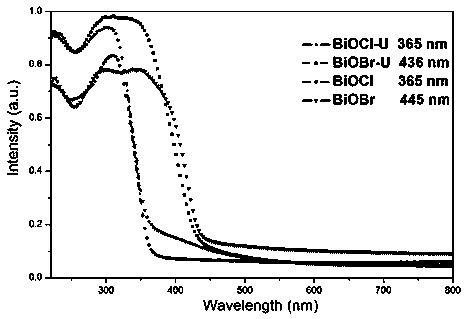
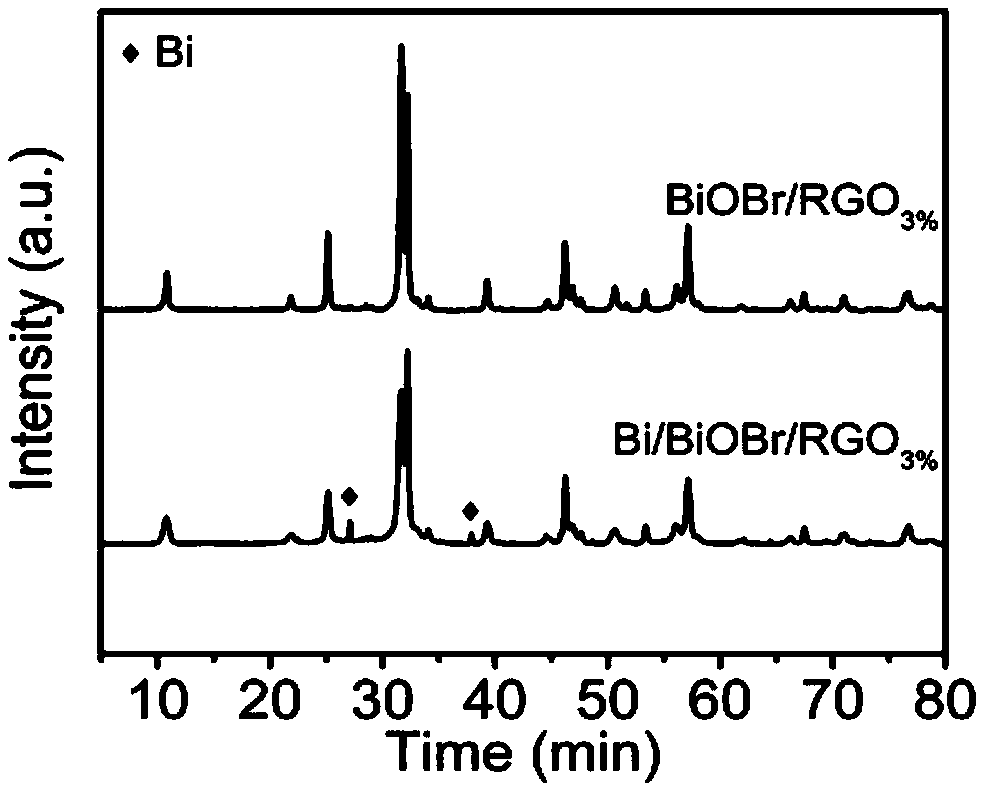
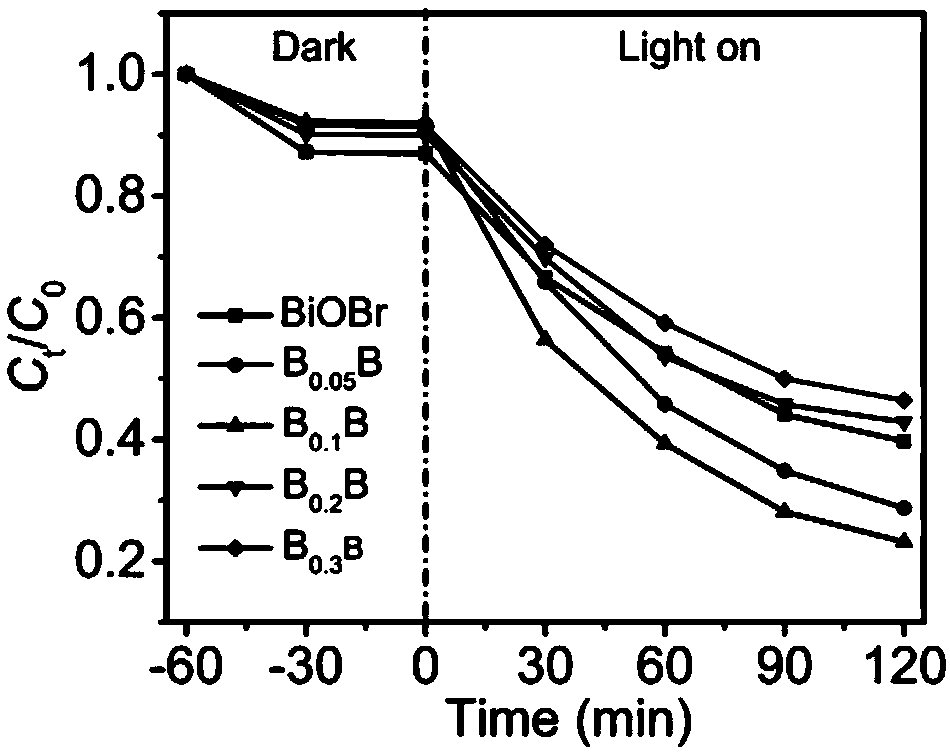
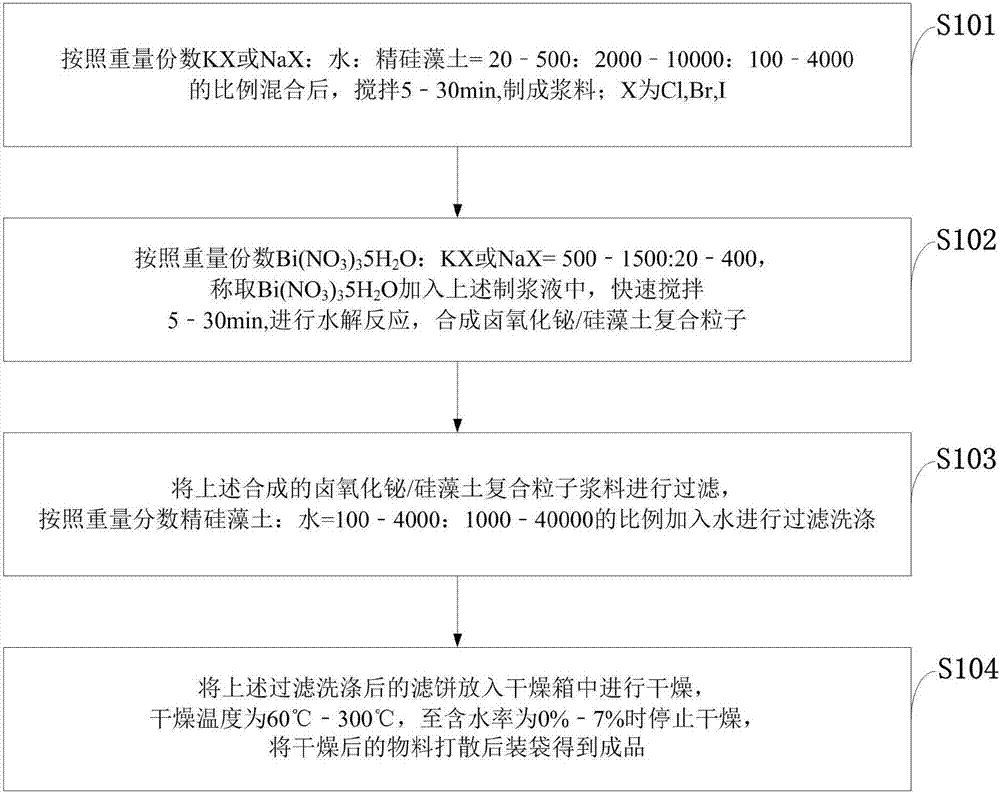
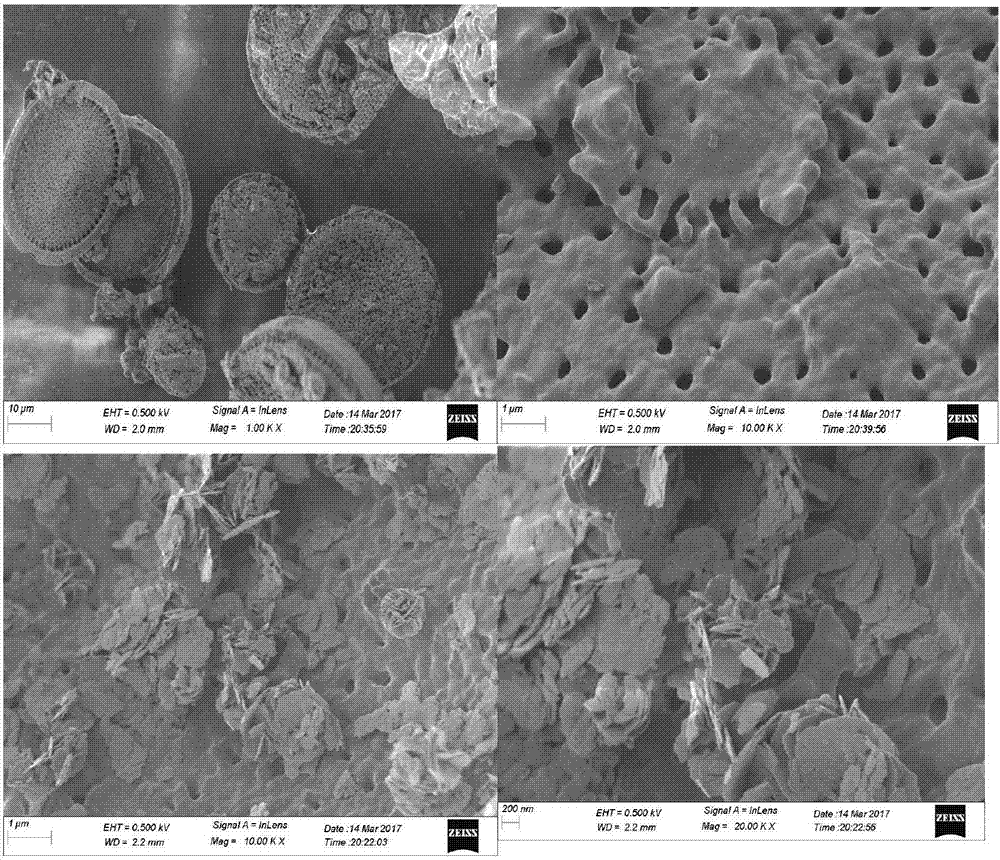
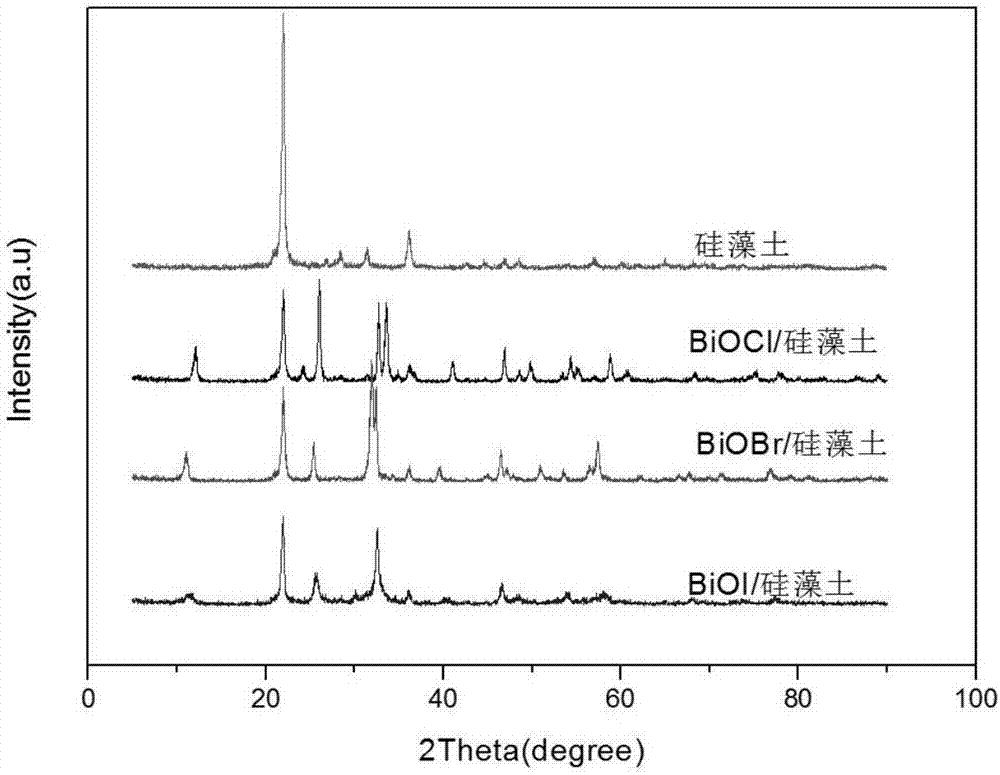
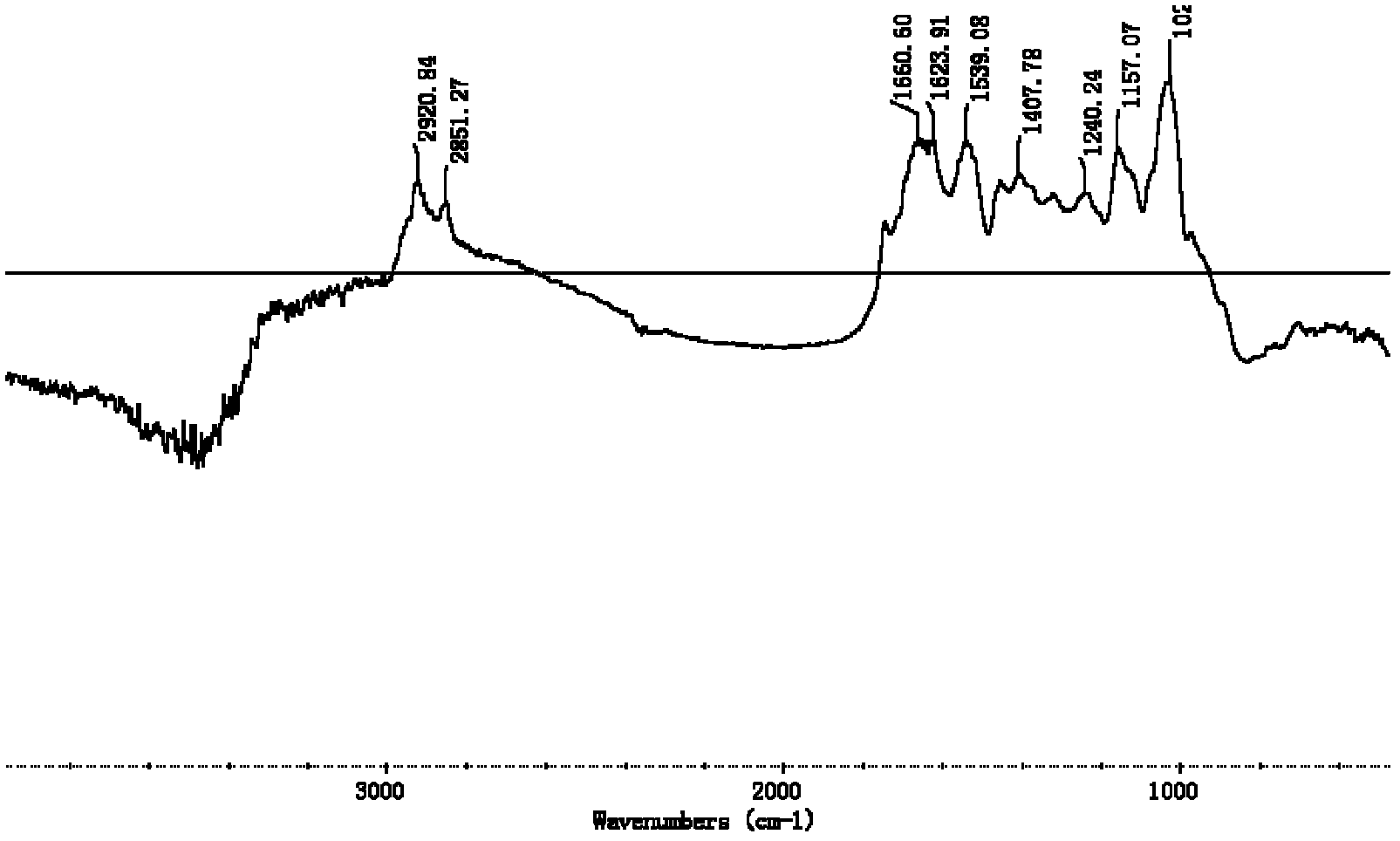
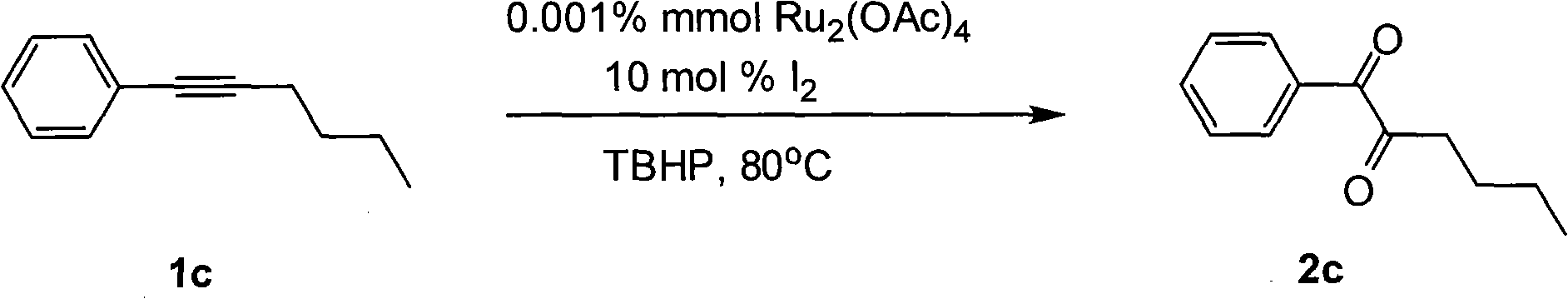Patents
Literature
579 results about "Potassium bromide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Potassium bromide (KBr) is a salt, widely used as an anticonvulsant and a sedative in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, with over-the-counter use extending to 1975 in the US. Its action is due to the bromide ion (sodium bromide is equally effective). Potassium bromide is used as a veterinary drug, as an antiepileptic medication for dogs.
