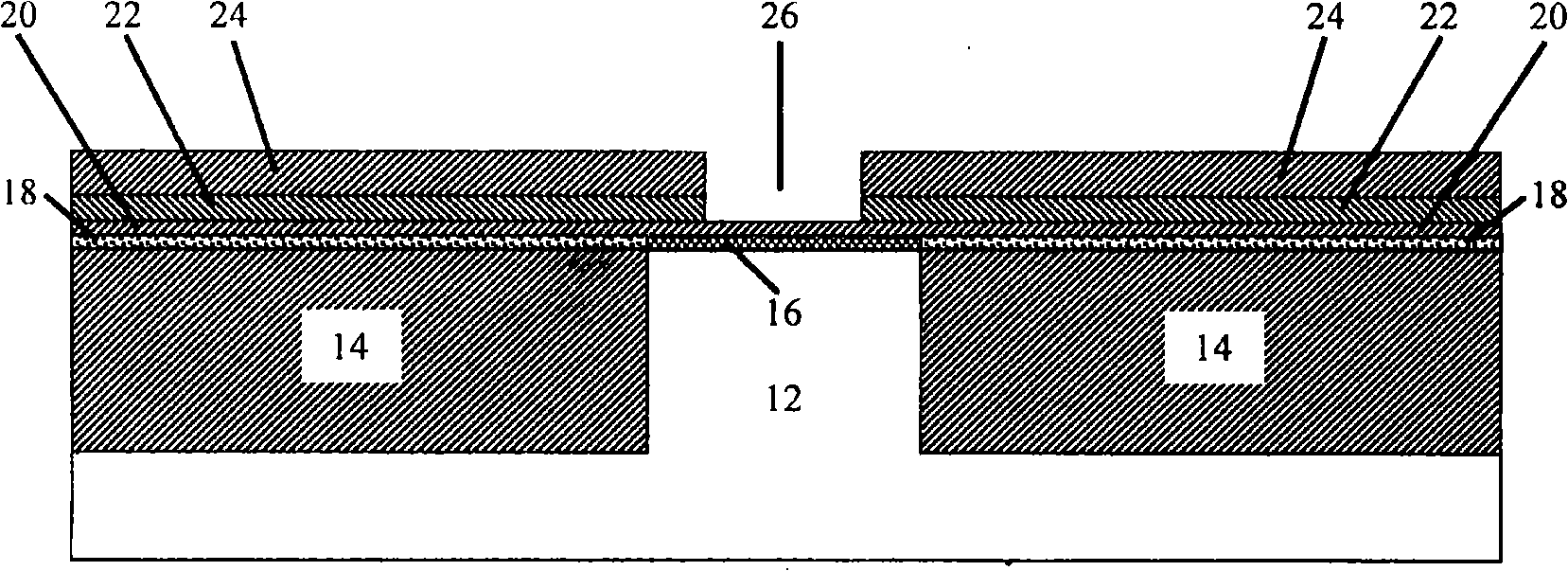
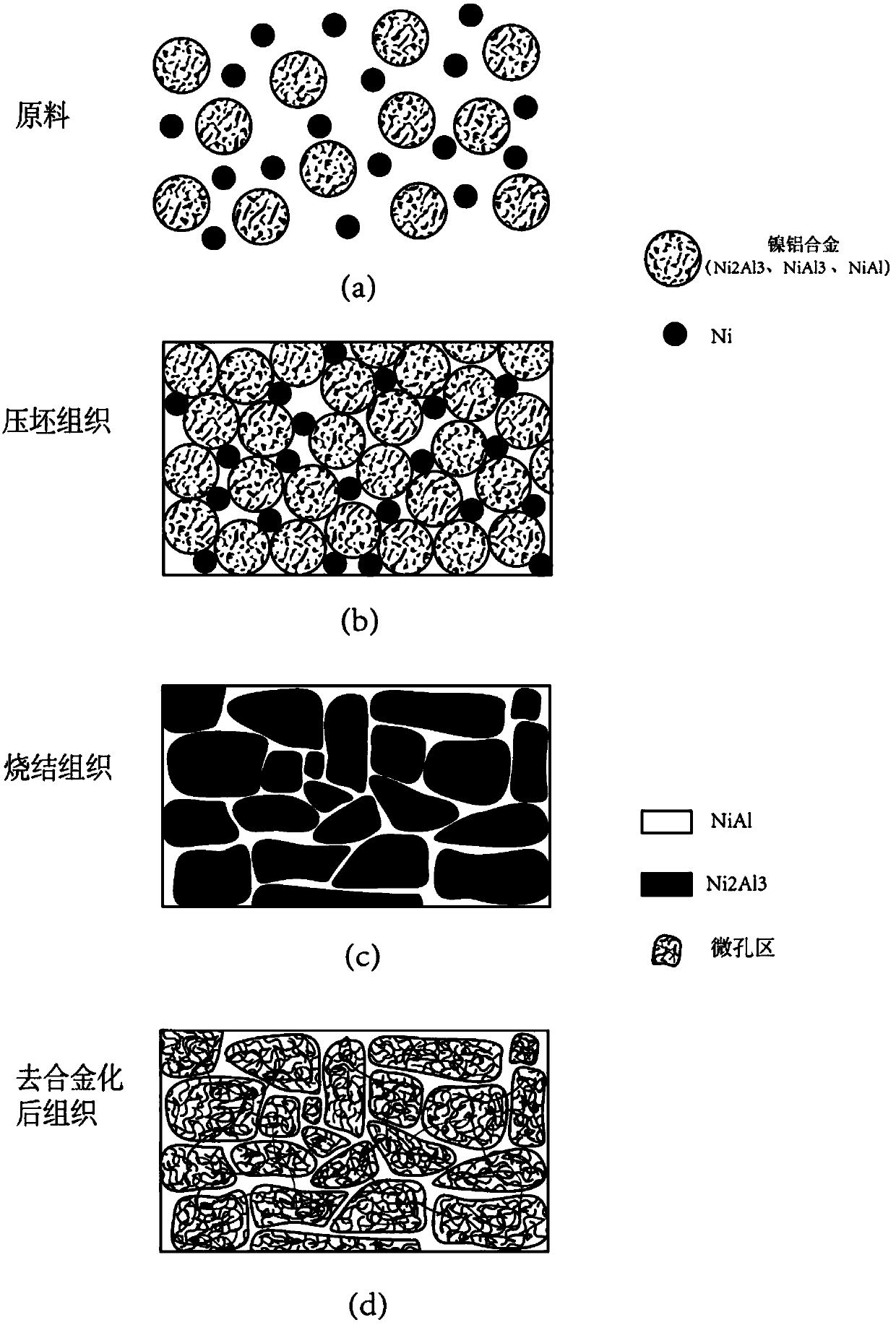
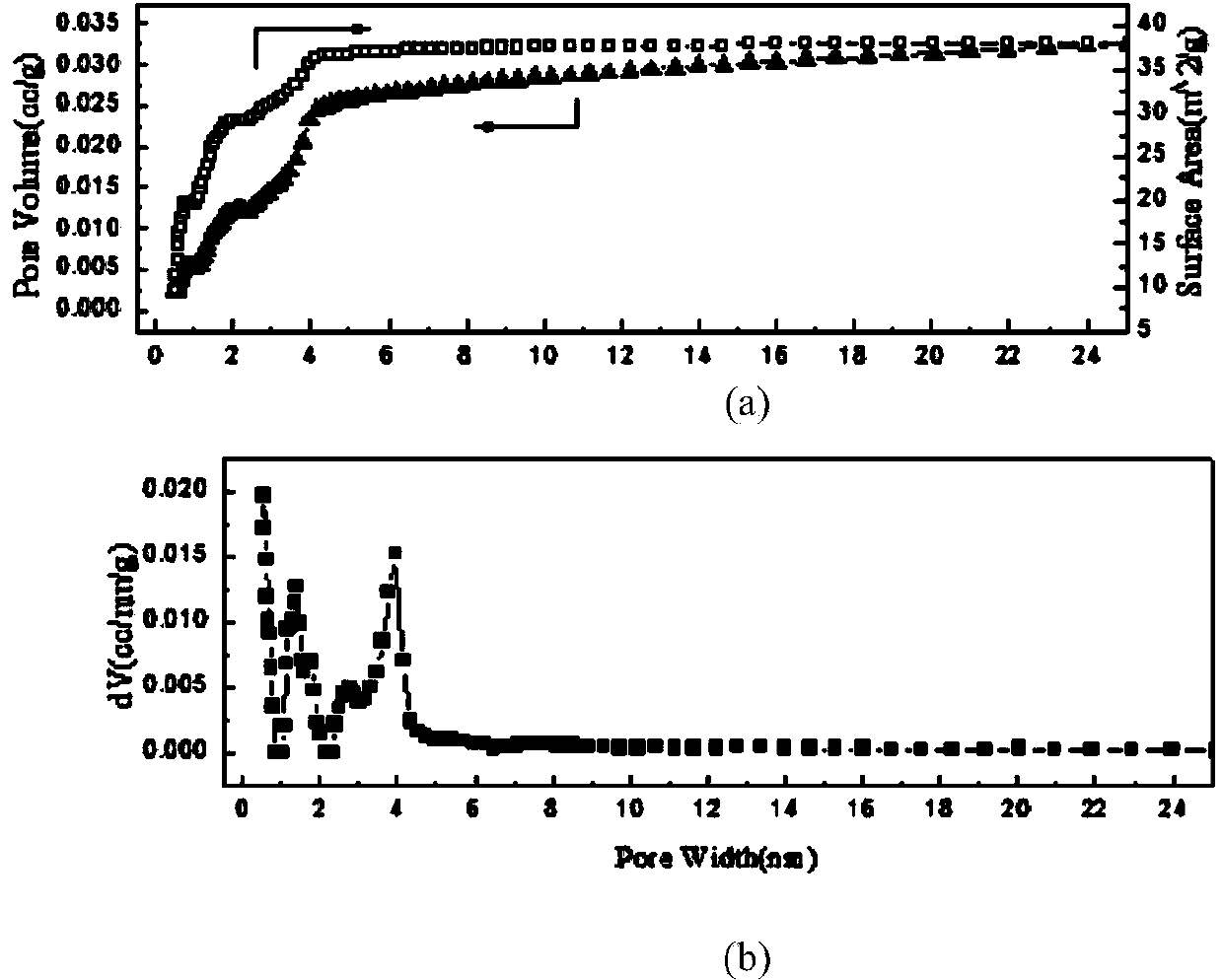
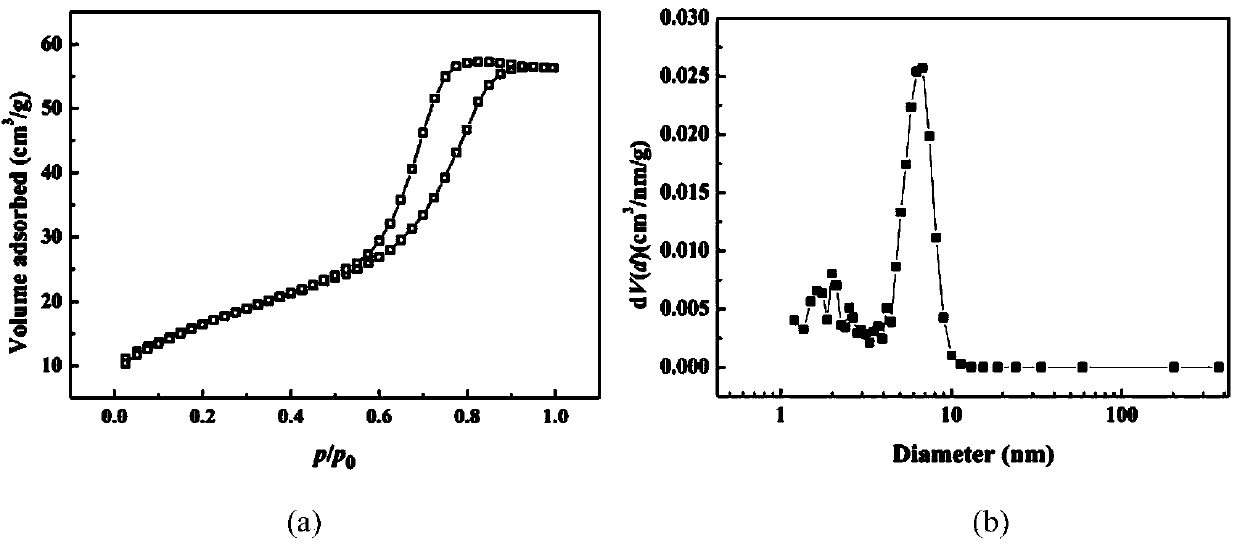
Patents
Literature
349 results about "Selective leaching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Selective leaching, also called dealloying, demetalification, parting and selective corrosion, is a corrosion type in some solid solution alloys, when in suitable conditions a component of the alloys is preferentially leached from the material. The less noble metal is removed from the alloy by a microscopic-scale galvanic corrosion mechanism. The most susceptible alloys are the ones containing metals with high distance between each other in the galvanic series, e.g. copper and zinc in brass. The elements most typically undergoing selective removal are zinc, aluminium, iron, cobalt, chromium, and others.
Method for recovering rare earth from rare earth-containing aluminum-silicon materials
ActiveCN101705380AAvoid enteringLess fixed investmentProcess efficiency improvementMolecular sieveSelective leaching
The invention relates to a method for recovering rare earth from rare earth-containing aluminum-silicon materials, which comprises the following steps: taking the rare earth-containing aluminum-silicon materials including rare earth-loaded molecular sieves, catalyst wastes, and the like as raw materials, conducting prioritized selective leaching by acid so as to lead the majority of the rare earth and a small amount of aluminum to be dissolved and separated from silicon and other impurities, leading the rare earth to form precipitates and be separated from the aluminum by adopting a double salt precipitation or oxalate precipitation method, and then recovering and purifying the rare earth. The method has the advantages of directly realizing the extraction of the rare earth from the aluminum-silicon materials including the molecular sieves and the like, with over 98% purity of the obtained rare earth, and avoiding impurities such as aluminum, silicon and the like entering the rare earth; and meanwhile, the technology also has the characteristics of little fixed investment, low production cost and easiness for realizing industrialized production.
Owner:GRIREM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Method for selectively recycling lithium from lithium iron phosphate waste
ActiveCN106910959AEfficient leachingLow costWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementHypochloriteSelective leaching
The invention discloses a method for selectively recycling lithium from lithium iron phosphate waste through a direct oxidization method. The method is characterized by comprising the steps that the lithium iron phosphate waste is added into a water solution, meanwhile, an oxidizing agent is added, stirring is carried out, lithium iron phosphate and the oxidizing agent react to generate iron phosphate, lithium ions enter the solution, and therefore a pure lithium-containing solution and iron phosphate solids are obtained. The adopted oxidizing agent comprises one or a mixture of persulfate, ozone, oxygen, pypocholoride and hydrogen peroxide. The molar weight of the oxidizing agent is 0.6-20 times that of lithium iron phosphate. The lithium-containing solution can be directly used for preparing a high-purity lithium product. According to the method, efficient and selective leaching of lithium can be achieved simply by adding a certain amount of oxidizing agent, and the method is mild in reaction condition, short in process and simple in equipment.
