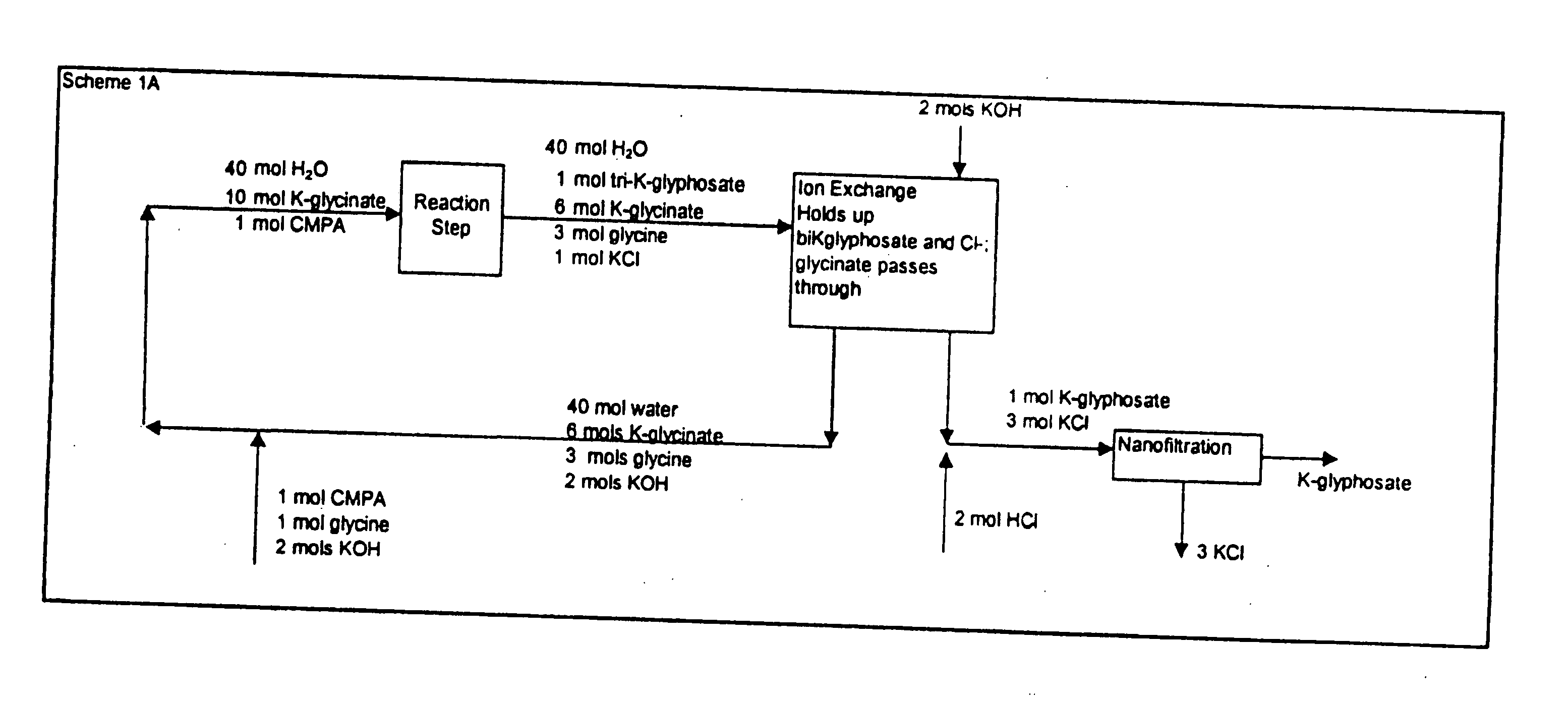
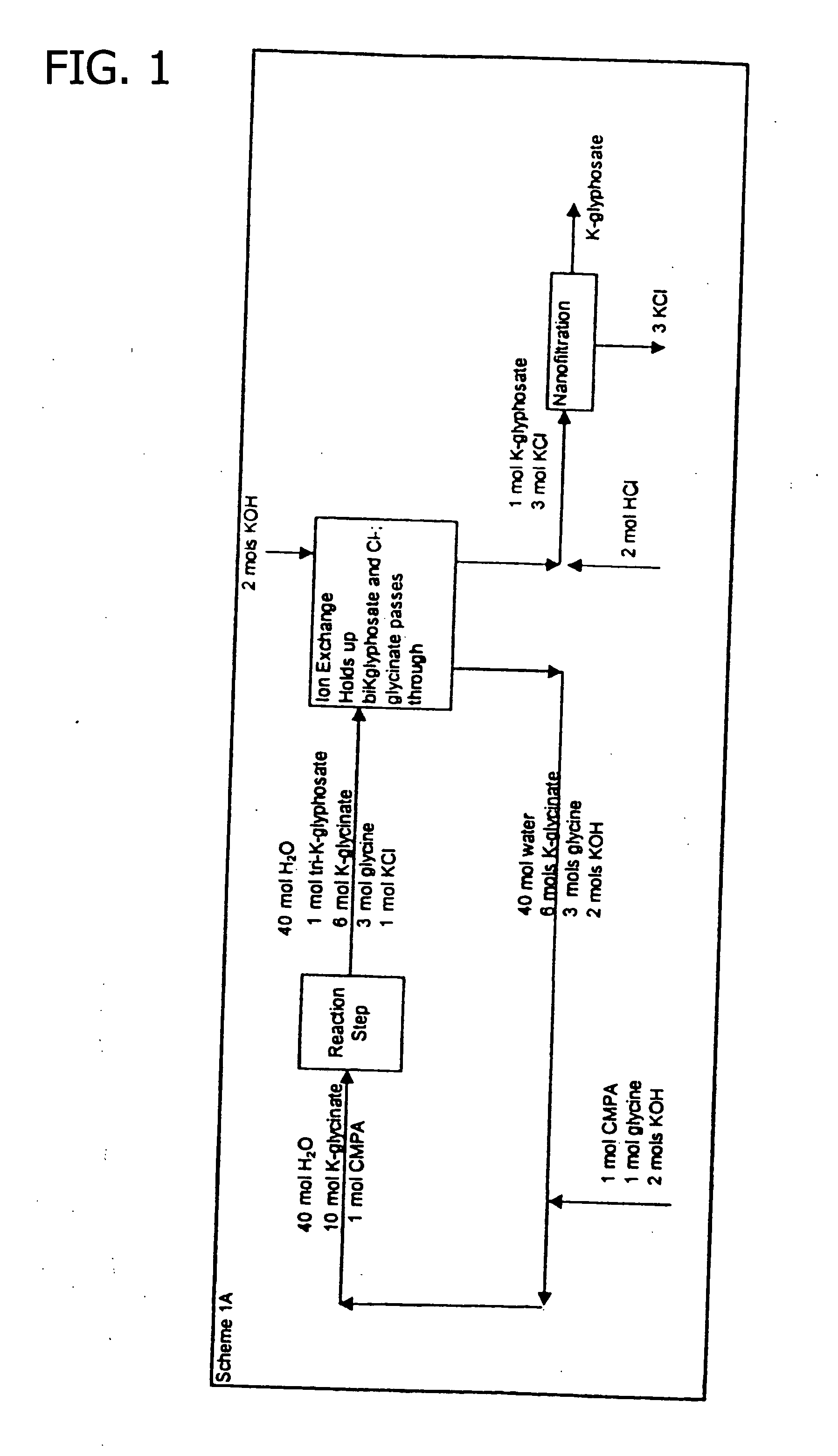
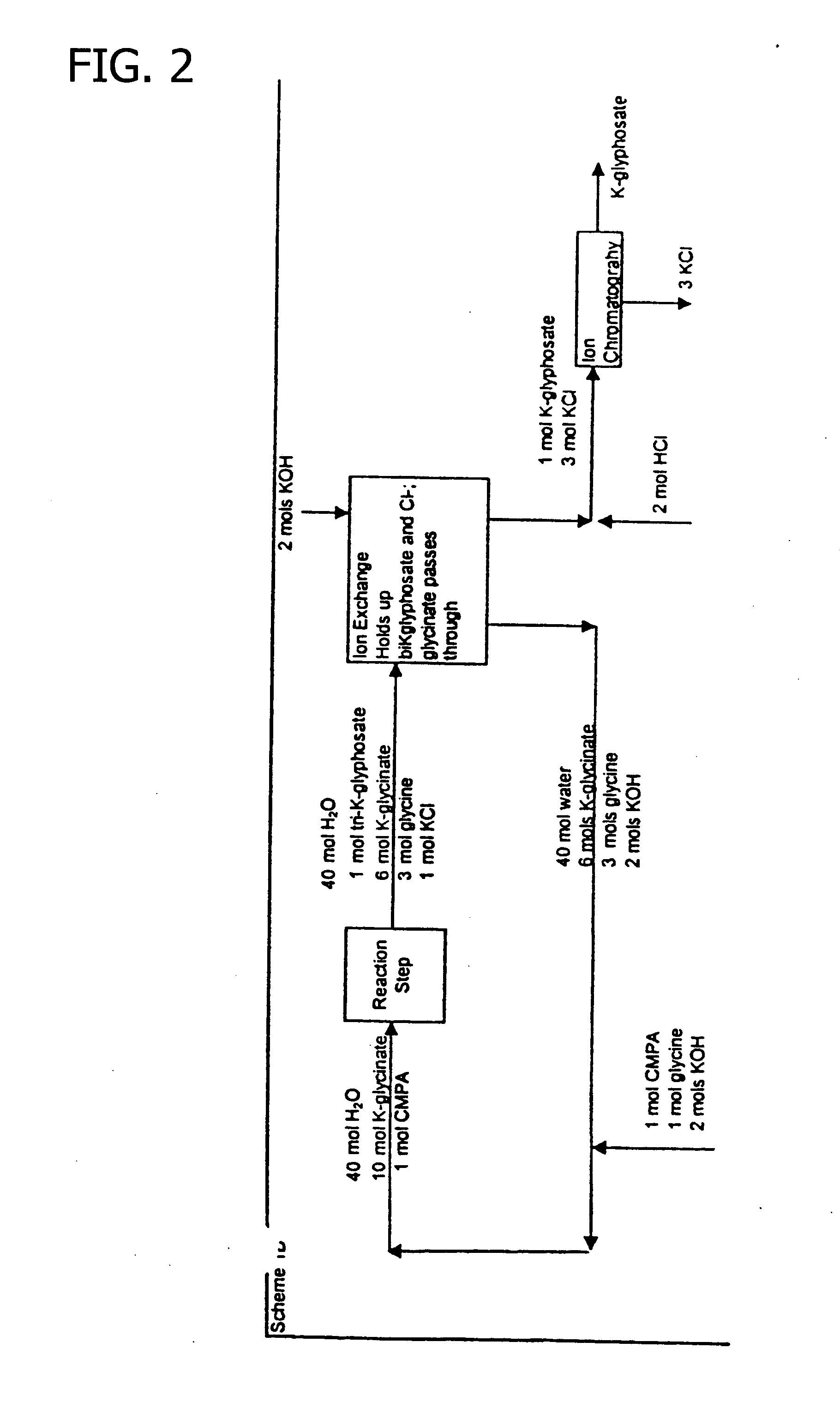
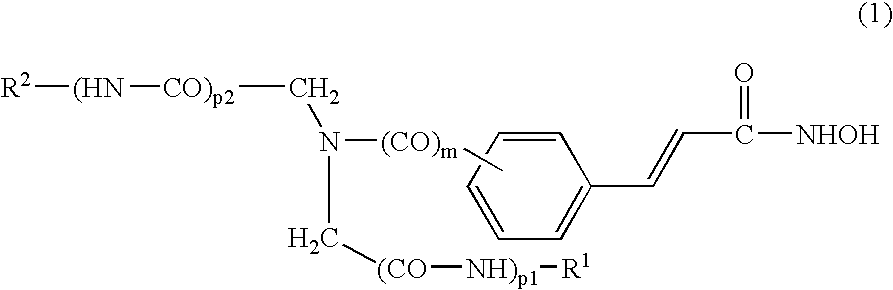
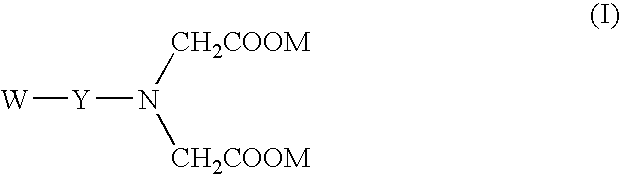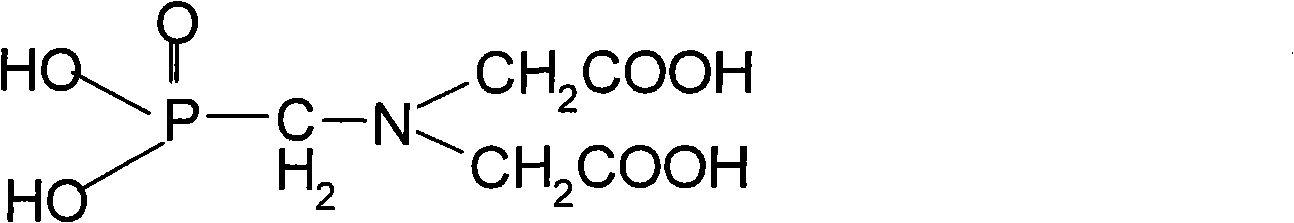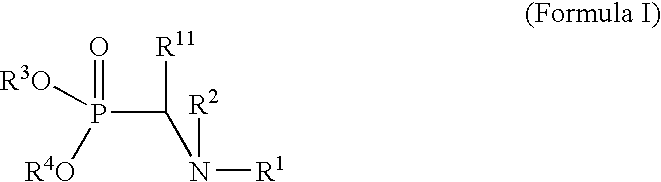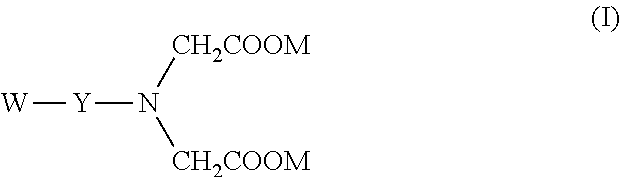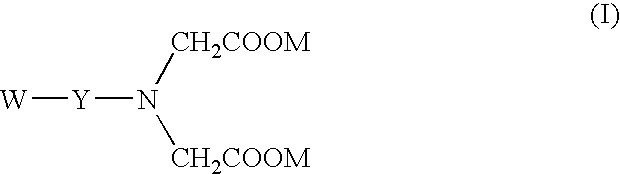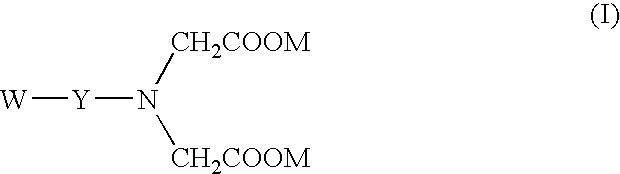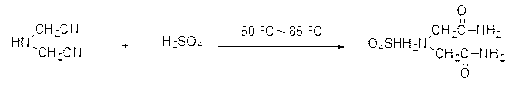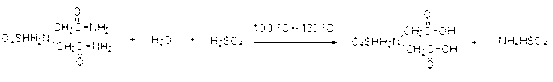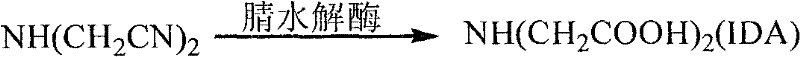Patents
Literature
252 results about "Imidodiacetic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
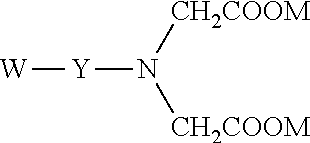
Iminodiacetic acid, HN(CH2CO2H)2, often abbreviated to IDA, is a dicarboxylic acid amine (the nitrogen atom forms a secondary amino group, not an imino group as the name suggests). The iminodiacetate anion can act as a tridentate ligand to form a metal complex with two, fused, five membered chelate rings.
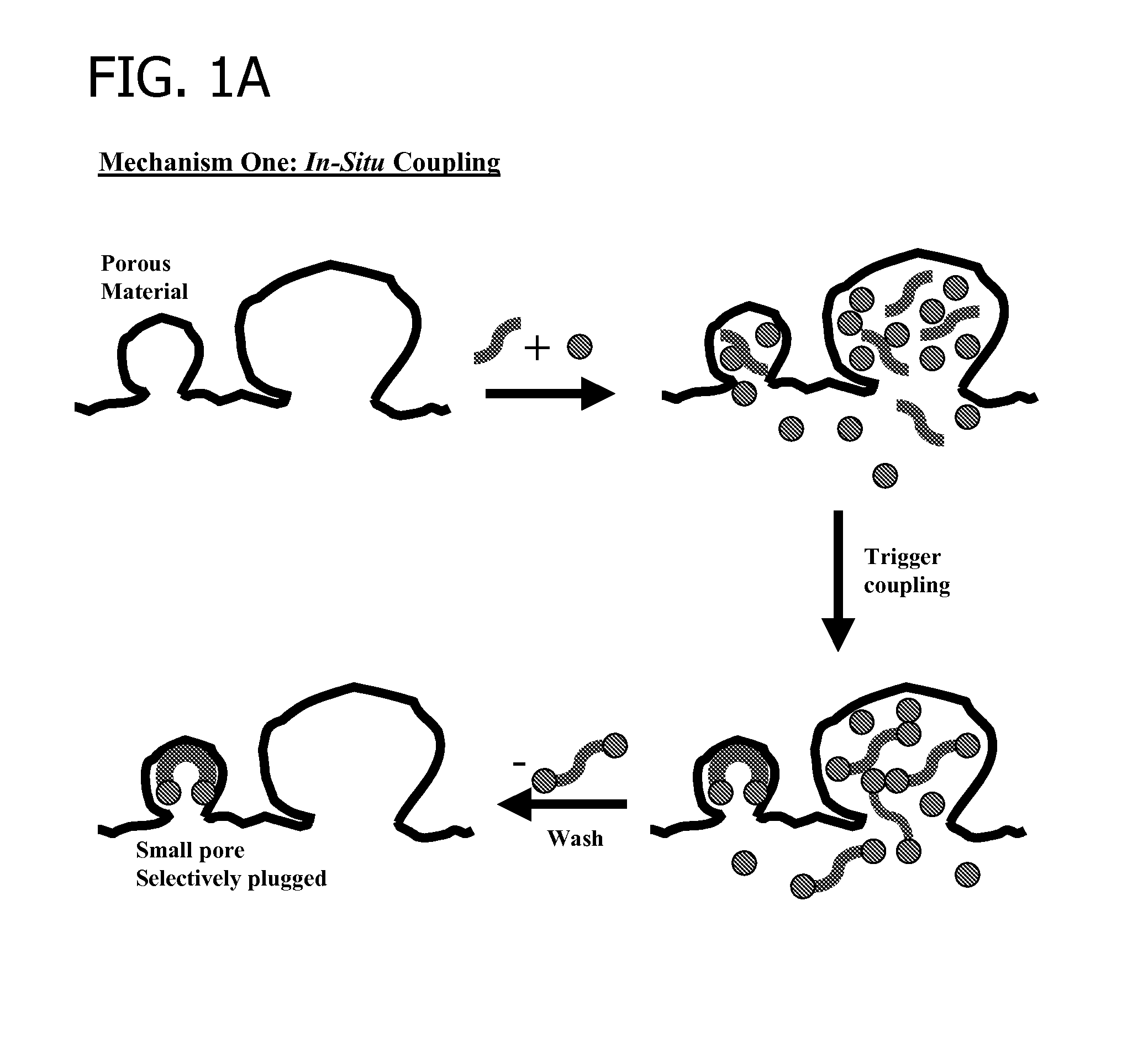
Breaker and displacement fluid and method of use
ActiveUS20080200354A1Sufficient hydrostatic controlEasy to placeFlushingDrilling compositionWater basedEmulsion
A method of cleaning a wellbore prior to the production of oil or gas is disclosed, wherein the wellbore has been drilled with an invert emulsion drilling mud that forms an invert emulsion filter cake. The method may include the steps of circulating a breaker fluid into the wellbore, where the breaker fluid includes an aqueous fluid, and imino diacetic acid or salt thereof. Optionally an acid buffering agent, and a weighting age are also included. The breaker fluid is formulated such that after a predetermined period of time and the filter cake present in the wellbore or on the wellbore face is substantially degraded. Other methods may also include drilling the wellbore with a water-based drilling mud that forms a water-based filter cake, wherein the method may include the steps of circulating a breaker fluid into the wellbore, where the breaker fluid may include an aqueous fluid, and an iminodiacetic acid or a salt thereof.
