Rapid identification method for pathogenic fungi
A technology of pathogenic fungi and fungi, which is applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, and microbial measurement/inspection, can solve the problems of high reagent and labor costs, long time-consuming, and many fungal hyphae, etc., to save time and cost Low, easy-to-operate effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] A method for rapidly identifying pathogenic fungi, specifically comprising the steps of:
[0036] (1) Cultivate the fungus to be identified: inoculate the fungus to be identified on PDA medium, and culture in dark at 28°C until the colony grows to 2-3 cm to obtain fungal mycelium.
[0037] (2) DNA extraction of fungi by microwave method: use an inoculation needle to take 2 mg of fresh mycelium (that is, the above-mentioned fungal mycelium) grown on PDA medium into a sterilized 1.5ml centrifuge tube, add 1×TE buffer After oscillating for a few seconds, place in a microwave oven, microwave at 750W for 2 minutes, take it out and put it on ice for 7 minutes, then centrifuge (10000rpm, 1.5min) and transfer the supernatant to a fresh centrifuge tube In the process, the fungal DNA extract was obtained.
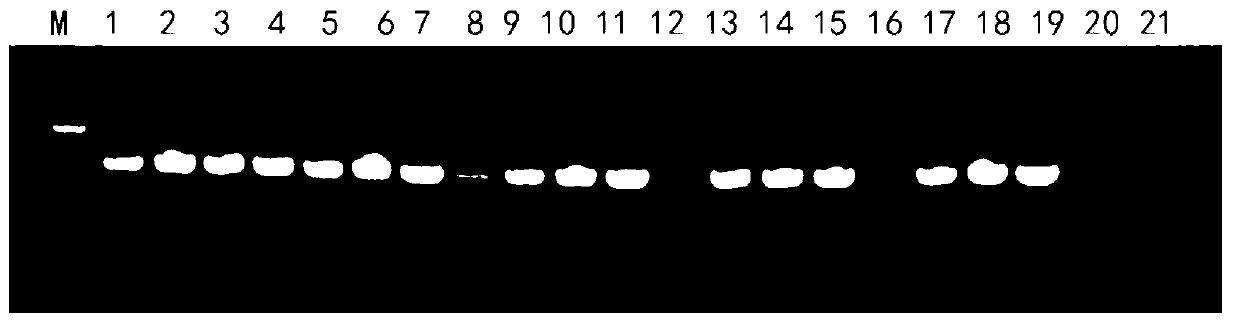
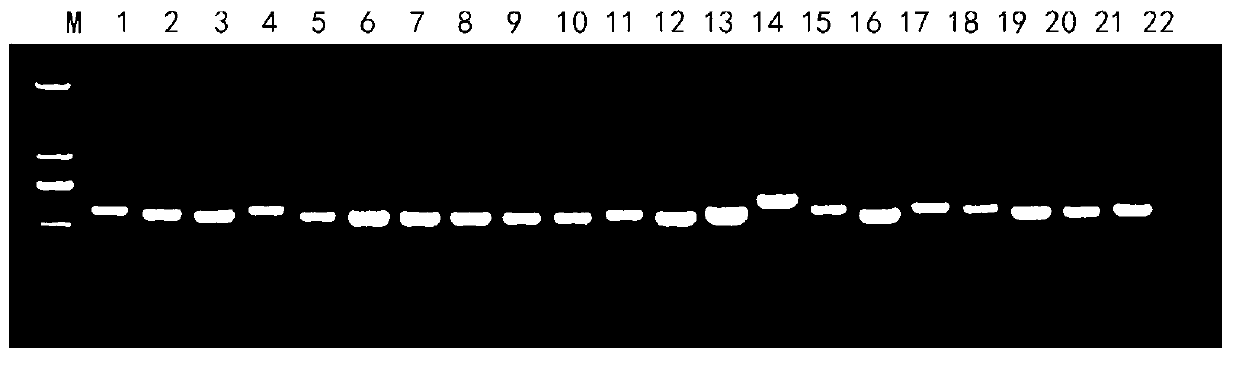
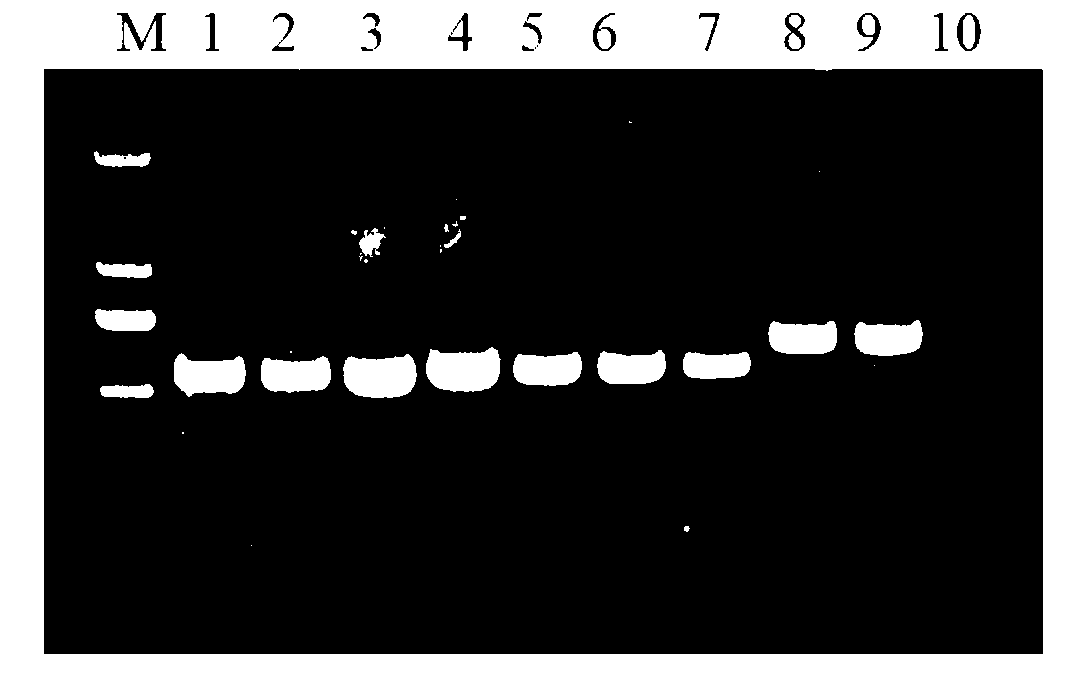
[0038] (3) Use fungal universal primers ITS1 and ITS4 to perform PCR amplification on the fungal DNA extract. The PCR amplification system is: 10×Taq buffer 2 μl, 10 pmol of ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] The identification objects in this example include fungal hyphae (mycelium of fungi), sclerotia and conidia, including three main steps of extraction of fungal DNA, amplification of specific PCR fragments, and sequence determination of amplified fragments.
[0050] A method for quickly identifying pathogenic fungi, the specific operation steps are roughly the same as in Example 1, the difference is: (1) Cultivate the fungi to be identified: Aspergillus flavus, Pyrophyllum, Alternaria, Fusarium and white silk fungus were respectively inoculated on PDA medium, cultured in dark at 28°C for 1 to 4 days, until the colony grew to 2-3cm, and Aspergillus flavus, Pyrophyllum, Alternaria, Fusarium and The hyphae of white silk fungus (i.e. fungal mycelium); at the same time, inoculate peanut white silk fungus on PDA medium and culture it in dark at 28°C until 10d to obtain the sclerotium of peanut white silk fungus; Culture medium (CZA) medium was cultivated in the dark at 28°C fo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com