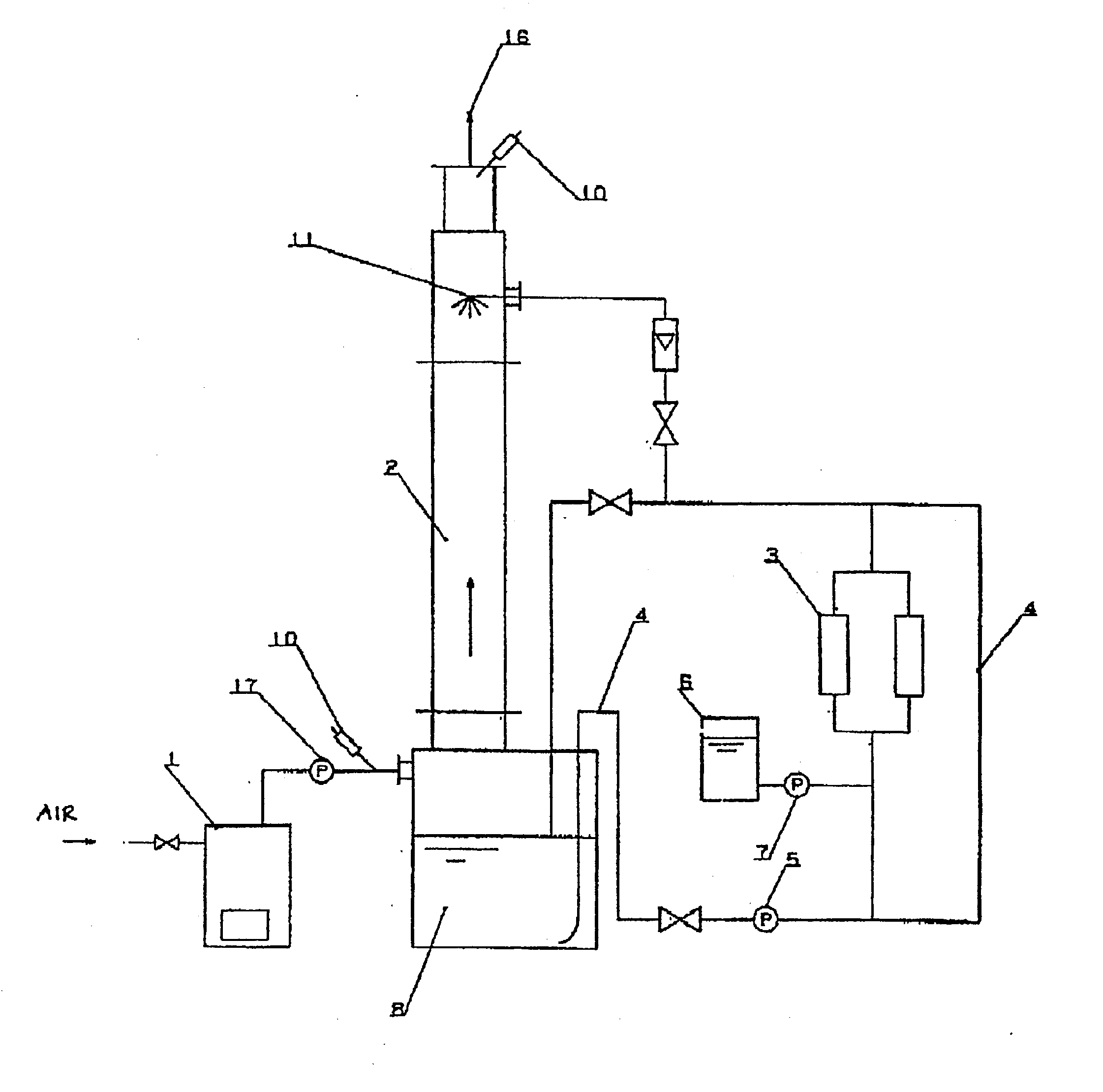
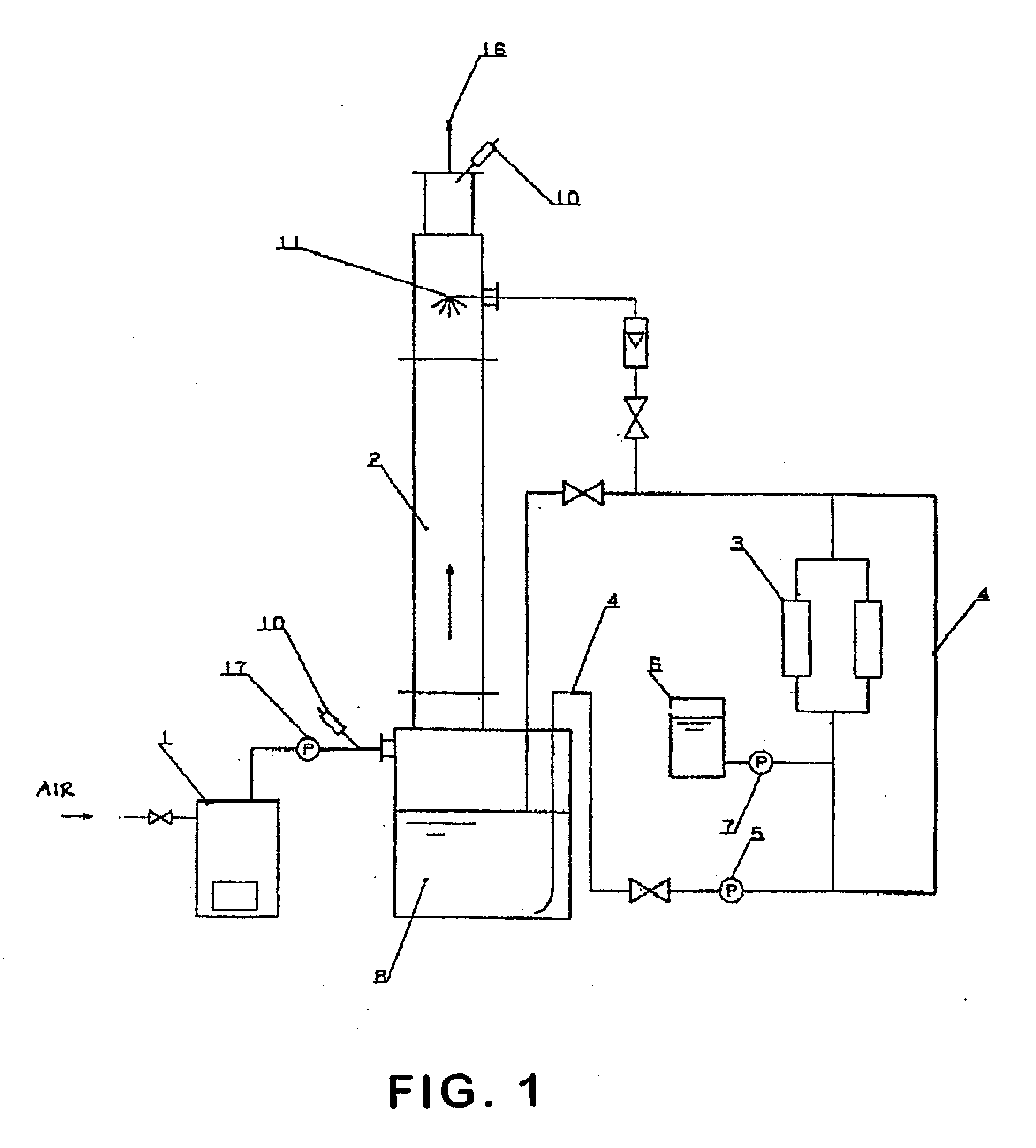
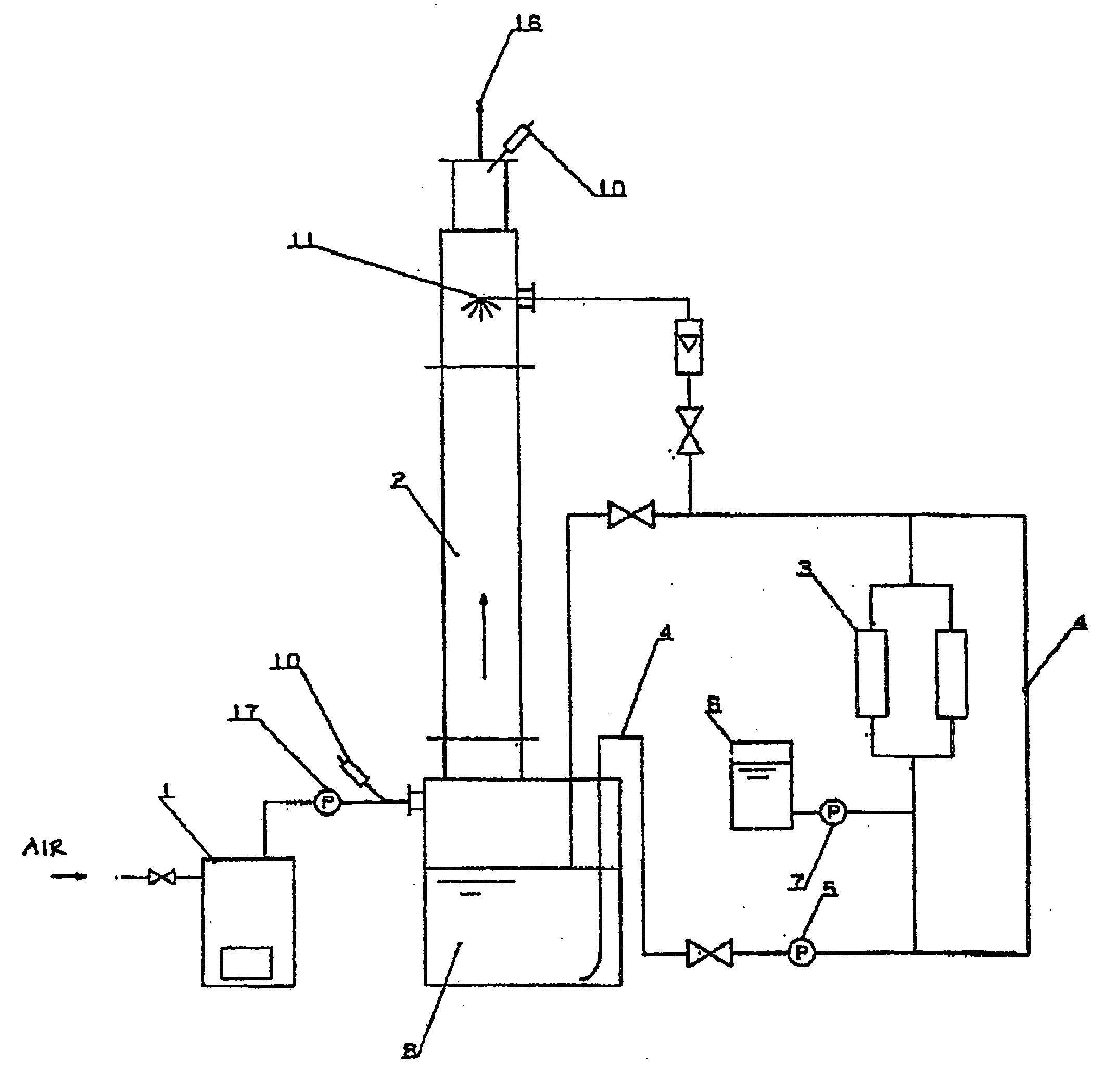
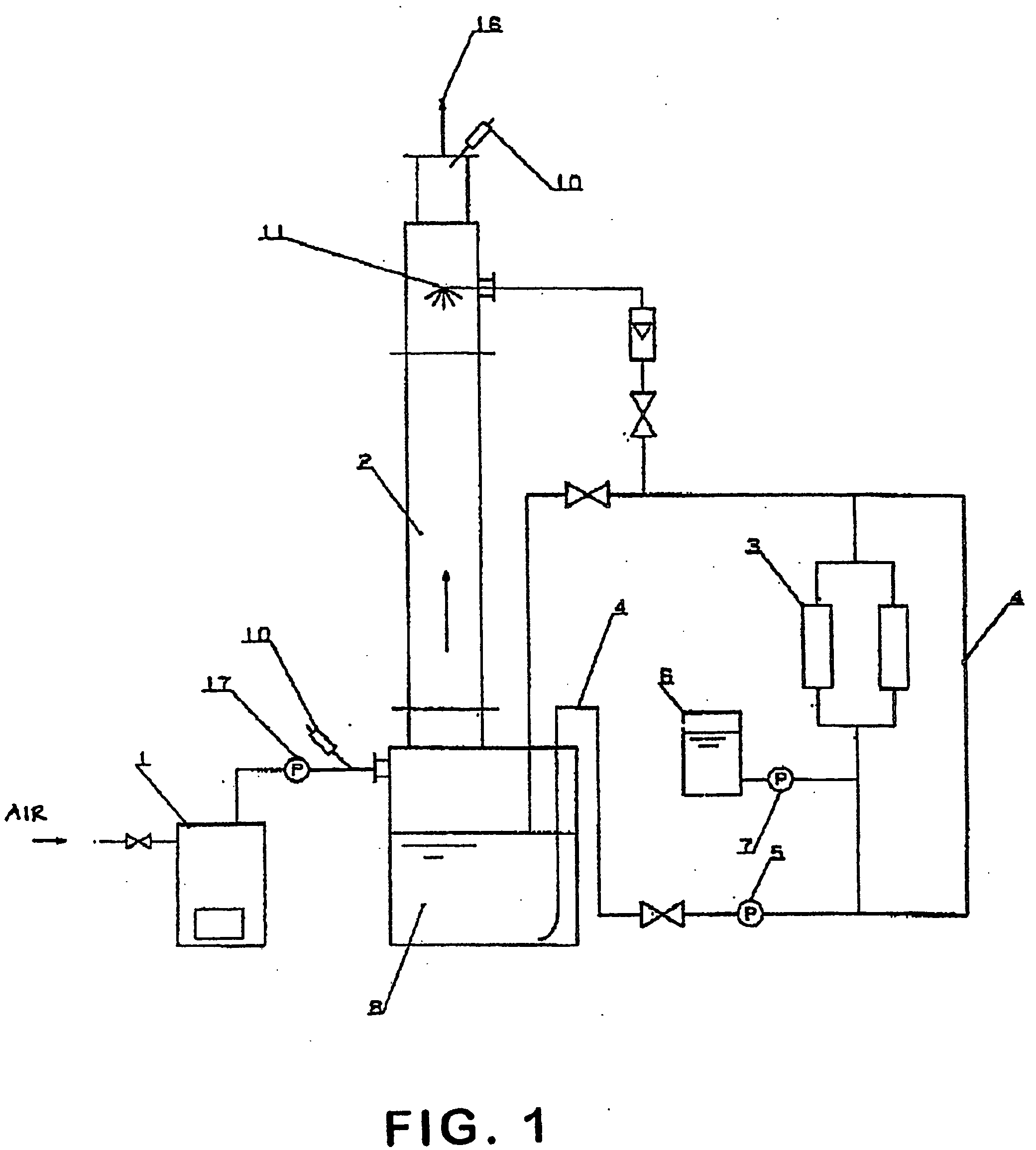
Method and device for deodorization and purification of exhaust gas or flue gas
InactiveUS20030164309A1Easy can be electrolyzedHigh densityCyanogen compoundsLighting and heating apparatusHazardous substancePotassium hydroxide
A method and device for removing, deodorizing and purifying odor, smoke and harmful substances from exhaust gas or flue gas employs a water solution containing hypohalogen acid such as hypochlorous acid soda, an alkaline electrolyte such as potassium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide and a saline electrolyte such as sodium chloride, potassium chloride, sodium bromide or potassium bromide which is electrolyzed to produce an electrolytic water solution which is fed to a deodorizing tower and brought into contact with exhaust gas or flue gas to remove odor, smoke and harmful substances in the exhaust gas or flue gas.
Owner:OMEGA CO LTD
Method and device for deodorization and purification of exhaust gas or flue gas
InactiveUS20060124444A1Reduce needRemove films of protein oil and fatsLighting and heating apparatusExhaust apparatusElectrolysisHazardous substance
A method and device for removing, deodorizing and purifying odor, smoke and harmful substances from exhaust gas or flue gas employs a water solution containing hypohalogenous acid compounds such as sodium hypochlorite, an alkaline electrolyte such as potassium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide and a saline electrolyte such as sodium chloride, potassium chloride, sodium bromide or potassium bromide which is electrolyzed to produce an electrolytic water solution which is fed to a deodorizing tower and brought into contact with exhaust gas or flue gas to remove odor, smoke and harmful substances in the exhaust gas or flue gas.
Owner:NAKAMURA SHINICHI +2
Fungicidal and parasiticidal fire-retardant powder
InactiveUS20150368560A1Reduce weightReduce the amount requiredFireproof paintsBiocidePhosphateFire retardant
Fire-retardant powder comprising at least 30% by weight of mono ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and / or di-ammonium monohydrogen phosphate, at least 5% by weight of alkaline bicarbonate, at least 3% by weight of silica, and at least 5% by weight of a compound selected from the group consisting of: sodium chloride, potassium chloride, potassium bromide, potassium sulfate, magnesium carbonate hydroxide pentahydrate, magnesium chloride hexahydrate, iron(II) sulfate heptahydrate, zinc (II) chloride, and combinations thereof. The invention also relates to building materials preferably comprising natural fibers and comprising at least 5% by weight, and at most 30% of a powder according to the invention.
Owner:SOLVAY SA
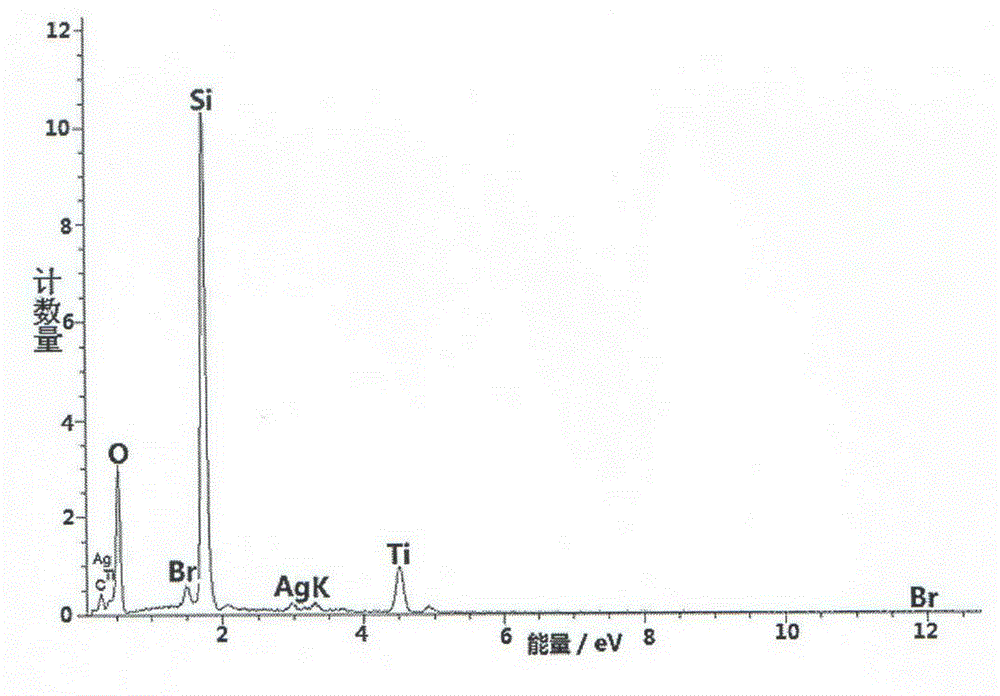
Preparation method of glass fiber loaded silver-silver bromide-titanium oxide composite material
ActiveCN103599800ASimple and fast operationEasy to scalePhysical/chemical process catalystsFiberVisible light photocatalytic
The invention provides a preparation method of a glass fiber loaded silver-silver bromide-titanium oxide composite material. The method comprises the following steps: with an organic or inorganic titanium compound as a titanium source and glass fibers as a carrier, obtaining a spherical titanium dioxide (TiO2) nano particle loaded threaded glass fiber composite material by a hydrolysis method under an acidic condition; impregnating the composite material in an ethylene glycol solution containing silver nitrate, and subsequently, adding dropwise an ethylene glycol solution containing potassium bromide to generate an AgBr-TiO2 / glass fiber composite material; and finally, reducing partial Ag<+1> in the AgBr-TiO2 / glass fiber composite material into metal Ag, thus obtaining an Ag-AgBr-TiO2 / glass fiber composite photocatalyst. The method provided by the invention realizes even loading of a nano-material having visible light catalytic activity on the surface of the threaded glass fibers by a two-step method; the method has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, easy large-scale production and the like; the obtained Ag-AgBr-TiO2 / glass fiber composite material has relatively high visible light catalytic activity.
