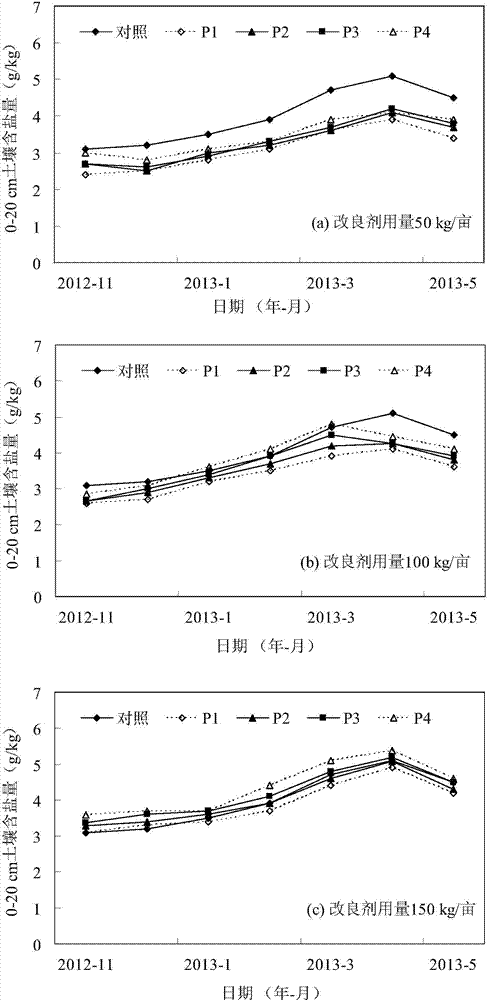
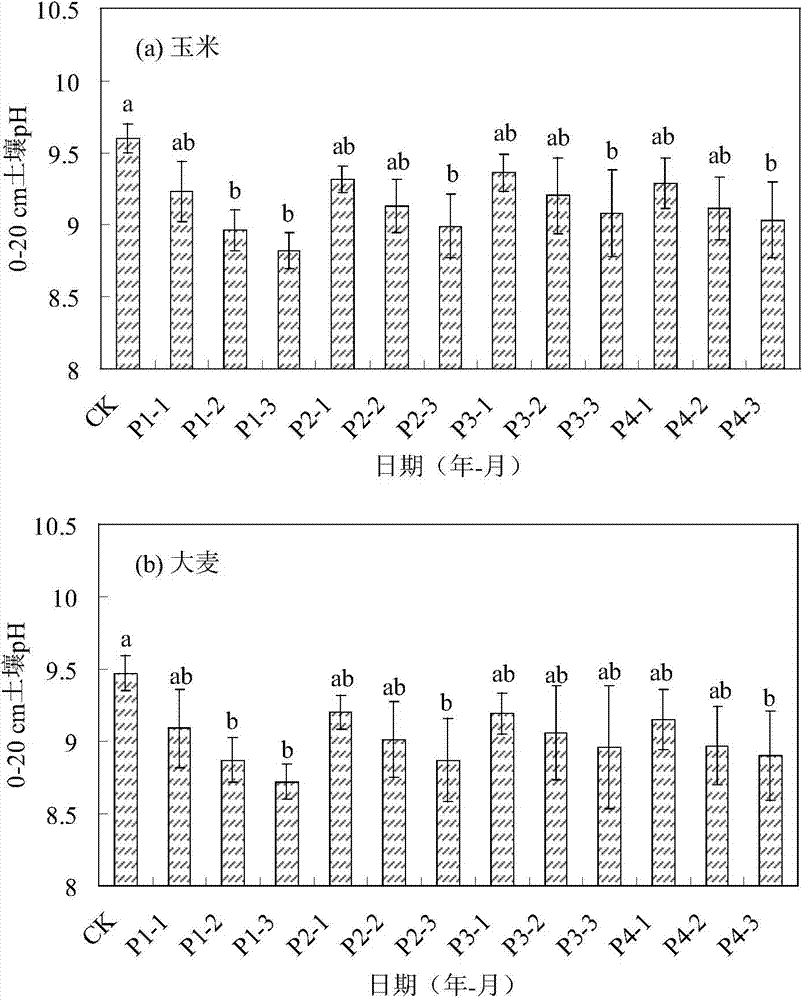
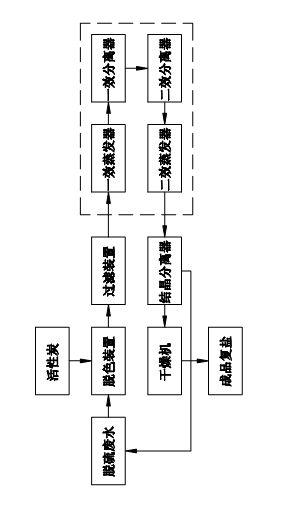
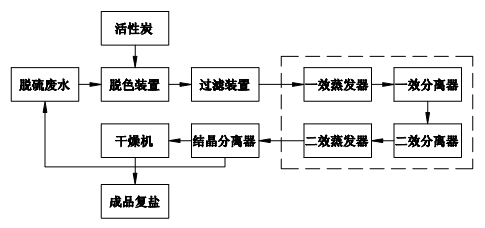
Patents
Literature
466 results about "Double salt" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A double salt is a salt that contains more than one cation or more than one anion, and is obtained by combination of two different salts which were crystallized in the same regular ionic lattice. Examples of double salts include alums (with the general formula MᴵMᴵᴵᴵ[SO₄]₂·12H₂O) and Tutton's salts (with the general formula [Mᴵ]₂Mᴵᴵ[SO₄]₂·6H₂O). Other examples include potassium sodium tartrate, ammonium iron(II) sulfate (Mohr's salt), and bromlite. Aluminium sulfacetate, Al₂SO₄(CH₃CO₂)₄, is an example of a double salt with two distinct anions; another is the salt Tl₄(OH)₂CO₃ where hydroxyl-centred triangles of thallium, [Tl₃(OH)]²⁺, are a recurring structural motif.
Method for recovering rare earth from rare earth-containing aluminum-silicon materials
ActiveCN101705380AAvoid enteringLess fixed investmentProcess efficiency improvementMolecular sieveSelective leaching
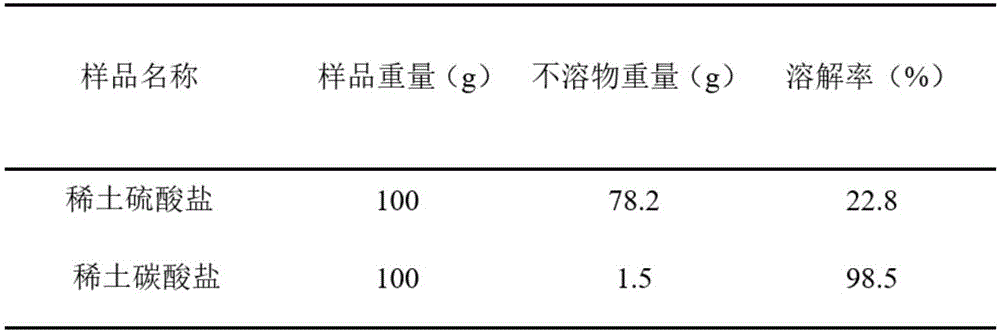
The invention relates to a method for recovering rare earth from rare earth-containing aluminum-silicon materials, which comprises the following steps: taking the rare earth-containing aluminum-silicon materials including rare earth-loaded molecular sieves, catalyst wastes, and the like as raw materials, conducting prioritized selective leaching by acid so as to lead the majority of the rare earth and a small amount of aluminum to be dissolved and separated from silicon and other impurities, leading the rare earth to form precipitates and be separated from the aluminum by adopting a double salt precipitation or oxalate precipitation method, and then recovering and purifying the rare earth. The method has the advantages of directly realizing the extraction of the rare earth from the aluminum-silicon materials including the molecular sieves and the like, with over 98% purity of the obtained rare earth, and avoiding impurities such as aluminum, silicon and the like entering the rare earth; and meanwhile, the technology also has the characteristics of little fixed investment, low production cost and easiness for realizing industrialized production.
Owner:GRIREM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Process for preparing detergent particles having coating or partial coating layers
InactiveUS7022660B1Improved surface and appearance and flow propertyImprove surface propertiesInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsDetergent mixture composition preparationDouble saltWater soluble
A process for preparing a detergent particle having a coating layer of a water-soluble material is provided. The process comprises providing a particle core of a detergent active material and the particle core is then at least partially covered by a particle coating layer of a water soluble coating material including double salt combinations of alkali metal carbonates and sulfates that reduces the surface area of the particle.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
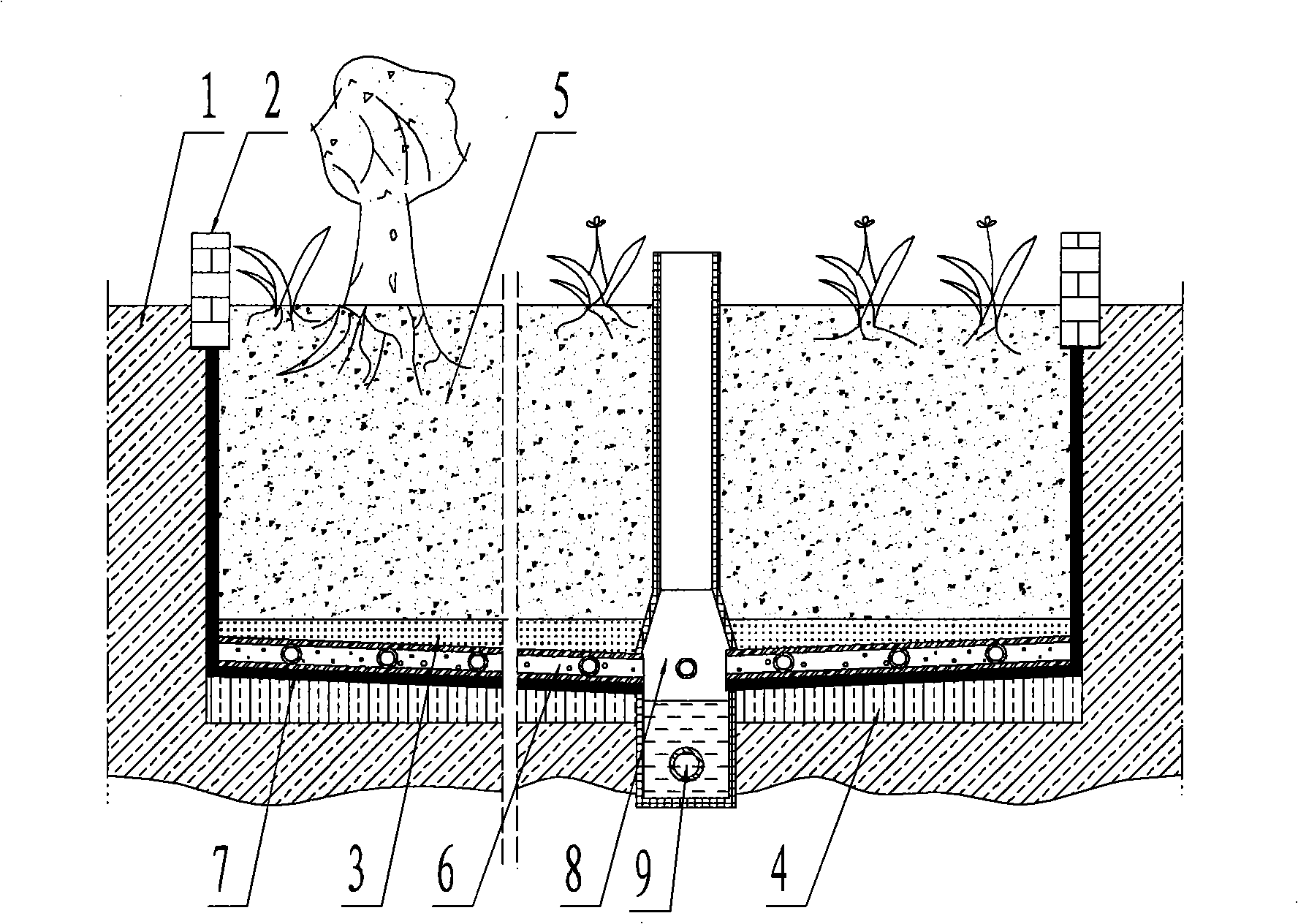
Shallow water level double salt-affected soil raw soil planting and greening method
InactiveCN101283656APrevent immersionGuaranteed independenceSoil lifting machinesConstructionsEngineeringDouble salt
The invention relates to a technology for afforestation and planting in areas with shallow water level and heavily-salted soil and solves the problems of high cost for foreign soil replacement and short duration. The technical proposal is that: the process realizes the original soil planting by building an integral isolation zone in the greening area and controlling a microcirculation system inside the isolation zone and desalting with fresh water. The process comprises the following steps: A. building an isolation zone; B. desalting with fresh water until the salt content in soil is below 0.2%; and C. planting seedlings for afforestation. The technology solves the technical problems of high cost for foreign soil replacement and short duration of afforestation and greening in coastal areas with shallow water level and heavily-salted soil; and has the advantages of overcome serious erosion of underground salt water to soil mass, good desalting effect, reduced afforestation cost, improved soil structure, low requirements for raw materials for afforestation, applicability for various seedlings, easy maintenance and management and low cost.
Owner:CANGZHOU ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Transformation liquid for preparation of corrosion-resistant oxidation film on aluminium alloy surface and method of use thereof
InactiveCN101139708AImprove corrosion resistanceGood adhesionMetallic material coating processesHigh resistancePersulfate
The invention discloses a transforming solution for preparing anti-corrosion compound oxidation film on an aluminum alloy surface and a using method for the oxidation film. The invention is characterized in that, the transforming solution is a film-forming promoter containing rare-earth salt (nitrate or sulfate and compound salt of cerium, praseodymium, and neodymium), such compound oxidant as radical of permanganate, nitrate and perchlorate, etc., film-forming promoter of vanadium salt and strontium salt, etc.; the transforming solution contains no sexavalent chromium, is environmental friendly; the reaction speed is improved by the compound oxidant and the film-forming promoter, no heating is needed for the chemical transforming, the treating time is 1-5 min. The invention can rapidly prepare under room temperature compound oxidation film comprising compound rare-earth oxide, alumina and manganese oxide with good resistance to corrosion on aluminum alloy surface. The treating solution from the invention is of rapid film-forming speed, simple process, even film layer, high resistance to corrosion, and low environmental pollution, etc.
Owner:陈东初 +2
Ammonium sulfate nitrate
Ammonium sulfate nitrate composite materials useful as fertilizers having desirable levels of nitrate ions, superior stability against detonation, higher density, greater resistance to moisture, and a method for their manufacture. The ammonium sulfate nitrate composites have as essential constituents ammonium sulfate and the NH4SO4.2(NH4NO3) double salt with less than 5 wt. % in combined total of the more hazardous NH4SO4.3(NH4NO3) double salt and ammonium nitrate. The composites of the invention are formed by reacting ammonium sulfate with ammonium nitrate in a molar ratio of about 0.9:1 to about 1.1:1 in the presence of a small amount of water in a narrow range of temperatures and then cooling to solidification at a sufficiently rapid rate to prevent macroscopic segregation of the reaction products.
