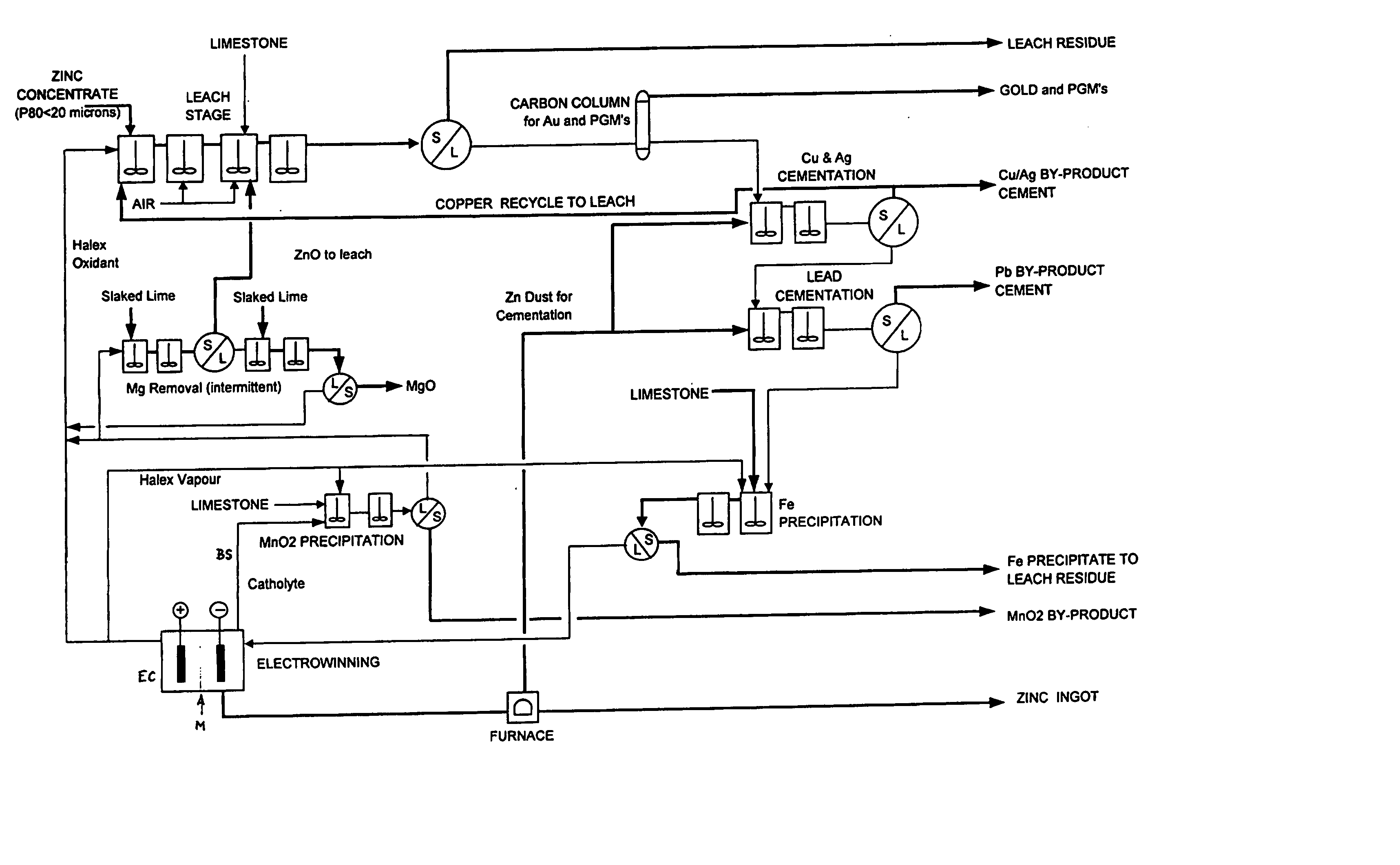
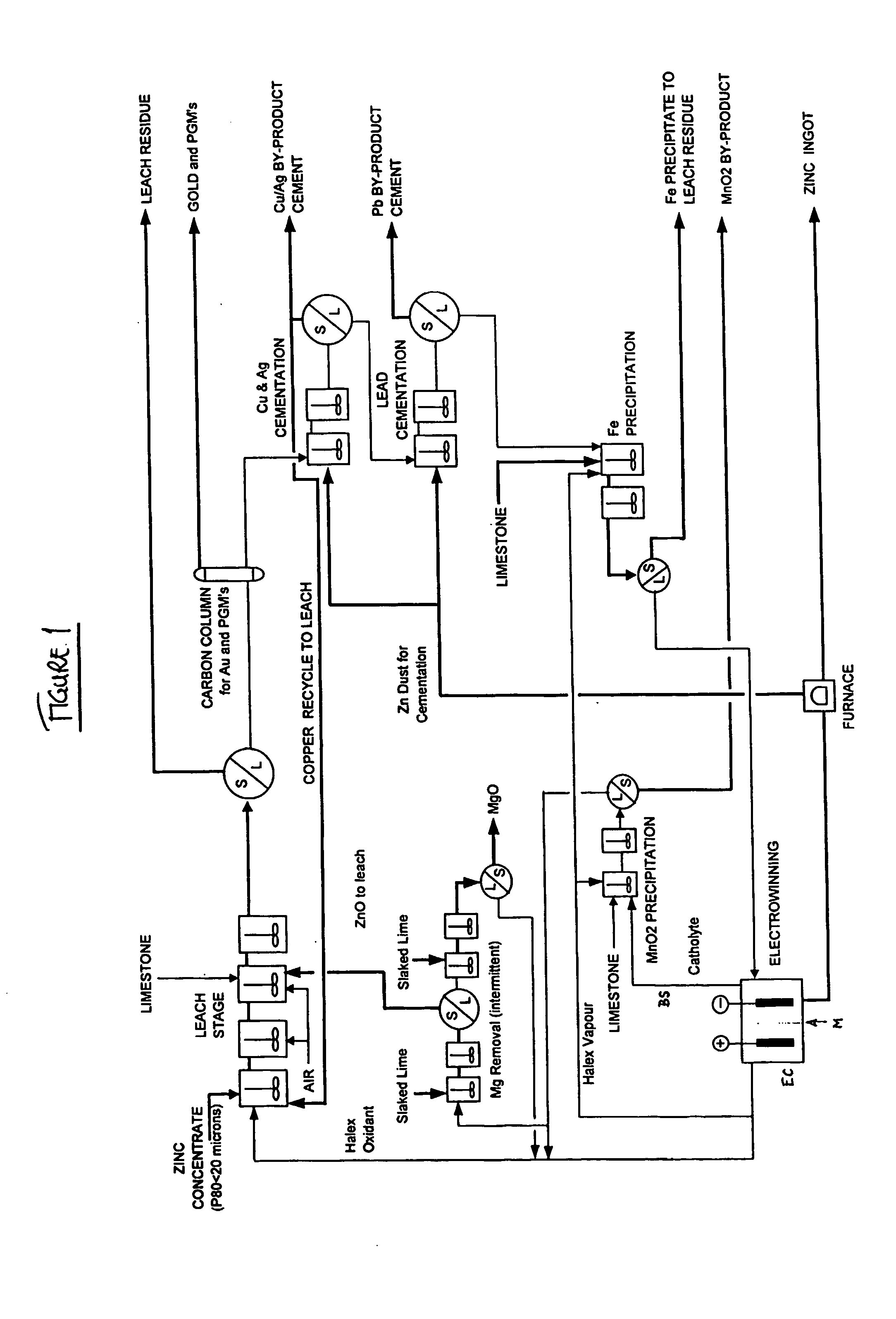
Zinc recovery process
InactiveUS20040237720A1Improve filtering effectEh is decreasedPhotography auxillary processesSolvent extractionZinc metalManganese
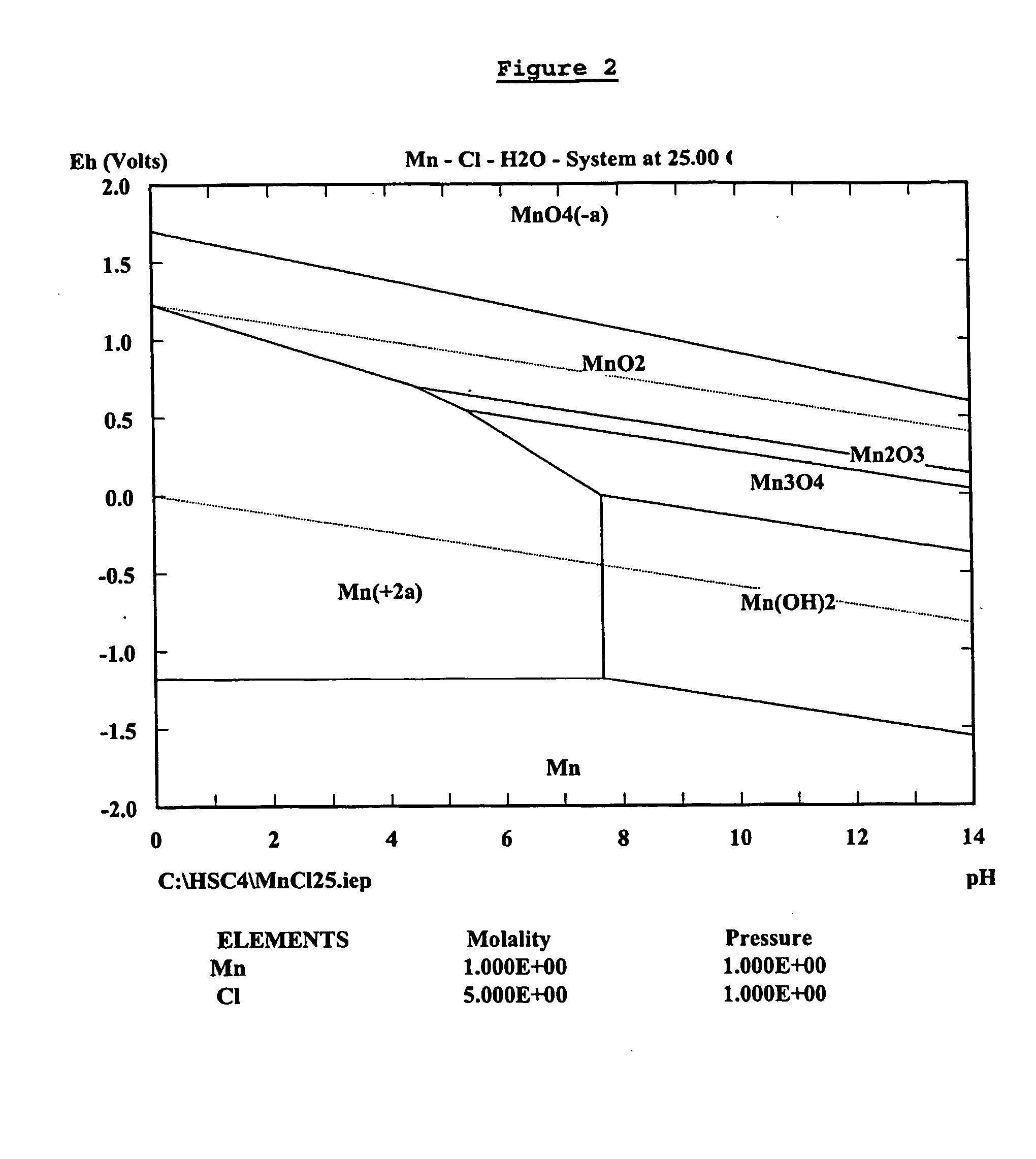
A process for the recovery of zinc metal from a zinc mineral includes the steps of leaching the zinc mineral in a solution including a halide species formed from two or more different halides, to leach the zinc into the solution. The zinc-bearing solution is then electrolysed to yield zinc metal and to generate the halide species. The electrolysed solution including the halide species is then returned to the leaching step. A portion of the electrolysed solution can be removed as a bleed stream from a cathode compartment of an electrolytic cell of the electrolysis process and processed to remove manganese as manganese dioxide precipitate by adding thereto limestone, and the halide species from an anode compartment of the electrolysis process. In this regard, the pH and Eh of the solution can regulated in a manner that favours the formation of the manganese dioxide precipitate over the formation of a precipitate of zinc.
Owner:INTEC INT PROJECTS
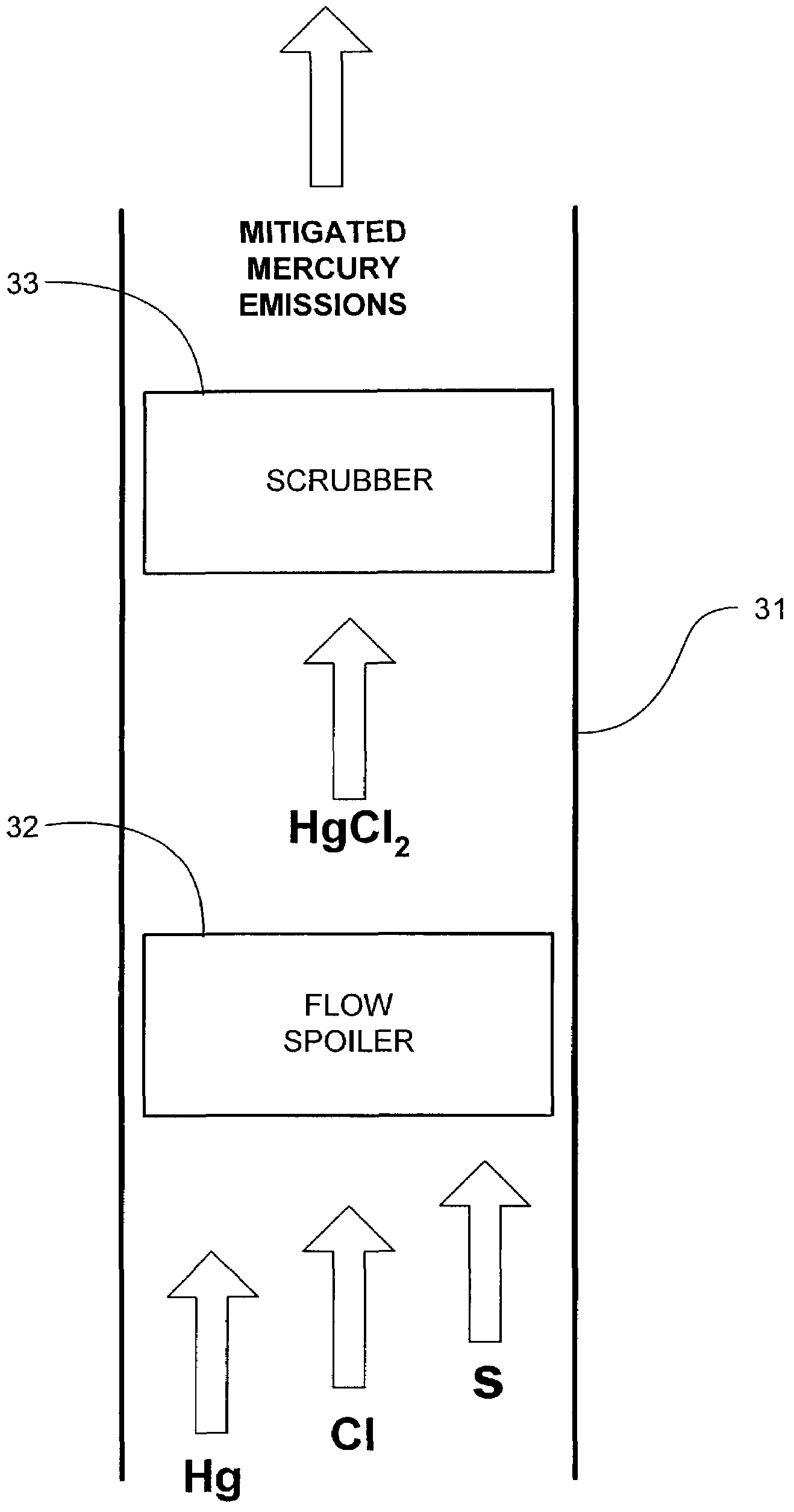
Method and apparatus for mitigating mercury emissions in exhaust gases
InactiveUS7517511B2Mitigating mercury emissionNitrogen compoundsUsing liquid separation agentMercury DichlorideExhaust fumes
Mercury emissions in an exhaust gas are mitigated. Mercury dichloride is formed upon a surface from a substantial portion of the mercury in the exhaust gas. The mercury dichloride sublimes from the surface, and the sublimed mercury dichloride is subsequently removed from the exhaust stream.
Owner:SCHOFIELD KEITH
II-II-VI alloy quantum dot, as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108546553ANo self-nucleationUniform shape and sizeMaterial nanotechnologyZinc sulfidesMain group elementQuantum dot
The invention provides an II-II-VI alloy quantum dot, as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of S1, reacting a precursor containing secondII group elements and a precursor containing first VI group elements to form an II-VI semiconductor nanocluster; S2, mixing the II-VI semiconductor nanocluster and the precursor containing the first II group elements, and obtaining a first system containing the II-II-VI alloy quantum dot through cation exchange and in-situ growth. The II-VI nanocluster formed at the beginning of nucleating is located at a nanocrystalline nucleation and growth intermediate state and is small in size, the precursor containing the first II group elements is added for carrying out cation exchange, first II group element atoms easily enter the innermost of the II-VI nanocluster so as to form an II-II-VI nanocluster similar to an alloy, and during the continuous growth process, the first II group element atoms are gradually outwards diffused to the whole particle so as to obtain the narrow half-width alloy quantum dot.