Owner:中科瑞丽分离科技无锡有限公司
Preparation method of agricultural fungicide difenoconazole
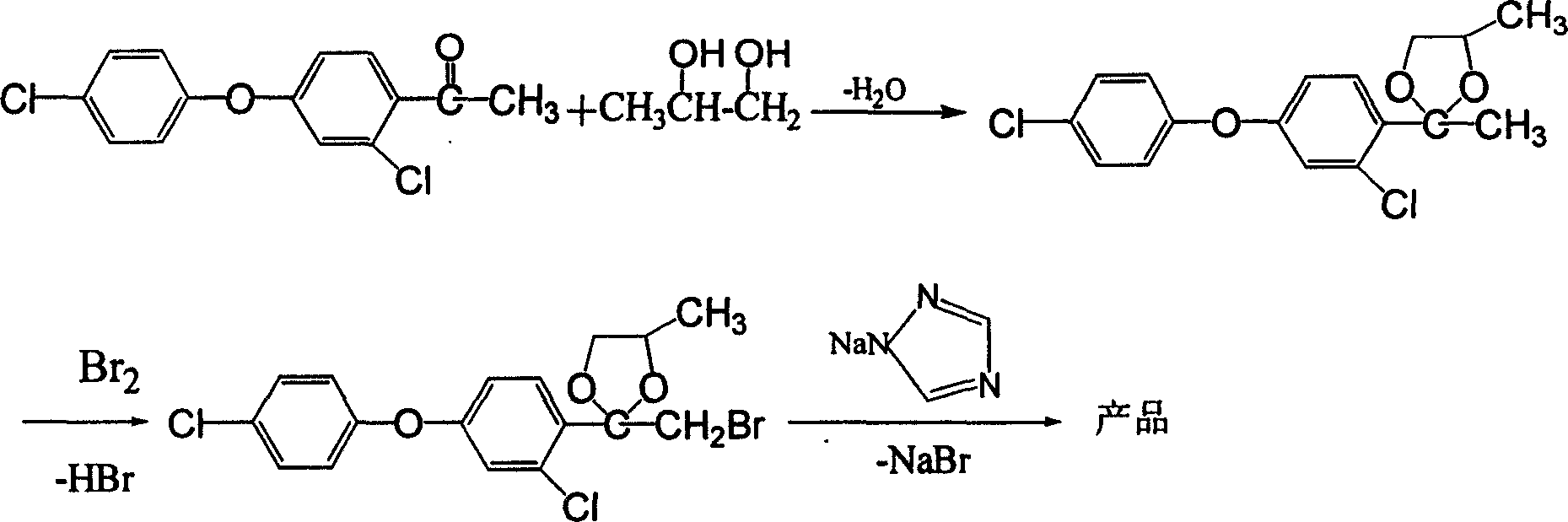
A method for preparing agricultural germicid, include the steps: 4-(4-) -2-chloro acetophenone propylene glycol generate cyclics-3-chlorine-4-(2,4-dimethyl-1,3-dioxane-2-group)benz-4'-, the reaction happens with catalyst-paratoluenesulfonic acid existing in the solvent, the density mess ratio is 5-50%. When catalyst-paratoluenesulfonic acid exists, the cyclics reacts with bromine, generating bromide-3-chlorine-4-(4-methyl-2- -1,3-dioxane-2-group)benz-4'-chlorine, the bromidereacts with 1,2,4- with potassium bromide as catalysis in acutesolvent, whose density mess ratio is 15-50%, acquiring the target compound. The invention has increased the productive efficiency of by more than 20%.
Owner:JIANGSU GENGYUN CHEM CO LTD
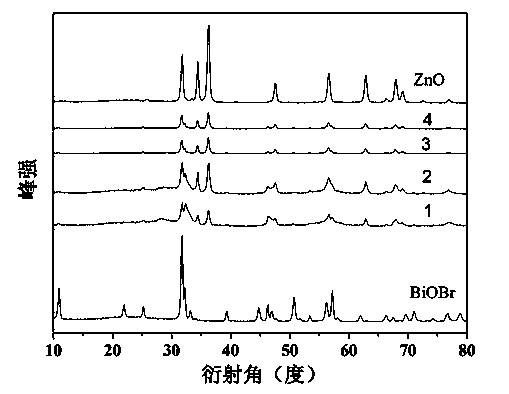
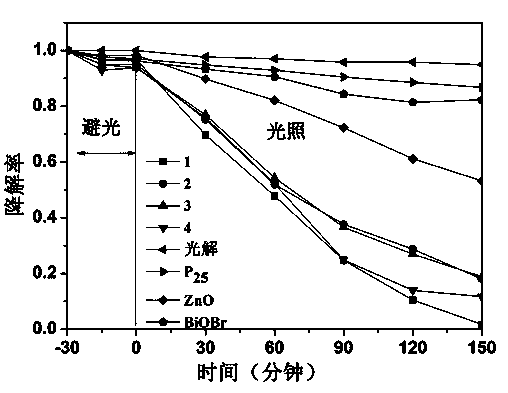
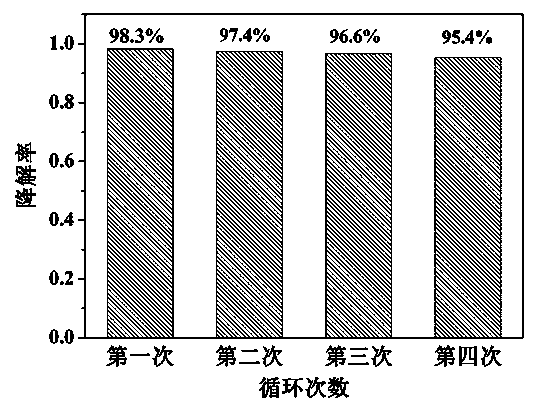
Preparation method of BiOBr/ZnO nano photocatalyst powder
InactiveCN103464184AHigh reuse ratePromote degradationPhysical/chemical process catalystsBismuth compoundPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method of BiOBr / ZnO nano photocatalyst powder, belonging to the field of nano photocatalyst preparation. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of adding two bromine compounds CTAB (cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide) and potassium bromide or sodium bromide at a proper proportion and a zinc-containing compound into an ethanol solvent, adding a bismuth-containing compound, and uniformly mixing; transferring the solution into a Teflon high-pressure reaction kettle, and performing a solvothermal reaction at certain temperature to generate precipitates; washing the precipitates with water and ethanol, and drying at 80 DEG C to obtain novel efficient BiOBr / ZnO nano photocatalyst powder. The method disclosed by the invention is quick, simple, convenient and high in operability, and the prepared BiOBr / ZnO heterojunction nano photocatalyst powder has perfect photocatalytic degradation efficiency on organic pollutants as well as good reusability.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
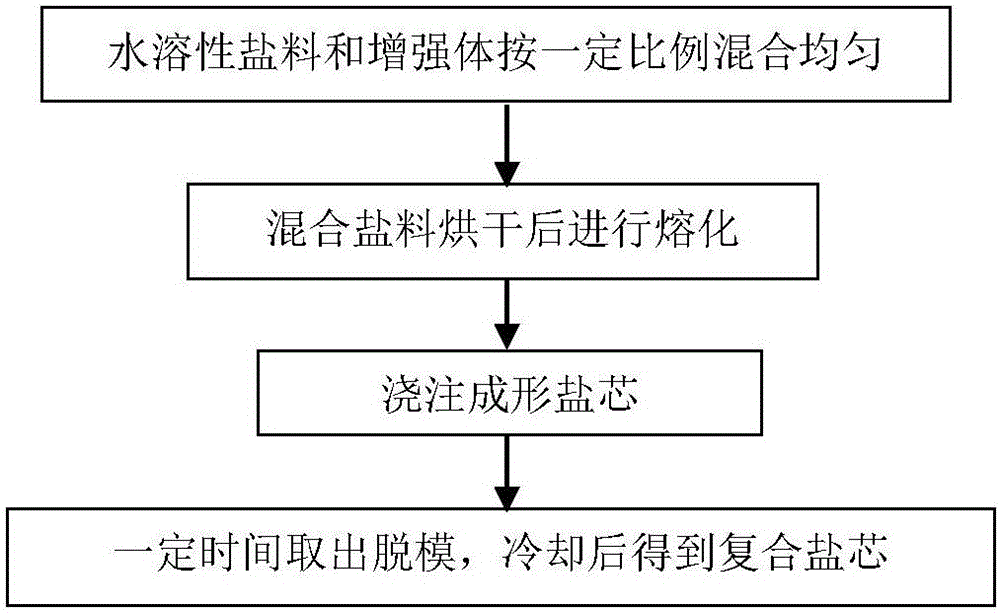
High-strength composite salt core material for low-melting-point alloy casting, salt core and preparation method
ActiveCN106670376AImprove flexural strengthReduce energy consumptionFoundry mouldsFoundry coresAlloySodium nitrate
The invention belongs to the technical field of casting, and particularly relates to a high-strength composite salt core material for low-melting-point alloy casting. The high-strength composite salt core material comprises, by mass, 70%-100% of water-soluble inorganic salt and 0%-30% of a reinforcement, wherein the water-soluble inorganic salt comprises one of low-melting-point salts including potassium nitrate and sodium nitrate, and at least one of high-melting-point salts including potassium chloride, sodium chloride, potassium bromide and sodium bromide, and positive ions of the low-melting-point slats are the same as positive ions of the high-melting-point salts. The invention further discloses a preparation method of a high-strength composite salt core, and an obtained salt core product. The prepared composite salt core has extremely high bending strength, excellent hygroscopicity and small volume shrinkage, and the comprehensive performance is excellent. In addition, the preparation technique of the high-strength composite salt core is simple, raw materials are cheap, and industrial production is easy.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
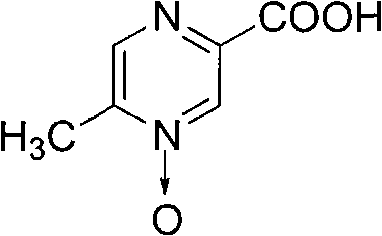
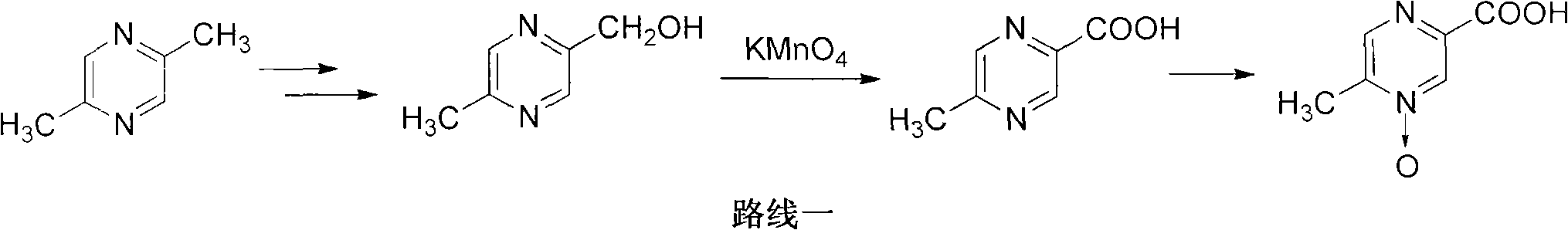
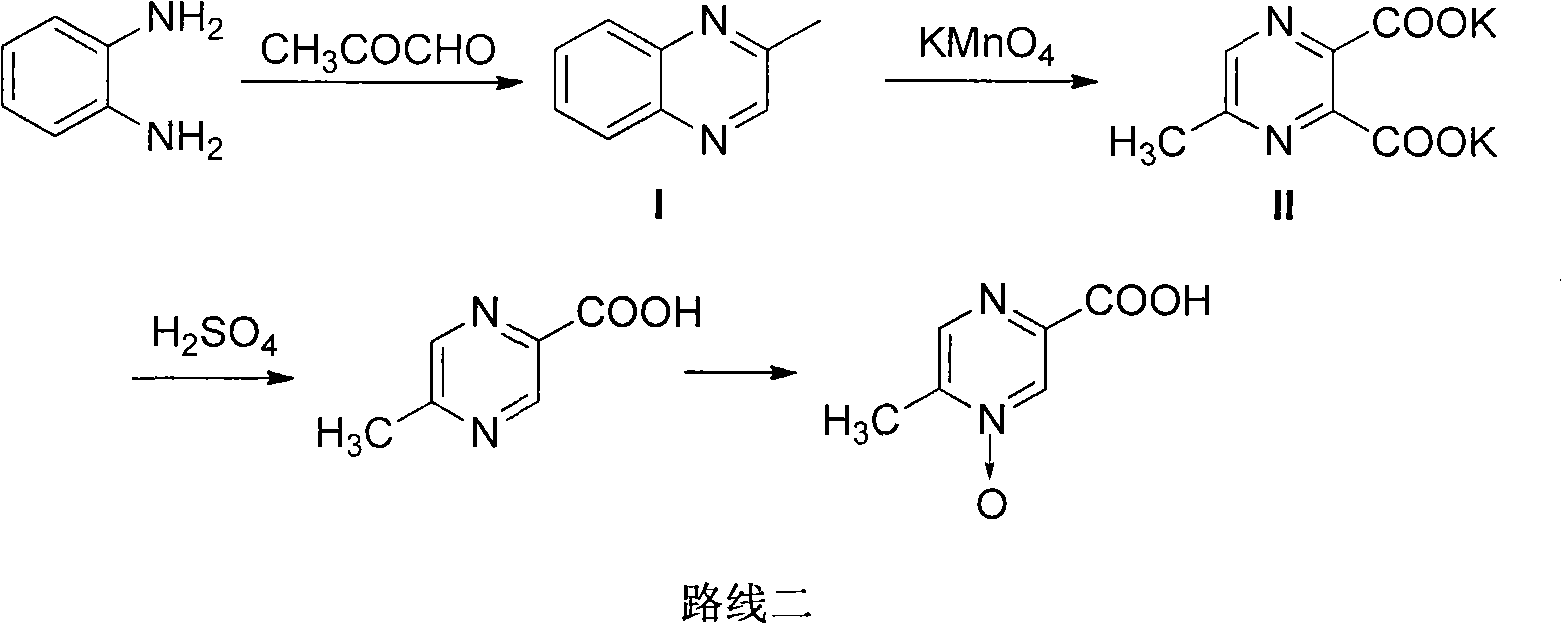
Preparation method of acipimox
InactiveCN103508963AReduce usageEasy to get materialOrganic chemistryAcetic anhydrideCarboxylic acid
The invention relates to a preparation method of acipimox for treating hyperlipidemia, belonging to the field of medicines. The invention provides an acipimox synthesis process which is simple and easy to operate. The preparation method comprises steps of with 2, 5-dimethylpyrazine as a raw material, carrying out nitrogen oxidation, reaction with acetic anhydride and alkaline hydrolysis to obtain 2-hydroxymethyl-5-methylpyrazine; directly oxidizing a post-treatment fluid by using 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-1-piperidinyloxy / sodium hypochlorite / potassium bromide to obtain 5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxylic acid, wherein the post-treatment fluid is not needed to be dried and concentrated; oxidizing 5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxylic acid by using hydrogen peroxide / sodium tungstate to obtain acipimox.
