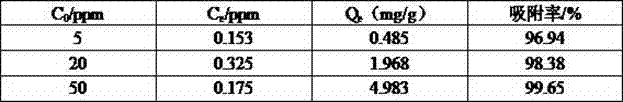
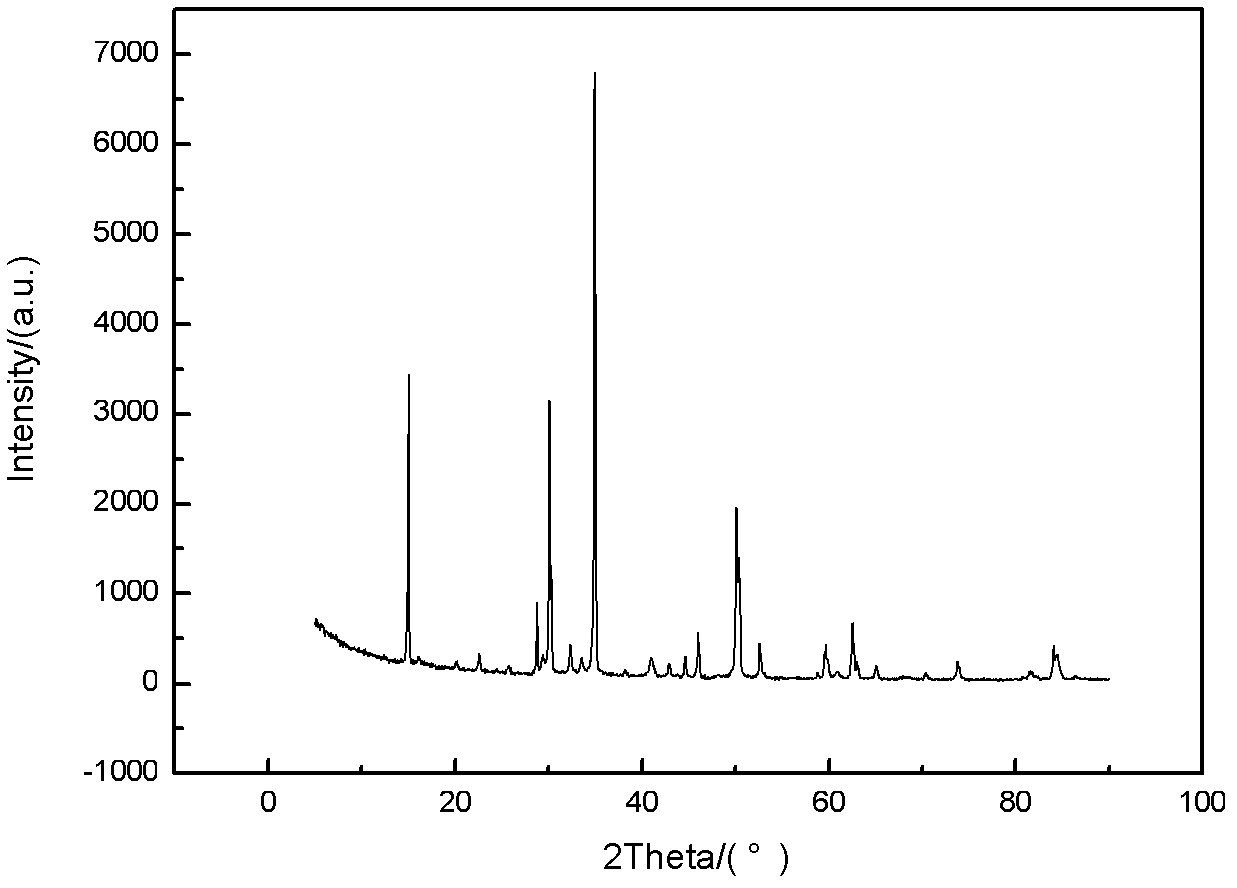
Patents
Literature
377 results about "Magnesium chloride hexahydrate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A: Magnesium chloride hexahydrate is the magnesium salt of the hydrochloric acid, HCl. Its molecular formula is Cl2H12MgO6 or MgCl2(H2O)6 and its molar mass is 203.3 grams per mole. It is highly soluble in water.
Fungicidal and parasiticidal fire-retardant powder
InactiveUS20150368560A1Reduce weightReduce the amount requiredFireproof paintsBiocidePhosphateFire retardant
Fire-retardant powder comprising at least 30% by weight of mono ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and / or di-ammonium monohydrogen phosphate, at least 5% by weight of alkaline bicarbonate, at least 3% by weight of silica, and at least 5% by weight of a compound selected from the group consisting of: sodium chloride, potassium chloride, potassium bromide, potassium sulfate, magnesium carbonate hydroxide pentahydrate, magnesium chloride hexahydrate, iron(II) sulfate heptahydrate, zinc (II) chloride, and combinations thereof. The invention also relates to building materials preferably comprising natural fibers and comprising at least 5% by weight, and at most 30% of a powder according to the invention.
Owner:SOLVAY SA
Process for producing high purity magnesia
InactiveCN1704337ANo pollutionShort technical routeChlorine/hydrogen-chlorideMagnesium chloridesSulfate radicalsPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a process for preparing high purity magnesium oxide products, which consists of using brine containing magnesium chloride from sea, lakes or crude magnesium chloride hexahydrate as raw material, purifying the brine through vacuum crystallization method, removing boron, sulfate radicals, calcium ions and soluble impurity substance in the raw material, finally carrying out dynamic calcinations.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
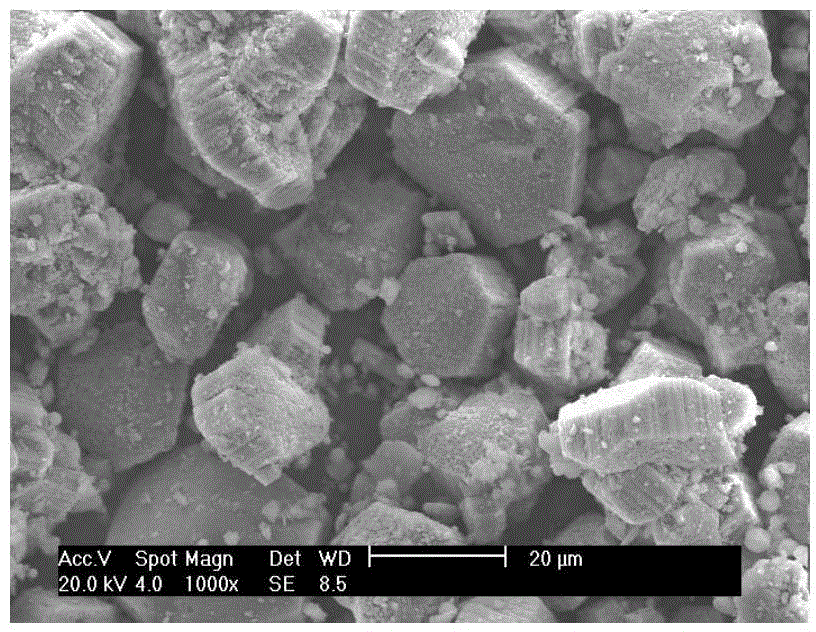
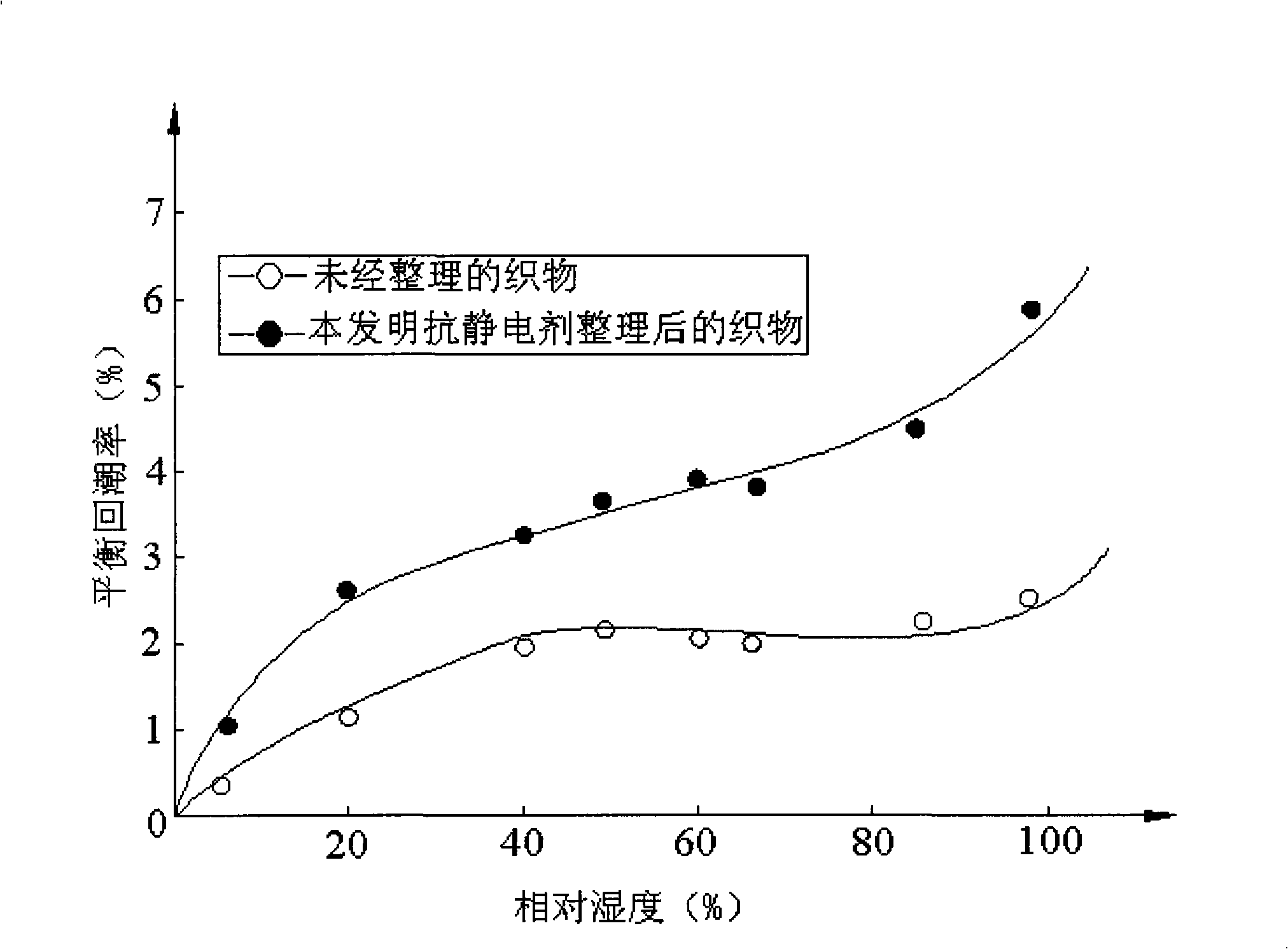
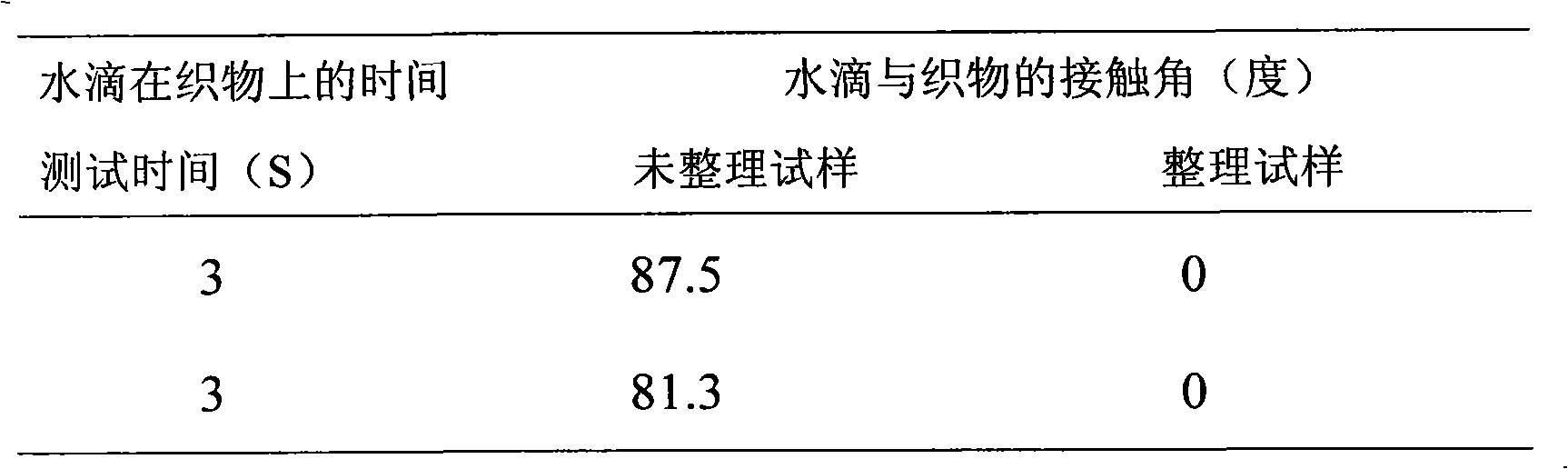
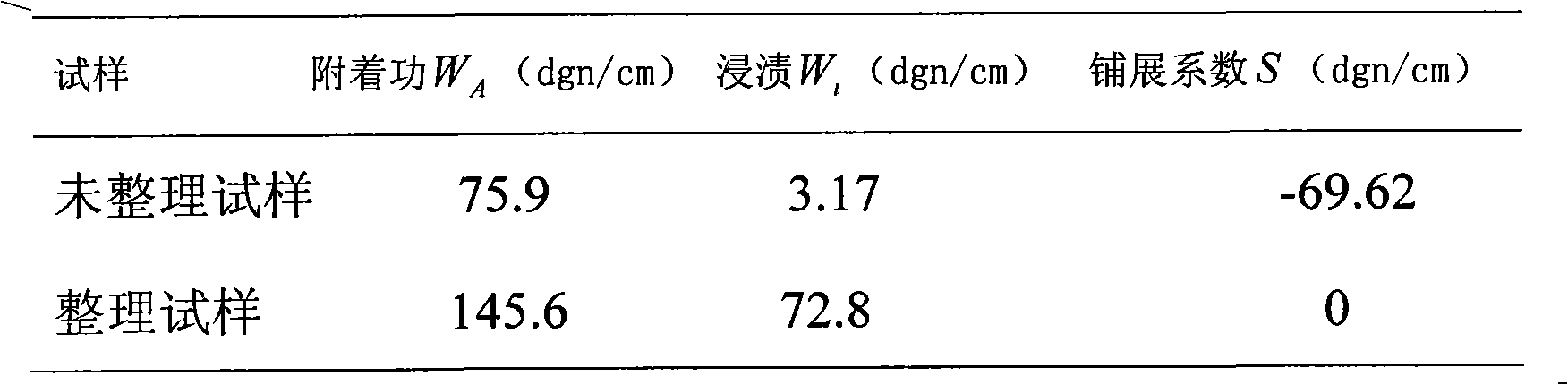
Dacron hydrophilic antistatic agent, preparing method and dacron afterfinish method
The invention discloses a polyester fabric hydrophilic antistatic agent which consists of the following components by weight percentage: 8 to 18 percent of DMT, 38 to 48 percent of glycol, 16 to 26 percent of polyoxyethylene, 6 to 16 percent of zinc acetate, 4 to 14 percent of diantimony trioxide and 3 to 8 percent of triphenyl phosphate, and the total amount of all the components is 100 percent. Interchange esterification and condensation polymerization are carried out to all the components so as to obtain the hydrophilic antistatic agent. The hydrophilic antistatic agent is adopted to prepare fabric-washing treatment liquid, and during the process the magnesium chloride hexahydrate is added and a two-dipping-two-rolling method is adopted to deal with the polyester fabric, and then the fabric is dried so as to complete the later finishing to the terylene fabric. The hydrophilic antistatic agent of the invention has stable antistatic capability, good washing resistance and low price. Adopting the antistatic agent to the later finishing of dacron can save the baking process of applied process so as to reduce energy cost and enhance the wearing property of polyester fiber and corresponding fabrics so as to meet the simulation requirement to polyester fabrics of costume fabric market.
Owner:XI'AN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Compound chloride-based environment-friendly snowmelt agent
InactiveCN101691481AAvoid Decomposition DefectsEasy to operateOther chemical processesSodium metasilicateDecomposition
The invention relates to a compound chloride-based environment-friendly snowmelt agent, which comprises a main component of a chloride mixture of calcium chloride dihydrate and magnesium chloride hexahydrate, contains various additives of sodium citrate, disodium hydrogen phosphate, sodium metasilicate, urea and the like and can contain abscisic acid or indoleacetic acid or a mixture thereof, sodium tartrate, humic acid or a salt thereof. The snowmelt agent in the invention can reduce the corrosivity to a metal object and a concrete structure effectively, improves the anti-salinization capabilities of a seed, a plant and soil, can be used when the temperature is as low as -25 DEG C, and solves the problems of bad snow melting effect caused by an autologous freezing point characteristic when a sodium chloride-based snowmelt agent is used and high cost caused by using an anhydrous calcium chloride-based snowmelt agent under the condition. The invention also provides a use method of the snowmelt agent, which places the main component and each additive separately without preparing a finished product of the snowmelt agent in advance and compounds the snowmelt agent on the spot before using. The method can avoid the problems of wetting, hardening and the like of the finished product of the snowmelt agent in the processes of storing and transporting, can avoid the defects of high-temperature energy consumption in the process of preparing compound granules (such as coating and granulating) and the capability of causing decomposition of the additives, has simple operations and a low cost, and is particularly suitable for on-site mechanical shed work.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF TRANSPORTATION SCI +1
