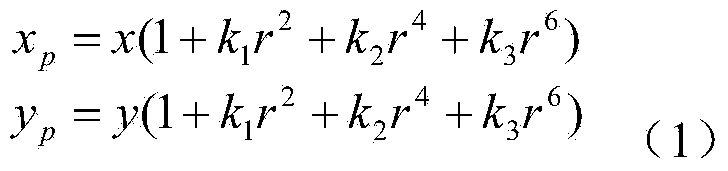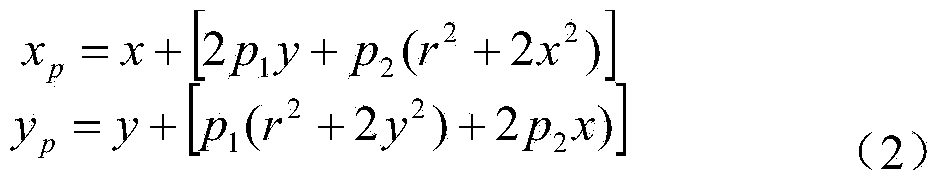Patents
Literature
1565 results about "Non targeted" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Non-Targeted Metabolomics. The non-targeted metabolomics approach aims to study both known and unknown metabolites. To comprehend the huge chunks of data this may yield, one must couple it with advanced chemometric methods such as multivariate analysis, so that these can be grouped into smaller manageable chunks.
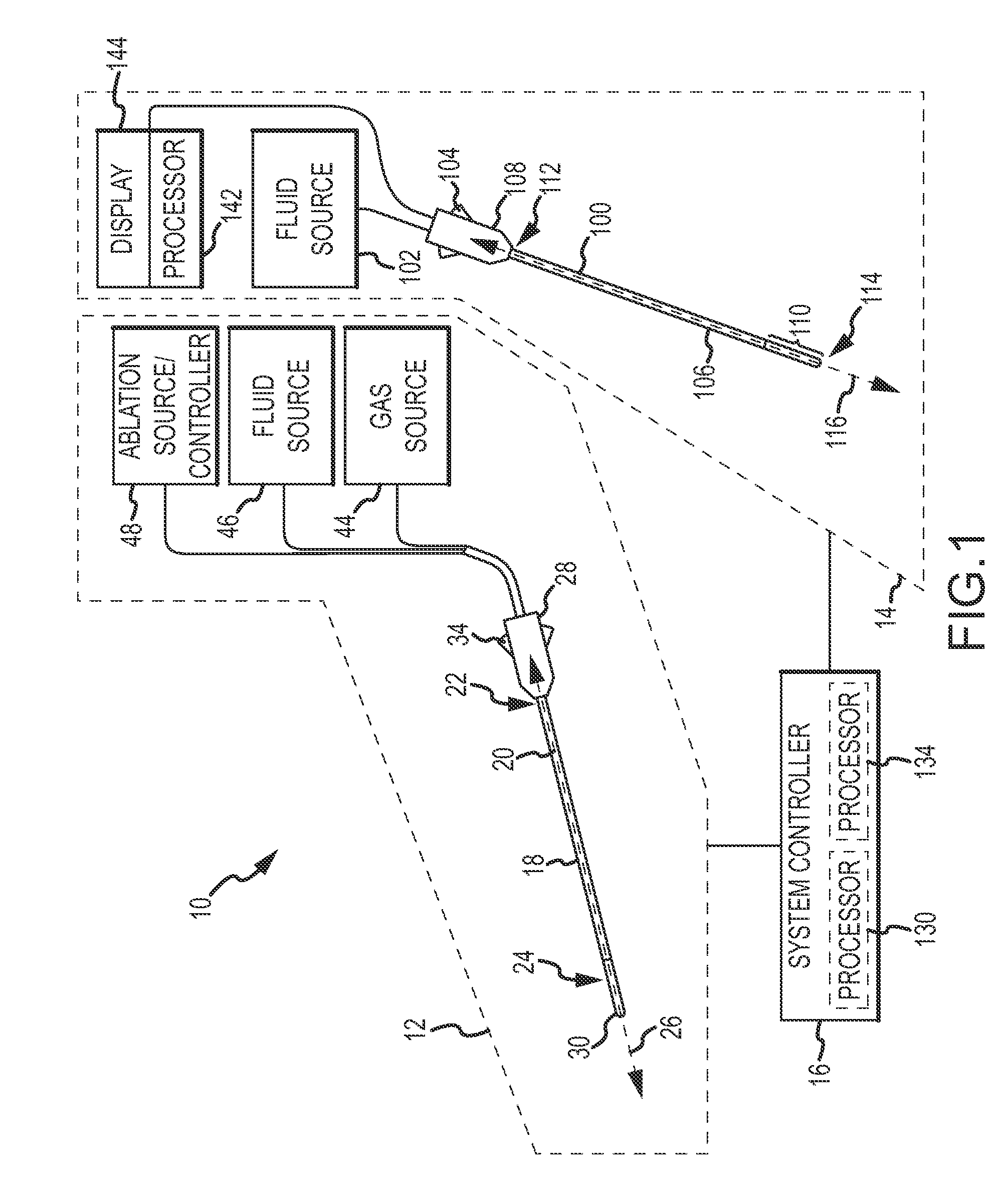
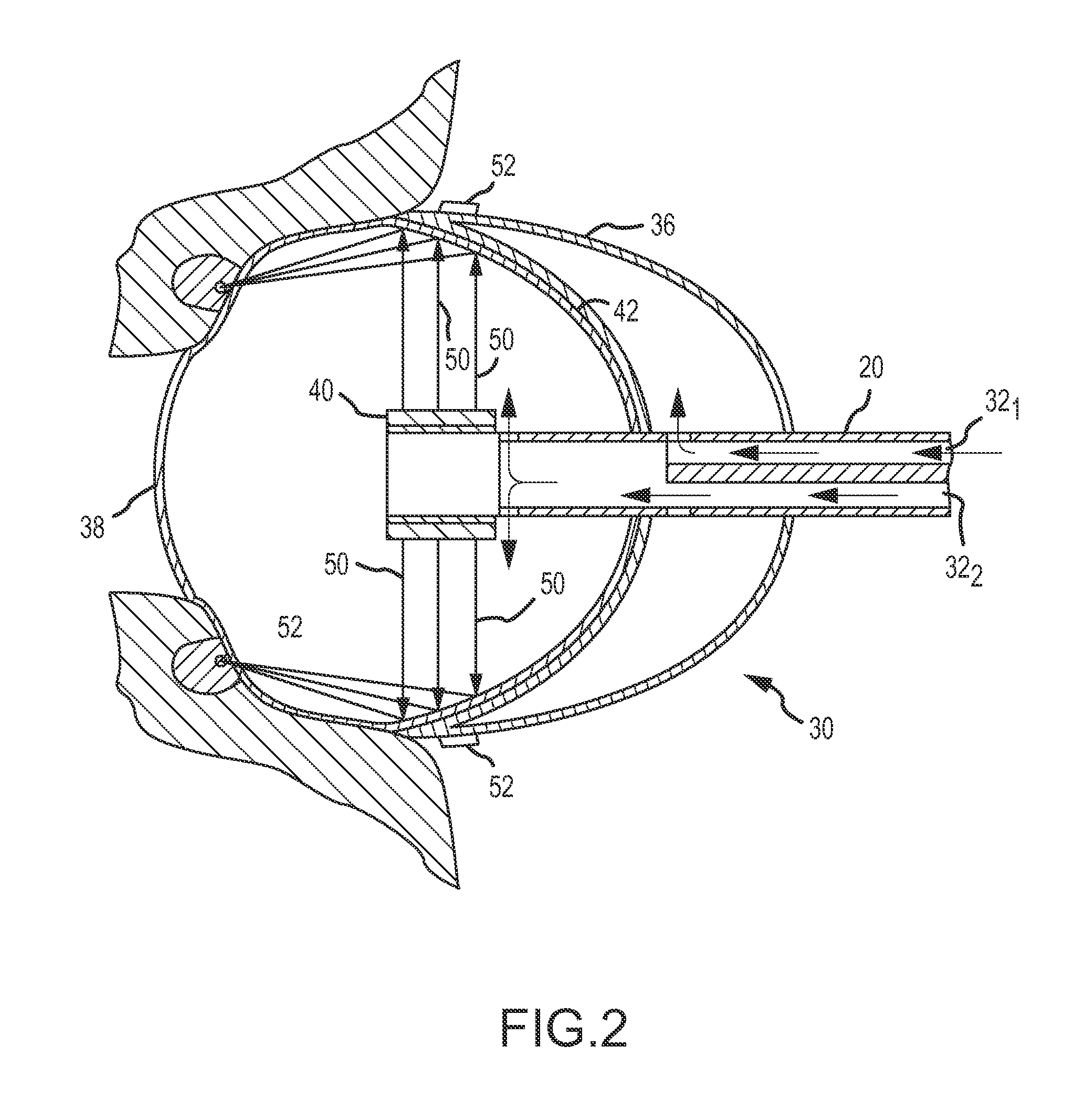
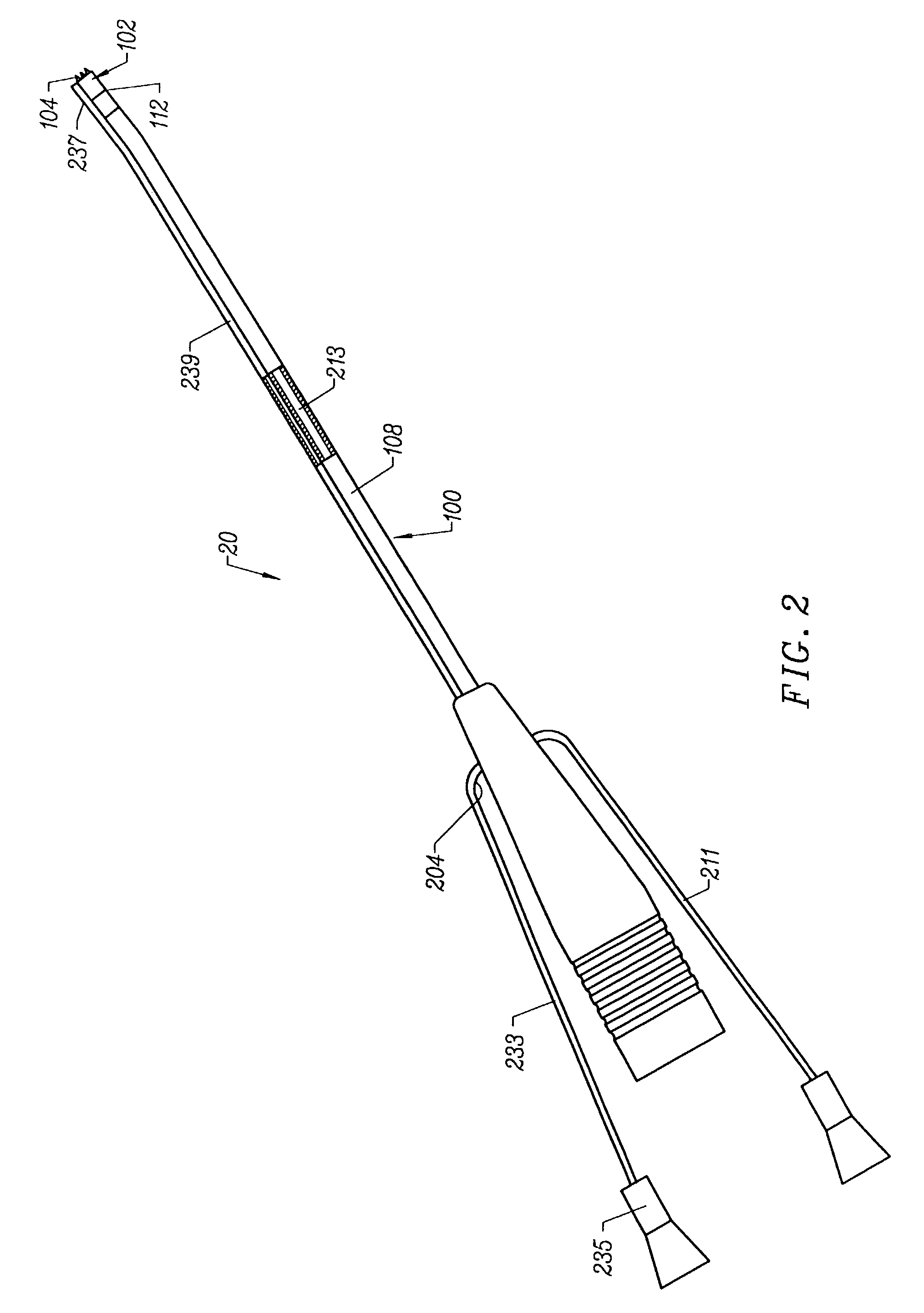
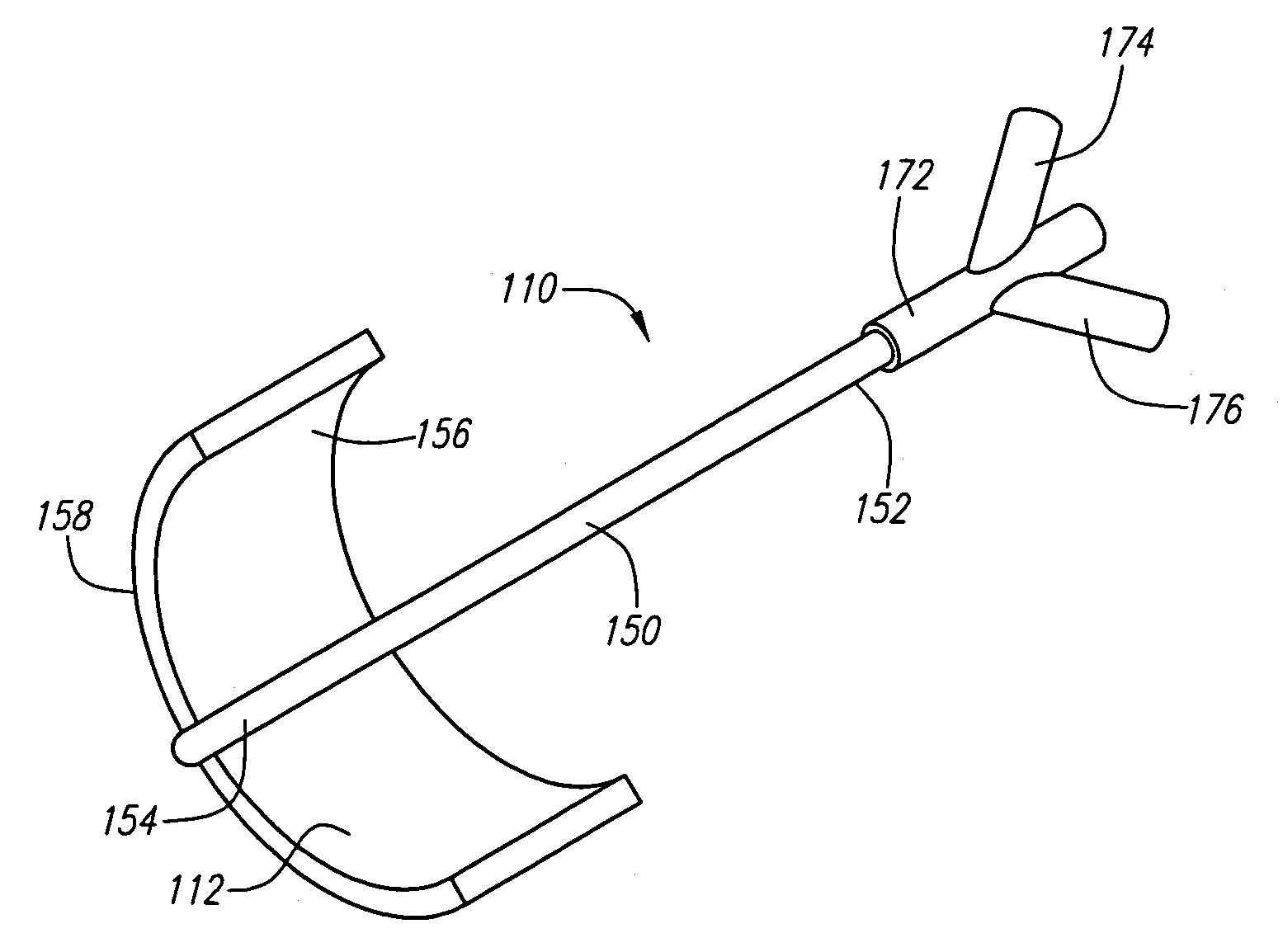
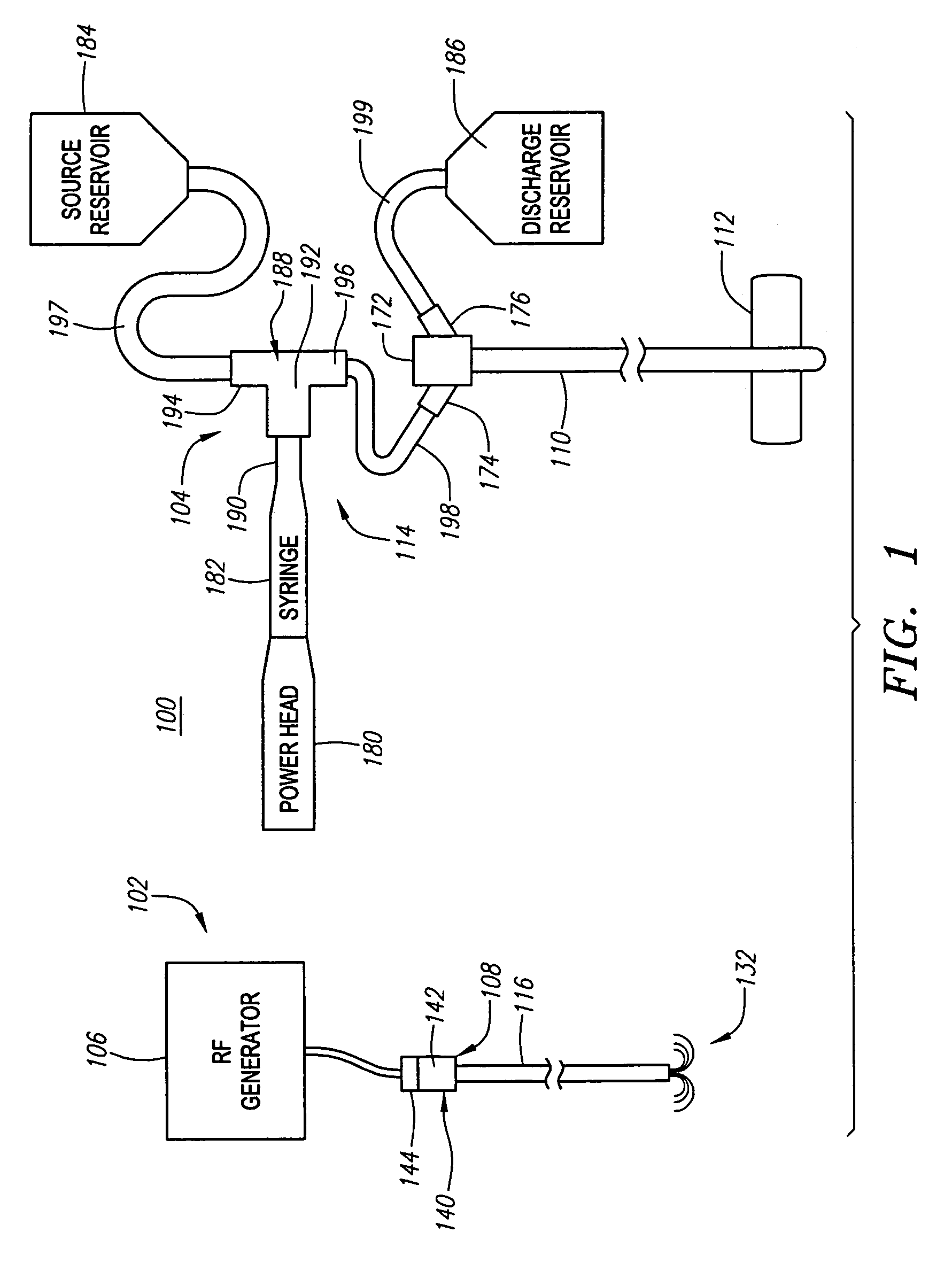
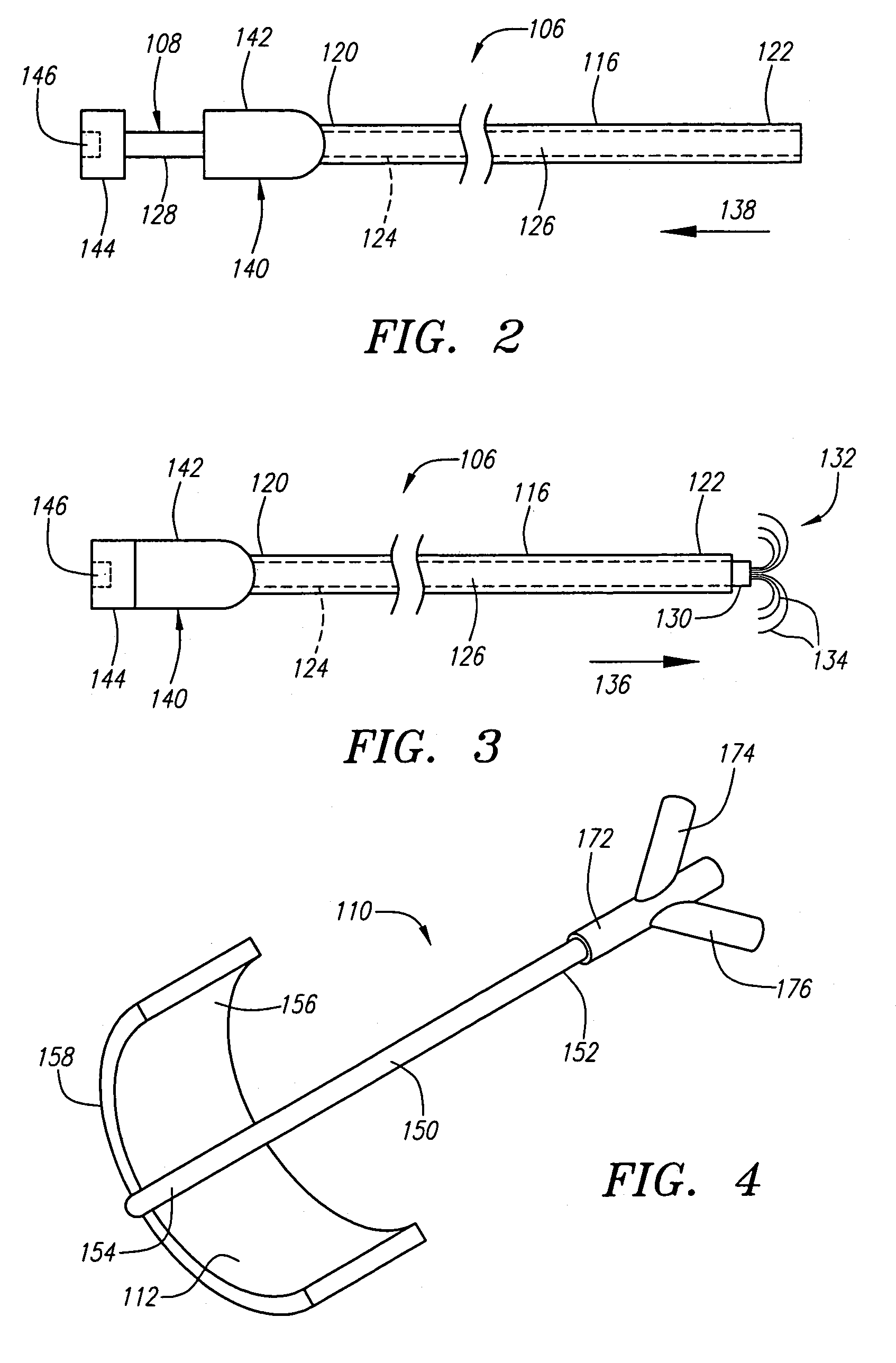
Dual mode electrosurgical clamping probe and related methods
