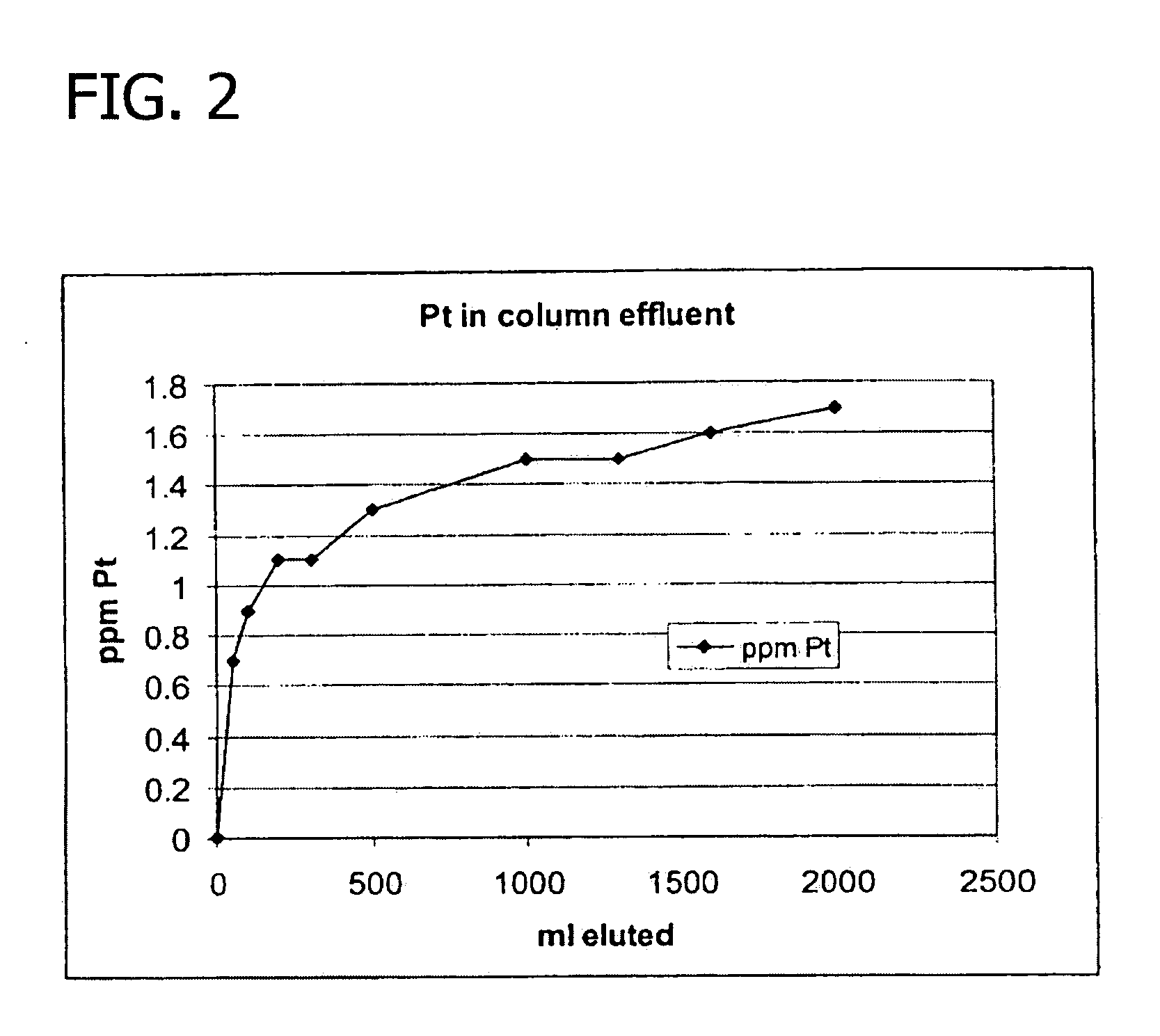
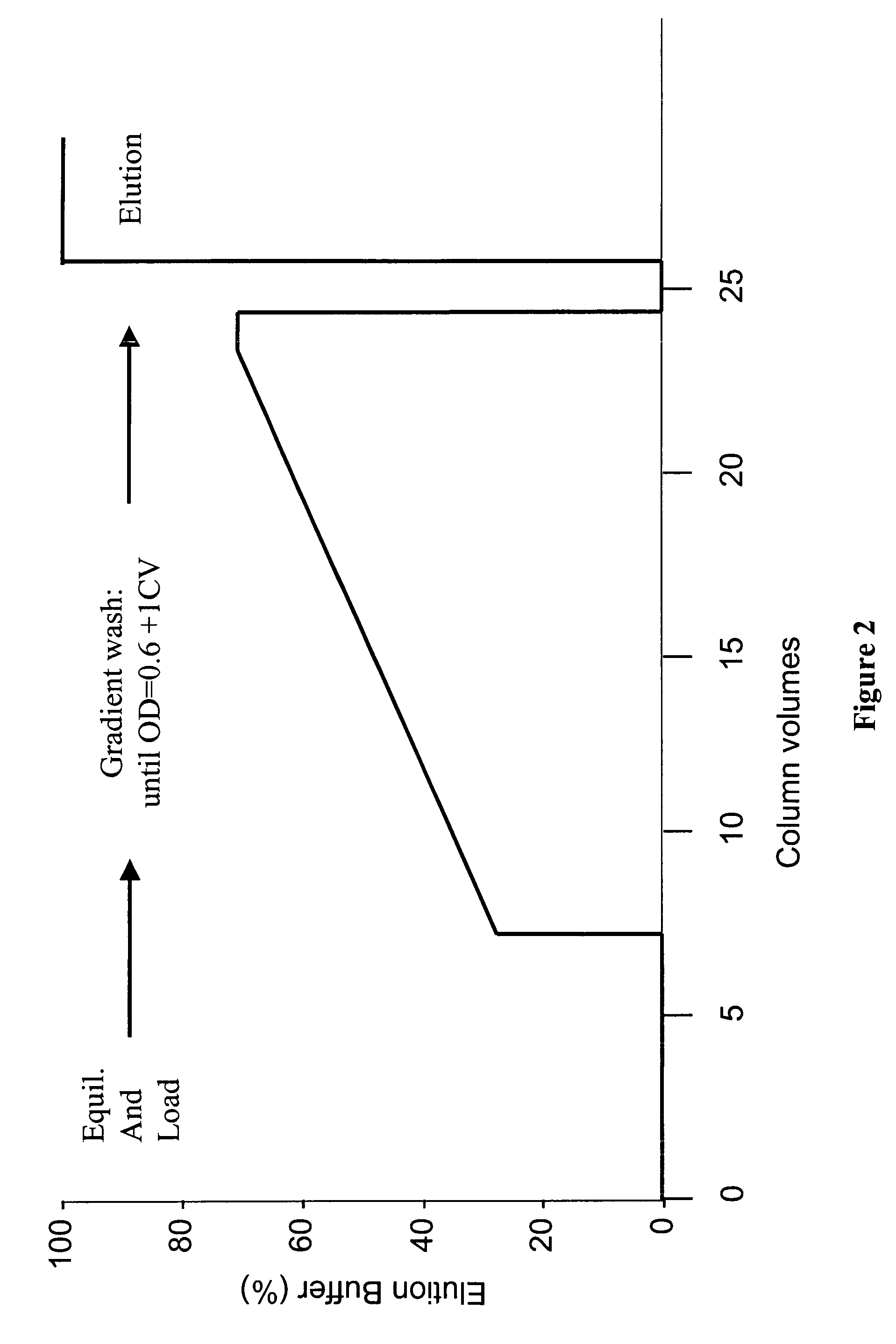
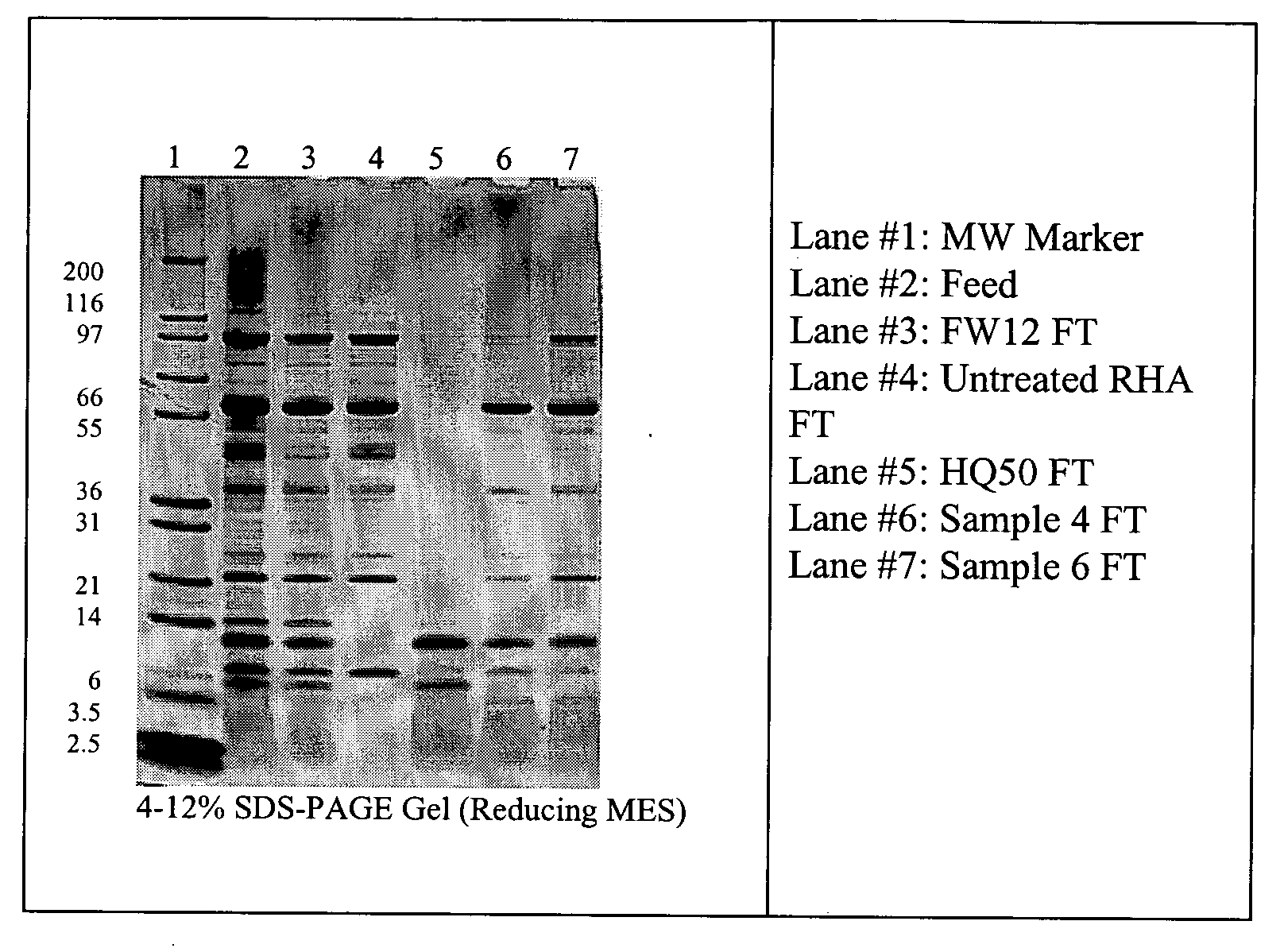
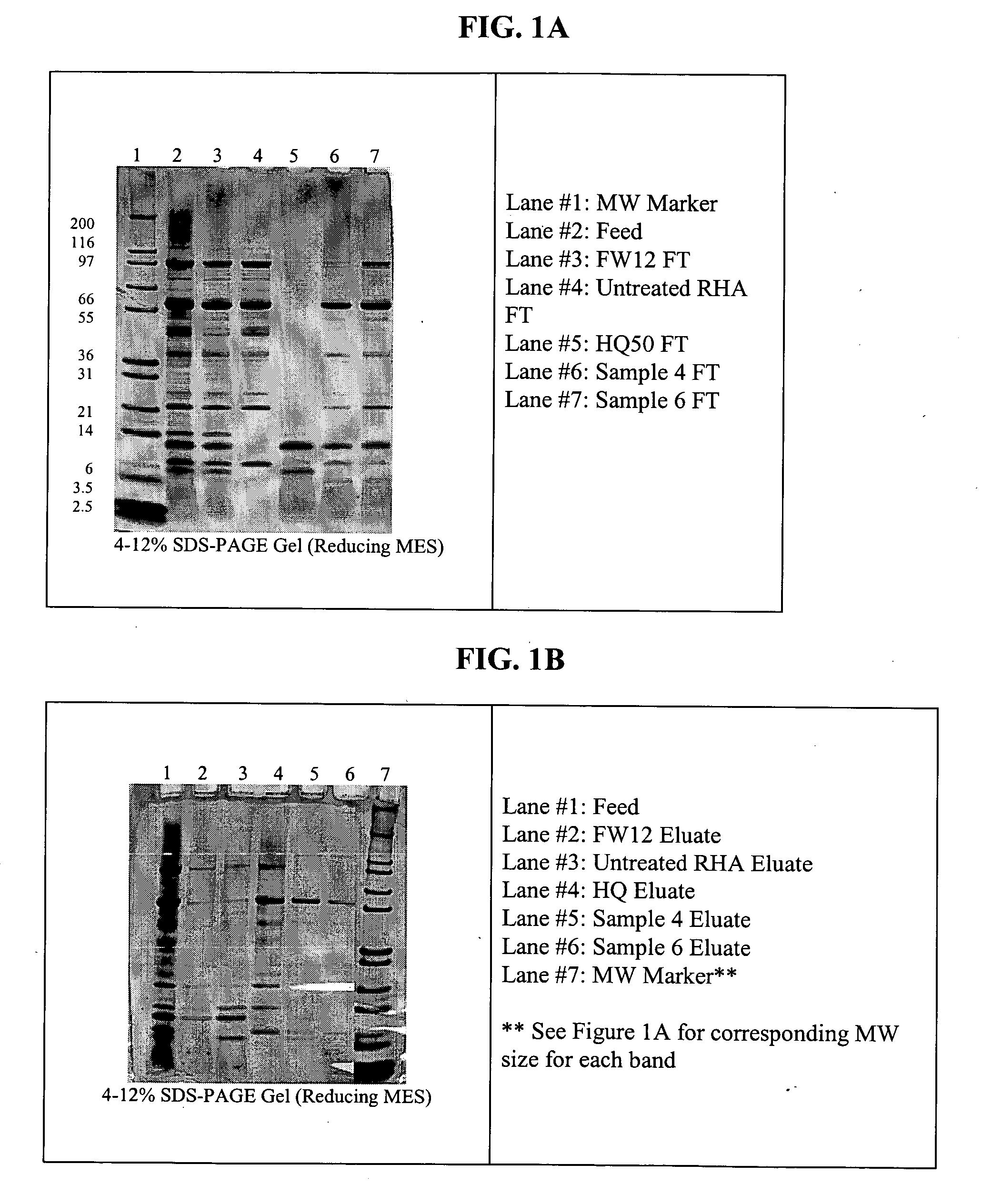
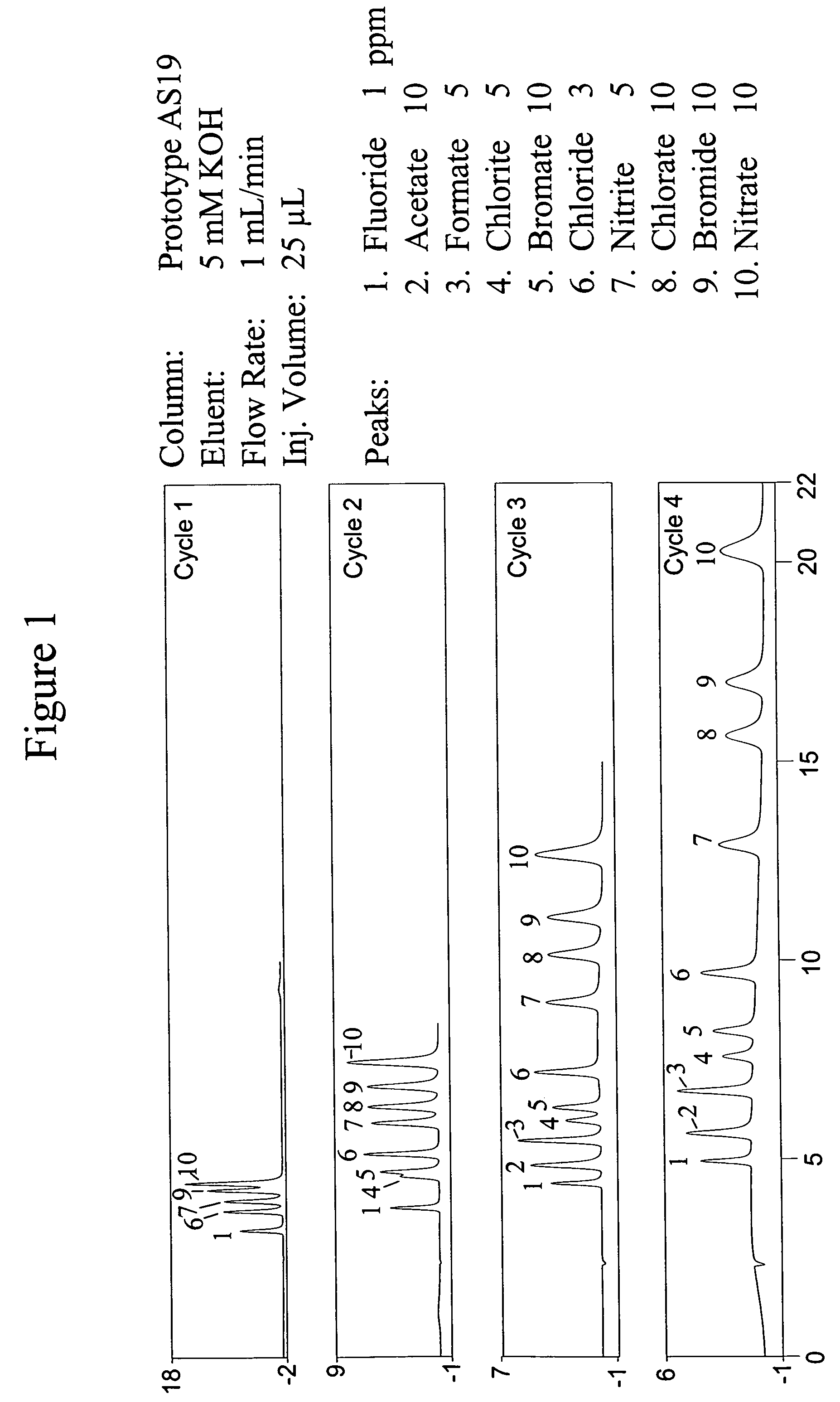
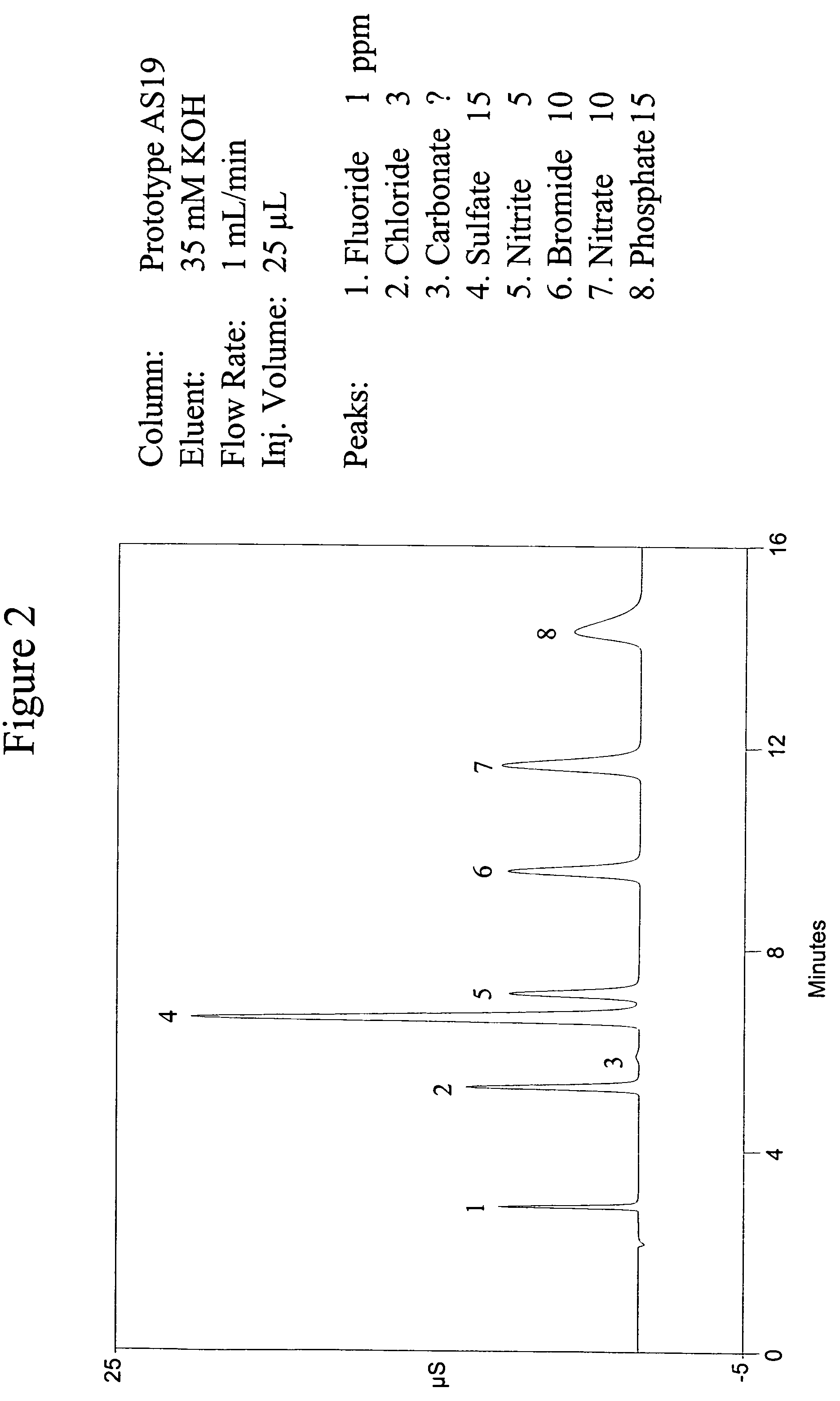
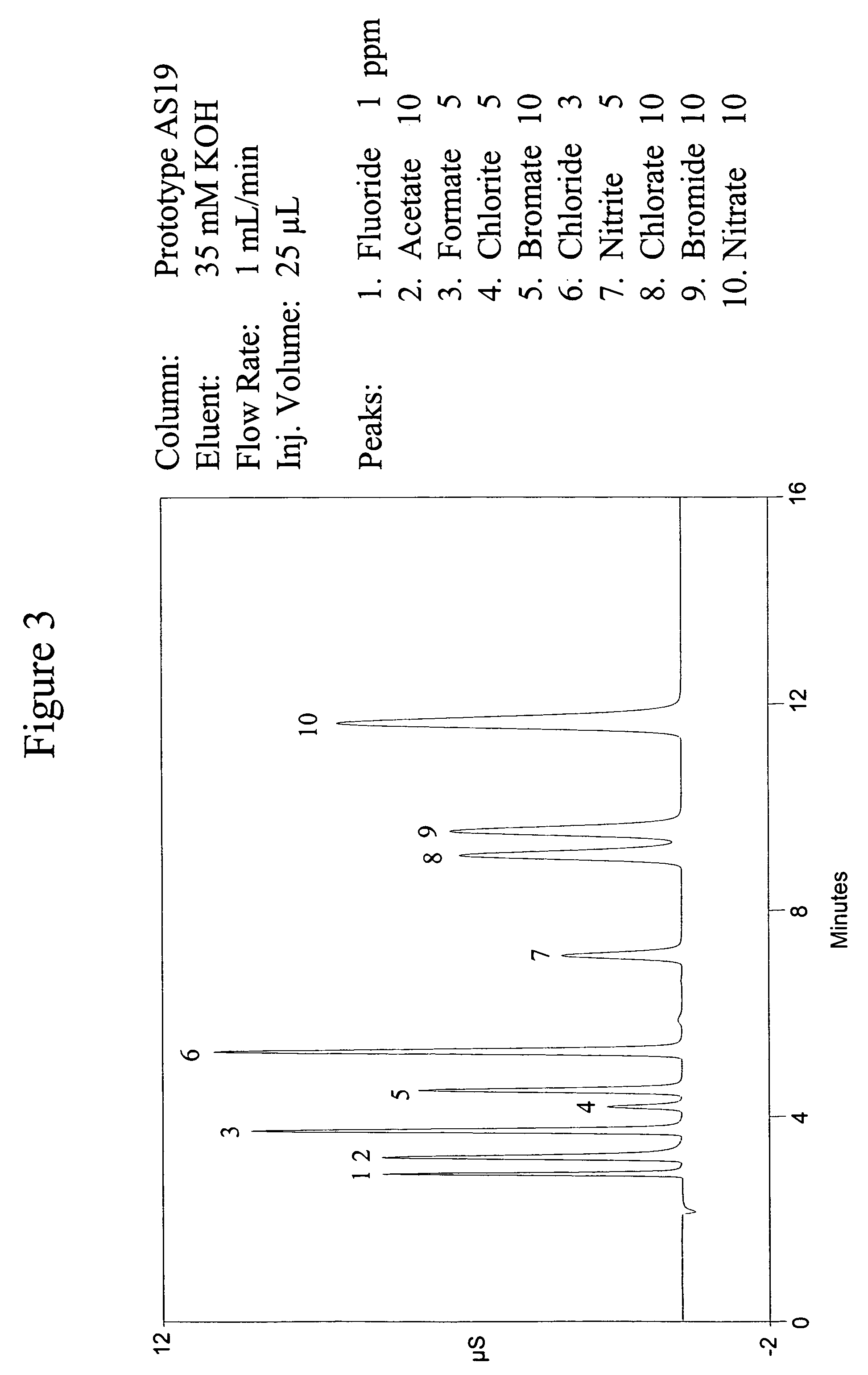
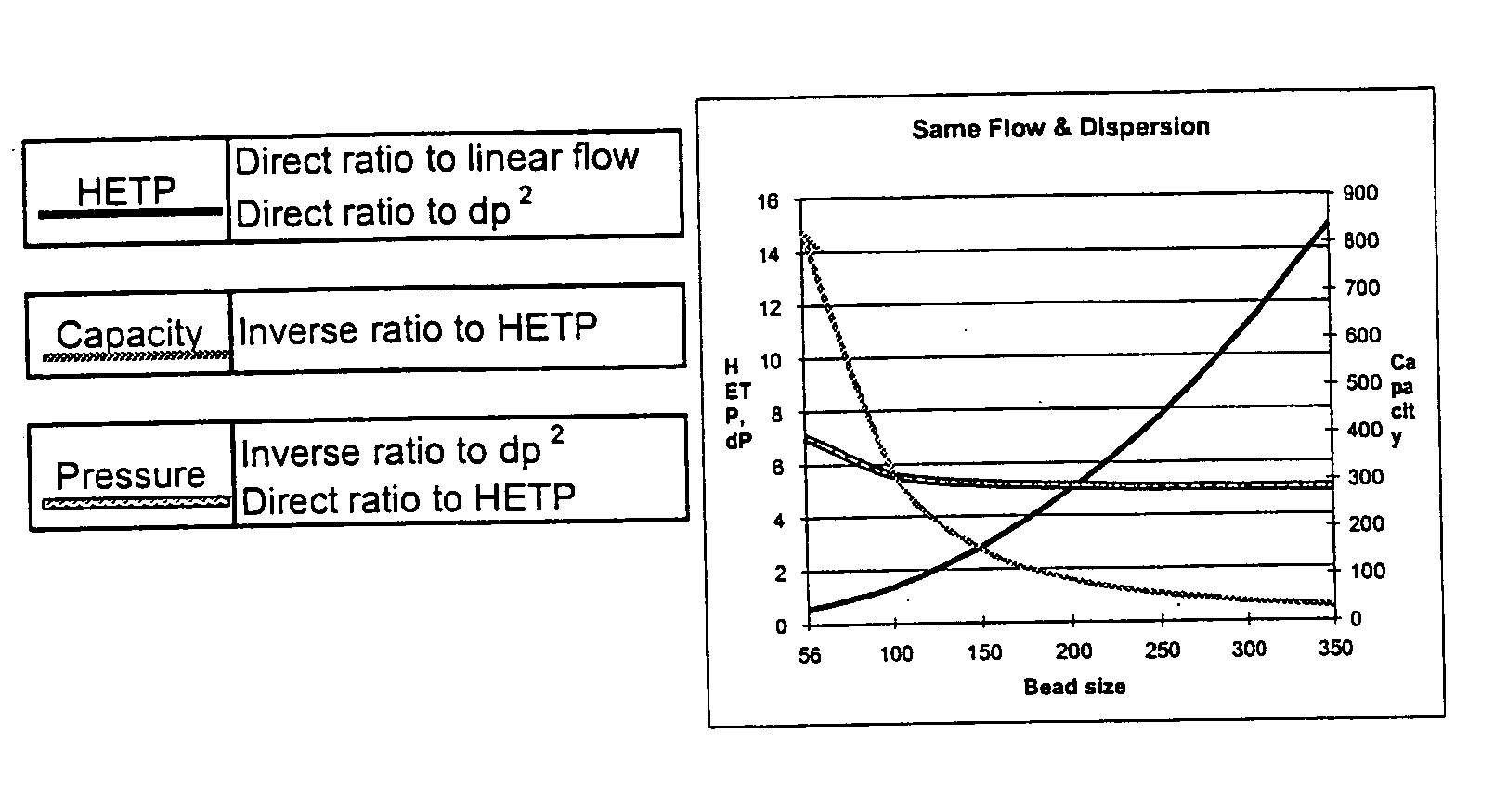
Patents
Literature
1407results about "Complex ion-exchangers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
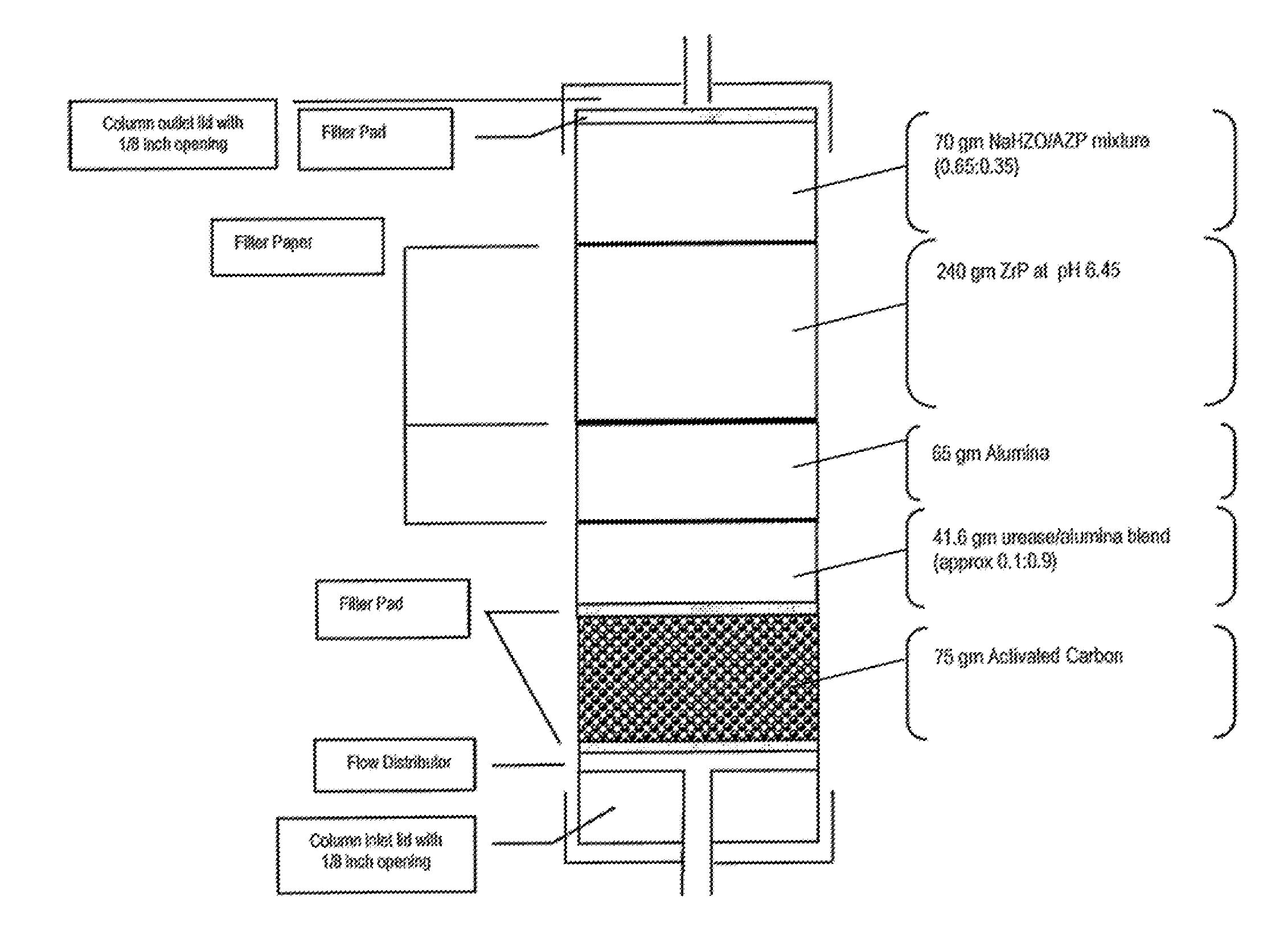
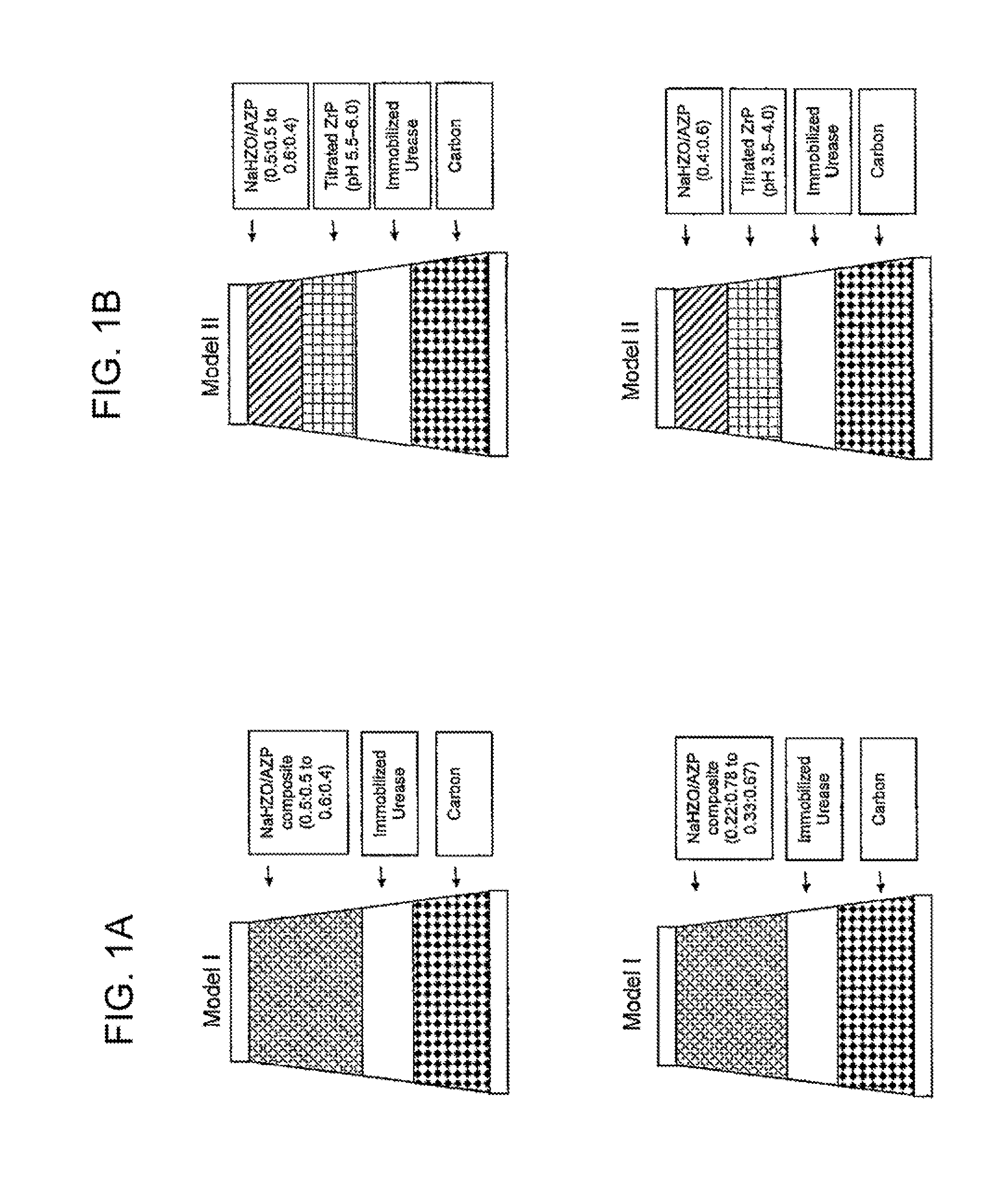
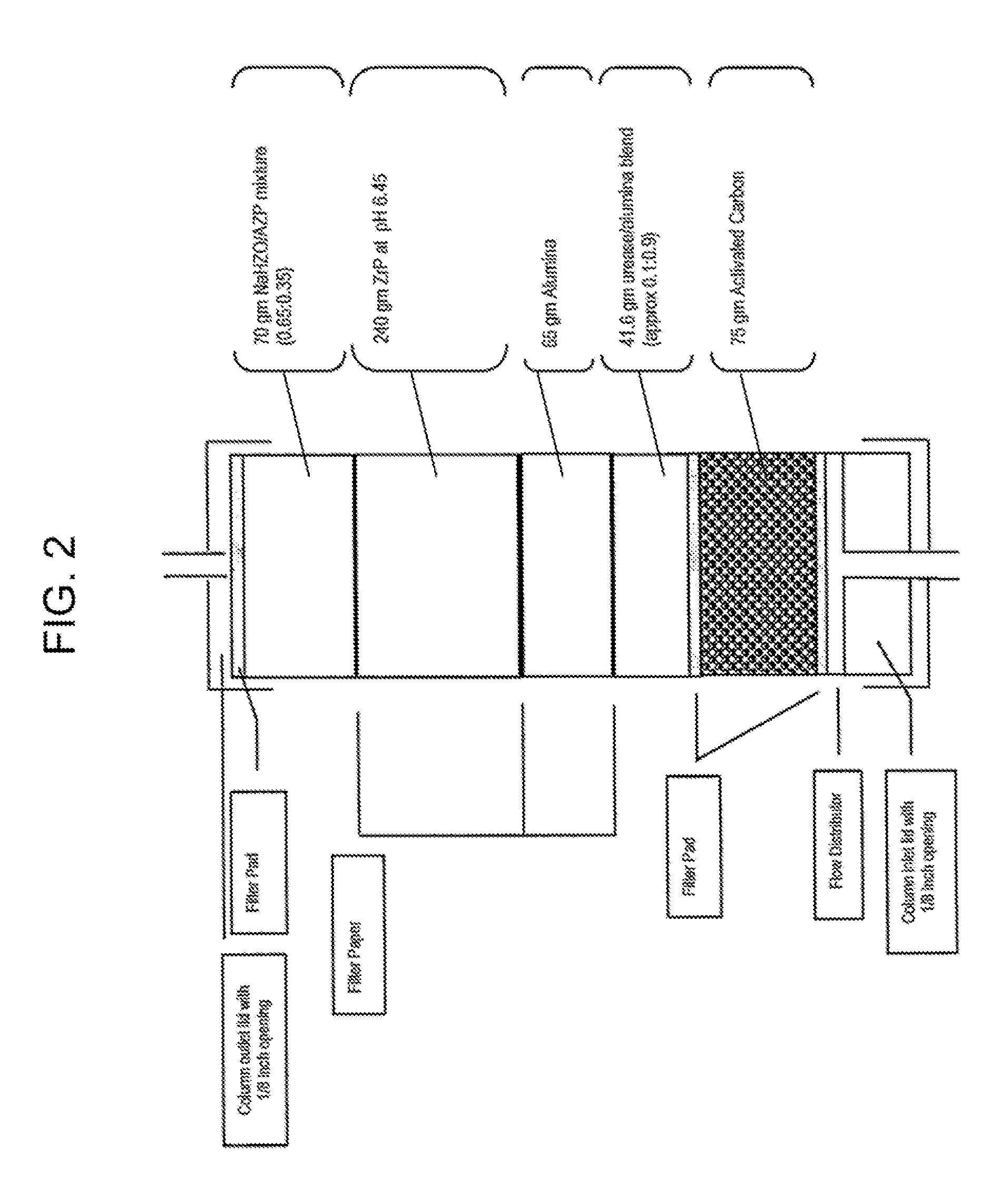
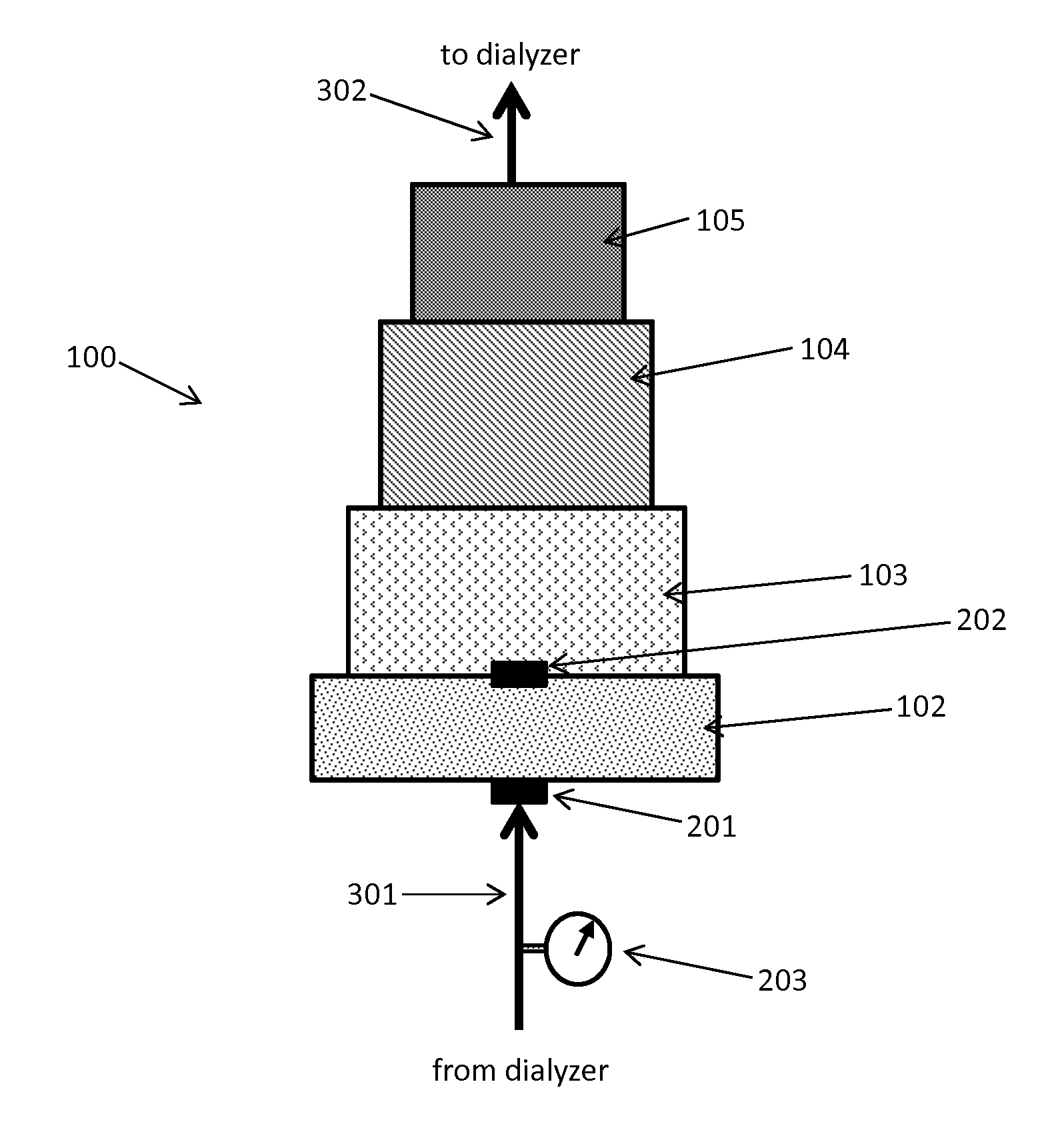
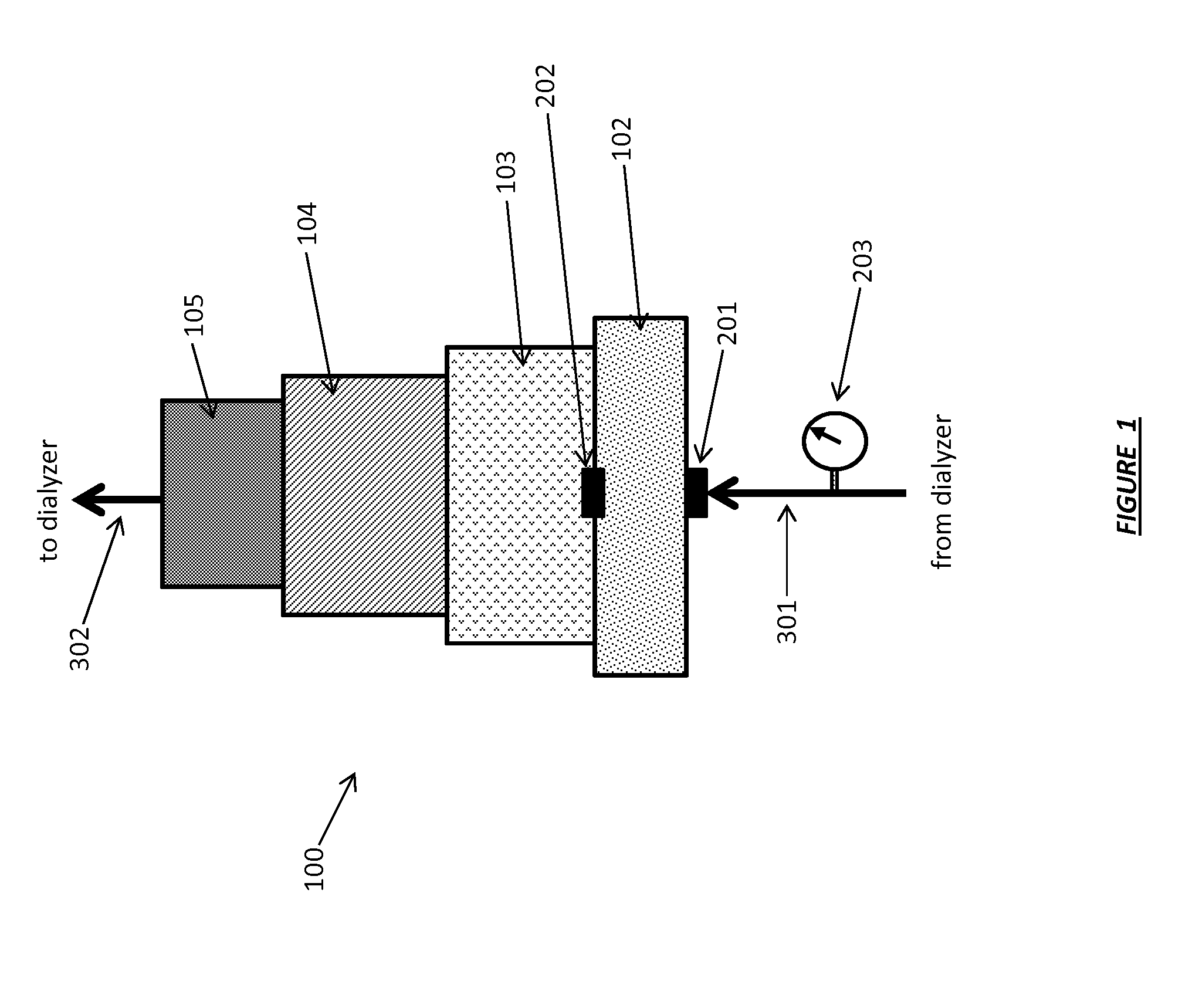
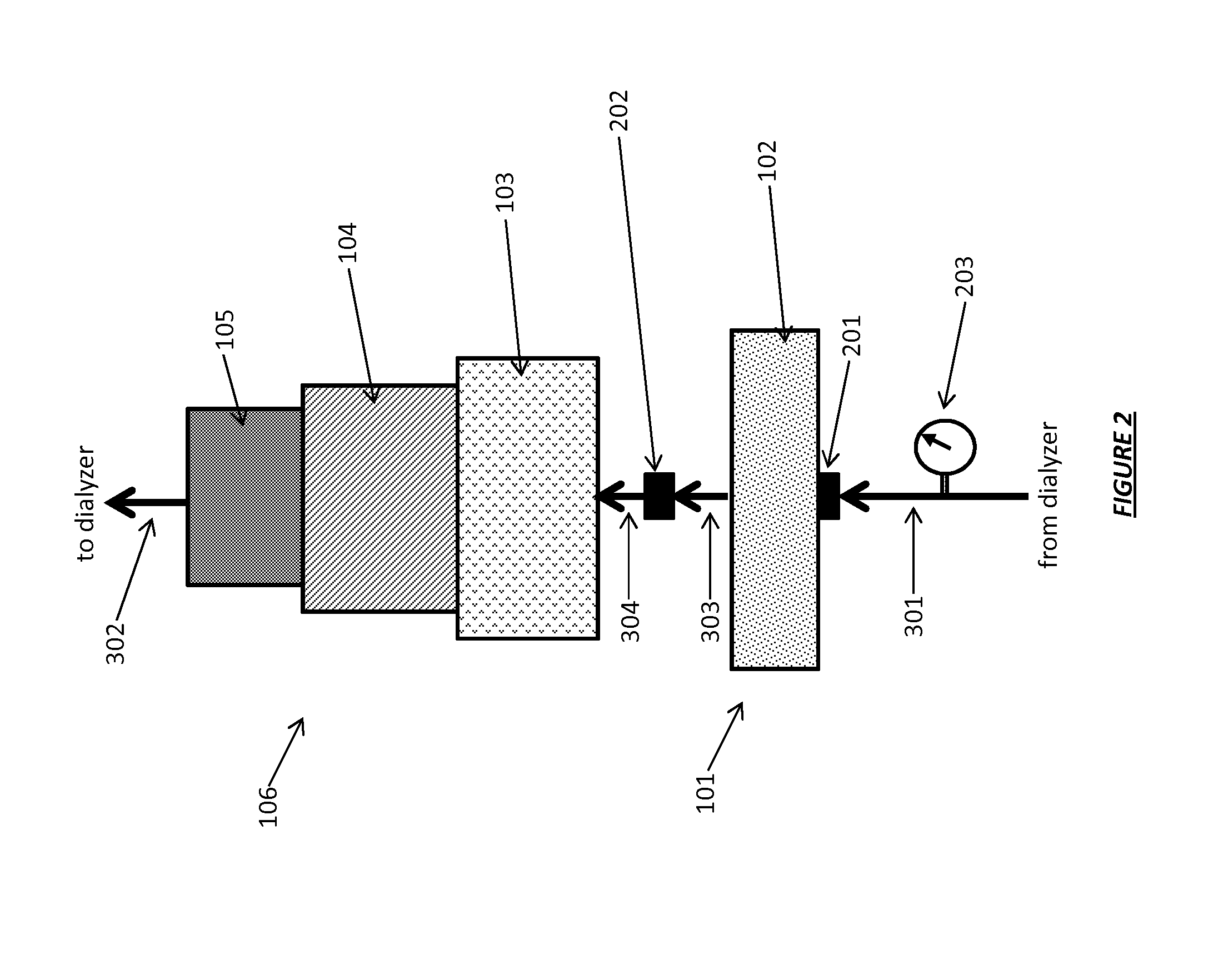
Acid Zirconium Phosphate and Alkaline Hydrous Zirconium Oxide Materials For Sorbent Dialysis
ActiveUS20100078387A1Avoid disadvantagesRestore balanceCation exchanger materialsOrganic anion exchangersIon exchangeDialysis fluid
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
Positively charged membrane
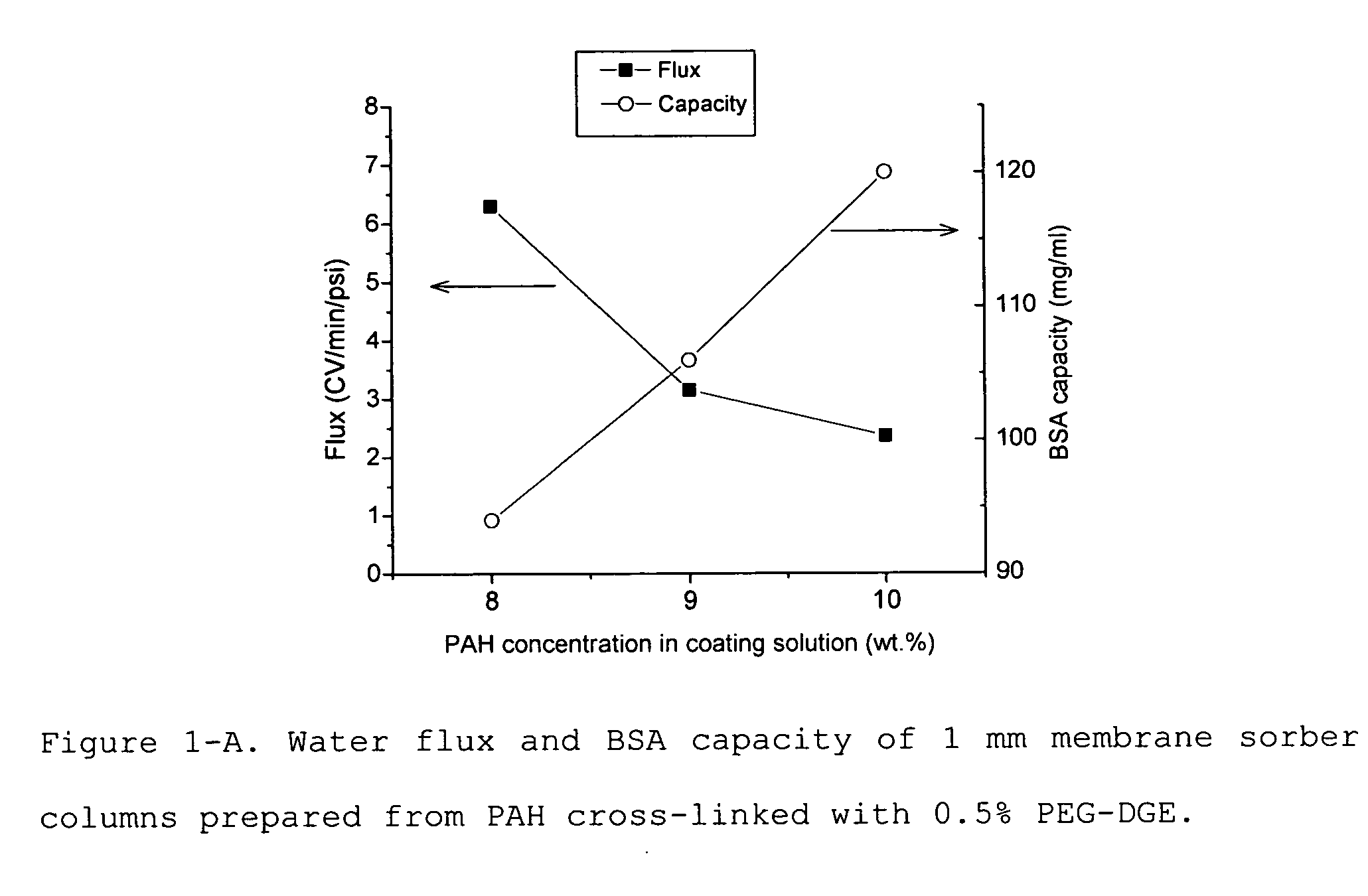
InactiveUS6780327B1High rateHigh charge densityCation exchanger materialsIon-exchanger regenerationPorous substrateFiltration
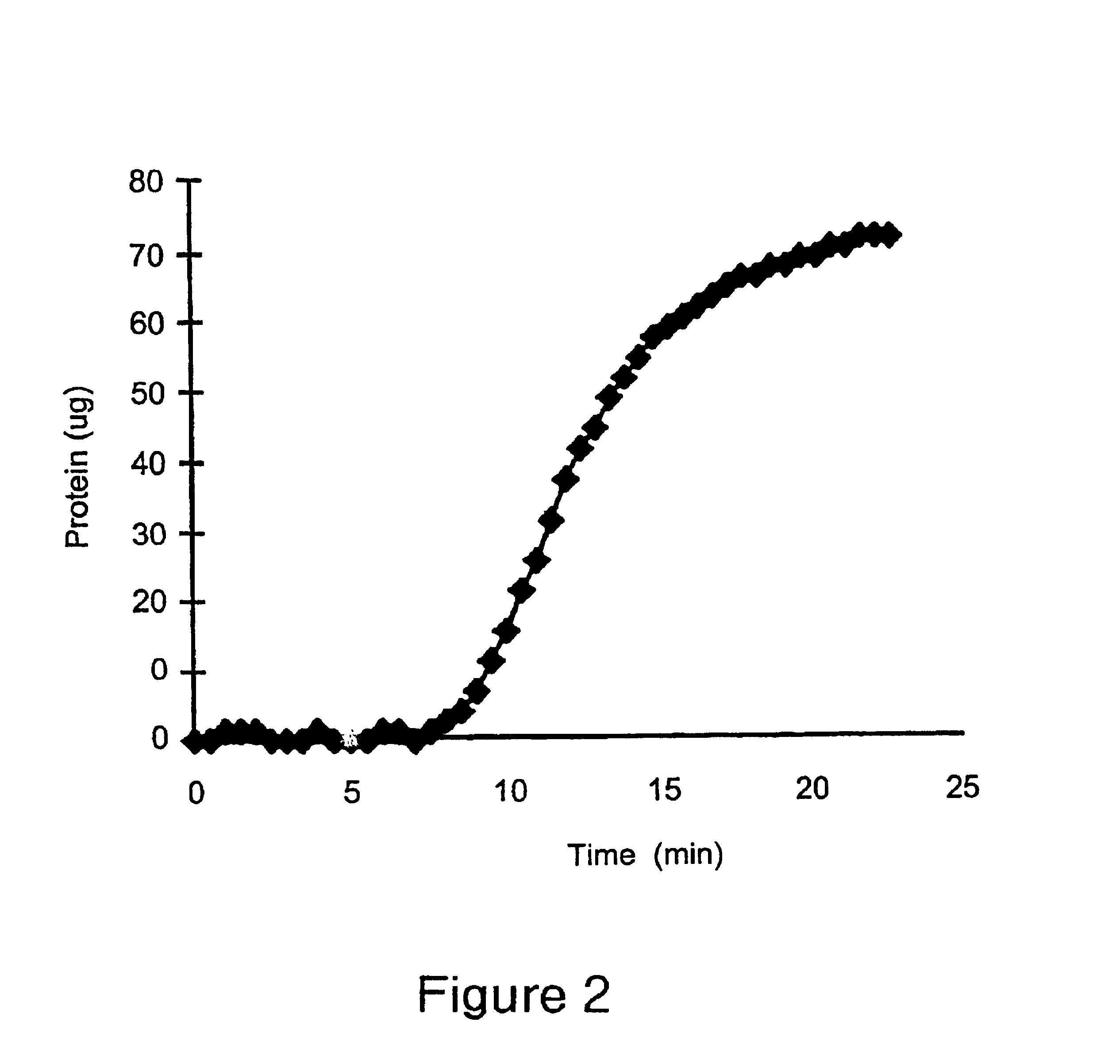
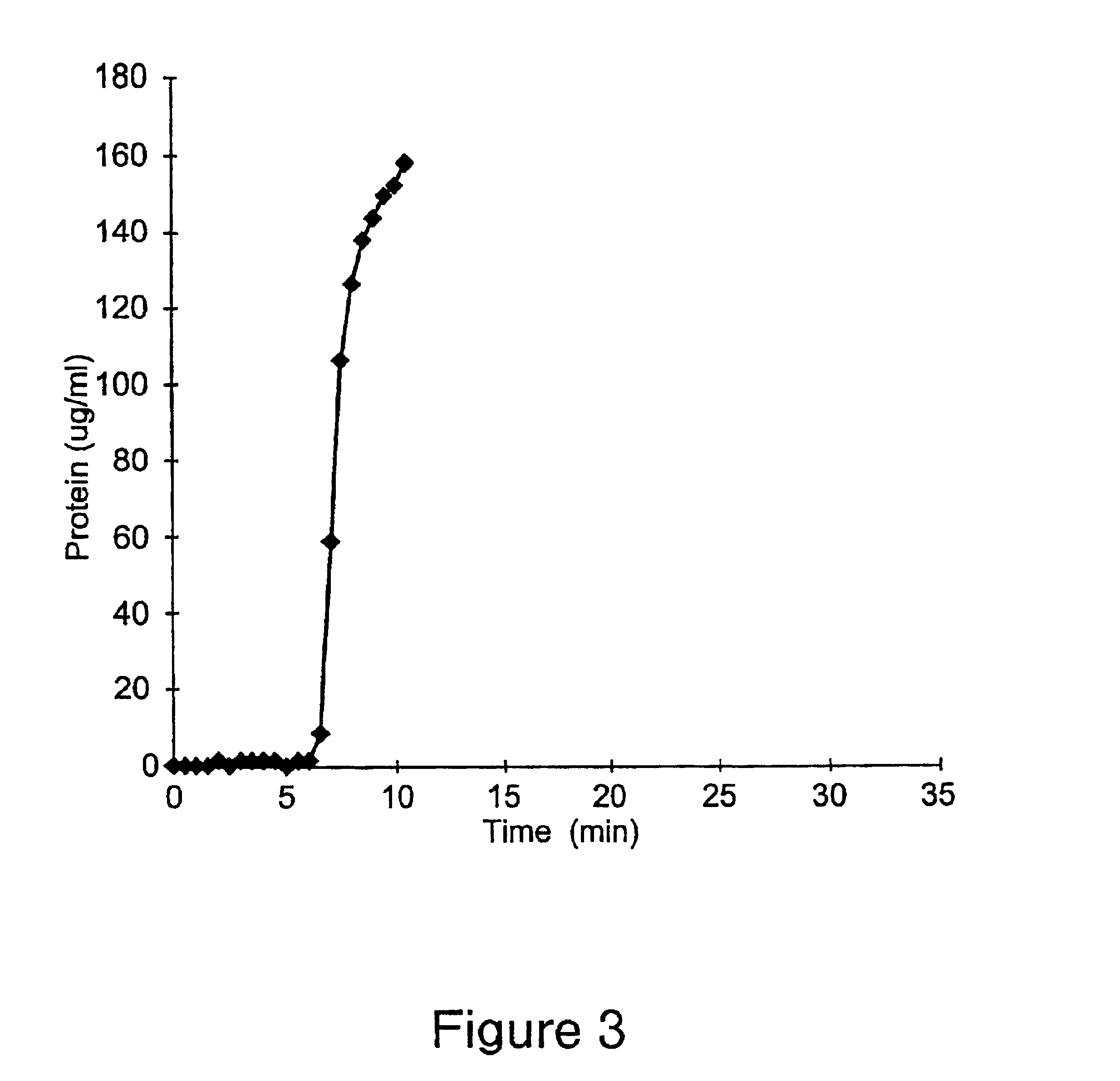
The present invention provides a positively charged microporous membrane having a protein binding capacity about 25 mg / ml or greater comprising a hydrophilic porous substrate and a crosslinked coating that provides a fixed positive charge to the membrane. The present invention further provides a positively charged microporous membrane comprising a porous substrate and a crosslinked coating comprising pendant cationic groups. The membranes of the present invention find use in a variety of applications including ion-exchange chromatography, macromolecular transfer, as well as detection, filtration and purification of biomolecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, endotoxins, and the like.