Controlled release of surfactants for enhanced oil recovery
ActiveUS8946132B2Reduce surface tensionEnhanced overall recoveryFlushingDrilling compositionCalcium Chloride HexahydrateMetal salts
A controlled release composition comprising an aqueous sulfonate solution; an anionic surfactant; and a salt selected from aluminum nitrate nanohydrate, calcium chloride dehydrate, magnesium chloride hexahydrate, cobalt chloride hexahydrate, and other metal salts. Methods of delivering a controlled release of surfactants composition, the method comprising the steps of: delivering a solution into a reservoir, the solution comprising an aqueous sulfonate solution; an anionic surfactant; and a salt selected from aluminum nitrate nanohydrate, calcium chloride dehydrate, magnesium chloride hexahydrate, cobalt chloride hexahydrate, and other metal salts; and delivering water to the reservoir.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
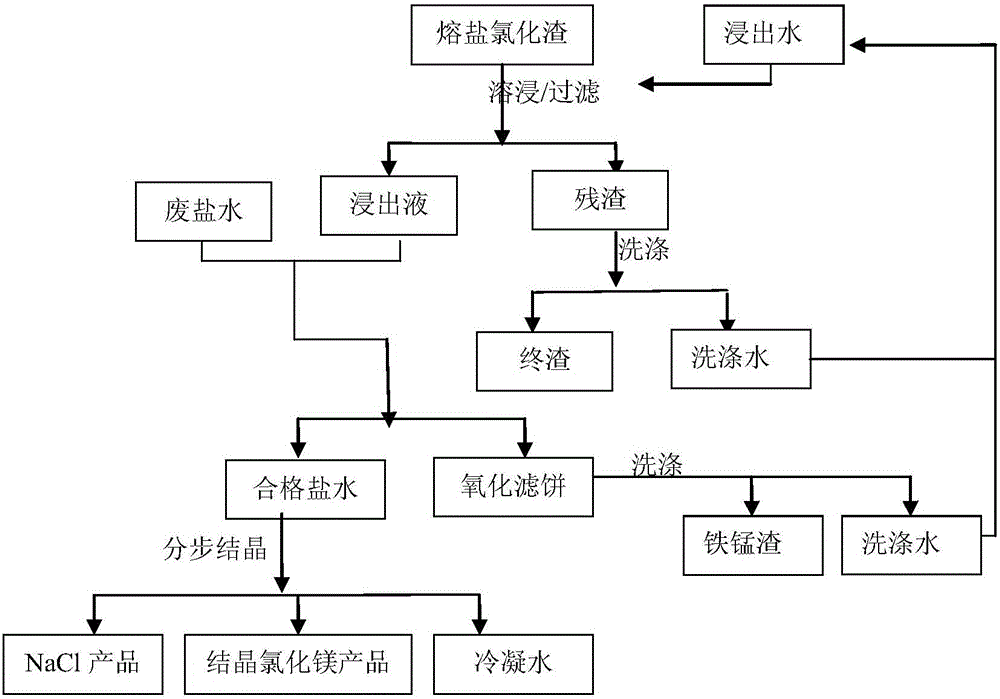
Resourceful treatment method for fused salt chlorination residues
ActiveCN105883911ASimple processReduce processing costsSolid waste disposalTitanium tetrachlorideChemical industryElectrolysis
The invention discloses a resourceful treatment method for fused salt chlorination residues. According to the method, high-oxidizability alkaline waste salt water generated through fused salt chlorination tail gas purification or chloro-alkali chemical industry tail gas absorption waste liquor is used for treating leachate of the fused salt chlorination residues so as to recover NaCl, magnesium chloride hexahydrate and ferro-manganese residues, and low-cost resourceful treatment for the fused salt chlorination residues is achieved. Waste is treated with waste, the pollution problem of the fused salt chlorination residues is solved, NaCl, MgCl2 and ferro-manganese raw materials in the fused salt residues are recovered and used, and the resourceful treatment method has good economic benefits, has great significance in eliminating development bottleneck of technology application of preparing TiCl4 through titanium residue fused salt chlorination, can be widely applied to domestic and overseas fused salt chlorination-magnesium thermal electrolysis titanium sponge and fused salt chlorination titanium sponge enterprises and has wide popularization prospects.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Temperature-resistant foam-stabilizing type low interfacial tension foaming agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105542741AImprove stabilityReduce interfacial tensionDrilling compositionSodium bicarbonateBetaine
The invention discloses a temperature-resistant foam-stabilizing type low interfacial tension foaming agent and a preparation method thereof. The temperature-resistant foam-stabilizing type low interfacial tension foaming agent comprises the following raw material components by mass percent: 0.18-0.25% of an anionic surfactant, 0.05-0.1% of an amphoteric surfactant, 0.08-0.15% of a nonionic surfactant and 99.2-99.69% of mineralized water, wherein the anionic surfactant is one of fatty acid polyoxyethylene ether sodium sulfate and disodium laureth sulfosuccinate; the amphoteric surfactant is one of erucamidopropyl sultaine and cocoamidopropyl betaine; the nonionic surfactant is one of coconutt diethanol amide and polyoxyethylene ether; the mineralized water is a mixed water solution of sodium chloride, sodium sulfate, sodium hydrogen carbonate, anhydrous calcium chloride and magnesium chloride hexahydrate. The temperature-resistant foam-stabilizing type low interfacial tension foaming agent, disclosed by the invention, has the advantages of high temperature resistance, good foam stability, low interfacial tension and the like.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
Preserving fluid of hepatic cells for biological artificial liver and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101919381APrevent acidificationImprove buffering effectDead animal preservationArtificial liverHydroxyethyl starch
