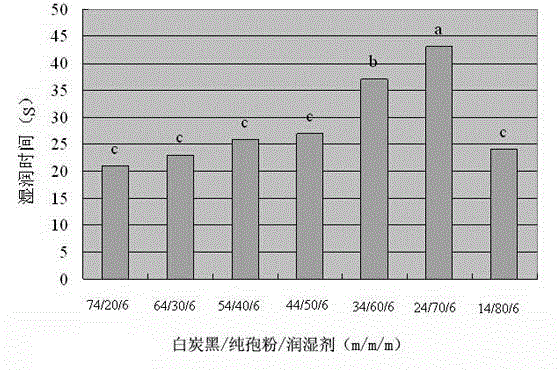
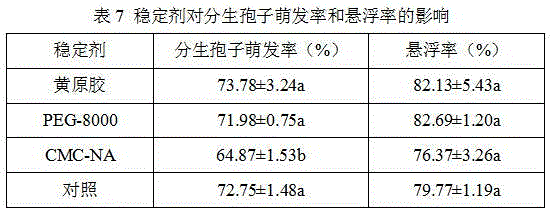
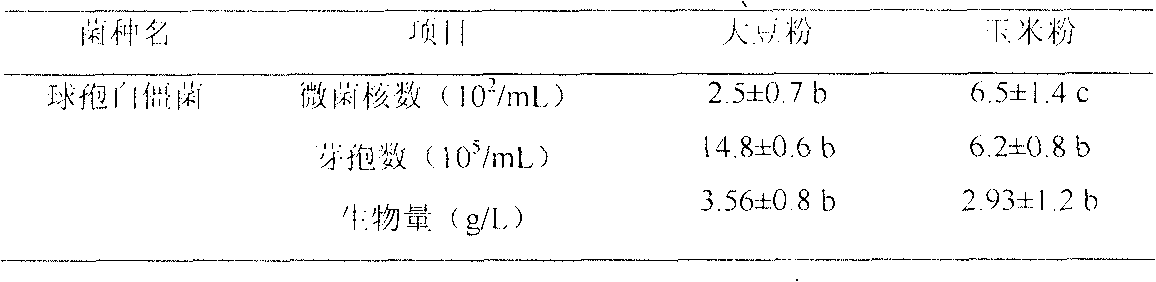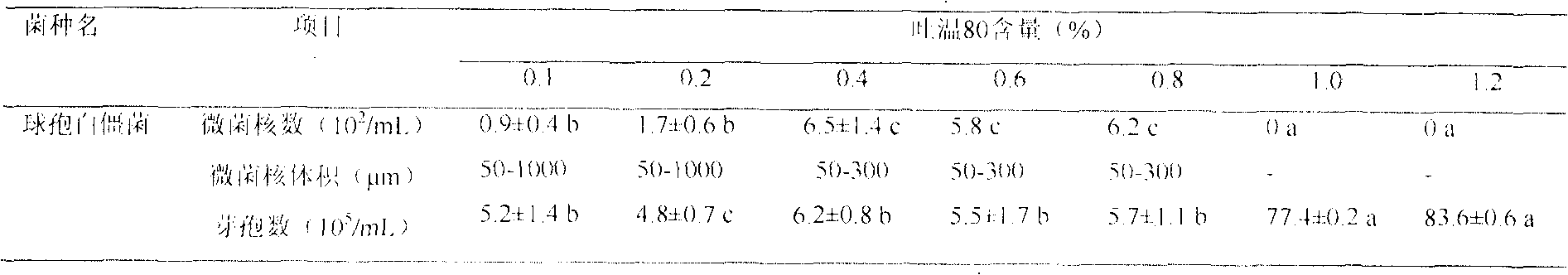Patents
Literature
505 results about "Conidium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A conidium (plural conidia), sometimes termed an asexual chlamydospore or chlamydoconidium (plural chlamydoconidia), is an asexual, non-motile spore of a fungus. The name comes from the Greek word for dust, κόνις kónis. They are also called mitospores due to the way they are generated through the cellular process of mitosis. The two new haploid cells are genetically identical to the haploid parent, and can develop into new organisms if conditions are favorable, and serve in biological dispersal.
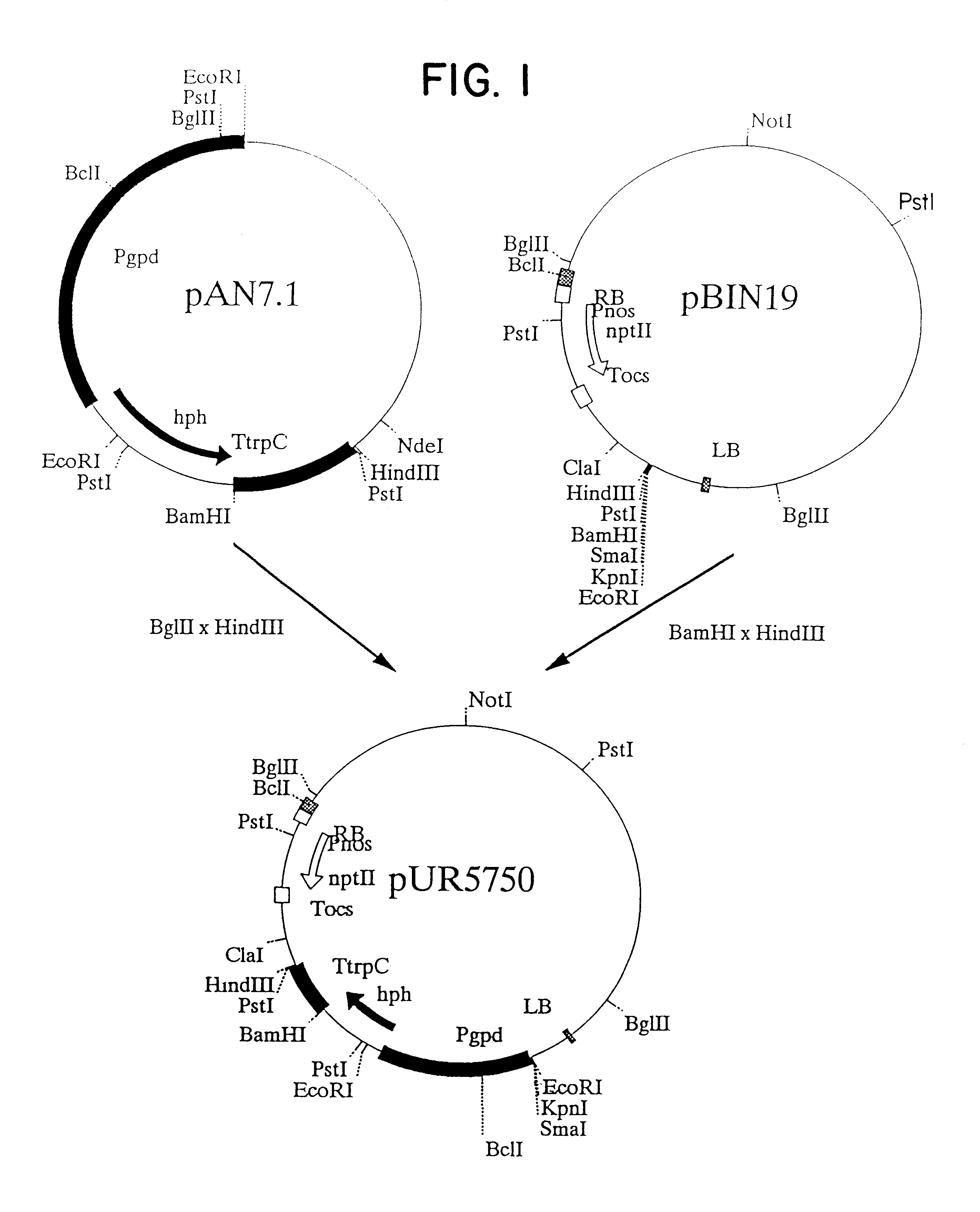
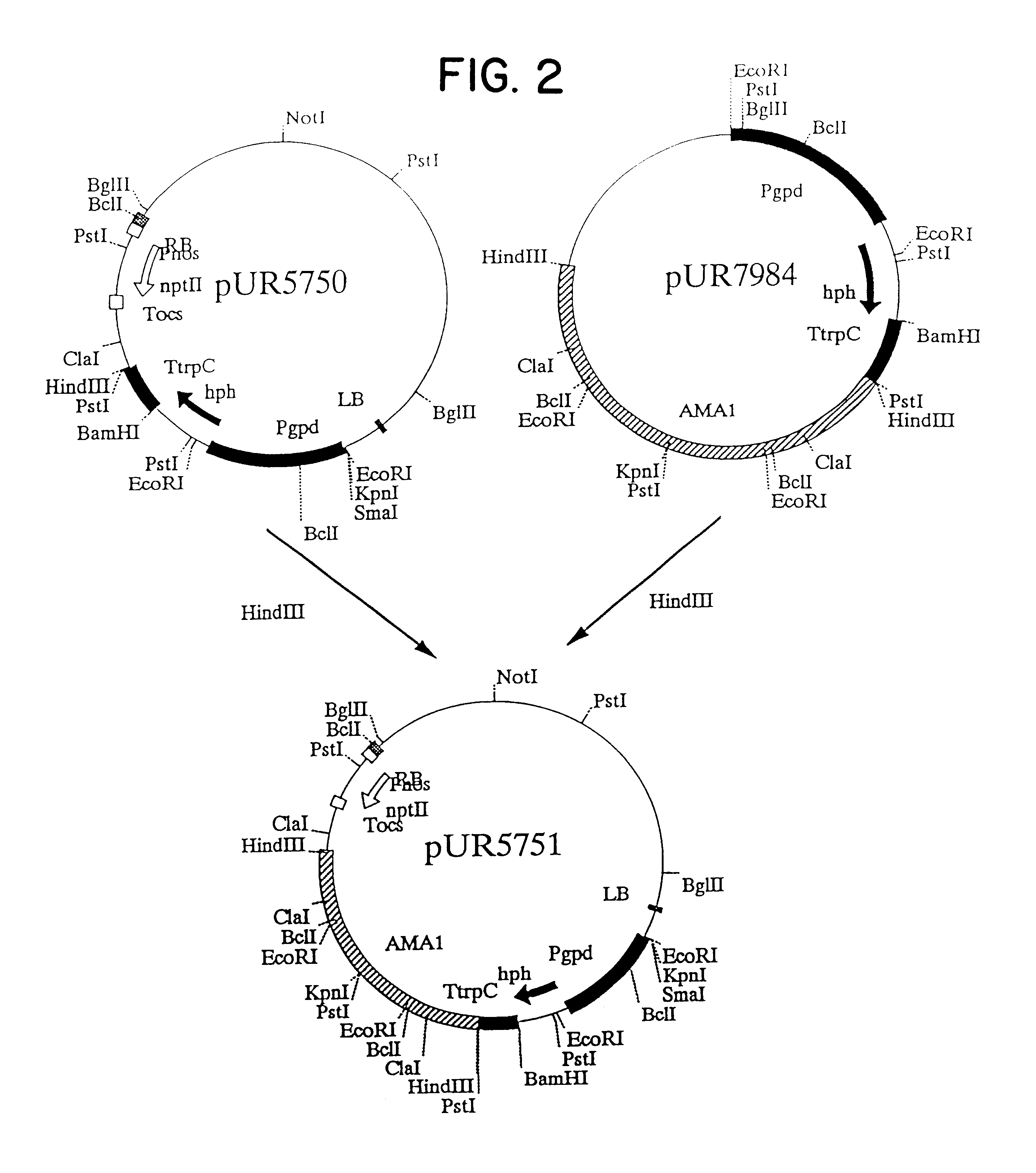
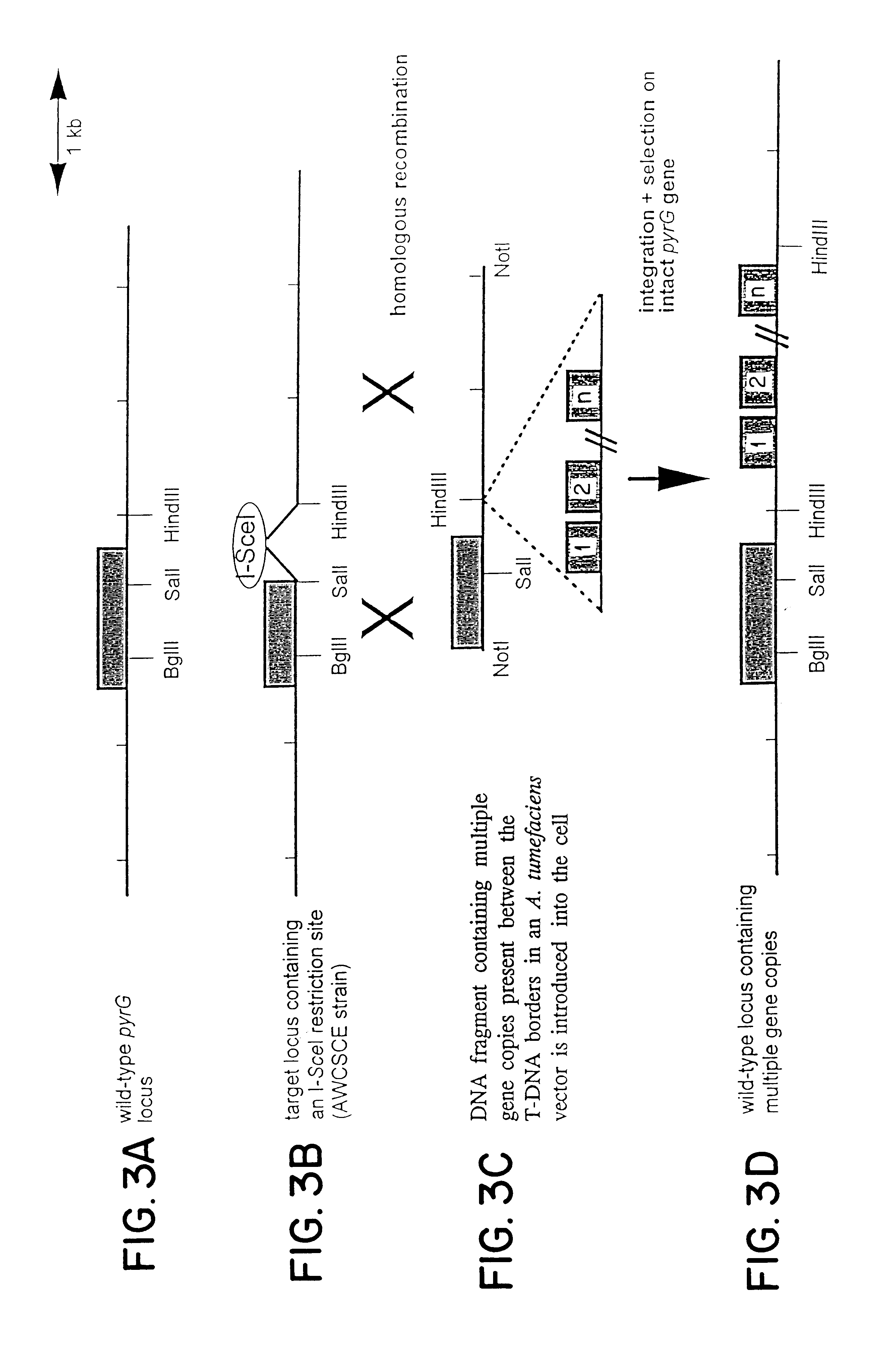
Agrobacterium mediated transformation of moulds, in particular those belonging to the genus Aspergillus
The invention relates to Agrobacterium mediated transformation of moulds comprising species of the fungal sub-divisions Ascomycotina, Basidiomycotina, Deuteromycotina, Mastigomycotina, and Zygomycotina.Examples demonstrate the transformation of Aspergillus awamori (both protoplasts and conidia), Aspergillus nidulans, Aspergillus niger, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, Fusarium solani pisi, Neurospora crassa, Trichoderma reesei, Pleurotus ostreatus and Agaricus bisporus (all conidia), and Fusarium graminearum (both conidia and rehydrated freeze dried ATCC material).Especially for Aspergillus awamori the transformation frequency is much higher than with conventional mould transformation techniques.It has further been found that not only one expressable gene can be introduced into these moulds, but even multiple copies of such gene, which, moreover, can be targeted e.g. in the chromosomal pyrG locus, as exemplified for A. awamori. These multiple copies can be of a gene encoding a desired, homologous or heterologous, protein.
Owner:UNILEVER PATENT HLDG BV
Production and use of endophytes as novel inoculants for promoting enhanced plant vigor, health, growth, yield reducing environmental stress and for reducing dependency on chemical pesticides for pest control
InactiveUS20090105076A1Improve scalabilityPrevent degradationBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyFungal endophyte
A process and method for the production of endophytes as plant inoculant products, specifically Clonostachys rosea strain 88-710, for the promotion of plant vigor, health, growth and yield are disclosed. The endophyte, Clonostachys rosea strain 88-710 produces a fungal conidial preparation by utilizing a discrete solid substrate fermentation system, namely Potato Dextrose Agar or Malt Extract Agar. Additionally, the endophyte, Clonostachys rosea strain 88-710, can act as an inoculant to stimulate and have an additive effect with rhizobium bacteria on the production of nitrogen fixing nodules on legumes and growth enhancement e.g. beans, soybeans, peas and alfalfa. As well, Clonostachys rosea strain 88-710, can combine with rooting hormones, e.g. indole-3-butyric acid (IBA) to provide inoculant and rooting benefits to cuttings / transplants of plants.