InactiveUS6974453B2Minimize damageAvoid and minimize currentCannulasEnemata/irrigatorsDual modeSurgical department
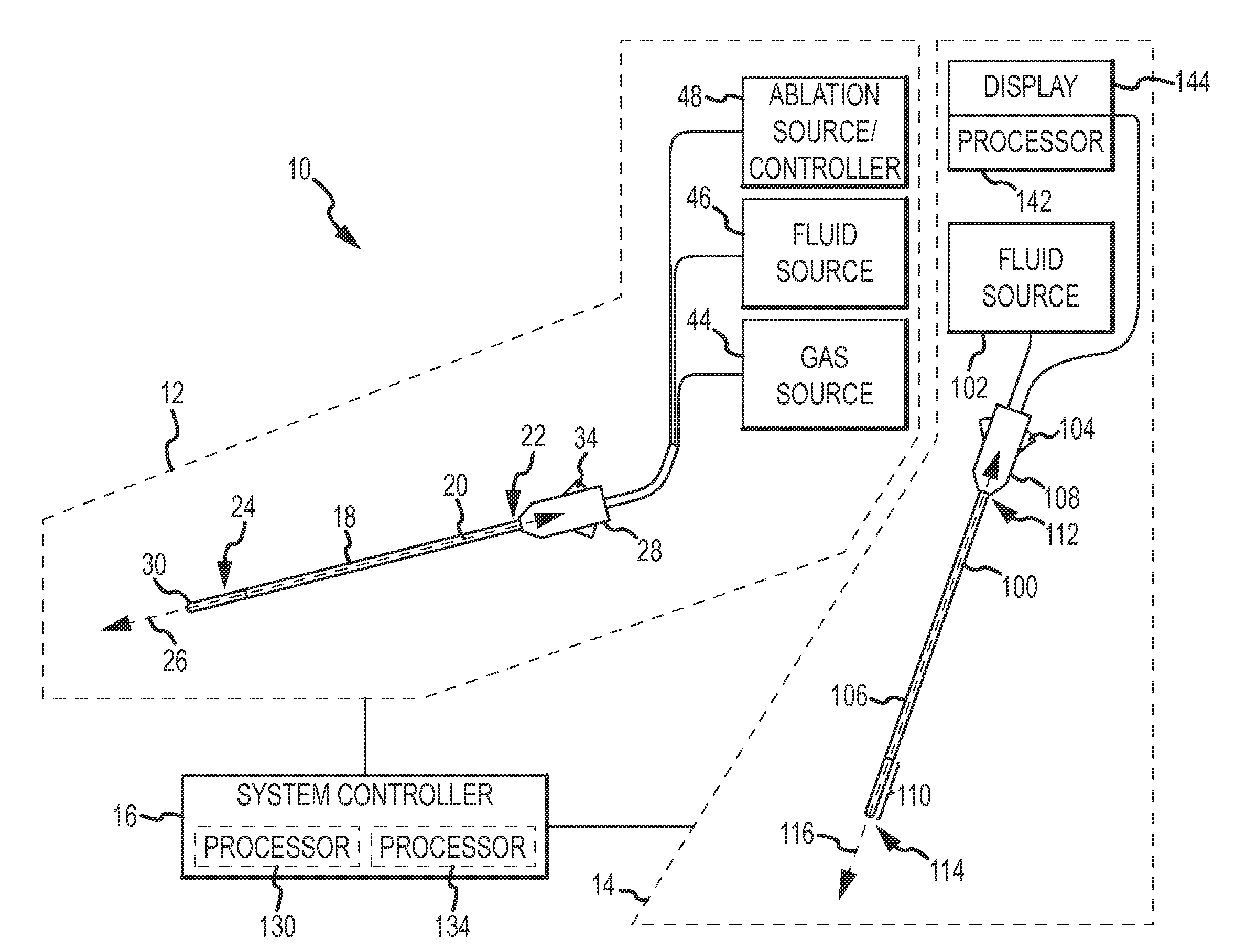
The present invention provides systems, apparatus and methods for selectively applying electrical energy to body tissue in order to ablate, contract, coagulate, or otherwise modify a target tissue or organ of a patients. An electrosurgical apparatus of the invention includes a shaft having a shaft distal end bearing an active electrode and a return electrode. At least one of the active electrode and the return electrode is moveable such that the shaft distal end can adopt a closed configuration or an open configuration. The apparatus can operate in an ablation mode or a sub-ablation mode. The closed configuration is adapted