Owner:PALL CORP
Adsorption/separation method and a medium for adsorption/separation
InactiveUS6428707B1Increase productionImprove productivityChromatographic cation exchangersCation exchanger materialsChemistrySeparation method
A method for adsorption of a substance from a liquid sample on a fluidized bead or stirred suspension, in which the beads used comprise a base matrix and exhibit a structure having affinity to the substance, characterized in that the structure is covalently bound to the base matrix via an extender. Populations of beads in which the beads contain a filler incorporated in a base matrix and an extender are also described.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIOPROCESS R&D
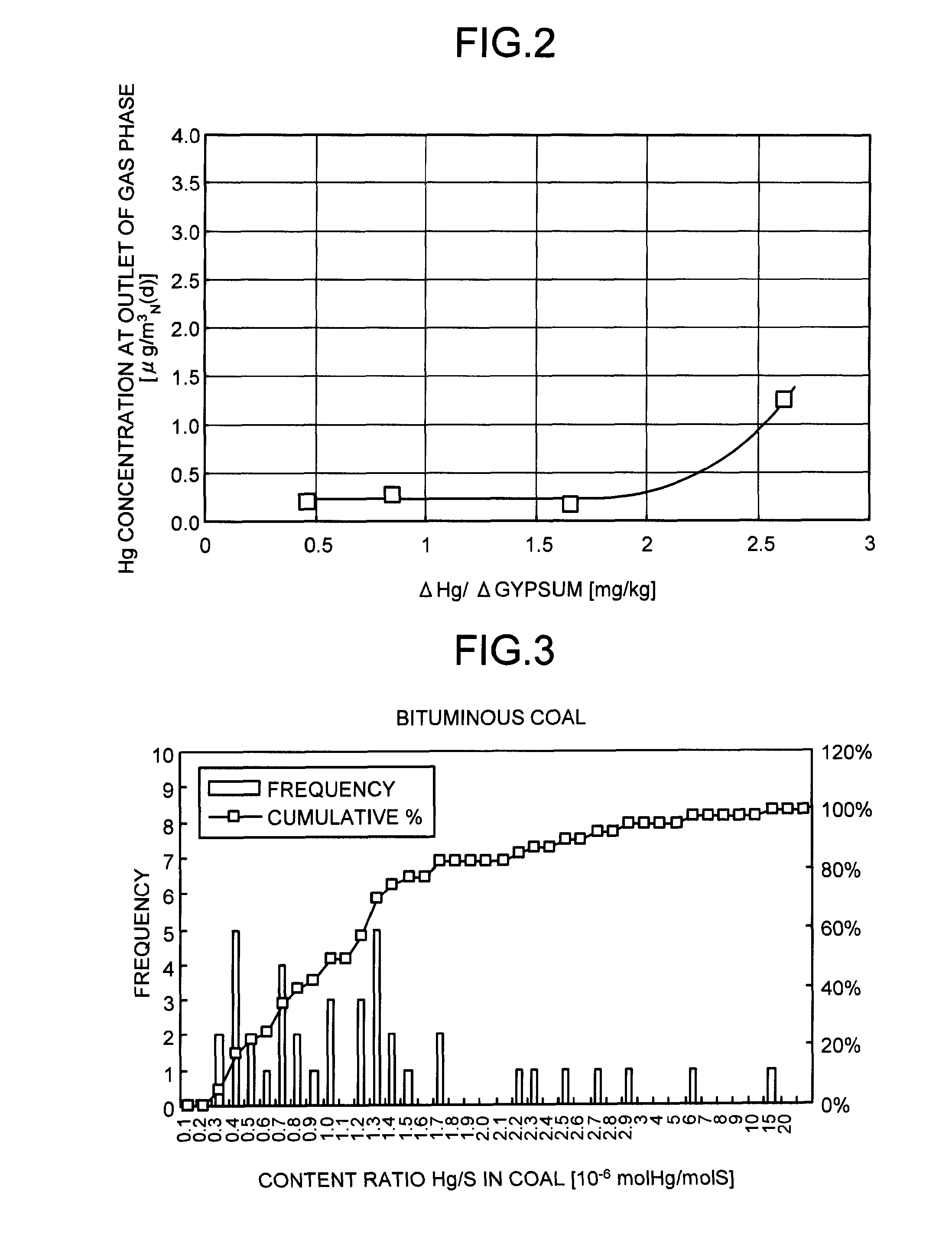
Flue gas control system of coal combustion boiler and operating method thereof
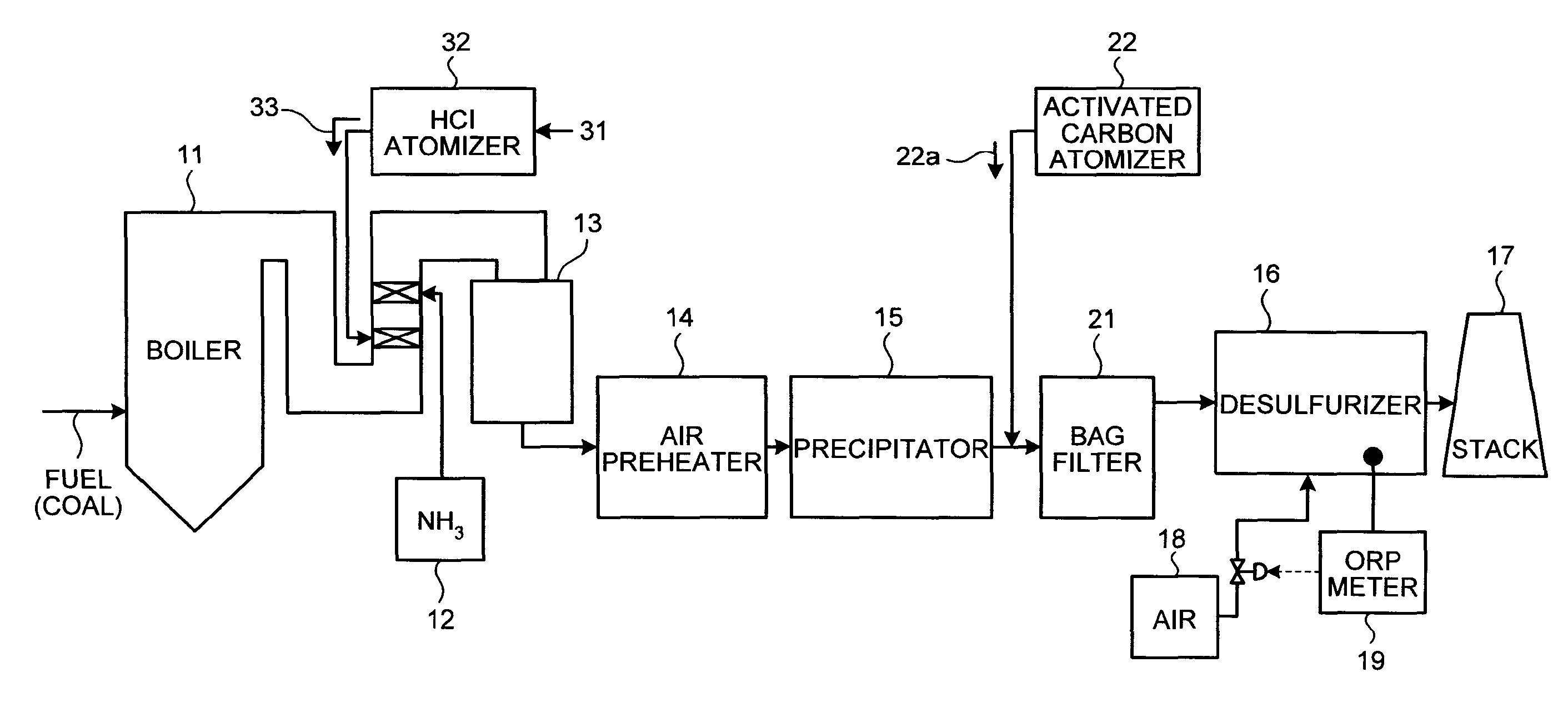
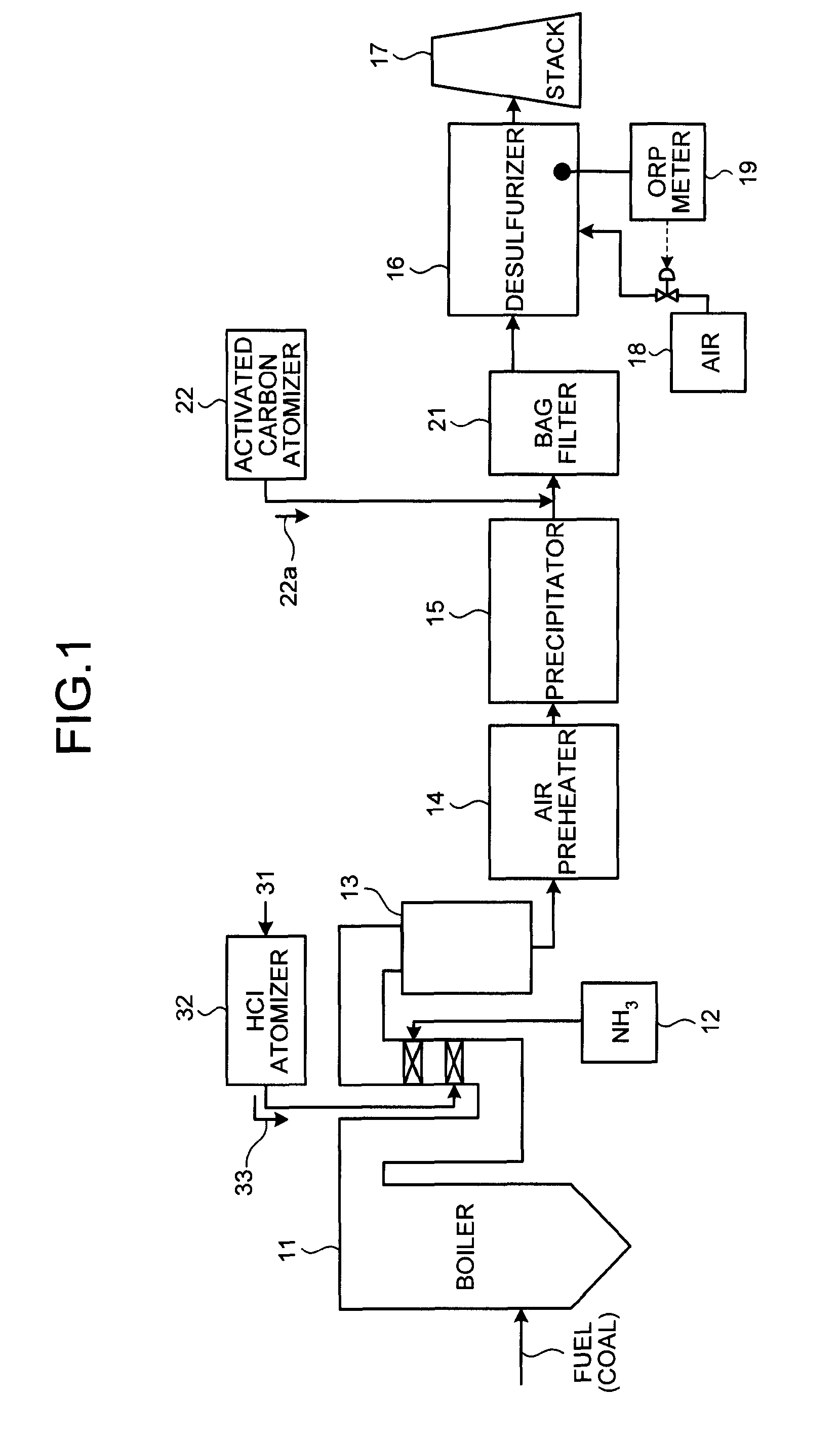
ActiveUS8071060B2Reduce operating costsCombination devicesNitrogen compoundsAir preheaterParticulates
A flue gas control system of a coal combustion boiler comprises an HCl atomizer that sprays hydrogen chloride to flue gas from a coal combustion boiler that uses coal as a fuel; NOx removing apparatus that removes nitrogen oxides by ammonia denitration by adding ammonia to the flue gas after spraying hydrogen chloride and oxidizes mercury; an air preheater that recovers heat in the gas after removal of nitrogen oxides; a precipitator that removes particulates in the gas; an activated carbon atomizer that sprays activated carbon into the gas after particulate collection; a bag filter that