Method of cultivating microorganisms having nitrile hydratase activity
A technology of nitrile hydratase and cultivation methods, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, adding compounds to stimulate growth, enzymes, etc., can solve problems such as low enzyme production rate, low microbial growth rate, and few microorganisms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
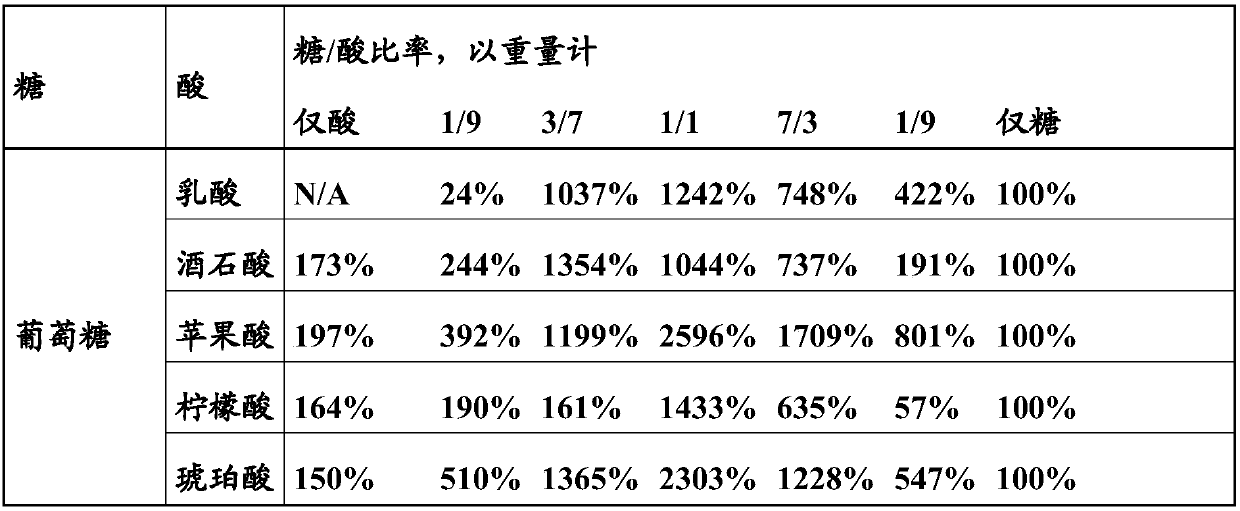
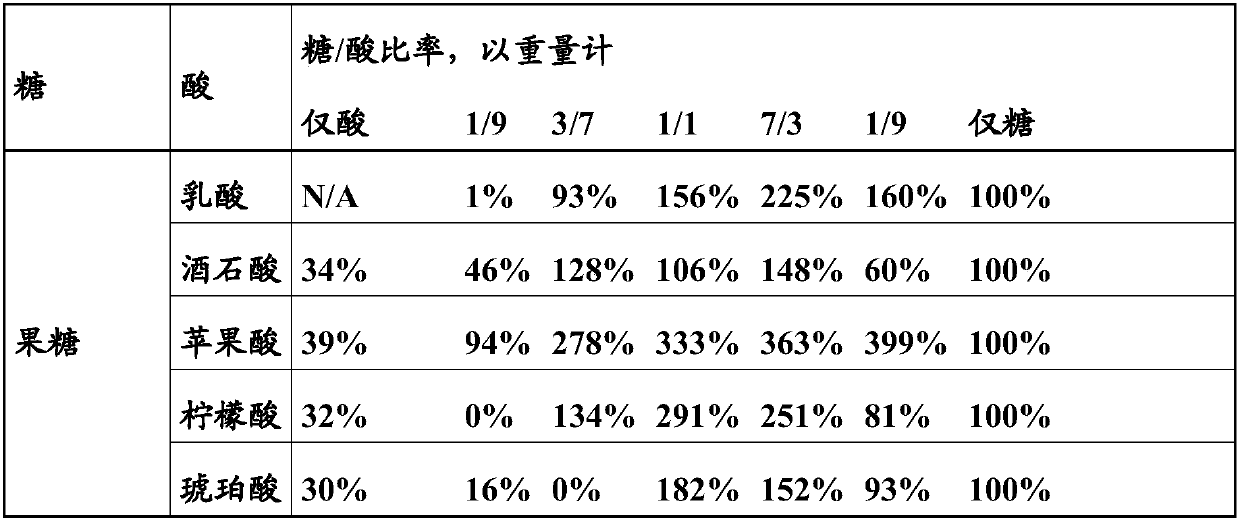
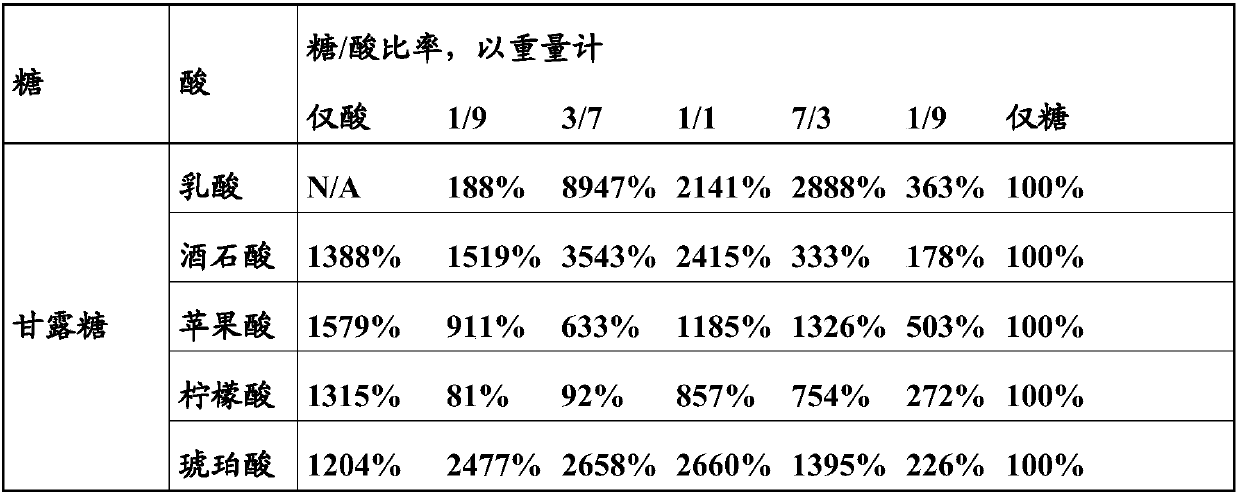
[0046] Culture of Rhodococcus
[0047] In a microfermentation system, different sugar / organic acid ratios were evaluated against different Rhodococcus strains, Rhodococcus rhodochrous "CIBA" (NCIMB 41164) and Rhodococcus rhodochrous "J1" (FERM BP-1478)).
[0048] Basal medium containing yeast extract (Biospringer) (1.25g / l), KH 2 PO 4 (10g / l), K 2 HPO 4 (10g / l), (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 (1g / l), MgSO 4 *7H 2 O(0.375g / l), CaCl 2 *2H 2 O (25mg / l), trace element solution (2.5g / l) (see below), Co(NO 3 ) 2 (31.2mg / l), defoamer P2000 (BASF) (62.5mg / l), urea (7g / l) and ammonium glutamate (2.5g / l), in H 2 O middle.
[0049]Trace element solution: citric acid monohydrate (40g / l), ZnSO 4 *7H 2 O(11g / l), (NH 4 ) 2 Fe(SO 4 ) 2 *6H 2 O(8.5g / l), MnSO 4 *H 2 O (3g / l) and CuSO 4 *5H 2 O(0.8g / l), in H 2 O middle.