Owner:ADJUVANTS PLUS INC
Paecilomyces lilacinus, culture method of paecilomyces lilacinus and use of paecilomyces lilacinus in prevention and control of diseases and pests of crops
The invention discloses a paecilomyces lilacinus strain and its culture method and use. The paecilomyces lilacinus strain is paecilomyces lilacinus CPLI0708, is preserved in the China general microbiological culture collection center (CGMCC) and has an accession number of CGMCC No.8450. The culture method of the paecilomyces lilacinus strain comprises the following steps of A, bacterial strain activation: carrying out bacterial strain streak cultivation activation on a PDA inclined plane, B, bacterial strain liquid fermentation culture: transferring the activated bacterial strain into a triangular flask with a liquid medium and carrying out shaking culture, and C, bacterial strain solid fermentation culture: mixing a carrier, a nutrition matrix and water according to a volume ratio to form a uniform mixture which is a solid fermentation medium, putting the solid fermentation medium into a fresh-keeping bag, inoculating the solid fermentation medium with a liquid fermentation seed, carrying out stirring to obtain a uniform mixture and carrying out culture. The bacterial strain conidiospore has strong effects of killing sucking-type insects such as greenhouse aphids and whitefly and the fermentation broth has strong effects of killing larvas of soybean cyst nematode and can be used for pollution-free vegetable production.
Owner:谢明
Biological weed control compound and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101856036ADoes not affect sensitivityDoes not affect virulenceBiocideAnimal repellantsSporeSynergy
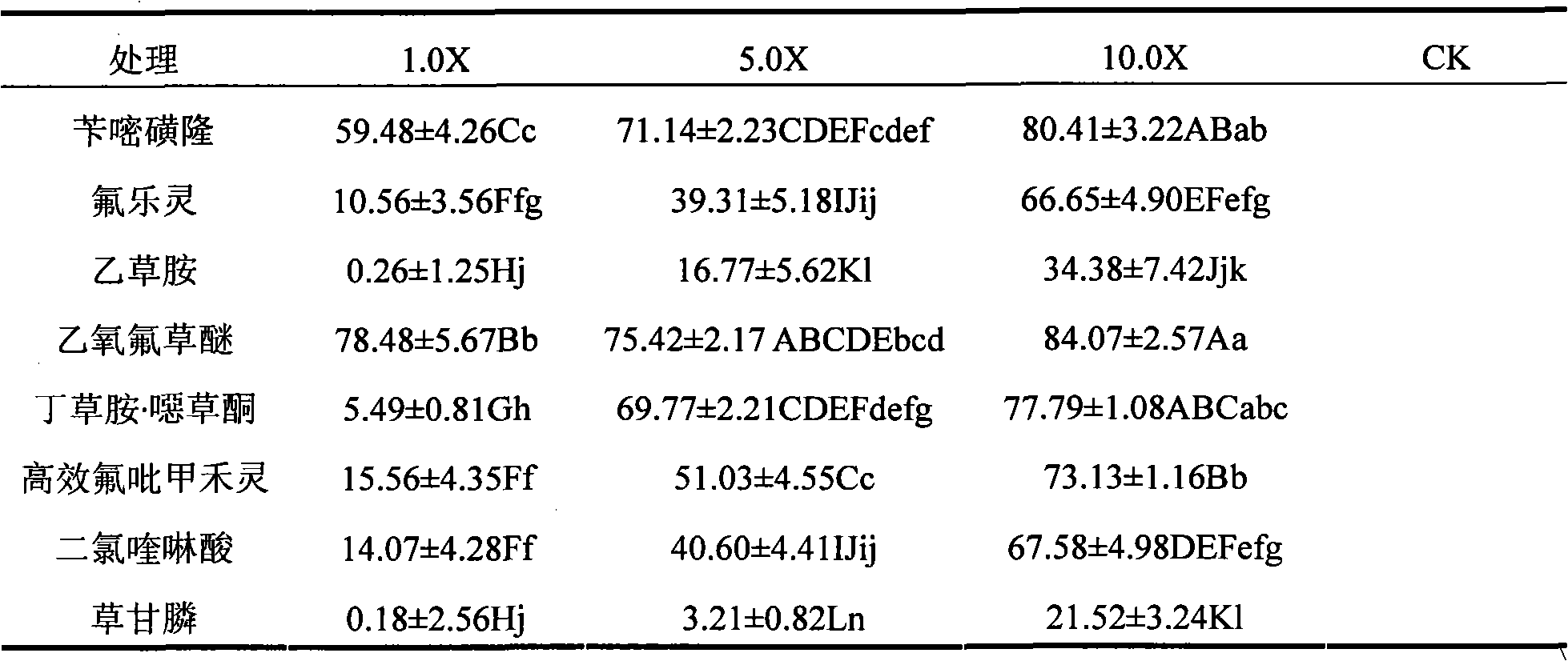
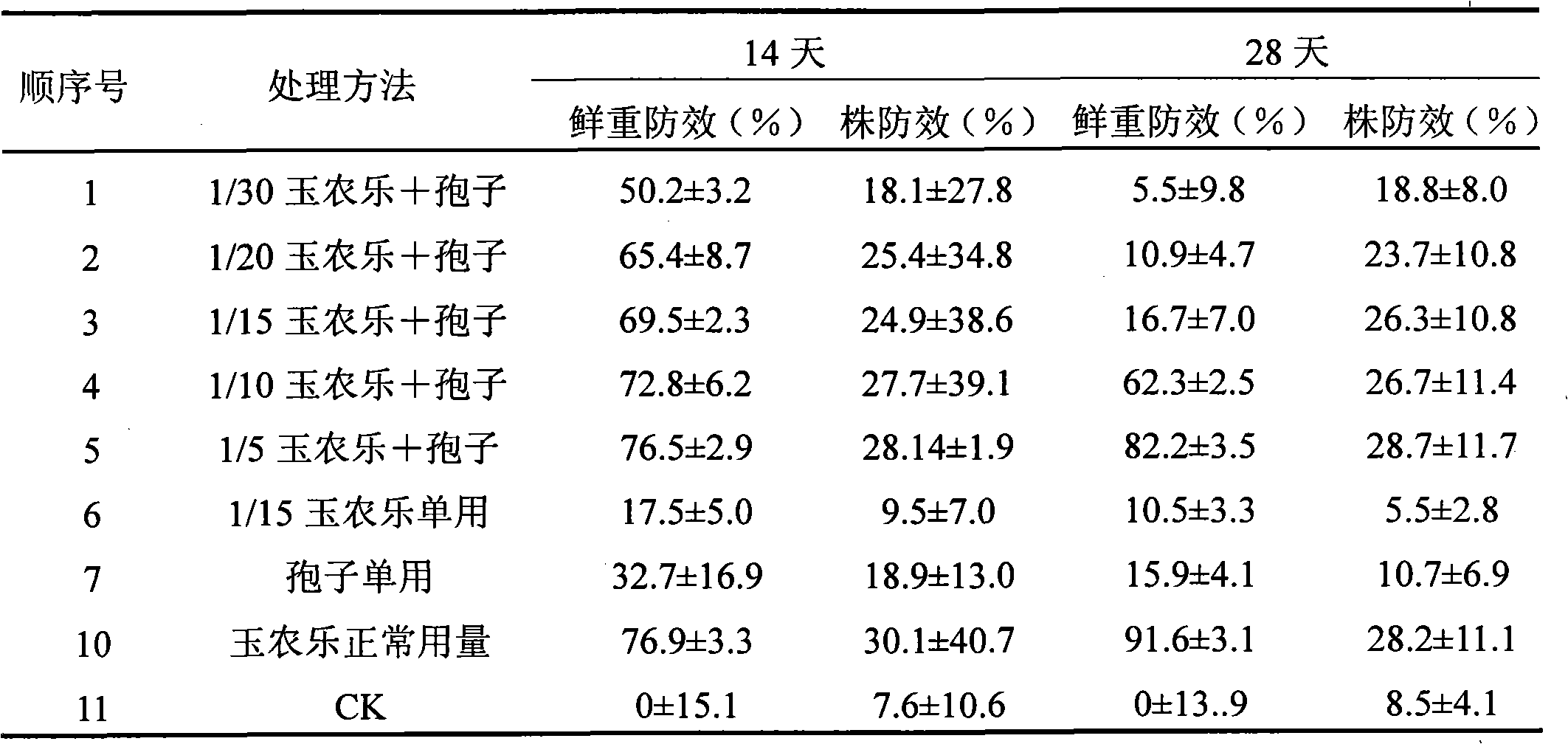
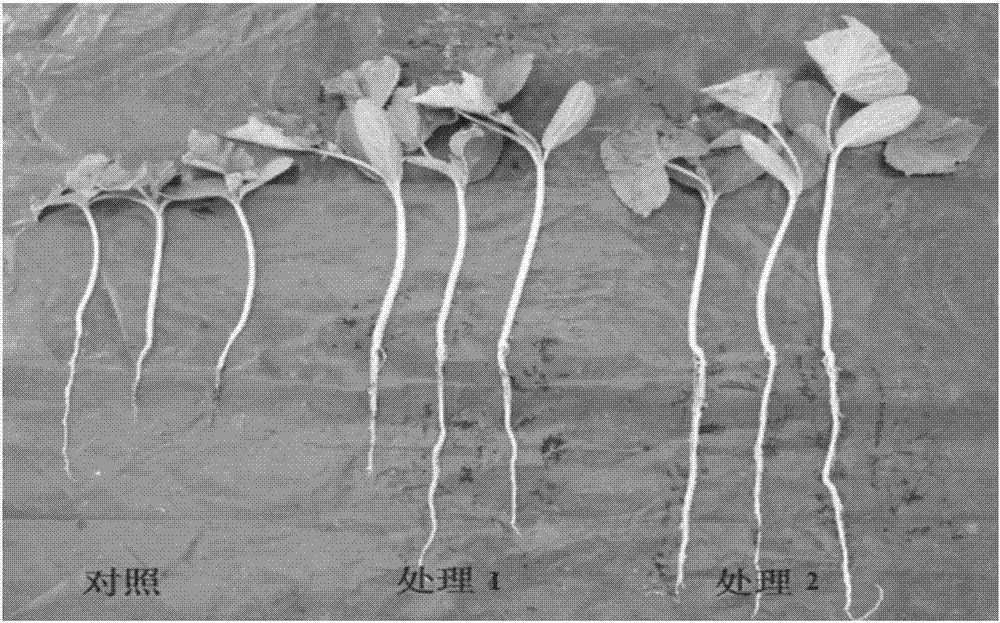
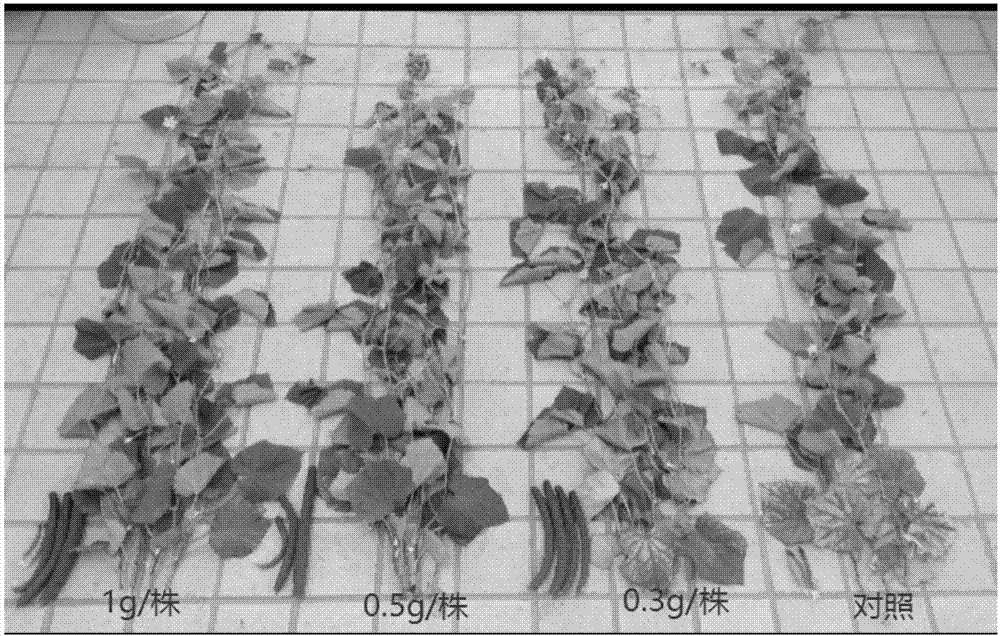
The invention discloses a weed control compound and a preparation method thereof. The weed control compound is mainly composed of conidium of Curvularia fungus strain QZ-2000 with preservation number CGMCC NO.0640 and a chemical herbicide, wherein the concentration of the conidium is 1-10g / L, and the concentration of the chemical herbicide is 1 / 20-1 / 3 of a conventional dosage. The invention adopts that the conidium is compounded with the chemical herbicide; on one hand, conidium dosage is lowered, biological prevention and cure cost is lowered, and the chemical herbicide performs the synergy when compound compared with the situation that only spore is adopted; on the other hand, lowers pollution of chemical herbicide is lowered.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Trichoderma asperellum with growth-promoting effect and culture method and application thereof
