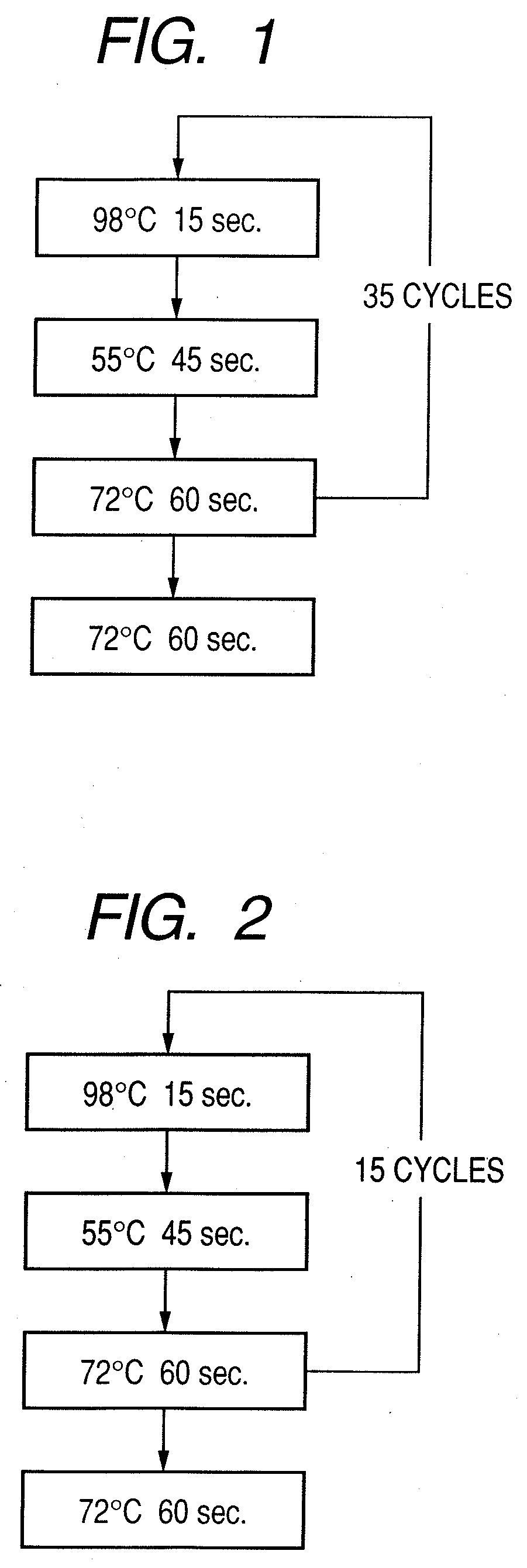
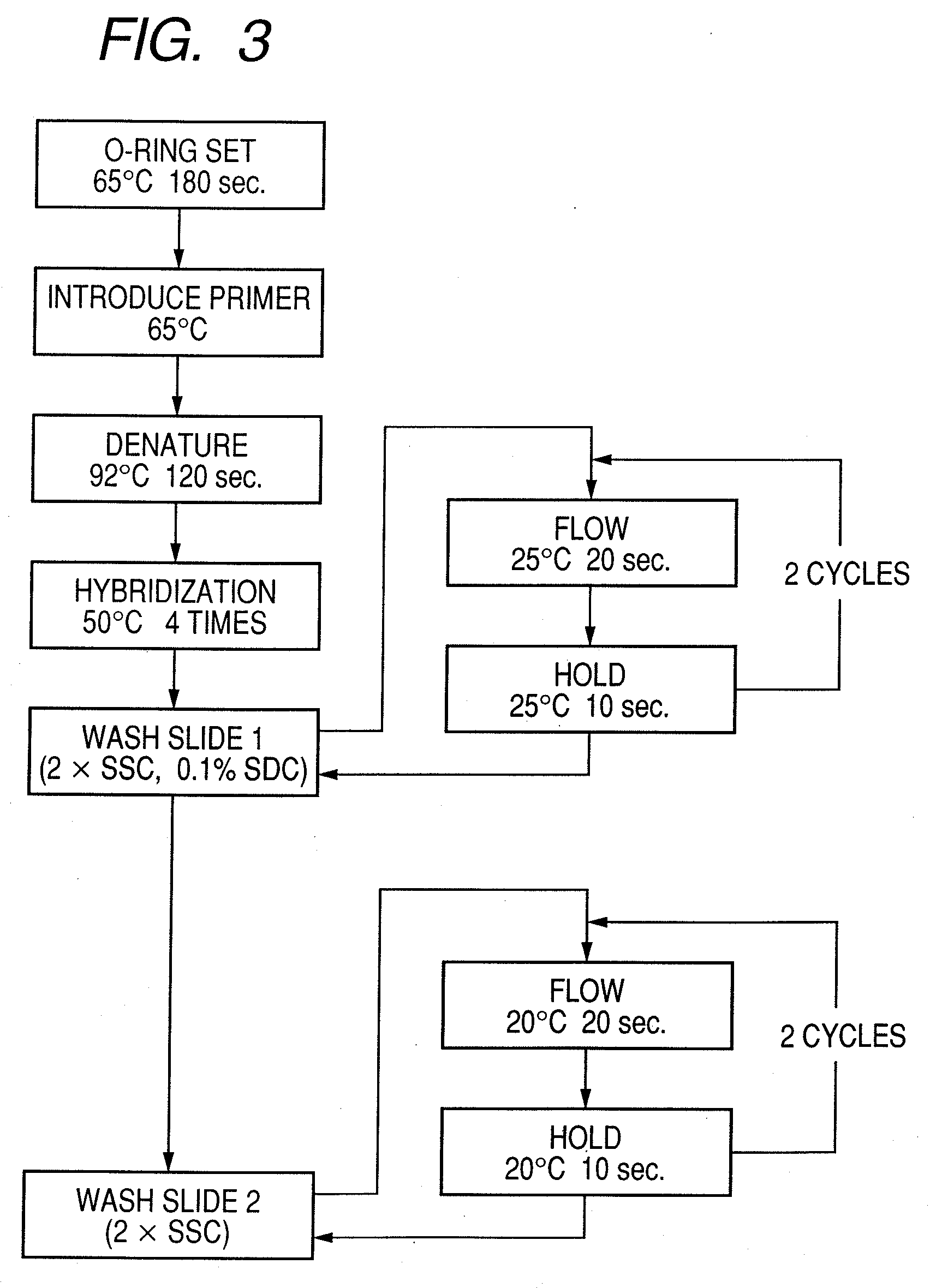
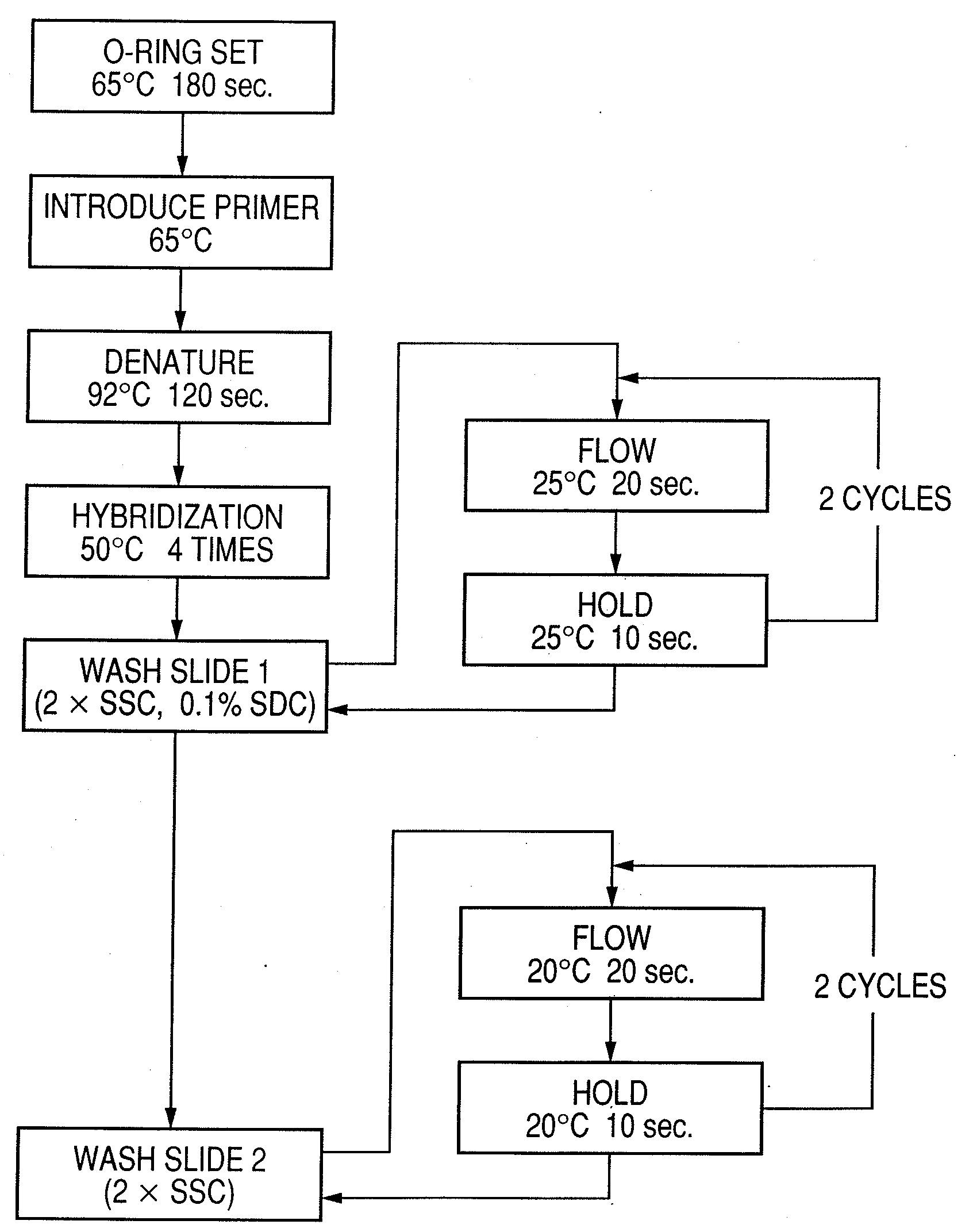
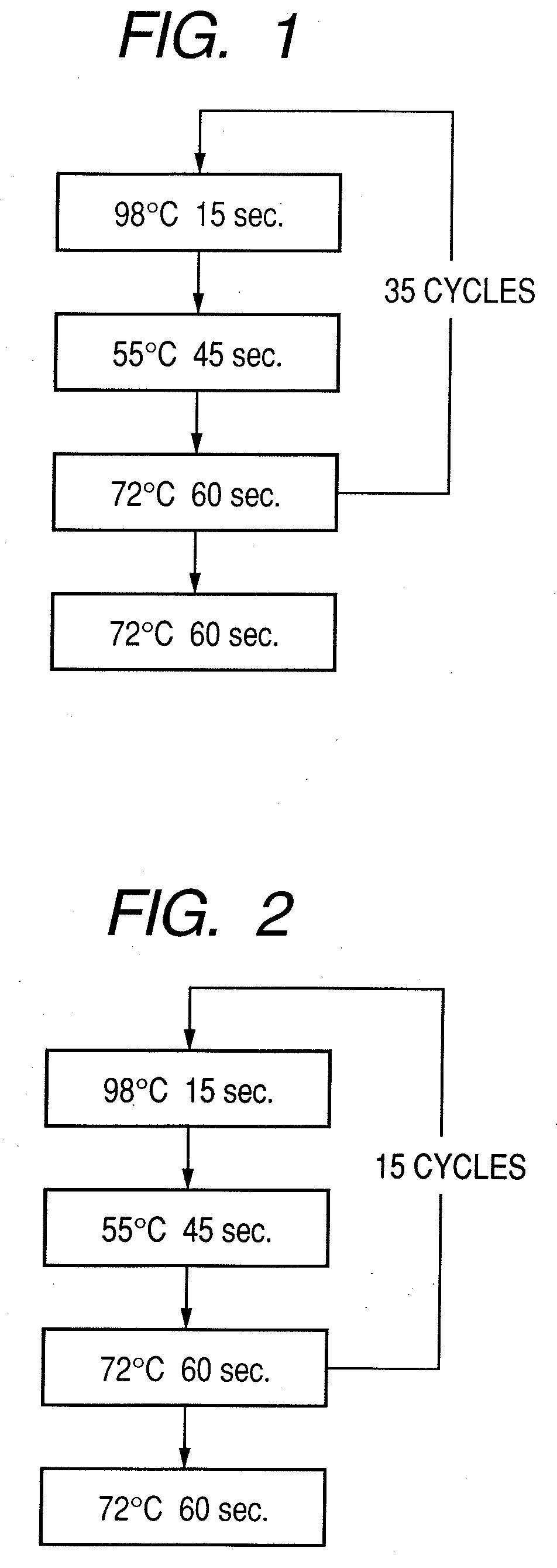
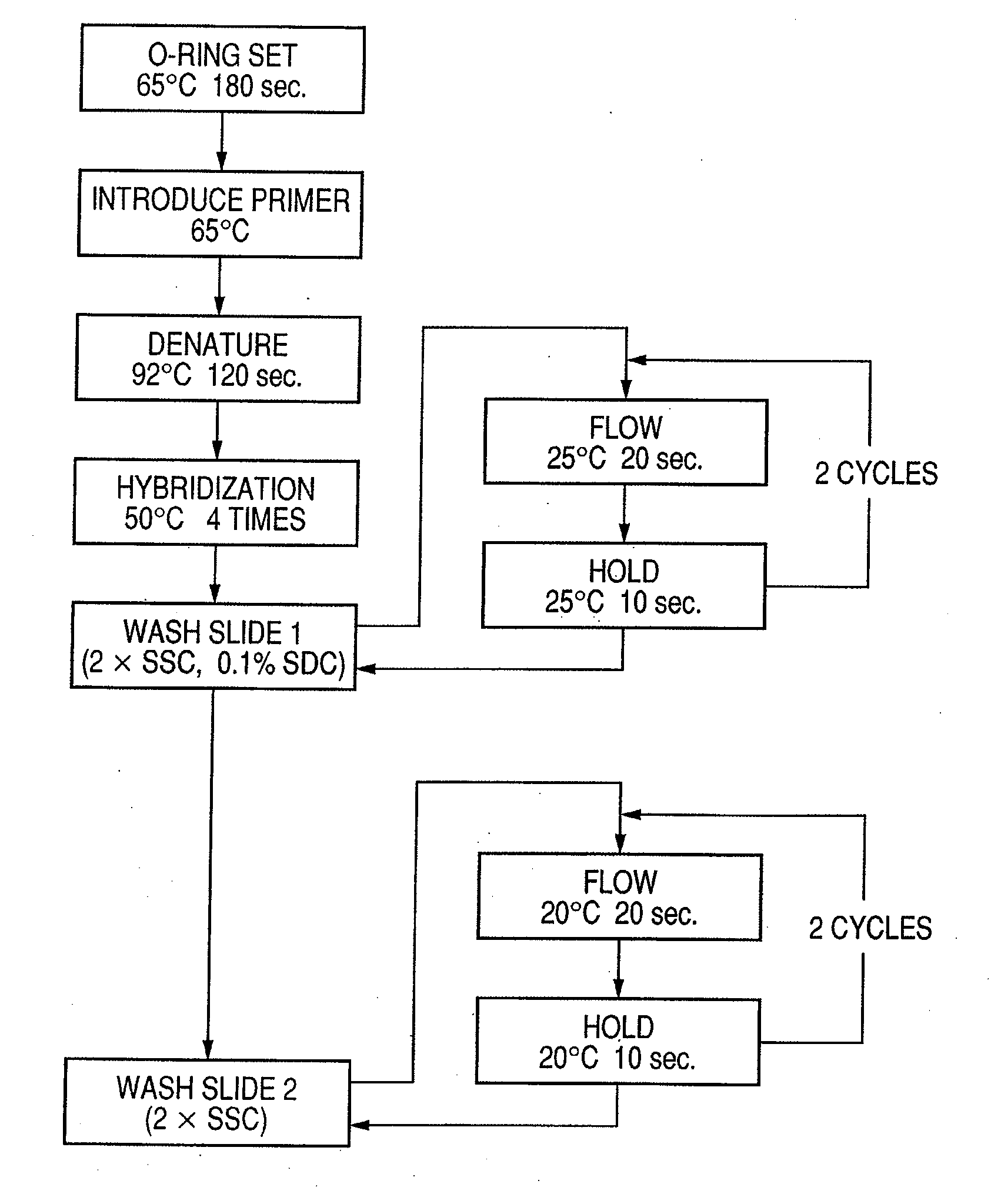
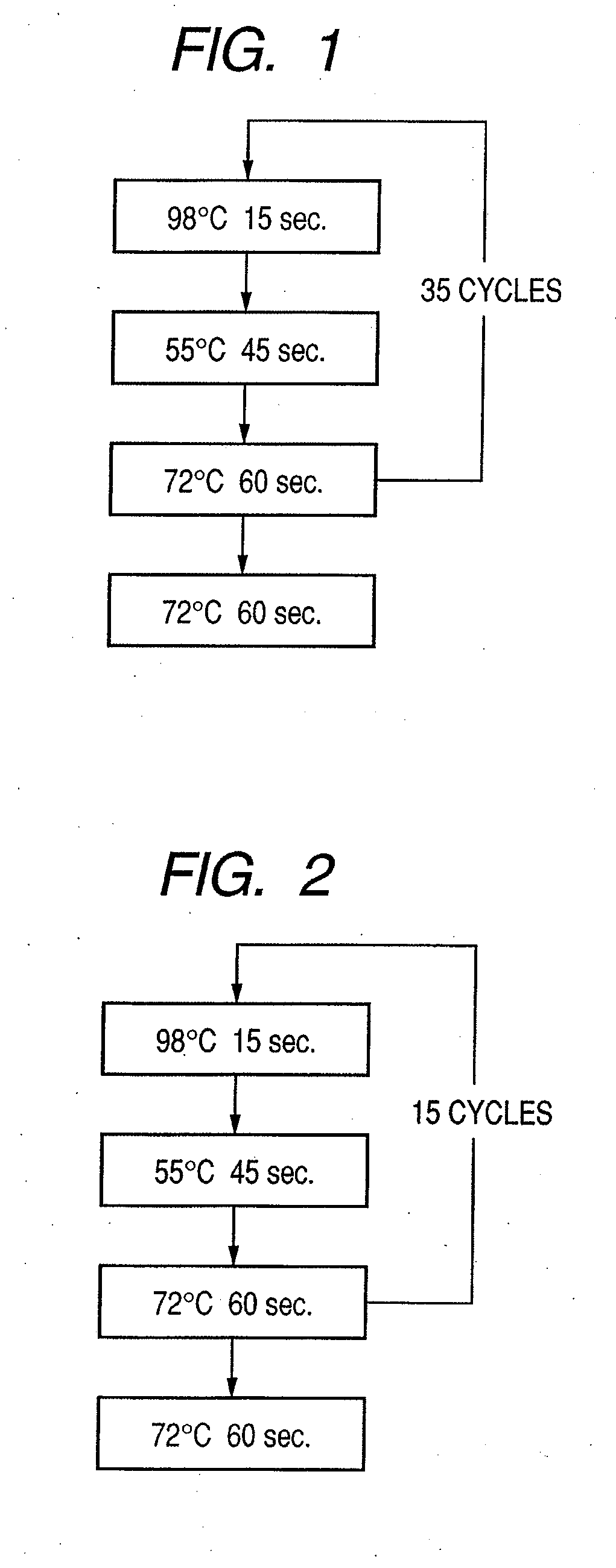
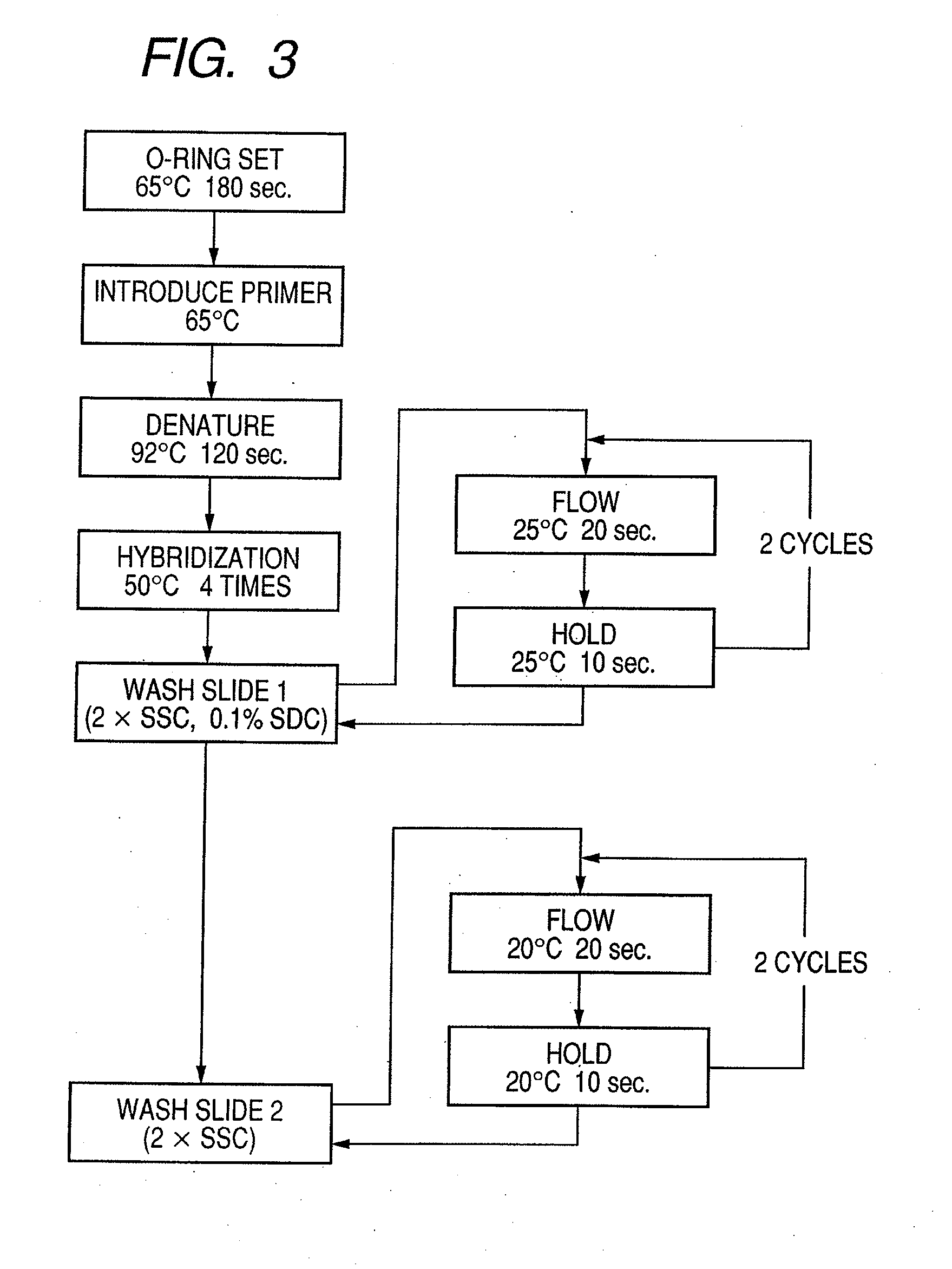
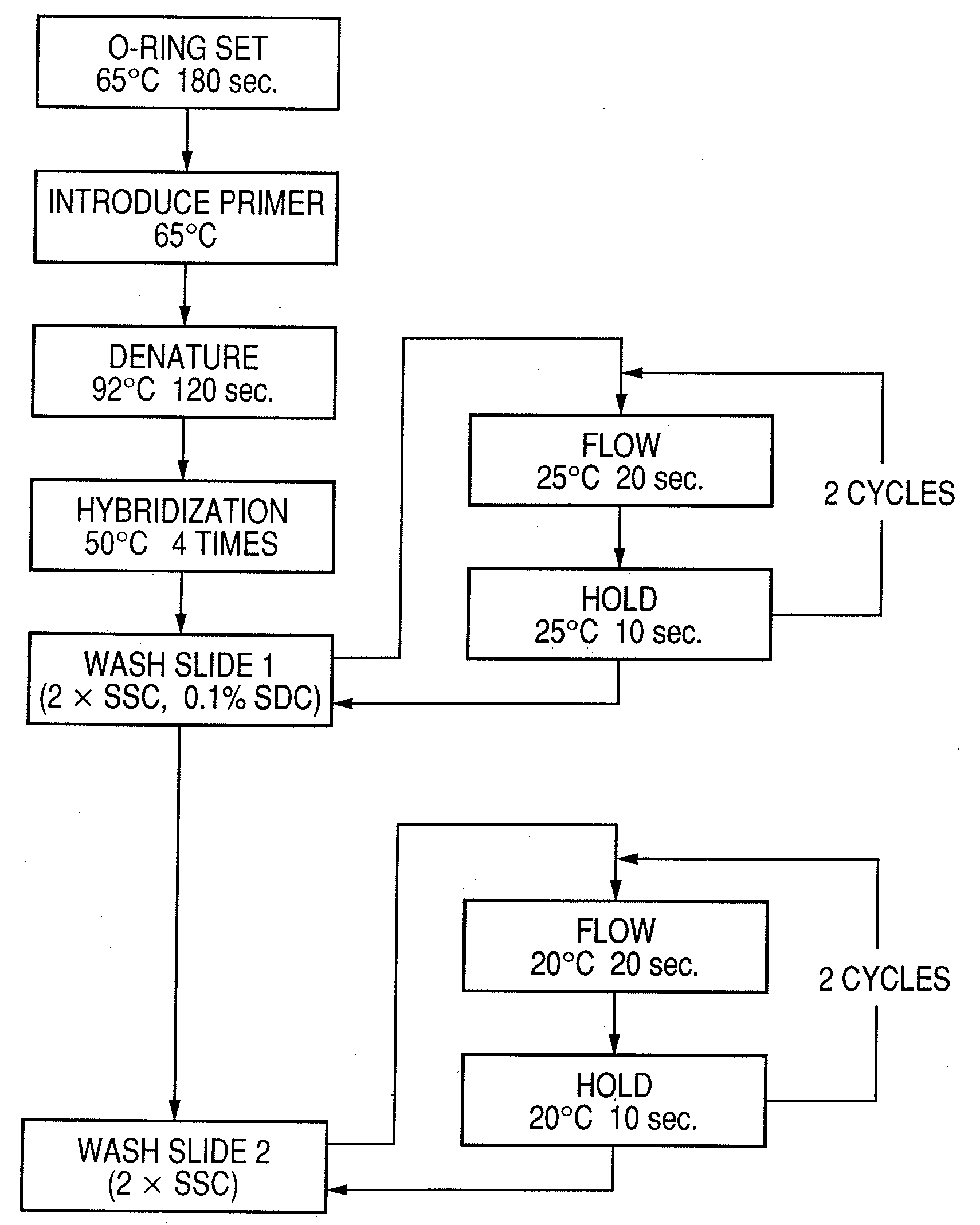
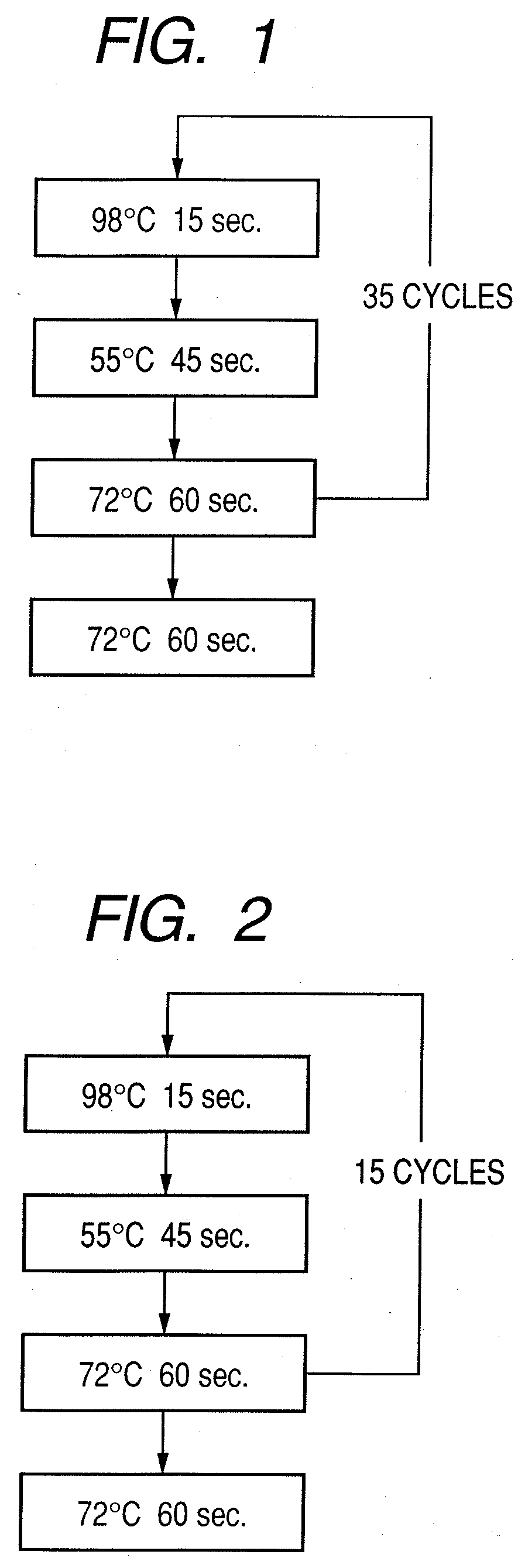
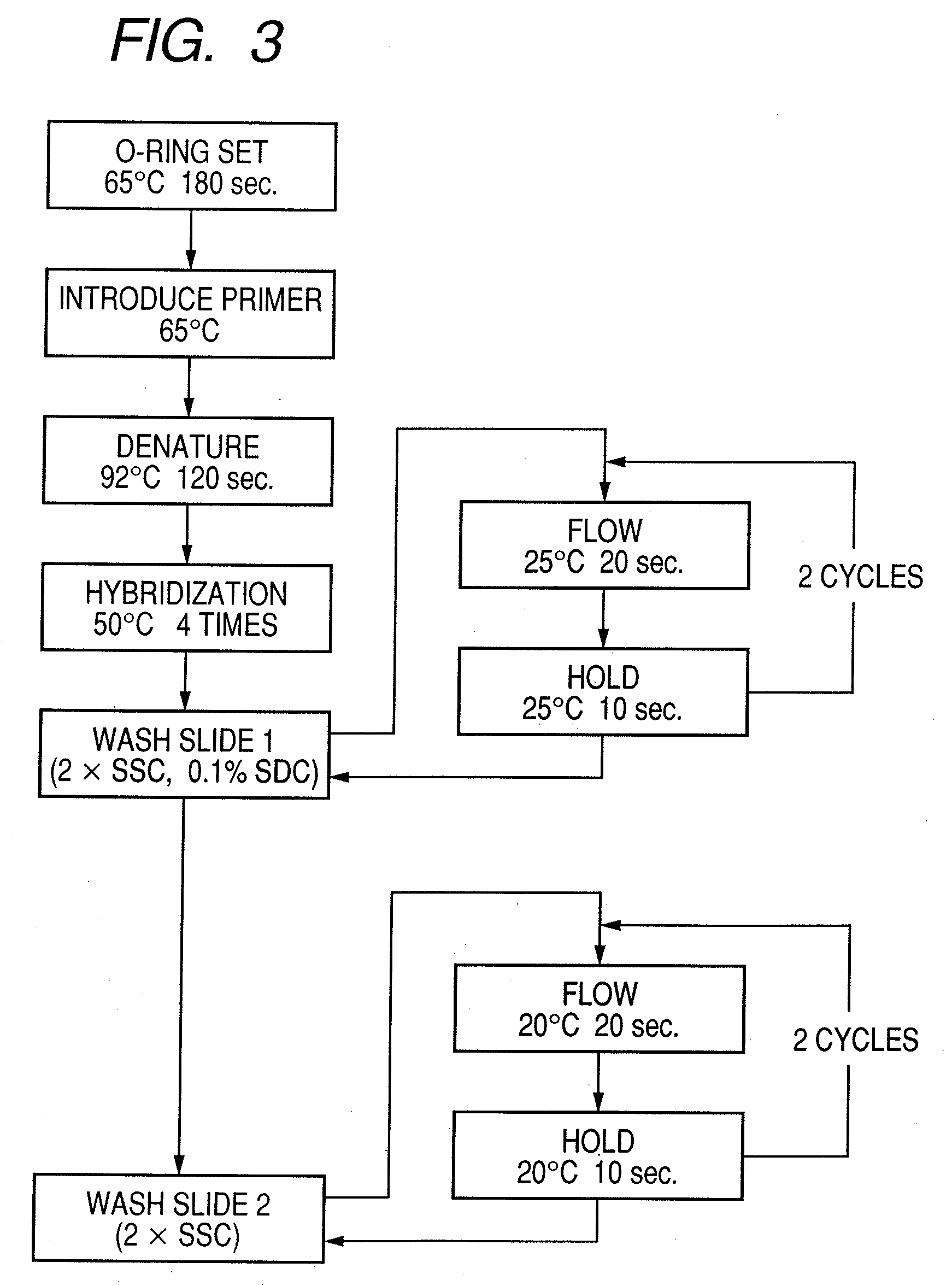
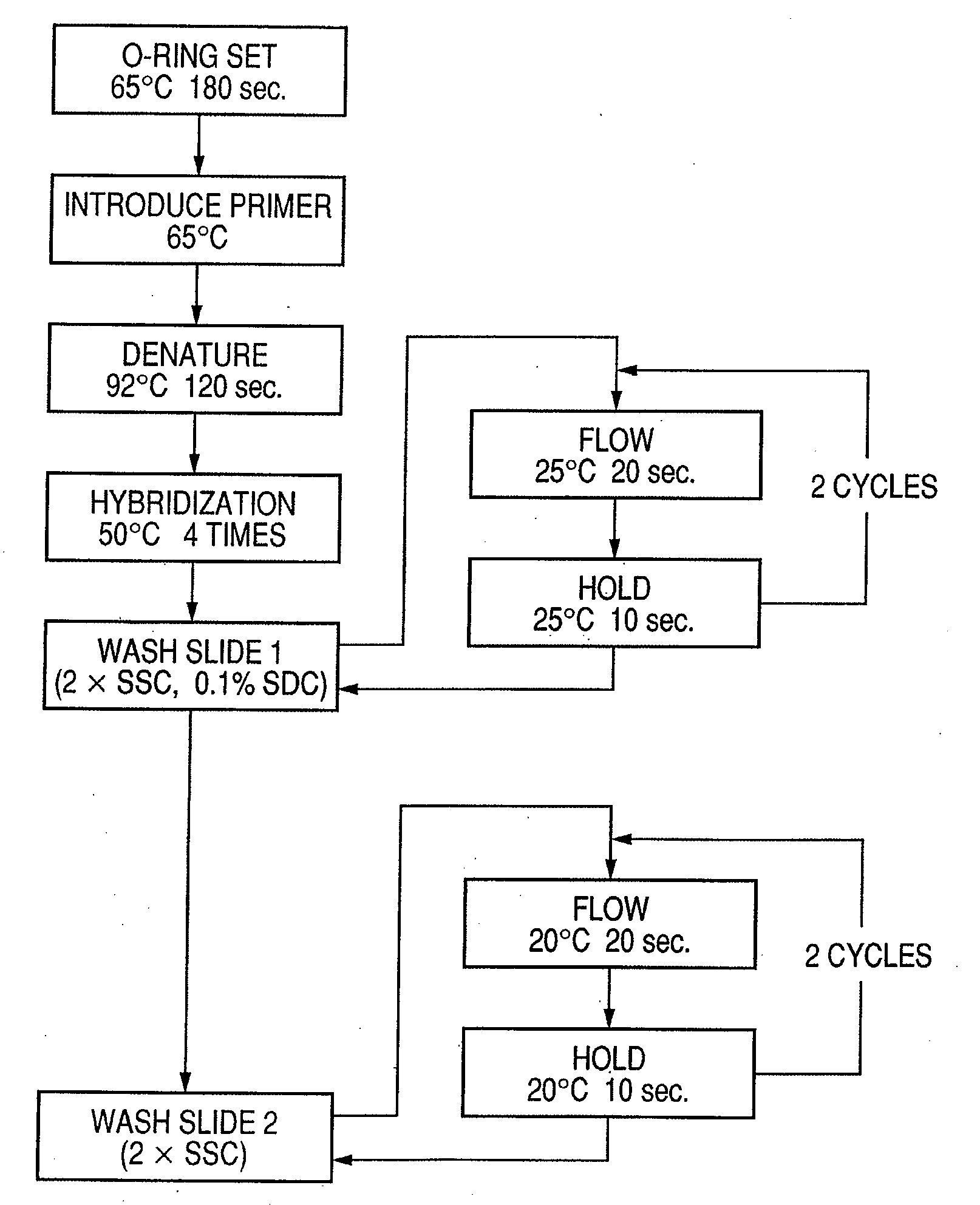
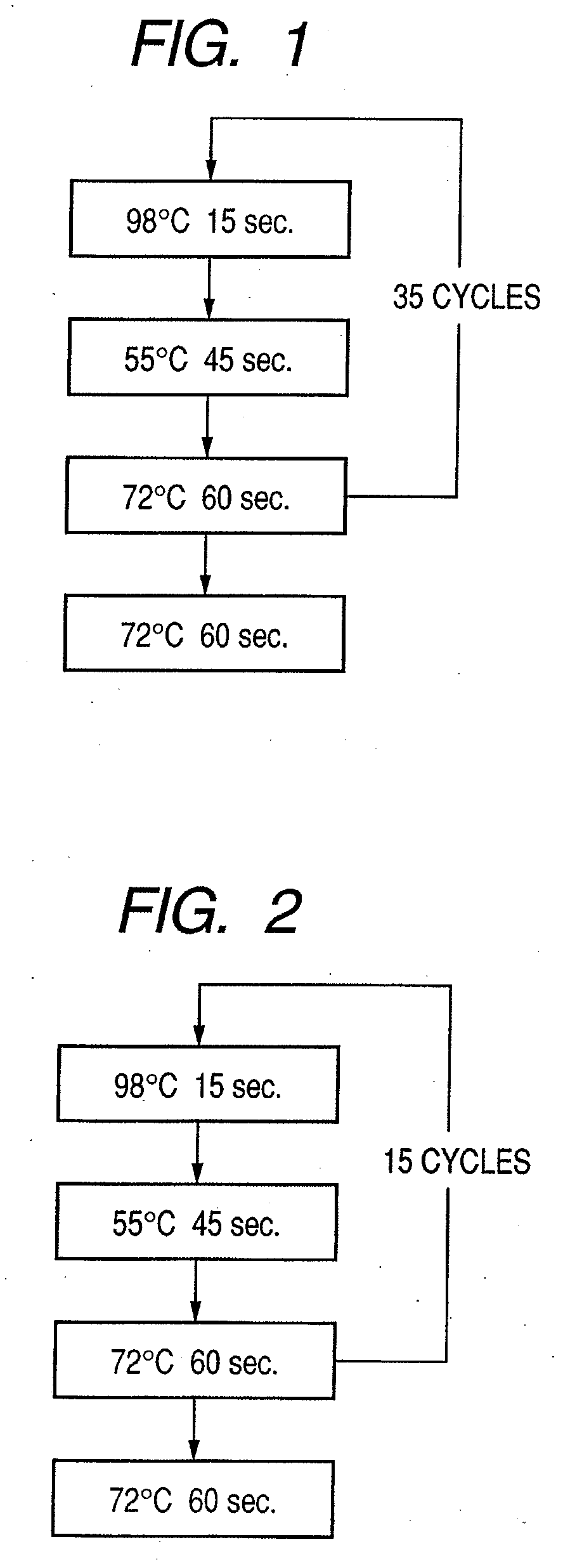
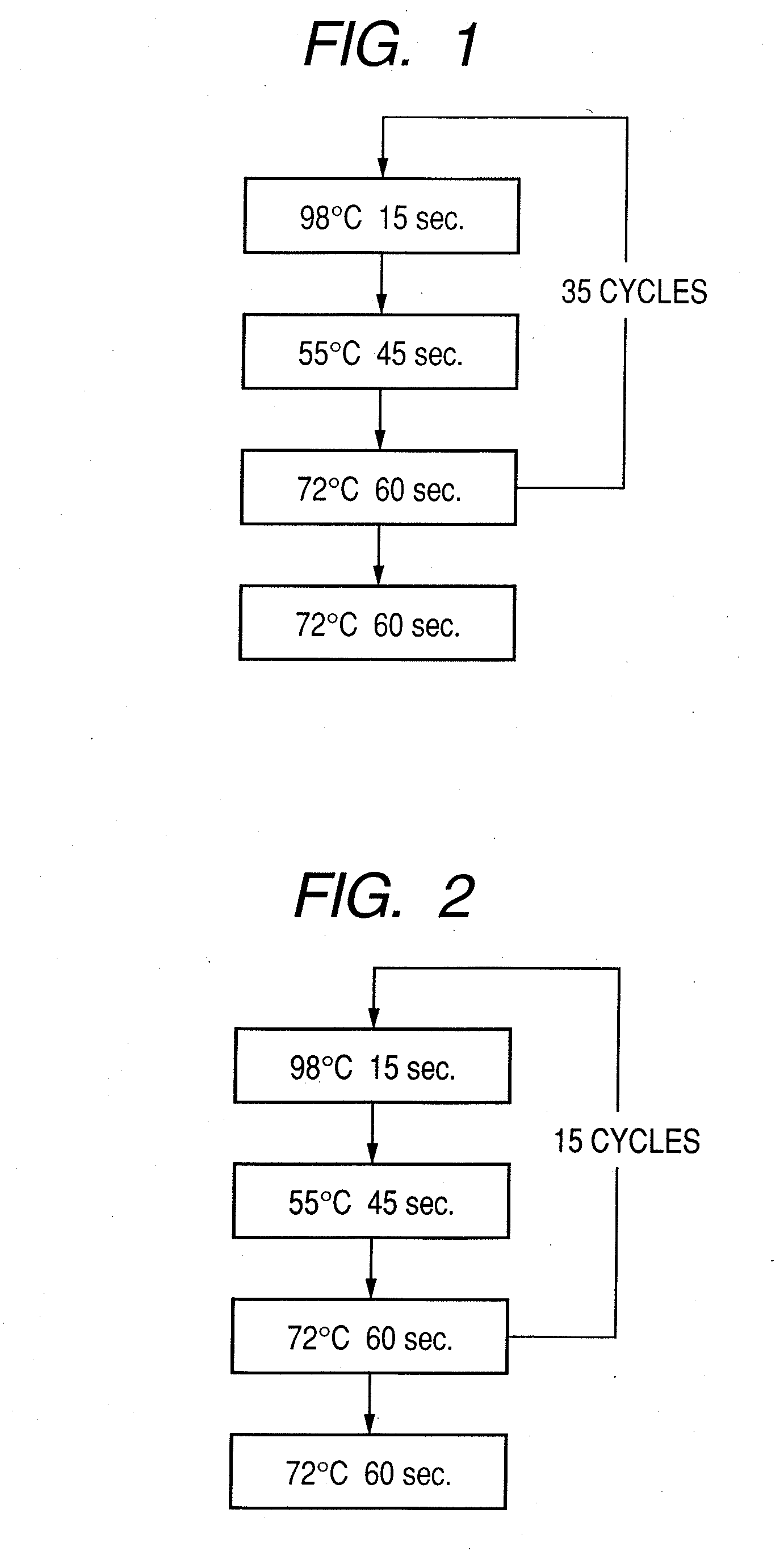
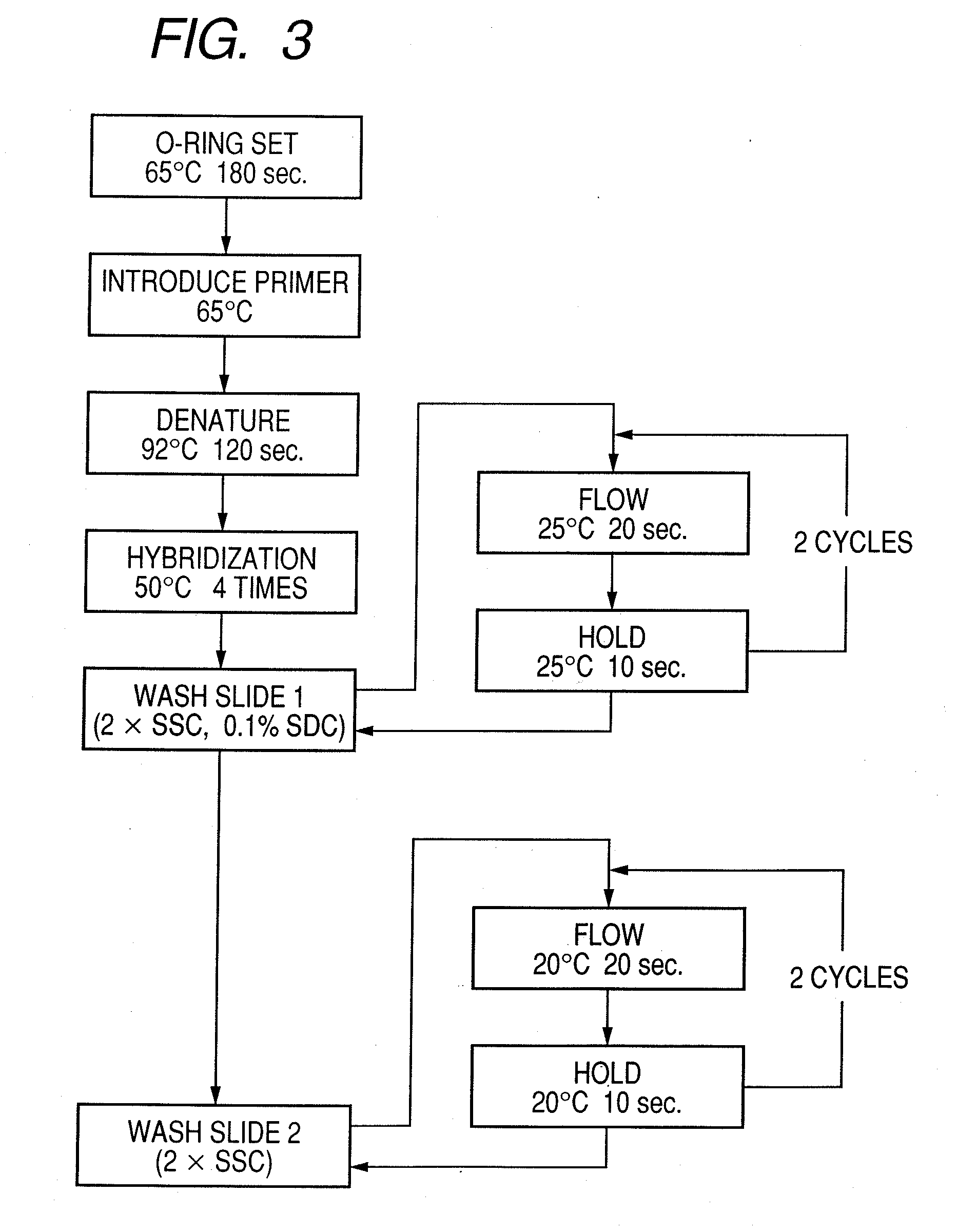
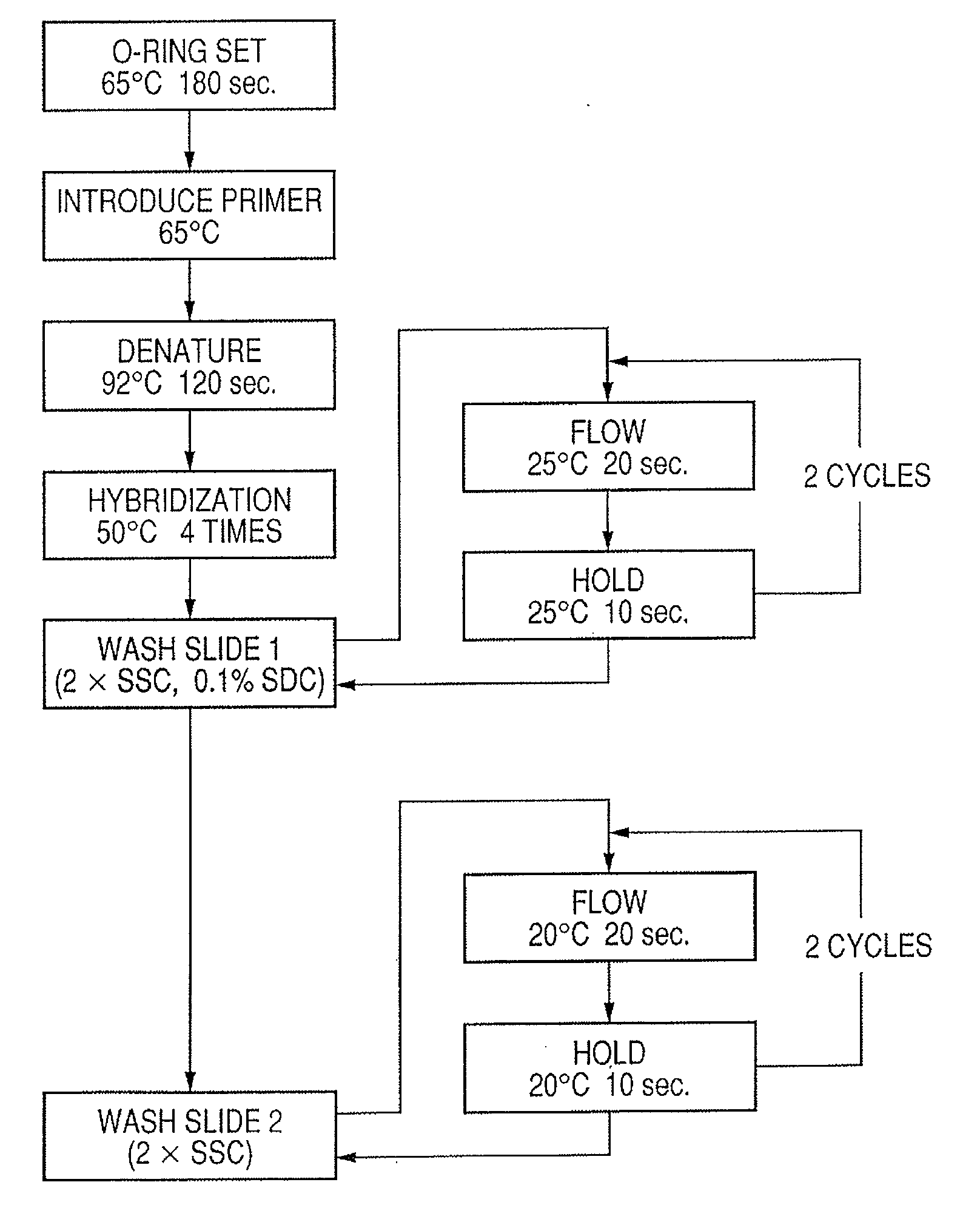
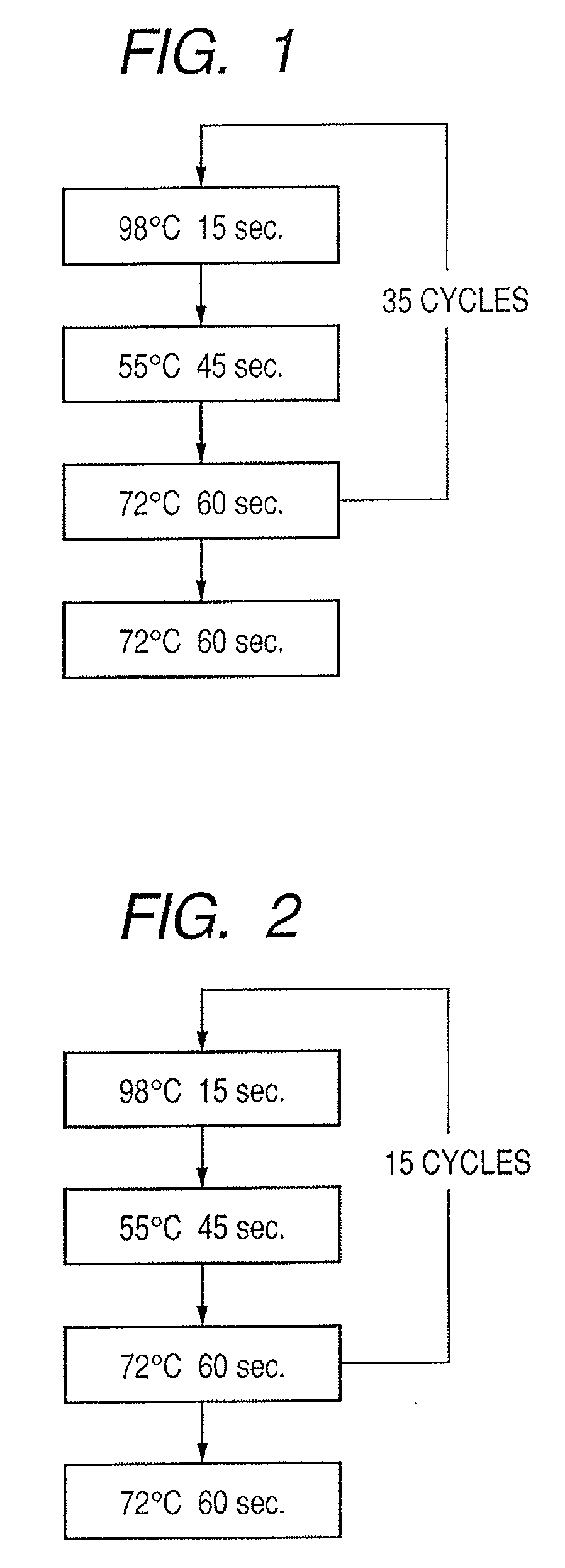
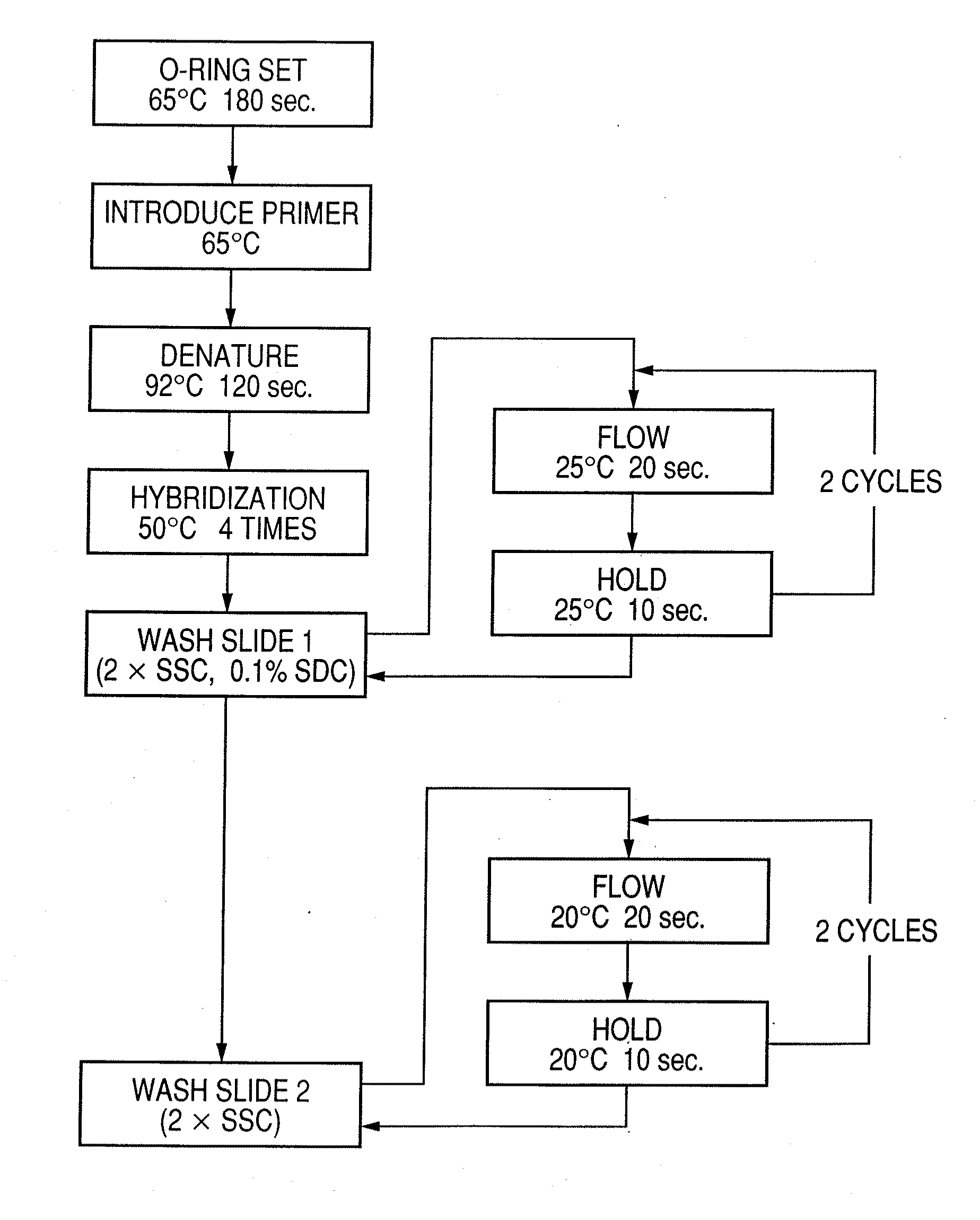
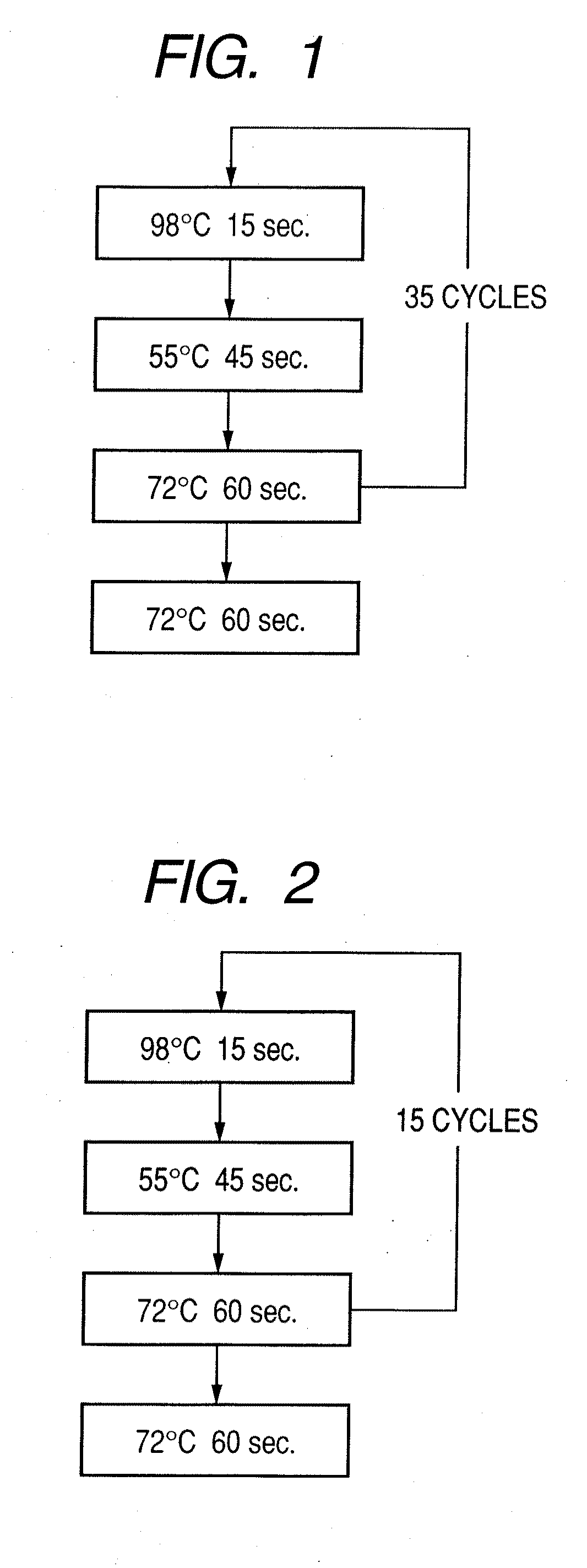
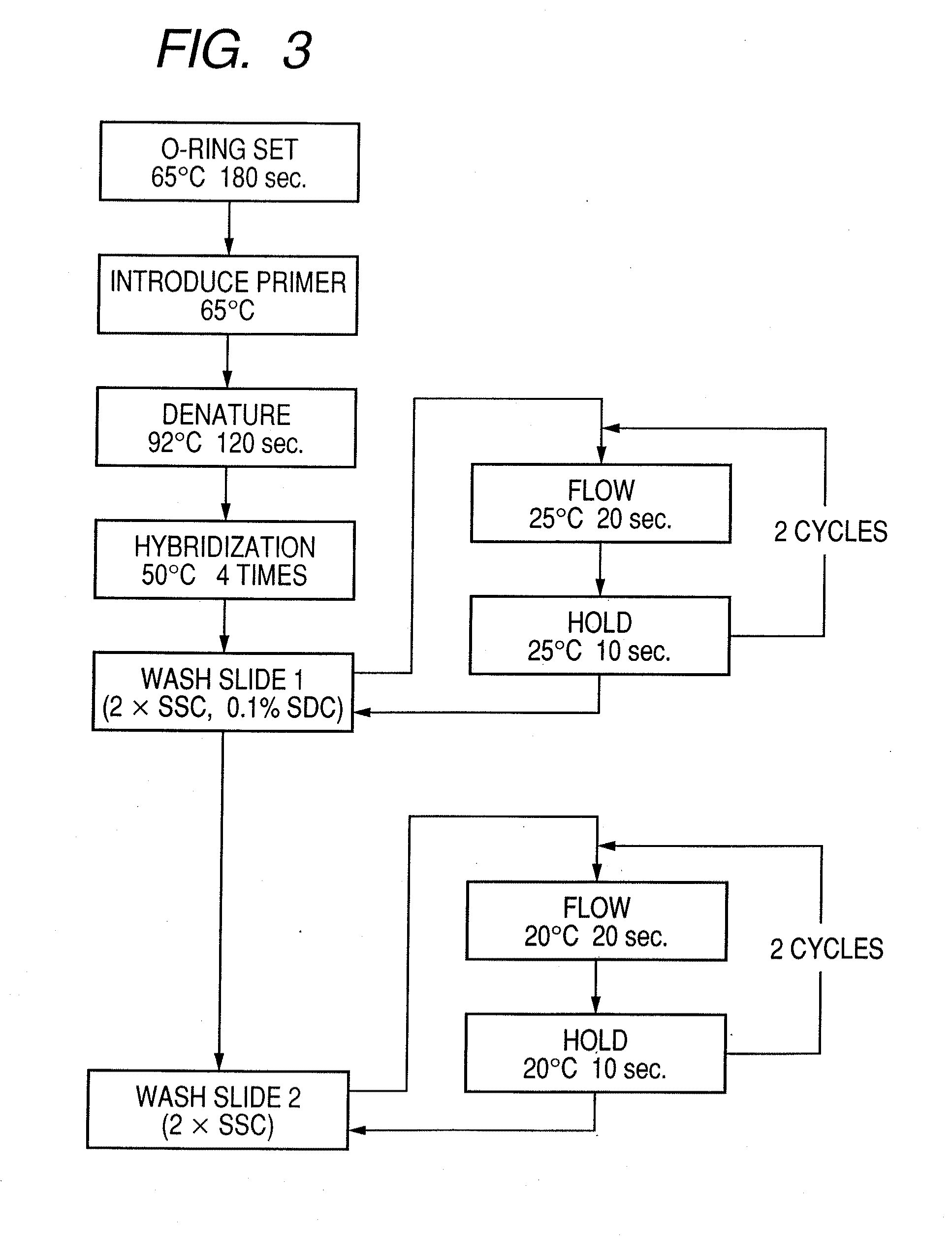
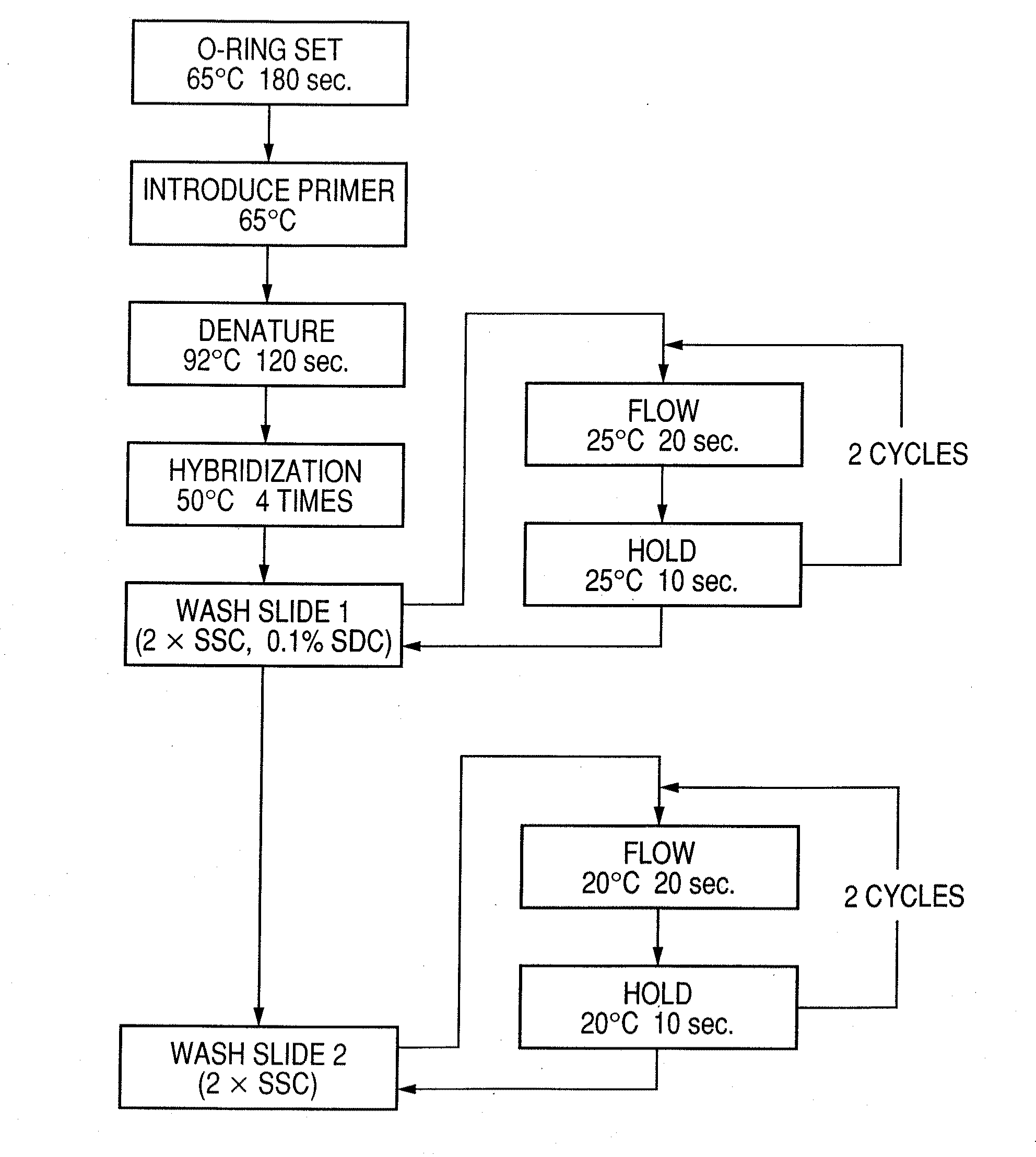
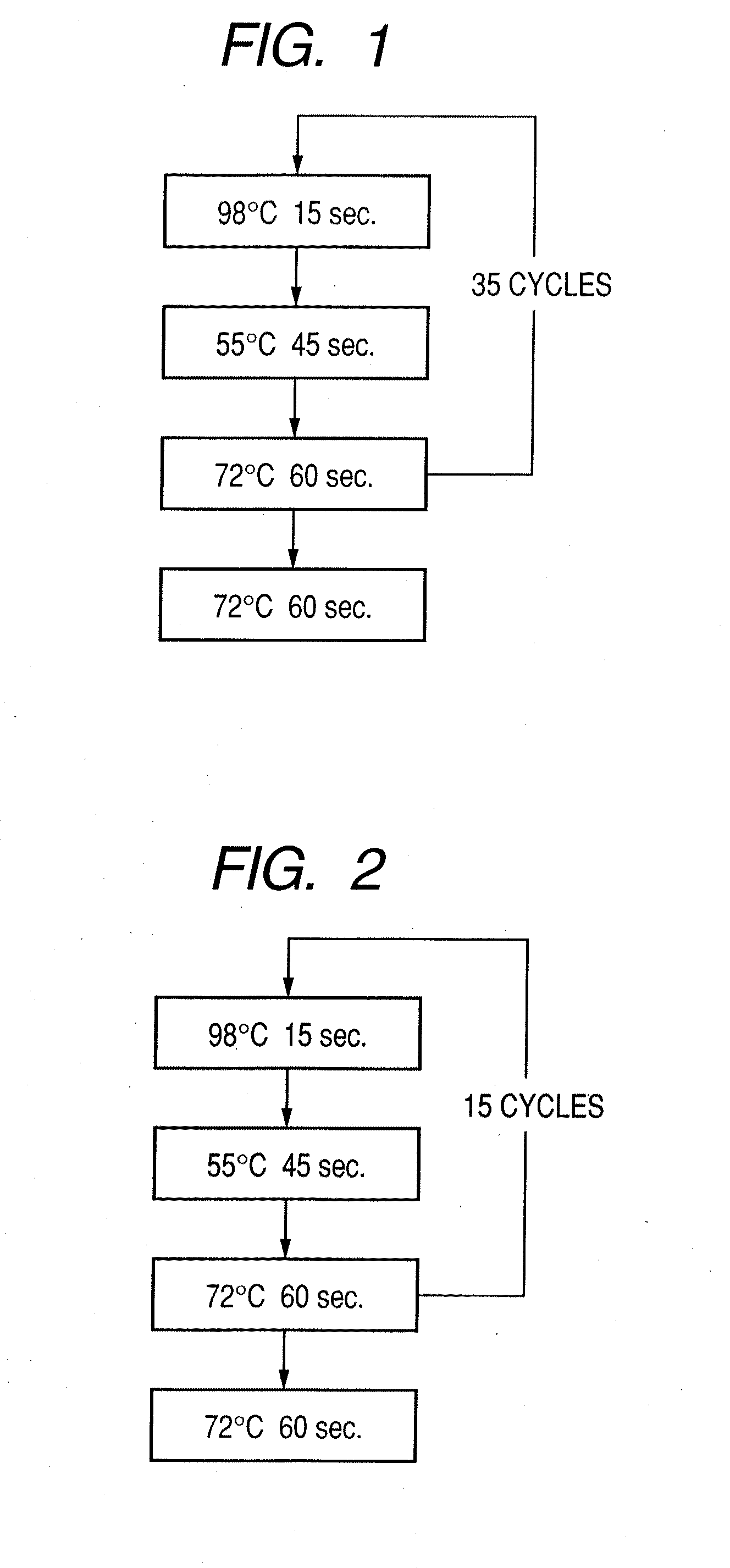
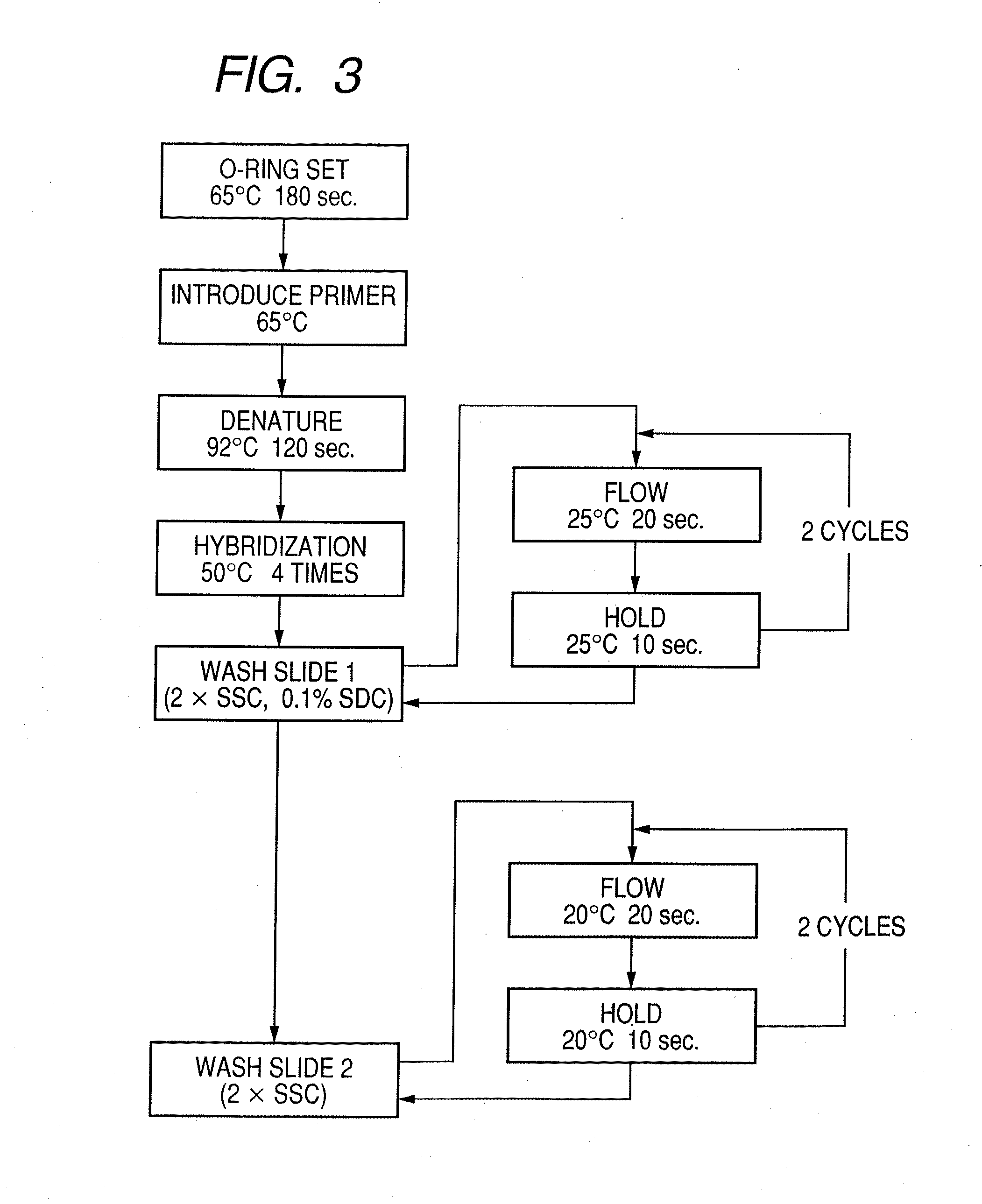
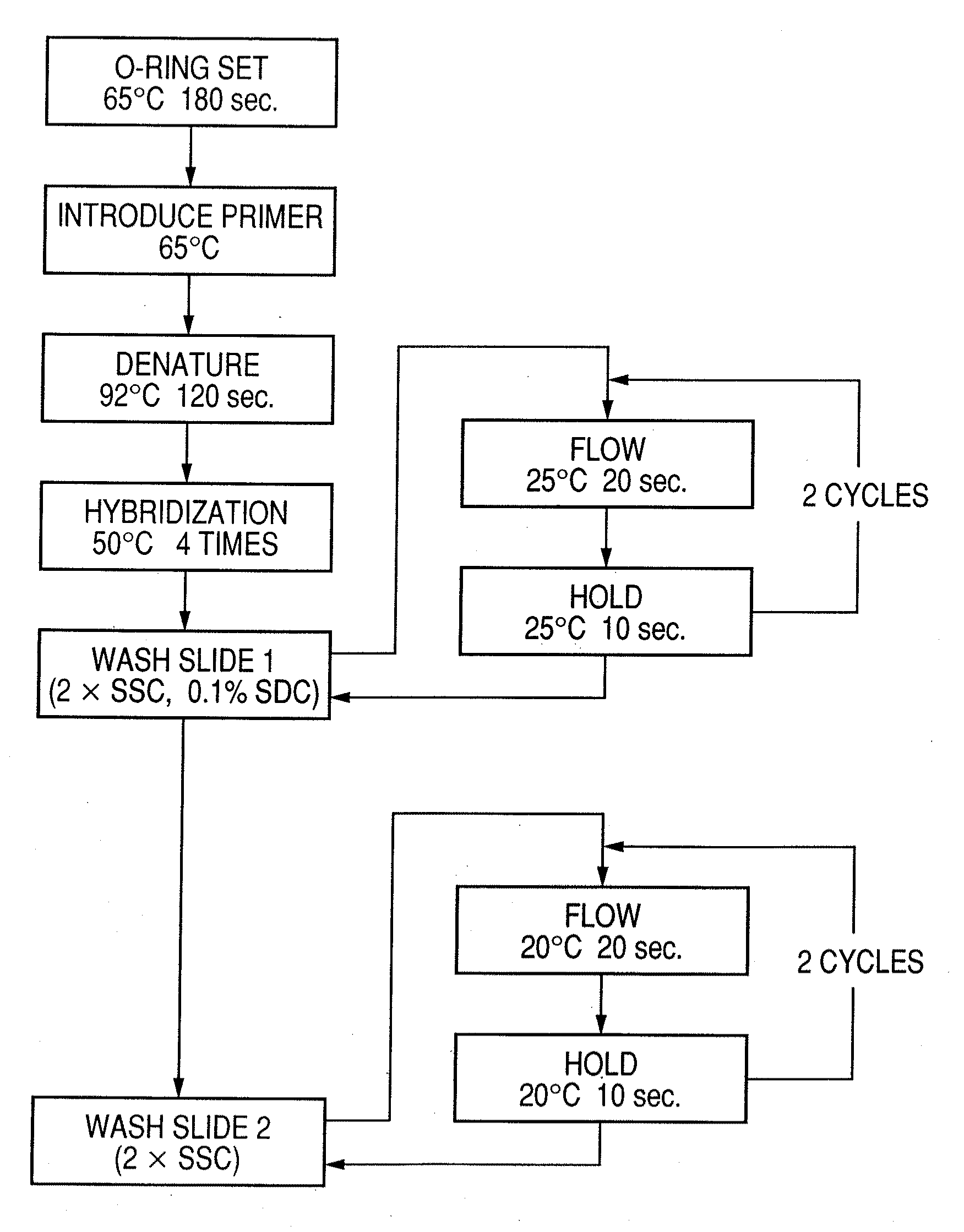
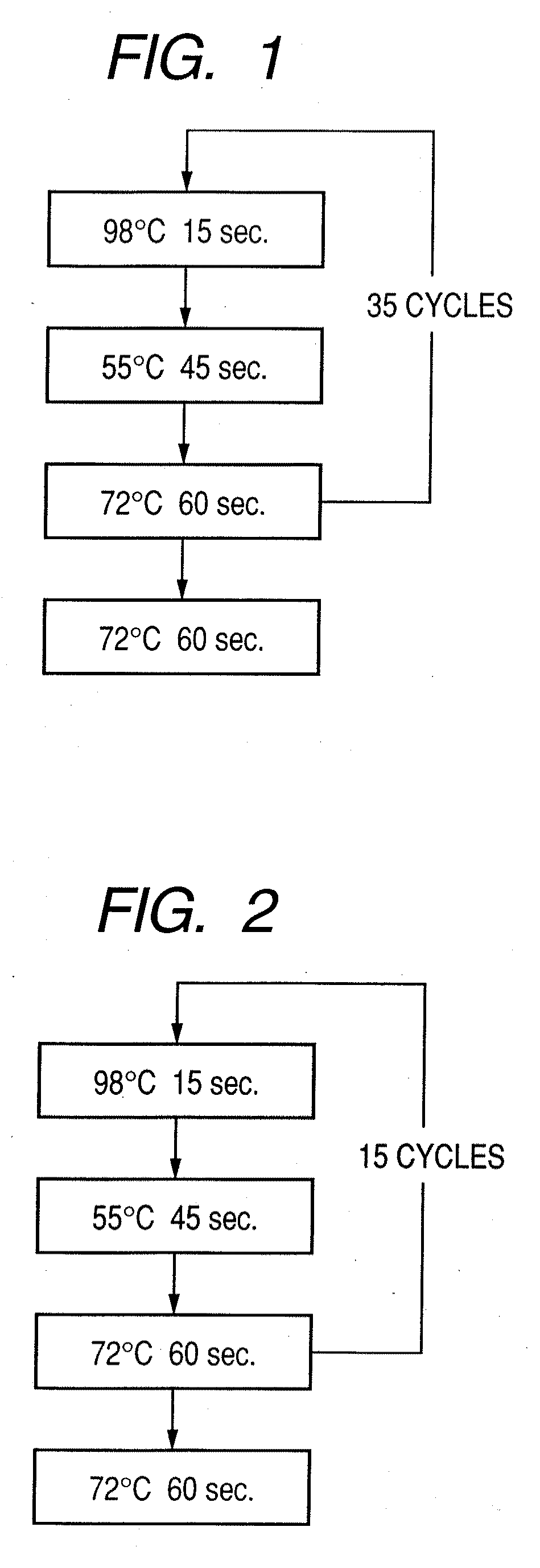
Patents
Literature
87 results about "Fungal DNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
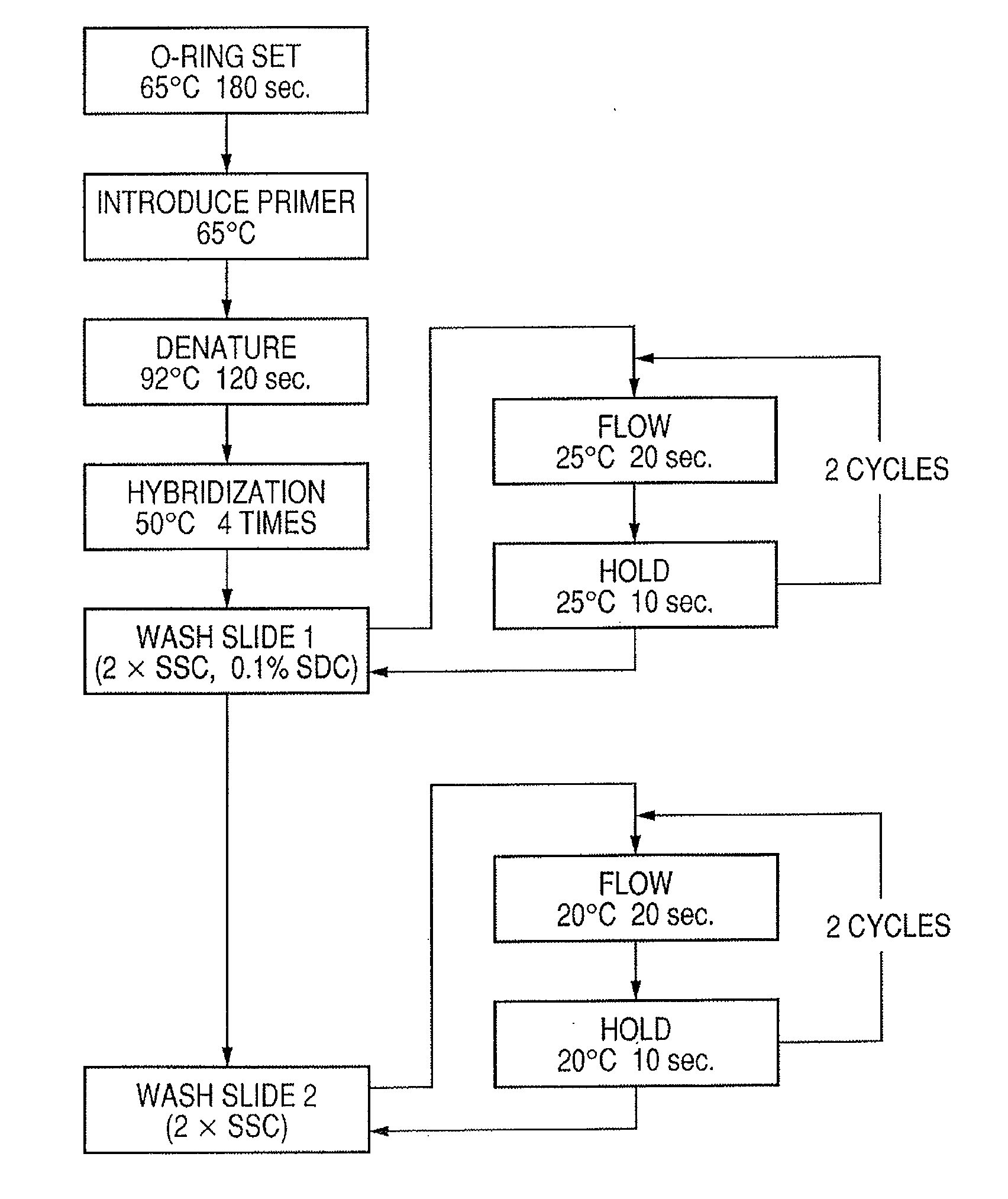
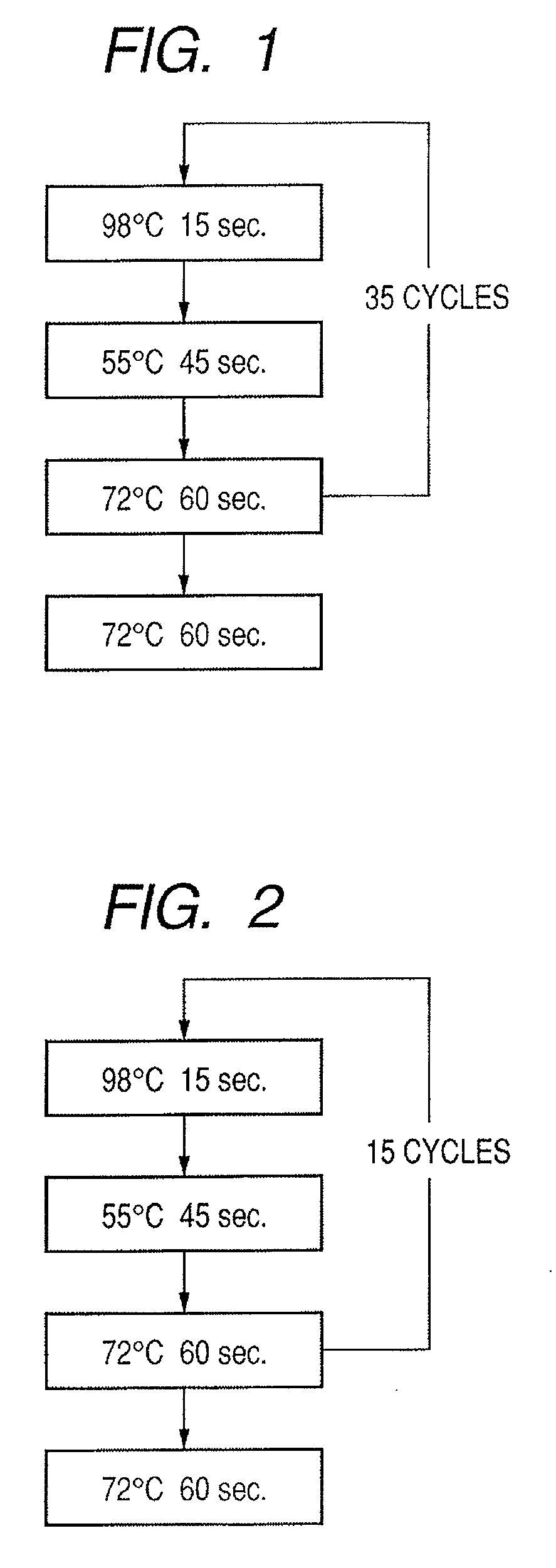
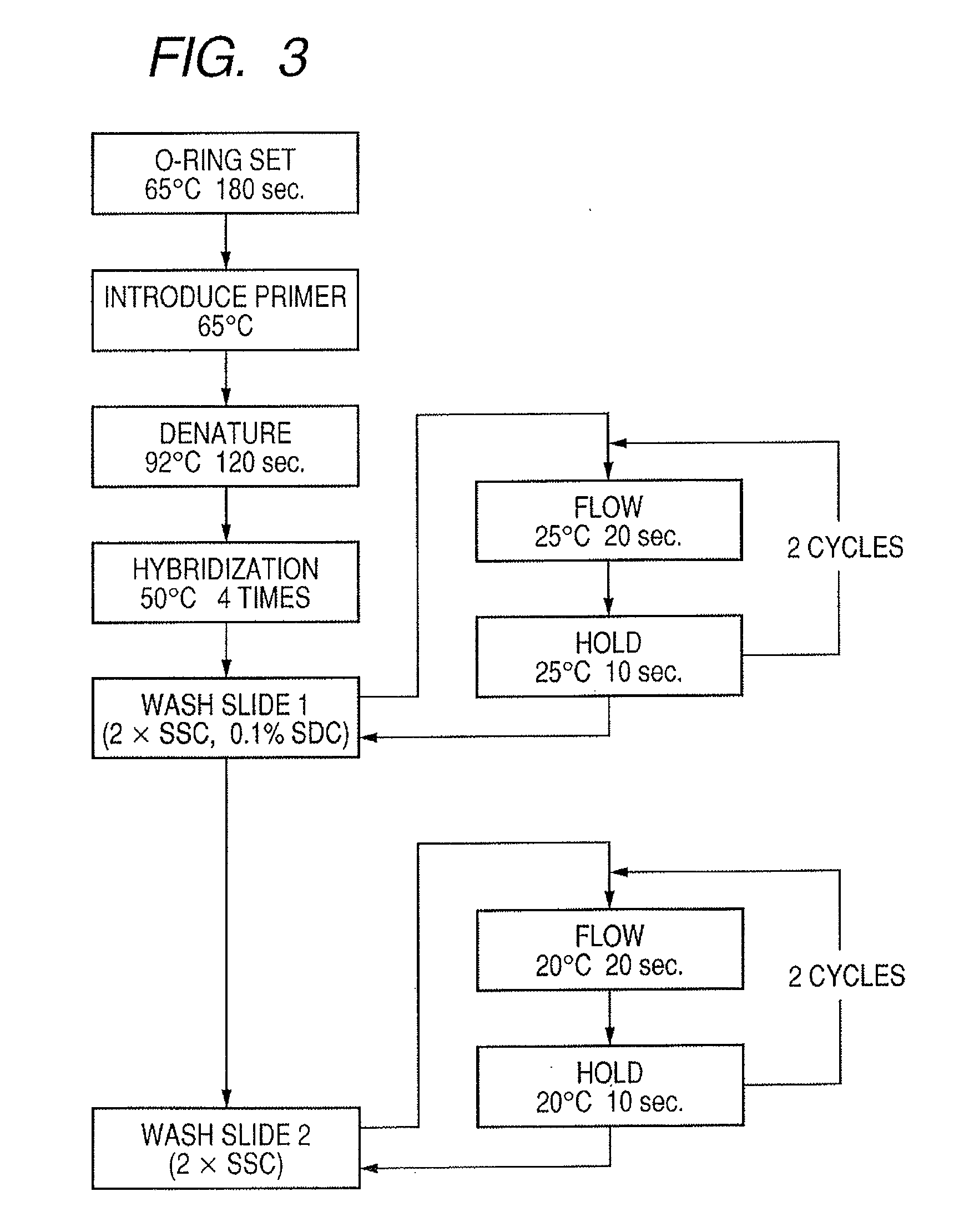
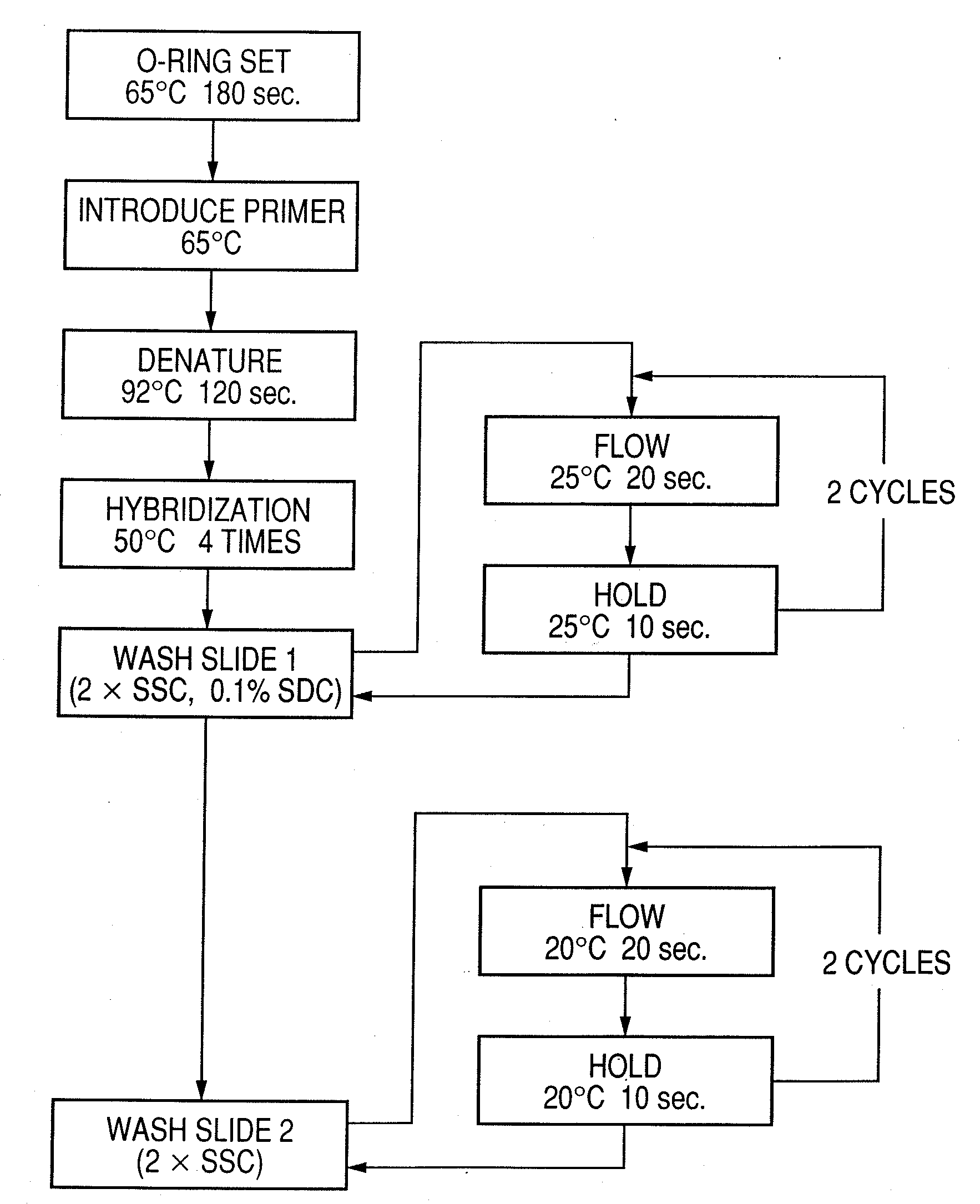
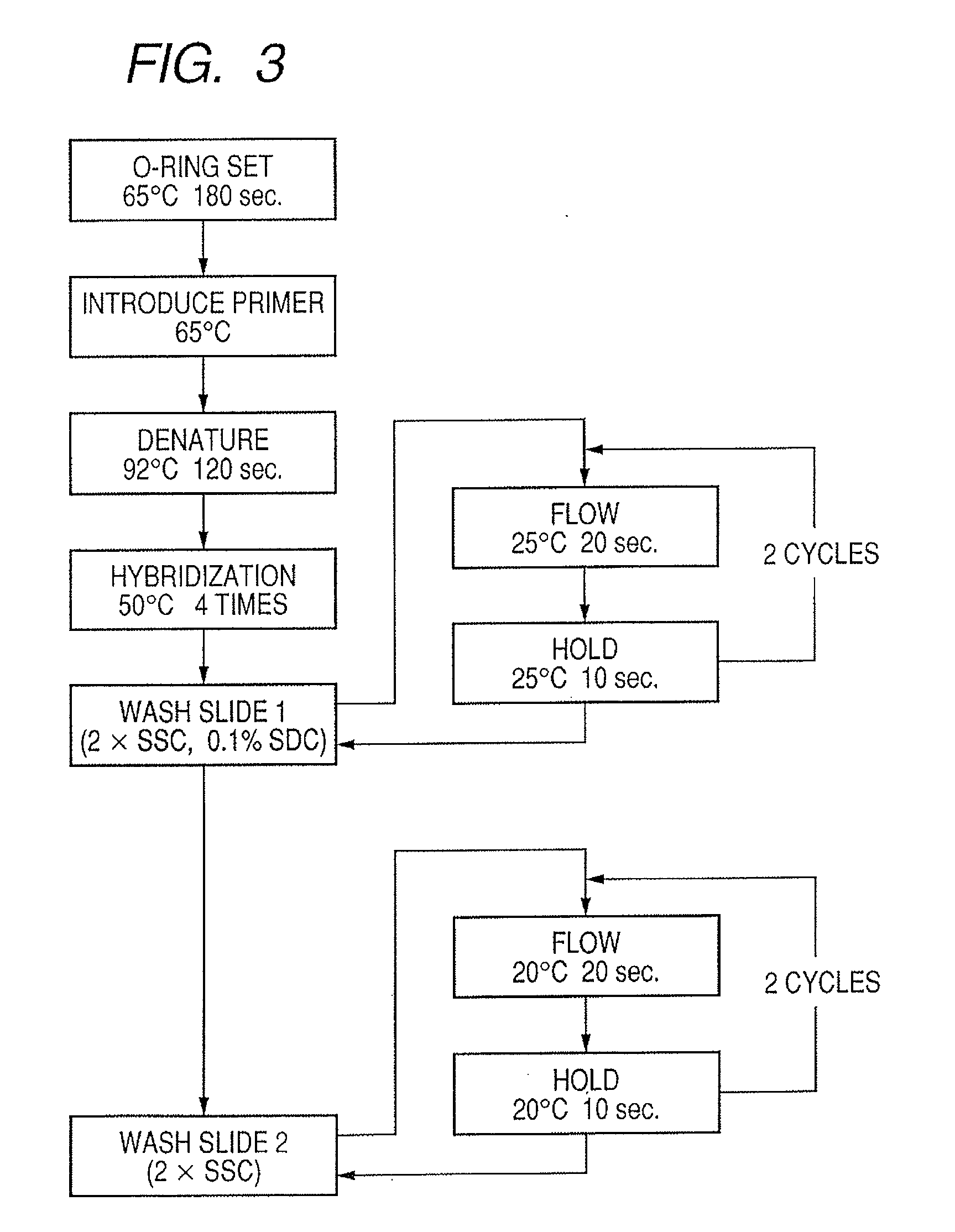
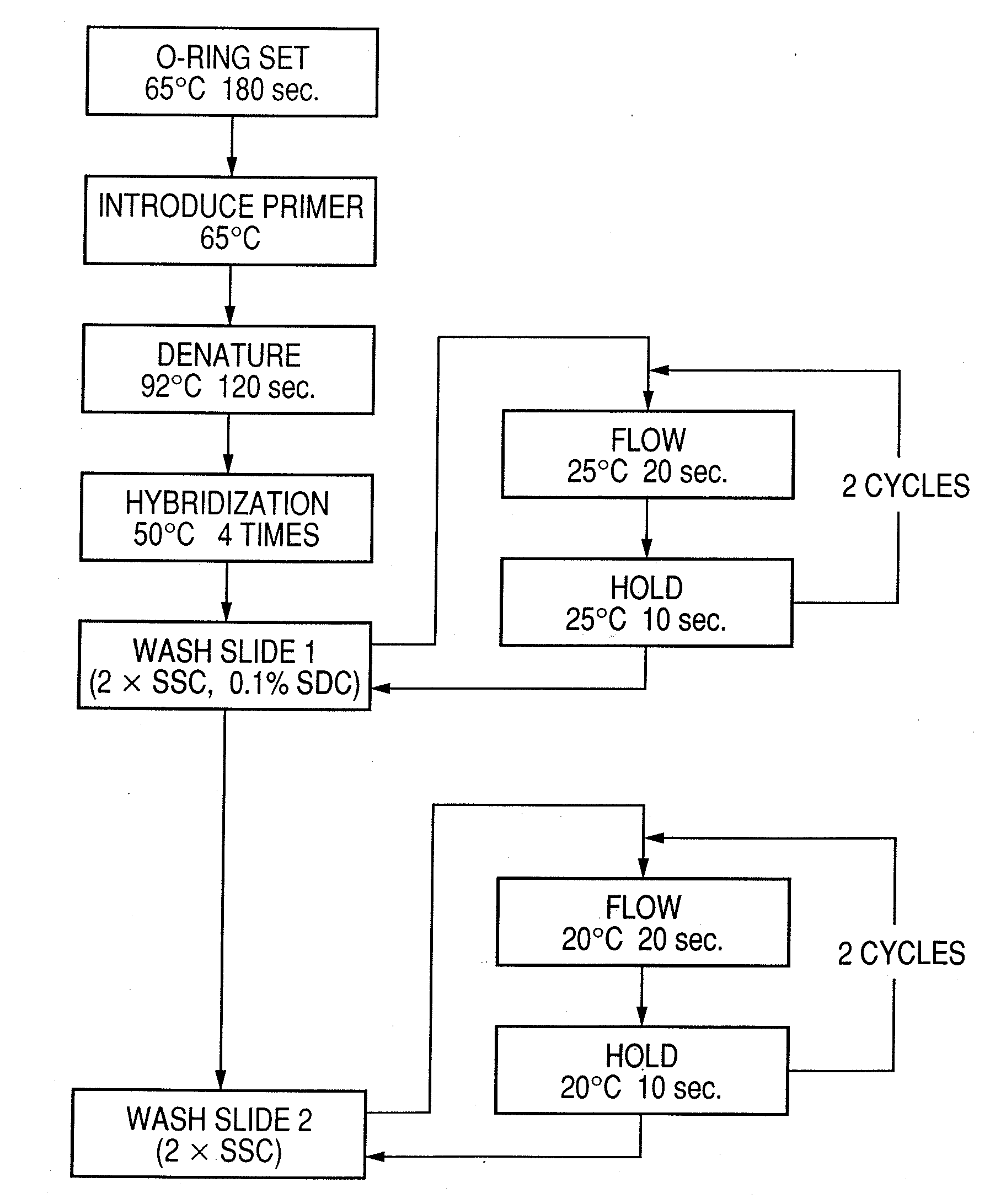
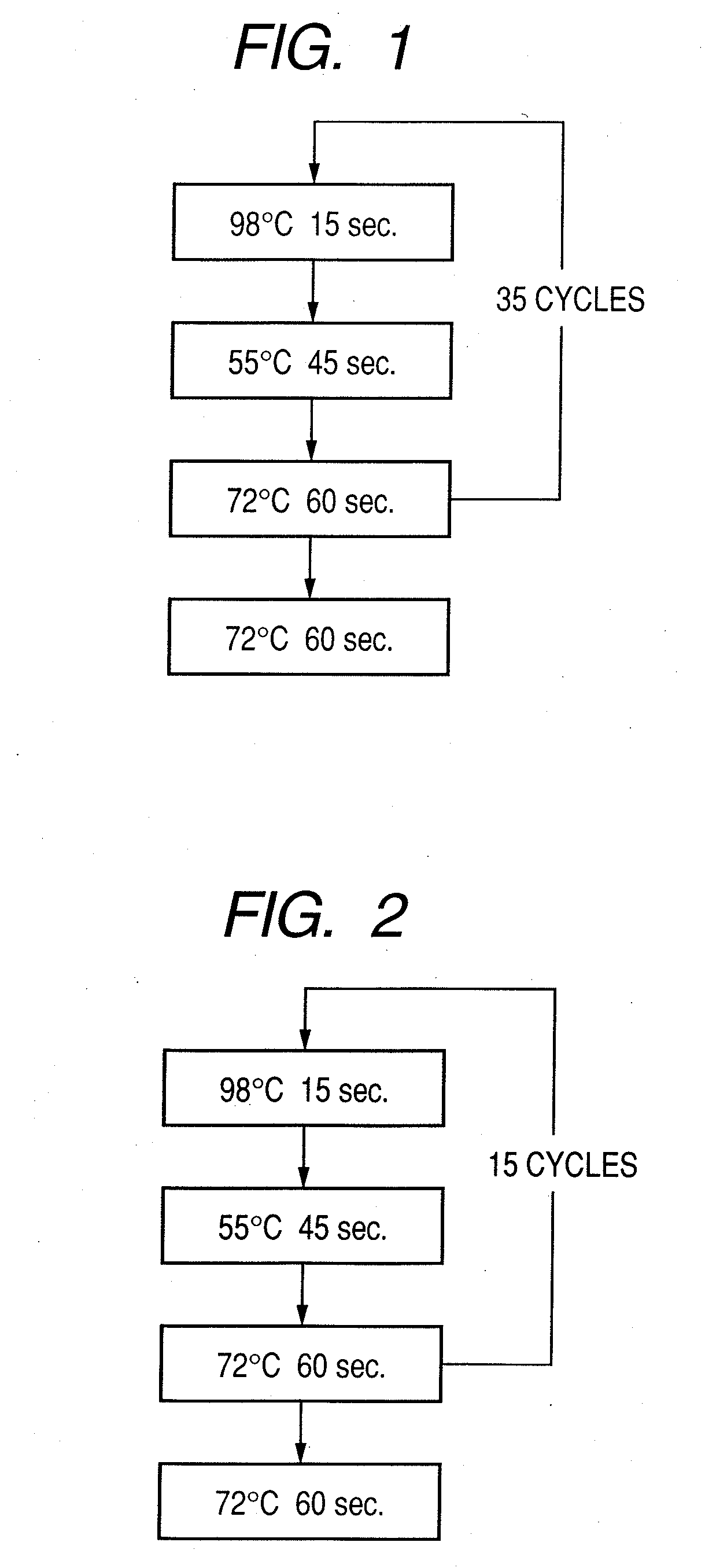
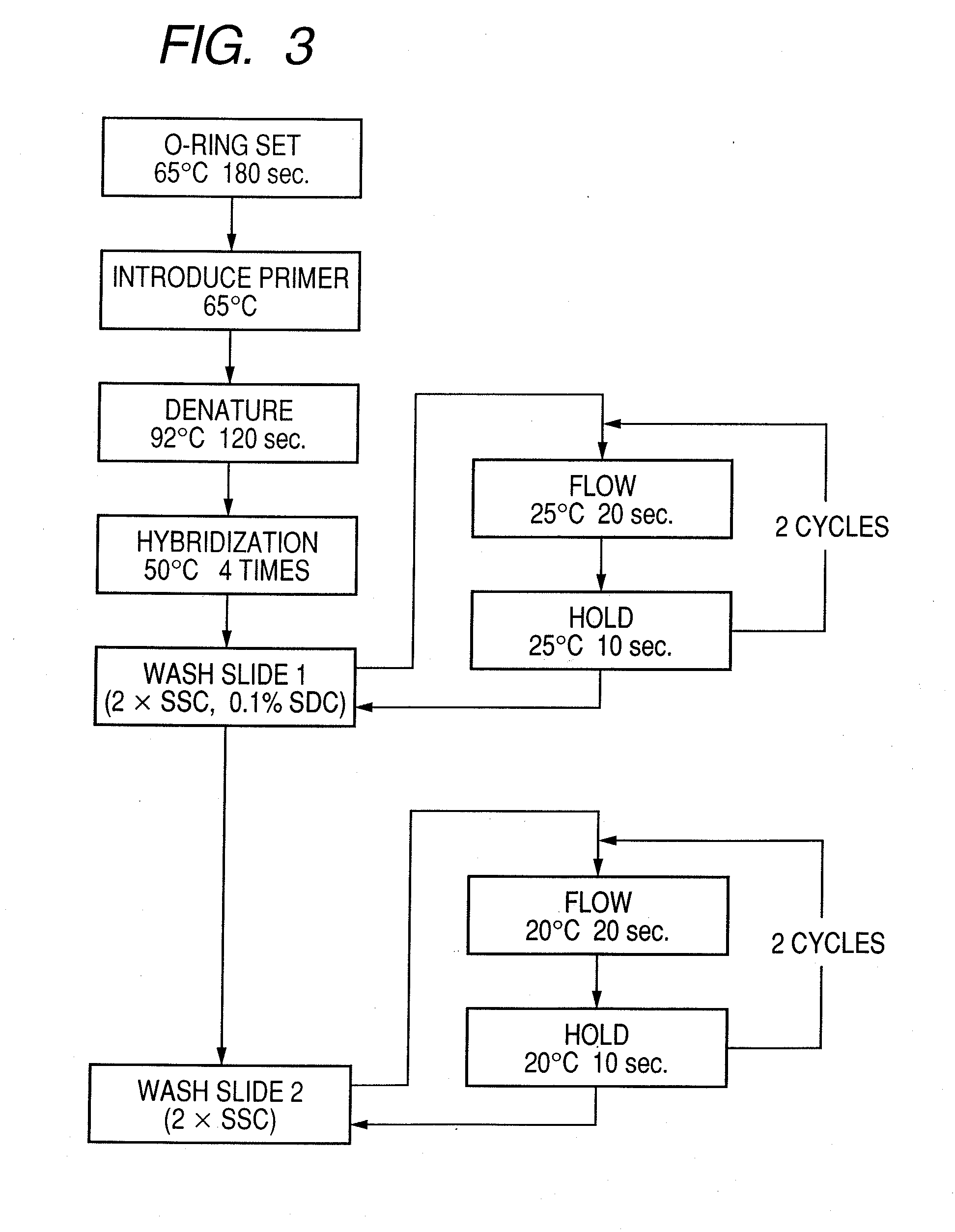
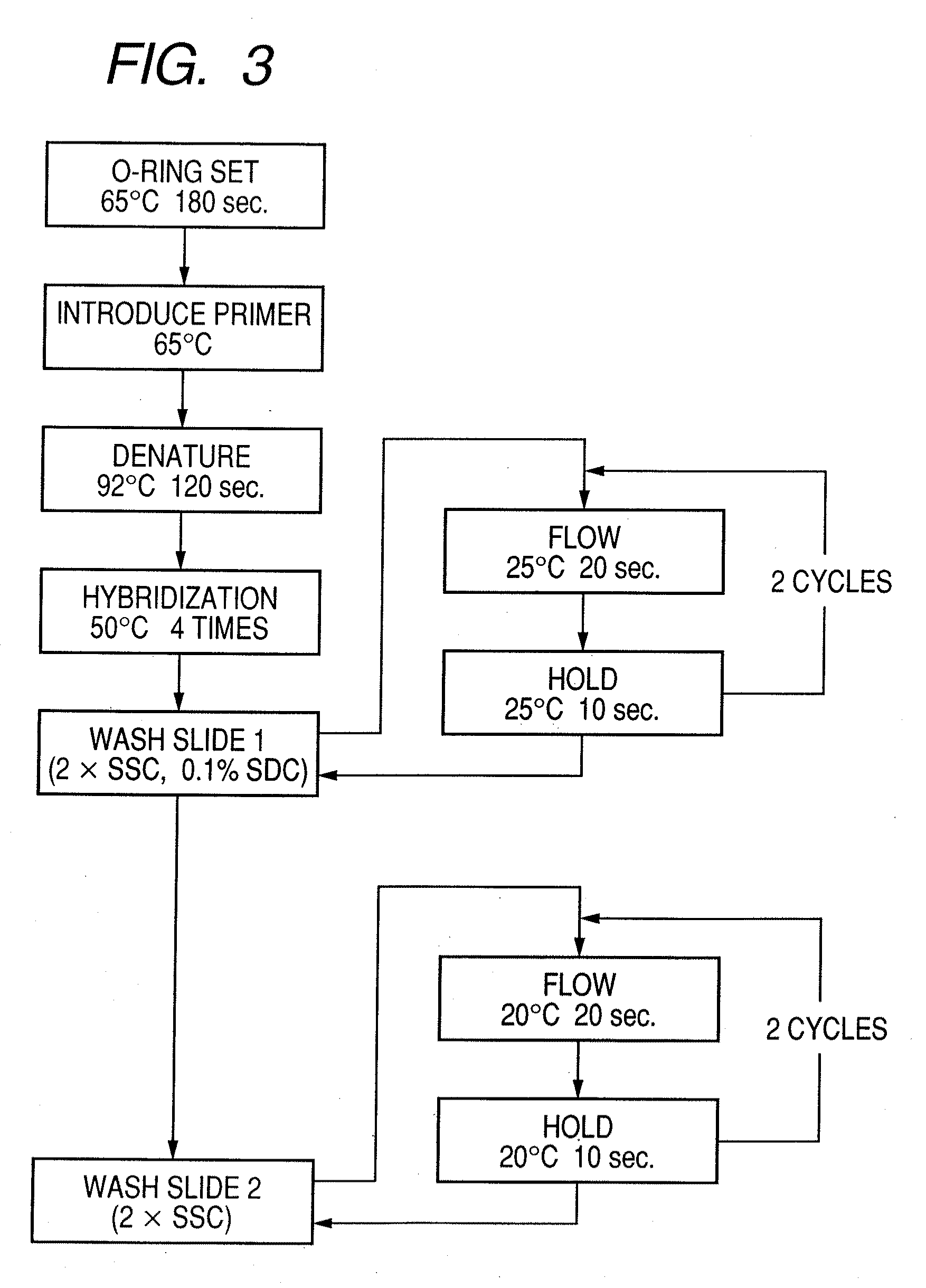
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
InactiveUS20080299575A1Accurate identificationQuickly and more detectAnimal cellsSugar derivativesMicrobiologyOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 2 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
