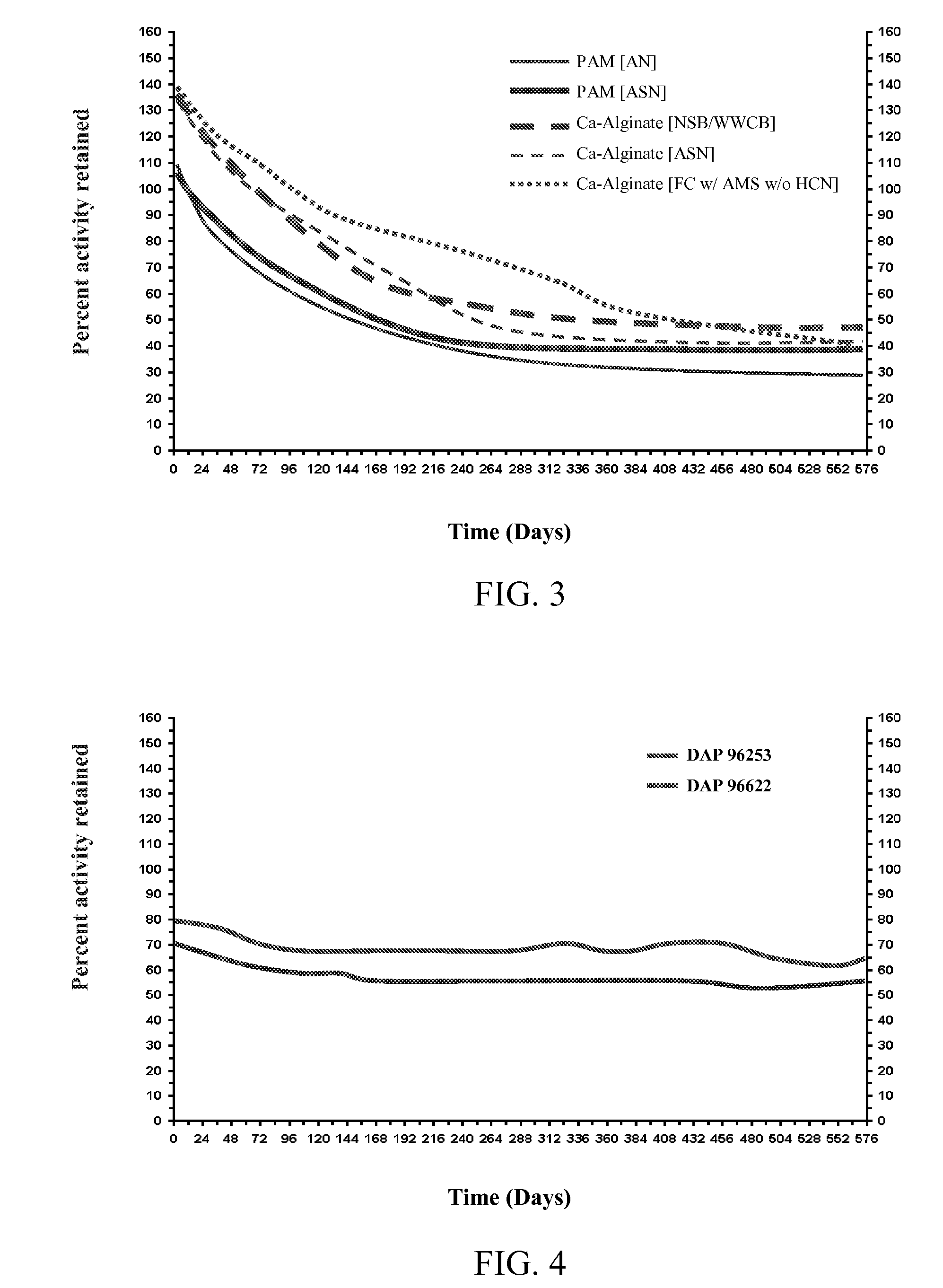
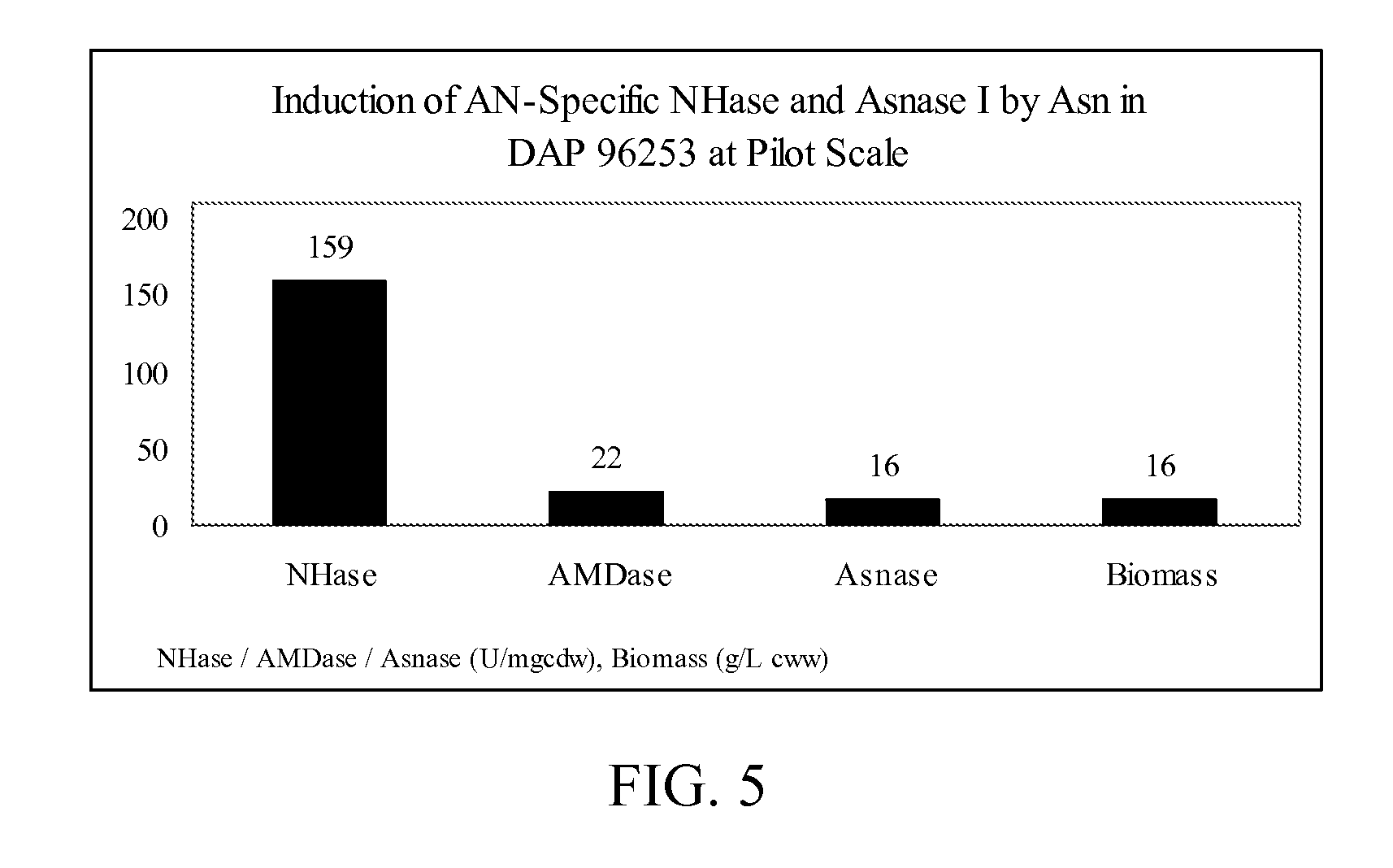
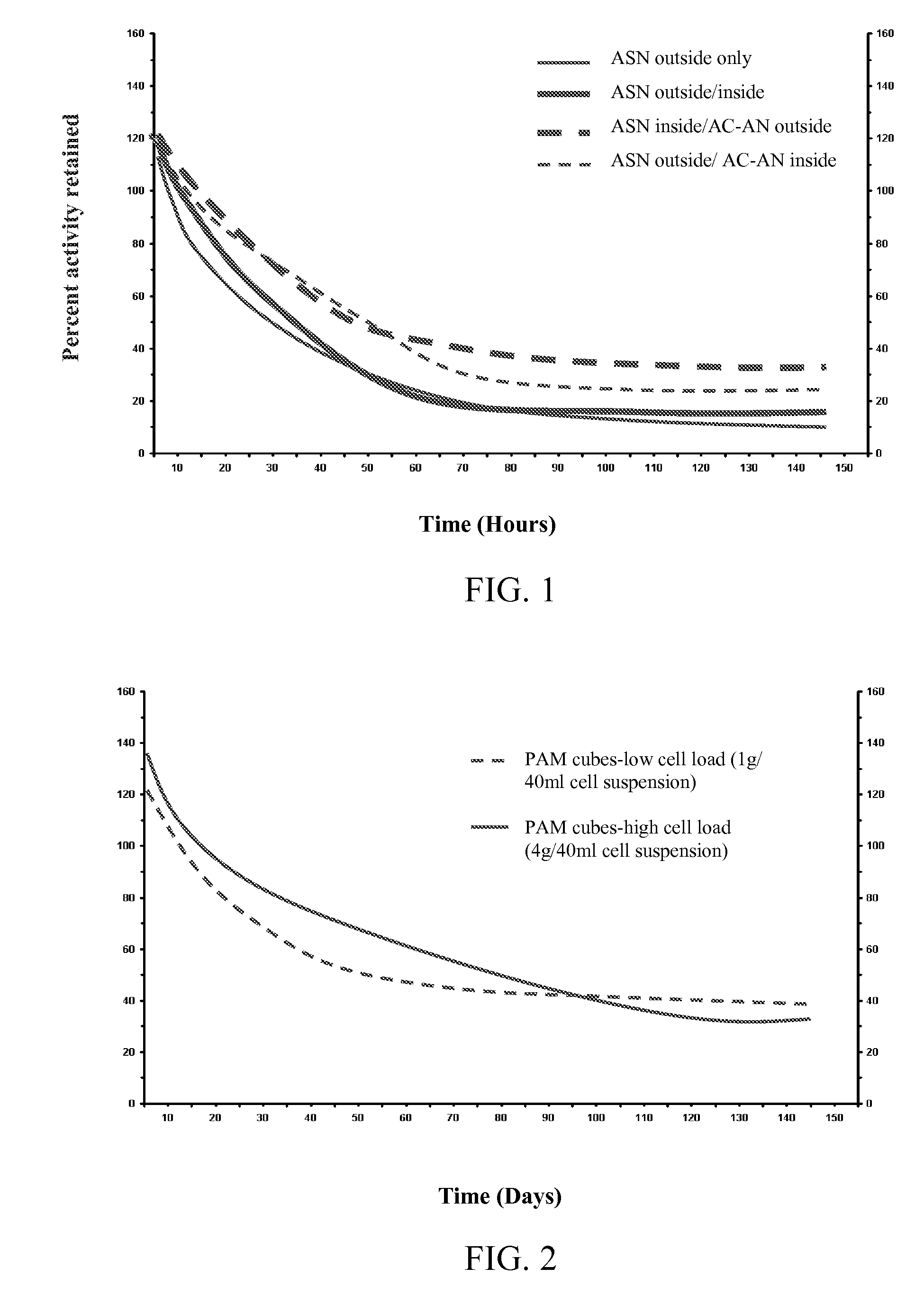
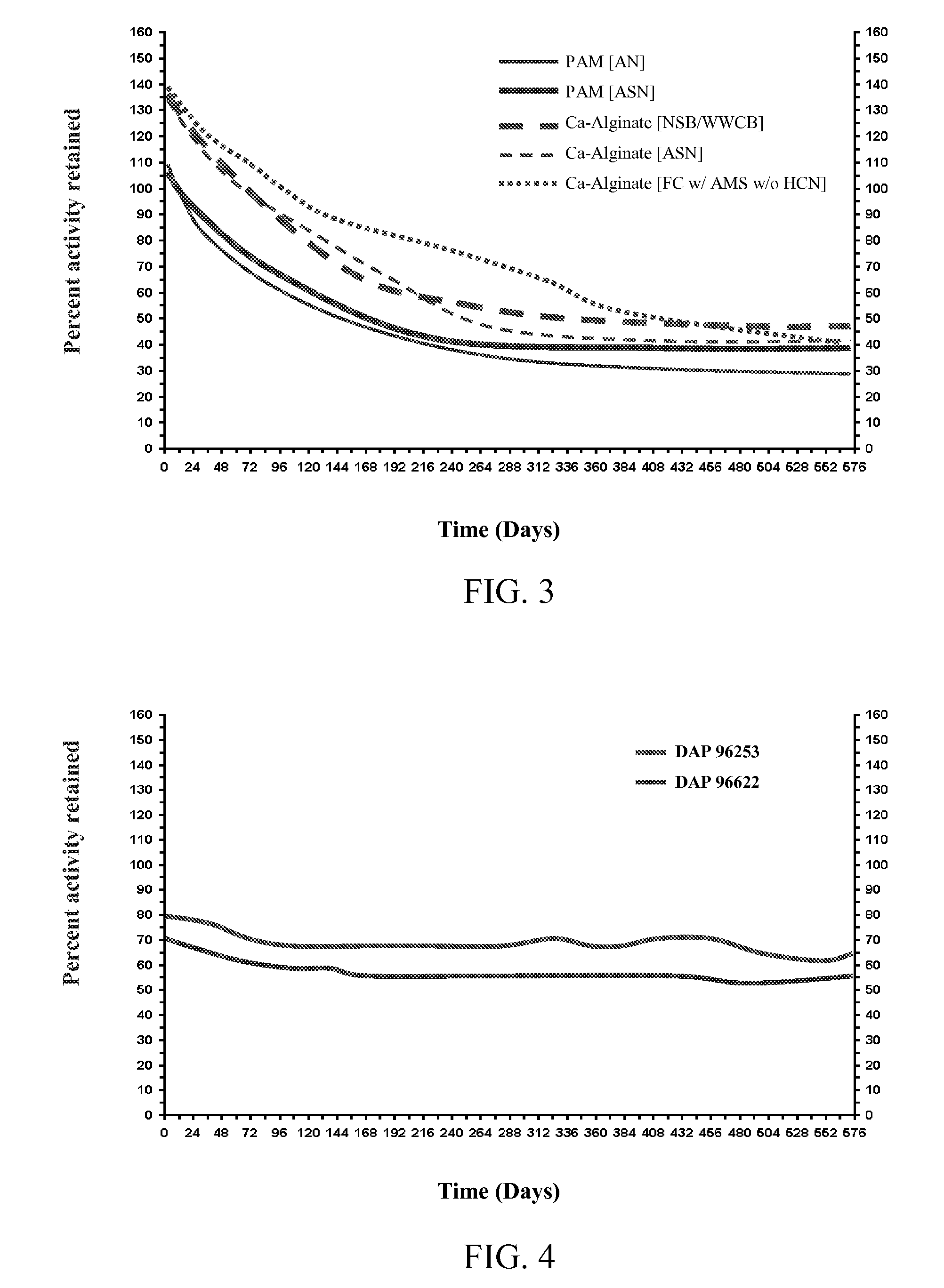
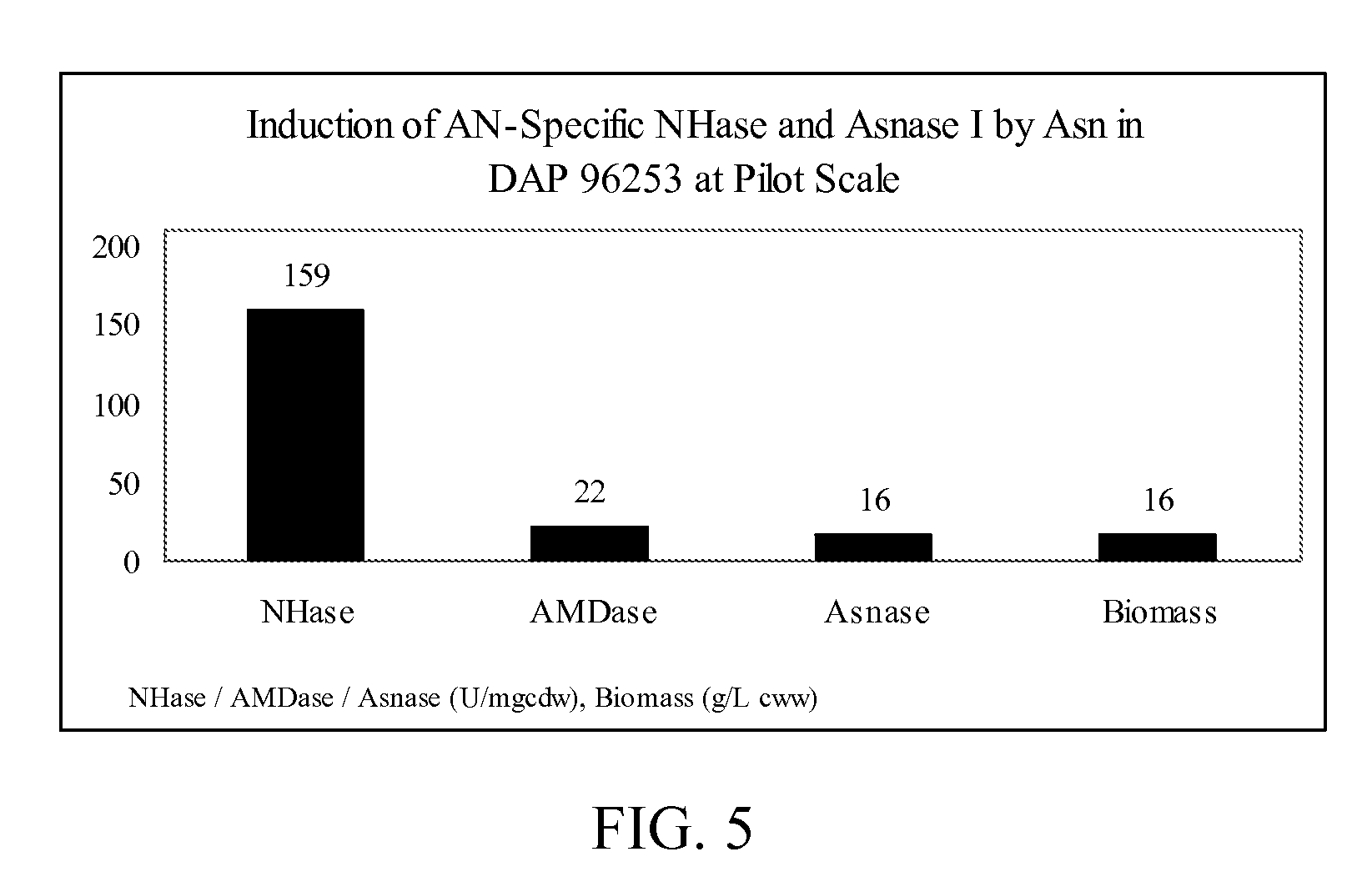
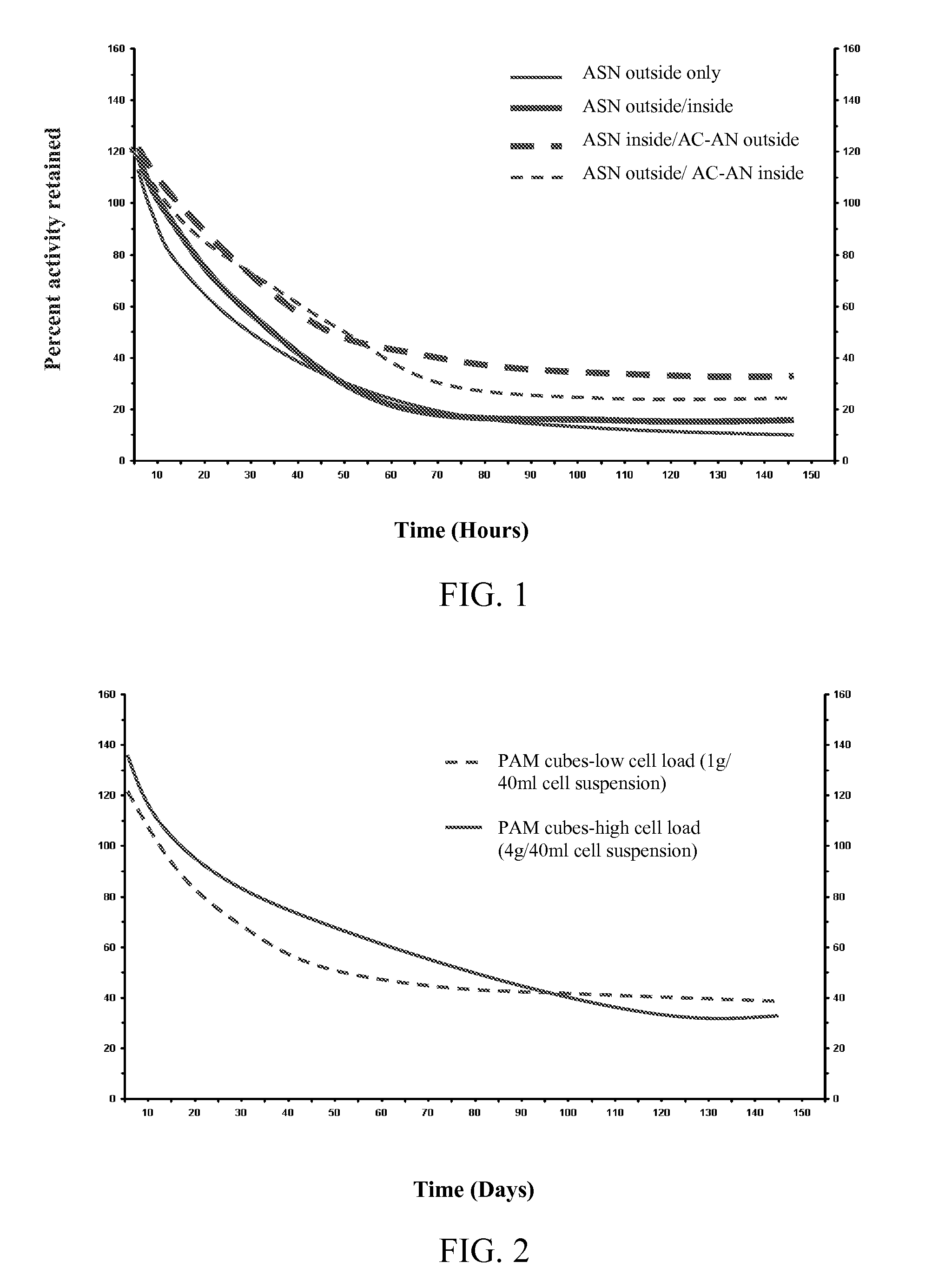
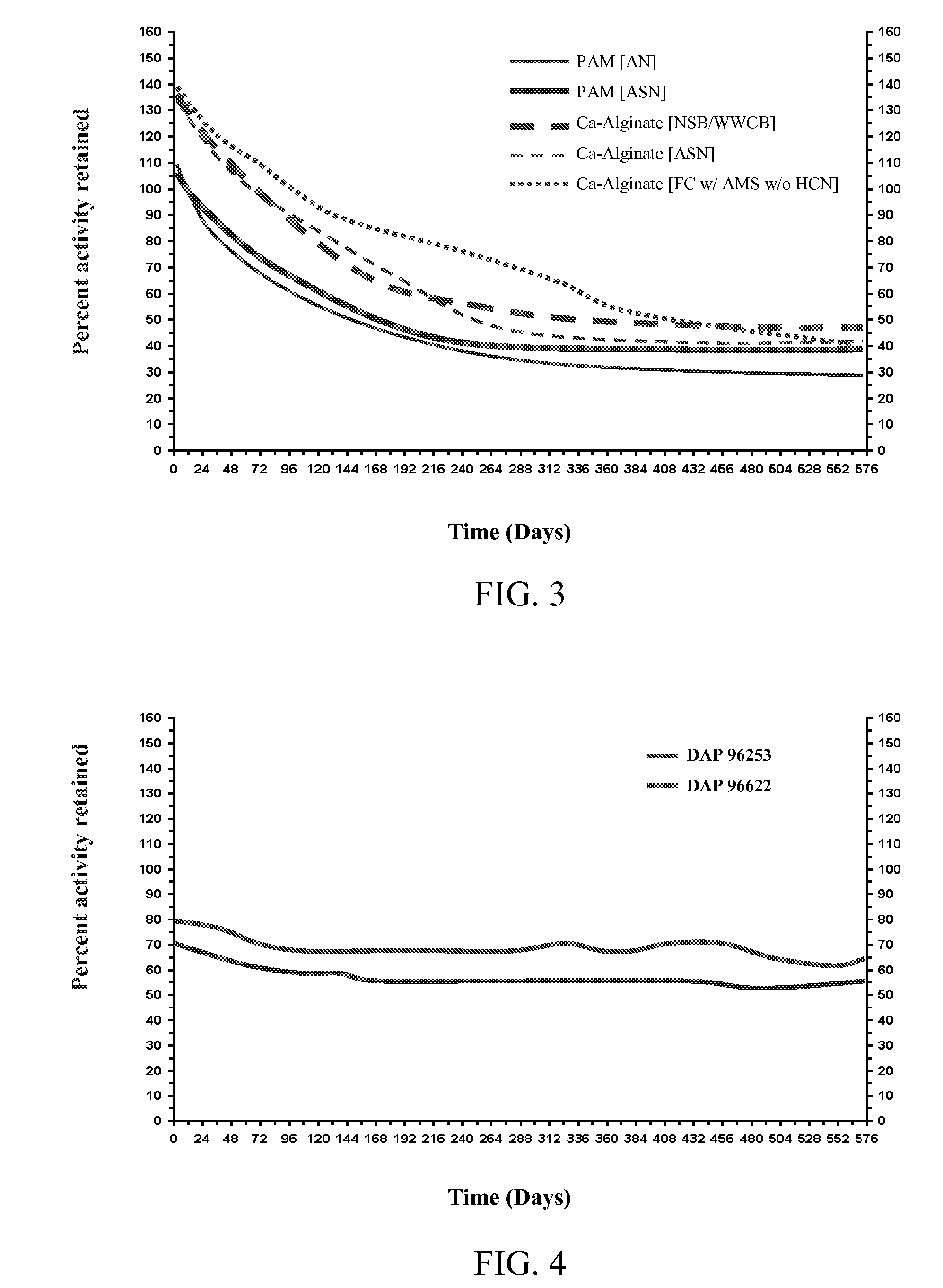
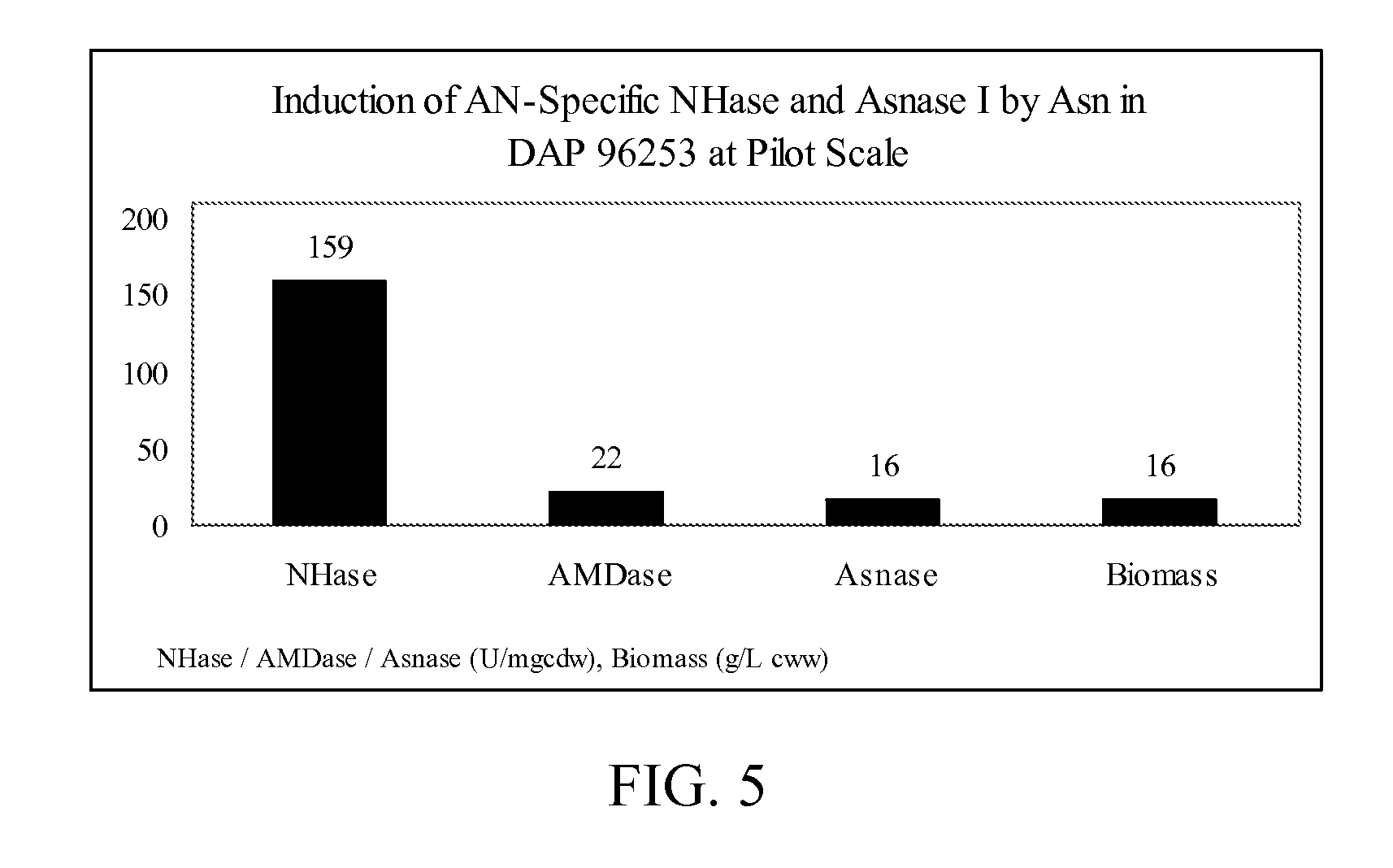
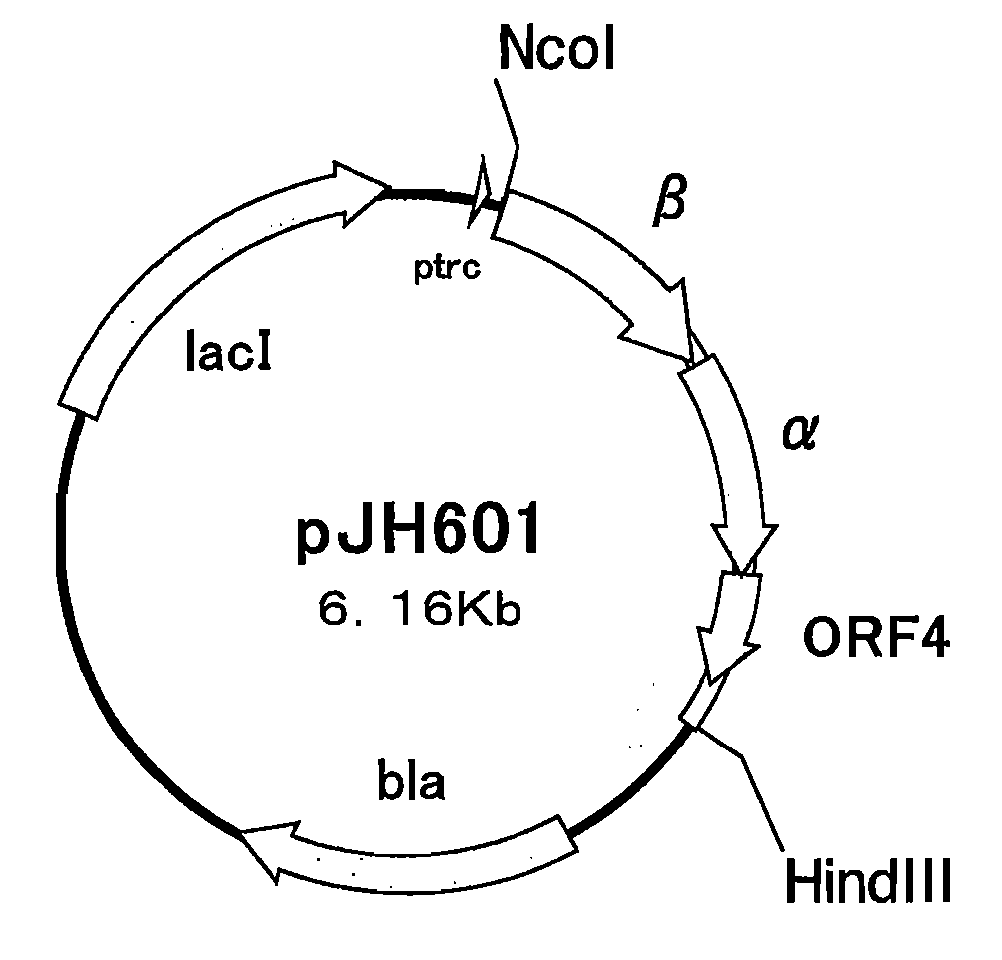
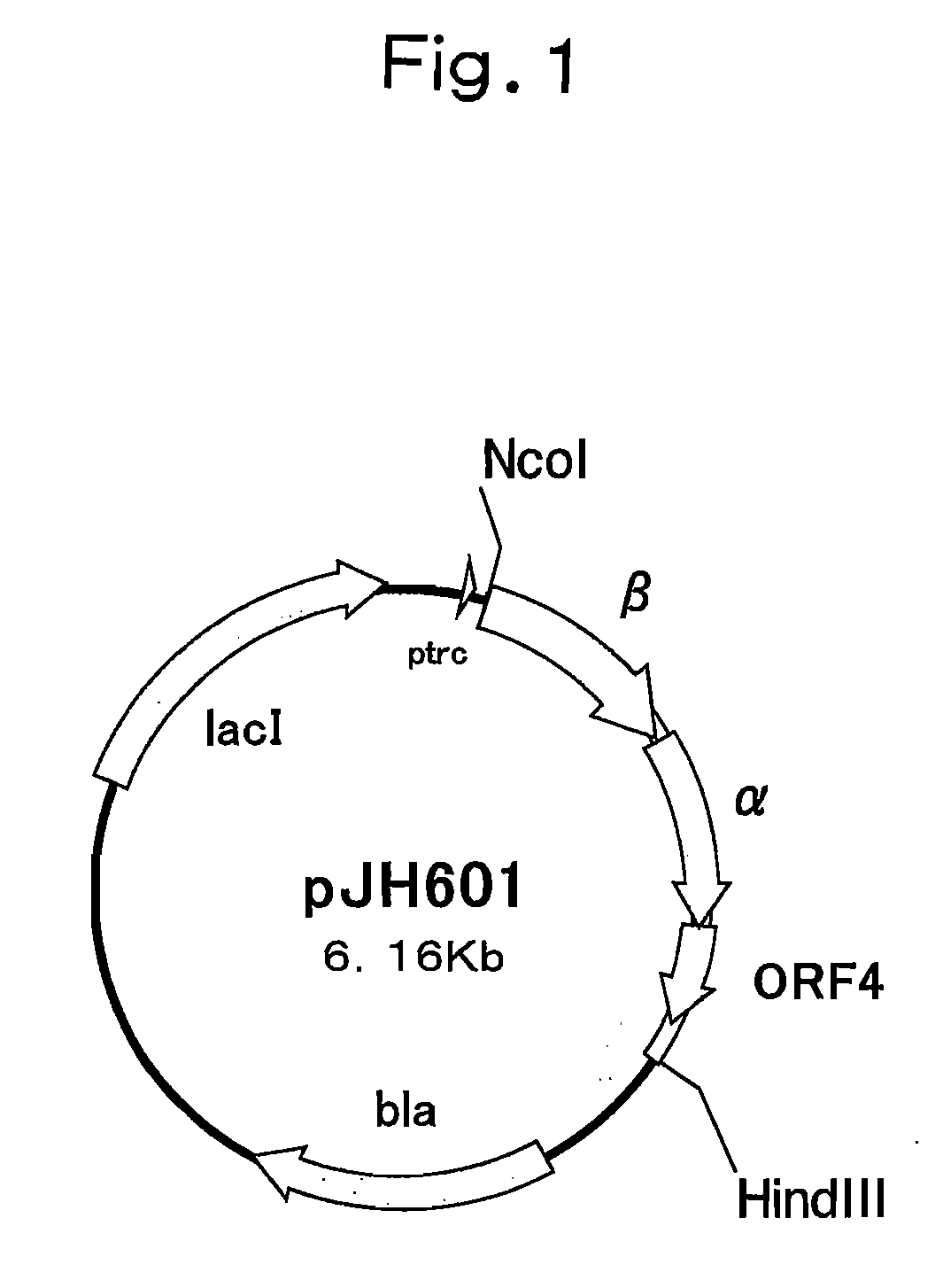
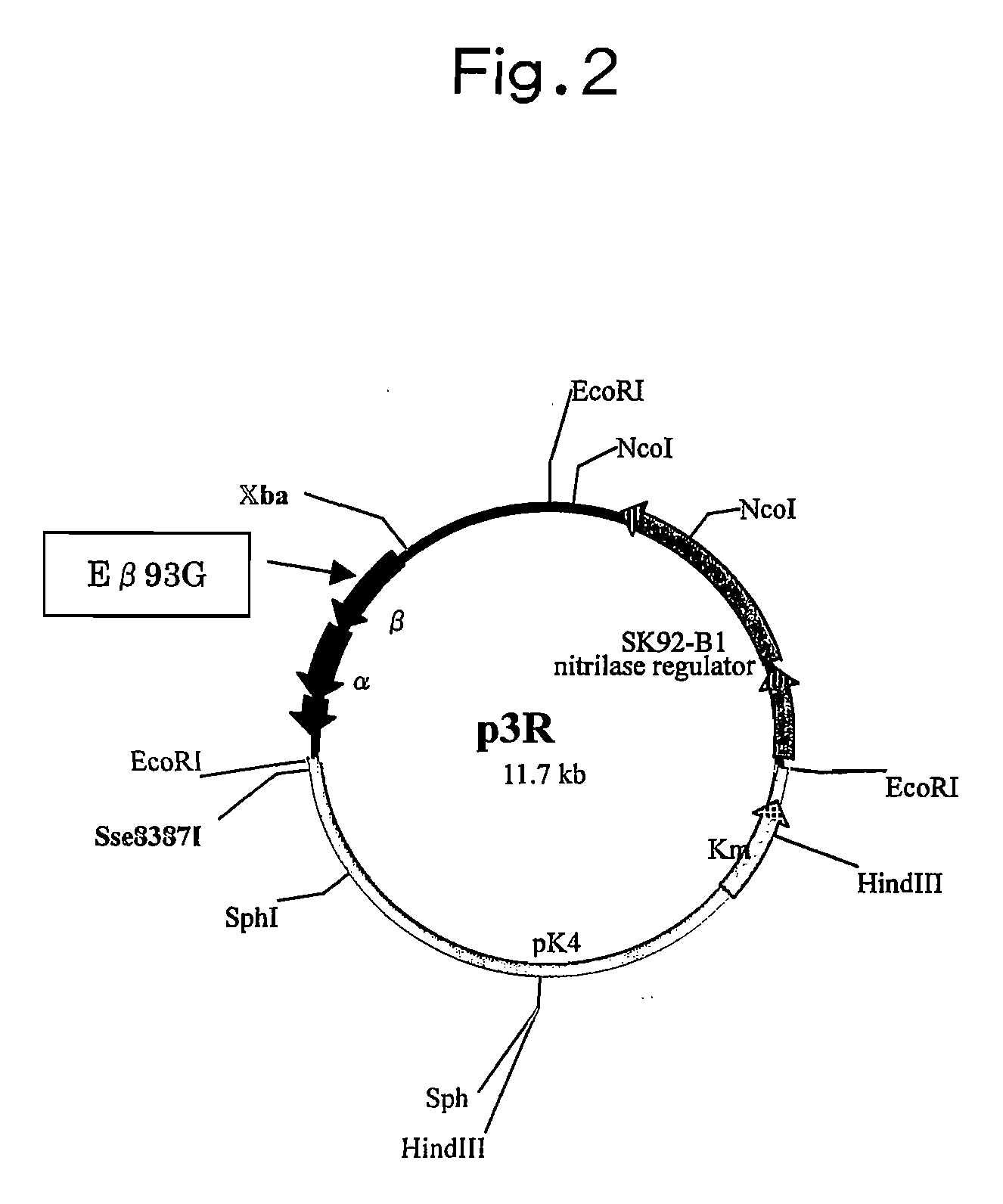
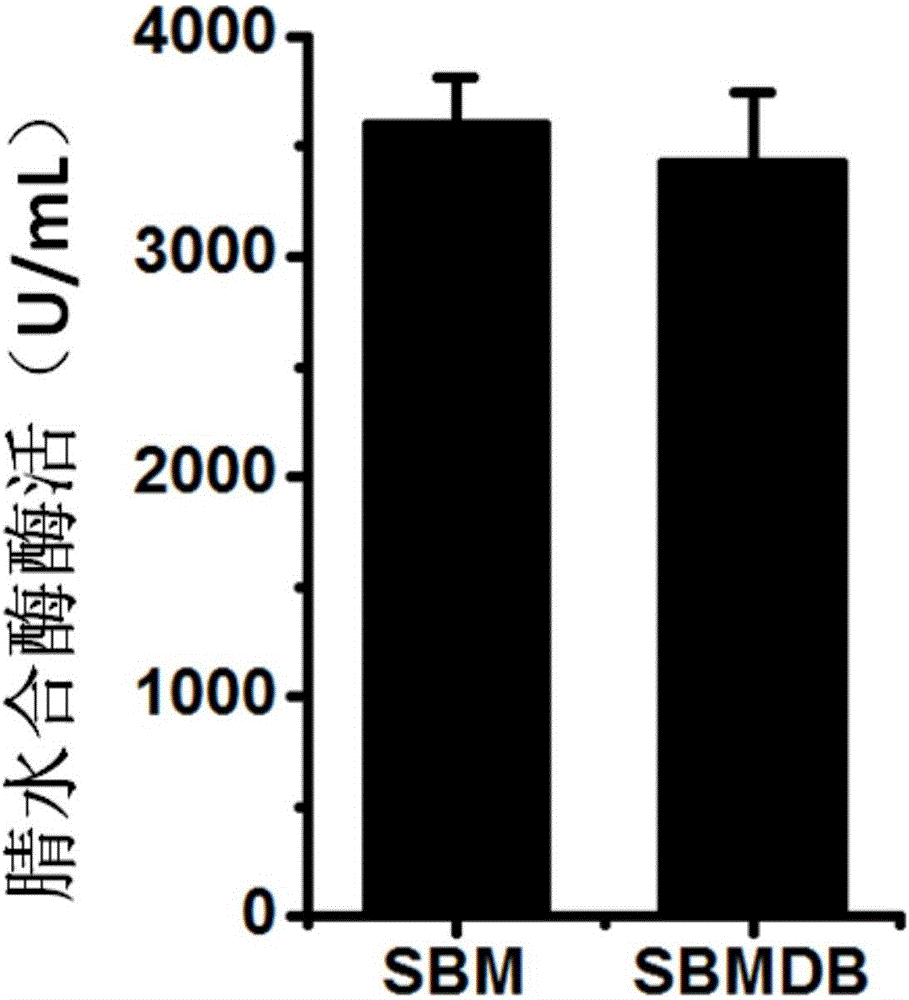