collects activated carbon having adsorbed mercury; a desulfurizer that removes sulfur oxides in the flue gas after removal of activated carbon; a stack that discharges the gas which has undergone desulfurization to outside; and an ORP meter that measures an oxidation reduction potential for feeding air to a slurry absorbent in the desulfurizer.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
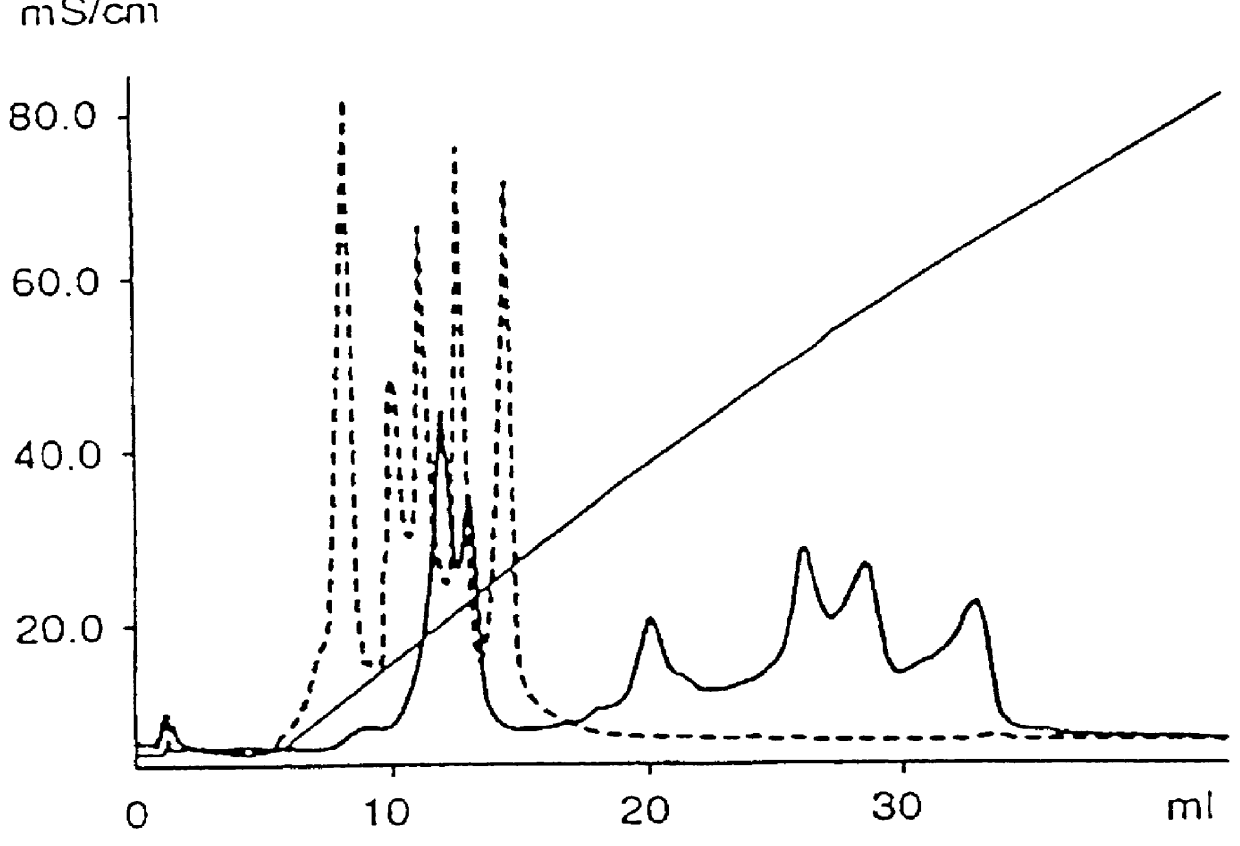
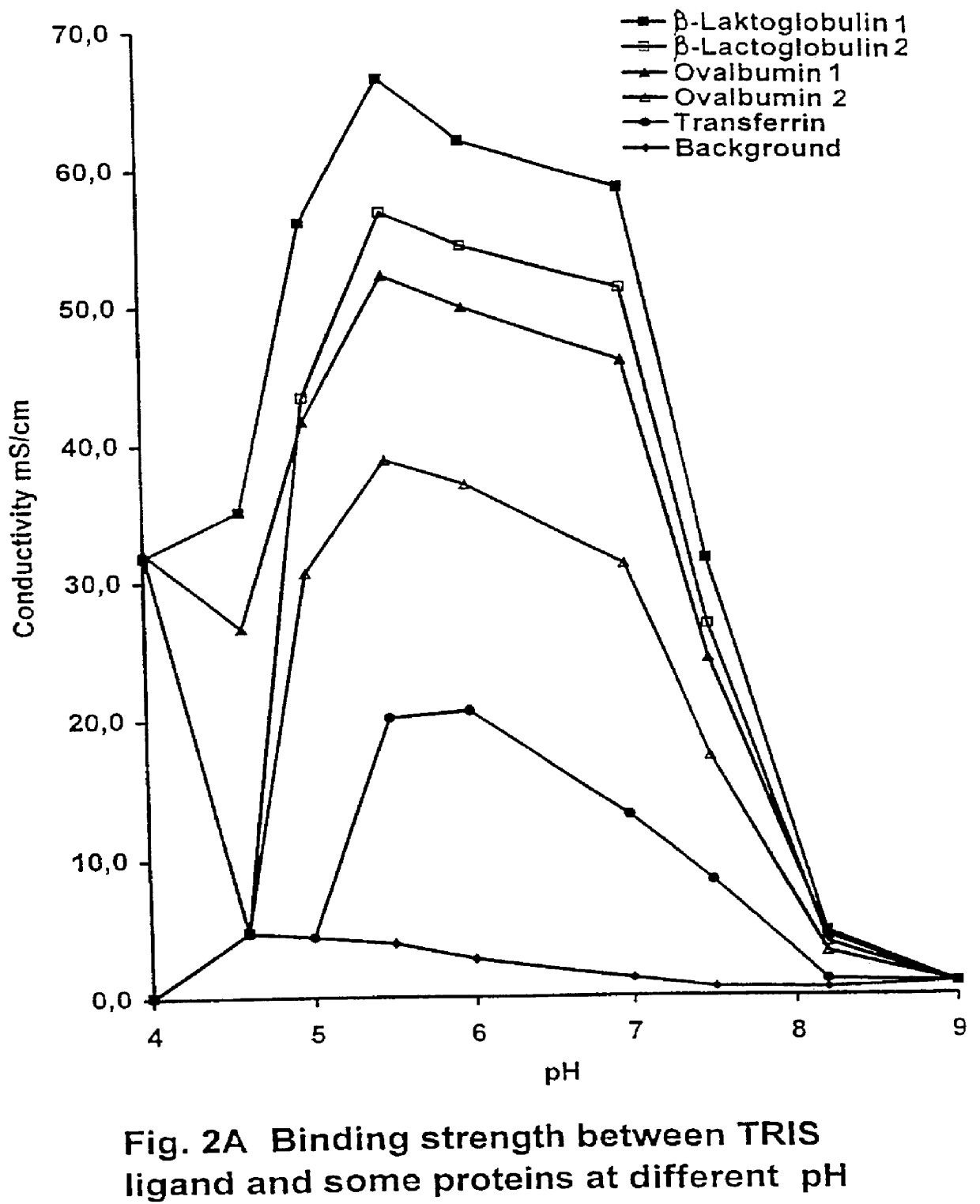
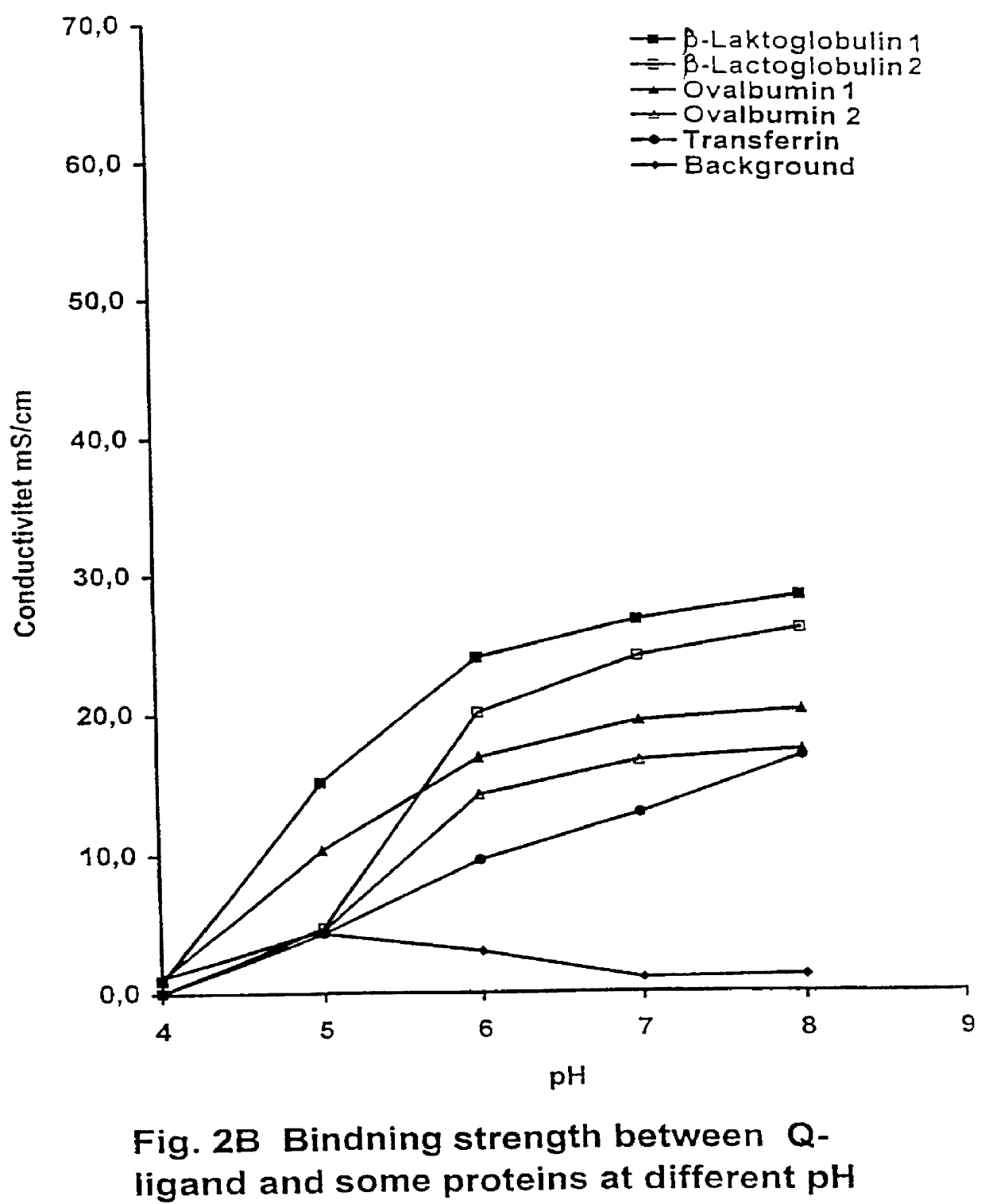
Process for chromatographic separation of peptides and nucleic acid, and new high affinity ion exchange matrix
InactiveUS6090288ACation exchanger materialsComponent separationChromatographic separationTransferrin
PCT No. PCT / SE97 / 00237 Sec. 371 Date Dec. 29, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Dec. 29, 1998 PCT Filed Feb. 14, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 29825 PCT Pub. Date Aug. 21, 1997Process for separating off a peptide or a nucleic acid by an anion exchanger (I) characterized in that a) the anion exchanger (I) exhibits ligands, which (i) contain a primary, secondary or tertiary amino group and (ii) are covalently bound to an organic polymer (matrix), b) there on a carbon atom at a distance of 2 or 3 atoms away from an amino nitrogen in the ligands is a hydroxyl group or a primary, secondary or tertiary amino group, and c) the maximum elution ionic strength in the pH range 2-14 for at least one of the proteins transferrin, ovalbumin 1, ovalbumin 2, beta -lactoglobulin 1 and beta -lactoglobulin 2 on the anion exchanger is higher than the elution ionic strength required for a quaternary comparative ion exchanger.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIOPROCESS R&D
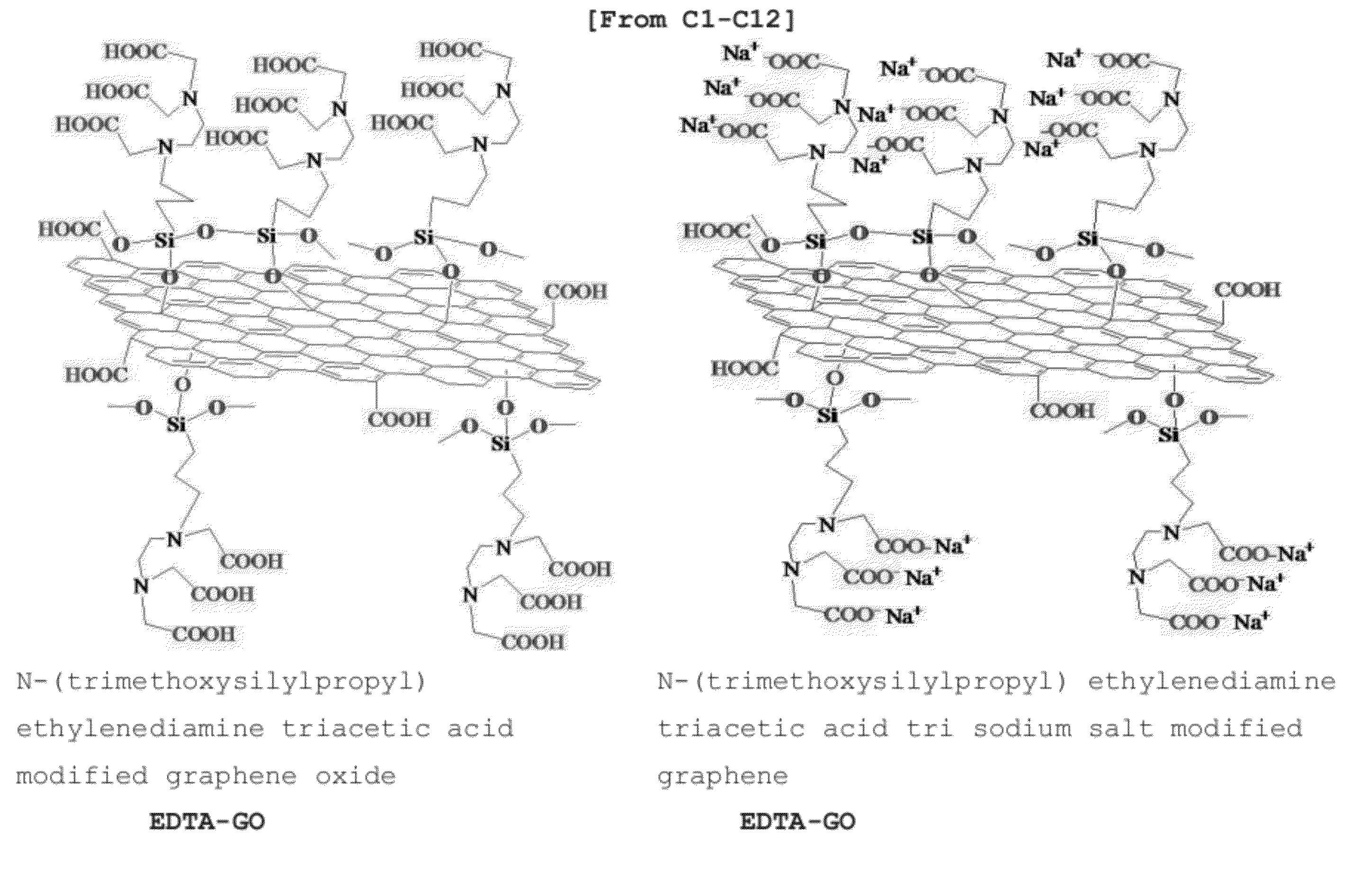