Owner:ADVANSIX RESINS & CHEM LLC
New dietary supplement composition for obesity and inflammation
InactiveUS20050282772A1Affect activityPromote migrationBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsDouble saltChemistry
The present invention relates to dietary supplement phytochemical compositions, comprising calcium, potassium double salt of (−)-hydroxycitric acid and glucosamine hydrochloride, and optionally boswellic acids, curcuminoids, 5-hydroxytryptophan, chondroitin sulfate and L-carnitine. The claimed compositions are useful in dietary supplements, nutritional supplements or pharmaceutical preparations for weight loss and inflammatory epidemics.
Owner:LAILA NUTRACEUTICALS
Process for producing coated detergent particles
InactiveUS6858572B1Fine surfaceGood lookingInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsNon-ionic surface-active compoundsSulfateDouble salt
A process for preparing detergent particles having a coating layer of a water-soluble inorganic material is provided. The detergent particle comprises a particle core of a detergent active material. This particle core is then at least partially covered by a particle coating layer of a water soluble inorganic material. Particularly preferred are non-hydratable inorganic coating materials including double salt combinations of alkali metal carbonates and sulfates. The particle coating layer may also include detergent adjunct ingredients such as brighteners, chelants, nonionic surfactants, co-builders, etc. The process includes the steps of passing the particle core through a coating mixer such as a low speed mixer or fluid bed mixer and coating the particle core with a coating solution or slurry of the water soluble inorganic material. Upon drying, the resultant detergent particles have improved appearance and flow properties and may be packaged and sold as a detergent material or mixed with various other detergent ingredients to provide a fully formulated detergent composition.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Compositions comprising ammonium nitrate double salts
ActiveUS20070199357A1Reduce detonation sensitivityReduce sensitivityAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersPotassium nitrateDetonation
Preferred aspects of the present invention provide ammonium nitrate compositions comprising ammonium nitrate and at least a second compound, said second compound being present under conditions and in amounts effective to substantially reduce the detonation sensitivity of the composition and / or to otherwise improve a desired property of the composition. In certain embodiments, the second compound is selected from the group consisting of ammonium sulfate, ammonium phosphate, calcium nitrate, potassium nitrate, magnesium nitrate, ammonium molybdenate, ammonium hexaflouralsilicate, neodymium hydroxynitrate, and combinations of two or more of these. In preferred embodiments, at least a substantial portion of the ammonium nitrate in the composition is in the form of a double salt with one or more of said second compounds. In highly preferred embodiments, the present compositions consist essentially of one or more double salts of ammonium nitrate and a second compound as described herein.
Owner:ADVANSIX RESINS & CHEM LLC
Process of extracting white tungsten concentrate from tungstenic iron ores or tungstenic waste residues
ActiveCN104046800AImprove conversion rateInhibitionShaft furnaceProcess efficiency improvementDesorptionResource utilization
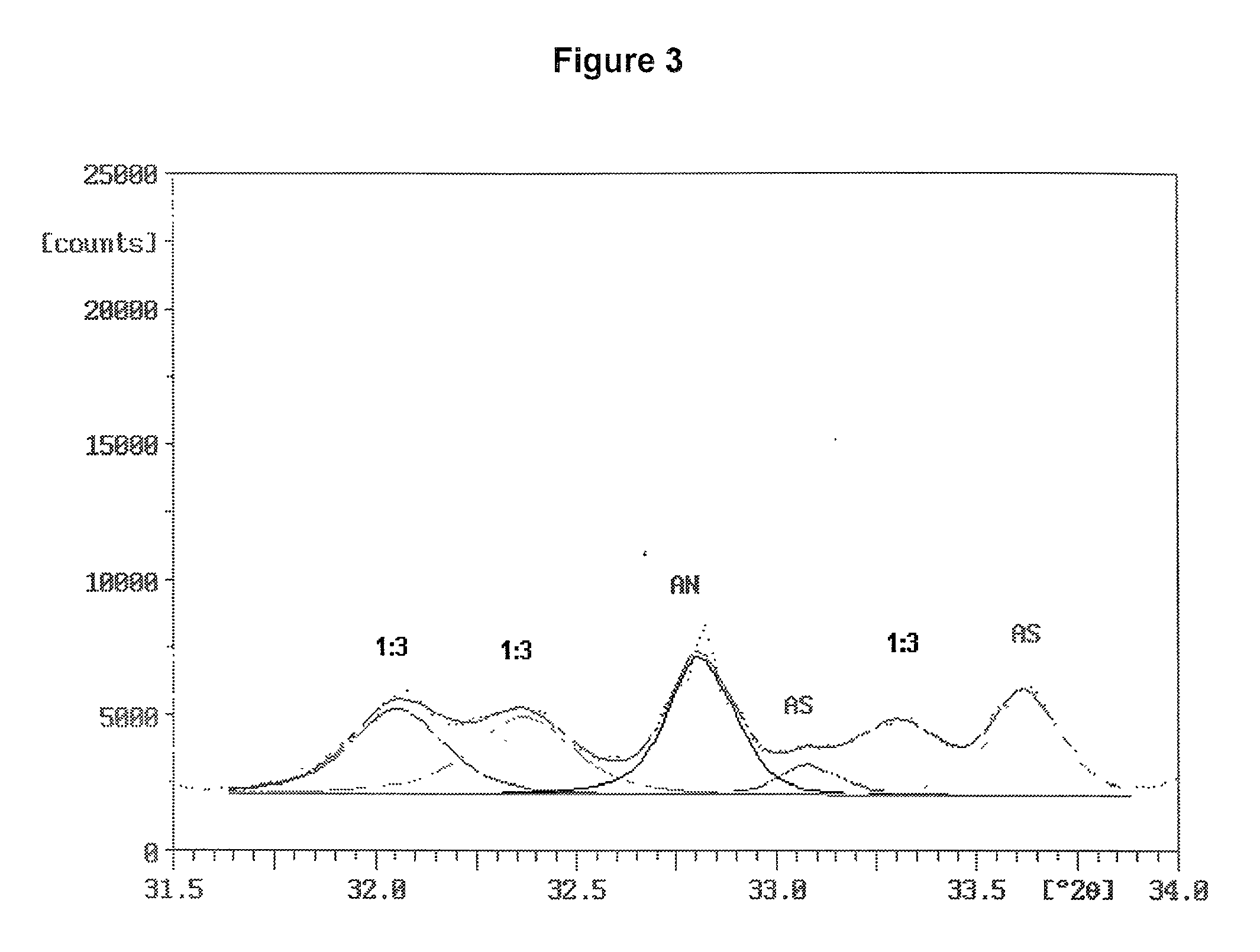
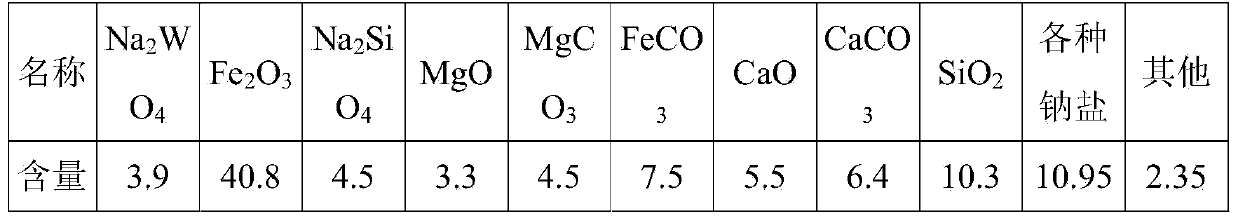
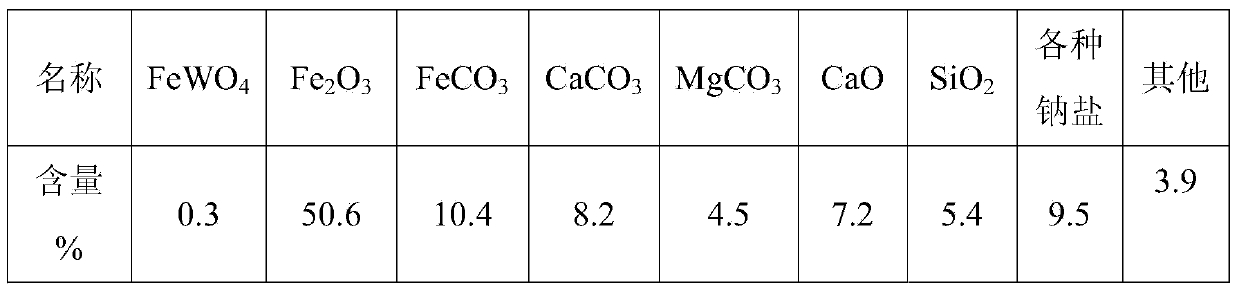
The invention discloses a process of extracting white tungsten concentrate from tungstenic iron ores or tungstenic waste residues. The process comprises the following steps: after smashing tungstenic iron ores or tungstenic waste residues, mixing with sodium carbonate and double salt and pressing to form pellets; then, calcining at an appropriate temperature; leaching the calcined pellets by use of a ball-mill; then carrying out resin ion exchange, desorption, impurity removal and crystallization on leach liquor to finally obtain the white tungsten concentrate. The process can be used for effectively separating high grade white tungsten concentrate from tungstenic iron ores or tungstenic waste residues with extremely low grade of tungsten, is low in energy consumption, low in production cost, small in discharge capacity and environment-friendly, and can be used for effectively realizing comprehensive resource utilization, thereby satisfying the industrialized production.
Owner:湖南天泰天润新能源科技有限公司
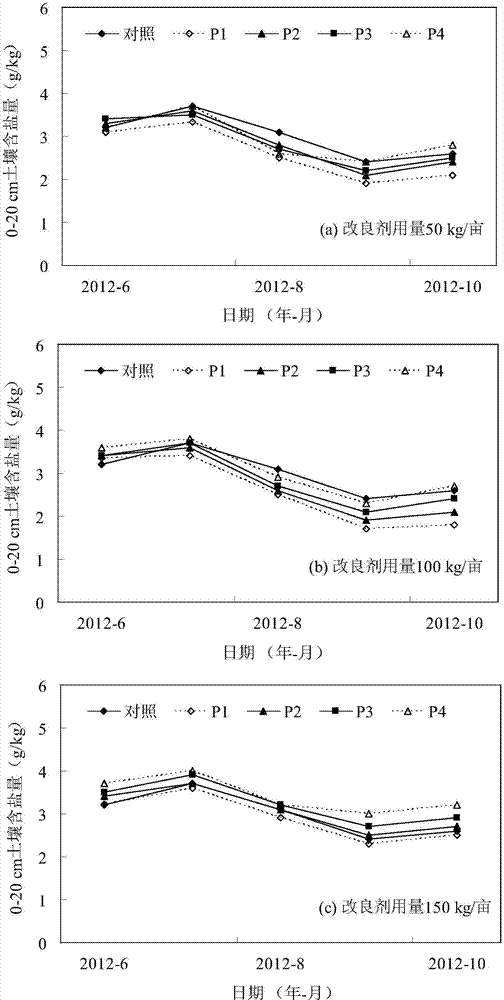
Chemical improvement conditioner suitable for coastal beach and strongly saline-alkaline land and application method thereof
InactiveCN104276903AShorten the governance cycleIncreased rinse volumeOther chemical processesClimate change adaptationAlkali soilDry season
The invention relates to a chemical improvement conditioner suitable for a coastal beach and a strongly saline-alkaline land and an application method thereof. The chemical improvement conditioner comprises the following components in parts by weight: 50-70 parts of ardealite, 20-30 parts of humic acid, 5-10 parts of aluminum sulfate and 3-5 parts of potassium dihydrogen phosphate. The chemical improvement conditioner disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple improver component and preparation process, clarity in principle, low cost and quick effect. The application method of the chemical improvement conditioner aiming at different planting modes and soil salinity conditions provides an optimized application mode of 'less use for dry farming, more use for water farming, less use for a dry season, more use for a rainy season, more use for double salt and less use for light salt' by comprehensively considering the plant modes, soil salt contents and the rainfall difference of different seasons, thereby improving the desalting and alkali-improving efficiency, farthest decreasing the residues of an improver in soil and realizing multiple purposes of salt leaching, soil improvement and fertility improvement of the coastal beach and the saline-alkaline land.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Desulfuration waste water treatment process
ActiveCN102020369AQuick extractionHigh purityMultistage water/sewage treatmentEconomic benefitsWastewater
The invention discloses a desulfuration waste water treatment process which comprises the following the steps of: firstly leading waste water to be desulfurated into a decoloration device, adding active carbon for absorbing decoloration, and then filtering by a filtering device; carrying out negative pressure concentration on the waste water subjected to absorbing decoloration and filtering through a double effect evaporimeter device so as to ensure that the density of the waste water is 1.25-1.30 times that of water; and finally cooling the concentrated waste water to 35-50 DEG C in a crystallization separator for crystal-liquid separation, wherein the discharged waste liquid can be recycled; and drying crystals into sulfur containing double salt in a dryer. The desulfuration waste water treatment process can effectively reduce the double salt content of desulfuration liquid in a desulfuration system, treat the desulfuration waste water of the desulfuration system and improve desulfuration efficiency; moreover, the recycled double salt products have certain economic benefit.
