Processing method of GaN basis light emitting diode surface coarsing
A technology for light-emitting diodes and surface roughening, which is applied to electrical components, circuits, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of inconspicuous surface roughening, increased processing complexity, irregular surface undulations, etc., to increase the number of corrosion pits, The effect of good roughening effect, enhancing effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
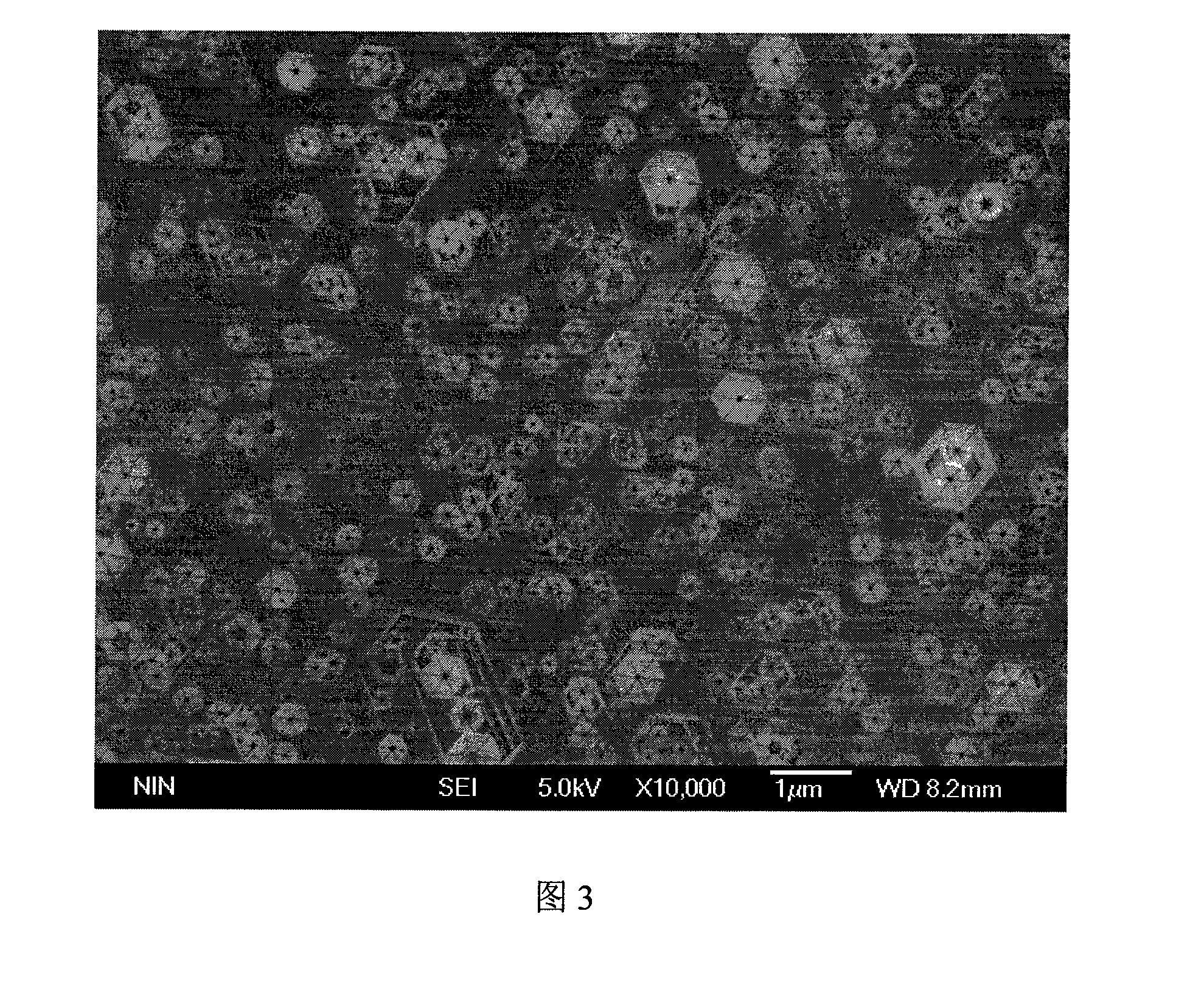
[0023] Referring to FIG. 1 , it is a schematic diagram of the GaN-based LED surface roughening treatment process of the present invention. Its specific implementation process is described as follows:
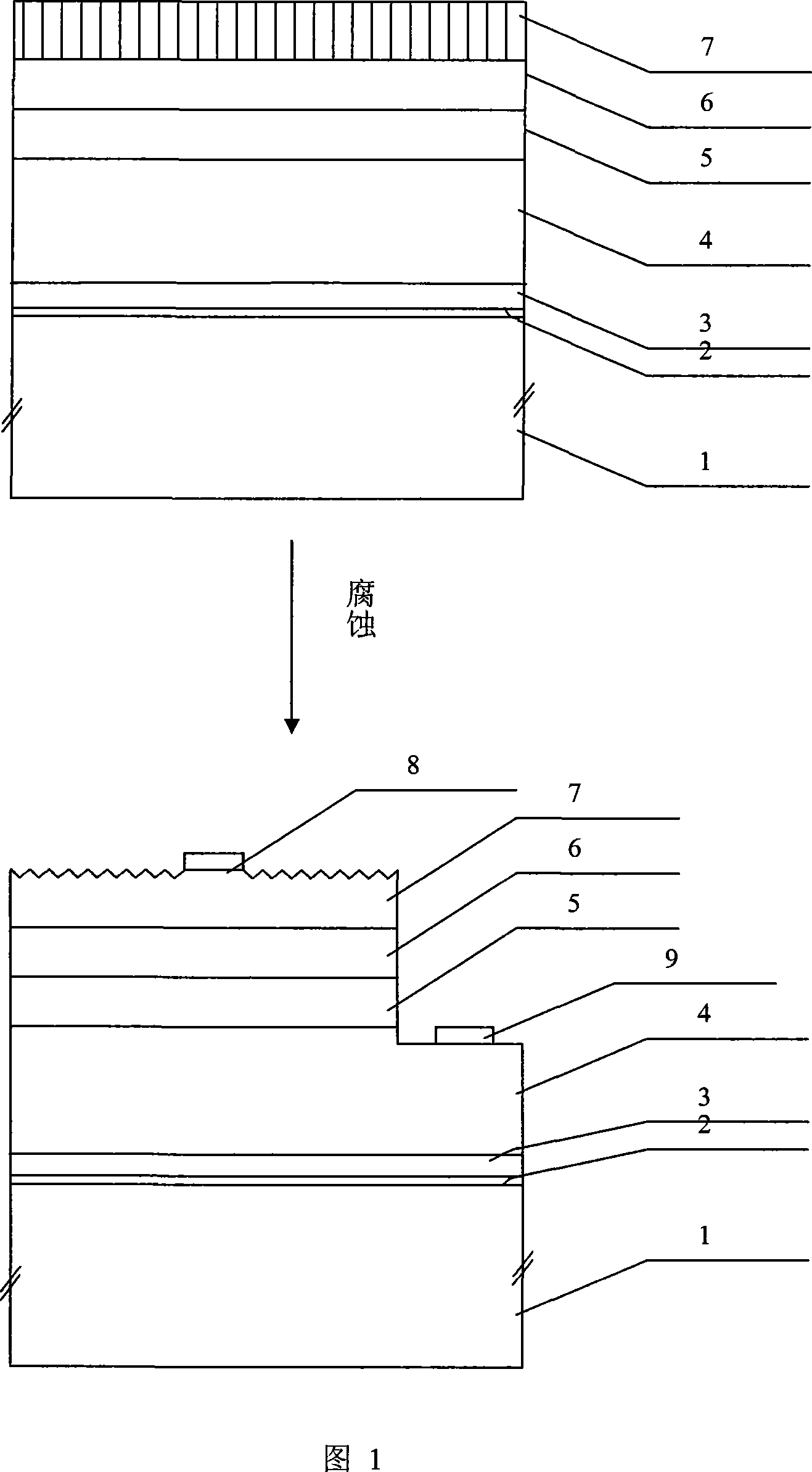
[0024] 1. Grow the p-type GaN cap layer in the GaN-based LED epitaxial wafer at a low temperature of 600°C to 750°C, so that the dislocation of the cap layer propagates in the direction perpendicular to the epitaxial surface without bending, so that the cap The dislocation density of the layer increases without affecting the optoelectronic properties of the device. The upper figure in Figure 1 is a schematic cross-sectional view of the GaN-based LED epitaxial wafer structure with low-temperature p-GaN as the cap layer. The vertical line in the cap layer in the figure indicates that this layer contains a large number of dislocations that propagate perpendicular to the surface.
[0025] 2. Under the set etching temperature and time, the LED epitaxial wafer is etched with molten K...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com