Patents
Literature
433results about How to "Good genetic stability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bacillus licheniformis strain, application thereof and method for producing poly-gamma-glutamic acid thereby
InactiveCN101603015AShort fermentation cycleIncrease productivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus licheniformisSubmerged fermentation
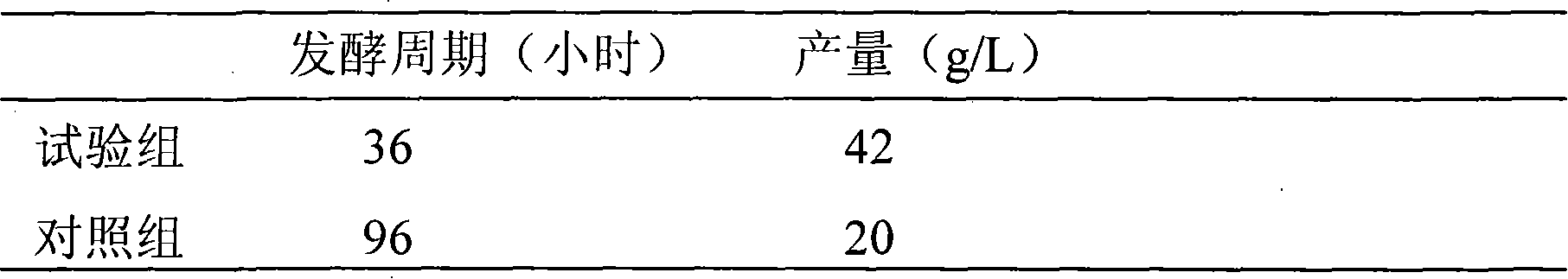
The invention discloses a bacillus licheniformis strain which is preserved as bacillus licheniformis WX-02 with the preserving number of NO: M208065 and the preserving date of April 24th, 2008 and the preserving unit of CCTCC. The invention also discloses an application of the bacillus licheniformis strain and a method for producing poly-gamma-glutamic acid by using the bacillus licheniformis strain. Poly-gamma-glutamic acid products are produced by processes of seed solution preparation and liquid submerged fermentation, and the strain has stable genetic performance of the strain, high production efficiency and low production cost. When the bacillus licheniformis strain of the invention and the fermentation method thereof are used for preparing 3000L of poly-gamma-glutamic acid, the yield of a fermentation tank can reach 35.05g / l.
Owner:HEBEI WELCOME PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD +1
Bacterial strain for producing prodigiosin and method thereof
InactiveCN102002469AIncrease productivityGood genetic stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCarbon sourceCulture mediums
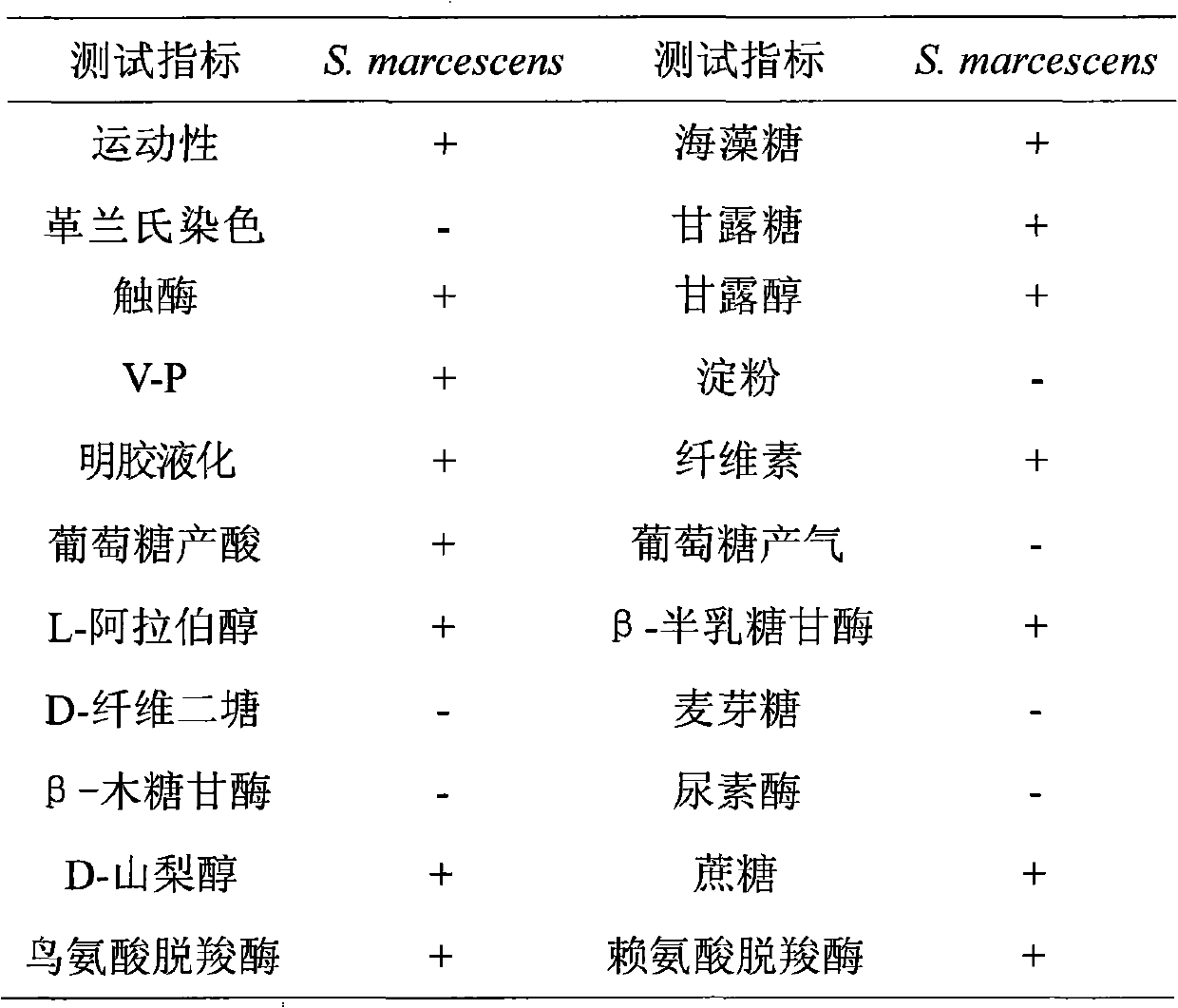
The invention provides a bacterial strain for producing prodigiosin, belonging to Serratia marcescens, wherein the preservation number of the bacterial strain is CGMCC No.4074. The bacterial strain provided by the invention has the advantages that the haematochrome can be efficiently synthesized within a liquid fermentation culture medium by using the bacterial strain and the production efficiency is high. The bacterial strain provided by the invention has low requirements to the carbon source and nitrogen source, the carbon source can be a single carbon source or a mixed carbon source and the nitrogen source can be a single nitrogen source or a mixed nitrogen source. The bacterial strain provided by the invention is continuously reproduced for more than ten generations, the genetic stability of the bacterial strain is good and the operation is simple.