ActiveUS20080299574A1Accurate identificationQuickly and more detectAnimal cellsSugar derivativesPathogenicityOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 4 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
InactiveUS20080305488A1Accurate identificationQuickly and more accurately detect a target fungusSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobiologyOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 3 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
InactiveUS20080299572A1Accurate identificationQuickly and more accurately detect a target fungusSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobiologyOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 3 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
InactiveUS20080293065A1Accurate identificationQuickly and more detectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPathogenicityOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 2 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
InactiveUS20080299576A1Accurate identificationQuickly and more detectAnimal cellsSugar derivativesMicrobiologyOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 2 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
InactiveUS20090011419A1Accurate identificationQuickly and more accurately detect a target fungusSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobiologyOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 2 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
InactiveUS20080299578A1Accurate identificationQuickly and more accurately detect a target fungusSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPathogenicityOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 3 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
InactiveUS20080293066A1Accurate identificationQuickly and more detectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobiologyOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 3 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
InactiveUS20080299569A1Accurate identificationQuickly and more detectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobiologyOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 2 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
InactiveUS20080299577A1Accurate identificationQuickly and more detectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobiologyOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 2 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
InactiveUS20080299570A1Accurate identificationQuickly and more detectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobiologyOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 3 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
InactiveUS20080293064A1Accurate identificationQuickly and more detectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPathogenicityOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 2 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
InactiveUS20090068661A1Accurate identificationQuickly and more detectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPathogenicityOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 4 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
InactiveUS20090233282A1Accurate identificationQuickly and more detectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobiologyOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 4 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Rapid identification method for pathogenic fungi
