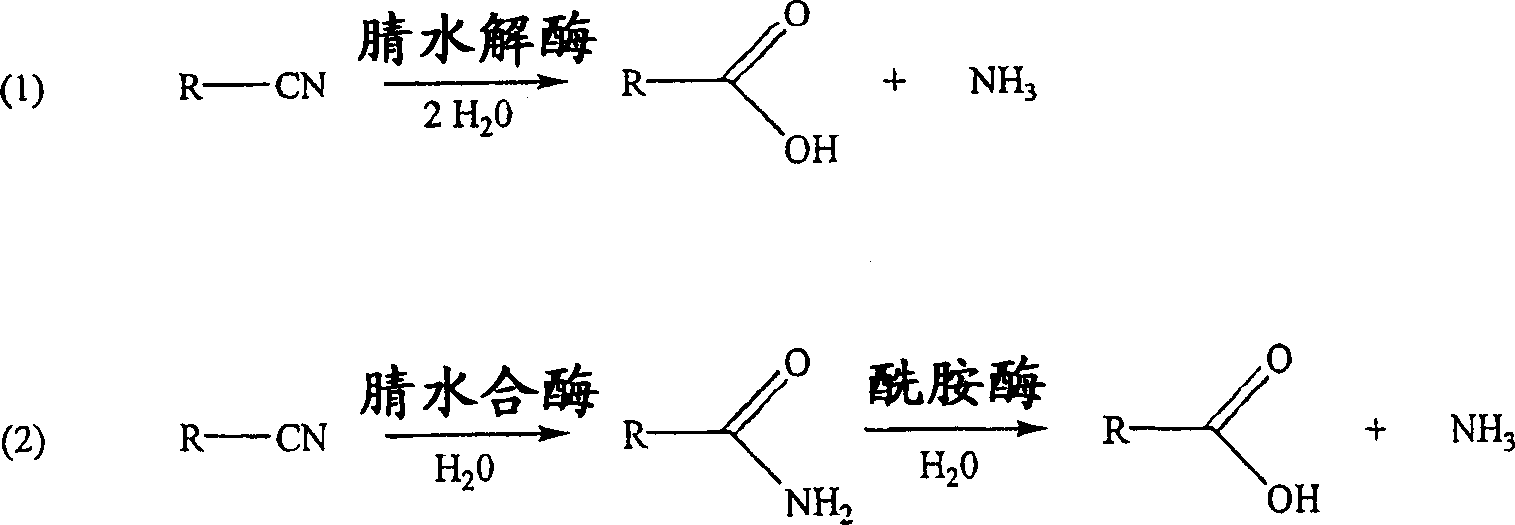
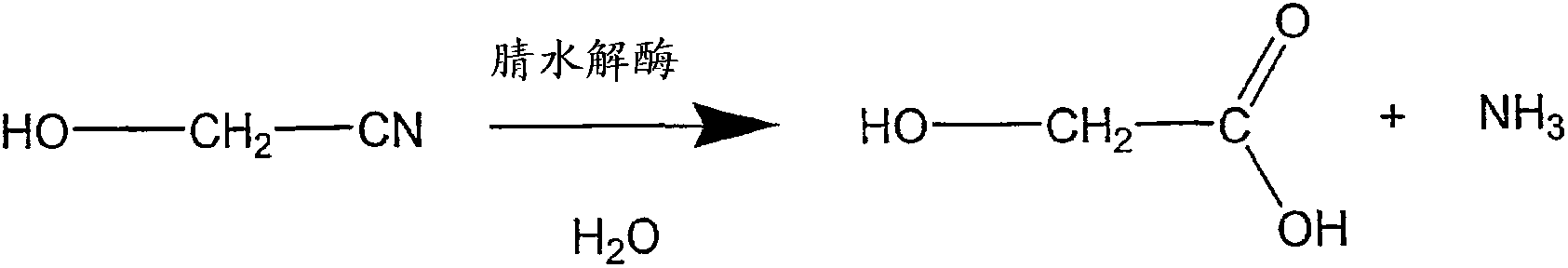
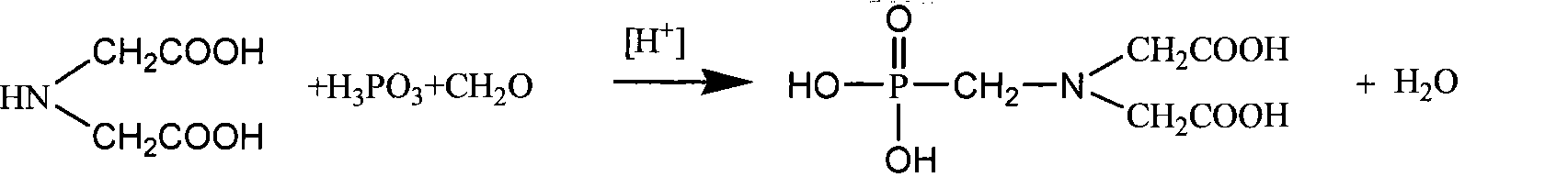
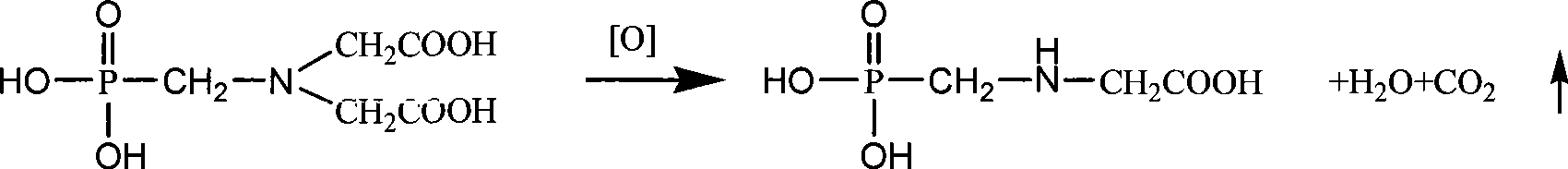
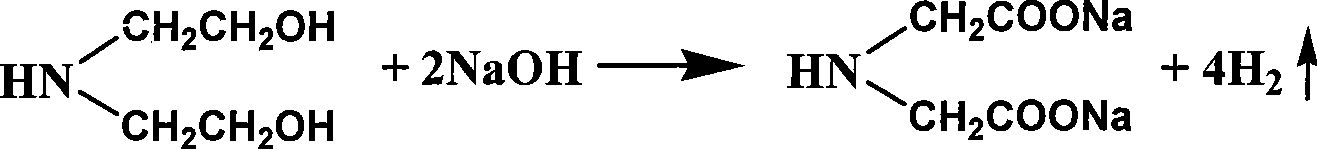
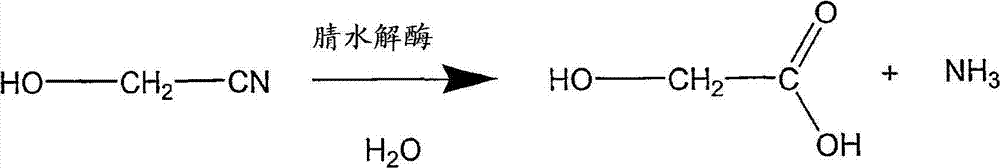
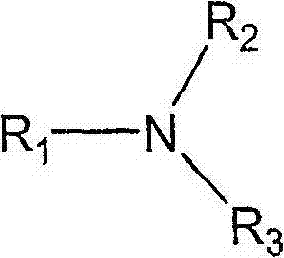
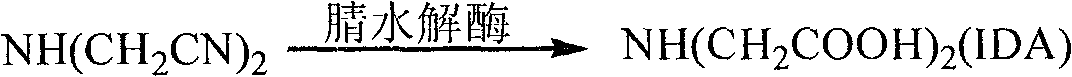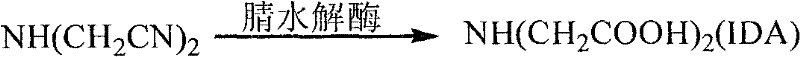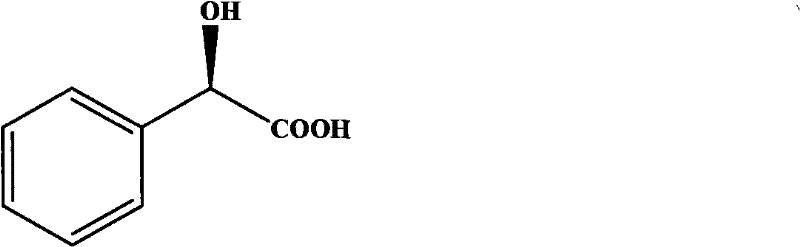Patents
Literature
49 results about "Nitrilase activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Production of 3-hydroxycarboxylic acid using nitrilase
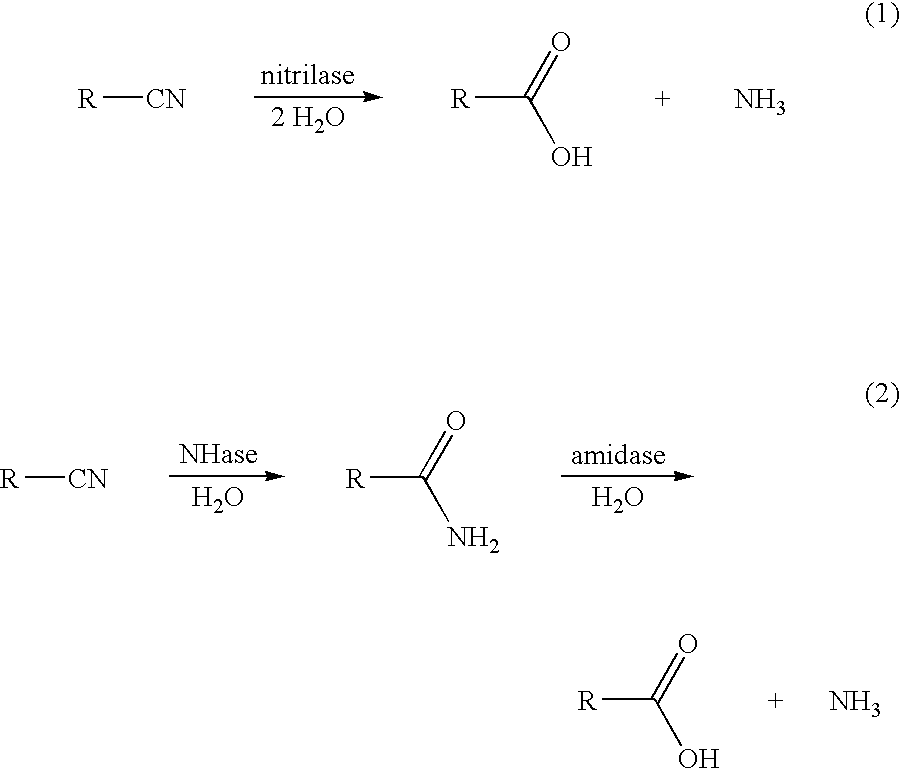
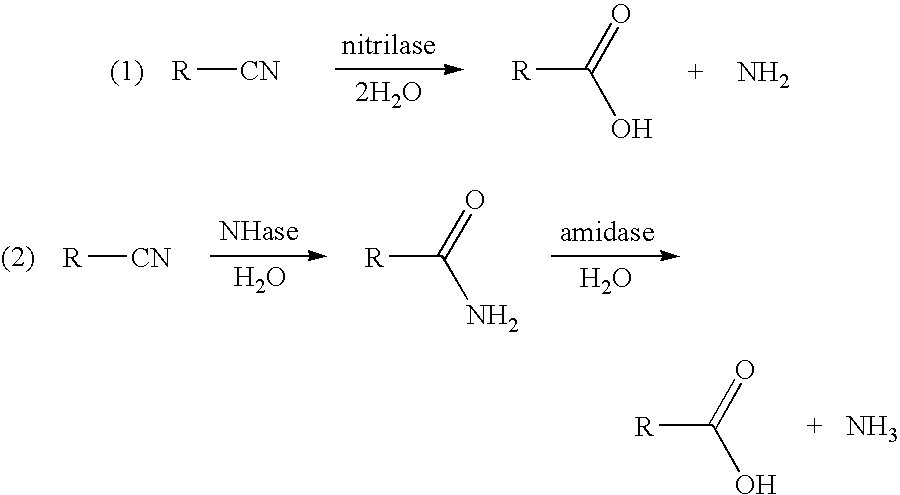
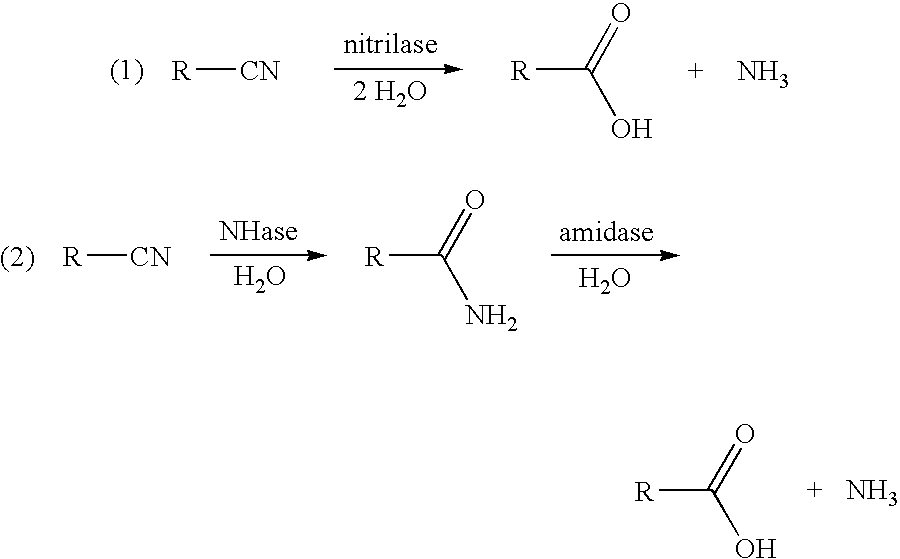
This invention relates to nitrilase mutants having improved nitrilase activity for converting 3-hydroxynitriles to 3-hydroxycarboxylic acids. More specifically, the Acidovorax facilis 72W (ATCC 55746) nitrilase gene was mutated using error-prone PCR and site-directed mutagenesis to create nitrilase enzymes having improved nitrilase activity for converting 3-hydroxynitriles (e.g., 3-hydroxybutyronitrile or 3-hydroxyvaleronitrile) to the corresponding 3-hydroxycarboxylic acids. A process using these improved mutants to produce the 3-hydroxycarboxylic acids is also provided.
Owner:PURETECH SCI LLC
Enzymatic production of glycolic acid
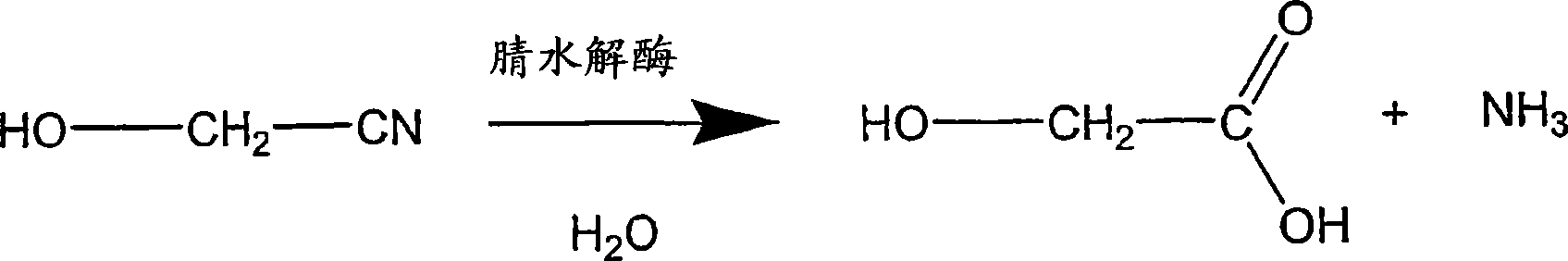
Various methods are provided for the enzymatic production of glycolic acid from glycolonitrile. These methods include: 1) use of Acidovorax facilis 72W nitrilase mutants having improved nitrilase activity for converting glycolonitrile to glycolic acid, and 2) methods to improve