Owner:NANJING TECH CORP LTD
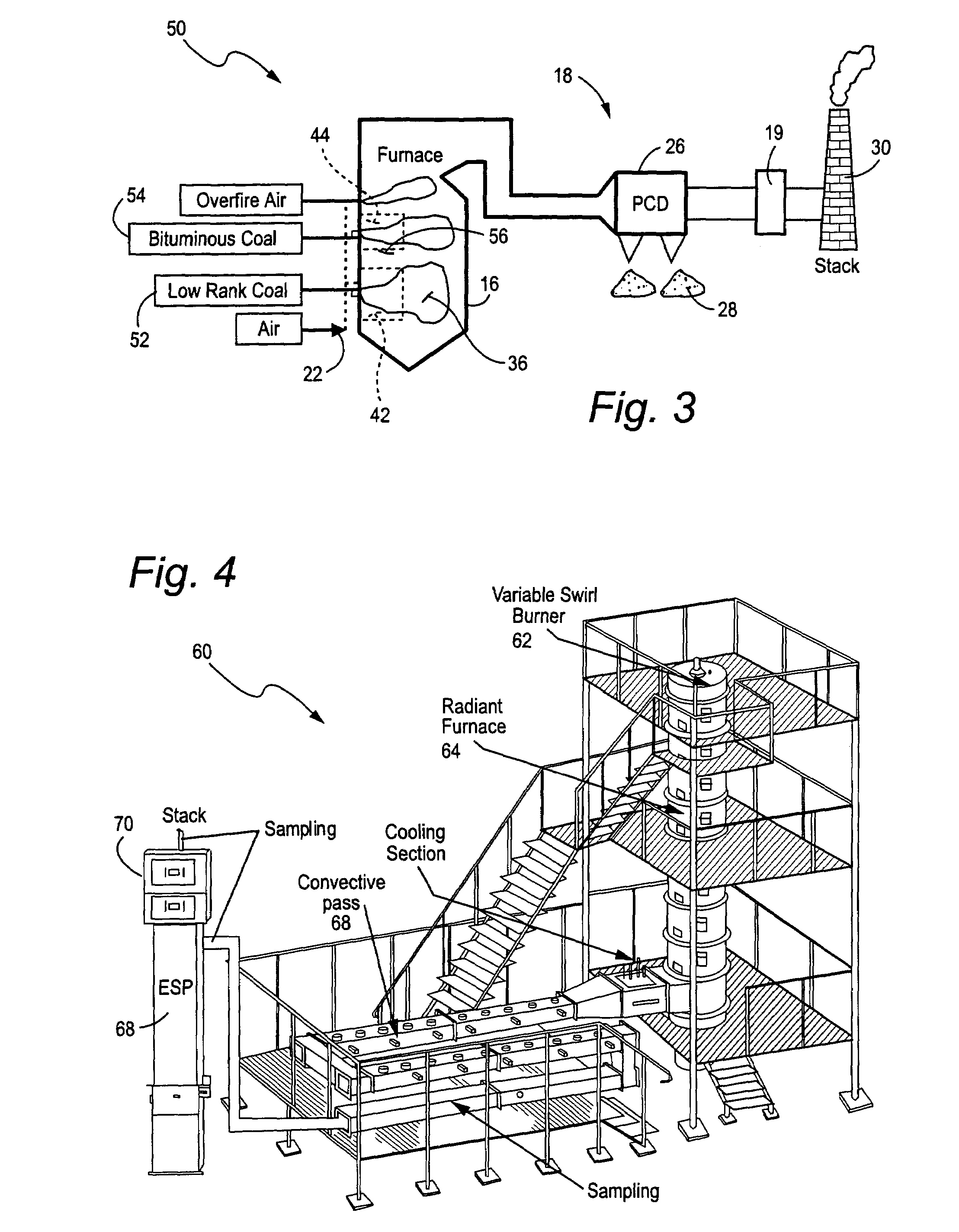
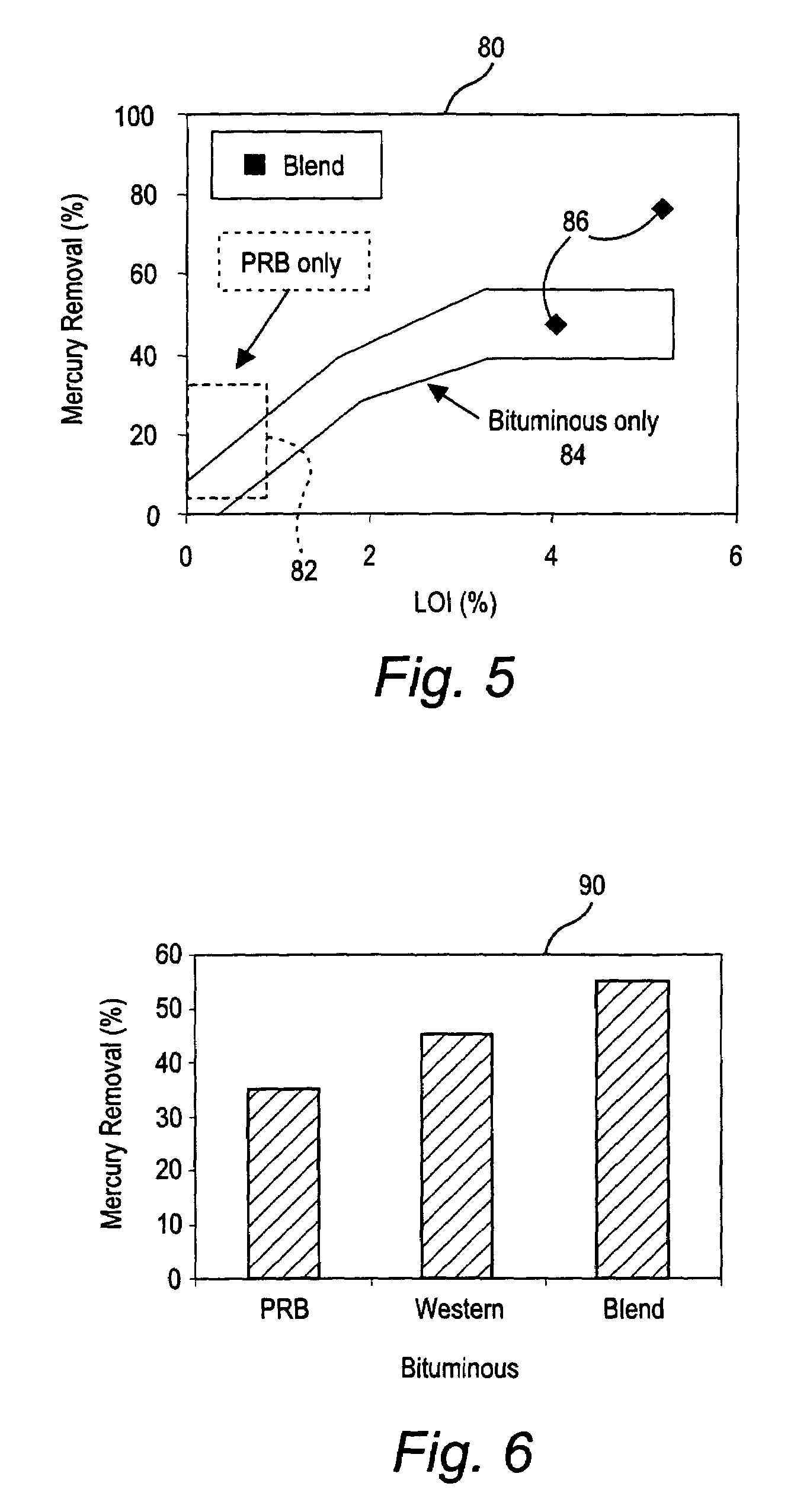
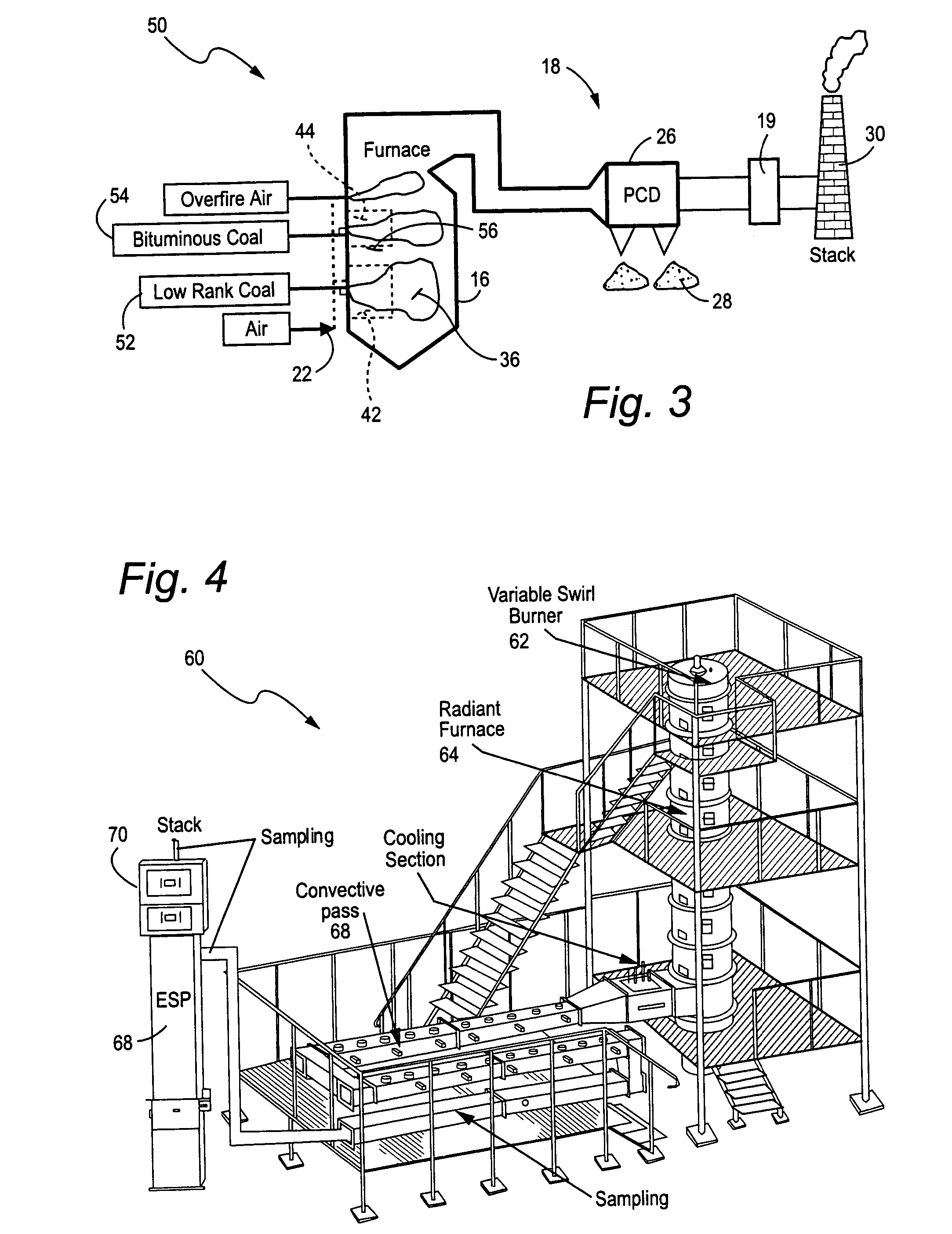
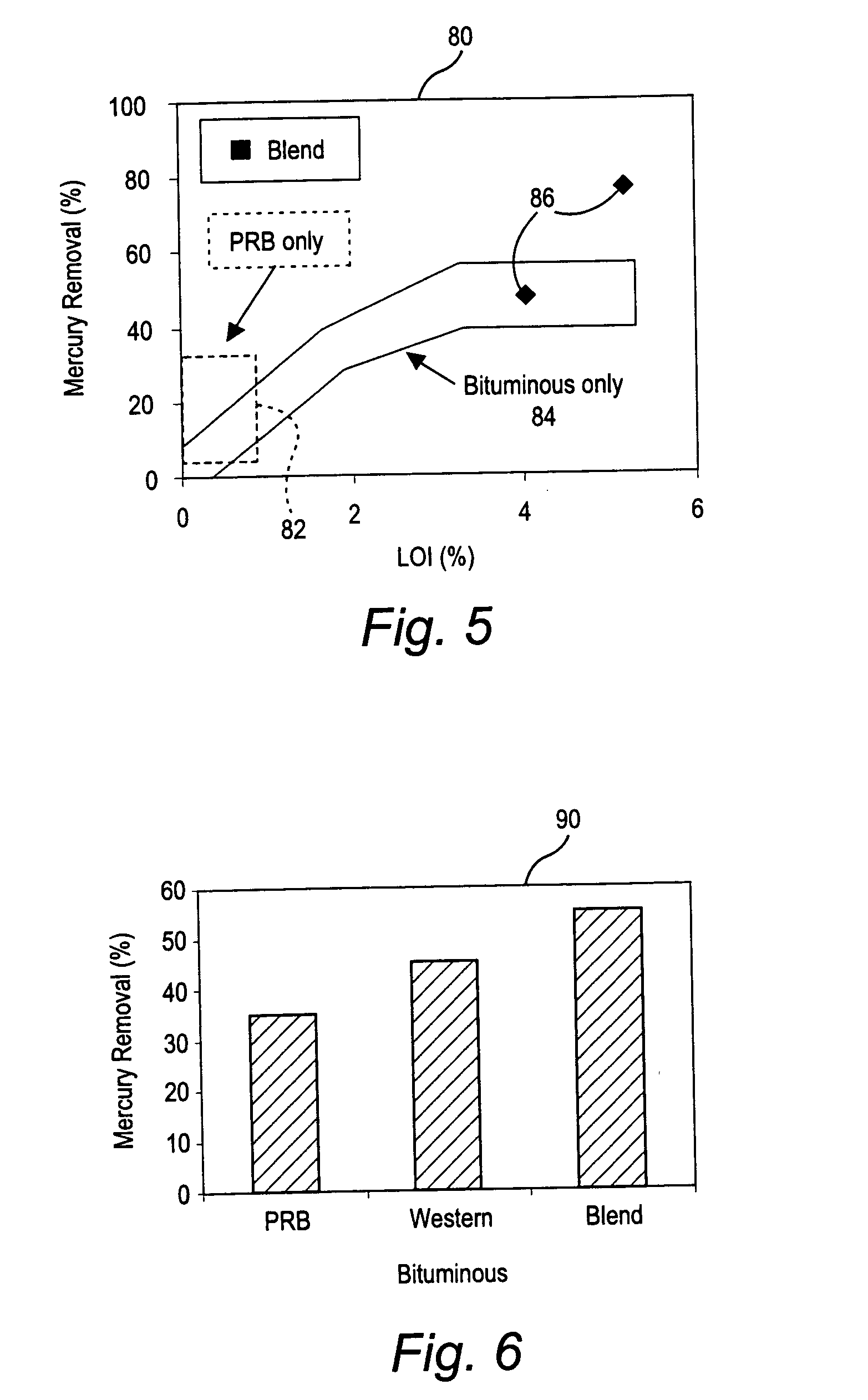
Mercury reduction system and method in combustion flue gas using coal blending
ActiveUS7381387B2Reduce gas emissionsGas treatmentUsing liquid separation agentCombustion systemCombustion
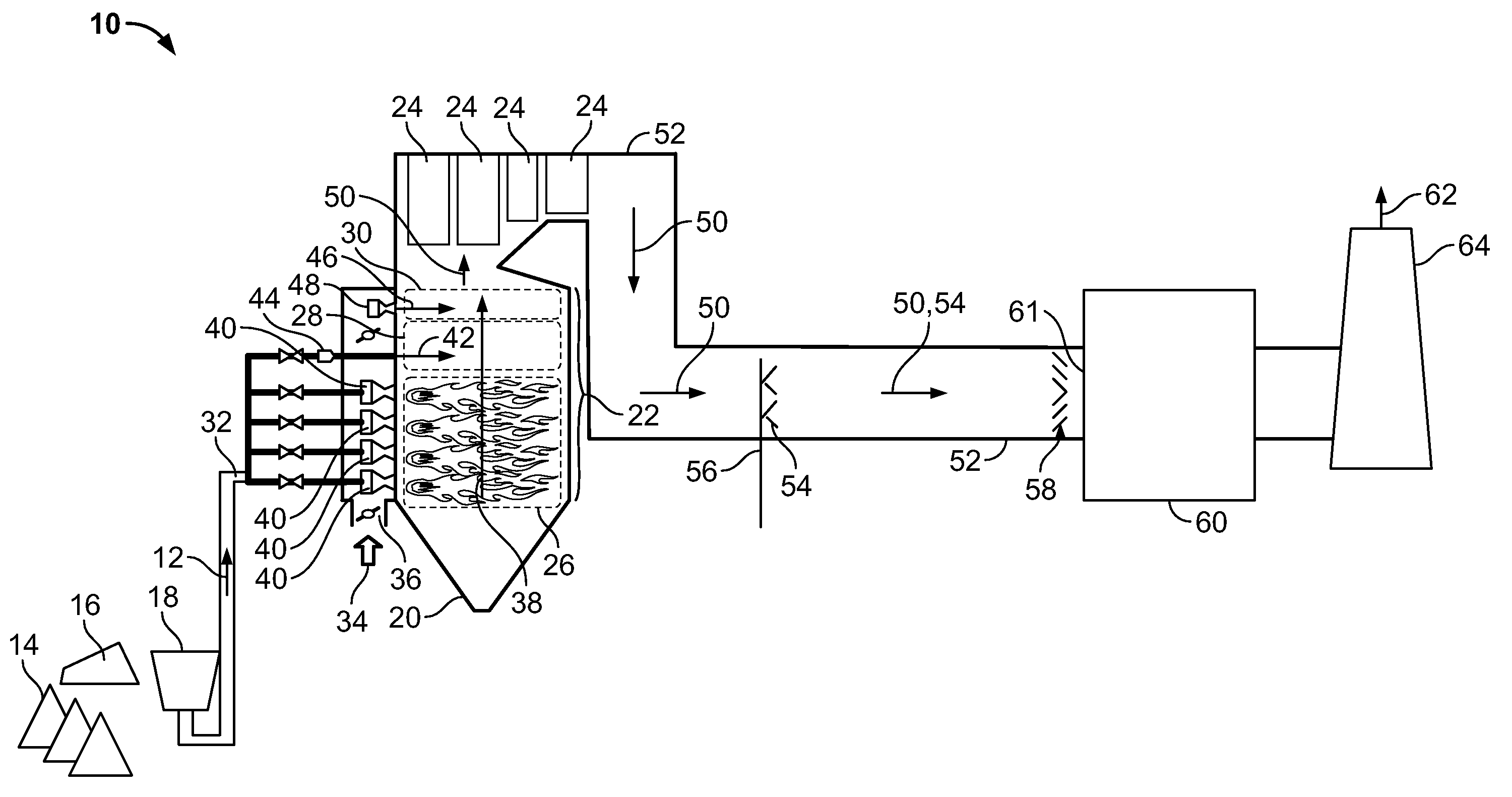
A method to reduce mercury in gas emissions from the combustion of low rank coal in a combustion system including: combusting coal having a low chlorine content in the combustion system, wherein elemental mercury (Hg0) is released in the flue gas produced by the combustion of the low rank coal; releasing chlorine into the flue gas by combusting a coal having a high chlorine in the combustion system; reacting the elemental mercury and released chlorine in the flue gas to oxidize the mercury; adsorbing at least a portion of the oxidized mercury generated by the combustion of the coal with an adsorbent in the flue gas, and collecting the adsorbent with the oxidized mercury in a combustion waste treatment system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
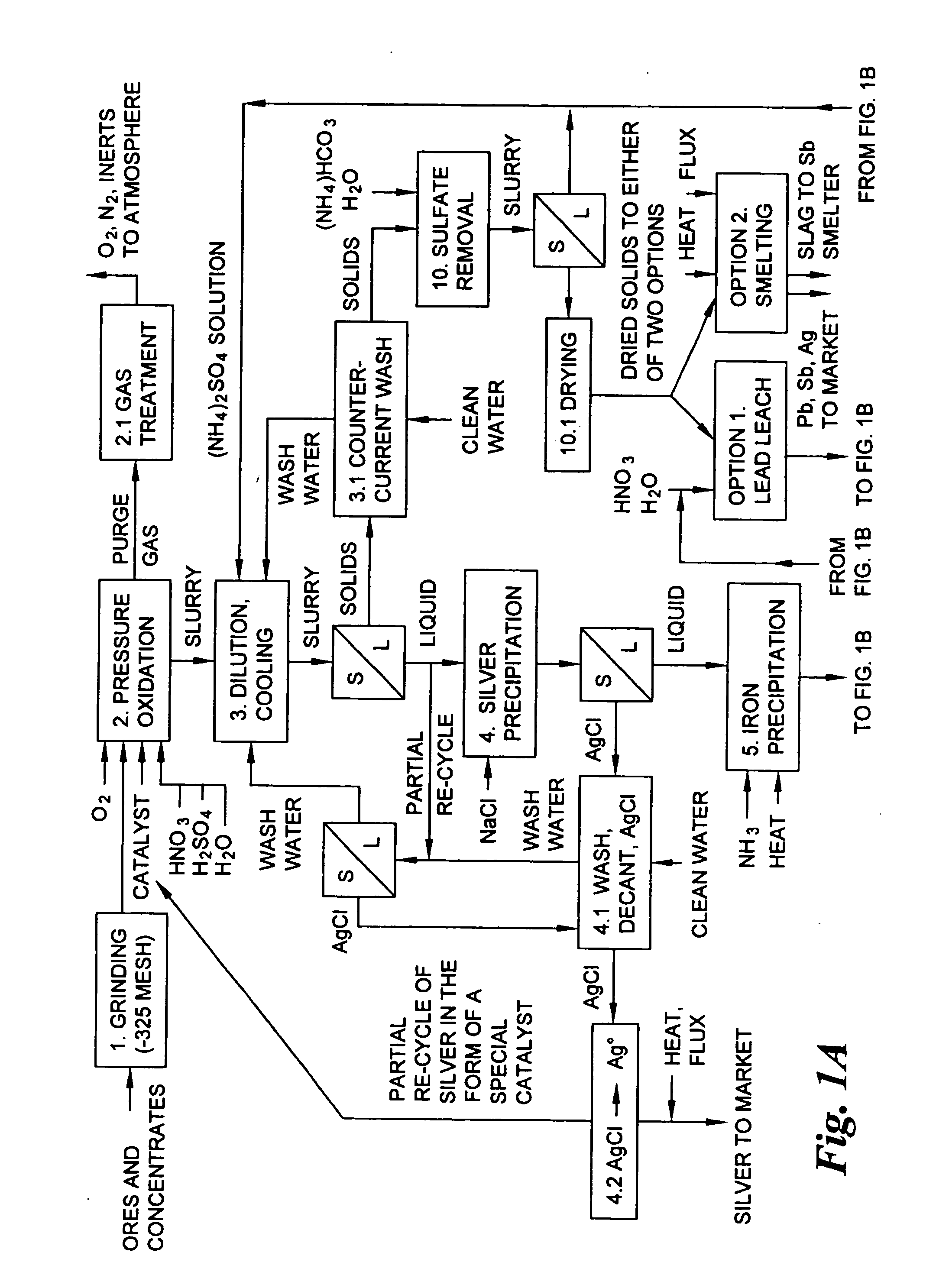
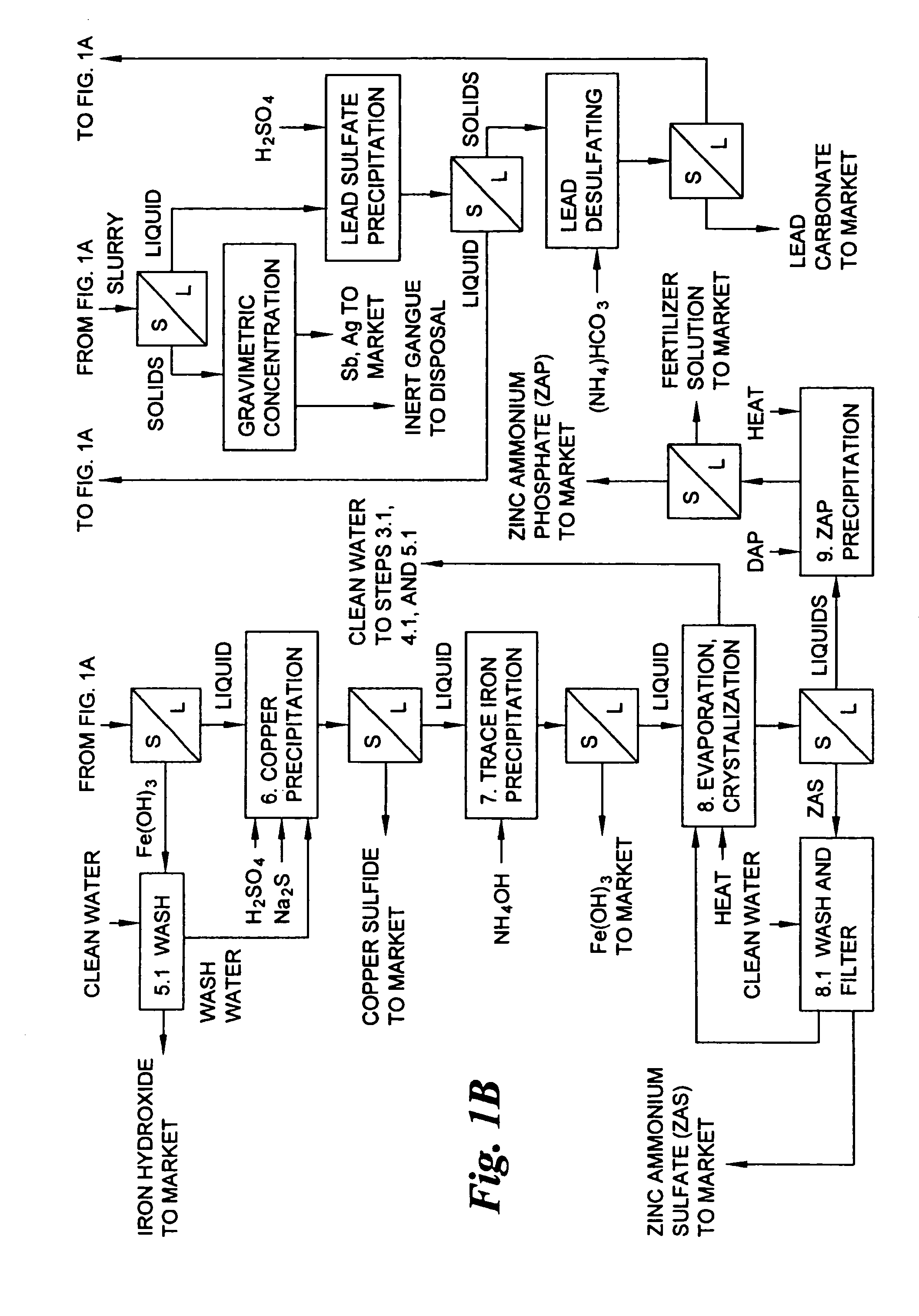
Hydrometallurgical process for the treatment of metal-bearing sulfide mineral concentrates
InactiveUS20070098609A1Improve efficiencyReduce the amount requiredSolvent extractionGold compoundsAmmonium compoundsMetallic sulfide
A hydrometallurgical process for the treatment of complex silver-bearing sulfide ores and concentrates that recovers substantially all silver, lead, antimony, zinc, copper and sulfur, along with the chemical reagents utilized during the process. Finely ground ores and concentrates are leached under heat and pressure with water, sulfuric acid, nitric acid, oxygen, and a catalyst, and are further treated to recover silver in the form of silver chloride; iron in the form of iron hydroxide; copper and all traces of soluble toxic metals as sulfides; zinc as zinc ammonium sulfate and specifically nitric acid, sulfuric acid, oxygen, ammonia, and ammonium compounds as valuable fertilizer products.
Owner:ROYAL SILVER PANAMA
Process for producing nano-powders and powders of nano-particle loose aggregate
InactiveUS7238331B2Speed up the processSimple structureCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesMaterial nanotechnologyPrillNanoparticle
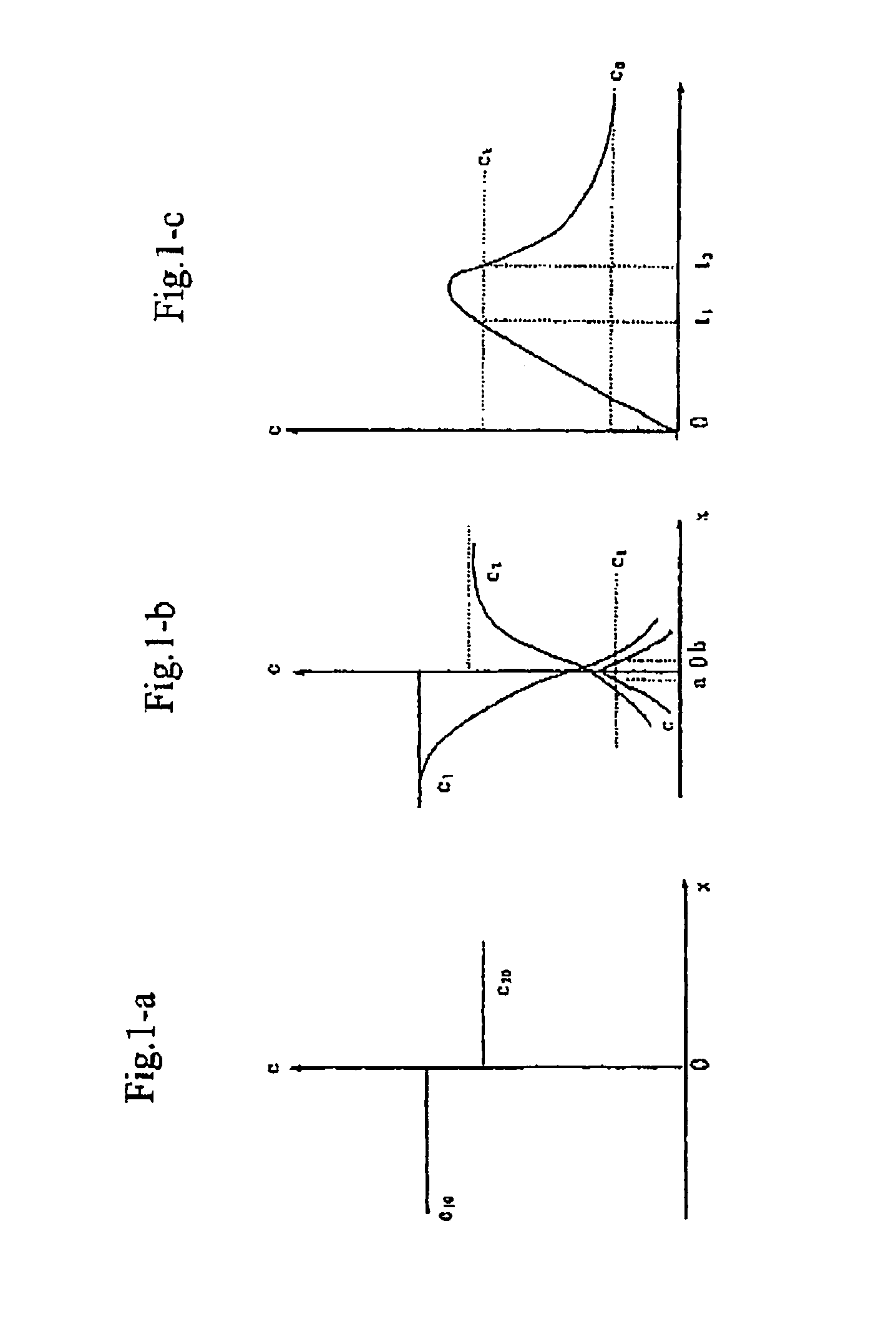
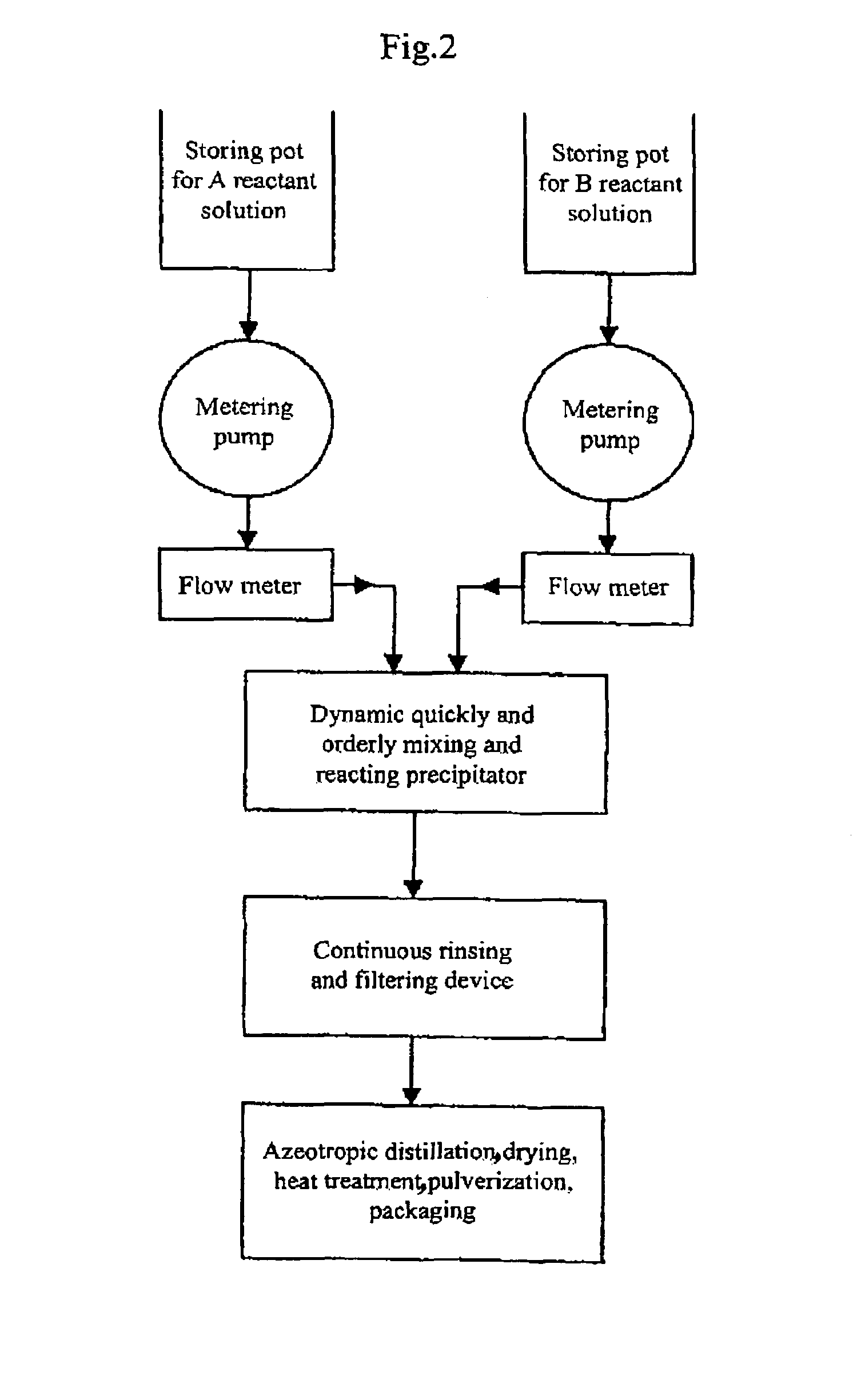
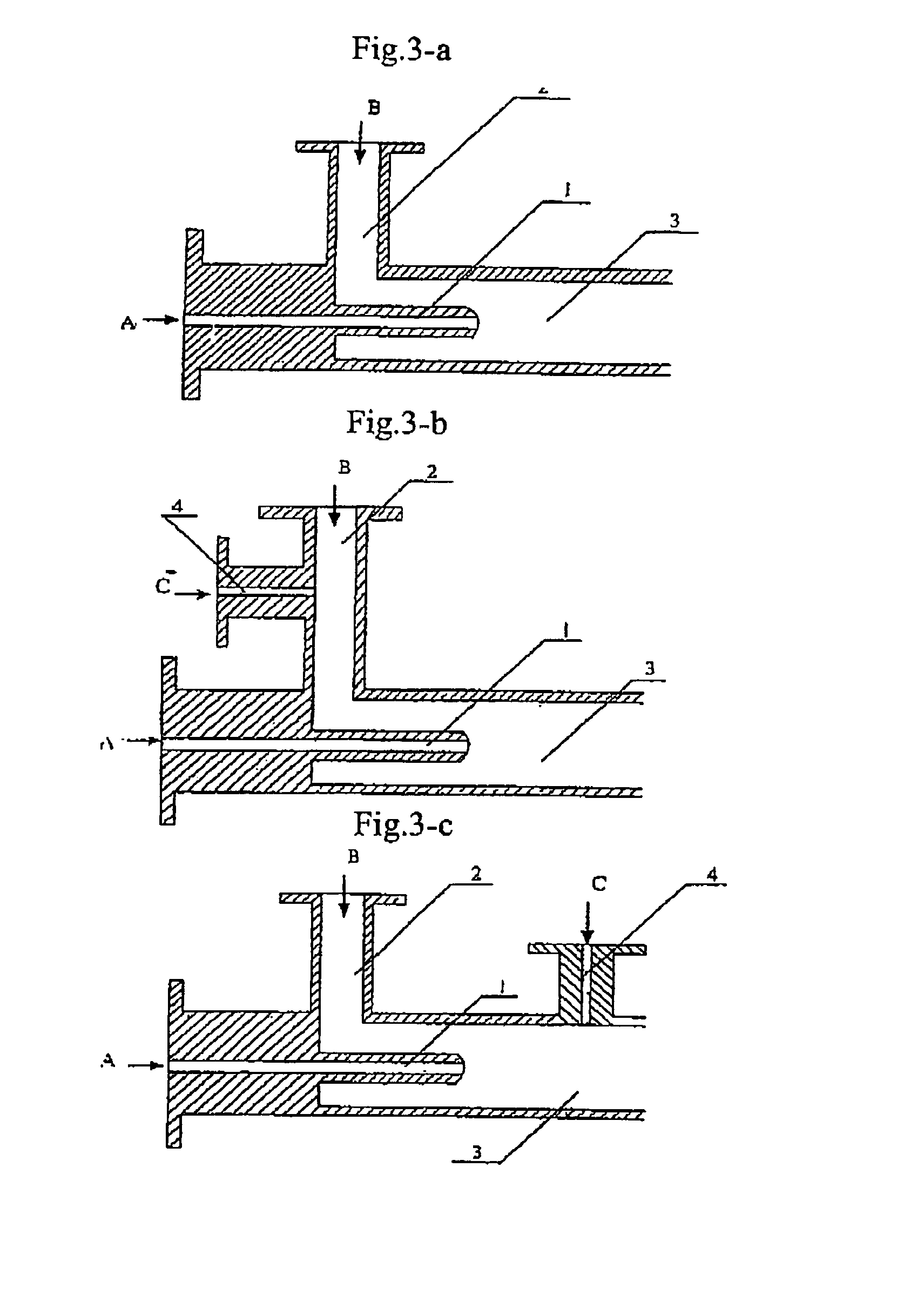