[0050] The medium was then supplemented with 10 g / l of a carbon source (sugar, organic acid or a mixture of both, as indicated in the table below). Use H 3 PO 4 or...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Determination of nitrile hydratase activity
[0062] Take a sample from the culture medium of embodiment 1, and with 50mmol / l KH 2 PO 4 Buffer (pH7.0) was diluted 1:10 (v / v). The obtained solution was treated with 50mmol / l KH 2 PO 4 Buffer (pH 7.0) was further diluted 1:20 (v / v) to achieve a final dilution factor of 1:200 for the medium.
[0063] reaction:
[0064] 875 μl KH 2 PO 4 Buffer (pH 7.0) was pipetted into 2ml Eppendorf tubes. Add 100 μl of diluted medium and pre-incubate the mixture in a thermostatic mixer at 500 rpm for 5 min at 25 °C. After pre-incubation, the reaction was started by adding 25 μl of acrylonitrile. The reaction was carried out at 25°C and 1,000 rpm for 10 minutes.
[0065] Sample Preparation:
[0066] After a reaction time of 10 minutes, the reaction was quenched by transferring 300 μl of the reaction solution to a 1.5 ml Eppendorf tube containing 300 μl of 1.4% (m / v) hydrochloric acid. The mixture was vortexed briefly and cent...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com