Owner:WEIHAI WEITAI PHARMA TECH DEV
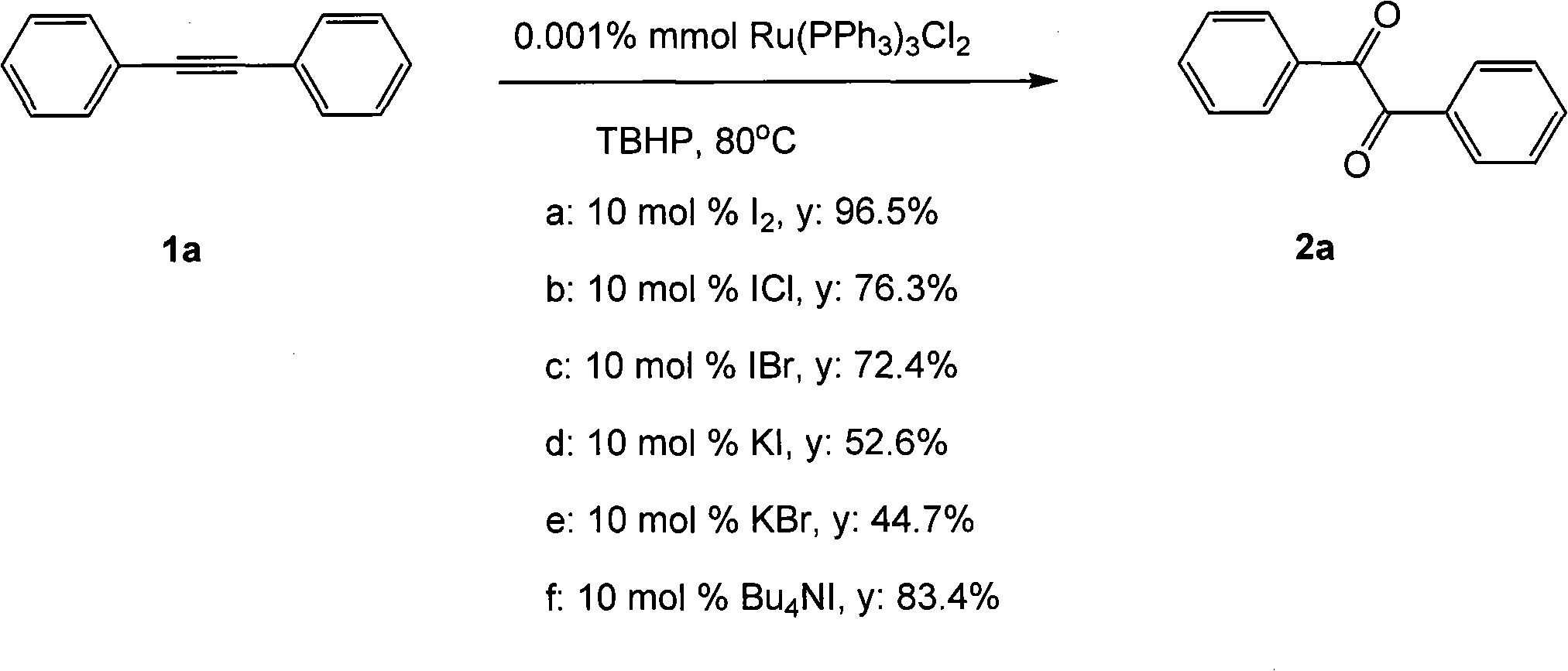
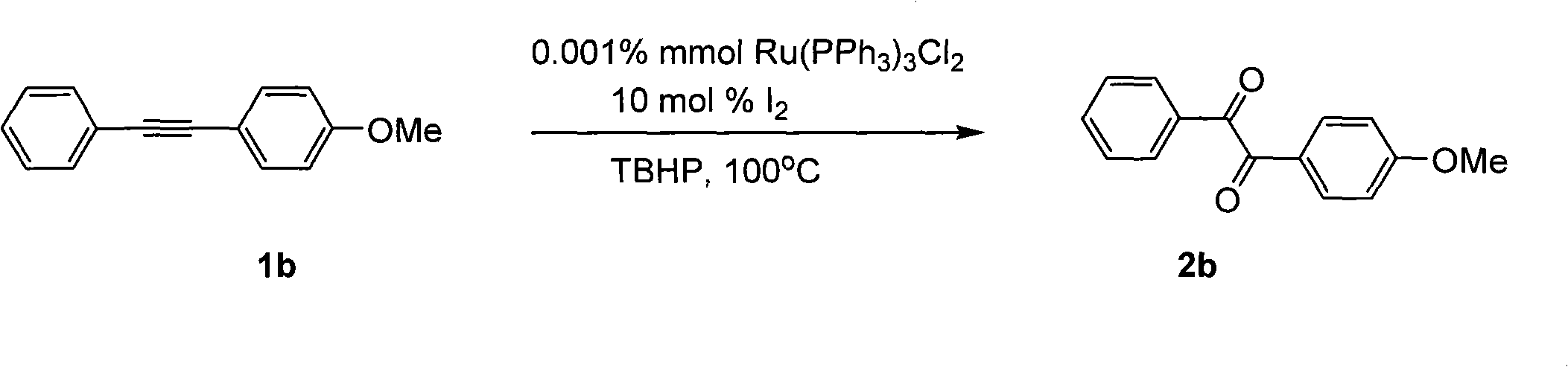
Method for preparing 1, 2-diketone by catalyzing and oxidizing alkynes
InactiveCN101624322AMild reaction conditionsMeet the requirementsCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationOrganic compound preparationCatalytic oxidationKetone
The invention belongs to the field of catalysis and oxidization, and particularly discloses a method for preparing 1, 2-diketone by catalyzing and oxidizing alkynes. The method comprises the following steps: taking alkynes R1-C-C-R2 (acetylenic link exists between C and C) as a reaction substrate, taking one of TBHP, m-chloroperoxybenzoic acid and p-benzoquinone as a oxidant, taking one of dichloro (p-cymene) ruthenium (II) dimer, tri (triphenylphosphine) ruthenous chloride, ruthenium acetate, ruthenium dichlorophenyl (II) dimer, ruthenium trichloride, BINAP ruthenous chloride, dodecacarbonyltriruthenium and tricarbonyldichlororuthenium (II) dimer as a catalyst, taking one of iodine, iodine chloride, iodine bromide, potassium iodide, tetrabutyl ammonium iodide and potassium bromide as a cocatalyst, and taking 1, 4-dioxane as a solvent to react under 40 DEG C to 100 DEG C for 4 to 24 h to prepare the 1, 2-diketone. The method is economic, environmental-friendly and mild.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Multistage macroscopical fingerprint method for identifying non-separated extracted infrared spectrum of medicinal materials in Chinese traditional medicine
InactiveCN1447110AAccelerate modernizationHigh speedColor/spectral properties measurementsTesting medicinal preparationsMiddle infraredUltrasound attenuation
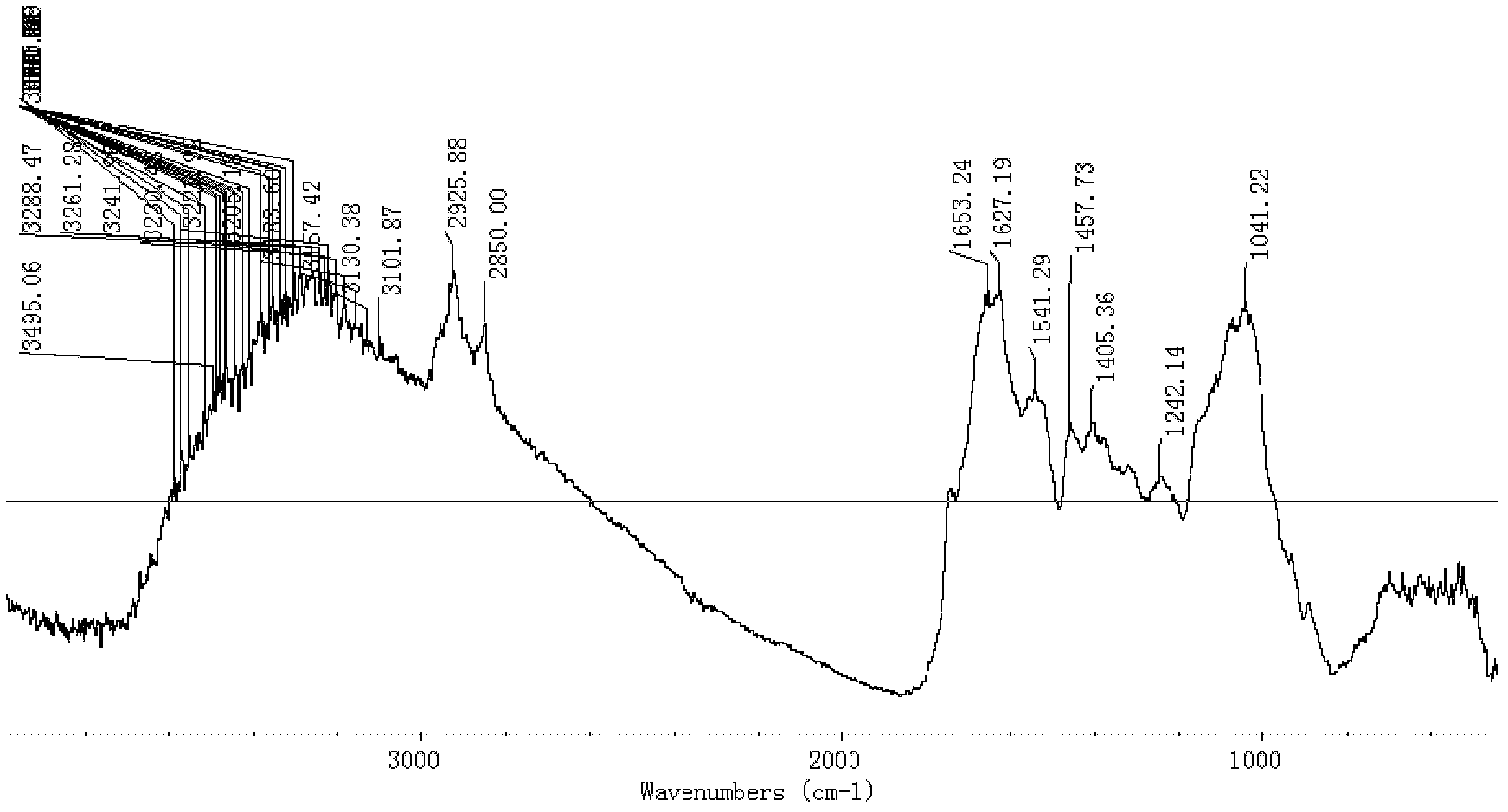
This invention relates to a method for verifying unseparately extracted multilever macro-finger makrs with infrared spectrum of Chinese medicine characterizing in cutting, crushing, and screening medicine to add potassium bromide powder into the medicine powder smaller than 200 mesh for table sampling to determine the middle infrared spectrum, diffuse reflection near infrared, diffuse reflection middle infrared spectrum, reflection spectrum and attenuation total reflection spectrum to get and draw the second-order derivative spectrum diagram of related spectrum, to determine the samples two-dimensional celated infrared spection to be compared in level.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for distinguishing pearl powders from shell powders
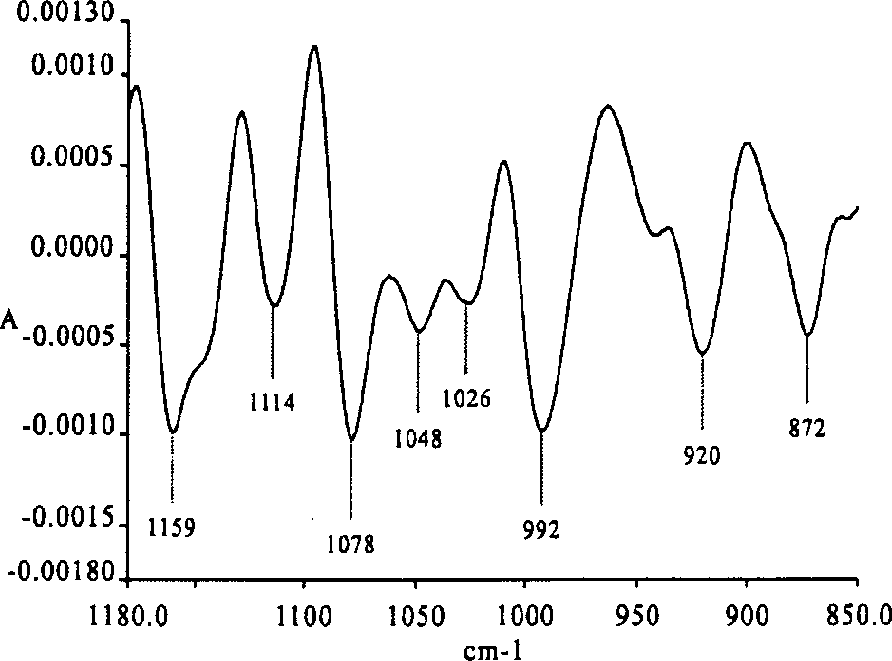
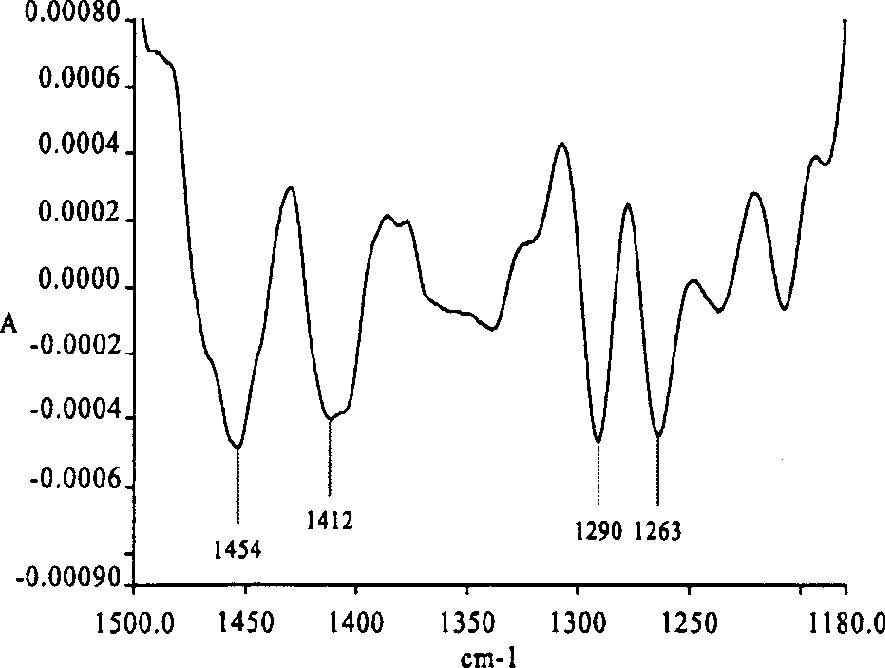
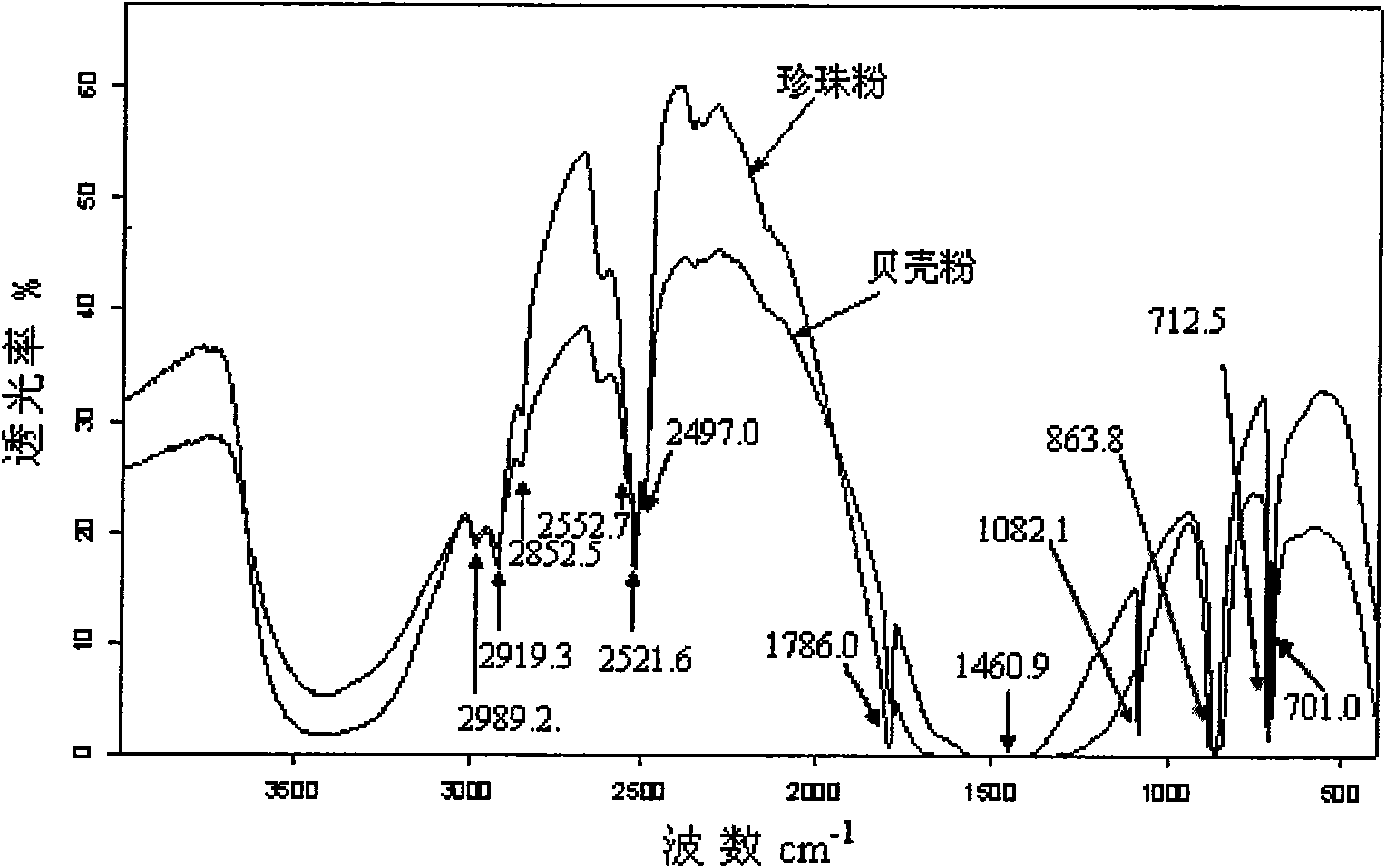
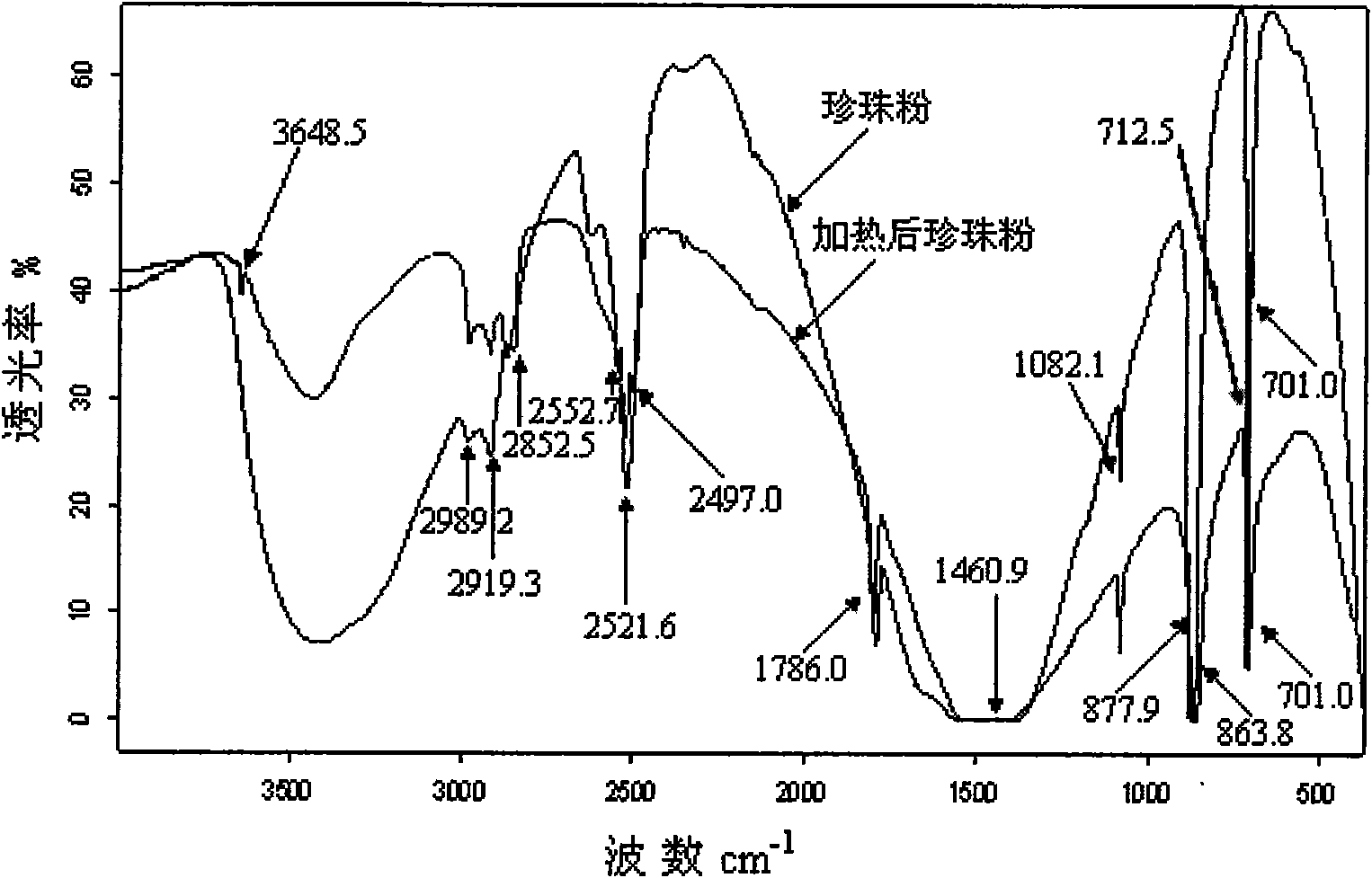
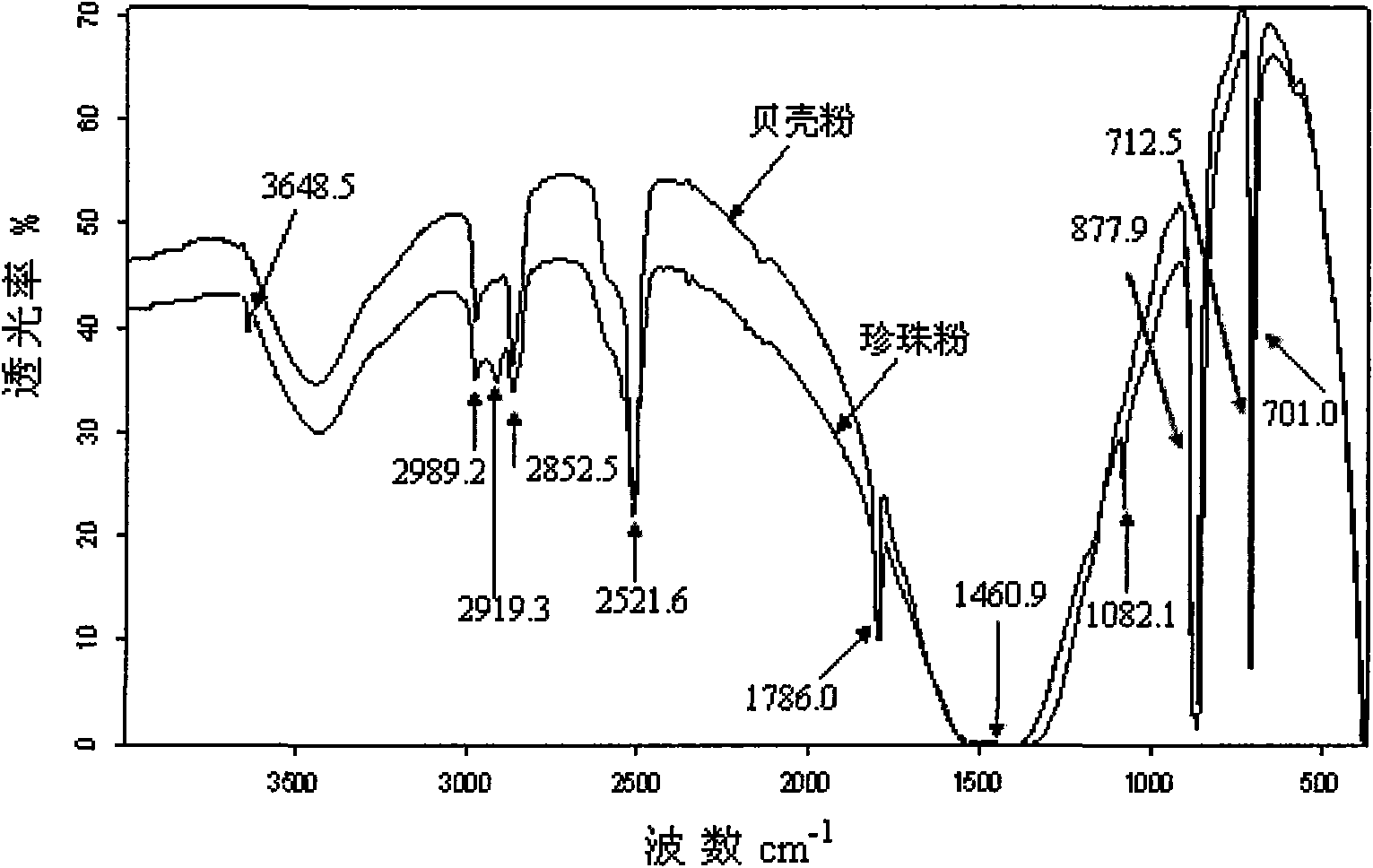
InactiveCN101620176AEasy to distinguishSimple methodPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsAragonitePotassium bromide
The invention relates to a method for distinguishing pearl powders from shell powders, comprising the following steps: the pearl powders and the shell powders are calcined and then respectively mixed with potassium bromide to be made into transparent flakes, then the infrared spectrum of the transparent flakes is measured under the conditions of resolution of 4 cm<-1> and scanning for 16 times with the scanning range of 400-4000 cm <-1>, the pearl powders and the shell powders are distinguished according to the characteristic peak of 701.0 cm <-1>, 1082.1 cm <-1>, 2919.3 cm<-1> and 3468.5 cm <-1>; as organic substances in the calcined pearl powders are partially decomposed, the crystal type of calcium carbonate changes from the aragonite type to the calcite type, and the calcium carbonate starts to decompose; the organic substances in the shell powders are almost totally decomposed, the aragonite type calcium carbonate is totally converted into the calcite type calcium carbonate, and the calcium carbonate does not start to decompose into calcium oxide yet, therefore, the method can be used for distinguishing the pearl powders from the shell powders. Compared with the prior distinguishing method, the method can simply, rapidly and effectively distinguish the pearl powders from the shell powders with obvious phenomenon.