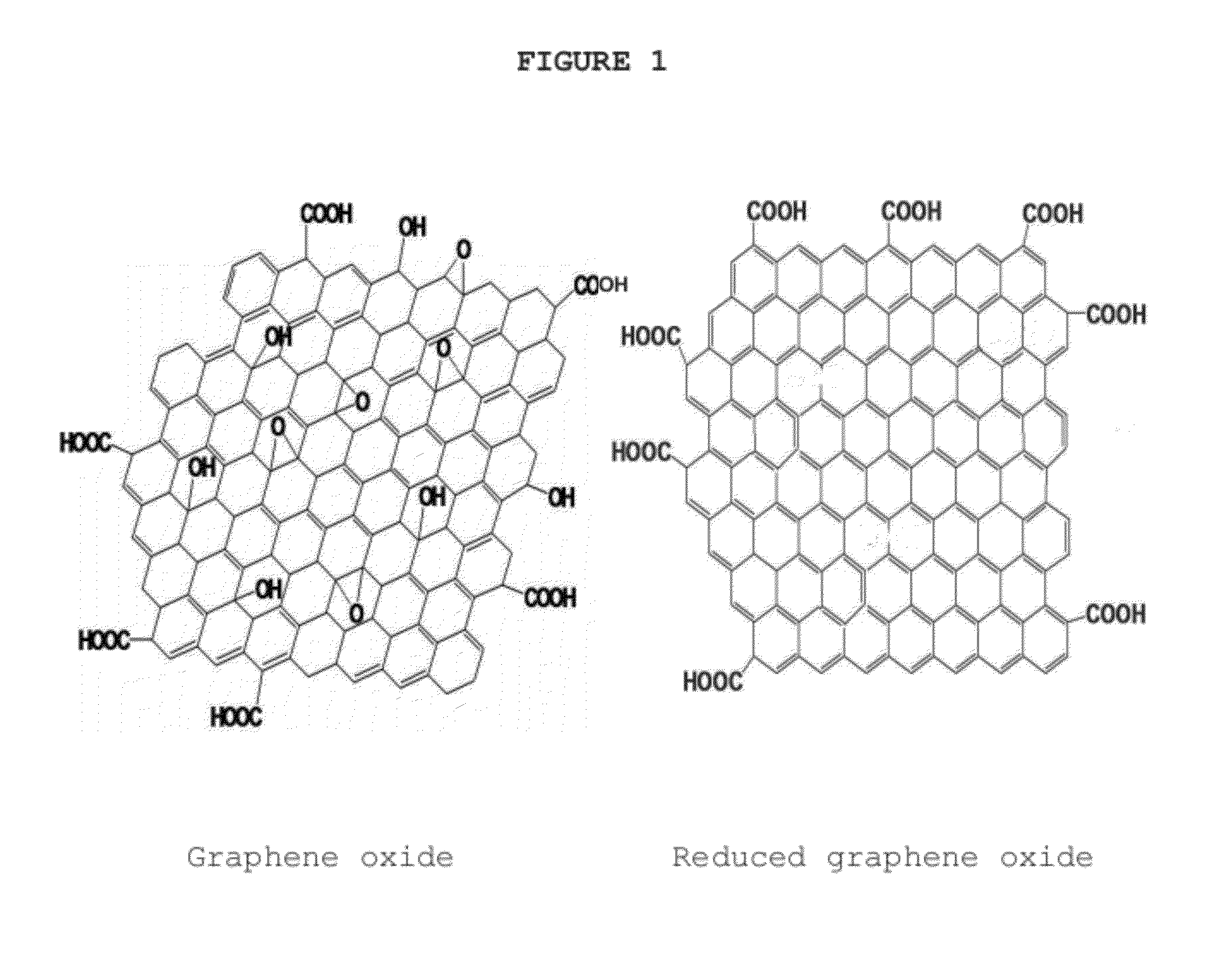
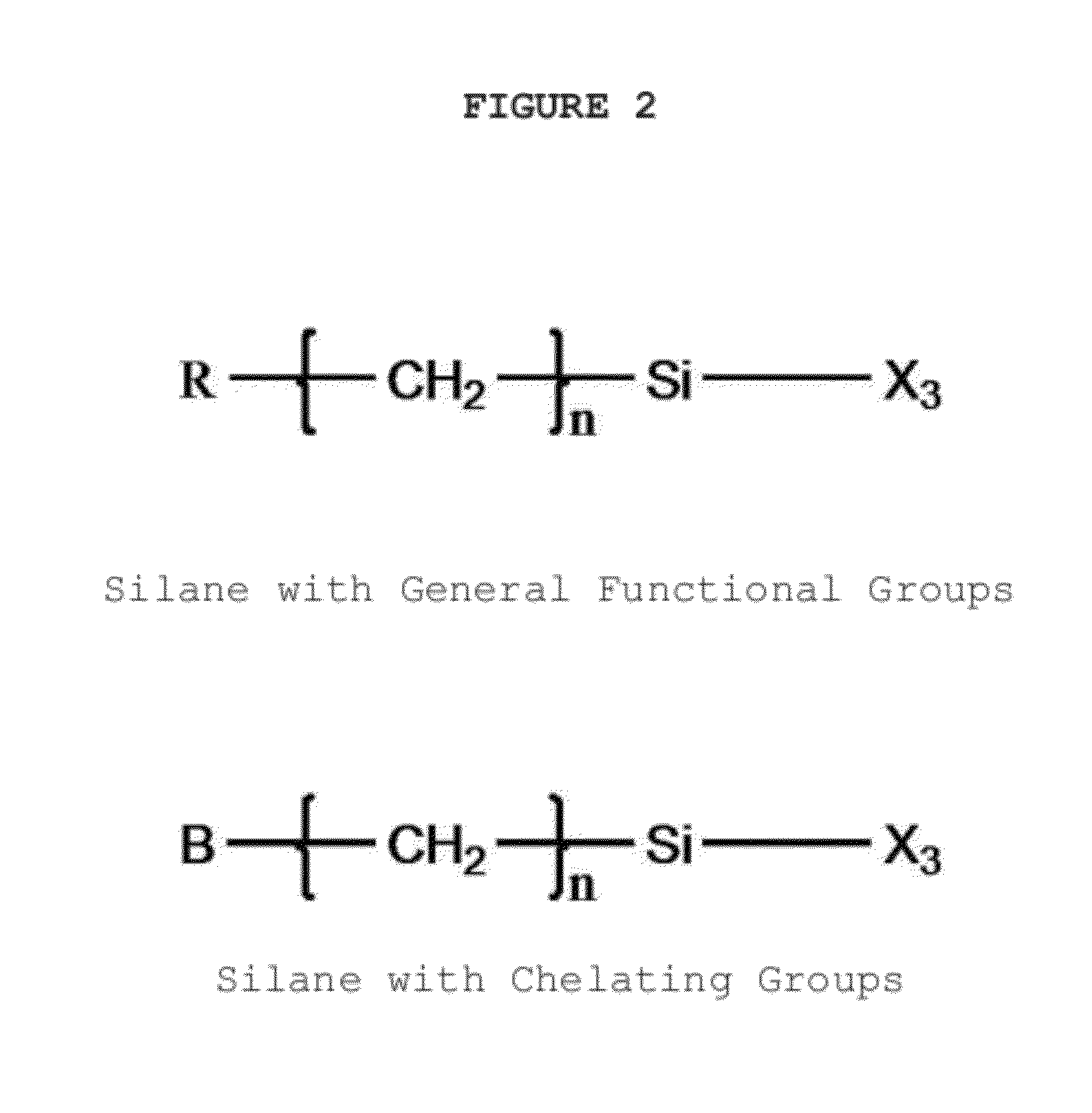
Chelating agent modified graphene oxides, methods of preparation and use
InactiveUS20120330044A1Improve performanceSilicon organic compoundsMaterial nanotechnologyGrapheneOxide
The invention is directed to chelating agent modified graphene oxides having the following formula G(AB)x; wherein G is graphene oxide, A is selected from the group consisting of —(CH2)m—, —NH—, —S—, —O—Si(—OR1)2(—CH2)m—, —C(═O)—, —C(═O)—O—, —C(═O)—O(CH2)m—, —C(═O)—NH—, —C(═O)—NH—(CH2)m—, —P(═O)2—O—, wherein m is 1-12 and R1 is H, or C1-C12 alkyl; and B is a chelating moiety; wherein the ratio of basic graphene oxide units:x is from about 1:0.00001 to about 1:0.5. Such chelating modified graphene oxides have broad applications in diverse technical fields.
Owner:JINING LEADERNANO TECH L L C
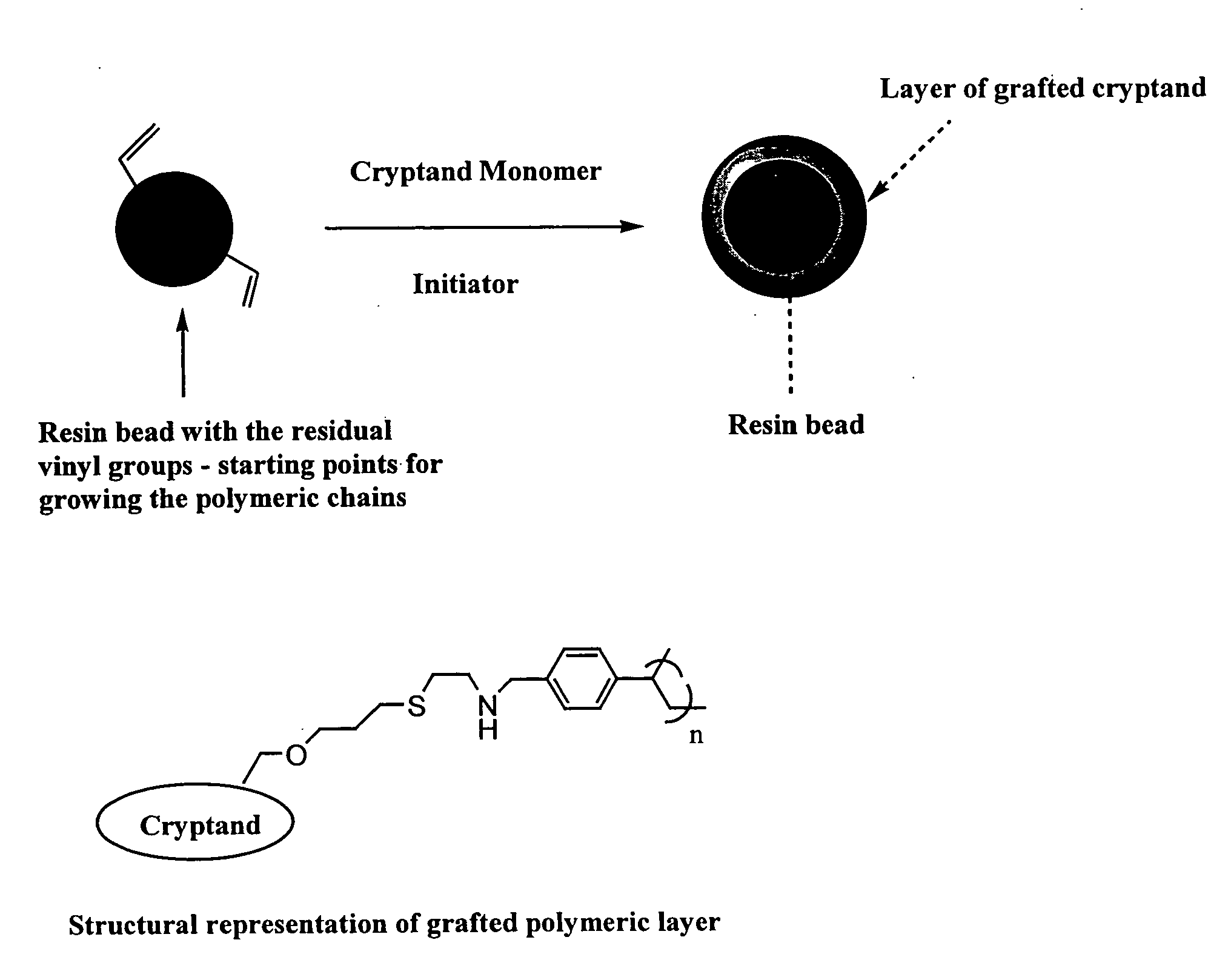
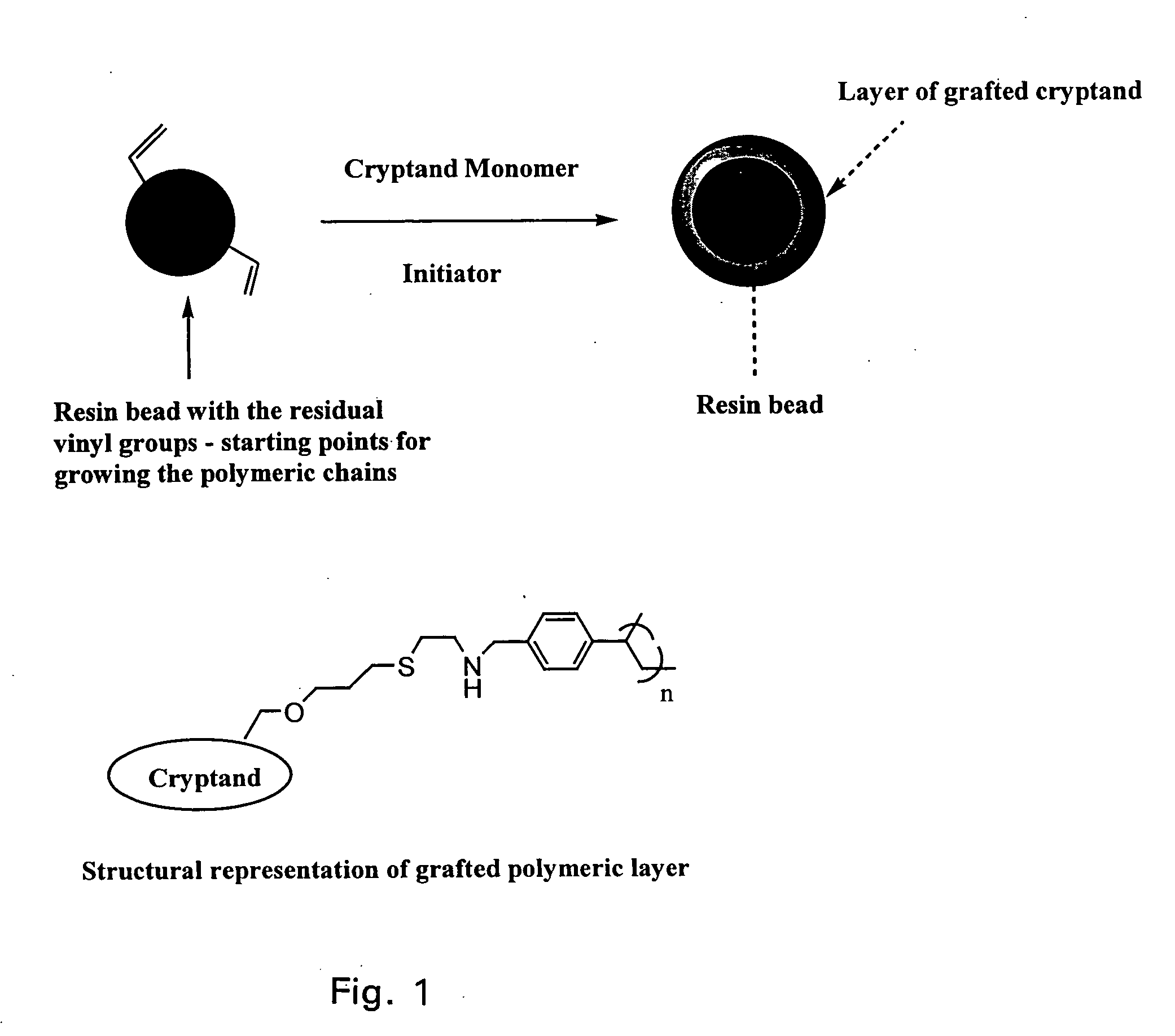
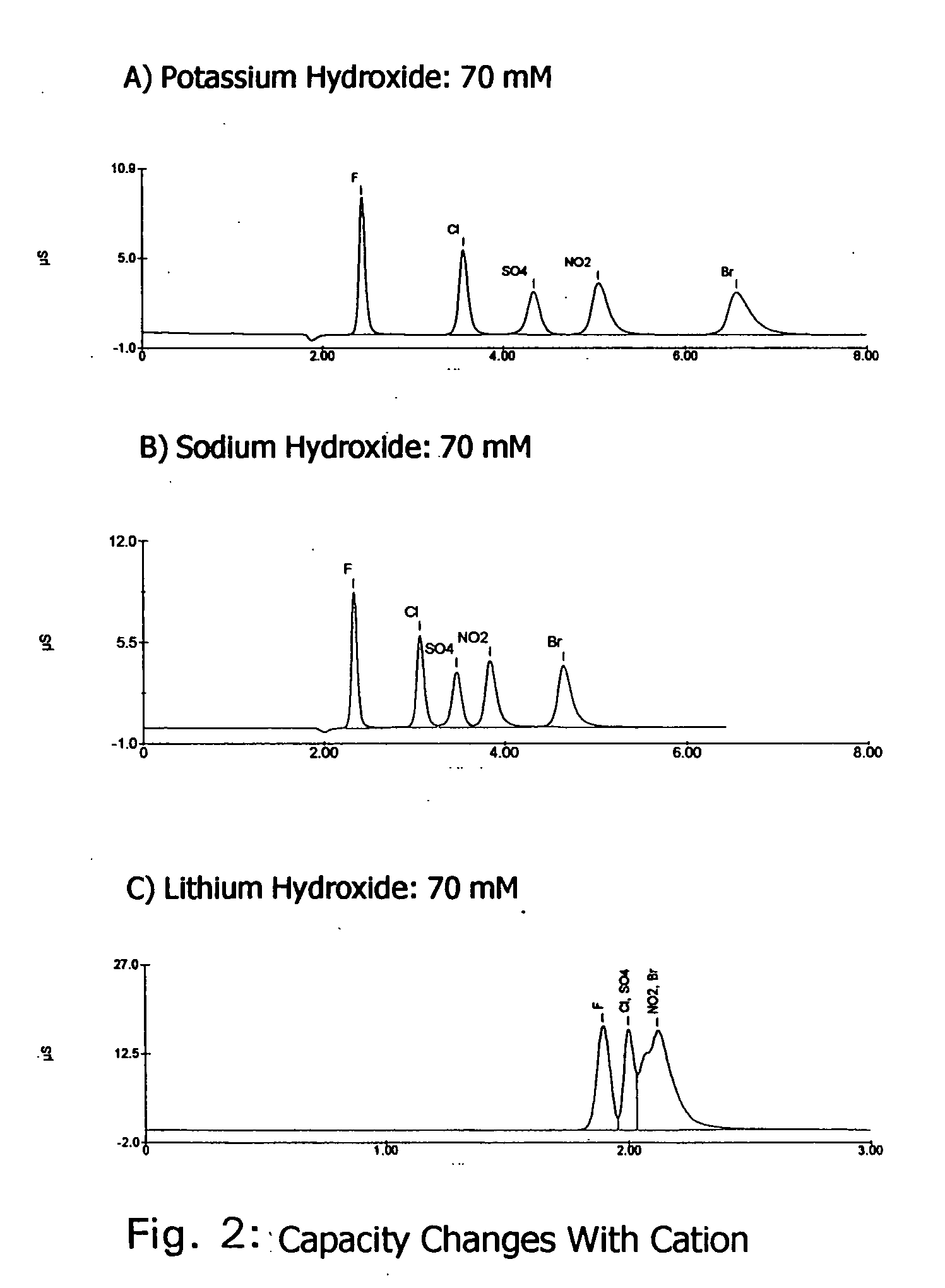
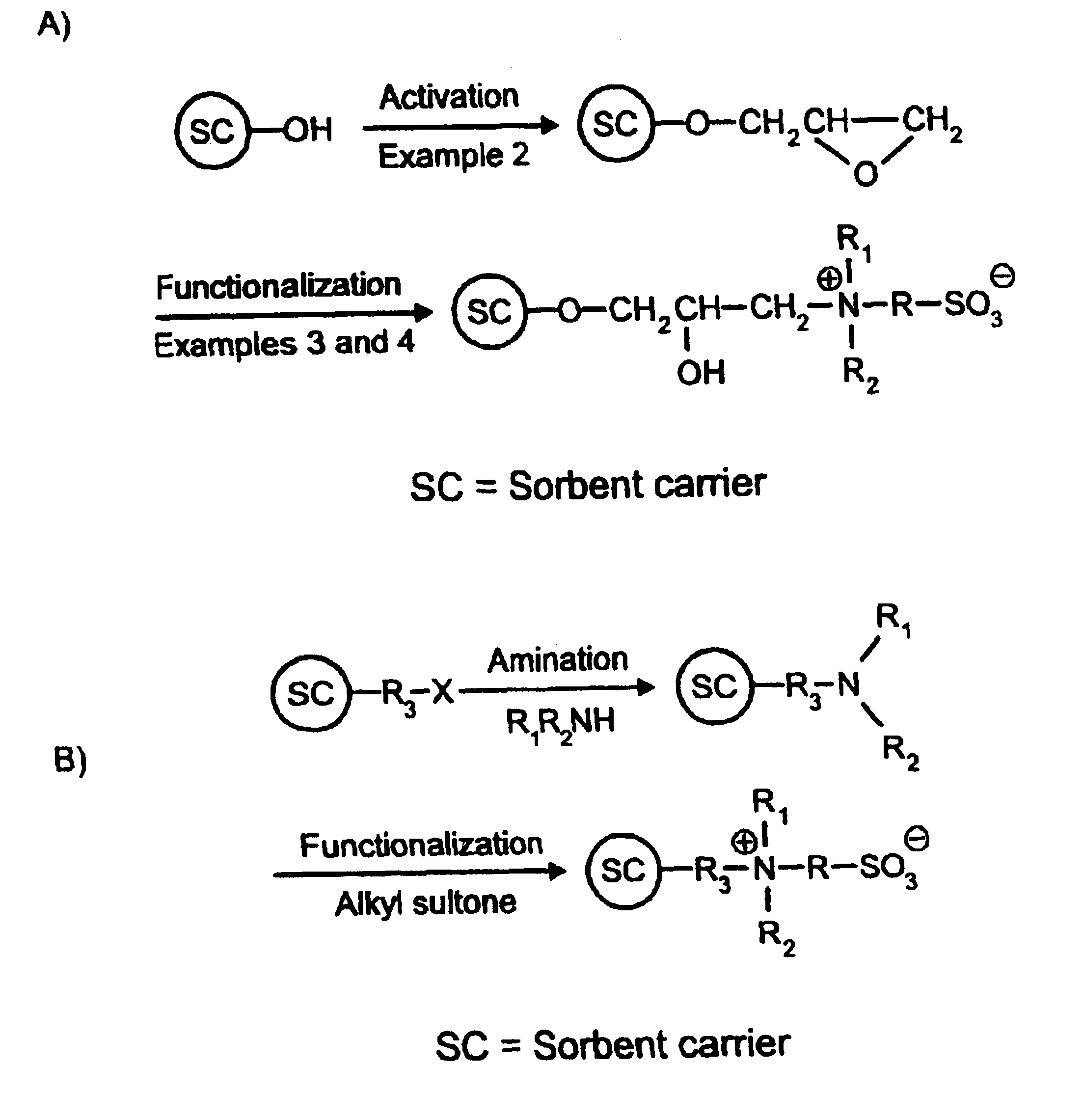
Ion exchange cryptands covalently bound to substrates
InactiveUS20050133453A1Ion-exchange process apparatusOther chemical processesIon exchangeIon binding
One embodiment of the invention comprises an ion exchange composition formed by reacting unsaturated carbon to carbon moieties pendant from derivatized ion binding cryptands with a support substrate under free radical activation conditions to form a covalent bond therebetween. In another embodiment, a cryptand ion exchange composition is made by covalently bonding unsaturated carbon to carbon moieties pendant from a derivatized ion binding cryptands with unsaturated carbon to carbon moieties pendant from a support substrate under free radical activation conditions to form covalent bond.
