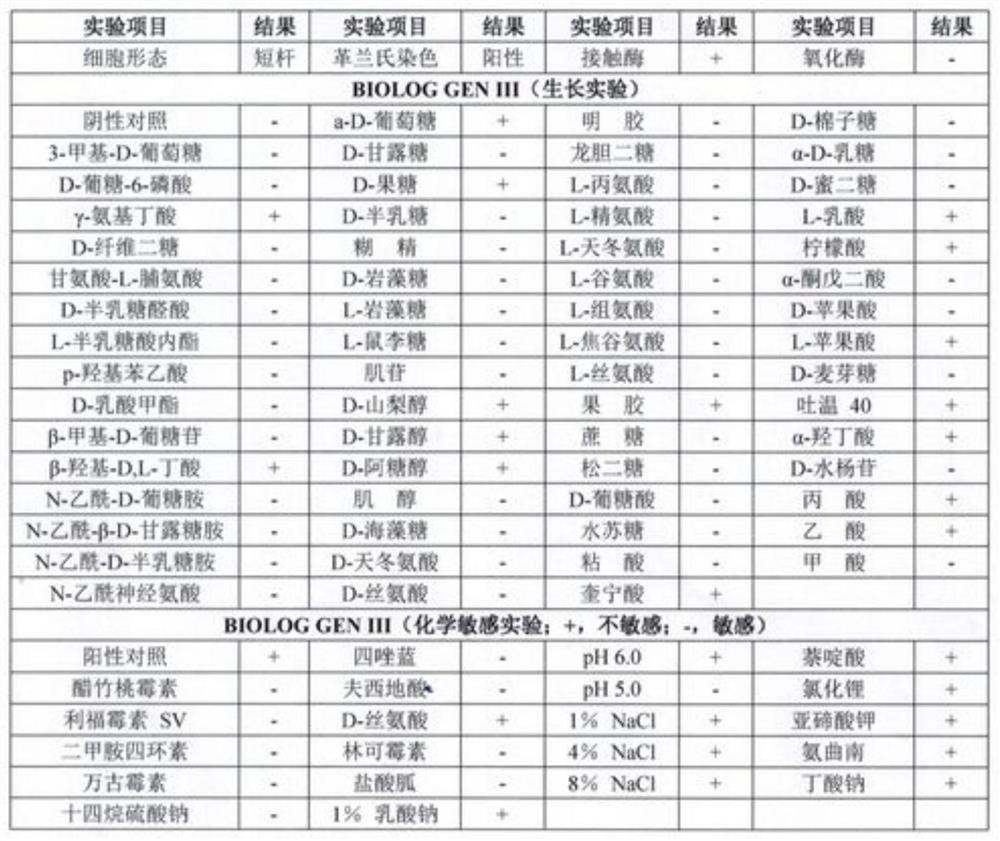
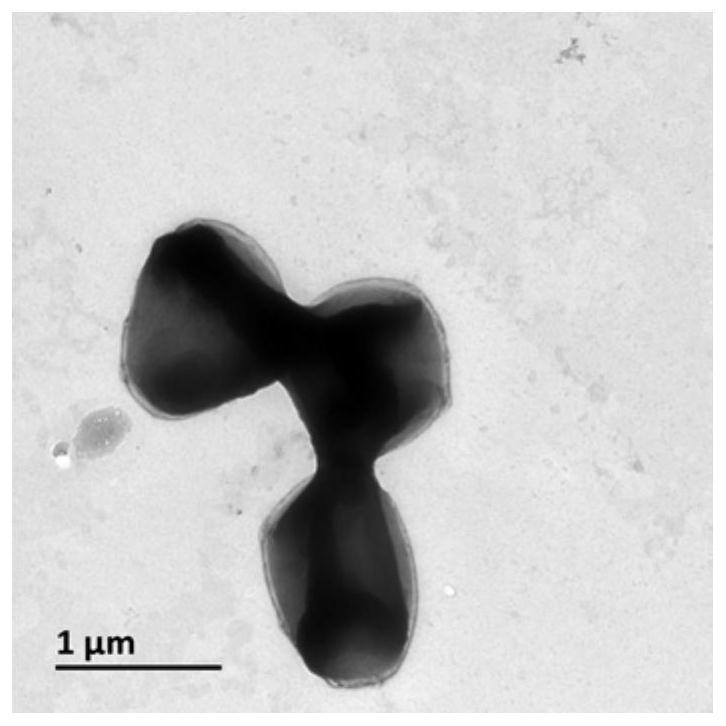
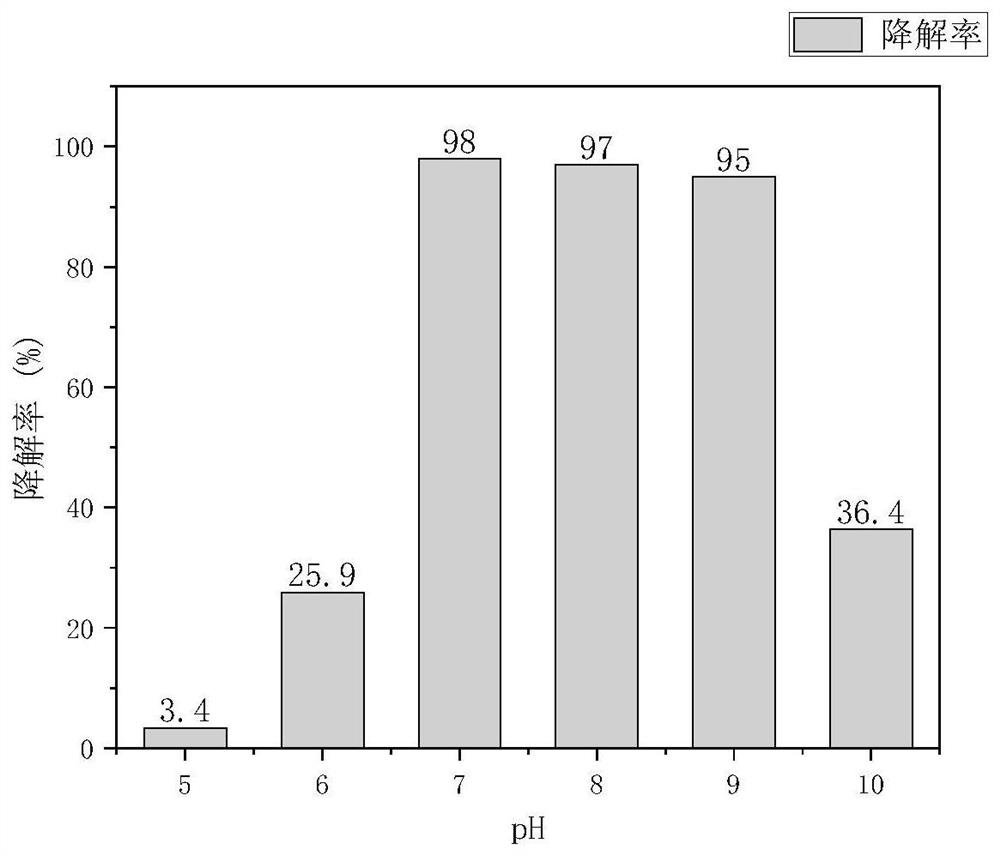
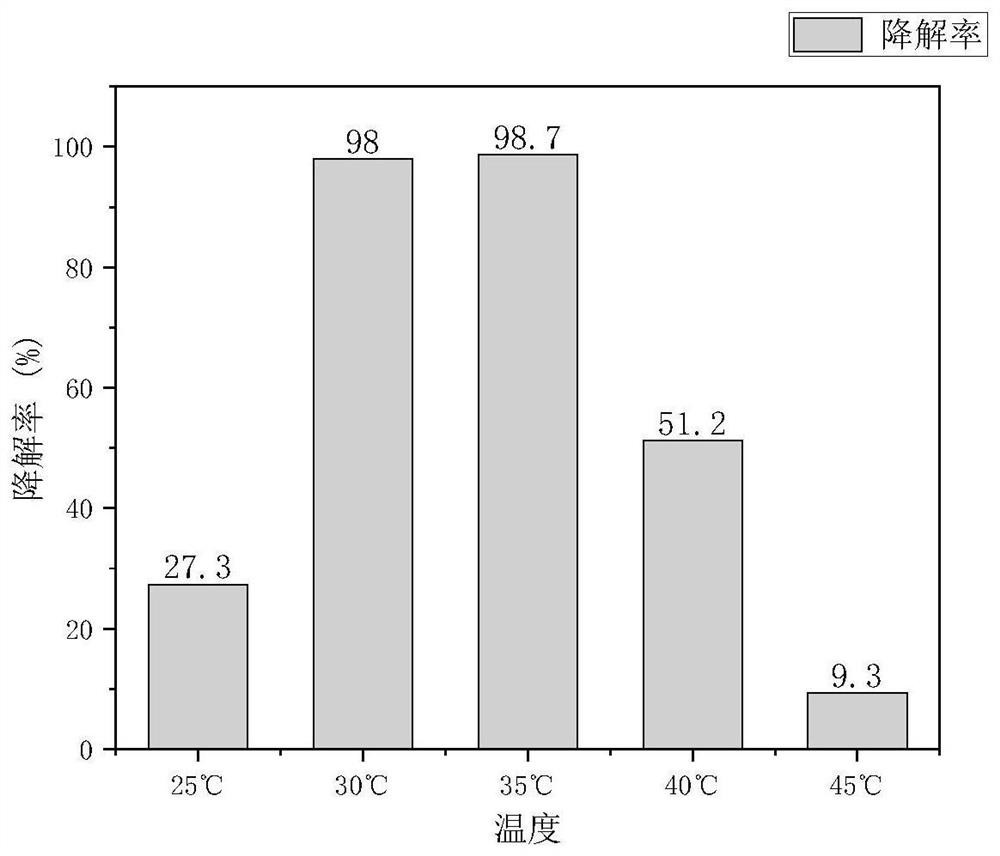
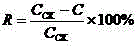Patents
Literature
31 results about "Rhodococcus rhodochrous" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Rhodococcus rhodochrous is a bacterium used as a soil inoculant in agriculture and horticulture.
Method for biodegradation of organic phosphorus pesticide wastewater
ActiveCN105967436AHigh removal ratePromote degradationMultistage water/sewage treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentElectrolysisAspergillus niger
The invention discloses a method for biodegradation of organic phosphorus pesticide wastewater, wherein the method comprises the following steps: after wastewater is subjected to electrolysis purification, adding a mixture composed of limestone and calcium chloride, putting an oxidizing agent, forming a calcium salt, and filtering to remove the calcium salt; weighing bacillus amyloliquefaciens Ba2015036, bacillus subtilis, rhodococcus rhodochrous strains R-MS6, aspergillus niger strains J15 and aspergillus niger strains J27 according to the proportion, to prepare a biodegradable agent; sending a part of the obtained wastewater into an SBR reactor, staying for 24 h, then putting a proper amount of the biodegradable agent, carrying out closed aeration for 2 d, and then continuously feeding water with the speed progressively increased at the speed rate of 5%; and adding a proper amount of ferrous sulfate into the wastewater treated by the SBR reactor, carrying out a coagulation reaction, and filtering. Through reasonable selection, proportion and culture of the dominant degrading strains, the biodegradation rate is increased, and at the same time, with collaboration of electrolytic purification, oxidizing agent treatment and SBR reactor treatment, the removal rate of organic phosphorus is greatly increased.
Owner:NANTONG VOCATIONAL COLLEGE
Composite fungicide for treating sludge and sludge treatment method
ActiveCN106635927ASpeed up fermentationColor back to normalFungiBacteriaRhodopseudomonas capsulataBacteroides
The invention relates to a composite fungicide for treating sludge and a sludge treatment method. The composite fungicide is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 3 to 8 parts of purple sulfur bacteria, 3 to 8 parts of green sulfur bacteria, 3 to 8 parts of rhodopseudomonas, 3 to 8 parts of rhodopseudomonas capsulata, 3 to 8 parts of rhodococcus rhodochrous, 3 to 8 parts of white-rot fungi, 3 to 8 parts of phosphorus-accumulating bacteria, 3 to 8 parts of anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria, 3 to 8 parts of lactobacillus plantarum, 3 to 8 parts of streptomycete, 3 to 8 parts of candida utilis, as well as saccharomyces cerevisiae, lactobacillus lactis, lactobacillus acidophilus, aspergillus niger, aspergillus oryzae, bacillus subtilis and bacillus licheniformis.
Owner:哈尔滨明慧生物技术开发有限公司
Method for cultivation of the nitrile-hydratase-producing strain Rhodococcus rhodochrous M33
The invention relates to a method for cultivation of the nitrile-hydratase-producing strain Rhodococcus rhodochrous M33, using a culture medium which is based on a 12 to 60 mM phosphate buffer, covers the demand of the cells for phosphorus and maintains the pH in the range of 5.5 to 9.0 during cultivation, and to which acetic acid is added in doses as the new source of carbon after consumption of the initially supplied quantity of glucose. The invention also relates to the culture medium used in the method.