Owner:钱国英 +2
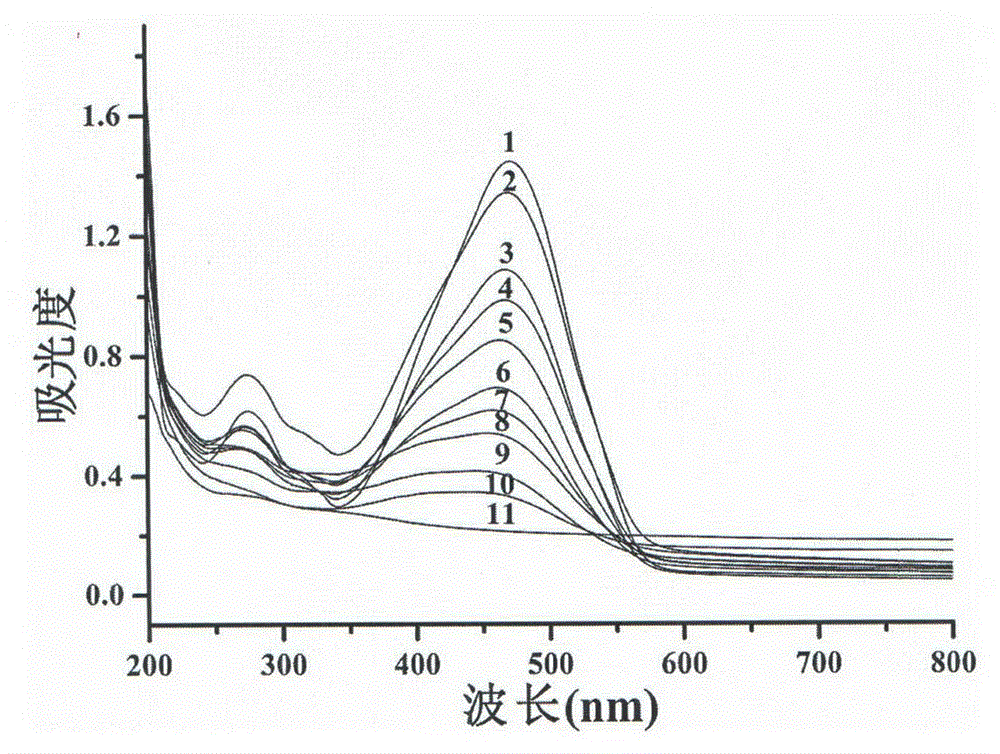
Flaky titanium dioxide/bismuth oxybromide composite photocatalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104785280AEvenly distributedImprove photocatalytic activityPhysical/chemical process catalystsBismuth oxybromideSolar power
The invention discloses a flaky titanium dioxide / bismuth oxybromide composite photocatalyst and a preparation method thereof. The composite photocatalyst is a heterogeneous composite material formed by depositing bismuth oxybromide on a titanium dioxide nanometer sheet. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dispersing the titanium dioxide nanometer sheet, thioglycollic acid, potassium bromide in deionized water in an ultrasonic manner, uniformly mixing to obtain a solution, and dissolving bismuth nitrate in ethylene glycol to obtain a solution; mixing the two solutions obtained in the former step to obtain a milky emulsion, stirring, leaving the emulsion to stand, and performing centrifugal separation and washing to obtain the composite photocatalyst. In the preparation process, through adjusting ratio of titanium dioxide to bismuth oxybromide, composite structures in different particle diameters can be obtained. The composite photocatalyst is simple in preparation technology; particularly, through thioglycollic acid, bismuth oxybromide can be uniformly distributed on the titanium dioxide (TiO2) sheet; the composite photocatalyst shows a more excellent photocatalytic activity compared with that of the titanium dioxide nanometer sheet under visible light, and has the potential practical application prospect of photocatalytic degration of organic pollutants through solar power light in the processing technology.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Formulation of plant source hard capsule case and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN1927186AHigh transparencyImprove stabilityPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCapsule deliveryCarrageenanLocust bean gum
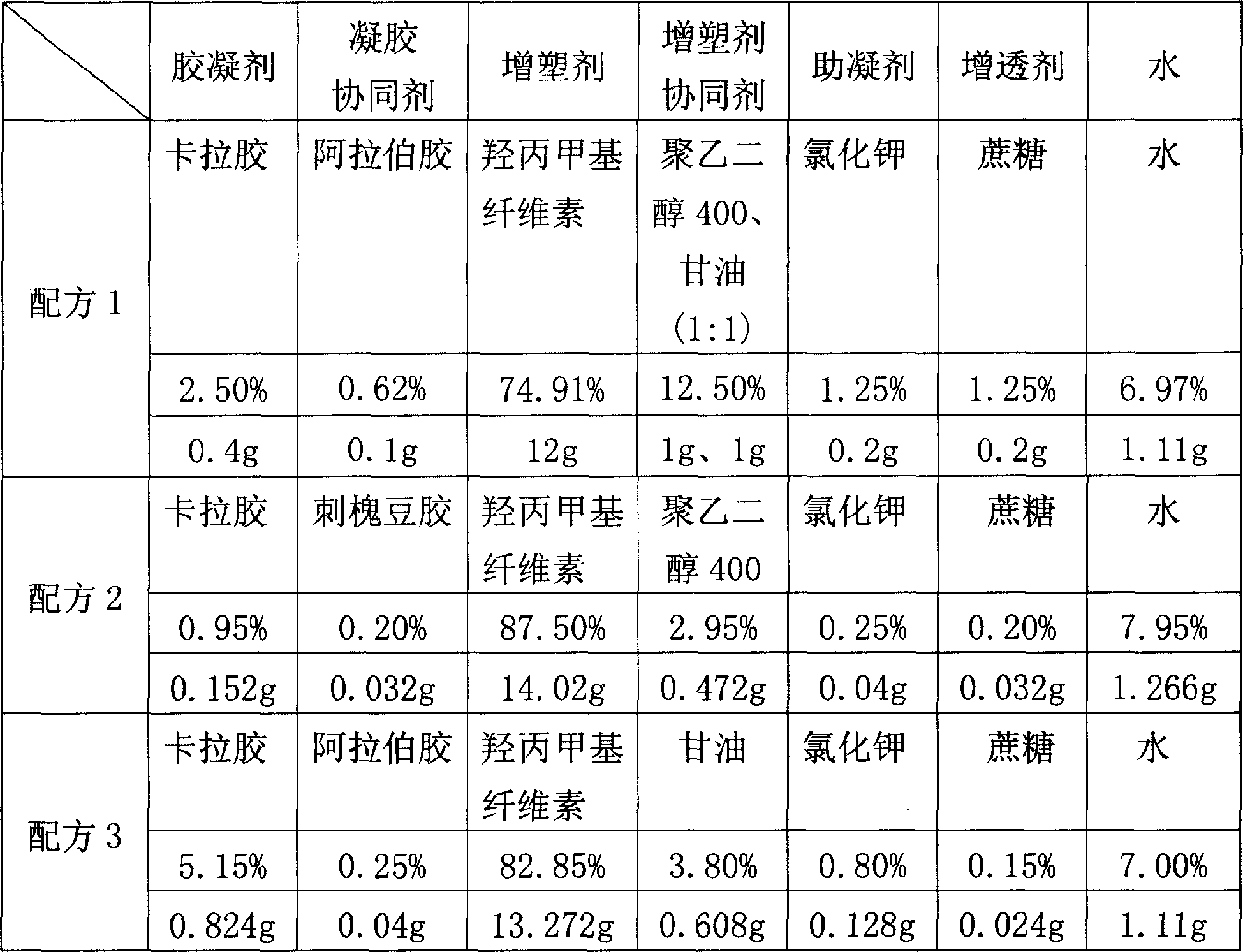
The invention relates to a formulation of plant source hard gelatin capsule shells and process for preparation, wherein the formulation includes (by weight ratio) 0.01-1.00% of potassium bromide, 0.02-0.80% of sucrose, 0.01-0.80% of acacia gum or locust bean glue, 0.10-2.00% of carrageenan, 0.50-5.20% of plasticizer synergistic agent, 70-90% of distilled water, 9.00-29.00% of methyl hydroxypropylcellulose.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
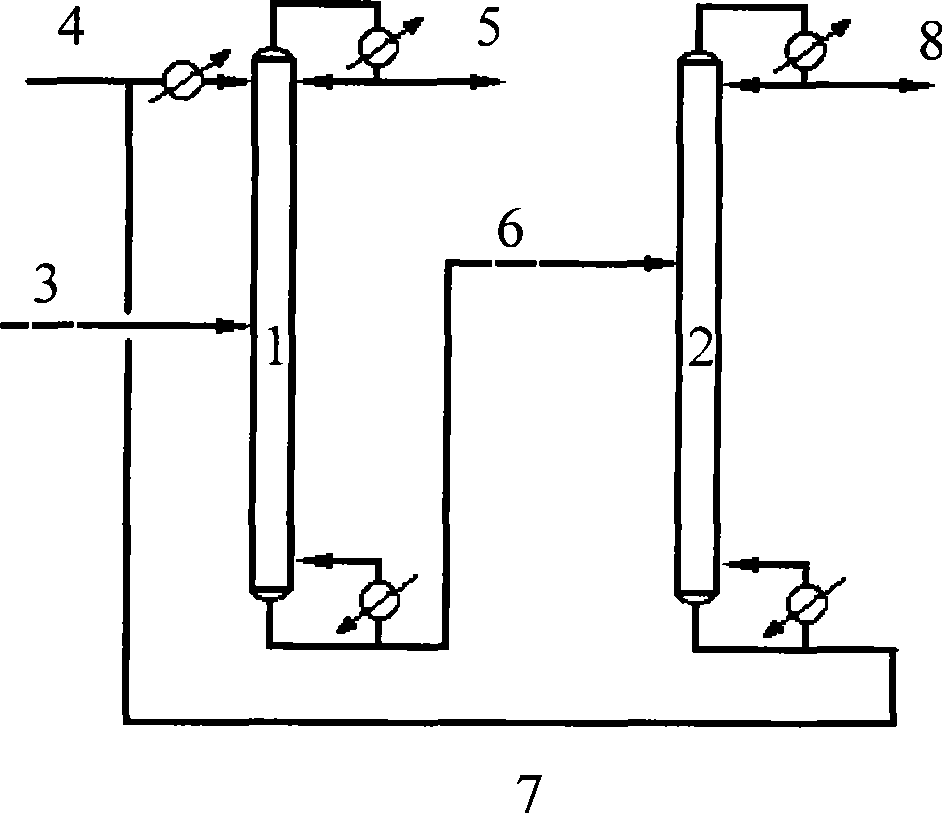
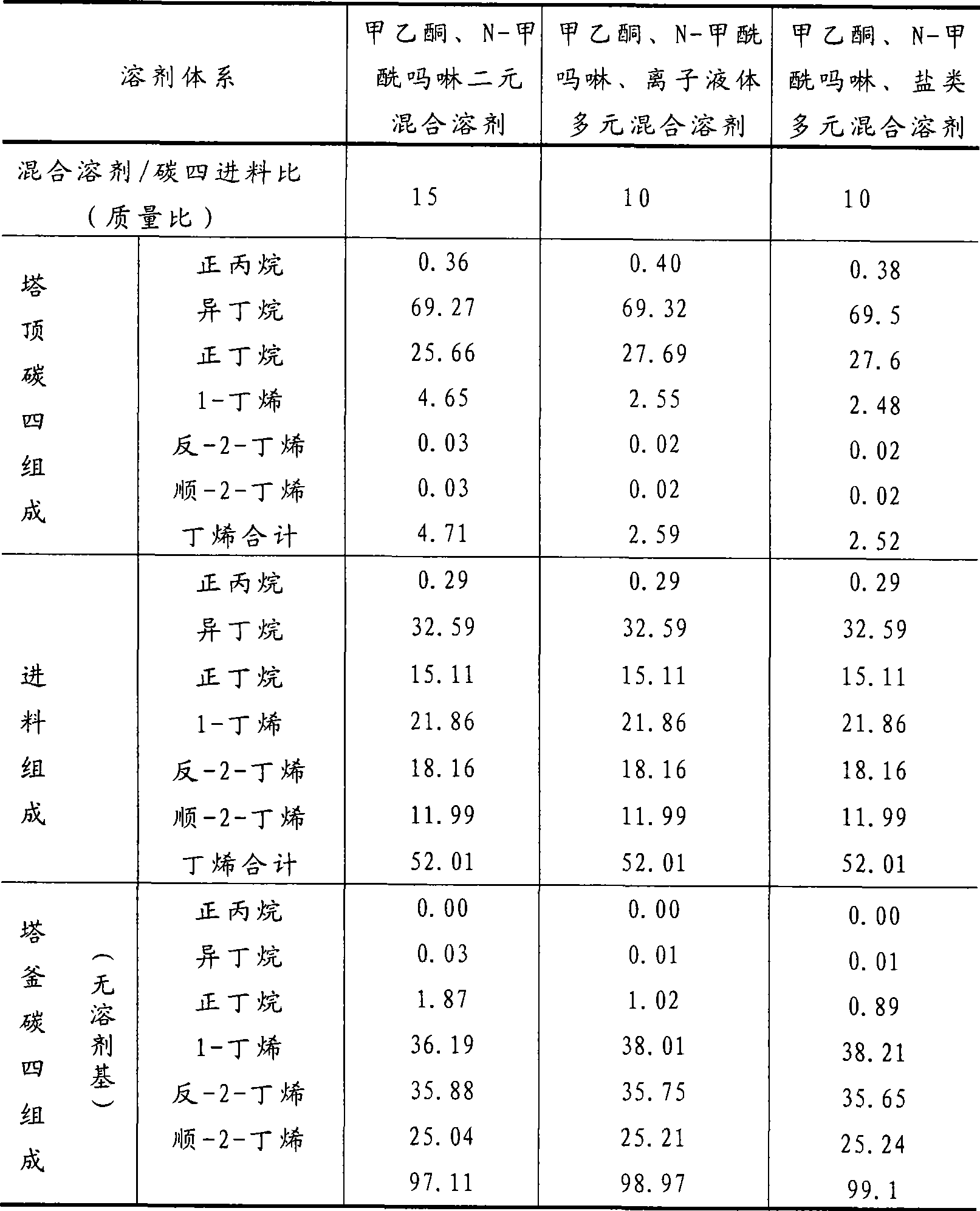
Method for separating butane and butene by using multiple mixed solvent
InactiveCN101417913ARetain solubilityImprove solubilityDistillation purification/separationBulk chemical productionSodium sulfocyanateTetrafluoroborate
The invention relates to a method for spearing butane from butylene with the multicomponent compound of ionic liquid, saline, ethyl methyl ketone and N-formylmorpholine. The content of ionic liquid in the multicomponent compound is 1.0 to 95 percent; the content of the saline in the multicomponent compound is 0.5 to 20 percent; the electropositive ion of the ionic liquid is iminazole electropositive ion, alkyl imidazole electropositive ion or alkyl quaternary ammonium ion, or the compound thereof; the electronegative ion is tetrafluoroborate electronegative ion, hexafluorophosphoric acid electronegative ion, nitrate ion, tetrachloro aluminic acid iron, heptachlor bi aluminic acid iron, chloride ion, bromine electronegative ion or the mixture; and the ionic liquid can be dimethylformamide potassium thiocyanate compound salt, dimethylformamide sodium sulfocyanate compound salt, or the compound; the saline is potassium thiocyanate, sodium sulfocyanate, ammonium thiocyanate, sodium nitrate, potassium nitrate, sodium iodide, potassium iodide, zinc chloride, copper chloride, zinc chloride, potassium bromide, or the compound thereof.