catalyst stability and / or productivity. The methods to improve catalyst stability / productivity include use of reaction stabilizers, running the reactions under substantially oxygen free conditions, and controlling the concentration of substrate in the reaction mixture.
Owner:PURETECH SCI LLC
Enzymatic production of glycolic acid
ActiveUS20060160199A1Facilitate recombinant expressionSugar derivativesBacteriaPtru catalystNitrilase activity
Various methods are provided for the enzymatic production of glycolic acid from glycolonitrile. These methods include: 1) use of Acidovorax facilis 72W nitrilase mutants having improved nitrilase activity for converting glycolonitrile to glycolic acid, and 2) methods to improve catalyst stability and / or productivity. The methods to improve catalyst stability / productivity include use of reaction stabilizers, running the reactions under substantially oxygen free conditions, and controlling the concentration of substrate in the reaction mixture.
Owner:PURETECH SCI LLC
Production of 3-hydroxycarboxylic acid using nitrilase
This invention relates to nitrilase mutants having improved nitrilase activity for converting 3-hydroxynitriles to 3-hydroxycarboxylic acids. More specifically, the Acidovorax facilis 72W (ATCC 55746) nitrilase gene was mutated using error-prone PCR and site-directed mutagenesis to create nitrilase enzymes having improved nitrilase activity for converting 3-hydroxynitriles (e.g., 3-hydroxybutyronitrile or 3-hydroxyvaleronitrile) to the corresponding 3-hydroxycarboxylic acids. A process using these improved mutants to produce the 3-hydroxycarboxylic acids is also provided.