Owner:山东潍焦集团薛城能源有限公司
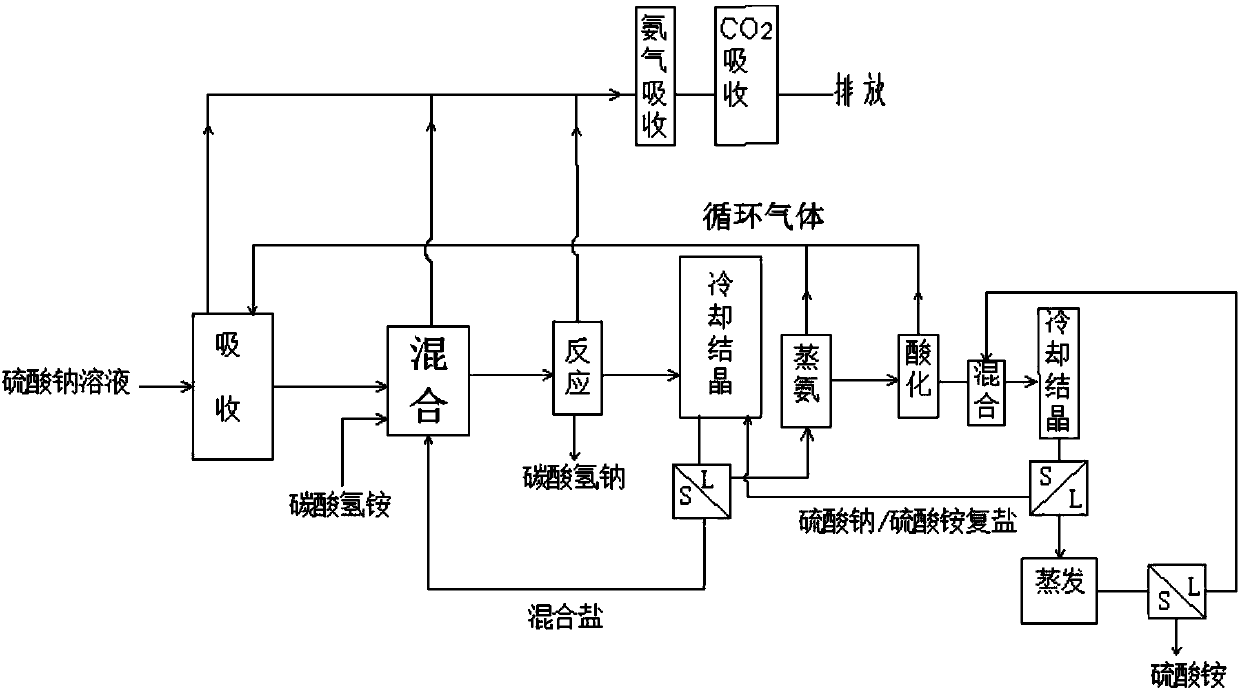
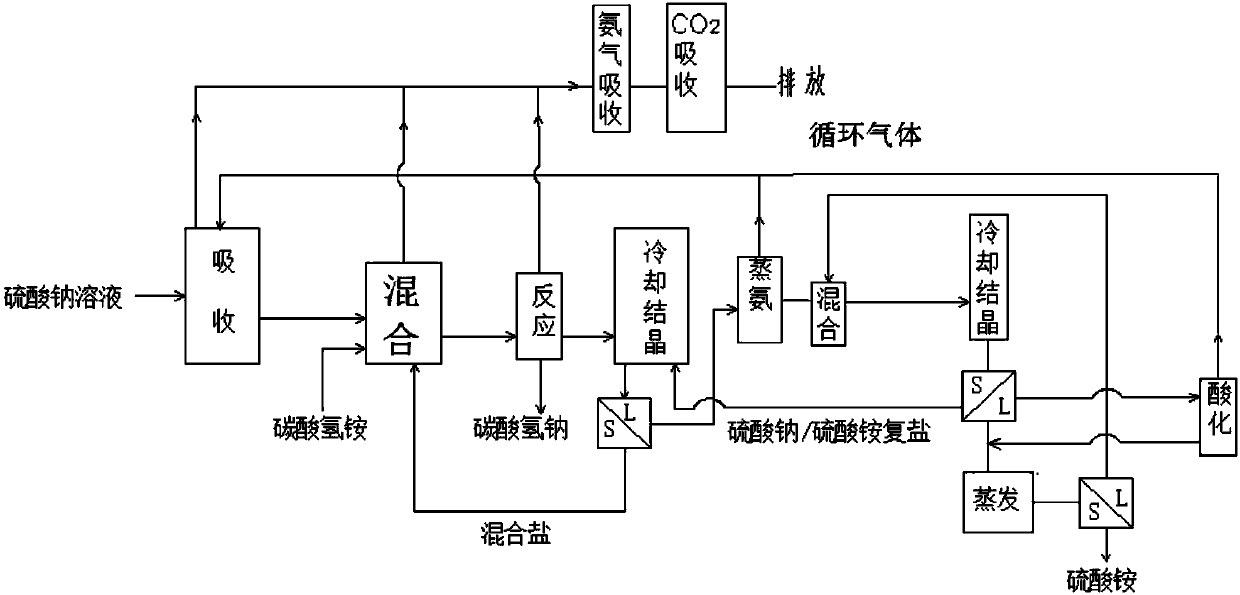
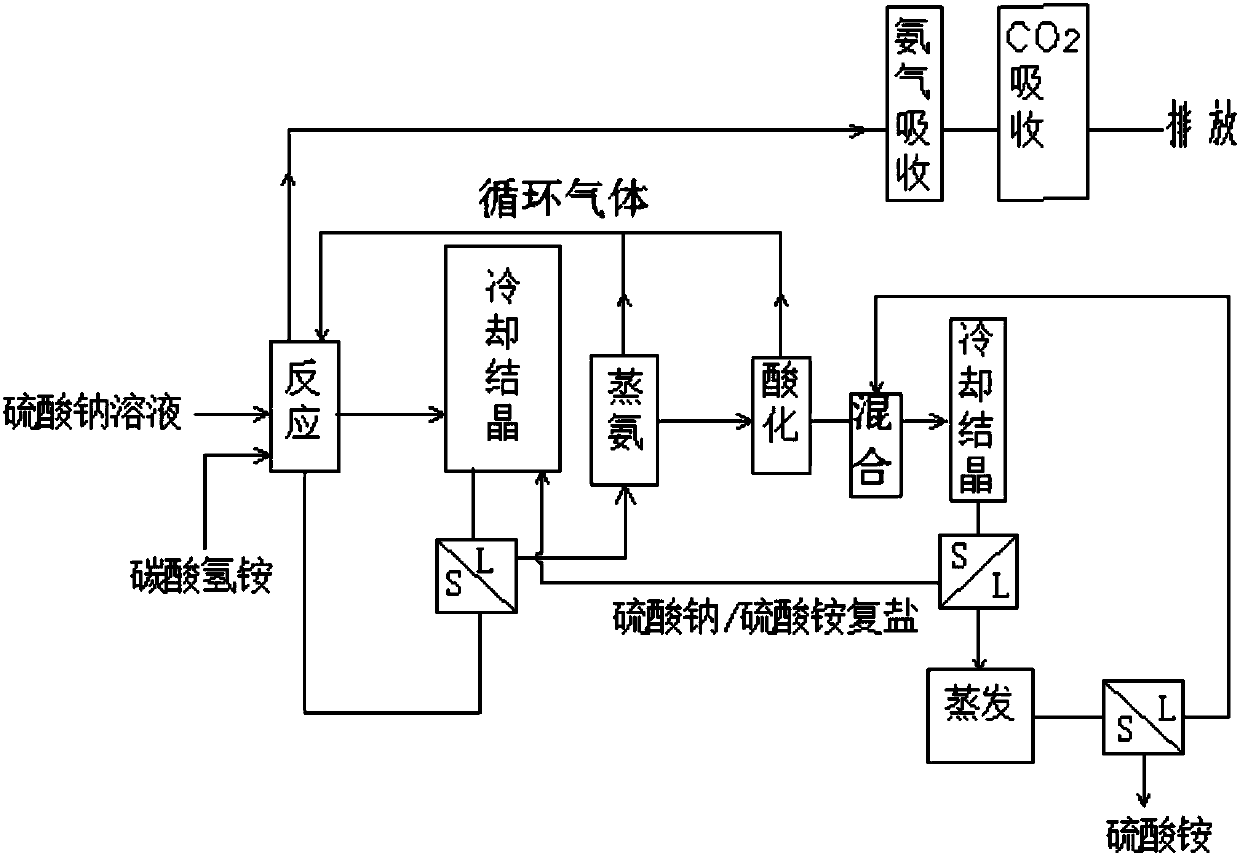
Method for producing sodium hydrogen carbonate and ammonium sulfate by using sodium sulfate solution
ActiveCN108046295ASolve pollutionImprove absorption rateCarbonate preparationAmmonia compoundsSodium bicarbonateHydrogen
The invention relates to a method for producing sodium hydrogen carbonate and ammonium sulfate by using a sodium sulfate solution, and belongs to the technical field of chemical engineering. The method comprises the following steps: a, absorbing circulating gas by using the sodium sulfate solution at -5 to 10 DEG C to obtain absorbing liquid; b, mixing the absorbing liquid, ammonium hydrogen carbonate and / or mixed salt at -5 to 20 DEG C to obtain mixed slurry; c, performing sealed reaction on the mixed slurry to obtain sodium hydrogen carbonate and reaction mother liquid; d, mixing the reaction mother liquid and complex salt to obtain salt mixture and primary frozen mother liquid after freezing; e, distilling the primary frozen mother liquid to obtain carbon dioxide, ammonium circulating gas and ammonium steaming mother liquid; f, adjusting the ammonium steaming mother liquid by acid to obtain an acidified solution and gas; g, mixing and freezing the acidified solution and crystallizedmother liquid to obtain complex salt and secondary frozen mother liquid; and h, evaporating and concentrating the secondary frozen mother liquid to separate out ammonium sulfate. The method is low inenvironmental pollution and high in raw material utilization rate.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
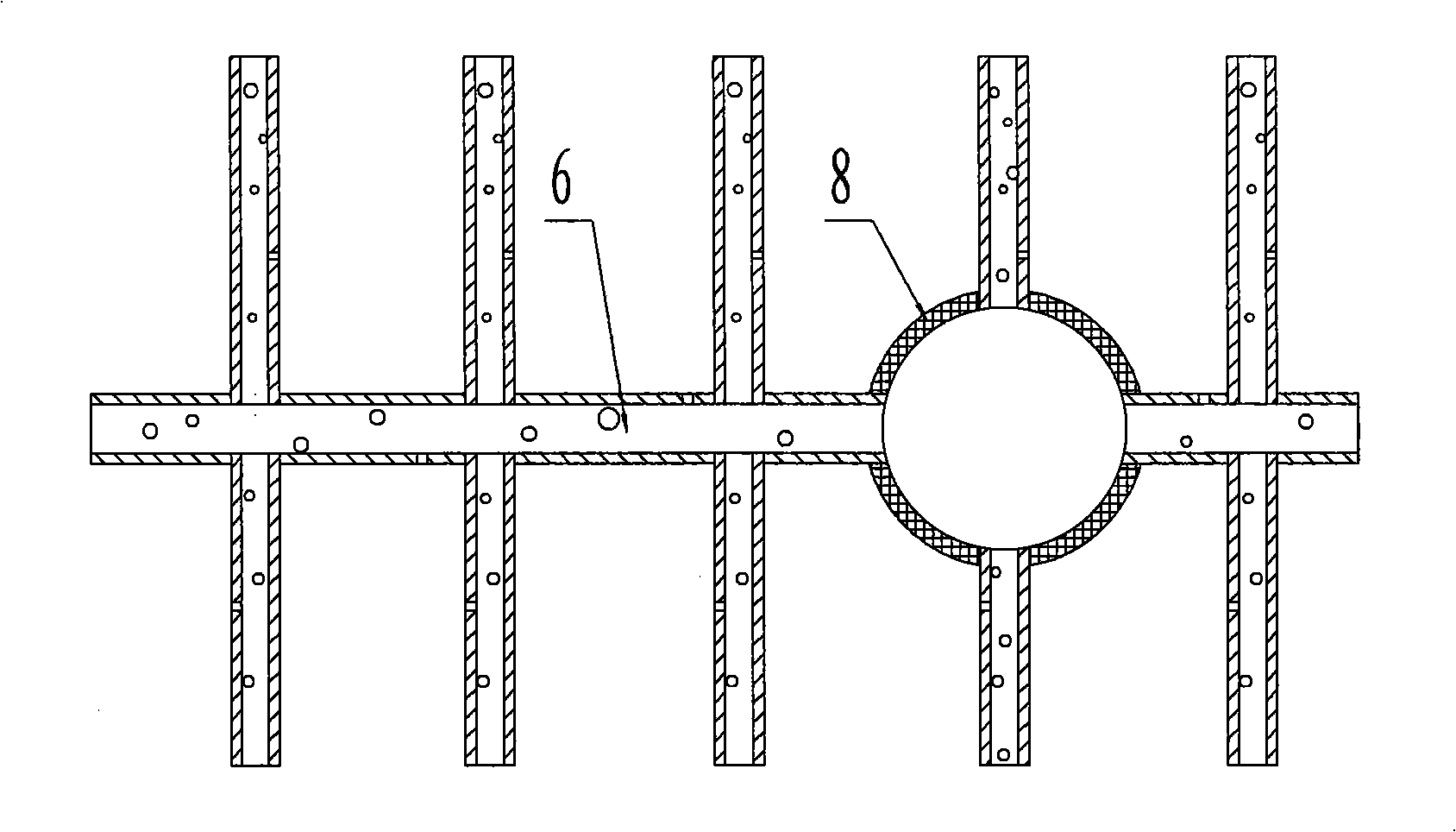
Saline-alkali soil treatment method
The invention relates to a saline-alkali soil treatment method. The method comprises the steps of establishing a concealed pipe salt drainage system under coastal original saline-alkali soil, and enabling concealed pipes of the concealed pipe salt drainage system to be 1m-2m away from the ground; enabling a rubble layer and a zeolite and rubble mixing layer which have a total thickness of 15-35cm to be laid above the concealed pipes, enabling the rubble layer and the zeolite and rubble mixing layer to form double salt separation layers, enabling the volume ratio of zeolite to rubble to be (0.5-1):(0.8-3) in the zeolite and rubble mixing layer, and after the laying is finished, laying a geotextile on a surface layer of the zeolite and rubble mixing layer; enabling furfural residue and the original soil to be evenly mixed according to the volume ratio of (0.5-2):(10-20), performing backfill and compaction, and forming a furfural residue and original soil improvement layer; watering the soil slowly until moisture in the soil reaches a saturated state and then irrigating the soil with great water, and eliminating salt in the soil through the concealed pipe salt drainage system until the average total salt content of the salt in soil within one meter is smaller than or equal to 0.5%. The saline-alkali soil treatment method is a comprehensive treatment method integrating various modes in engineering, water conservancy, physics and biology and the like.
Owner:BEIJING ORIENT LANDSCAPE
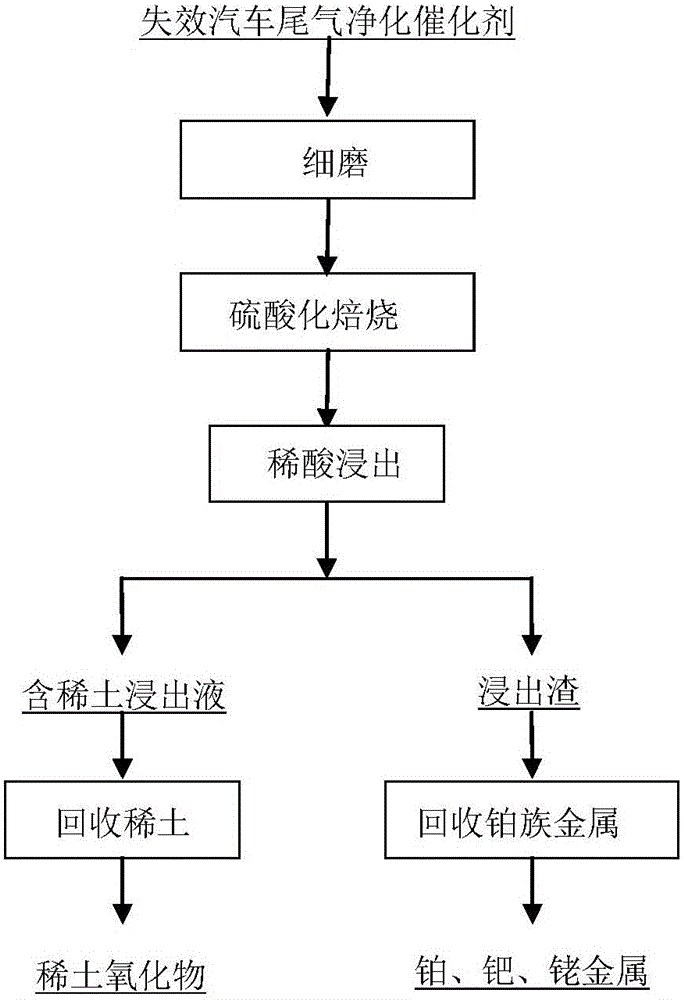
Method for recycling rare earth and platinum group metal from spent automobile emission purification catalyst
The invention discloses a method for recycling rare earth and platinum group metal from a spent automobile emission purification catalyst. The method comprises the following steps that 1, fine grinding is carried out; 2, sulfatizing roasting is carried out; 3, dilute acid leaching is carried out, wherein a roasted product in the second step is subjected to dilute sulfuric acid leaching, and a rare earth sulfate solution and platinum group metal bearing insoluble slag are obtained after filtering and separating; 4, the rare earth is recycled, wherein sodium sulfate is added to the rare earth sulfate solution obtained in the third step, rare earth sulfate double salt precipitation is generated, and lanthanum-cerium rare earth oxide is prepared; and 5, the platinum group metal is recycled, wherein hydrochloric acid and chlorine are adopted in the insoluble slag obtained in the third step for leaching of the platinum group metal, and leachate is subjected to treatment through an existing separating and purifying refining process, so that platinum, palladium and rhodium of the platinum group metal are obtained. Compared with the prior art, the method can be adopted for effectively recycling the rare earth and the platinum group metal from the spent automobile catalyst, the method is simple and practicable, all needed equipment is mature and universal equipment in the field of metallurgy, and the production cost is low.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PRECIOUS METALS
Beneficiation reagent, synthesis method and method for comprehensively utilizing generated waste gases
The invention discloses a beneficiation reagent, a synthesis method and a method for comprehensively utilizing generated waste gases. The beneficiation reagent is formed by solid-phase synthesis of inorganic or organic raw materials and comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 300 to 700 parts of a nitrogen-containing compound, 500 to 800 parts of chlorine salt, 400 to 650 parts of carbonate, 80 to 160 parts of strong alkali, 50 to 500 parts of cyanide complex double salt, 0 to 300 parts of cyanate, 5 to 20 parts of potassium sulfide, 50 to 200 parts of carbon and 0 to 100 parts of lime nitrogen. The beneficiation reagent is prepared by the following steps: mixing the raw materials uniformly; adding the mixed raw materials into a reaction kettle; quickly heating to 500 to 1,200 DEG C; maintaining high temperature for 1 to 2 hours; and cooling and crushing to obtain the product. Ammonia gas and carbon dioxide generated in a synthesis process are absorbed by a sodium sulfate solution to generate byproducts sodium carbonate and ammonium sulfate. The invention has the advantages of low production cost, simple operation, low toxicity and easy control. The product can be widely applied to leaching of noble metals such as gold oxide ores and silver oxide ores, floatation inhibitors and metal heat treatment and electroplating industries.