The present invention discloses a process for producing nano-powders and powders of nano-particle loose aggregate, which includes: (a) providing at least two reactant solutions A and B capable of rapidly reacting to form deposits; (b) supplying the at least two reactant solutions A and B at least at the reaction temperature into a mixing and reaction precipitator respectively, in which mixing reaction and precipitation are continuously carried out in sequence, the mixing and reaction precipitator being selected from at least one of a tubular ejection mixing reactor, a tubular static mixing reactor and an atomization mixing reactor; and (c) treating the deposit-containing slurry continuously discharged from the mixing reaction precipitator.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH LIAONING
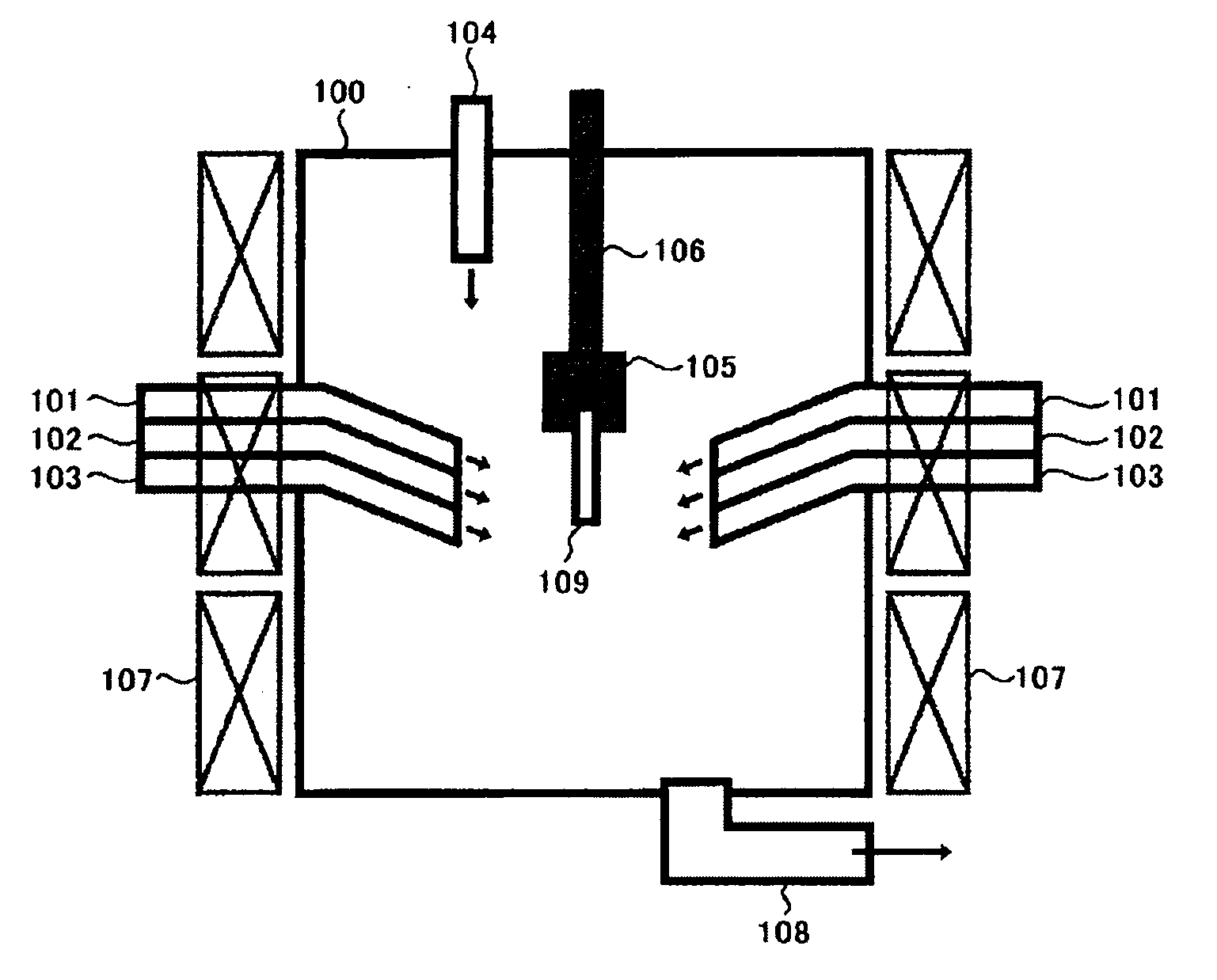
Method and apparatus for removing mercury from combustion exhaust gas
A method for reducing mercury emissions in combustion flue gas is provided. The method includes combusting coal such that a flue gas flow is created. The flue gas flow includes at least mercury and carbon-containing fly ash. The method further includes cooling the flue gas flow within a duct and creating turbulence in the flue gas flow. The mercury is removed from the flue gas flow.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Biooxidation process for recovery of metal values from sulfur-containing ore materials
InactiveUS6383458B1Increase ratingsIncrease attractivenessTransuranic element compoundsSolvent extractionParticulatesPartial oxidation
A process for the recovery of one or more metal values from a metal ore material comprising those of one or more values and a matrix material having a sulfur content wherein the sulfur is present in an oxidation-reduction state of zero or less comprisinga. forming particulates from particles of said ore and an inoculate comprising bacteria capable of at least partially oxidizing the sulfur content;b. forming a heap of said particulates;c. biooxidizing the sulfur content andd. recovering those one or more metal values.
Owner:NEWMONT USA LTD
Recovery of the transition metal component of catalyst used in heavy feed hydroconversion
The invention relates to a process for recovering the transition metal component of catalysts used in the hydroconversion of heavy hydrocarbonaceous materials. In accordance with the invention, a slurry of a transition metal catalyst and hydrocarbon is catalytically desulfurized resulting in a desulfurized product and a solid residue containing the transition metal. The transition metal may be recovered by coking the residue and then dividing the coker residue into two portions are combusted with the flue dust from the first combustion zone being conducted to the second combustion zone. The flue dust from the second combustion zone is treated with ammonia and ammonium carbonate in order to obtain ammonium molybdate.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
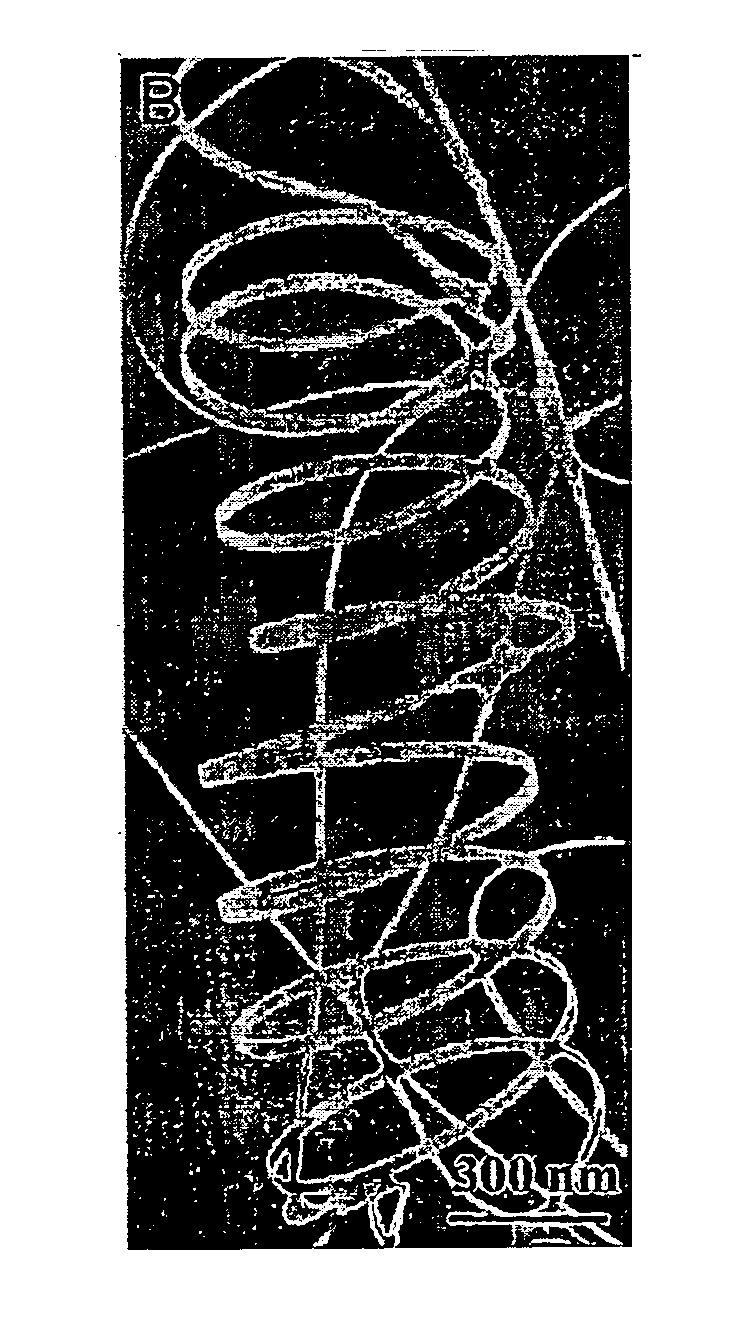
Semiconducting oxide nanostructures