The invention provides preserving fluid of hepatic cells for a biological artificial liver and a preparation method thereof. The preserving fluid is a solution compounded by ultrapure water. The solution contains the following components within the concentration range: 15-25mmol / L of disodium hydrogen phosphate, 1-10mmol / L of sodium hydrogen phosphate dehydrate, 4-6mmol / L of potassium citrate monohydrate, 10-30mmol / L of sodium chloride, 5-10mmol / L of magnesium chloride hexahydrate, 3-10mmol / L of disodium adenosine triphosphate, 1-5mmol / L of reducing glutathione, 0.1-0.5mmol / L of alpha-lipoic acid, 100-150mmol / L of trehalose (C6H12O5), 200 / 0.510-50g / L of hydroxyethyl starch and 2-10mg / L of matrine. The preparation method of the preserving fluid comprises the following steps of: accurately weighing all components according to the concentration requirements of the components, wherein the alpha-lipoic acid is weighed in a dark place; completely dissolving the other components except the alpha-lipoic acid by using the right amount of ultrapure water; sufficiently dissolving the alpha-lipoic acid in the dark place; and adding the ultrapure water to full dose. The preserving fluid can well protect the cell activity of the hepatic cells for the biological artificial liver and the special functions of the hepatic cells at low temperature so as to satisfy the short-term low temperature preservation of a large-scale hepatic cell bank for the biological artificial liver and / or the hepatic cell protection in the long-distance transportation process.
Owner:ZHUJIANG HOSPITAL SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
Producing method of calcium hydrogen phosphate
InactiveCN102659089AImplement in-place loopImprove cycle efficiencyPhosphorus compoundsResource utilizationDecomposition
The invention relates to a producing method of calcium hydrogen phosphate. The producing method includes firstly, utilizing hydrochloric acid to decompose phosphorite powders to obtain a mixture of phosphoric acid and calcium chloride, subjecting the mixture to defluorination purification, and using ammonia to neutralize the phosphoric acid to obtain a calcium hydrogen phosphate product; secondly, after the phosphoric acid is separated, using the ammonia and carbon dioxide to convert redundant calcium to a calcium carbonate product, using magnesium oxide to distill the ammonia out of remaining ammonium chloride in a solution in a boiling state, circulating the distilled ammonia to a neutralization procedure, subjecting remaining a magnesium chloride solution after ammonia distillation to evaporation concentration to obtain magnesium chloride-water (1 / 6), subjecting magnesium chloride hexahydrate to dehydration at the temperature of 120 DEG C to obtain magnesium chloride-water (1 / 2), then subjecting the magnesium chloride-water (1 / 2) to pyrogenic decomposition at the temperature between 550 DEG C and 600 DEG C to release hydrogen chloride, subjecting the hydrogen chloride obtained by the pyrogenic decomposition to water absorption, returning to the process of acid hydrolysis of phosphorite, and finally subjecting the magnesium oxide to returning to the process of the ammonia distillation. The producing method of the calcium hydrogen phosphate has the advantages that the resource utilization ratio is high, large-scale production of the phosphorite by means of a hydrochloric acid processing method can be achieved, acid-base media can be completely circulated, phosphorous gypsum or calcium chloride are prevented from discharging, and the like.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Waterproof film spraying material, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides a waterproof film spraying material, and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding 1-20 parts of 60 wt% above glycerol into 100 parts of magnesium acrylate monomer water solution, uniformly mixing, adding 0-30 parts of magnesium chloride hexahydrate, and evenly mixing until no visible agglomerated particles exist in the solution, thereby obtaining the waterproof film spraying material. The waterproof film spraying material, which is used as a main material, can be sprayed and mixed with an oxidizer and a reducer to instantaneously form a gel, and the gel is bonded to the treated base surface to form a film layer. The waterproof film spraying material can not crystallize in a high-altitude low-temperature envelopment, thereby ensuring the continuity of the main material and effectively ensuring the smoothness of the waterproof film spraying construction in the region.
Owner:成都市嘉洲新型防水材料有限公司
Heating curable and waterproof halogenation resistant magnesium oxychloride construction materials and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101016214AHigh strengthNon-refluxSolid waste managementCeramicwareHalogenMagnesium chloride hexahydrate
The invention discloses a new typed heat solidifying and water-tolerant koenenite architectural material without returning halogen and making method, which comprises the following parts: 100g 80%-85% light-burnt magnesia, 18-25g not less than 44% magnesium chloride hexahydrate, 10-45g II-grade coal dust, 15-20g supernatant reacted by 25-35g sulfuric acid and 25-35g refuse, water, foam with grain size not more than 1mm.