Owner:YUNNAN KEENLY NEW MATERIAL
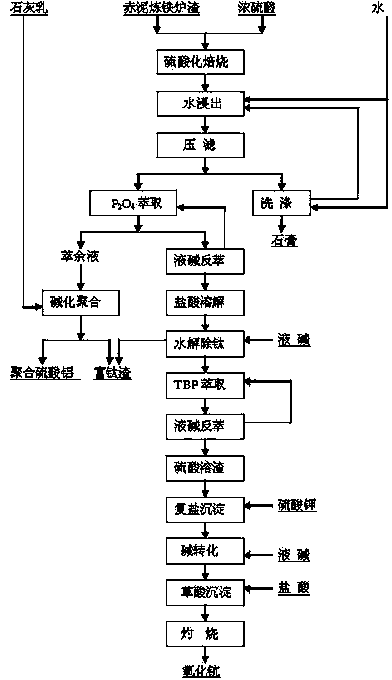
Method for recycling scandium from red mud slag
The invention provides a method for recycling scandium from red mud slag. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out sulfating roasting on red mud iron slag, soaking the processed slag in water, filtering so as to obtain filter residue gypsum, extracting the filtrate, carrying out a back extraction treatment on the organic phase with an alkaline solution of alkali metal, collecting the precipitate, dissolving the precipitate with hydrochloric acid, filtering, then adjusting the pH value of the filtrate with an alkaline solution of alkali metal, heating to carry out hydrolysis so as to turn titanium element into precipitate, filtering, collecting the filtrate; extracting the titanium-free filtrate with tributyl phosphate, then carrying out a back extraction treatment on the organic phase with an alkaline solution of alkali metal, collecting the precipitate, dissolving the precipitate with sulfuric acid, filtering, adding potassium sulfate into the filtrate to carry out double-salt reactions, then adding an alkaline solution of alkali metal into the double salt to carry out alkali conversion, collecting the precipitate, dissolving the precipitate with hydrochloric acid, adding oxalic acid into the solution to generate scandium oxalate precipitate, and collecting the precipitate. The method has the advantages of simple technology and easy operation, comprehensively utilizes the red mud, and eliminates the pollution to the environment and incident hazard caused by red mud piles.
Owner:GUIZHOU BRANCH CHINA ALUMINUM IND
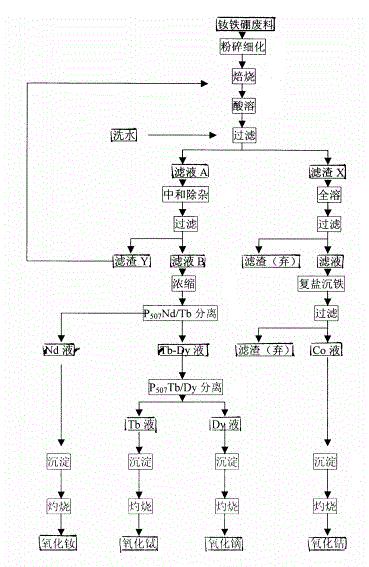
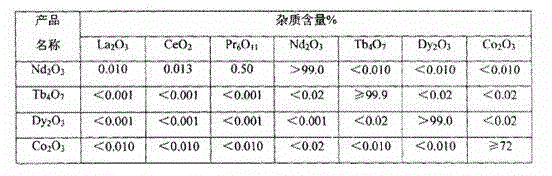
Neodymium, iron and boron waste recycling process with approximately zero wastewater discharge
InactiveCN102912134ANo pollution in the processEasy extractionProcess efficiency improvementDissolutionDouble salt
The invention discloses a neodymium, iron and boron waste recycling process with approximately zero wastewater discharge. The method is characterized in that recycling and separating for neodymium, terbium, dysprosium and cobalt in neodymium, iron and boron waste are researched, means such as fine grinding and crushing for the waste, oxidizing roasting, prior dissolution in hydrochloric acid, neutralization and impurity removal, double-salt iron settling and extraction separation are selected according to chemical properties of elements contained in the waste, valuable elements in the neodymium, iron and boron waste are successfully extracted, and neodymium oxide, terbium oxide, dysprosium oxide and cobalt oxide which are high in purity are obtained. The neodymium, iron and boron waste recycling process is simple, the production cost is low, an obvious economical benefit is realized, environmental pollution is prevented, and the process is applicable to industrial continuous production. Besides, the extraction rates of manufactured neodymium oxide, terbium oxide, dysprosium oxide and cobalt oxide products are maximized, and quality indexes of the manufactured neodymium oxide, terbium oxide, dysprosium oxide and cobalt oxide products meet industrial standards or customer standards.
Owner:XINFENG BAOGANG XINLI RARE EARTH
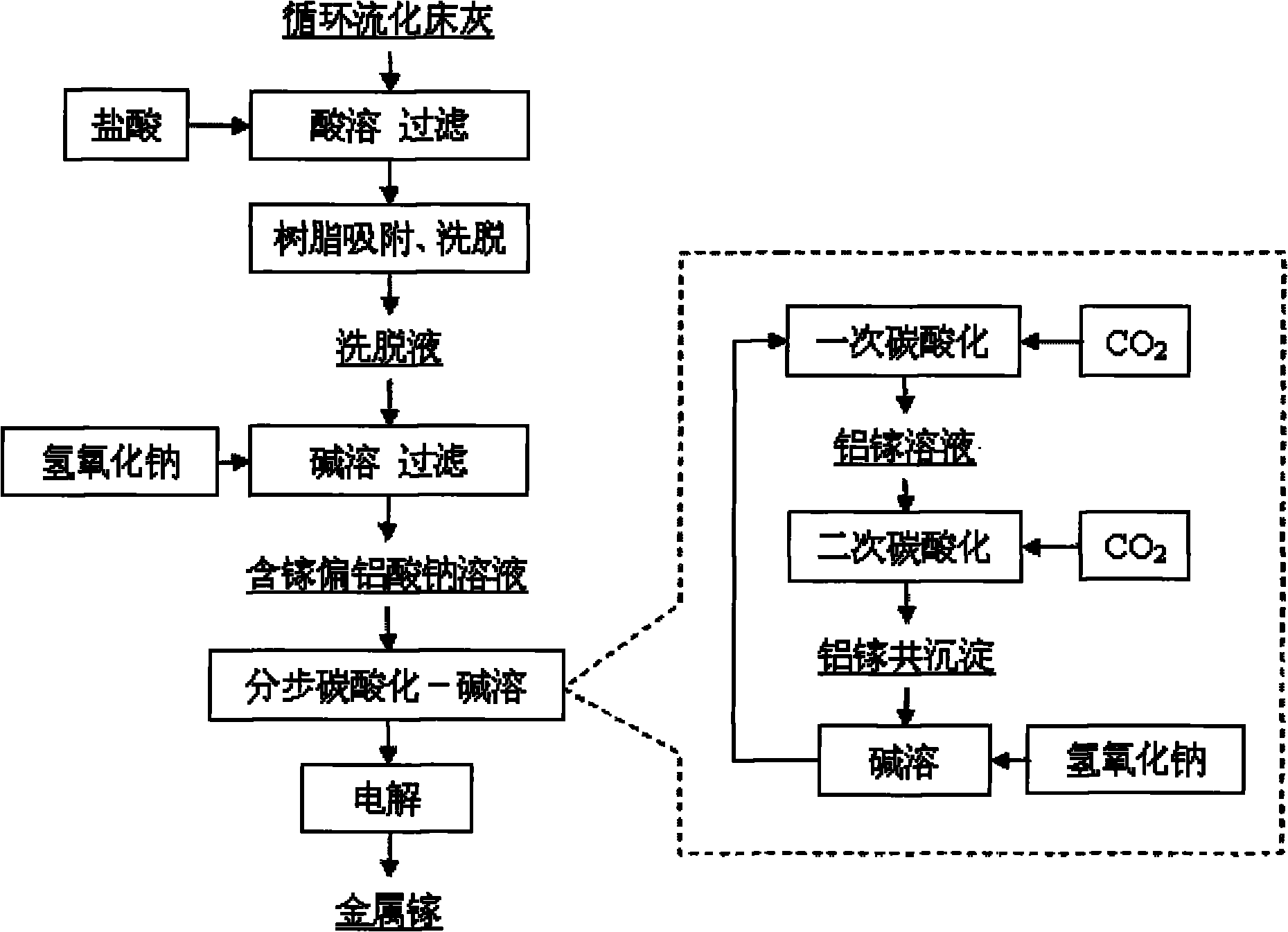
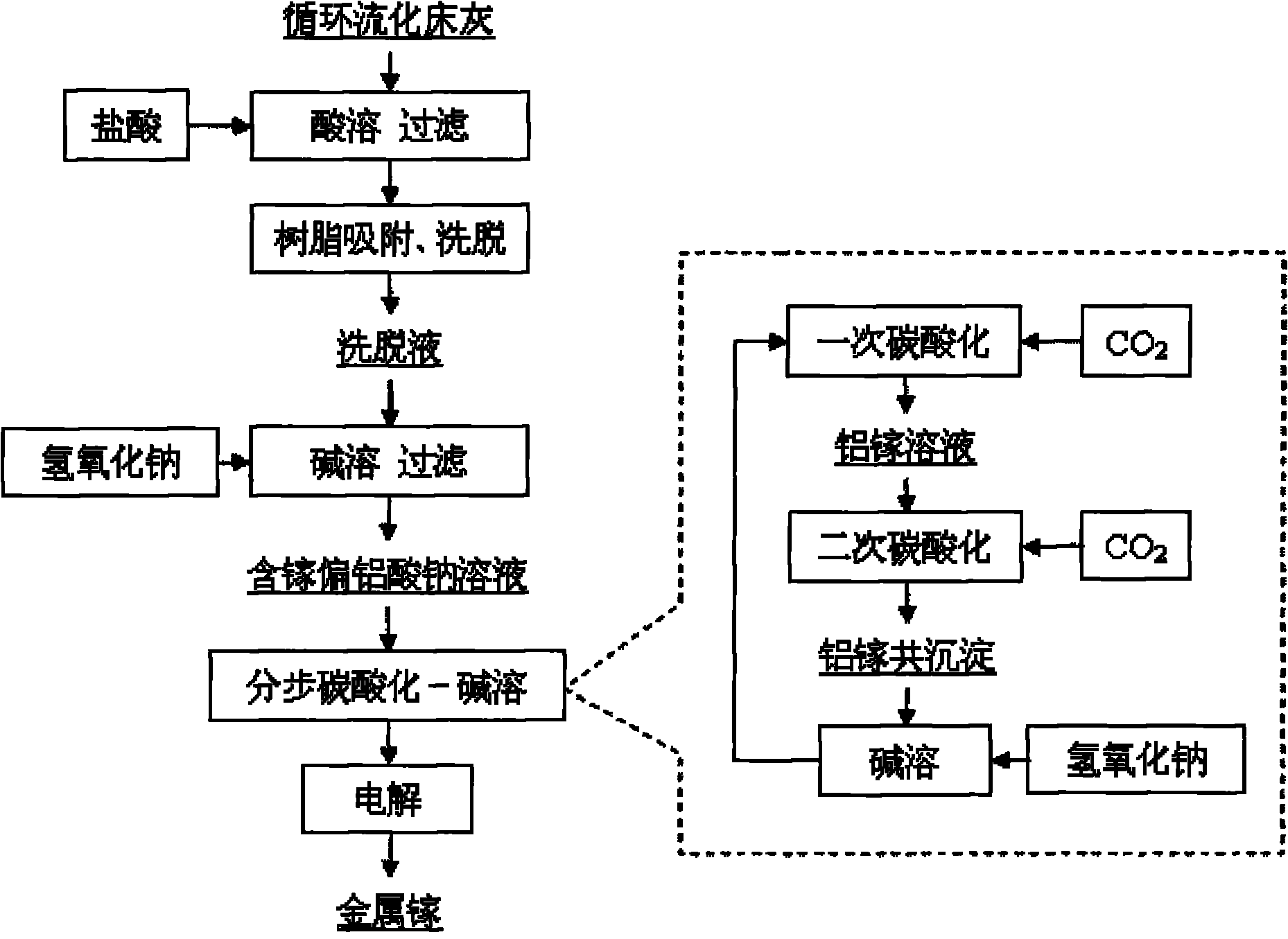
Method for extracting gallium from fly ash
InactiveCN101864525AHigh extraction rateOmit high temperature calcination activation stepHigh gradient magnetic separatorsProcess efficiency improvementElectrolysisDouble salt
The invention discloses a method for extracting gallium metal from fly ash of a fluidized bed. The method comprises the following steps of: crushing the fly ash, performing wet magnetic separation to remove iron, and reacting the fly ash with hydrochloric acid to obtain hydrochloric acid extract; b) introducing the hydrochloric acid extract into a macroreticular cation resin column for gallium adsorption and eluting the resin column by using eluant to obtain eluent; c) adding sodium hydroxide solution into the eluent to perform reaction to obtain gallium-containing sodium metaaluminate solution; d) introducing carbon dioxide into the gallium-containing sodium metaaluminate solution for carbonation to separate the gallium from the aluminum so as to obtain aluminum gallium double salt of which the mass ratio of the gallium to aluminum oxide is greater than 1 to 340; and e) adding the aluminum gallium double salt into the sodium hydroxide solution to perform reaction so as to obtain the gallium-containing aluminum alkaline solution by adjusting the alkalinity and performing concentration; and finally performing electrolysis to obtain the gallium metal. The method has the advantages of simple process, high yield, low cost and stable product quality; and the obtained gallium metal product has gallium content of greater than or equal to 99.9 percent and reaches 3N level.