Owner:ASHLAND LICENSING & INTPROP LLC
Strain-of Rhodococcus rhodochrous NCIMB 41164 and its use as producer of nitrile hydratase
ActiveUS7575912B2Increase enzyme activityHigh nitrile hydratase activitySugar derivativesBacteriaUrea derivativesMicroorganism
A microorganism which is Rhodococcus rhodochrous strain NCIMB 41164 or a mutant thereof. A method of culturing the microorganism in a culture medium comprising urea or urea derivative is claimed. A nitrite hydratase obtainable from the microorganism is claimed. Also claimed is a process of preparing an amide from the corresponding nitrite wherein the nitrite is subjected to a hydration reaction in an aqueous medium in the presence of a biocatalyst selected from the group consisting of a microorganism which is a Rhodococcus rhodochrous strain NUMB 41164, a mutant thereof and a nitrite hydratase obtainable from Rhodococcus rhodochrous strain NCIMB 41164 or a mutant thereof. Also claimed is a method of storing the Rhodococcus rhodochrous NUMB 41164.
Owner:CIBA SPECIALTY CHEM WATER TRATMENTS +1
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degrading bacterium Q3 and application thereof
InactiveCN110468065AGood restorativeImprove repair effectBacteriaWater contaminantsPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonMicroorganism
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganisms, in particular to a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degrading bacterium and application thereof in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon degradation. The degrading bacterium is Rhodococcus rhodochrous, belongs to gram-positive bacteria, and has a deposit number of CGMCC No. 16446. The degrading bacterium screened by the invention has a widerange of degradable substrates and strong degradation performance, can efficiently degrade various high- and low-cyclic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon monomers, and especially have strong tolerance to high-concentration pyrene solution. Meanwhile, the strain can grow normally under neutral and alkaline conditions and under a salt concentration of less than 8%. The strain can be used for removingor degrading various polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon monomers, especially removing or degrading composite high-cyclic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil and water environment.
Owner:INST OF URBAN ENVIRONMENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Nitrile degradation biofilm formed genetically engineered bacterium and application of genetically engineered bacterium in nitrile-containing wastewater treatment
InactiveCN104293725AEnrich resourcesHas film-forming abilityBacteriaHydrolasesGenetically engineeredMicrobiological culture