Owner:DIONEX CORP
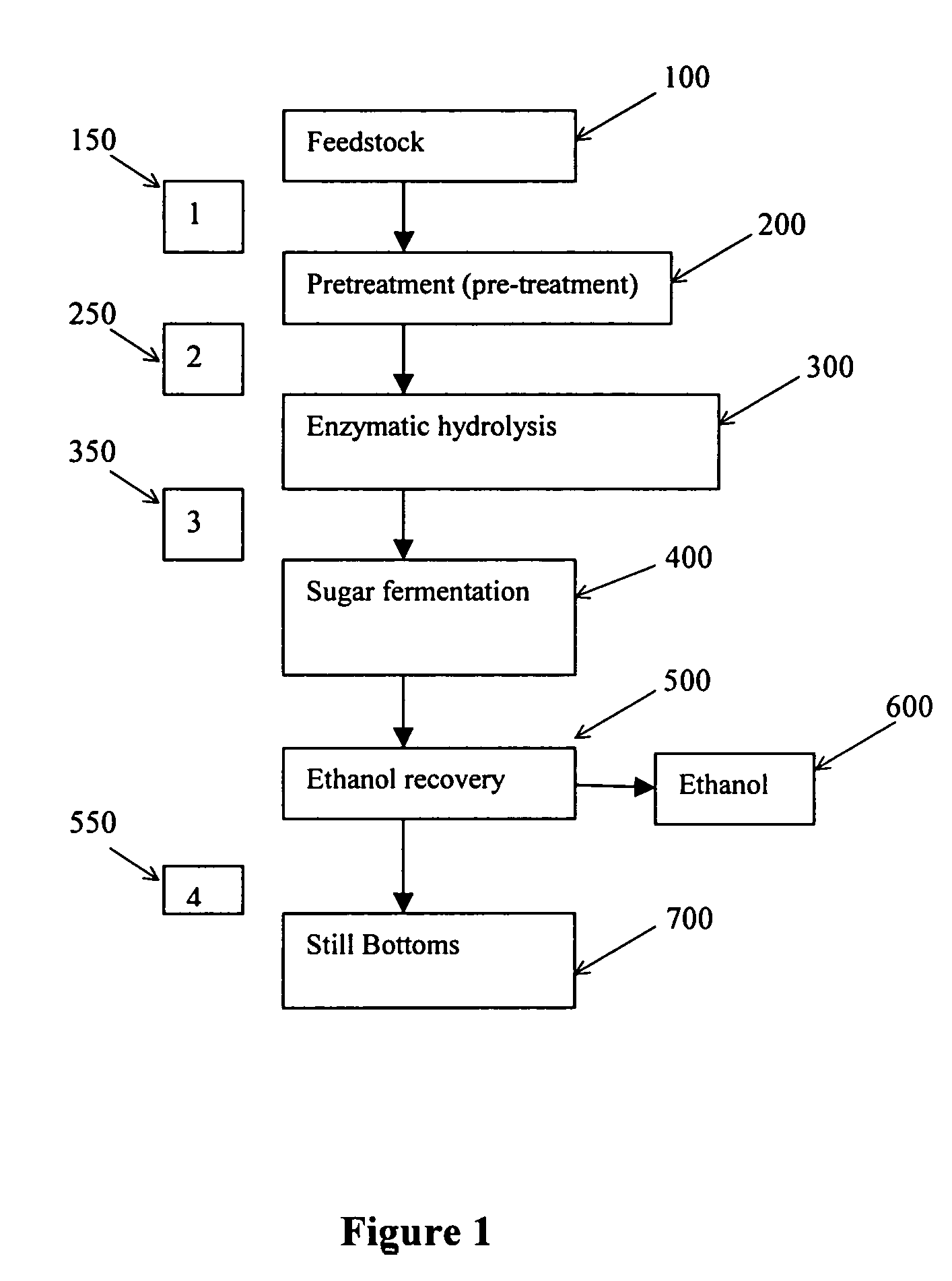
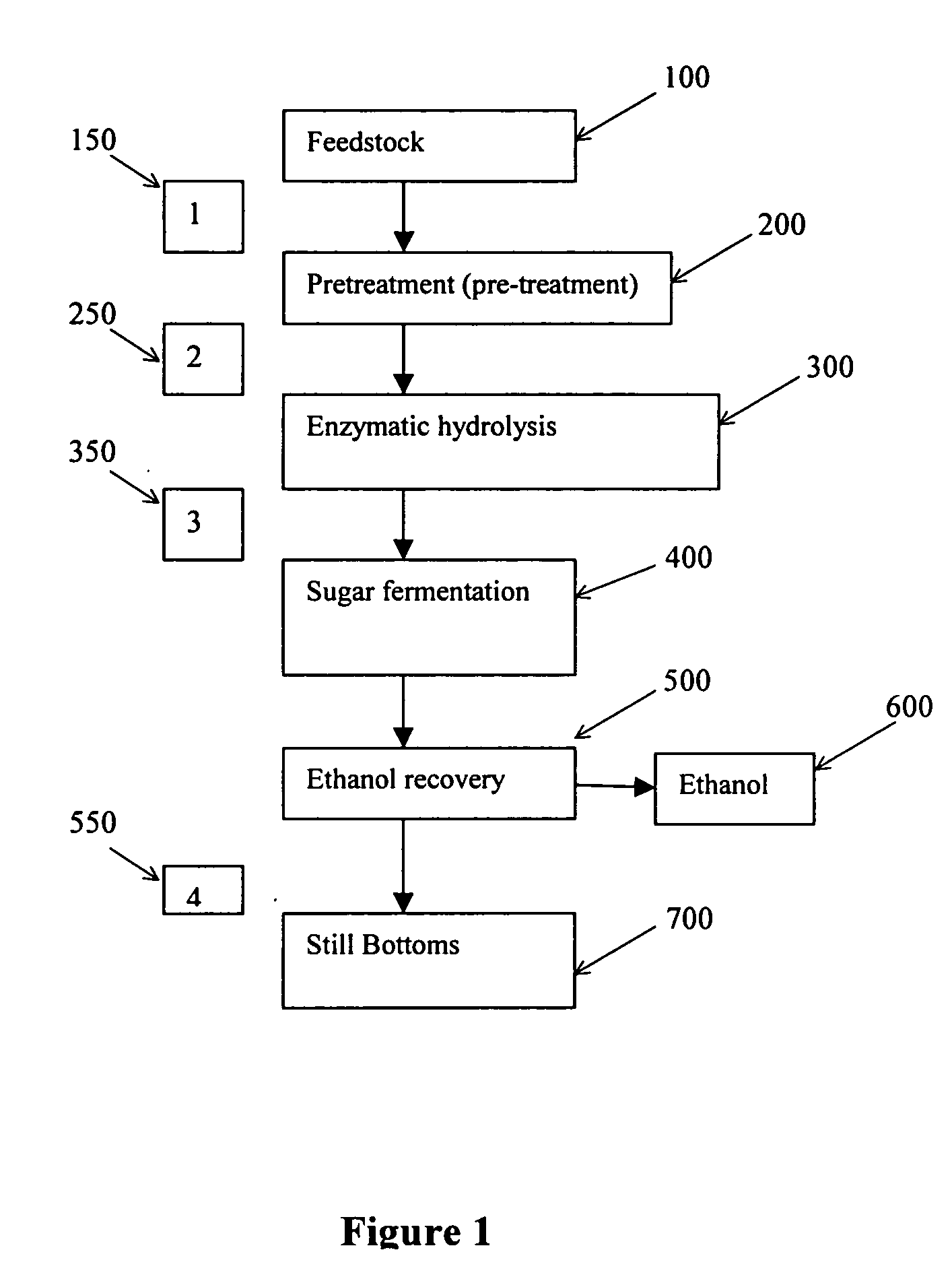
Recovery of inorganic salt during processing of lignocellulosic feedstocks
ActiveUS7585652B2Reduce inhibitionMeet cutting requirementsMagnesium fertilisersIon-exchanger regenerationCelluloseInorganic salts
A method for recovering inorganic salt during processing of a lignocellulosic feedstock is provided. The method comprises pretreating the lignocellulosic feedstock by adding an acid to the feedstock to produce a pretreated lignocellulosic feedstock. A soluble base is then added to the pretreated lignocellulosic feedstock to adjust the pH and produce a neutralized feedstock. The neutralized feedstock is then enzymatically hydrolyzed to produce an enzyme hydrolyzed feedstock and a sugar stream. Inorganic salt is recovered from either a stream obtained from the lignocellulosic feedstock prior to the step of pretreating, a stream obtained from the pretreated lignocellulosic feedstock, a stream obtained from the neutralized feedstock, a stream obtained from the sugar stream, or a combination of these streams. The inorganic salt may be concentrated, clarified, recovered and purified by crystallization, electrodialysis drying, or agglomeration and granulation, and then used as desired, for example as a fertilizer.
Owner:IOGEN ENERGY CORP
Media for membrane ion exchange chromatography based on polymeric primary amines, sorption device containing that media, and chromatography scheme and purification method using the same
ActiveUS20090050566A1Improve bindingGood removal effectCation exchanger materialsIon-exchanger regenerationPurification methodsSorbent
Media and devices, such as anion exchangers including such media, wherein the media is a membrane having a surface coated with a polymer such as a polyallylamine. The resulting membrane offers stronger binding of protein impurities and superior removal of host cell proteins from biological samples than conventional ligands based on quaternary ammonium salts, including trimethylammonium ligands. Also described is a chromatography scheme and method for purifying monoclonal antibodies, wherein the anion exchange sorber is placed downstream of an affinity column (such as Protein A or Protein G affinity column) and optionally one or more polishing devices such as cationic exchange columns. Little or no dilution of the cation exchanger pool (or affinity column exchange pool where no cation exchanger is used) is necessary to lower the conductivity of the sample. The sorber functions well to strongly bind host cell proteins and other impurities in biological samples even at high conductivities and pH.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