Owner:CHINA SHENHUA ENERGY CO LTD +1
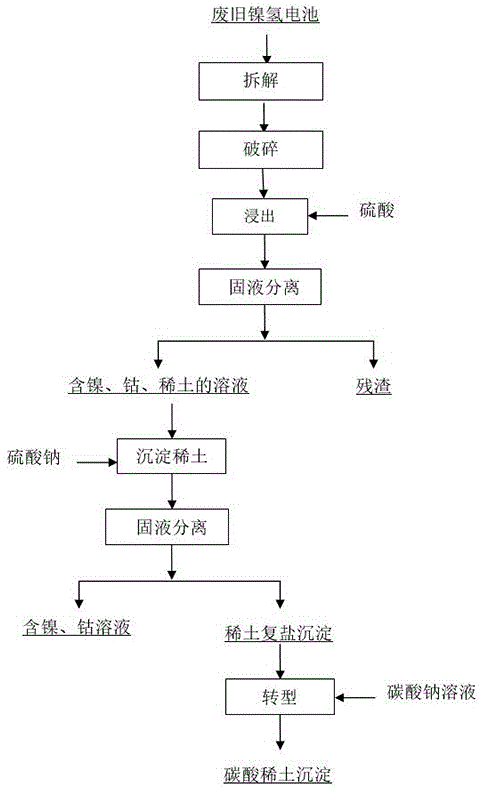
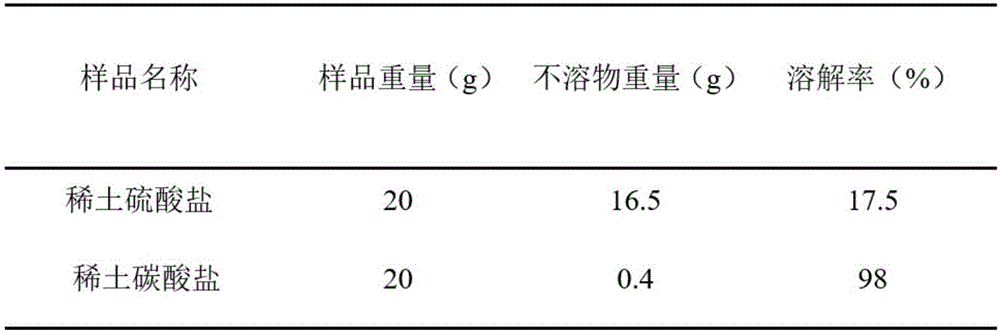
Method for recycling rare earth from waste nickel-hydride battery and conducting transformation
ActiveCN106222456AEasy to recycleImprove solubilityWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementReaction temperatureRare earth
The invention discloses a method for recycling rare earth from a waste nickel-hydride battery and conducting transformation. The method comprises seven steps including the first step of crushing treatment, the second step of acid leaching treatment, the third step of primary solid-liquid separation, the fourth step of primary sedimentation treatment, the fifth step of secondary solid-liquid separation, the sixth step of sulfuric acid rare earth double salt transformation treatment and the seventh step of rare earth sedimentation extraction. Compared with rare earth sulfate, carbonic acid rare earth sediment is easy to dissolve, the carbonic acid rare earth sediment can be better conducted to further deep processing and can be well separated from nickel and cobalt in the waste nickel-hydride battery, recycling of the rare earth is facilitated, and other valuable metal can be recycled. The reaction is conducted under the normal pressure, the reaction temperature is low, and therefore energy consumption is low. The waste nickel-hydride battery is crushed under the temperature condition of 15 DEG C, volatilization of harmful substances of the waste nickel-hydride battery can be reduced, and the waste nickel-hydride battery can be easier to crush; and to prevent temperature rise of the waste nickel-hydride battery due to collisions in the crushing process, it is most proper to crush the waste nickel-hydride battery in winter.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED
Preparation method for preparation containing glucosamine and application thereof
InactiveCN101947234AHeavy metal active ingredientsPowder deliveryGlucosamine SulfateGlucosamine Hydrochloride
The invention discloses a preparation method for preparation containing glucosamine and an application thereof. The preparation is characterized in that the major component is one or the combination of more of the glucosamine, glucosamine hydrochloride, glucosamine sulfate sodium chloride double salt or potassium chloride double salt, and chondroitin sulfate. The preparation method is simple, convenient and time-saving to operate and is easy for large industrialized production.
Owner:南京威尔曼药物研究所有限公司
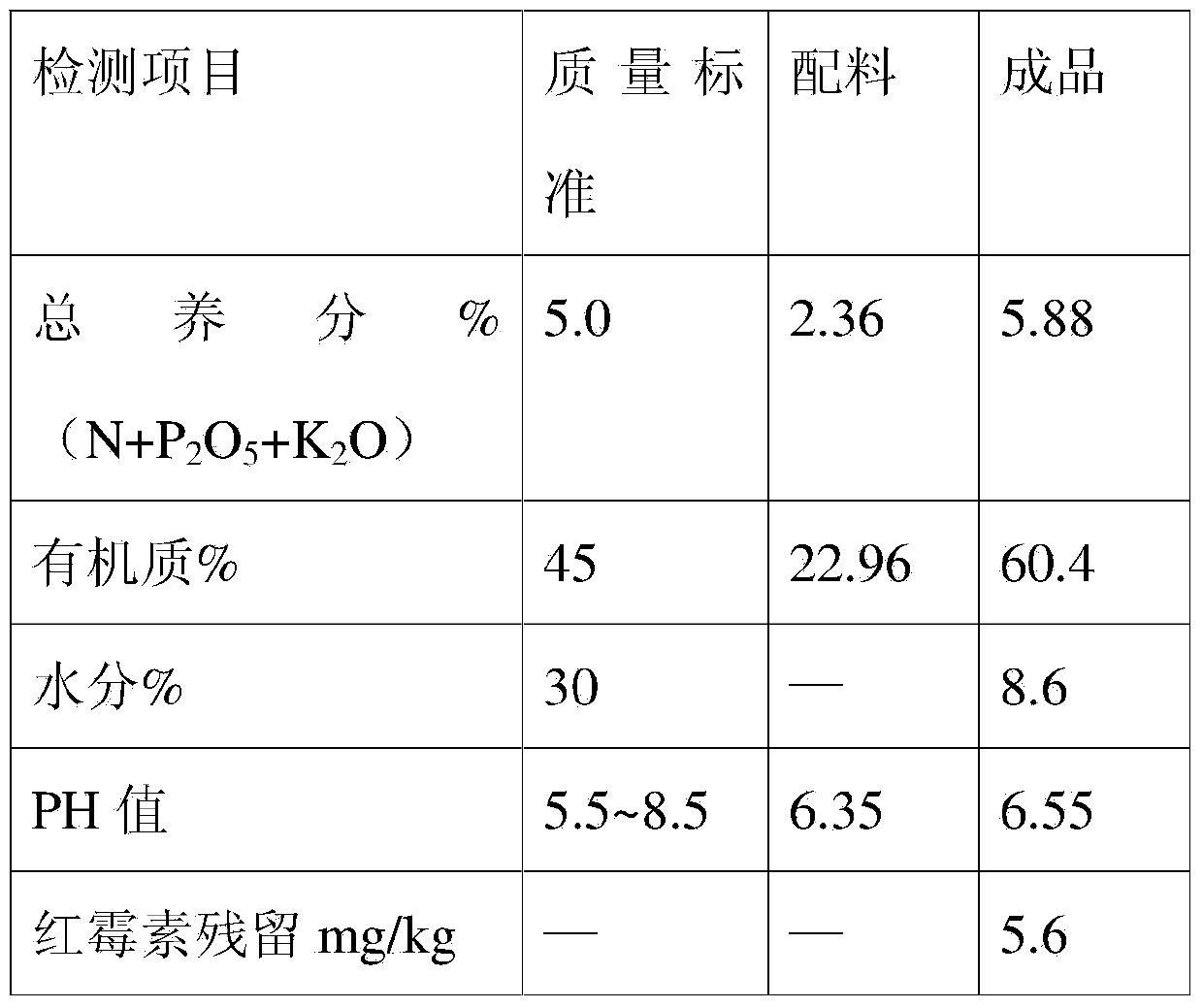
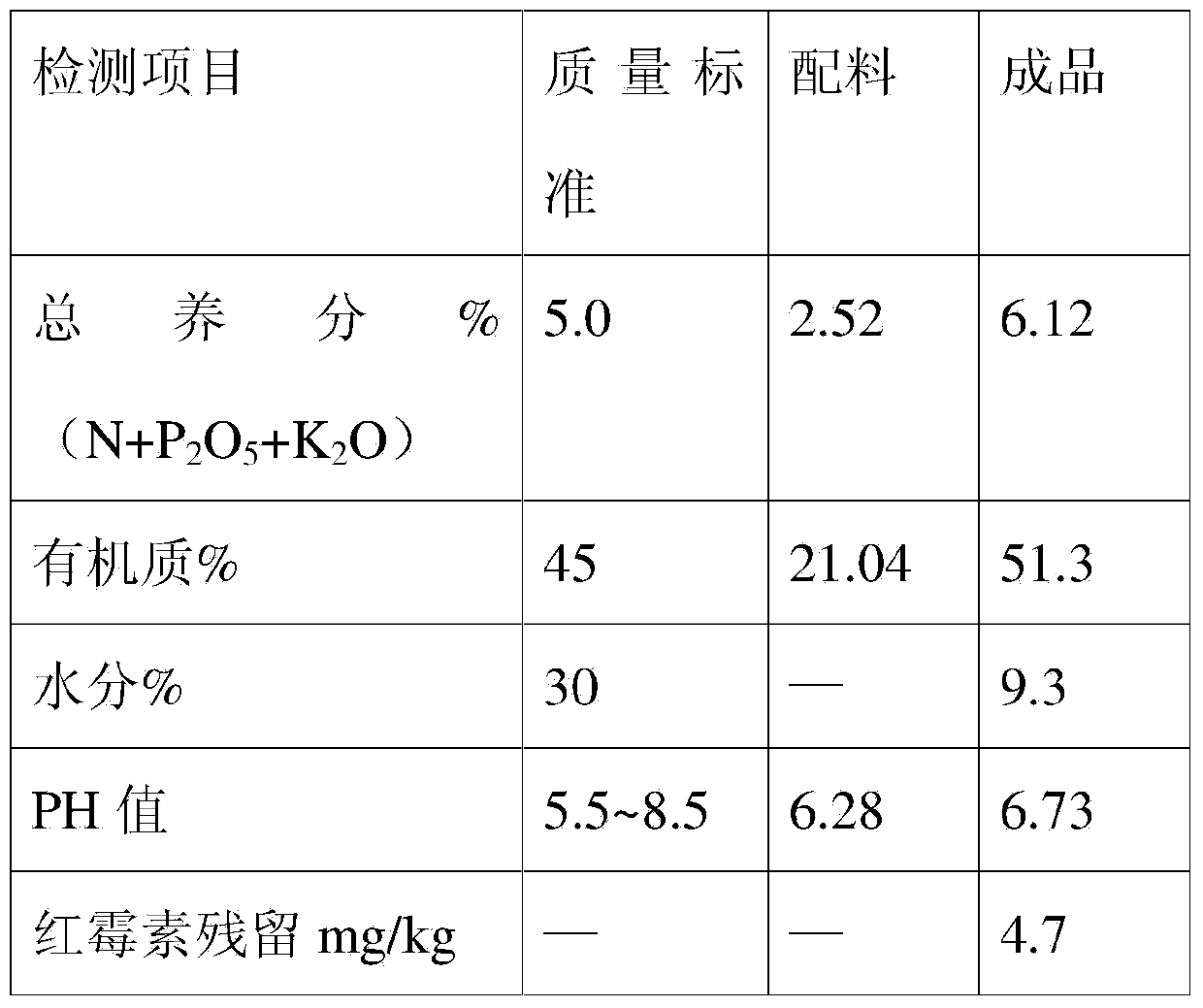
Method for producing organic fertilizer by using erythromycin waste residue and tetracycline urea double salt mother liquor
The invention relates to a method for producing an organic fertilizer by using erythromycin waste residue and tetracycline urea double salt mother liquor. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: evenly mixing erythromycin waste residue hydrolysate obtained by heating and hydrolyzing under an acid condition with dialysate of the tetracycline urea double salt mother liquor separated by an organic membrane in a manner of nanofiltration separation at a volume ratio of (2-3):1; then adding 5-10% of ammonium humate and 10-15% of bentonite based on total volume; evenly stirring, detecting that the total nutrient (N+P2O5+K2O) is greater than or equal to 2.0%, the organic matter is greater than or equal to 20% and the dry matter is greater than or equal to 35%; spraying and pelletilizing when the PH is 5.5-8.5, drying until the moisture is smaller than or equal to 20%, and sieving, so as to obtain the product, namely the organic fertilizer. By adopting the method, the organic fertilizer is prepared from the hydrolyzed erythromycin waste residue hydrolysate obtained by hydrolytic degradation and the dialysate of the tetracycline urea double salt mother liquor separated by the organic membrane by nanofiltration separation in a mixing manner, so that the problem of environmental pollution of antibiotic residues is ended; reutilization of resources is taken in; new economic benefits are brought about for enterprises; furthermore, the method is sufficient in raw materials, and low in manufacturing cost.