The invention provides a nitrile degradation biofilm formed genetically engineered bacterium and application of the genetically engineered bacterium in nitrile-containing wastewater treatment, and belongs to the bioengineering technology. The genetically engineered bacterium Bacillus subtilis N4-pHT01-Nitr with the preservation number of CGMCC No.9484 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on July 25, 2014. The bacterium is prepared by inserting a nitrilase gene in Rhodococcus rhodochrous BX2 into Bacillus subtilis N4 for expressing by means of gene engineering. The bacterium is capable of generating a biofilm and degrading acetonitrile, the OD570nm value of biofilm formation capacity is 1.45 when the bacterium is culture in synthetic wastewater at 37 DEG C and 60r / min for 48 hours; and the residual concentration of acetonitrile is 23.56mg / L after the bacterium is oscillated and cultured in 800mg / L acetonitrile-containing synthetic wastewater at 37 DEG C and 160rpm for 48 hours. The bacterium has strong acetonitrile impact resistance, acetonitrile in synthetic wastewater is reduced from 800mg / L to 0.32mg / L when the wastewater is output, and the COD value of the synthetic wastewater is reduced from 487mg / L to 16.39mg / L when the wastewater is output. The bacterium provides a novel method to nitrile-containing wastewater treatment by utilizing a biofilm method.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Microorganism
ActiveUS20090269822A1Easy to produceHigh activityBacteriaHybrid cell preparationUrea derivativesHydration reaction
A microorganism which is Rhodococcus rhodochrous strain NCIMB 41164 or a mutant thereof. A method of culturing the microorganism in a culture medium comprising urea or urea derivative is claimed. A nitrile hydratase obtainable from the microorganism is claimed. Also claimed is a process of preparing an amide from the corresponding nitrile wherein the nitrile is subjected to a hydration reaction in an aqueous medium in the presence of a biocatalyst selected from the group consisting of a microorganism which is a Rhodococcus rhodochrous strain NCIMB 41164, a mutant thereof and a nitrile hydratase obtainable from Rhodococcus rhodochrous strain NCIMB 41164 or a mutant thereof. Also claimed is a method of storing the Rhodococcus rhodochrous NCIMB 41164.
Owner:SOLENIS TECH CAYMAN
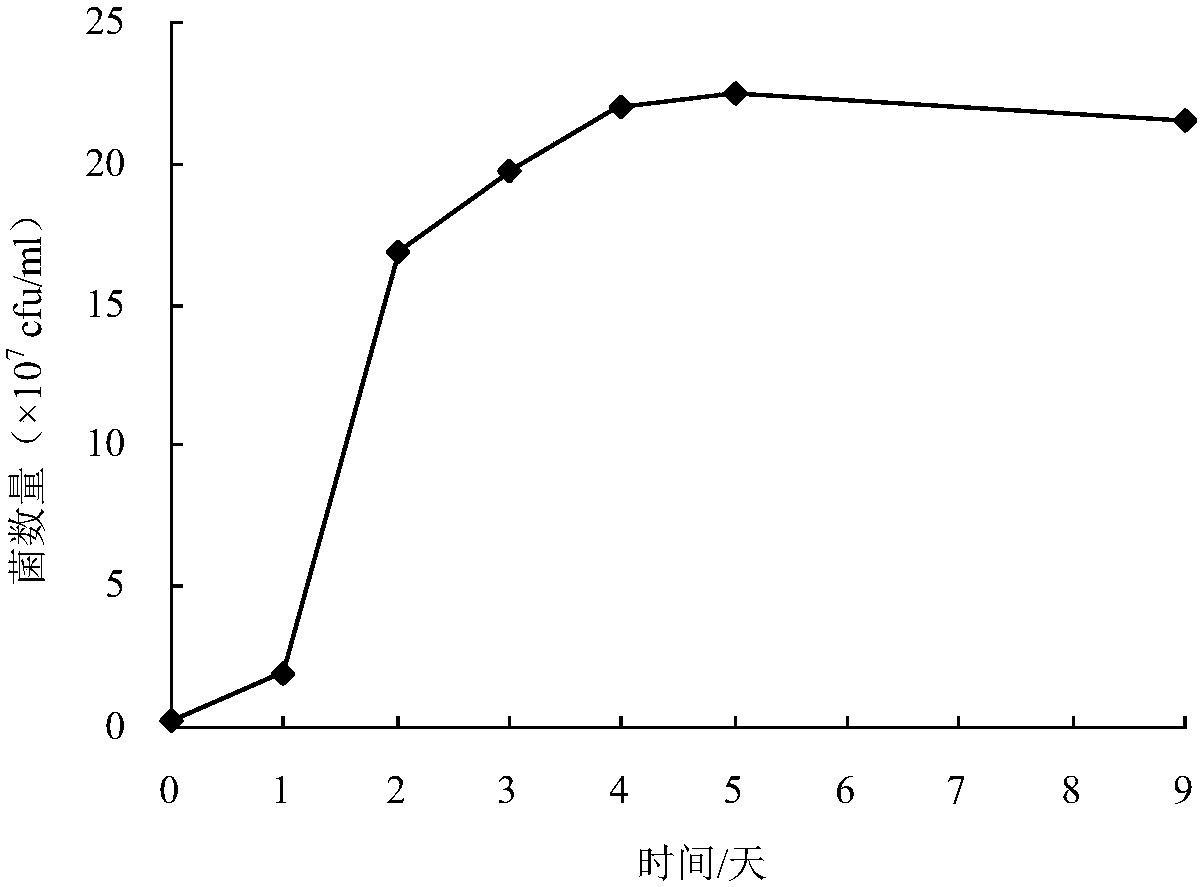
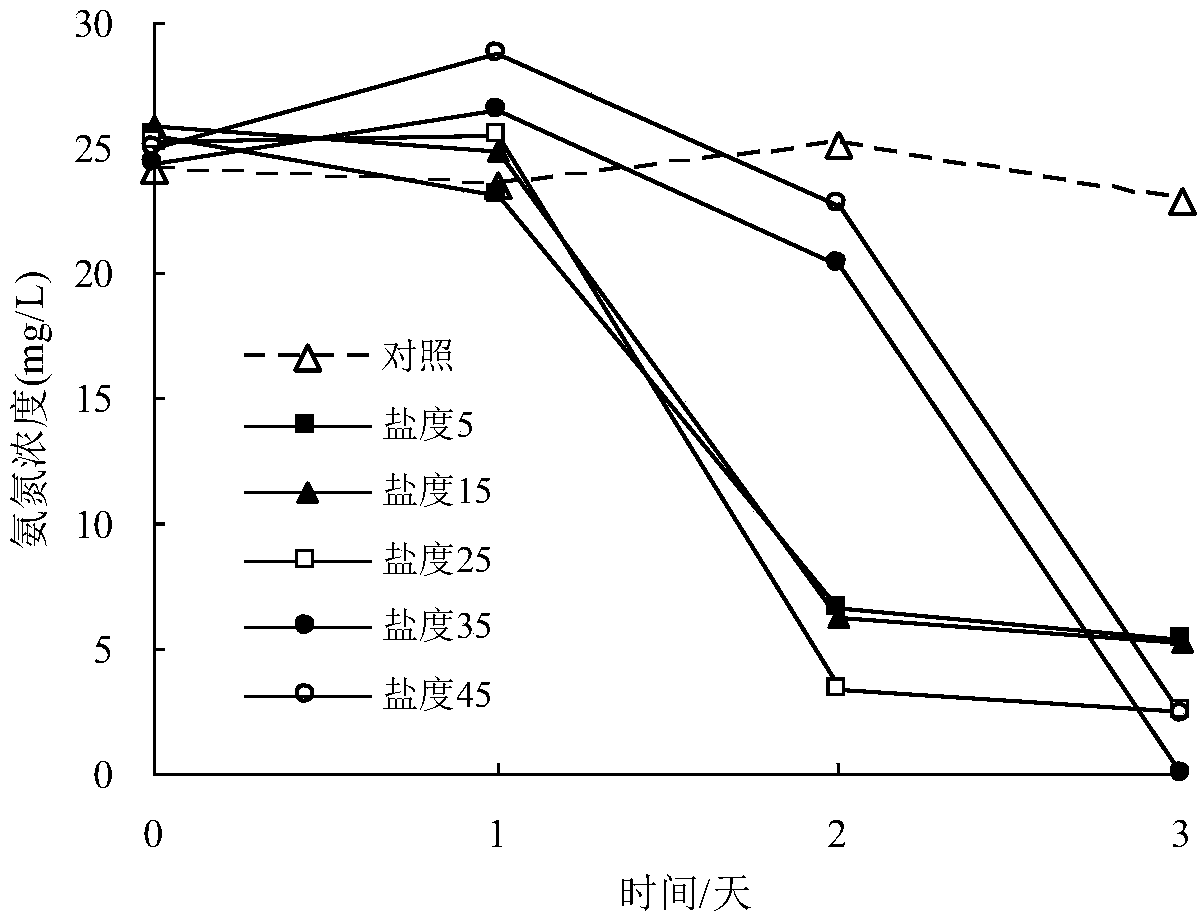
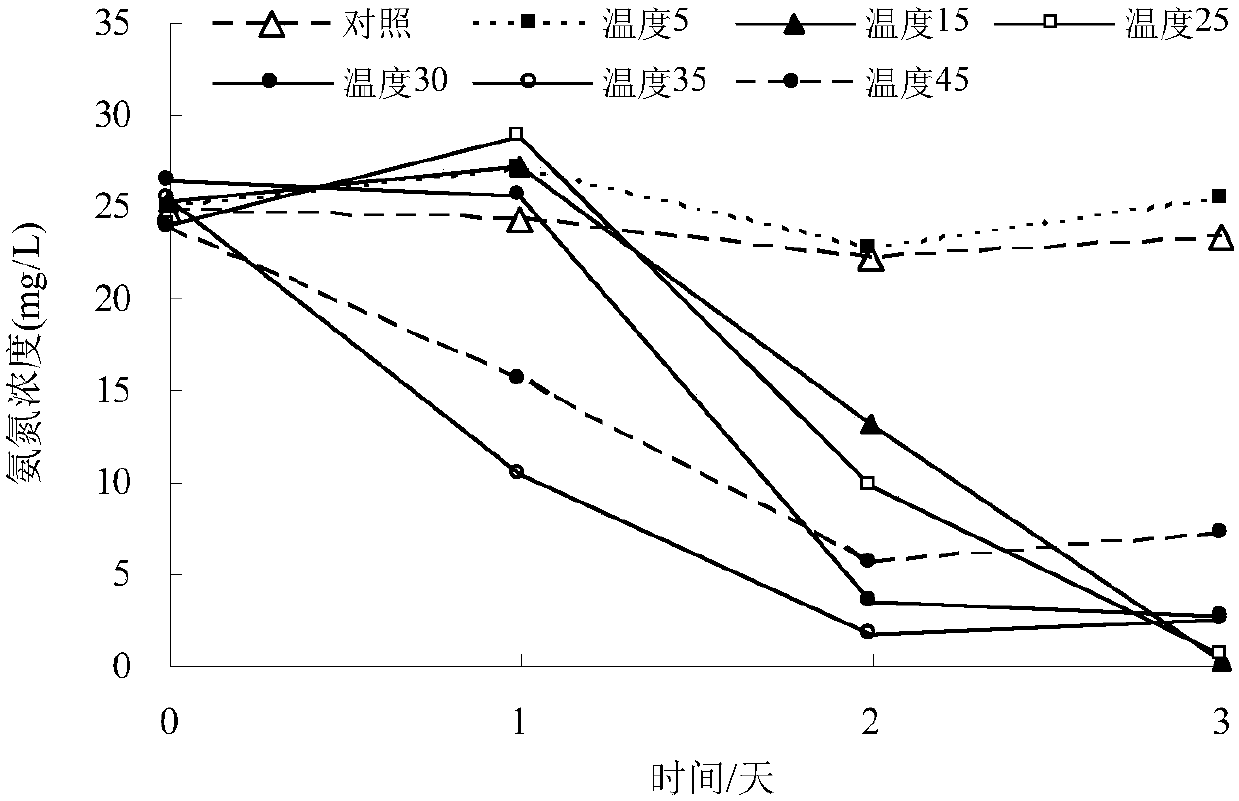
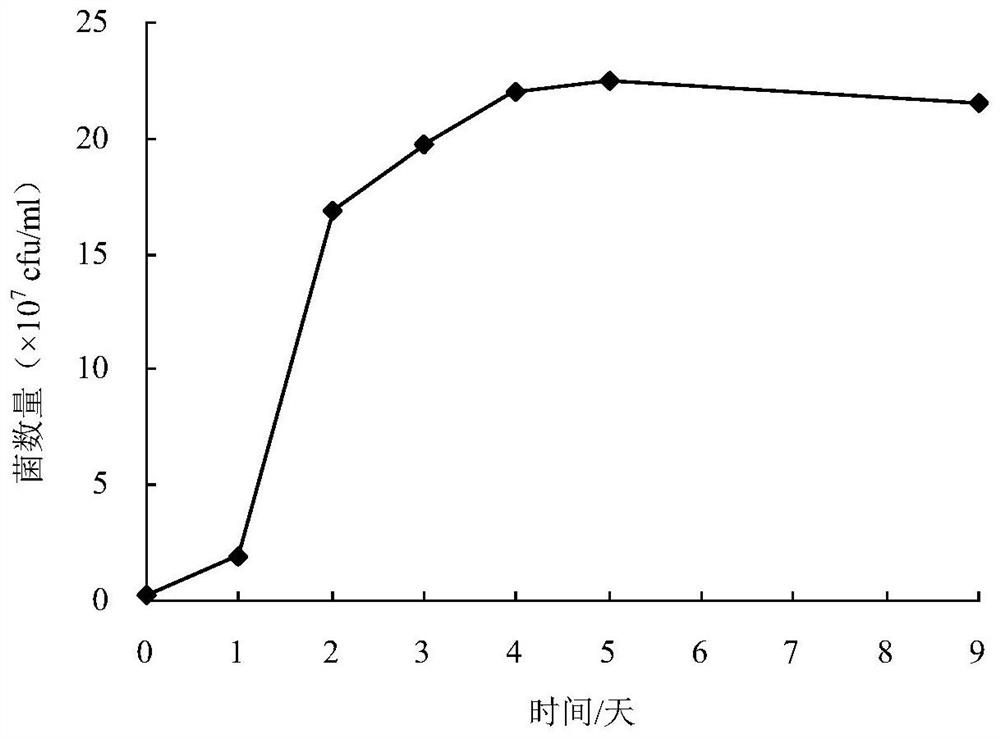
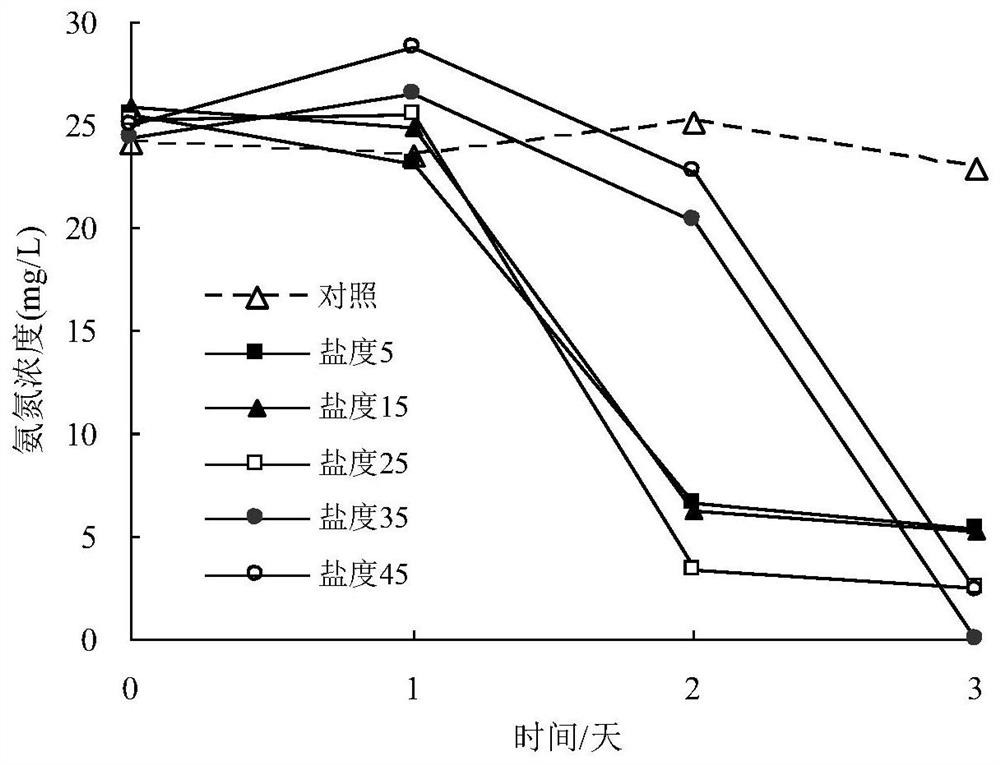
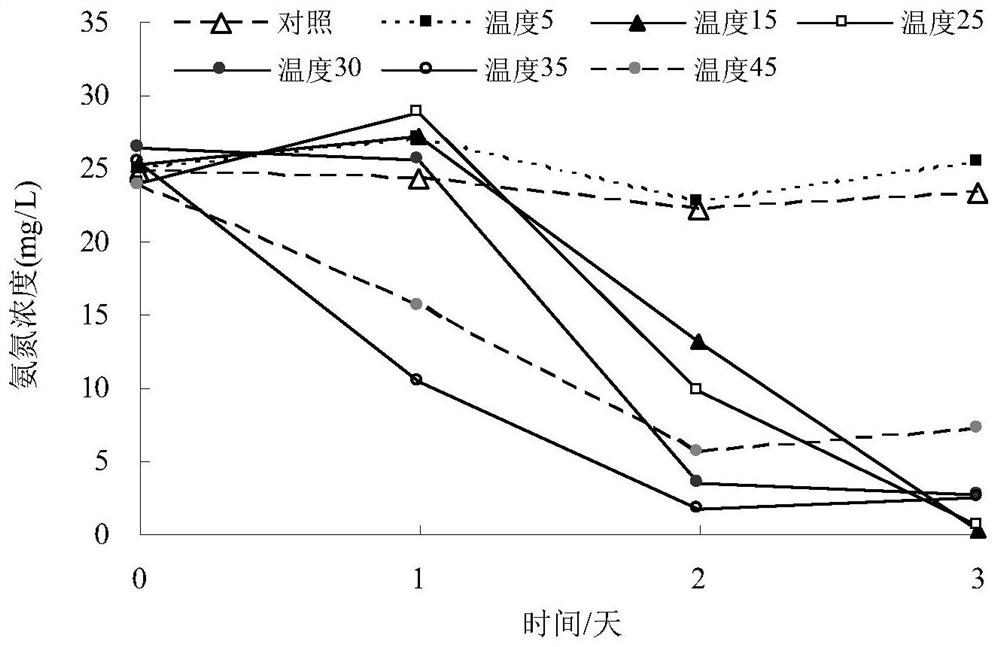
Rhodococcus rhodochrous bacterial strain XHRR1 for purifying ammonia in aquatic water and application thereof
ActiveCN107828679AGood removal effectImprove environmental adaptabilityBacteriaWater contaminantsMicrobiologyBacterial strain