Briefly described, new types of nanostructures and methods of fabrication thereof are disclosed. A representative nanostructure includes a free-standing, helical semiconductor oxide nanostructure. The free-standing, helical semiconductor oxide nanostructure includes a nanobelt having a substantially rectangular cross-section. The the nanobelt is about 5 nanometers to about 200 nanometers in width and about 3 nanometers to about 50 nanometers in height, and the radius of the helical semiconductor oxide nanostructure is about 200 to 5000 nanometers.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Gasoline sulfur reduction in fluid catalytic cracking
InactiveUS6923903B2Improving reduction in sulfur contentImprove catalytic stabilityCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsReduction ActivityMolecular sieve
The sulfur content of liquid cracking products, especially the cracked gasoline, of the catalytic cracking process is reduced by the use of a sulfur reduction catalyst composition comprising a porous molecular sieve which contains a metal in an oxidation state above zero within the interior of the pore structure of the sieve as well as a cerium component which enhances the stability and sulfur reduction activity of the catalyst. The molecular sieve is normally a faujasite such as USY. The primary sulfur reduction component is normally a metal of Period 3 of the Periodic Table, preferably vanadium. The sulfur reduction catalyst may be used in the form of a separate particle additive or as a component of an integrated cracking / sulfur reduction catalyst.
Owner:WR GRACE & CO CONN +1
Method for treating exhaust gas
An object of the present invention is to provide a new method for treating an exhaust gas, which can effectively treat an exhaust gas containing a nitrogen oxide and metal mercury over a long term, and also can be applied to treatment of a large volume of an exhaust gas. As a means of achieving this object, a method according to the present invention for treating an exhaust gas comprises performing a reaction of changing metal mercury into mercury halide in the presence of a halogen compound and treatment of a nitrogen oxide, using a Ti—V-containing catalyst, upon treatment of an exhaust gas containing a nitrogen oxide and metal mercury.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Solid acid catalyst and method of using same
A catalyst composition includes an oxygen compound of an element selected from Group IVB or Group IVA of the Periodic Table of the Elements; an oxygen compound of an element selected from Group VIB or Group VIA of the Periodic Table of the Elements; and at least about 1% by weight based upon total catalyst weight of fumed silica particles. The catalyst composition is advantageously employed in hydrocarbon conversion processes such as isomerization.