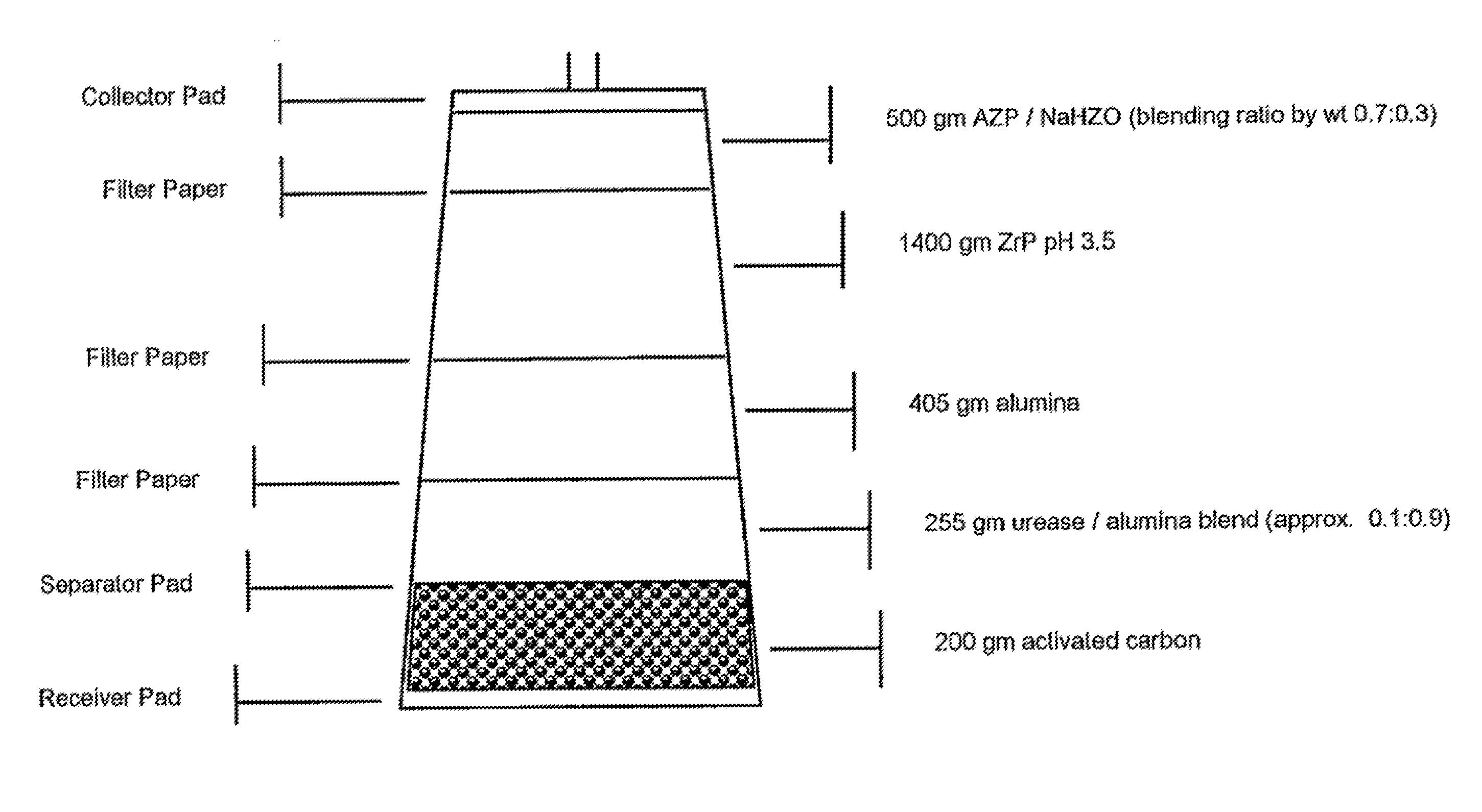
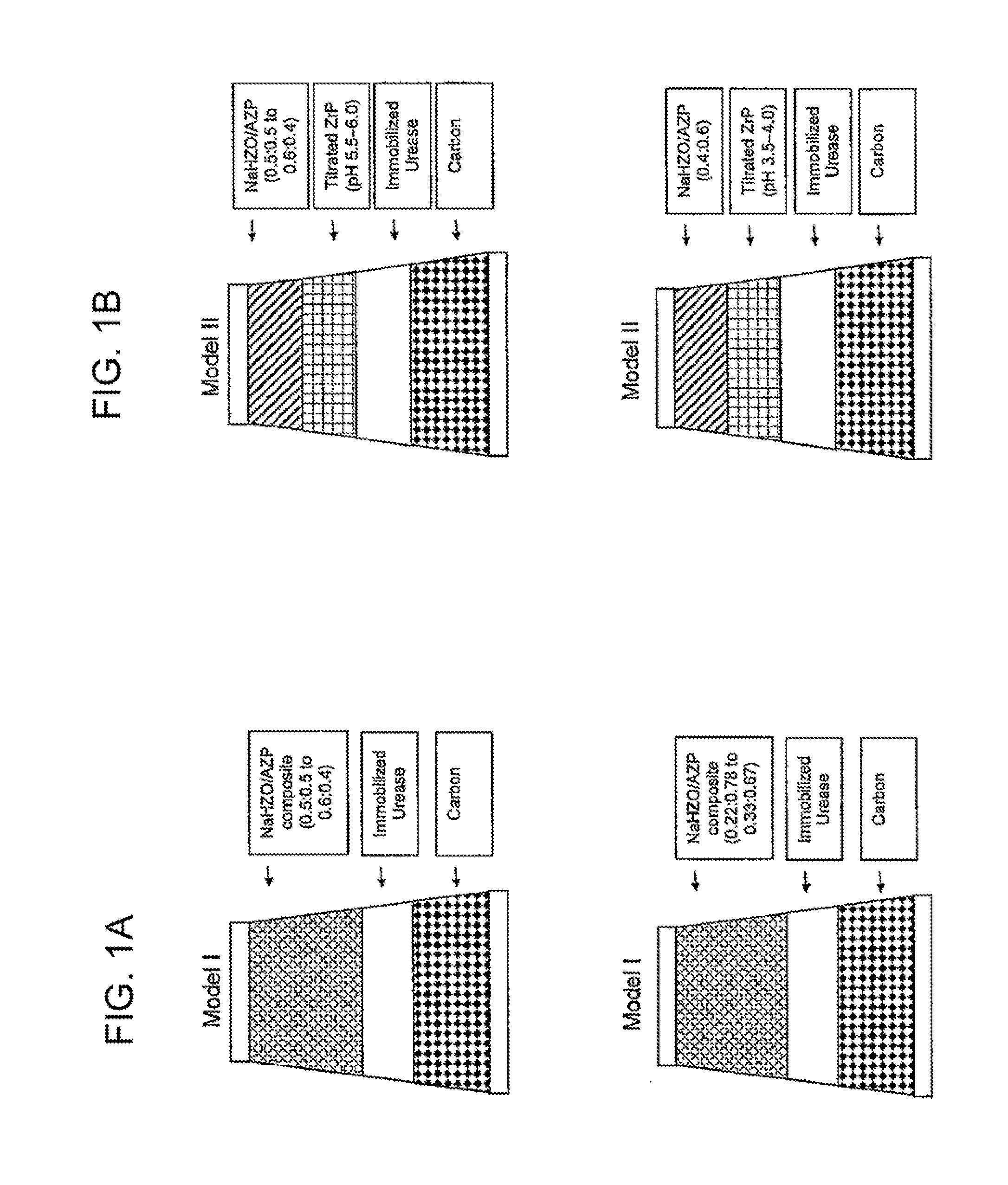
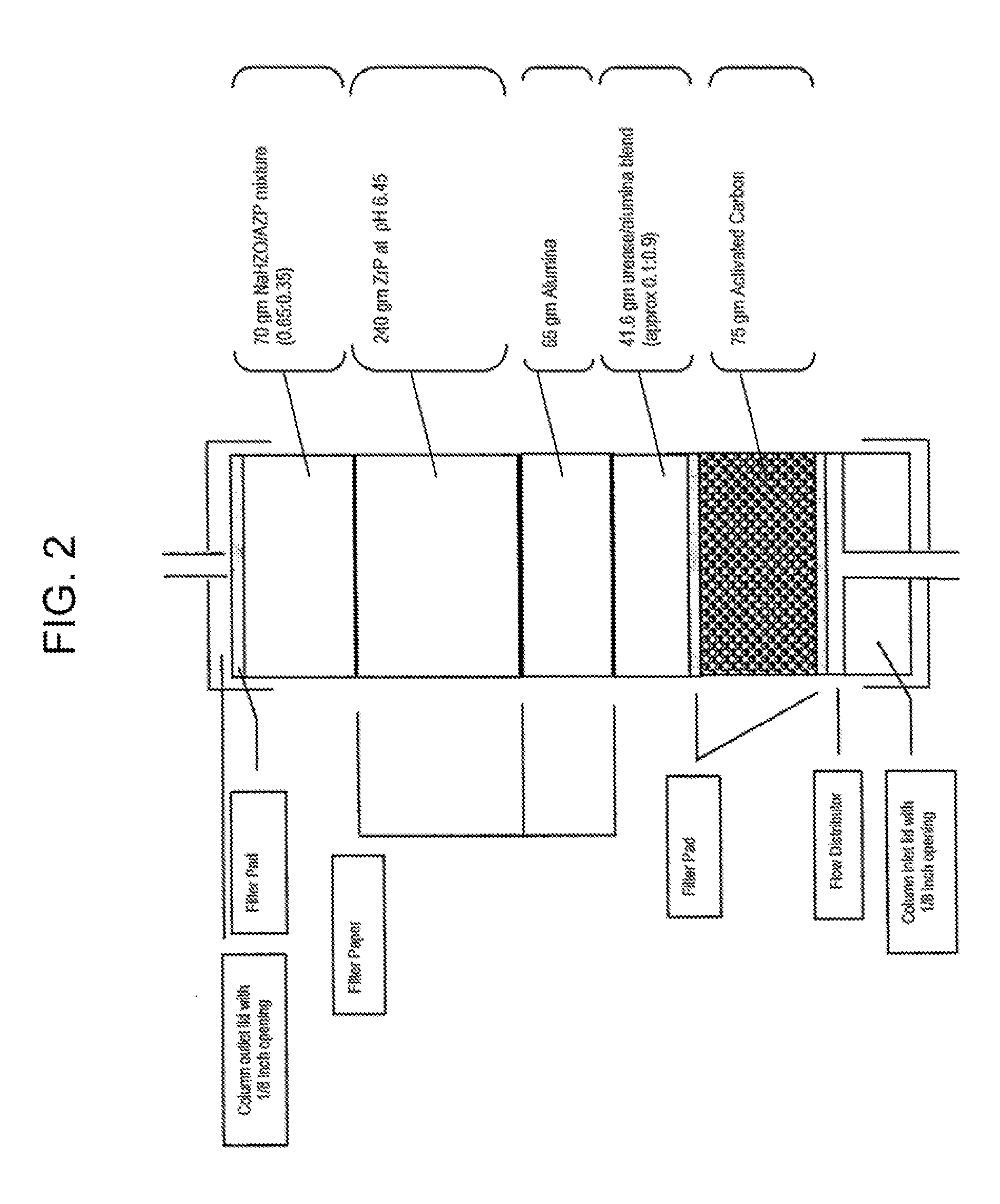
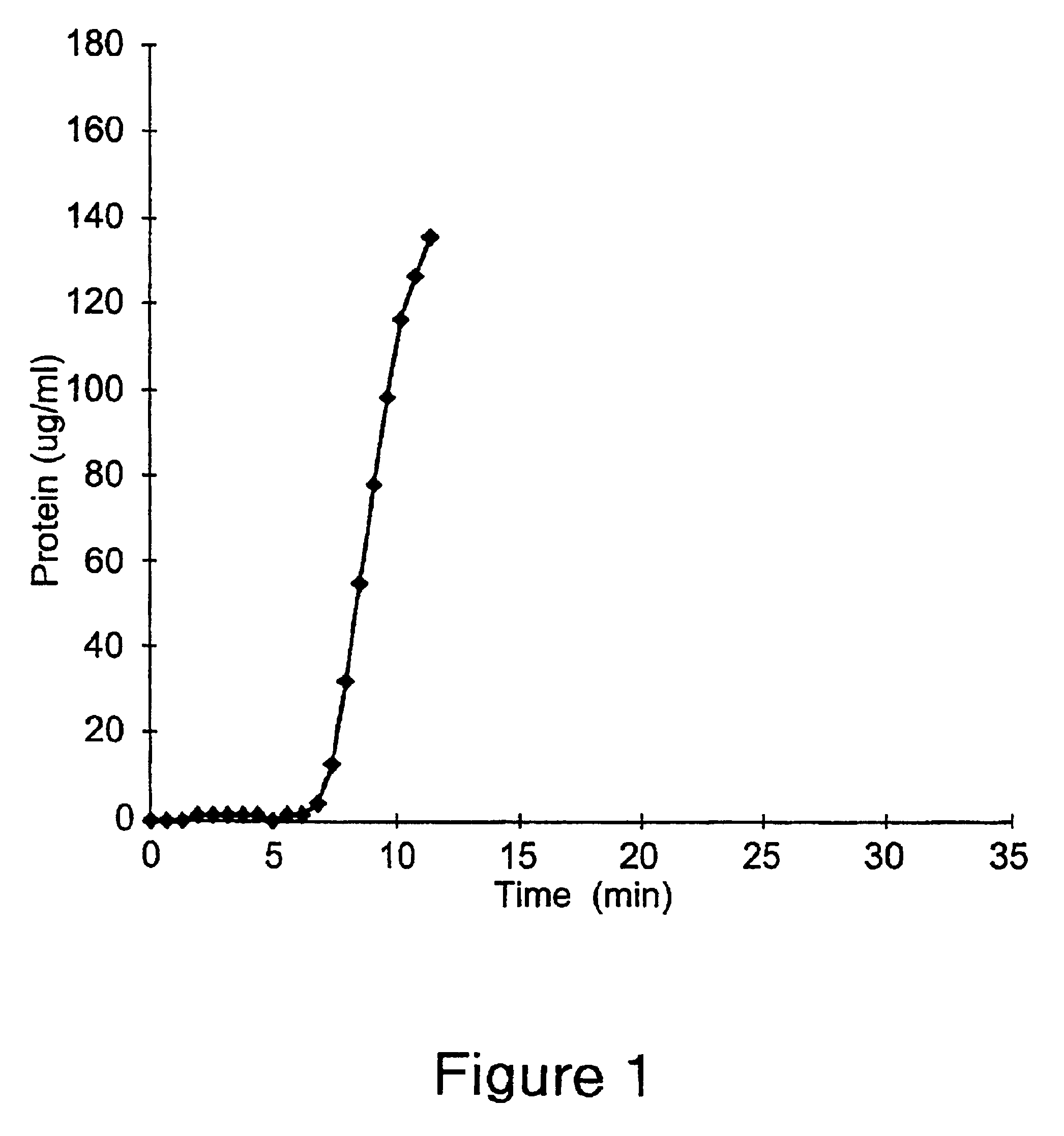
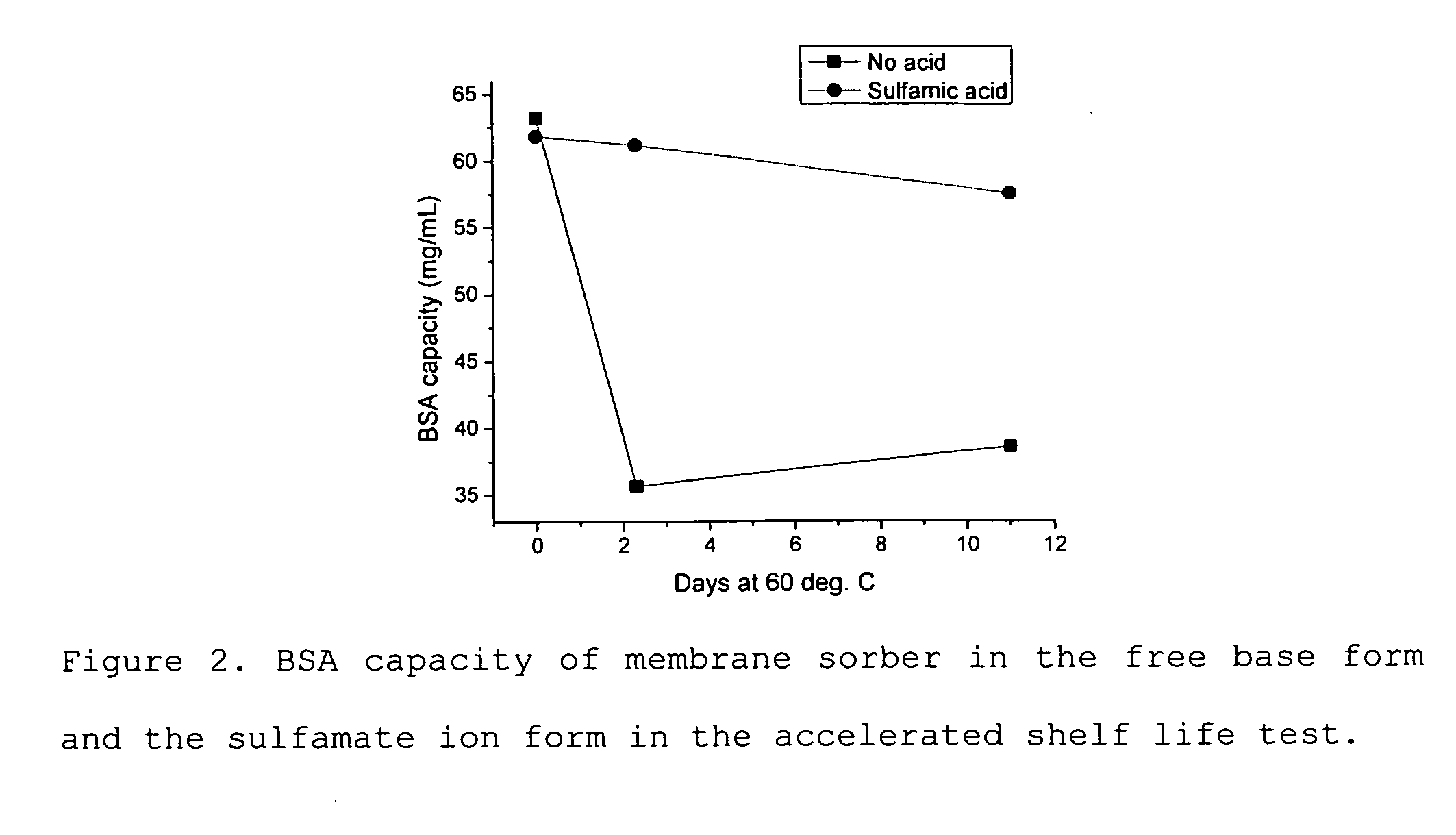
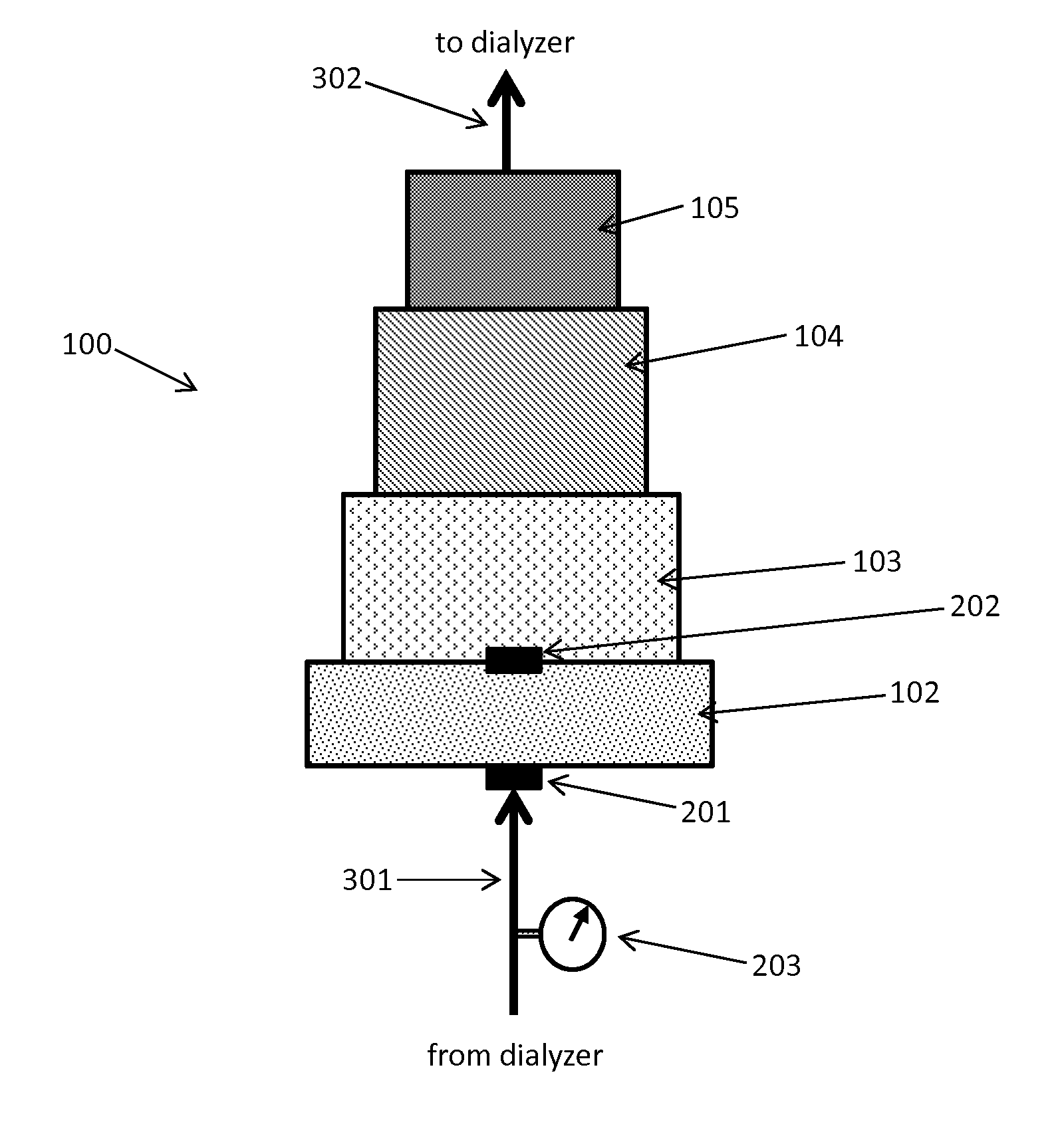
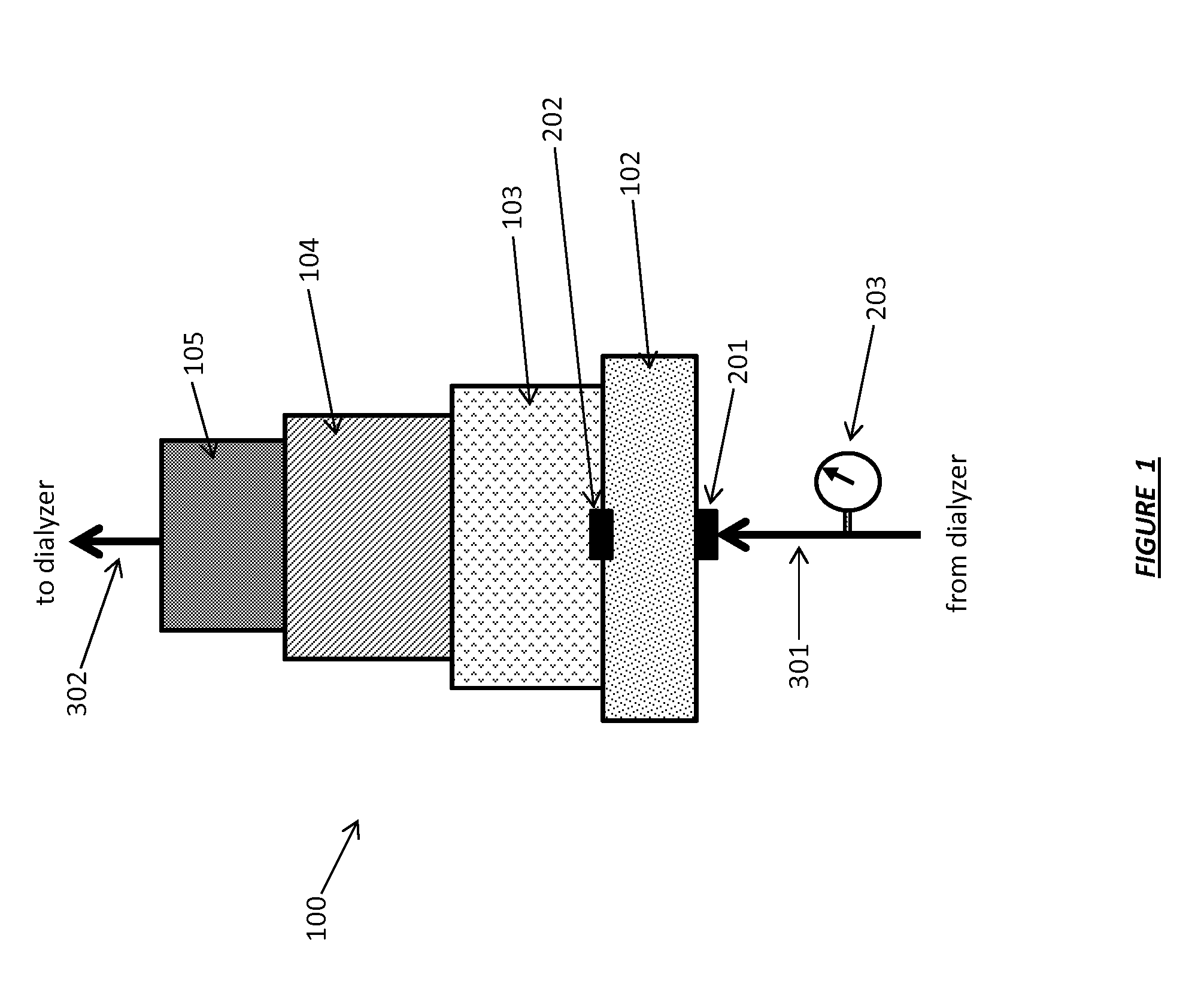
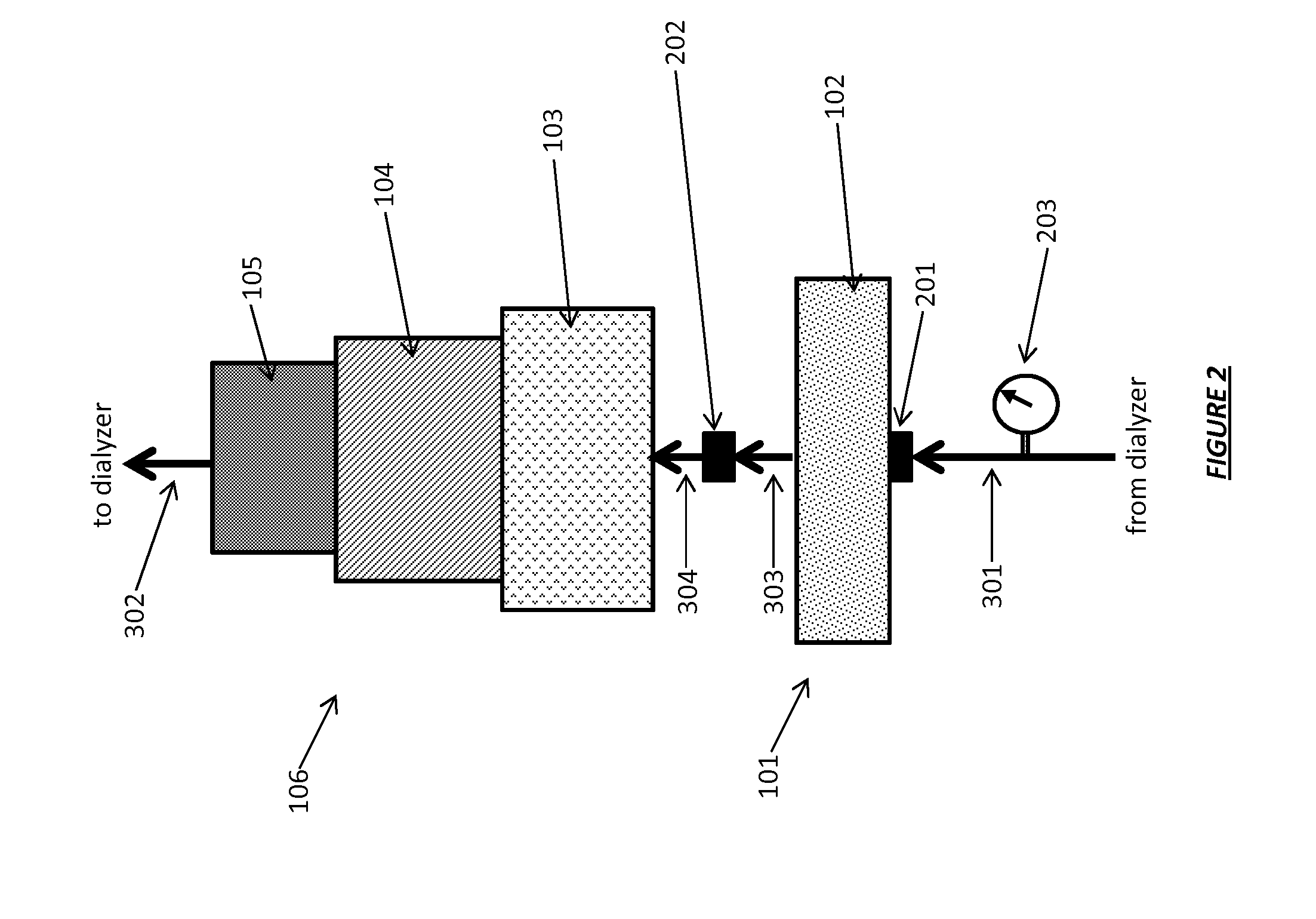
Acid zirconium phosphate and alkaline hydrous zirconium oxide materials for sorbent dialysis
ActiveUS8409444B2Avoid disadvantagesRestore balanceCation exchanger materialsSolvent extractionIon exchangeDialysis fluid
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
Recirculating dialysate fluid circuit for blood measurement
ActiveUS20140190886A1Short balance timeIncreasing dialysateCation exchanger materialsSolvent extractionMonitoring systemBiomedical engineering
A blood based solute monitoring system for measuring at least one blood solute species that has a first recirculation flow path in fluid communication with a dialyzer. The first recirculation flow path is configured to allow a fluid to recirculate through a dialyzer such that the concentration of at least one solute species in the fluid becomes equilibrated to the solute species concentration of the blood in a blood compartment of the dialyzer. The blood solute monitoring system has at least one sensor to measure a fluid characteristic.
Owner:MOZARC MEDICAL US LLC
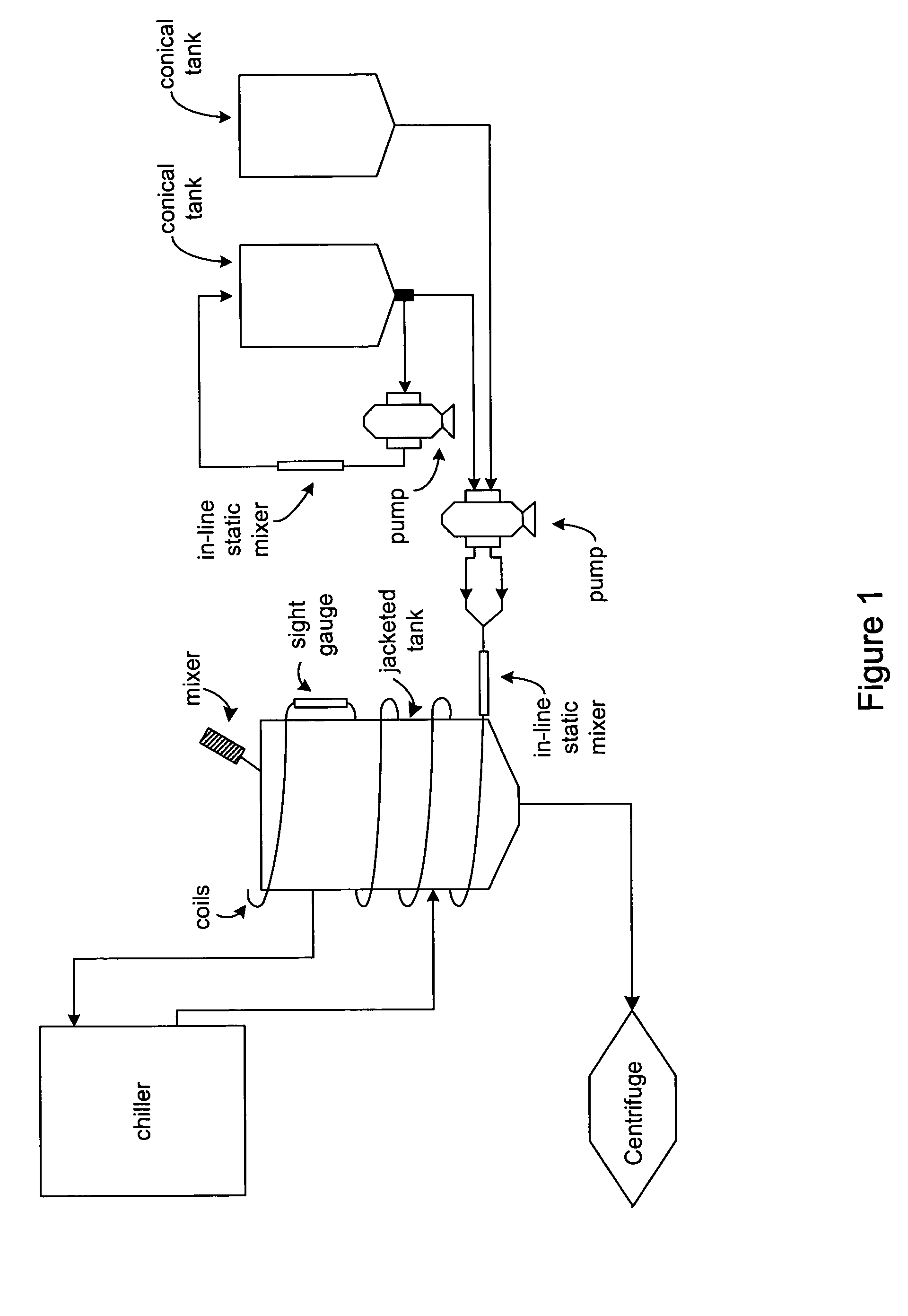
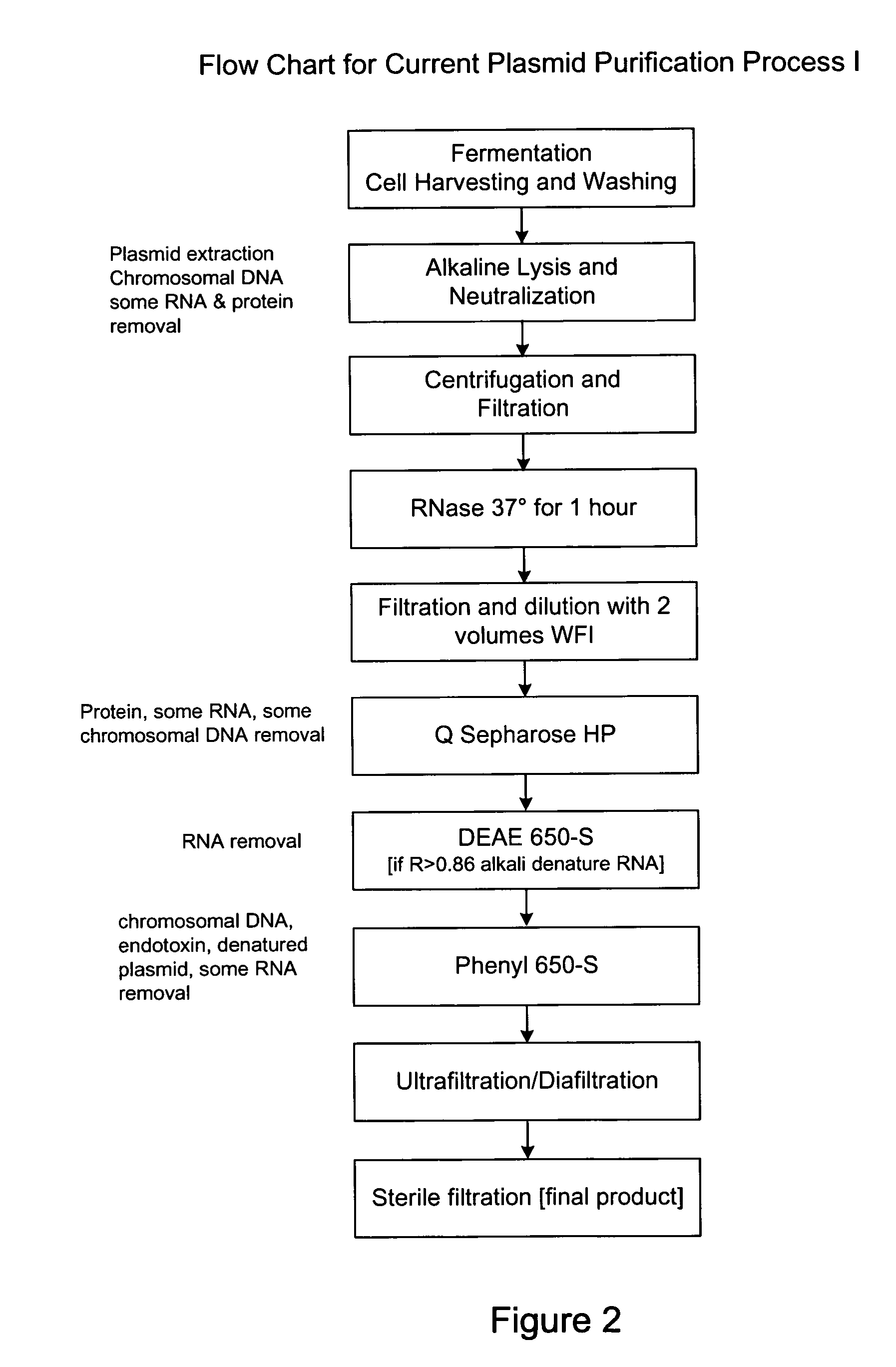
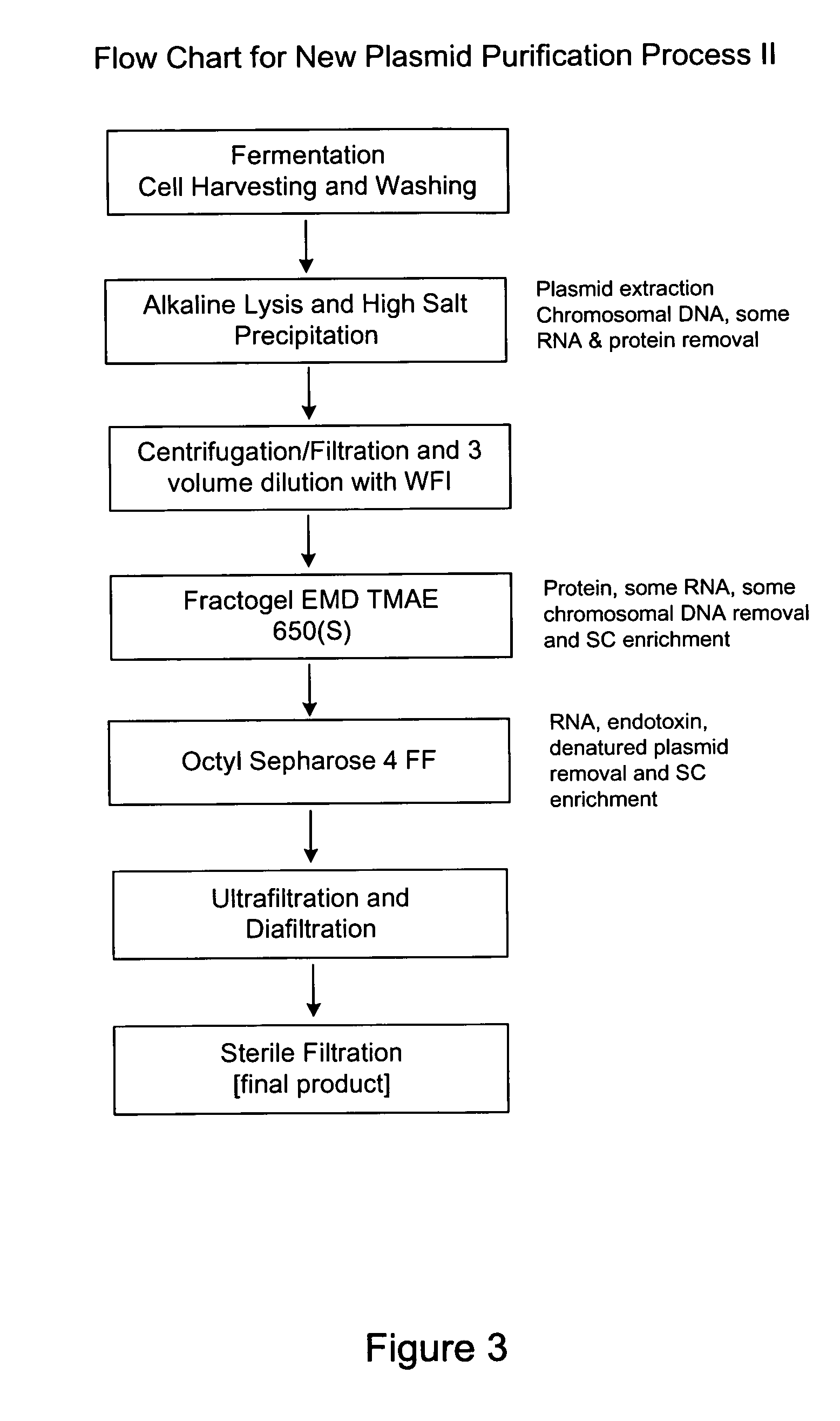
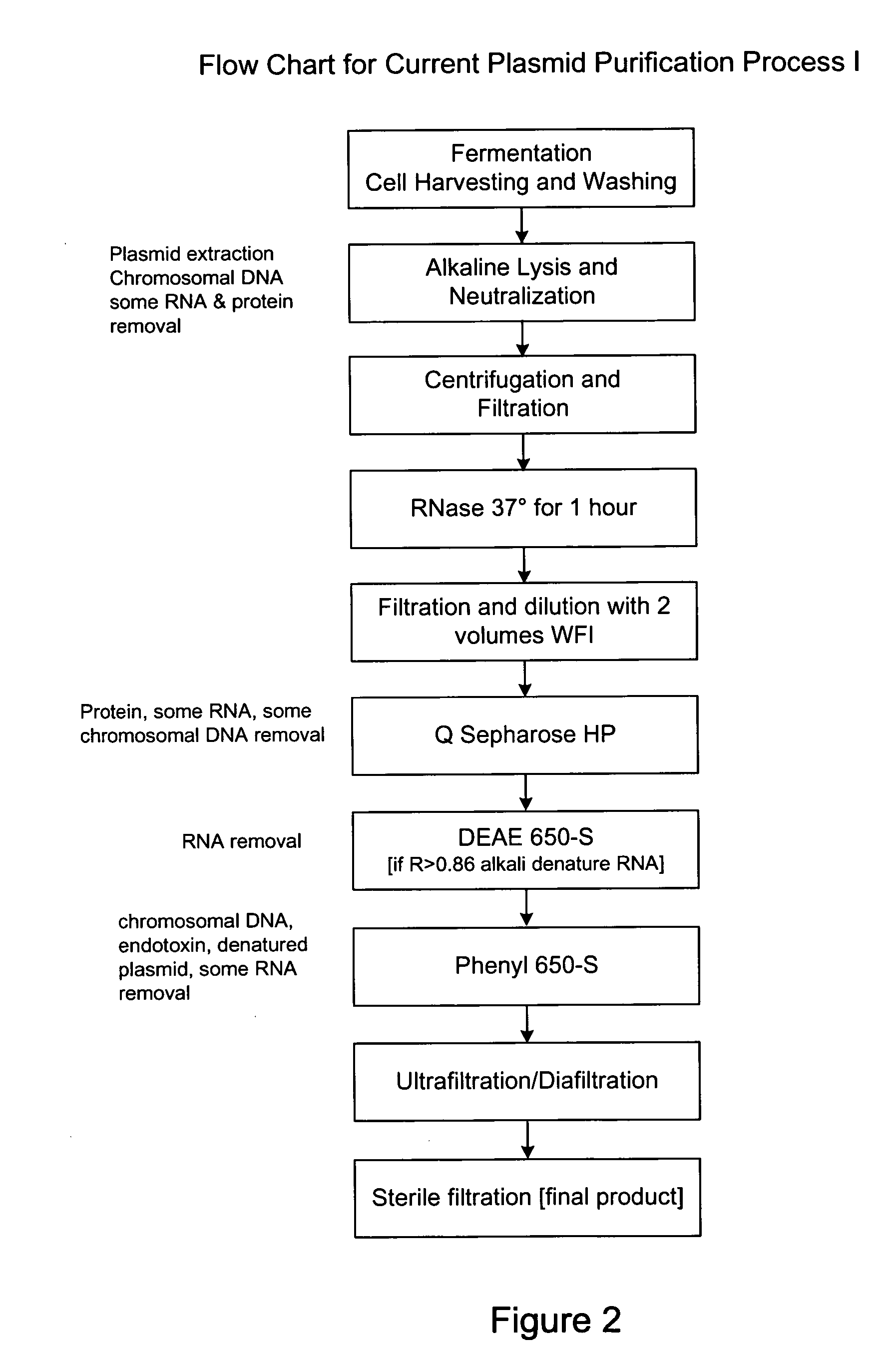
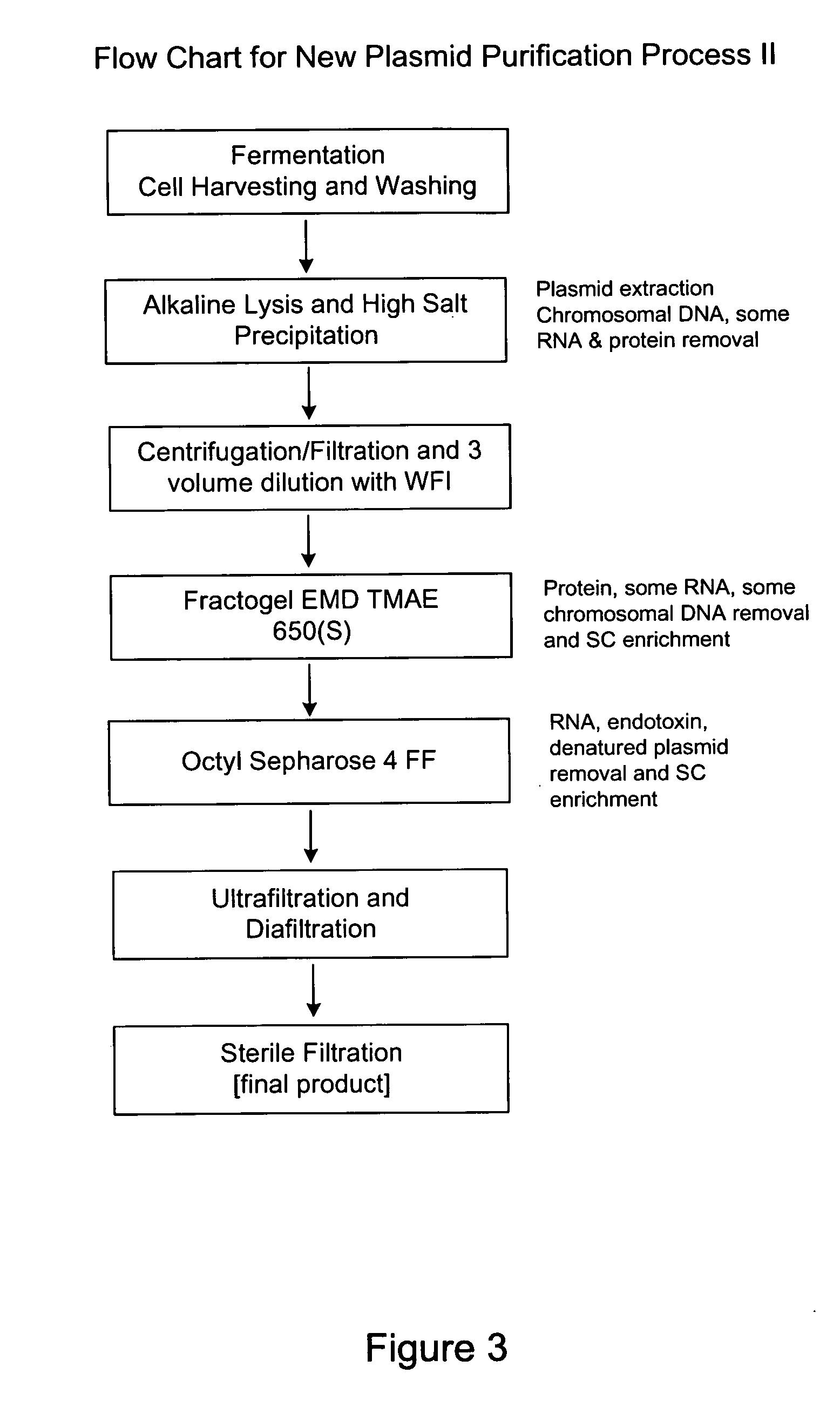
Process and equipment for plasmid purification
InactiveUS8236495B2Easy to operateConsistent levelCation exchanger materialsOrganic anion exchangersEscherichia coliLysis
A scalable alkaline lysis process, including procedures and devices for the isolation of large quantities (grams and kilograms) of plasmid DNA from recombinant E. coli cells. Effective, controllable, and economical operation, and consistent low level of host chromosomal DNA in the final plasmid product. Involves a series of new unit operations and devices for cell resuspension, cell lysis, and neutralization.