Owner:GUANGDONG GUANGHUA SCI TECH
Preparation method for small silicon-based nano hollow array with orderly heights
InactiveCN102173376ASmall sizeCycle controllableDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingMagnetic storagePolystyrene
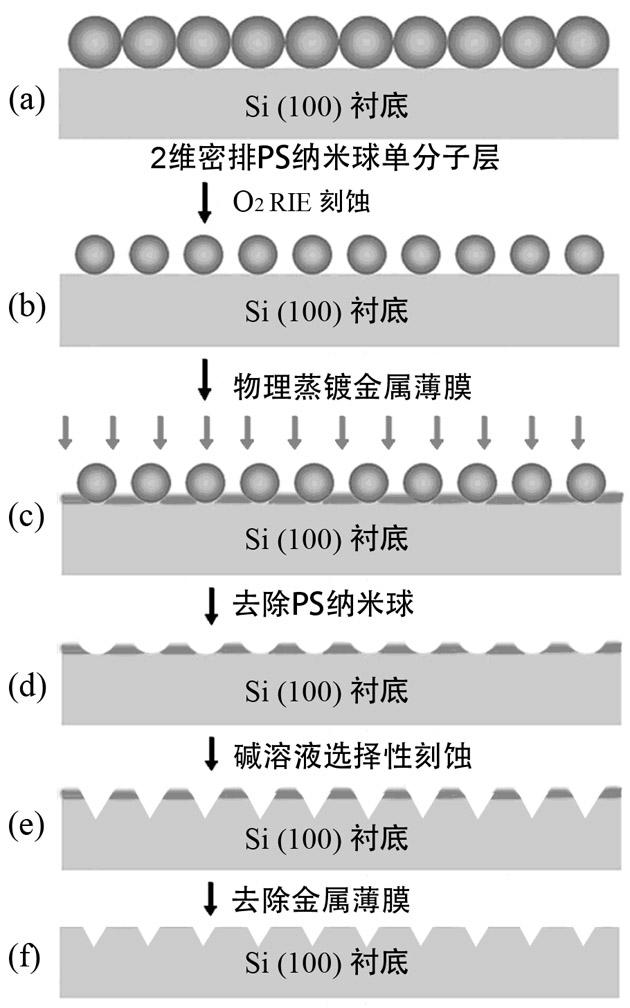
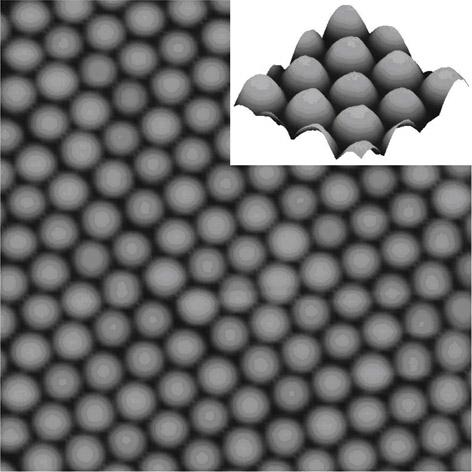
The invention relates to a preparation method for a small silicon-based nano hollow array with orderly heights, belonging to the technical field of nano-structure preparation. The preparation method employs large-diameter polystyrene nano-spheres which are self-mounted into a single-layer nano-sphere film serving as masks on a Si substrate. After going through multiple technical procedures such as reaction ion lithography, direct current sputtering metal films, selective corrosion and the like, the mask is converted into a small inverted-pyramidal nano-hollow array, which is a two-dimensionalhexagonal dot array. The cycle of the nano-hollow arrays is determined by the diameters initially selected for the polystyrene nano-spheres. The invention is likely to be used in fields of growth of controllable quantum structures, photonic crystal manufacturing, quantum logic operation, magnetic storage media, etc.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Selective leaching agent and recycling method for metal components in positive electrode material
ActiveCN107230811ASelective leaching achievedImprove leaching efficiencyWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingSelective leachingLithium carbonate
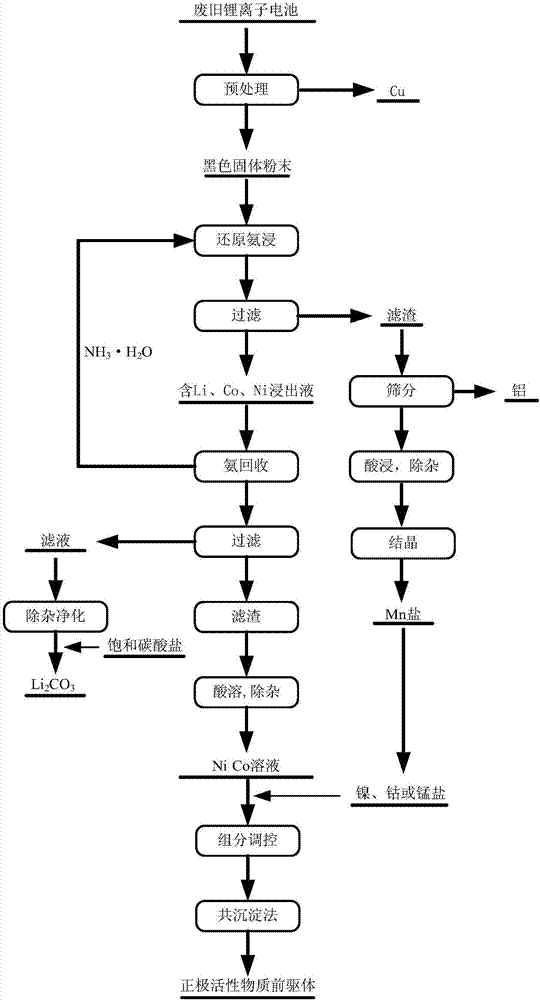
The invention provides a selective leaching agent and recovery method for metal components in positive electrode materials. The leaching agent is a solution containing a reducing agent, ammonium salt and ammonia water, and the reducing agent is a reducing substance under alkaline conditions. , the concentration of ammonia water in the leaching agent is 0-10 mol / L, the concentration of ammonium ion is 0-8 mol / L, and the concentration of reducing agent is 0-2 mol / L. The leaching agent provided by the invention has a wide range of sources, cheap raw materials, high leaching selectivity and leaching rate (up to 90%), and the prepared lithium carbonate has a purity of 99%, which is used to reclaim Li, Co and Ni in positive electrode materials. The introduction of hetero ions in the existing acid leaching process is avoided, the separation and purification process is simplified, the recycling of the leaching agent is realized, the treatment cost is reduced, and the method is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
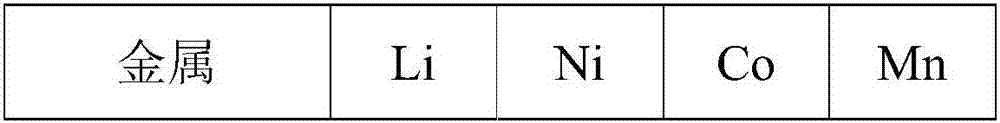
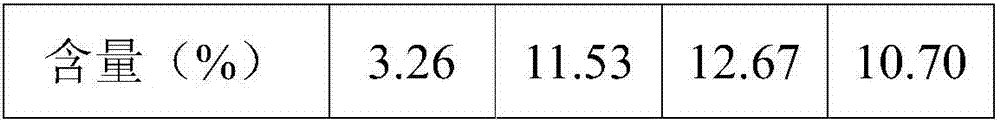
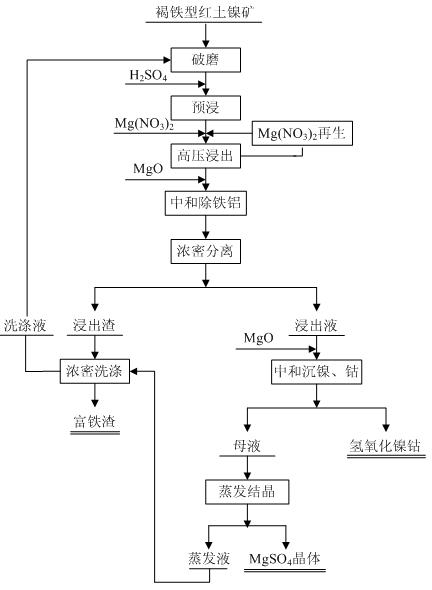
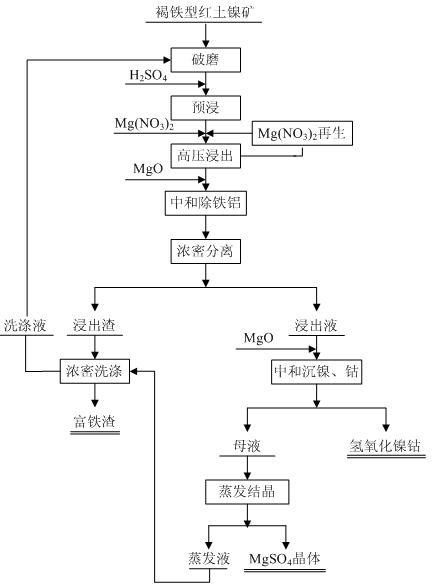
Method for leaching limonitic laterite nickel ore
InactiveCN102534206AReduce consumptionEasy to operate and controlProcess efficiency improvementSlagSlurry
The invention discloses a method for leaching limonitic laterite nickel ore and relates to a process method for recovering nickel, cobalt and iron through treatment of laterite nickel ore by wet process. The method is characterized in that the technical process comprises: (1) grinding raw limonitic laterite nickel ore into fine powder, making slurry, adding sulfuric acid, heating the slurry and leaching the slurry; (2) adding Mg(NO3)2 into the pre-leached slurry, heating with stirring, pressurizing the slurry and leaching the slurry; 3) at the end of leaching, neutralizing the slurry, removing iron and aluminum from the slurry, and separating to obtain a leaching solution and a leaching residue; and 4) washing the leaching residue to obtain washing liquid and iron-enriched slag, neutralizing the leaching solution, precipitating nickel and cobalt, obtaining nickel and cobalt hydroxides, evaporating a mother solution from which nickel and cobalt are separated to crystallize magnesium sulfate and comprehensively recovering magnesium sulfate. The method realizes the high-efficiency selective leaching of nickel and cobalt, the leaching rate reaches over 90 percent, the iron leaching rate is lower than 0.8 percent and iron-enriched slag with an iron content of over 55 percent is obtained.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
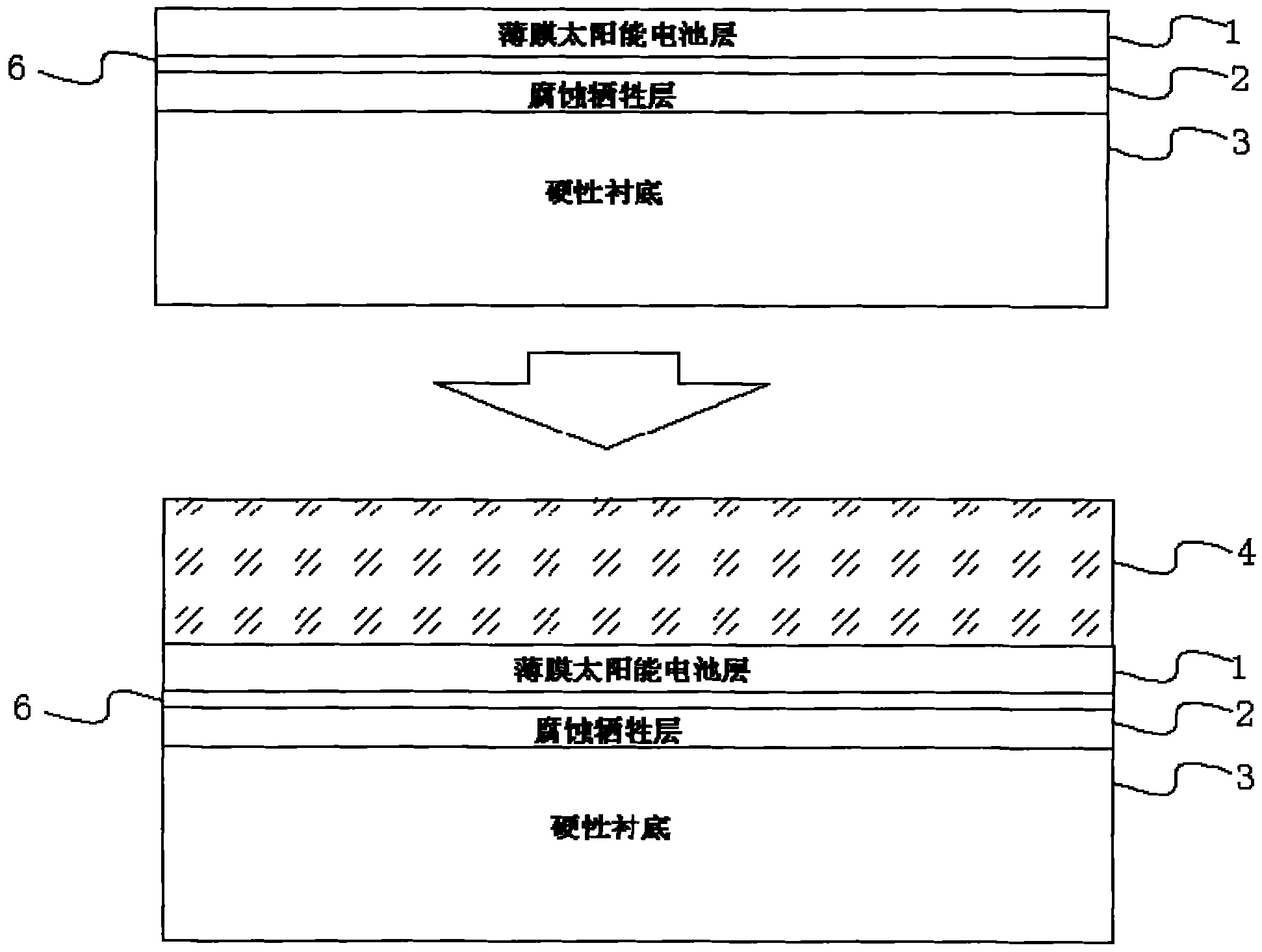
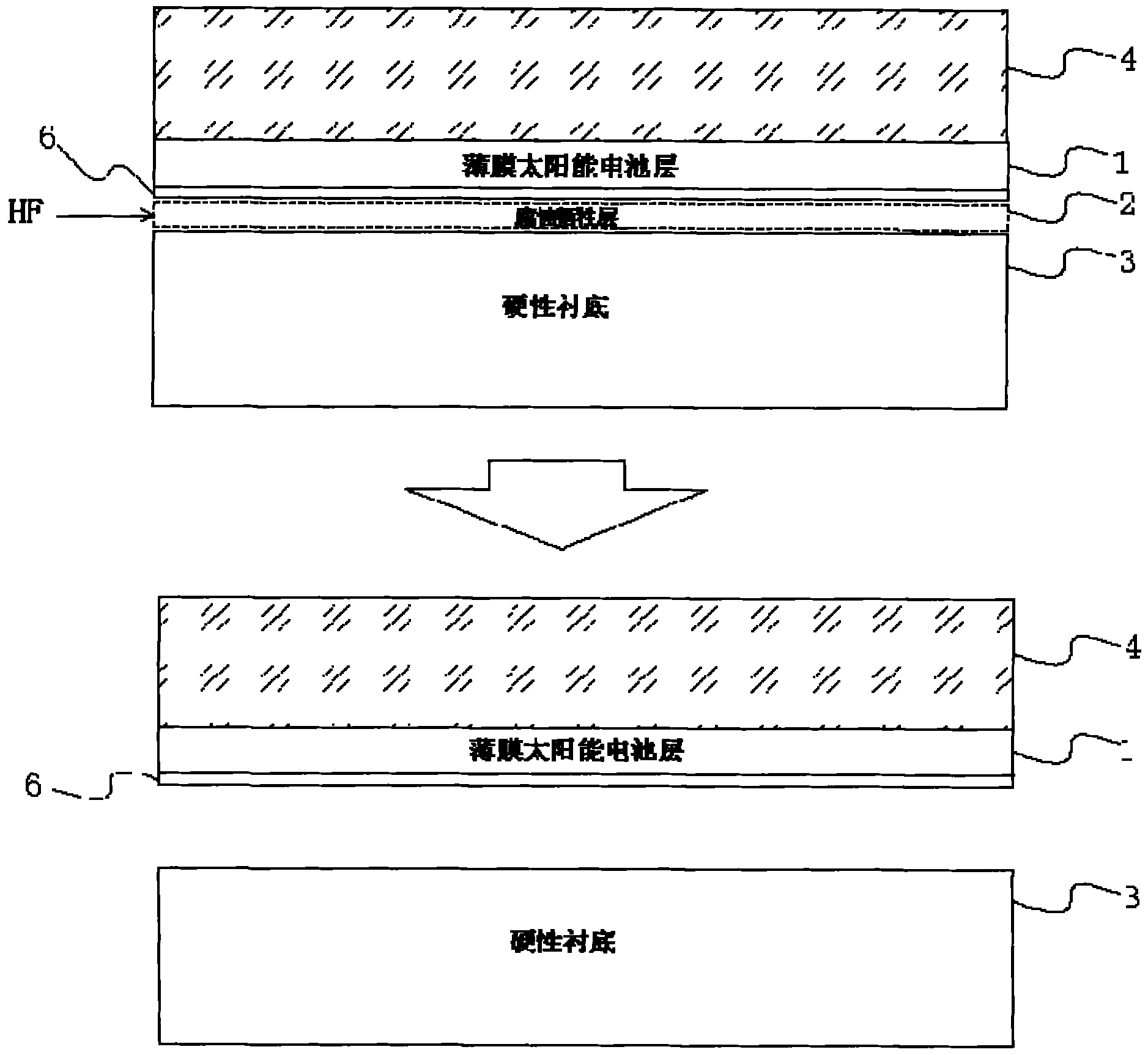
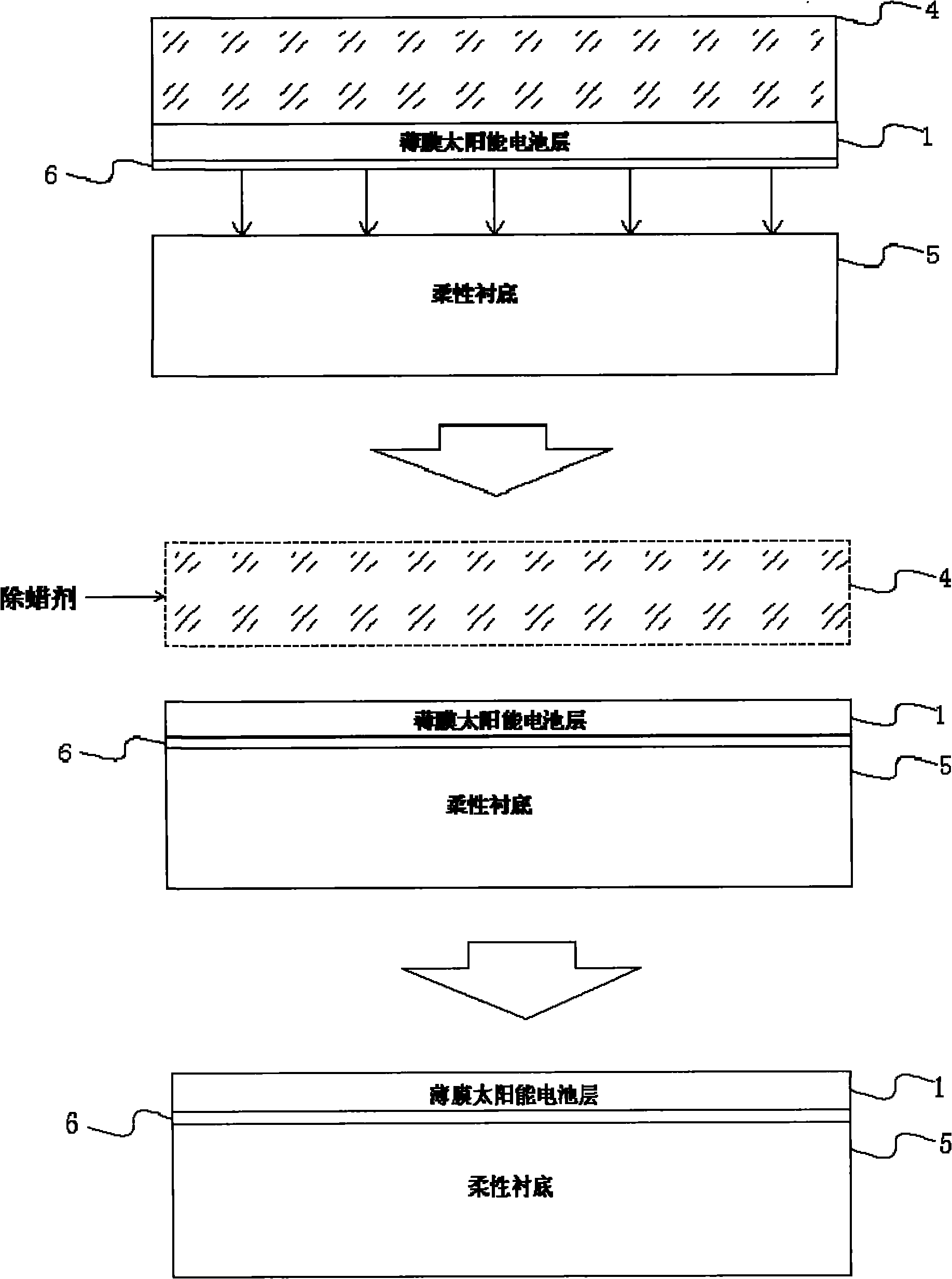
Stripping transfer method of substrate of thin film solar cell
InactiveCN102157623AImprove flexibilityLight weightFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesWaxSelective leaching
The invention relates to a stripping transfer technology of a substrate of a thin film solar cell, particularly comprising the following steps of: firstly depositing and growing a corrosion sacrifice layer on a rigid substrate; then depositing and growing a solar cell layer on the completely grown corrosion sacrifice layer; heating black waxes for thawing on the solar cell layer, and naturally condensing to normal temperature to fix on the surface of the solar cell layer to form a support layer; placing the solar cell layer with the support layer in selective corrosive liquid to soak at the normal temperature for 6-8 hours so that the corrosion sacrifice layer positioned between the solar cell layer and the rigid substrate is completely corroded to be eliminated; transferring and fixing the solar cell layer stripped from the rigid substrate to a flexible substrate under the action of the support layer; and finally dissolving to eliminate the support layer fixed on the surface of the solar cell layer by adopting a dissolving agent. The invention realizes the lightweight and the flexibleness of the thin film solar cell, thereby enlarging the application range of the thin film solar cell.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Method for preparing crystalline silicon nanometer and micrometer composite texture surface
InactiveCN102610692AImprove light trappingPromote absorptionFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesSelective leachingScale structure
The invention relates to a method for preparing a crystalline silicon nanometer and micrometer composite texture surface. The method is technically characterized by comprising carrying out cleaning and texture surface making for a crystalline silicon wafer and forming a micrometer-scale texture surface; then uniformly covering a layer of discontinuous nanometer-scale precious metal particles on the surface of the silicon wafer; selectively corroding the surface of the silicon wafer by the aid of chemical corrosive liquid, and forming a nanometer-scale texture surface; and finally cleaning and removing the precious metal particles by the aid of chemical liquor. The composite texture surface prepared by the method has a micrometer-scale structure and a nanometer-scale structure, the structure of the texture surface is finer, a light trapping effect of the surface of the silicon wafer is greatly improved, short-circuit current of a battery can be effectively increased, and accordingly photoelectric conversion efficiency of the battery is enhanced.
Owner:REALFORCE POWER