Owner:MI
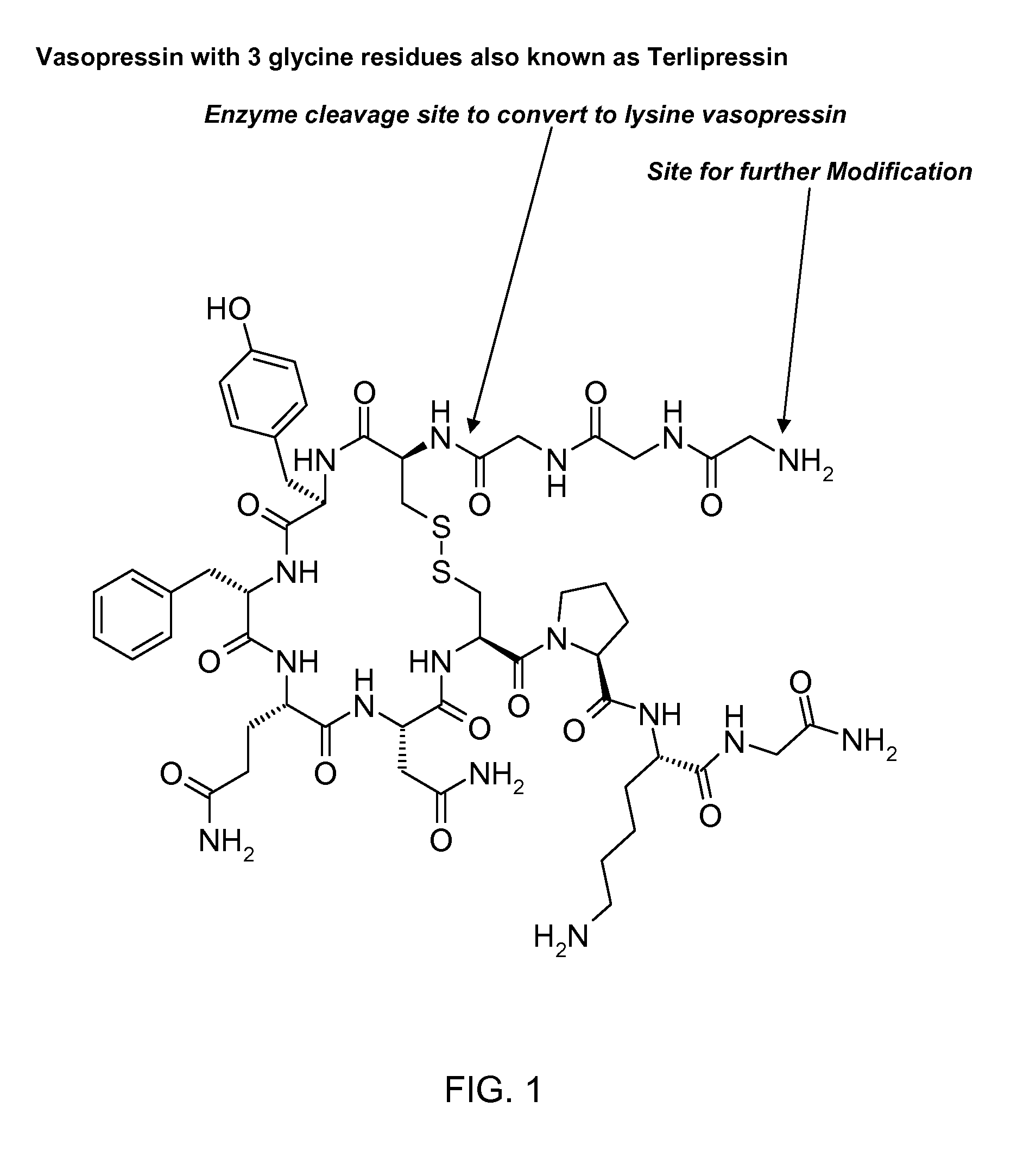
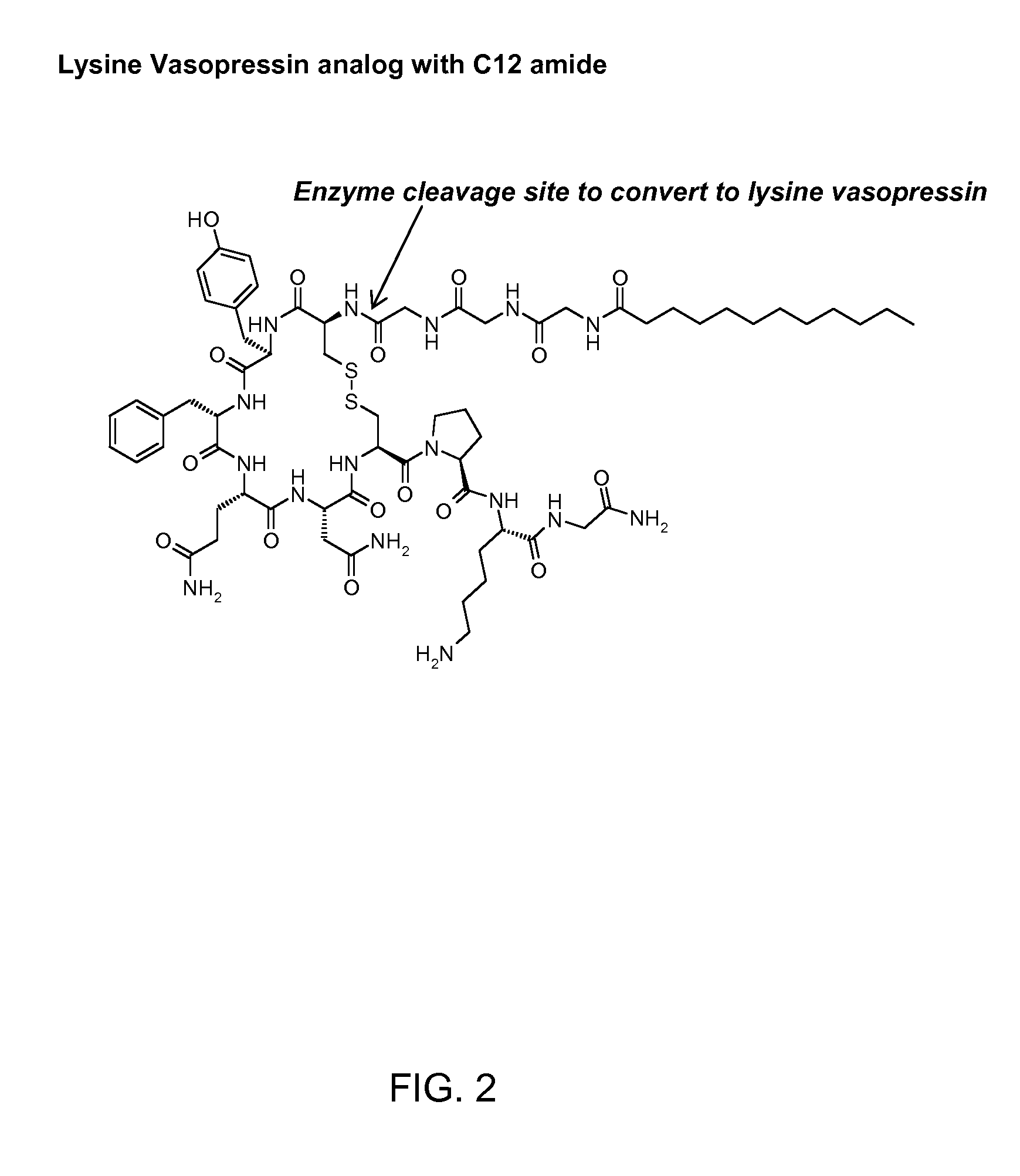
Composition for long-acting peptide analogs
ActiveUS20090088387A1Increase perfusionImprove the level ofAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsHalf-lifeArginine
The invention describes compositions of peptide analogs that are active in blood or cleavable in blood to release an active peptide. The peptide analogs have a general formula: A-(Cm)x-Peptide, wherein A is hydrophobic moiety or a metal binding moiety, e.g., a chemical group or moiety containing 1) an alkyl group having 6 to 36 carbon units, 2) a nitrilotriacetic acid group, 3) an imidodiacetic acid group, or 4) a moiety of formula (ZyHisw)p, wherein Z is any amino acid residue other than histidine, His is histidine, y is an integer from 0-6; w is an integer from 1-6; and p is an integer from 1-6; wherein if A has alkyl group with 6 to 36 carbon units x is greater than 0; and Cm is a cleavable moiety consisting of glycine or alanine or lysine or arginine or N-Arginine or N-lysine, wherein x is an integer between 0-6 and N may be any amino acid or none. The peptide analogs are complexed with polymeric carrier to provide enhanced half-life.
Owner:PHARMAIN CORP
Cleaning Composition
ActiveUS20090281017A1Improve abilitiesGood removal effectOrganic detergent compounding agentsNon-surface-active detergent compositionsIminodiacetic acidGlycine
The invention relates to compositions and methods for cleaning integrated circuit substrates. The compositions are in the form of an aqueous solution and include a quaternary ammonium hydroxide compound and a chelating compound. The chelating compound includes either boric acid or at least one N-substituted aminocarboxylate selected from the group consisting of N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)glycine(bicine), N-tris(hydroxymethyl)methyl glycine (tricine) and mixtures thereof, and can optionally include glycine, Iminodiacetic acid (IDA), Nitrilo trizacetic acid (NTA), Ethylenediammine Tetraacetic acid (EDTA), or mixtures thereof.
Owner:EKC TECH
Comprehensive processing method of N-phosphonomethyliminodiacelic acid mother liquor
ActiveCN101348266AHigh degree of automationReduce energy consumptionElectrolysis componentsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsElectrolysisFiltration
The invention relates to a process for comprehensively treating a mother liquor containing sodium chloride, obtained by the synthesis of an IDA line n-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid. The treated sodium chloride meet the quality requirement for producing caustic soda by electrolysis, in particular, the concrete treatment steps comprises: an n-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid, an n-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid homolog and a dense liquid richly concentrated on the inner side of the film of the sodium filtration film condensed mother liquor are used to recover the n-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid, and coarse sodium chloride is obtained by the dehydration crystallization of a weak liquor; the coarse sodium chloride is treated to obtain refined sodium chloride which can be directly used for producing caustic soda by electrolysis. By the comprehensive treatment method of the invention, the n-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid of the n-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid mother liquor can be effectively recovered, the by-product sodium chloride in the waste water can be fully utilized, thereby thoroughly meeting the requirements on economy, energy conservation and environmental protection.
Owner:JIANGSU YANGNONG CHEM +1
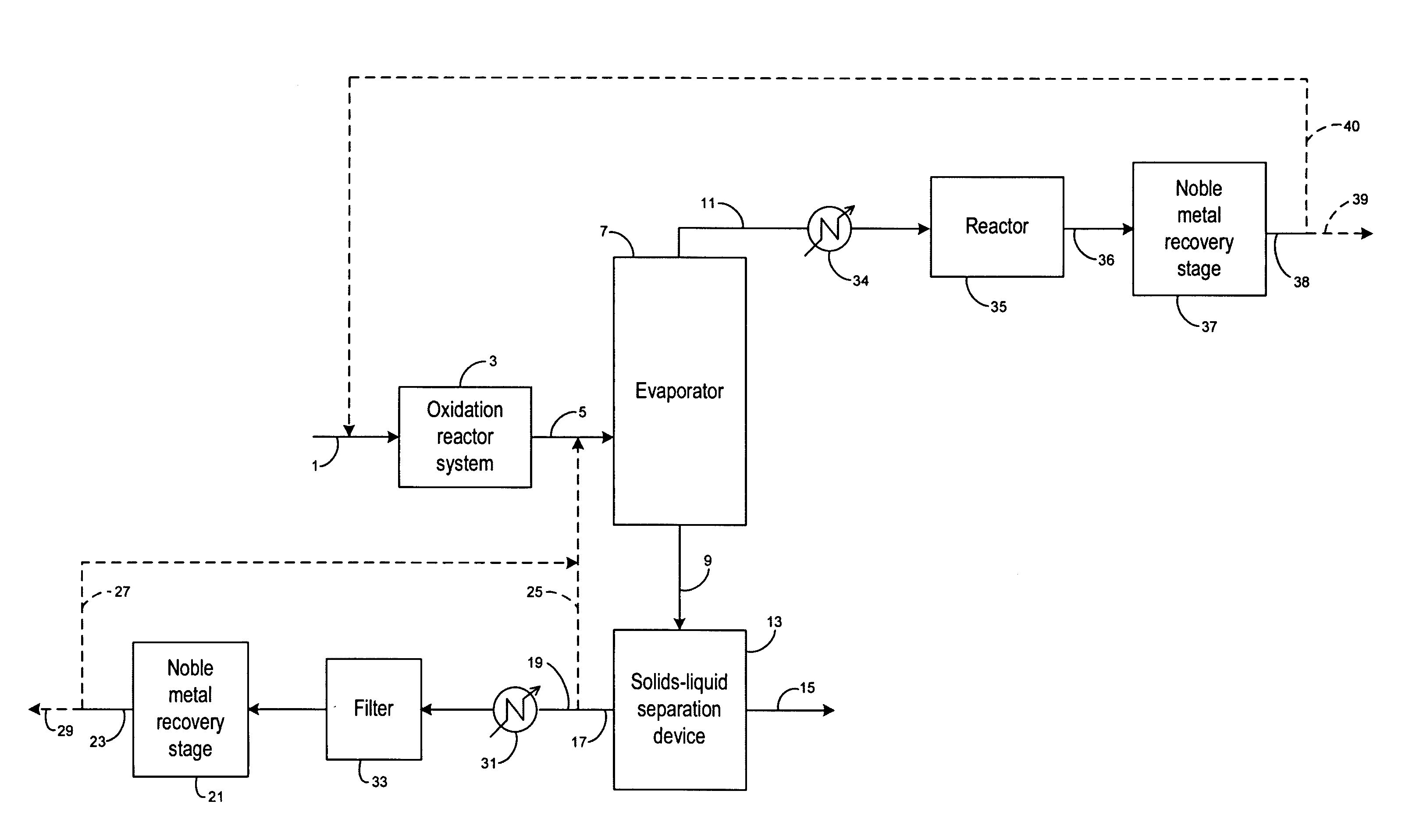
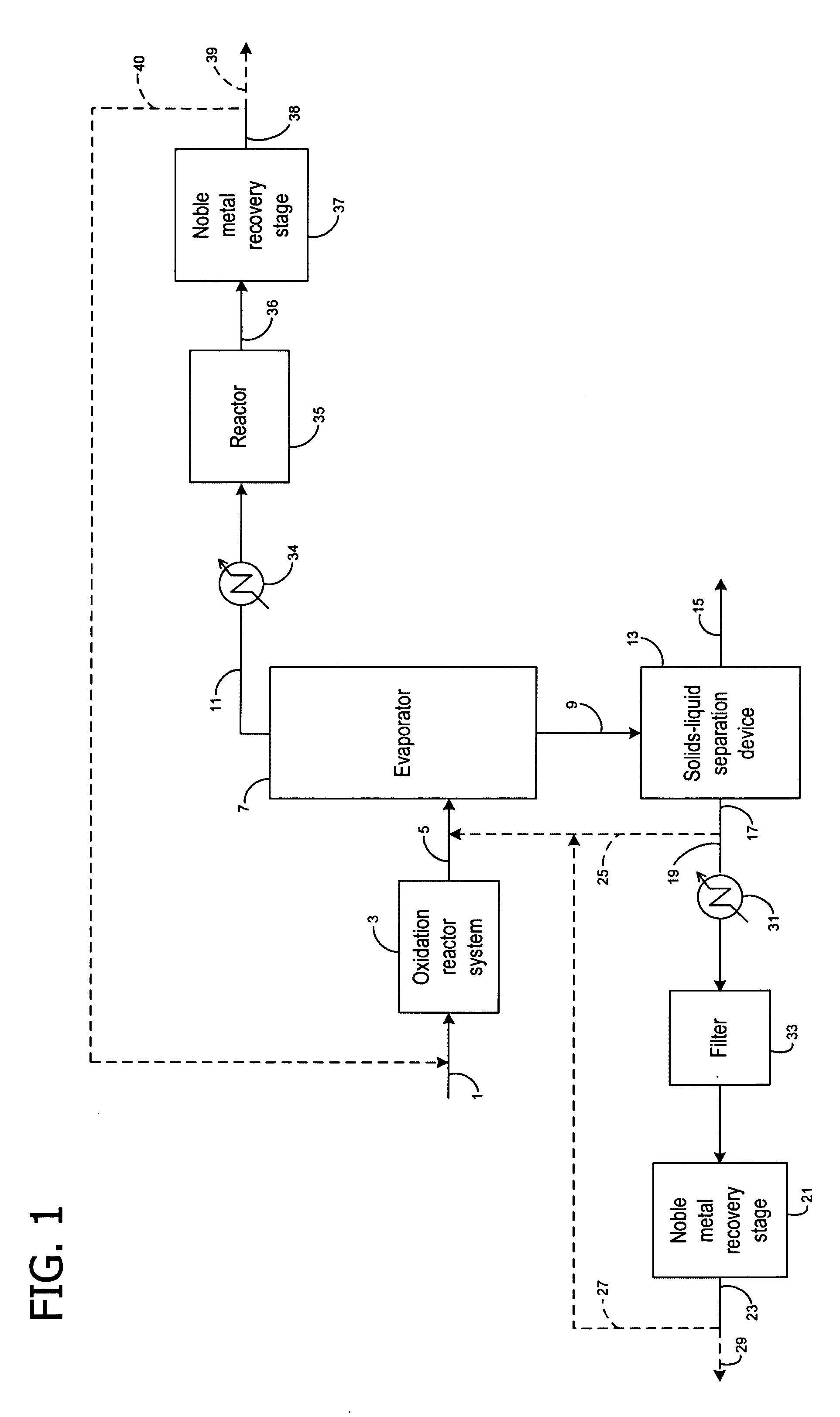
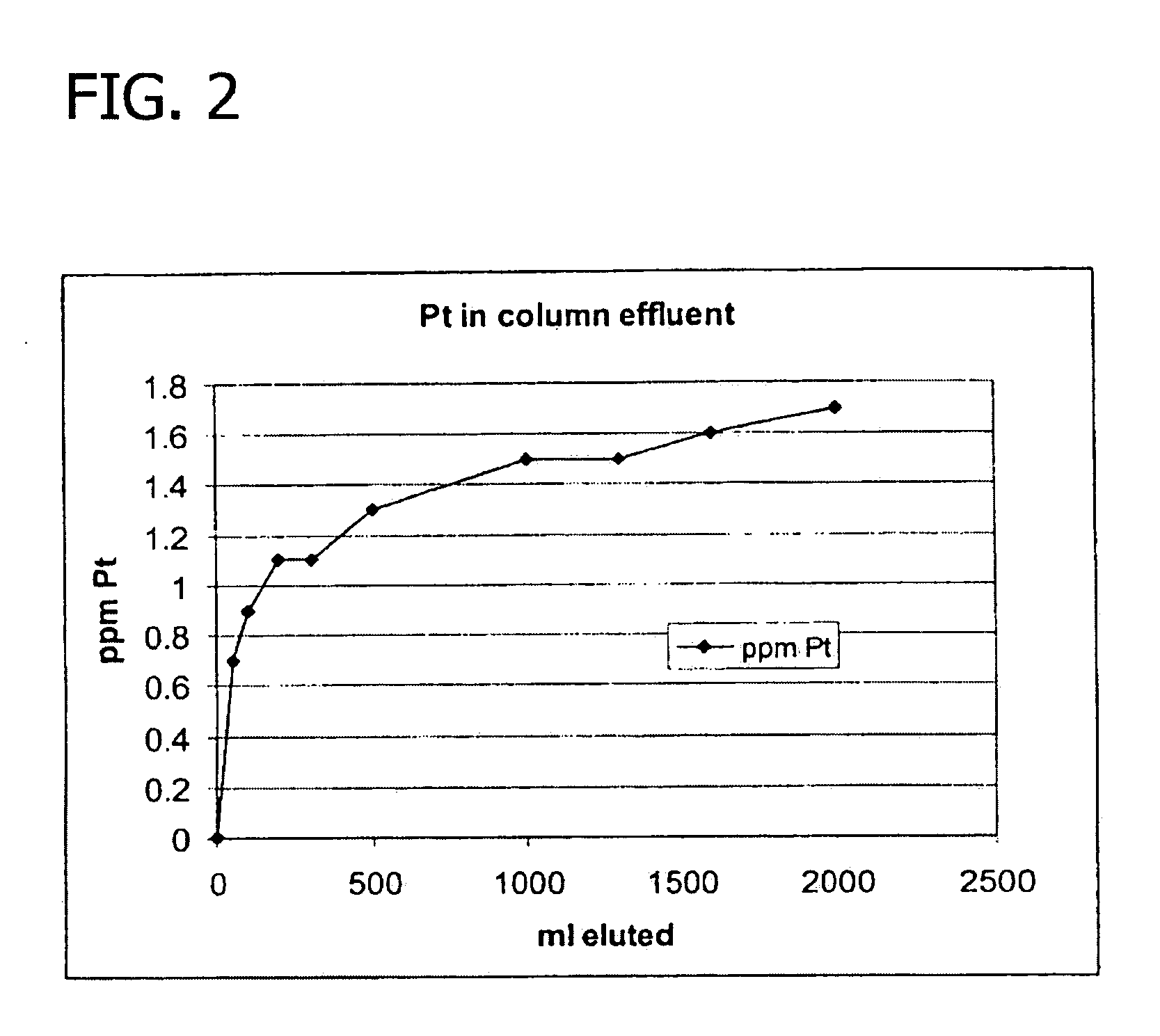
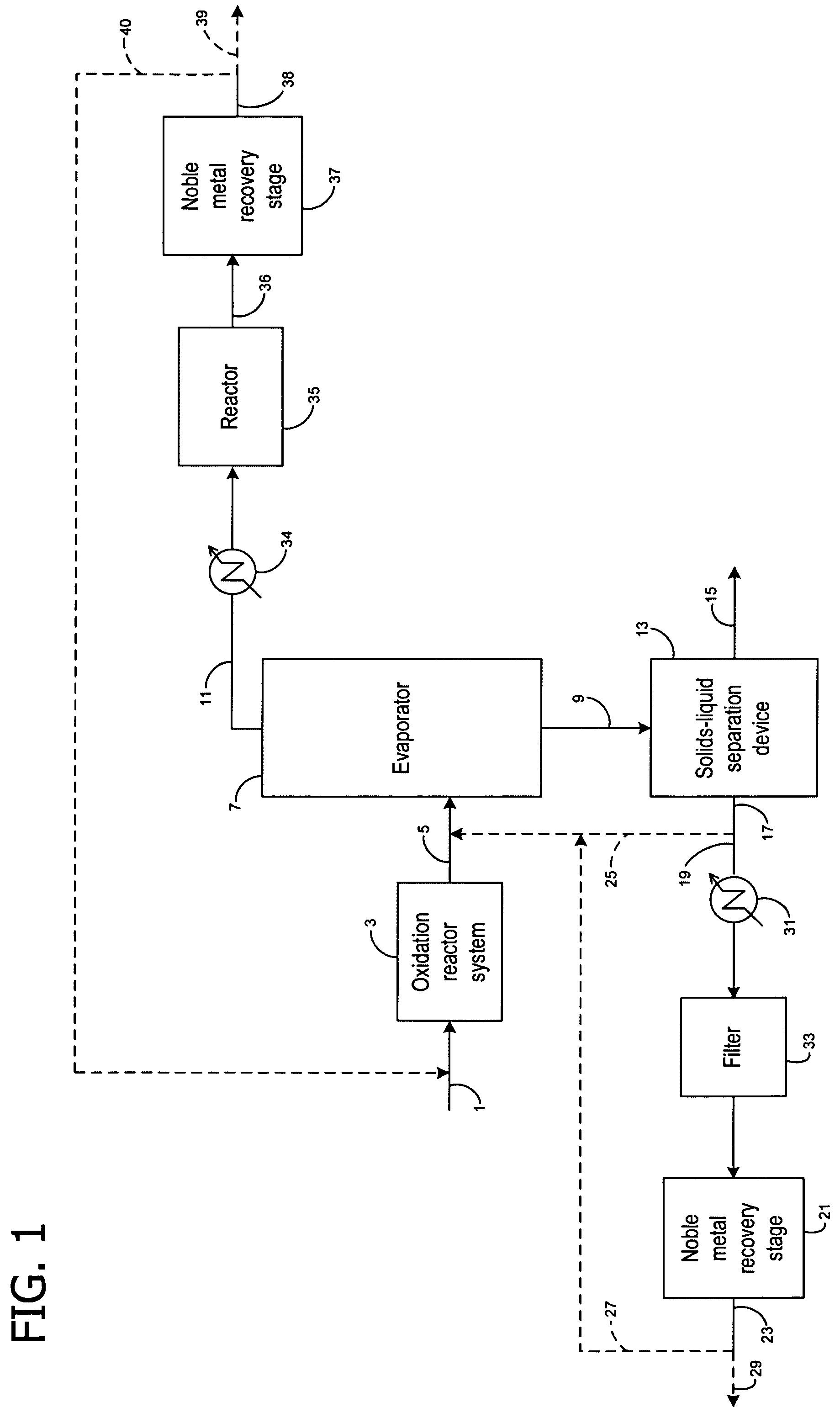
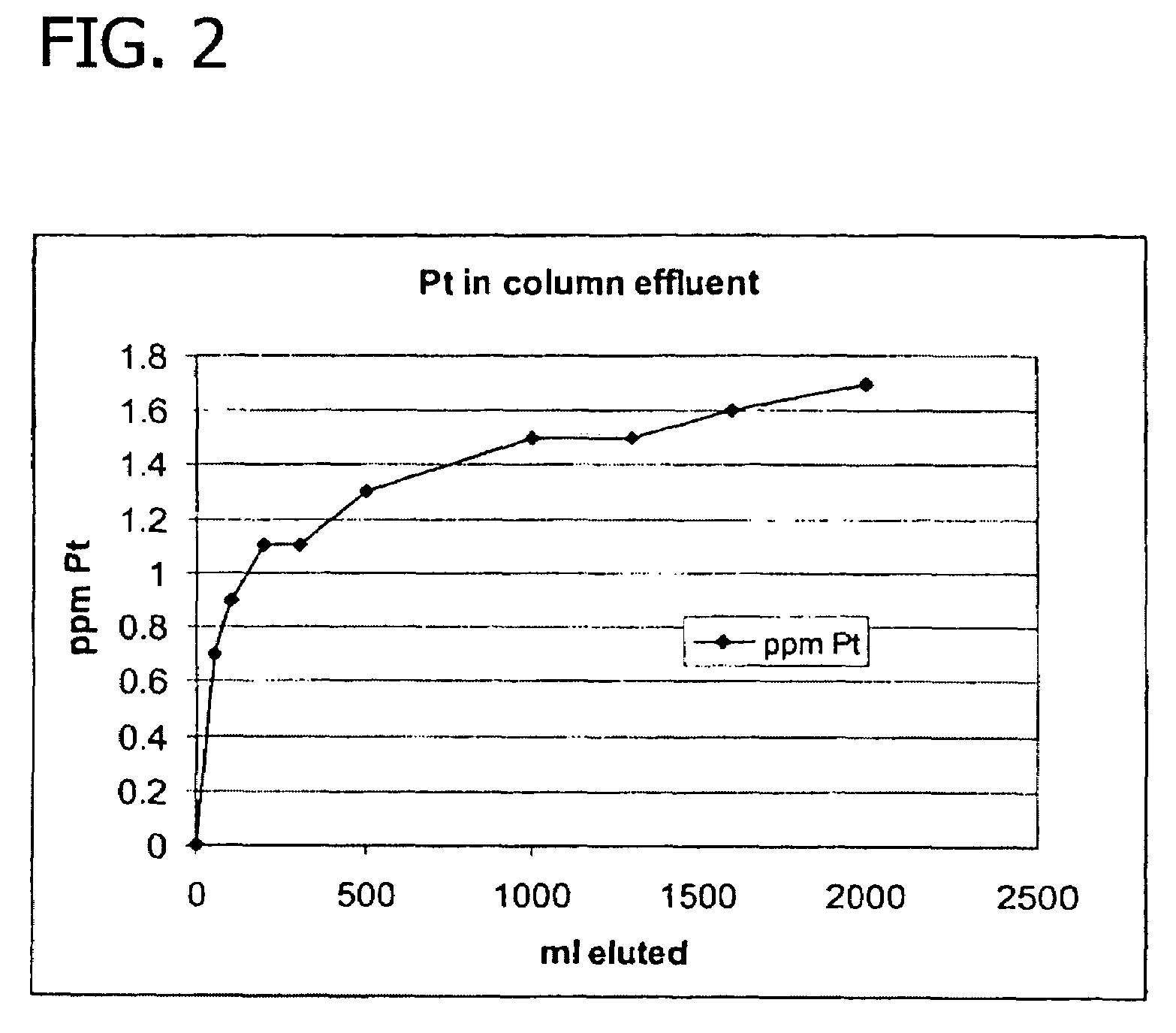
Recovery of noble metals from aqueous process streams
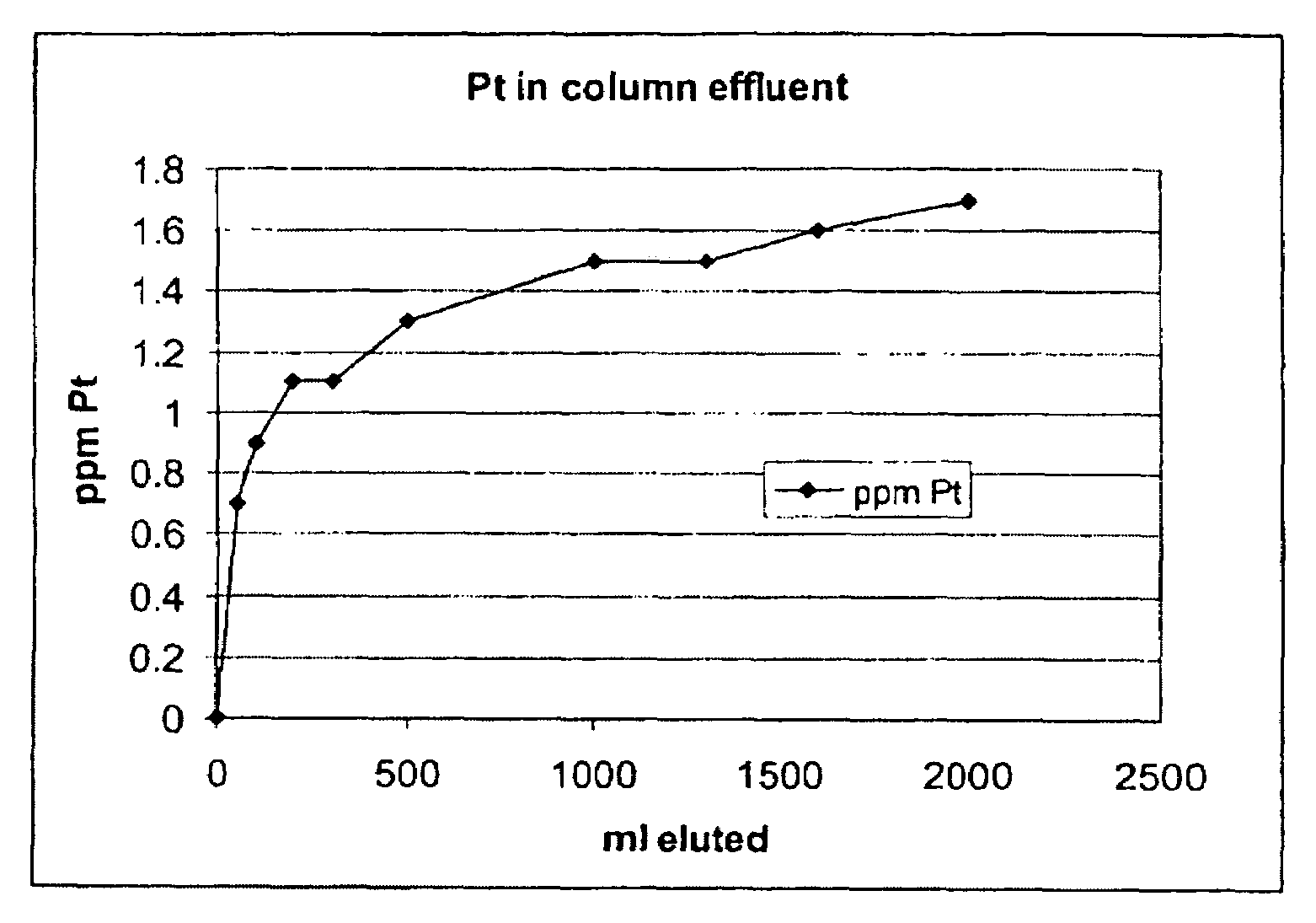
ActiveUS20060106248A1Reduce operating costsPhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic anion exchangersIon-exchange resinImidodiacetic acid
This invention generally relates to processes for recovering solubilized noble metals from aqueous process streams, in particular, aqueous process streams generated in the preparation of an N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine product, for example, by noble metal-catalyzed oxidation of an N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid substrate. The process includes contacting the aqueous process stream with a noble metal adsorption media such as an ion exchange resin to remove solubilized noble metal from the process stream.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
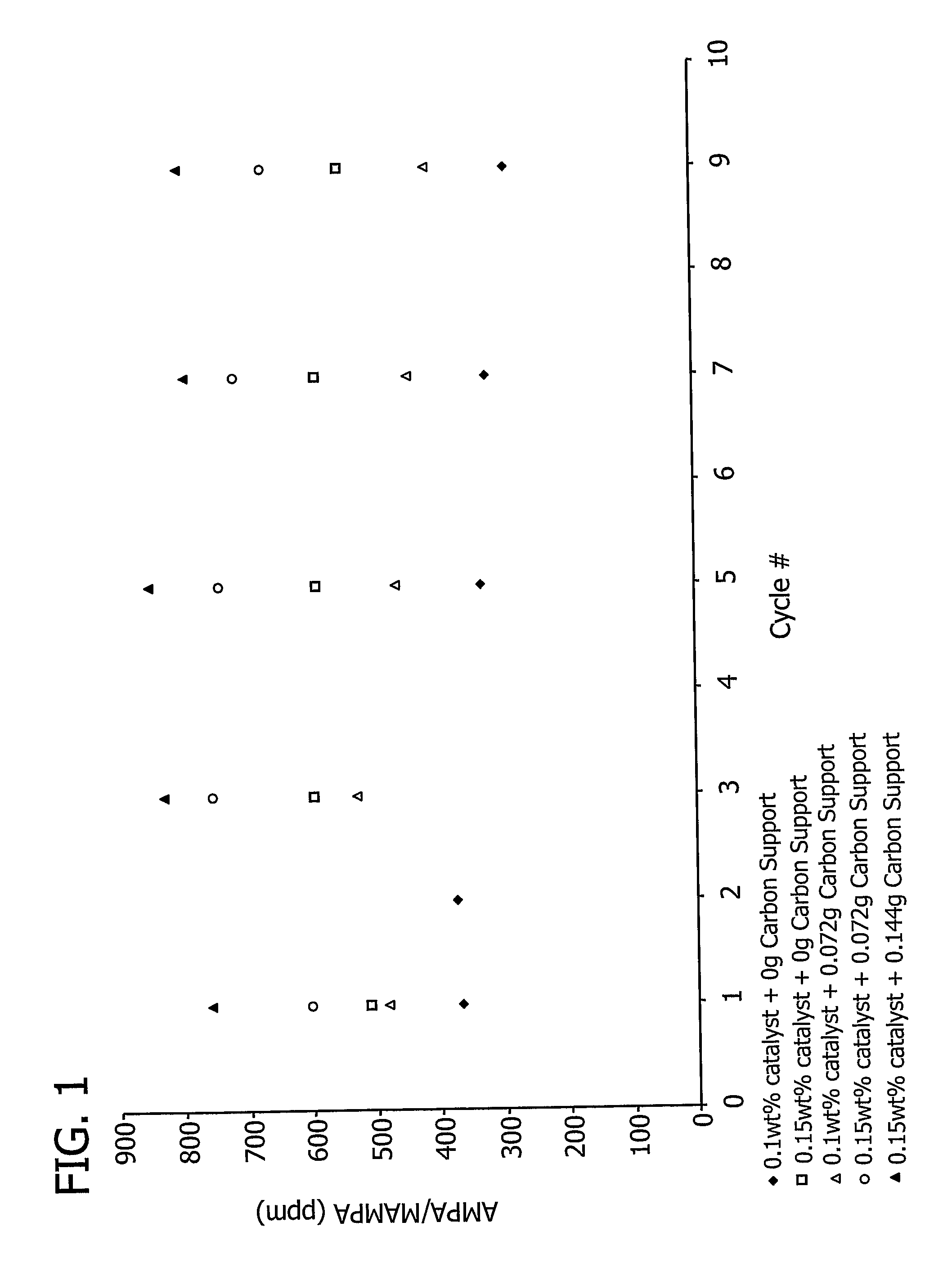
Metal utilization in supported, metal-containing catalysts
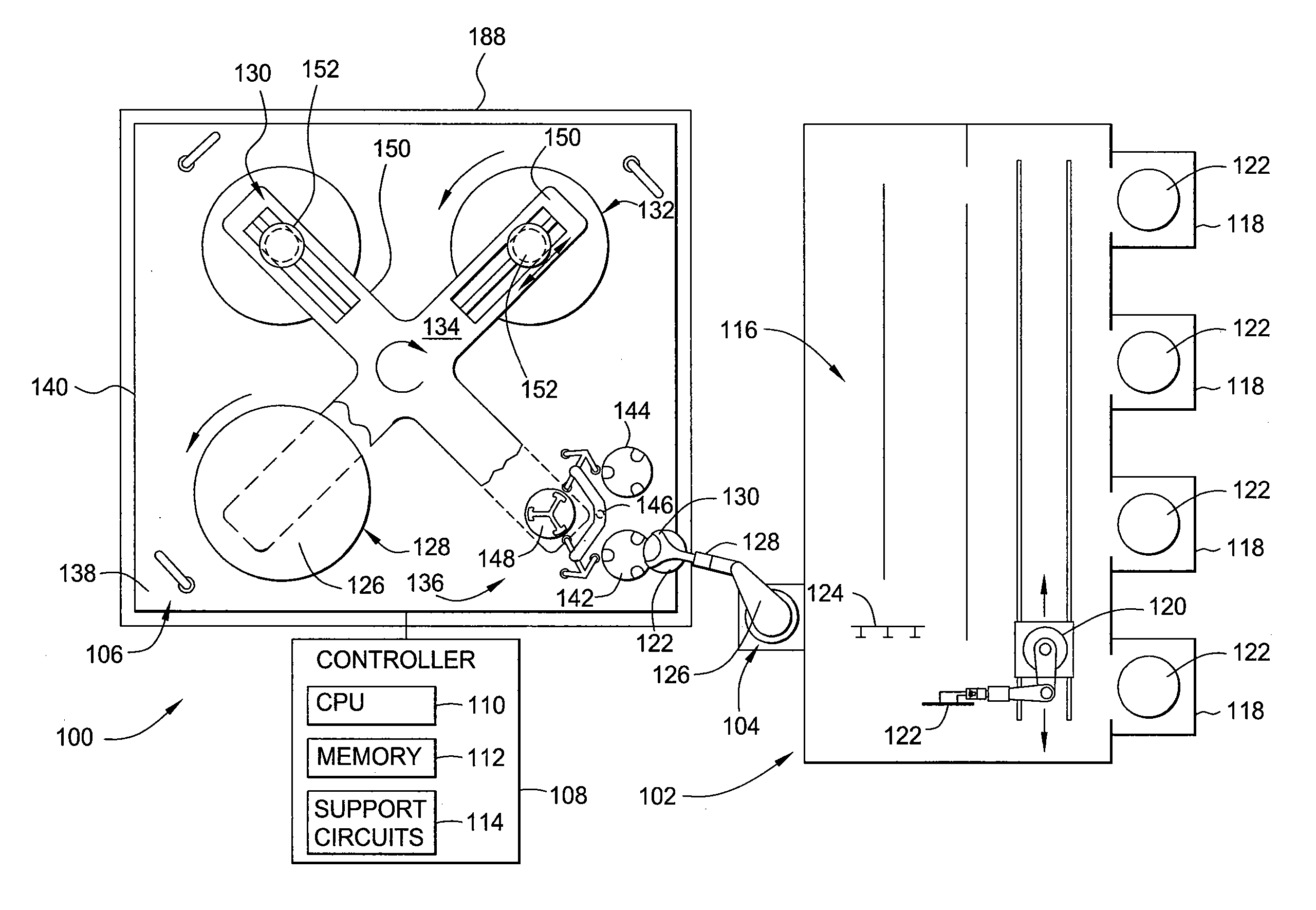
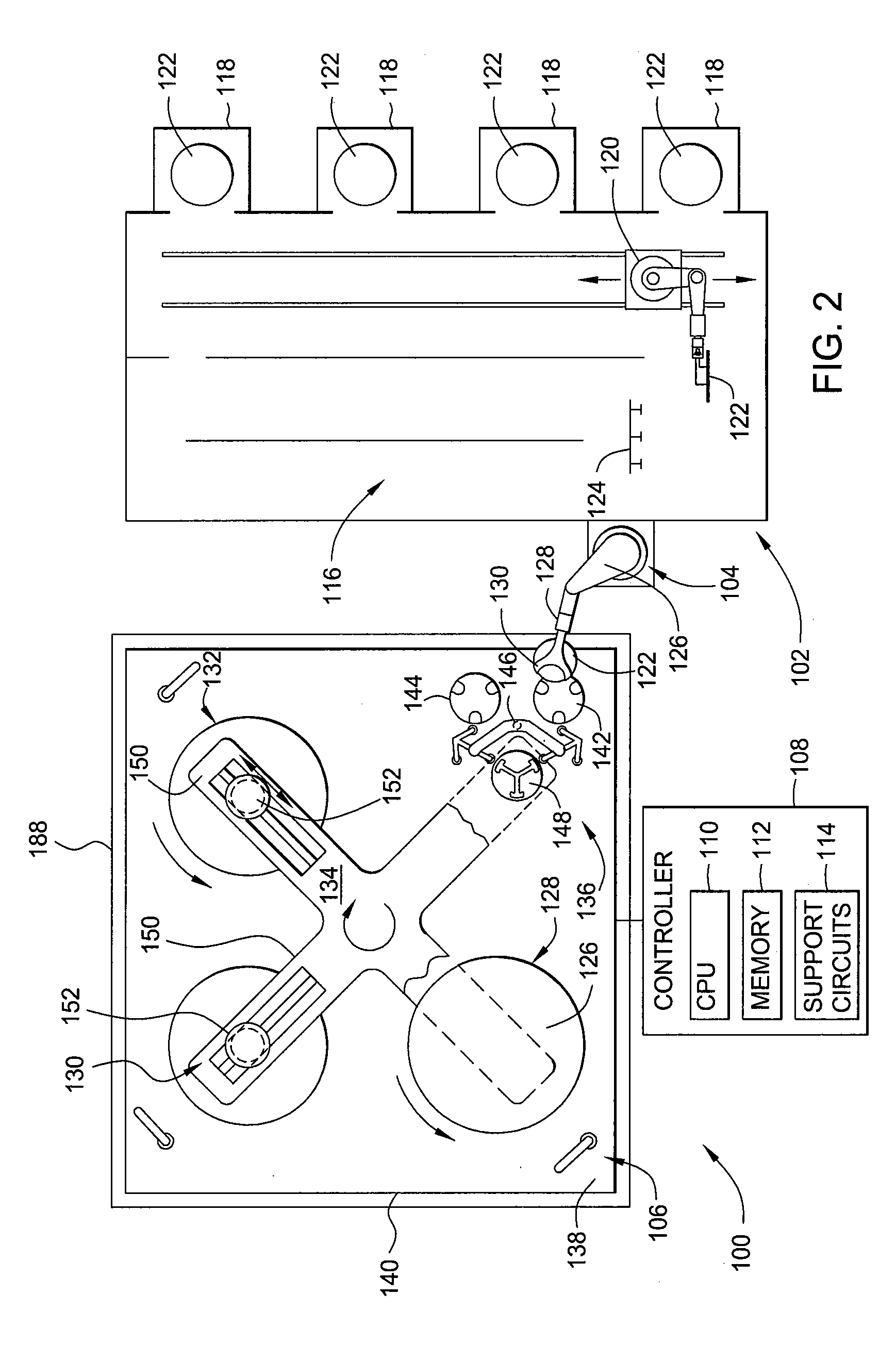
ActiveUS20090326262A1Reduce riskGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPorous substratePlatinum
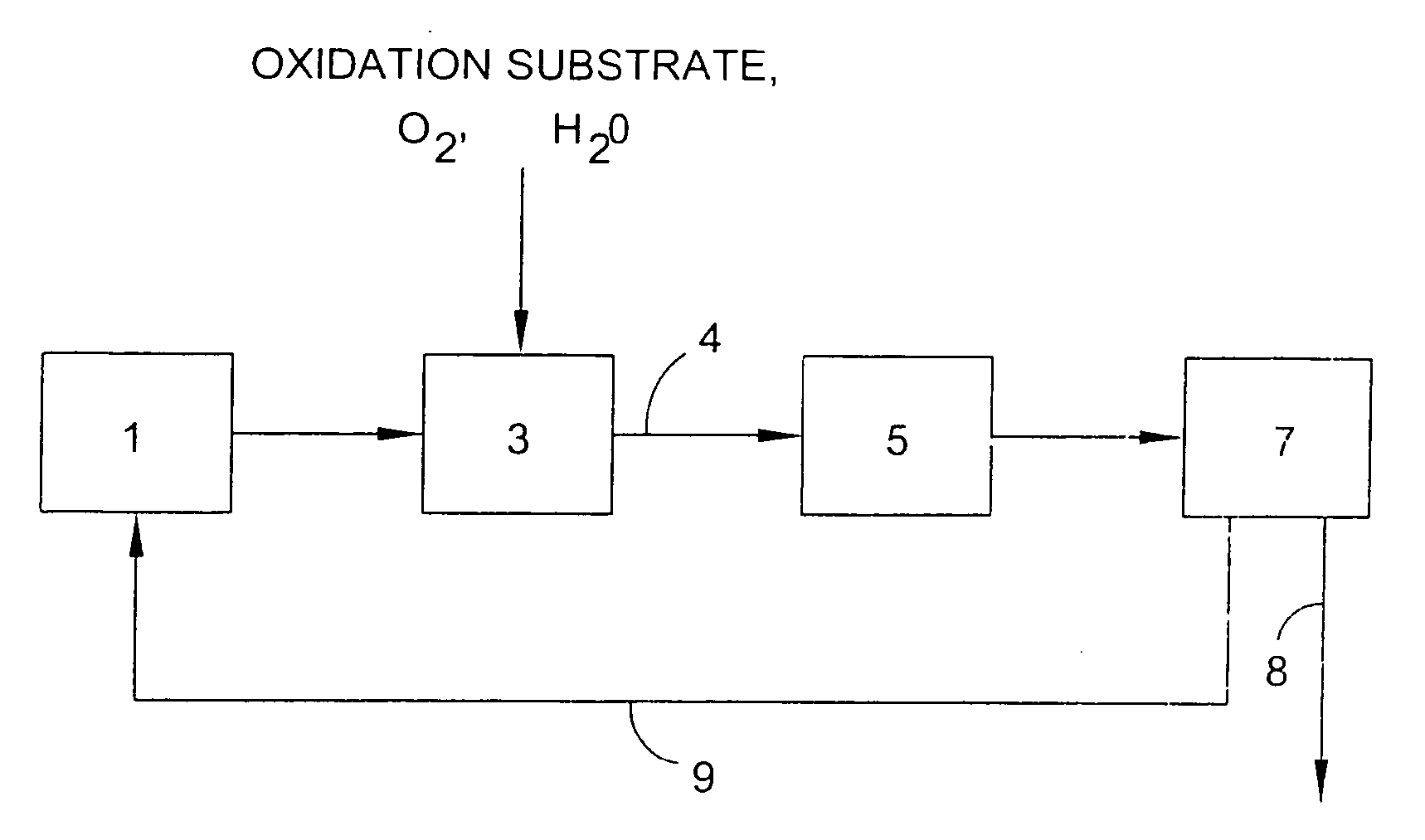