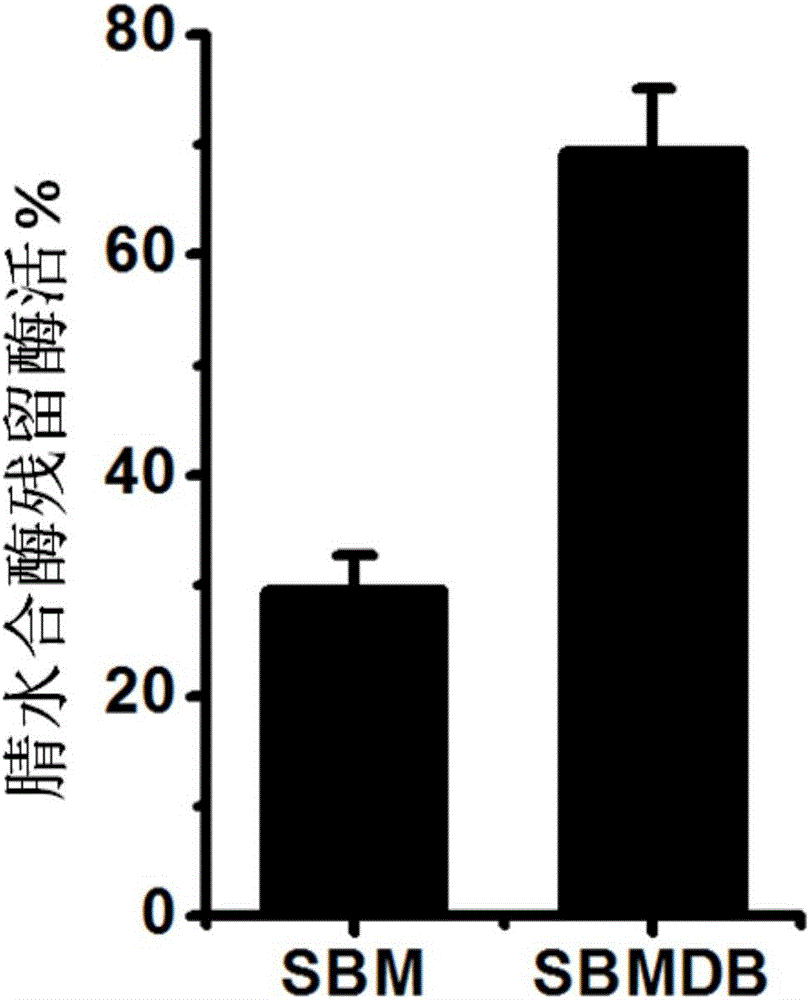
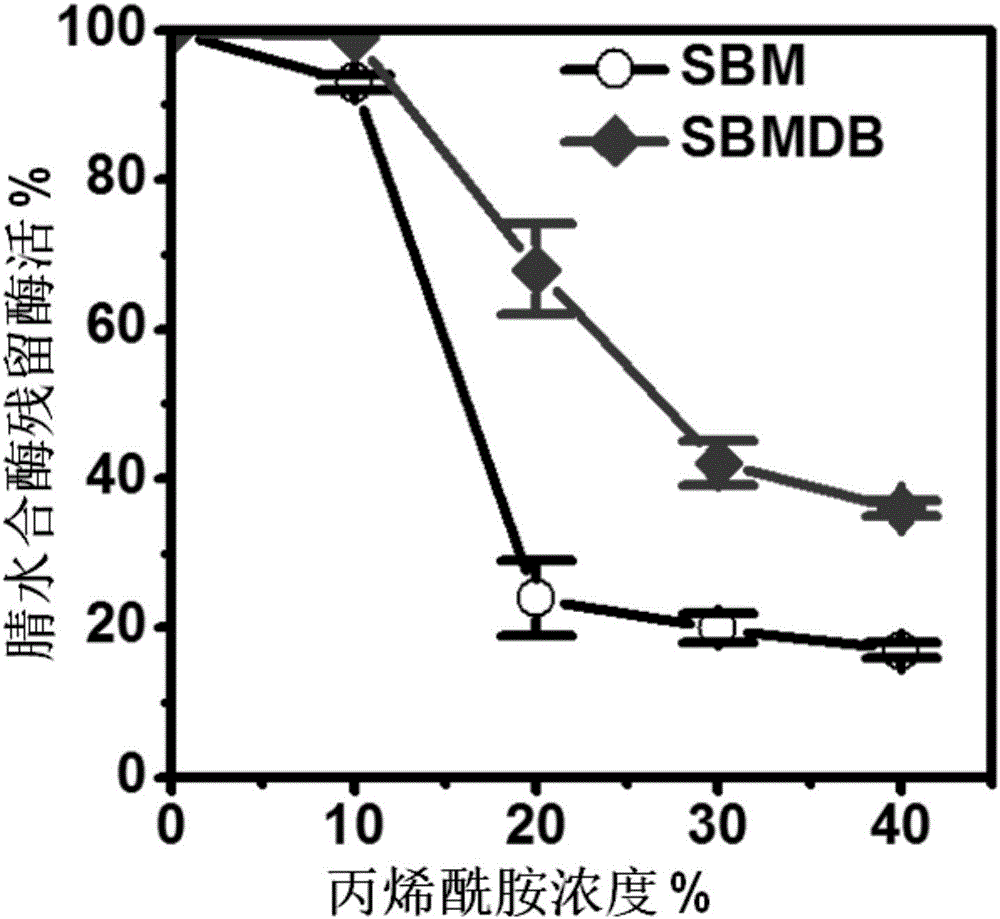
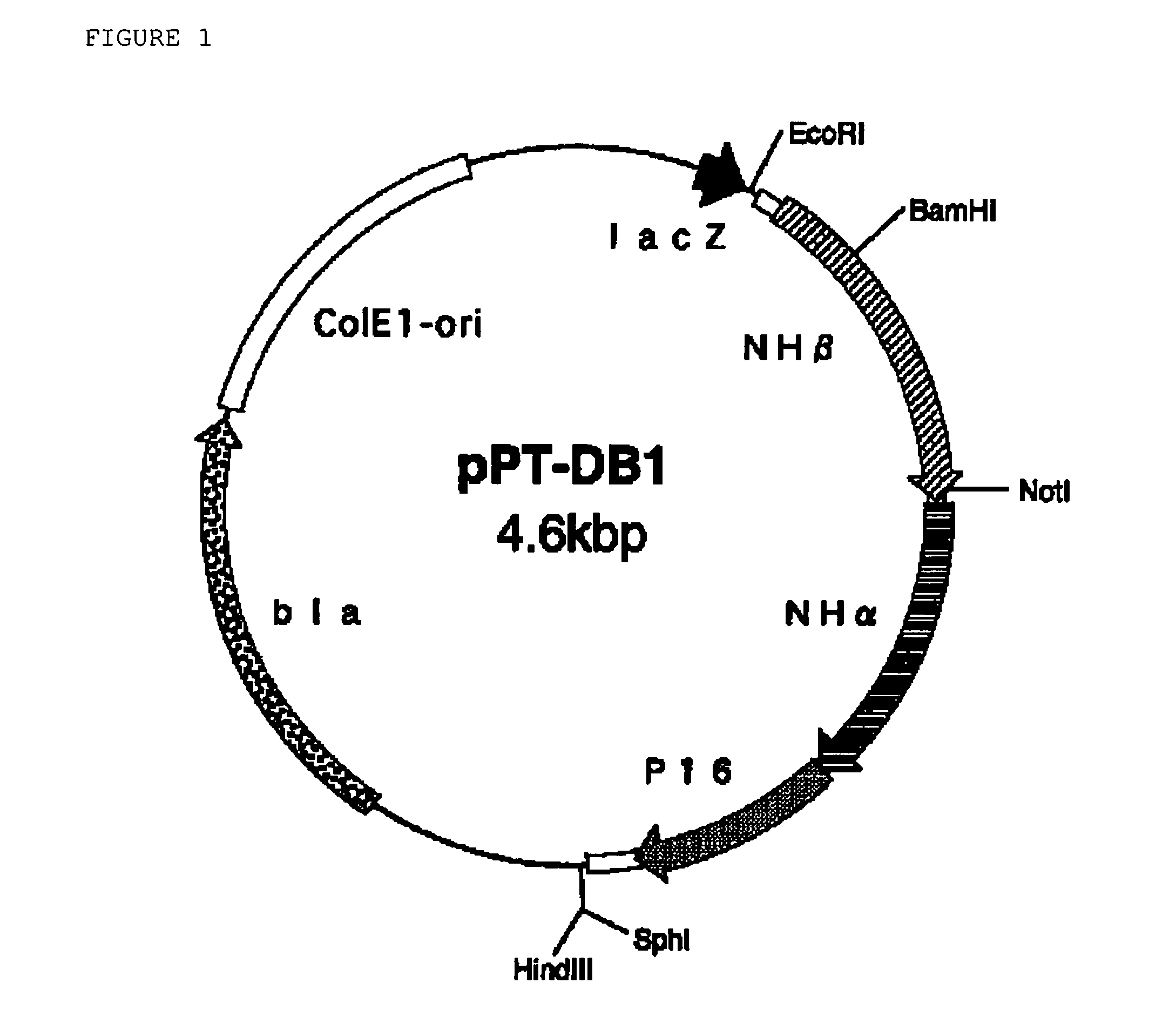
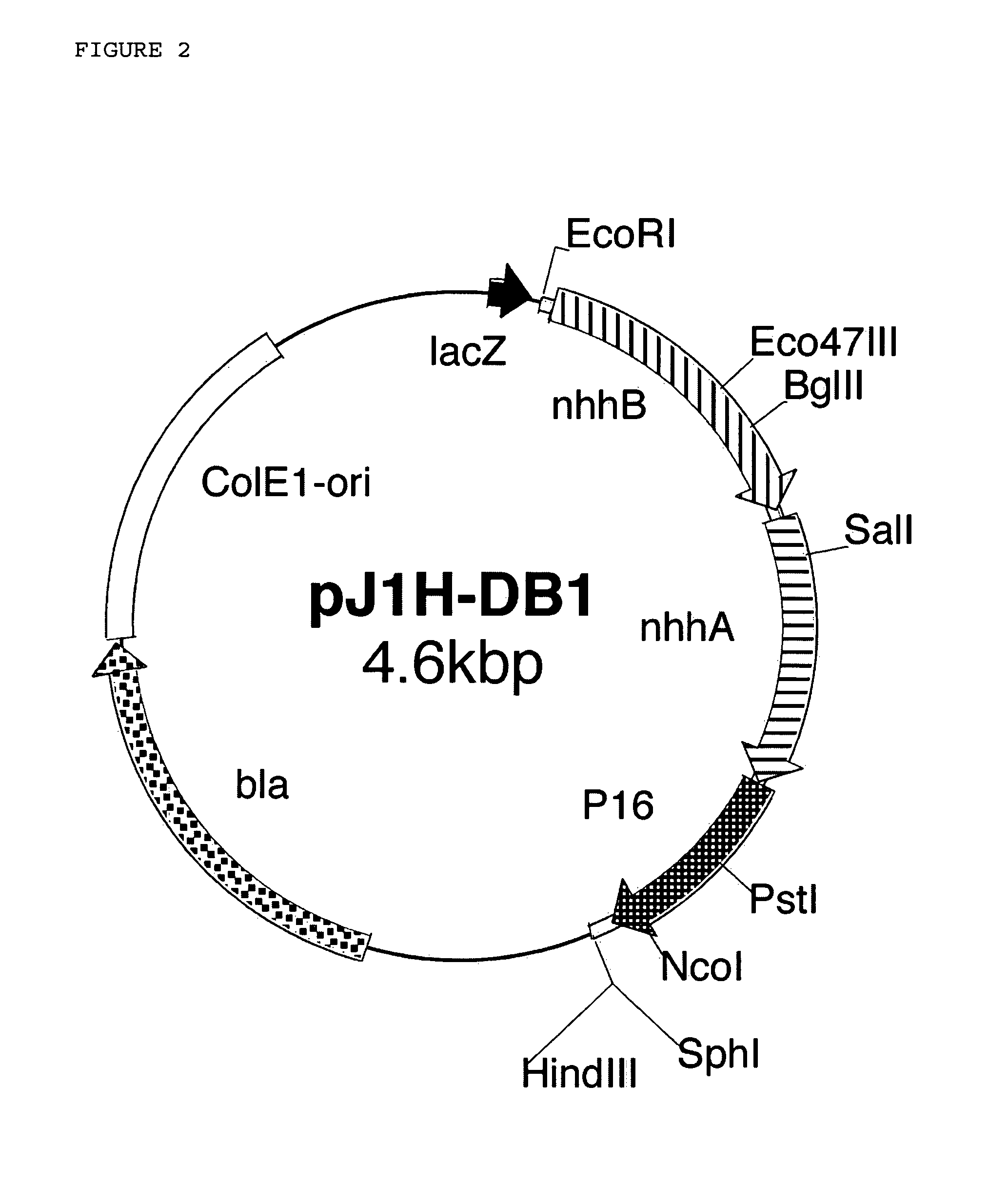
Patents
Literature
32 results about "Nitrile hydratase activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
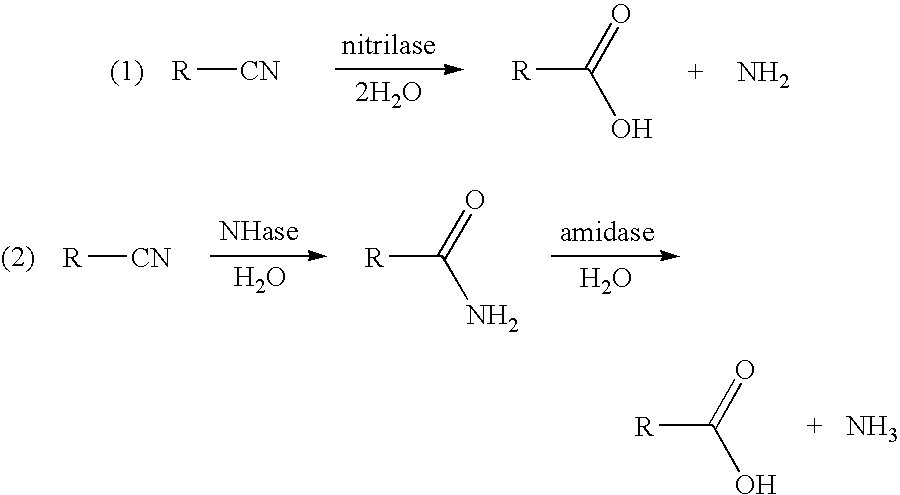
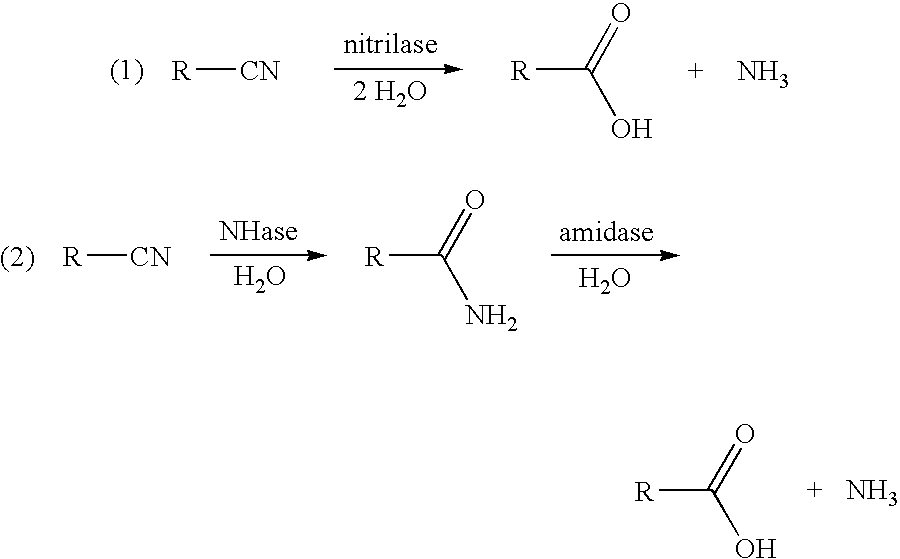
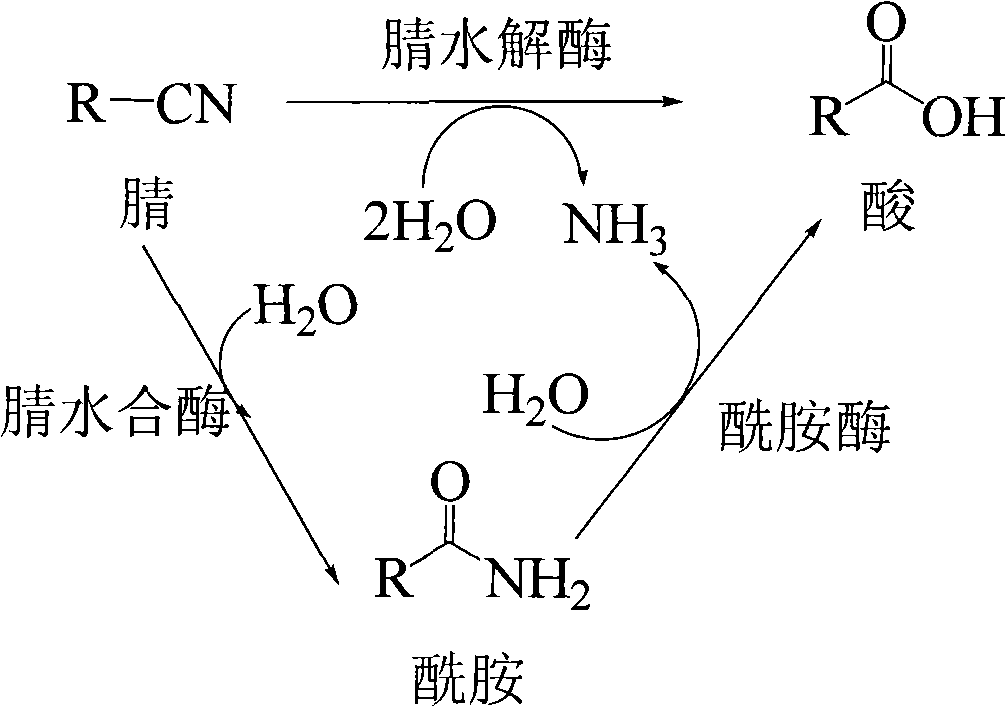
Catalysis of the reaction: an aliphatic amide = a nitrile + H2O. [EC:4.2.1.84]