Owner:刘世权
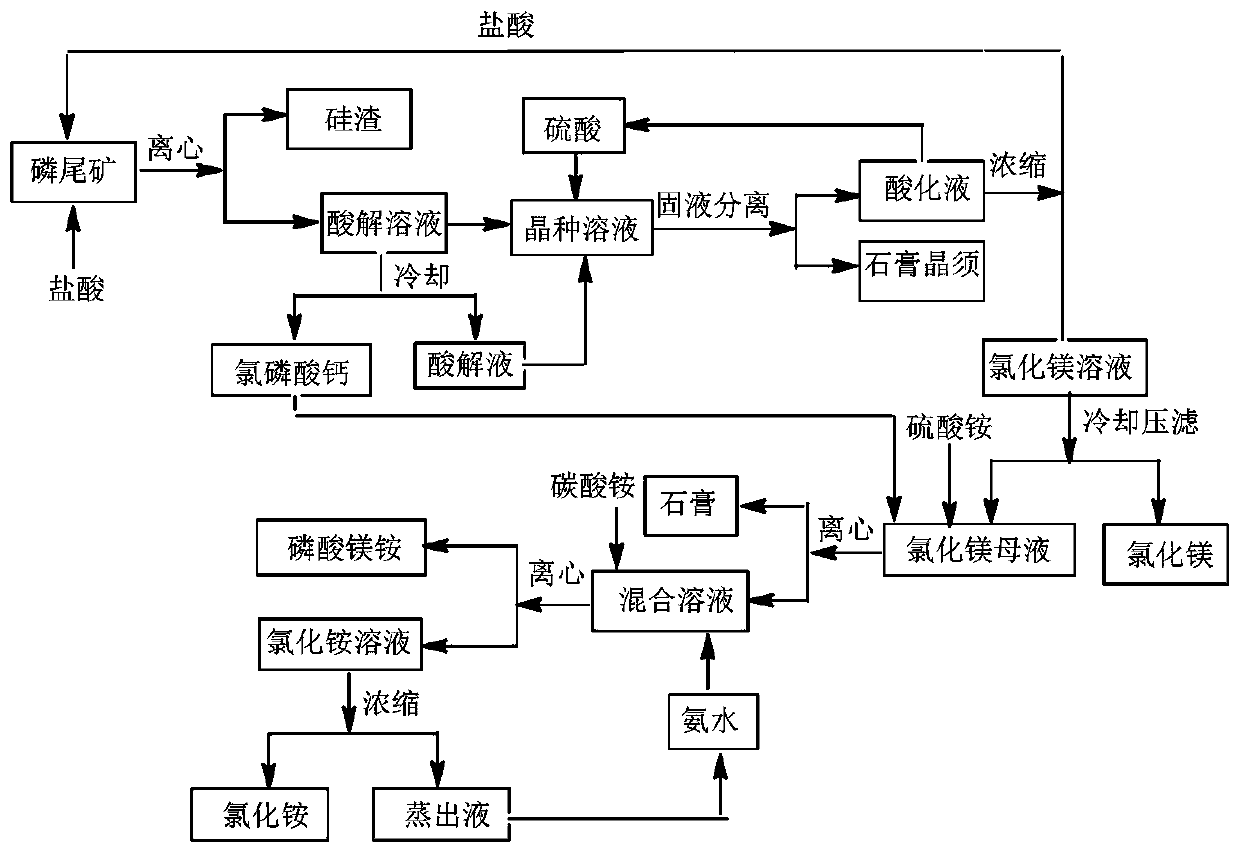
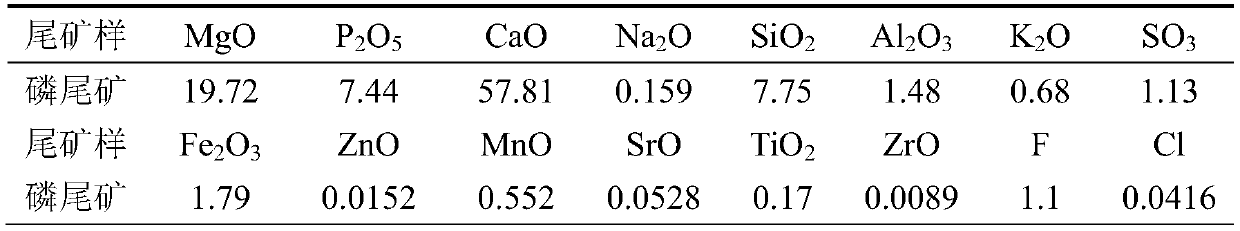
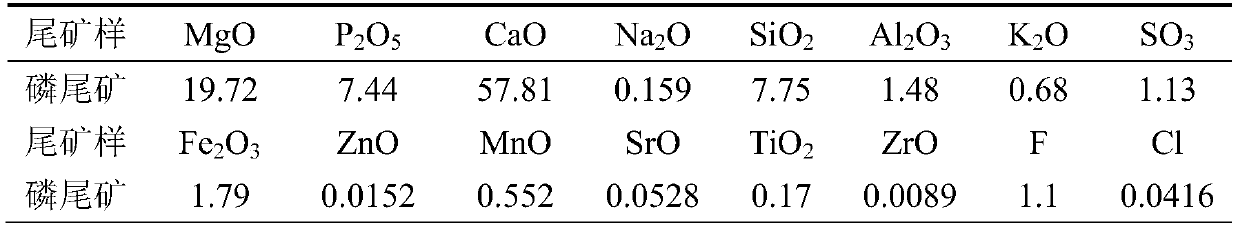
Method for preparing gypsum whiskers, magnesium chloride, ammonium magnesium phosphate and ammonium chloride from phosphate tailings
ActiveCN110817911AHigh recovery rateSolve the bottleneck problem that cannot be consumed in large quantitiesPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsMagnesium phosphatePhosphoric acid
The invention provides a method for preparing gypsum whiskers, magnesium chloride, ammonium magnesium phosphate and ammonium chloride from phosphate tailings. The method comprises the following steps:adding an acidizing fluid into phosphate tailings in batches, dropwise adding hydrochloric acid to react, separating silicon slag and an acidolysis solution, and cooling and crystallizing the acidolysis solution to obtain calcium chlorophosphate and acidolysis solution; adding concentrated sulfuric acid into the acidizing fluid, dropwise adding the acidolysis fluid for reaction, and performing centrifugal separation after reaction to obtain gypsum whiskers and the acidizing fluid; heating and concentrating the acidizing fluid, crystallizing to obtain a magnesium chloride solution, and centrifugally separating the magnesium chloride solution to obtain magnesium chloride hexahydrate and a magnesium chloride mother liquor; adding ammonium sulfate and calcium chlorophosphate into the magnesium chloride mother liquor for reaction, filtering to obtain gypsum and a filtrate after the reaction is finished, dropwise adding ammonia water into the filtrate, cooling and filtering to obtain ammonium magnesium phosphate and an ammonium chloride solution; heating, concentrating, and cooling the ammonium chloride solution to obtain ammonium chloride crystals and a crystallization mother liquor, and after centrifugal separation, preparing a 5 to 20% ammonia water solution from the crystallization mother liquor and ammonia water. According to the technical scheme, the recovery rate of phosphorus reaches 99%, and the recovery rate of calcium reaches 95%.
Owner:三峡公共检验检测中心
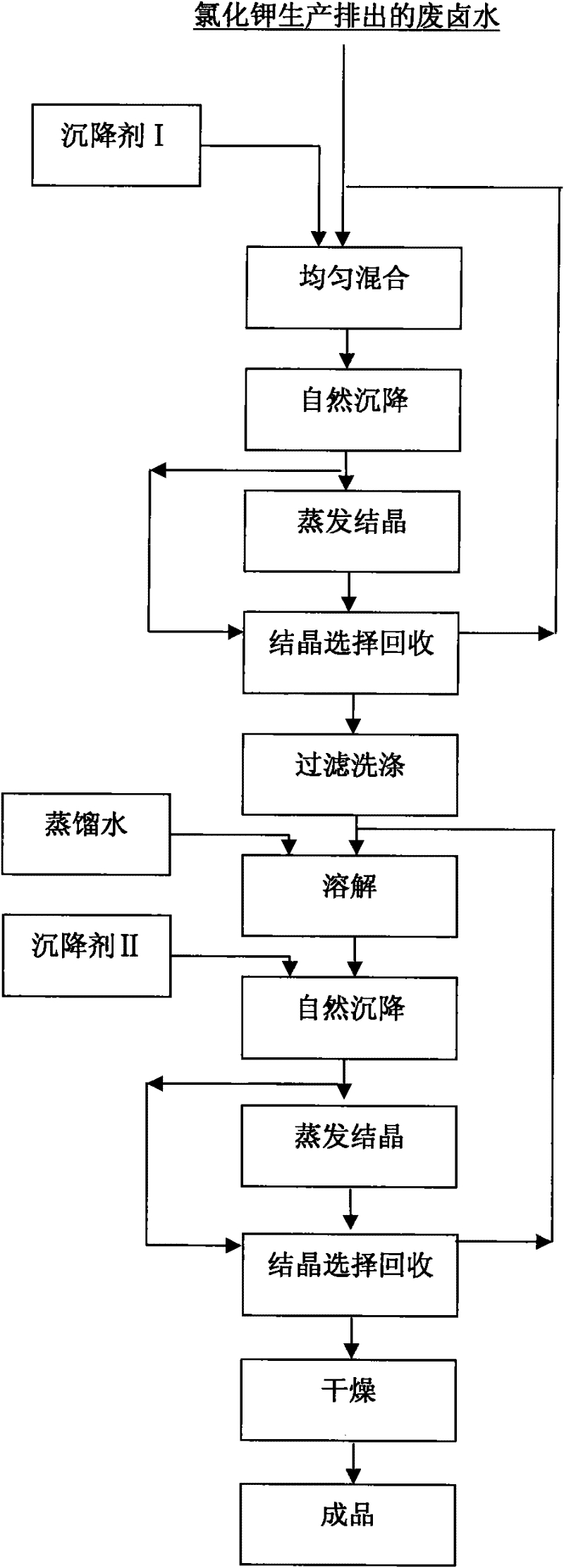
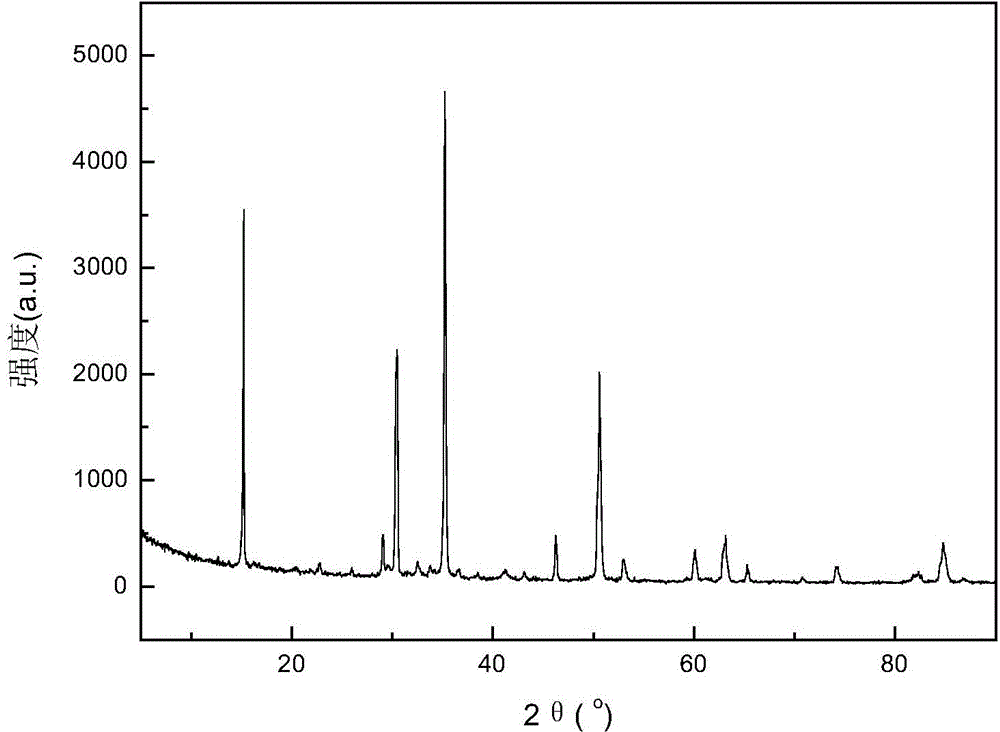
Method for preparing high-purity magnesium chloride hexahydrate from waste brine
The invention provides a method for removing trace impurities in magnesium chloride by using waste brine discharged in potassium chloride production as a raw material by an improved two-stage recrystallization technique. Each stage of the crystallization technique comprises the following steps: 1) free settling, 2) natural evaporation and crystallization, 3) size-grading selective recycling, 4) filtration, (5) saturated magnesium chloride solution washing and the like. By using the method, trace impurities, such as boron, sulfur, ferrum and the like, in magnesium chloride can be reduced to less than 5 ppm, and the purity of the product magnesium chloride hexahydrate is higher than 99.5%. The invention has the characteristics of low energy consumption and low cost, is simple to operate, and is applicable to refining magnesium metal, flame retardant, magnesium hydroxide or any other raw material by an electrolytic process.