for clamping and coagulating a target tissue while the apparatus is operating in the sub-ablation mode, while the open configuration is adapted for ablating the target tissue via molecular dissociation of tissue components. A method of the present invention comprises clamping a target tissue or organ with an electrosurgical probe. A first high frequency voltage is applied between the active electrode and the return electrode to effect coagulation of the clamped tissue. Thereafter, a second high frequency voltage is applied to effect localized molecular dissociation of the coagulated tissue. The present invention allows the ablation or modification of the target tissue with minimal or no damage to surrounding, non-target tissue.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
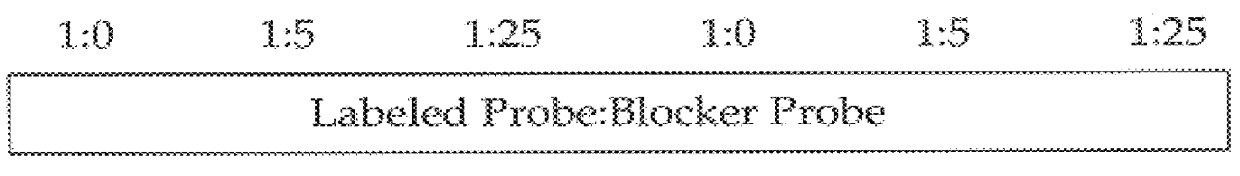
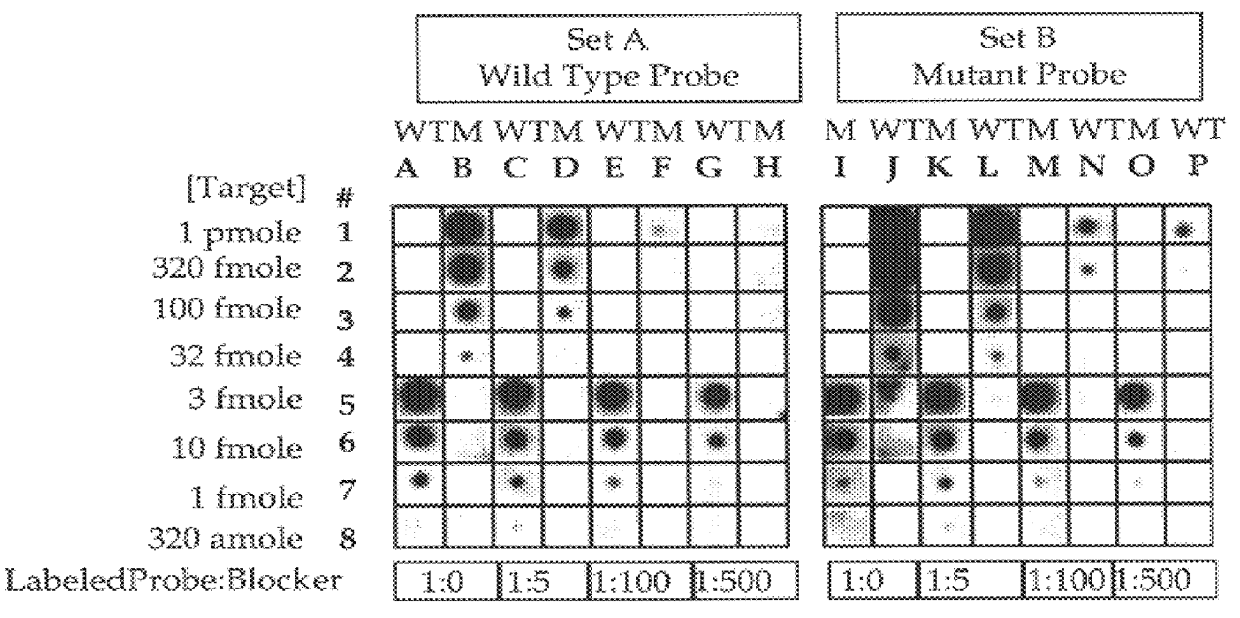
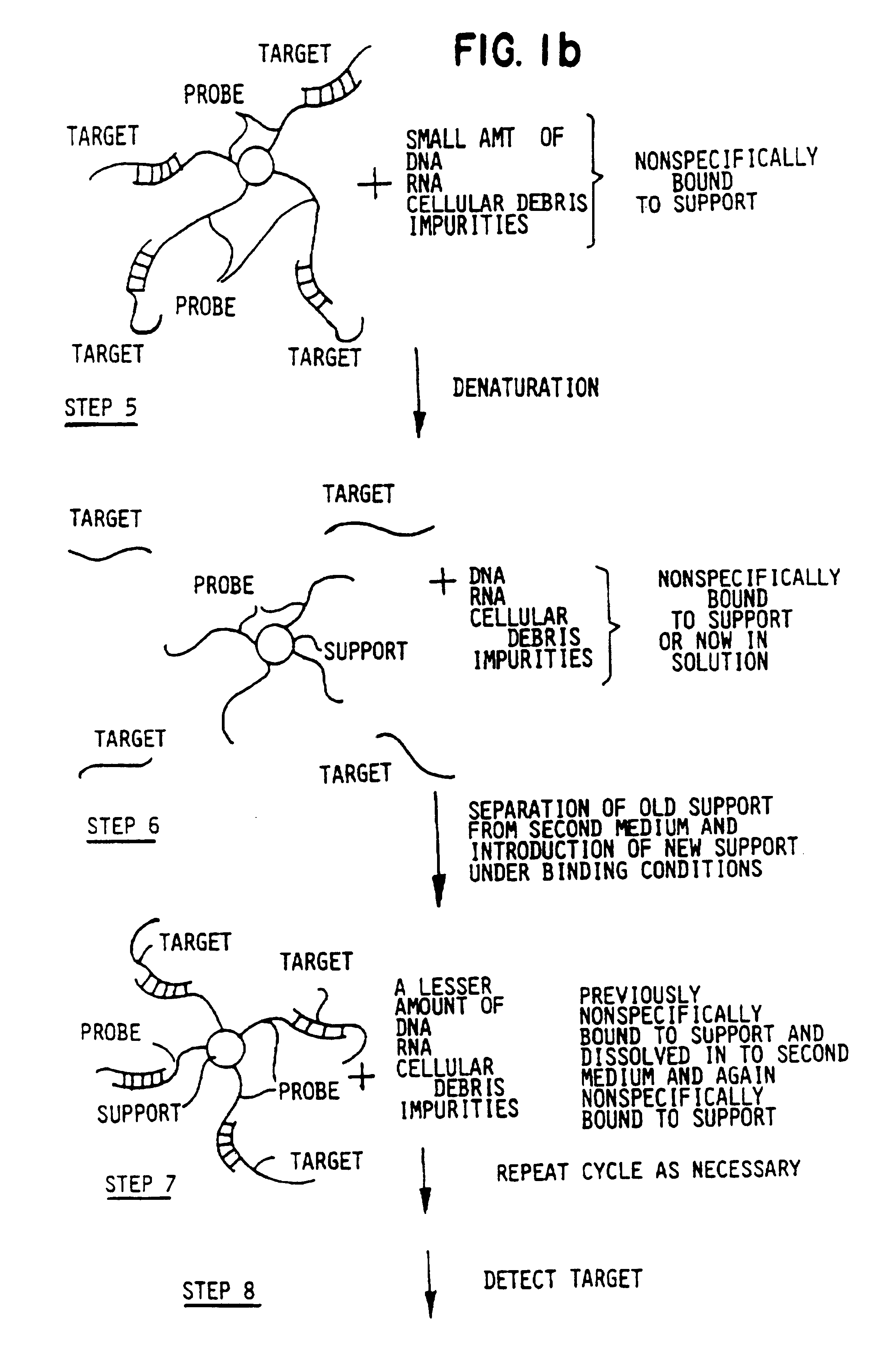
Methods for suppressing the binding of detectable probes to non-target sequences in hybridization assays
InactiveUS6110676AIncrease assayEasy to addSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleic Acid ProbesTrue positive rate
This invention relates to methods, kits and compositions suitable for the improved detection, analysis and quantitation of nucleic acid target sequences using probe based hybridization assays. The invention is more specifically directed to methods, kits and compositions suitable for suppressing the binding of detectable nucleic acid probes or detectable PNA probes to non-target nucleic acid sequences in an assay for a target nucleic