Rhodococcus nitrile hydratase
InactiveUS7288402B2High expressionExtended service lifeSugar derivativesBacteriaMicroorganismNucleotide
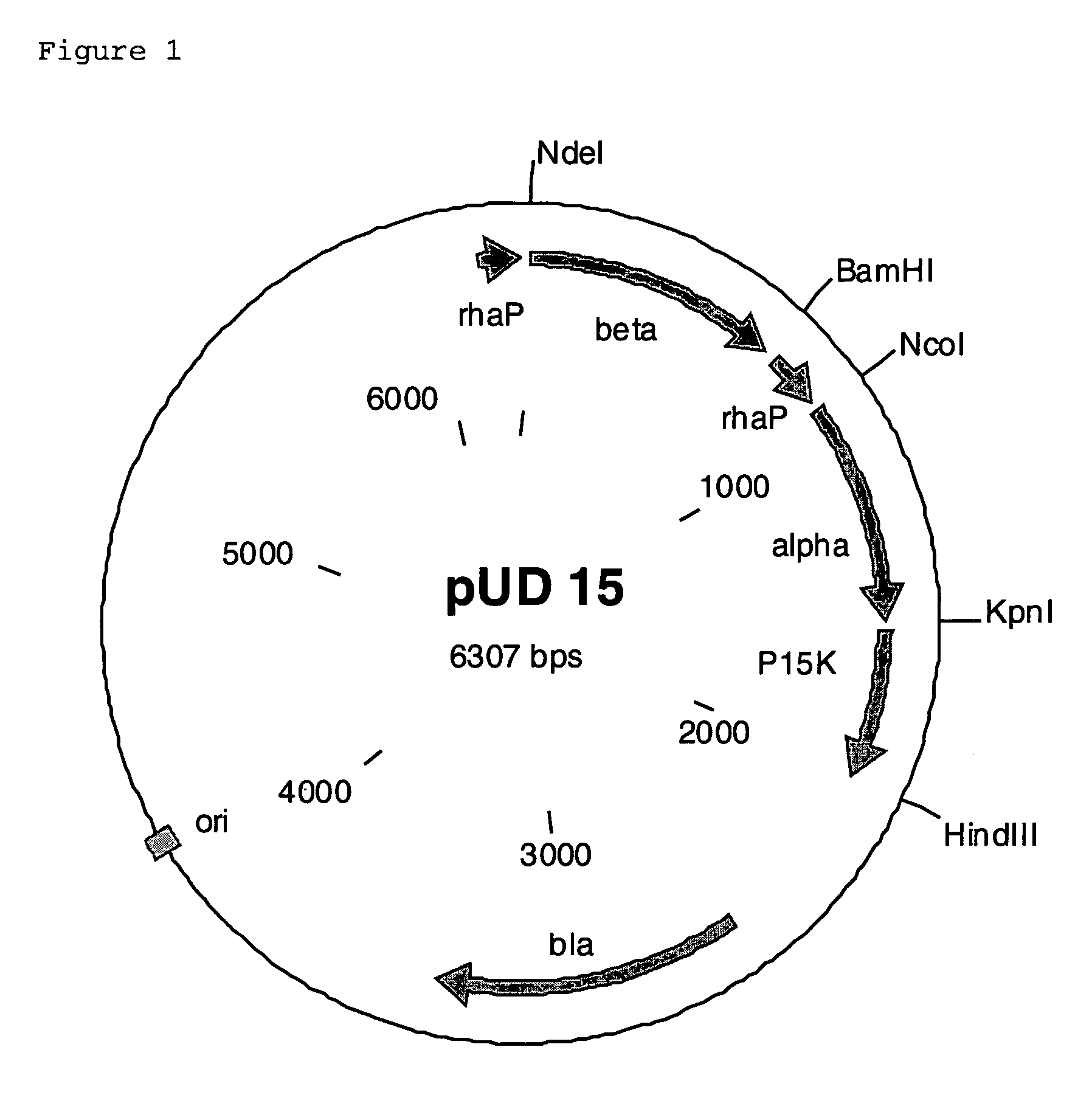
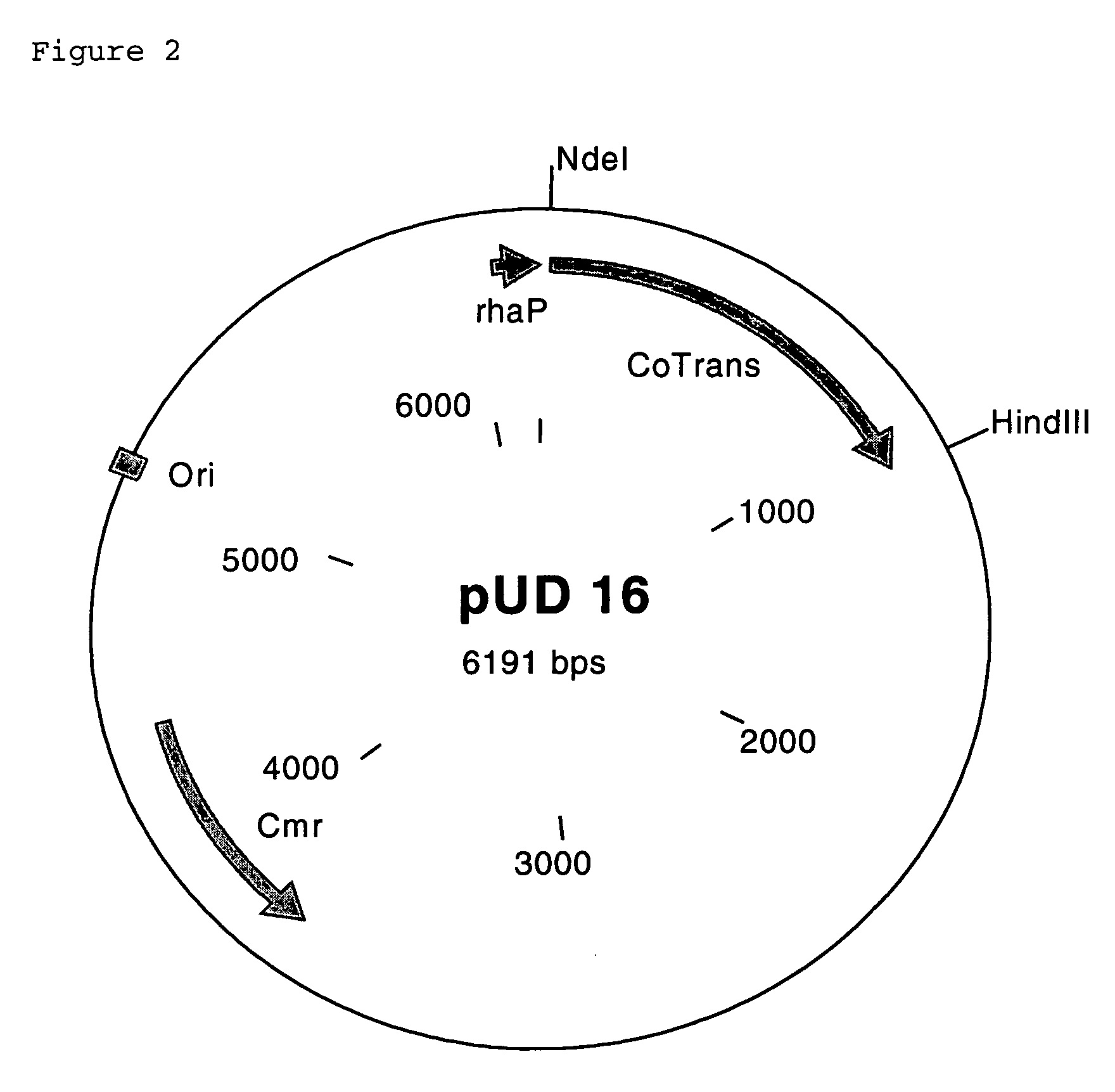
The invention relates to a Rhodococcus polynucleotide cluster which contains nucleotide sequences which encode polypeptides having the activity of a nitrile hydratase, of an auxiliary protein P15K which activates this enzyme and of a cobalt transporter, to transformed microorganisms in which the nucleotide sequences encoding these proteins are present in increased quantity, and to the use of the transformed microorganisms for preparing amides from nitriles.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Induction and stabilization of enzymatic activity in microorganisms
ActiveUS20070184528A1Improve stabilityCommercially useful levelSugar derivativesBacteriaMicroorganismNitrile hydratase activity
The present invention is directed to methods for inducing desired activity in enzymes or microorganisms capable of producing the enzymes. The invention is further directed to methods of stabilizing activity in microorganisms. In specific embodiments, the invention provides methods for inducing and stabilizing nitrile hydratase activity, amidase activity, and asparaginase I activity. The invention further provides compositions comprising enzymes or microorganisms having induced and / or stabilized activity.