Owner:ABB LUMMUS GLOBAL INC
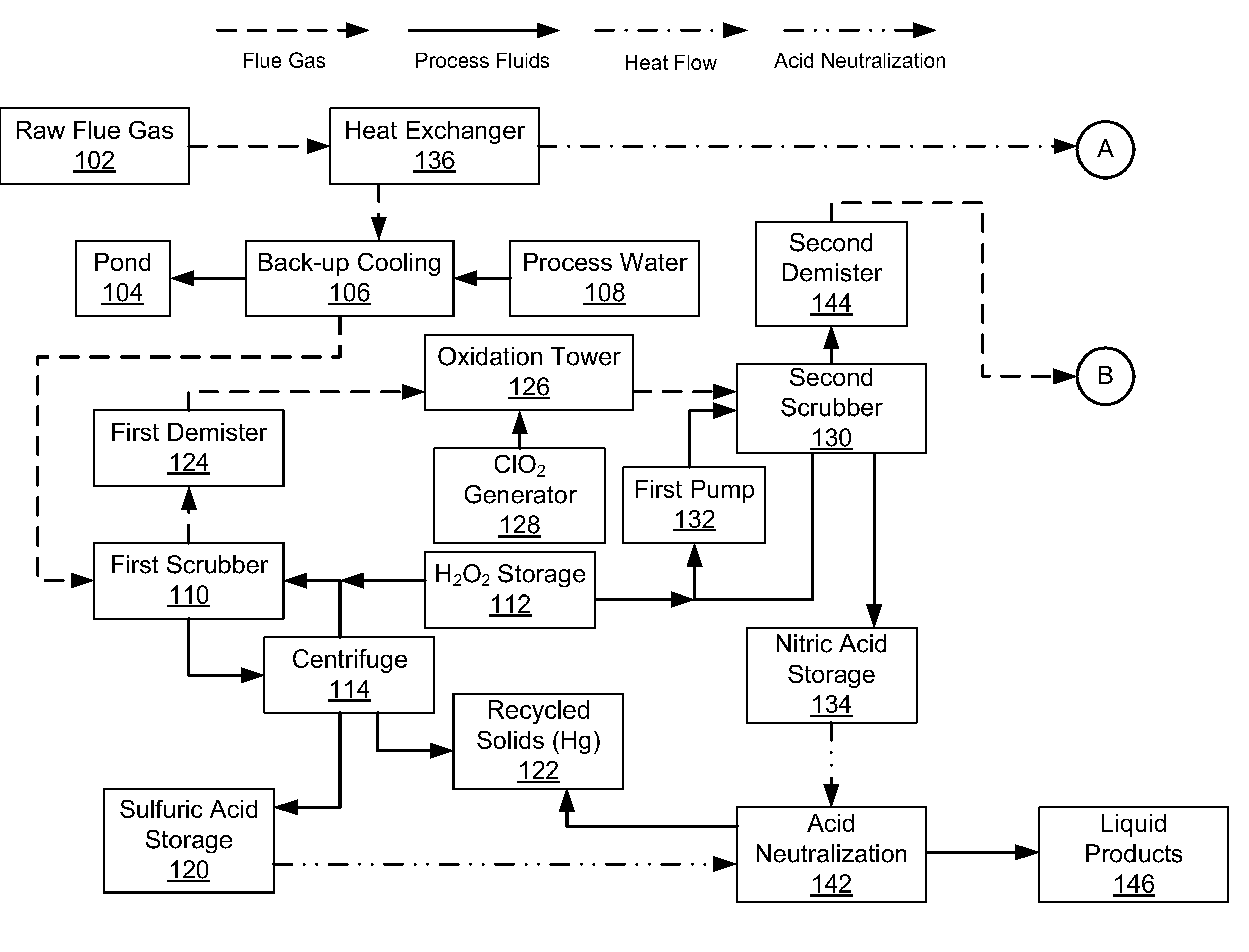
Emission Control System
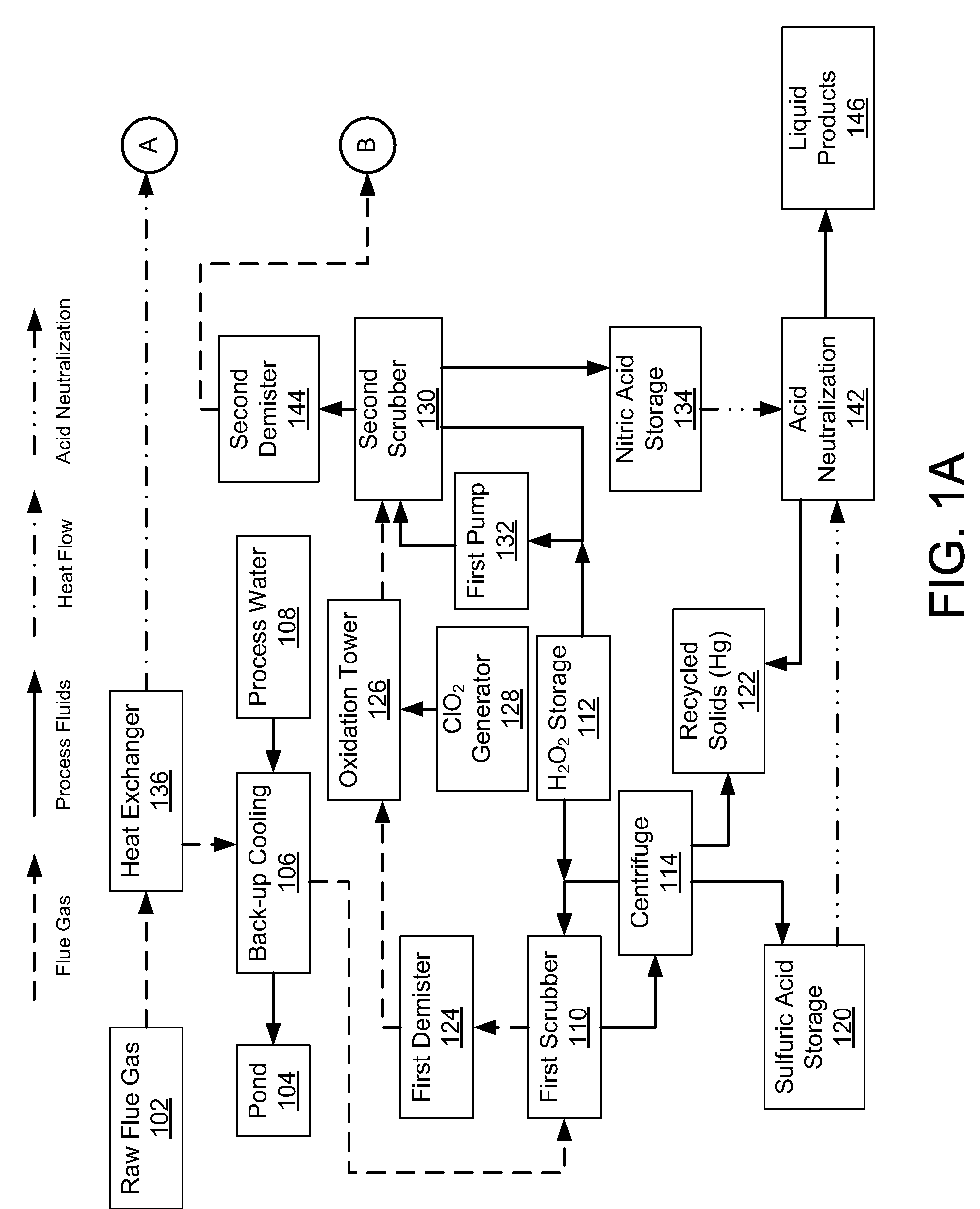
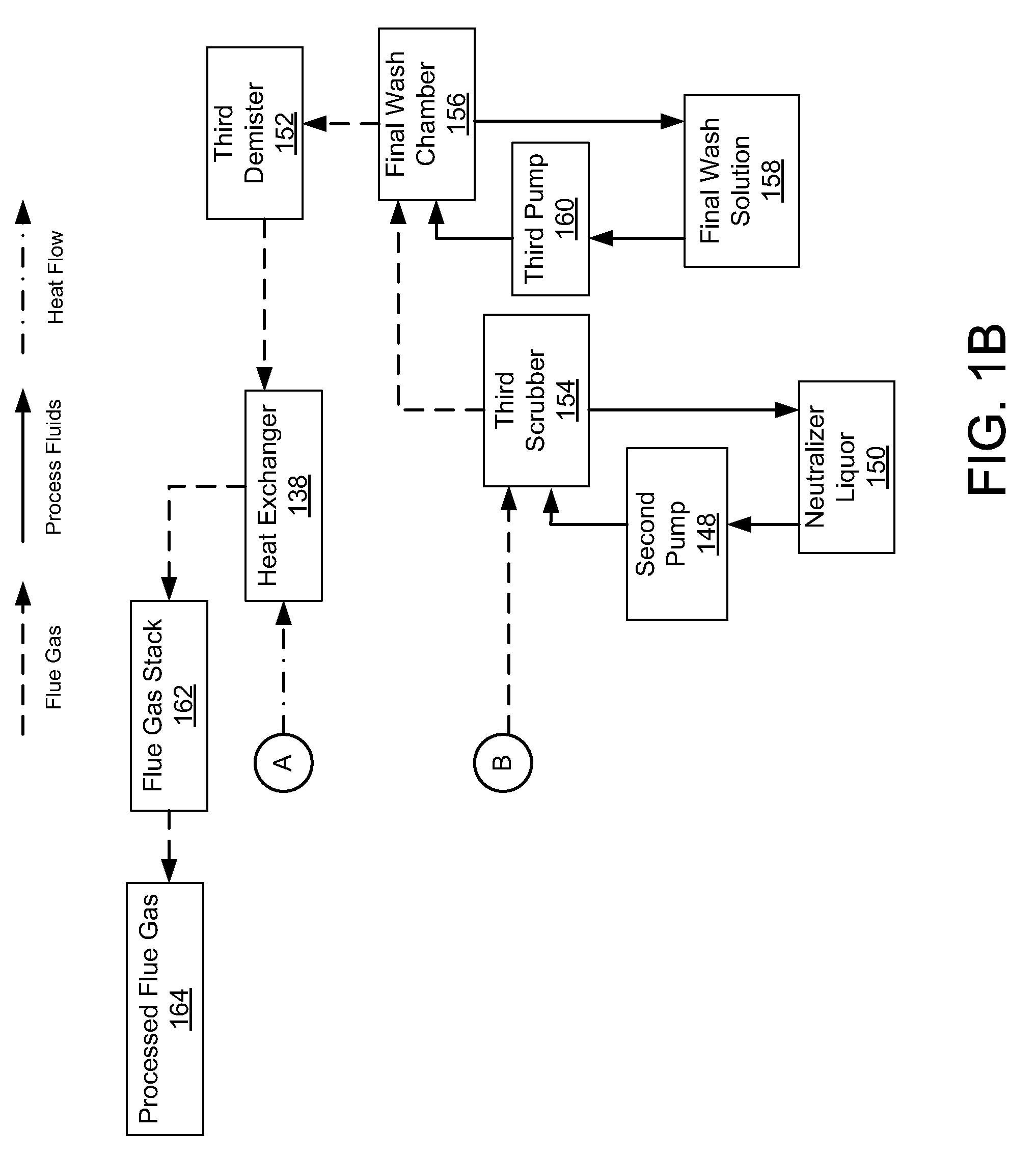
InactiveUS20080241030A1Reduce mercury emissionEmission reductionCombination devicesNitrogen compoundsChlorine dioxideControl system
Methods and apparatus utilizing chlorine dioxide and hydrogen peroxide are useful to reduce emissions of NOx, SOx, and heavy metals, e.g., mercury, emissions from combustion flue gas streams.
Owner:NASA
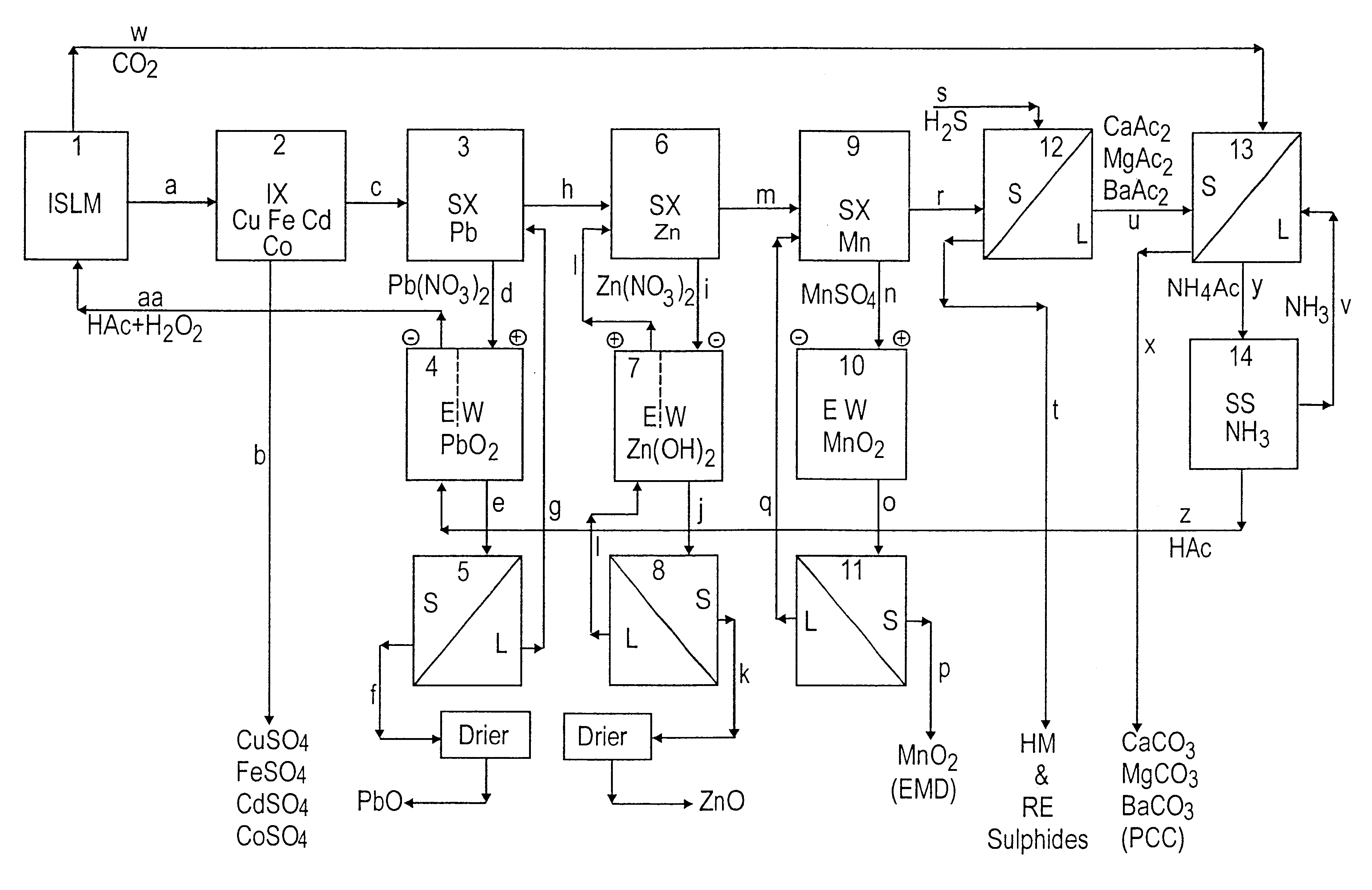
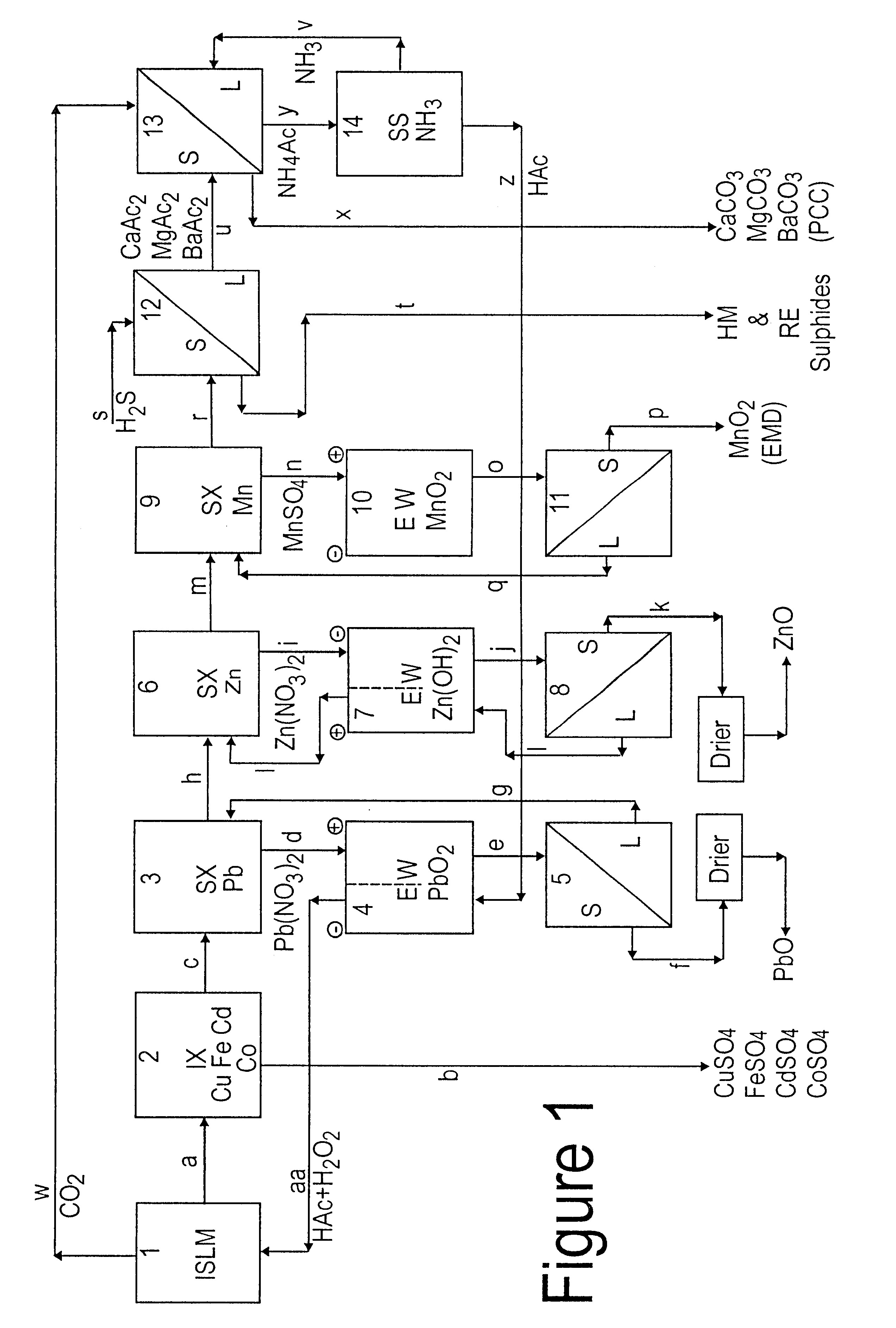
Lead, zinc and manganese recovery from aqueous solutions
InactiveUS6517701B1Low costShorten the timePhotography auxillary processesElectrolysis componentsIon exchangeManganese
Aqueous solutions containing lead, zinc and manganese are treated to recover these metals by sequential solvent extraction steps. Solvent extractants are selected to extract preferentially lead, then zinc and then manganese in that order. Any interfering metals are removed (as by ion exchange) before extraction. The loaded extractant phases are stripped with selected acids and lead, zinc and manganese each recovered from the strip solutions. Optionally calcium can be recovered when present. A preferred type of extractant (for lead especially) is substituted monothiophosphinic acids. A closed loop system is described which is advantageous with leachate from sulphide and carbonate ores.