Generally, the present invention relates to improvements in metal utilization in supported, metal-containing catalysts. For example, the present invention relates to methods for directing and / or controlling metal deposition onto surfaces of porous substrates. The present invention also relates to methods for preparing catalysts in which a first metal is deposited onto a support (e.g., a porous carbon support) to provide one or more regions of a first metal at the surface of the support, and a second metal is deposited at the surface of the one or more regions of the first metal. Generally, the electropositivity of the first metal (e.g., copper or iron) is greater than the electropositivity of the second metal (e.g., a noble metal such as platinum) and the second metal is deposited at the surface of the one or more regions of the first metal by displacement of the first metal. The present invention further relates to treated substrates, catalyst precursor structures and catalysts prepared by these methods. The invention further relates to use of catalysts prepared as detailed herein in catalytic oxidation reactions, such as oxidation of a substrate selected from the group consisting of N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid or a salt thereof, formaldehyde, and / or formic acid.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Detection of biological warfare agents
InactiveUS6838292B1High sensitivity and selectivityHigh specificity and selectivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOrganic moleculesTerbium
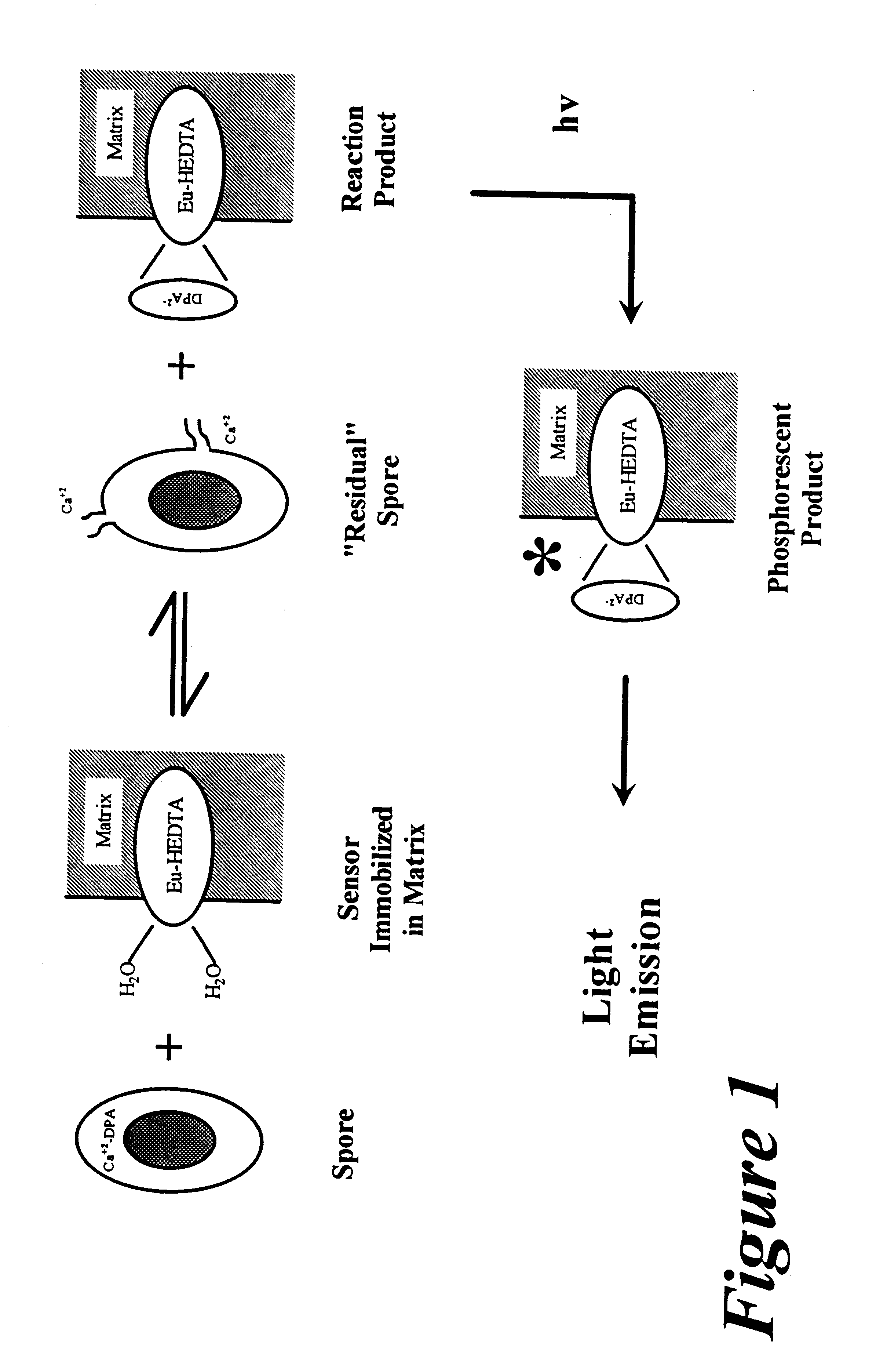
Methods and devices are provided for the detection of bacterial agents such agents as Bacillus anthracis and Clostridium botulinum with high sensitivity and selectivity. More specifically, methods and devices are based on a phosphorescence-emission detection system using chelate-stabilized lanthanides (e.g, Eu(III), Tb(III), and Sm(III)) to detect various spore-specific small organic molecules (e.g., dipicolinic acid, diaminopimelic acid, n-acetlymuramic acid, and the like). By careful selection of the chelating agent or ligand coordinated to the lanthanide, both high specificity and selectivity can be obtained. Examples of suitable and preferred sensor systems include N-(2-hydroxyethyl)ethylenediaminetriacetic acid (HEDTA) and N-(2-hydroxyethyl)iminodiacetic acid (HEIDA) combined with europium (III) and / or terbium (III). The chelate-stabilized lanthanides react with the spore-specific “target” molecules to form a characteristically phosphorescent product which can then be detected.