Self-alignment elevated external base area or heterojunction bipolar transistor and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101359682AHigh speedHigh frequencyTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSelective leachingMedia layer
The invention discloses a self-aligning bipolar transistor with an uplifted extrinsic base region or a heterojunction bipolar transistor and a fabrication method thereof, belonging to the technical field of semiconductor device fabrication. Firstly, a plurality of medium layers are deposited on a base; an emitter region window is formed through etching, then a medium inner wall is formed in the window; the medium layers (a plurality of) are selectively eroded on the basis of forming emitter region material through deposition or growing and etching, and then an uplifted extrinsic base region is formed through selective epitaxy method at the place vacated by the medium layers which are selectively eroded; and self-alignment of the uplifted extrinsic base region and the emitter region is realized due to the isolation action of the medium inner wall in the emitter region window, thus effectively reducing the base resistance of the device and thereby improving the speed, the frequency and the noise performance of the device.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Preparation method of high-strength nano-porous nickel film
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-strength nano-porous nickel film, and belongs to the technical field of a nano-porous metal film material, in particular discloses a method for preparing a high-strength nano-porous metal film material combining a micron-sized reinforcing framework and nano-sized pores through mixing alloy and metal powder, implementing powder metallurgy to obtain an alloy sheet, and further dealloying the sintered alloy sheet. The preparation method, through preparing a film precursor by powder metallurgy and selective corrosion in junction with dealloying, can increase the number of pores, and simultaneously keep high strength; aperture of the nano-porous metal film is adjustable from 0.5nm to 100nm when controlling various reaction conditions and parameters. The entire process, which is implemented in a stable environment, is safe, reliable, pollution-free, simple, low in cost and up to industrial demand, so that the prepared nano-porous metal film material is applicable to such aspects as biological medicine, organic synthesis, organic solvent micro and nano-filtration, catalysis and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
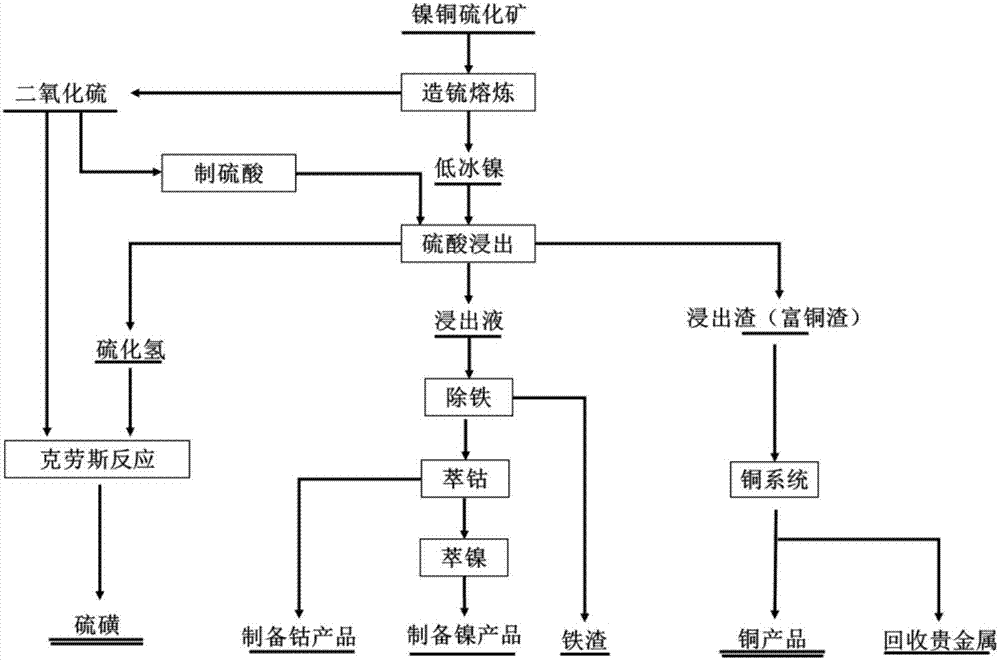
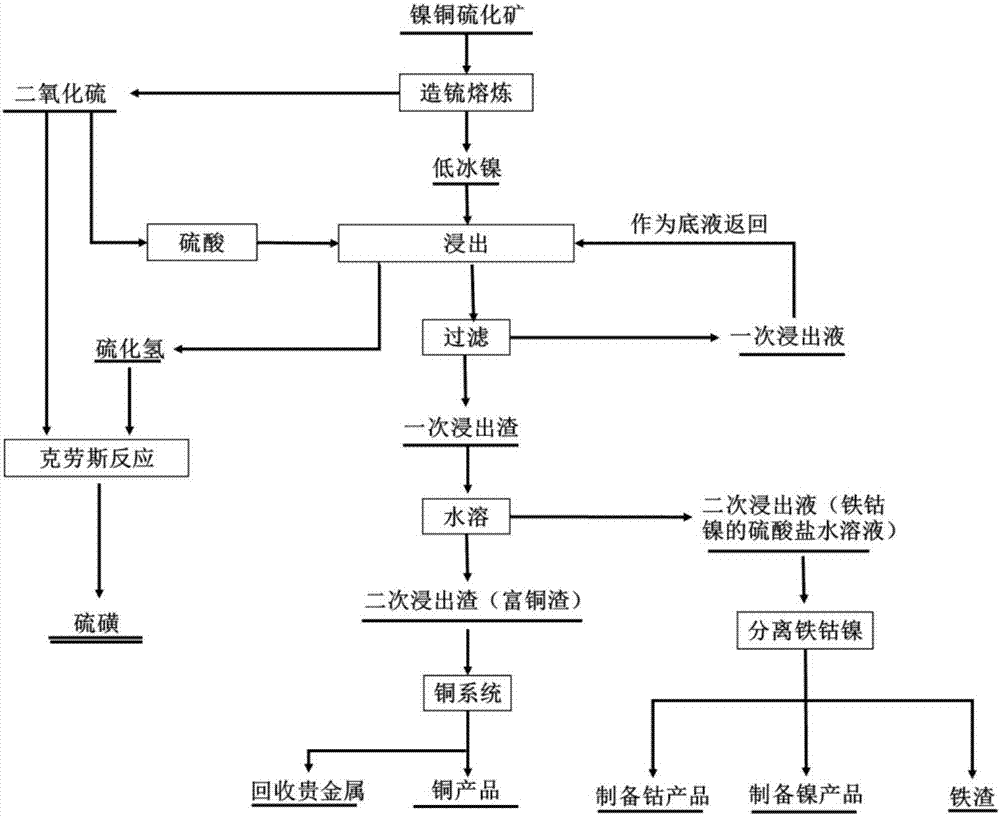
Method for comprehensively utilizing copper-nickel sulfide ores and system thereof
ActiveCN107058730AAvoid lostEfficient recyclingProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionSelective leaching
The invention provides a method for comprehensively utilizing copper-nickel sulfide ores and a system thereof. The method comprises the steps that (1), low nickel mattes obtained by matte smelting of the copper-nickel sulfide ores is subjected to normal pressure selective leaching directly through sulfuric acid, and hydrogen sulfide gas, leaching liquor and leaching residues are collected separately, wherein the temperature of normal pressure selective leaching is 25-80 DEG C; and (2), the leaching liquor in the step (1) is subjected to iron removal, iron-removed liquor and iron removal residues are collected separately, the iron-removed liquor is used for extracting of nickel and cobalt, the iron removal residues are used for iron making, and / or the leaching residues in the step (1) are sent to a copper smelting system to be smelted to obtain copper and precious metals. According to the method for the comprehensively utilizing the copper-nickel sulfide ores, deep separation of the nickel and the copper can be achieved, the recovery rates of the nickel, the copper, the cobalt and the precious metals are high, and high pure sulfur is output, so that storage is facilitated; and the process is simple, short in procedure, less in energy consumption and low in cost, and large-scale industrial production is easy.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Process for preparing ordered porous aluminum oxide thin film
InactiveCN101104944AHole spacing controllableReduce the possibility of breakdownAnodisationLow voltageAluminum substrate
The invention provides a preparation method in the field of material technology, specifically a preparation method of ordered porous aluminum oxide film. The preparation method comprises: firstly, electrolytically polishing an aluminum sheet; then, pre-oxidizing for a certain period of time under a low voltage and raising the oxidation voltage to a predetermined value and oxidizing for a certain period of time; and finally, selectively eroding the aluminum substrate to facilitate the observation of orderly structure of the bottom of aluminum oxide film. By the pre-oxidation under low voltage and the addition of ethanol in oxalic acid electrolyte, the oxidation under high voltage can be performed stably without breakdown under enlarged operational conditions. The method can produce highly-ordered porous aluminum oxide film within an extremely-short oxidation period and can control the pore distance in a range from 300nm to 360nm. The inventive method is simple and efficient, and promotes the application of porous aluminum oxide template in the fields of industry and nano material synthesis.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
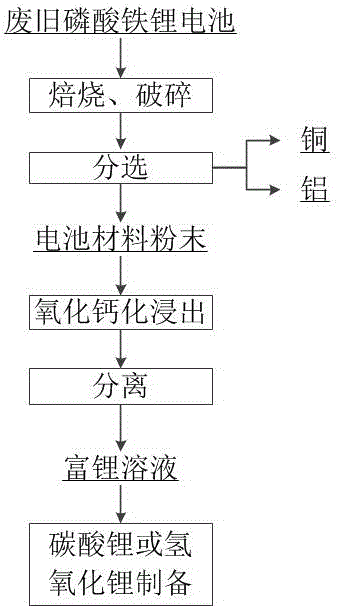
Method for recovering lithium in waste and old lithium iron phosphate batteries
ActiveCN106848472AHigh purityImprove recycling efficiencyWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingWater insolubleLithium hydroxide
The invention provides a method for efficiently recovering lithium in waste and old lithium iron phosphate batteries. The method comprises that waste and old lithium iron phosphate batteries are roasted and sorted to form lithium-containing positive pole powder, lithium-containing positive pole powder and a calcium-containing alkaline solution undergo a reaction under conditions of oxidation so that iron and phosphate radical are converted into a water-insoluble compound and lithium is converted into water soluble lithium hydroxide, and the reaction products are filtered so that a lithium hydroxide solution is obtained and can be used for further preparation of lithium hydroxide or lithium carbonate products. The method replaces the conventional wet acid leaching method in waste and old lithium iron phosphate battery recovery and is free of a strong acid so that production of a large amount of high-salt waste water is avoided. The method realizes selective leaching of lithium, prevents iron impurities from entering the leaching liquid from the source, can produce a high-purity lithium product, has simple processes, utilizes chemical agents having wide sources, has simple process conditions, can prepare a high-purity lithium product through a one-step method, greatly improves recovery efficiency of waste and old lithium iron phosphate batteries and has a good industrial application prospect.