The invention discloses rhodococcus rhodochrous bacterial strain XHRR1 for purifying ammonia in aquatic water. A preservation name of the bacterial strain XHRR1 is rhodococcus rhodochrous XHRR1, and the classification is named as rhodococcus rhodochrous XHRR1, the preservation unit is China Center for Type Culture Collection, the preservation address is Wuhan China, the preservation date is August3, 2017, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 2017437. The bacterial strain XHRR1 has higher purification capacity for the ammonium in the aquatic water, is good in environment adaptability andhas no unfavorable influence on the cultured prawns. The invention also discloses application of the rhodococcus rhodochrous bacterial strain XHRR1 in purifying the ammonia in the aquatic water.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI +1
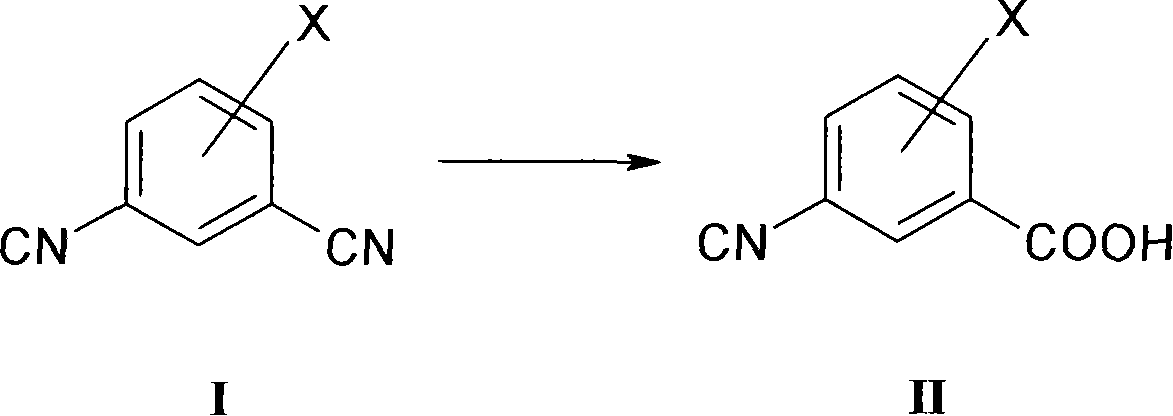
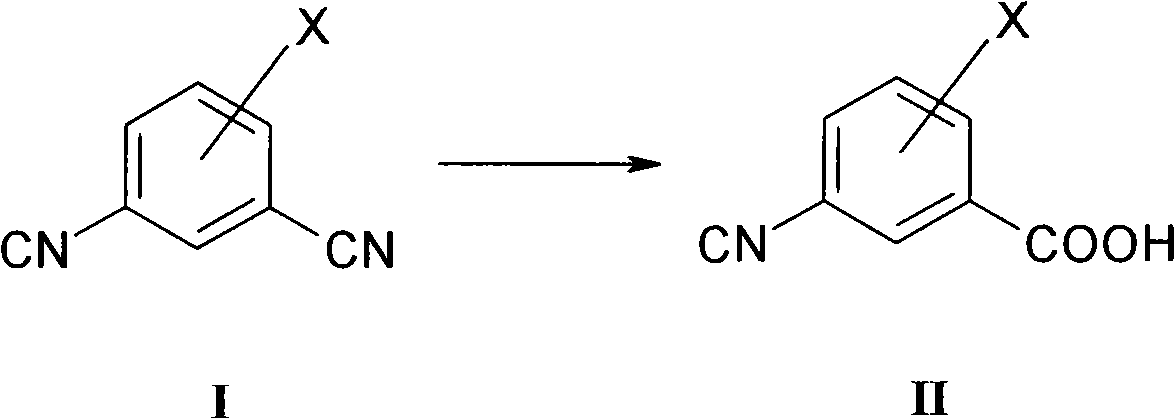
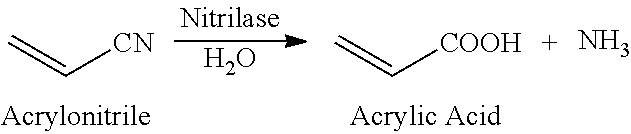
New process for converting aromatic halo-substituted dinitriles into halo-substituted cyanocarboxylic acids
The present invention is directed to a process for converting aromatic halo-substituted dinitriles into the corresponding cyanocarboxylic acids in the presence of a nitrilase such as Rhodococcus rhodochrous.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
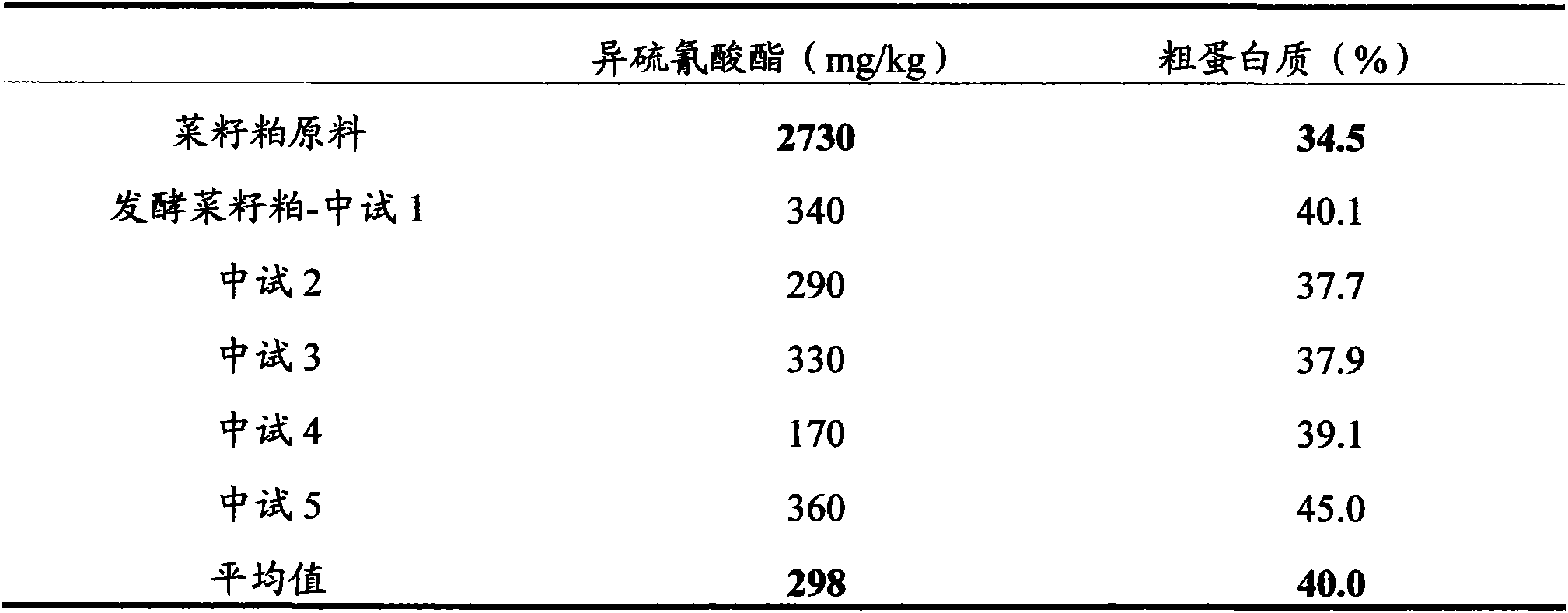
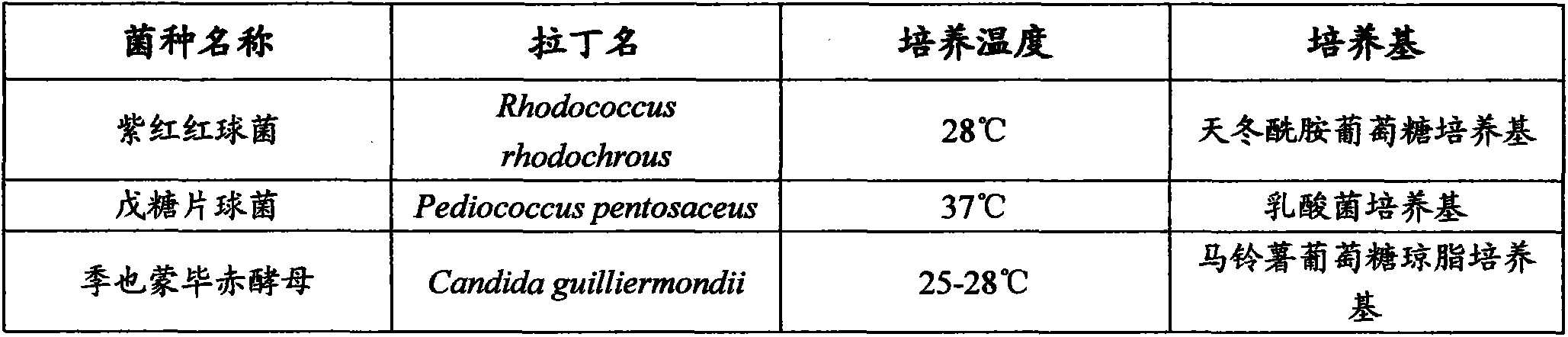
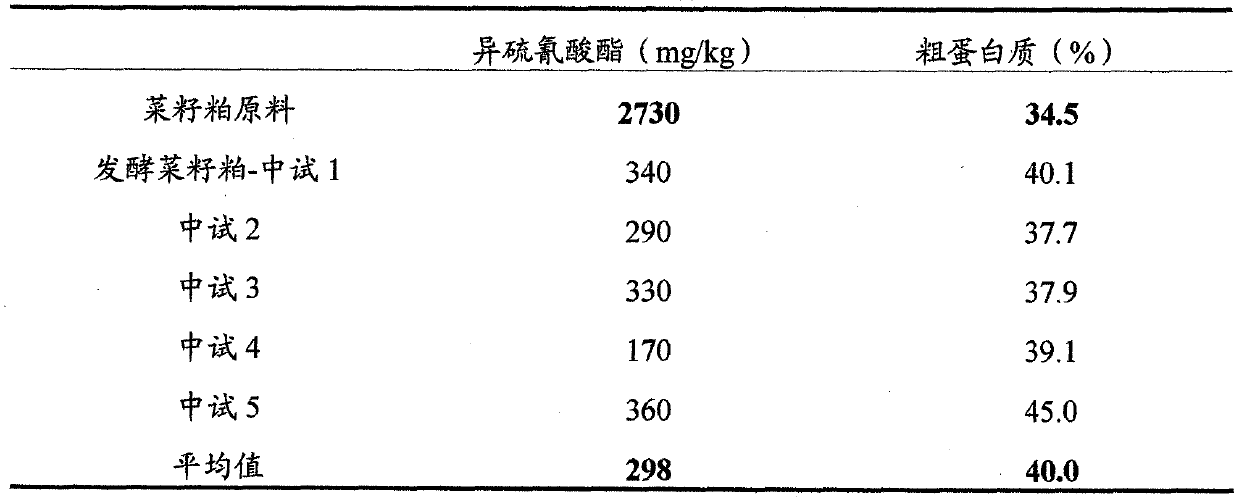
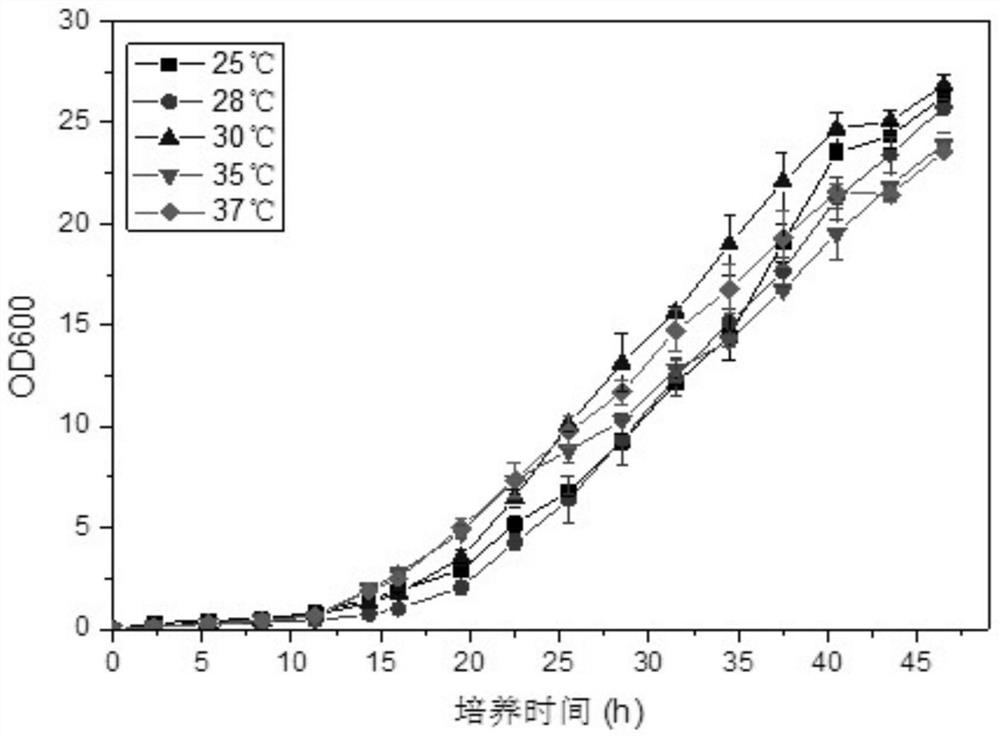
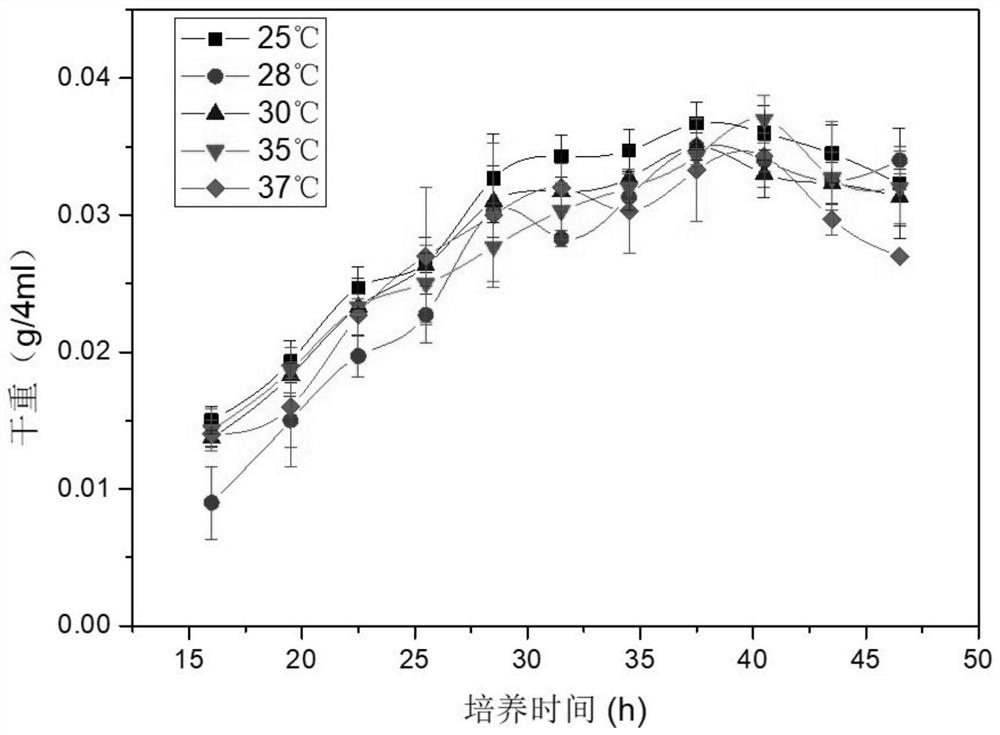
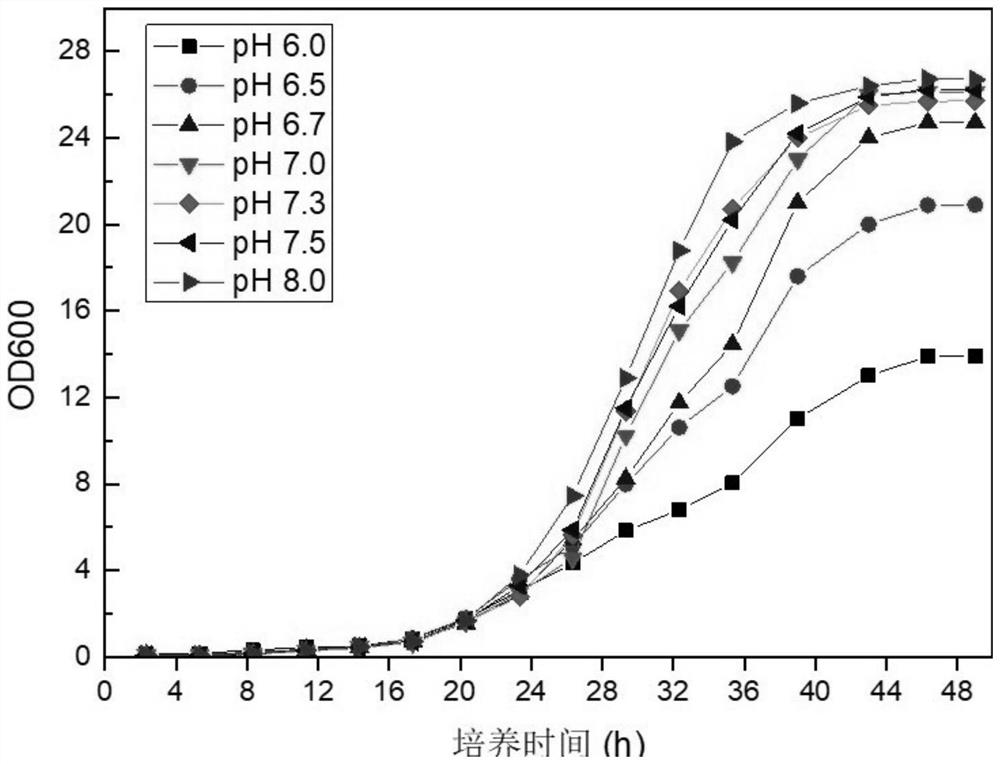
Microorganism combination solid-state fermentation method for reducing content of butyl isosulfocyanate in rapeseed dregs
InactiveCN103704466AReduced isothiocyanate contentShort fermentation timeFungiBacteriaMicroorganismRapeseed
The invention discloses a microorganism combination solid-state fermentation method for reducing the content of butyl isosulfocyanate in rapeseed dregs. Solid-state fermented rapeseed dregs of the combination of three microorganisms of Rhodococcus rhodochrous, Pediococcus pentosaceus and Candida guilliermondii are adopted for reducing the content of the butyl isosulfocyanate in the rapeseed dregs. The method comprises the following steps: preparation and pretreatment of a rapeseed dreg raw material, preparation of a fermented seed solution, inoculation of the three microorganisms in a proportion, solid fermentation, and preparation of a fermented rapeseed dreg finished product. According to the method, the Rhodococcus rhodochrous is firstly used for enabling the rapeseed dregs to be fermented in a solid state, and is combined with Pediococcus pentosaceus and Candida guilliermondii for use; compared with other technical schemes, the method can greatly reduce the content of the butyl isosulfocyanate in the rapeseed dregs obviously; moreover, the fermentation time is shorter, and the efficiency is high.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Rhodococcus rhodochrous for expressing mpd genes and construction method thereof
InactiveCN102174457APromote degradationEfficient degradationBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliStenotrophomonas sp.
