Neodymium, iron and boron waste recycling process with approximately zero wastewater discharge
A technology of waste recycling and neodymium iron boron, applied in the direction of process efficiency improvement, etc., can solve the problems of low recovery rate of heavy rare earths, secondary pollution of the environment, high cost, etc., and achieve no environmental pollution, significant economic benefits, and low production costs Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
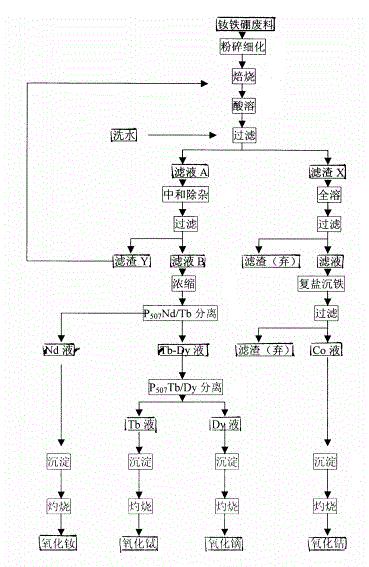
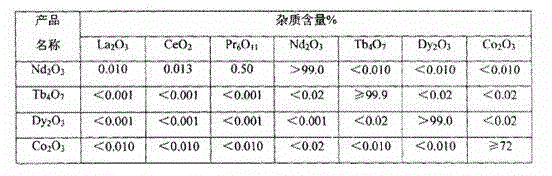
[0020] Finely pulverize 1OOOKG NdFeB waste into 300-mesh powder, oxidize and burn at 550°C for 150 minutes, put it into the reaction tank, add water 15OOKG and 500KG hydrochloric acid, beat and heat to make the reactor temperature reach 100°C, Stir the reaction for 5 hours, cool to 25°C and filter to separate solid and liquid to obtain solid X and liquid A. Add liquid A to hydrogen peroxide 20KG ammonium bicarbonate 100KG, stir at 90°C for 35 minutes to neutralize and remove impurities, then filter to obtain solid Y and liquid B. The solid Y returns to the roasting process and repeats the above steps; the liquid B undergoes the separation of 40 grades of neodymium and terbium and 70 grades of terbium and dysprosium in the PS07-sulfonated kerosene-hydrochloric acid system to obtain neodymium chloride, terbium chloride, and dysprosium chloride respectively. solution, and then precipitate and burn separately to obtain neodymium oxide, terbium oxide, and dysprosium oxide products ...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Finely pulverize 1OOOKG NdFeB waste into 200-mesh powder, oxidize and burn at 650°C for 100 minutes, put it into the reaction tank, add 800KG water and 300KG oxalic acid, beat and heat to make the reactor temperature reach Stir and react at 100°C for 7 hours, cool to 25°C and filter to separate solid and liquid to obtain solid X and liquid A. Add liquid A to 3KG of quicklime, 60KG of sodium chlorate, stir at 90°C for 45 minutes to neutralize and remove impurities, and then filter to obtain solid Y and liquid B. The solid Y returns to the roasting process and repeats the above steps; the liquid B undergoes the separation of 40 grades of neodymium and terbium and 70 grades of terbium and dysprosium in the P507-sulfonated kerosene-hydrochloric acid system to obtain neodymium chloride, terbium chloride, and dysprosium chloride respectively. solution, and then precipitate and burn separately to obtain neodymium oxide, terbium oxide, and dysprosium oxide products that meet th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com