Owner:URIGEN PHARMA INC
Recovery of inorganic salt during processing of lignocellulosic feedstocks
ActiveUS20050244934A1Decreases acid requirementReduce inhibitionMagnesium fertilisersIon-exchanger regenerationCelluloseInorganic salts
A method for recovering inorganic salt during processing of a lignocellulosic feedstock is provided. The method comprises pretreating the lignocellulosic feedstock by adding an acid to the feedstock to produce a pretreated lignocellulosic feedstock. A soluble base is then added to the pretreated lignocellulosic feedstock to adjust the pH and produce a neutralized feedstock. The neutralized feedstock is then enzymatically hydrolyzed to produce an enzyme hydrolyzed feedstock and a sugar stream. Inorganic salt is recovered from either a stream obtained from the lignocellulosic feedstock prior to the step of pretreating, a stream obtained from the pretreated lignocellulosic feedstock, a stream obtained from the neutralized feedstock, a stream obtained from the sugar stream, or a combination of these streams. The inorganic salt may be concentrated, clarified, recovered and purified by crystallization, electrodialysis drying, or agglomeration and granulation, and then used as desired, for example as a fertilizer.
Owner:IOGEN ENERGY CORP
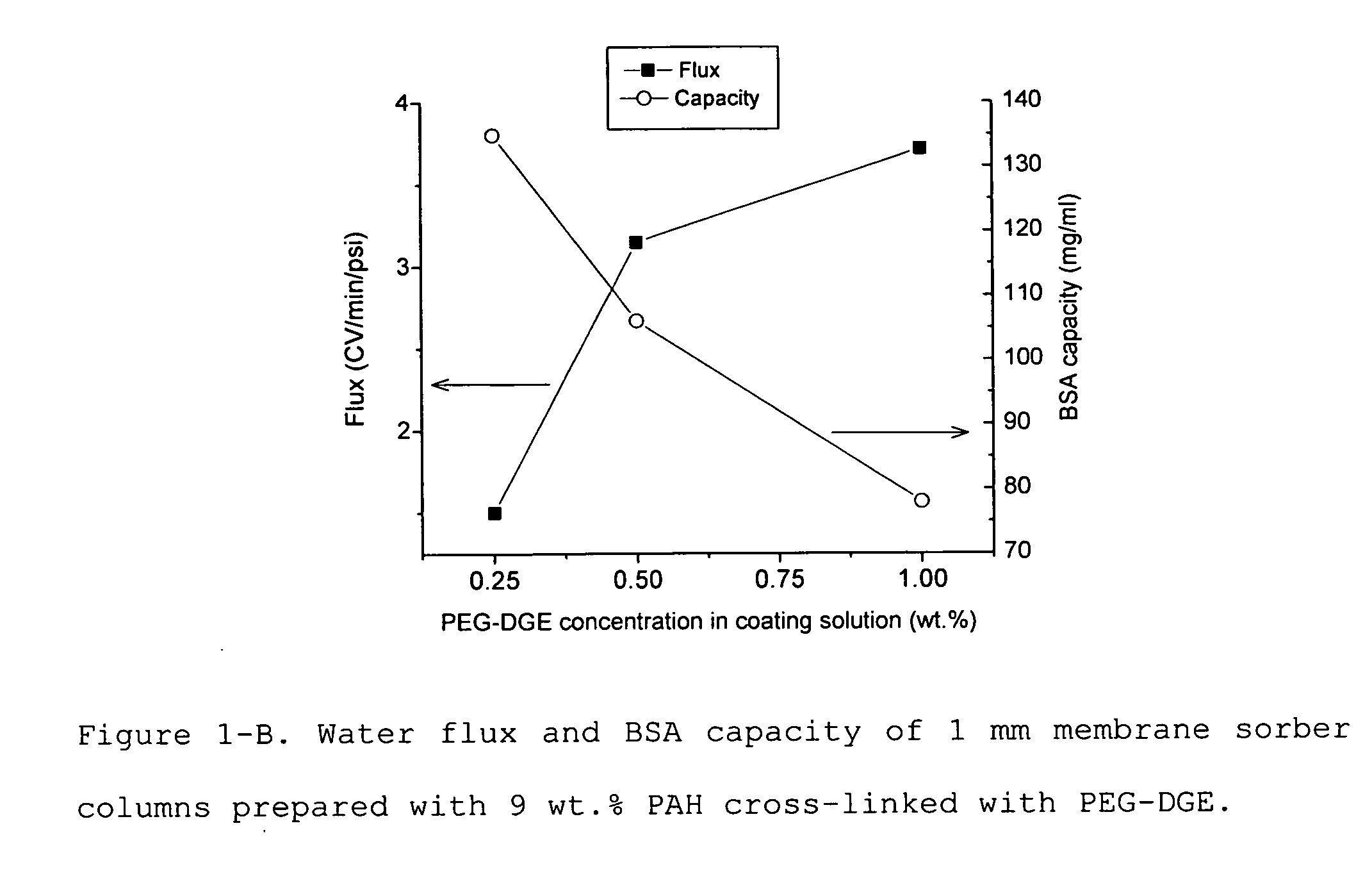
Positively charged membrane
The present invention provides a positively charged microporous membrane having a protein binding capacity of about 25 mg / ml or greater comprising a hydrophilic porous substrate and a crosslinked coating that provides a fixed positive charge to the membrane. The present invention further provides a positively charged microporous membrane comprising a porous substrate and a crosslinked coating comprising pendant cationic groups. The membranes of the present invention find use in a variety of applications including ion-exchange chromatography, macromolecular transfer, as well as detection, filtration and purification of biomolecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, endotoxins, and the like.
Owner:PALL CORP
Process and equipment for plasmid purfication
InactiveUS20060106208A1Easy to operateConsistent levelCation exchanger materialsIon-exchanger regenerationLysisGram
A scalable alkaline lysis process, including procedures and devices for the isolation of large quantities (grams and kilograms) of plasmid DNA from recombinant E. coli cells. Effective, controllable, and economical operation, and consistent low level of host chromosomal DNA in the final plasmid product. Involves a series of new unit operations and devices for cell resuspension, cell lysis, and neutralization.
Owner:URIGEN PHARMA INC
Amine-aldehyde resins and uses thereof in separation processes
InactiveUS20060151397A1Highly versatileEffective isolationWaste water treatment from quariesWaste water treatment from ceramic industriesParticulatesKaolin clay
Amine-aldehyde resins are disclosed for removing a wide variety of solids and / or ionic species from the liquids in which they are suspended and / or dissolved. These resins are especially useful as froth flotation depressants in the separation of bitumen from sand and / or clay or in the beneficiation of clay (e.g., kaolin clay) from an impure clay-containing ore. The resins are also useful for treating aqueous liquid suspensions to remove solid particulates, as well as for removing metallic ions in the purification of water.
Owner:INGEVITY SOUTH CAROLINA
Methods, system and devices for analyzing a biological fluid sample following ion exchange
Devices, methods and systems effective to evaluate a physical or chemical property of an ion exchange resin-treated biological fluid sample are provided.
Owner:CANTIMER
Fluid circuits for sorbent cartridge with sensors
ActiveUS20140190885A1Cation exchanger materialsOrganic anion exchangersSorbentMechanical engineering
A system for measuring at least one fluid characteristic at various stages within a sorbent system that has a sorbent cartridge that has at least one material layer and at least one fluid passageway in at least one location in the sorbent system to provide a diverted sample stream from the various stages. At least one fluid characteristic of the diverted sample stream is measured.
Owner:MOZARC MEDICAL US LLC
Chromatography method and a column material useful in said method
InactiveUS6884345B1Chromatographic cation exchangersCation exchanger materialsNatural sourceStationary phase
A novel sorbent suitable for use as a stationary phase in a chromatography column, the core of which consists of an organic polymer of synthetic or natural origin. Further, the carrier exhibits a plurality of covalently bonded non-aromatic zwitterionic groups on its surface. Additionally, the invention also relates to a method for purifying a particular biological macromolecule, such as a protein or a nucleic acid, by zwitterionic ion exchange chromatography as well as an ion exchange column suitable for use in the zwitterionic ion exchange chromatography.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Filter cartridge for fluid for treating surface of electronic device substrate
InactiveUS20070007196A1Suitable for useIon-exchange process apparatusMembranesHydrofluoric acidCompound (substance)
It is the purpose of the present invention to provide filter cartridges which can suitably be utilized in purifying chemical fluids for treating the surface of an electronic device substrate to be used in the semiconductor industry, particularly fluids containing a basic compound such as ammonia and an ammonium salt, or hydrofluoric acid (HF). The filter cartridges relating to the present invention which are used in removing metallic impurities contained in a chemical fluid for treating the surface of an electronic device substrate by treating the chemical fluid, is characterized by having a filter material incorporated therein, into which functional groups compatible with the existing morphology of the metallic impurities to be removed are incorporated in compliance with the constituents of the chemical fluid to be treated and the types of the metallic impurities to be removed.
Owner:EBARA CORP
Protein purification
InactiveUS20120065381A1Improve conductivityCation exchanger materialsOrganic anion exchangersIon chromatographyMulti pollutant
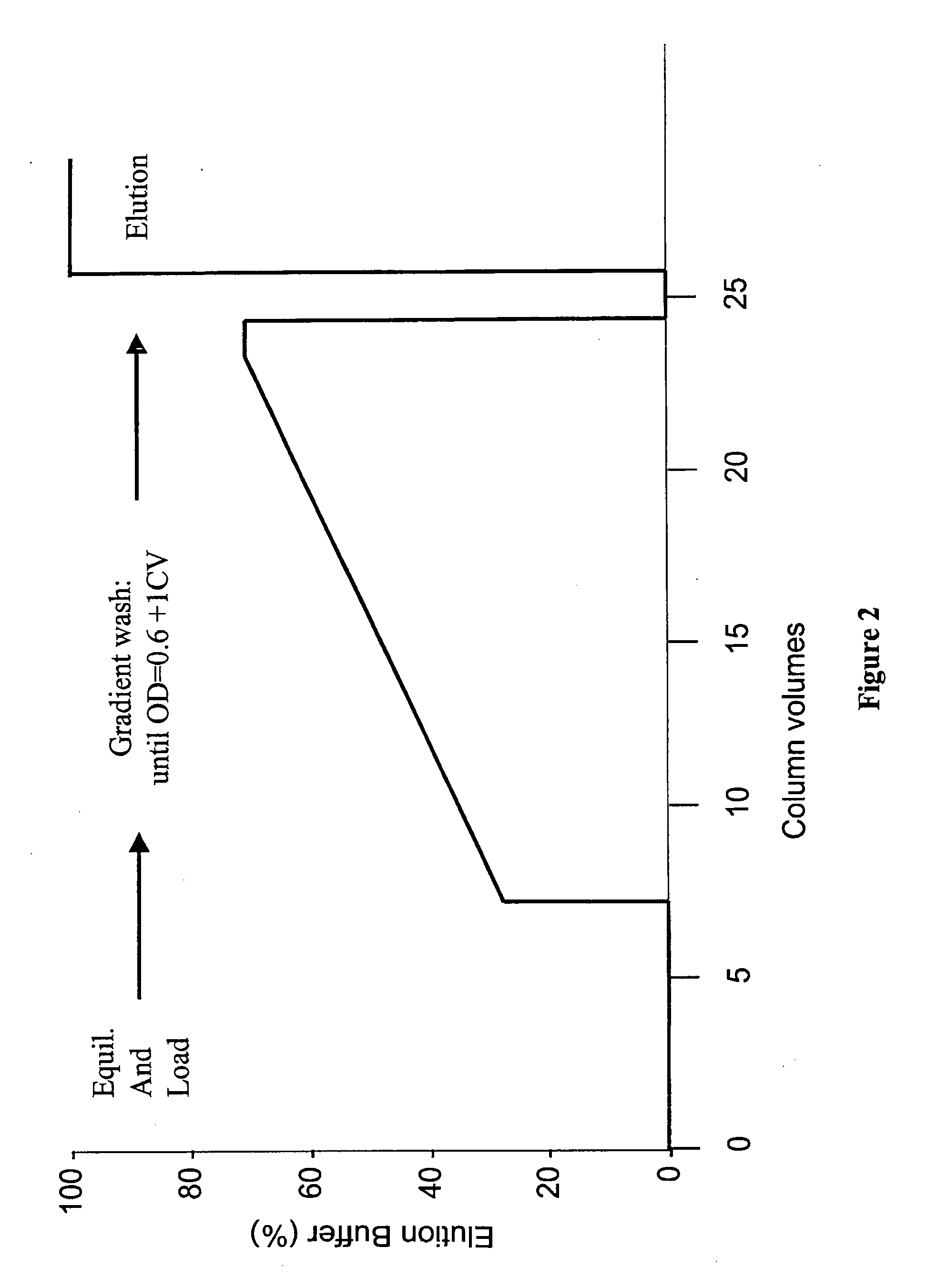
A method for purifying a polypeptide by ion exchange chromatography is described in which a gradient wash is used to resolve a polypeptide of interest from one or more contaminants.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
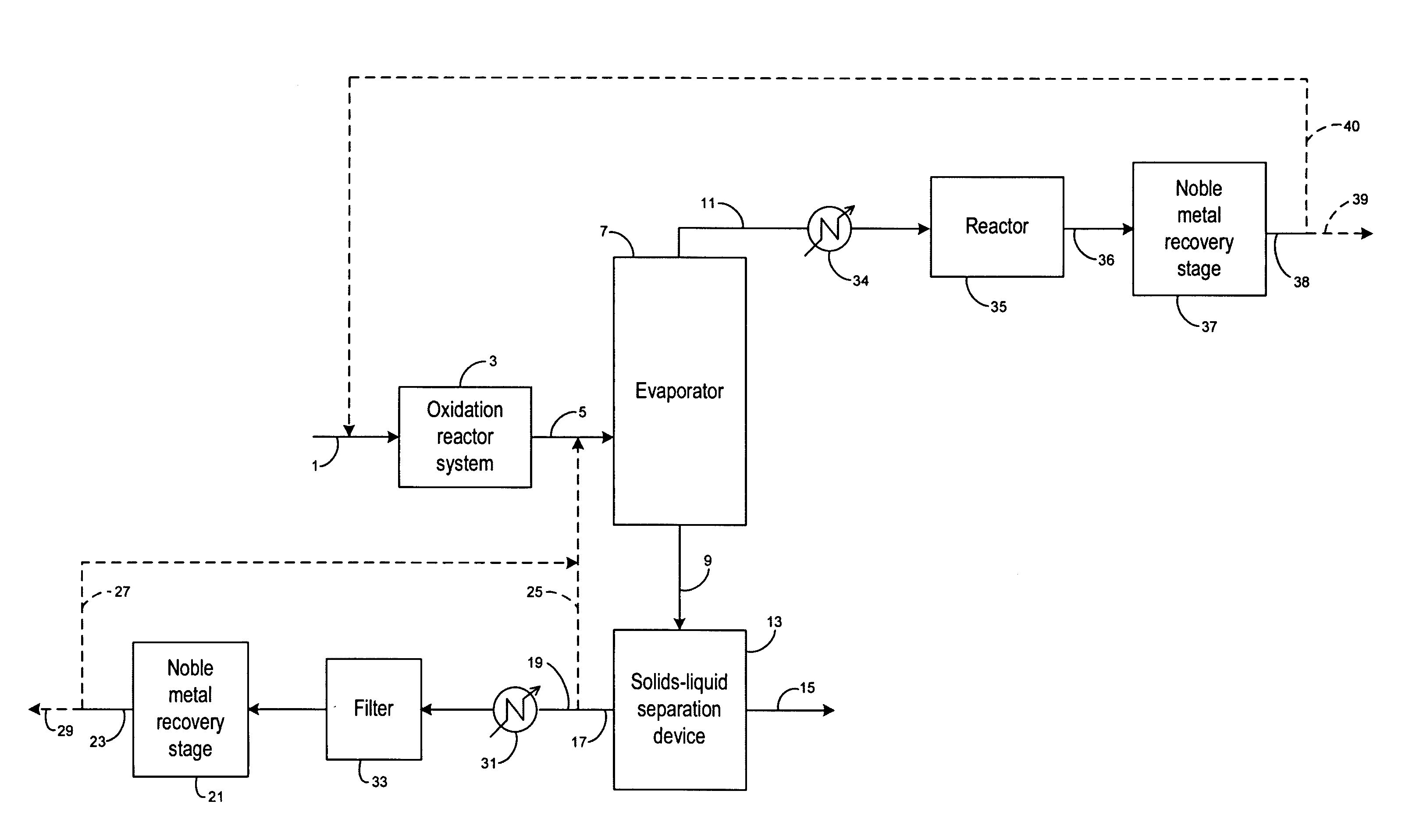
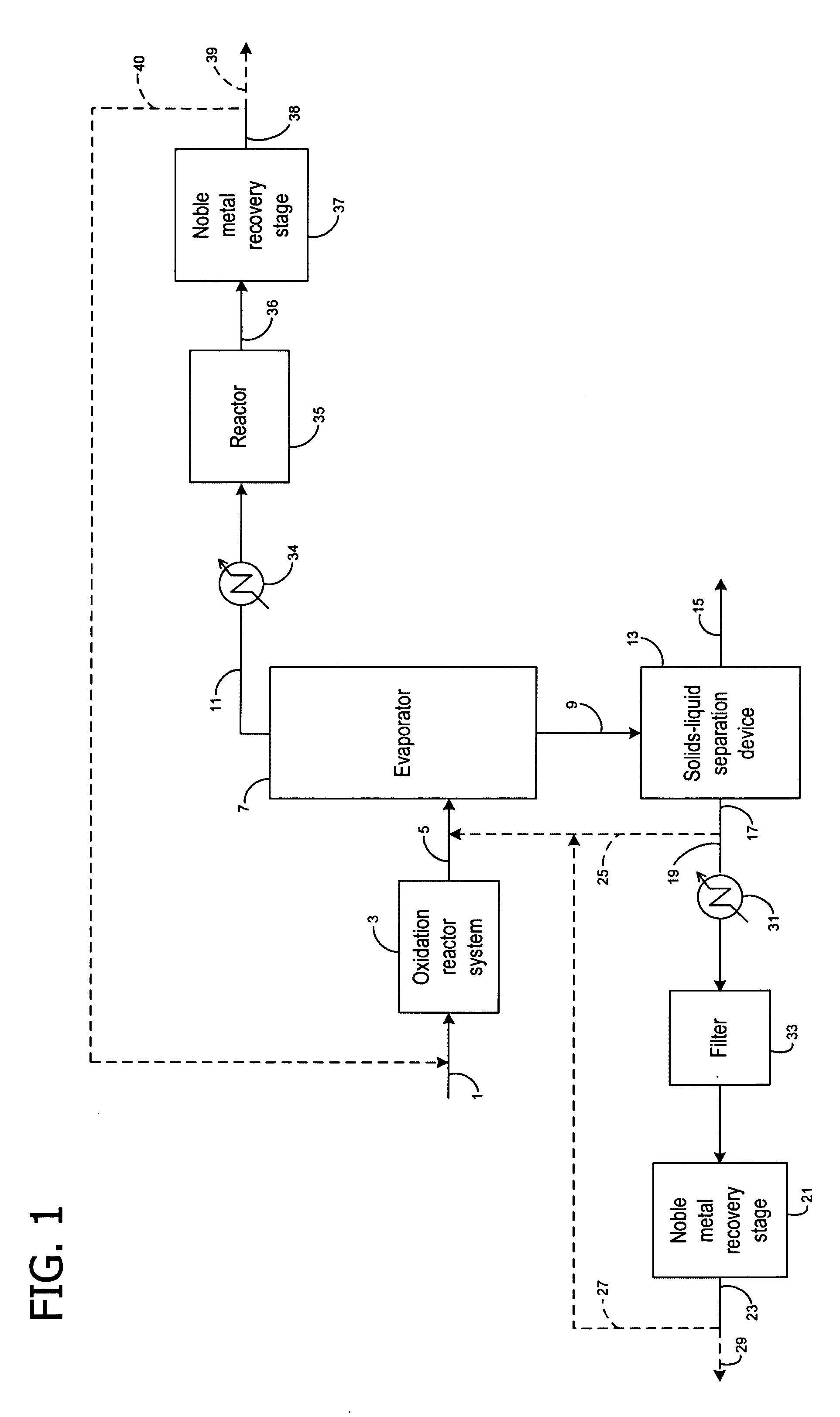
Recovery of noble metals from aqueous process streams
ActiveUS20060106248A1Reduce operating costsPhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic anion exchangersIon-exchange resinImidodiacetic acid
This invention generally relates to processes for recovering solubilized noble metals from aqueous process streams, in particular, aqueous process streams generated in the preparation of an N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine product, for example, by noble metal-catalyzed oxidation of an N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid substrate. The process includes contacting the aqueous process stream with a noble metal adsorption media such as an ion exchange resin to remove solubilized noble metal from the process stream.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Protein purification
ActiveUS8044017B2Improve conductivityPowder deliveryCation exchanger materialsIon chromatographyMulti pollutant
A method for purifying a polypeptide by ion exchange chromatography is described in which a gradient wash is used to resolve a polypeptide of interest from one or more contaminants.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Method of separating components in a sample using silane-treated silica filter media
The present invention provides methods for separating one or more components of interest from a sample containing particulates and soluble materials. The method comprises the steps of: (a) filtering a sample through silica filter media whose surface silanol groups have reacted with one or more silanes, and (b) simultaneously capturing particulates and binding a soluble component to the silica filter media. The bound soluble component of interest is subsequently eluted from the silica filter media. In one embodiment of the invention, unwanted soluble materials are captured by the treated silica filter media and desired component of interest is recovered from the flow-through. In another embodiment of the invention, different components of interest are recovered from both the eluate and the flow-through. Preferred treated silica filter media are silane-treated rice hull ash or diatomaceous earth with functional quaternary ammonium group or functional sulphonate group. Particulates suitable for the present invention, for example, are microorganisms.