Owner:CENTAUR MINING EXPLORATION
Method for effecting solvent extraction of metal ions using hydrocarbon soluble aminomethylene phosphonic acid compounds
Solvent extraction of one or more metal ions from an aqueous solution in the presence of hydrocarbon-soluble aminomethylenephosphonic acid derivatives.
Owner:BASF AG +1
Method of removing mercury from mercury contaminated materials
InactiveUS7214254B2The process is compact and efficientThe equipment is compact and efficientZinc compoundsProcess efficiency improvementMercury levelMicrowave irradiation
A method of reducing mercury levels in a mercury contaminated material using microwave energy. The method comprises the steps of (a) placing the mercury contaminated material in a microwave reactor; (b) providing a stream of gas in the microwave reactor, the stream causing agitation of the mercury contaminated material; and (c) exposing the mercury contaminated material to microwave radiation so as to raise the temperature to at least 357° C., producing a vapour phase which contains mercury and a treated material. The method also allows for a simultaneous reduction of mercury and carbon levels in the material to be treated as well as the use of a carbon-free material in the reactor.
Owner:HENDRIX HLDG CO INC +1
Hydrometallurgical process for a nickel oxide ore
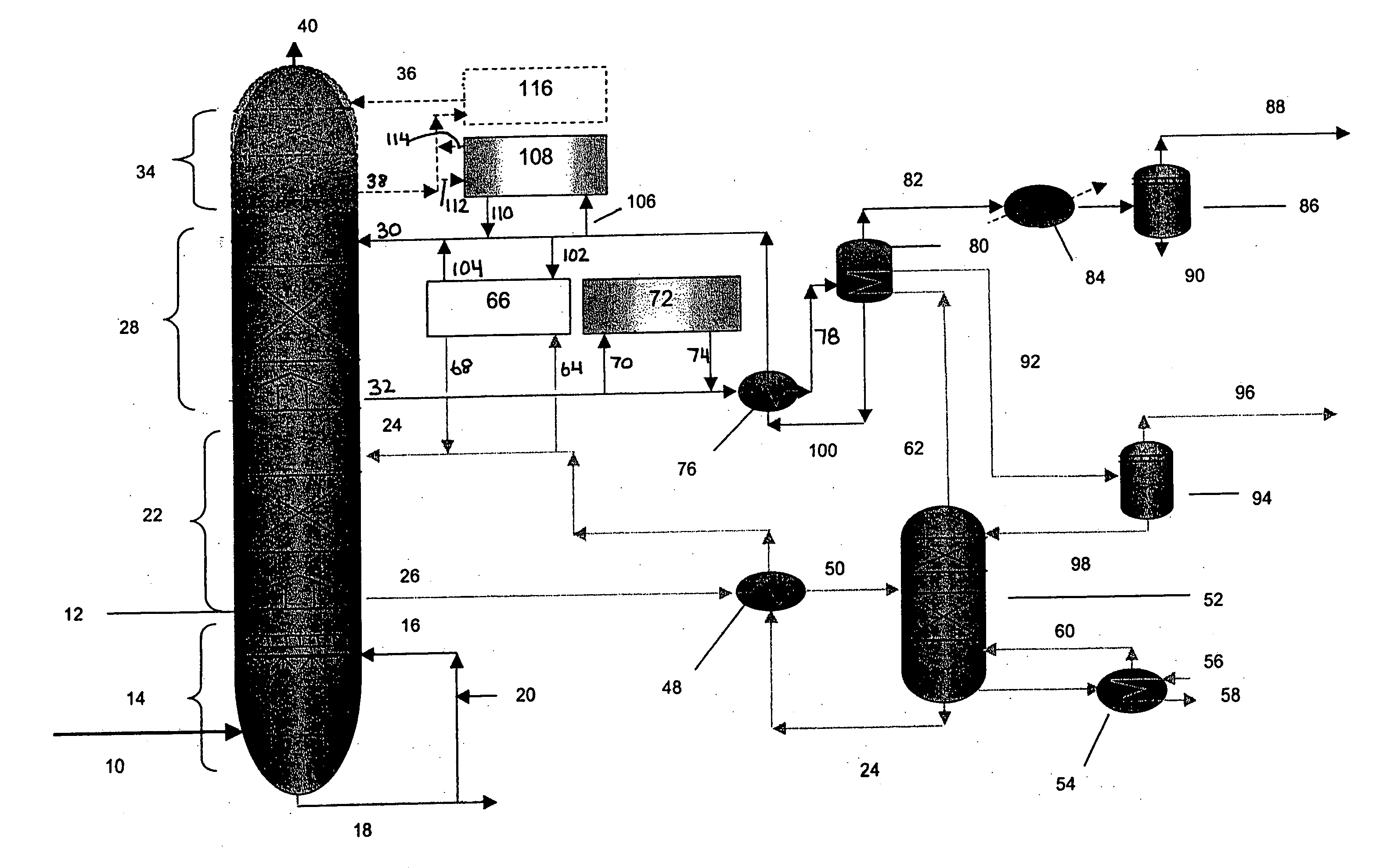
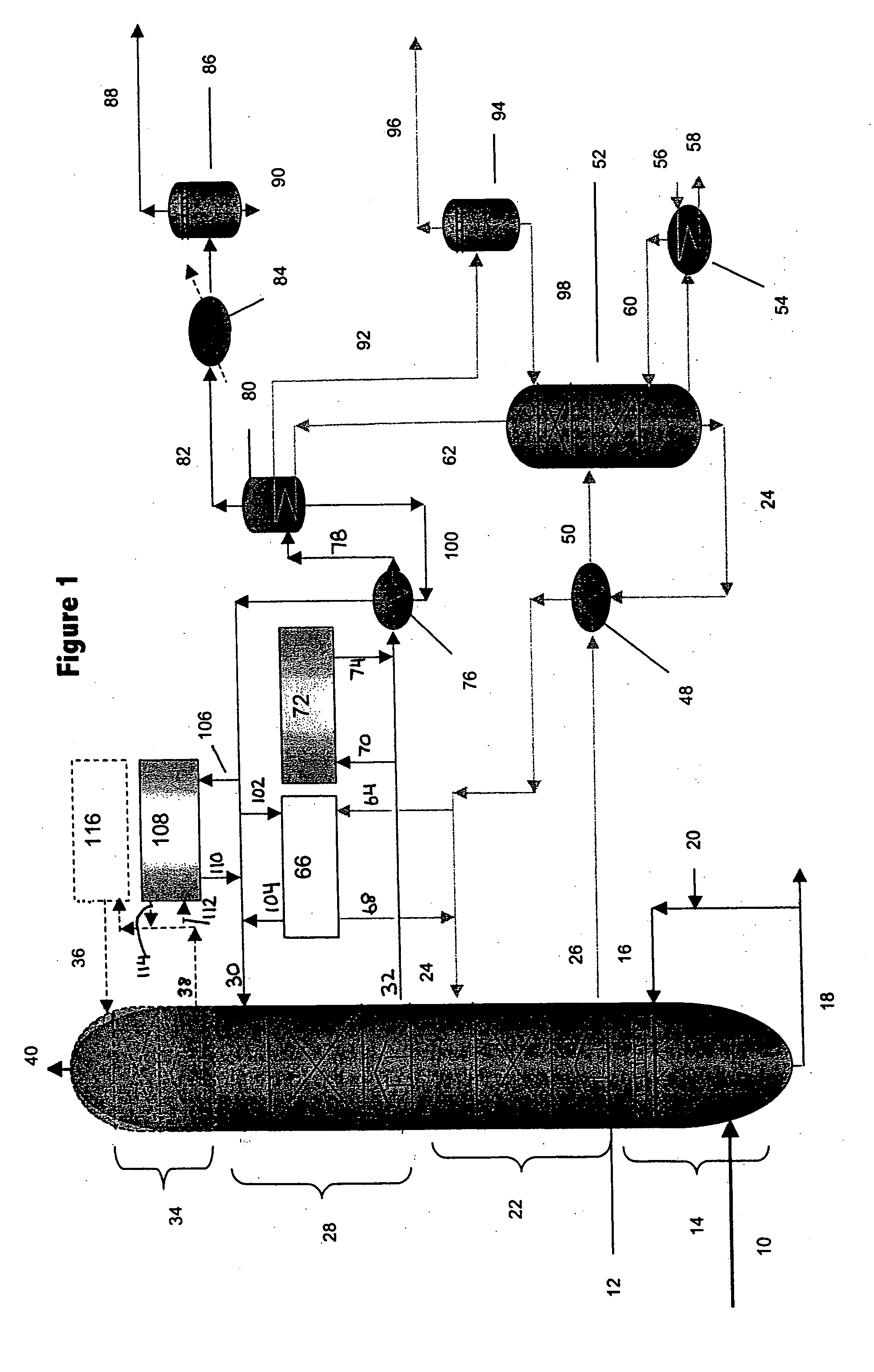
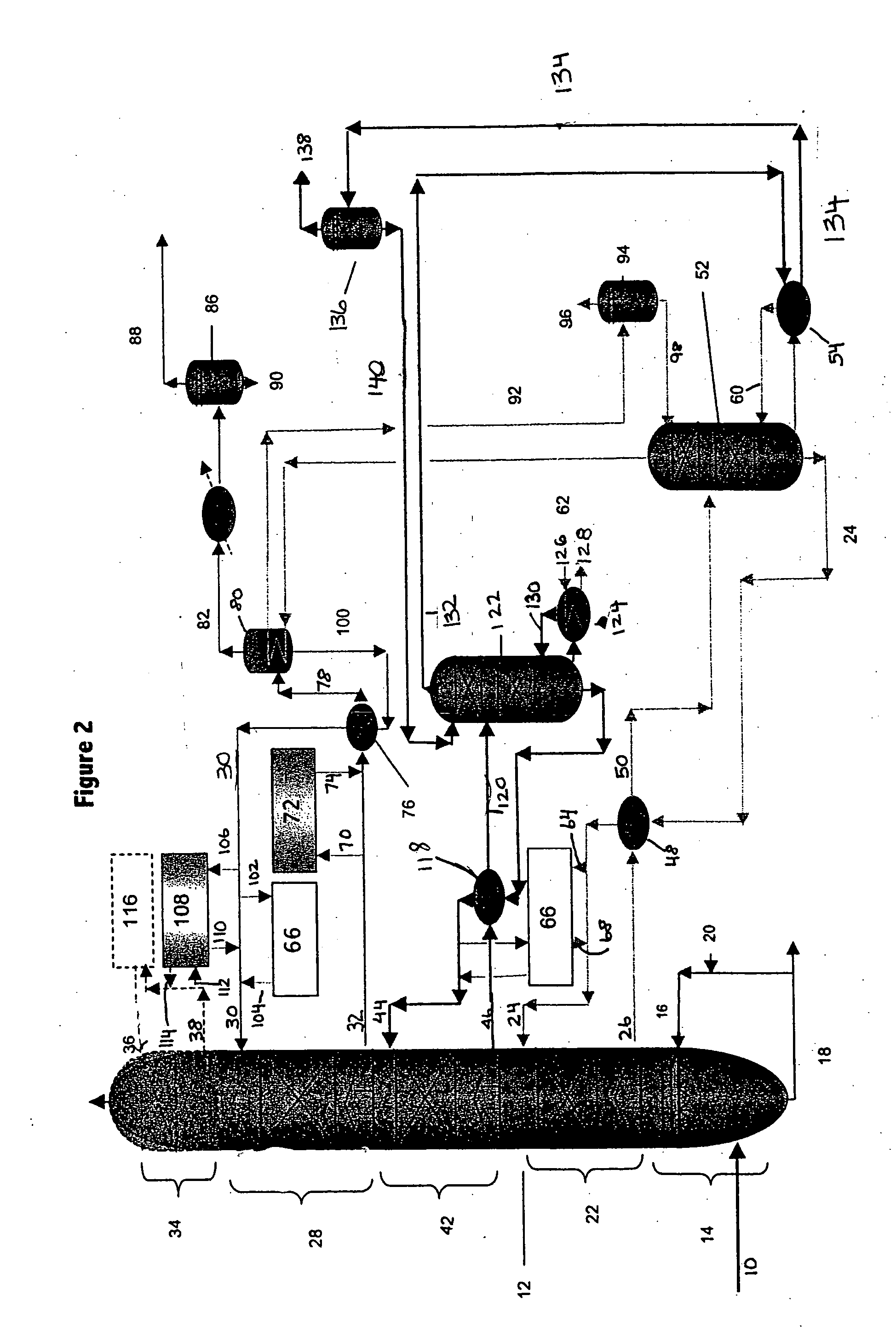
ActiveUS20100018350A1Reduce usageReduce operating costsSolvent extractionHydrogen sulfidesLiquid wasteSulfate
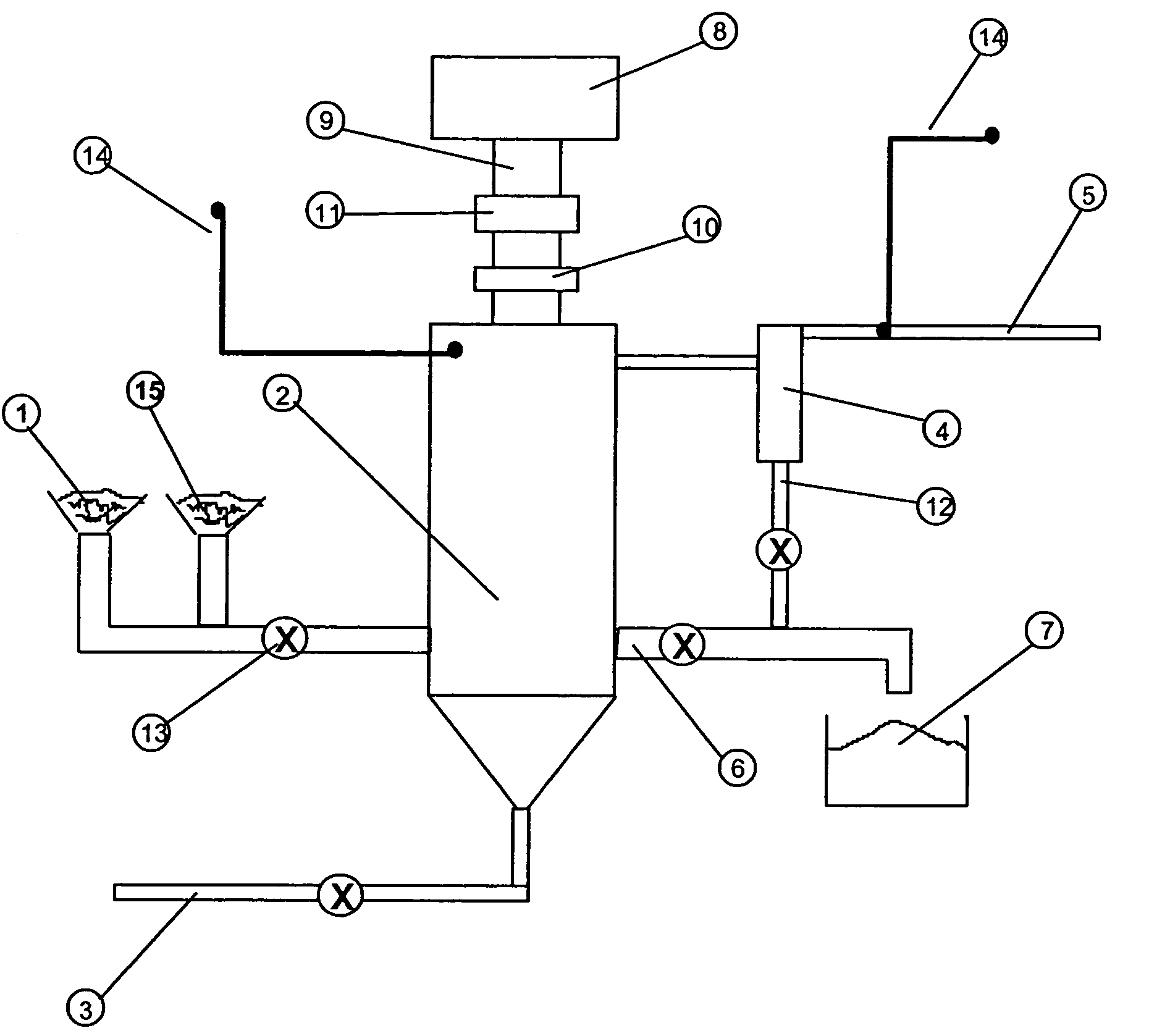
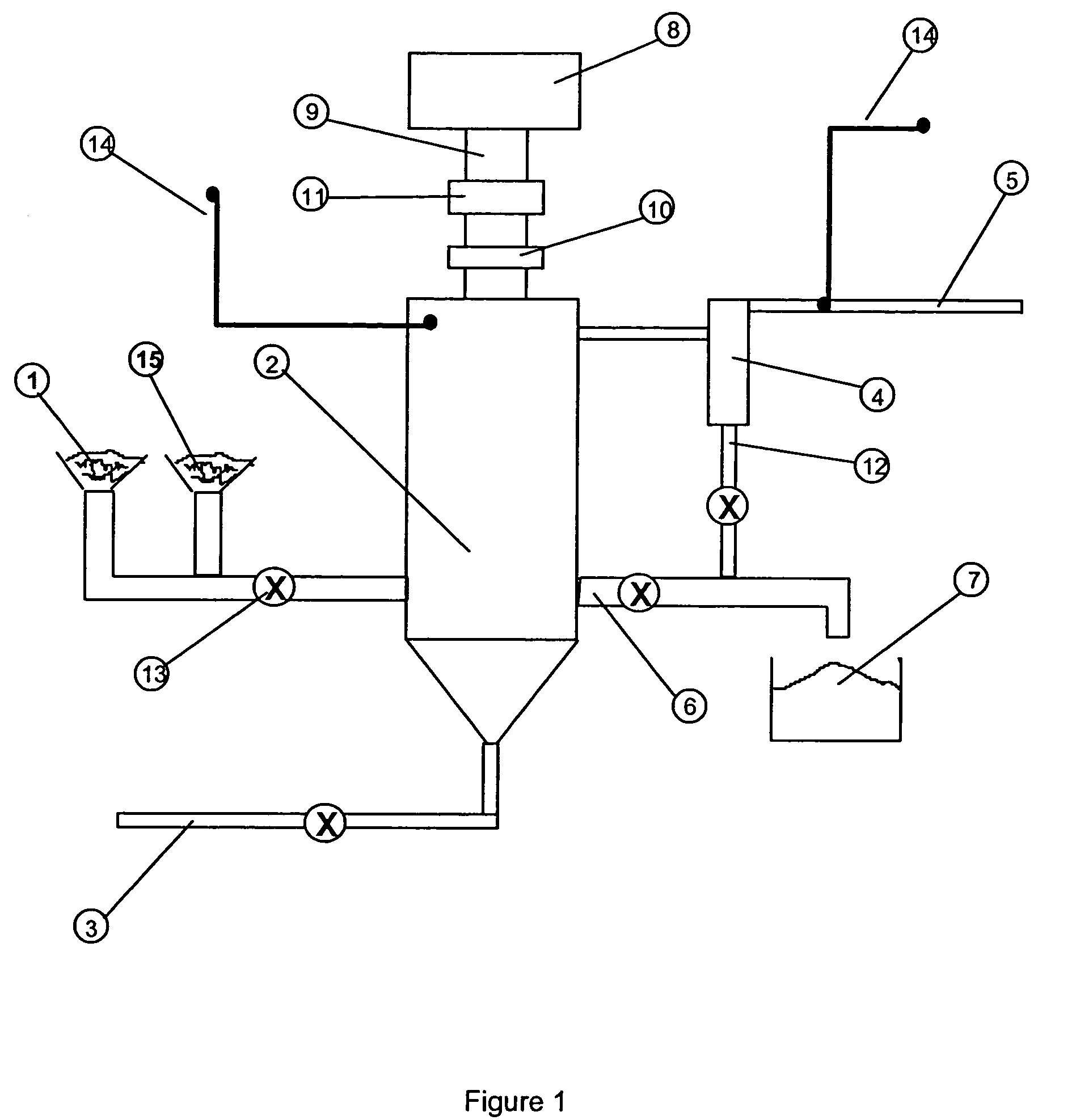
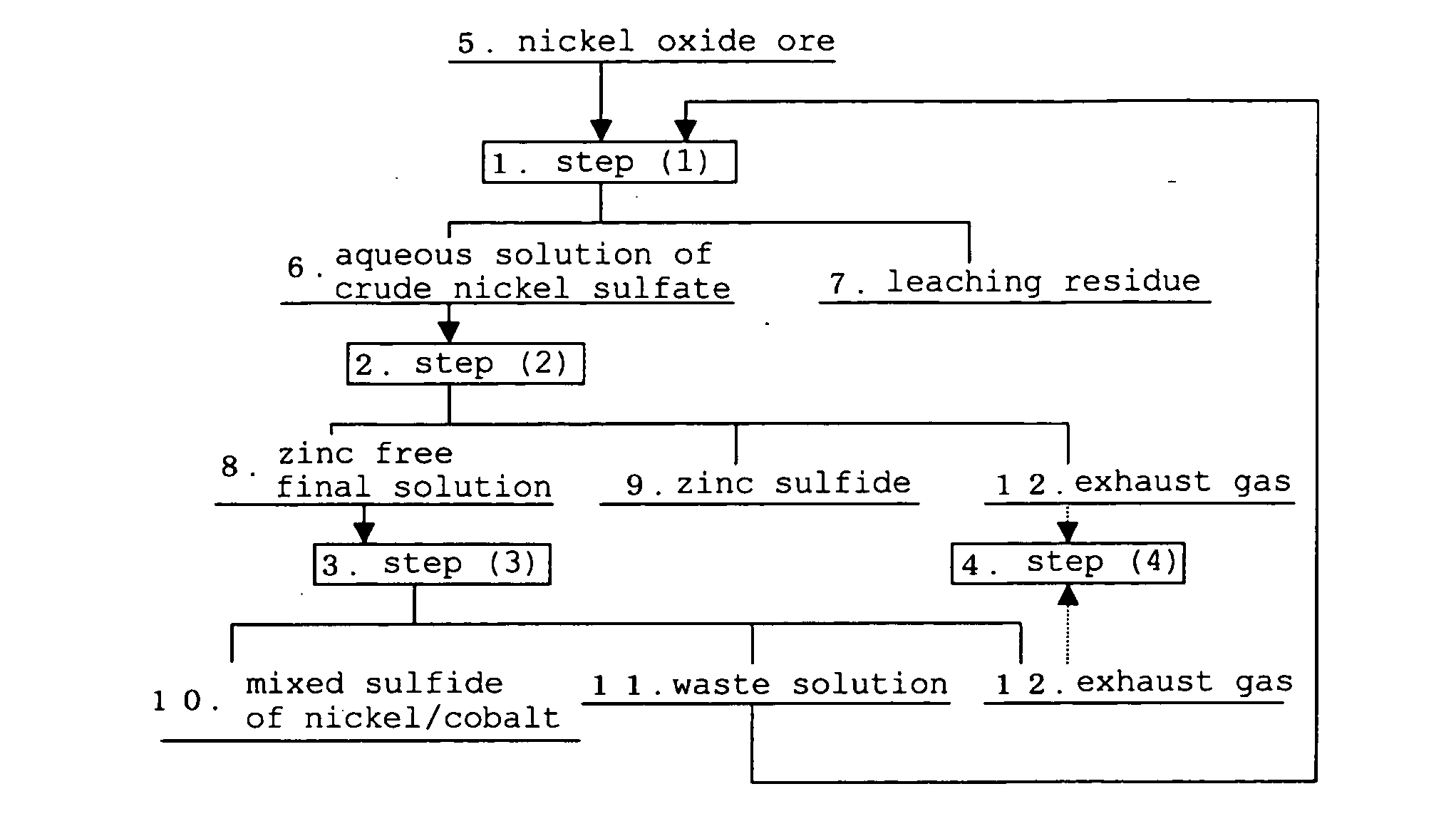
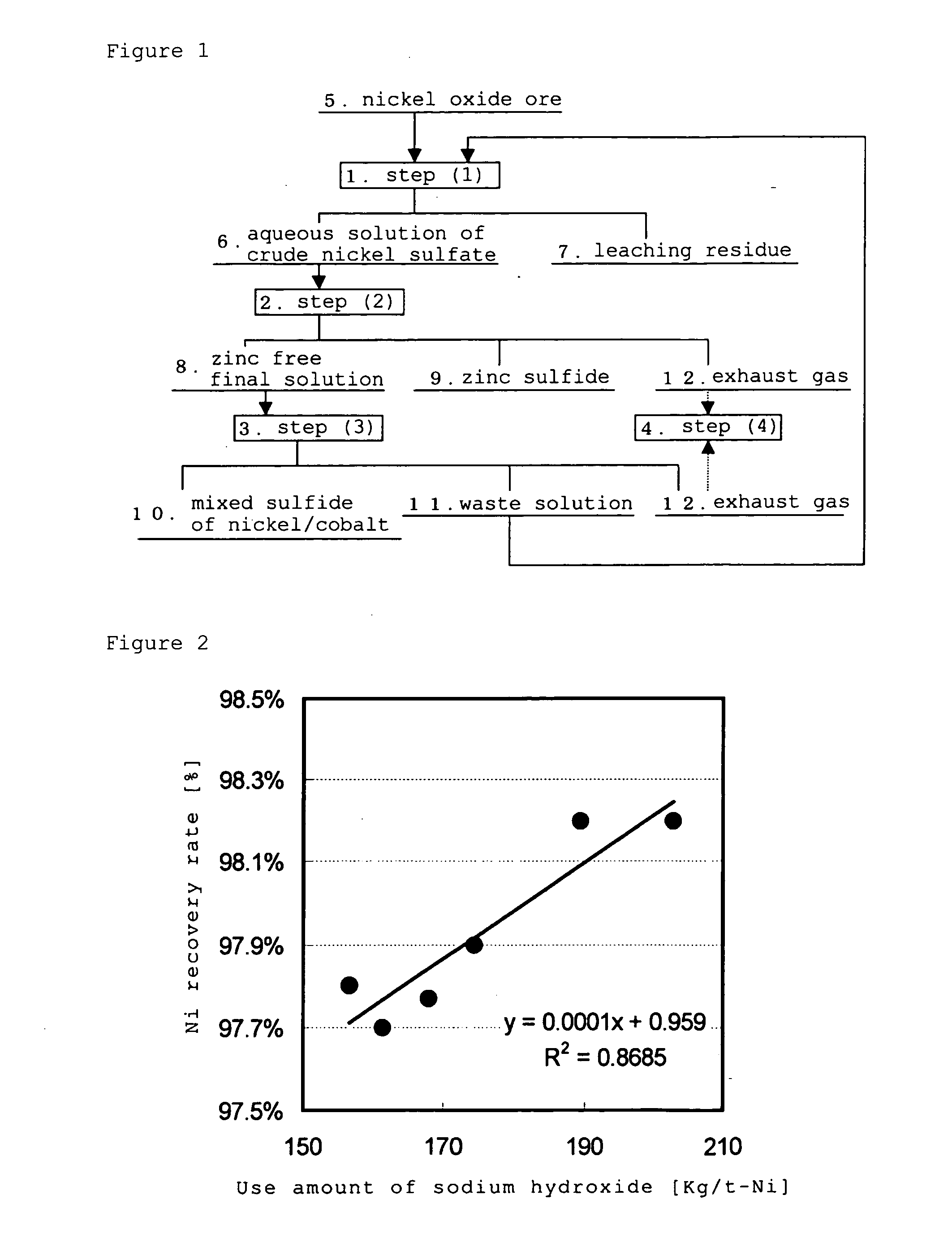
The hydrometallurgical process for a nickel oxide ore comprising a step (1) for obtaining an aqueous solution of crude nickel sulfate by High Pressure Acid Leach of a nickel oxide ore; a step (2) for obtaining a zinc free final solution formed; a step (3) for obtaining a waste solution; and a step (4) for scrubbing a hydrogen sulfide gas in exhaust gas, wherein utilization efficiency of hydrogen sulfide gas is enhanced while maintaining nickel recovery rate.It is characterized in that at least one kind of the following operations (a) to (d) is adopted.(a) to adjust total volume (m3) of the sulfurization reactor (B) in the above step (3), at a ratio of 0.2 to 0.9, relative to input mass (kg / h) of nickel to be introduced;(b) to evaporate, under negative pressure, slurry in the above step (3), and to add hydrogen sulfide gas recovered to the above step (3);(c) to reuse exhaust gas from the sulfurization reactor in the above step (3), and add it to the step (2); and(d) to subject the waste solution in the above step (3) and exhaust gas in the above step (4) to countercurrent contact, then to introduce the exhaust gas to the scrubber again and to charge waste solution from the scrubber into the sulfurization reactor in the step (3).
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
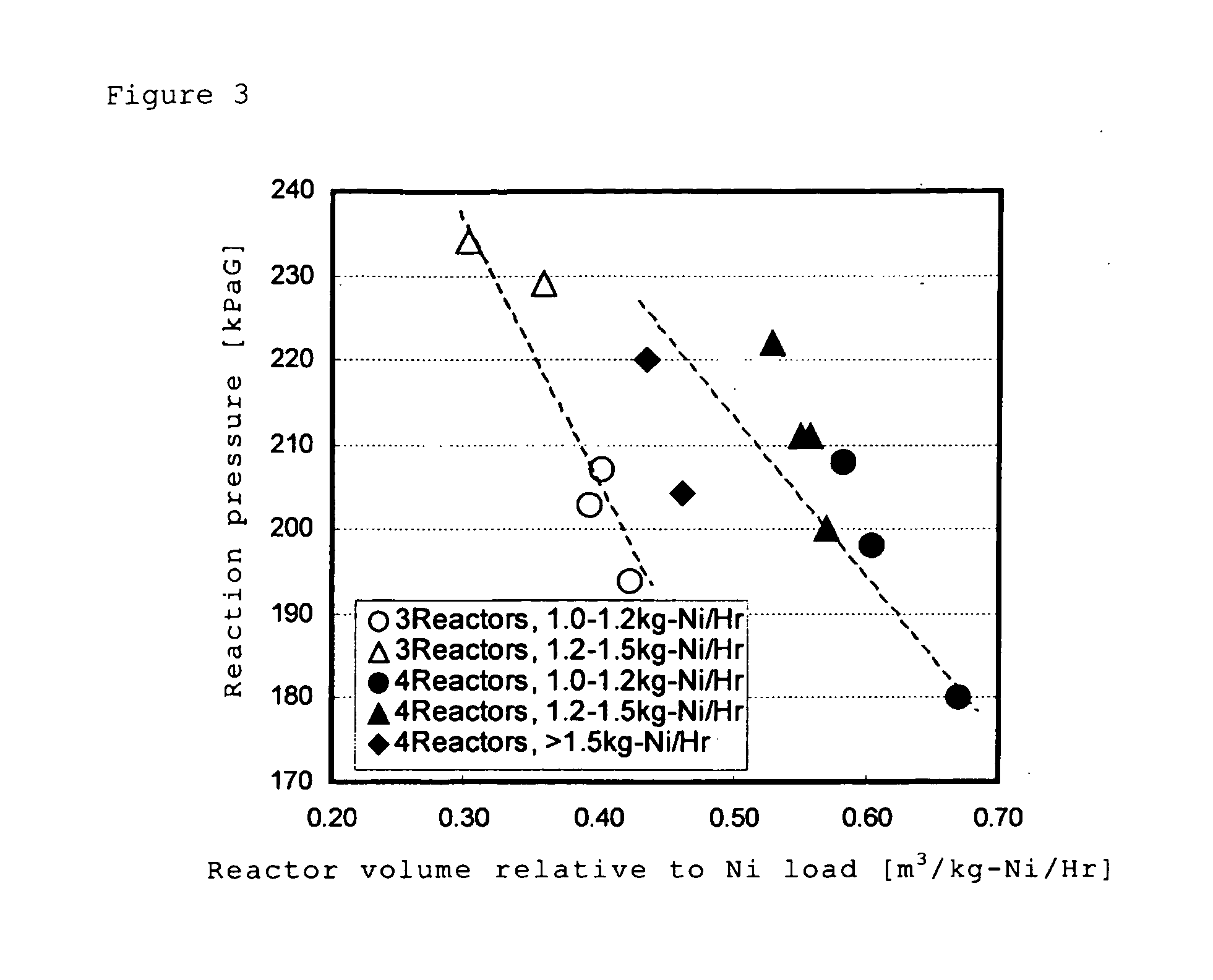