Owner:JIAXING UNIV
Method and application for improving application efficiency of gene targeting technique in aspergillus terreus
ActiveCN104894165AHigh gene targeting efficiencyHigh homologous recombination efficiencyFungiMicroorganism based processesBinding siteLIG4
The invention discloses a method and application for improving application efficiency of a gene targeting technique in aspergillus terreus, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, by taking Aspergillus terreus as an initial bacterium, knocking off a ku80 gene or an lig4 gene so as to increase the exogenous DNA homologous recombination probability of a strain; secondly, establishing a pyrG gene deletion uracil auxotroph stain, establishing a inheritance conversion system based on a pyrG gene as a screening tag; and finally, cutting off the screening tag by using a Cre / LoxP specific binding site recombinant system, thereby obtaining a uracil auxotroph stain which can be applied to genetic modification again. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, an efficient aspergillus terreus gene targeting platform can be established, the method has the advantages that high homologous recombination efficiency can be achieved, the bidirectional screening of the conversion system can be achieved, a screening tag cutting method is simple and feasible, the screening tag can be recycled, and the like, and basic support can be provided for efficient genetic modification of aspergillus terreus by using the gene targeting technique.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for carrying out taking off poison and quick breeding by using strawberry anther
InactiveCN101049090AIncreased rate of culture differentiationBreak through the predicament of low traditional differentiation ratePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsAlcoholBud
A detoxicating fast reproduction method of strawberry by anther culture includes such steps as taking the flower bud of strong strawberry, storing at 4 deg.C in refrigerator for 72 hr, disinfecting with the mixture of alcohol, corrosive sublimate and tween, sucking surface water by aseptic suction paper, taking anther, and sequentially culturing in colli inducing culture medium, regrowing culture medium, secondary culture medium, and rooting culture medium.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for propagating dendrobium candidum test-tube plantlets
ActiveCN101810140AIncrease profitGrow neatlyMicrobiological testing/measurementHorticulture methodsAxillary budShoot
The invention provides a mthod for propagating dendrobium candidum test-tube plantlets, which comprises the following steps: a. adopting dendrobium candidum stem sections or stem section axillary buds as explants, wherein chloroplasts of the stem sections or the stem section axillary buds have gene sequences with the GenBank login number of FJ530946; and b. carrying out the processes of axillary bud survival and growth, cespitose shoot inducement and multiplication, and plantlet formation, wherein the culture conditions include the culture room temperature of 26+ / -2 DEG C, the illumination intensity of 20001x, the pH value between 5.8 and 6.0, the light source of a fluorescent lamp or an LED light source, and the illumination time of 12 h per day. The method of the invention aims at the defects of the existing dendrobe tissue culture method, improves the existing dendrobe tissue culture method, and provides a fast propagation method of the dendrobium candidum germchits. The method can meet the requirements of germchits required by large-scale production in a short time, and has the characteristics of low cost, regular germchit growth, simplicity and easy implementation of a domestication method, good inheritance stability and the like.
Owner:SICHUAN WANAN DENDROBIUM IND DEV
Avermectin B1a high-yielding strain and application thereof
InactiveCN102634471AHigh compositionReduce other componentsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLithium chlorideUltraviolet
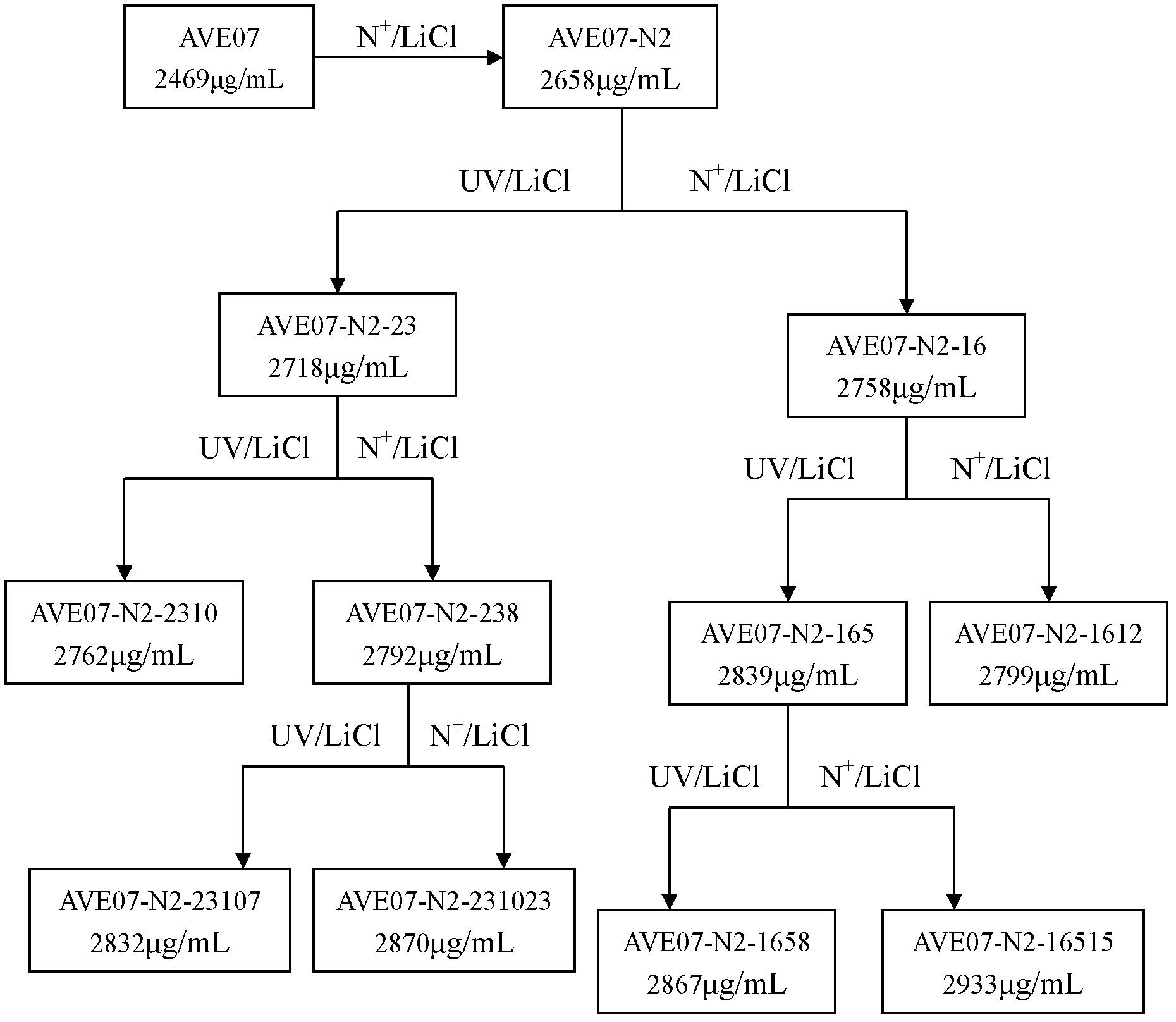
The invention discloses an avermectin B1a high-yielding strain, which is classified and named streptomyces avermitilis AVE 07-N2-16515, and is preserved in a China type culture preservation centre (CCTCC) with the preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2012094. The avermectin B1a high-yielding strain disclosed by the invention is obtained by combining low-energy nitrogen ion implantation-lithium chloride (N<+>-LiCl) compound mutation with ultraviolet ray-lithium chloride (UV-LiCl) compound mutation, primarily screening, and performing shake-flask fermentation secondary screening, and is used as a starting strain for next mutation, so that the target strain AVE07-N2-16515 is finally screened. The obtained strain can greatly increase the avermectin B1a component and reduce other components in fermentation products, and is good in hereditary stability. The strain is fermented in a 5L fermentation tank to produce avermectin B1a by utilizing glucose as a quick-acting carbon source and cornstarch as a delayed-action carbon source, the titer can achieve 3048 mu g / m, which is improved by 23.4% as compared with the original starting strain AVE07; and the strain can be applied on industrial production, greatly improves a fermenting unit, and has great economic application value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Recombinant low-virulent vaccine strain of chicken infectious bursal disease viruses (IBDV) and application thereof
ActiveCN101935637ANon-pathogenicGood spiritsViral antigen ingredientsMicroorganism based processesProtective antigenOrganism
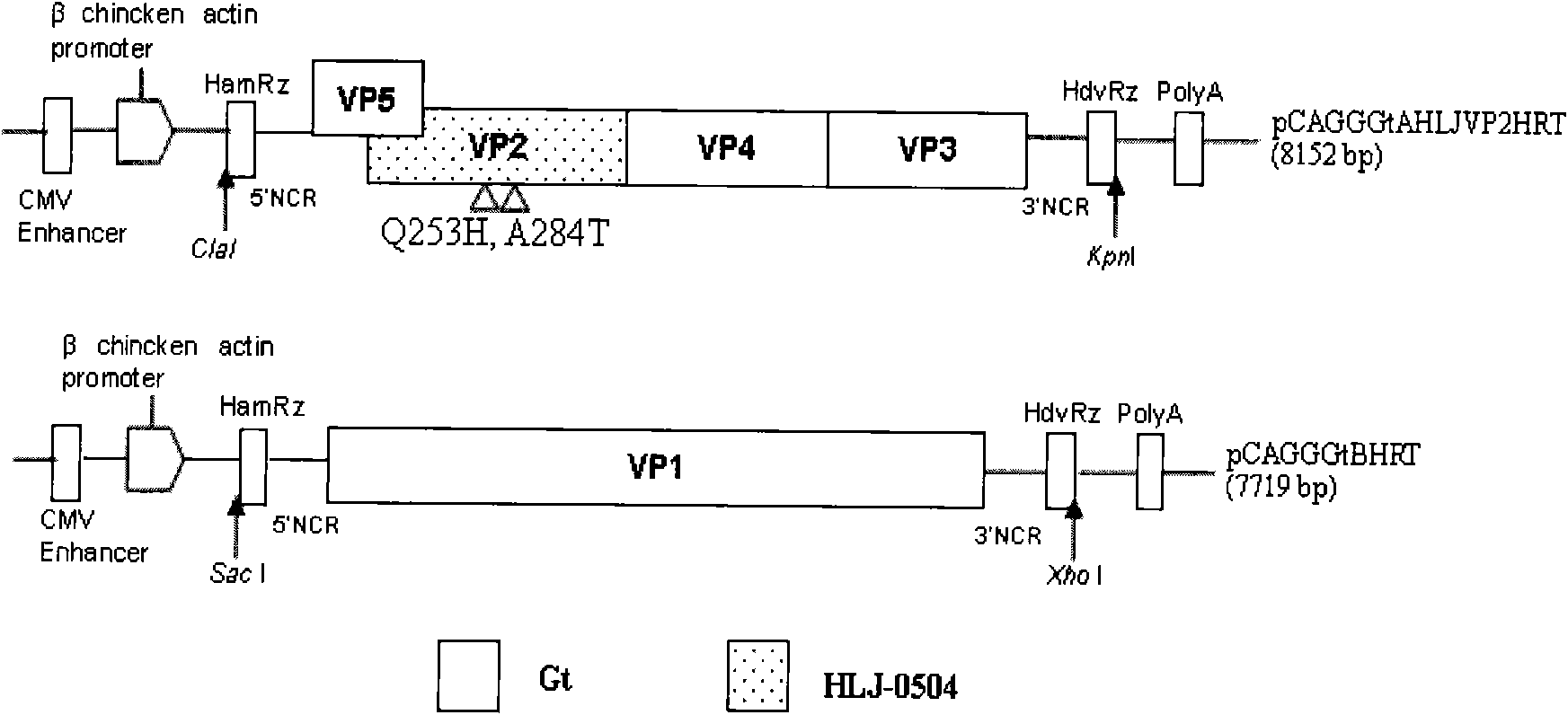