ActiveCN107142213APromote growthAvoid infectionBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyTrichoderma asperellum
The invention relates to a solid fermentation production method of trichoderma asperellum. The trichoderma asperellum bacterial strain used in the method is preserved in the general microbiological center of Chinese general microorganism strain preservation management committee, the preservation date is October 27th, 2015, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.11528. The trichoderma asperellum is subjected to strain activation, shake flask seed preparation, primary liquid seed culture and then solid fermentation. A solid fermentation culture medium for solid fermentation is composed of rice husks, corn straw powder, wheat bran or corn powder and inorganic salt. According to the solid fermentation method of the trichoderma asperellum, a large quantity of conidia can be generated, the spore number of the substrate trichoderma asperellum can reach up to 1*109-1*1010 cfu / g, the fermentation viable count is high, neither pollution nor waste materials are generated in the production process, and the efficiency of the production technology is high. Fermentation products obtained after fermentation have obvious growth-promoting effects on crops and greatly improve the economic benefit of the crops.
Owner:KINGENTA ECOLOGICAL ENG GRP +1
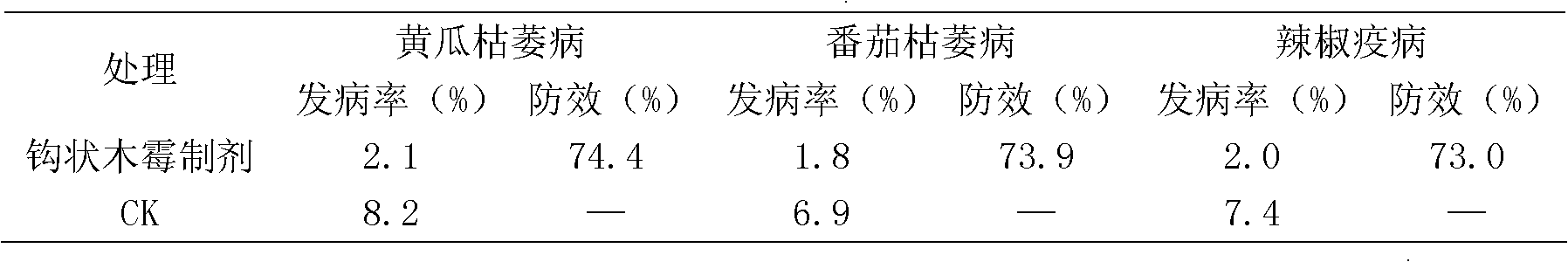
Application of trichoderma strains in preparation of biopesticide for preventing and controlling cucumber fusarium wilt
The invention relates to the application of trichoderma strains in preparation of biopesticide for preventing and controlling cucumber fusarium wilt. The trichoderma strains are Trichoderma harzianum SH2303CGMCC NO.4963. The main components for preventing and controlling the cucumber fusarium wilt are conidia of the Trichoderma harzianum SH2303; and the biopesticide can be seed coating agents or granules. The trichoderma strains in the application has high growth speed and high sporulation quantity; the confrontation pathogens inhibition rate in vitro reaches 43.01 percent; the inhibition rate of a non-volatile inhibitor to the cucumber fusarium wilt is 41.33 percent; the inhibition rate of a volatile inhibitor to the cucumber fusarium wilt is 11.49 percent; the chitinase activity is 3.9573U; the beta-1,3-glucanase enzyme activity is 0.5092U; the extracellular protease enzyme activity is 3.0678 U; the prevention effect aiming at the living bodies of the cucumber fusarium wilt is 71.43 percent; the overall proportion of the antibiosis secondary metabolites, having antagonism, in the strains is 30.28 percent; and the trichoderma strains can effectively prevent and treat the disease of the cucumber fusarium wilt.