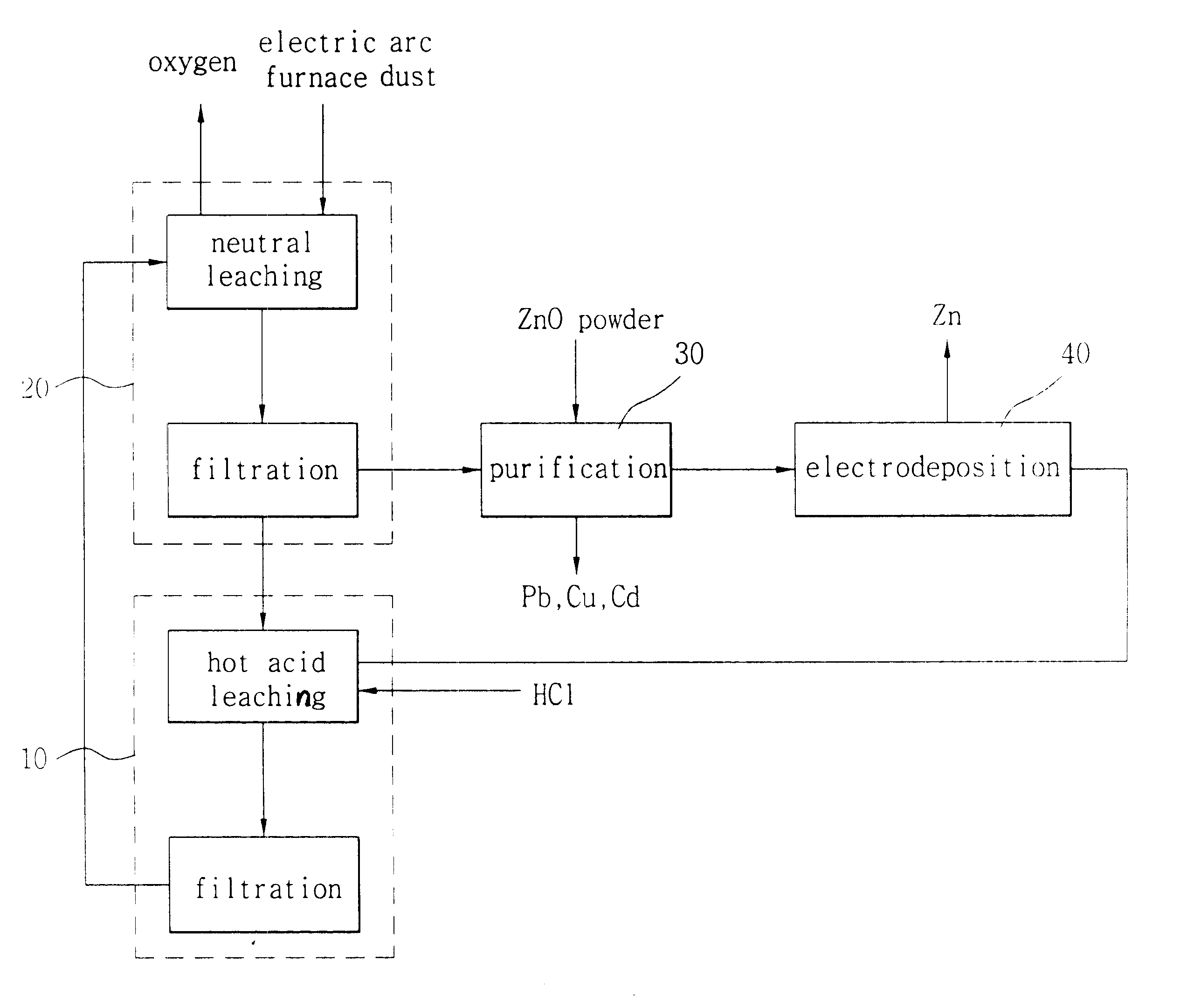
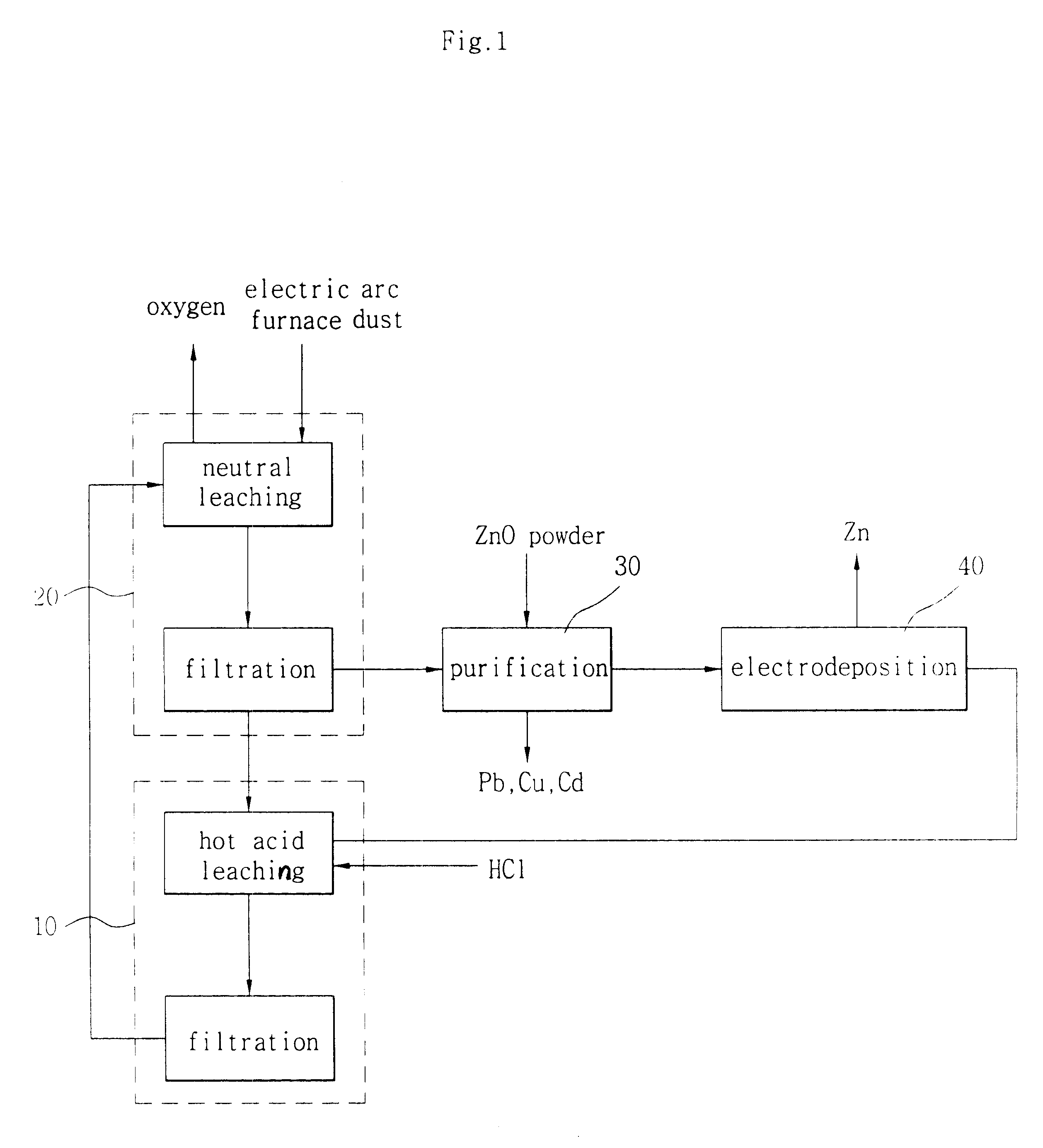
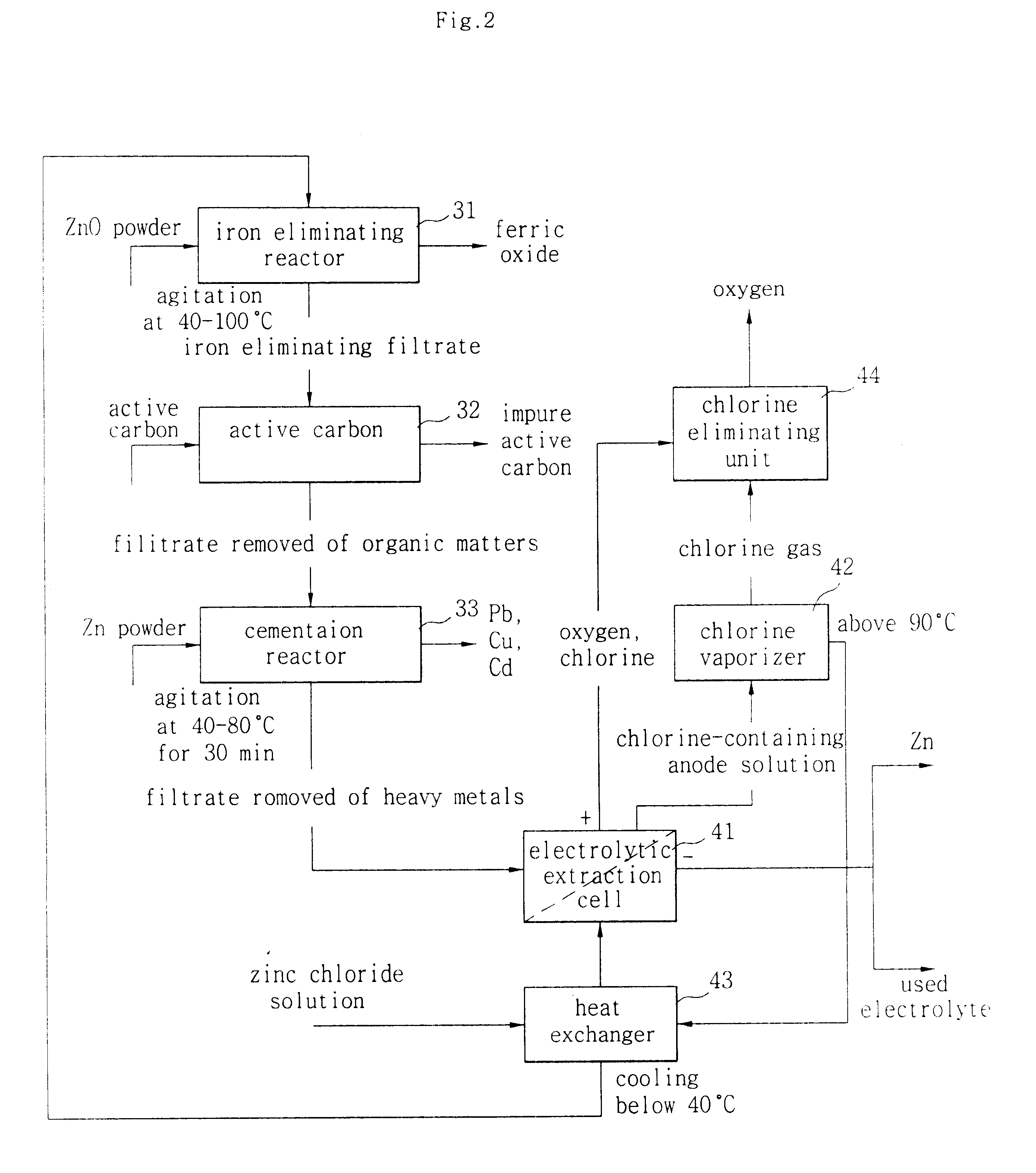
Hydrometallurgical method for recovery of zinc from electric arc furnace dust
InactiveUS6338748B1Current efficiency is deterioratedLow costPhotography auxillary processesSolvent extractionMembrane currentElectric arc furnace
The process uses hydrochloric acid solutions to extract zinc from electric arc furnace dusts containing zinc oxide and zinc ferrite. To selectively leach zinc and minimize iron dissolution by precipitating as FeO.OH and Fe2O3, hot acid leaching with the aqueous solution containing 37 g / l-74 g / l HCl and 104 g / l-270 g / l ZnCl2 is used. New dust is introduced to remove iron from the filtrate of the hot acid leaching. The zinc chloride solutions purified by activated carbon and metallic zinc powder is electrolysed in electrowinning cells which had cation exchange membrane to produce high purity zinc metal and to regenerate hydrochloric acid. Electrolysing an aqueous solution of zinc chloride with Zn concentration of 50-130 g / litre below 40° C. in a cell divided by cation exchange membrane, whereby coherent zinc is yielded at the cathode with high current efficiency of exceeding 90%. HCl is directly regenerated with a very small loss below 2% and low energy consumption below 5.0 kWh / kg-Zn during Zn-electrodeposition at a cathodic current density in the range of 300-2000 A / m2, and a membrane current density in the range of 750-2000 A / m2. The spent electrolyte with 1-2N HCl is used to leach the residue in the hot acid leaching vessel.
Owner:SANGWON ENC +1
Method for preparing inorganic pigments, resulting inorganic pigments, and apparatus therefor
PCT No. PCT / FR96 / 01202 Sec. 371 Date May 27, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date May 27, 1998 PCT Filed Jul. 30, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 06215 PCT Pub. Date Feb. 20, 1997A method for preparing inorganic pigments from steel mill dust, particularly electric steel mill dust, wherein (a) the dust is separated into a magnetic fraction and a non-magnetic fraction; (b) the non-magnetic fraction is subjected to a basic leaching reaction; (c) the resulting solid batch is rinsed until neutralized and then separated; (d) the resulting batch is calcined at 450-650 DEG C.; (e) the calcined batch is treated with sulfuric acid in the presence of a catalyst; (f) the inorganic pigments are recovered; and (g) the solutions from (c) and (e) are used to precipitate other pigments.
Owner:RECUPAC
Mercury reduction system and method in combustion flue gas using coal blending
ActiveUS20050036926A1Reduce mercury in gas emissionReduce gas emissionsGas treatmentUsing liquid separation agentCombustion systemSorbent