Owner:张英才
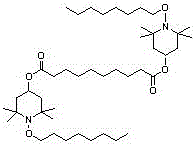
Synthesis method of light stabilizer HS-112
InactiveCN106699639AReduce generationThe reaction steps are simpleOrganic chemistryChemical synthesisCalcium Chloride Hexahydrate
The invention discloses a synthesis method the a light stabilizer bis(1-octyoxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidyl) sebacate, belongs to the field of organic chemical synthesis. The bis(1-octyoxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidyl) sebacate is the material, ethanol solution is the solvent, and magnesium hydrate or magnesium chloride hexahydrate is the catalyst. Oxidation reaction is conducted with the action of aquae hydrogenii dioxidi which is used as the oxidant to generate bis(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-1-piperidinyloxy-4-yl)sebacate free radicals. Then molybdenum trioxide is used as the catalyst, normal octane is used as the material and solvent to react with the bis(2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-1-piperidinyloxy-4-yl)sebacate free radicals to obtain the light stabilizer HS-112. The method uses two steps to synthesize the HS-112. The process is simple, the reaction time is short the side effects are few, the pollution is minimal, the production cost is low, the reaction yield rate is high, and therefore the industrial application prospect is good.
Owner:GANSU RES INSTION OF CHEM IND GRICI
Method for preparing high-strength alpha-semi-hydrated gypsum from flue gas desulfurization gypsum
The invention belongs to the field of material science, and relates to a method for preparing high-strength alpha-semi-hydrated gypsum from flue gas desulfurization gypsum. The method comprises the following steps: 1) preparing desulfurization gypsum slurry: sufficiently mixing the flue gas desulfurization gypsum and water according to a solid-liquid mass ratio of 1: (4-10), and warming to 80-95 DEG.C; 2) adding a habit modifier to prepare mixed slurry: adding the habit modifier in the desulfurization gypsum slurry according to a condition that the mass ratio of the flue gas desulfurization gypsum to the habit modifier is 1: (0.5-1.5), wherein the habit modifier is a mixture of magnesium chloride hexahydrate and magnesium sulfate hexahydrate in a mass ratio of 1: (0.1-0.2), continuously warming to boil, and refluxing; 3) adding a crystal habit modifier: adding the crystal habit modifier in the mixed slurry obtained in the step 2) according to a condition that the mass ratio of the flue gas desulfurization gypsum to the crystal habit modifier is 1: (1%-5%); and 4) crystal transforming. The uniform short hexagonal prism alpha-semi-hydrated gypsum can be prepared by the method simple in process, the rupture strength reaches 14.4 MPa, and the compressive strength reaches 44.5 MPa.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Preparation method for modified biological carbon which efficiently adsorbs soil inorganic phosphorus and dissolves organic phosphorus at same time and application
InactiveCN107459025AEfficient reuseWide variety of sourcesAgriculture tools and machinesOther chemical processesSoil scienceMagnesium chloride hexahydrate
The invention provides modified biological carbon which efficiently adsorbs soil inorganic phosphorus and dissolves organic phosphorus at the same time. The modified biological carbon is prepared according to the following steps: (1) collecting air-dried yak excrement, smashing the collected yak excrement, and sieving the smashed yak excrement; (2) preparing an impregnating liquid containing magnesium ions with a certain concentration by using magnesium chloride hexahydrate; (3) mixing the sieved yak excrement with the modification impregnating liquid uniformly according to a proportion; (4) placing the mixture of the treated yak excrement and the impregnating liquid in a shaking bed, and performing impregnation fully; (5) filtering impregnated yak excrement out, placing filtered yak excrement in a drying oven, and performing drying; and (6) performing slow-speed pyrolysis on dried yak excrement in a muffle furnace under nitrogen protection to obtain the modified biological carbon. According to the invention, the dried yak excrement is fired into the modified biological carbon, thus high-efficiency recycling of biological matter is realized, the modified biological carbon can efficiently adsorb the soil inorganic phosphorus and dissolve the organic phosphorus at the same time, and agricultural non-point source pollution is effectively controlled.
Owner:INST OF URBAN ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
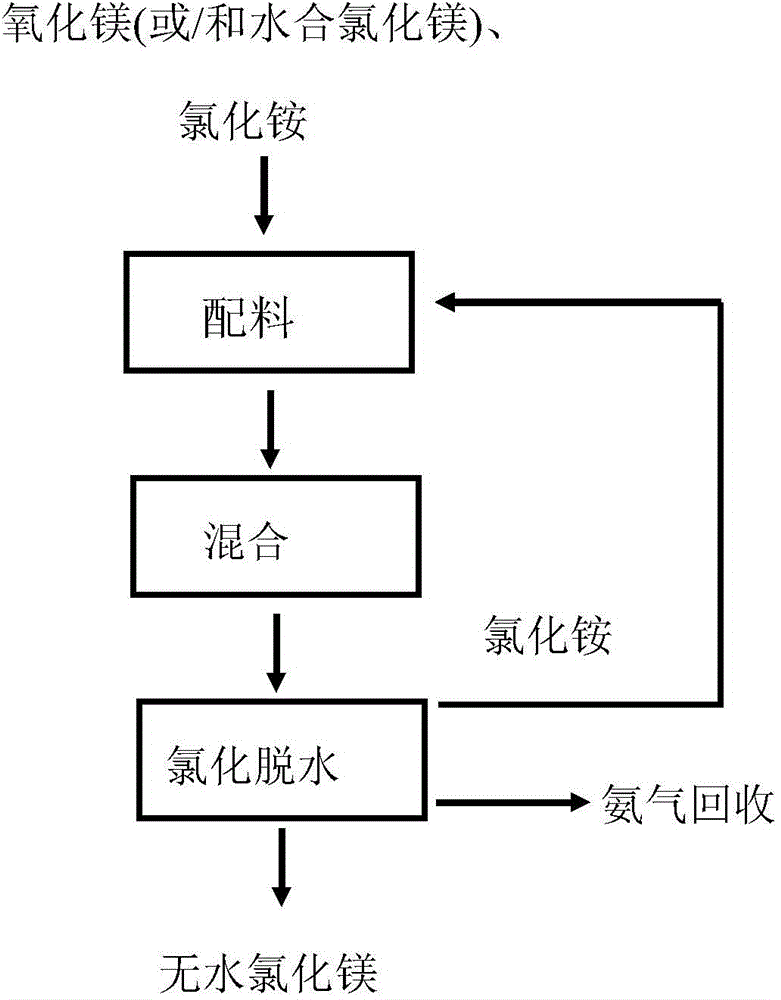
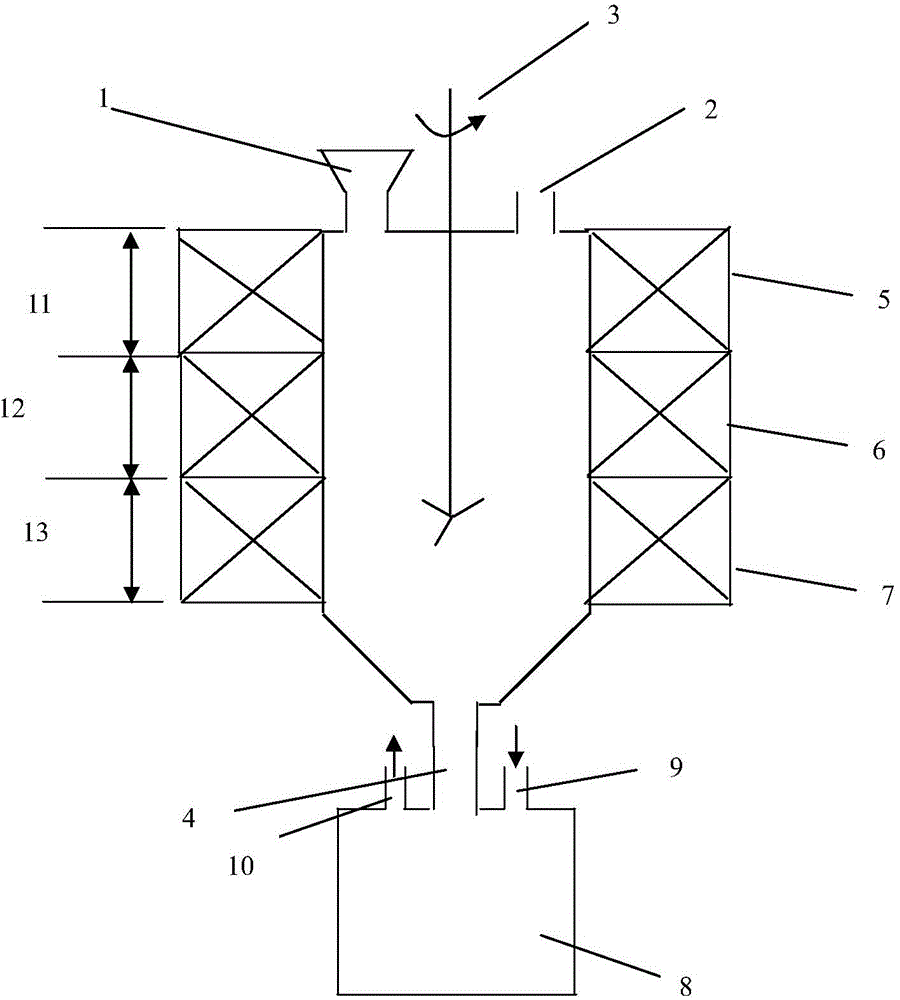
Method and device for preparing anhydrous magnesium chloride
The invention relates to a device for preparing anhydrous magnesium chloride and a preparation method which uses the device. The device is a chlorination dehydration furnace and comprises a storage cabin, wherein the upper part of the storage cabin is a preheating zone; the middle part of the storage cabin is a double salt forming zone; the bottom of the storage cabin is an ammonium removing zone; the storage cabin is connected with an outlet and has certain sealing property. The preparation method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing magnesium oxide and / or hydrated magnesium chloride and ammonium chloride, adding the mixture into the chlorination dehydration furnace, and heating, thereby preparing anhydrous magnesium chloride; and repeating the above operation steps when the anhydrous magnesium chloride is discharged out, thereby achieving continuous production. A method for preparing anhydrous magnesium chloride by using the rich magnesite and magnesium chloride hexahydrate resources in China is provided by the invention, continuous production of anhydrous magnesium chloride is achieved, the production efficiency is improved, the production cost is lowered, and the cost of environment protection is lowered; the prepared anhydrous magnesium chloride is high in purity, the content of the main impurity magnesium oxide in the anhydrous magnesium chloride can be controlled to be 0.5% or even less than 0.1%, and the anhydrous magnesium chloride can be used for preparing magnesium metal in an electrolysis manner and has very good industrial and commercial prospect.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing magnesite products
The invention discloses a method for preparing magnesite products. The method comprises the following steps: (1) taking a veneer as a mould; (2) evenly mixing magnesium oxide, magnesium chloride hexahydrate, plant fiber powder, modified liquid and an adhesive at room temperature and forming slurry through stirring; (3) pouring the formed slurry into the mould, and solidifying to obtain the magnesite products. The method has the advantages of omitting the processes such as moulding, demoulding and decorating, and the method can realize the large-scale production.