acid sequence to thereby improve the reliability, sensitivity and specificity of the assay. The methods, kits and compositions of this invention are particularly well suited to the detection and analysis of nucleic acid point mutations.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC +1
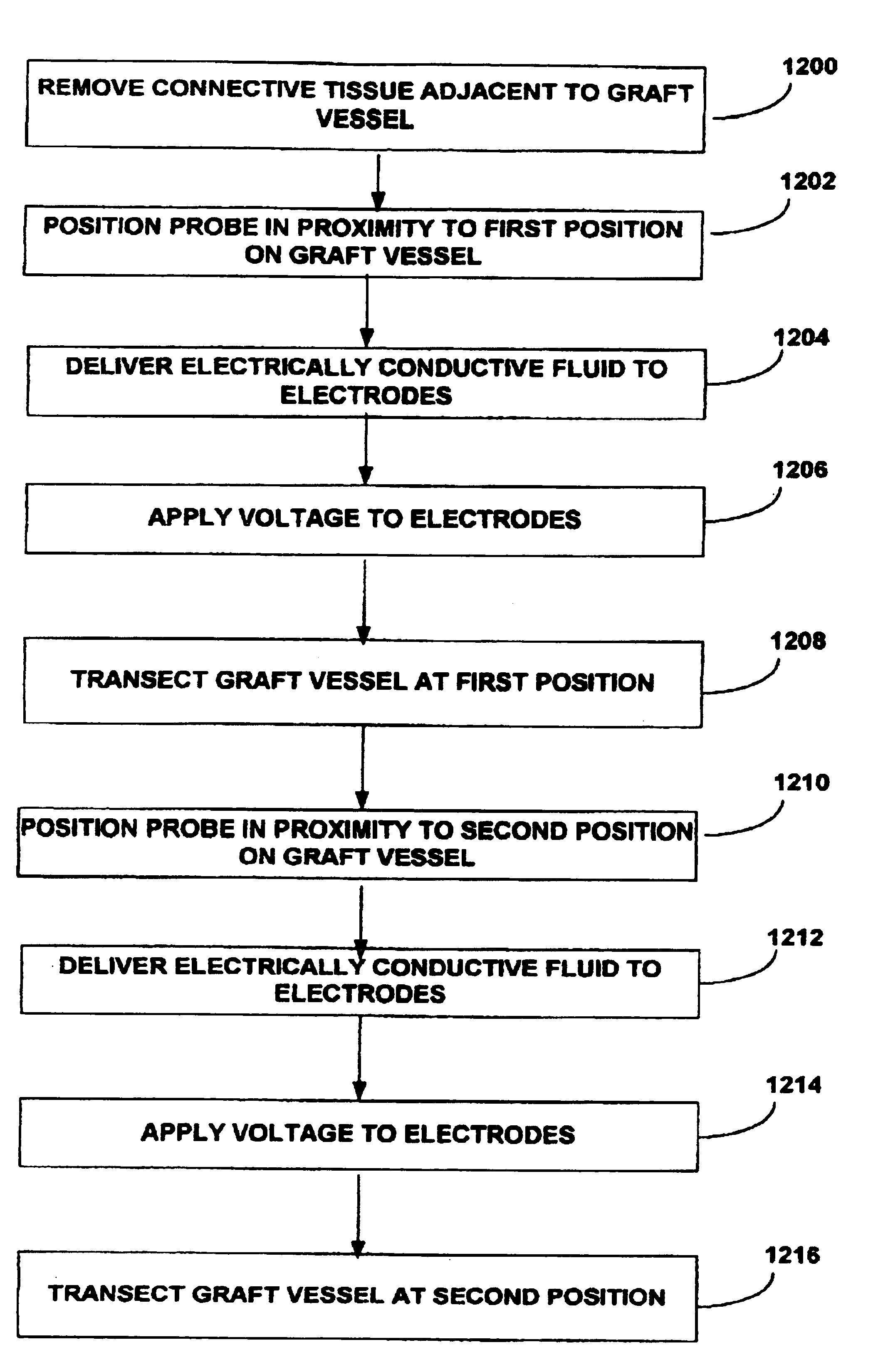
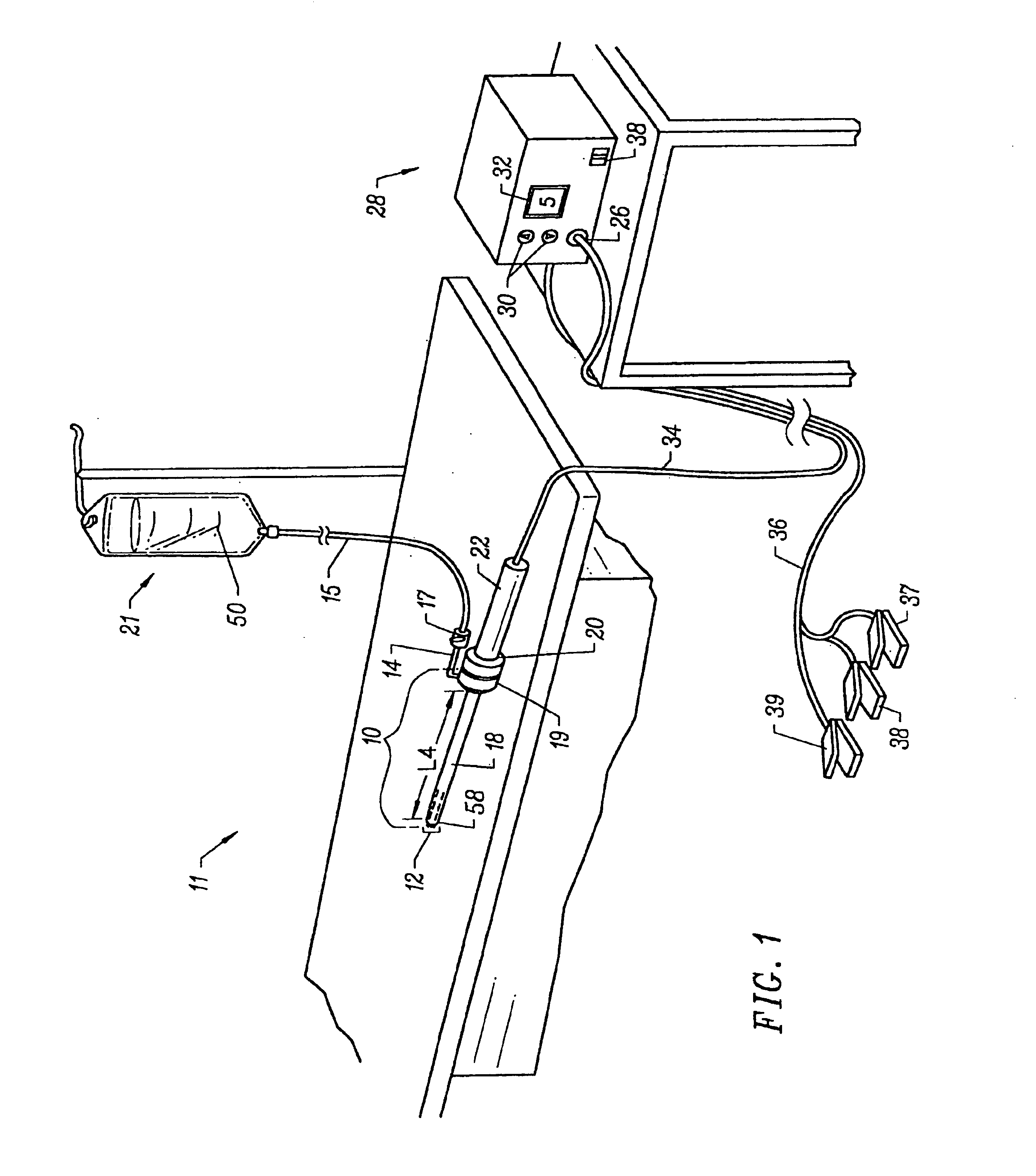
Method for harvesting graft vessel
InactiveUS6915806B2Improves surgeon 's viewThermal damage is minimizedCannulasEnemata/irrigatorsSaphenous veinsMammary artery
The present invention provides systems, apparatus and methods for selectively applying electrical energy to body tissue in order to incise, dissect, harvest or transect tissues or an organ of a patient. The electrosurgical systems and methods are useful, inter