Owner:YANTAI UNIV
Modified lime sulphur and application thereof in gold leaching technology
ActiveCN103243222AReduce dosageImprove stabilityProcess efficiency improvementLead nitrateCalcium peroxide
The invention discloses a modified lime sulphur and an application thereof in a gold leaching technology. The modified lime sulphur comprises a stabilizer sodium-hexametaphosphate, oxidants-calcium peroxide and potassium cyanate, and additives-lead nitrate and soluble bromides (such as sodium bromide, potassium bromide, calcium bromide and the like). The modified lime sulphur is used as a gold leaching agent so as to effectively recover gold from gold-containing ores, gold concentrate powder and gold-containing wastes. The modified lime sulphur has the characteristics that the modified lime sulphur is easy to synthesize; the preparation cost is low; the preparation process is environment-friendly and toxic-free; and when the prepared modified lime sulphur is used for gold leaching, the gold leaching technology is simple, and the gold leaching velocity is high; and moreover, the modified lime sulphur is suitable for more ores than cyaniding gold leaching.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Electrochemical synthesis method for tetra-n-butylammonium tribromide
InactiveCN101054680ANothing producedConvenient sourceElectrolysis componentsElectrolytic organic productionElectrolysisSynthesis methods
The present invention relates to an electrochemistry synthetic method of tetributyl tribromide of ammonium and belongs to the field of chemical formulation preparing technology. Sadi synthetic method in accordance with the present invention is as follow: dissolving tetrabutyl ammonium bromide in a aqueous solution of bromium salts such as ammonium bromide, potassium bromide or sodium bromide, magnetic-stirring it until reaching a entire solubilization, and then restirring it after adding organic solvent such as methylene dichloride or acetonitrile therein; putting the solution into an electrolytic tank of non-diaphragm type, selecting platinum meshwork as cathode and anode, inputting a constant electrical current for electroanalysis; electrolyzing for 3 hours under normal temperature and magnetic stirring to obtain tetributyl tribromide of ammonium in oil phase finally; washing the oil phase with distilled water, evaporating the organic solvent off and exposing it to air for a period of time, after the product solidifies, washing it with water, performing a recrystallization with methanol to obtain high-purity tetributyl tribromide of ammonium solid.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
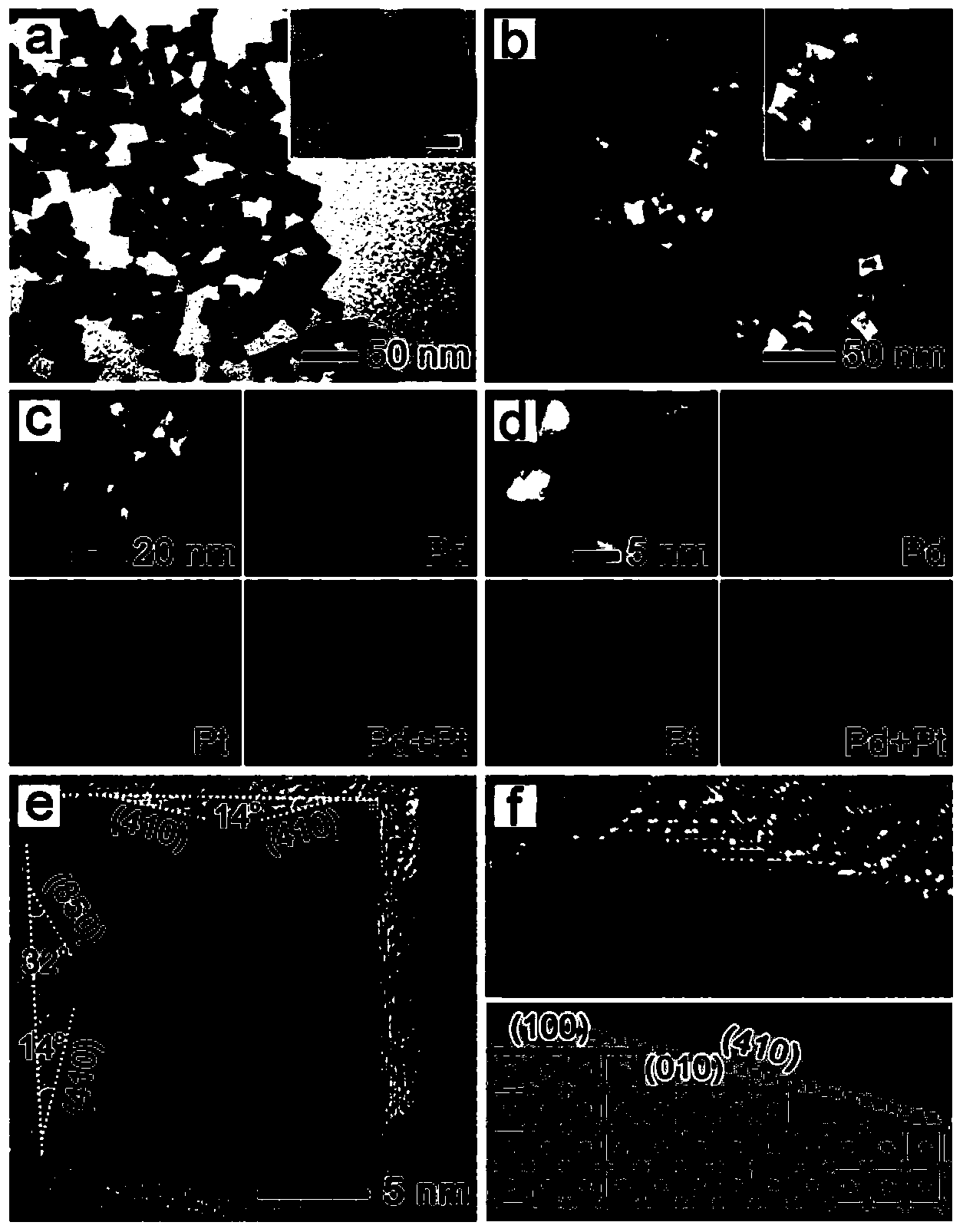
Preparation method of platinum-palladium alloy nanocrystalline
ActiveCN103668462AUniform sizeGood dispersionPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsPotassium bromideSodium tetrachloropalladate
The invention discloses a preparation method of platinum-palladium alloy nanocrystalline. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving chloroplatinic acid and sodium tetrachloropalladate into ethylene glycol to obtain a mixed solution I; dissolving polyvinylpyrrolidone, ascorbic acid and potassium bromide into ethylene glycol to obtain a mixed solution II; heating the mixed solution II to 100-150 DEG C while continuously stirring, and adding the mixed solution I into the mixed solution II to obtain the platinum-palladium alloy nanocrystalline, wherein the molar concentration of the potassium bromide is 0.1-0.4 mol / L. By the preparation method, the platinum-palladium alloy nanocrystalline with a concave hexahedral shape can be prepared by one step; reagents used in the preparation method are relatively simple and non-toxic and harmless; the preparation method is simple, and easy to implement; the prepared platinum-palladium alloy nanocrystalline has the concave hexahedral shape and has the characteristics of high-index crystal surface exposure, uniform particle size, and controllable components.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
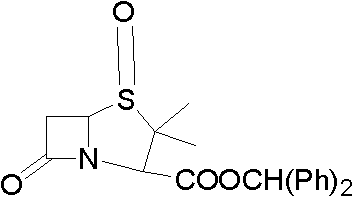
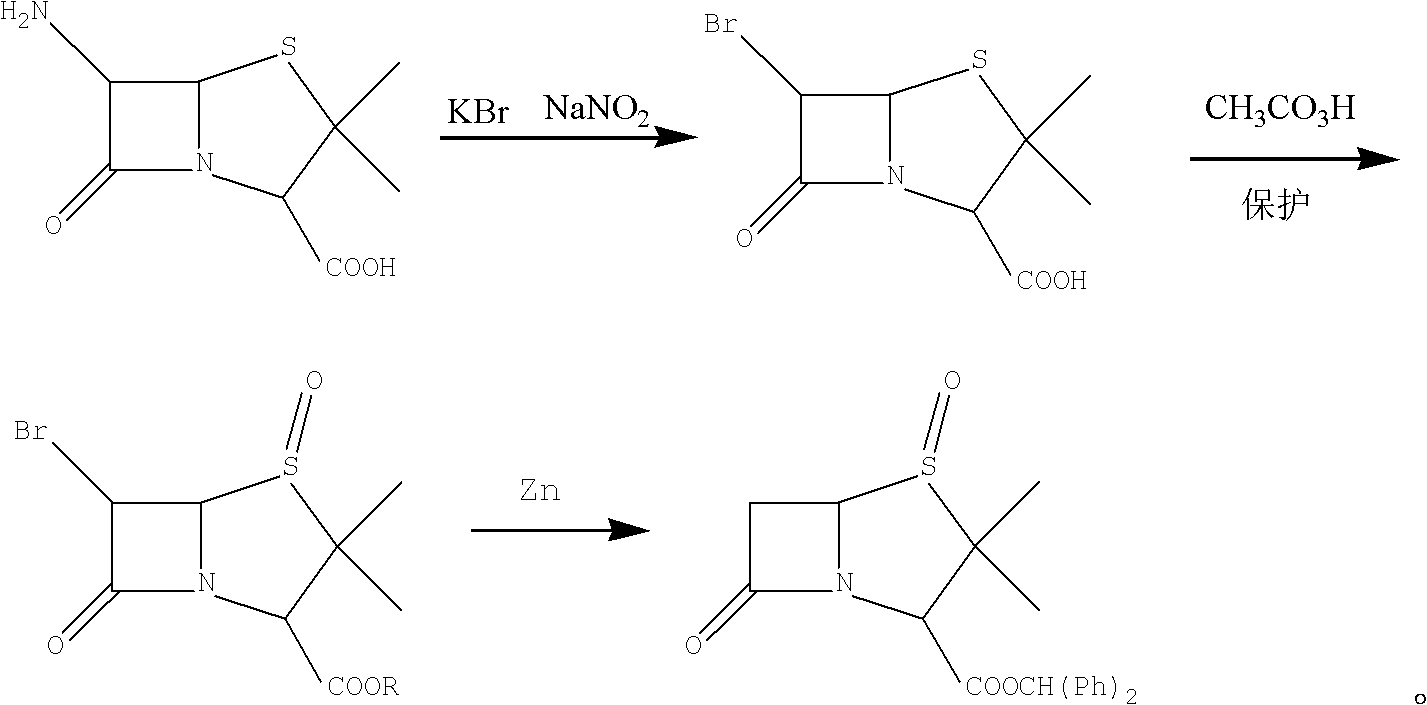
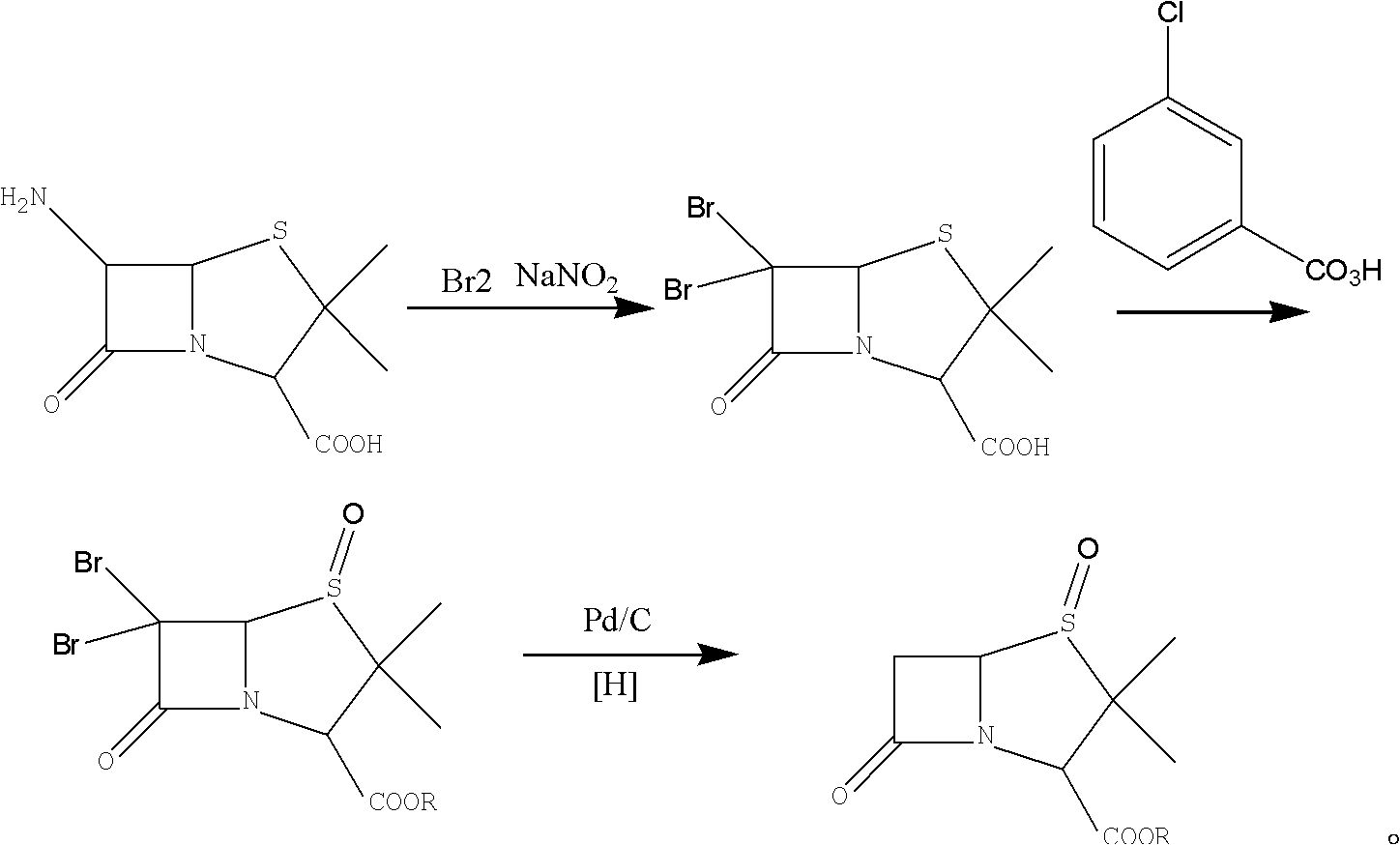
Method for preparing penicillanic acid sulfoxide diphenyl methyl ester
ActiveCN101935324AQuality improvementIncrease profitOrganic chemistryHigh pressureMeta-Chloroperoxybenzoic acid
The invention provides a method for preparing penicillanic acid sulfoxide diphenyl methyl ester. Penicillanic acid sulfoxide is prepared by the following four-step reaction. Hydrobromic acid is used as a brominating agent for substituting potassium bromide and bromine, and hydrogen peroxide is used as an oxidant for substituting peracetic acid and chloroperoxybenzoic acid, so the preparation method is safe and environment-friendly; in addition, the hydrogen peroxide is reacted with a compound (iii) under the catalysis action of acetyl molybdenum pyruvate so that the reaction mole yield can be obviously improved and reaches 90 percent; zinc powder which substitutes palladium and carbon is used as a reducing agent, so high-pressure equipment is not needed in the reaction; and the preparation method simplifies the process operation step, is easy for industrialized production, and reduces the production cost.