Owner:江西圣保罗新型材料有限公司
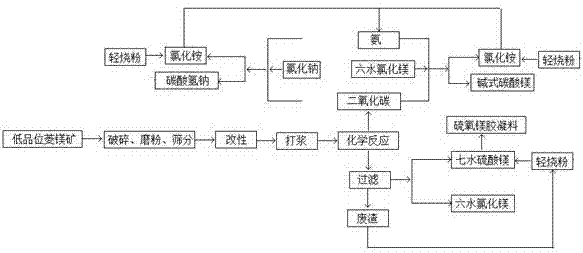
Low-grade magnesite comprehensive utilization method
ActiveCN107417146ARealize comprehensive utilizationRealize resource utilizationMagnesium carbonatesMagnesium chloridesChemical reactionMagnesite
The invention discloses a low-grade magnesite comprehensive utilization method, and relates to a magnesite utilization method. The method comprises the following steps: using low-grade magnesite as a raw material, wherein the magnesium oxide content is less than or equal to 40%, crushing, grinding and sieving, modifying by a surfactant, and directly chemically reacting with a sulfuric acid or a hydrochloric acid to prepare magnesium sulfate heptahydrate or magnesium chloride hexahydrate, and recycling and using carbon dioxide; enabling the modified magnesite powder to chemically react with the sulfuric acid (or the hydrochloric acid), generating the magnesium sulfate heptahydrate or the magnesium chloride hexahydrate, recycling and releasing the carbon dioxide; circularly using generated magnesium chloride and steamed ammonia gas; and enabling filtered residue, silico-calcium and light roasting powder to react with the magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, and preparing a magnesium oxysulfate binding material. The whole process is zero release, the magnesite is completely used, and the comprehensive utilization of the magnesite is realized.
Owner:丹东金硼肥业有限公司
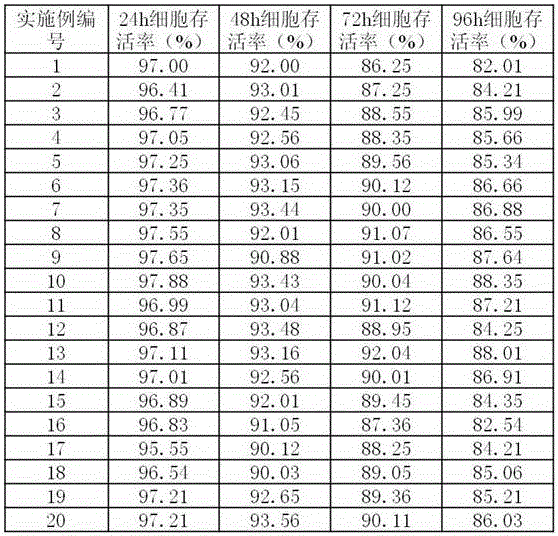
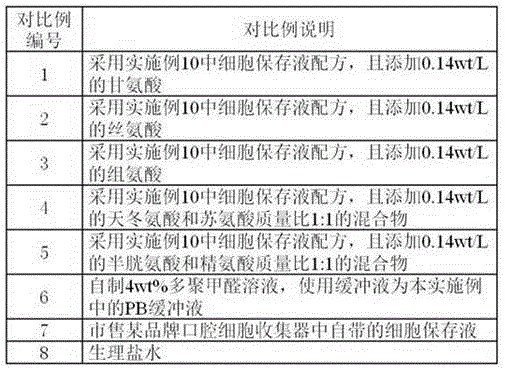
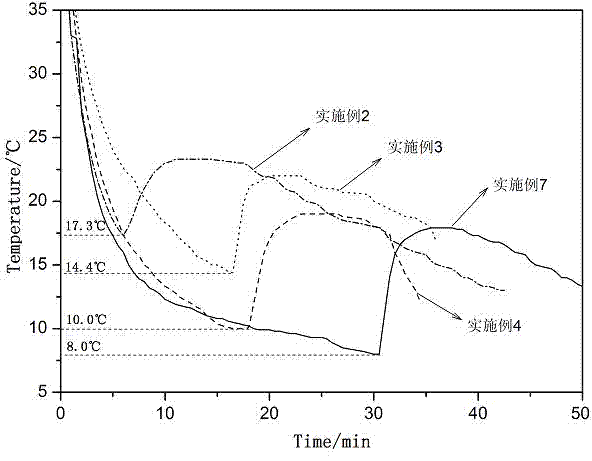
Cell preservation solution as well as preparation method and use method thereof
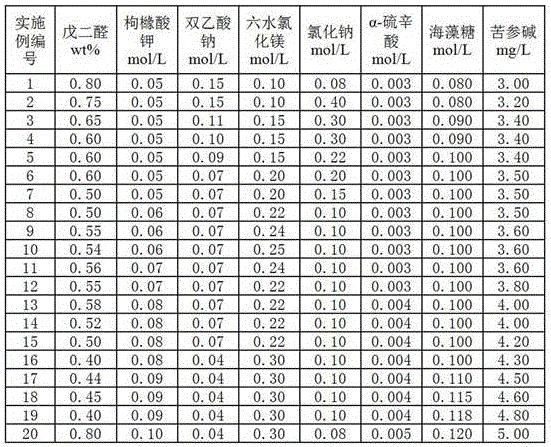
InactiveCN106614525AEasy to fixHigh activityDead animal preservationAlpha-Lipoic AcidSodium diacetate
The invention discloses a cell preservation solution. The cell preservation solution is a solution prepared from ultra pure water. The solution is a paraform preservation solution. The solution also comprises 0.4-0.8wt% of glutaraldehyde, 0.05-0.1mol / L potassium citrate, 0.035-0.15mol / L sodium diacetate, 0.1-0.3mol / L magnesium chloride hexahydrate, 0.08-0.4mol / L sodium chloride, 0.003-0.005mol / L alpha-lipoic acid, 0.08-0.12mol / L trehalose and 3-5mg / L matrine. The pH value of the cell preservation solution is 7.1-7.4, and the osmotic pressure of the cell preservation solution is 290-315mmol / L. According to the preservation solution disclosed by the invention, the cell preservation time is greatly prolonged, besides, the preparation method is simple, and the application range is wide.
Owner:MIRACLEAN TECH
Phase change energy storage material for heat preservation at night and preparation method
InactiveCN103205242ALower eutectic pointLower melting temperatureHeat-exchange elementsCalcium Chloride HexahydrateMagnesium chloride hexahydrate
The invention relates to a phase change energy storage material for heat preservation at night. The medium consists of a CaC12-MgCl2-H2O water salt system and a nucleating agent; the CaC12-MgCl2-H2O water salt system consists of 80-95 % of calcium chloride hexahydrate, 1-7 % of magnesium chloride hexahydrate and 3-15 % of deionized water by mass; and the content of the nucleating agent is 0.5-2.0 % of the total amount of the CaC12-MgCl2-H2O water salt system. The phase change energy storage material has the advantages of high phase change latent heat, relatively low melting temperature and adjustable solidification temperature, can be used for avoiding the phase separation phenomenon, and can be applied to different seasons and different regions.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing anhydrous magnesium chloride by utilizing magnesium chloride hexahydrate
ActiveCN102491384AReduce dosageEasy to recycleMagnesium chloridesStrontium chloride hexahydrateMagnesium chloride hexahydrate
The invention relates to a method for preparing anhydrous magnesium chloride by utilizing magnesium chloride hexahydrate. The method comprises the following steps of (1) mixing and ball-milling the magnesium chloride hexahydrate and ammonium chloride to obtain ammonium camallite or mixture containing the ammonium camallite, (2) heating the mixture and performing preliminary dehydration to preparelower-water ammonium camallite or mixture containing the lower-water ammonium camallite, and (3) placing a covering on the product obtained in the step (2) and performing heating and reaction to prepare anhydrous magnesium chloride. The method for preparing the anhydrous magnesium chloride by utilizing the magnesium chloride hexahydrate can shorten production process of the anhydrous magnesium chloride, improve production efficiency and reduce production cost and input cost for environmental protection.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Low-pollution flame-retardant thermal expansion microspheres and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108084333AEfficient flame retardant effectLow toxicityHeat resistant fibresFiltrationMicrosphere
The invention discloses low-pollution flame-retardant thermal expansion microspheres and a preparation method thereof, and relates to a preparation technology of a chemical product. The preparation method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing deionized water, sodium hydroxide, magnesium chloride hexahydrate, an aqueous sodium dodecyl sulfate solution and sodium chloride to obtain a waterphase protection solution; uniformly mixing surface-modified hydroxide, an unsaturated olefinic monomer polymer, an oil-soluble flame retardant, an inert hydrocarbon and an initiator in the presenceof a dispersing agent and an auxiliary agent to obtain an oil phase; under a stirring condition, dropwise adding the oil phase into the water phase protection solution, performing a suspension polymerization reaction to obtain stable liquid drops, then raising the temperature, then performing a reaction under an anoxic condition to obtain a suspension, performing suction filtration on the suspension, and drying to obtain the flame-retardant thermal expansion microspheres. The low-pollution flame-retardant thermal expansion microspheres have the most important characteristics of a highly-effective flame-retardant effect, relatively low toxicity and relatively low pollution.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Fireproof and insulating light composite glass magnesium board and its preparation method
The invention discloses a fireproof and insulating light composite glass magnesium board and its preparation method. The board is prepared by the following raw materials by weight: magnesium chloride hexahydrate, a modifier, light calcined powder, calcined forsterite, forsterite or serpentine raw ore. The method comprises the steps of: 1. using magnesium chloride hexahydrate to prepare a solution, and adding a modifier so as to form a liquid mixture; 2. grinding forsterite raw ore powder and calcined ore powder, and mixing the powder with light calcined powder, then stirring them well; 3. subjecting the mixed powder into a double-shaft paddle mixer for mixing, stirring, and metering; 4. delivering the well stirred material into a template, which is automatically placed on a template processing roller platform by means of a plate-sucking machine, then conducting pouring, wrapping a reinforced glass fiber cloth, then conducting rolling, thickness setting and moulding; 4. sending the moulded plate to maintenance, and putting the product plate in a trimming machine for shaping, performing inspection, thus obtaining a qualified product. The method of the invention has simple process and convenient operation, and is conducive to implementation. The glass magnesium board provided in the invention has the advantages of high efficiency insulation, plate structure, no thermal bridge andcold bridge, excellent heat insulating performance, flame resistance and weatherability, as well as excellent flame retardancy and refractability.