Owner:NINGXIA QIYUAN PHARMA
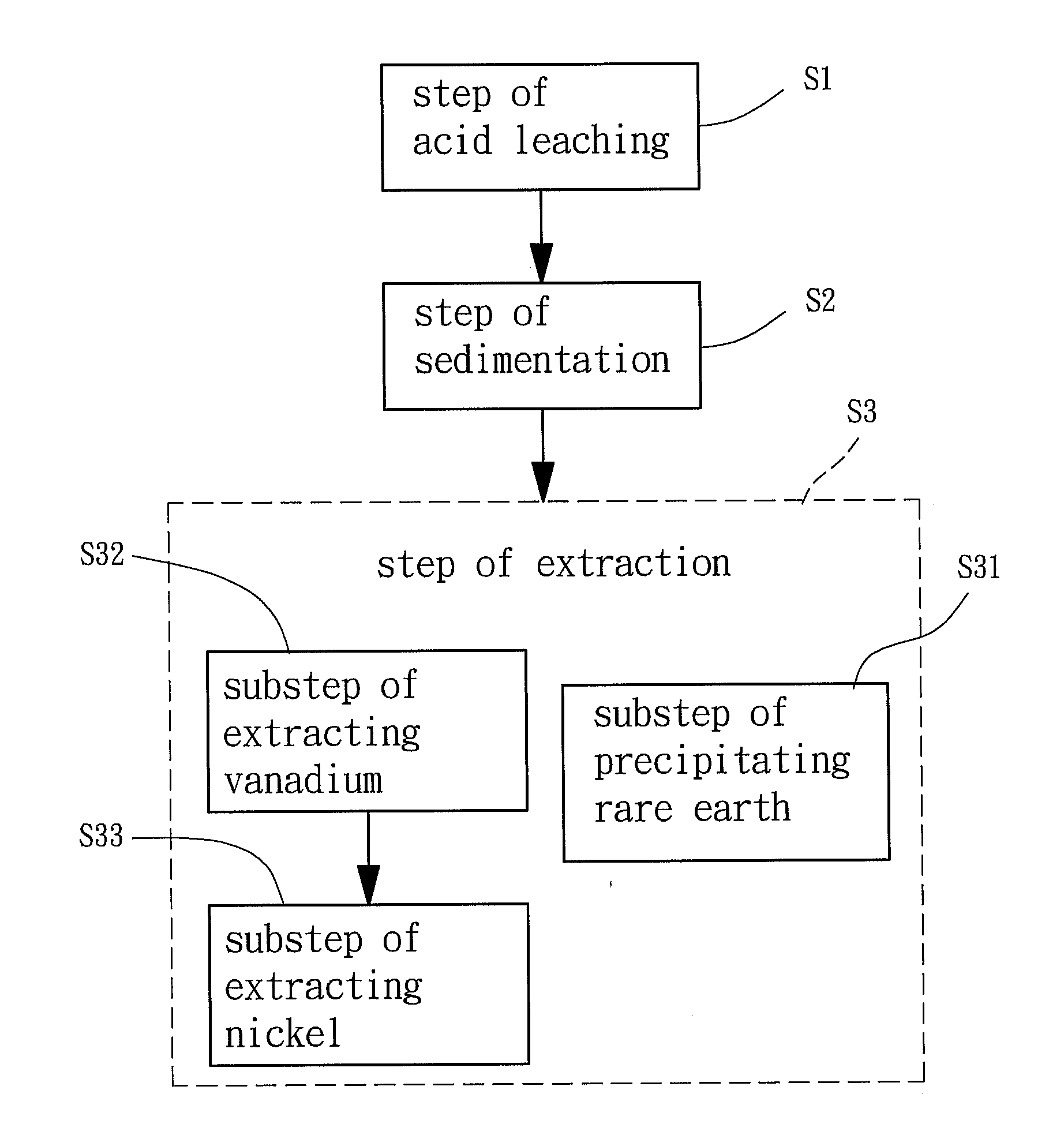
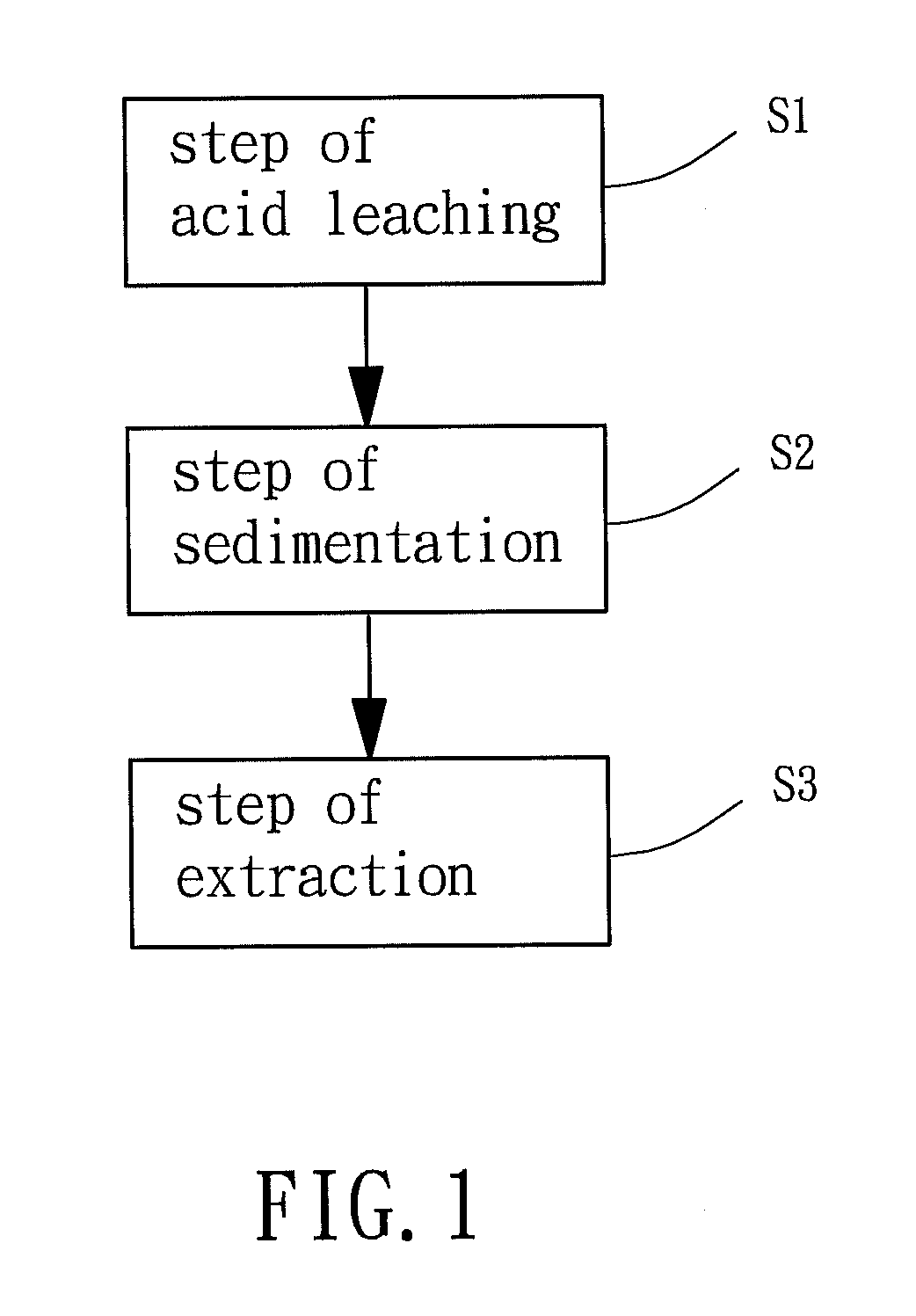
Method for recovering rare earth, vanadium and nickel
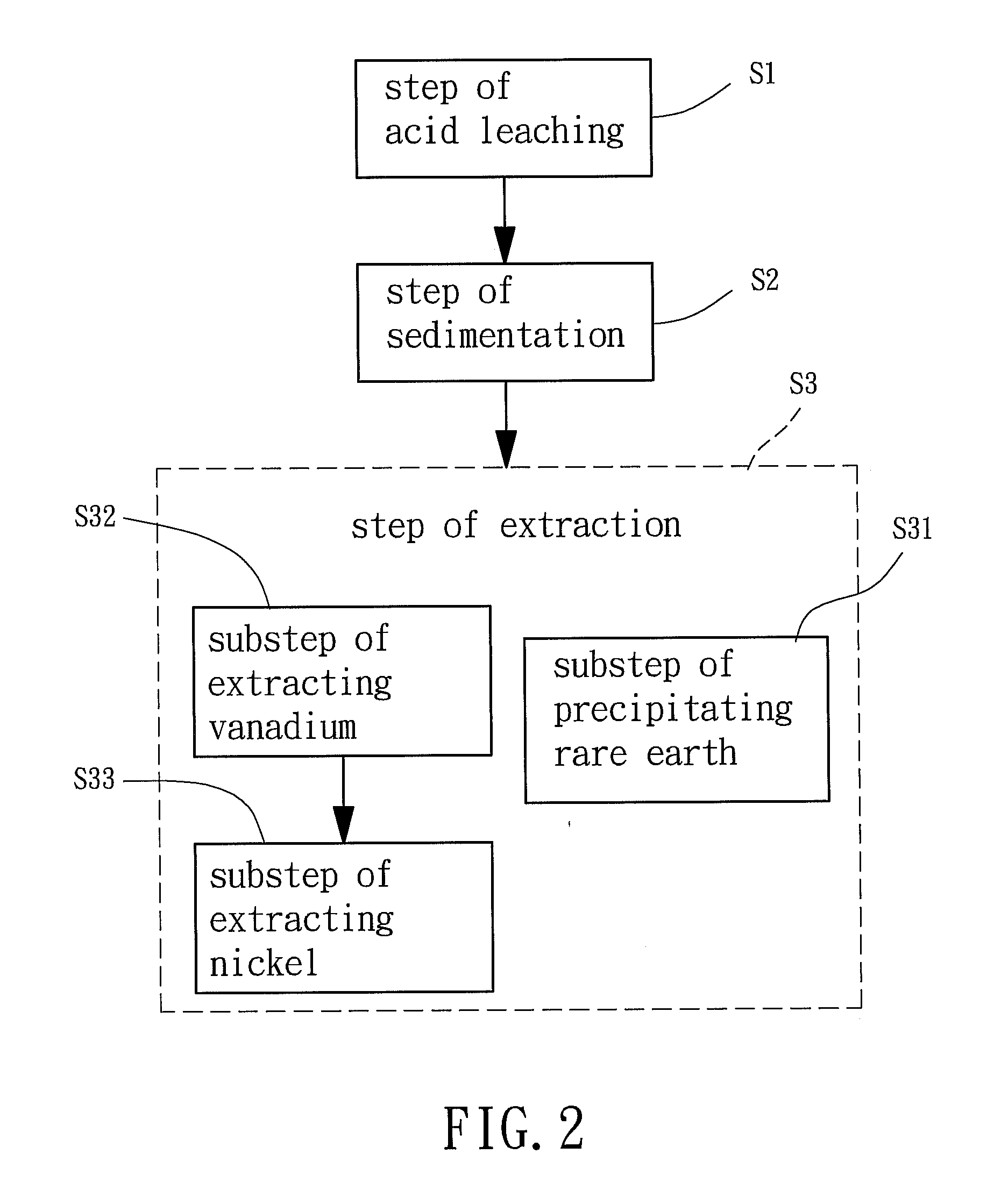
ActiveUS20130091989A1Quality improvementEffective recoveryProcess efficiency improvementFiltrationSlag
A method for recovering rare earth, vanadium and nickel from waste vanadium-nickel catalysts, comprising steps of: acid leaching, by soaking waste vanadium-nickel catalysts into a sulfuric acid solution and obtaining a mixture containing alumina silica slag; sedimentation, by filtering out the alumina silica slag from the mixture to obtain a filtrate, and then adding a salt into the filtrate to precipitate rare earth followed by isolating a sediment of rare earth double salts and a liquid solution via filtration; and extraction, by providing and adding an alkali into the sediment of rare earth double salts followed by further soaking the rare earth double salts in an acid solution to precipitate rare earth, and adding an oxidizer into the liquid solution to adjust the pH value thereof and then extracting vanadium and nickel from the liquid solution via an ion-exchange resin.
Owner:HONG JING INVESTMENT CO
Comprehensive recovery method of rare metal ore
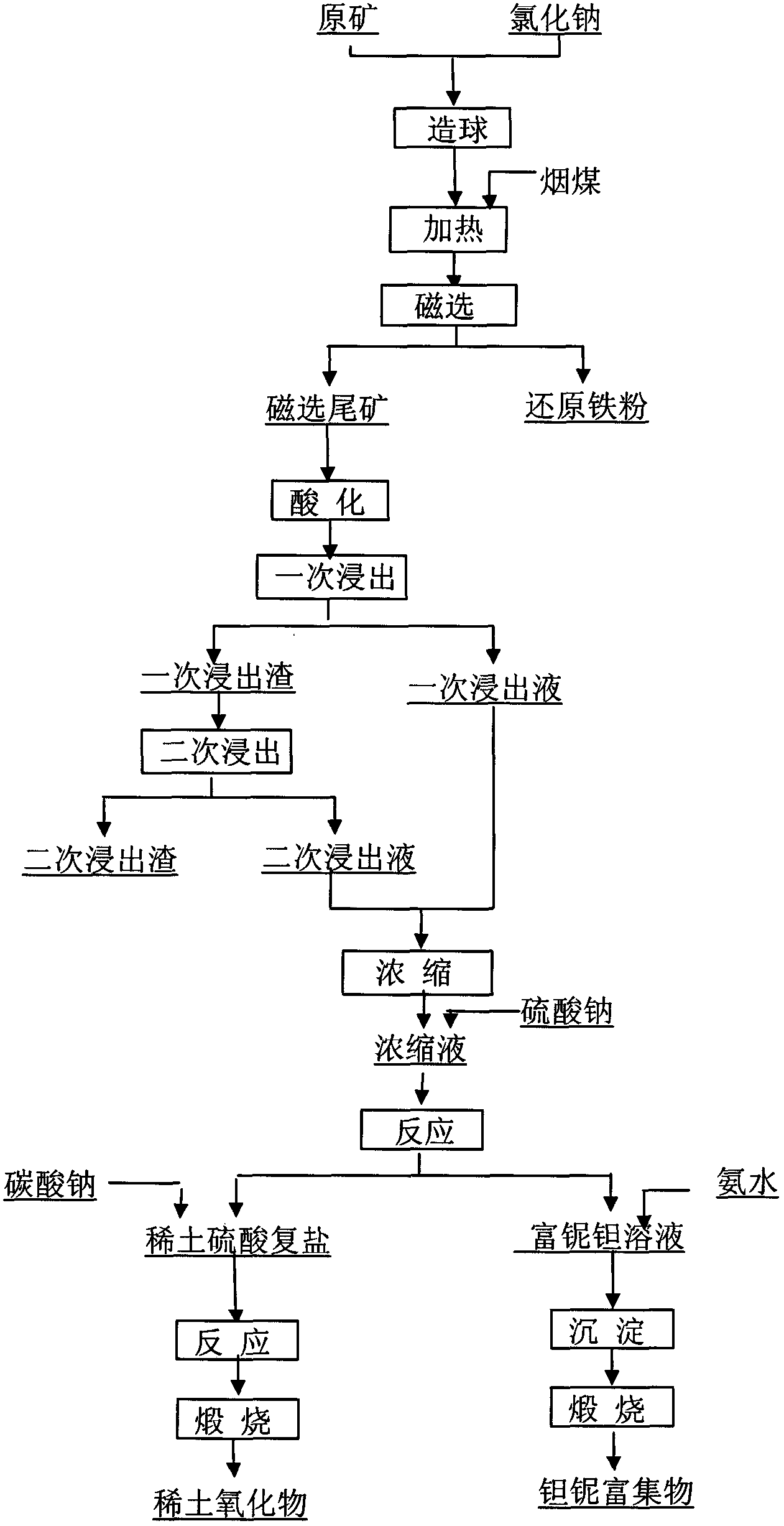
ActiveCN102703682AAchieve recyclingMagnetic separationProcess efficiency improvementRecovery methodNiobium
The invention discloses a comprehensive recovery method of rare metal ore. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: grinding the raw ore, adding sodium chloride, and uniformly mixing and pelletizing; drying the pellets and uniformly mixing with soft coal; performing heating, grinding and magnetic separation to obtain the reduced iron powder and magnetic separation tailings; adding concentrated sulfuric acid into the magnetic separation tailings for acidification; adding water for primary leaching; performing solid-liquid separation to obtain the primary leaching liquid and primary leaching slag; adding water into the primary leaching slag, leaching and performing solid-liquid separation to obtain secondary leaching liquid and secondary leaching slag; stockpiling the secondary leaching slag; mixing the primary leaching liquid and the secondary leaching liquid; concentrating; adding sodium sulfate to the concentrate; reacting and performing solid-liquid separation to obtain the rare-earth sulphate double salt and solution rich in niobium and tantalum; adding sodium carbonate solution to the rare-earth sulphate double salt; reacting to obtain rare-earth carbonate; calcining to obtain rare earth oxide; adding ammonia water to adjust the pH value of the solution rich in niobium and tantalum; stirring and performing solid-liquid separation to obtain niobium and tantalum precipitates; and calcining the precipitates to obtain the niobium and tantalum concentrate. The invention provides a comprehensive recovery method of rare earth, niobium and tantalum from the rare metal ore.