The invention relates to a rapid identification method for pathogenic fungi, which specially comprises the following steps: (1) culturing fungi on a solid culture medium; (2) taking fresh fungi, and extracting the DNA of the fungi by using a microwave method; (3) amplifying DNA fragments between ribosomal spacers of the fungi by using ITS1 and ITS4 primers through PCR (polymerase chain reaction); (4) after recovering the PCR fragments, carrying out sequence determination on the fragments; and (5) carrying out comparison on the obtained sequences by using the Blast of NCBI. According to the invention, the identification of unknown pathogenic fungi can be performed within a shorter time and under relatively simple experimental conditions, thereby facilitating the rapid diagnosis for diseases occurring in fields so as to guide the prevention and control of diseases. According to the method, through the identification on 21 kinds of pathogenic fungi on different crops, and the coincidence rate is 100% through sequence comparison. The method is not only applicable to the identification on fresh mycelia, but also is applicable to the identification on conidium and sclerotium of pathogenic fungi, and has the characteristics of rapidness and high efficiency.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A kit for extracting pathogen nucleic acids from a phlegm sample in a high-flux and automatic manner
A kit for extracting pathogen nucleic acids from a phlegm sample in a high-flux and automatic manner is disclosed. The kit includes a phlegm digestion agent, a lysis liquid, magnetic beads, a washing liquid and an eluant. The phlegm digestion agent is a NaOH solution having a concentration of 1-6 M. The lysis liquid is an acidic solution the pH of which is not more than 3, and which is prepared from a guanidine salt having a concentration of 2-8 M, a surfactant, a pH buffer medium and a metal