Owner:PURETECH SCI LLC
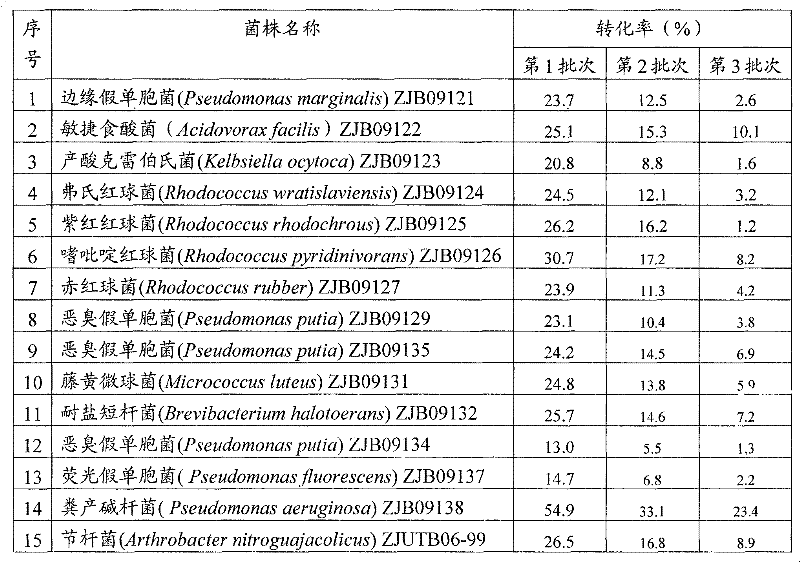
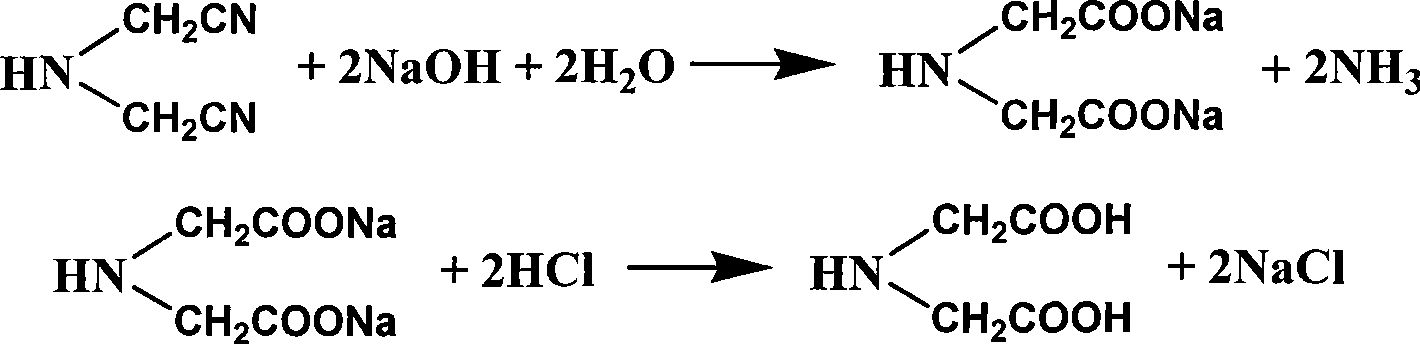
Method for preparing iminodiacetic acid by catalyzing iminodiacetonitrile with microbes
ActiveCN101629192AEfficient productionBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismIminodiacetic acid
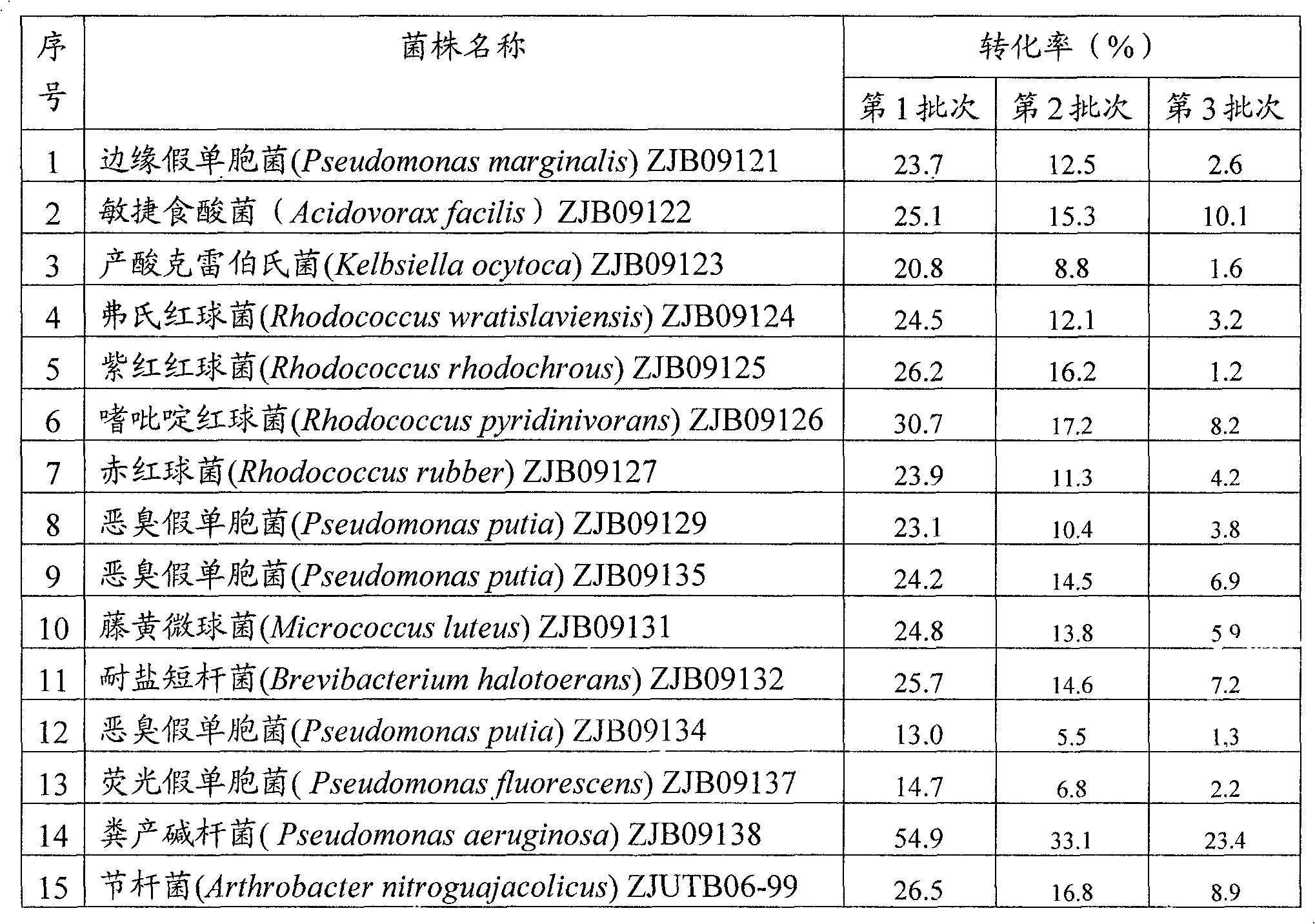
The invention provides a method for preparing iminodiacetic acid by catalyzing iminodiacetonitrile with microbes, which comprises the following steps: using bacterial strains which produce nitrilase to obtain the nitrilase through enzyme production cultivation; and taking the nitrilase as a biological catalyst to biologically catalyze the iminodiacetonitrile to prepare the iminodiacetic acid. The invention also relates to a screening method of the microbes which produce the nitrilase and the bacterial strains with nitrilase activity obtained by the screening method. The invention provides the basis for producing the iminodiacetic acid by biologically catalyzing the iminodiacetonitrile, thereby having important application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Process for producing glycolic acid from formaldehyde and hydrogen cyanide
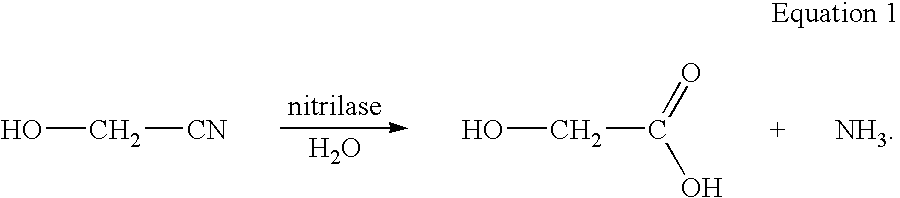
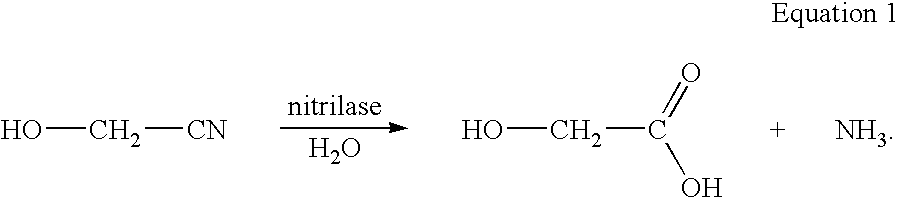
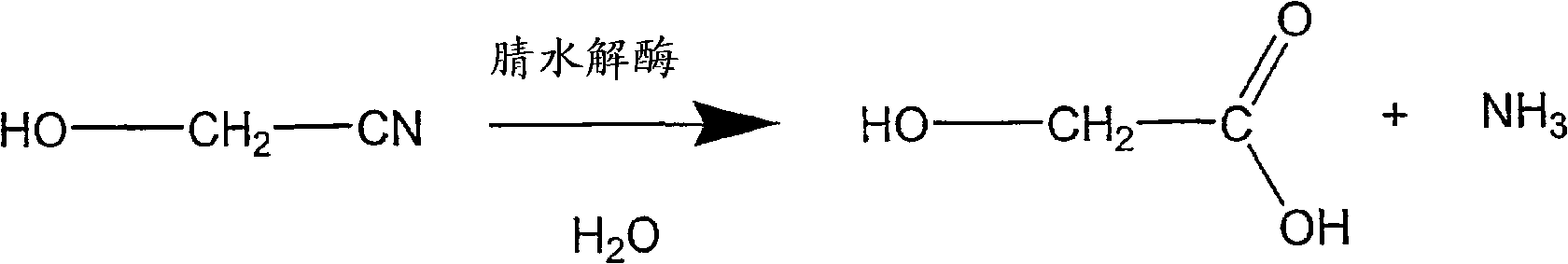
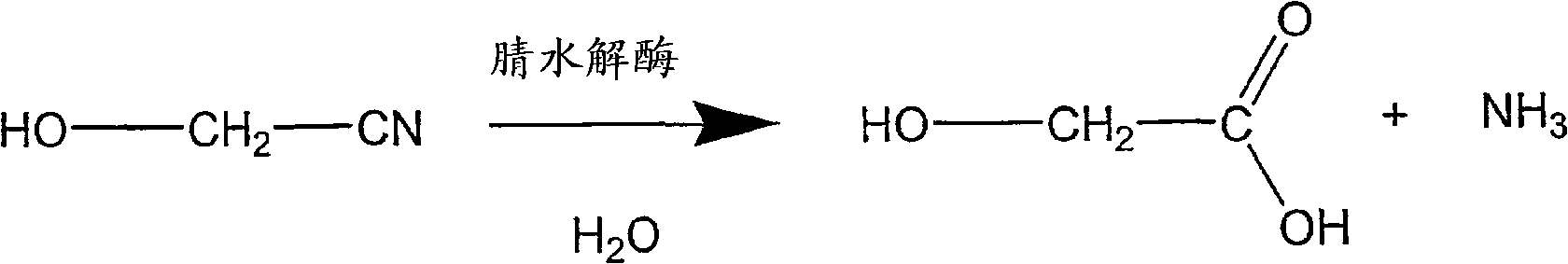
A process is provided for producing glycolic acid from formaldehyde and hydrogen cyanide. More specifically, heat-treated formaldehyde and hydrogen cyanide are reacted to produce glycolonitrile having low concentrations of impurities. The glycolonitrile is subsequently converted to an aqueous solution of ammonium glycolate using an enzyme catalyst having nitrilase activity derived from Acidovorax facilis 72W (ATCC 57746). Glycolic acid is recovered in the form of the acid or salt from the aqueous ammonium glycolate solution using a variety of methods described herein.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Method for preparing iminodiacetic acid from iminodiacetonitrile by microorganism catalysis
ActiveCN101629192BEfficient productionBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyIminodiacetic acid