Owner:江西祥太生命科学有限公司
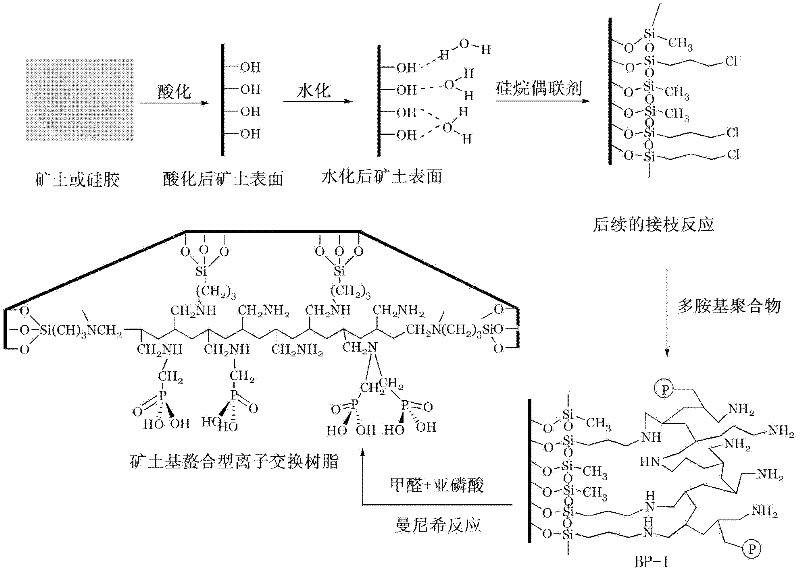
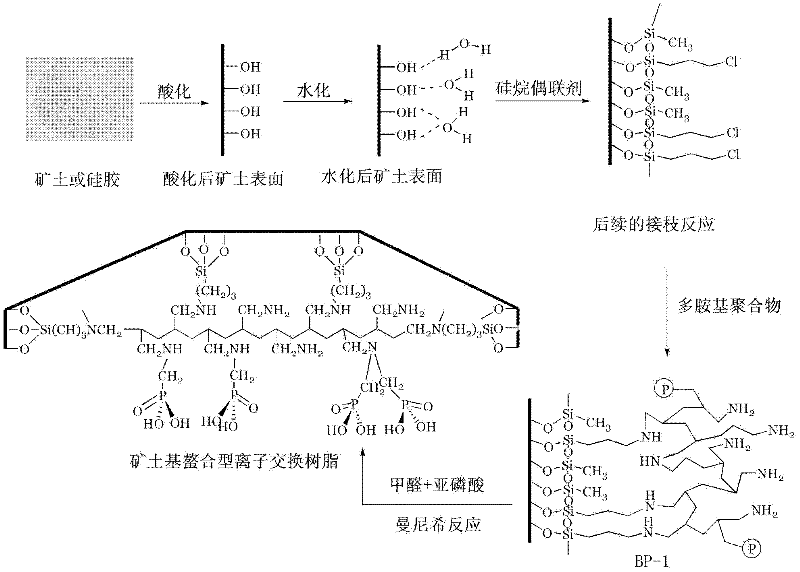
Preparation method for chelating ion exchange resin using inorganic substance as matrix
ActiveCN102391399AImprove performanceIncrease the ion exchange capacityComplex ion-exchangersPhosphorous acidHydration reaction
The invention belongs to the technical field of macromolecular ion exchange resin, and relates to a preparation method for chelating ion exchange resin. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: acidizing a matrix by using acid under the heating condition; washing the matrix by using deionized water until the matrix is neutral; allowing damp air in a sodium bromide or potassium bromide saturated solution reaction kettle to enter the matrix which is treated in the previous steps, so that a water molecule single layer is generated on the surface of the matrix; performing silanization reaction on the hydrated matrix, alkane and a silane coupling agent to obtain a silanized matrix; performing grafting reaction on the silanized matrix and multi-amino polymer to obtain a functional resin material; and performing Mannick reaction on the functional resin material, formaldehyde and phosphorous acid so as to obtain the final chelating ion exchange resin using an inorganic substance as the matrix. The method has the advantages that the operation process is short and the method is convenient to operate. A reagent is not required to be added into an ion exchange column when noble metal ions are adsorbed, so pollution and wastes are avoided.
Owner:GANZHOU RARE EARTH MINERAL IND
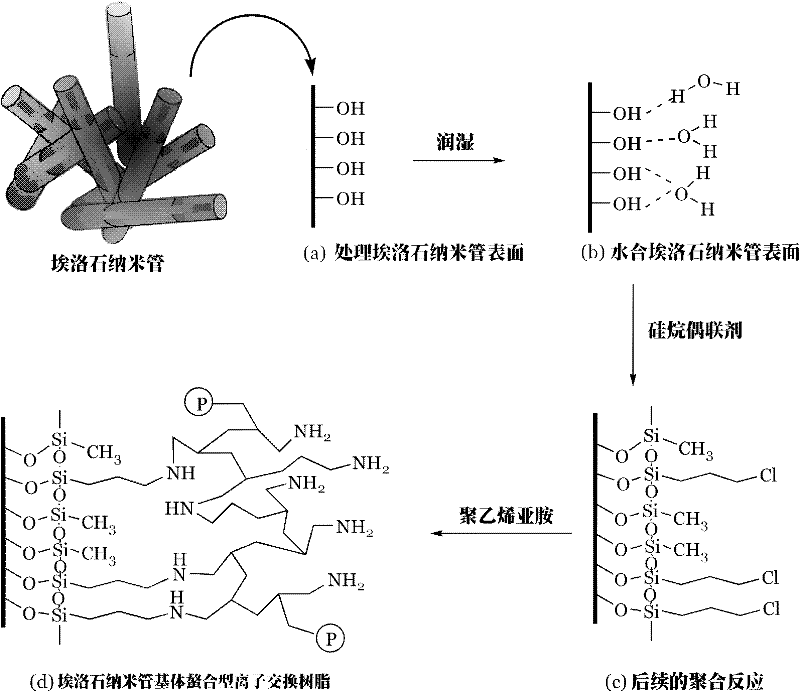
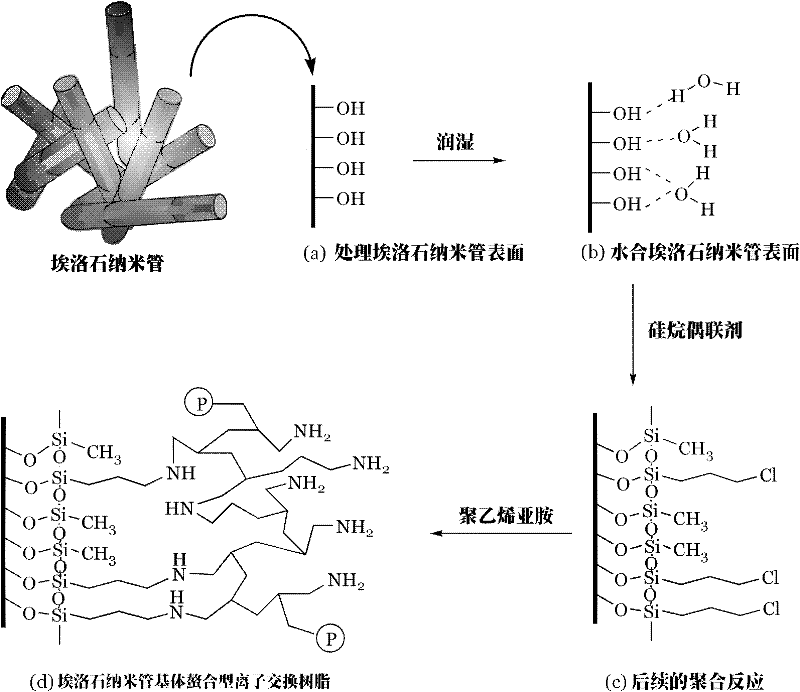
Preparation method of chelating type ion exchange resin with natural halloysite nanotube (HNT) as matrix
InactiveCN102250347AImprove performanceIncrease the ion exchange capacityComplex ion-exchangersAlkaneHalloysite
The invention relates to a preparation method of a chelating type ion exchange resin. The preparation method of a chelating type ion exchange resin with a natural halloysite nanotube as the matrix is characterized by comprising the steps of: taking a halloysite nanotube as the matrix and subjecting the halloysite nanotube to an acidification treatment under the condition of heating, and then washing the halloysite nanotube with deionized water until the acidified halloysite nanotube becomes neutral; introducing the humid air from a sodium bromide / potassium bromide saturated liquid reaction vessel into the water vapour saturated gas with the last step treated halloysite nanotube placed inside, thus obtaining a hydrated halloysite nanotube; subjecting the hydrated halloysite nanotube, alkane and a silane coupling agent to a silanization reaction so as to obtain a silanized halloysite nanotube, then conducting a grafting reaction to the silanized halloysite nanotube and an ethyleneimine polymer, thus obtaining the product. Characterized by brief operation process and convenient operation, the method of the invention has no need for any reagent to be added into an ion exchange column when absorbing precious metal ions, without any pollution and waste generated.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
CsPbBr3 (cesium-lead-bromide) perovskite quantum dot fluorescent glass for display of wide color gamut and preparation method and application thereof
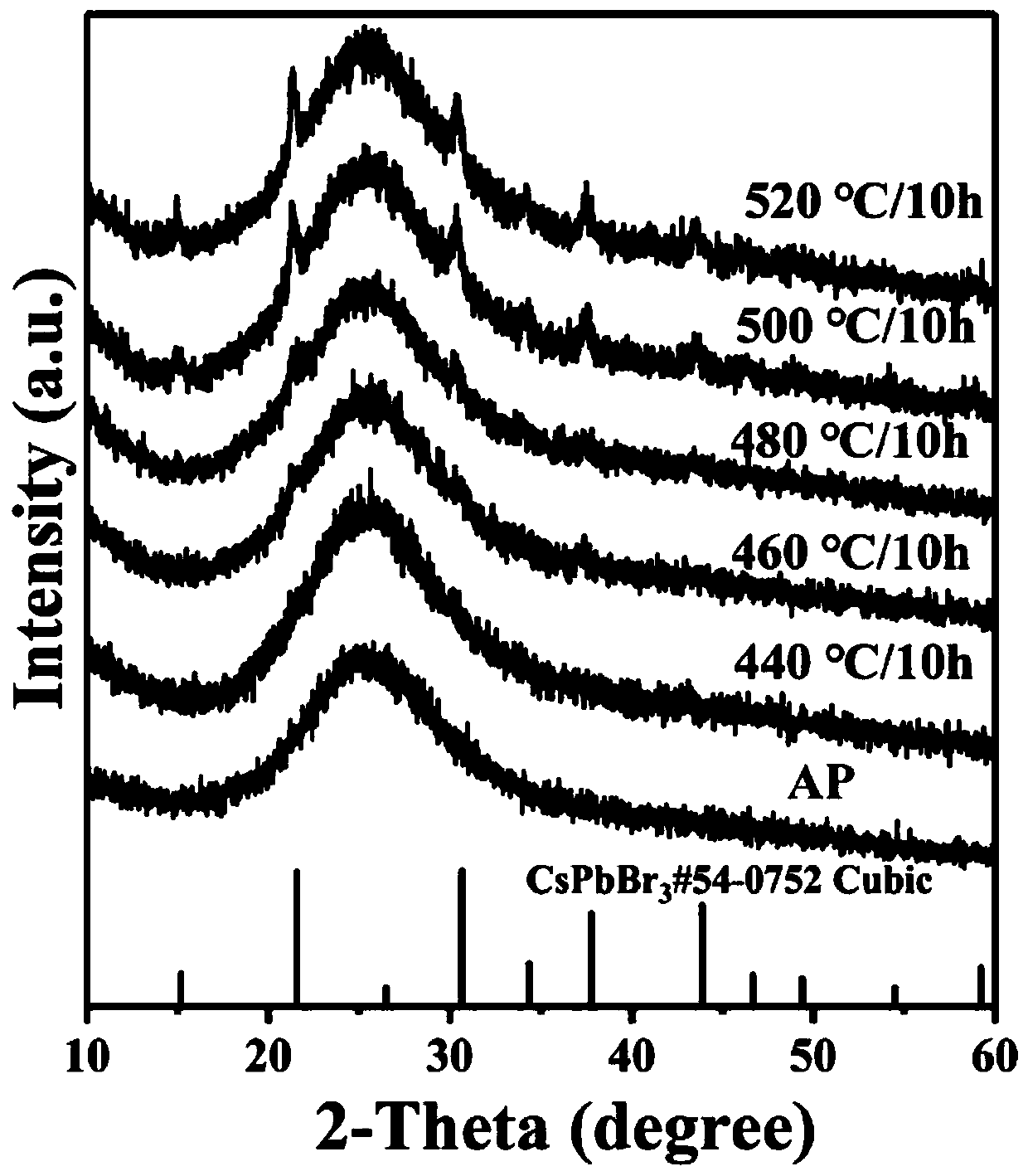
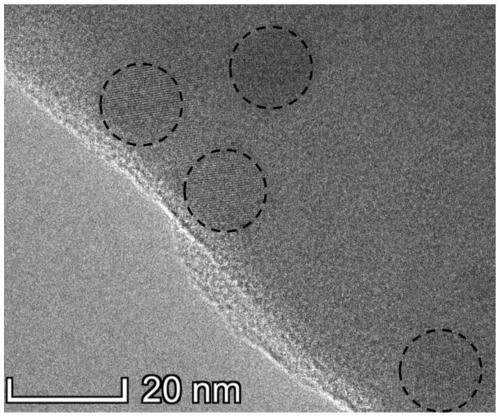
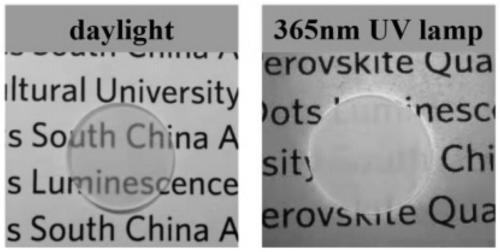
ActiveCN110294597AImprove internal quantum efficiencyImprove thermal stabilitySemiconductor devicesFluorescenceGermanium dioxide
The invention belongs to the technical field of display of fully-organic perovskite quantum dots, and discloses a CsPbBr3 (cesium-lead-bromide) perovskite quantum dot fluorescent glass for display ofwide color gamut and a preparation method and application thereof. The CsPbBr3 perovskite quantum dot fluorescent glass comprises the following components in percentage by mole: 0 to 45% of SiO2 (silicon dioxide), 0 to 45% of GeO2 (germanium dioxide), 30 to 40% of B2O3 (boron oxide), 2 to 8% of Al2O3 (aluminum oxide), 3 to 7% of MCO3 (metal carbonate), 1 to 5% of ZnO (zinc oxide), 5 to 15% of CsBr(cesium bromide) or Cs2CO3 (cesium carbonate), 2 to 10% of PbBr2 (lead bromide) or PbO (lead oxide), and 3 to 15% of NaBr (sodium bromide) or KBr (potassium-bromide), wherein M is Ca (calcium) or Sr(strontium); the sum of the components in percentage by mole is 100%. The CsPbBr3 perovskite quantum dot fluorescent glass has the advantages that the technology is simple, and the operation is easy;after in-situ crystallization, the quantum efficiency is higher, the light emitting stability is obviously improved, and the broad application prospect is realized.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
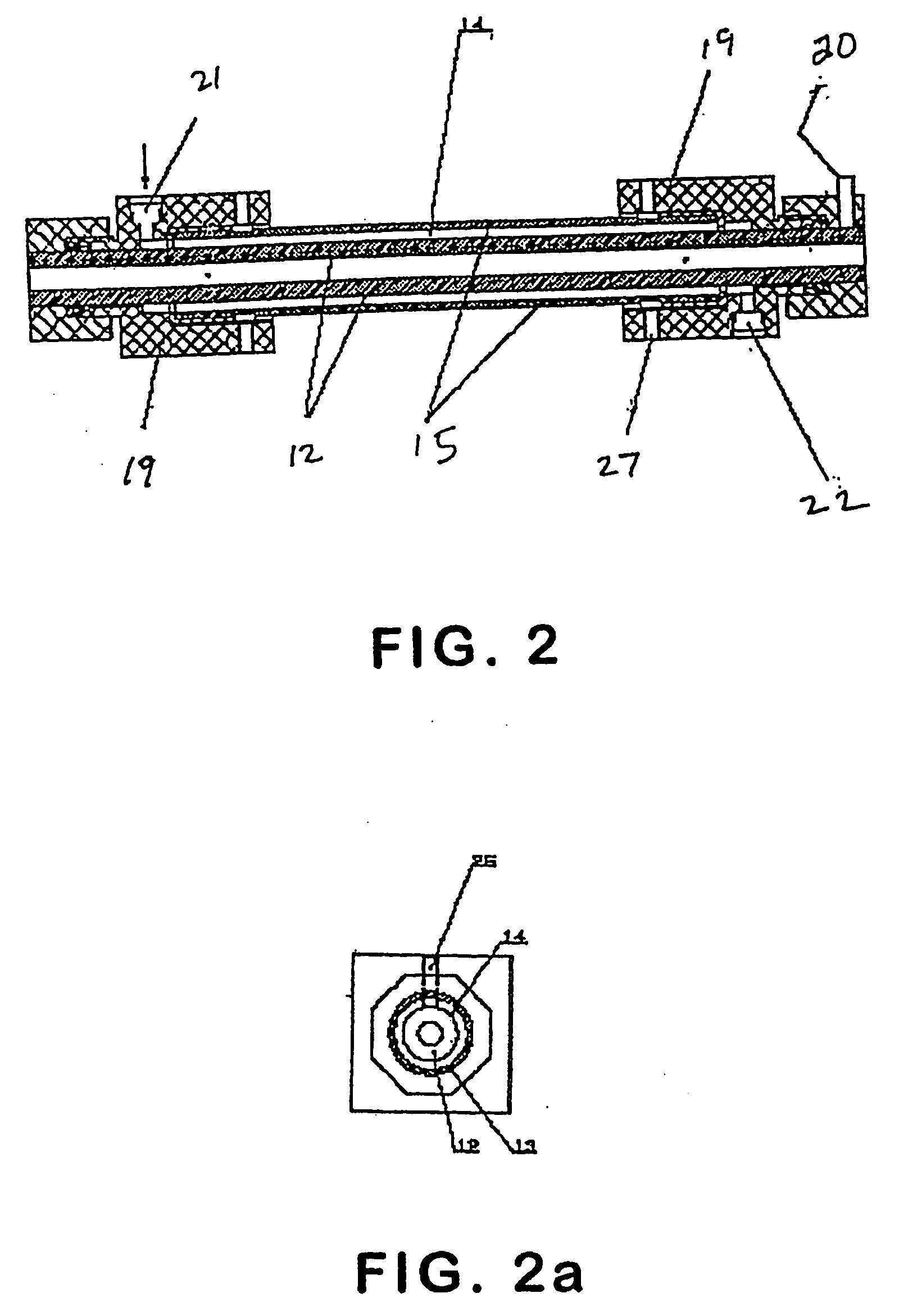
Palladium-103 and io-125 compound sealed seed source, source core and source core preparation method
ActiveCN101797392AEvenly distributedCompact distributionRadioactive preparation carriersAntineoplastic agentsChemical platingSodium iodide
The invention belongs to the technical field of medical preparations containing radioactive substances, in particular to a palladium-103 and io-125 compound sealed seed source, a source core and a source core preparation method. A palladium-103 and io-125 compound film covers on a carrier to form the source core, and the palladium-103 and io-125 compound sealed seed source is prepared in a way that the source core is welded and sealed in a titanium pipe or titanium alloy pipe. The source core preparation method of the palladium-103 and io-125 compound sealed seed source comprises the steps of: 1, inoculating a nano palladium seed crystal: dipping a carrier bar into a chloroform solution of palladium diacetate, and then dipping into an alkaline ammonia solution of hydrazine; 2, carrying out chemical plating on palladium-103 and silver: putting the carrier bar into a mixed solution of palladium chloride, silver nitrate, ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid, ammonium hydroxide and hydrazine to enable the surface of a carrier to be uniformly coated with a layer of palladium-103 and silver; and 3, carrying out chemical absorption of iodine-125: putting the carrier bar into a mixed solution of sodium bromide or potassium bromide, sodium iodide or potassium iodide, sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide, and potassium ferricyanide.