alia, for accessing, dissecting, and transecting a graft blood vessel, such as the internal mammary arteries (IMA) or the saphenous vein, for use in a by-pass procedure. A method of the present invention comprises positioning an electrosurgical probe adjacent the target tissue so that one or more active electrode(s) are brought into at least partial contact or close proximity with a target site in the presence of an electrically conductive fluid. A high frequency voltage is then applied between the active electrode and one or more return electrode(s). During application of the high frequency voltage, the electrosurgical probe may be translated, reciprocated, or otherwise manipulated such that the active electrode is moved with respect to the tissue. The present invention volumetrically removes the tissue at the point of incision, dissection, or transection in a cool ablation process that minimizes thermal damage to surrounding, non-target tissue.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
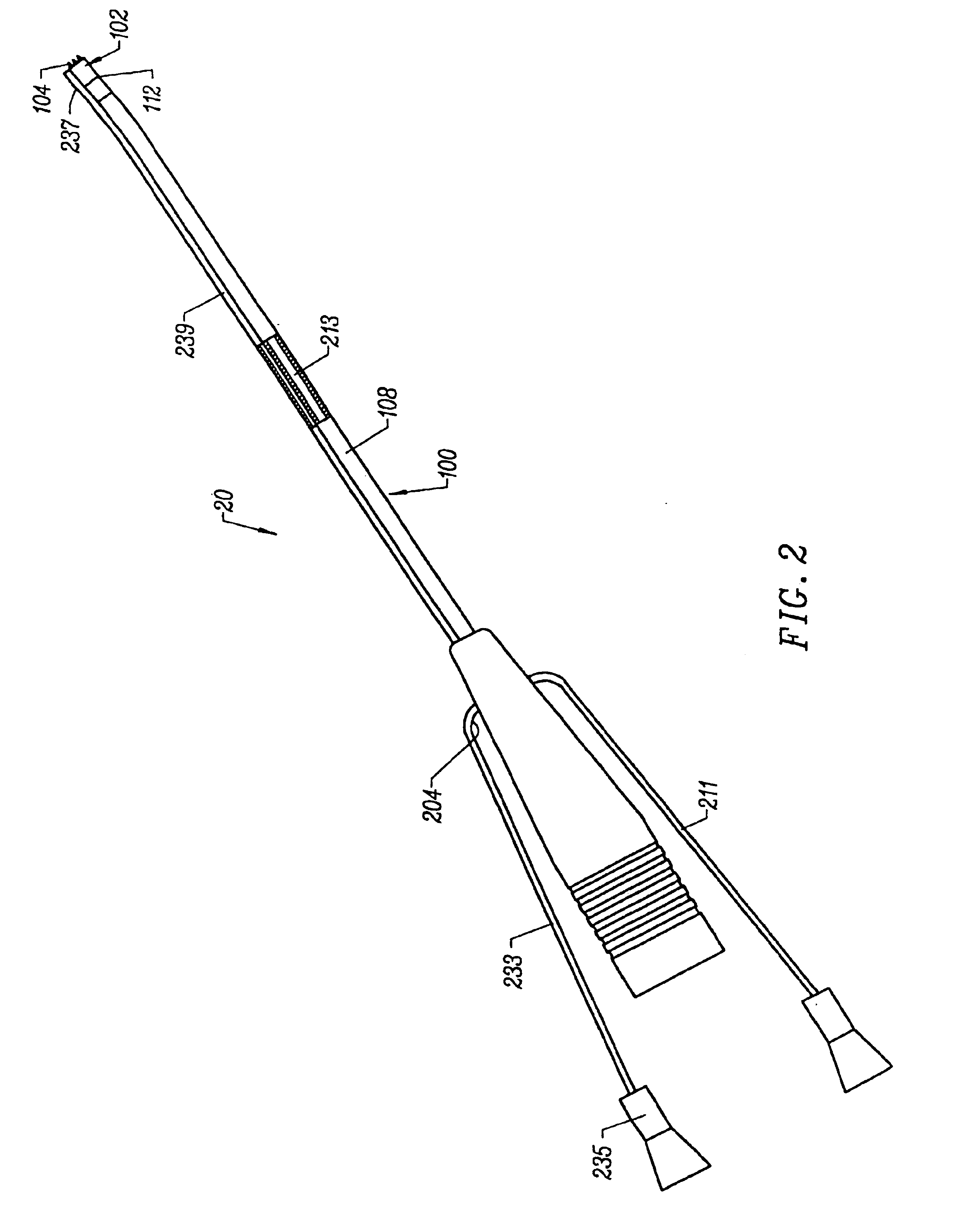
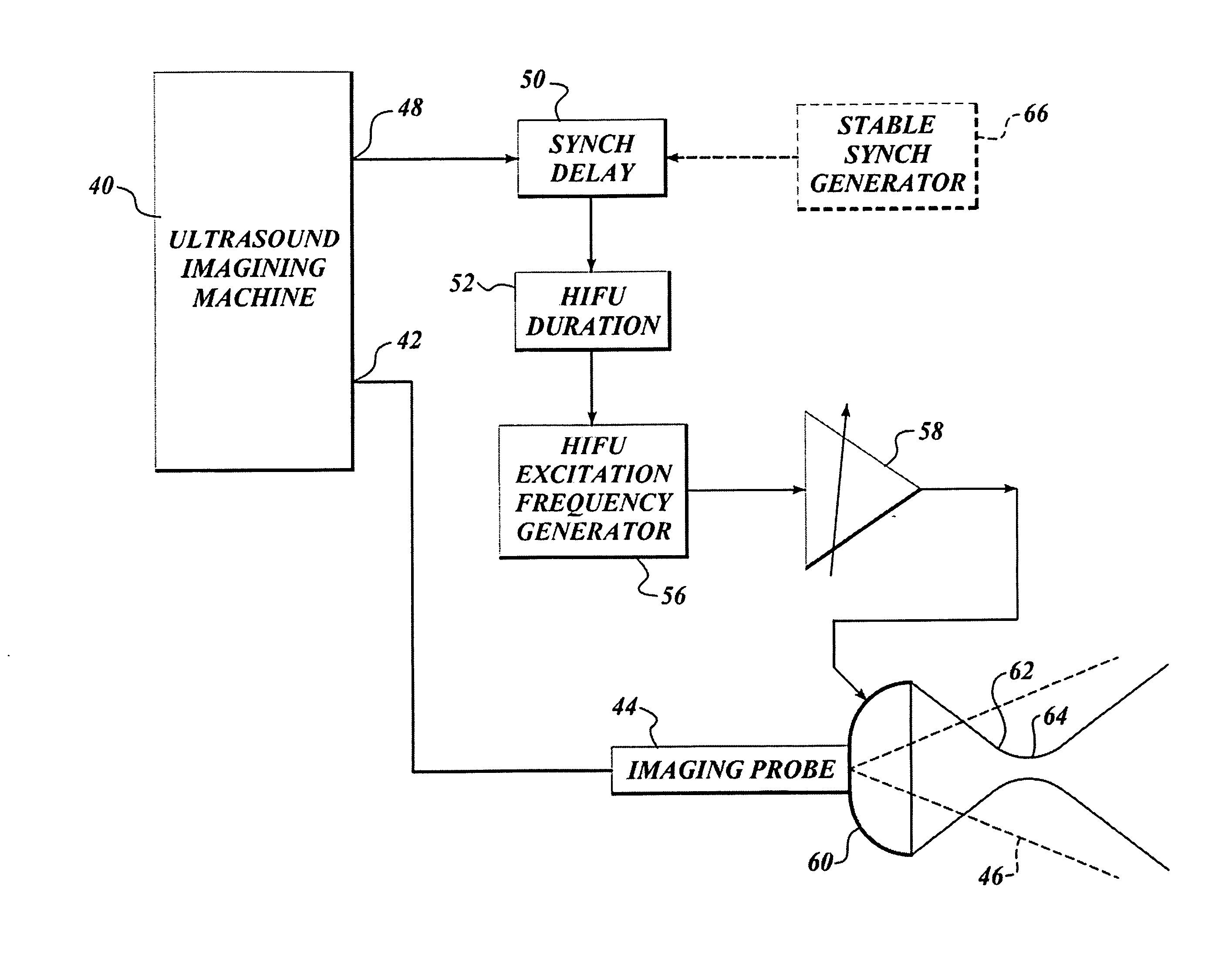
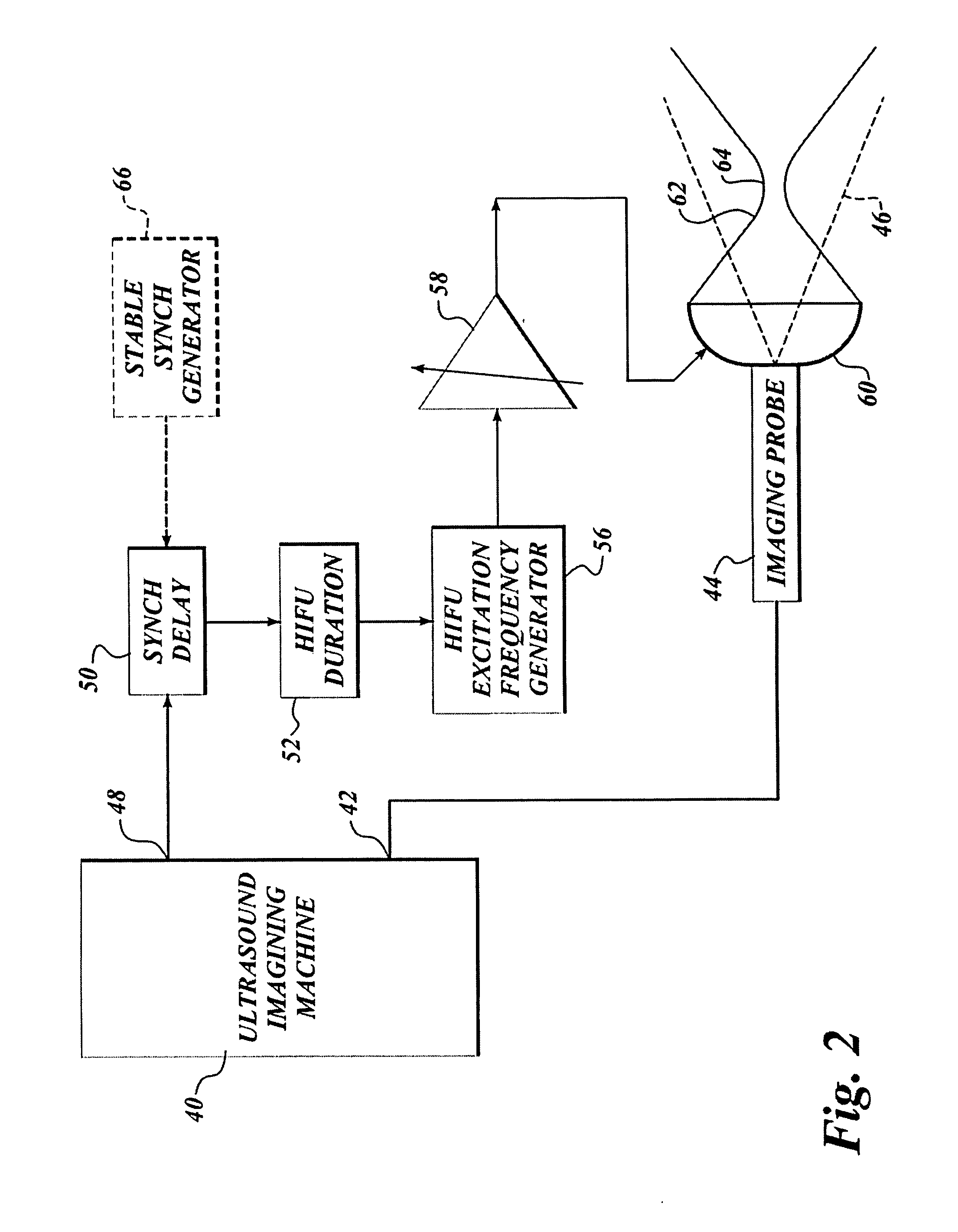
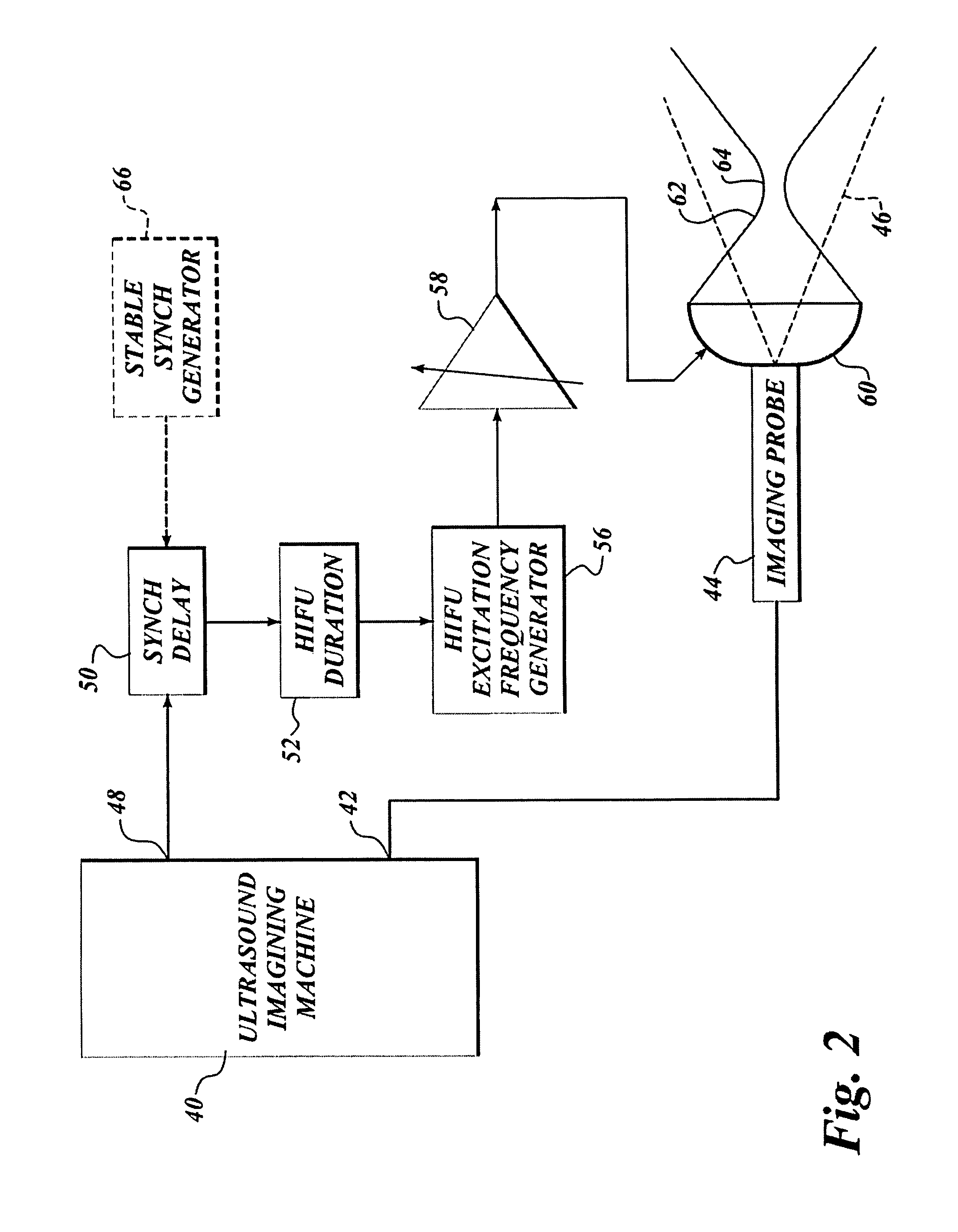
Use of contrast agents to increase the effectiveness of high intensity focused ultrasound therapy
InactiveUS20050038340A1Easy to useGood choiceUltrasound therapyBlood flow measurement devicesCavitationUltrasound contrast media
Ultrasound contrast agents are used to enhance imaging and facilitate HIFU therapy in four different ways. A contrast agent is used: (1) before therapy to locate specific vascular structures