The invention discloses a recombinant low-virulent vaccine strain of chicken infectious bursal disease viruses (IBDV) and application thereof. In the invention, a major protective antigen gene VP2 of an epidemic superhigh virulent strain is cloned, the nucleotide of the gene VP2 is modified by mutation and then used for replacing a corresponding segment of a Gt genome of a low-virulent strain of the IBDV, so that the infectious clone of a recombinant genome of the IBDV is constructed, and the recombinant low-virulent vaccine strain is saved and identified by using an IBDV reverse genetic operation system. The microbial collection number of the vaccine strain is CGMCC No.3749. The recombinant low-virulent vaccine strain of the invention has high replicability, genetic stability and safety. The immune effect of the low-virulent vaccine strain of the invention is as good as that of the medium-virulent vaccine strain, but is superior to that of the low-virulent vaccine strain. The biological safety of the low-virulent vaccine strain of the invention is superior to that of the medium-virulent vaccine strain. As the vaccine strain, the recombinant low-virulent vaccine strain of the invention has the characteristics of high efficiency and low toxicity, is a good candidate vaccine strain and can be used for controlling chicken infectious bursal disease.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Bacillus subtilis for preventing and controlling plant fungal disease and application of bacillus subtilis
InactiveCN102965320ABroad antibacterial spectrumGood genetic stabilityBiocideBacteriaLaboratory cultureSclerotium
The invention relates to efficient bacillus subtilis for preventing and controlling plant fungal disease and promoting plant growth. The bacillus subtilis is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) with a preservation number of CGMCC No.6788. The bacillus subtilis related by the invention has a high capacity of inhibiting the growth of plant pathogenic fungi, has high hereditary stability, does not pollute the environment, is ecologically safe, and can be widely applied to prevention and control of plant pathogenic fungi, especially Pythium aphanidermatum, Fusarium, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Botrytis cinerea. The bacillus subtilis is singly used or is used together with other organic and inorganic nutrients required in the growth of plants to be prepared into a biological compound fertilizer which has the advantages of remarkable continuous cropping resistance, premature senility resistance, and control of dead seedlings and rotten roots and is capable of ensuring correct color and large fruits, and increasing output and improving quality of improved products.
Owner:赵斌 +2
Method for producing momordica grosvenori group seedling with single culture medium
InactiveCN101218896AEasy to operateQuality improvementHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureAxillary budMomordica
A method for producing a grosvenor momordica tissue culture seedling by a single culture medium uses an MS solid medium during the producing process and is characterized in that the angustimycin of 0.1 to 0.5mg L<1> is added into a normal MS solid medium to produce the grosvenor momordica tissue culture seedling. As the medium singly prepared by the angustimycin can be simultaneously used on each technical tache of 'axillary bud explant starting', 'proliferation and expanding propagation' and 'proliferated seedling rooting', thereby greatly simplifying the producing operation procedures of the grosvenor momordica tissue culture seedling. In particular, the angustimycin can effectively control the generation of a callus during the culturing process of the grosvenor momordica tissue culture seedling in particular, which is beneficial to the genetic stability; thereby improving the quality of the tissue culture seedling.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Method for promoting paeonia suffruticosa seedling growth and application thereof
InactiveCN104206417ABreak dormancyShorten the flowering processBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPaeonia suffruticosaActive agent
The invention relates to a method for promoting paeonia suffruticosa seedling growth and application thereof. Specifically, the invention provides a paeonia suffruticosa seedling treatment fluid, which comprises: a paeonia suffruticosa seedling growth active agent (gibberellin and / or 6-benzyladenine) and a surfactant, and also can include an agronomically acceptable soluble calcium salt. The growth active agent can break epicotyl dormancy of paeonia suffruticosa seeds, improve the germination rate / germination potential of paeonia suffruticosa seeds, accelerate the paeonia suffruticosa seed growth process, and promote seedling emergency or flowering of paeonia suffruticosa seed seedlings / tissue culture seedlings. The surfactant can make active substances fully enter cells. And the soluble calcium salt is closely related to multiple physiological functions of cells.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Hansenula polymorpha expression system, hansenula polymorpha construction method and application of hansenula polymorpha
ActiveCN103045492AThe mutation site is clearLow back mutation rateFungiMicroorganism based processesHigh level expressionGenetic engineering
The invention provides a hansenula polymorpha expression system, a hansenula polymorpha construction method and application of hansenula polymorpha. The expression system contains uracil auxotroph hansenula polymorpha AU-0501, of which the preservation number is CGMCC NO.7013. The uracil auxotroph hansenula polymorpha AU-0501 provided by the invention has the advantages of definite mutation site, low reverse mutation frequency, good hereditary stability, high biological expression quantity and the like, plays a significant role in researching and producing gene engineering vaccine, has the advantages of higher yield and low cost as compared with other eukaryotic expression systems adopted at present. The invention further provides an expression vector applied to the hansenula polymorpha expression system and a construction method of the expression vector. Two or more genes can be expressed simultaneously through the expression vector. Two target genes can be expressed in a hansenula polymorpha auxotroph cell at a high level without interference.