The invention provides a method for preparing iminodiacetic acid by microorganism catalyzing iminodiacetonitrile. The method is to use a nitrilase-producing bacterial strain to obtain nitrilase through enzyme-producing culture, and use nitrilase as a biocatalyst to biocatalyze Iminodiacetonitrile is prepared to give iminodiacetic acid. The present invention also relates to a screening method for microorganisms producing nitrilase and a bacterial strain with nitrilase activity obtained by screening using the method. The invention provides a basis for producing iminodiacetic acid by using biocatalytic iminodiacetonitrile, and has important application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Production of iminodiacetic acid by microorganism catalytic processes and bacterial strain thereof
ActiveCN101392276AReduce outputLow impurity contentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacterial strainFermentation
The invention discloses a method for producing diglycolamidic acid, namely, the key intermediate synthesized by glyphosate through biological catalysis and a new strain used in the process. The method takes iminodiacetonitrile as a raw material and a microbial enzyme with nitrilase activity obtained from the fermentation culture of Alcaligenes faecalis ZJUTB10 as a catalyst and obtains the diglycolamidic acid as a product by going through hydrolysis reaction under certain condition. The beneficial effects of the method are mainly reflected by little waste water produced during the reaction process, little pollution, mild reaction conditions, low energy consumption, high conversion rate and high yield and being easy for industrialized production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
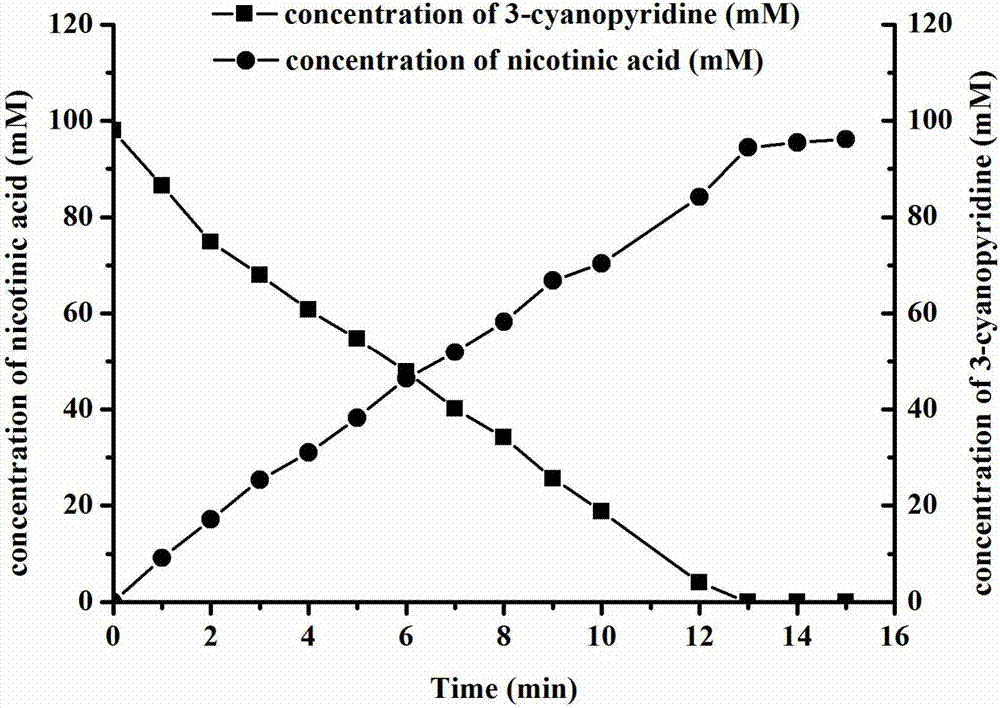
Bacillus subtilis for high yield of recombinant nitrilase and application of bacillus subtilis
ActiveCN107254429AImprove security levelReduce manufacturing costBacteriaHydrolasesHydrolase GenePseudomonas putida
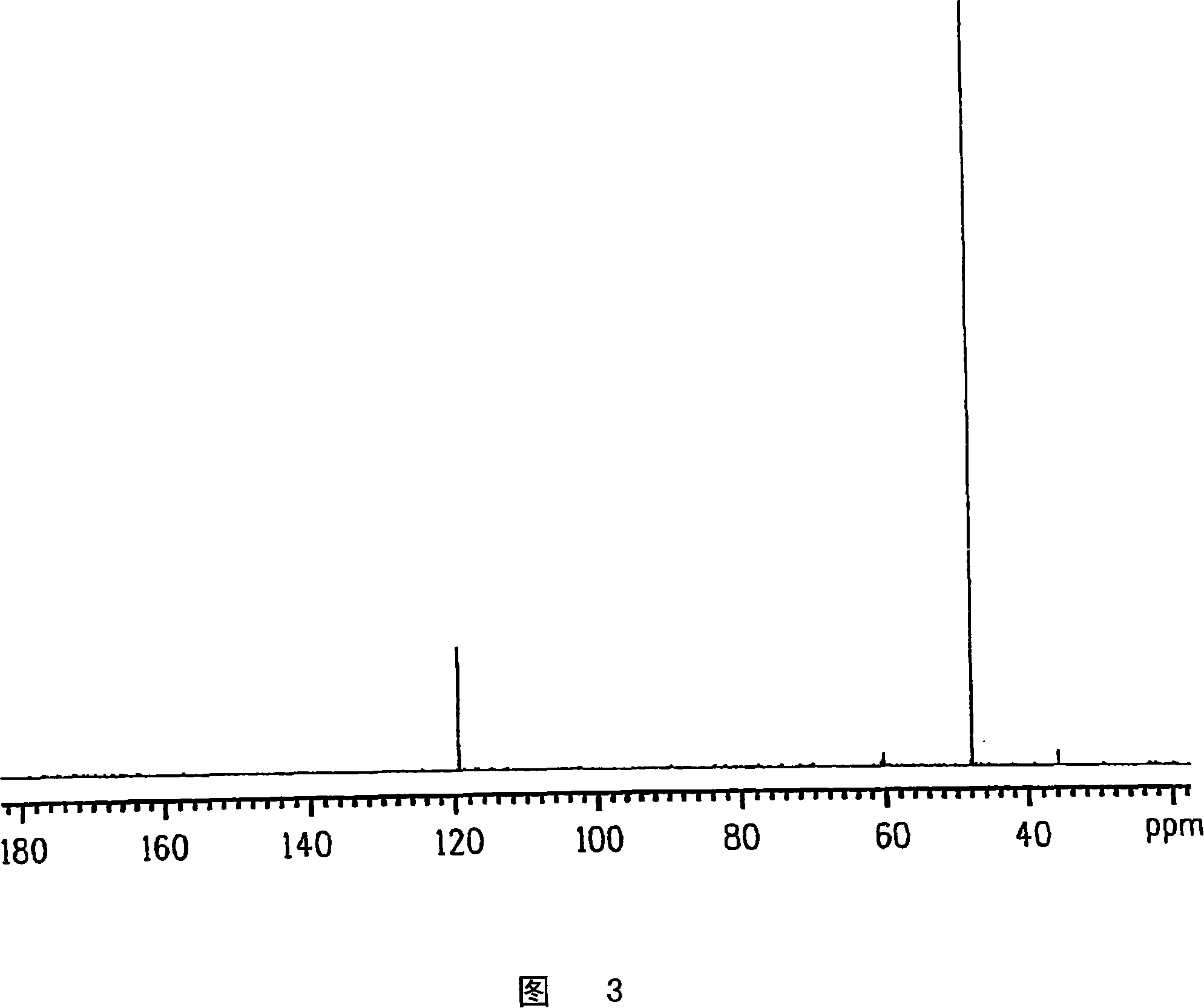
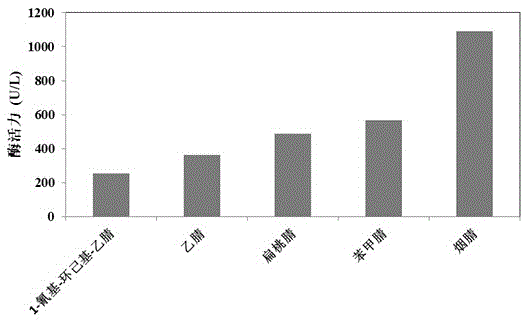
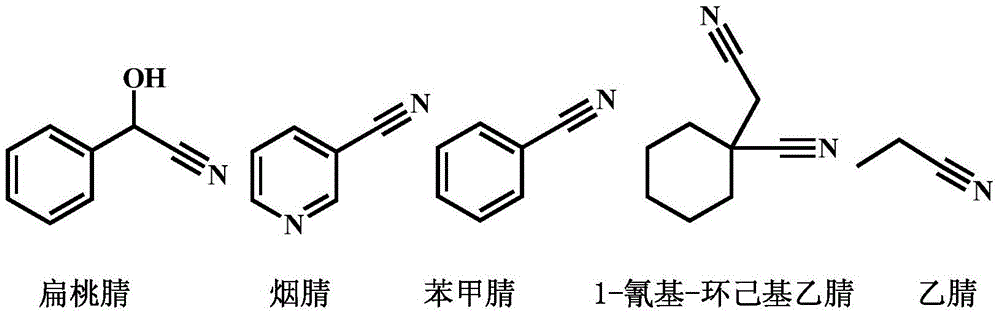