Owner:ALION SEIENCE & TECH CORP +1
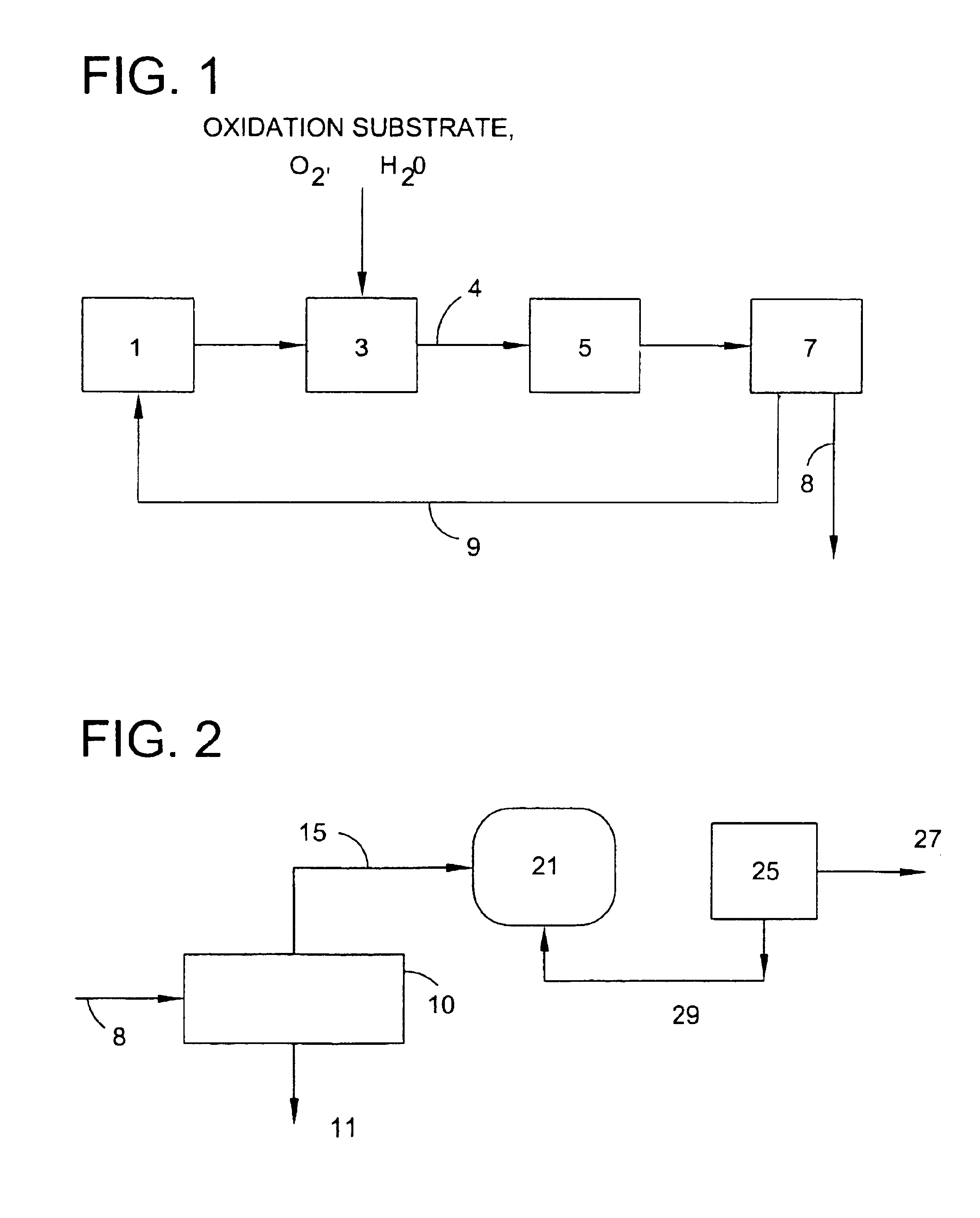
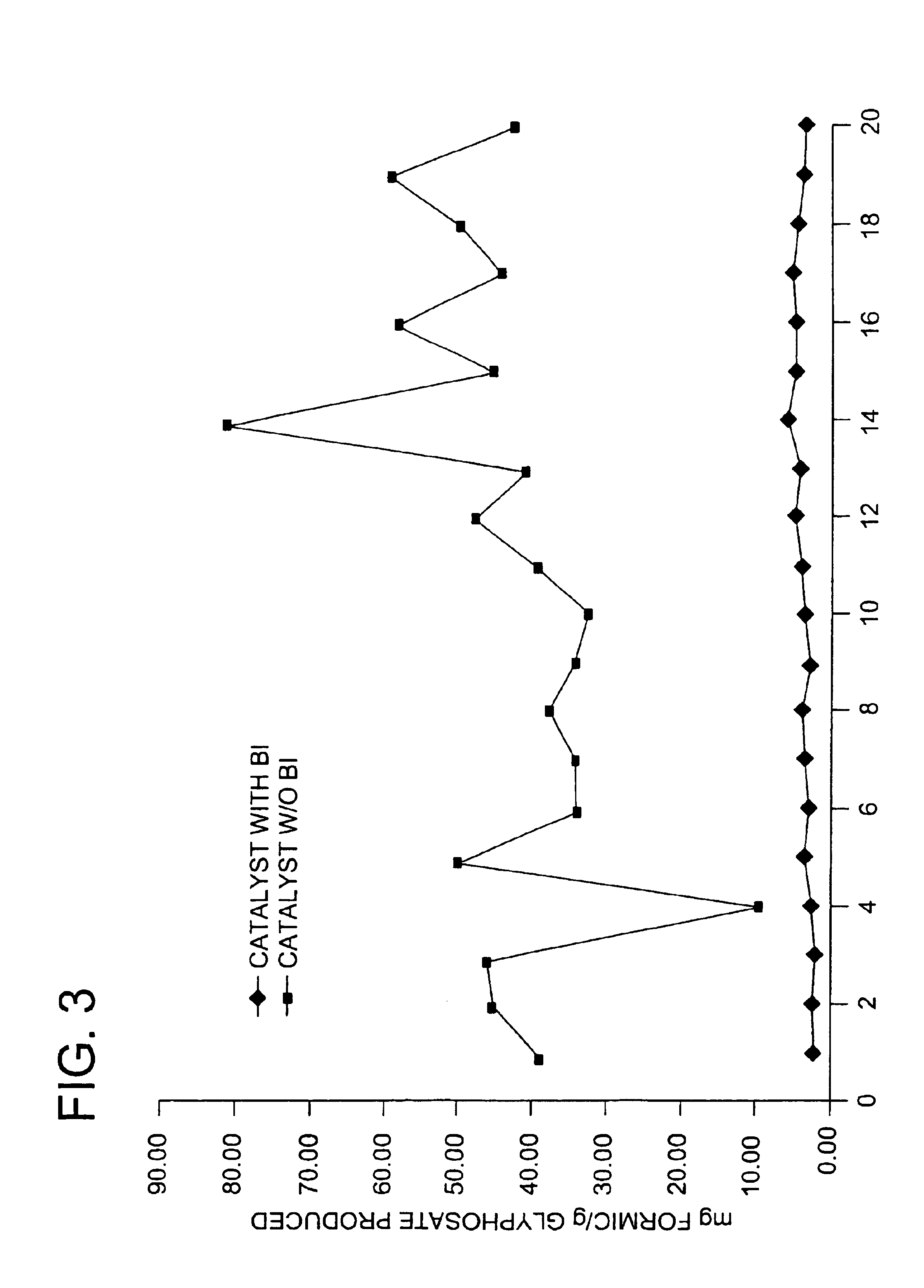
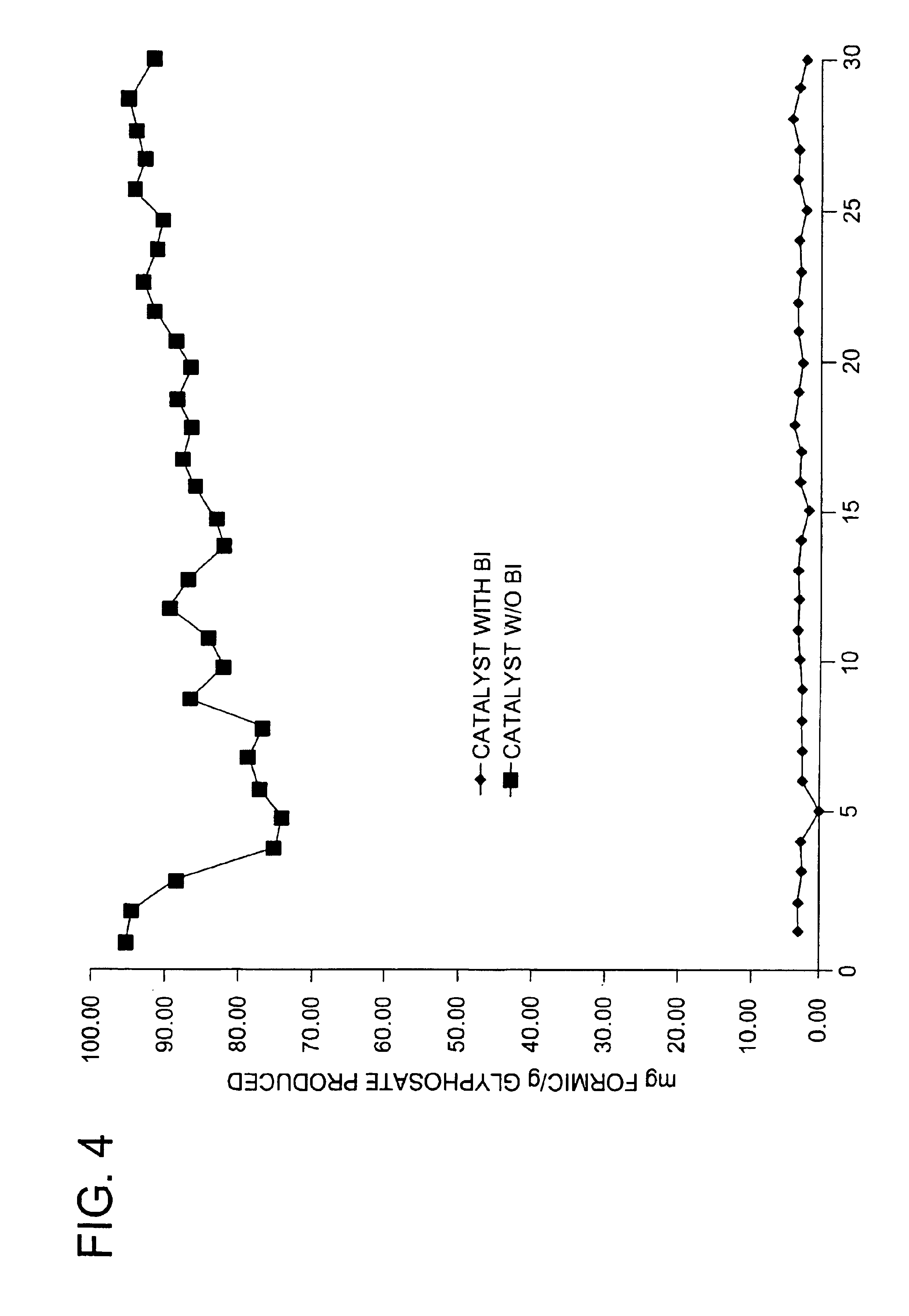
Use of a supplemental promoter in conjunction with a carbon-supported noble-metal-containing catalyst in liquid phase oxidation reactions
InactiveUS6963009B2Promote oxidationHigh activityBiocideGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsTe elementMethyl group
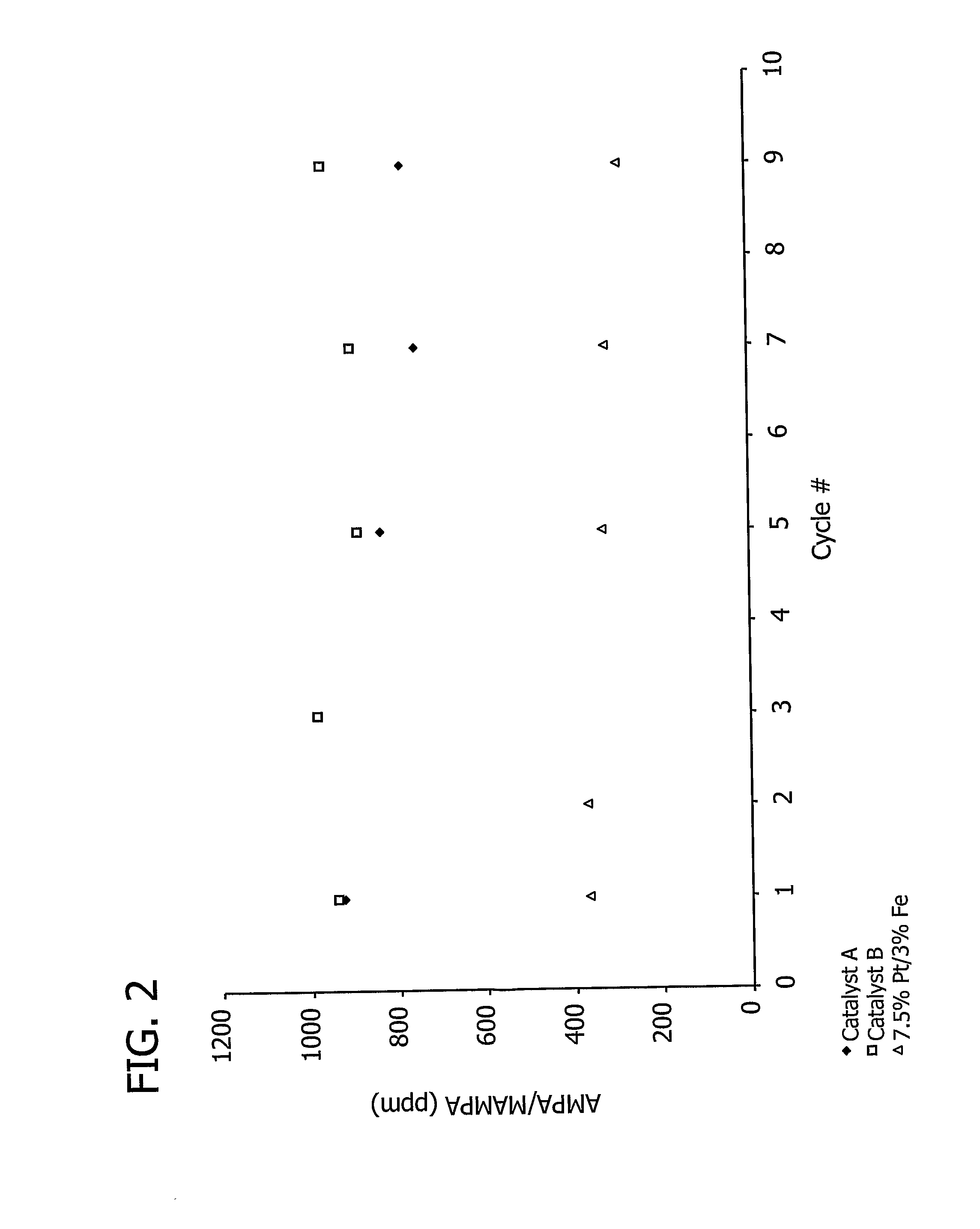
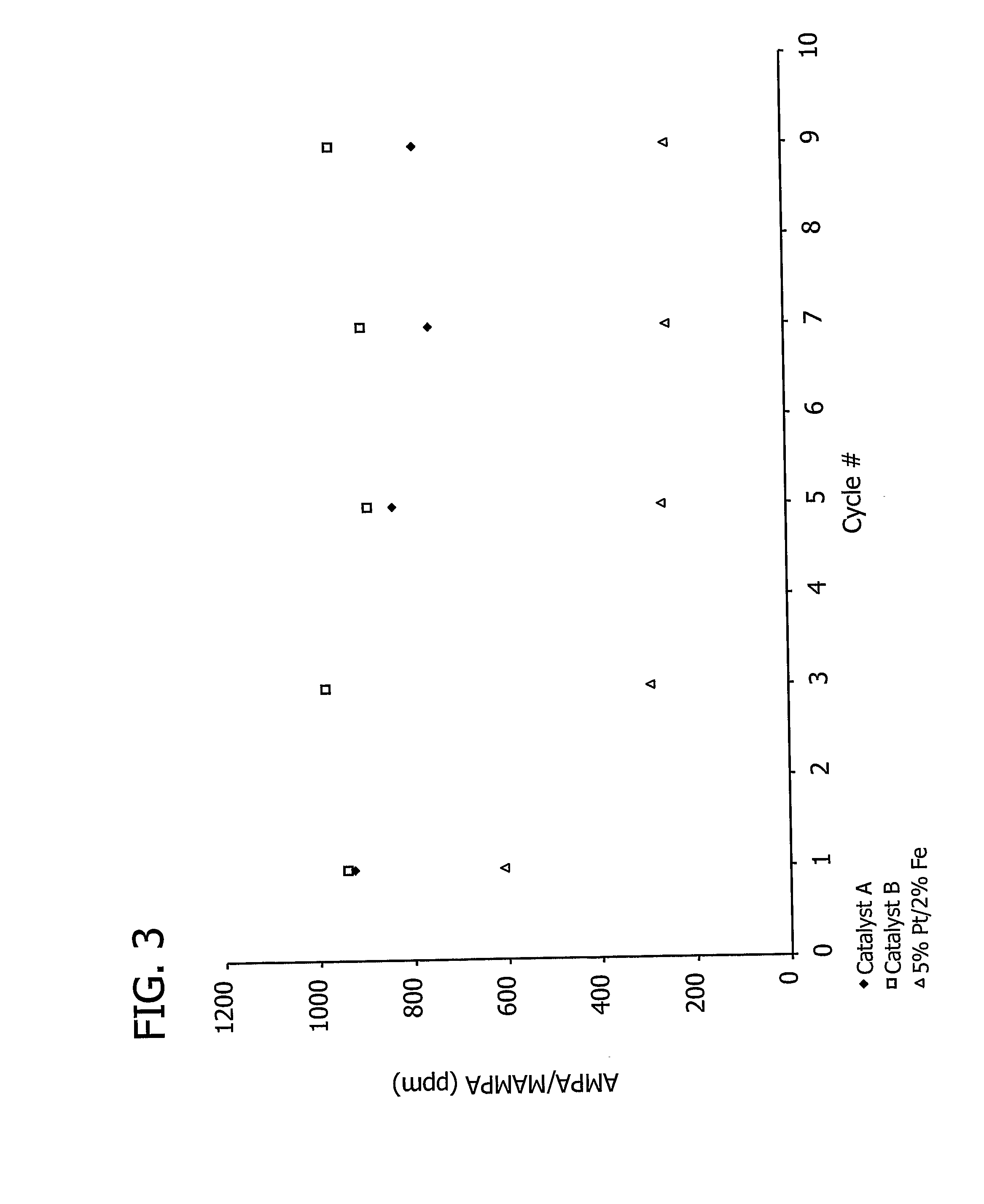
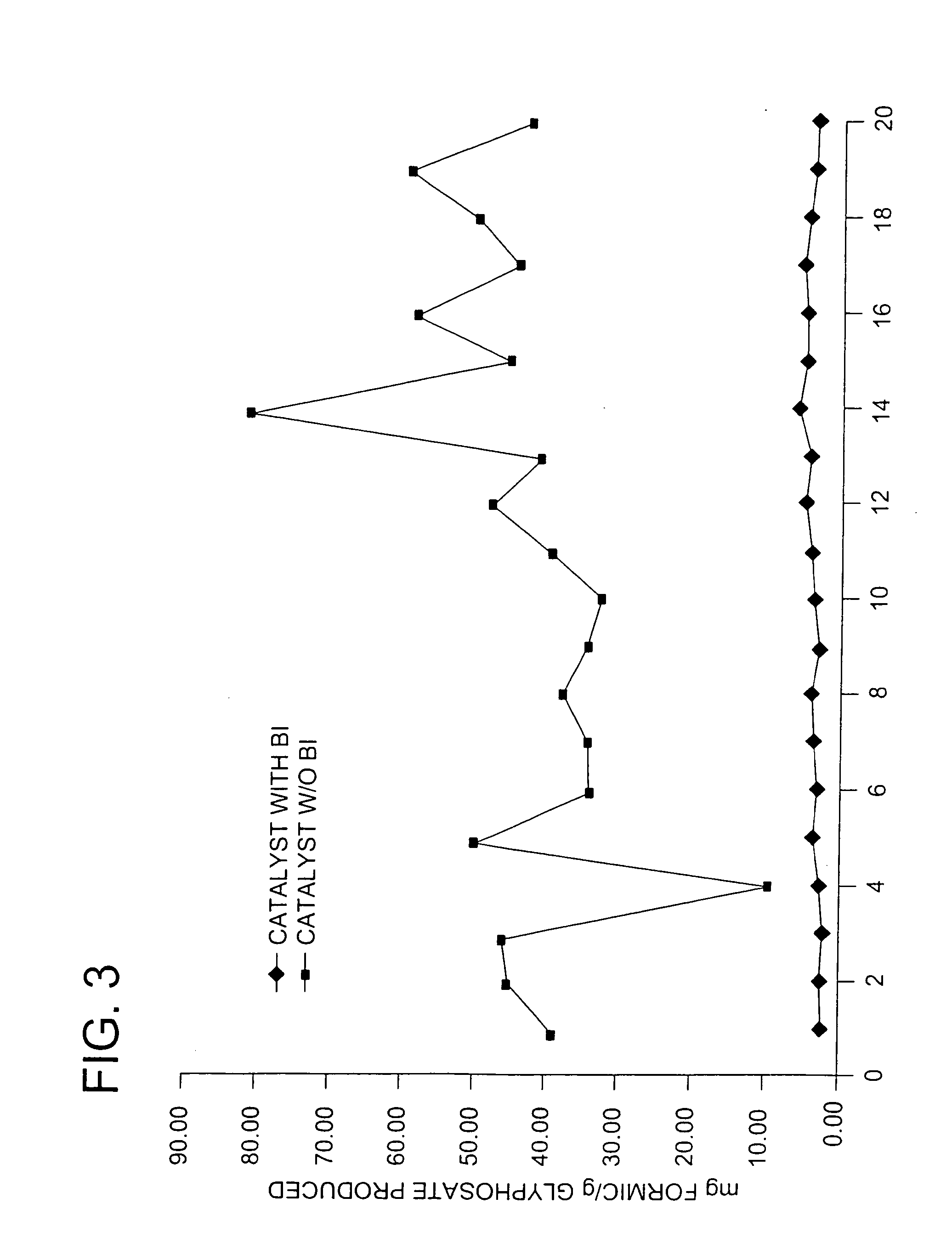
This invention relates to the use of a supplemental promoter in conjunction with a noble-metal-containing catalyst comprising a carbon support in catalyzing liquid phase oxidation reactions.In a particularly preferred embodiment, a supplemental promoter (most preferably bismuth or tellurium) is used in conjunction with a noble-metal-containing catalyst comprising a carbon support in a liquid phase oxidation process wherein N-(phosphonomethyl) iminodiacetic acid (i.e., “PMIDA”) or a salt thereof is oxidized to form N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine (i.e., “glyphosate”) or a salt thereof. The benefits of such a process include oxidation of the formaldehyde and formic acid by-products, and, consequently, decreased final concentrations of those by-products as well as other undesirable by-products, most notably N-methyl-N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine (i.e., “NMG”).
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Oxidation catalyst and its use for catalyzing liquid phase oxidation reactions
ActiveUS20100130774A1Group 5/15 element organic compoundsCatalyst activation/preparationCatalytic oxidationImidodiacetic acid
This invention relates to the field of heterogeneous catalysis, and more particularly to oxidation catalysts including carbon supports having deposited thereon a noble metal and one or more optional promoters and to methods for their preparation. The invention further relates to the field of heterogeneous catalytic oxidation reactions, including the preparation of secondary amines by the catalytic oxidation of tertiary amines, such as the oxidation of an N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid to produce an N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine product.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Well treatment fluid
A method of drilling with a wellbore fluid, wherein the wellbore fluid forms a filtercake on a wellbore wall, that includes pumping the wellbore fluid with an oxidative degradable polymer and an inactivated oxidant; forming a filtercake in a downhole environment by the pumping of the wellbore fluid into a well and allowing some of the fluid to filter into a subterranean rock formation to produce a filtercake comprising the oxidative degradable polymer and inactivated oxidant; and removing the filtercake formed by the wellbore fluid from the wellbore walls by exposing the filterckae with a breaker fluid comprising an aqueous fluid, and at least one iminodiacetic acid or a salt thereof is disclosed.
Owner:MI +1
Treatment process for wastewater from N-(Phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid production
InactiveCN101428935AReduce processing costsPromote environmental protectionTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentSteam pressureFiltration
The invention discloses a method for treating PMIDA (N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid) production wastewater, which comprises the following steps: 1) the PMIDA production wastewater is sent into equipment with a compound evaporator and a vacuum system, and is separated into a saturated concentrated solution containing sodium chloride and evaporable water at a steam pressure of between 0.1 and 0.4MPa and a vacuum degree of between 0.05 and 0.08MPa; the concentrated solution containing the sodium chloride is cooled to crystallize the sodium chloride; and the solid-liquid separation is performed; 2) separating medium is sent into a curing container, a curing agent is added, and innoxious solid mud and a filtrate are obtained after the washing and filtration; 3) after the evaporable water and the filtrate are mixed, a neutralizing agent is used to adjust the pH value to between 6 and 8; 4) an oxidant is added in neutralized wastewater for oxidation; and 5) a treated oxidized liquid is aerated and then enters the prior biochemical system to obtain treated water. The method can greatly reduce the treatment cost for the PMIDA production wastewater, can also extract partial useful constituents in the PMIDA production wastewater, can be recycled, and is favorable for the environmental protection.