Owner:CROWPIERCE TECH LLC
Induction and stabilization of enzymatic activity in microorganisms
InactiveUS7531344B2Improve stabilityCommercially useful levelBacteriaHydrolasesMicroorganismNitrile hydratase activity
The present invention is directed to methods for inducing desired activity in enzymes or microorganisms capable of producing the enzymes. The invention is further directed to methods of stabilizing activity in microorganisms. In specific embodiments, the invention provides methods for inducing and stabilizing nitrile hydratase activity, amidase activity, and asparaginase I activity. The invention further provides compositions comprising enzymes or microorganisms having induced and / or stabilized activity.
Owner:CROWPIERCE TECH LLC
Induction and stabilization of enzymatic activity in microorganisms
ActiveUS7531343B2Improve stabilityCommercially useful levelBacteriaHydrolasesMicroorganismNitrile hydratase activity
The present invention is directed to methods for inducing desired activity in enzymes or microorganisms capable of producing the enzymes. The invention is further directed to methods of stabilizing activity in microorganisms. In specific embodiments, the invention provides methods for inducing and stabilizing nitrile hydratase activity, amidase activity, and asparaginase I activity. The invention further provides compositions comprising enzymes or microorganisms having induced and / or stabilized activity.
Owner:CROWPIERCE TECH LLC
Method of maintaining or improving a nitrile hydratase activity
ActiveUS20050014243A1Maintains nitrile hydratase activityImproves nitrile hydratase activityBacteriaHydrolasesNitrile hydratase activityOxidizing agent
The object of this invention is to provide a method which not only maintains the nitrile hydratase activity of a nitrile hydratase-containing cell or a treated material of the cell under conditions where the cell does not grow, but also improves the nitrile hydratase activity of a nitrile hydratase-containing cell or a treated material of the cell whose activity was once reduced. This invention relates to a method of maintaining or improving a nitrile hydratase activity which comprises bringing a nitrile hydratase-containing cell or a treated material of the cell into contact with an oxidizing agent under conditions where the cell does not grow, as well as a method of producing an amide compound from a nitrile compound, which comprises using the cell brought into contact with an oxidizing agent or a treated material of the cell.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Nitrile Hydratase
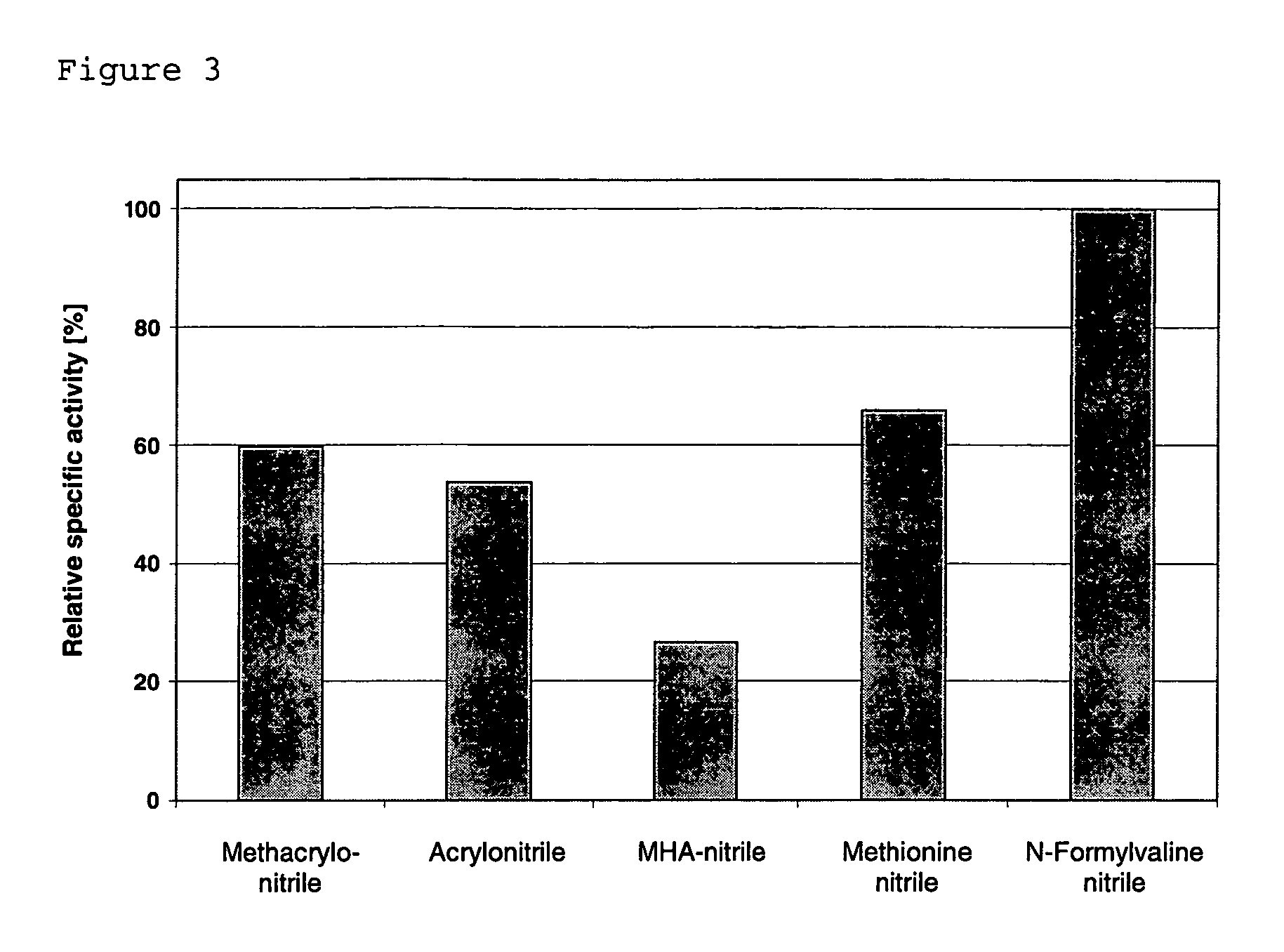
The present invention provides: a protein having an improved nitrile hydratase activity, whereby heat resistance has been improved when compared with a wild-type nitrile hydratase activity, wherein the amino acid sequence of a nitrile hydratase is modified; a gene DNA encoding the above protein; a recombinant vector having the above gene DNA; a transformant or transductant having the above recombinant vector; a nitrile hydratase collected from a culture of the above transformant or transductant, and a production method thereof; and a method for producing an amide compound.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Method of maintaining or improving a nitrile hydratase activity
ActiveUS7244595B2Maintain activityHigh activityBacteriaHydrolasesNitrile hydratase activityOxidizing agent
The object of this invention is to provide a method which not only maintains the nitrile hydratase activity of a nitrile hydratase-containing cell or a treated material of the cell under conditions where the cell does not grow, but also improves the nitrile hydratase activity of a nitrile hydratase-containing cell or a treated material of the cell whose activity was once reduced. This invention relates to a method of maintaining or improving a nitrile hydratase activity which comprises bringing a nitrile hydratase-containing cell or a treated material of the cell into contact with an oxidizing agent under conditions where the cell does not grow, as well as a method of producing an amide compound from a nitrile compound, which comprises using the cell brought into contact with an oxidizing agent or a treated material of the cell.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Aqueous acrylamide solution containing saccharide
InactiveUS7129217B2Reduce the amount requiredHigh viscosityBiocideSugar derivativesNitrile hydratase activityAqueous solution
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Preparation of lactams from aliphatic alpha omega -dinitriles
A process for the preparation of five-membered or six-membered ring lactams from aliphatic alpha , omega -dinitriles has been developed. In the process an aliphatic alpha , omega -dinitrile is first converted to an ammonium salt of an omega -nitrilecarboxylic acid in aqueous solution using a catalyst having an aliphatic nitrilase (EC 3.5.5.7) activity, or a combination of nitrile hydratase (EC 4.2.1.84) and amidase (EC 3.5.1.4) activities. The ammonium salt of the omega -nitrilecarboxylic acid is then converted directly to the corresponding lactam by hydrogenation in aqueous solution, without isolation of the intermediate omega -nitrilecarboxylic acid or omega -aminocarboxylic acid. When the aliphatic alpha , omega -dinitrile is also unsymmetrically substituted at the alpha -carbon atom, the nitrilase produces the omega -nitrilecarboxylic acid ammonium salt resulting from hydrolysis of the omega -nitrile group with greater than 98% regioselectivity, thereby producing only one of the two possible lactam products during the subsequent hydrogenation. A heat-treatment process to select for desirable regioselective nitrilase or nitrile hydratase activities while destroying undesirable activities is also provided.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Modified nitrile hydratase and application thereof
ActiveCN107177581AImprove stress resistanceImprove heat resistanceBacteriaFermentationHigh concentrationMicroorganism
The invention discloses modified nitrile hydratase and application thereof in the technical field of enzyme engineering and industrial microorganisms. A method for obtaining the modified nitrile hydratase disclosed by the invention is that Pro of 133 site of a alpha subunit of an amino acid sequence shown as by a sequence table SEQ ID NO:2 and Asp of 215 site of a beta subunit of an amino acid sequence shown as by a sequence table SEQ ID NO:1 are respectively replaced with Cys, so that a disulfide bond is formed between the two subunits. Stress resistance and heat resistance of the modified nitrile hydratase disclosed by the invention and product tolerance are all obviously improved, and activity of the nitrile hydratase is not lowered. The modified nitrile hydratase can be catalyzed to obtain a high-concentration acrylamide product, and can be recycled repeatedly.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method For Producing Amide Compound
InactiveUS20090171051A1Efficient productionExcellent toneHydrolasesOrganic compound preparationSolubilityBenzene
[Problems] The present invention provides a method for efficiently producing a corresponding amide compound from a nitrile compound by a reaction using a nitrile hydratase and a method for producing an amide-based polymer excellent in quality from the amide compound. In addition, the present invention provides a method for more efficiently producing an acrylamide with higher quality by a microbial catalyst containing a nitrile hydratase and the like and a method for producing an acrylamide-based polymer, which is excellent in hue, has a good balance between the water solubility and the high molecular weight and is also excellent in quality, by using the acrylamide.[Means for Solving the Problems] The method for producing an amide compound of the present invention is characterized in that in a method for producing an amide compound from a nitrile compound in an aqueous medium in the presence of a catalyst having a nitrile hydratase activity, the concentration of benzene in the aqueous medium is 4.0 ppm or less. In addition, the method for producing an amide-based polymer of the present invention is characterized by homopolymerizing the amide compound or by copolymerizing the amide compound and at least unsaturated monomer copolymerizable with the amide compound. Further, the method for producing acrylamide of the present invention is characterized by hydrating acrylonitrile having a concentration of acrolein of 1 ppm or less by a microbial cell containing a nitrile hydratase or a processed product of the microbial cell in an aqueous medium. Furthermore, the method for producing an acrylamide-based polymer of the present invention is characterized by homopolymerizing the acrylamide or by copolymerizing the acrylamide and at least one unsaturated monomer copolymerizable with the acrylamide.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Nitrile hydratase variant
The amino acid sequence of a mutant which is obtained by introducing a novel mutation into a Pseudonocardia thermophila JCM3095-derived nitrile hydratase consisting of two types of heterogeneous subunits, and the base sequence of the gene are provided. The nitrile hydratase is modified by specifying the region to be modified in the stereostructure / amino acid sequence of the nitrile hydratase, and applying alteration such as substitution, insertion, deletion or the like, to the amino acids in the amino acid sequence which are corresponding to the amino acid residues forming the region. Also provided is a method for modifying an enzyme having a nitrile hydratase activity.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Aqueous acrylamide solution containing saccharide
InactiveUS20050153421A1Reduce the amount requiredGuaranteed production demandBiocideBacteriaNitrile hydratase activityAqueous solution
This invention provides an aqueous solution of acrylamide that is useful as a starting material for high-quality polyacrylamide. Starting materials for polyacrylamide are an aqueous solution of acrylamide containing a saccharide and an aqueous solution of acrylamide containing a saccharide produced with the use of a biocatalyst having nitrile hydratase activity.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
3-hydroxycarboxylic acid production and use in branched polymers
This invention relates to a process for the preparation of a 3-hydroxycarboxylic acid from a 3-hydroxynitrile. More specifically, 3-hydroxyvaleronitrile is converted to 3-hydroxyvaleric acid in high yield at up to 100% conversion, using as an enzyme catalyst 1) nitrile hydratase activity and amidase activity or 2) nitrilase activity of a microbial cell. 3-Hydroxyvaleric acid is used as a substitute for ε-caprolactone in the preparation of highly branched copolyester.