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis for high yield of recombinant nitrilase and application of the bacillus subtilis in nicotinic acid synthesis and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. A method comprises the following steps: performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on a Pseudomonas putida CGMCC 3830 nitrilase gene coding sequence, connecting with a pMA5 plasmid, establishing a recombinant plasmid pMat-NIT, and transforming into Bacillus subtilis WB600, thereby obtaining a recombinant bacterium, namely B.subtilis WB600 (pMA5-NIT) which is capable of efficiently expressing nitrilase, wherein the recombinant bacterium is named as Bacillus subtilis NIT-2 and is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.14255. With recombinant bacillus subtilis free cells as a catalyst, 3-cyanopyridine can be completely transformed to generate nicotinic acid. The invention provides a bacillus subtilis strain for high yield of recombinant nitrilase, and the bacillus subtilis strain has outstanding nitrilase activity and is short in recombinant bacterium fermentation period, high in catalysis efficiency and good in application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
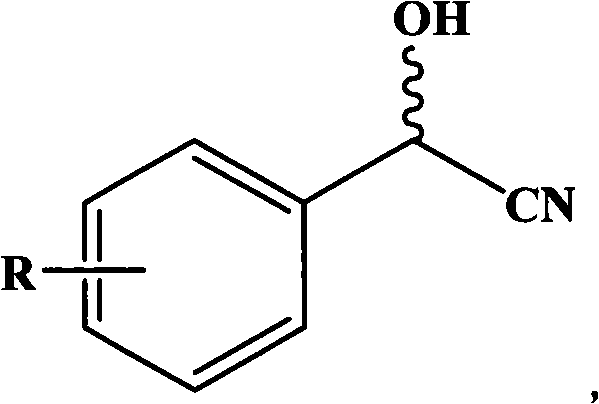
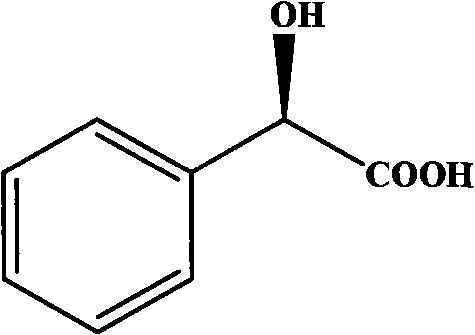
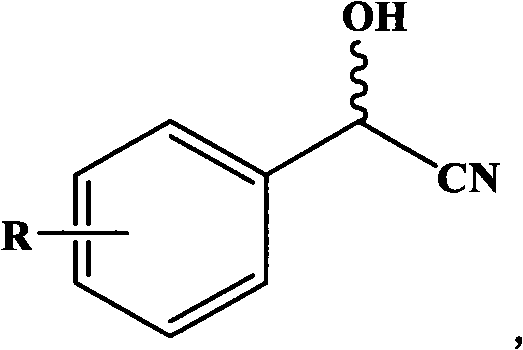
Gene for coding nitrilase of alcaligenes and method for preparing single enantiomorph of mandelic acid using same
InactiveCN101701222AGood effectGreat potential for industrial application developmentHydrolasesMicroorganismsMandelonitrileNitrilase activity
The invention relates to a base sequence for coding nitrilase of alcaligenes, relating to a carrier comprising the base sequence and a transformant comprising the base sequence or the carrier, wherein the carrier comprises the base sequence, or a composite unit connecting the base sequence with a corresponding signal sequence. The invention also relates to an amino acid sequence coded by the base sequence, and further relates to a technical method for preparing single enantiomorph of mandelic acid and analogue thereof from corresponding mandelonitrile by utilizing the recombinant expression nitrilase as catalyst.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