Owner:BEIJING MINHAI BIOTECH
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens separated from fermented soya beans and used for producing protease
The invention discloses bacillus amyloliquefaciens separated from fermented soya beans and used for producing a protease and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens is separated from traditional fermented soya beans by adopting a separation and purification technique. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens which is identified and named according to the microbial taxonomy is collected in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on December 10. 2014 with the collection number of CCTCC M 2014639. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens used for producing protease is easy to culture and is highly safe during production, the screened strain for liquid fermenting and culturing has the enzyme activity of 148-2,231U / mL, has good genetic stability; the metabolite is easy to separate and purify; a foundation is laid for the scientific pure culture in the traditional fermented soya bean industry.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Fibrinolytic-enzyme-producing Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain separated from traditional fermented black beans
InactiveCN104877936AGrow fastImprove production safetyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMetabolitePlasmin
The invention discloses a fibrinolytic-enzyme-producing Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain separated from traditional fermented black beans, belonging to the technical field of bioengineering. The strain is separated and purified from traditional fermented black beans, is named Bacillus amyloliquefaciens by taxonomic identification, and is collected by China Center for Type Culture Collection on December 10th, 2014; and the collection number is CCTCC M2014638. The fibrinolytic-enzyme-producing Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain is easy to culture, and has the advantages of high production safety and favorable hereditary stability. The enzyme activity of the strain liquid after fermentation and culture is up to 324.6-410.2 IU / mL. The metabolite fibrinolytic enzyme can be easily separated and purified. The separation of the strain lays foundation for implementing scientific axenic culture in traditional fermented black bean industry.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Dioscoreae Oppositae 'Qi' tissue culture seedling raising method
InactiveCN102511398AGood genetic stabilityLow costHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureAlcoholPeat
The invention provides a Dioscoreae Oppositae 'Qi' tissue culture seedling raising method, which comprises the steps of explant selection and disinfection, callus tissue induction, adventitious bud differentiation, rooting culture, seedling training, transplanting and the like. By taking the nodular stem segments of the potted Dioscoreae Oppositae 'Qi' as explants, after the explants are disinfected by alcohol with volume concentration of 70 percent and sodium hypochlorite with weigh percentage of 2 percent, the callus tissue induction, the adventitious bud differentiation and the rooting culture are conducted on MS+NAA+BA culture mediums, and rooted seedlings are transplanted in mixed mediums for culture, wherein the mixed mediums comprise vegetable garden soil, mountain sand and peat, with the mass ratio of 4:1:1. Compared with traditional Dioscoreae Oppositae 'Qi' seedling raising methods such as a direct root tuber planting method, a cutting breeding method and the like, the Dioscoreae Oppositae 'Qi' tissue culture seedling raising method has the advantages that the genetic stability of the seedlings is good, the breeding cycle is short, the breeding coefficient is high, the operation is simple and the factory production of the seedlings can be realized. By adopting the method, not only can the problems that the quantity of the used seminal roots for the production of the Dioscoreae Oppositae 'Qi' is large, the cost is high and the characters of strain is degenerated be solved, but also technical supports can be provided for the high quality and high yield and the industrialization of the Dioscoreae Oppositae 'Qi' through large-scale seedling breeding.
Owner:黄石理工学院
Tissue culture method of gynura divaricata
InactiveCN102246694ALow pollution rateNo pollution in the processCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsAxillary budSucrose