Owner:广东省资源综合利用研究所
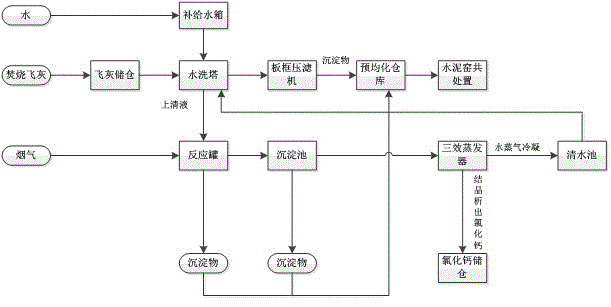
Method for recovering calcium salt by treating high Cl high CO2 burning flue gas and waste burning fly ash water washing lotion
InactiveCN104128080AEmission reductionReduce pollutionCalcium/strontium/barium chloridesDispersed particle separationDouble saltHigh carbon dioxide
The invention discloses a method for recovering calcium salt by treating high Cl high CO2 burning flue gas and waste burning fly ash water washing lotion, which comprises the following steps: 1) flue gas and the water washing lotion are co-operated; 2)multiple-effect evaporation is carried out for recovering calcium salt. In the step 1) burning flue gas is introduced in a fly ash water washing lotion until pH value of the water washing lotion is reduced to 6-9; acidic gas such as hydrogen chloride in the flue gas is absorbed and neutralized by high alkalescence water washing lotion, calcium-heavy metal-chloride ion double salt is formed; carbon dioxide is slightly dissolved in water to form the calcium-heavy metal-carbonate ion double salt, and then the calcium-heavy metal-carbonate ion double salt is fixed; wherein pH of the water washing lotion is reduced to 6-9 from 11-13 which exceeds a national discharge standard; concentration of heavy metal ions such as zinc, copper, chromium and cadmium in the water washing lotion is reduced, and the heavy metal ions are conversed to calcium-heavy metal double salt sediment. In the step 2), a lot of residual calcium salt resource in the water washing lotion is recovered through multiple-effect evaporation. The invention realizes the harmlessness and resource treatment for two wastes of high chlorine high carbon dioxide burning flue gas and garbage burning fly ash water washing lotion.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
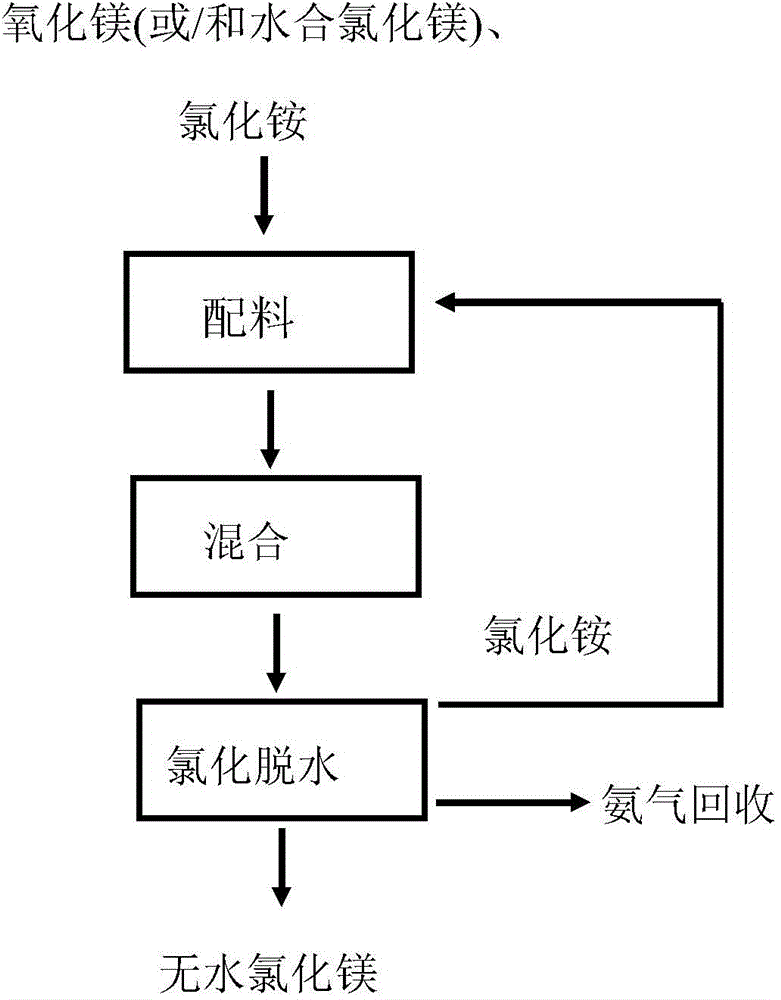
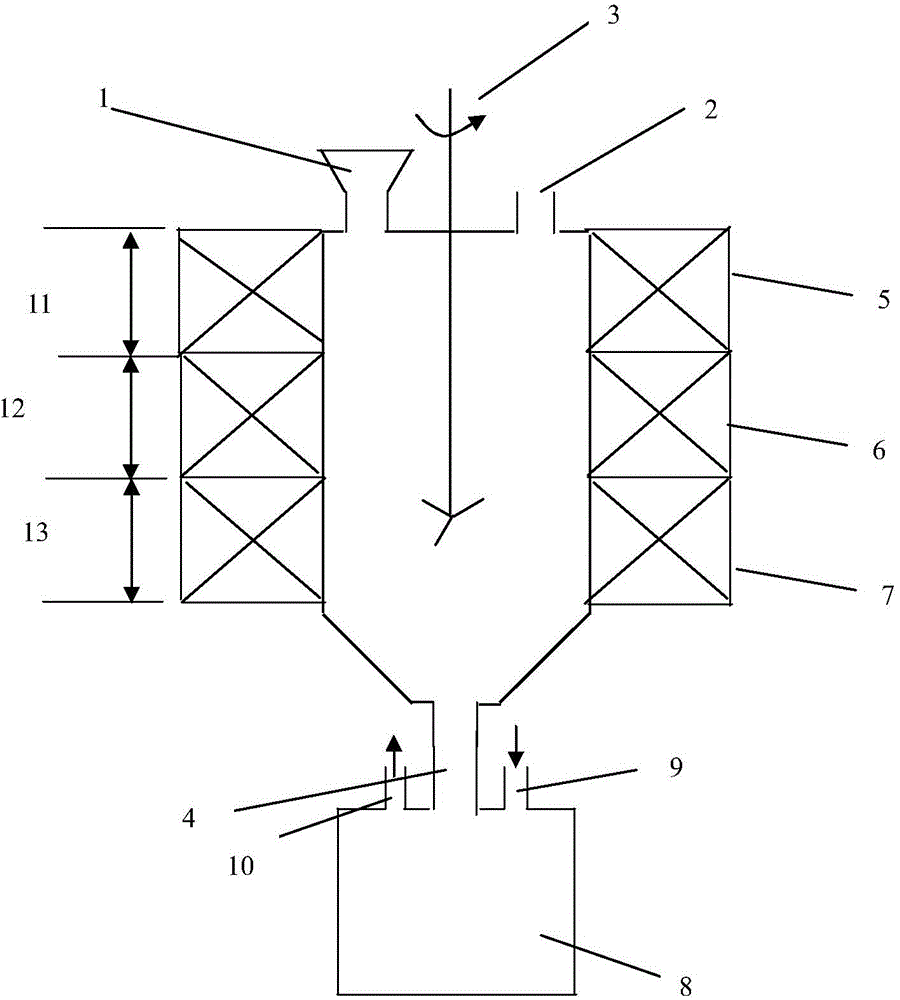
Method and device for preparing anhydrous magnesium chloride
The invention relates to a device for preparing anhydrous magnesium chloride and a preparation method which uses the device. The device is a chlorination dehydration furnace and comprises a storage cabin, wherein the upper part of the storage cabin is a preheating zone; the middle part of the storage cabin is a double salt forming zone; the bottom of the storage cabin is an ammonium removing zone; the storage cabin is connected with an outlet and has certain sealing property. The preparation method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing magnesium oxide and / or hydrated magnesium chloride and ammonium chloride, adding the mixture into the chlorination dehydration furnace, and heating, thereby preparing anhydrous magnesium chloride; and repeating the above operation steps when the anhydrous magnesium chloride is discharged out, thereby achieving continuous production. A method for preparing anhydrous magnesium chloride by using the rich magnesite and magnesium chloride hexahydrate resources in China is provided by the invention, continuous production of anhydrous magnesium chloride is achieved, the production efficiency is improved, the production cost is lowered, and the cost of environment protection is lowered; the prepared anhydrous magnesium chloride is high in purity, the content of the main impurity magnesium oxide in the anhydrous magnesium chloride can be controlled to be 0.5% or even less than 0.1%, and the anhydrous magnesium chloride can be used for preparing magnesium metal in an electrolysis manner and has very good industrial and commercial prospect.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
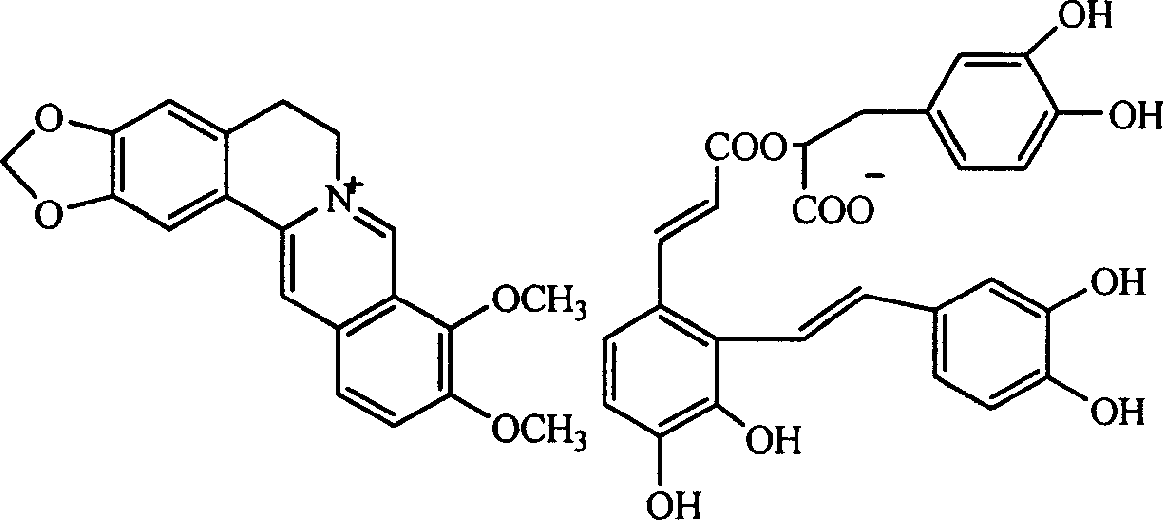
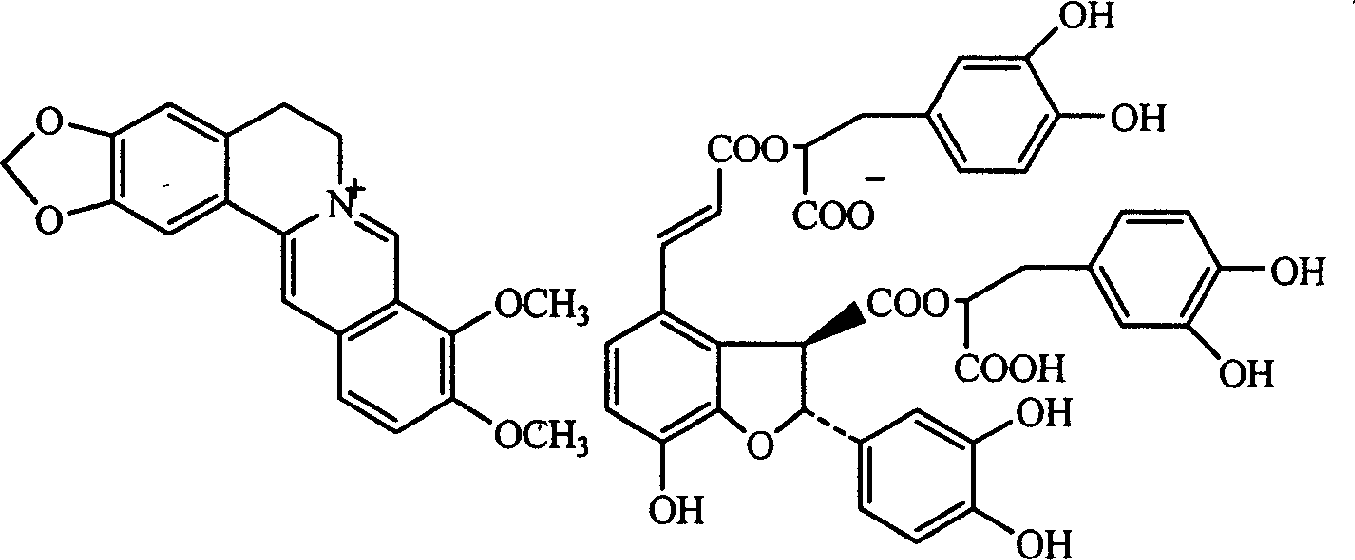
Salviolic acid berberine double salt, its preparation method and application
InactiveCN1651433AReduce solubilityGood water solubilityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiabetes mellitusBerberine
A berberine danshinolate used to prepare the medicines for treating chronic hepatism, diabetes, and its complications is prepared from berbeine and danshinolic acid or its derivative, which includes danshinolic acid A or B or their derivatives and metallic salts, the metallic salts of the derivatives of danshinolic acid A or B, and the red sage root's extract containing danshinolic acid A or B.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
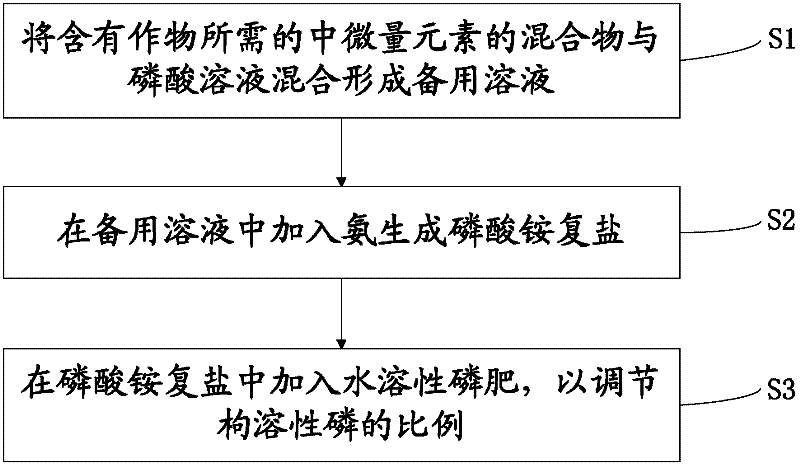
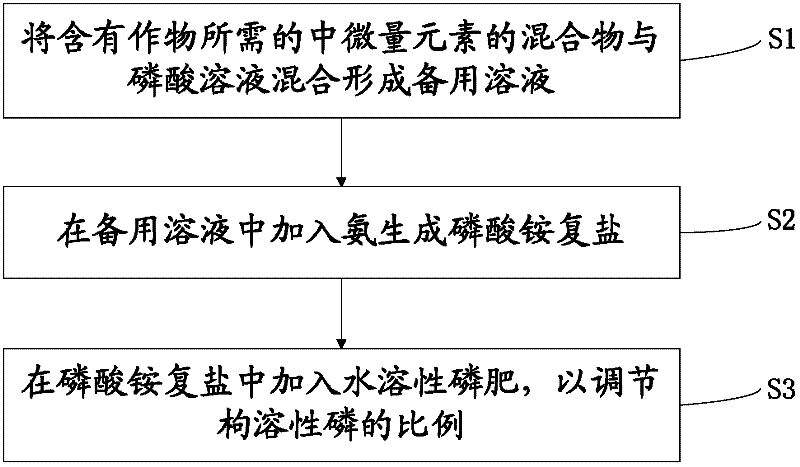
Preparation method of anti-aging, long-acting and multifunctional phosphate fertilizer
The invention provides a preparation method of an anti-aging, long-acting and multifunctional phosphate fertilizer. The method comprises the following steps of: (S1) mixing a mixture, which includes one or more of medium trace elements desired in the crop, with a phosphate solution so as to form a spare solution; and (S2) adding ammonia to the spare solution so as to generate ammonium phosphate double salt. The phosphate fertilizer prepared by using the preparation method of the anti-aging, long-acting and multifunctional phosphate fertilizer, which is provided by the invention, has the advantages of uneasiness for fixing the phosphate, long fertilizer action, aging resistance, multiple medium trace elements, comprehensive nutrients, speed lowering interdependence and convenience in use; the crop root development can be promoted; and the crop photosynthetic capacity can be improved.