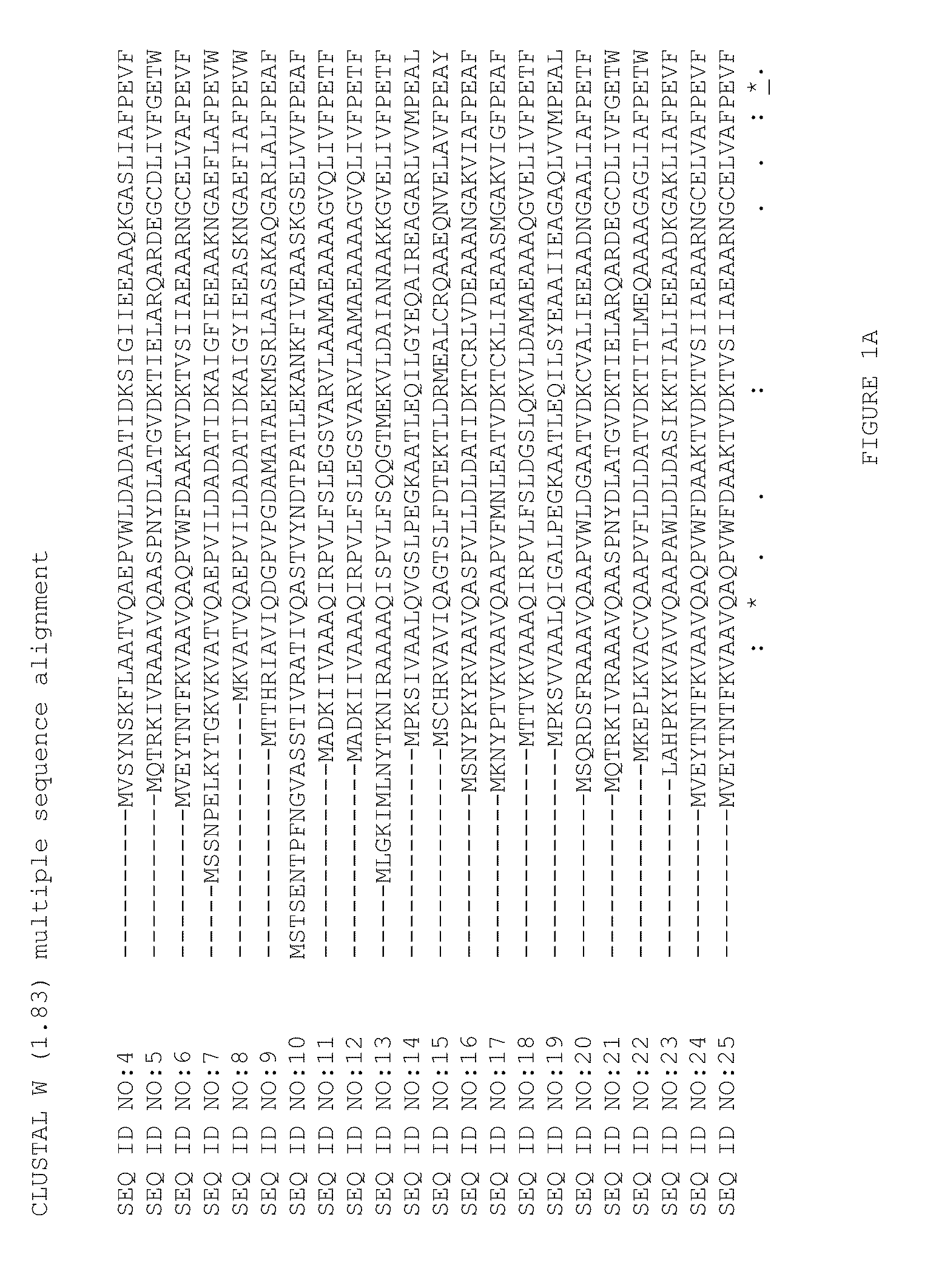
Nitrilase mutant with improved catalytic activity and reaction specificity and application
ActiveCN112359036AHigh activityImprove responseBacteriaHydrolasesHigh concentrationMethyl palmoxirate
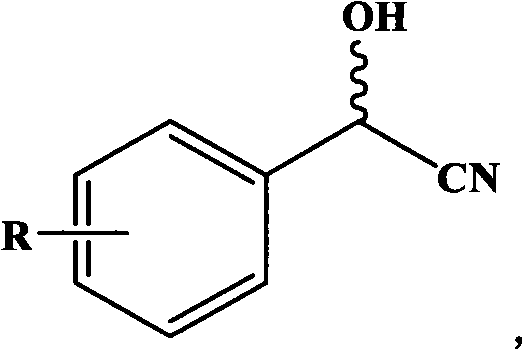
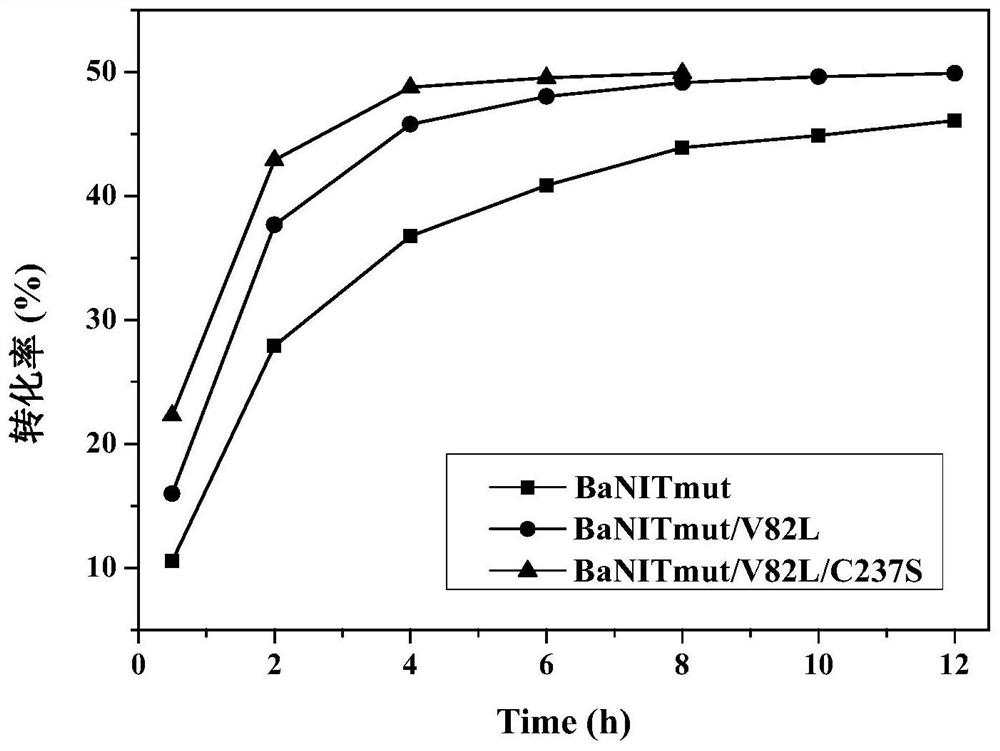
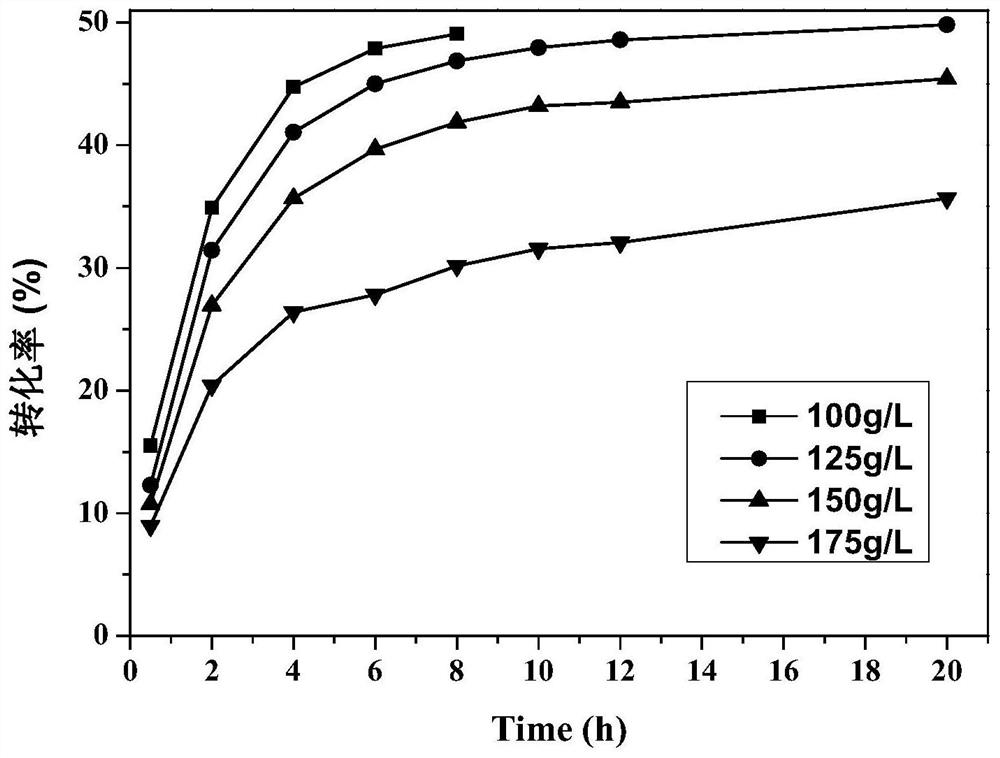
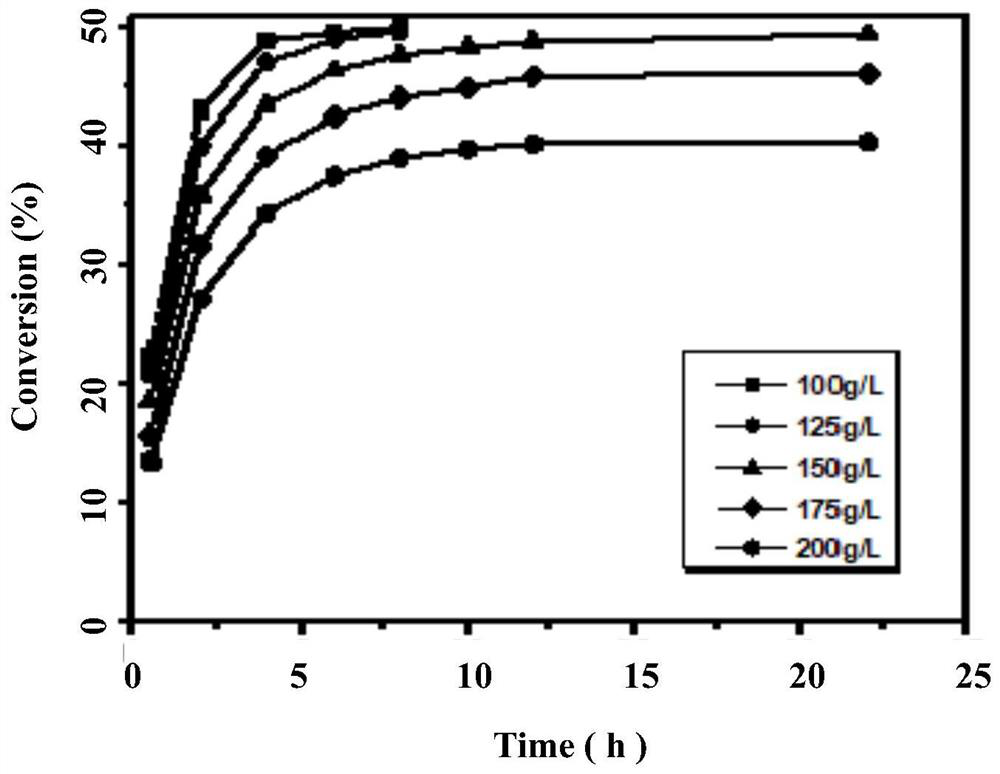
The invention discloses a nitrilase mutant and application thereof in hydrolysis of racemic isobutyl butyronitrile to synthesize a pregabalin chiral intermediate (S)-3-cyano-5-methyl hexanoic acid andbelongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The nitrilase mutant BaNITmut / V82L with the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.4 or the double mutant BaNITmut / V82L / C237S with the amino acidsequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.6 can catalyze high-concentration IBSN hydrolysis, and amide byproducts are remarkably reduced. The nitrilase activity and the reaction specificity are improved througha directed evolution technology, industrial production cost is greatly reduced, and the method has a good application prospect in industrial production of the pregabalin chiral intermediate (S)-3-cyano-5-methyl caproic acid.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Immobilized microbial nitrilase for production of glycolic acid
ActiveUS20090111158A1High retention rateSpecific activitySugar derivativesHydrolasesGluconic acidNitrilase activity
The present invention provides a process for preparing an enzyme catalyst having nitrilase activity for hydrolysis of glycolonitrile to glycolic acid with improved retention of recovered catalyst activity in consecutive batch reactions with catalyst recycle, said process comprising pretreating the enzyme catalyst with glutaraldehyde. The glutaraldehyde-pretreated enzyme catalyst has improved specific activity when compared to non-glutaraldehyde-pretreated enzyme catalysts, and thereby, has improved overall catalyst activity and productivity.