Owner:AXALTA COATING SYST IP CO LLC
Nitrile hydratase
The present invention provides: a protein having an improved nitrile hydratase activity, whereby heat resistance has been improved when compared with a wild-type nitrile hydratase activity, wherein the amino acid sequence of a nitrile hydratase is modified; a gene DNA encoding the above protein; a recombinant vector having the above gene DNA; a transformant or transductant having the above recombinant vector; a nitrile hydratase collected from a culture of the above transformant or transductant, and a production method thereof; and a method for producing an amide compound.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Method of cultivating microorganisms having nitrile hydratase activity
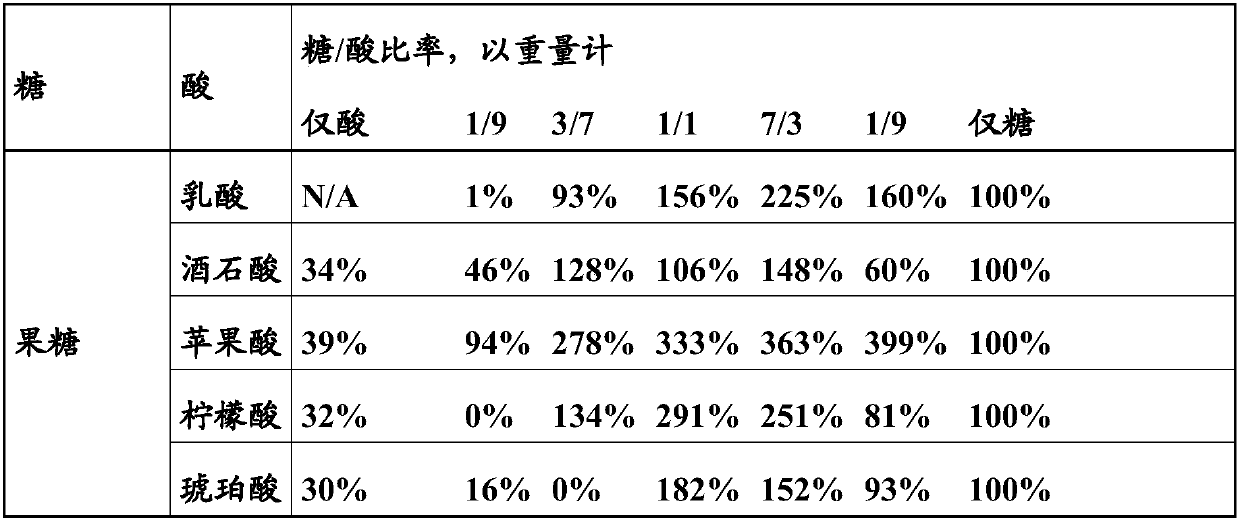
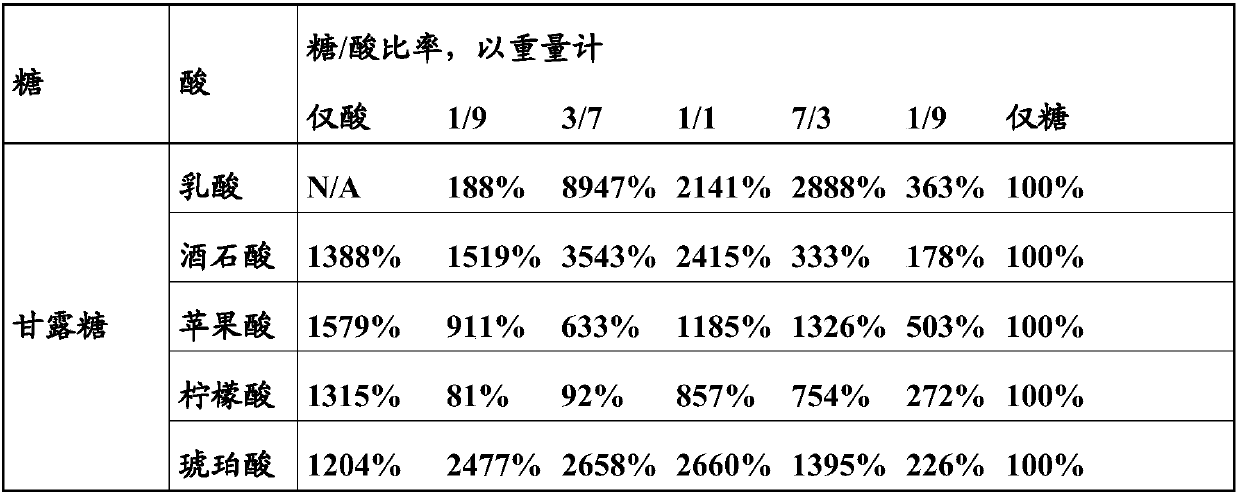
The present invention relates to methods for cultivating a nitrile hydratase producing microorganism, compositions for cultivating a nitrile hydratase producing microorganism, and use of compositions comprising a saccharide and an organic acid for cultivating a nitrile hydratase producing microorganism. The composition provided in and to be employed in context with the present invention is particularly suitable for inducing both, growth and nitrile hydratase production of corresponding microorganisms.
Owner:BASF AG
Method for reducing enzyme usage amount in process of producing acrylamide by virtue of microbiological method
ActiveCN106467921AReduce consumptionReduce the number of storage devicesFermentationHydration reactionMicroorganism
The invention provides a method for reducing a nitrile hydratase usage amount in a process of producing acrylamide by virtue of a microbiological method. In a process of producing the acrylamide by catalyzing a hydration reaction in the microbiological method, the quality of the acrylamide is optimized when a fermentation broth storage time of nitrile hydratase cells is 96-240h; and when the storage time is longer than or equal to 240h, the activity of the nitrile hydratase in a fermentation broth drops, the usage amount of the fermentation broth is increased and the quality of the obtained acrylamide is reduced. According to the method provided by the invention, by mixing the nitrile hydratase cell fermentation broth with the storage time shorter than or equal to 24h and the nitrile hydratase cell fermentation broth with the storage time longer than or equal to 240h, the activity and the quality of the nitrile hydratase are improved, so that the method for reducing the usage amount of the nitrile hydratase is achieved. With the application of the method provided by the invention, the usage amount of the nitrile hydratase in the production process is reduced, the consumption of raw materials of a fermentation medium is relieved and the stability of the quality of an acrylamide solution is improved, and the method is conducive to the subsequent production of the acrylamide. When the method provided by the invention is applied to the industrial production of the acrylamide by virtue of the microbiological method, the finished product is stable in various technical indicators.
Owner:SICHUAN GUANGYA POLYMER CHEM
Method for improving nitrile hydratase activity of bacillus subtilis
InactiveCN106520744AControlled growing environmentIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesOxygen
The invention discloses a method for improving the nitrile hydratase activity of bacillus subtilis. The method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out slant culture; (2) carrying out seed culture; and (3) carrying out fermentation culture. The method has the advantages that on one hand, the nutrition components in the fermentation medium are changed, namely, the fermentation medium contains Tween-80 0.1-1 g / ml%, NH4Cl 0.1-1 g / ml%, and urea 0.01-1 g / ml%, a glucose-Co<2+> coupling fed batch process is adopted, and a supplementary material formed by mixing glucose and inducer IND is added; on the other hand, the growth environment of bacteria can be controlled, namely, in the fermentation process, by adding ammonium hydroxide, the pH is controlled to be 6.8-7.5, the temperature is controlled to be 25-35 DEG C, the oxygen quantity is maintained to be 1-3 vvm, and thus the purpose of greatly improving the enzymatic activity during the nitrile hydratase fermentation production is achieved.
Owner:ANHUI RUIBANG BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Process for producing amide compound using microbial catalyst
This invention relates to a process for producing an amide compound from a nitrile compound using a microbial catalyst, wherein a microbial cell having nitrile hydratase activity of 50 U or higher per mg of dry cell at a reaction temperature of 10° C. is brought into contact with a nitrile compound in an aqueous medium without being immobilized. This method utilizes a microbial cell that exhibits high nitrile hydratase activity in the reaction without being entrap-immobilized. Thus, an amide compound can be effectively produced from a nitrile compound without problems of decreased reaction speed or lowered amount produced per unit cell amount, which are caused by entrap-immobilization. Accordingly, an amide compound can be produced within a very short period of time in the case of a batch reaction and with a very small-scale facility in the case of a continuous reaction.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
3-Hydroxycarboxylic acid production and use in branched polymers
Owner:AXALTA COATING SYST IP CO LLC
Preservation method of microbial cells and suspension of microbial cells
ActiveCN102010826BReduce laborLow costMicroorganism based processesMicroorganism preservationMicroorganismMicrobial fuel cell
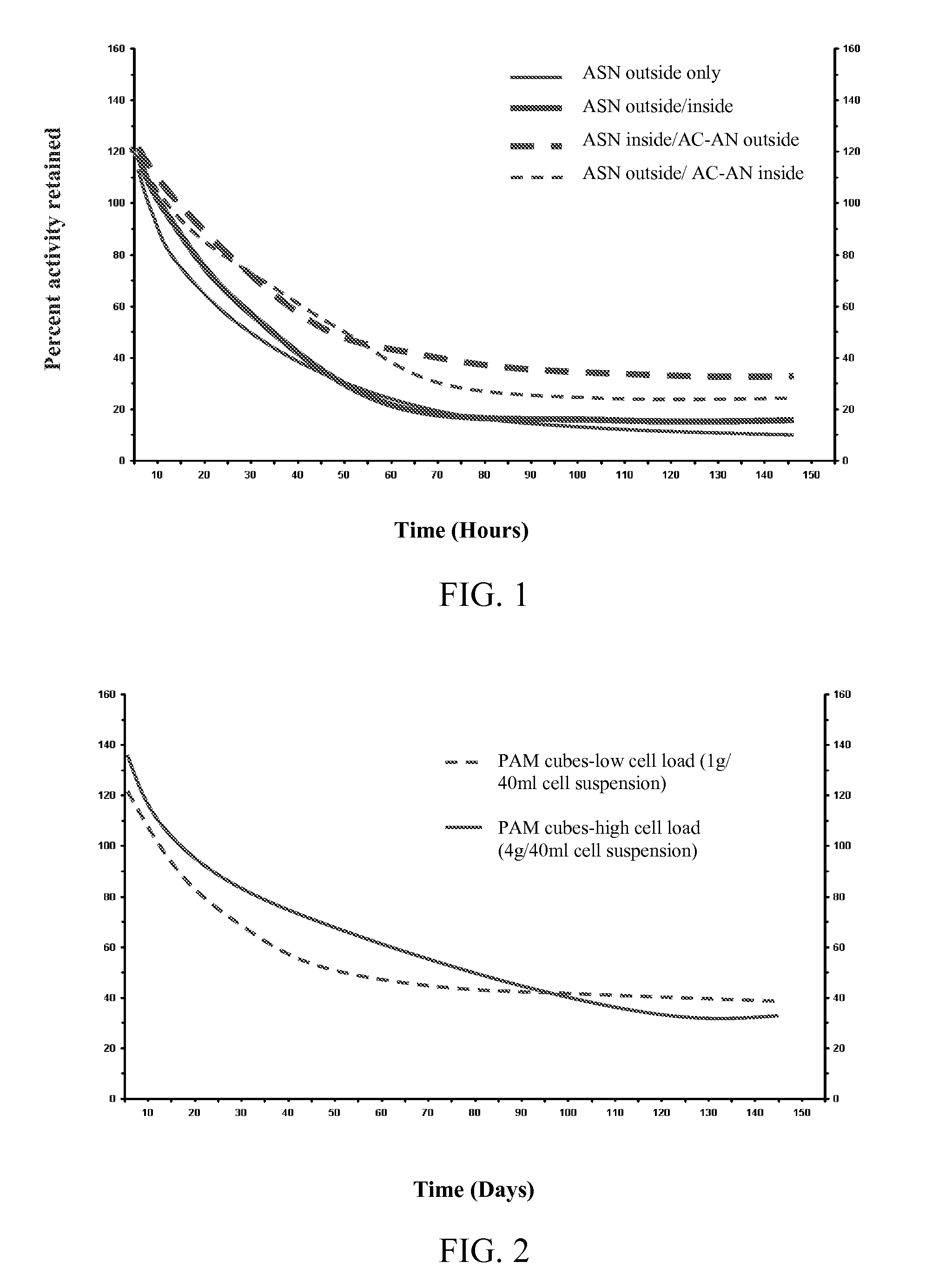
The present invention provides a cheap and simple microbe for replacing that of the prior art, and a preserving method thereof. The invention relates to the preserving method of microbe and is characterized in that: the microbes with nitrile hydratase activity are dispersed in a dispersion medium with a concentration that the mass of dry microbe is 4-20wt%.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
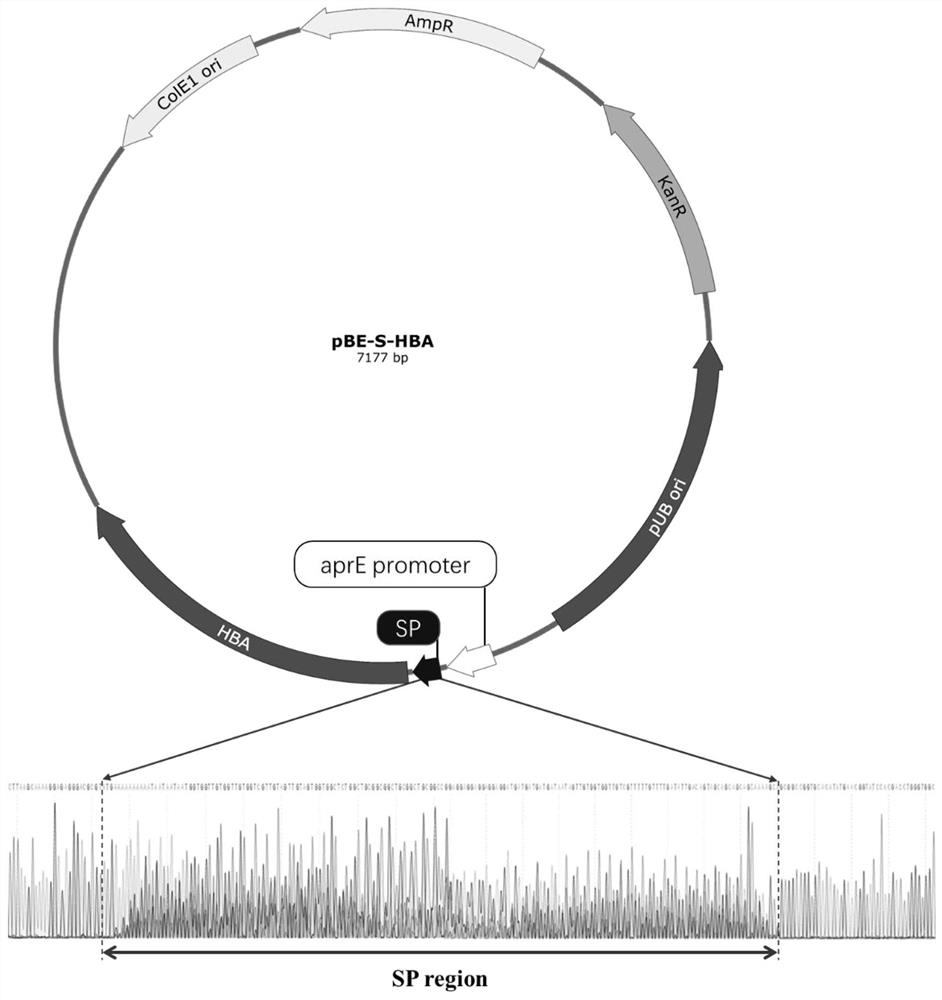
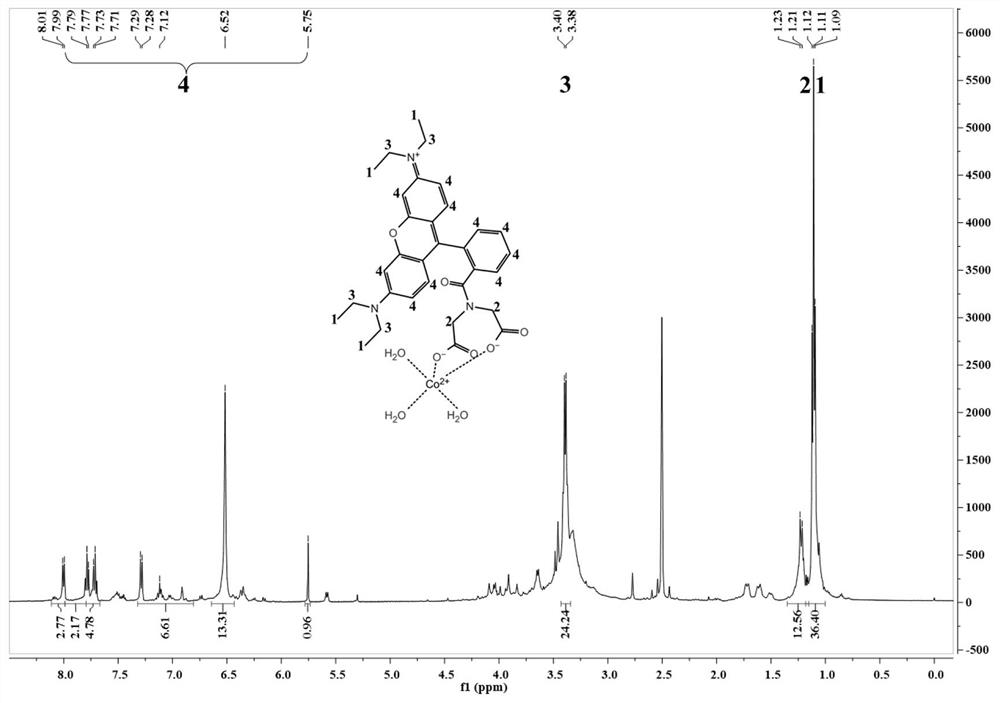
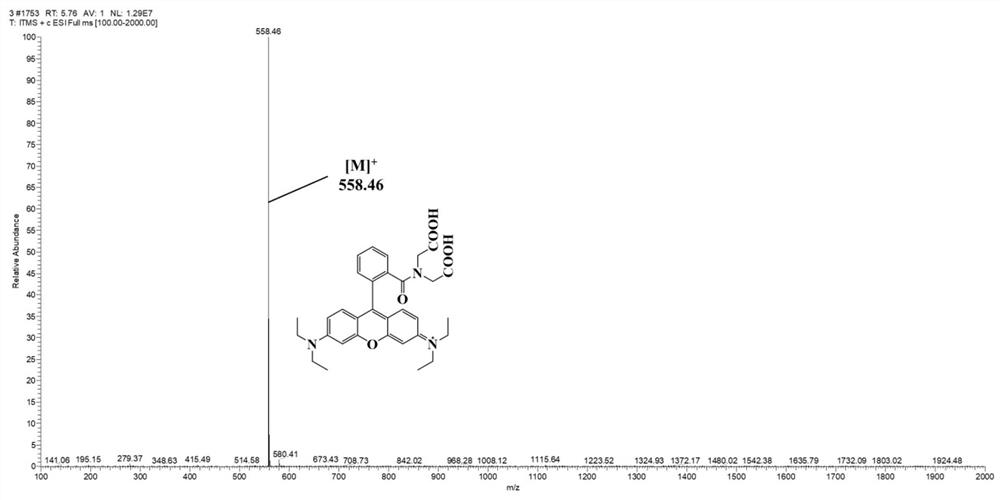
High-throughput screening method of signal peptide library based on fluorescent probe Rho-IDA-CoII