Owner:HTA CO LTD
Preparation method of ethylene carbonate
InactiveCN109134422AReduce adverse effectsReduce power consumptionOrganic chemistryOrganic solventSodium iodide
The invention belongs to the field of lithium battery electrolyte additive preparation, and particularly relates to a preparation process of ethylene carbonate. The method comprises: making monochloroethylene carbonate react with organic amine in an organic solvent in the presence of a catalyst; wherein the catalyst is a mixture of potassium bromide, sodium bromide, sodium iodide, potassium iodide, or any combination thereof and 18-crown ethers-6, tetrabutylammonium bromide or a combination thereof. The preparation method of the ethylene carbonate can improve a yield, the reaction condition ismild and environment-friendly.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG HUASHENG CHEM CO LTD
Ultra-thin bismuth oxyhalide nanosheet as well as preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN108380226AImprove stabilityHigh catalytic efficiencyHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesGaseous fuelsPotassiumHydrolysis
The invention discloses an ultra-thin bismuth oxyhalide nanosheet as well as preparation and application thereof. The ultra-thin bismuth oxyhalide nanosheet is prepared by using bismuth nitrate pentahydrate, potassium chloride or potassium bromide as raw materials, and hydroxypropyl guar gum as a thickening agent, and adopting a hydrolysis method at low temperature. The preparation method providedby the invention has a simple process and low costs, and is green, environmentally friendly and easy to control and produce in a large scale; the guar gum is added as the thickening agent in the preparation process, various raw materials are mixed more uniformly, so that an occurrence of agglomeration of macromolecular particles in the preparation process is avoided, and preparation of a more ultra-thin bismuth oxyhalide photocatalyst with a larger specific surface area is facilitated; and the prepared ultra-thin bismuth oxyhalide nanosheet is a nano-scale layered structure, can respond in avisible light range, has stronger stability, higher catalytic efficiency, and a significant effect and huge application space in the field of photocatalytic reduction of CO2.
Owner:NANYANG NORMAL UNIV
Preparation method, product and application of Bi/BiOBr/RGO composite photocatalyst
ActiveCN109550509ASuitable for industrial productionImprove photocatalytic performancePhysical/chemical process catalystsPhotocatalytic degradationGlycol synthesis
The invention discloses a preparation method, product and application of a Bi / BiOBr / RGO composite photocatalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving a bismuth source in anethylene glycol solution to form a bismuth salt solution; dissolving potassium bromide in distilled water to form a potassium bromide solution; slowly adding the potassium bromide solution into the bismuth salt solution to obtain a potassium bromide-bismuth salt mixed solution; carrying out ultrasonic treatment on graphite oxide in distilled water to obtain a graphene oxide suspension liquid, adding the graphene oxide suspension liquid into the potassium bromide-bismuth salt mixed solution, carrying out a solvothermal reaction, carrying out cooling to room temperature after the reaction is finished, carrying out suction filtration, collecting precipitates and carrying out washing to obtain the composite photocatalyst. According to the invention, ethylene glycol is used as a solvent and areducing agent, and the flower-like Bi / BiOBr / RGO composite photocatalyst is simply and rapidly prepared through a one-step solvothermal method. The composite photocatalyst is free of toxicity, is environmentally friendly, and is suitable for industrial production. Under visible light, the composite photocatalyst can be used for photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B, and the photocatalytic performance of the composite photocatalyst is greatly improved.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Method for improving efficiency of perovskite solar cell
InactiveCN111599923APromote secondary growthIncrease the average particle sizeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPtru catalystHole transport layer
The invention provides a method for improving the efficiency of a perovskite solar cell. The method comprises the following steps: depositing a layer of lithium-magnesium heavily doped nickel oxide asa hole transport layer on an ITO glass substrate; then respectively spin-coating the surface with a perovskite precursor solution A and a doped precursor solution, wherein the perovskite precursor solution A is prepared by adding methylamine iodine and lead iodide into a DMF solvent and uniformly mixing, and the doped precursor solution is prepared by adding bismuth nitrate, potassium bromide anda guanidyl catalyst into a perovskite precursor solution B prepared from methylamine iodine, lead iodide and a DMF solvent. According to the method provided by the invention, a perovskite absorptionlayer with a double-layer structure is formed by adding a secondary growth process on the basis of an original crystal growth process, so that the carrier transfer efficiency in perovskite is effectively improved, and the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the solar cell is improved.
Owner:CHENDU NEW KELI CHEM SCI CO LTD
Method for preparing bismuth oxyhalide - diatomite composite photocatalyst
InactiveCN107029757AImprove photocatalytic performancePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationHazardous substancePotassium
The invention belongs to the technical field of catalysts and discloses a method for preparing a bismuth oxyhalide - diatomite composite photocatalyst. Raw material refined diatomite is taken as a carrier, bismuth nitrate pentahydrate, potassium chloride, potassium bromide and potassium iodide are taken as precursors, a normal temperature direct hydrolysis method is adopted to directly synthesize the bismuth oxyhalide - diatomite composite photocatalyst, the composite material is filtered, washed and dried, and then the finished product is obtained. BiOX is successfully loaded on a diatomite rotary screen and is of a flaky hierarchical structure; and on equal conditions, the degradation rate of rhodamine B reaches 86.7% under the conditions that the initial dye concentration is 15 mg / L, the catalyst dosage is 0.15 g and a 50 W LED blue light lamp shines for 50 min. A preparation process is simple, raw materials are easy to obtain, the product can thoroughly remove harmful substances in air and water under visible light, the cost is low, and the method has good application prospect.
Owner:HUNAN CITY UNIV
Method for quickly identifying true and false cordyceps mycelia
The invention discloses a method for quickly identifying true and false cordyceps mycelia. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) tabletting and scanning a potassium bromide blank film to obtain a standard sample spectrum; (2) tabletting and scanning a sample, namely accurately weighing the cordyceps mycelium which is crushed and screened via a 80-meshe sieve and fine potassium bromide powder, grinding and uniformly mixing the two powder, uniformly laying the mixed powder in a pressure membrane, and pressurizing the mixed powder for 1 min so as to obtain a sample sheet, and carrying out Sample scanning on the pressed sample sheet into a fourier infrared spectrometer scanning chamber, thus obtaining a cordyceps mycelium sample spectrum; and (3) comparing the similarity of the cordyceps mycelium sample spectrum and a standard sample spectrum, wherein the criterion is that the similarity of the cordyceps mycelia is higher than 0.95. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for quickly identifying the true and false cordyceps mycelia on the basis of the difference of spectral absorption of the cordyceps mycelium; the detection is fast, samples are not damaged, and the use quantity of the cordyceps mycelia is little; and the samples are subjected to full wave infrared spectrum scanning, so that the information of the samples is complete.
Owner:TIANJIN TIANSHI BIOLOGICAL DEV +2
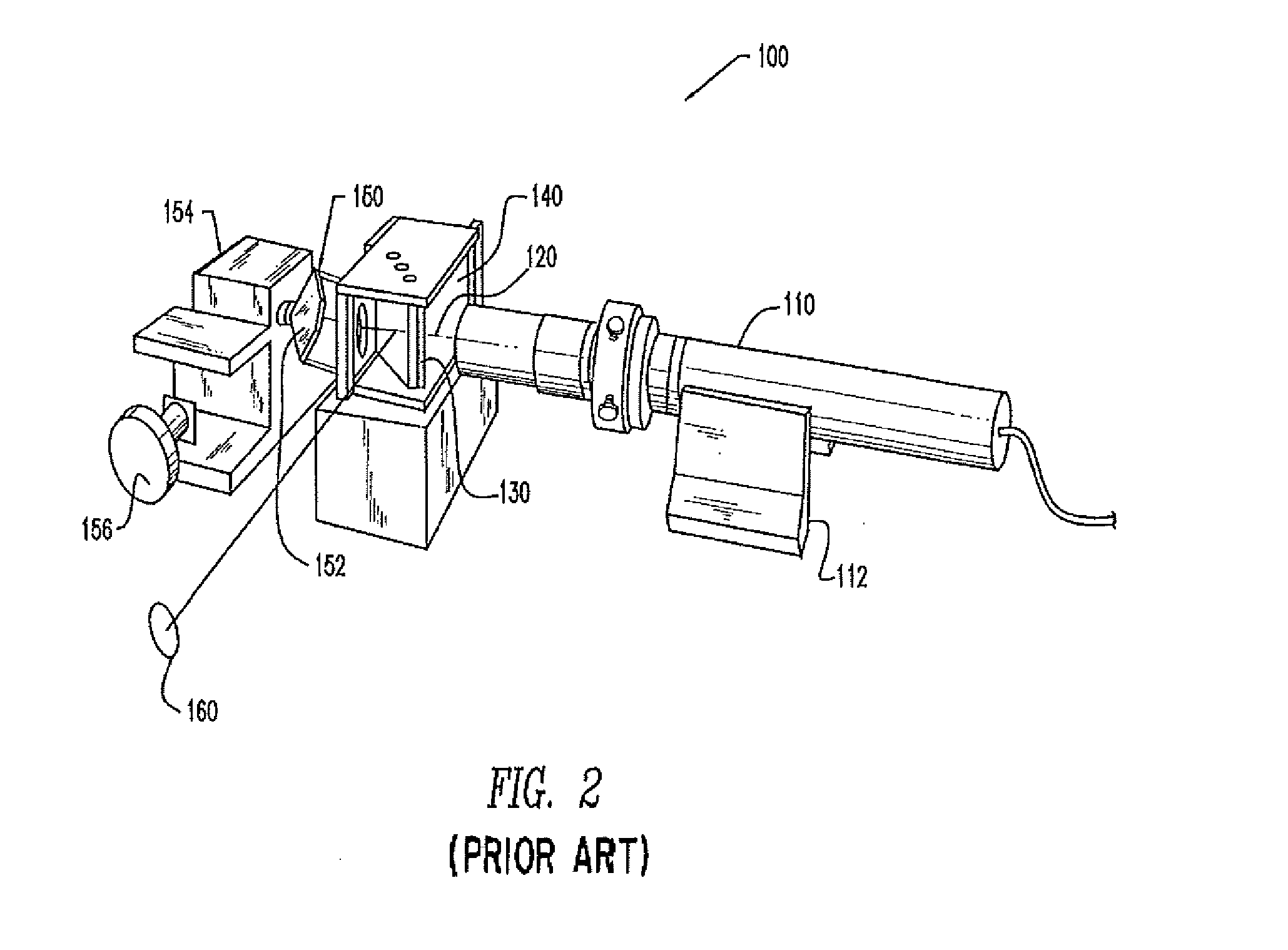
Interferometer, optical assembly and method of mounting same
ActiveUS20140029010A1Reduces and eliminates tiltingReduces and eliminates and bendingMirrorsInterferometric spectrometryOptical instrumentationEngineering
A frame for optics used in interferometers that may include different materials having substantially similar, identical, or as close as practicable coefficients of thermal expansion from the material(s) used to make the beamsplitter and / or compensator without warping, bending, tilting or distorting the optics. The beamsplitter and / or compensator are mounted onto the frame of the interferometer using a three-point method of mounting, preferably using three pins for each component. Preferably, the pins are made of the same material as the beamsplitter and compensator, and all three components are made of Potassium Bromide (“KBr”) or Calcium Fluoride (“CaF2”) such that the optic instrument can operate to scan into the mid or far infrared. Stability in optical alignment is therefore achieved without requiring the optic instrument include only one material. The invention provides stability in situations where it is not possible to utilize a single material for every component of the interferometer.
Owner:PLX
Density adjustable type composite weighted fracturing fluid
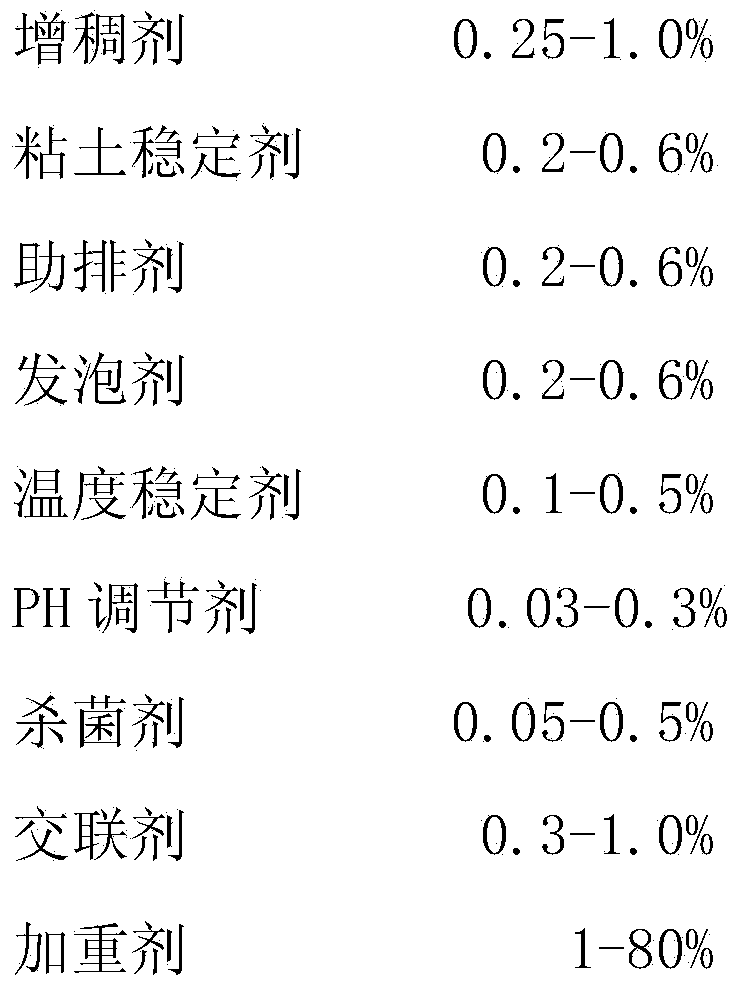
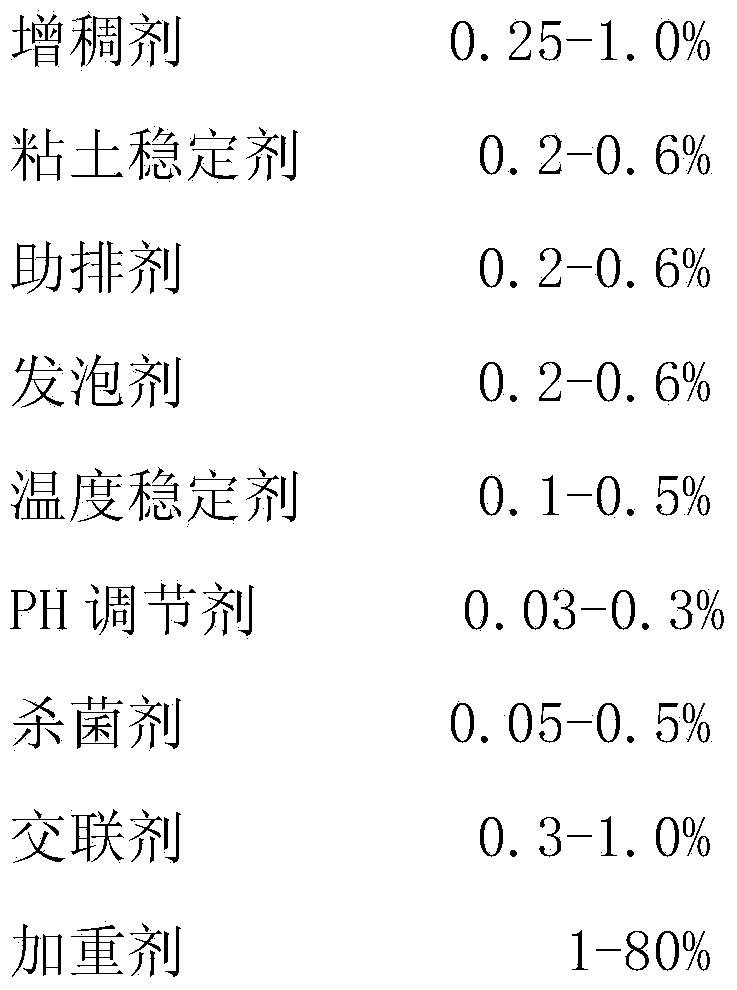
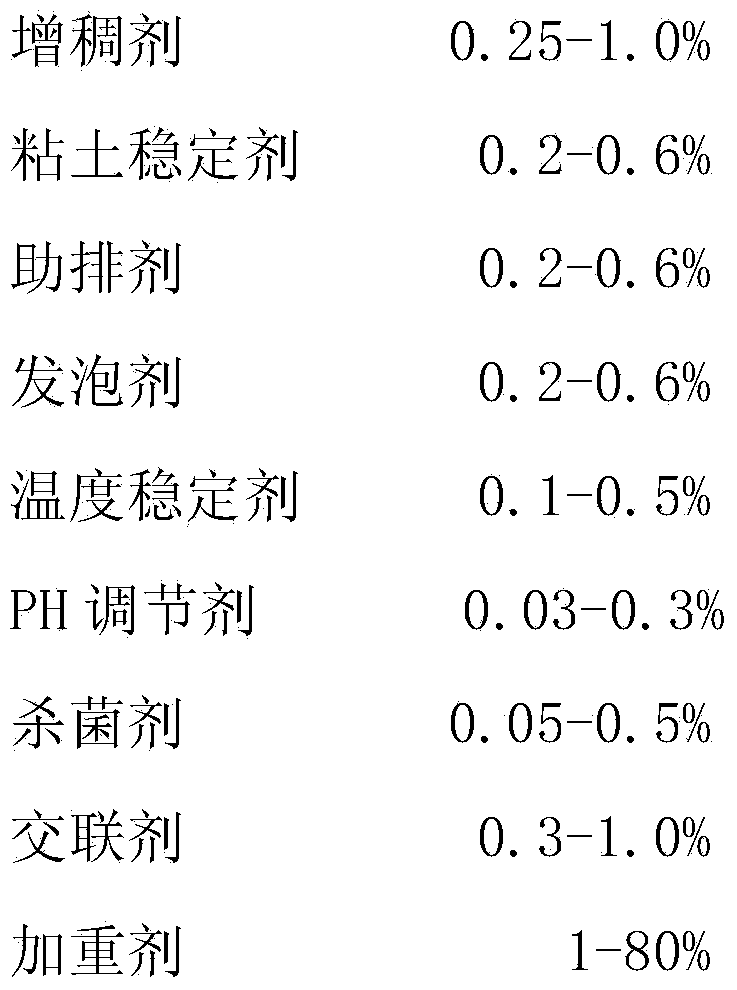
The invention discloses density adjustable type composite weighted fracturing fluid. The density adjustable type composite weighted fracturing fluid is prepared from the following components in percentage by mass: 0.25-1.0% of thickening agent, 0.2-0.6% of clay stabilizer, 0.2-0.6% of cleanup agent, 0.2-0.6% of foaming agent, 0.1-0.5% of temperature stabilizer, 0.03-0.3% of PH regulator, 0.05-0.5% of sterilizing agent, 0.3-1.0% of crosslinking agent, 1-80% of weighting agent and the balance of water, wherein the weighting agent is one of or a mixture of two of sodium chloride, potassium chloride, sodium bromide and potassium bromide. The density adjustable type composite weighted fracturing fluid disclosed by the invention can be applied to the fracturing construction of deep well compact oil and gas reservoirs and is capable of effectively achieving the purposes of reducing construction pressure, thus a ground pressure-bearing manifold can be protected.
Owner:CNPC BOHAI DRILLING ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com