Owner:PURETECH SCI LLC
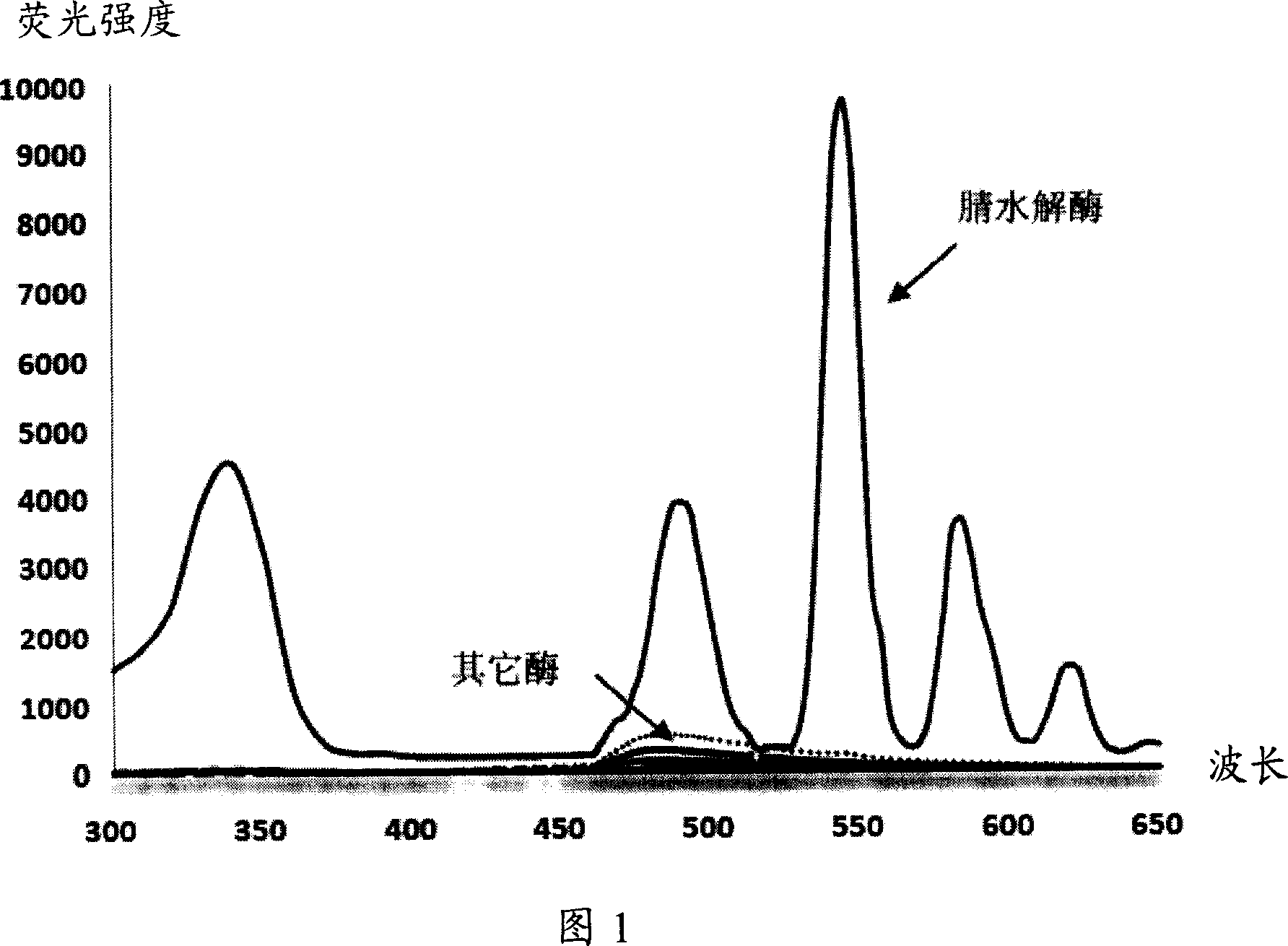
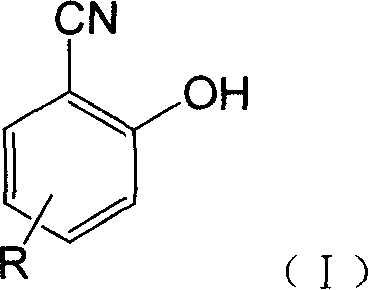
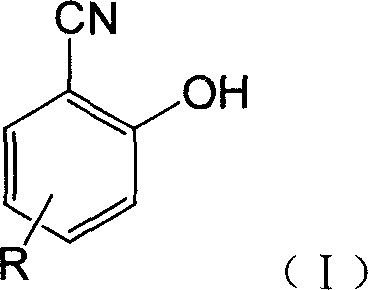
Fluorescent detecting method for nitrile hydrolitic enzyme activity
InactiveCN1945288AStable in natureHigh purityOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementNitrilase activityHydrolase activity
The fluorescent detecting method for nitrile hydrolase activity includes hydrolyzing fluorescent probe with nitrile hydrolase and measuring the fluorescence strength to obtain nitrile hydrolase activity data. The fluorescent probe is made of salicyl nitrile compound in the structure as shown. The present invention has the advantages of simple preparation of fluorescent probe, stable property and high purity of the fluorescent probe, and high detection sensitivity, precision and speed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Enzymatic production of glycolic acid
Various methods are provided for the enzymatic production of glycolic acid from glycolonitrile. These methods include: 1) use of Acidovorax facilis 72W nitrilase mutants having improved nitrilase activity for converting glycolonitrile to glycolic acid, and 2) methods to improve catalyst stability and / or productivity. The methods to improve catalyst stability / productivity include use of reaction stabilizers, running the reactions under substantially oxygen free conditions, and controlling the concentration of substrate in the reaction mixture.
Owner:高纯技术科学有限责任公司
Immobilized microbial nitrilase for production of glycolic acid
ActiveUS20090111148A1Specific activityFully understandSugar derivativesHydrolasesCross-linkGluconic acid
The present invention is directed to a process for improving the specific activity of a dehydrated enzyme catalyst having nitrilase activity for hydrolysis of glycolonitrile to glycolic acid upon rehydration. In particular, a process is provided comprising pretreating an enzyme catalyst having nitrilase activity with glutaraldehyde, immobilizing the gutaraldehyde-preteated enzyme catalyst and chemically cross-linking the enzyme catalyst prior to dehydration. Upon rehydration, the enzyme catalyst exhibits improved specific nitrilase activity as compared to enzyme catalysts having nitrilase activity that are dehydrated and rehydrated without the processing described herein.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Enzymatic production of glycolic acid
Various methods are provided for the enzymatic production of glycolic acid from glycolonitrile. These methods include: 1) use of Acidovorax facilis 72W nitrilase mutants having improved nitrilase activity for converting glycolonitrile to glycolic acid, and 2) methods to improve catalyst stability and / or productivity. The methods to improve catalyst stability / productivity include use of reaction stabilizers, running the reactions under substantially oxygen free conditions, and controlling the concentration of substrate in the reaction mixture.
Owner:高纯技术科学有限责任公司
Method for stabilizing nitrilase activity and preserving microbial cells
A method for preserving immobilized or unimmobilized microbial cells having nitrilase activity and for stabilizing the nitrilase activity of unimmobilized or immobilized microbial cells has been developed. The unimmobilized or immobilized microbial cells are stored in an aqueous solution containing from about 0.10 M to the saturation concentration of an inorganic salt of bicarbonate or carbonate, including ammonium, sodium and potassium salts of bicarbonate or carbonate. Aqueous suspensions containing at least 100 mM bicarbonate or carbonate limit microbial contamination of the stored enzyme catalyst, as well as stabilize the desired nitrilase activity of the unimmobilized or immobilized cells. Microorganisms which are characterized by a nitrilase activity and are stabilized and preserved by this method include Acidovorax facilis 72-PF-15 (ATCC55747), Acidovorax facilis 72-PF-17 (ATCC55745), Acidovorax facilis 72W (ATCC55746), and transformed microbial cells having nitrilase activity, preferably Escherichia coli SS1001 (ATTCCPTA-1177) which is transformed with Acidovorax facilis 72W nitrilase activity.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Gene for coding nitrilase of alcaligenes and method for preparing single enantiomorph of mandelic acid using same
InactiveCN101701222BGood effectGreat potential for industrial application developmentHydrolasesMicroorganismsBase JMandelonitrile
The invention relates to a base sequence for coding nitrilase of alcaligenes, relating to a carrier comprising the base sequence and a transformant comprising the base sequence or the carrier, wherein the carrier comprises the base sequence, or a composite unit connecting the base sequence with a corresponding signal sequence. The invention also relates to an amino acid sequence coded by the basesequence, and further relates to a technical method for preparing single enantiomorph of mandelic acid and analogue thereof from corresponding mandelonitrile by utilizing the recombinant expression nitrilase as catalyst.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
3-hydroxycarboxylic acid production and use in branched polymers
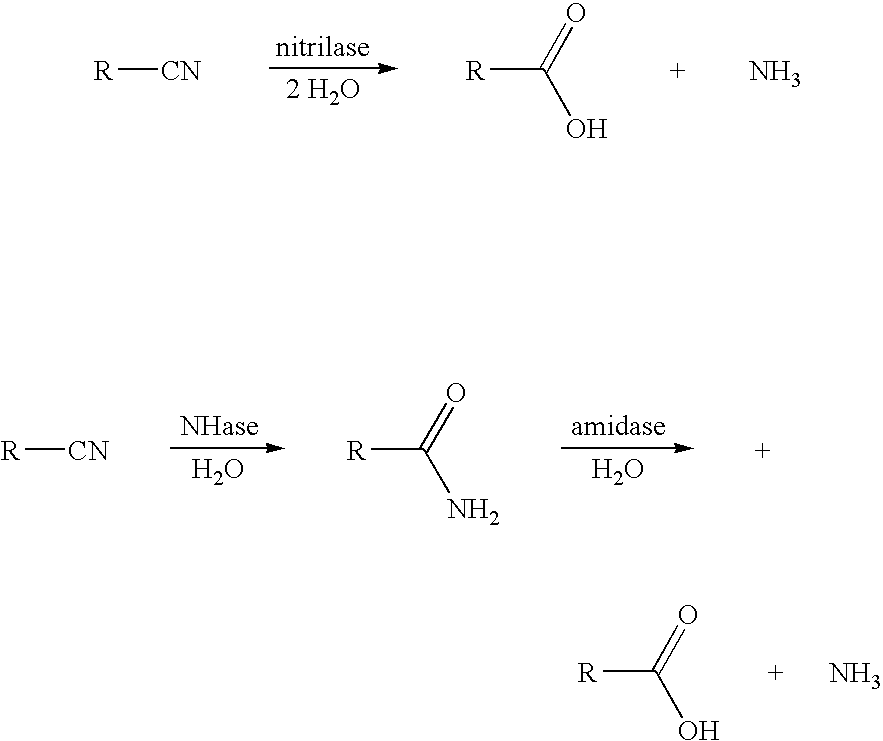
This invention relates to a process for the preparation of a 3-hydroxycarboxylic acid from a 3-hydroxynitrile. More specifically, 3-hydroxyvaleronitrile is converted to 3-hydroxyvaleric acid in high yield at up to 100% conversion, using as an enzyme catalyst 1) nitrile hydratase activity and amidase activity or 2) nitrilase activity of a microbial cell. 3-Hydroxyvaleric acid is used as a substitute for ε-caprolactone in the preparation of highly branched copolyester.