Owner:SINO SCI PROCESS BEIJING SCI&TECH CO LTD
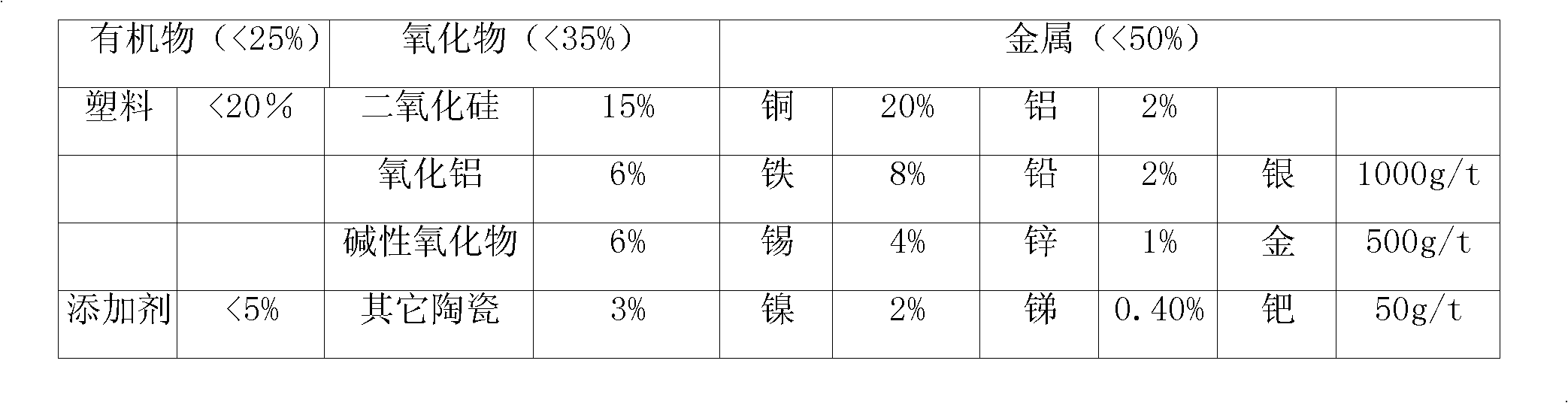
Method for extracting valuable metals from electronic waste
InactiveCN101575715AAdaptableMinor metal recoveryPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionSelective leaching
The invention discloses a method for extracting valuable metals from electronic waste. The method comprises the following concrete steps: smashing; oxidant ammoniac leaching; separating organic components; purifying leaching solution and electrodepositing to obtain the final products of organic granules, gold / silver / palladium powder and cathode copper, more concretely, the method comprises the following steps: carrying out the selective leaching on the smashed electronic waste by an oxidant ammoniac system; separating the organic granules on the basis of the characteristic that the organic components in the smashed electronic waste float on the surface layer of the leaching solution, for the density of the organic components is lower, whereas the valuable metals, such as Au, Ag, Pd, Cu, Ni, Cd, Zn and Pb, enter the solution; then, extracting the valuable metals of Au, Ag and Pd from the leaching solution by replacement; and finally obtaining the electrodeposit copper by the electro-deposition method, and extracting the metals of Ni, Pb, Zn and Cd from the electrolyte by the open-circuit method after the enrichment of the electrolyte. The invention has the outstanding advantages of high material adaptability, high metal recovery rate and low environmental pollution, and achieves the balance between the environmental benefit and the economic benefit.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Processing method of GaN basis light emitting diode surface coarsing
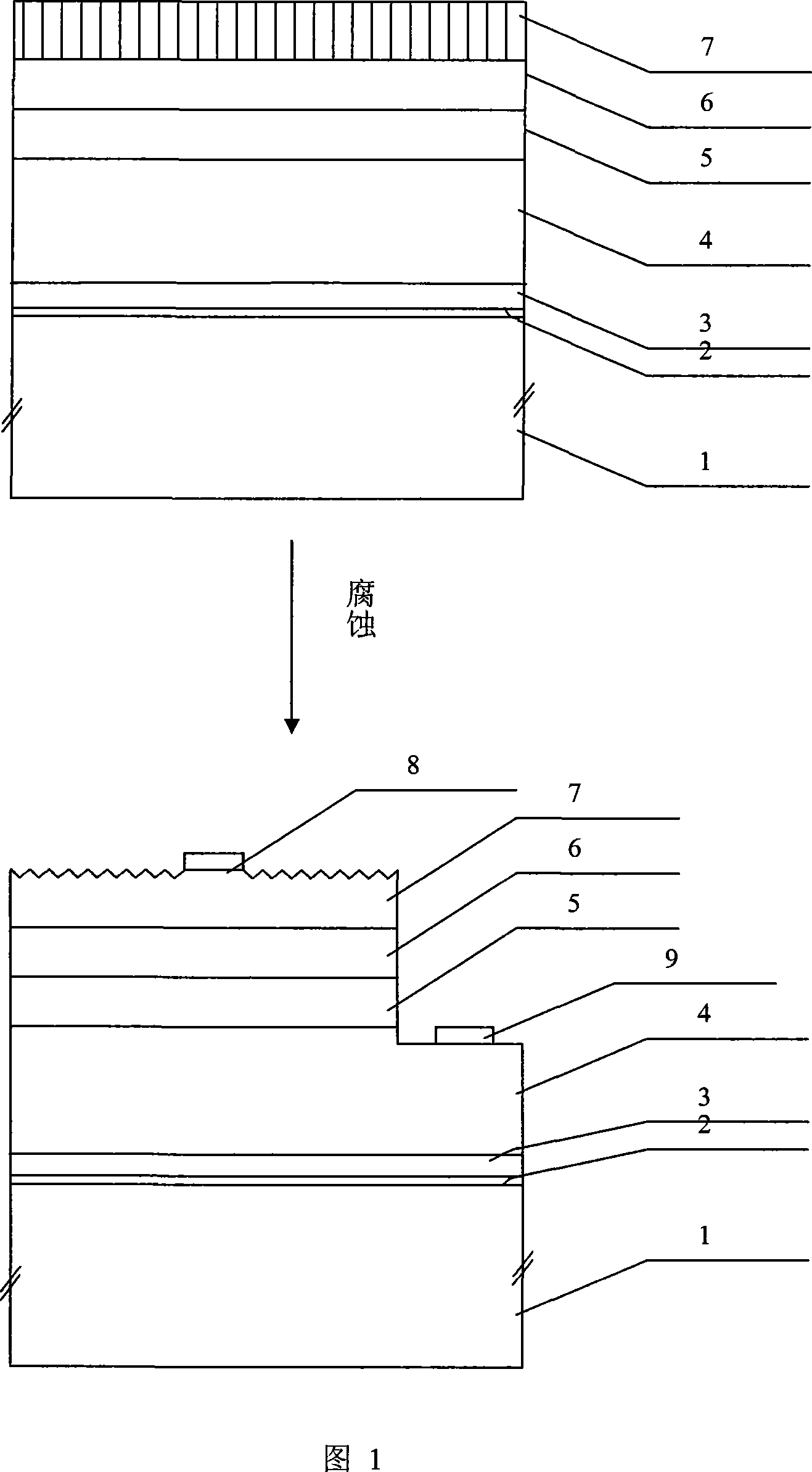
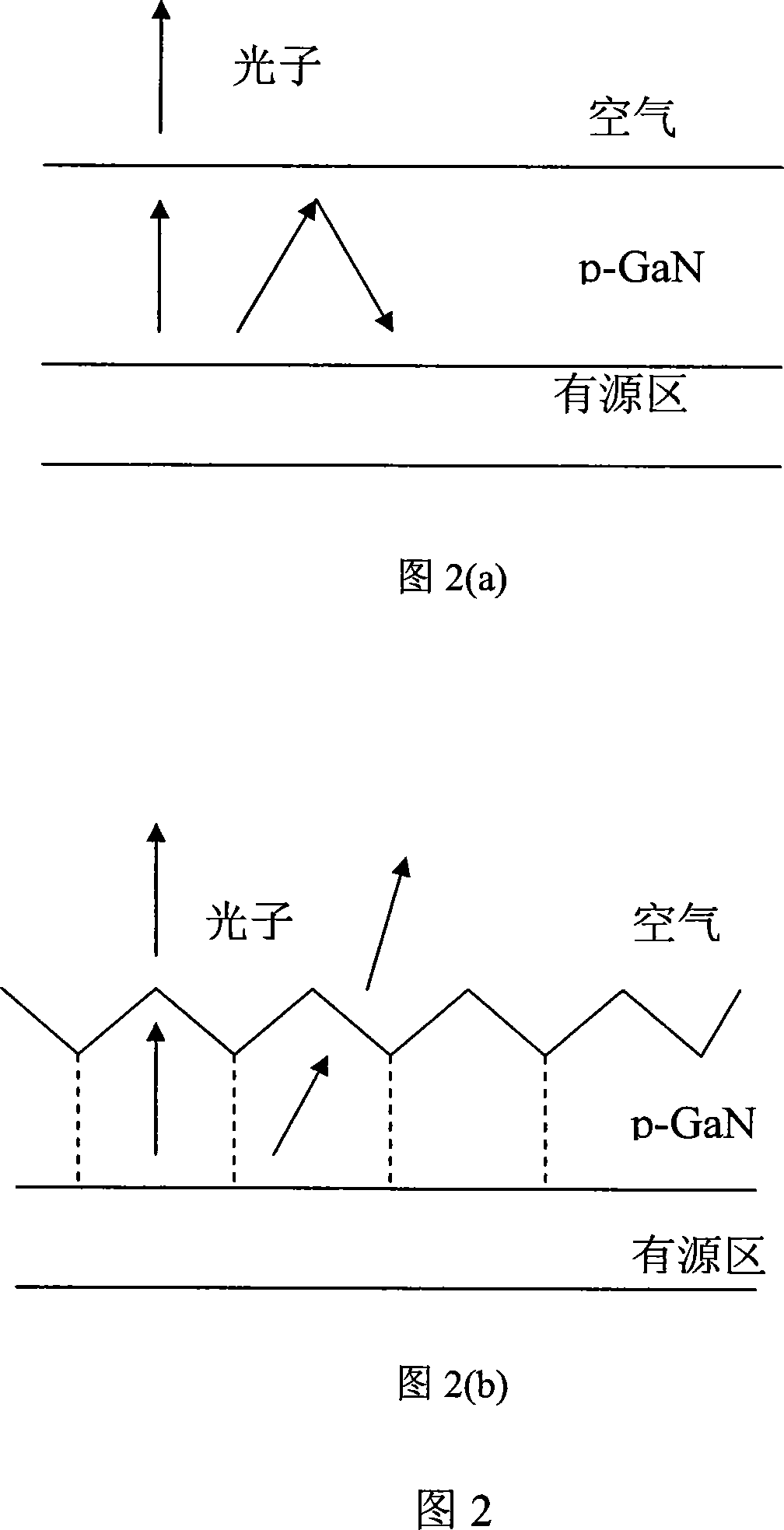
InactiveCN101226977AIncrease chance of surface intersectionIncrease chance of intersectionSemiconductor devicesManufacturing technologySelective leaching
The invention discloses a processing method of coarsening the surface of a GaN based lighting diode, which relates to the technical field of preparing semiconductor optoelectronic devices. The aims are that under the state that other photoelectric characteristics of the devices are not affected, and the light removal rate is improved using the method. The implementation procedure of the method are that V1ing, a P type GaN cap layer in an extension wafer of the GaN based lighting diode grows in a low temperature of 600-750 DEG C, the dislocation of the cap layer is spread along a direction which is perpendicular to an extensional surface, the bend does not produce, thereby increasing the dislocation density of the cap layer and not affecting the photoelectric characteristics of the devices. V2ing, the extension wafer of the lighting diode is eroded by melted KOH in a given corrosion temperature and time, the high-density dislocation which is perpendicular to the extensional surface in the P type GaN layer is optionally eroded, and dense corrosion pits whose shapes are regular are formed on the surface of the device. The processing method is capable of improving the luminous efficiency of the device.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method and system for recovering main associated elements from copper-nickel sulfide ore
ActiveCN107012324AAchieve deep separationImprove efficiencyProcess efficiency improvementSlagNickel sulfide
The invention provides a method and system for recovering main associated elements from copper-nickel sulfide ore. The method comprises the following steps: 1, continuously adding low-grade nickel matte and a leaching reaction solution into a reaction base solution, carrying out selective leaching, and collecting hydrogen sulfide gas, a first leaching solution and a first leaching residue, wherein the leaching reaction liquid is sulfuric acid with the mass fraction being 60-95%; 2, adding water into the first leaching residue for dissolving the first leaching slag, and collecting a second leaching solution and a second leaching residue; and 3, removing iron from the second leaching solution, collecting an iron-removed solution used for extracting nickel and cobalt and an iron-removed residue used for iron making, and / or sending the second leaching residue to a copper smelting device for smelting to obtain copper and noble metal. According to the method, deep separation of the nickel and the copper can be realized, and recovery of the nickel, the copper, the cobalt, the noble metal and sulfur can be effectively realized. The method is simple in process, short in flow and high in efficiency, is a clean and efficient element recovery process and is easy for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for leaching extracted vanadium from vanadium-containing raw material roasted clinker through ammonium oxalate