chelating agent. Centrifugation is not needed during extraction of nucleic acids of pathogens (including bacteria, viruses and fungi) in the phlegm sample by using the kit, thus facilitating automatic operation. The kit can extract DNAs and RNAs of bacteria, viruses and fungi in the phlegm sample so that the kit is high in universality. An extraction process is free of organic and toxic solvents so that the kit is safer. Extracted nucleic acids are high in purity so that value of a pathogen clinical sample in disease diagnosis is improved.
Owner:AUTOBIO DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
Probe, probe set, probe carrier, and testing method
ActiveUS8049001B2Accurate identificationQuickly and more accurately detect a target fungusAnimal cellsSugar derivativesMicrobiologyOligonucleotide
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 4 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification fast detection method of producing candida albicans fungi
InactiveCN101381775AGuaranteed reliabilityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMonilinia laxaBetaine
The invention relates to a rapid detection method for candida albicans by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Reagents used by the method comprises a loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction solution, a Bst DNA polymerase and a color development reagent, wherein the reaction solution contains reaction buffer, dNTP, magnesium sulfate, an upstream inner primer 5-CACATTTTGGATAAGGTTCACCATT-ATAGAAACCTCAAGATTTCCGT-3, a downstream inner primer 5-TCGTGTTCGTGAAAGTGAAGATAAT-CTTTCTATCATCCAAATCGTAGA-3, an upstream outer primer 5-ACCGTTGATTTCCAATTCG-3, a downstream outer primer 5-TTAACTTGAGCCATGGAGAT-3, and glycine betaine. The method for detection of candida albicans comprises the steps of DNA extraction of the fungi, loop-mediated isothermal amplification of the candida albicans, and chromogenic detection. The method has the characteristics of rapidness, strong specificity, high sensitivity and low cost.