Owner:侨昌生物科技(上海)有限公司
Method for preparing and regenerating phomopasis asparagi protoplast
InactiveCN103451110AHigh number of preparationsHigh regeneration rateFungiMicroorganism based processesMyceliumEtioplasts
The invention discloses a method for preparing and regenerating a phomopasis asparagi protoplast, which relates to the technical field of fungus protoplast preparation and regeneration in cell engineering. The method comprises the following detailed operation steps of: (1) preparing a phomopasis asparagi conidium suspension; (2) preparing a fresh mycelium; (3) performing enzymolysis on mycelium cell walls; (4) separating the protoplast; and (5) regenerating the protoplast. The method is easy to operate, low in requirements on equipment and short in enzymolysis time and regeneration period, and effectively enhances the efficiency of preparation and regeneration of the protoplast.
Owner:VEGETABLE & FLOWER INST JIANGXI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Artificial culturing method for cicade flower
InactiveCN101225362AHigh pathogenicityLess susceptible to infectionFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroscopic observationBacterial strain
The invention discloses a culturing method of artificially cicada fungus, which comprises the following steps: (1) select original bacterial strains with fast growth speed, compact and chubby bacterial colonies and obvious angle distortion and separation in later culturing phase from the paecilomyces cicada bacterial strains in the nature reserves; the bacterial strains with the typical conidial production structure when observing the angle distortion using a microscope is the paecilomyces cicada heterokaryotic bacterial strains; (2) after culturing the paecilomyces cicada of the paecilomyces cicada heterokaryotic bacterial strains in culture media for a week, use the 0.05% tweenum 80 water to separate the conidia from the paecilomyces cicada spores in the inclined plane of the test tubes or culture dishes, and then dilute the conidia into the paecilomyces cicada spore liquid with the concentration being 1*10<6>-1*10<7> conidia / ml; put the infection bodies in the paecilomyces cicada spore liquid for infection and culture for two to three weeks with normal temperature of 20 to 28 DEG C to get cicada fungus. The culturing method of artificially cicada fungus has the advantages that: the method is simple and practical; infection bodies the same as the cicada fungus collected in natural mountain forests can be gotten; the method is endowed with market popularization value.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Rapid identification method for pathogenic fungi