The invention provides a method for leaching extracted vanadium from vanadium-containing raw material roasted clinker through ammonium oxalate. The method includes the steps that a mixture of a vanadium-containing raw material and an additive is roasted to obtain a vanadium-containing raw material clinker; the vanadium-containing raw material clinker leaches extracted vanadium in an ammonium oxalate solution, and extracted vanadium tailings and a vanadium-containing leaching solution are obtained after solid-liquid separation. The method is high in vanadium selective leaching rate which can reach 90% or above, the content of vanadium-containing solution impurities obtained after leaching is small, the acidity and the alkalinity are proper, the purification and impurity removal process can be simplified or omitted, and subsequent vanadium precipitation and preparation of high-purity vanadium products are facilitated. No salt-containing waste water is generated. A leaching agent, namely the ammonium oxalate solution, used in the method does not volatilize, and the problem of ammonia volatilization is avoided. Besides, the leaching technology is simple in process, the method is friendly to the operation environment, and production cost is low.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
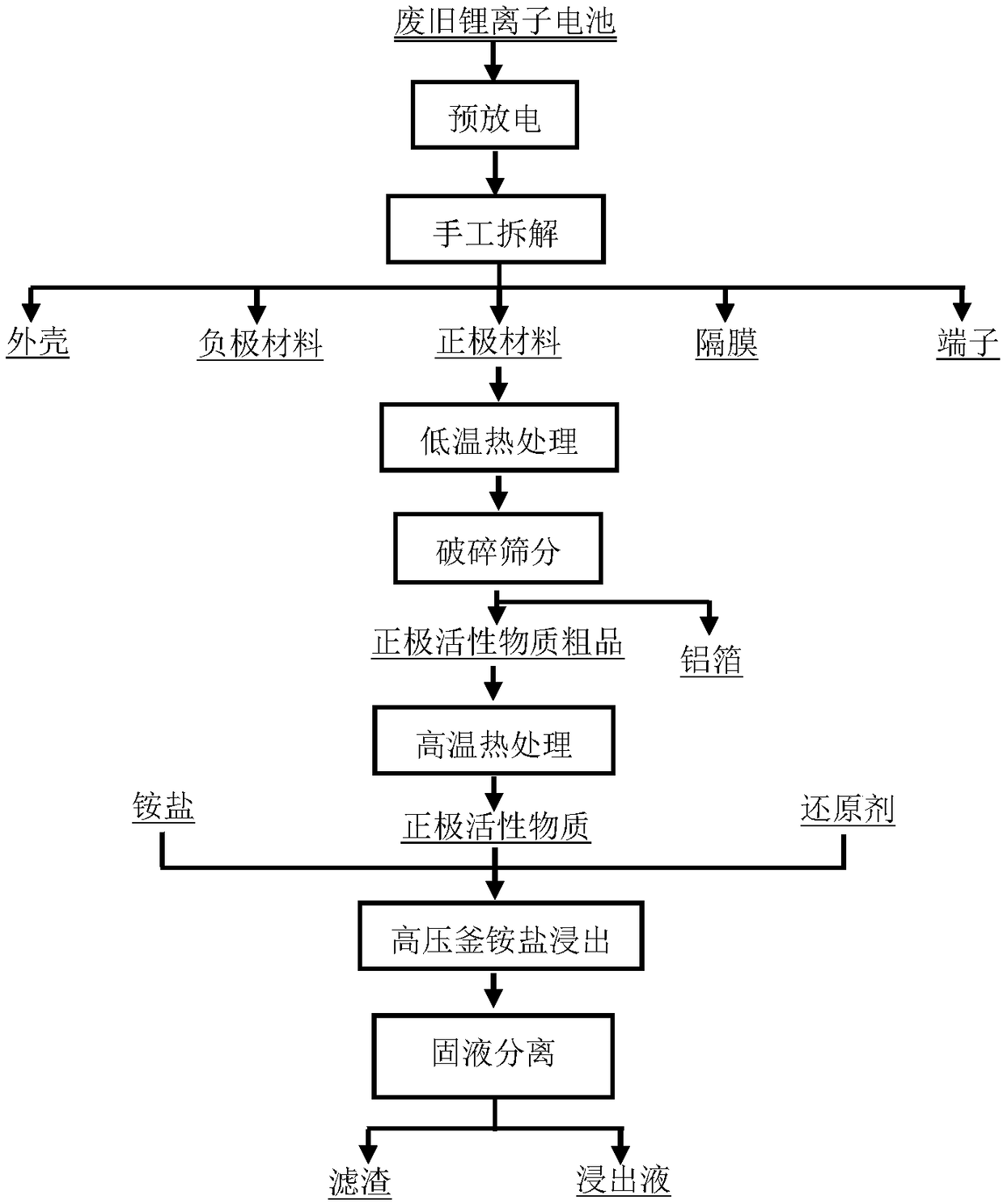
Method for leaching metals in anode material of waste lithium ion battery
InactiveCN108486376AImprove leaching rateHigh selectivityWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementManganeseHigh pressure
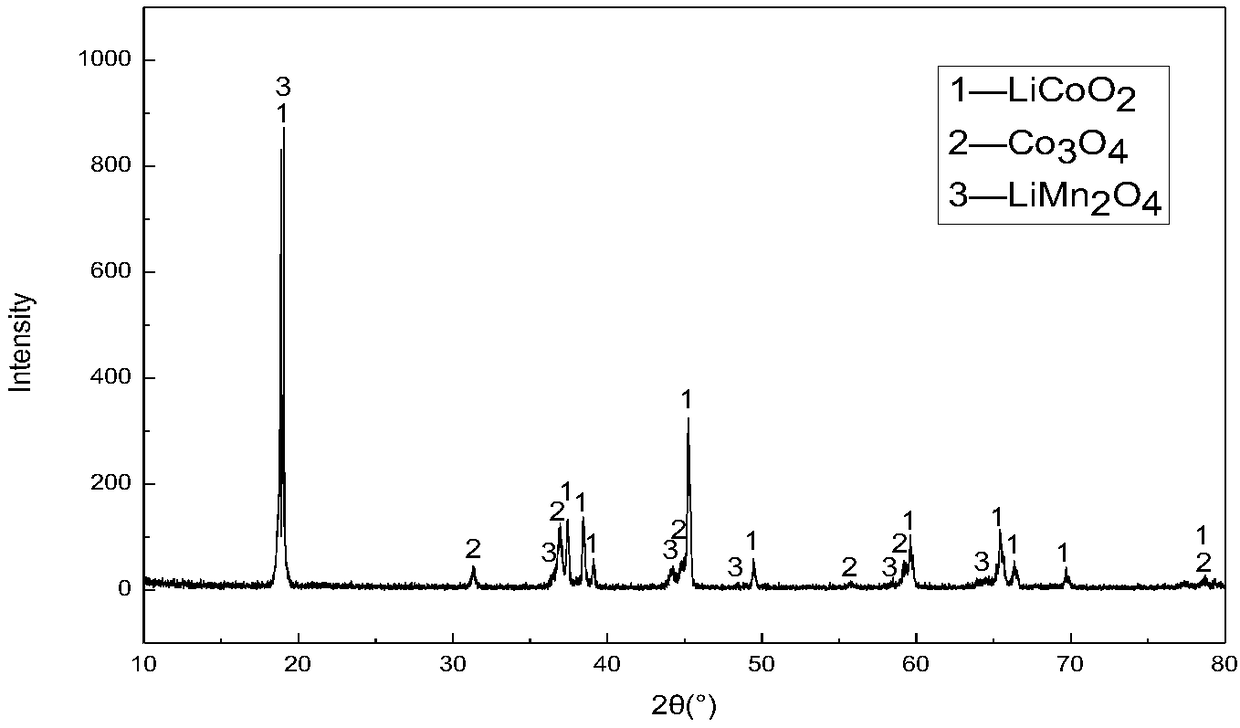
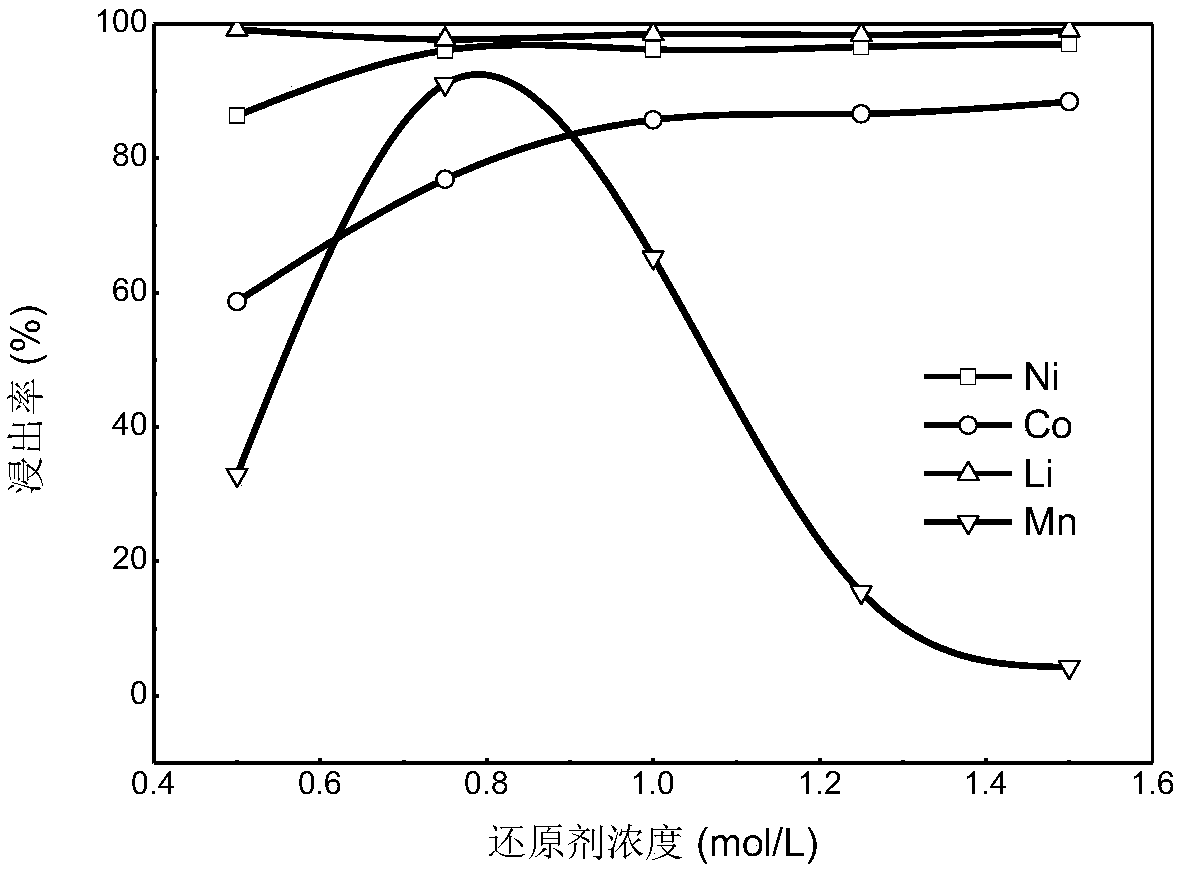
The invention relates to a method for leaching metals in an anode material of a waste lithium ion battery. The method for leaching the metals in the anode material of the waste lithium ion battery comprises the steps that anode active substances are obtained after the waste lithium ion battery is pretreated, then the anode active substances are made to react with an ammonium salt solution containing a reducing agent, solid-liquid separation is conducted after the reaction, and thus, leachate and filter residues are obtained. According to the method, the process is simple, the metal leaching rate is high, and the metal selectivity is high; by controlling the type and quantity of the reducing agent used in the leaching process, selective leaching of the metals can be achieved, for instance,when the anode material contains metals such as Li, Co and Mn, the reducing agent is ammonium sulfite, the leaching rate of Mn is 90% when the concentration of the reducing agent is 0.75 mol / L, and the leaching rate of Mn is 4% when the concentration of the reducing agent is 1.5 mol / L; the impurity content of the leachate is low, so that the cost for the subsequent impurity removal procedure is low; and the leaching process is conducted in a high-pressure kettle, emission of poisonous gas is avoided in the operation process, and the operation environment is good.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Portable type metal wire stretching stress corrosion testing device
InactiveCN104007058AAccurate measurementAchieving Selective ErosionWeather/light/corrosion resistancePull forceSelective leaching
The invention provides a portable type metal wire stretching stress corrosion testing device which comprises a loading body device (1), a stress corrosion container (2), a sensor system (3) and a dedicated clamp (4). A test piece is fixed through the loading body device (1), pull force is exerted on the test piece through a loading nut, the magnitude of force is measured and displayed by the sensor system (3), and the stress corrosion container (2) can perform selective and multi-point corrosion on the stretched test piece and an electrochemical test can be carried out. The dedicated clamp (4) can be connected with the test piece and an acoustic emission testing system so as to perform acoustic emission testing. The device has the advantages of being convenient to loading, convenient to carry, high in precision, capable of being repeatedly used, and capable of performing selective corrosion and multi-point simultaneous corrosion.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
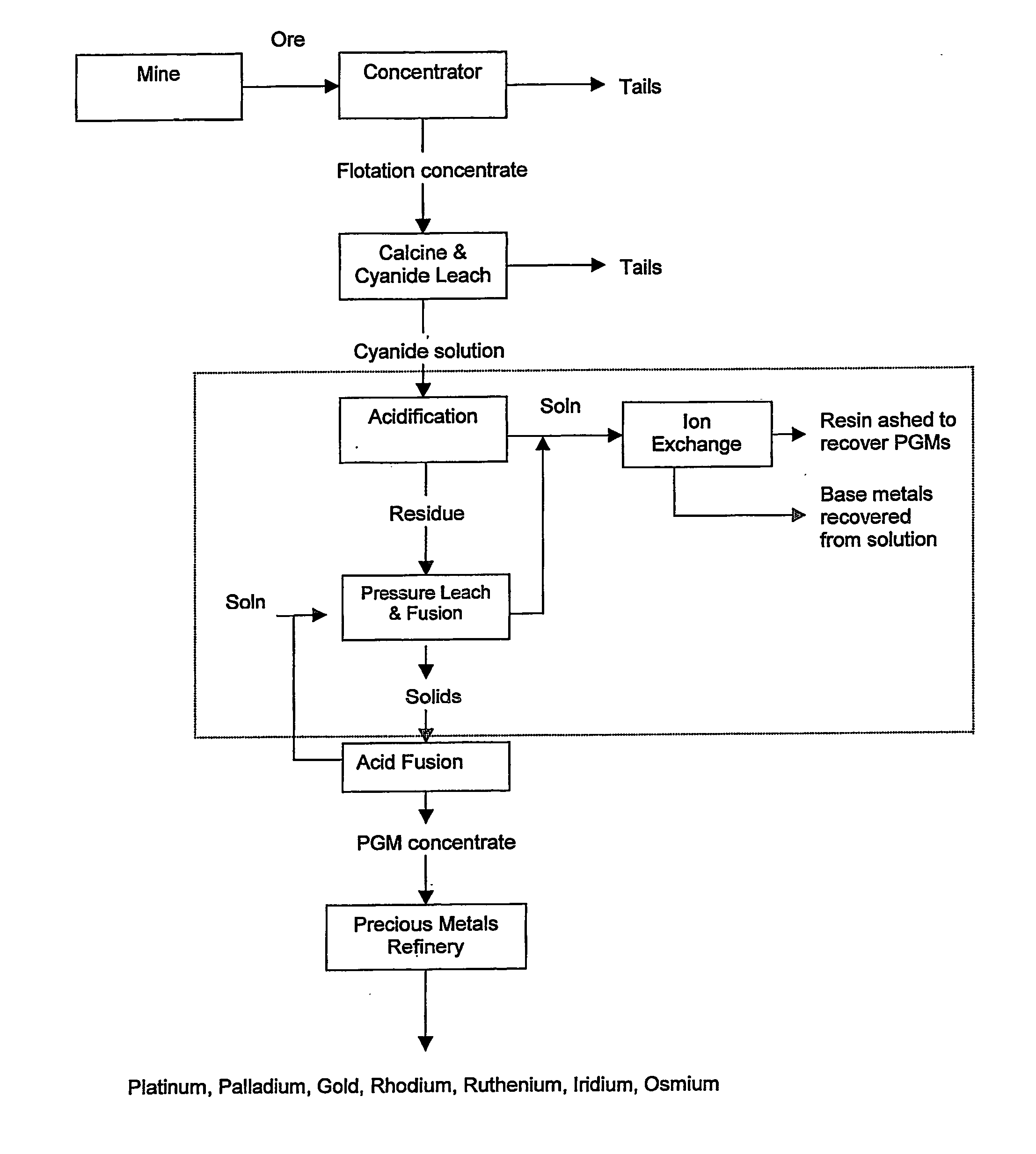
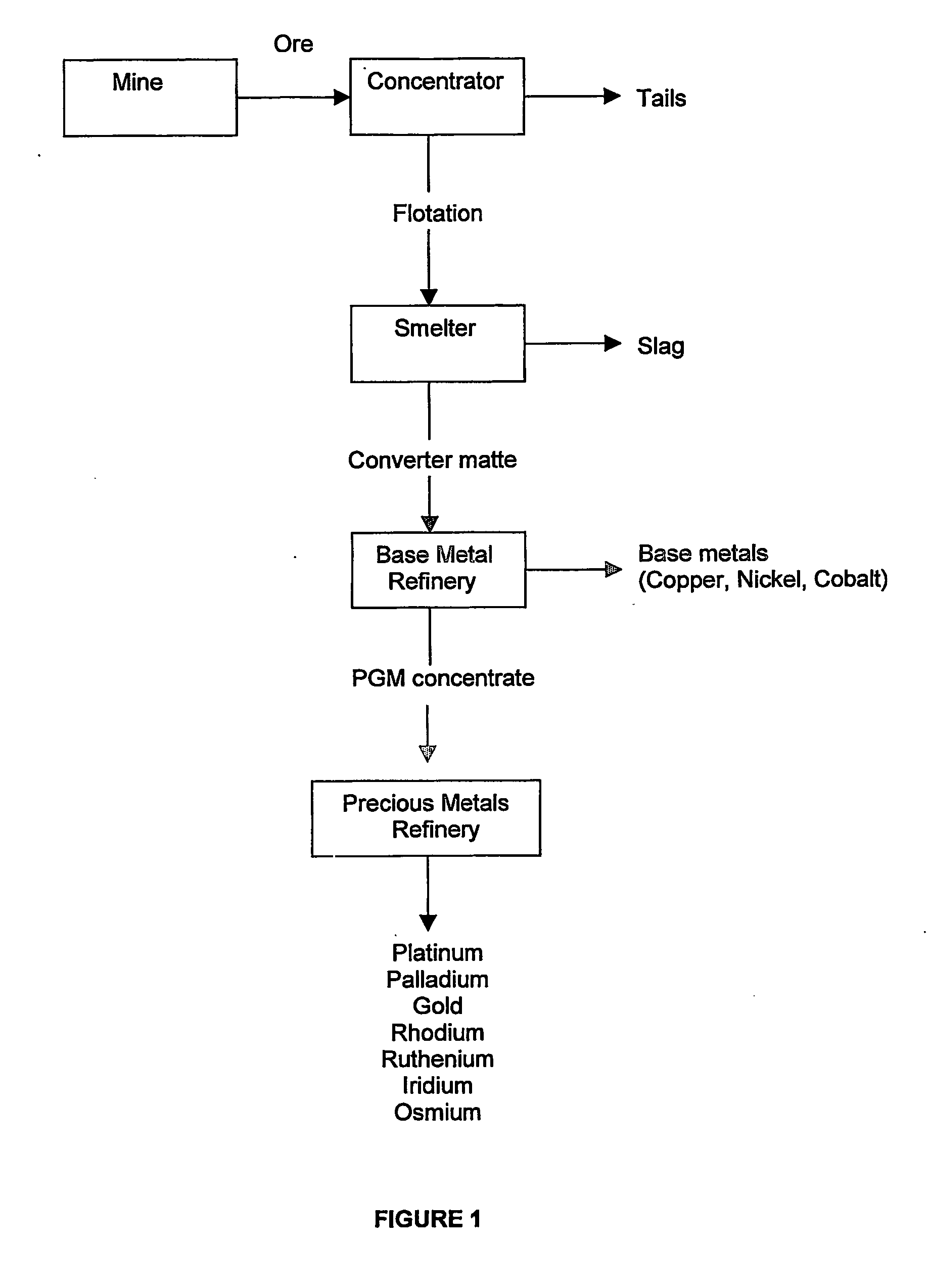
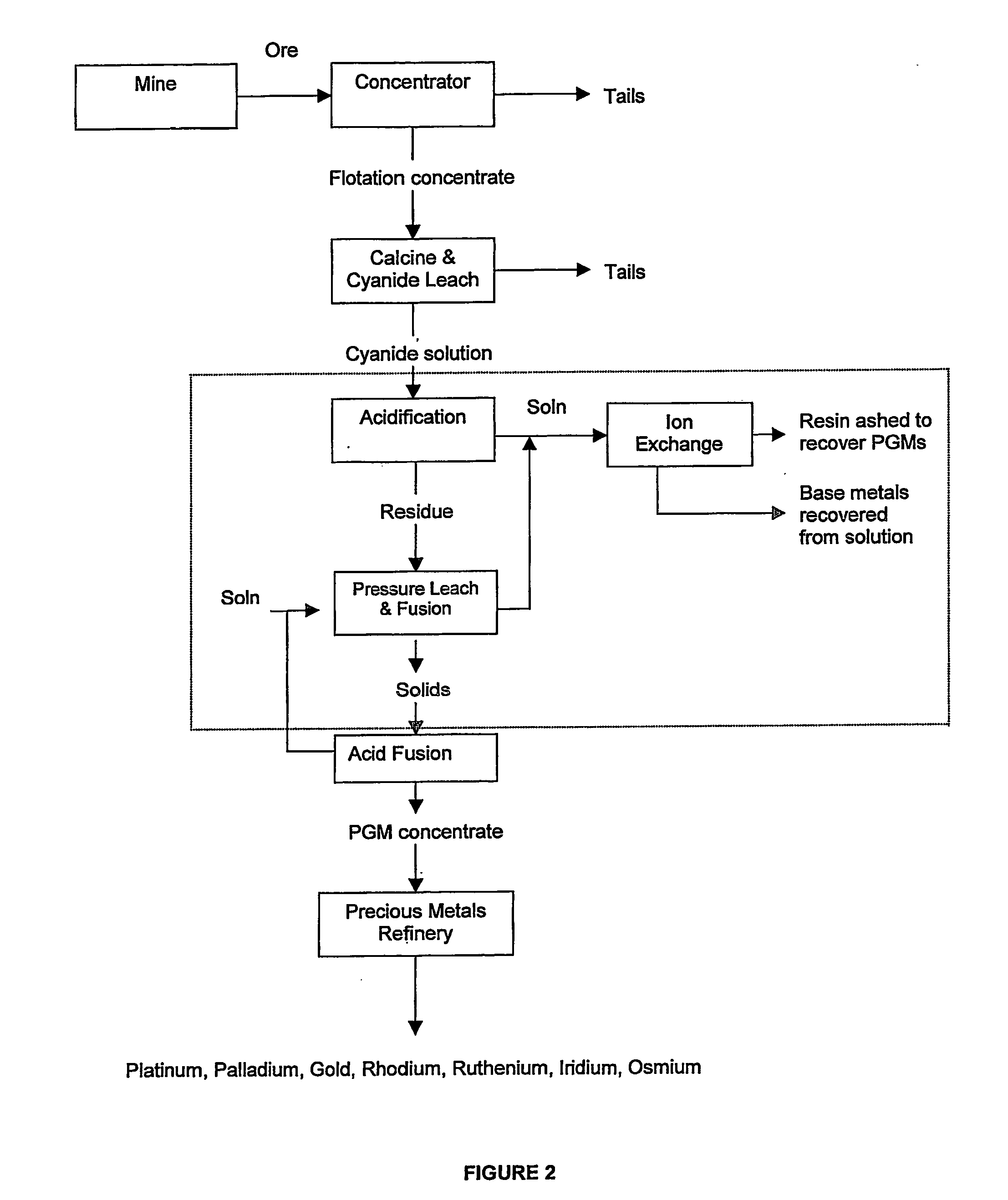
Recovery of platinum group metals
A process of recovering platinum group metals (PGMs) from a pregnant solution or leachate containing PGM values and base metals, typically a cyanide solution or leachate. A non-selective precipitation of the PGM values and base metals to form an insoluble precipitate comprising the PGM values and base metals is followed by selective leaching of the precipitate. The selective leaching forms a leach solution containing the base metals and a residue containing the PGM values, or a leach solution containing the base metals and PGM values and a depleted residue. The base metals are recovered from the leach solution and the PGM values are recovered from the residue or the leach solution, depending on the selective leaching. The non-selective precipitation of the PGM values and base metals is carried out by controlled reduction of the pH of the pregnant solution or leachate to a pH of about 2.
Owner:LONMIN
Selective heap leaching gold extraction process for gold mine containing copper
ActiveCN101818247AReduce consumptionImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementSelective leachingHydrometallurgy