Owner:宜昌弘林华镁矿业投资有限公司
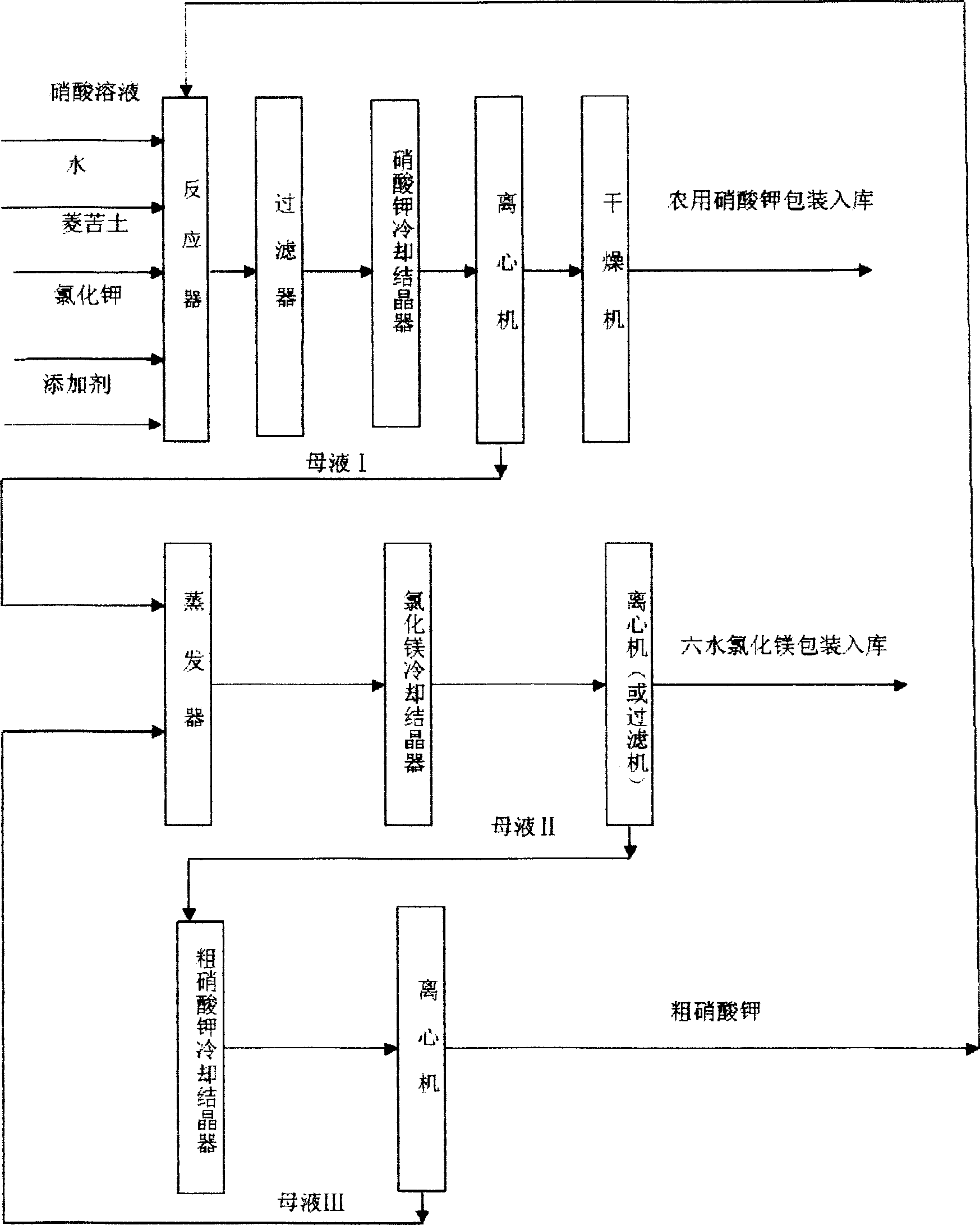
Technological process of preparing potassium nitrate and magnesium chloride
InactiveCN1673083ALow costWide variety of sourcesAlkali metal nitrate preparationMagnesiaMagnesium chloride hexahydrateMother liquor
The technological process of preparing potassium nitrate and magnesium chloride includes the following steps: adding powdered magnesite into nitric acid solution to react, adding potassium chloride for reacting with coarse potassium nitrate, adding additive, maintaining the temperature to deposit, filtering, cooling to crystallize, centrifugally separating and drying to obtain potassium nitrate product for farm use; mixing mother liquor I and mother liquor III, evaporating to concentrate, and cooling to crystallize and separate magnesium chloride hexahydrate crystal; cooling mother liquor II to crystallize, and centrifugally separating to obtain coarse potassium nitrate and mother liquor III. The technological process is simple, low in power consumption, hermetically circulated and without waste produced.
Owner:HUNAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Silicone acrylic emulsion modified magnesium-containing inorganic adhesive for straws and preparation method of silicone acrylic emulsion modified magnesium-containing inorganic adhesive
ActiveCN105694739AHigh strengthImprove water resistanceMacromolecular adhesive additivesInorganic adhesivesAdhesivePolymer chemistry
The invention discloses a silicon acrylic emulsion modified magnesium-containing inorganic adhesive for straws. The adhesive is prepared from, by weight, 100 parts of magnesium chloride hexahydrate, 44-61 parts of magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, 218-298 parts of light calcined magnesia, 167-202 parts of water, 10-43 parts of silicone acrylic emulsion and 4-9 parts of dispersant. Adhered products prepared with the adhesive are high in water resistance, strength and toughness and appropriate in coagulation rate. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the silicone acrylic emulsion modified magnesium-containing inorganic adhesive. The method includes steps: feeding water into a reaction kettle, heating, adding the magnesium chloride hexahydrate, and stirring at a constant speed to obtain a magnesium chloride solution; slowly adding the magnesium sulfate heptahydrate into the magnesium chloride solution, and stirring at a constant speed; adding the light calcined magnesia into the reaction kettle, and stirring at a constant speed; slowing dripping the silicone acrylic emulsion into the reaction kettle, adding the dispersant after dripping is finished, stirring and cooling to obtain the adhesive.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
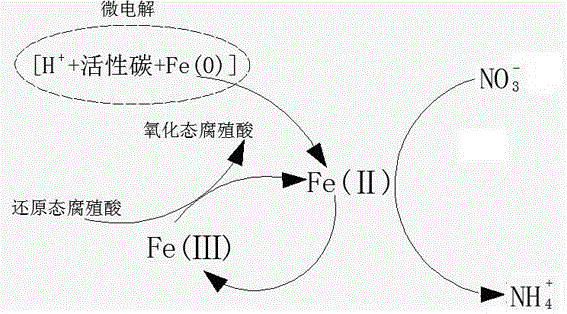
Method of removing nitrate nitrogen in wastewater
ActiveCN104891722AImprove reduction efficiencyGood removal effectMultistage water/sewage treatmentHydration reactionSodium phosphates
The invention discloses a method of removing nitrate nitrogen in wastewater. The method includes the steps of S1, adjusting pH, to be specific, collecting wastewater in a container resistant to acid and alkali, and adjusting the pH of the wastewater to 2 to 4; S2, performing denitrification, to be specific, adding humic acid, activated carbon and scrap iron into the wastewater, the pH of which is adjusted, performing stirring to allow reaction under isolation with the external air, performing solid-liquid separation, and collecting liquid to a chemical settling pond; S3, allowing chemical settling, to be specific, adding sodium phosphate dibasic dodecahydrate and magnesium chloride hexahydrate into the chemical settling pond under aerated stirring, performing solid-liquid separation after chemical settling reaction, and collecting supernate as treated water. The novel efficient reducing aid, the humic acid, is used with iron-carbon micro-electrolysis, the denitrification process is enhanced, and the removal efficiency of the nitrate nitrogen in the wastewater is improved. Additionally, the method helps effectively remove chemical reduction products and thoroughly remove the nitrate nitrogen from the wastewater.