The invention relates to a rapid identification method for pathogenic fungi, which specially comprises the following steps: (1) culturing fungi on a solid culture medium; (2) taking fresh fungi, and extracting the DNA of the fungi by using a microwave method; (3) amplifying DNA fragments between ribosomal spacers of the fungi by using ITS1 and ITS4 primers through PCR (polymerase chain reaction); (4) after recovering the PCR fragments, carrying out sequence determination on the fragments; and (5) carrying out comparison on the obtained sequences by using the Blast of NCBI. According to the invention, the identification of unknown pathogenic fungi can be performed within a shorter time and under relatively simple experimental conditions, thereby facilitating the rapid diagnosis for diseases occurring in fields so as to guide the prevention and control of diseases. According to the method, through the identification on 21 kinds of pathogenic fungi on different crops, and the coincidence rate is 100% through sequence comparison. The method is not only applicable to the identification on fresh mycelia, but also is applicable to the identification on conidium and sclerotium of pathogenic fungi, and has the characteristics of rapidness and high efficiency.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
High purity cnidicin and its preparation method and medicinal composition using said compound as active component
InactiveCN1724529AOptimizing the Extraction and Separation ProcessGood reproducibilityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryStability studyAcute toxicity testing
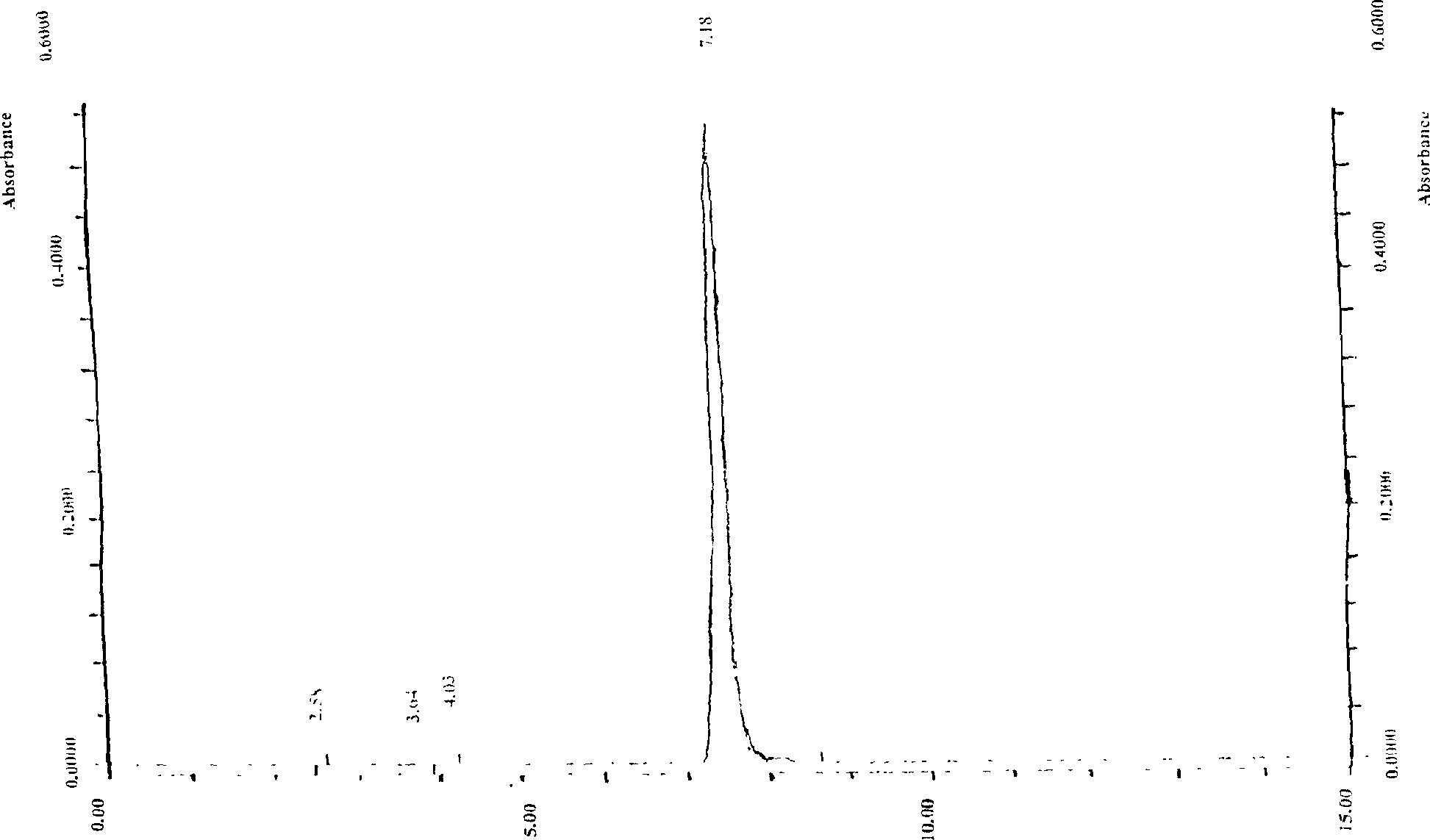
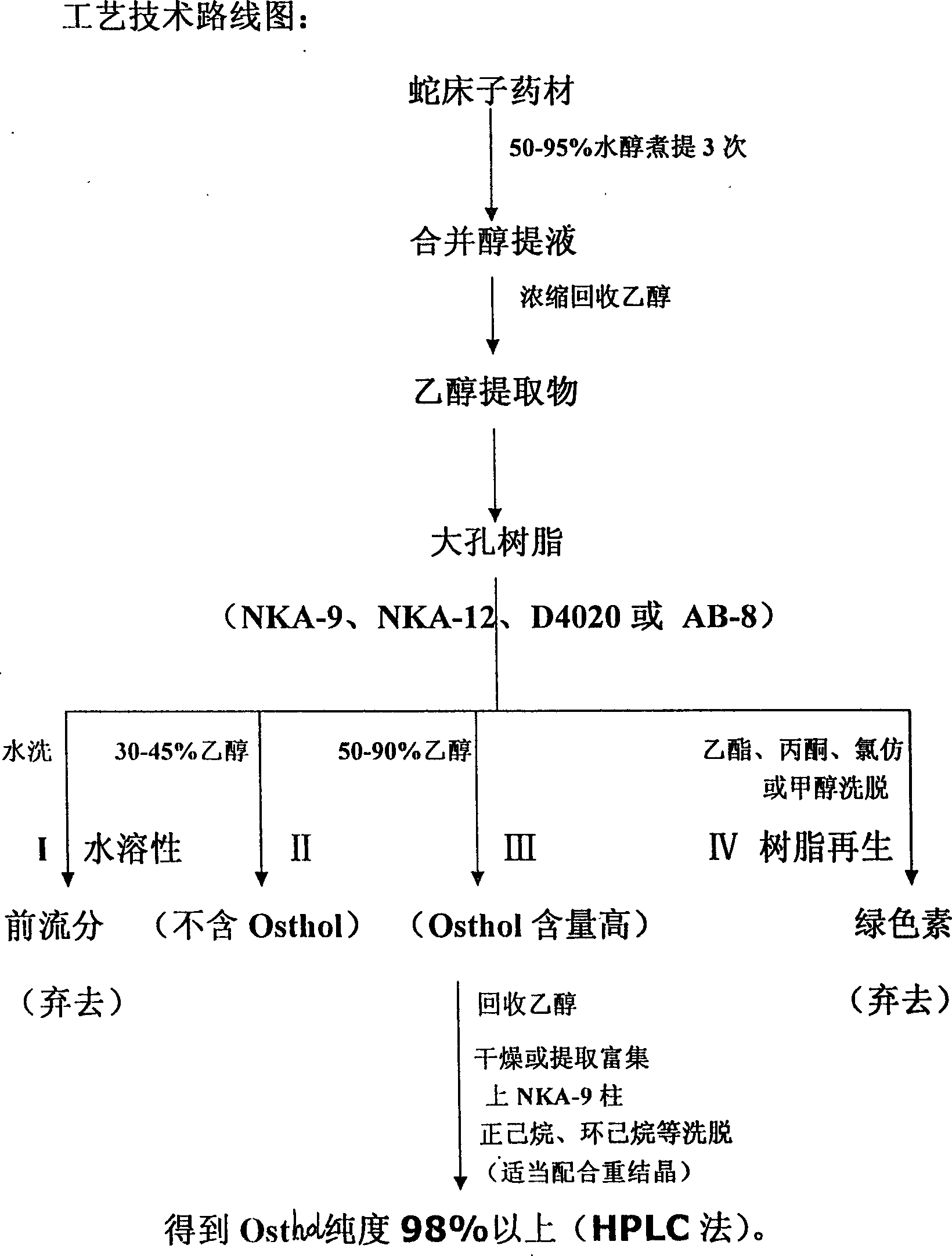
The invention discloses a high- purity of osthol, structure proof with spectral analysis, method for preparation, stability study, acute toxicity study, the drug compositions containing osthol, and new drug utilities of the natural product. By the technique steps of extracted Chinese pharmacy conidium fruit with alcohol, decolorizing and enriching by large-hole adsorption resin, and separating and purifying, it can prepare osthol with a purity of above 98%. The study expresses that the osthol has a clear utility of anti-cancer, anti-auto lymphoma, and so on.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
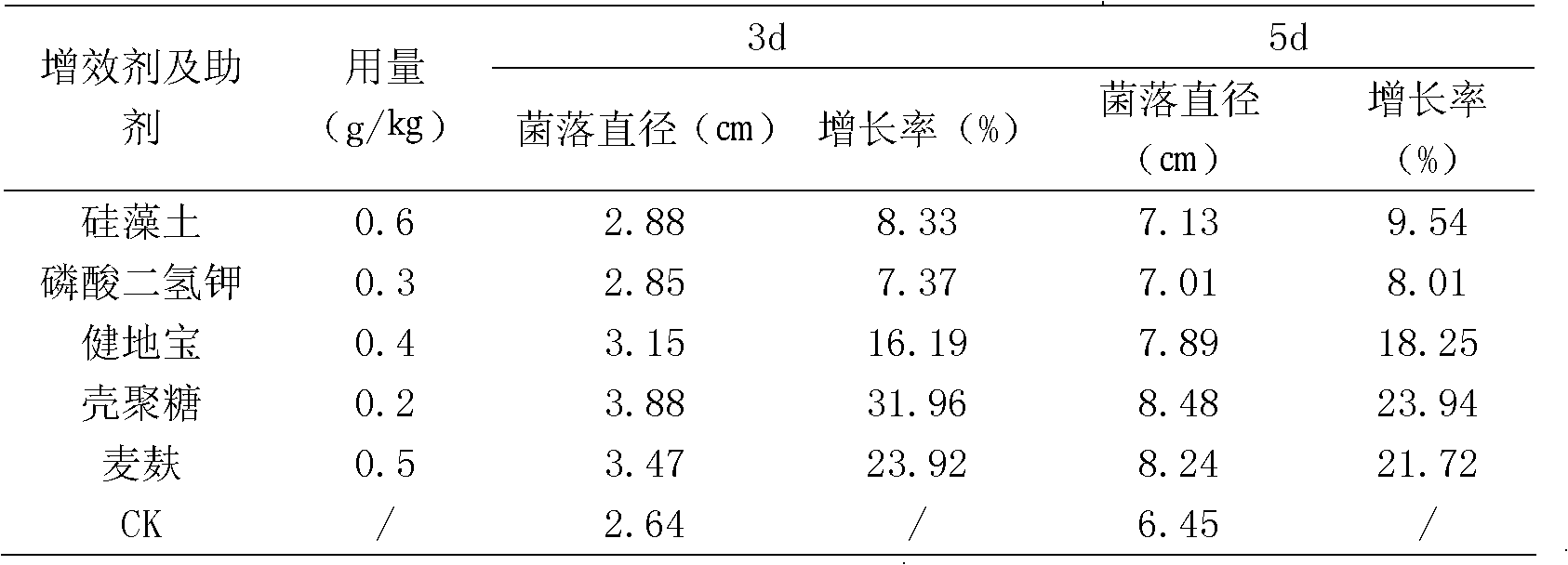
Method for preparing Trichderma bacteria conididium powder and use thereof
The invention discloses a manufacturing method and the application for a wood fungus conidium dust agent. It gains wood fungus from separating leaf of vegetables, purifying and transplanting to PDA test tube bevel to be used as mother fungus, adjusting temperature, pH value, and oxygen supplying quantity to produce spore liquid, and gaining large quantity of dry proofing conidium by adopting solid fermenting, mixing crashed condium and superfine diatomite to form wood fungus conidium dust agent. The method could be used to prevent vegetable producing.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV +1
Method for Encapsulation of Microparticles
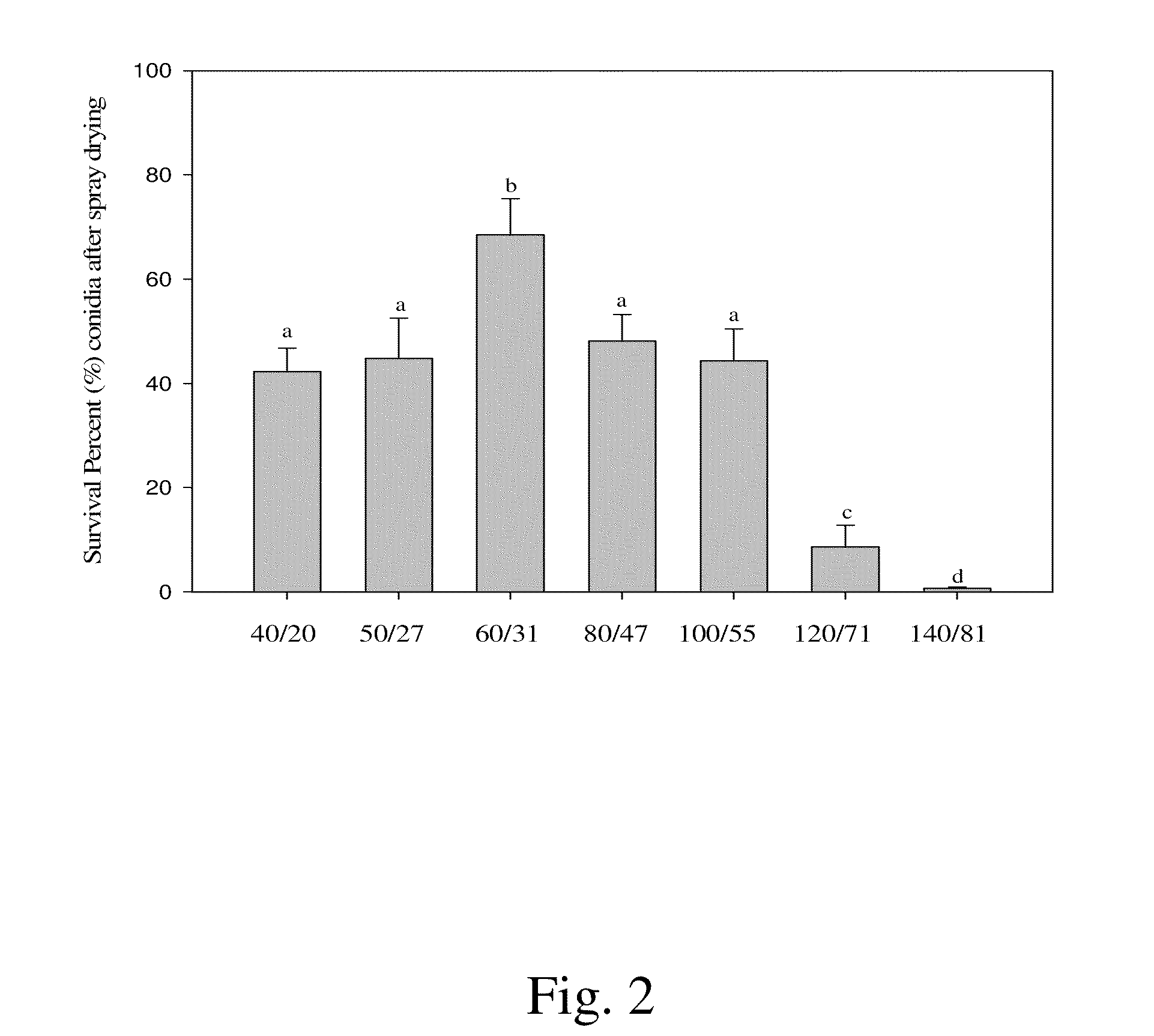
A method for encapsulation of microparticles (e.g., fungal conidia), involving (i) suspending microparticles in an aqueous solution containing at least one sugar to form an aqueous suspension wherein the concentration of said sugar is about 0.1 to 10% w / v, and (ii) spray drying said aqueous suspension with a spray dryer, wherein the inlet temperature of said spray dryer is about 40° C. to about 140° C. and the outlet temperature of said spray dryer is about 20° C. to about 80° C.