The invention discloses a selective heap leaching gold extraction process for gold mine containing copper, belonging to the field of hydrometallurgy. The process comprises the steps of: smashing and heaping gold mine containing copper; carrying out alkali treatment on the mine; then adding ammonium salt and sodium cyanide according to a certain proportion to realize the selective leaching of the gold and the restriction to the leaching of the copper; and finally absorbing and extracting the gold from leaching solution by conventional active carbon. The invention has the advantages of simple process method, short procedure, simple equipment, easy implementation, high gold leaching efficiency, low consumption of sodium cyanide, low energy consumption, little investment and low cost, and is the gold extraction method with easy realization of industrialized production and favorable economical benefit.
Owner:ZIJIN MINING GROUP
Cascade recovery method for arsenic-containing antimony-containing gold ore difficult to process
ActiveCN105063354AAddressing the Impact of Recycling RatesHigh recovery ratePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementRecovery methodMaterials science
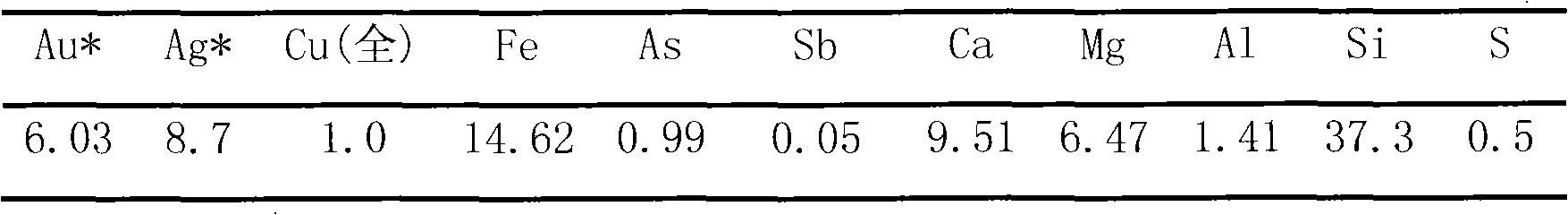
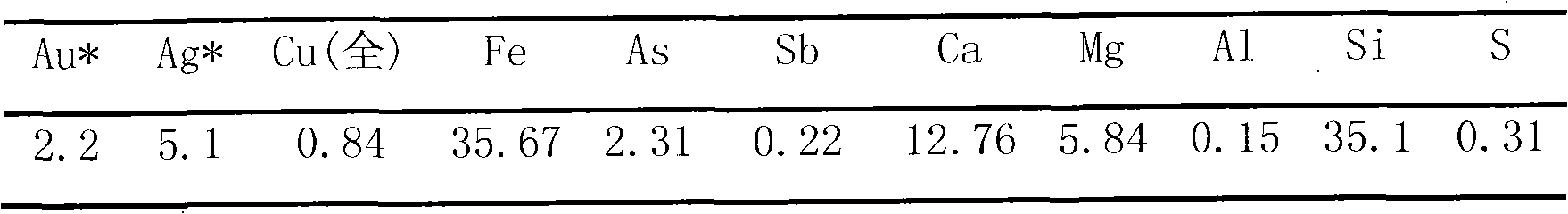
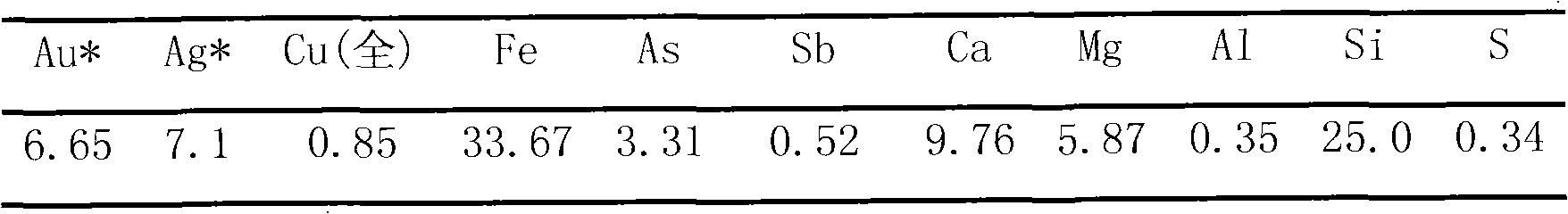
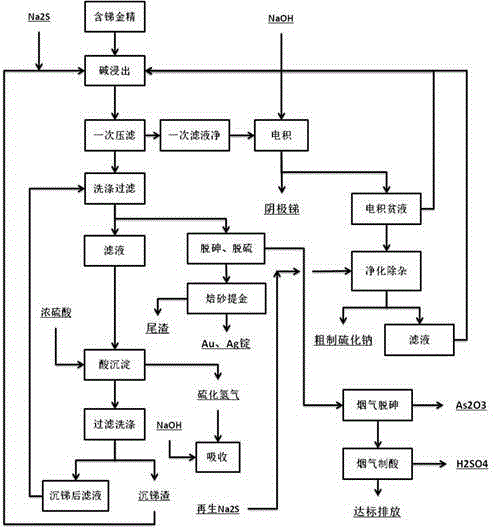
The invention provides a cascade recovery method for arsenic-containing antimony-containing gold ore difficult to process, and relates to a method for separating and extracting antimony, arsenic and gold of the gold ore difficult to process. The method is characterized in that the recovery process includes the steps that (1) sodium sulphide is added under the alkaline condition, and antimony leaching is carried out; (2) electrodeposition is conducted on leaching liquid to obtain cathode antimony liquid; (3) leaching residues are washed, and concentrated sulfuric acid is added into the washed liquid for antimony deposition; (4) the leaching residues are roasted for arsenic removal and desulfuration, so that pozzuolite enters smoke, the smoke is chilled and crystallized to recover arsenic trioxide, and acid making with smoke is achieved after arsenic recovery; and (5) gold and silver in the roasted residues are separated after antimony, arsenic and sulphur are extracted. The method is special for the arsenic-containing antimony-containing gold ore difficult to process, the influences of arsenic and antimony on the recovery rate of noble metal are effectively eliminated, the problem that arsenic and antimony are difficult to separate is solved through selective leaching, valuable elements such as antimony, arsenic and sulphur are comprehensively recycled, and the recovery rate of gold and silver is also increased. According to the technology, raw material adaptability is high, the technology process is short, and energy consumption is low.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
Carbide crystal material with two-dimensional lamellar structure and preparation method thereof
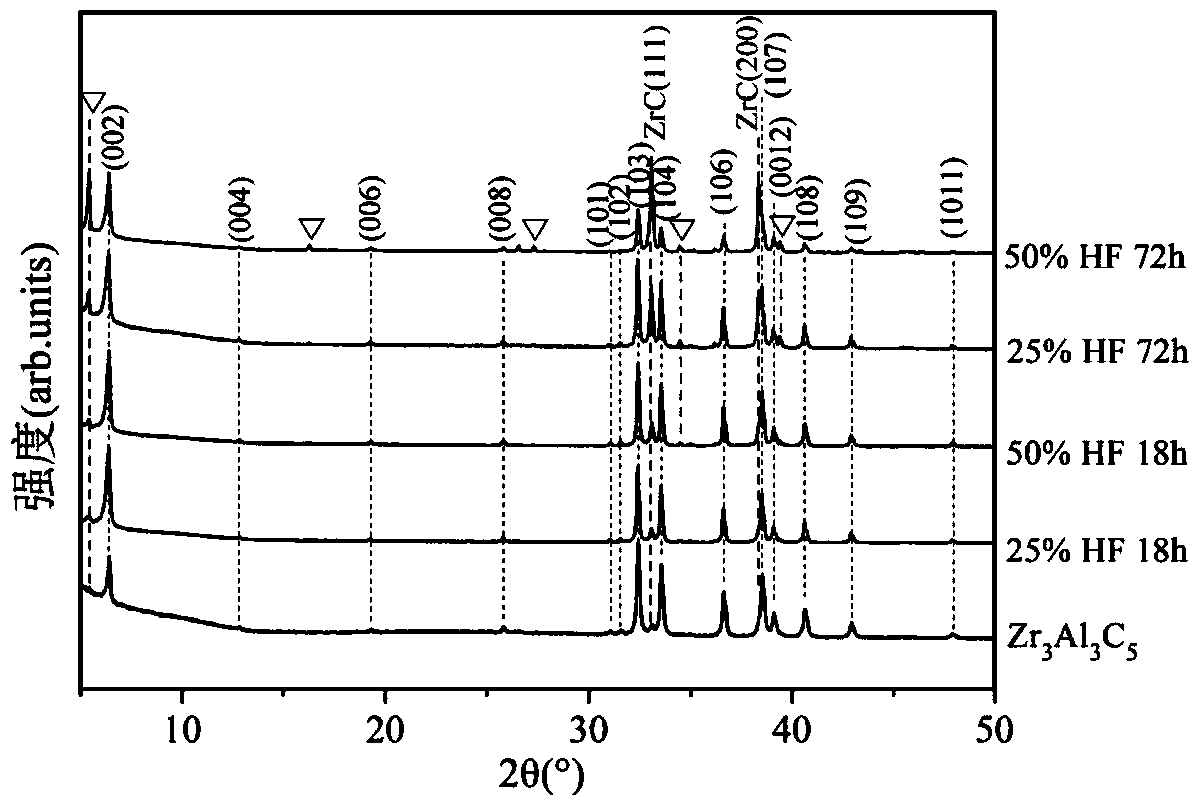
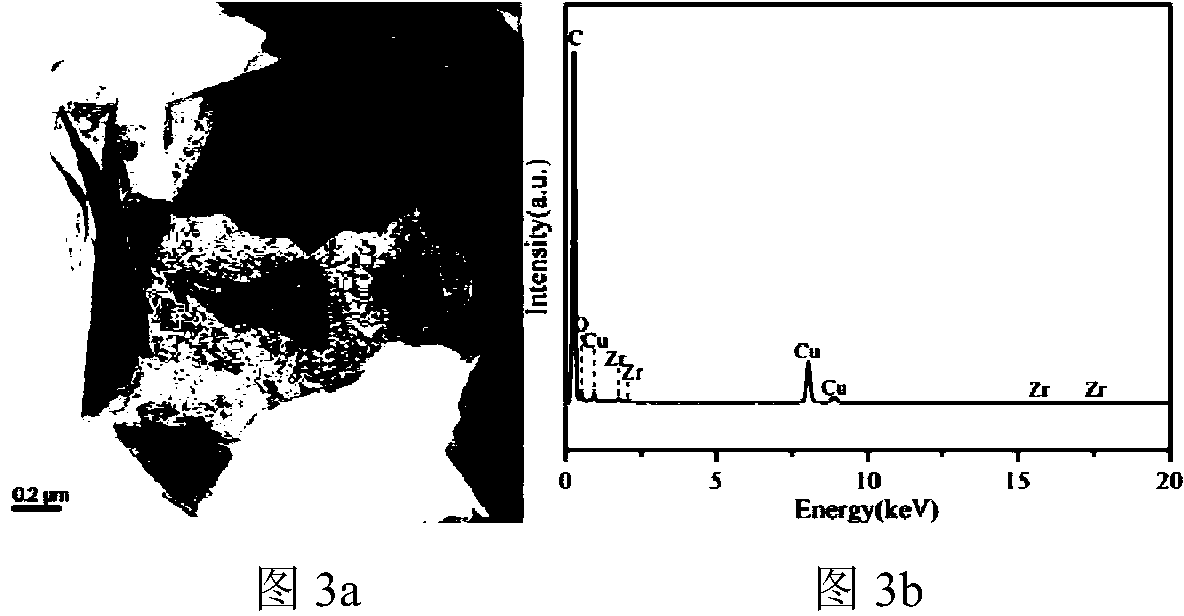
ActiveCN104762660ALarge molar contentHigh affinityPolycrystalline material growthSingle crystal growth detailsTransition metal carbidesElectrical conductor
The invention provides a carbide crystal material with a two-dimensional lamellar structure. The carbide crystal material with the two-dimensional lamellar structure is composed of transition metal elements and carbon element, and the atomic ratio of the transition metal elements to the carbon element is less than or equal to 1. According to the preparation method of the carbide crystal material with the two-dimensional lamellar structure, ternary or polybasic Zr / Hf / Y-Al / Si / Ge-C lamellar ceramic material is used as a precursor and is subjected to selective corrosion so that an Al-C lamella with a weak valence bond can be peeled off and corroded, thus obtaining the carbide crystal material with the two-dimensional lamellar structure. The method is simple and practicable, and has the advantage that the composition elements, element stoichiometric ratio, morphology and structure of the carbide crystal material with the two-dimensional lamellar structure are all designable and controllable. The carbide crystal material with the two-dimensional lamellar structure has good applications in the fields of electrode materials for electrochemical energy storage, functional macromolecular conductive fillers, sensors, catalysts, transparent conductors and the like.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
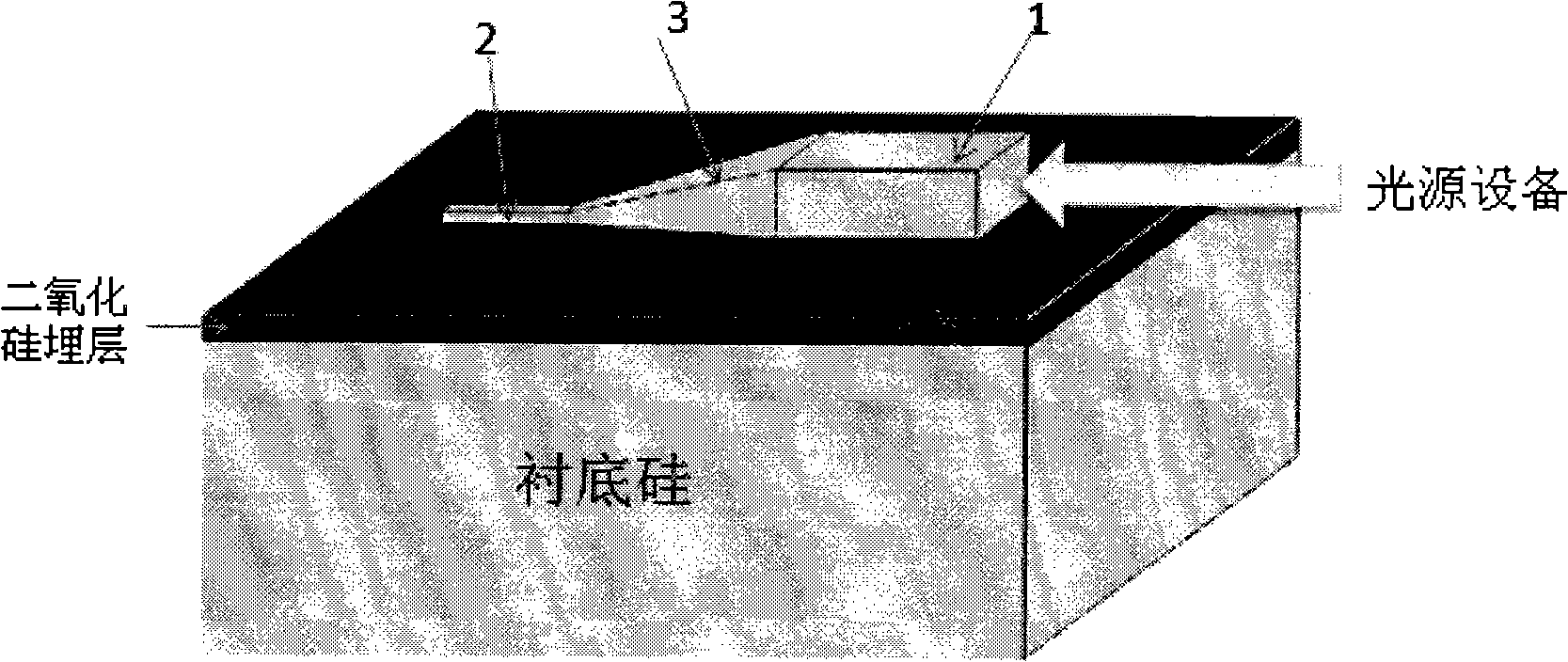
Isolator silicon based three-dimensional wedge-shaped spot-size converter and method for making same
InactiveCN101308230AImprove coupling efficiencySimple processPhotomechanical apparatusCoupling light guidesControllabilityElectron
The invention relates to an SOI-based (silicon on insulator) three-dimensional wedge-shaped spot-size converter based on micromachining as well as a making method thereof, which are used for realizing the high efficiency coupling between light source equipment such as optical fibers and small-sized optoelectronic devices such as silica-based wave guide. The spot-size converter is made by utilizing selectivity corrosion characteristics of different crystal faces of a silicon wafer and adopting the bulk silicon micro-machining technique, and belongs to the microelectronics and solid electronics fields. The converter is made by adopting SOI materials and utilizing micromachining processes such as photolithography, anisotropy corrosion and dry etching for processing, so as to obtain the three-dimensional wedge-shaped spot-size converter structure having linear variation in both the vertical and horizontal directions, thereby effectively improving the coupling efficiency of optical and optoelectronic devices such as general optical fibers and small-sized plane wave guide. The making method of the invention has the advantages of simple processes, good compatibility, and strong controllability and practicability.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for separating and recovering copper from waste electronic appliances