The invention discloses a tissue culture method of gynura divaricata. The method comprises the steps of: inductive culture: inoculating on MS start medium without any hormone to induce generation of axillary bud; multiplication culture: inoculating on the medium MS+6BA, 0.2 mg / L+sucrose 20 g / L+ of agar 6 g / L for multiplication; and rooting culture: rooting on MS+IBA 0.1 mg / L+sucrose 20 g / L+agar 6 g / L, or MS+IBA 0.3 mg / L+IAA 0.3 mg / L+sucrose 20 g / L+agar 6 g / L, wherein the culture temperature is 25+ / -1 DEG C, the illumination intensity is 20,001x, and the illumination time is 16 h / d. The method disclosed by the invention can quickly and efficiently produce healthy and uniform high-quality gynura divaricata seedlings with pure characteristics at large scale.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
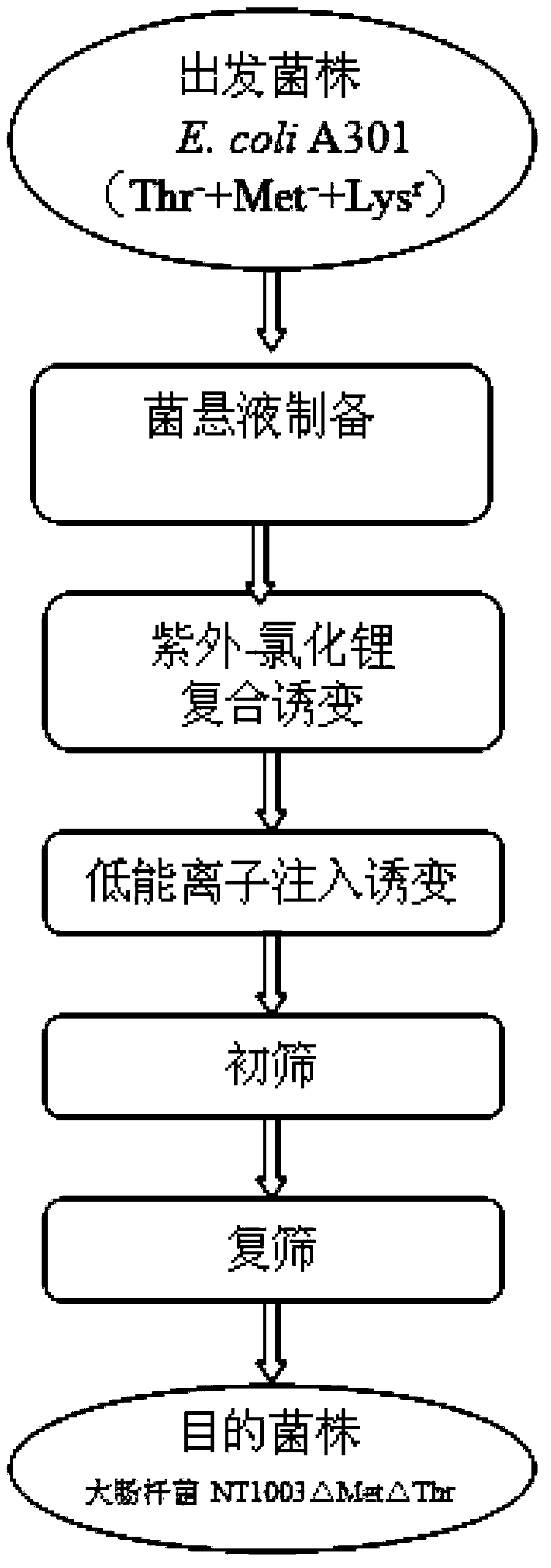
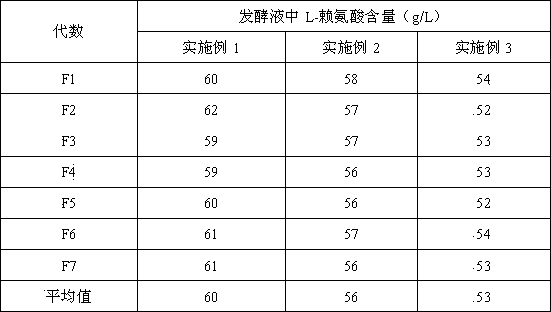
Strain for producing L-lysine and method thereof for producing L-lysine
ActiveCN103361289AL-Lysine BoostIncreased L-lysine contentBacteriaMutant preparationMicrobiologyEnterobacter
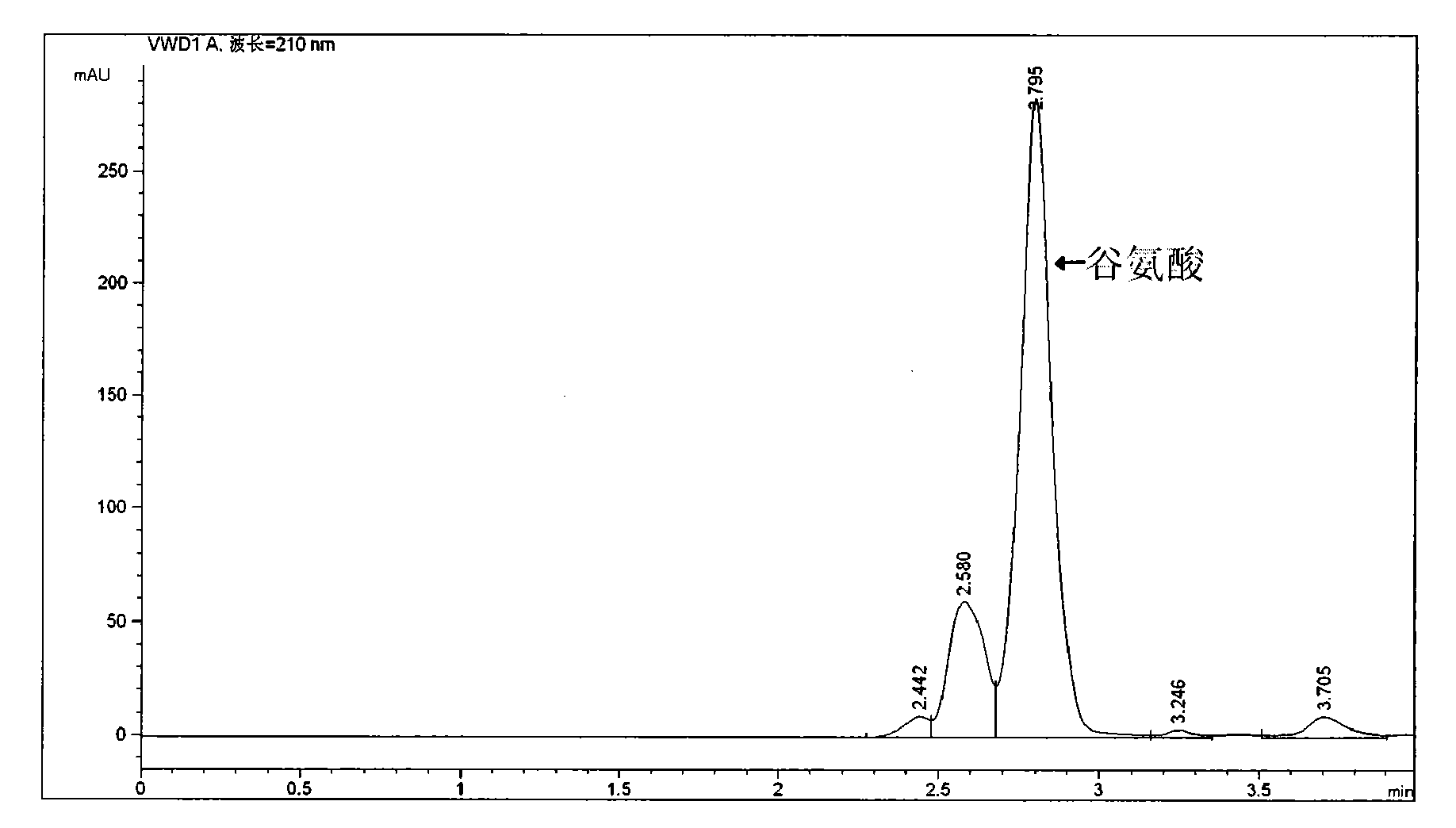
The invention relates to a strain for producing L-lysine, which is classified and named as Escherichiacoli NT1003 delta Met delta Thr and is collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on May 30, 2013, and the collection number is CCTCC NO: M2013239. The invention further provides a mutation screening method of the strain and a method for producing the L-lysine by utilizing the strain. After continuous passage is performed on the Escherichiacoli NT1003 delta Met delta Thr strain for 7 times, the content of the L-lysine in a fermentation solution is about 60g / L and has no significant change, so that the genetic stability is good.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Tissue culture method of dioscorea opposita stem with axillary buds
InactiveCN102657092AHigh reproductive coefficientImprove reproductive efficiencyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyAxillary bud
The invention discloses a tissue culture method of a dioscorea opposita stem with axillary buds. A dioscorea opposita stem with axillary buds is selected as an explant, and through a series of operations of bud induction, mulitiplication and rooting culture, a dioscorea opposita test-tube plantlet is finally formed. The method includes medium components for a plurality of stages of cultivation and a processing method, and a complete tissue culture seedling can be acquired within about twenty days. Through the method, dioscorea opposita tissue culture seedling can be acquired through the induction of the explant of the dioscorea opposita stem with axillary buds, so indoor mass propagation of the test-tube plantlets is feasible, and breeding and industrial production of dioscorea opposita tuber can be realized. The tissue culture method has the characteristics of high propagation coefficient, fast propagation speed, high propagation efficiency and good genetic stability and is free of the influence of environment conditions, and the seedlings have fewer virus.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Micro-propagation method for white birch with purple leaf
InactiveCN101502237AShort reproductive cycleImprove efficiencyHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBetula platyphyllaObserved Survival
The present invention relates to a micropropagation method of purple-leaf birch, and relates to a micropropagation method. The invention settles the problems of long breeding cycle, long propagation efficiency, high cost and low survival rate. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: 1. sterilizing the explant; 2. cutting the explant to stem segment, and then executing induction cultivation for obtaining micro-branch; 3. cutting the micro-branch to stem segment and proliferating in the culture medium; and 4. executing invigoration culture to the proliferated micro-branch, sticking into a rooting substrate for executing rooting culture for finishing the micropropagation of purple-leaf birch. The micropropagation method of purple-leaf birch of the invention has the advantages of short propagation period, high efficiency and excellent genetic stability. The propagation efficiency is that the purple-leaf birch propagates for 30-40 times every 30-40 days. The method of the invention also has the advantages of simple operating technique, labor saving, time saving and low cost. The cost is saved by 30%-50% compared with the prior art. Furthermore the rooting rate and survival rate of seedling propagation equally can obtain 100%.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +2
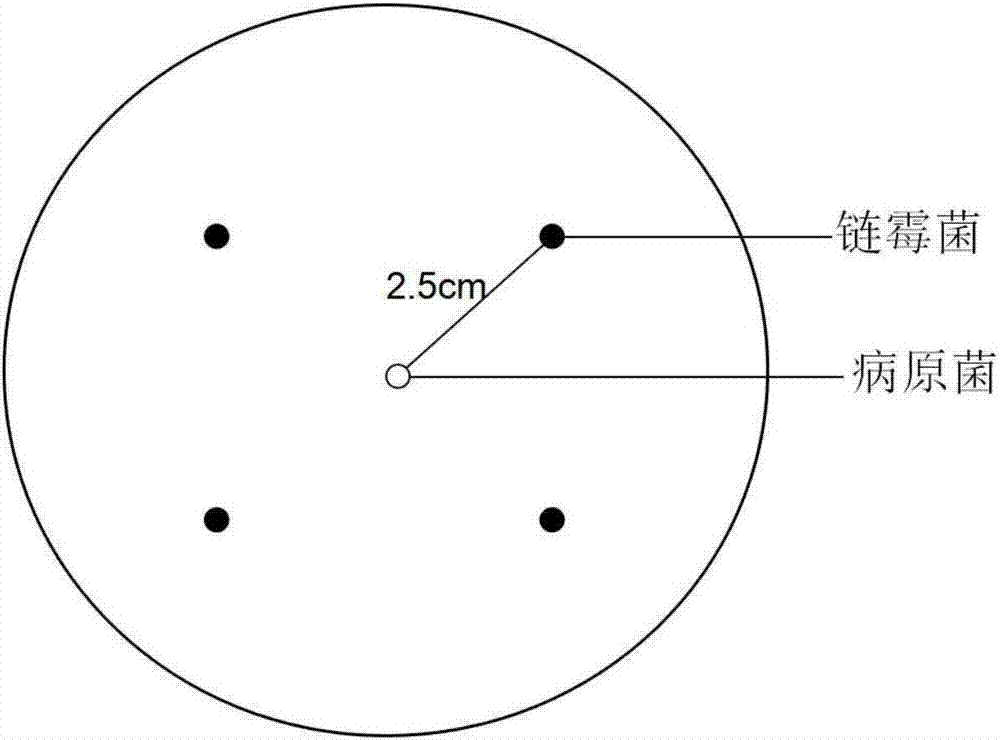
Streptomyces albidoflavus and application thereof in apple tree rot prevention and treatment
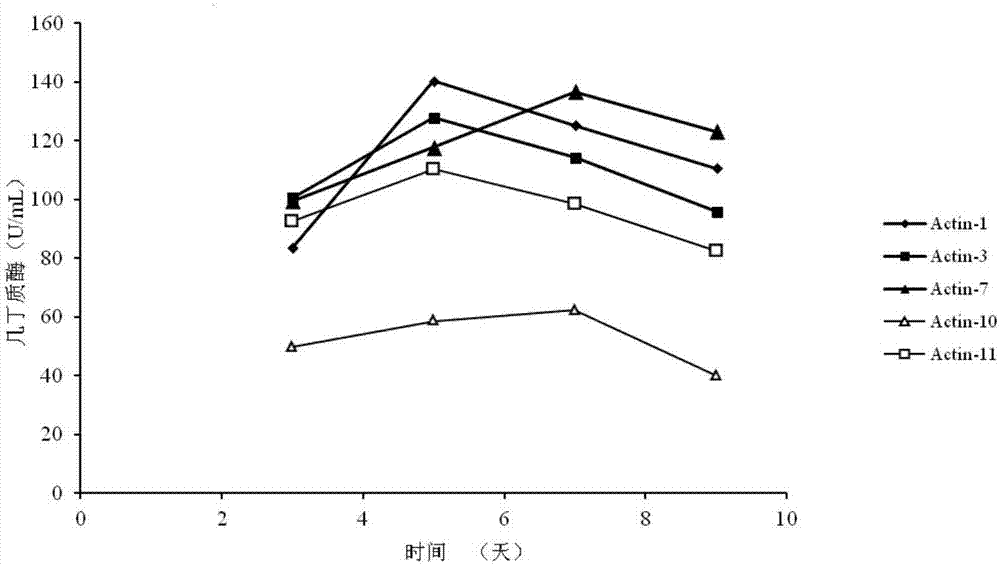
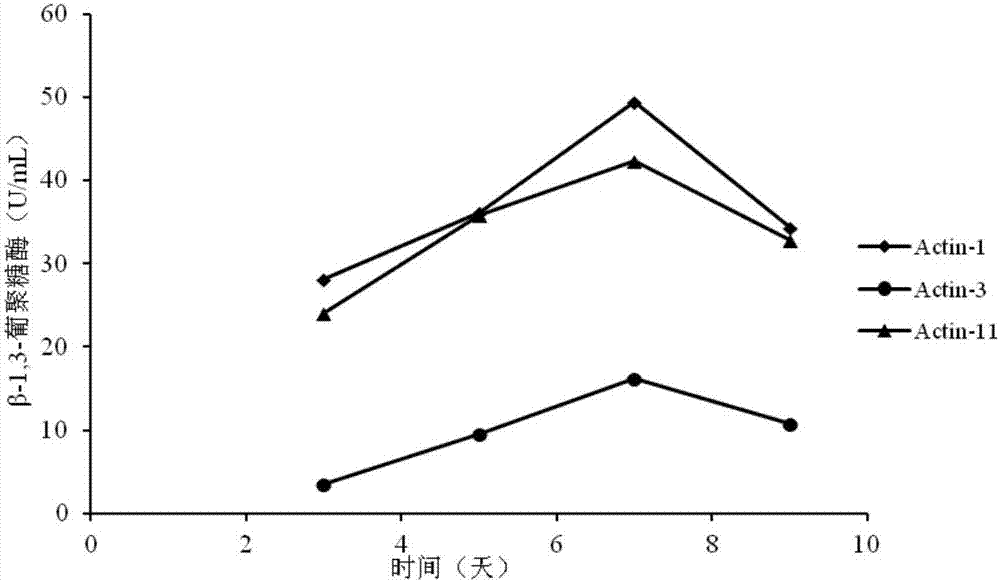
ActiveCN106906172AConducive to long-term colonizationStrong antibacterial active substanceBiocideBacteriaActive matterTherapeutic effect