Owner:DOW CORNING CORP
Preparing monomeric metal ion chelator containing diacetyl glycine group linked to proteinaceous molecule
A precursor for the construction of chelated metal conjugates which demonstrate improved assay performance and utility in minimizing non-specific binding while maintaining specificity for target molecules is disclosed. The precursor has tridentate functionality towards multivalent ions such as iron and nickel and contains a diacetyl glycine group covalently linked via an amide to a molecule such as a proteinaceous molecule providing a primary amide group for amide bond formation. The precursor is preferably prepared in monomeric form by reacting nitrilotriacetic acid or a salt thereof in an aqueous medium at an alkaline pH of at least 8 with a proteinaceous molecule containing a primary amine group in the presence of a carbodiimide. The proteinaceous molecule may be bovine serum albumin or an enzyme such as alkaline phosphatase or horseradish peroxidase.
Owner:PIERCE BIOTECHNOLOGY
Coated ion exchanged substrate and method of forming
ActiveUS7291395B2Promote formationEasy to synthesizeChromatographic cation exchangersLiquid surface applicatorsIon exchangeAminal
A method for making an ion exchange coating (e.g., a chromatographic medium) on a substrate comprising (a) reacting at least a first amine compound comprising amino groups, with at least a first polyfunctional compound, in the presence of a substrate to form a first condensation polymer reaction product, with a first unreacted excess of either at least said first amino group or polyfunctional compound functional moieties, irreversibly attached to the substrate, and (b) reacting at least a second amine compound or at least a second polyfunctional compound with unreacted excess in the first condensation polymer reaction product to form a second condensation polymer reaction product, and repeating the steps to produce the desired coating. A coated ion exchange substrate so made.
Owner:DIONEX CORP
Separation system and process
InactiveUS20040251204A1Cation exchanger materialsIon-exchanger regenerationIon-exchange resinSeparation system
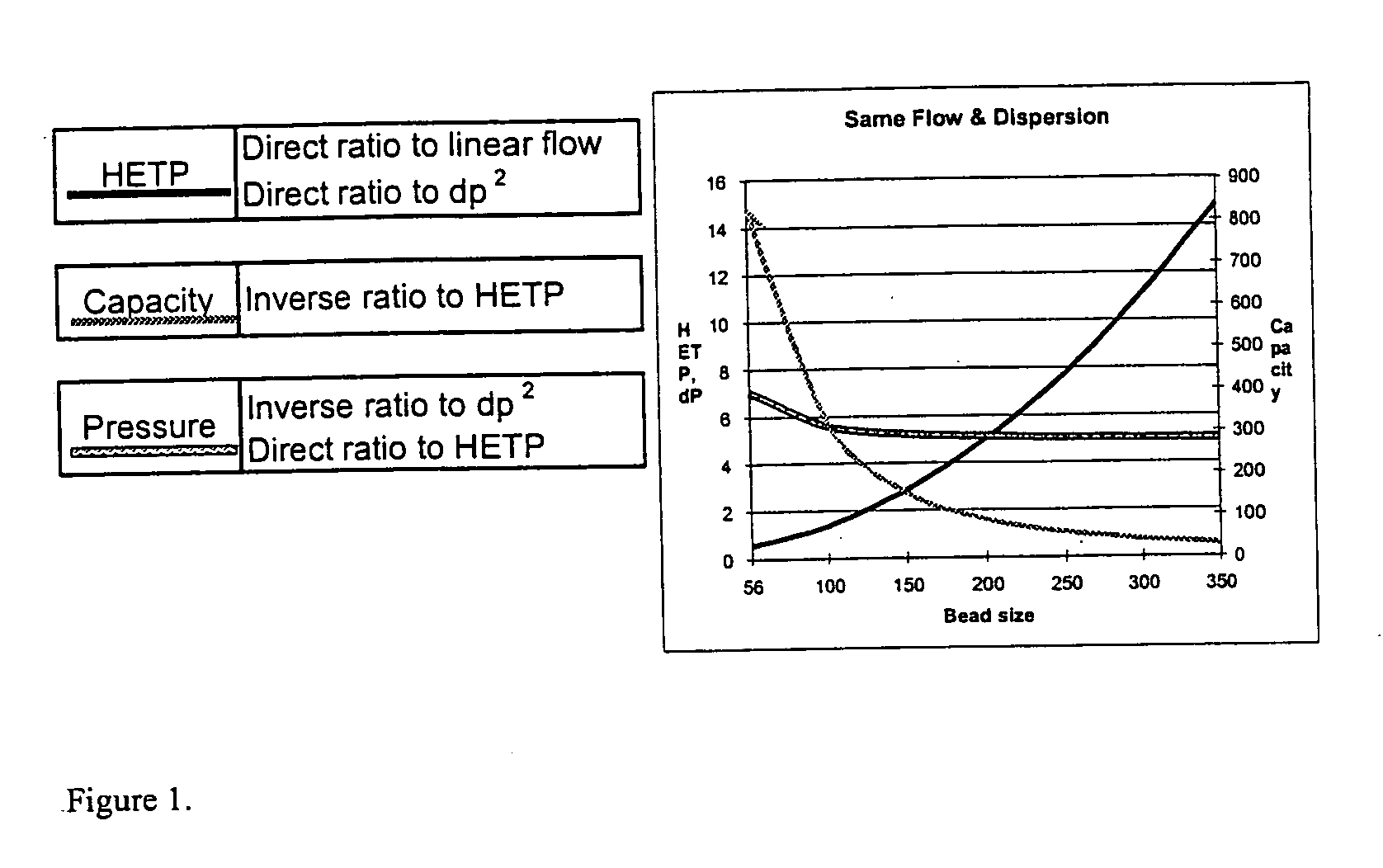
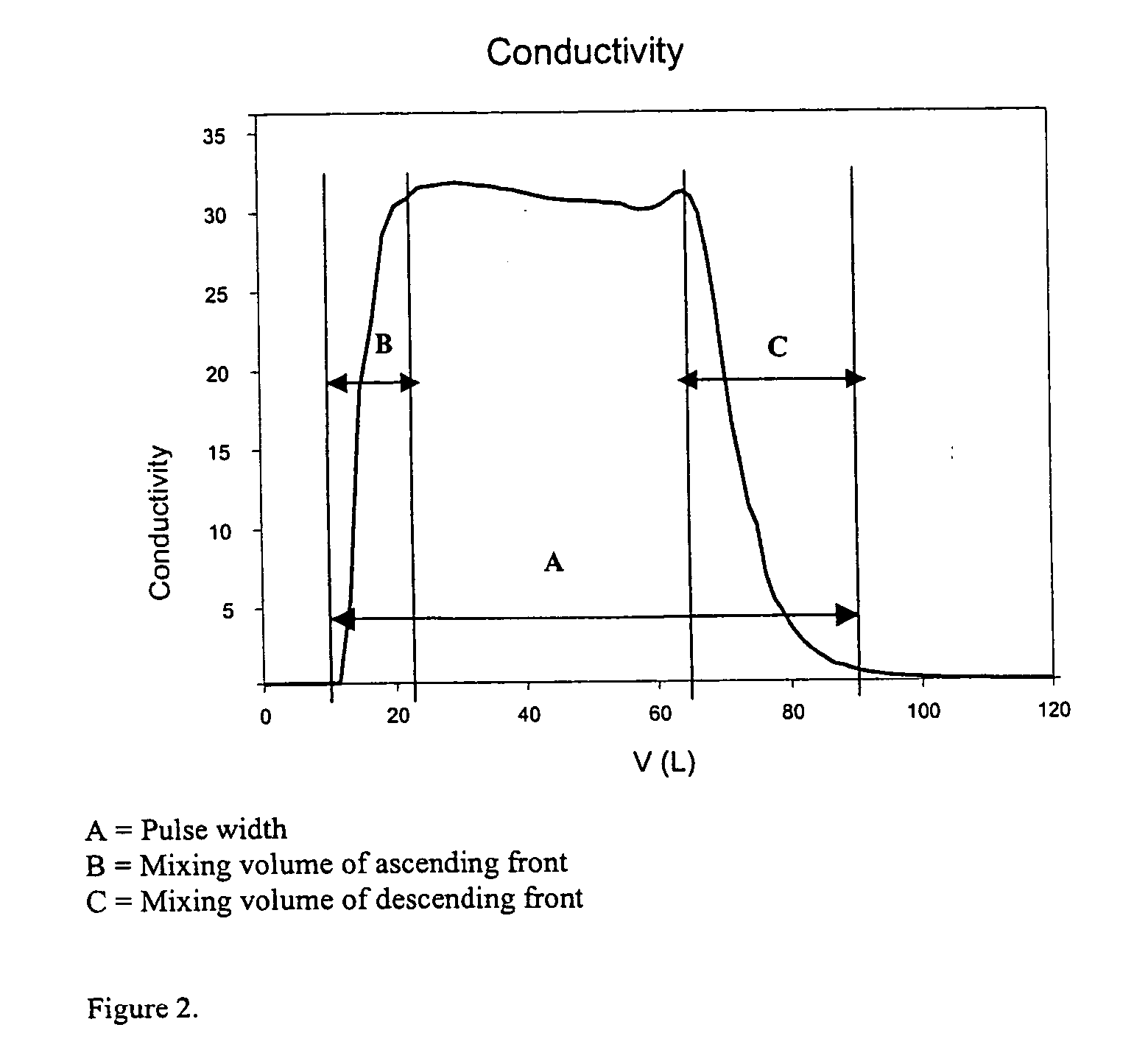
The invention relates to a system and a process for fractionating a solution into two or more fractions. The system of the invention comprises at least two compartments having a diameter of at least about one meter and including a uniform packing of a polymer-based ion exchange resin with a bead size in the range of about 50 to about 250 mum. The mixing volume of the fluid fronts in the system of the invention is not more than 5% of the volume of the compartment.
Owner:FINPHIDE
Separation of sugars, sugar alcohols, carbohydrates and mixtures thereof
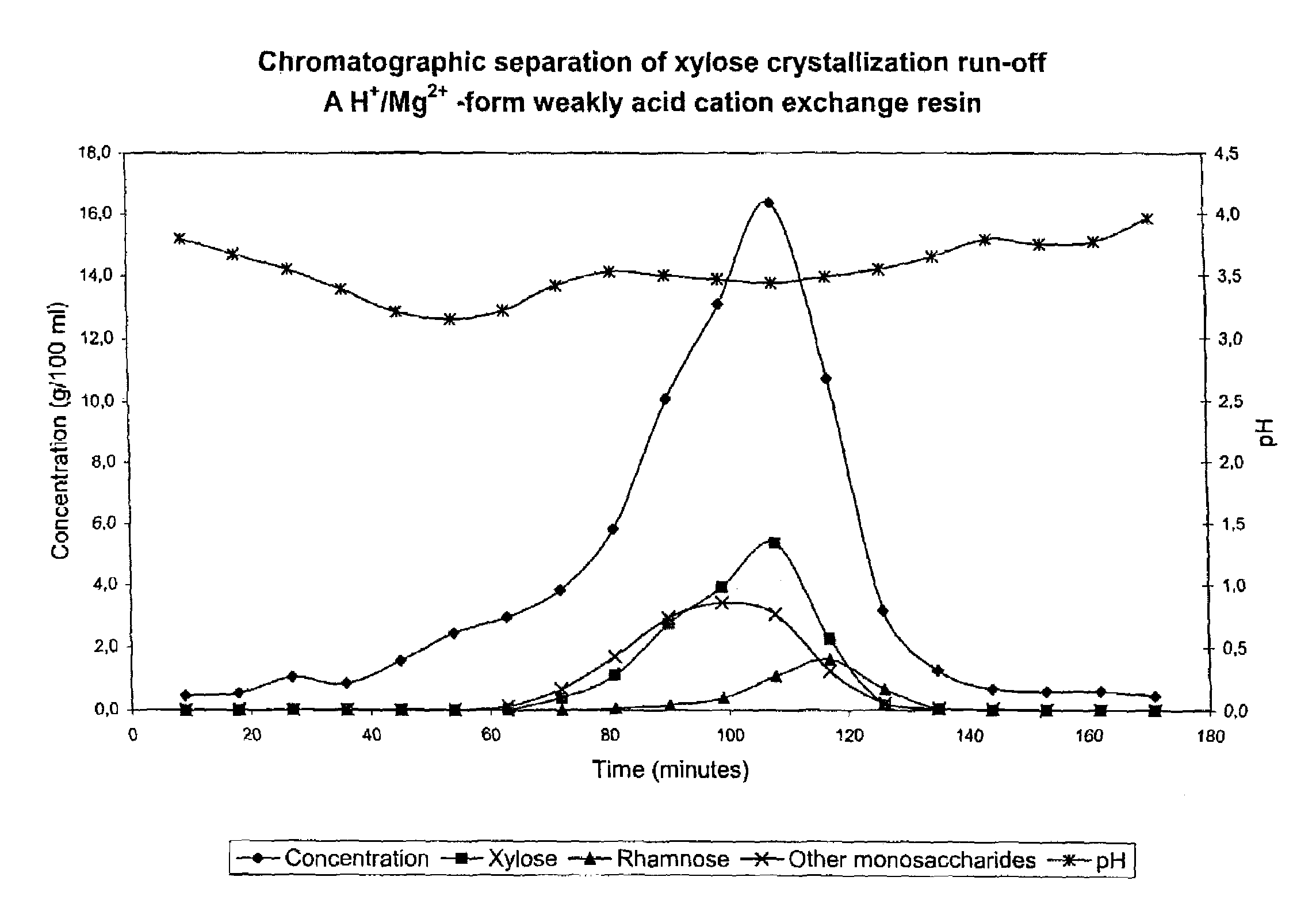
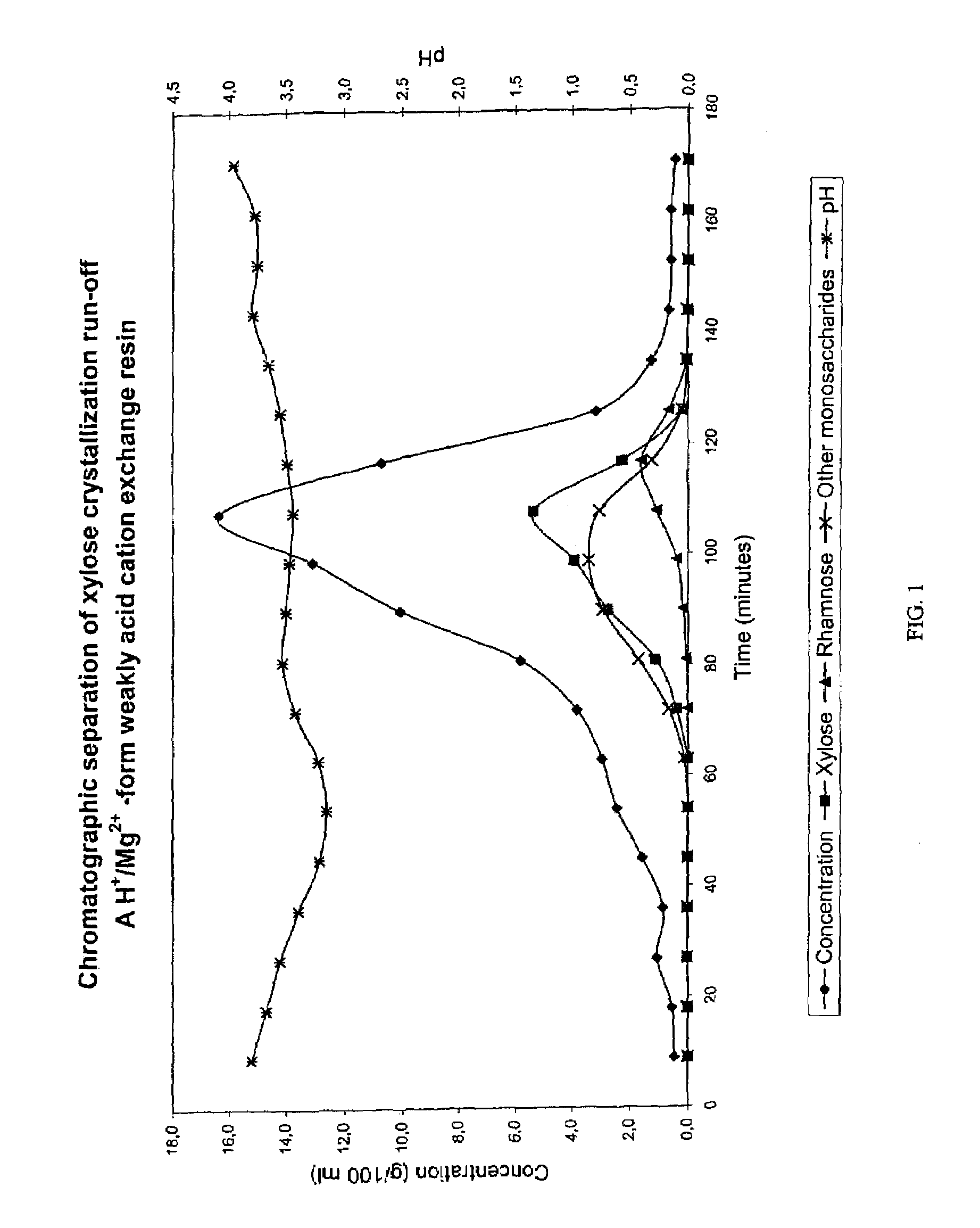
InactiveUS7361273B2Efficient separationCation exchanger materialsIon-exchanger regenerationChromatographic separationAlcohol sugars
The present invention relates to a method of separating sugars and sugar alcohols from each other. More particularly the present invention relates to the use of a weakly basic anion exchange resin in a chromatographic separation process. The advantage of the present invention compared with the prior art is that it is especially suitable for separating reducing sugars in acidic conditions as well as for example in weakly acidic conditions. The method using chromatographic separation comprises at least one step where a weakly basic anion exchange resin is used in a chromatographic column or in a part of a column.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
High purity chromatographic materials comprising an ionizable modifier
ActiveUS20130319086A1Enhancing pore geometryCation exchanger materialsComponent separationChromatographic separationChromatographic column
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
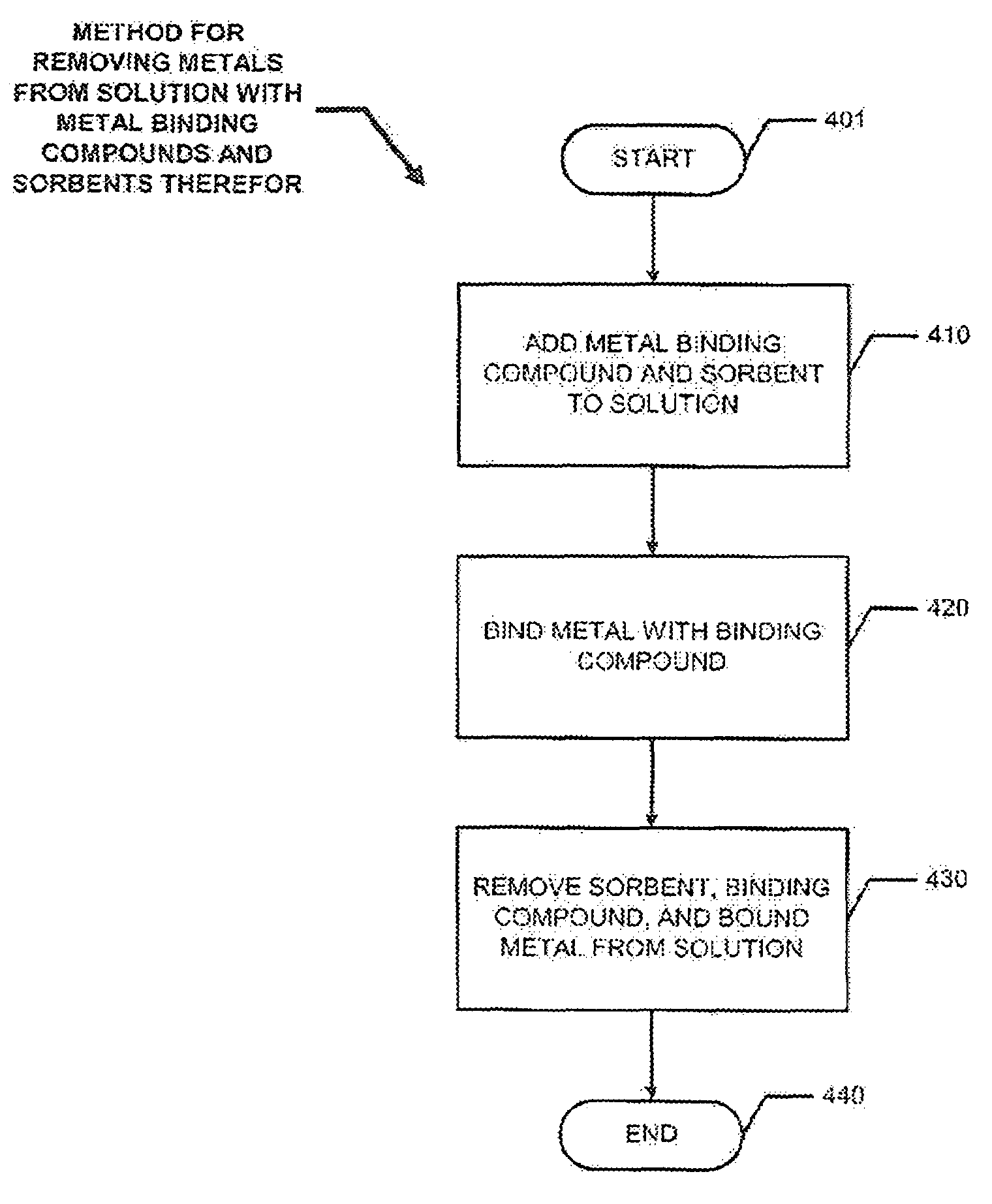
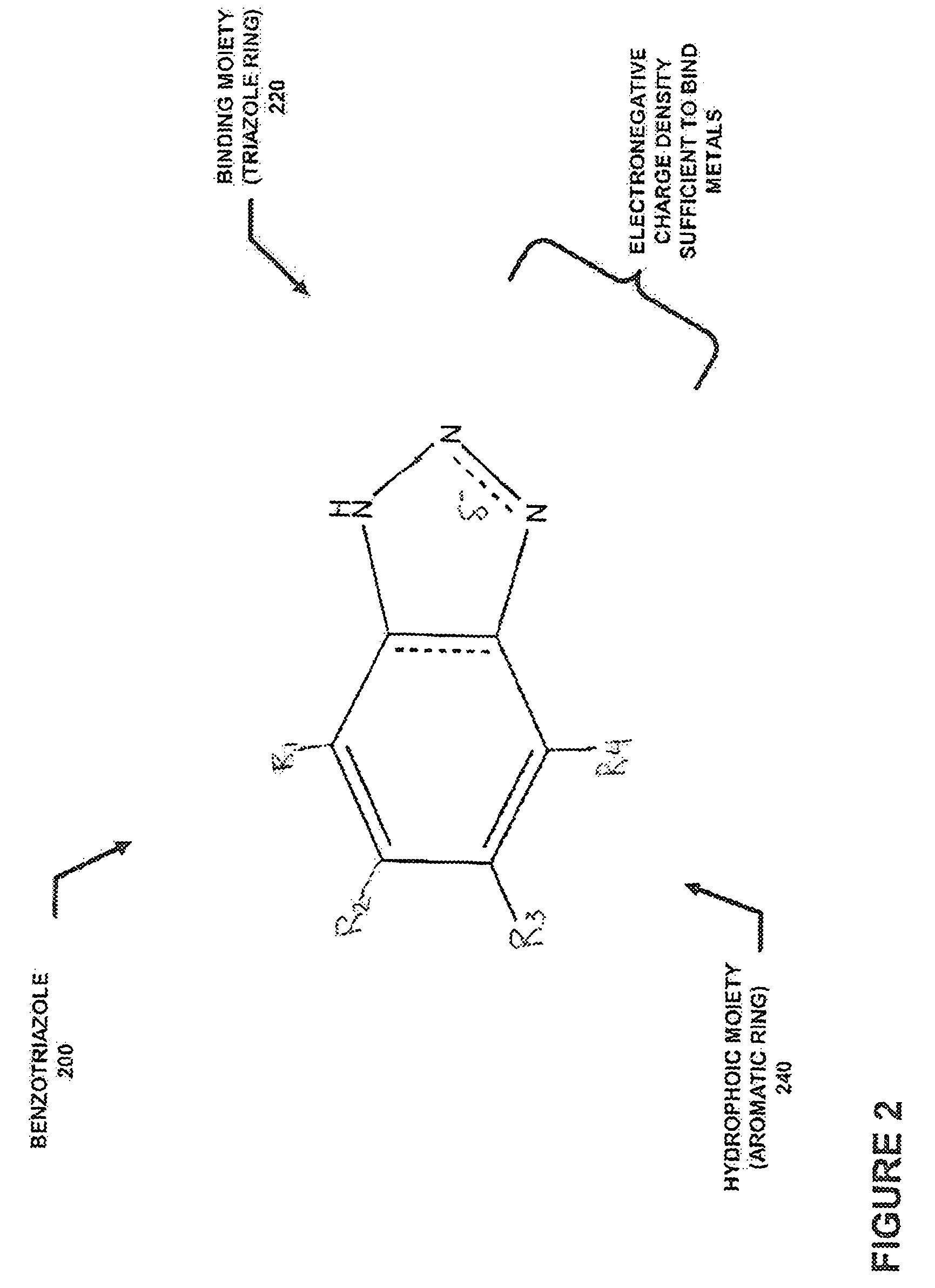
Removing metals from solution using metal binding compounds and sorbents therefor
ActiveUS7361279B2Reduce hydrophilicityWaste water treatment from quariesWater treatment parameter controlSorbentWastewater
Removing metals from metal containing acidic solutions, such as contaminated waters and industrial wastewaters, is described. An amphipathic, heterocyclic, metal-coordinating compound (an extraordinaiy ligand) and a sorbent are added to a solution, such that the addition, at a specific acidic pH of the solution, causes at least some of the metal-coordinating compound to bind with some of the metal cations and at least some of the metal-coordinating compound sorbs to the sorbent, along with any metal cations bound therewith. The compound and the sorbent may be added to the solution, either together or independently, so that the compound may bind the metal. The metal binding compound may be a benzotriazole, a benzothiazole, or another compound to bind a metal. The sorbent is selected to interact with the metal-coordinating compound in sequestering the metal from solution as part of a complexation. Thereafter, the ligand-metal complex may be removed from the solution.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com