InactiveCN102643995AIncrease contentEasy to recycleProcess efficiency improvementCopper sulfateMetal recycling
The invention relates to a method for separating and recovering metal from waste electronic appliances; aiming at the problems of high cost and complicated technological process in the existing metal recovery of waste electronic appliances, and the current situation that except the recovery of most valuable gold, the recovery of other metal elements is not fully considered about, the invention particularly provides a method for separating and recovering copper from the waste electronic appliances, which is low in production cost, quick and simple. According to the method, blocks or powder of the crushed waste electronic appliances, or metal powder which is obtained by sorting the powder is taken as raw material, and hydrochloric acid solution and sulfuric acid solution containing an oxidizing agent are respectively used as leaching reagents, the metal copper is recovered from the raw material by two-step selective leaching, and finally, copper sulfate pentahydrate or metal copper can be obtained.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
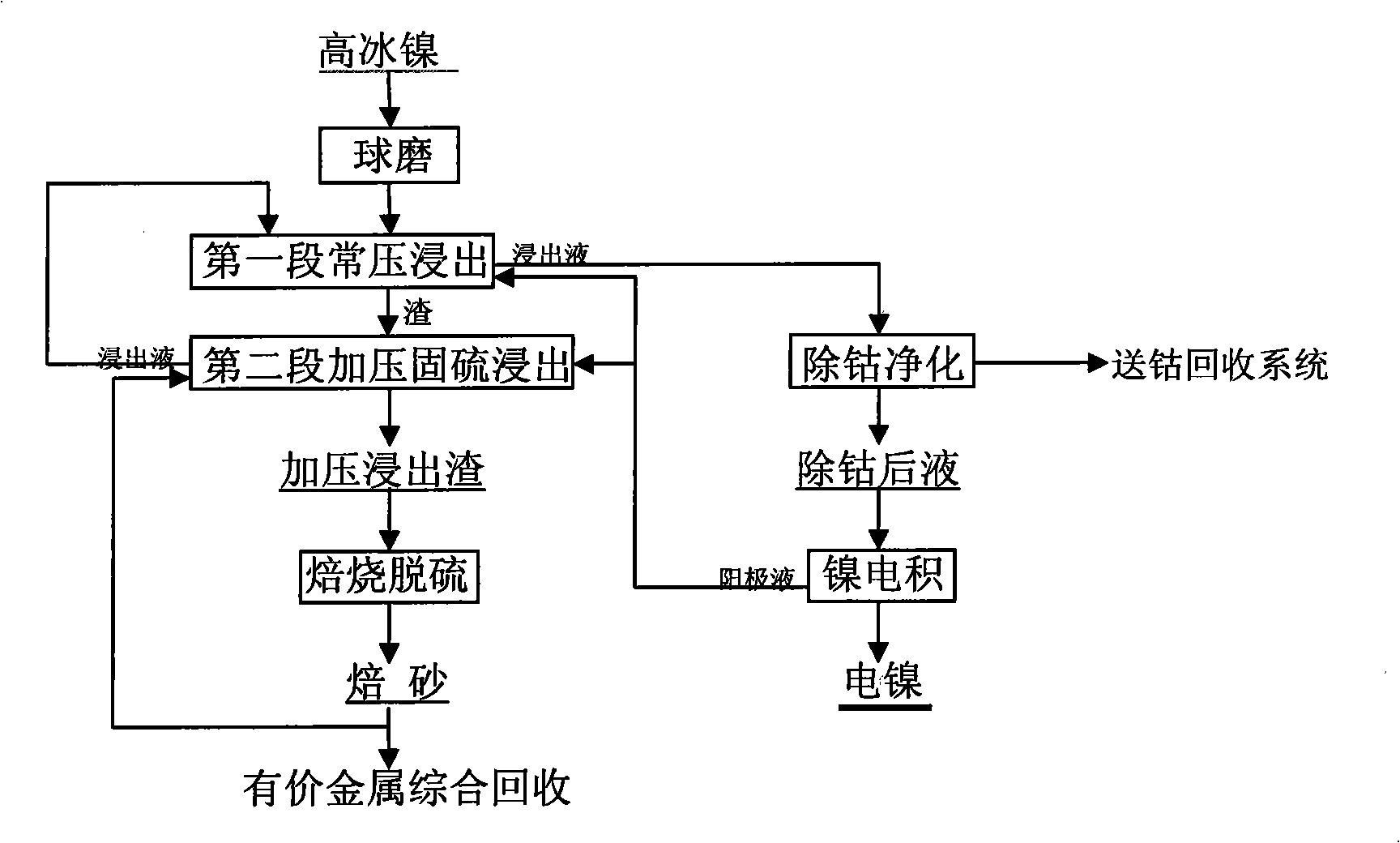
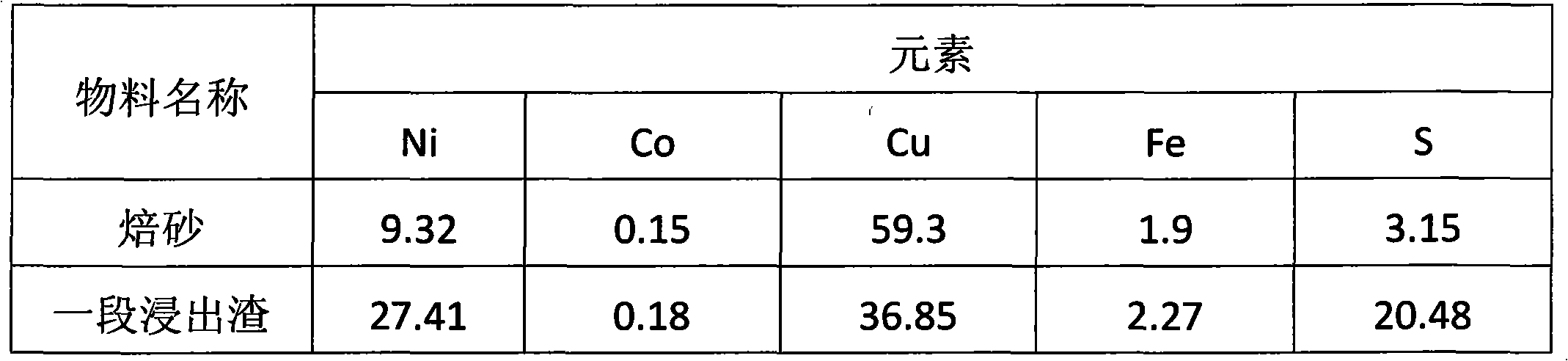
Method for producing cathode nickel by selective leaching-electrodeposition of high nickel matte
InactiveCN101886167AHigh recovery rateAdaptablePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionSelective leaching
The invention discloses a method for producing cathode nickel by the selective leaching-electrodeposition of high nickel matte, which relates to a method for producing the cathode nickel by hydrometallurgical refining of the high nickel matte. The method is characterized in that the cathode nickel production process comprises the following steps of: (1) performing first-stage normal-pressure leaching on the high nickel matte; (2) removing cobalt from first-stage normal-pressure leachate for purification and producing electric nickel by electrodeposition; (3) adding a sulphur fixing agent into a first-stage leaching residue to perform second-stage pressing and sulphur fixing leaching, and returning the leachate which is obtained by the second-stage pressing and sulphur fixing leaching to perform first-stage normal-pressure leaching; and (4) desulfurating and roasting the leaching residue obtained by the second-stage pressing and sulphur fixing leaching to obtain a roasted product, and returning the roasted product which is used as the sulphur fixing agent in the step (3). The method of the invention effectively solves the problem of acid excess of a production system, has a high nickel recovery rate and low production cost, is highly adapted to different high nickel matte raw materials and favorable for environmental protection, and can obviously reduce the waste water emission in the production.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
Method for manufacturing sensor structure based on charge transfer
InactiveCN102214042AIncrease viewable areaReduced precision requirementsInput/output processes for data processingChemical platingEvaporation
The invention relates to a method for manufacturing a sensor structure based on charge transfer. The method comprises the following steps of: manufacturing transparent conductive layers on two surfaces of a base material by a vacuum-sputtering film coating, vacuum ion film coating, vacuum thermal evaporation film coating or coating method; manufacturing metal reinforcement layers on the surfaces of the upper and lower transparent conductive layers by the vacuum-sputtering film coating, vacuum ion film coating or vacuum thermal evaporation film coating method, an electroplating method or a chemical plating method; forming patterns of a first transparent conductive layer, a first lead wire electrode group, a second transparent conductive layer and a second lead wire electrode group on the two surfaces of the base material by a selective erosion method; manufacturing protection layers on the surfaces of the first lead wire electrode group and the second lead wire electrode group by a screen-printing method, a roller transfer-printing method or a photoetching method; and putting a workpiece processed by the process into a selective etching solution to remove the metal reinforcement layers covered on the transparent conductive layers. Compared with the conventional method, the method has the advantages that: the processing procedures are reduced, the process difficulty is lowered, the processing efficiency is improved and the qualification rate is increased greatly, and the manufacturing cost is low.