Owner:SICHUAN BEIER CHEM GROUP
Use of a supplemental promoter in conjunction with a carbon-supported, noble-metal-containing catalyst in liquid phase oxidation reactions
InactiveUS20060020143A1High activityPromote oxidationBiocideOrganic chemistry methodsTe elementChemistry
This invention relates to the use of a supplemental promoter in conjunction with a noble-metal-containing catalyst comprising a carbon support in catalyzing liquid phase oxidation reactions, a process for making of an improved catalyst comprising such a supplemental promoter, and an improved catalyst comprising such a supplemental promoter. In a particularly preferred embodiment, a supplemental promoter (most preferably bismuth or tellurium) is used in conjunction with a noble-metal-containing catalyst comprising a carbon support in a liquid phase oxidation process wherein N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid (i.e., “PMIDA”) or a salt thereof is oxidized to form N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine (i.e., “glyphosate”) or a salt thereof. The benefits of such a process include increased oxidation of the formaldehyde and formic acid by-products, and, consequently, decreased final concentrations of those by-products as well as other undesirable by-products, most notably N-methyl-N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine (i.e., “NMG”).
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Gravel-packing carrier fluid with internal breaker
A method of gravel packing a hole in a subterranean formation having a filter cake coated on the surface thereof that includes injecting into the hole a gravel pack composition comprising gravel and a carrier fluid comprising a base fluid and at least one iminodiacetic acid or salt thereof is disclosed.
Owner:MI
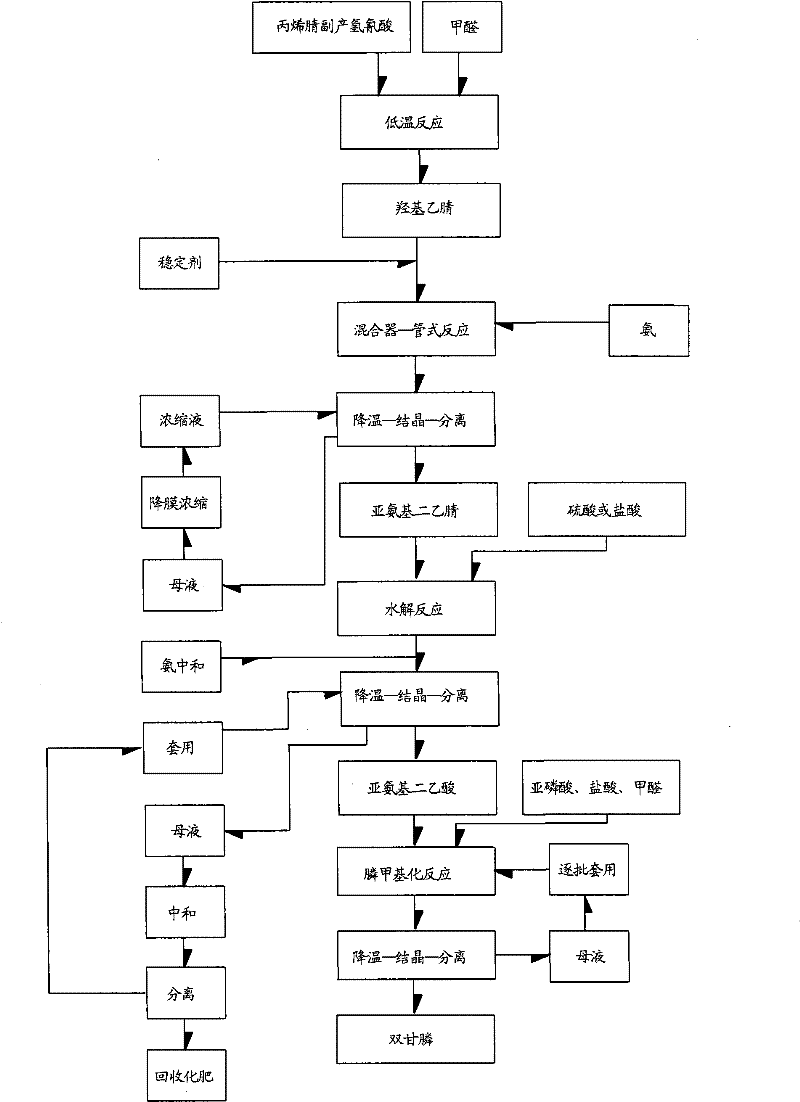
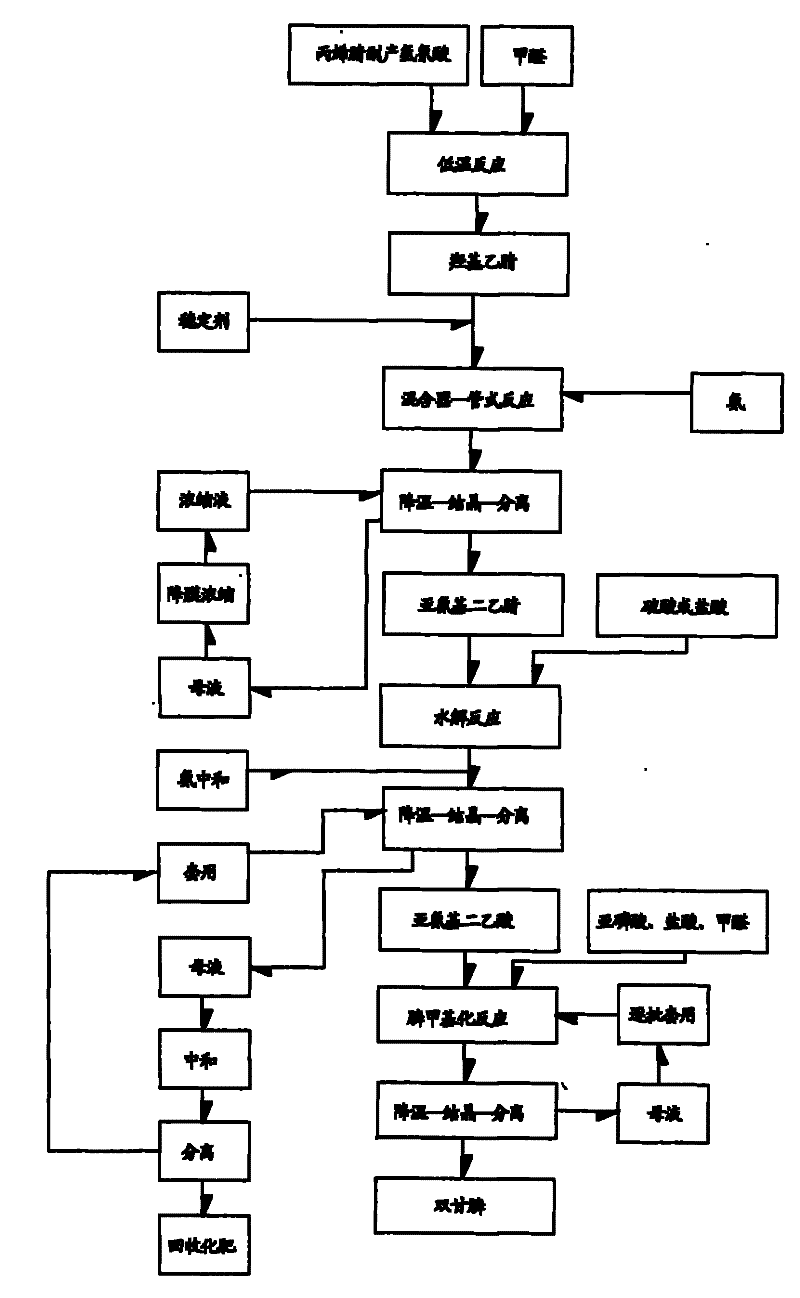
Environmental-friendly new method for preparing N-phosphonomethyl iminodiacetic acid by utilizing acrylonitrile byproduct hydrocyanic acid
InactiveCN101747369AQuality improvementHigh yieldGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsIminodiacetic acidControl system
The invention relates to an environmental-friendly new method for preparing N-phosphonomethyl iminodiacetic acid by utilizing acrylonitrile byproduct hydrocyanic acid, belonging to the comprehensive utilization of acrylonitrile device byproduct hydrocyanic acid in industrial scale. The method includes that: step first, acrylonitrile byproduct hydrocyanic acid is used for preparing hydroxyl acetonitrile, and then iminodiacetonitrile is prepared; step two, the obtained iminodiacetonitrile is used for preparing iminodiacetic acid by acid hydrolysis method; and step three, the obtained iminodiacetic acid is used for preparing N-phosphonomethyl iminodiacetic acid. No report of preparing PMIDA by utilizing acrylonitrile byproduct hydrocyanic acid in industrial scale is seen, and the inventor uses local materials, utilizes the advantages of being adjacent to Qilu petrochemical and having resource of hydrocyanic acid (4000 ton / year) transmitted by pipeline and initially provides the method for preparing PMIDA by utilizing acrylonitrile byproduct hydrocyanic acid in industrial scale. The invention solves the problem of region restriction of product production caused by inconvenient transportation of hydrocyanic acid. A gas and liquor mixer is applied to iminodiacetonitrile reaction, and by virtue of DCS control system, quality and yield of iminodiacetonitrile are improved.
Owner:YINGKOU YINGXIN CHEM TECH CO LTD
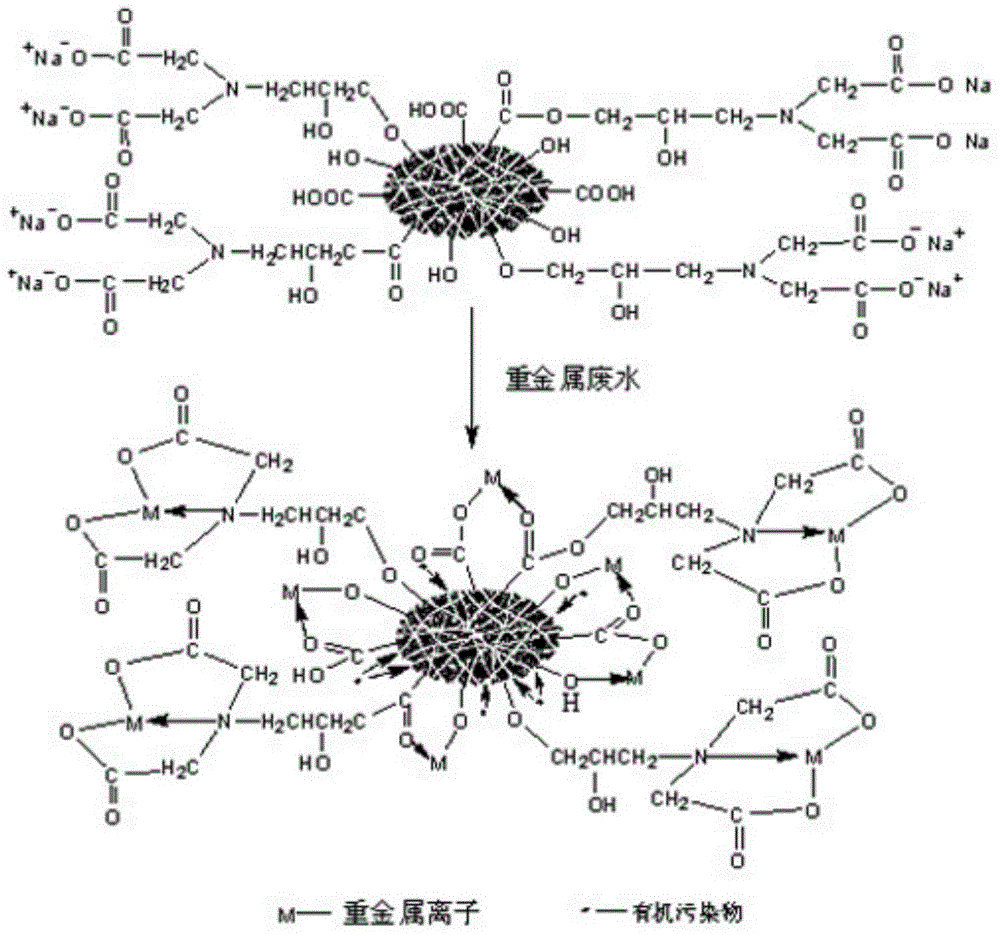
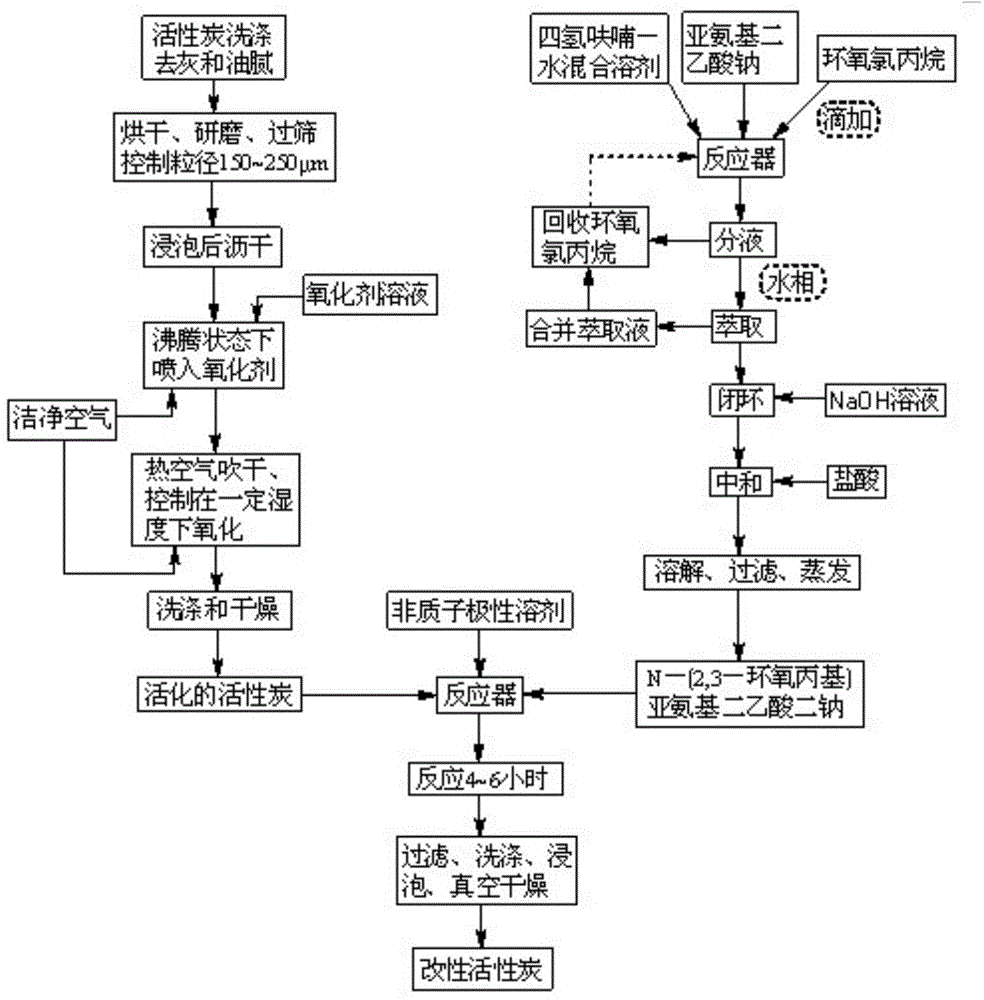
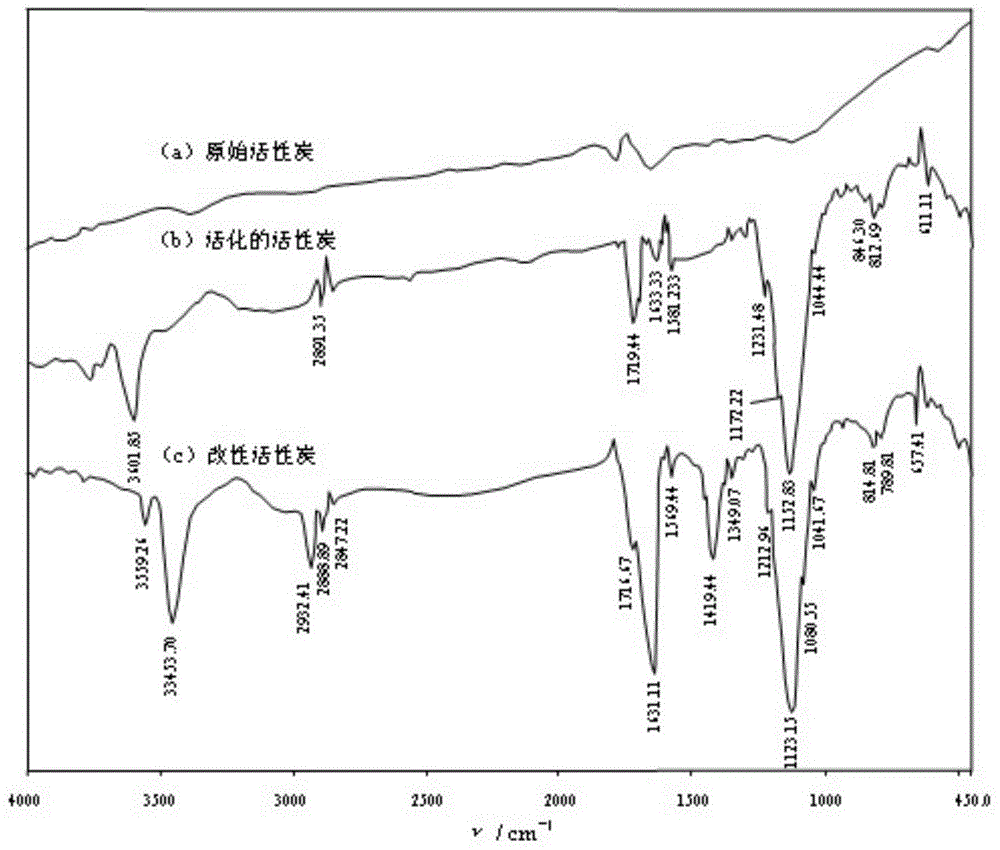
Preparation method of modified activated carbon used for heavy metal wastewater treatment
ActiveCN104525129AReduce oxidationMaintain structural propertiesOrganic chemistryOther chemical processesActivated carbonEpoxy
The invention discloses a preparation method of modified activated carbon used for heavy metal wastewater treatment. The preparation method comprises the steps that firstly, activated carbon is washed, dried, ground, sieved and soaked, so that pores of the activated carbon are filled with water; secondly, clean air is blown so that the activated carbon can be in a boiling state, and an oxidizing agent is sprayed for controllable oxidation; thirdly, N-(2,3-glycidyl) iminodiacetic acid disodium allows iminodiacetic acid disodium to be connected to the surface of the activated carbon through epoxy group ring opening. According to the prepared modified activated carbon, hydroxyls, carboxyls and iminodiacetic acid groups having a strong effect on heavy metal ions are introduced only on the surface, the original hole channel structure feature of the activated carbon is maintained, the capacities of strong heavy metal adsorption and organic pollutant removal are both achieved, and the dual purposes of removing heavy metal and organic pollution can be achieved by one step through adsorption via activated carbon. Meanwhile, the adsorbed heavy metal is easy to recycle, the activated carbon is easy to regenerate, the cycle service life of the activated carbon is long, no secondary pollution will occur, and therefore the preparation method has good application and popularization prospects.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and composition for polishing a substrate
InactiveUS20070290166A1Reduce saggingReduce insensitivityOther chemical processesSurface treatment compositionsPotassium hydroxideMonopotassium phosphate
Compositions and processes for producing compositions for removing conductive material, such as copper or copper alloys, from a substrate with reduced dishing and reduced insensitivity to overpolishing are provided. Embodiments include polishing compositions for electrochemical mechanical polishing of a substrate surface comprising a conductive material, the compositions having a pH of between about 3.0 to about 9.0, such as between about 4.0 to about 7.0, for example between about 5.0 to about 6.5. The polishing compositions comprise one or more inorganic based electrolytes, such as potassium phosphate monobasic, one or more chelating agents, such as citric acid, imidodiacetic acid, glycine, or salts thereof, such as ammonium citrate, one or more corrosion inhibitors, such as benzotriazole, a basic pH adjusting agent, such as ammonium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide or combinations thereof, one or more oxidizers, such as hydrogen peroxide or ammonium persulphate (APS), and a solvent, such as deionized water.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Cleaning composition comprising a chelant and quaternary ammonium hydroxide mixture
ActiveUS7825079B2Improve abilitiesGood removal effectOrganic detergent compounding agentsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGlycineIminodiacetic acid
Owner:EKC TECH
Recovery of noble metals from aqueous process streams
ActiveUS7687663B2Reduce operating costsPhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic anion exchangersIon-exchange resinImidodiacetic acid
This invention generally relates to processes for recovering solubilized noble metals from aqueous process streams, in particular, aqueous process streams generated in the preparation of an N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine product, for example, by noble metal-catalyzed oxidation of an N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid substrate. The process includes contacting the aqueous process stream with a noble metal adsorption media such as an ion exchange resin to remove solubilized noble metal from the process stream.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
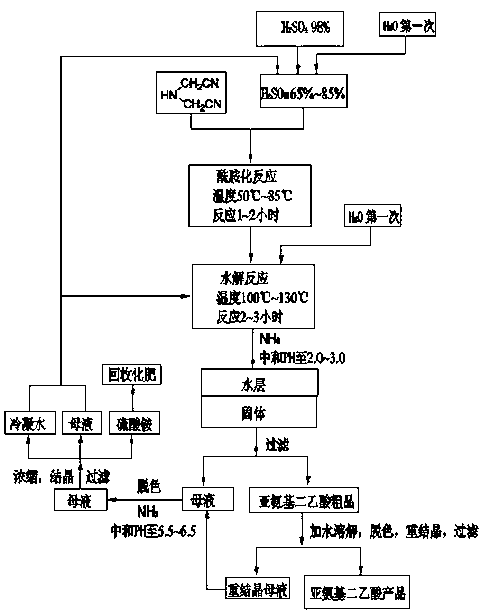
Environmentally-friendly clean production method of iminodiacetic acid
ActiveCN103232355AAvoid it happening againAvoid pollutionOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationAlkaline hydrolysisHydrolysis
The invention discloses an environmentally-friendly clean production method of iminodiacetic acid. According to the method, the iminodiacetic acid product is prepared from iminodiacetonitrile serving as the starting raw material through the steps of performing sulfuric acid hydrolysis, performing ammonia or ammonia water neutralization, decoloring, recrystallizing and the like; ammonium sulfate is separated out by decoloring, concentrating and crystallizing mother liquid; and condensate water and the mother liquid are recycled and applied to the next time of sulfuric acid dilution. By adopting the method, a large amount of sodium sulfate generated by alkaline hydrolysis is avoided, and corrosion to equipment and pollution to operation environment caused by hydrochloric acid hydrolysis are avoided; the reaction mother liquid can be completely reused and the iminodiacetic acid which the mother liquid contains can be completely recycled, so the yield is increased, water consumption is greatly reduced, no emission of waste liquid is realized, and the method is a completely environmentally-friendly clean process; and in addition, after the iminodiacetic acid and the mother liquid are decolored by active carbon, accumulation of colored impurities is greatly reduced and the product quality is high.