The invention relates to rhodococcus rhodochrous for expressing mpd genes and a construction method thereof. The rhodococcus rhodochrous R-D3 for expressing the mpd genes can rapidly degrade residues of Dursban (a pesticide) in a water body. The construction method comprises the following steps: 1. extracting the genome DNA of a slightly acidophilic stenotrophomonas G1 bacterial strain; 2. carrying out amplification to obtain the PCR (polymerase chain reaction) product of the G1 bacterial strain; 3.connecting the PCR product of the G1 strain and pET-28a (+), an escherichia coli plasmid and constructing pET-C, a sequencing recombinant plasmid; and 4. constructing pDA71-C, an expressive recombinant plasmid, constructing an electrically transformed rhodococcus rhodochrous R-D3 bacterial strain of pDA71-C, an expressive recombinant plasmid to obtain the rhodococcus rhodochrous R-D3 for expressing the mpd genes.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Rhodococcus rhodochrous strain and use thereof in the production of acrylic acid
ActiveUS11485962B2Improve energy efficiencyReduce unwanted intermediate productsHydrolasesFermentationNitrile hydrataseProtein
Owner:AECI LTD
A strain of Rhodococcus rhodochrous and its method for producing nicotinamide
ActiveCN111424061BIncrease vitalityGood genetic stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHydration reactionPtru catalyst
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and in particular relates to a strain of Rhodococcus rhodochrous and a method for producing nicotinamide; including steps such as preparation of a Rhodococcus rhodochrous catalyzer, hydration reaction and the like, using nitrile hydratase produced by fermentation of Rhodococcus rhodochrous as a catalyst, using pure Water is used as a reaction system, and 3-cyanopyridine is catalyzed and converted into nicotinamide by means of flow addition or batch addition; the nitrile hydratase-producing Rhodococcus rhodochrous bacterium provided by the invention has good genetic stability, low culture cost, and produces nitrile The hydratase has high enzymatic activity, and this strain can be directly used to convert 3-cyanopyridine into nicotinamide. During the catalytic reaction, pure water is used as the reaction system, and the final reaction concentration of the reaction solution can reach more than 400g / L, avoiding the introduction of exogenous impurities, and at the same time, it is beneficial to the extraction and separation operation, and the industrial application has advantages.
Owner:山东昆达生物科技有限公司
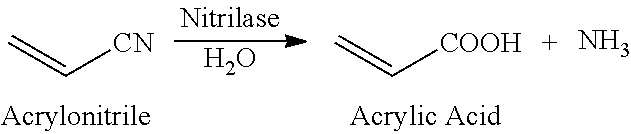
Rhodococcus jj-3 and its application in degrading acrylic acid
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
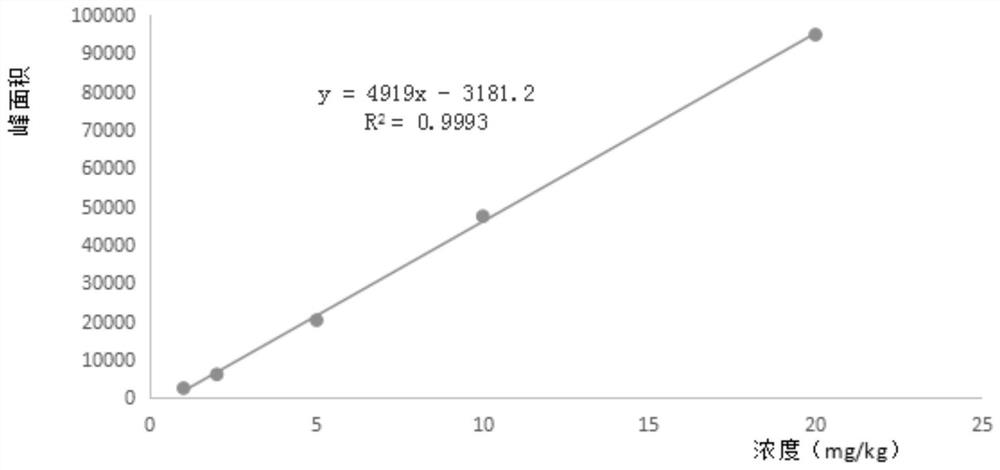
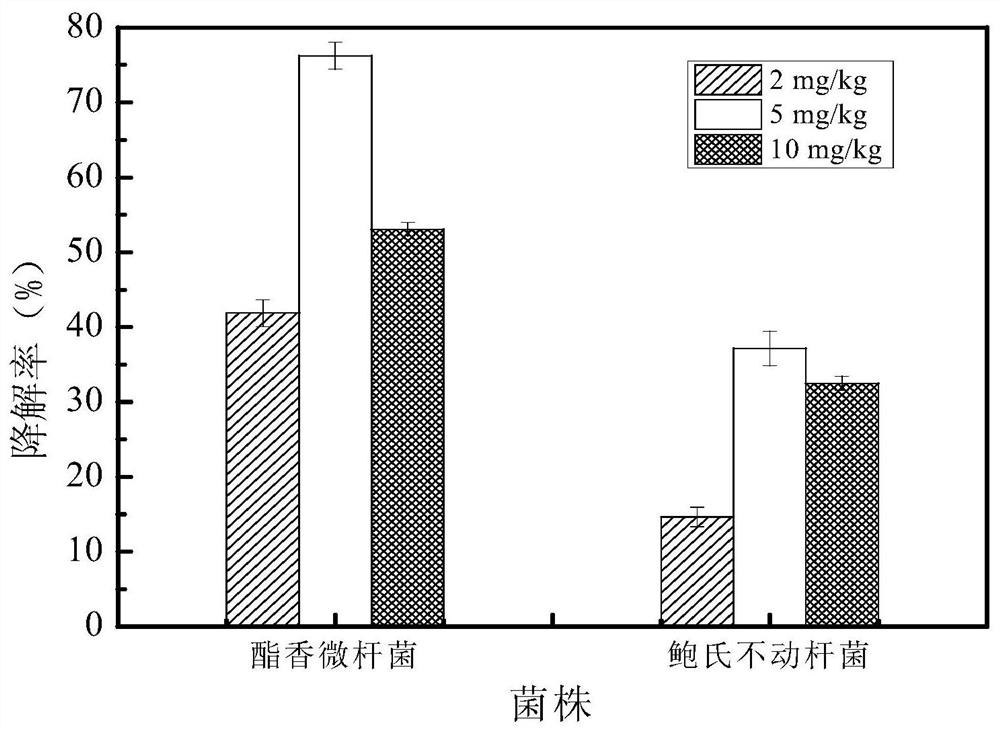
A strain of Rhodococcus rhodochrous that efficiently degrades cyhalothrin and its application
ActiveCN108410759BSolve the problem of pesticide residuesImprove securityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNicotiana tabacumPesticide residue
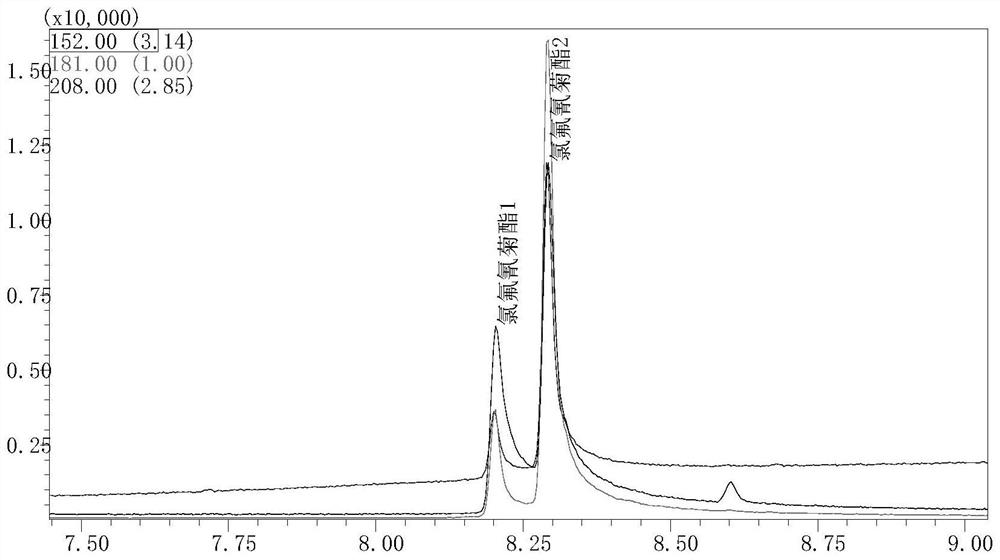
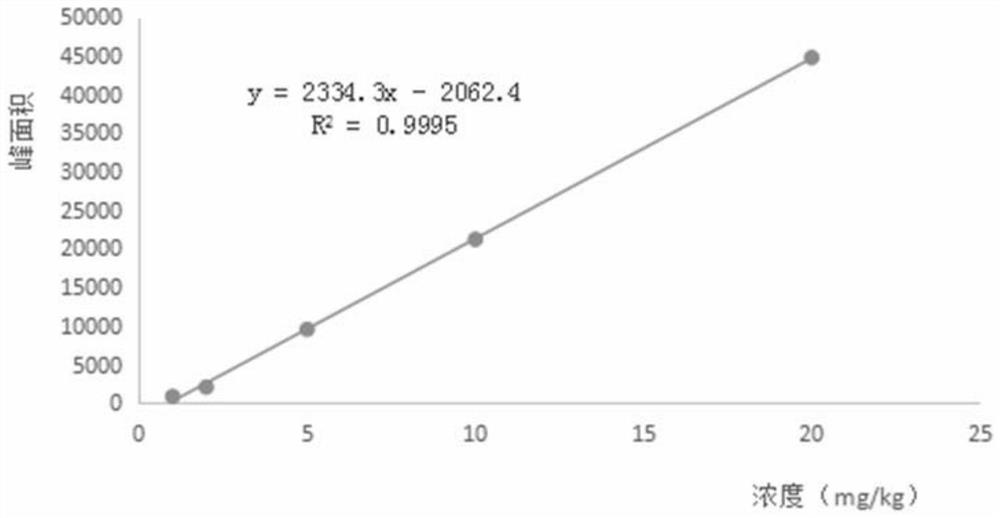
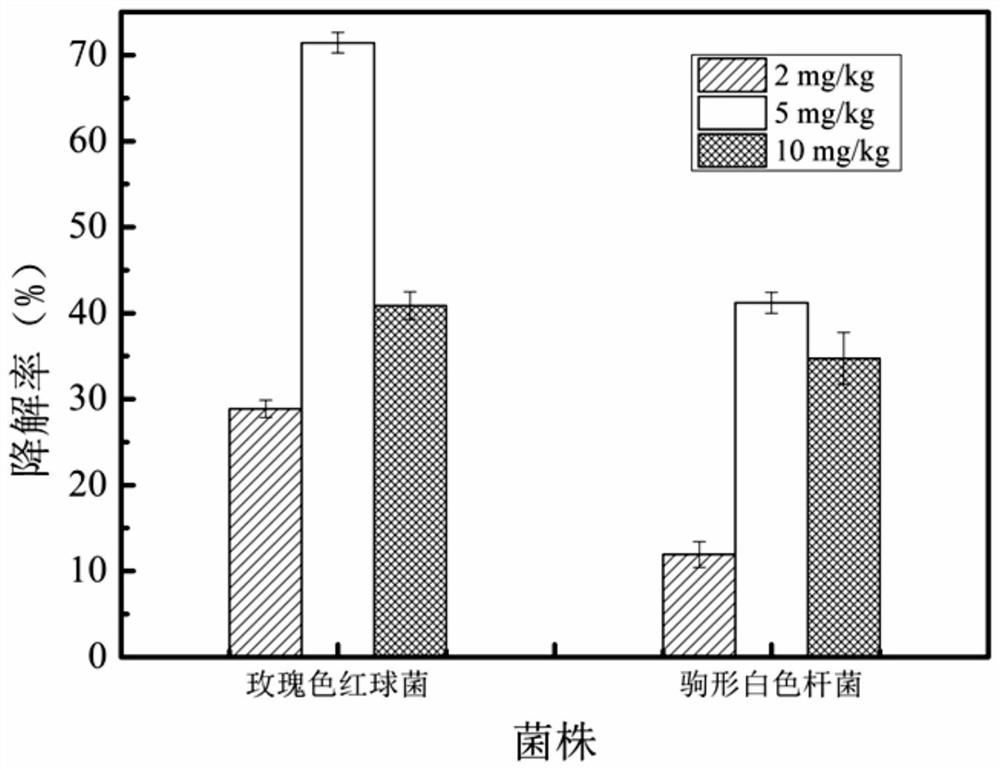
The invention discloses a rhodococcus rhodococcus capable of efficiently degrading cyhalothrin and an application thereof. The present invention takes microbial resources in the traditional fermentation process as the research object, screens and obtains the degrading bacteria for cyhalothrin that is used more in the planting process of tobacco and other crops, has a large residual amount, and has a long degradation cycle. The degrading bacteria is rose red The Rhodococcus rhodochrous L5 strain, derived from Fenjiu Daqu, has high safety and can efficiently degrade cyhalothrin at a concentration of 5 mg / kg, and has a certain effect on the degradation of low-concentration cyhalothrin pesticide residues in crops such as tobacco leaves. The application prospect provides a safe and effective biodegradation way to improve the quality and safety of tobacco products and solve the problem of pesticide residues in tobacco leaves and other crops.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
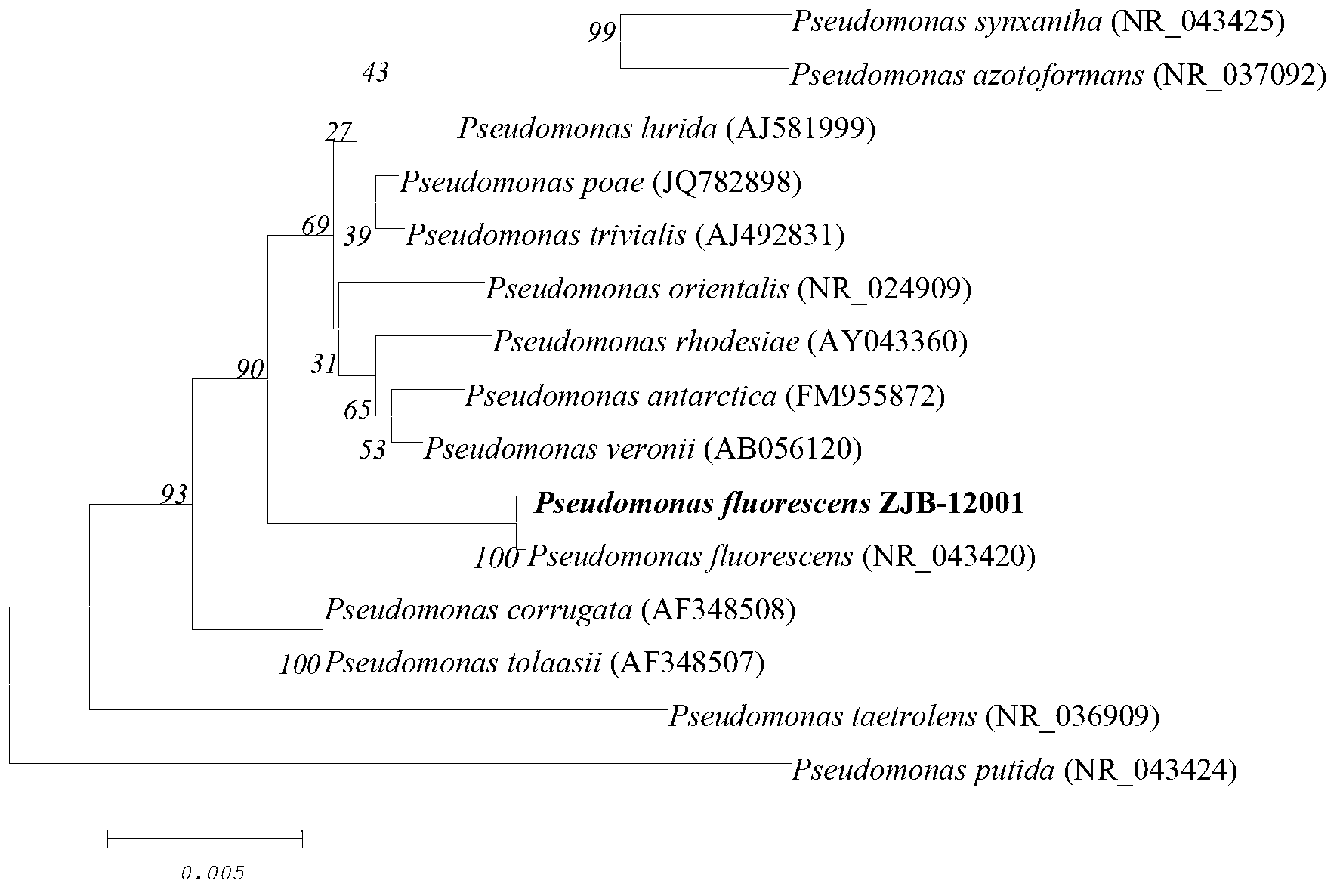
Pseudomonas fluorescens and application thereof in biosynthesizing methionine
ActiveCN103289928AEfficient productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyMethionine biosynthesis
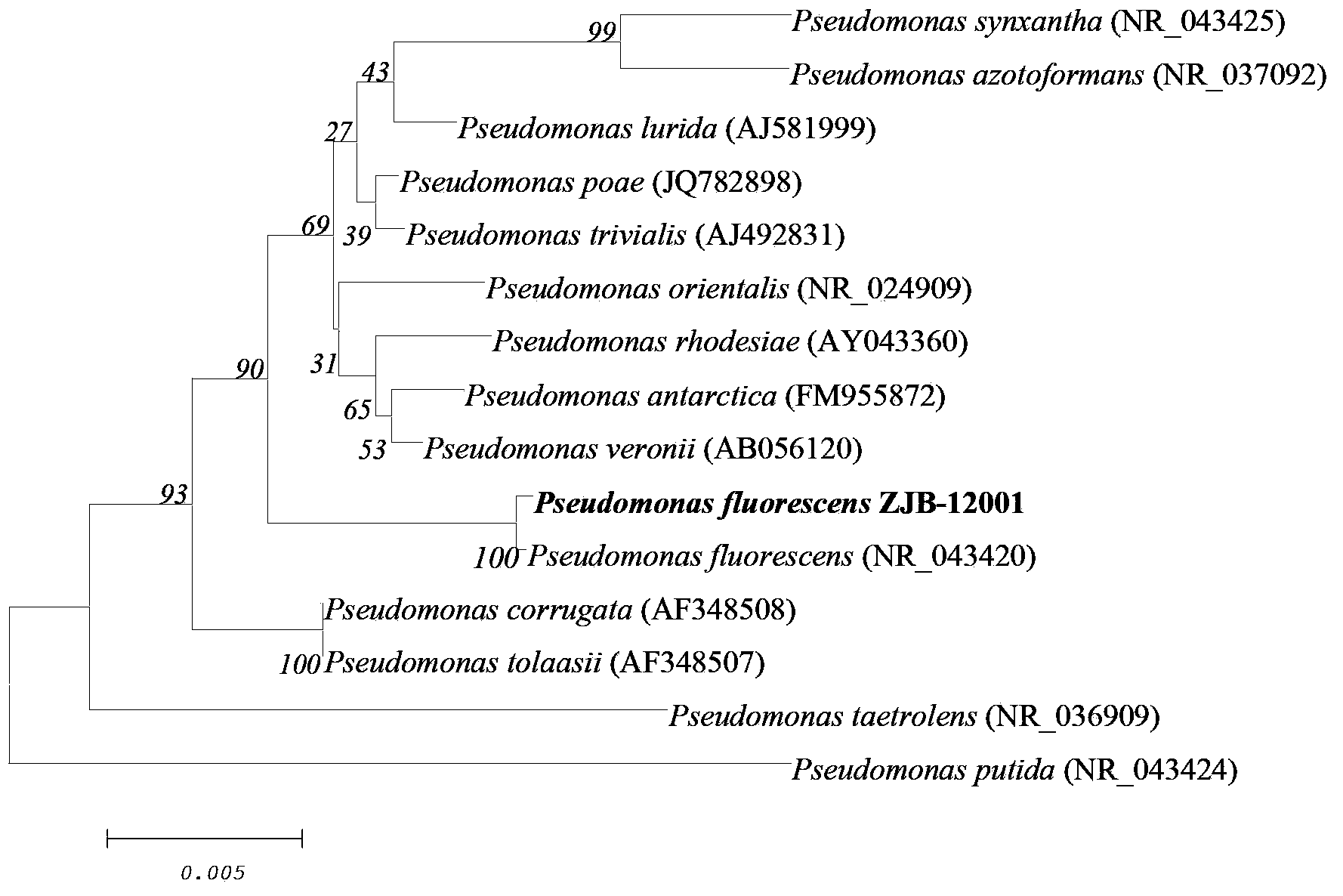