The invention discloses streptomyces albidoflavus Actin-1. The streptomyces albidoflavus Actin-1 can grow and propagate with apple tree rot pathogenic bacterium mycelium as nutrition, long-term colonization of biocontrol bacteria on apple tree rot scabs is promoted, a long-term biological prevention and treatment function is achieved, meanwhile, the streptomyces albidoflavus Actin-1 is induced to generate multiple ectoenzyme cell wall hydrolytic enzymes, and pathogenic bacterium cells disintegrate in combination with the enzyme dissolving function; high antibacterial active matter can be generated, the bacteriostasis rate on the apple rot pathogenic bacteria is 89.82%, a good antibacterial effect is achieved on botryosphaeria berengeriana and other pathogenic bacteria, the bacteriostasis rate ranges from 76.08% to 87.10%, and broad spectrum bacteriostasis performance is achieved. The streptomyces albidoflavus Actin-1 is adopted as main biocontrol bacteria for preventing and treating the apple tree rot and other fruit and vegetable pathogenic bacteria, and the advantages of being good in prevention and treatment effect (100%), high in efficiency, low in recurrence rate (0), high in environment adaption capacity, high in stability, not likely to generate resistance to drugs and the like are achieved. Important significance is achieved on improving the prevention and treatment effect on the apple tree rot and other fruit and vegetable pathogenic bacteria, preventing pathogenic bacterium relapse and protecting the environment.
Owner:陕西枫丹百丽生物科技有限公司
Large-scale artificial planting method for Xinjiang saussurea involucrata
InactiveCN102487720AGood genetic stabilityLow equipment requirementsSeed and root treatmentHorticultureOperating instructionGenetically engineered
The invention relates to a large-scale artificial planting method for Xinjiang saussurea involucrata. The method comprises the steps of selecting seeds, accelerating germination, selecting proper nutritional soil, sowing, transplanting, performing field management and the like. By the method, a standard saussurea involucrata planting operating instruction is established, and the flowering and propagation period of the saussurea involucrata is greatly shortened; and the method is suitable for industrialized culture of the saussurea involucrata, and lays a foundation for good variety breeding and transgenic research of the saussurea involucrata.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Astaxanthin high-yield strain and application thereof
InactiveCN104178430AEnhanced Astaxanthin ComponentsHigh compositionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNitroso
The invention discloses an astaxanthin high-yield strain and application thereof. The astaxanthin high-yield strain is classified to be named as Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous VR-032 and collected in CCTCC (China Center For Type Culture Collection), and the collection number is CCTCCM2014190. According to the invention, a target strain VR-032 is finally screened by virtue of nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis by adopting a strain which is obtained by fermentation and screening based on a shake flask and has high astaxanthin yield as an initial strain of a next round of mutagenesis, and the strain can be used for more greatly increasing astaxanthin components contained in a fermentation product and decreasing other components and has good hereditary stability. According to the astaxanthin high-yield strain disclosed by the invention, the sugar cane is utilized as a fermentation carbon source, the yield of the astaxanthin obtained by fermentation by utilizing the low-cost sugar cane as the carbon source in a 5L fermentation tank is up to 68.7mg / L, the yield of the astaxanthin is increased by 20.8% compared with that of an original initial strain, and the astaxanthin high-yield strain can be applied to industrial production, greatly improving the fermentation unit and achieving significant economic application value.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Propagation method of Chinese yam exsomatize
InactiveCN101637125AGood genetic stabilityBreeding takes up little spaceHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureForest yamBiology
The invention discloses a propagation method of Chinese yam exsomatize, aiming at providing a propagation method of Chinese yam exsomatize with good genetic stability, less propagation usage space, and convenient storage and transportation. The technical scheme of the invention comprises the following steps of: (1) inducing the formation of Chinese yam protocorm; (2) propagating the Chinese yam protocorm; (3) differencing the Chinese yam protocorm; (4) rooting regeneration plant of the Chinese yam protocorm; and (5) hardening and transplanting the regeneration plant of the Chinese yam protocorm. The method is used for the propagation of the Chinese yam.