A method to reduce mercury in gas emissions from the combustion of low rank coal in a combustion system, said method including: combusting coal having a low chlorine content in the combustion system, wherein elemental mercury (Hg0) is released in the flue gas produced by the combustion of the low rank coal; releasing chlorine into the flue gas by combusting a coal having a high chlorine in the combustion system; reacting the elemental mercury and released chlorine in the flue gas to oxidize the mercury; adsorbing at least a portion of the oxidized mercury generated by the combustion of the coal with an adsorbent in the flue gas, and collecting the adsorbent with the oxidized mercury in a combustion waste treatment system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
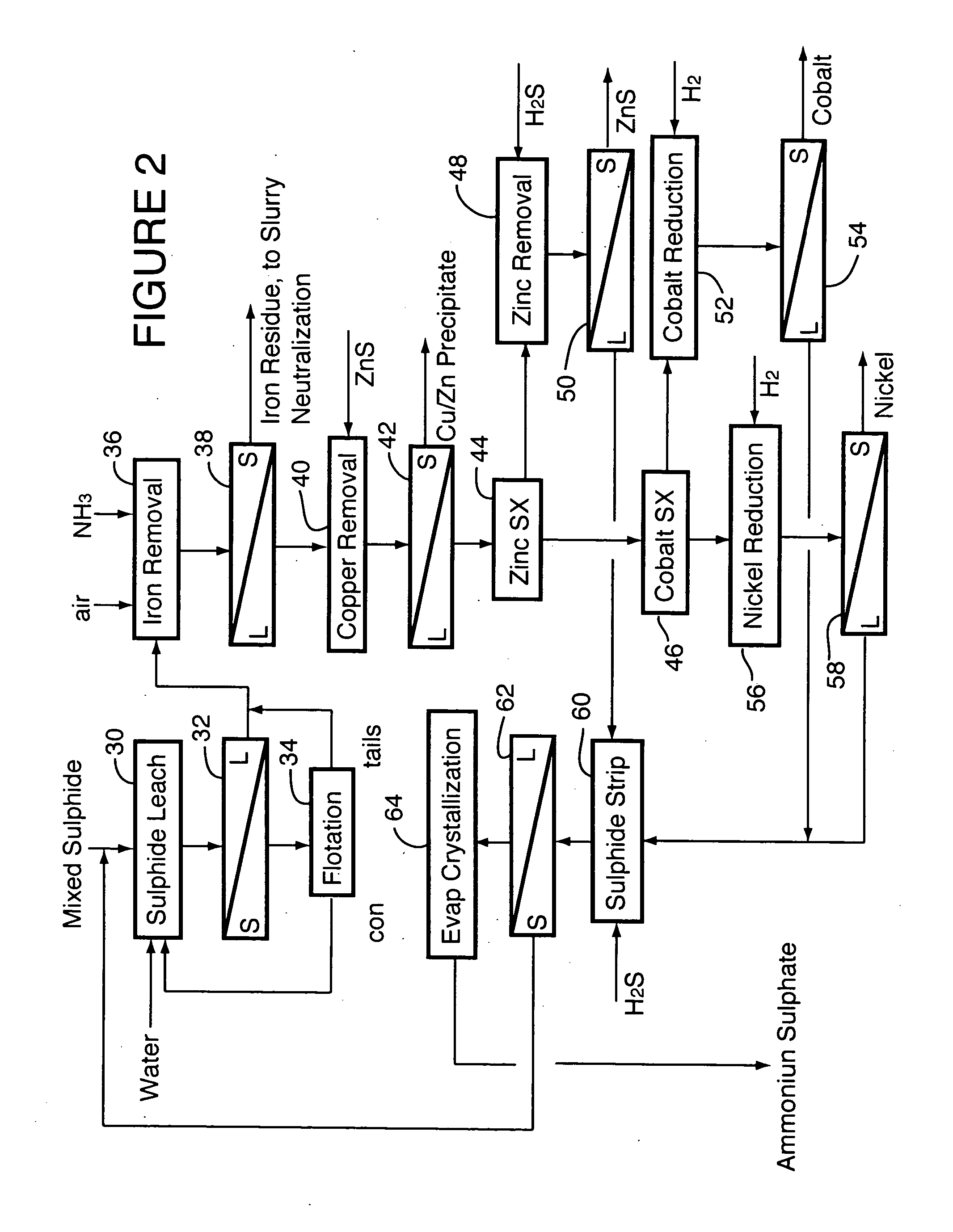
Recovery of nickel, cobalt, iron, silica, zinc and copper from laterite ore by sulfuric acid leaching
ActiveUS7387767B2Efficient separation and recoveryHigh purityCobalt sulfidesSolvent extractionFree solutionSlurry
A process for recovering nickel and cobalt values from nickel- and cobalt-containing laterite ores as an enriched mixed nickel and cobalt sulphide intermediate and for producing nickel and cobalt metal from the nickel and cobalt sulphide intermediate. The laterite ore is leached as a slurry in a pressure acid leach containing an excess of aqueous sulphuric acid at high pressure and temperature, excess free acid in the leach slurry is partially neutralized to a range of 5 to 10 g / L residual free H2SO4 and washed to yield a nickel- and cobalt-containing product liquor, the product liquor is subjected to a reductant to reduce any Cr(VI) in solution to Cr(III), the reduced product liquor is neutralized to precipitate ferric iron and silicon at a pH of about 3.5 to 4.0, and the neutralized and reduced product liquor is contacted with hydrogen sulphide gas to precipitate nickel and cobalt sulphides. The precipitated nickel and cobalt sulphides can be leached in a water slurry in a pressure oxidation leach, the leach solution subjected to iron hydrolysis and precipitation, the iron-free solution contacted with zinc sulphide to precipitate copper, the iron- and copper-free solution subjected to zinc and cobalt extraction by solvent extraction to produce a nickel raffinate, the nickel raffinate contacted with hydrogen gas to produce nickel powder and the cobalt strip solution from the solvent extraction step contacted with hydrogen gas to produce cobalt powder.
Owner:SHERRITT INC
Waste gas treatment process including removal of mercury
InactiveUS20060286017A1Lower levelNitrogen compoundsUsing liquid separation agentPERMANGANATE IONMercury vapour
A process for removing contaminants from a waste gas stream comprises treating the waste gas stream to remove at least one of SO2 and NOx and to obtain a lean stream having a reduced level of at least one of SO2 and NOx and, contacting the lean gas stream with a mercury absorbent solution comprising permanganate to remove mercury vapour and to obtain a mercury lean stream and a mercury rich absorbent solution. The mercury rich absorbent solution may be subsequently treated on a batch basis to remove precipitated manganese dioxide and obtain a solution containing mercury ions.
Owner:CANSOLV TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com