Owner:US SEC AGRI +1
Bacillus velenzensis and application thereof to biological control
ActiveCN111254086AGrowth inhibitionReduce diseasePlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyAMARANTHUS CAUDATUS SEED
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural microorganisms, in particular to Bacillus velenzensis and application thereof to biological control. The Bacillus velenzensis disclosed bythe invention is Bacillus velezensis Bv-6, and a preservation number is CCTCC NO:M20191106. The Bacillus velenzensis fermented solutions or powder can effectively inhibit growth of mycelia of important pathogens (Sclerotinia sclerotiorum(Lib.)de Bary, Botrytis cinerea Pers. and Blackleg) on rapes, and germination of conidiophores and ascospores; and through seed soaking treatment of the fermentedsolutions, the seeds of the rapes can be normally germinated and grown, and the edisease resistance of plants can be improved. In addition, the Bacillus velenzensis has the characteristics of being high in proliferation speed, high in stability, high in temperature resistance and free of toxicity. Therefore, the Bacillus velezensis strain Bv-6 has the potential of developing and utilizing the function of the biological control.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Water Dispersible Formulation for Delivery of Biocontrol Fungi to Reduce Aflatoxin
InactiveUS20090060965A1Prevention of aflatoxin contaminationAvoid contaminationBiocideEdible seed preservationWater dispersibleAspergillus flavus
A formulation containing conidia of non-toxigenic strains of fungi is a useful biocontrol agent for preventing toxin contamination in agricultural commodities, especially those for human and animal consumption such as peanuts, corn, cotton and tree nuts. The formulation of the invention is a water dispersible granule formulation suitable for spraying and includes non-toxigenic and / or non-aflatoxigenic Aspergillus flavus strains capable of inhibiting growth of fungi which produce aflatoxin and further capable of suppressing production of aflatoxin by the toxigenic fungi. A method of preparing the formulation is shown.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF AGRI THE
Method for preparing trichoderma fungicide
InactiveCN102676445ASolve pollutionSolve the problem of not being able to fully recycleMicroorganism based processesSpore processesBiotechnologySporeling
The invention discloses a method for preparing a trichoderma fungicide, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1) carrying out seed culture on trichoderma strains; 2) diluting the trichoderma seeds obtained in the step 1) by using sterile water so as to obtain a trichoderma spore suspension; 3) carrying out liquid state fermentation on the trichoderma spore suspension obtained in the step 2) so as to obtain liquid trichoderma fermentation broth; and 4) placing the liquid trichoderma fermentation broth obtained in the step 3) in a destarched potato residues solid medium to carry out solid state cultivation. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that: 1, according to the technical scheme provided by the invention, easy-to-take and cheap destarched potato residues are adopted for producing the trichoderma fungicide, therefore, the problems of high cost and complex formula and the like are solved, and the problem that potato residues cause environmental pollution and can not be fully recycled is also solved; and 2, according to the technical scheme provided by the invention, the number of produced trichoderma conidia can be as high as 3.2*1012 cfu / g substrates, and the spore production quantity is 100 times as large as that in the prior art, thereby improving the output capacity, and further saving the cost.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Early-flue-cured tobacco quality improving method with eurotium cristatum
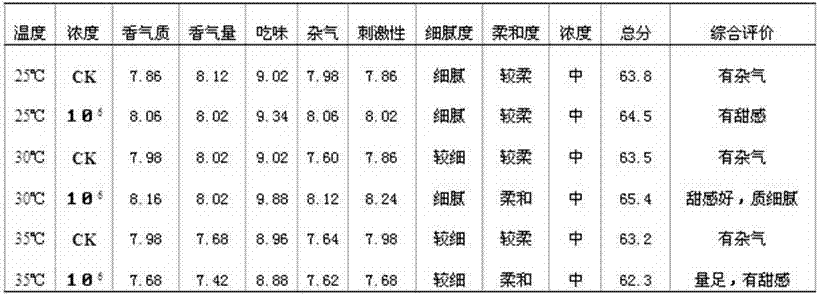
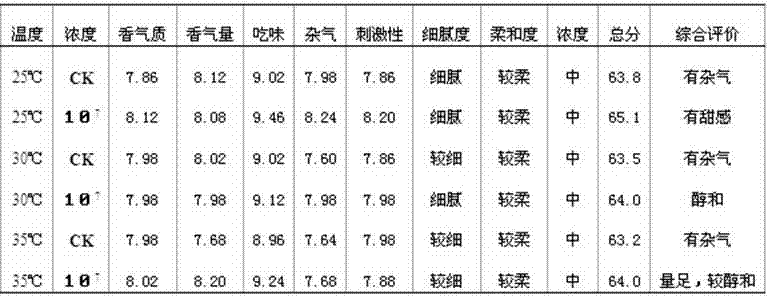
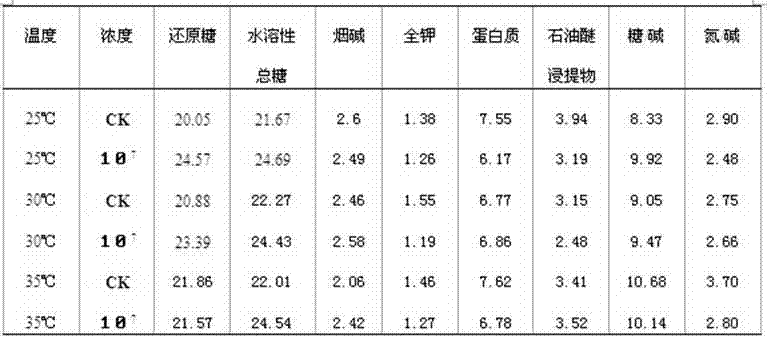
The invention discloses an early-flue-cured tobacco quality improving method with eurotium cristatum. The method comprises the steps that (1) the eurotium cristatum is cultured in an activation mode; (2) conidium bacterial colony culturing is carried out, a conidium bacterial colony culture medium is prepared and is formed into a flat plate, bacterial colonies of bacterial strain slopes from the step (1) are planted on the flat plate in a point mode and are cultured for 5-7 days in an inverting mode until the bacterial colonies overgrow on the flat plate; (3) spore suspension is prepared, conidium generated according to the step (2) is inoculated and is washed off with asepsis water and then is prepared to be the spore suspension which is used as inoculant to be evenly sprayed on early-flue-cured tobacco. When processing conditions are that culturing temperature is 30 DEG C and spore concentration is 106 and 107, aroma of the early-flue-cured tobacco becomes good, impurity odor and irritation are relieved, smoke sweet feeling is improved and is fine, pure and mild, after taste is pure and comfortable, nicotine is lowered, and whole tobacco quality is improved.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV +1
Trichoderma harzianum fermentation process, wettable powder and application thereof
ActiveCN105802863AGood control effectSignificant germination promoting effectBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyPlant disease
The invention relates to a Trichoderma harzianum fermentation process, wettable powder and application thereof and aims at solving the problems of high cost and poor plant disease and pest prevention and control effect when a Trichoderma harzianum strain is made into stable wettable powder.The Trichoderma harzianum fermentation process includes following steps: 1, selecting and treating raw materials; 2, preparing a Trichoderma harzianum solid-state fermentation culture medium; 3, fermenting Trichoderma harzianum.A preparation process of the wettable powder includes: mixing conidia powder obtained by Trichoderma harzianum fermentation, a wetting agent, a dispersant, a synergist X and a carrier well to obtain the wettable powder.The wettable powder has effect of promoting germination of tomato seeds and has remarkable effect on treating and controlling tomato powdery mildew, gray mold and leaf mold.The Trichoderma harzianum fermentation process and the wettable powder are used for promoting germination of the tomato seeds and preventing and controlling tomato diseases and pests.
Owner:黑龙江省加垄农业技术开发有限公司
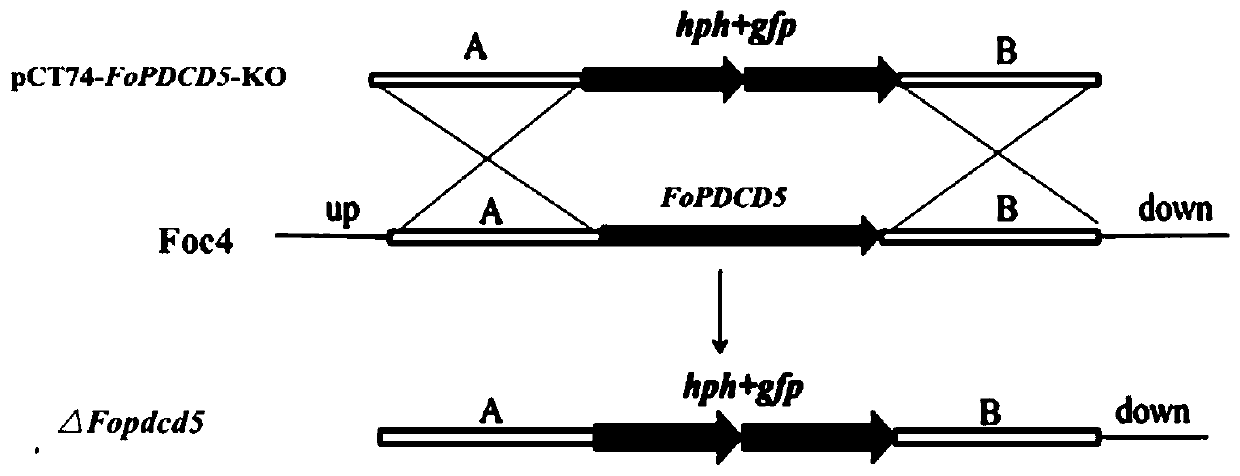
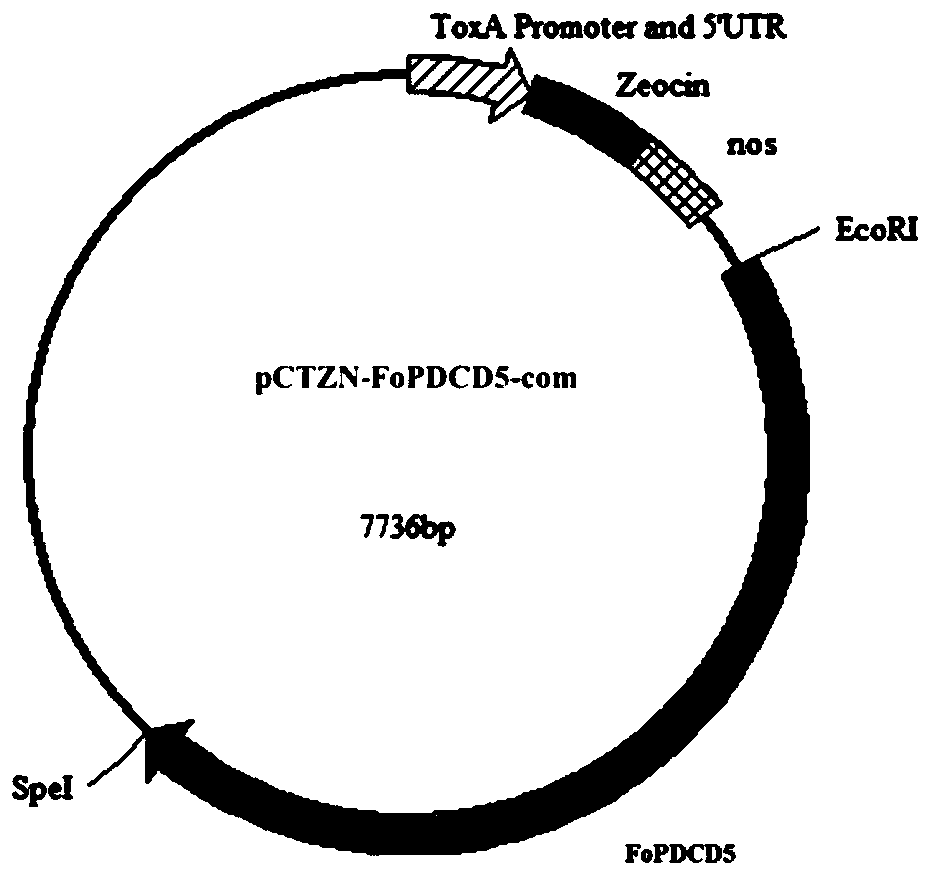
Application of gene FoPDCD5 (Program Cell Death Protein 5) to regulation of pathogenicity of fusarium oxysporum
ActiveCN110669773AReduce pathogenicityIn-depth elucidation of pathogenic molecular mechanismsBiocideFungicidesBiotechnologyWild type
The invention discloses application of a gene FoPDCD5 (Program Cell Death Protein 5) to regulation of pathogenicity of fusarium oxysporum, and belongs to the field of plant genetic engineering. According to the application of the gene FoPDCD5 to regulation of the pathogenicity of the fusarium oxysporum, the gene is knocked out from the fusarium oxysporum by a homologous recombination method, and aknockout mutant [delta]Fopdcd5 is obtained; by constructing a gene complement vector, the gene complement vector is introduced into a [delta]Fopdcd5 protoplast; and by using a method of random insertion, the gene is completed into the knockout mutant, a complement mutant [delta]Fopdcd5-com is obtained. A pathogenicity test shows that pathogenicity of the knockout mutant [delta]Fopdcd5 is significantly reduced; and pathogenicity of the complement mutant [delta]Fopdcd5-com is restored to a wild-type level. The application of the gene FoPDCD5 to regulation of the pathogenicity of the fusarium oxysporum proves that the FoPDCD5 is necessary for production of conidia of the fusarium oxysporum and response to oxidative stress and pathogenicity. The application is helpful to elucidate a pathopoiesia molecular mechanism of the fusarium oxysporum thoroughly, and target genes are provided for development of effective fungicides.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Trichoderma hamatum biological agent for controlling soil borne disease for greenhouse vegetable cultivation
ActiveCN102499265APromote growthImprove field control effectPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyDisease
The invention relates to a biological agent, in particular to a trichoderma hamatum biological agent for controlling soil borne disease for greenhouse vegetable cultivation. The biological agent is prepared through the following steps: preparing trichoderma hamatum enlarging culture; preparing trichoderma hamatum seed fermentation liquor; preparing solid fermentation culture medium; preparing trichoderma hamatum fermentations; smashing the trichoderma hamatum fermentations obtained through the step d and wheat bran respectively before use and sieving through a sieve of 60 to 80 meshes; mixingthe raw materials obtained through the step e with bergmeal, chitosan, potassium dihydrogen phosphate and biochemical fulvic acid, stirring uniformly and mixing completely to obtain jade-green powder, and determining that the content of conidiospore is 108 per gram, thereby obtaining the product. The product provided by the invention can not only effectively control soil borne disease for greenhouse vegetable cultivation but also can improve soil, is pollution-free and nuisanceless, can activate soil, has a wide range of application, and can improve the microenvironment of soil as well as induce and improve broad spectrum resistance of crops so as to promote growing of the crops.