Owner:CHONGQING UNISPLENDOUR CHEM
Method for treating glyphosate waste water and reducing the emission of carbon dioxide
ActiveCN101591084ARealize resourcesEmission reductionOrganic chemistryWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisHexamethylenetetramineFormate
The invention relates to a method for treating glyphosate waste water and reducing the emission of carbon dioxide. The glyphosate waste water is obtained by extracting glyphosate after the N-phosphonomethyliminodiacetic acid is oxidized in the process of preparing the glyphosate by using an iminodiacetic acid method. Urotropine finished products are prepared by the following steps: (1) adding alkali into the glyphosate waste water, and adjusting and controlling the pH value to between 3 and 5 to obtain corresponding formate solution; (2) performing condensing separation on the solution of the step (1) by a film integration method to obtain 5 to 25 percent formate solution and 0.5 to 5 percent obenzaldehyde water solution (1); (3) performing evaporating, dehydration and solid-liquid separation on the formate solution of the step (2) to obtain formate wet powder and 0.5 to 5 percent benzaldehyde water solution (2), and drying the formate wet powder to obtain the finished product; (4) adding ammonia accounting for 1.5 to 3 percent the benzaldehyde water solution (1) and the benzaldehyde water solution (2) to obtain 0.3 to 4 percent urotropine water solution, and improving the concentration of the urotropine to between 10 and 25 percent by film separation; and (5) evaporating, separating and drying the urotropine solution to obtain the urotropine finished product.
Owner:HANGZHOU TIAN CHUANG ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
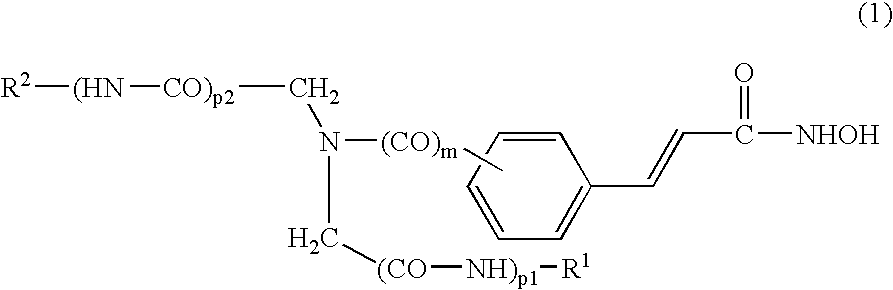
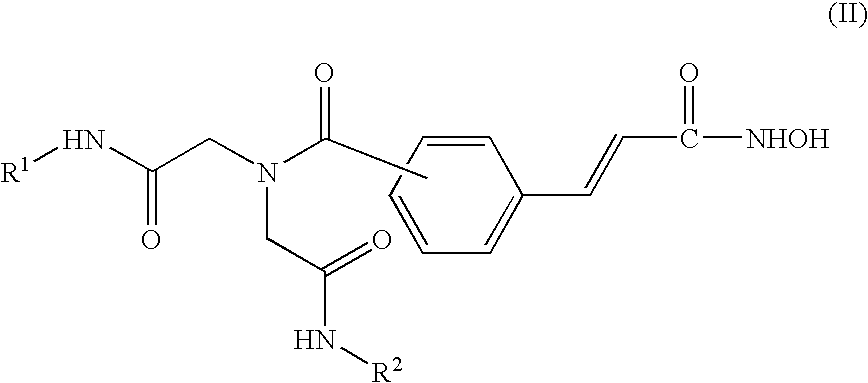
Histone deacetylase inhibitors
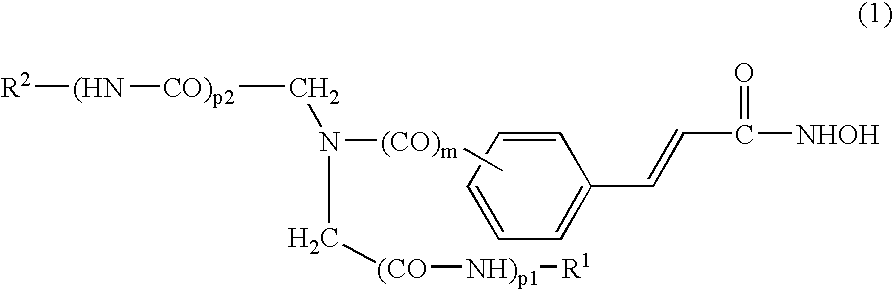
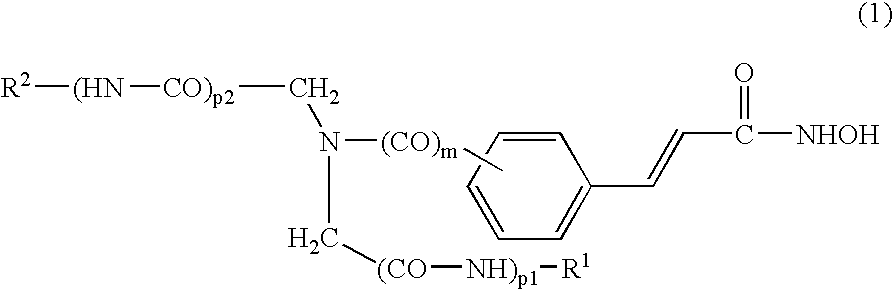
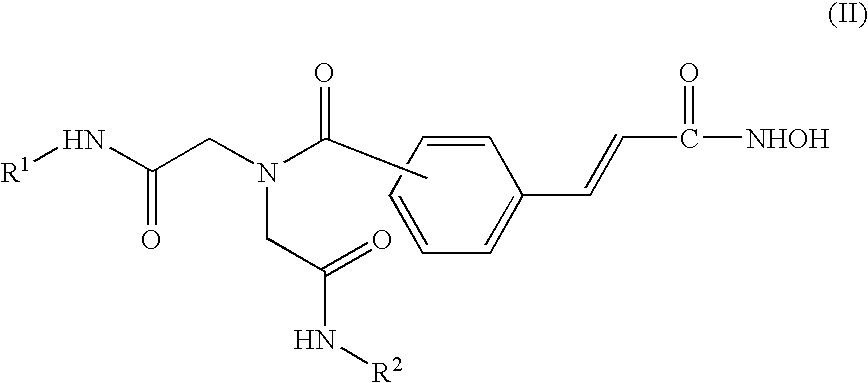
This invention relates to iminodiacetic acid and diamine hydroxamic acid derivatives, that are inhibitors of histone deacetylase (HDAC), and are useful in the prevention and / or treatment of cellular proliferative diseases, for example cancer, autoimmune, allergic and inflammatory diseases, diseases of the central nervous system (CNS) such as neurodegenerative diseases, and in the prevention and / or treatment of restenosis.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Method for treating N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid wastewater
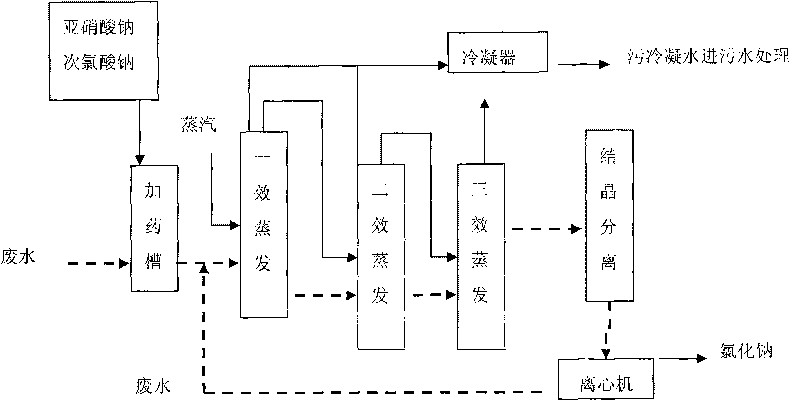
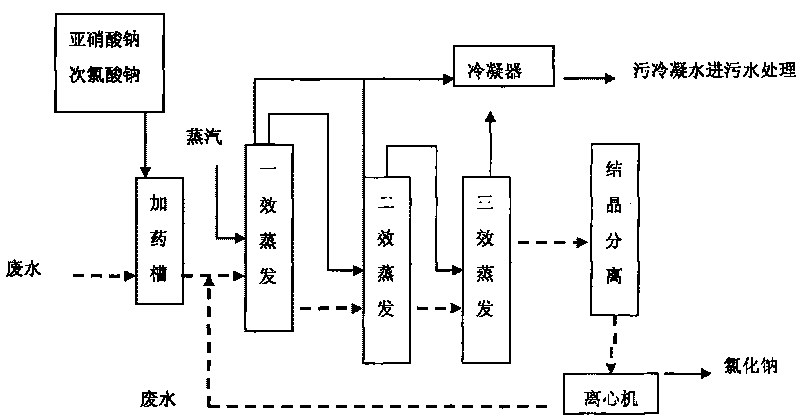
ActiveCN101717131AReduce CODReduce salt contentNature of treatment waterWater/sewage treatment by heatingEvaporationCatalytic oxidation
The invention relates to a wastewater treatment process, in particular to a method for treating N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid wastewater by a coupling catalytic oxidation technology. The method comprises the following concrete steps of: adding catalytic oxidizers of sodium nitrite and sodium hypochlorite into the N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid wastewater in a mixing tank, filtering after stirring evenly, putting the wastewater into a multi-effect evaporation device, concentrating under the conditions that the temperature is 65-100 DEG C and the vacuum degree is from -0.05MPa to -0.09MPa and crystallizing a concentrate under the condition that the COD concentration of effluent water is below 5000mg / L to precipitate sodium chloride which can reach the standard of industrial salt. The invention has simple and convenient operation, strong controllability, simple equipment, cost reduction, less energy consumption and no secondary pollution; the invention is suitable for treating and reclaiming the N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid wastewater.
Owner:JINGBO AGROCHEM TECH CO LTD
Oligonucleotide labeling reactants and their use
InactiveUS20040260080A1Highly simplifiedSimple methodSugar derivativesGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsAlkyl transferIminodiacetic acid
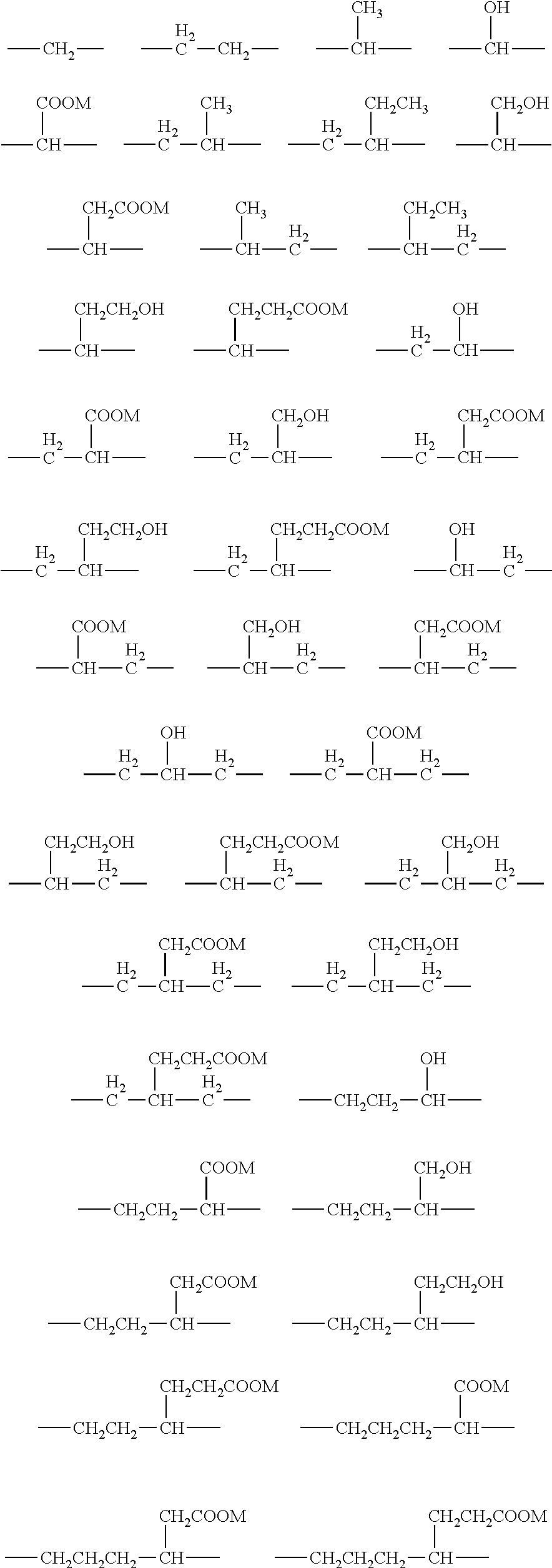
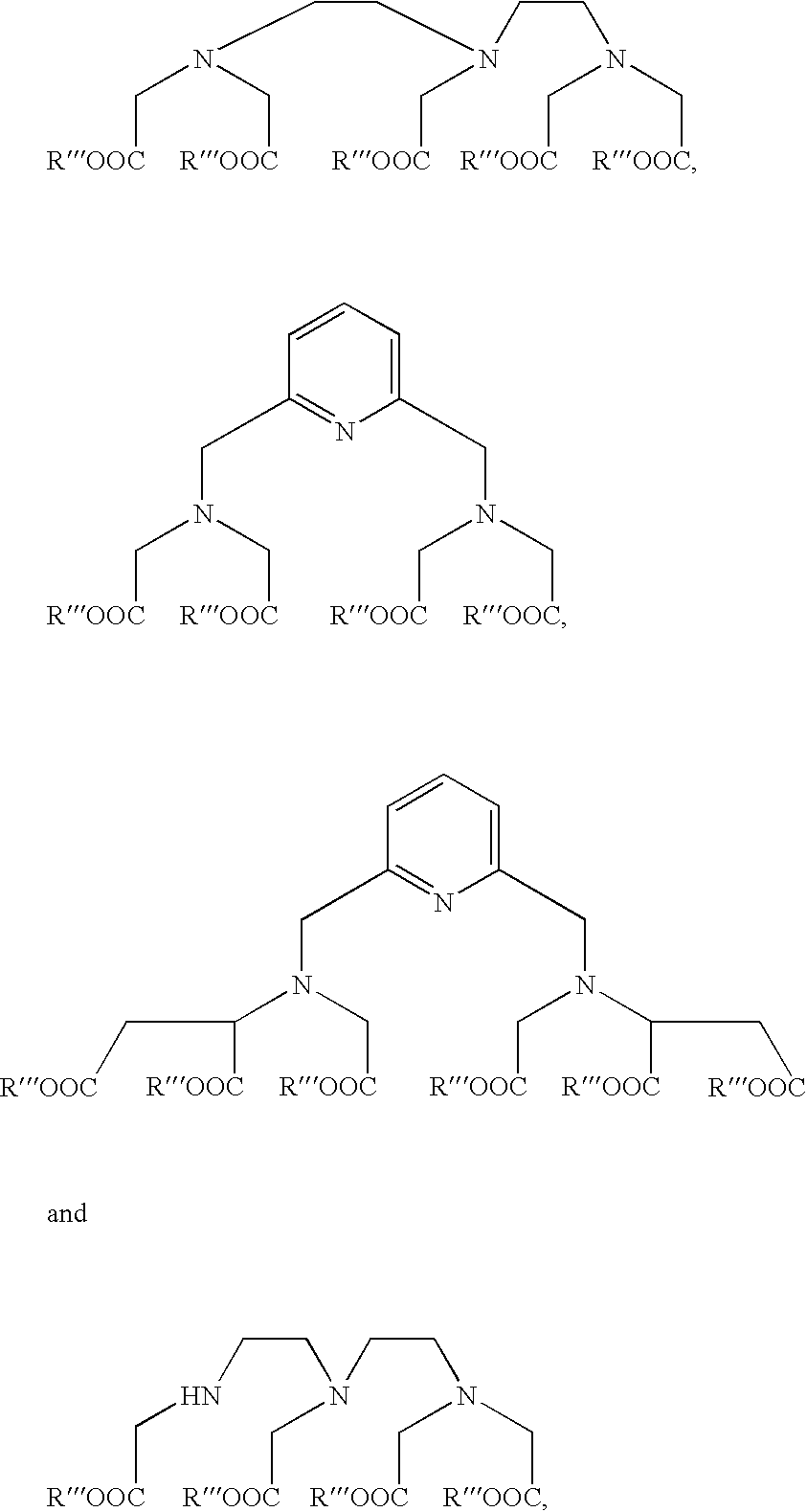
The invention relates to a novel labeling reactant of formula (I) suitable for labeling an oligonucleotide wherein: R is a temporary protecting group. A is either a phosphorylating moiety or a solid support tethered to a bridge point Z via a linker arm E. E' is a linker arm between G and Z. G is a bivalent aromatic structure, tethered to two iminodiacetic acid ester groups N(COOR''')2 or G is a structure selected from a group consisting of or G is a protected functional group. The invention further concerns a method for direct attachment of a conjugate group to an oligonucleotide structure enabling the attachment of a desired number of these groups during chain assembly. The method comprises a Mitsonobu alkylation.