Owner:AVIC FERTILIZER
Wet process phosphoric acid purification technology of nonphosphate precipitation
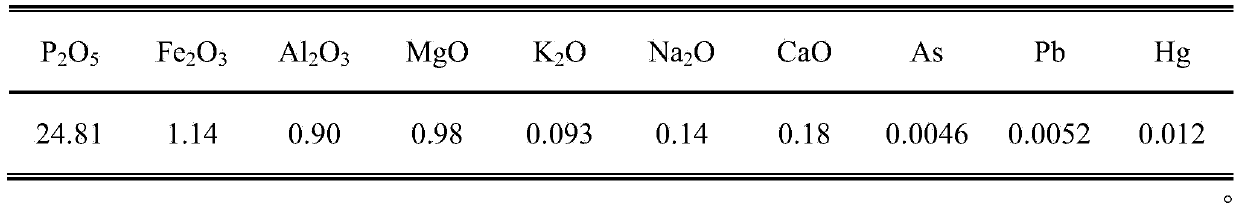
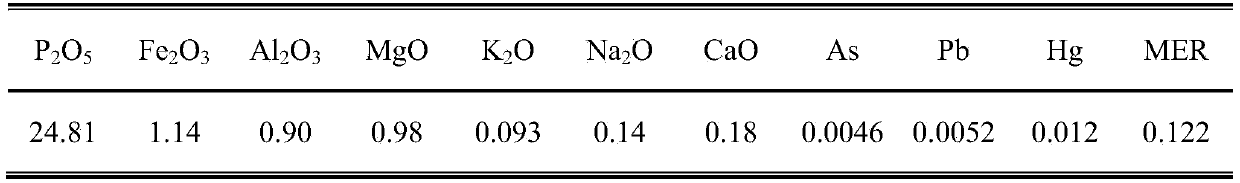
ActiveCN105366654AMeet the concentrationWater soluble fertilizerPhosphorus compoundsChemical industryHigh concentration
The invention discloses a wet process phosphoric acid purification technology of nonphosphate precipitation and belongs to the field of phosphorus chemical industry. According to the wet process phosphoric acid purification technology of nonphosphate precipitation, an agent is combined with anions and cations in diluted phosphoric acid to generate an indissolvable double salt which is precipitated in a form of nonphosphate, so that a purpose of wet process phosphoric acid purification is achieved, thereby satisfying the demand of producing a high-concentration phosphate fertilizer, a water soluble fertilizer and an industrial phosphate product. The method can remove iron, magnesium, aluminum, arsenic, lead, sodium, potassium, sulfate radicals and the like stably in wet process phosphoric acid and has characteristics of being simple in reaction condition, short in a process flow, wide in an agent source, low in a treatment cost, high in a P2O5 recovery rate and the like, so that sesquioxide-removal, heavy metal removal and desulfuration by a one-step method are realized. The removal rates of iron, magnesium and aluminum in the treated wet process phosphoric acid separately reaches above 97%, 70% and 15%; arsenic and lead in diluted acid are less than 5 ppm; sodium (calculated by NaO) and potassium (calculated by K2O) are separately lower than 0.025% and 0.083%; sulfate radicals are lower than 0.16%; and the P2O5 recovery rate is higher than 98.5%.
Owner:YUNNAN PHOSPHATE CHEM GROUP CORP
Method for separating copper and nickel from sulfuric acid solution containing copper and nickel
ActiveCN105018728AEfficient separationEfficient recyclingProcess efficiency improvementDouble saltDissolution
The invention provides a method for separating copper and nickel from a sulfuric acid solution containing copper and nickel. Ammonium sulfate salt or ammonia is added to the sulfuric acid solution containing copper and nickel, the copper and nickel in the sulfuric acid solution are separated out by crystallization in an ammonium sulfate double salt mode, and copper, nickel and ammonium sulfate double salt mixed crystals and liquid obtained after crystallization are obtained after filtering. The liquid obtained after crystallization is returned to the copper and nickel sulfuric acid solution preparation process for reuse. After water is added to the mixed crystals for dissolution, copper and nickel inside are separated and recycled through selective electro-deposition or selective solvent extraction or selective sulfuration, and ammonium sulfate is recycled in the technological process. The method has the advantages that the copper and nickel recovery rate is high, the separation effect is good, and the production cost is low; operation is easy and convenient, and environment friendliness is achieved; the method is suitable for industrial production applications for separating and recycling copper and nickel from the sulfuric acid solution containing copper and nickel.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
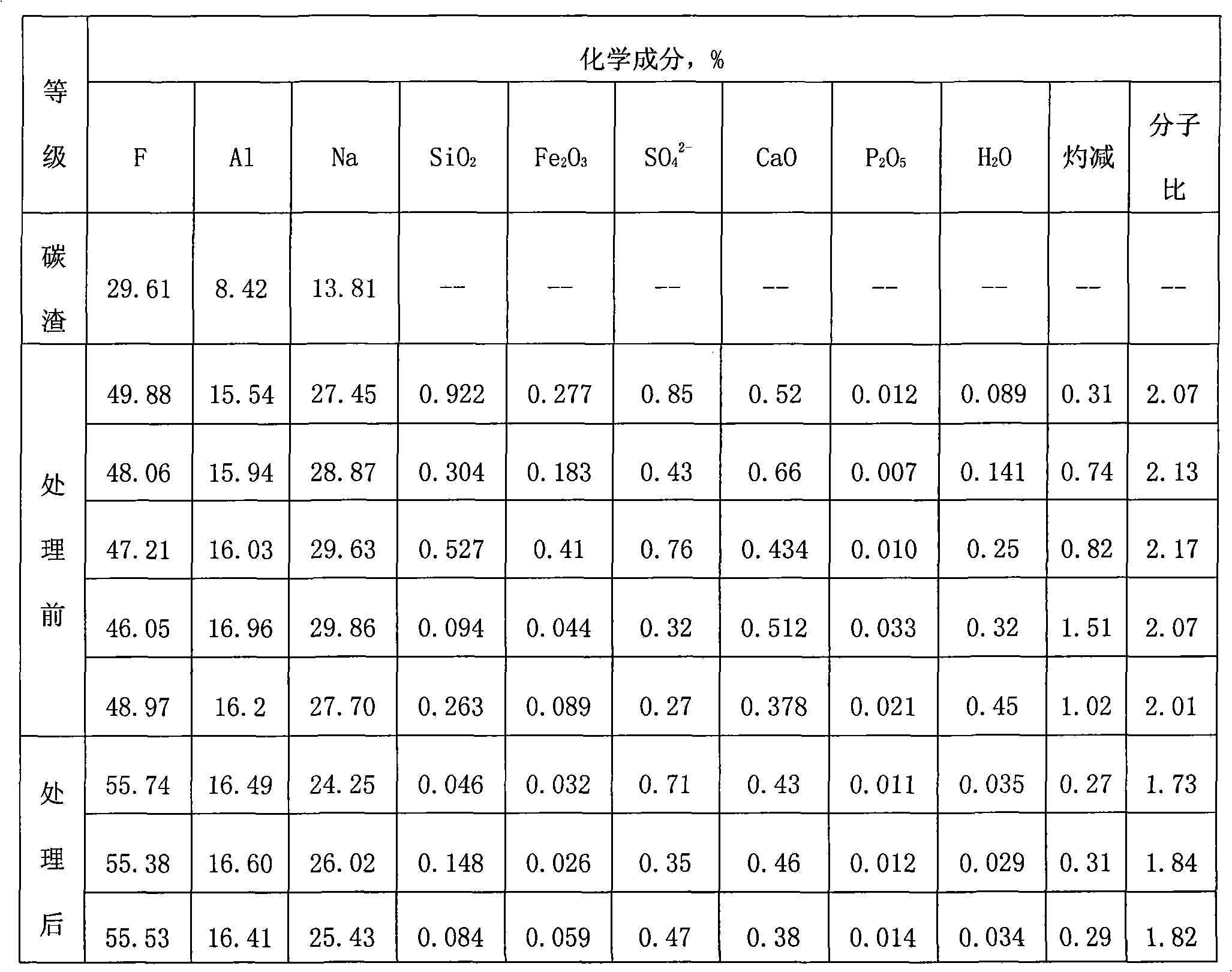
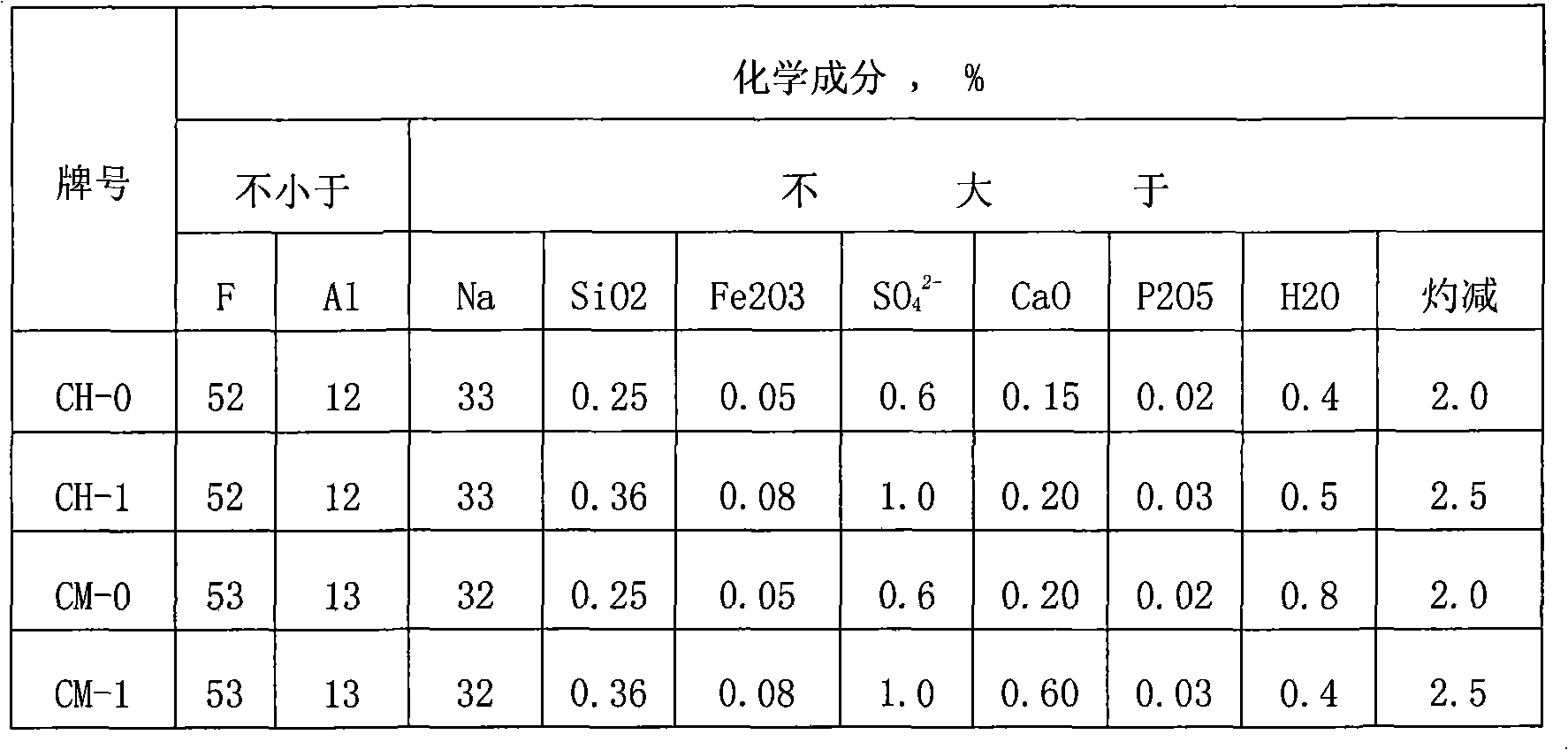
Method for preparing kryocide
The invention relates to a method for preparing cryolite, which takes carbon residue of aluminum factories and ammonium fluoroaluminate as raw materials which are then reacted with each other in a solid phase. The method adopts a great deal of waste residue of the electrolytic aluminum factories - the carbon residue and waste residue of the aluminum section industry - the ammonium fluoroaluminate as the raw materials, thereby the method creates a source of raw materials for producing villiaumite, relieves the dependency on fluorite, saves a large number of valuable resources, has low cost, greatly reduces the production cost, and relieves the ambient environmental pollution problem. Carbon powder containing about 10 percent of electrolyte obtained after flotation of the carbon residue can be dried and then used as auxiliary materials for adequate addition when bottom paste is manufactured, and used for building a novel groove. The compositions of electrolyte in a great deal of waste residue produced by the electrolytic aluminum factories - the carbon residue are the cryolite and alumina; the method converts the alumina in the electrolyte into aluminum fluoride; and the cryolite is double salt of sodium fluoride and the aluminum fluoride. Moreover, products during the reaction process of the method can be recycled, thereby the method greatly reduces the production cost to a certain degree, has good social benefit and economic benefit, and is easy to promote and apply.
Owner:DO FLUORIDE CHEM CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com