Owner:NINGXIA ACADEMY OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Production of insect-proof sick wooden mold and its use
Production of anti-insect and disease-proof mold and its use are disclosed. The process includes taking hamycin, Agrobacterium tumefaciens AGL-1 and gene plasmid pPBH with thuricin bacillosporin stored in normal way, preparing conidiospore suspension, converting the obtained tumefaciens and pPBH plasmid, activation culturing, culturing the activated fungus liquid of conidiospore suspension, tumefaciens and pPBH plasmid mutually, converting, screening and purifying. It can be used to prepare anti-insect and disease-proof mold and insect prevention of plant.
Owner:杨谦
Method for cultivating morchella single-spore strains by adopting 'artificial pollination'
ActiveCN106416751AEfficient formationGood for fruitingCultivating equipmentsPlant genotype modificationSporePollen
The invention belongs to the field of morchella cultivation and relates to a method for cultivating morchella single-spore strains by adopting 'artificial pollination'. The method promotes efficient formation of XY types of hyphae, facilitates final fruiting and plays the effects of improving the cultivation efficiency and increasing the yield. The cultivating method comprises the steps that (A) strain preparation is performed; (B) an X type of strains are sowed; (C) a Y type of spores produce pollen; (D) artificial pollination is performed; (E) management and harvesting are performed and the like. According to the method, a concept and a method of 'artificial pollination' are introduce to the edible fungi cultivation field, the Y type of microgonidium spores is fertilized to the X type of hyphae, strain hybridization is achieved, and the novel cultivation method is provided for morchella hybridization and crossbreeding.
Owner:四川省食用菌研究所
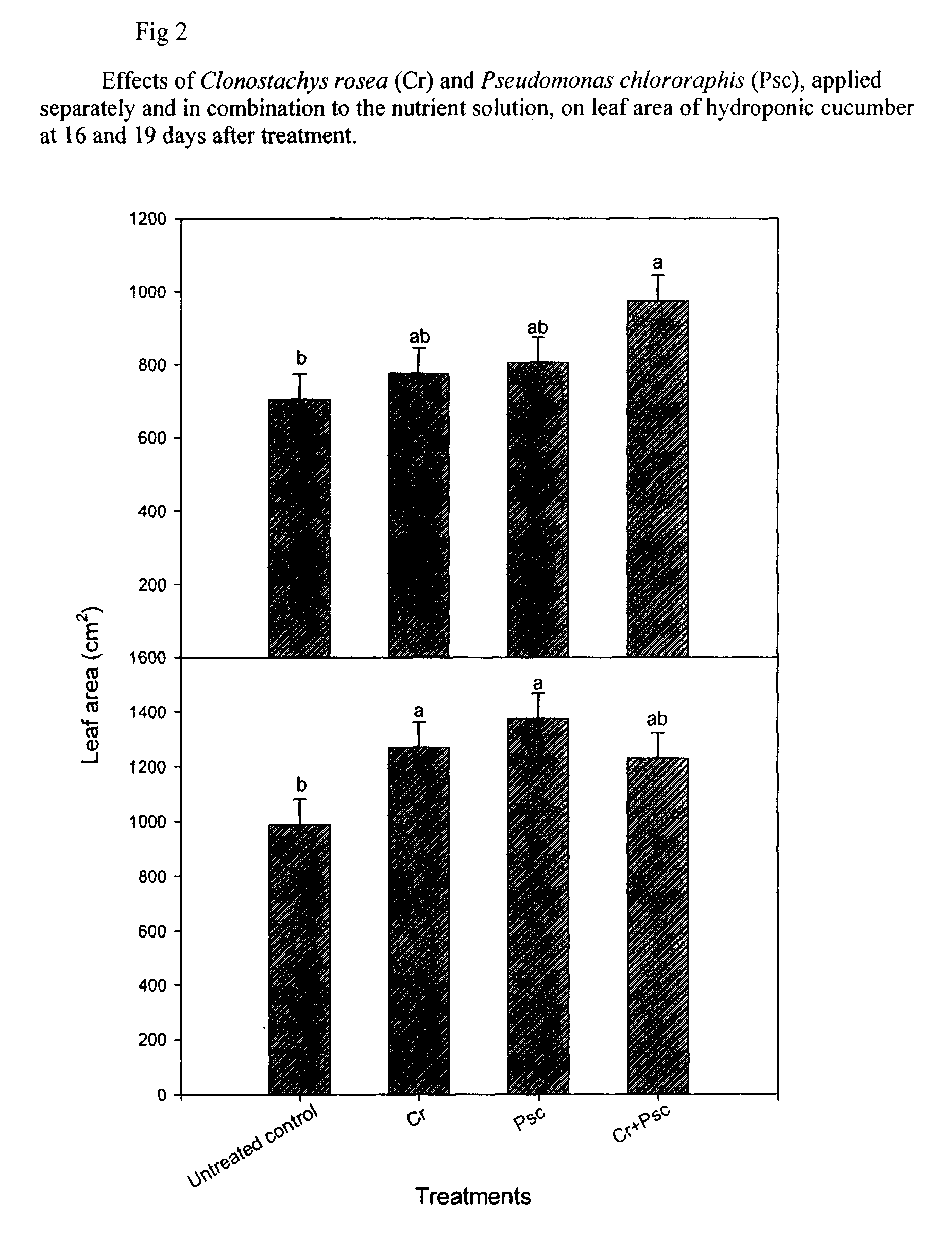
Clonostachys rosea Inoculated Plant Materials with Fungicides and Adjuvants
ActiveUS20160007613A1Reduce the environmentReduction of worker exposureBiocideBryophytesAdjuvantFungal endophyte
Clonostachys rosea strains have novel usefulness as inoculants of plants promoting plant vigor, health, growth, yield and a reduction of competitive stress caused by other fungi when used alone or sequentially with many fungicides in an integrated pest management system (IPM). Seed and foliar uses are shown to inoculate and subsequently achieve endophytic colonization of the portion of the plant treated. While the germinating conidia of this organism has been shown to tolerate several fungicide groups, the established mycelium of Clonostachys rosea is significantly more tolerant to systemic fungicides facilitating use in seed and foliar applications. Seed treatment and colonization may occur at any time after harvest resulting in endophyte enhanced seed that ignores or is marginally altered by other fungal organisms and may be suitable for Feed, Food and Seed uses.
Owner:ADJUVANTS PLUS USA
Culture method of sclerotium of beauveria bassiana and application thereof
Aiming at the defects of conidiospores as propagula of an insecticide of insect pathogenic fungi, the invention provides a technology of liquid culture of entomogenous fungus sclerotia, and the entomogenous fungus can be beauveria bassiana. The liquid culture method of entomogenous fungus sclerotia provided by the invention is required to control the liquid culture components and the culture conditions within a certain range. The cultured sclerotia can be stored for a long time after vacuum drying, and can still germinate mycelia and pathogenic conidiospores under suitable conditions. The micro-sclerotia prepared by drying have maintained activity, can germinate mycelia and spores after rehydration, and increase the potential of beauveria bassiana as a biocontrol factor for western flowerthrips in a soil-dwelling phase. The technology has low cost, long storage period of sclerotia, and is quite suitable for popularization.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Isaria fumosorosea conidia wettable powder and application thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of biological control of insect pests and particularly discloses isaria fumosorosea conidia wettable powder. The isaria fumosorosea conidia wettable powder is prepared from the following components in percentage by weight: 15-25% of conidia pure spore powder of isaria fumosorosea conidia IfB01, 1-5% of a wetting agent, 5-10% of a dispersant, 0.5-1.5% of an ultraviolet protective agent, 1-3% of a stabilizer and 60-74% of a carrier, wherein the carrier is white carbon black. The wettable powder can be used for preventing and treating bemisia tabaci and according to the indoor toxicity, the medial lethal concentration LC50 on the 13th day of treatment is 0.04*10<6> spores / mL while that of the pure spore powder is 0.07*10<6> spores / mL; the half lethal time LT50 when the concentration is 1*10<6> spore / mL is 8.76 days while that of the pure spore powder is 9.25 days. Treated by 2*10<7> spore / mL, for bemisia tabaci on tomatoes and cabbage mustards treated on the 14th days, the field control efficiencies are respectively 82.73% and 66.58% which are remarkably higher than those of other treatment.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Cultivation method and use of Bacillus foecalis alkaligenes from sea
InactiveCN101481671AInhibition of germinationReduced germination rateBiocideBacteriaHyphaHyphomycetes
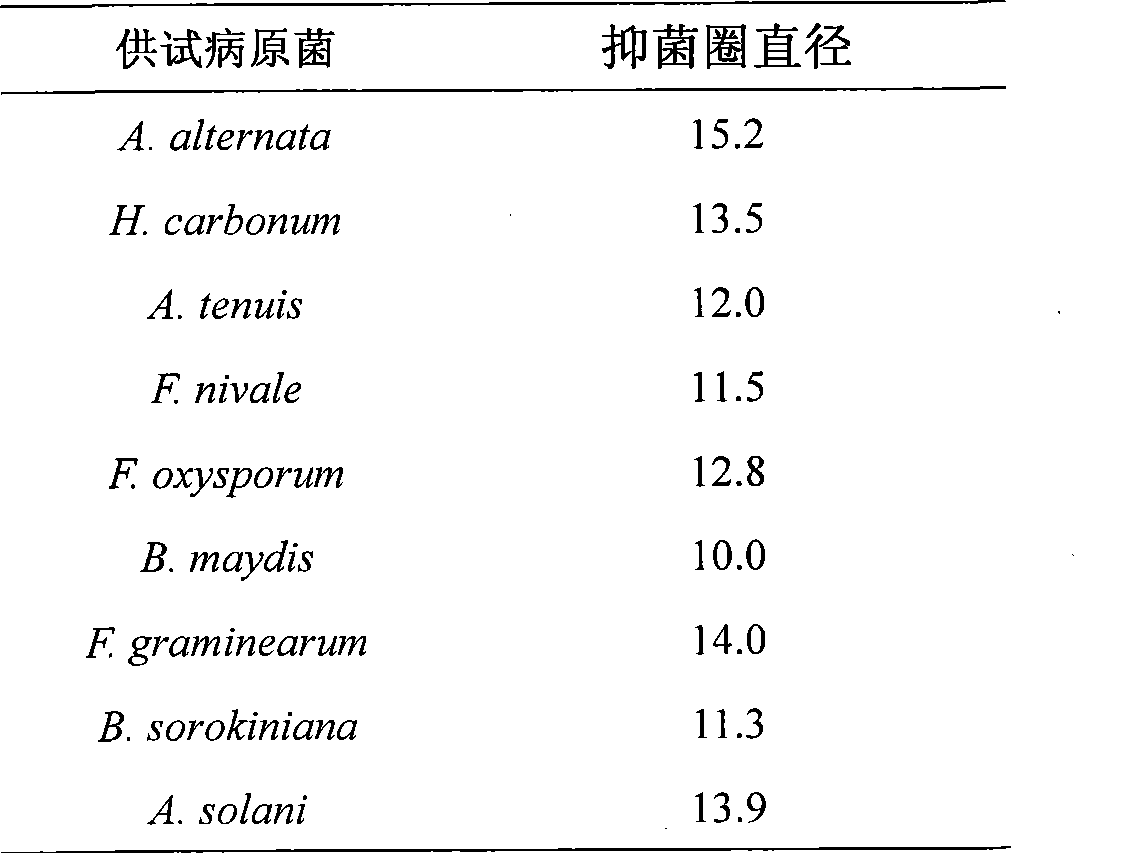
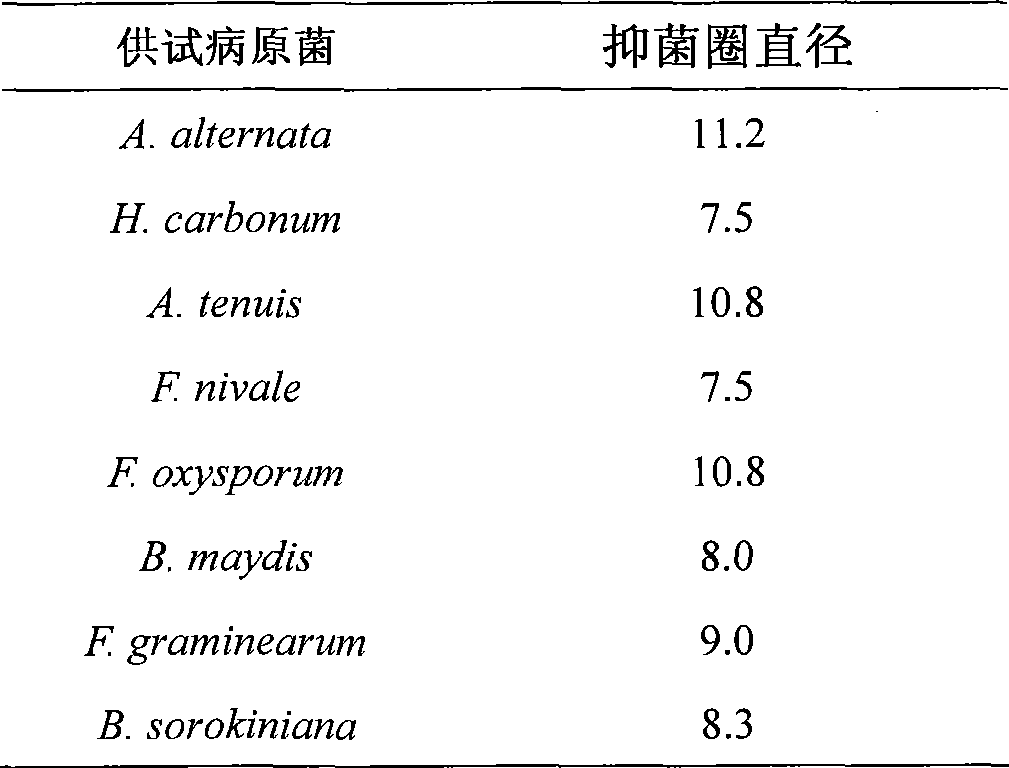
The invention relates to a culture method for Alcaligenes faecalis strain KZJ01 from oceans, characterized in that the Alcaligenes faecalis strain KZJ01 is obtained by the steps of enrichment culture, separation of strains, purification of strains, sieving of strains, authentication of strains and the like. The Alcaligenes faecalis strain KZJ01 obtained by the inventive culture method has the effect of inhibiting the growth of hypha of 9 plant pathogenic fungi and of inhibiting the germination of conidia of 2 plant pathogenic fungi therein.
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH
Method for producing liquid strain of cordyceps militaris
InactiveCN101861794AEase of evaluationEasy to controlHorticultureDipotassium phosphateMonopotassium phosphate