Owner:HENAN NORMAL UNIV
Pig viral infectious disease gene recombined live vaccine using canine II type adenovirus as carrier and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN1827172AGood genetic stabilityEasy to storePowder deliveryGenetic material ingredientsAntigenVp4 gene
This invention supplies a series of production techniques of gene recombination live vaccine of swine virus contagion with canine ó� adenovirus as carrier and finished goods. The viral live vectors vaccine takes swine important virus zymad protective antigens gene as object gene, which are chosen from HCV-E1, E2 gene, FMDV-VP1íóVP2íóVP3íóVP4 gene, TGEV-SíóNíóM gene, PEDV-SíóNíóM geneú¼SIV-HAíóNA geneú¼RV-GíóN gene, etc. The produced vaccines contain recombined swine influenza virus HA gene adenovirus carrier live vaccine, swine plague virus E2 gene adenovirus carrier live vaccine and recombination swine AsiaI foot-and-mouth disease virus VPI gene adenovirus carrier live vaccine. Recombination virus has good inheritance stability, and vaccine immunization can induct pig develop differential antiviral neutralization antibody. It has good immune protection effect and has no toxic side effect. The goods are facilitating for preserve and transportú”it has long storage life and simple technics, and it fits for commercial manufacture.
Owner:MILITARY VETERINARY RES INST PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Method for fusing protoplast of volvaria volvacea and pleurotus eryngii
InactiveCN101985617AStrong technical repeatabilityGood genetic stabilityHybrid cell preparationPleurotus eryngiiPleurotus
The invention provides a method for fusing protoplast of volvaria volvacea and pleurotus eryngii. The mycelium of the volvaria volvacea and pleurotus eryngii is in enzymolysis to prepare a protoplast; the thermal inactivation of the pleurotus eryngii protoplast serves as a mark, and a PEG (polyethylene glycol)-mediated chemical method is adopted to fuse the protoplast of volvaria volvacea and pleurotus eryngii; a fusant is screened at the temperature of 0 DEG C, and a fruiting experiment is carried out to obtain a fusion strain. The method provided by the invention can effectively fuse the protoplast of volvaria volvacea and pleurotus eryngii and obtain low temperature resistant new volvaria volvacea strain with the characteristics of pleurotus eryngii. The invention provides an effectivemethod for distant fusion creation between two edible fungusiaceae with obvious complementary character.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Tissue culture and rapid propagation method for campanumoea
InactiveCN101869074AHigh reproductive rateGood genetic stabilityCultivating equipmentsPlant tissue cultureSaccharumSucrose
The invention discloses a tissue culture and rapid propagation method for campanumoea, which comprises the following steps of: 1) selecting and pretreating an explant; 2) sterilizing the explants; 3) performing inducing culture; 4) performing propagation culture; 5) performing rooting culture; and 6) transplanting, wherein a basic culture medium is an MS basic culture medium, comprises 20 to 30g / L of cane sugar or white sugar and 7 to 9g / L of agar, and has the pH of 5.6 to 5.8; an inducing culture medium comprises MS, 0.1 to 5.0mg / L of cytokinin, 0.0 to 0.5mg / L of growth hormone and 30g / L of cane sugar or white sugar; a propagation culture medium comprises MS, 0.1 to 3.0mg / L of cytokinin, 0.0 to 0.5mg / L of growth hormone and 30g / L of cane sugar or white sugar; and a rooting culture medium comprises half MS, 0.1 to 1.0mg / L of growth hormone and 20g / L of cane sugar or white sugar. The method has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, strong pertinence of component formulas of the culture media, low vitrification rate of tissue culture seedlings, feasible operation, and capacity of making the campanumoea have high propagation coefficient and good genetic stability than wild campanumoea.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
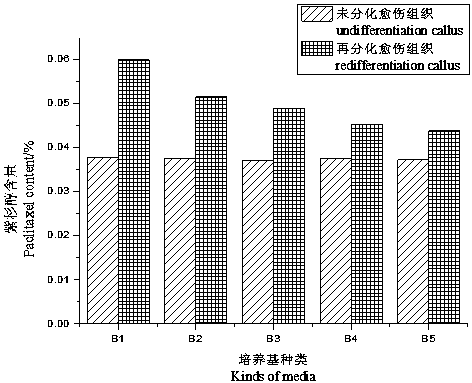
Induced redifferentiation method for improving paclitaxel content in calluses of Taxus wallichiana var. mairei
InactiveCN103651139APaclitaxel content increasedGood genetic stabilityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSecondary metaboliteTaxus species
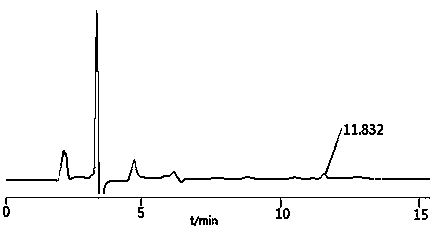
The invention provides a technology for inducing the redifferentiation of calluses of Taxus wallichiana var. mairei to improve or maintain the genetic stability of the cellular metabolism of the Taxus wallichiana var. mairei and improve the content of paclitaxel as a secondary metabolite of the Taxus wallichiana var. mairei. The technology comprises four steps of explant preprocessing, induced culture of calluses, calluses subculture and calluses redifferentiation induction. In the step of induced culture of calluses, subculture is performed four times with 20-35 days for each culture, the calluses with good color and right texture are transferred to an improved MS (Murashige & Skoog) culture medium in which 0.05-0.20mg / L6 of BA, 0.2-2.0mg / L of NAA, 0.1mg / L of KT and 0.5mg / L of CH are added for redifferentiation induction culture, after 45-75 days of the induction culture, tiny sprouts grow from the calluses of the Taxus wallichiana var. mairei, the calluses are harvested at the time, after samples are subjected to drying, weighing and a series of preprocessing, HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) is adopted to measure the content of the paclitaxel, and a result shows that the content of the paclitaxel is one time higher than that of the calluses which are not subjected to differentiation. In the improved MS culture medium, ammoniacal nitrogen is 2000-2600 mg / L and the nitrate nitrogen is 800-1000mg / L.