The invention provides a rhodococcus rhodochrous strain, namely, pseudomonas fluorescens ZJB-12001, and an application thereof in 2-amino-4-methylmercapto-butyronitrile synthetic methionine. The strain is preserved in the Chinese Typical Culture Collection Center which is located in Wuhan College, Wuhan, China, the postcode is 430072, the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 2012449, and the preservation date is November 8th, 2012. The pseudomonas fluorescens ZJB-12001 is applied to experiments for producing methionine in a biological catalysis mode, the result shows that the pseudomonas fluorescens ZJB-12001 can be used for effectively producing methionine in the biological catalysis mode, and the conversion rate of 20mM3-cyanopyridine within 60 minutes can be 60-75%, so that the pseudomonas fluorescens ZJB-12001 has a wide application prospect in the field of biological catalysis methionine production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Application of a kind of Rhodococcus rhodochrous and its preparation in the remediation of pyrethroid pesticide pollution
ActiveCN114107095BEfficient bioremediationPromote bioremediationBacteriaWater contaminantsRhodococcus strainGermplasm
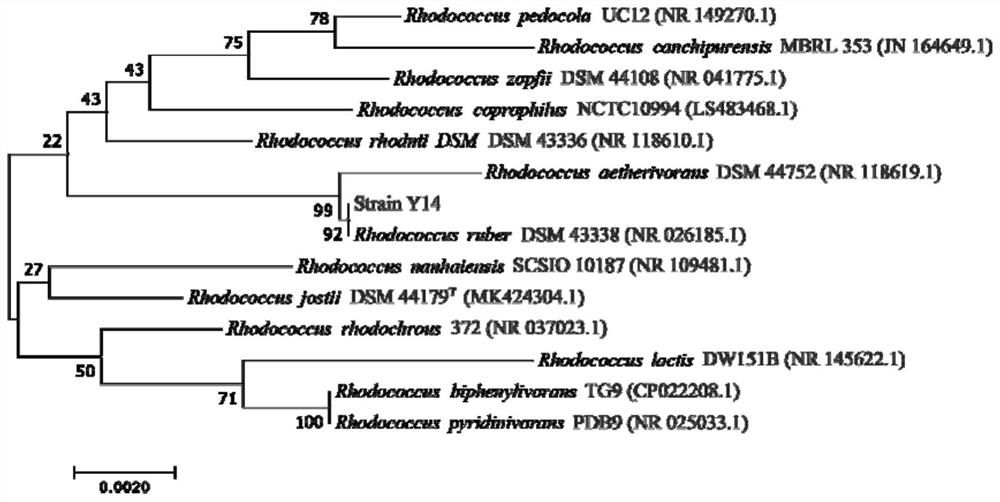
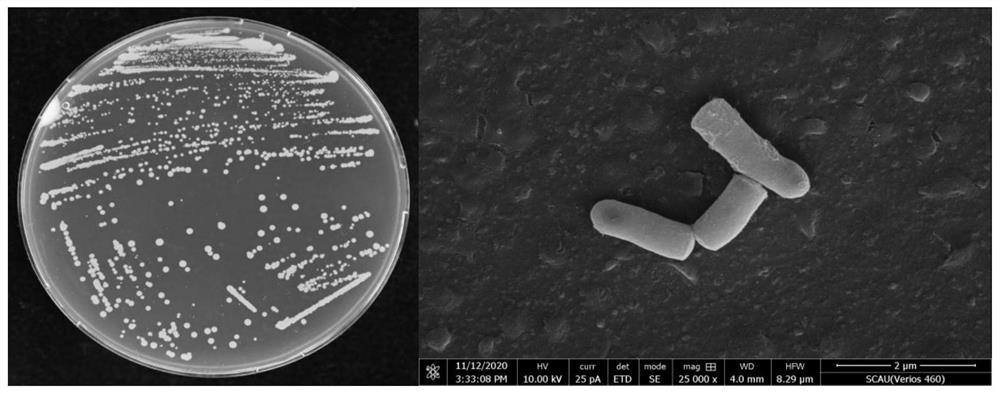
The invention discloses the application of Rhodococcus rhodochrous and its preparation in the remediation of pyrethroid pesticide pollution. The strain is the gram-positive bacterium Rhodococcus ruber strain Y14, and was deposited in the Guangdong Provincial Microbial Culture Collection Center on July 21, 2021, and the deposit number is GDMCC NO: 61813. The strain has significant biodegradation ability of pyrethroid insecticides, especially the highest activity to dextrofenothrin, and the number of bacterial cells is not less than 1.0×10. 6 CFU·mL ‑1 The suspension of 50mg·L in water after 6 days of treatment ‑1 D-Cyphenothrin is completely removed, and it also has a high-efficiency bioremediation effect on polluted soil. It provides a new idea to solve the problems of excessive pyrethroid pesticide residues and environmental pollution in agricultural production, and also enriches the germplasm resource bank of pesticide-degrading bacteria, which is of great practical importance for the production of non-toxic and pollution-free green agricultural products. Value.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Pseudomonas fluorescent and application thereof in biosynthesizing methionine
ActiveCN103289928BEfficient productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyMethionine biosynthesis
The invention provides a rhodococcus rhodochrous strain, namely, pseudomonas fluorescens ZJB-12001, and an application thereof in 2-amino-4-methylmercapto-butyronitrile synthetic methionine. The strain is preserved in the Chinese Typical Culture Collection Center which is located in Wuhan College, Wuhan, China, the postcode is 430072, the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 2012449, and the preservation date is November 8th, 2012. The pseudomonas fluorescens ZJB-12001 is applied to experiments for producing methionine in a biological catalysis mode, the result shows that the pseudomonas fluorescens ZJB-12001 can be used for effectively producing methionine in the biological catalysis mode, and the conversion rate of 20mM3-cyanopyridine within 60 minutes can be 60-75%, so that the pseudomonas fluorescens ZJB-12001 has a wide application prospect in the field of biological catalysis methionine production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Composite microbial agent for treating sludge and method for treating sludge
ActiveCN106635927BSpeed up fermentationColor back to normalFungiBacteriaPseudomonasLactobacillus acidophilus
The invention relates to a composite fungicide for treating sludge and a sludge treatment method. The composite fungicide is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 3 to 8 parts of purple sulfur bacteria, 3 to 8 parts of green sulfur bacteria, 3 to 8 parts of rhodopseudomonas, 3 to 8 parts of rhodopseudomonas capsulata, 3 to 8 parts of rhodococcus rhodochrous, 3 to 8 parts of white-rot fungi, 3 to 8 parts of phosphorus-accumulating bacteria, 3 to 8 parts of anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria, 3 to 8 parts of lactobacillus plantarum, 3 to 8 parts of streptomycete, 3 to 8 parts of candida utilis, as well as saccharomyces cerevisiae, lactobacillus lactis, lactobacillus acidophilus, aspergillus niger, aspergillus oryzae, bacillus subtilis and bacillus licheniformis.