Owner:黑龙江怀德环保有限公司
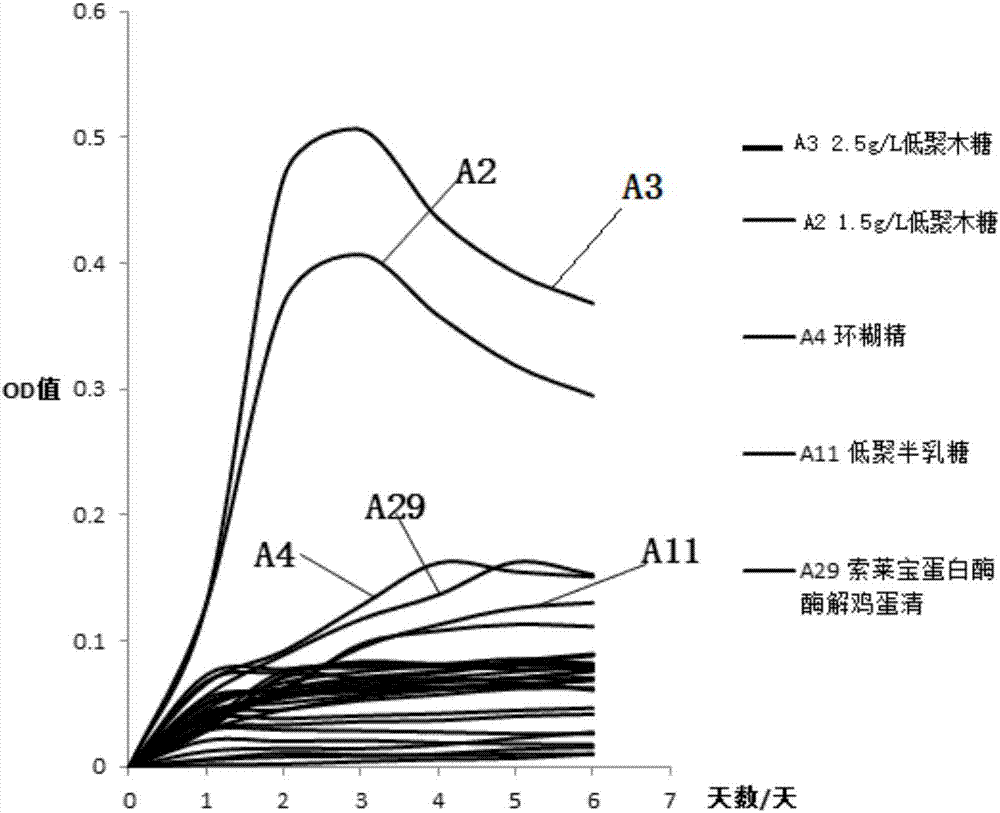
Ackerman myxobacteria culture medium and preparation method thereof
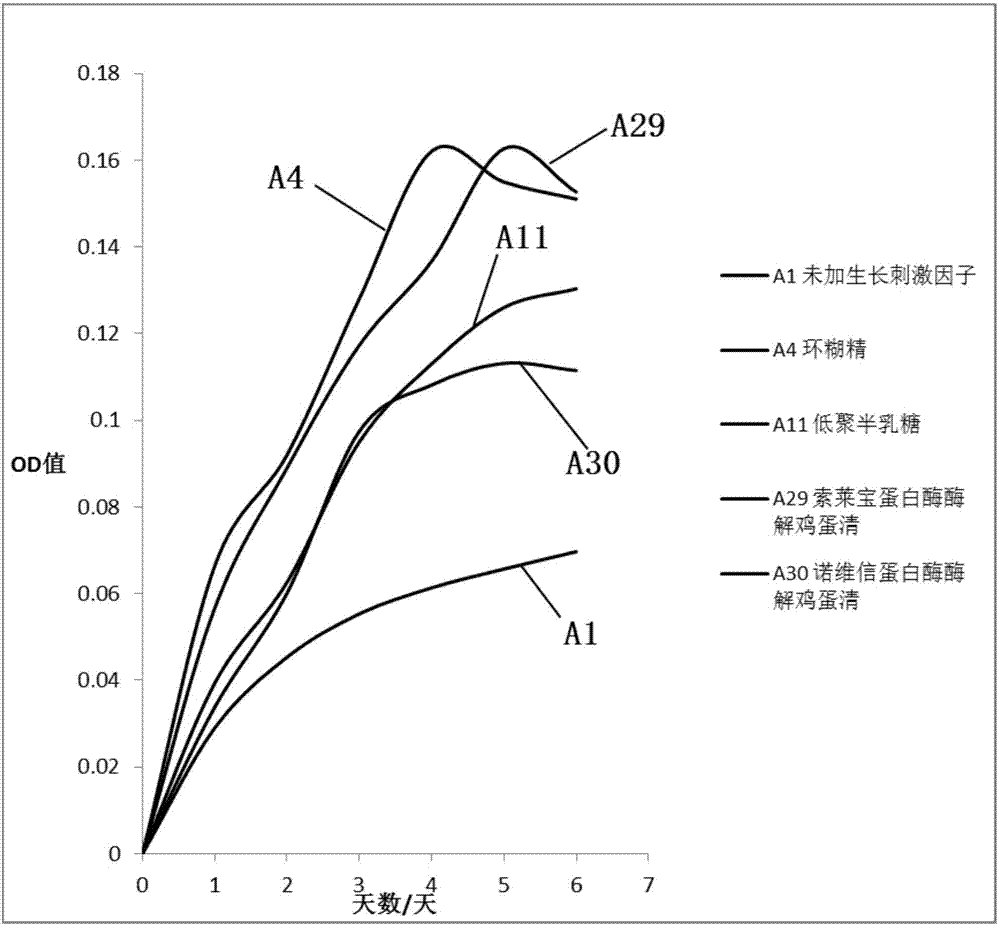
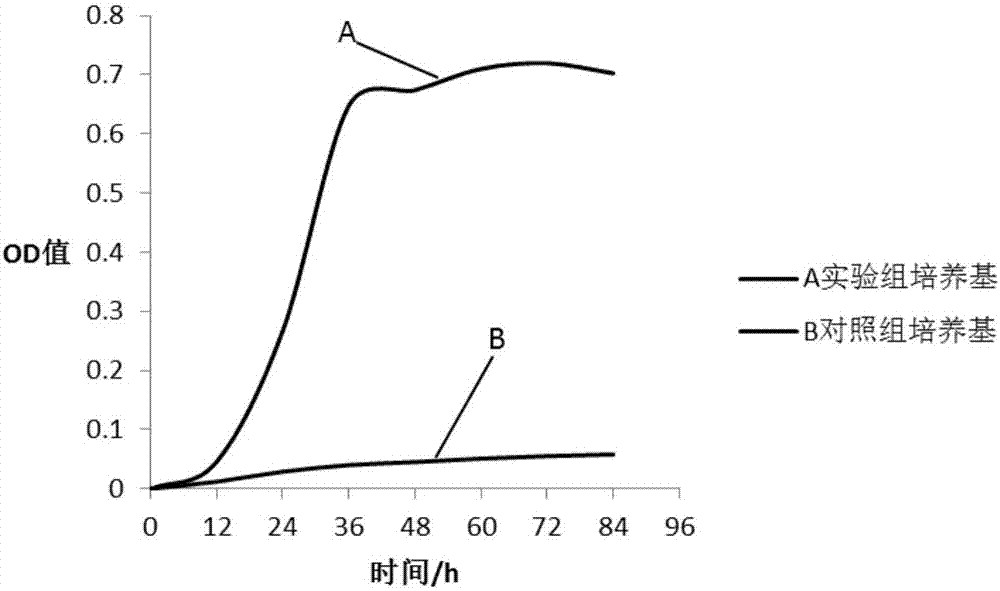
ActiveCN107384828APromote growthReduce incubation timeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesXyloseMagnesium chloride hexahydrate
The invention discloses an Ackerman myxobacteria culture medium and a preparation method thereof. The Ackerman myxobacteria culture medium per liter is prepared from the following raw materials: 0.4g of monopotassium phosphate, 0.53g of disodium hydrogen phosphate, 0.3g of ammonium chloride, 0.3g of sodium chloride, 0.11g of calcium chloride, 0.1g of magnesium chloride hexahydrate, 4g of sodium bicarbonate, 0.5mg of resazurin, 1mL of an acid trace solution, 1mL of an alkali trace solution, 1mL of a vitamin solution, 37g of a brain heart infusion, 1.5g of xylooligosaccharide, 5g of cyclodextrin and 30g of solarbio protease-enzymolyzed egg white. The culture medium is capable of solving the problem of slow growth of Ackerman myxobacteria, and significantly improving the growth rate and the bacteria solution concentration of Ackerman myxobacteria.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Porous cordierite block preparation method
The present invention discloses a porous cordierite block preparation method, which sequentially comprises: 1) at a room temperature, dissolving magnesium chloride hexahydrate, aluminum chloride hexahydrate and polyacrylamide in a solvent, adding tetramethyl orthosilicate in a dropwise manner, and continuously carrying out a stirring reaction for 50-70 min at a temperature of 50-70 DEG C; 2) naturally cooling the transparent clear solution obtained in the step 1) to a room temperature, adding propylene oxide, and uniformly stirring; 3) placing the homogeneous solution obtained in the step 2) into a container, sealing, and carrying out gelation for 3-5 min at a temperature of 35-45 DEG C; 4) placing the wet gel obtained in the step 3) in an environment with a temperature of 35-45 DEG C, and aging for 60-80 h; and 5) placing the aged gel obtained in the step 4) in an environment with a temperature of 50-70 DEG C, carrying out normal pressure drying for 72-96 h, and carrying out a heat treatment for 4-6 h at a temperature of 900-1300 DEG C. The porous cordierite block prepared by using the preparation method has characteristics of porous structure, high porosity and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Finishing process of knitted fabric
InactiveCN104452267AImprove wrinkle resistanceImprove antibacterial propertiesFibre treatmentMagnesium chloride hexahydrateAntibacterial property
The invention discloses a finishing process of a knitted fabric. The finishing process comprises the following steps: (1) putting 2.1 parts by mass of magnesium chloride hexahydrate, 1.2 parts by mass of potassium oxalate and 3.4 parts by mass of sodium hydroxide into 12.6 parts by mass of deionized water and stirring uniformly; (2) sequentially adding 1.7 parts by mass of solid nano titanium dioxide and 2.8 parts by mass of sodium tripolyphosphate and further stirring until the components are mixed uniformly so as to obtain finishing liquid; and (3) padding the fabric in the finishing liquid and drying at a constant temperature. According to the finishing process of the knitted fabric, the finished fabric is washable and has the excellent anti-wrinkle property and antibacterial property.
Owner:CHANGSHU HUABO WOOLEN TEXTILE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com