The invention provides a method for producing the liquid strain of cordyceps militaris. The method comprises the following steps: (1) inoculating the mother culture of cordyceps militaris to a dedicated strain culture medium to carry out the shaking culture; (2) moving the strain solution cultured in step (1) into a dedicated strain culture medium to carry out the amplification culture, wherein the inoculation amount accounts for 2% to 20% of the volume of the culture medium; (3) filtering the strain solution cultured in step (2) by using a sieve with the bore diameter thereof being 50 to 500 meshes to obtain the filtrate containing more than 107 conidia per ml; and (4) diluting the filtrate obtained in step (3) by using sterile water until the density thereof is 105 to 107 conidia per ml to obtain the liquid strain of cordyceps militaris. The method of the invention is applicable to inoculating and cultivating the fruit body of cordyceps militaris, wherein the dedicated strain culture medium contains carbon source, yeast nitrogen base, magnesium sulfate, monopotassium phosphate, dipotassium phosphate and agar.
Owner:和润通(重庆)供应链管理有限责任公司
Artificial preparation method of white muscardine silkworms
The invention discloses an artificial preparation method of white muscardine silkworms. The method includes the steps of 1, preparation of beauveria bassiana spore liquid, wherein white muscardine silkworm bodies are soaked and cleaned with sterile water, filtrate is obtained after filtering is completed, and the beauveria bassiana spore liquid is obtained after primary slant culture, secondary slant culture and tertiary slant culture; 2, pathogen toxin counteracting, wherein the beauveria bassiana spore liquid is rapidly sprayed to the silkworm bodies of 5-day-old or older silkworms within 45 min after the beauveria bassiana spore liquid is prepared, and a silkworm room is sealed for 1-1.5 h after the beauveria bassiana spore liquid is sprayed; 3, silkworm body culture, wherein the silkworm room is opened, the silkworm bodies are fed, and the silkworm bodies are fed once every other 3-4 h till the silkworm bodies die; 4, white muscardine silkworm culture, wherein the dead silkworm bodies are transferred to a silkworm rearing bed, the silkworm bodies continue to be cultured under the condition that the temperature is 25-28 DEG C and the humidity is 95-98% till the silkworm bodies are fossilized, and white mycelium conidia grow out; 5, preparation of the finished white muscardine silkworms, wherein white muscardine silkworms with the white mycelium conidia growing out are collected and then dried till the water content is smaller than 10%, and the finished white muscardine silkworms are obtained. The preparation period of the finished white muscardine silkworms is short, and the yield and quality are high.
Owner:SICHUAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI SERICULTURE INST +1
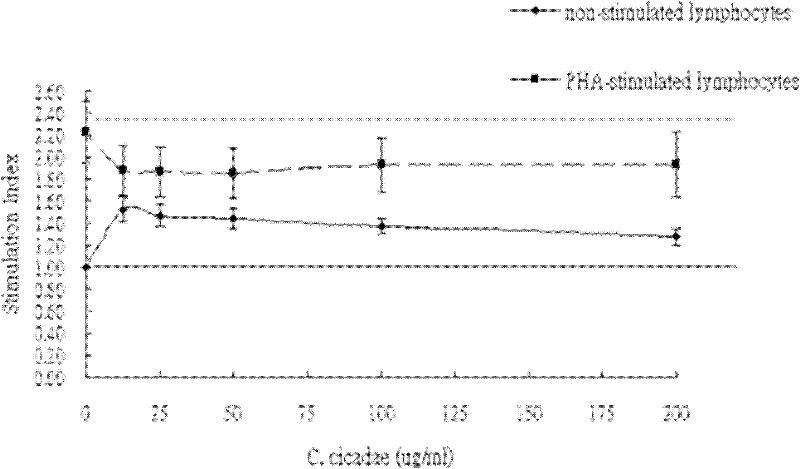
Medium for producing Paecilomyces cicadae spore, culture method thereof, culture product thereof and application thereof
ActiveCN102242079ASolve the problem of excess residueImmunomodulatoryCosmetic preparationsBiocideBiotechnologyLiquid medium
The invention belongs to the technical field of microbial fermentation, and specifically relates to media for producing Paecilomyces cicadae conidiospores, a culture method thereof, a culture product thereof and application thereof. The media for producing Paecilomyces cicadae conidiospores comprise a solid medium and a liquid medium. The culture method provided in the invention can produce considerable Paecilomyces cicadae conidiospores; the culture product of the method comprises components like polysaccharides, cordycepic acid, adenosine, triterpenoids and a plurality of amino acids, has the functions of regulating immunity, relieving fever and pain, improving renal function, lowering blood pressure, resisting radiation and tumor, reducing blood sugar, etc., and is applicable to the field of human healthy life; considerable spores are generated in the process of fermentation and the generated spores can be used as effective means of biological control, thereby solving the problem that the amount pesticide residues in agricultural products exceed the standard amount from the head stream.
Owner:ZHEJIANG BIOASIA PHARMA CO LTD
Single spore isolation method of fusarium oxysporum
The invention discloses a single spore isolation method of fusarium oxysporum. According to the method, a special spore spreading filament is adopted, and single conidia are directly separated from a conventional flat plate bacterial colony of fusarium oxysporum and are cultured to form a fusarium oxysporum strain with a single genetic composition. The single spore isolated culture method comprises the following implementation operation steps: (1) preparing a fusarium oxysporum spore-producing bacterial colony; (2) preparing spore spreading filaments; (3) preparing a spore spreading plate; (4) spreading conidia; (5) searching for monospores through microscopic examination; (6) cutting small square blocks loaded with single spores; and (7) forming a monospore isolated strain. The method has the following advantages: (1) a key appliance for separating spores is simple and easy to manufacture, and the separation operation is simple and easy; (2) the separation work consumes less time and labor; and (3) the working efficiency of fusarium oxysporum separation and the reliability of the separation result can be obviously improved.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Culture and preparation method for pyricularia oryza conidia
PendingCN105861412AReduced Chances of ContaminationSimple operation techniqueSpore processesSporeOryza
The invention discloses a culture and preparation method for pyricularia oryza conidia. According to the method, the multi-starting-point culture technology and the aerial mycelium conidium production technology are utilized for fast culturing and preparing the pyricularia oryza conidia. The method comprises the following implementation steps that 1, a conidium production culture medium is prepared; 2, a multi-starting-point transplanting thallus is prepared; 3, the multi-starting-point transplanting thallus is planted in a culture plate; 4, the conidia are prepared and cultured; 5, the conidia are eluted and separated. The method has the advantages that fastness and high efficiency are achieved, and conidia of a new generation can reach the ideal state of a high sporulation quantity after five days of culture usually; sterile operation can be kept in the whole culture process, and the contamination probability of a finished conidium solution is greatly reduced; the operation technology is simple, and the result sporulation quantity is large.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com