Owner:哈尔滨明慧生物技术开发有限公司
A kind of rhodococcus erythrococcus capable of degrading phthalates and its application
InactiveCN107151635BEfficient degradationAvoid degradationBacteriaWater contaminantsEthyl groupBioremediation
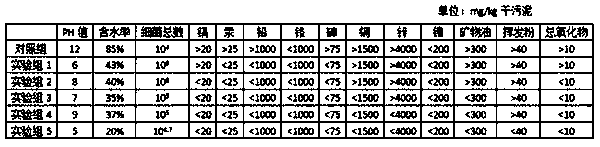
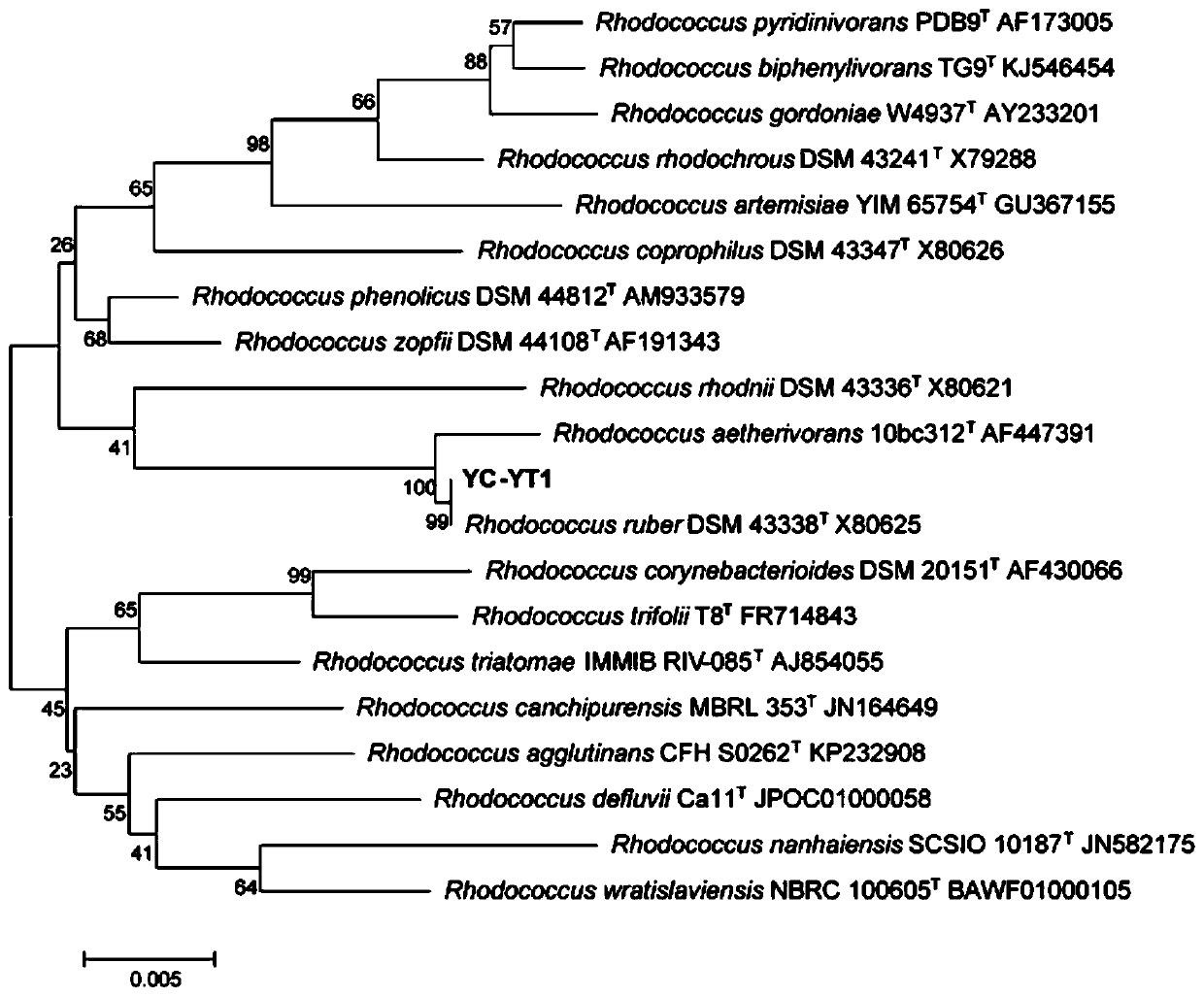
The invention provides a Rhodococcus ruber capable of degrading phthalates and an application thereof. The bacterium is YC-YT1, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.13959, which can degrade 85% of 100 mg / L bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate contained in inorganic salts within 12 hours, and within 5 days Can degrade 100mg / L bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate, dipropyl phthalate, butyl benzyl phthalate contained in inorganic salt culture medium 100%; Phthalates are also highly degradative. The Rhodococcus rubrum YC-YT1 of the present invention has a wide tolerance range for salt ion concentration, pH and temperature, can be applied to bioremediation and industrial wastewater treatment of environmental pollution caused by phthalates, and has good economic value and application prospects.
Owner:中国农业科学院研究生院
Rhodococcus rhodochrous and use thereof as catalyst for use in preparation of iminodiacetic acid from iminodiacetonitrile
ActiveCN102286409BEfficient productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismImidodiacetic acid
The invention discloses a method for preparing iminodiacetic acid from iminodiacetonitrile in presence of a biocatalyst and a strain. The method comprises: performing nitrilase production culture of nitrilase-producing strain to obtain nitrilase; and preparing iminodiacetic acid from iminodiacetonitrile under the biocatalytic action of the nitrilase serving as the biocatalyst. The method providesa basis for producing iminodiacetic acid from iminodiacetonitrile in the presence of the biocatalyst and has a bright application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Application of a kind of rhodococcus erythrococcus strain, bacterial preparation and its bacterial cell and extract
ActiveCN110184215BEnhanced immune functionEnhance anti-tumorBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsBiotechnologyMicroorganism
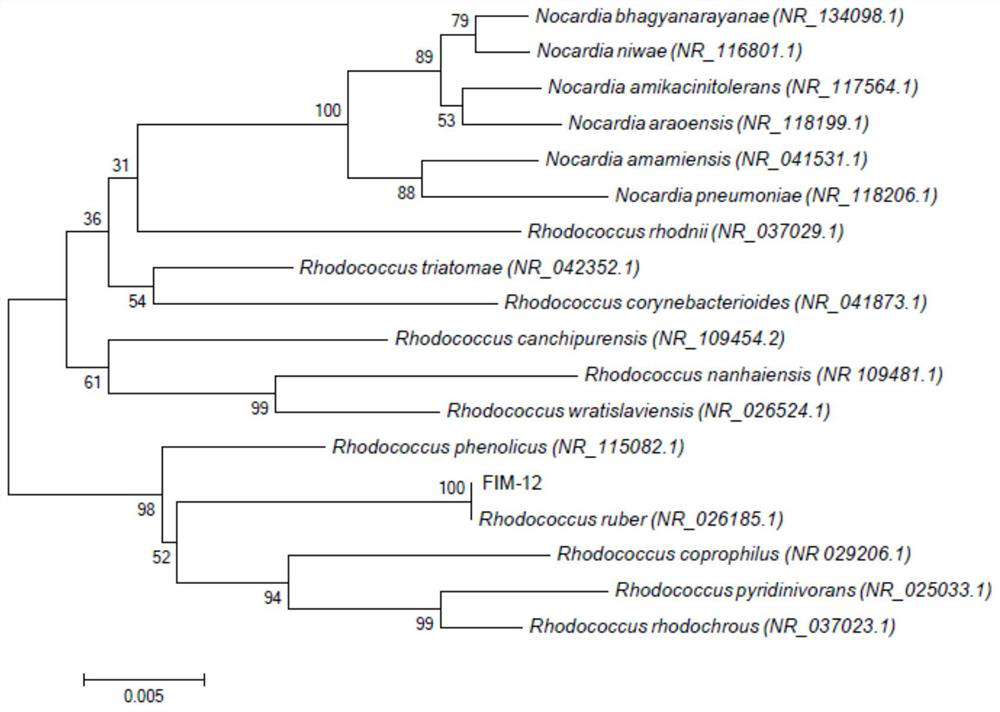
The present invention provides a strain of Rhodococcus ruber, a bacterial preparation and the application of its cells and extracts. The strain is Rhodococcus ruber FIM-12, which was preserved in China Microorganism Culture Collection on April 03, 2019 General Microbiology Center of the Management Committee, the preservation number is CGMCC No.17525; it can be used for microbial fermentation to prepare Rhodococcus cells and their extracts: Rhodococcus ruber (Rhodococcus ruber) FIM‑12 is fermented and cultured to collect bacterial cells and wash with purified water Wet cells are obtained; the wet cells are repeatedly frozen and thawed combined with ultrasonic breaking, and then extracted with absolute ethanol to obtain the Rhodococcus erythrococcus extract. The rhodococcus erythrococcus strain of the invention can be applied to industrial fermentation production to prepare rhodococcus erythrococcus cells and extracts of the rhodococcus erythrococcus. The prepared product has the functions of improving immune activity and tumor inhibition, and can be used as a production strain for further research and development.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF MICROBIOLOGY
A strain of Microbacterium asterifera that efficiently degrades fenvalerate and its application
ActiveCN108410760BImprove securityQuality improvementBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a strain of Rhodococcus rhodochrin capable of efficiently degrading fenvalerate and application thereof. The present invention takes microbial resources in the traditional fermentation process as the research object, screens and obtains the degrading bacteria for fenvalerate that is used more in the planting process of tobacco and other crops, has a large residual amount, and has a long degradation cycle. Microbacterium esteraromaticum E20 strain, derived from Fenjiu Daqu, has high safety and can efficiently degrade 5mg / kg of fenvalerate. It has a certain application prospect in the degradation of low-concentration fenvalerate pesticide residues in crops such as tobacco leaves. In order to improve the quality and safety of tobacco products and solve the problem of pesticide residues in tobacco leaves and other crops, it provides a safe and effective biodegradation pathway.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Rhodococcus rhodochrous strain and use thereof in the production of acrylic acid
ActiveUS20210340517A1Reduce unwanted intermediate productImprove energy efficiencyHydrolasesFermentationNitrile hydrataseProtein
A strain of Rhodococcus rhodochrous in which a gene coding at least part of a nitrile hydratase enzyme or any gene coding a protein involved in the transcription, translation or formation of at least part of the nitrile hydratase enzyme has been deactivated or rendered ineffective or a strain of Rhodococcus rhodochrous cultured under condition wherein the nitrile hydratase enzyme is been inhibited.