Owner:JISHOU UNIVERSITY
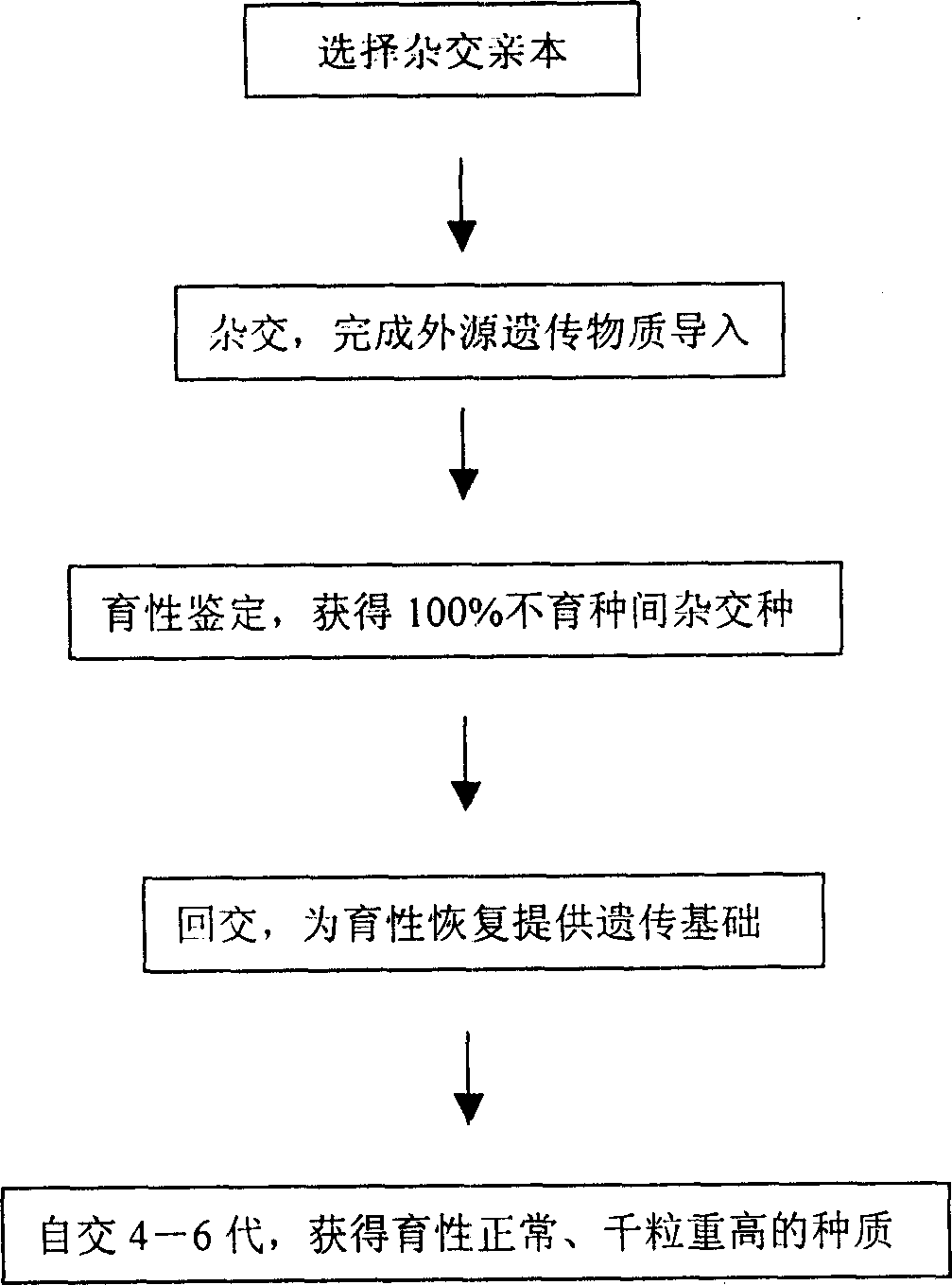
Wheat interspecific distant hybrid, secondary backcross and selfing breeding method
InactiveCN1813523AGood genetic stabilityReduce manufacturing costPlant genotype modificationGermplasmInterspecific hybridization
The present invention provides a wheat breeding method, including interspecific distant hybridization, secondary back cross and self-cross. Said method includes the following several procedures: a), parents selection; b), distant hybridization; c), hybridization combination and fertility identification; d), backcross; and e) self-cross. Besides, said invention provides the concrete steps and requirements of the above-mentioned every procedure.
Owner:DRY LAND FARMING INST OF HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Method for preparing apple tree valsa ceratosperma transformant and GFP (Green Fluorescent Protein) labelled strain
ActiveCN102994401AThe sporulation method is simpleSimple and fast operationFungiMicroorganism based processesFluorescencePolyethylene glycol
The invention aims to provide an apple tree valsa ceratosperma transformant and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: after mixing, co-culturing conidial suspensions of agrobacterium tumefaciens containing a binary vector and valsa ceratosperma, screening by using antibiotics to obtain the transformant. According to the method, the conidium of apple tree valsa ceratosperma is used as a receptor, agrobacterium tumefaciens is used as an amboceptor, the problems of difficulty in preparation of protoplast of the apple tree valsa ceratosperma and difficulty in genetic transformation of the valsa ceratosperma caused by low polyethylene glycol (PEG)-mediated transformation efficiency and the like are overcome; the transformation efficiency of the method can be up to 1 / 10<3> conidiums; simultaneously, the invention provides an apple tree valsa ceratosperma green fluorescent protein (GFP) labelled strain and a preparation method thereof; and the efficiency of the green fluorescent protein with strong expression in the transformant obtained by the method can be up to 96.7%.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Cultivation method for quickly obtaining lycium ruthenicum regeneration seedlings
ActiveCN107135950AReduce cultivation costHigh transplant survival rateSeed and root treatmentHorticulture methodsCataphyllBud
The invention belongs to the technical field of forest creatures, and discloses a cultivation method for quickly obtaining lycium ruthenicum regeneration seedlings. The cultivation method comprises the following steps: disinfection of seeds, obtaining of germfree seedlings, induction of a callus, obtaining of adventitious buds and induction of roots. According to the cultivation method, the callus is directly obtained from the germfree seedlings of lycium ruthenicum, and the lycium ruthenicum regeneration seedlings are cultivated through a tissue culture method; compared with a conventional method for inducing the callus through leaves or stems of the seedlings, the cultivation method has the advantages that the tissue culture time is greatly shortened, and cultivation cost of the lycium ruthenicum is greatly reduced; meanwhile, the cultivation efficiency is effectively improved, and the transplanting survival rate of the regeneration seedlings reaches up to 98 percent. The lycium ruthenicum obtained through the cultivation method has the characteristics of being high in genetic stability, low in cost, short in seedling growing period, high in reproduction coefficient, and easy and convenient to operate.
Owner:NANJING XIAOZHUANG UNIV
Antiphagin L-phenylalanine producing strain as well as breeding method and application thereof
InactiveCN102010847AFight infectionAddressing susceptibility to bacteriophage contaminationBacteriaMutant preparationBio engineeringFermentation broth
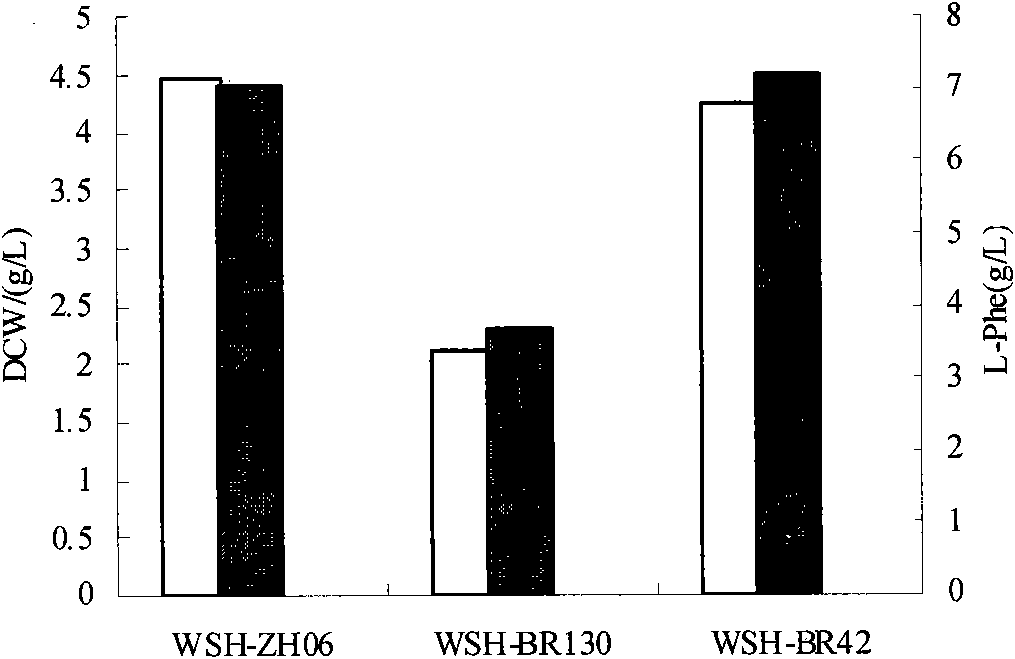
The invention discloses an antiphagin L-phenylalanine producing strain as well as a breeding method and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of bioengineering. The breeding method comprises the steps of: inducing and recombining a host bacterium WSH-Z06 of escherichia coli with nitrosoguanidine (NTG), breeding a strain with phage (CCTCC M) resistance by using phage separated from WSH-Z06(pAP-B03)(CCTCC M2010009) fermentation broth as a sieve, and transforming a plasmid pAP-B03 containing a L-phenylalanine synthase gene to finally obtain the antiphagin L-phenylalanine producing strain WSH-BR42(pAP-B03)(CCTCC M 2010008). Compared with a starting strain, the antiphagin L-phenylalanine recombinant strain WSH-BR42(pAP-B03) has the resistance to the phage (CCTCC M) and suffers from no influence to the growth speed and acid forming capability to the strain body. In the invention, the problem that the L-phenylalanine fermentation production is constantly polluted by the phage is solved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com