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT SHANDONG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
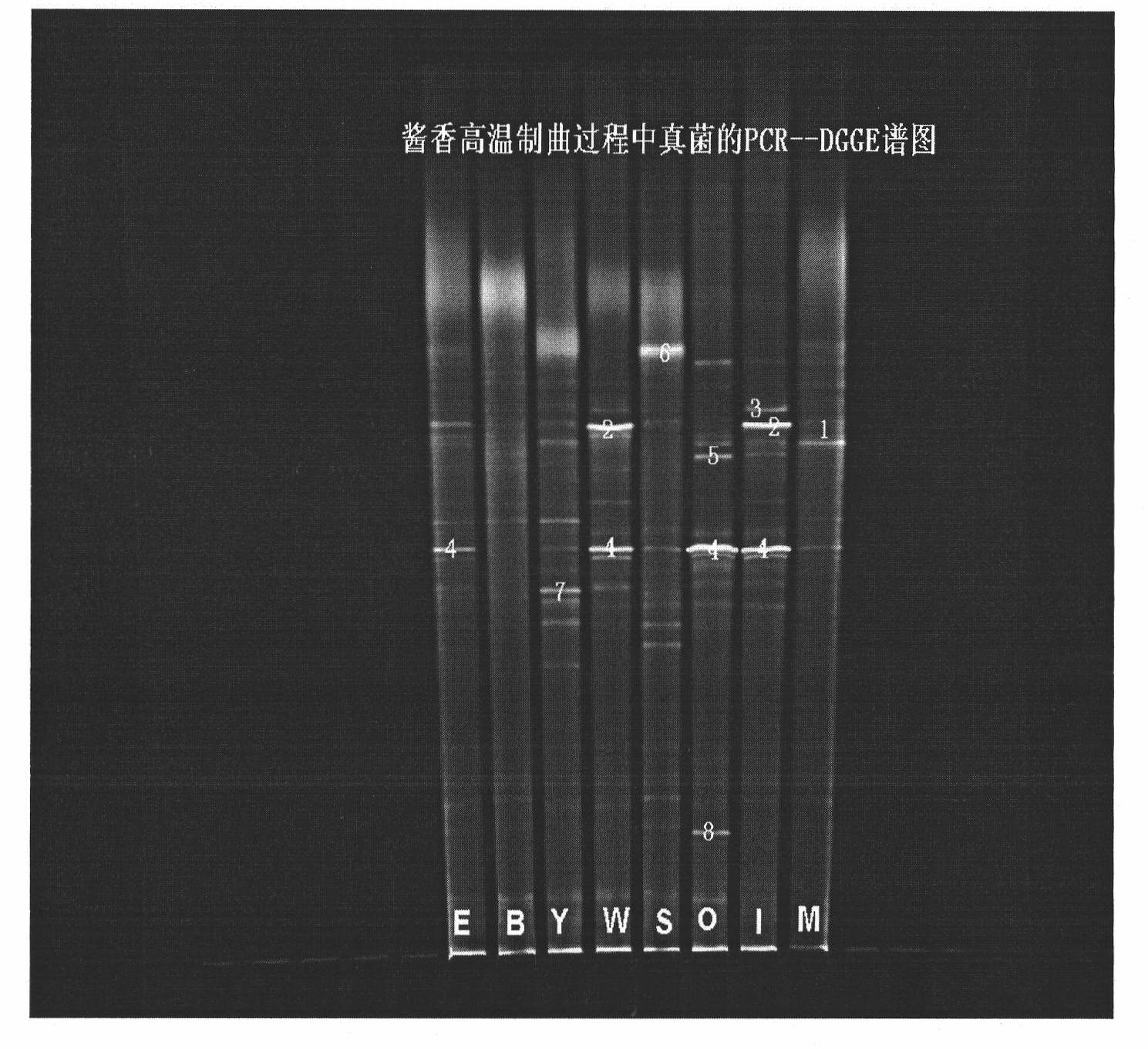
Method for identifying Maotai-flavor Daqu liquor
InactiveCN102071249AAvoid screeningAvoid enrichmentMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismMicrobiology
Owner:贵州国台酒业集团股份有限公司
Method for quickly extracting fungal DNA for PCR amplification
InactiveCN101696411AReduce lossesImprove extraction efficiencyMicroorganism based processesDNA preparationBiotechnologyMolecular identification
The invention discloses a method for quickly extracting fungal DNA for PCR amplification, which comprises the steps of: (1) culturing fungi to obtain fungal mycelia; (2) placing the fungal myceliua into a centrifugal tube filled with a lysate; (3) alternately freezing and thawing the centrifugal tube; and (4) centrifuging the thawed fungal mycelia, taking a supernatant, adding 95 percent ethanol into the supernatant, mixing the mixture evenly, quickly freezing the mixture by liquid nitrogen, centrifuging the mixture, removing a supernatant, and air-drying a precipitate to obtain the fungal DNA. The method has simple operation, is time-saving and labor-saving, reduces the loss of the fungal DNA during the grinding, does not need phenol and chloroform for extraction, and avoids the contact of a toxic reagent. The DNA extracted by the method has good integrity, high purity and high yield, can be directly used for a PCR amplification reaction, and can efficiently amplify a target product for cloning and sequencing. The method improves the extraction efficiency of the fungal DNA, reduces the cost for the extraction of the fungal DNA, and can effectively improve the molecular identification and detection efficiency of the fungi.
Owner:INST OF FOREST ECOLOGY ENVIRONMENT & PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Primers and kit for detecting fusarium on basis of loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology
InactiveCN102251055ASensitive detectionQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesUracil-DNA glycosylaseLoop-mediated isothermal amplification
The invention relates to a loop-mediated isothermal amplification kit and method for detecting fusarium. The kit comprises loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction liquid, UNG (uracil-DNA-glycosylase), Bst DNA polymerase, developer and fusarium positive DNA, wherein the reaction liquid contains forward / reverse inner and outer primers, of which the sequences are respectively SEQ ID NO: 1-4. The detection method comprises the steps of fungus DNA extraction, loop-mediated isothermal amplification and development detection. The loop-mediated isothermal amplification primers are designed according to the fusarium gene conserved region sequences, and the fusarium in the sample is detected by loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology. The invention has the advantages of high speed, high sensitivity, high specificity, low cost and the like; and the whole process is not related to toxic reagents, thereby ensuring the safety of operating personnel and environment. Meanwhile, the UNG adopted in the invention can thoroughly eliminate false positive caused by nucleic acid pollution in multiple detection processes.