PendingCN114231553ADiversity guaranteedAvoid lossMicrobiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesFluoProbesHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention discloses a high-throughput screening method of a signal peptide library based on a fluorescent probe Rho-IDA-CoII. Compared with a traditional screening method, the method has the advantages that the histidine tag fusion protein in the range of 50-500 ng can be accurately measured by using a fluorescent probe labeling quantitative method, high background fluorescence caused by complex samples and environmental pollution is avoided, and the application range is wide. The method comprises the following steps: screening bacillus subtilis recombinants capable of secreting and expressing active nitrile hydratase from a bacillus subtilis expression nitrile hydratase signal peptide library by virtue of a fluorescent high-throughput screening method, and detecting that the nitrile hydratase activity is 12.97 + / -0.77 U / mL in culture supernate of the bacillus subtilis recombinants. The recombinant capable of secreting and expressing the nitrile hydratase can be applied to industrial production of the nitrile hydratase and downstream application of the nitrile hydratase.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Methods for preserving and/or storing cells having a nitrilase or nitrile hydratase activity
The invention relates to a method for preserving and / or storing microorganisms which exhibit at least one nitrile hydratase or nitrilase enzyme activity, with the preservation and / or storage being effected in an aqueous medium which comprises at least one aldehyde, with the total aldehyde concentration being in a range from 0.1 to 100 mM / l.
Owner:BASF AG
Method for preserving enzyme
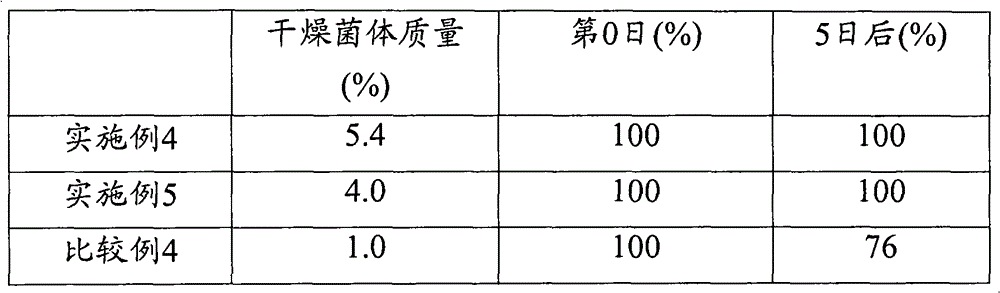
InactiveUS9353348B2Low costPreserved inexpensively and simplyBacteriaMicroorganism lysisNitrile hydratase activityHigh pressure
The problem is to provide a method for inexpensively and simply preserving an enzyme of a microbial biomass obtained by culturing and improve the enzyme activity during preservation. Provided is a method for preserving nitrile hydratase, characterized in that microbes having nitrile hydratase activity are cultured while being protected from light, and the resulting biomass is crushed using a high-pressure homogenizer and preserved while being protected from light.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Method for transporting microbial cells
ActiveCN103620030AThe preservation method satisfiesLabor savingHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismMicrobial fuel cell
A method for storing microbial cells having nitrile hydratase activity in a hermetically sealable container, and a method for transporting microbial cells having nitrile hydratase using the container are provided. The methods are characterized in that the vapor phase portion within the container is set to 2-20% (inclusive) of the total interior volume of the container, said vapor phase portion being filled with a suspension that contains the microbial cells.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Transport method of microorganisms
ActiveCN103620030BThe preservation method satisfiesLabor savingHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismGas phase
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
A strain of Escherichia coli recombinant strain heterologously expressing heat-resistant nitrile hydratase and its application
ActiveCN109251882BSimplify separation and purification stepsIncrease productivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHeterologous
The invention discloses a Escherichia coli recombinant strain heterologously expressing heat-resistant nitrile hydratase and application of the Escherichia coli recombinant strain, and belongs to thefield of bioengineering. According to the invention, the Escherichia coli recombinant strain having a high nitrile hydratase activity is obtained by constructing of recombinant Escherichia coli, and the recombinant nitrile hydratase obtained by fermentation has better thermal stability. In addition, the Escherichia coli recombinant strain can be used as a catalyst, and nicotinonitrile or acrylonitrile can be used as a substrate to carry out a whole-cell catalytic reaction to prepare nicotinamide or acrylamide. Compared with a chemical production method, the production process is safe and clean, and has no environmental pollution. Compared with an enzymatic method, the production process employs a cheap substrate, simplifies separation and purification steps of products, has high catalyticefficiency, and has a yield of the final product nicotinamide or acrylamide of 95% or above.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Method for synthesizing low-conductivity amide compound aqueous solution
InactiveCN110157751AReduce conductivityLow impurity contentMicroorganism based processesFermentationNitrile hydratase activityAqueous solution
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing a low-conductivity amide compound aqueous solution. The method for synthesizing the low-conductivity amide compound aqueous solution comprises the following steps that in a solution system with a biocatalyst with nitrile hydratase activity, a corresponding amide compound is synthesized from a nitrile compound, and the temperature in the synthesis process ranges from 9 DEG C to 14 DEG C. According to the method, acrylamide is synthesized through a microbiological method at a low temperature; for a 42% acrylamide product, the by-product crylic acid content is low (0.0846%), and the conductivity of the product is 400 micro Scm<-1>.
Owner:英德市云超聚合材料有限公司 +1
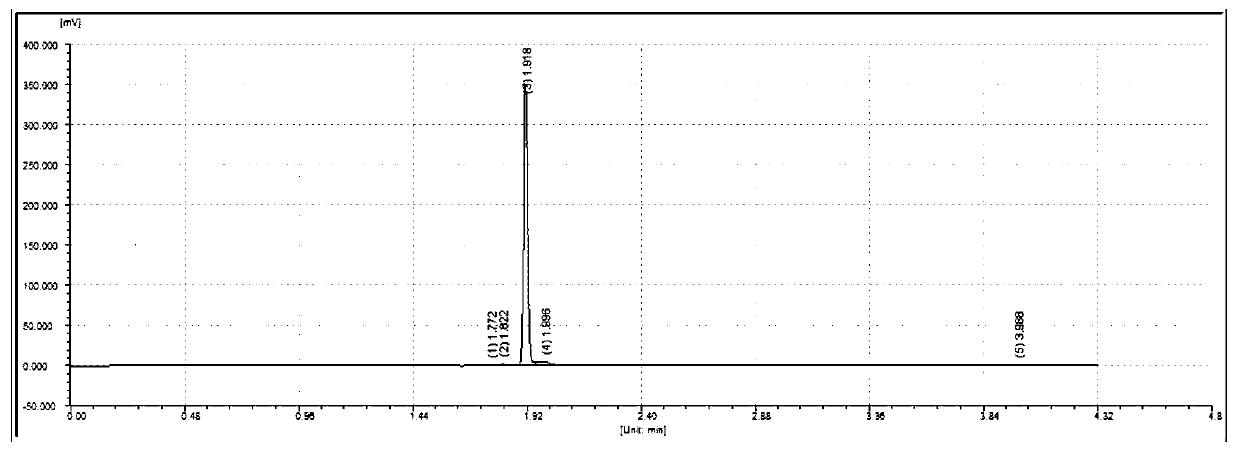
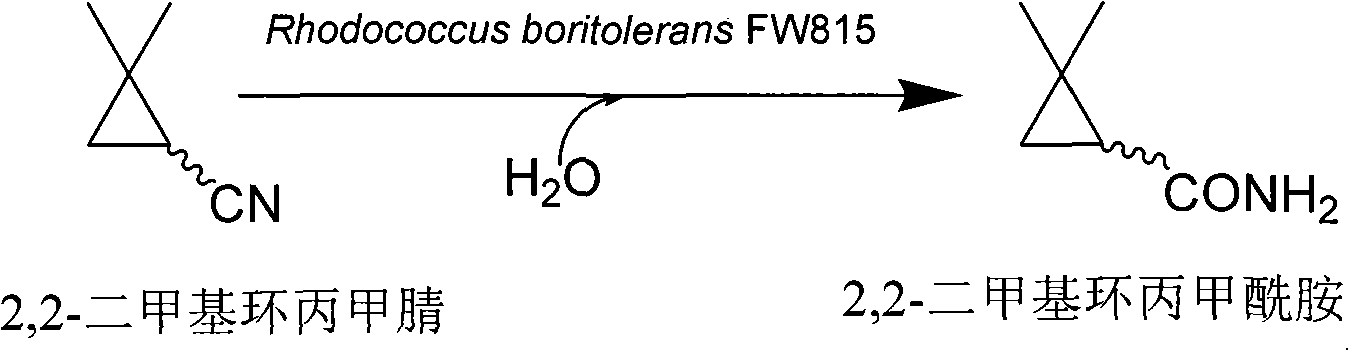
Method for preparing 2,2-dimethyl cyclopropanecarboxamide and bacterial strain thereof by biological catalysis
ActiveCN101481665BSimple compositionHigh biocatalytic efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNitrile hydratase activitySewage
The invention provides a Rhodococcus boritolerans FW815 enriched in soil and sewage and sieving high nitrile hydratase active mircoorganism strain, and a process that applies the strain to biological catalysis methods for the preparation of 2,2-dimethyl cyclopropane formamide. The 2,2-dimethyl cyclopropane formamide is prepared by converting 2,2-dimethyl cyclopropane formonitrile via the nitrile hydratase generated by the strain, wherein, the reaction medium is water, constituents of the reaction system are simple, the biological catalysis efficiency is high, the conversion time is short, theconversion rate for substrates is high, the yield of the 2,2-dimethyl cyclopropane formamide product is high and the extraction and purification processes are simple.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for preserving enzyme
InactiveUS20150050718A1Low costPreserved inexpensively and simplyBacteriaUnicellular algaeNitrile hydratase activityHigh pressure
The problem is to provide a method for inexpensively and simply preserving an enzyme of a microbial biomass obtained by culturing and improve the enzyme activity during preservation. Provided is a method for preserving nitrile hydratase, characterized in that microbes having nitrile hydratase activity are cultured while being protected from light, and the resulting biomass is crushed using a high-pressure homogenizer and preserved while being protected from light.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com