Owner:HOVINEN JARI +1
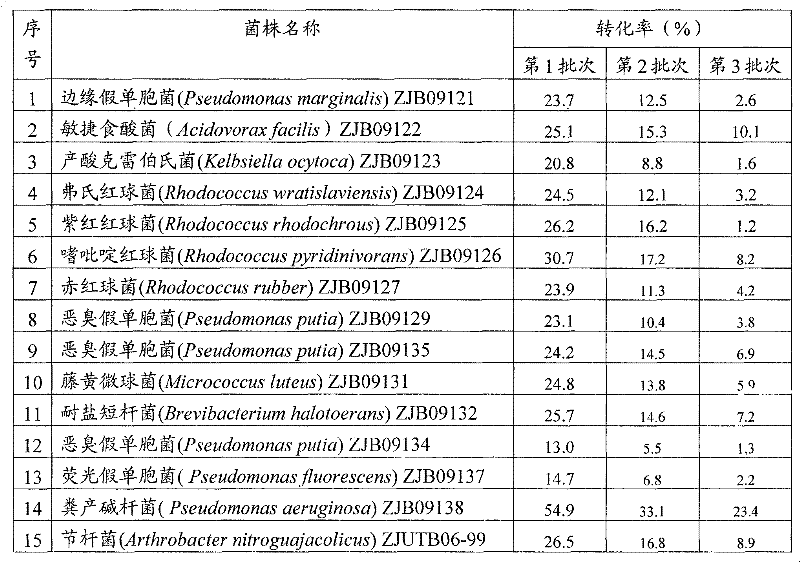
Method for preparing iminodiacetic acid from iminodiacetonitrile by microorganism catalysis
ActiveCN101629192BEfficient productionBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyIminodiacetic acid
The invention provides a method for preparing iminodiacetic acid by microorganism catalyzing iminodiacetonitrile. The method is to use a nitrilase-producing bacterial strain to obtain nitrilase through enzyme-producing culture, and use nitrilase as a biocatalyst to biocatalyze Iminodiacetonitrile is prepared to give iminodiacetic acid. The present invention also relates to a screening method for microorganisms producing nitrilase and a bacterial strain with nitrilase activity obtained by screening using the method. The invention provides a basis for producing iminodiacetic acid by using biocatalytic iminodiacetonitrile, and has important application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
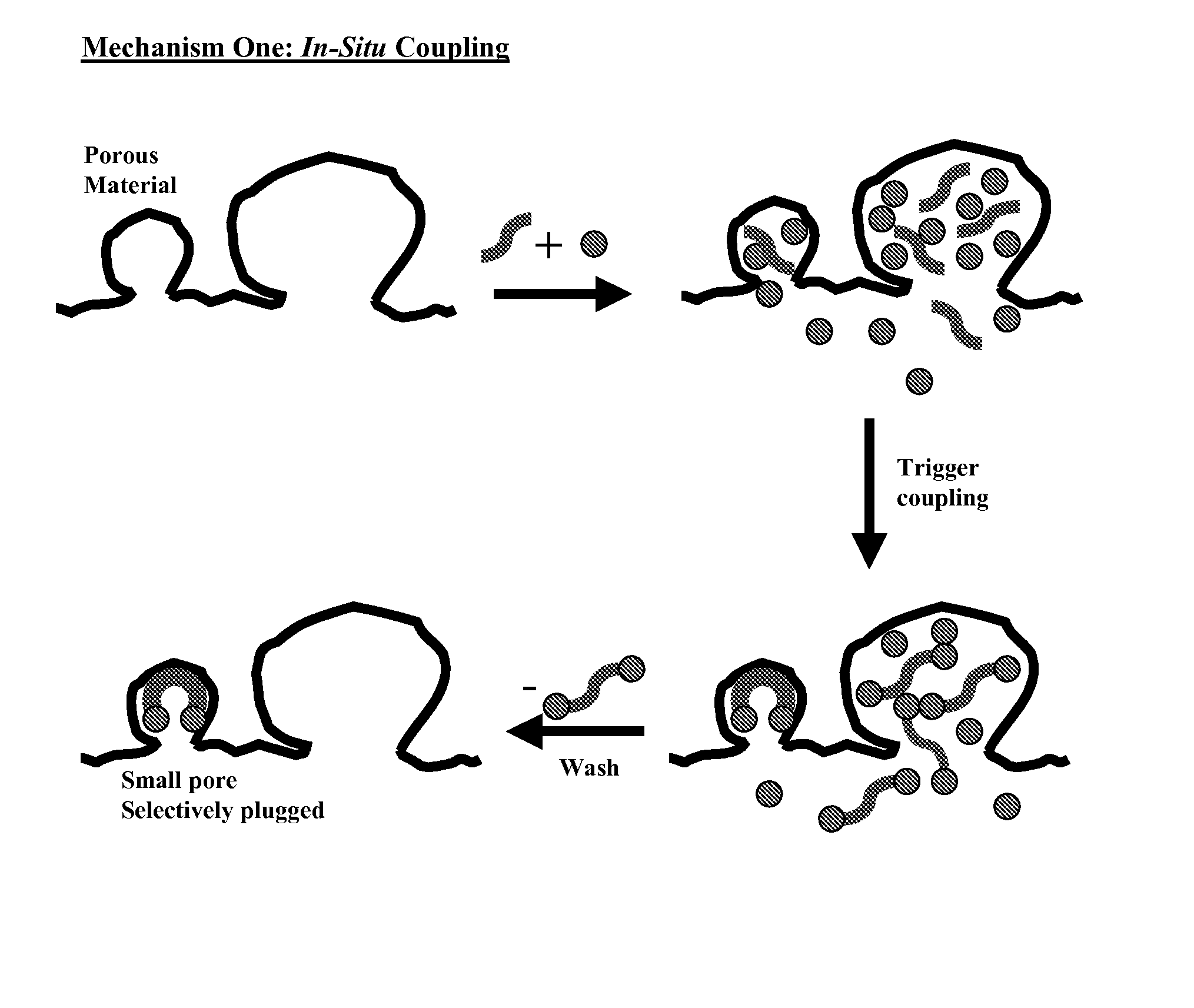
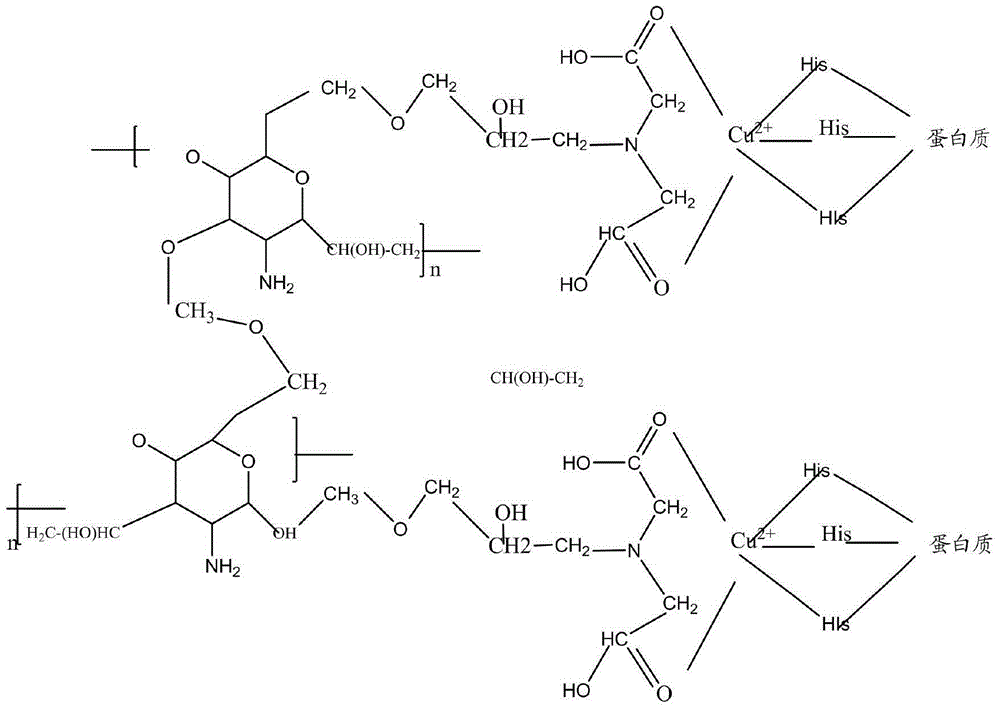
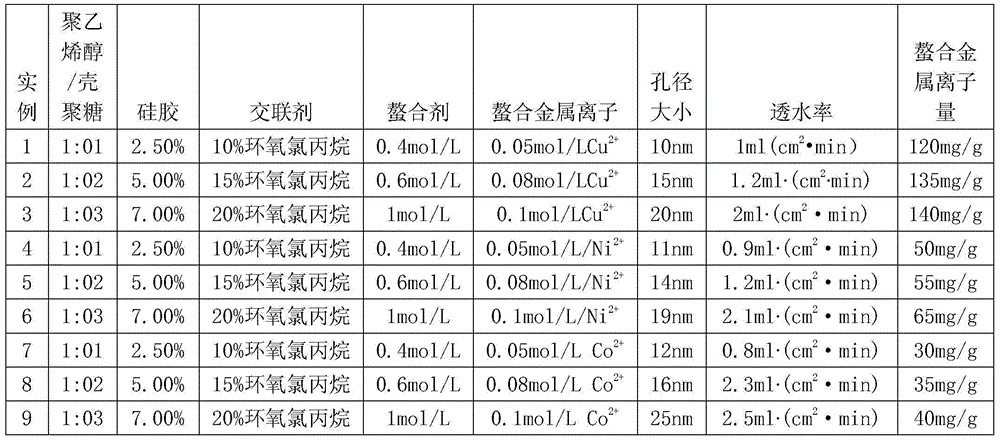
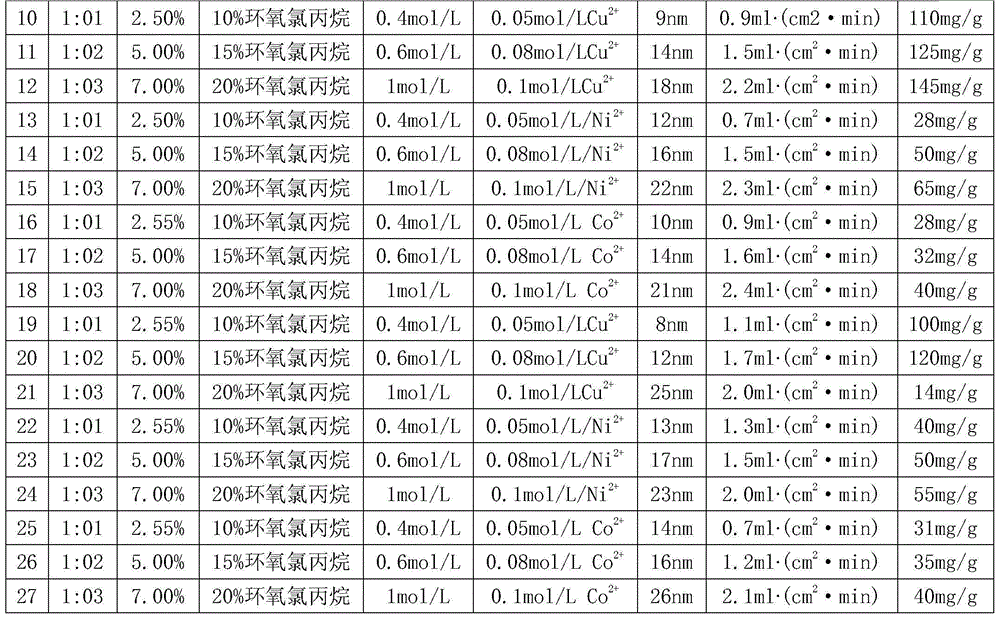
Preparation method and application of macroporous chitosan-polyvinyl alcohol crosslinking affinity membrane chelated with metal ions
InactiveCN105131329AAvoid churnImprove adsorption capacityPeptide preparation methodsEnzymesEpoxyDivalent metal ions
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of a macroporous chitosan-polyvinyl alcohol crosslinking affinity membrane chelated with metal ions. The preparation method of the membrane comprises the steps that chitosan, polyvinyl alcohol and silica gel are mixed to prepare a chitosan-polyvinyl alcohol membrane; processing and pore forming are performed with a sodium hydroxide solution; the chitosan-polyvinyl alcohol membrane is added in epoxy chloropropane and sodium hydroxide to obtain a macroporous chitosan-polyvinyl alcohol crosslinking membrane of a net structure; the macroporous chitosan-polyvinyl alcohol crosslinking membrane is steeped in a sodium carbonate solution containing iminodiacetic acid; the dried membrane is steeped in a solution containing divalent metal ions, and then the macroporous chitosan-polyvinyl alcohol crosslinking affinity membrane chelated with the metal ions is obtained. The macroporous chitosan-polyvinyl alcohol crosslinking affinity membrane chelated with the metal ions has the higher mechanical strength and has the efficient affinity adsorption capacity on protein containing histidine; the macroporous chitosan-polyvinyl alcohol crosslinking affinity membrane chelated with the metal ions is applied to separation of protein or enzymes containing the histidine, and the separation method comprises the steps of crude enzyme fluid preparation, specificity affinity adsorption of the membrane on the protein or enzymes containing the histidine, adsorption protein elution and membrane regeneration.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Method for reclaiming diglycolamidic acid from acidified mother liquor of diglycolamidic acid
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Process for the preparation of N-phosphonomethylglycine and derivatives thereof
N-phosphonomethylamines are produced by reaction of an amine substrate with a halomethylphosphonic acid or salt thereof, a hydroxymethylphosphonic acid or salt thereof, or a dehydrated self-ester dimer, trimer or oligomer of hydroxymethylphosphonic acid. Among the products that may be prepared according to the process are N-phosphonomethylaminocarboxylic acids such as (e.g.) glyphosate, N-phosphonomethylaminoalkanols such as (e.g.) hydroxyethlaminomethylphosphonic acid, and N-acylaminomethylphosphonic acids such as (e.g.) N-carbamylaminomethylphosphonic acid. Certain reactions are conducted with a substantial excess of amine reactant in order to drive the conversion while avoiding excessive formation of bis(N-phosphonomethyl)amine by-products. Other reactions use a secondary amine substrate (such as iminodiacetic acid) and can be conducted at substantial equimolar ratios of halomethylaminomethylphosphonic acid or hydroxyaminomethylphosphonic acid to secondary amine reactant without significant formation of bis(phosphonomethyl)amine by-products. Further disclosed is a process for the preparation of hydroxymethylphosphonic acid self-ester dimers, trimers and oligomers by azeotropic dehydration.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Auto cooling fluid
InactiveCN104087255AImprove stabilityGuaranteed cycleHeat-exchange elementsSilver carbonateSilver phosphate
The invention discloses auto cooling fluid, comprising the following raw materials in parts: 10-18 parts of diethylene glycol, 11-14 parts of oxalic acid, 13-15 parts of 1,2-propylene glycol, 12-15 parts of ethylene glycol ethyl ether acetate, 8-12 parts of triethyl phosphonoacetate, 8-12 parts of glufosinate-ammonium, 5-8 parts of N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid, 6-8 parts of styrene-acrylic-triazole, 6-7 parts of 1-hydroxybenzotriazole, 6-9 parts of benzotriazole, 2-3 parts of dimeticone, 1-3 parts of hydroxyl silicone oil, 3-4 parts of a dimethyl silicone polymer, 3-5 parts of butanol, 1-3 parts of sodium hydroxide, 2-3 parts of sodium peroxide, 2-4 parts of potassium chlorate, 1-3 parts of silver carbonate, 2-5 parts of silver phosphate and 150-160 parts of purified water. The auto cooling fluid has good stability, the microbial flora can be inhibited and killed, floccules, flotage, sediments and the like are prevented, effective circulation of the cooling liquid is ensured, the fault of a cooling liquid circulating system is relieved and prevented, the anti-corrosion effect is good, corrosion to the cooling liquid circulation system can be reduced and delayed, the fault of the cooling liquid circulating system is reduced, and the service life of the auto cooling liquid is prolonged.
Owner:梁胜光
Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors
This invention relates to iminodiacetic acid and diamine hydroxamic acid derivatives, that are inhibitors of histone deacetylase (HDAC), and are useful in the prevention and / or treatment of cellular proliferative diseases, for example cancer, autoimmune, allergic and inflammatory diseases, diseases of the central nervous system (CNS) such as neurodegenerative diseases, and in the prevention and / or treatment of restenosis.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
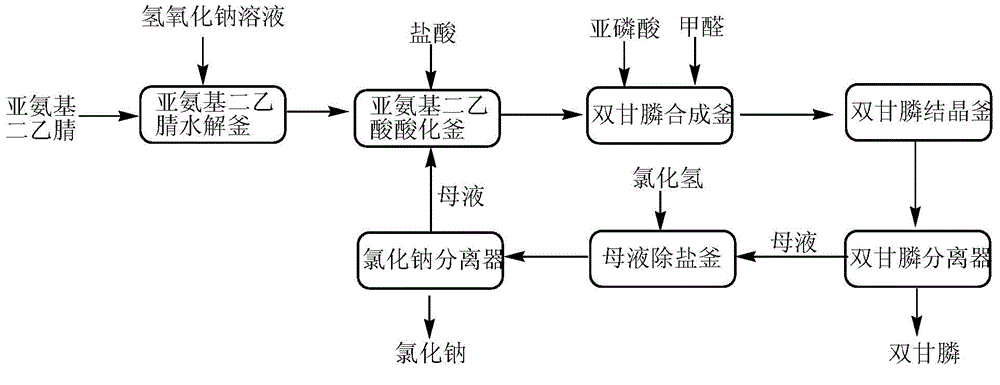
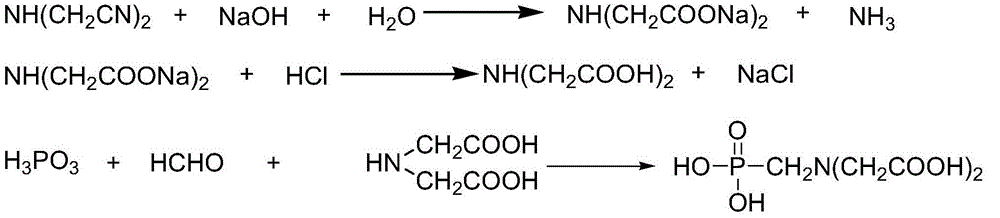
Method for producing N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid and recycling mother solution by hydrogen chloride desalinization
InactiveCN103554179AAvoid cumbersomeReduce consumptionGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsAlkali metal halide purificationPhosphorous acidHigh energy
The invention discloses a method for producing N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid and recycling a mother solution by hydrogen chloride desalinization, which comprises the following steps: 1) hydrolyzing iminodiacetonitrile with a sodium hydroxide solution to obtain disodium iminodiacetate; 2) adding hydrogen chloride to acidify the disodium iminodiacetate; 3) adding phosphorous acid and formaldehyde, heating to react to synthesize the N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid; 4) cooling, crystallizing, separating the solid, and drying to obtain the N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid product; 5) adding hydrogen chloride into the mother solution subjected to N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid separation until the concentration of the hydrogen chloride is 15-30% so as to precipitate sodium chloride, and separating and taking the sodium chloride out; and 6) returning the hydrogen-chloride-containing mother solution subjected to sodium chloride separation to the step 2) to acidify the disodium iminodiacetate. The method is simple and easy to implement, can avoid the problems of complex process and high energy consumption in the original desalinization technique for concentrating the mother solution, and can recycle excessive phosphorous acid, formaldehyde and dissolved N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid in the mother solution, thereby reducing the raw material consumption and enhancing the yield.
Owner:CHONGQING UNISPLENDOUR CHEM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com