Owner:SHANDONG EYE INST
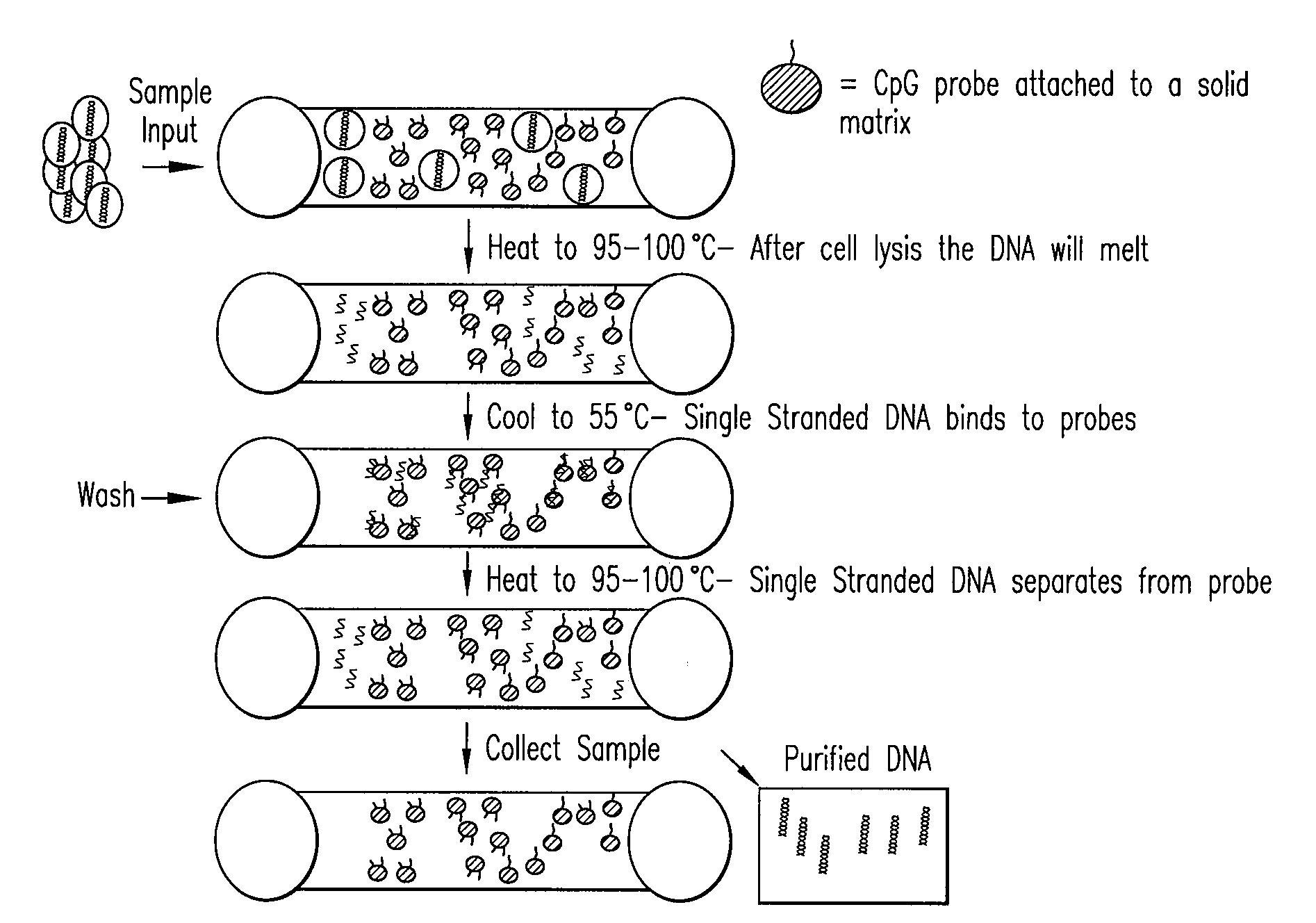
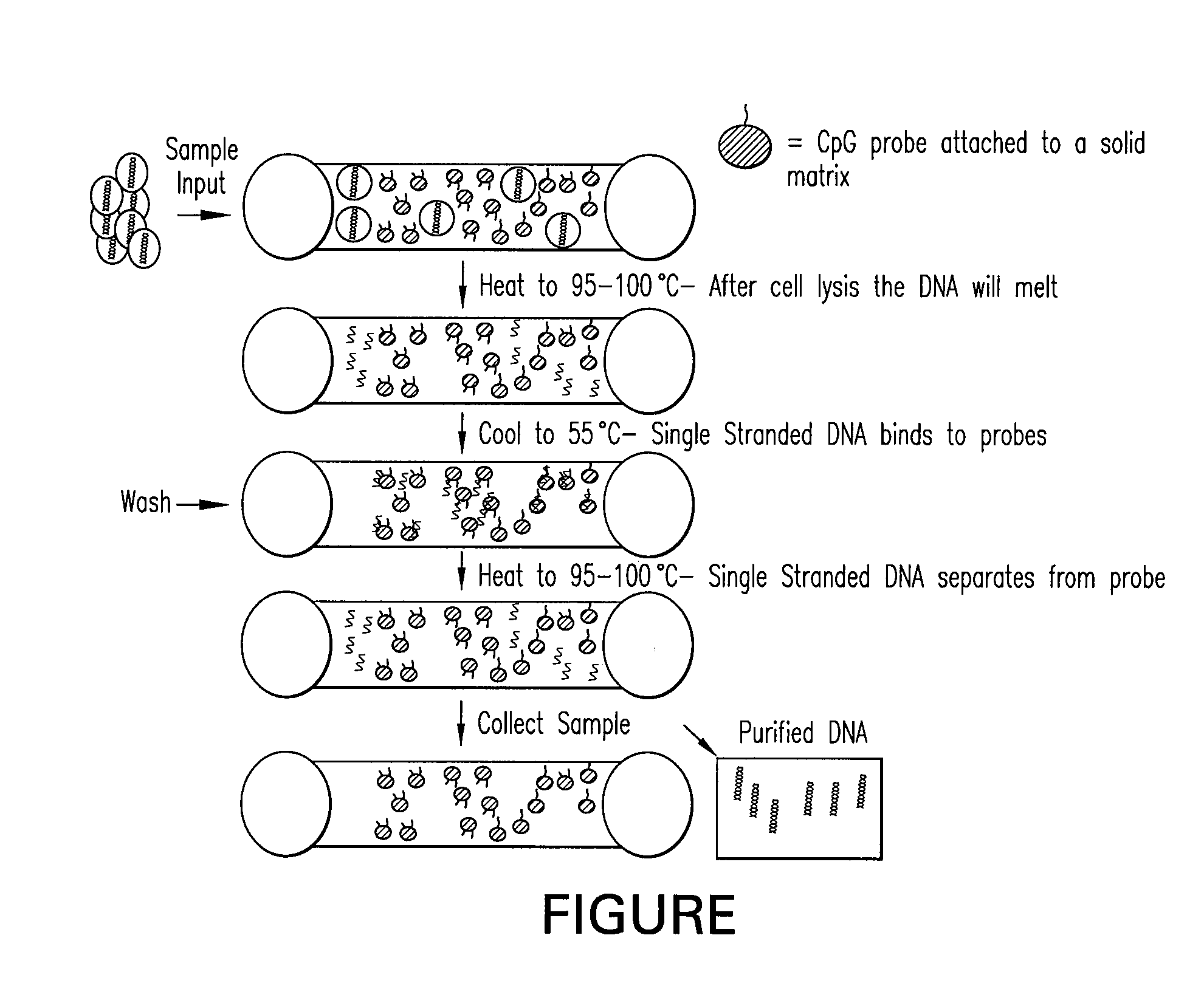
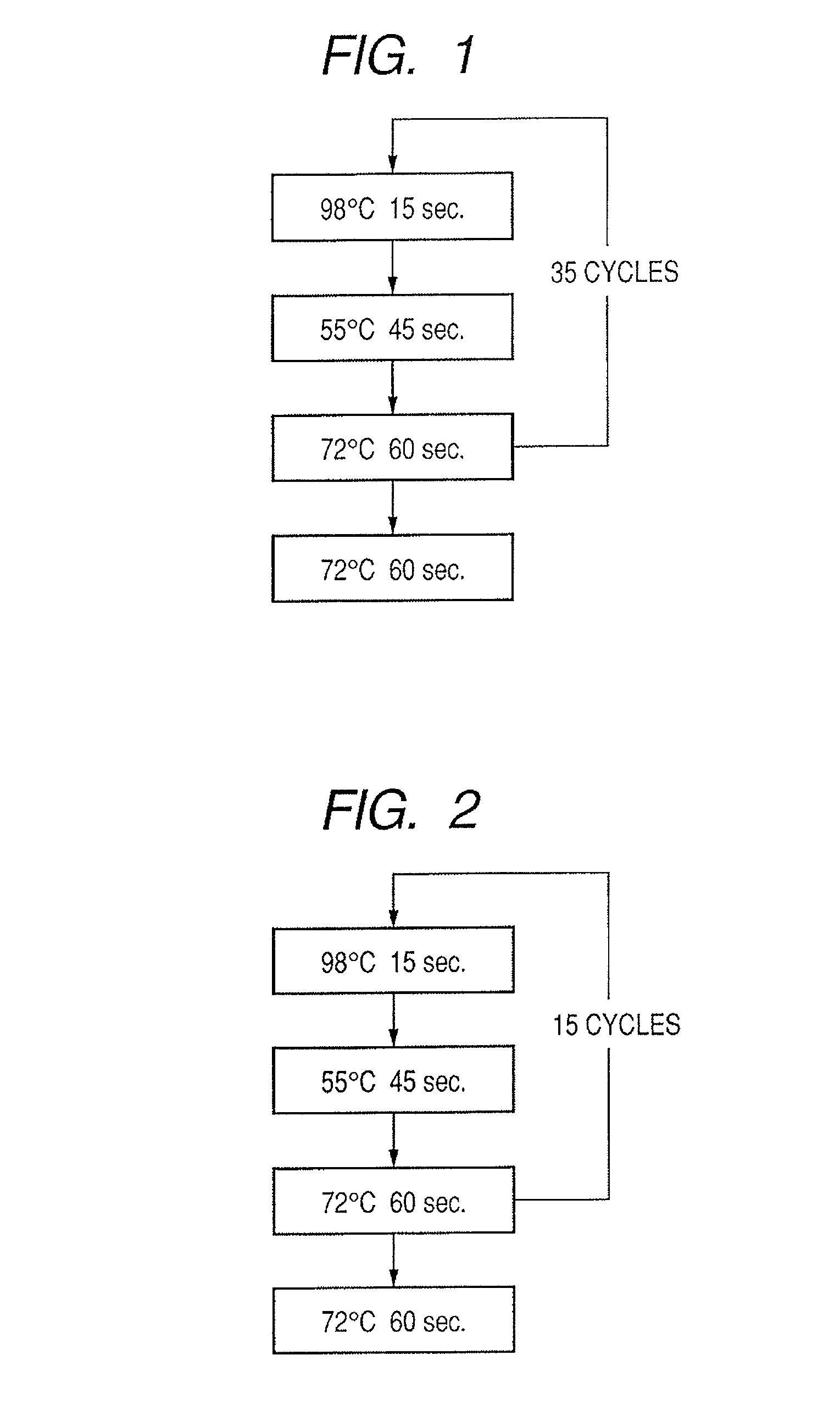
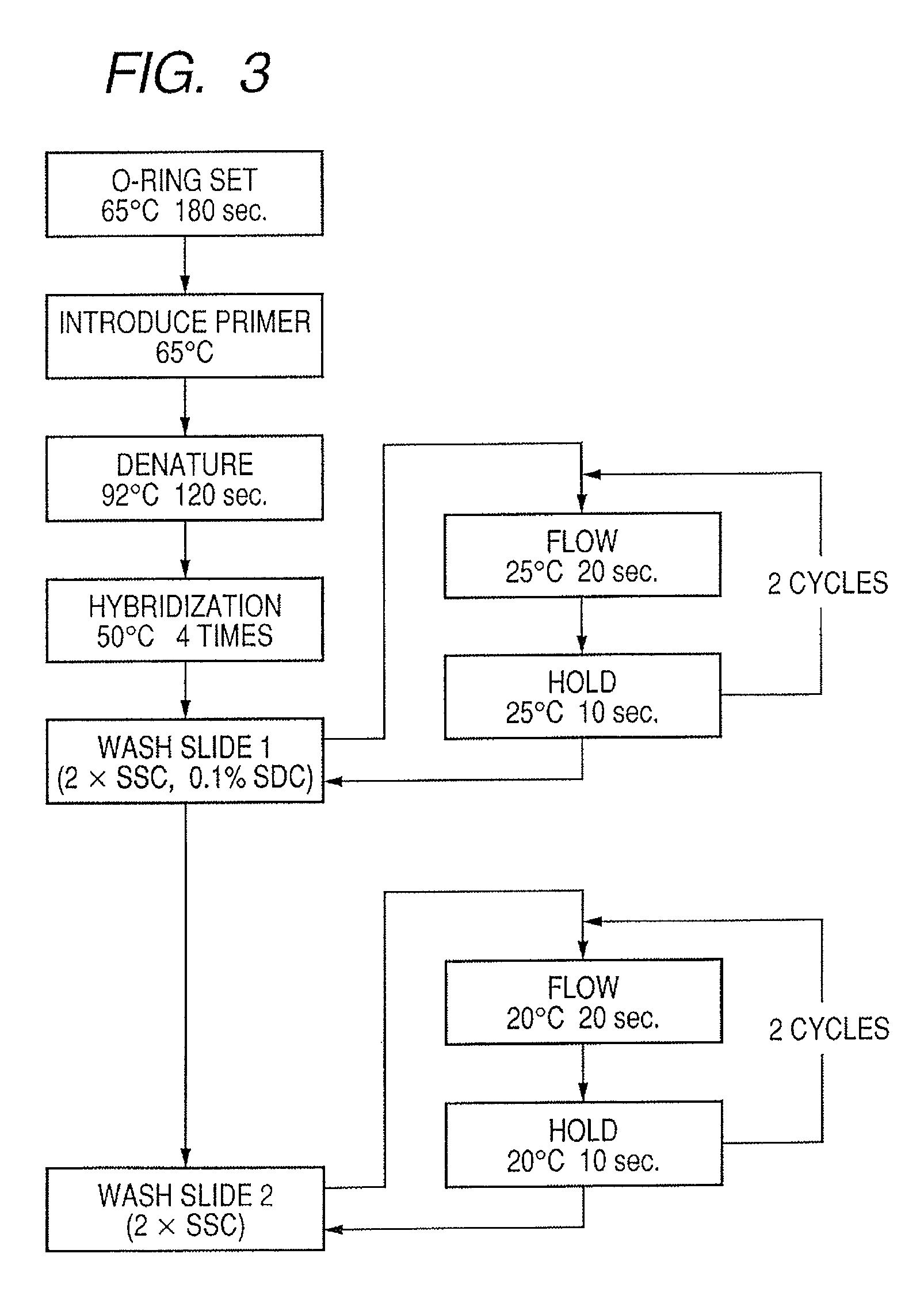
Method of Separating Target DNA from Mixed DNA
The present invention relates to methods of separating target DNA from mixed DNA in a sample. In some embodiments, the target DNA may be viral DNA, prokaryotic DNA, fungal DNA or combinations thereof. In some embodiments the mixed DNA includes target DNA and non-target DNA.
Owner:CANON US LIFE SCIENCES INC
Method for direct detection of fungal pathogens
ActiveUS7291465B2Quick and efficient qualitative identification and detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCompanion animalDNA
The present invention relates to a method and diagnostic kit for directly detecting the presence of a specific species of mold / fungi in a sample, particularly a species which is toxic to humans or animals including pets and livestock. The method involves releasing any fungal DNA from the sample and subjecting it to PCR amplification without the need for purifying the DNA.
Owner:KARAGEN PHARMA INC
SLS splitting liquor for rapid extraction of fungus DNA and uses thereof
The invention discloses a SLS lysis solution which can quickly extract fungal DNA. The SLS lysis solution contains following components (calculated by the total volume of solution): 1 - 3 g / 100ml of N-lauroyl sodium sarcosinate, 150 - 300mmol / L of Tris-HCl, 150 - 300mmol / L of NaCl, and 50 - 100mmol / L of EDTA; and the pH value is ranged from 7.5 to 8.5. The SLS lysis solution of the invention takes N-lauroyl sodium sarcosinate as the main functional component to make up the DNA extracting solution; and the DNA extracting solution can be used for extracting fungal DNA. Due to the excellent biologic degradability, the DNA extracting solution can be used for directly breaking the cell wall of pathogenic fungi, thereby avoiding the complicated physical processing of the cell-wall breaking in traditional method in extracting fungal DNA, and greatly simplifying the extracting of DAN.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Externally used Chinese medicine for treating tinea versicolor
InactiveCN101194954AHas a killing effectInhibition of synthesisHeavy metal active ingredientsAntimycoticsMalassezia furfurCnidium
The invention discloses an externally used traditional Chinese medicine for curing tinea versicolor, which is powder which is prepared by raw material with the following ratio by weight, such as sulfur 10-15%, density monk 20-30%, cuttlebone 20-30%, chuan paprika 10-15%, cnidium fruit 10-15% and dried alum 6-10%. The compatibility of the raw material of the invention has the function of detoxifying, destroying intectinal worms, sterilizing and relieving itching. The invention has a killing effect to malassezia furfur, and has a function of inhibiting fungi DNA to synthesize. The invention is a traditional Chinese medicine for effectively curing tinea versicolor, which is harmless to skin, and has the advantages of short course and quick results, which can not recur after healing, and effective rate can reach 100%.
Owner:韩曙光
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification fast detection method of producing ariatoxin fungi
InactiveCN101381771AGuaranteed reliabilityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementGlycineBetaine
The invention relates to a rapid detection method for aflatoxin-producing fungi by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Reagents used by the method comprises a loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction solution, a Bst DNA polymerase and a color development reagent, wherein the reaction solution contains reaction buffer, dNTP, magnesium sulfate, an upstream inner primer 5-CGACAGTTGTTGGGGCCTGC-TCCAGGACATGTGCAGACT-3, a downstream inner primer 5-CAGACAGTGTGGCAGGCATCT-CCGTGTGGATAACGAAGTGC-3, an upstream outer primer 5-TCACGGCCTTCATCATCGA-3, a downstream outer primer 5-ACCAGGGGAGTTGAGATCC-3, and glycine betaine. The method for detection of aflatoxin-producing fungi comprises the steps of DNA extraction of the fungi, loop-mediated isothermal amplification of the aflatoxin-producing fungi, and chromogenic detection. The method has the advantages of rapidness, strong specificity, high sensitivity and low cost.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT SHANDONG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Method of Separating Target DNA from Mixed DNA
The present invention relates to methods of separating target DNA from mixed DNA in a sample. In some embodiments, the target DNA may be viral DNA, bacterial DNA, fungal DNA or combinations thereof. In some embodiments the mixed DNA includes target DNA and non-target DNA.
Owner:CANON US LIFE SCIENCES INC
Probe, probe set and probe carrier for detecting Candida lusitaniae
InactiveUS7863000B2Accurate identificationQuickly and more accurately detect a target fungusSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCandida lusitaniaeMicrobiology
A probe, a set of probes, and a probe carrier on which the probe or the set of probes is immobilized, are provided for classification of fungus species. The probe or the set of probes is capable of collectively detecting fungus of the same species and distinguishingly detecting those fungus from fungus of other species. The probe is an oligonucleotide probe for detecting a pathogenic fungus DNA and includes at least one of base sequences of SEQ ID NOS. 1 to 2 and mutated sequences thereof.
Owner:CANON KK
Molecule identification method for taxol-producing endophytic fungi in yew
InactiveCN101302555AEliminate the extraction stepSimple preliminary identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular identificationEndophytic fungus
The invention discloses a molecular identification method in the molecular biology technical field. The detection method comprises the following steps that: endophytic fungi are separated from yew and are preserved and cultivated; mycelium of the cultivated endophytic fungi is scrubbed, precipitated and ground into powder; DNA of the endophytic fungi is extracted and purified; PCR augmentation, electrophoretic detection of a PCR product and the determination of a special gene sequence are performed; whether a strain produces taxol is distinguished by the fact that whether a special band with the size of 650bp can be augmented in the endophytic fungi; and the reliability of the result is further confirmed through a chemical detection program. The method performs simple, quick and accurate preliminary identification that whether the special gene sequence produces the taxol to the endophytic fungi, which lays the foundation for further research and development and use.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com