Owner:AECI LTD
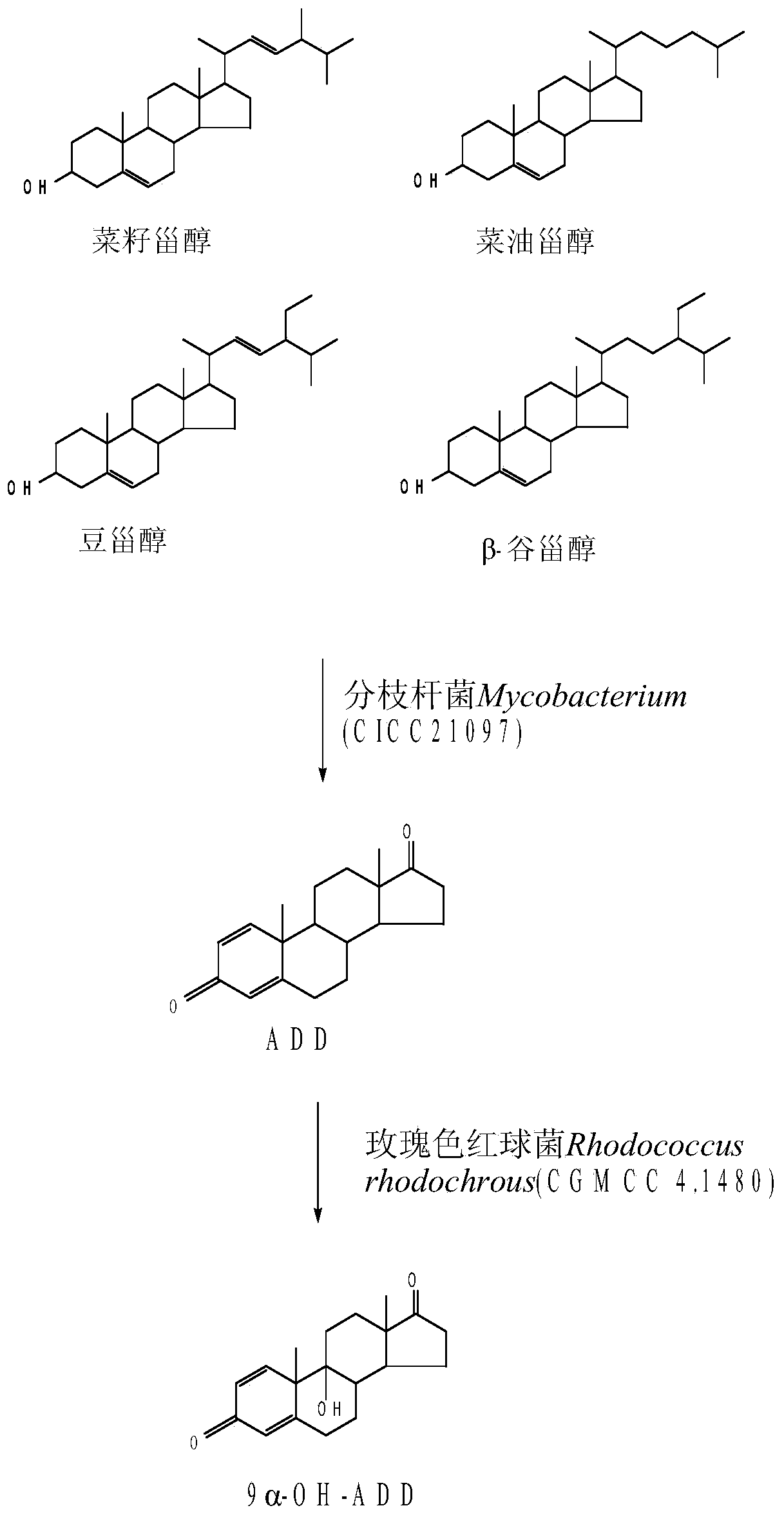
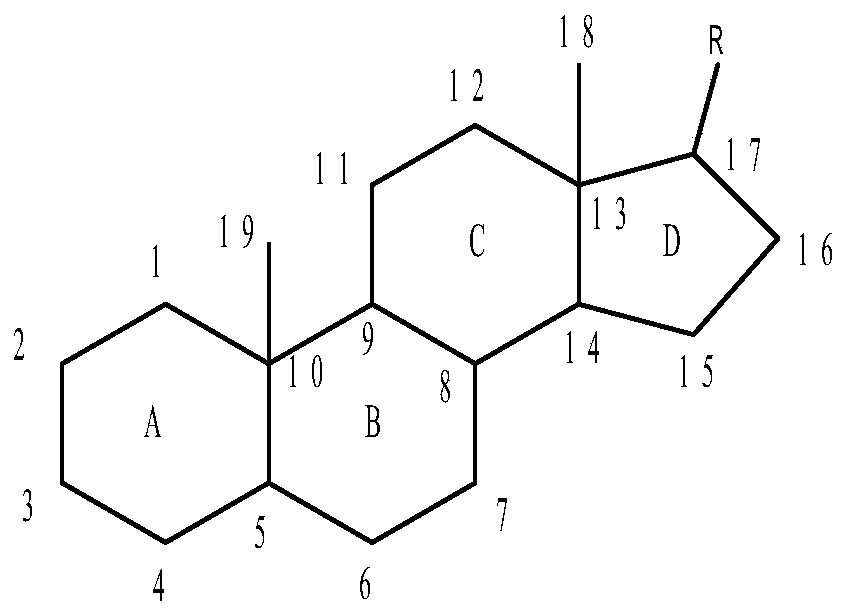
A kind of method for preparing 9α-hydroxy-androst-1,4-diene-3,17-dione
InactiveCN105219829BImprove utilization efficiencyHigh biotransformation rateSteroidsFermentationKetoneDissolution
The invention discloses a method for preparing 9 alpha-hydroxy-androstane-1,4-diene-3,17-dione. The method takes phytosterol as a substrate, utilizes two microbial mixed bacteria, namely Mycobacterium (CICC 21097) and Rhodococcus rhodochrous (CGMCC 4.1480) for fermentation to prepare 9 alpha-hydroxy-androstane-1,4-diene-3,17-dione. Besides, a compound dissolution promotor is added into a fermentation culture medium to ensure the highest rate of molar conversion from phytosterol to 9 alpha-OH-ADD reaches 84.3 percent. Meanwhile, purification in a two-step 9 alpha-hydroxy-androstane-1,4-diene-3,17-dione preparation method is omitted, and the consumption of a solvent is reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Method for biodegrading organophosphorus pesticide wastewater
ActiveCN105967436BHigh removal ratePromote degradationMultistage water/sewage treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentElectrolysisOrganophosphorus pesticides
The invention discloses a method for biodegradation of organic phosphorus pesticide wastewater, wherein the method comprises the following steps: after wastewater is subjected to electrolysis purification, adding a mixture composed of limestone and calcium chloride, putting an oxidizing agent, forming a calcium salt, and filtering to remove the calcium salt; weighing bacillus amyloliquefaciens Ba2015036, bacillus subtilis, rhodococcus rhodochrous strains R-MS6, aspergillus niger strains J15 and aspergillus niger strains J27 according to the proportion, to prepare a biodegradable agent; sending a part of the obtained wastewater into an SBR reactor, staying for 24 h, then putting a proper amount of the biodegradable agent, carrying out closed aeration for 2 d, and then continuously feeding water with the speed progressively increased at the speed rate of 5%; and adding a proper amount of ferrous sulfate into the wastewater treated by the SBR reactor, carrying out a coagulation reaction, and filtering. Through reasonable selection, proportion and culture of the dominant degrading strains, the biodegradation rate is increased, and at the same time, with collaboration of electrolytic purification, oxidizing agent treatment and SBR reactor treatment, the removal rate of organic phosphorus is greatly increased.
Owner:NANTONG VOCATIONAL COLLEGE
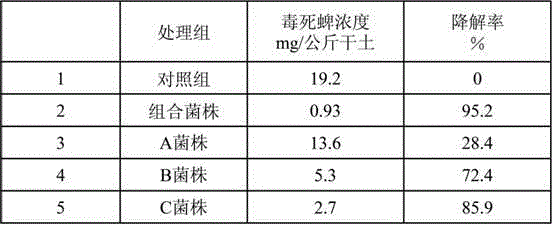
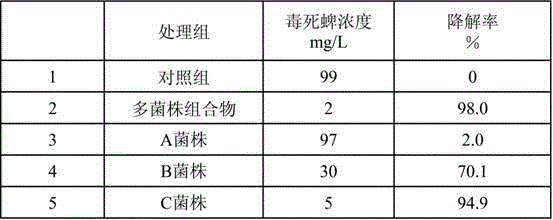
Multi-strain composition for high-efficiency degradation of organic phosphorus pesticides in environment
ActiveCN102296043BGive full play to the degradation abilityAdapt to the needs of governanceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPesticide residueStenotrophomonas sp.
The invention relates to a multi-strain composition for high-efficiency degradation of organic phosphorus pesticides in the environment, which consists of a strain A, a strain B and a strain C, wherein the strain A is rhodococcus rhodochrous R-D3 strain; the B strain is stenotrophomonas acidaminiphila G1; and the C strain is cupriavidus taiwanensis X1 strain. The strain A, strain B and strain C are inoculated onto and cultured in a Luria Broth (LB) liquid culture medium respectively to form bacterial solution A, bacterial solution B and bacterial solution C; the bacterial solution A, bacterial solution B and bacterial solution C are uniformly mixed according to a volume mixing ratio of (1-2):(1-2):(1-2); and thus, the multi-strain composition for high-efficiency degradation of organic phosphorus pesticides in the environment is obtained. The multi-strain composition can quickly degrade organic phosphorus pesticide residue to different degrees within 1 to 7 days, the degradation rate of the multi-strain composition reaches over 95 percent, and the pollution of organic phosphorus pesticides is eliminated effectively.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Microorganism combination solid-state fermentation method for reducing content of butyl isosulfocyanate in rapeseed dregs
InactiveCN103704466BReduced isothiocyanate contentShort fermentation timeFungiBacteriaMicroorganismRapeseed
The invention discloses a microorganism combination solid-state fermentation method for reducing the content of butyl isosulfocyanate in rapeseed dregs. Solid-state fermented rapeseed dregs of the combination of three microorganisms of Rhodococcus rhodochrous, Pediococcus pentosaceus and Candida guilliermondii are adopted for reducing the content of the butyl isosulfocyanate in the rapeseed dregs. The method comprises the following steps: preparation and pretreatment of a rapeseed dreg raw material, preparation of a fermented seed solution, inoculation of the three microorganisms in a proportion, solid fermentation, and preparation of a fermented rapeseed dreg finished product. According to the method, the Rhodococcus rhodochrous is firstly used for enabling the rapeseed dregs to be fermented in a solid state, and is combined with Pediococcus pentosaceus and Candida guilliermondii for use; compared with other technical schemes, the method can greatly reduce the content of the butyl isosulfocyanate in the rapeseed dregs obviously; moreover, the fermentation time is shorter, and the efficiency is high.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
A strain of Rhodococcus rhodochrous and its application as an immune adjuvant in the preparation of vaccines
ActiveCN109576180BWill not cause accidental infectionReduce pollutionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAnimals vaccinesCytokine
The invention discloses a rhodococcus strain and its application as an immune adjuvant in vaccine preparation. The Rhodococcus ruber of the present invention is also called Rhodococcus ruber (Rhodococcus ruber) RDC-01, and the preservation number is CGMCC NO.16640. The activity of cells can induce interferon and other cytokines. After inactivating the bacteria, adding it as an immune adjuvant to the oil emulsion inactivated vaccine can significantly promote the production of vaccine-induced animal antibodies. Compared with using the oil emulsion inactivated vaccine alone It can produce high-titer antibodies, is safe to use, has no short-term and long-term toxic and side effects, and has a good application prospect in the field of animal vaccine preparation.
Owner:北京利昂盛生物技术有限公司
A Rhodococcus rhodococcus strain xhrr1 for purifying ammonia in aquaculture water and its application
ActiveCN107828679BGood removal effectImprove environmental adaptabilityBacteriaWater contaminantsBiotechnologyRhodococcus strain
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com