Owner:南京福莱克斯光电科技有限公司
Method for efficiently recovering iron, scandium and aluminum from limonite type lateritic nickel ores
ActiveCN108998662AEfficient recyclingEfficient use ofPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisLaterite
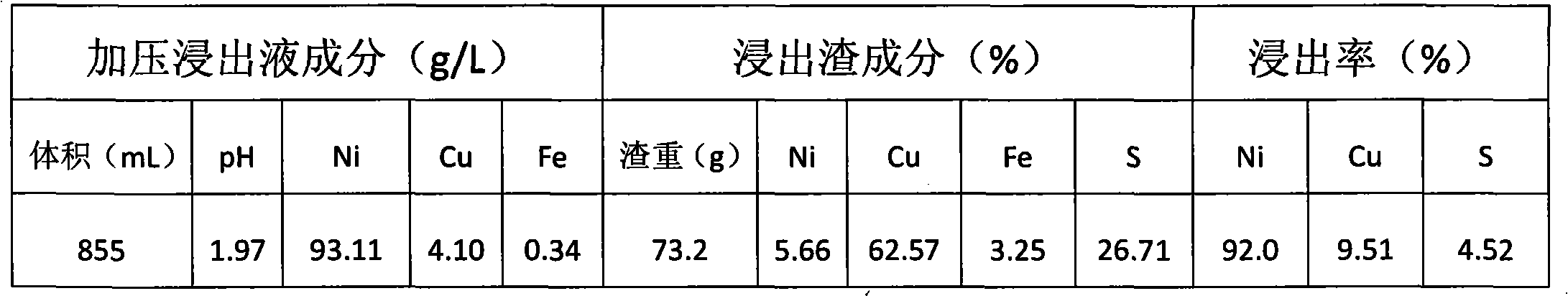
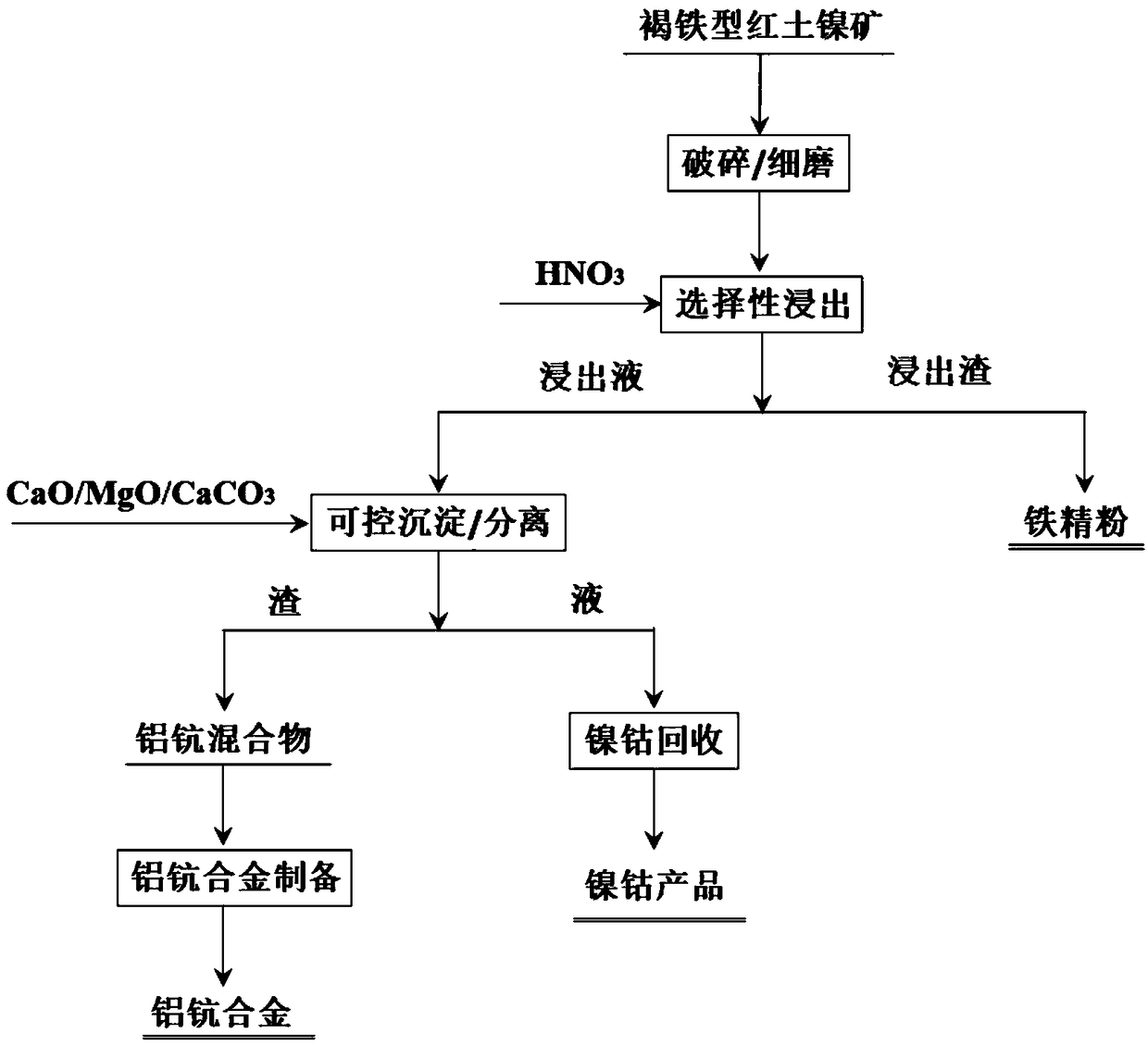
The invention discloses a method for efficiently recovering iron, scandium and aluminum from limonite type lateritic nickel ores. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out crushing or fine grinding on the limonite type laterite nickel ores to obtain ore powder; carrying out selective leaching on the ore powder through nitric acid to obtain sulfur-free iron ore concentrates, of which the iron content exceeds 60%; carrying out controllable sedimentation or separation on a leach solution by adding magnesium oxide, calcium oxide or calcium carbonate, so that an aluminum-scandium mixture is obtained; after baking dehydration of the aluminum and scandium mixture, adding an approximate amount of cryolite and carrying out molten salt electrolysis to directly prepare aluminum-scandiumalloy; and neutralizing a solution obtained through the controllable sedimentation or separation to prepare nickel and cobalt hydroxides, or carrying out extraction-electrodeposition on the solution to prepare nickel and cobalt products. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that under mild conditions without external pressurization, both selective nickel and cobalt leaching andefficient iron, scandium and aluminum recovery and utilization can be achieved, both the nickel and cobalt leaching rates can reach above 90%, the iron and scandium recovery rates can reach above 95%,and the aluminum recovery rate can reach 65%, so that iron, scandium, aluminum, nickel and cobalt in the limonite type lateritic nickel ores can be efficiently recovered and utilized.
Owner:MEISHAN SHUNYING POWER BATTERY MATERIALS CO LTD
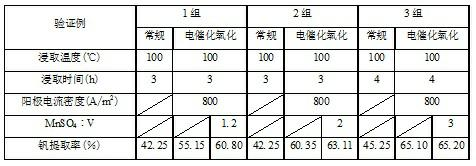
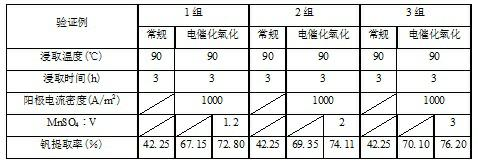
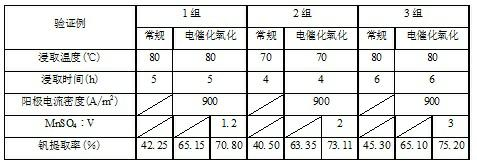
Method for leaching vanadium slag in converter by electro-catalytic oxidation
InactiveCN102134640AIncreased electrocatalytic oxidationHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementElectrodesSlagHigh energy
The method discloses a method for leaching vanadium slag in a converter by electro-catalytic oxidation. In the method, the vanadium slag in the converter is mixed with MnSO4 and H2SO4 to obtain slurry and then leaching is conducted by non-membrane electro-catalytic oxidation; and after the leached ore slurry is filtered and separated, the vanadium in the obtained leaching solution is extracted through conventional ammonium salt (ammonium sulfate) vanadium precipitation so as to prepare vanadium pentoxide. During the leaching, the low-valent vanadium which is not easily leached in the vanadium slag is oxidized into high-valent vanadium which is easily leached by an anode-generated strong oxidant Mn3+ so that the leaching rate of the vanadium is improved by using an electro-catalytic oxidation method to leaching the vanadium slag, therefore, the problems of high energy consumption and high pollution in the traditional leaching methods are avoided, otherwise, the method is also suitable for the extraction of the vanadium in the raw materials including vanadium and the selective leaching of molybdenite concentrate; meanwhile, the method has the characteristics of being good in selectivity, moderate in technological condition, free of pollution and the like, therefore, a novel environmentally friendly wet decomposition method is provided.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for extracting vanadium by leaching vanadium-contained raw material roasting clinkers through ammonium phosphate
ActiveCN105714102AReduce leachingEasy to manufactureProcess efficiency improvementSelective leachingWastewater
The invention provides a method for extracting vanadium by leaching vanadium-contained raw material roasting clinkers through ammonium phosphate. The method includes the steps that a mixture of a vanadium-contained raw material and an additive is roasted, and the vanadium-contained raw material clinkers are obtained; and the vanadium-contained raw material clinkers are leached in an ammonium phosphate solution to extract vanadium, and vanadium extracting tailings and a vanadium-contained leaching agent are obtained after solid-liquid separation is carried out. According to the method, the vanadium selective leaching efficiency is high and can reach more than 90%; meanwhile, leaching of impurity element is less, preparation of products with the high-purity vanadium is facilitated, and brine waste is avoided; the leaching agent-ammonium phosphate solution used in the method does not volatilize, and the problem of ammonia gas volatilization is avoided; and in addition, the leaching technological process of the method is simple, the operation environment is friendly, and the production cost is low.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
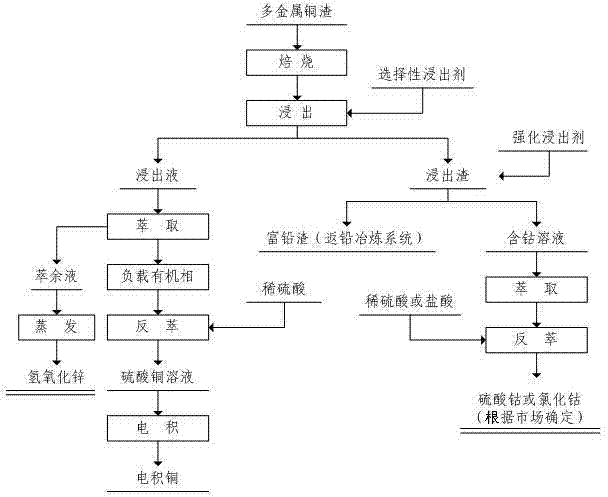
Method for producing electrodeposited copper from polymetallic copper slag
ActiveCN104846202AImprove leaching efficiencyHigh recovery ratePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementZinc hydroxideLead smelting
The invention discloses a method for producing electrodeposited copper from polymetallic copper slag, which includes the following steps: the polymetallic copper slag is roasted to oxidize, so that the complex states of valuable metals in the polymetallic copper slag are transformed into oxides, changed into a state which can be selectively leached; leaching first adopts selective leaching agent to leach copper and zinc, the leachate is extracted, reextracted and electrodeposited, so that electrodeposited copper is obtained, and raffinate is vaporized and crystallized, so that zinc hydroxide is obtained; mechanical intensified leaching agent is then used for intensely leaching leaching residue, so that cobalt, nickel and the like in the leaching residue are leached, lead, iron and the like are enriched into the slag, the lead-rich slag is adopted as material for lead smelting, the leachate is extracted and reextracted, so that cobaltous sulfate or cobalt chloride is obtained, and if the nickel content in the leachate is overhigh, multi-stage extraction can be carried out to separate cobalt and nickel, so that nickel sulfate or nickel chloride is produced. The method can comprehensively recover a variety of metals, the leaching efficiency is high, the recovery rate is high, the method is environment-friendly, and is easy to implement, the method ensures that all the valuable metals in the polymetallic copper slag can be effectively separated and recycled, and the solid waste utilization rate can reach more than 99 percent.
Owner:NORTHWEST RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com