Owner:AXALTA COATING SYST IP CO LLC
Method for preparing 2-hydroxy 4-methylthio butyric acid using nitrilase
The invention concerns a method for preparing 2-hydroxy 4-methylthio butyric acid and / or the ammonium salt thereof by enzymatic hydrolysis of 2-hydroxy 4-methythio butyronitrile characterised in that: a) in a first step a biological material having nitrilase activity is prepared, b) in a second step it is immobilised, c) in a third step, 2-hydroxy 4-methylthio butyronitrile is brought in the presence of the immobilised biological material, for obtaining the ammonium salt of 2-hydroxy 4-methylthio butyric acid, d) in a fourth step, optionally, the salt obtained in step c) is transformed into the corresponding acid, and e) in a fifth step, the product resulting from step c) or d) is concentrated.
Owner:ADISSEO IRELAND LIMITED IE
Process for producing glycolic acid from formaldehyde and hydrogen cyanide
ActiveCN101133161AOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationGluconic acidGlycollic acid
A process is provided for producing glycolic acid from formaldehyde and hydrogen cyanide. More specifically, heat-treated formaldehyde and hydrogen cyanide are reacted to produce glycolonitrile having low concentrations of impurities. The glycolonitrile is subsequently converted to an aqueous solution of ammonium glycolate using an enzyme catalyst having nitrilase activity derived from Acidovorax facilis 72W (ATCC 57746). Glycolic acid is recovered in the form of the acid or salt from the aqueous ammonium glycolate solution using a variety of methods described herein.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
Method for rapidly detecting activity of nitrilase
InactiveCN105548054ASignificant technological progressImprove securityColor/spectral properties measurementsWater bathsHplc method
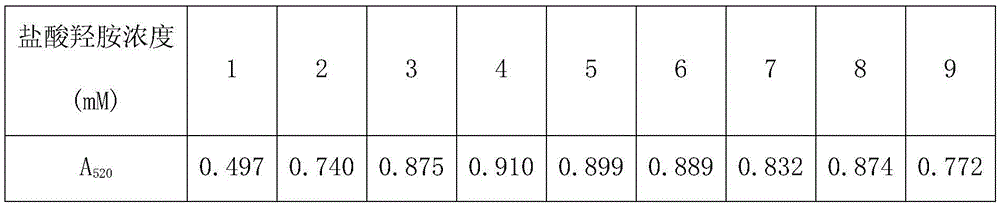
The invention discloses a method for rapidly detecting the activity of nitrilase. The method comprises the following steps: adding hydroxylamine hydrochloride and an ethanol solution of dicyclohexylcarbodiimide into a nitrilase reaction sample, vibrating the mixture to evenly mixing the solution, heating the solution by a water bath, then adding an ethanol solution of iron trichloride, fully carrying out color development, measuring the absorbance value at 520 nm by a ultraviolet spectrophotometer, and calculating the activity of nitrilase according to the absorbance value; the measured relative standard deviation (RSD) and recovery rate are 1-2% and 99-102%, and the results are identical with those of HPLC method. The provided method has the advantages of simpleness, rapidness, safety, cheapness, and precision, and can be applied to rapid screening and high flux screening of nitrilase.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
3-Hydroxycarboxylic acid production and use in branched polymers
Owner:AXALTA COATING SYST IP CO LLC
Enzymatic production of glycolic acid
Various methods are provided for the enzymatic production of glycolic acid from glycolonitrile. These methods include: 1) use of Acidovorax facilis 72W nitrilase mutants having improved nitrilase activity for converting glycolonitrile to glycolic acid, and 2) methods to improve catalyst stability and / or productivity. The methods to improve catalyst stability / productivity include use of reaction stabilizers, running the reactions under substantially oxygen free conditions, and controlling the concentration of substrate in the reaction mixture.
Owner:THE CHEMOURS CO FC LLC
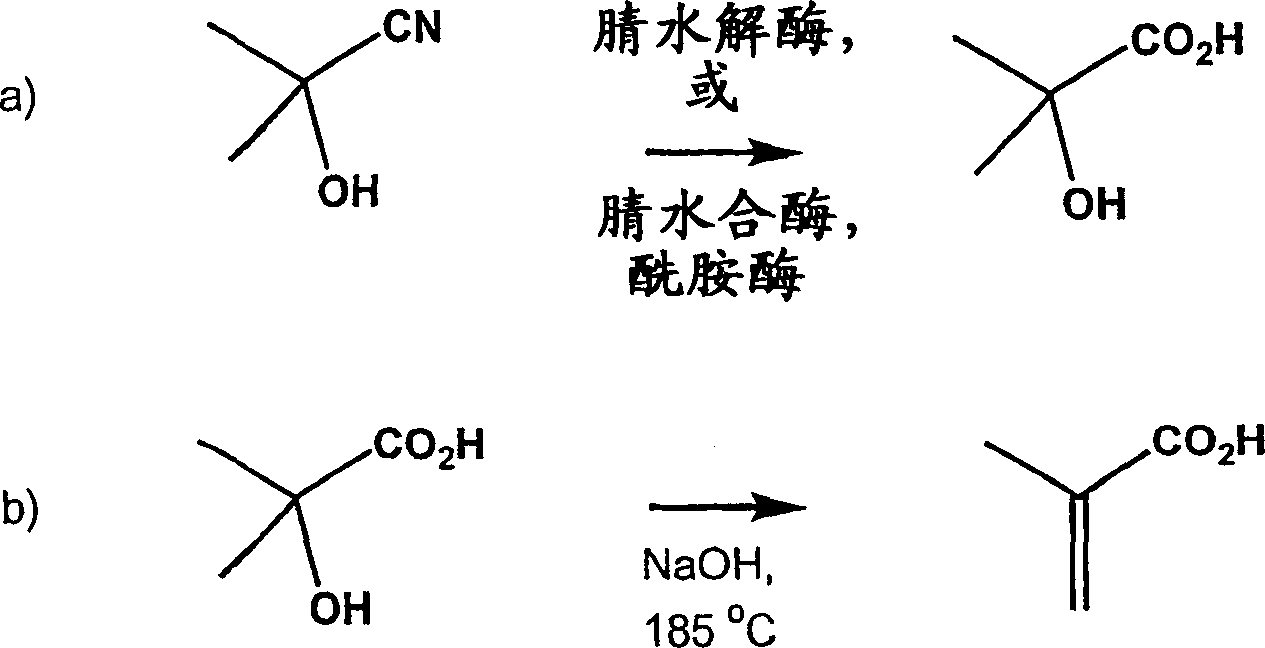
Method for producing 2-hydroxyisobutyric acid and methacrylic acid from acetone cyanohydrin
The present invention relates to a process for the production of 2-hydroxyisobutyric acid in which acetone cyanohydrin is converted to 2-hydroxyisobutyric acid using a catalyst having nitrilase activity or using a catalyst having combined nitrile hydratase and amidase activity acid. The invention also relates to the production of methacrylic acid in which 2-hydroxyisobutyric acid prepared with said catalyst is dehydrated to produce methacrylic acid.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Enzymatic production of glycolic acid
Various methods are provided for the enzymatic production of glycolic acid from glycolonitrile. These methods include: 1) use of Acidovorax facilis 72W nitrilase mutants having improved nitrilase activity for converting glycolonitrile to glycolic acid, and 2) methods to improve catalyst stability and / or productivity. The methods to improve catalyst stability / productivity include use of reaction stabilizers, running the reactions under substantially oxygen free conditions, and controlling the concentration of substrate in the reaction mixture.
Owner:高纯技术科学有限责任公司
Production of iminodiacetic acid by microorganism catalytic processes and bacterial strain thereof
ActiveCN101392276BReduce outputLow impurity contentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacterial strainFermentation
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Enzymatic production of glycolic acid
Various methods are provided for the enzymatic production of glycolic acid from glycolonitrile. These methods include: 1) use of Acidovorax facilis 72W nitrilase mutants having improved nitrilase activity for converting glycolonitrile to glycolic acid, and 2) methods to improve catalyst stability and / or productivity. The methods to improve catalyst stability / productivity include use of reaction stabilizers, running the reactions under substantially oxygen free conditions, and controlling the concentration of substrate in the reaction mixture.
Owner:HIGH PURITY TECH & SCI LLC
Sequestration of formaldehyde to stabilize nitrilase specific activity when converting glycolonitrile to glycolic acid
A process is provided to improve the specific activity of an enzyme catalyst having nitrilase activity when converting glycolonitrile to glycolic acid under aqueous reaction conditions. Inclusion of an effective amount of at least one amine protectant improves the specific activity and catalytic productivity of the enzyme catalyst.
Owner:PURETECH SCI LLC
Method for producing 3,6-dichloropyrimidine-2-carboxylic acid by biocatalysis
InactiveCN101906447BReduce poisonReduce inhibitionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationOrganic solvent
The invention belongs to the field of biochemical engineering, and discloses a method for producing 3,6-dichloropyrimidine-2-carboxylic acid by biocatalysis. In the method, a nitrilase-producing active cell is taken as a biocatalyst, and a substrate 3,6-dichloro-2-cyanopyridine is hydrolyzed into the 3,6-dichloropyrimidine-2-carboxylic acid in a water-organic solvent biphasic system at the temperature of between 15 and 35 DEG C. In the method, biocatalytic reaction is coupled with product separation, so that the toxicity and inhibition effect of the high-concentration substrate and the product on the cell is effectively overcome, and the product is effectively separated; therefore, the method has the advantages of simple operation, mild reaction condition, and suitability for industrialized production.
Owner:NANJING HUAZHOU PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com