for treatment; (2) to determine the focal point of a HIFU therapy transducer while the HIFU therapy transducer is operated at a relatively low power level, so that non-target tissue is not damaged as the HIFU is transducer is properly focused at the target location; (3) to provide a positive feedback mechanism by causing cavitation that generates heat, reducing the level of HIFU energy administered for therapy compared to that required when a contrast agent is not used; and, (4) to shield non-target tissue from damage, by blocking the HIFU energy. Various combinations of these techniques can also be employed in a single therapeutic implementation.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
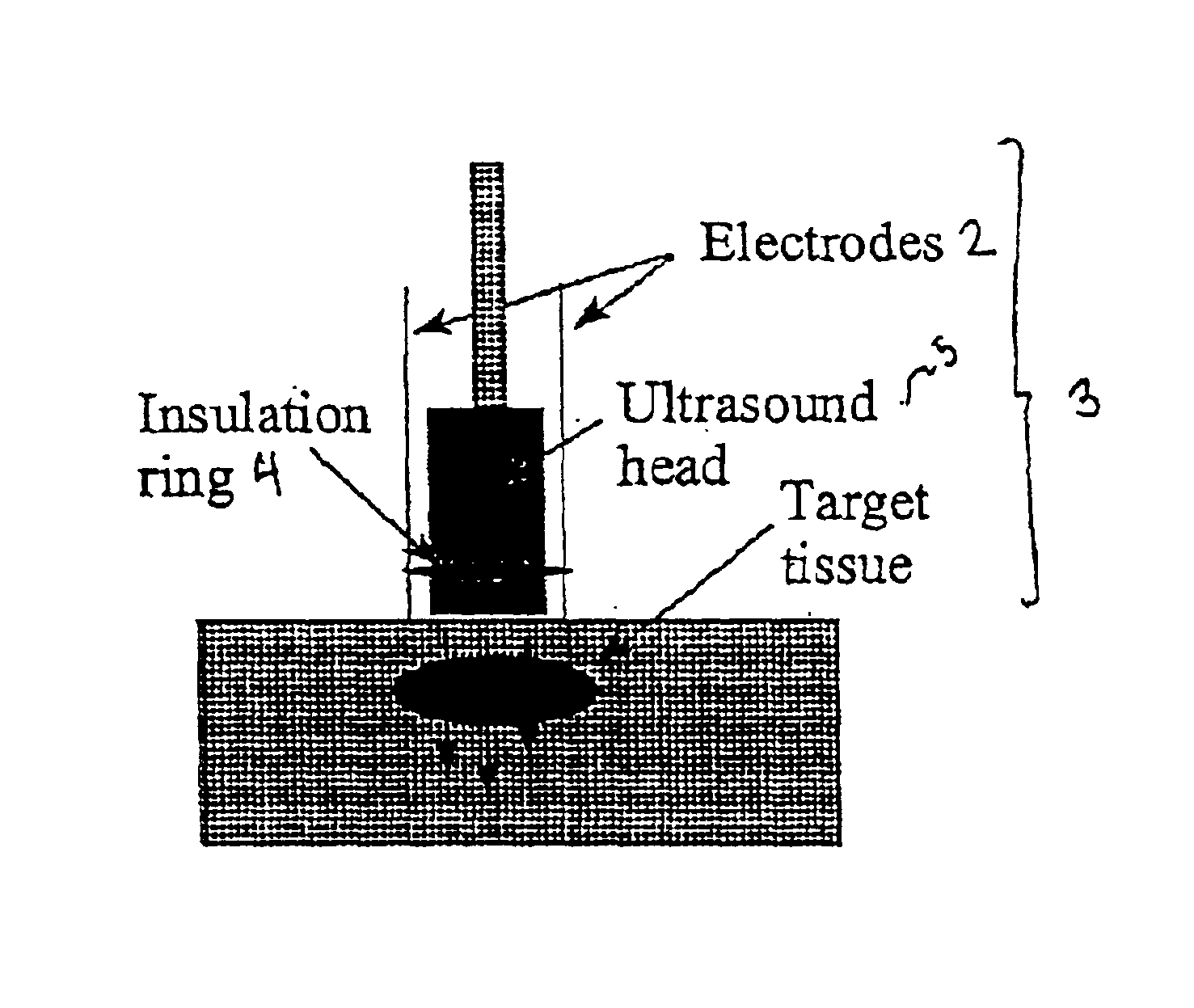
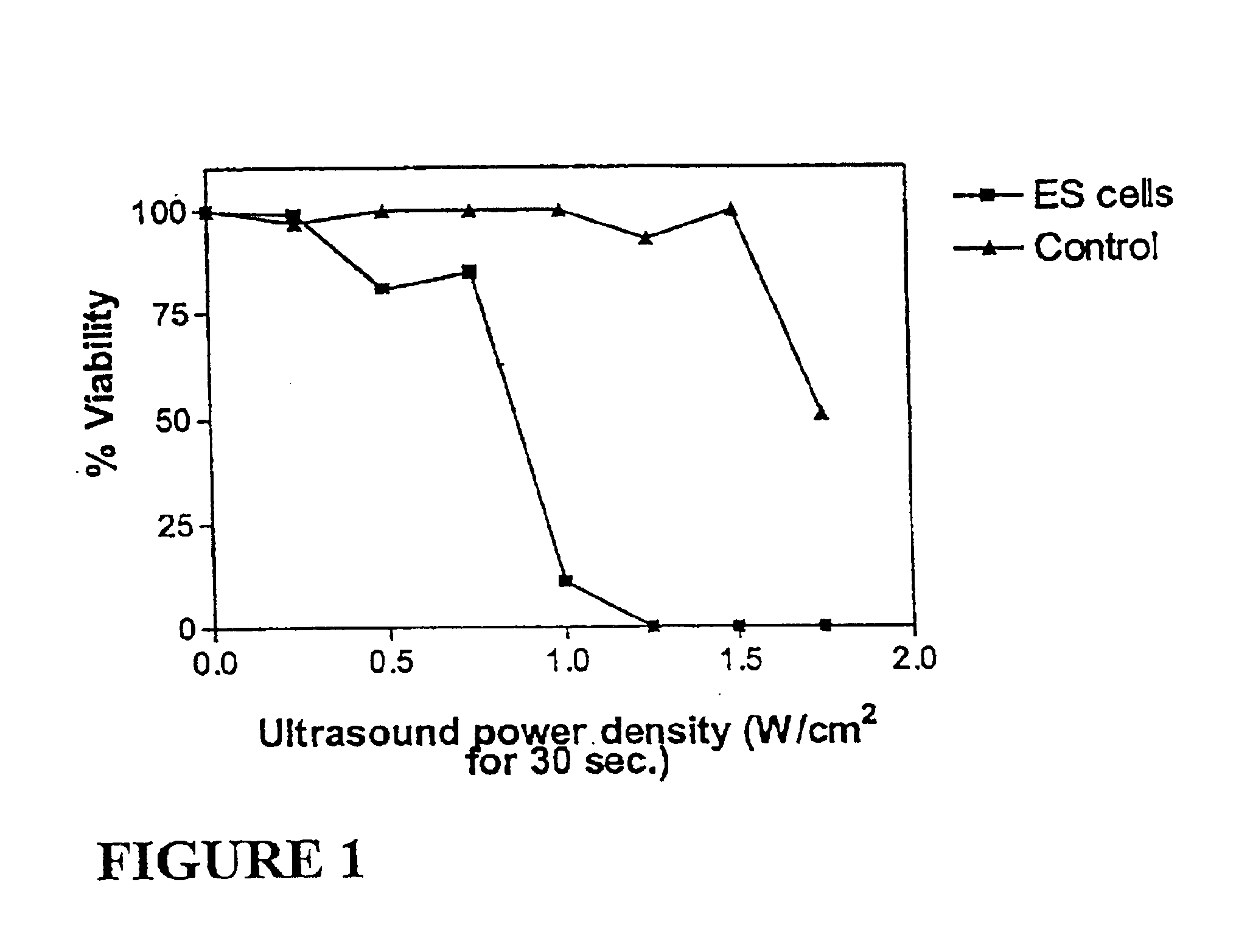
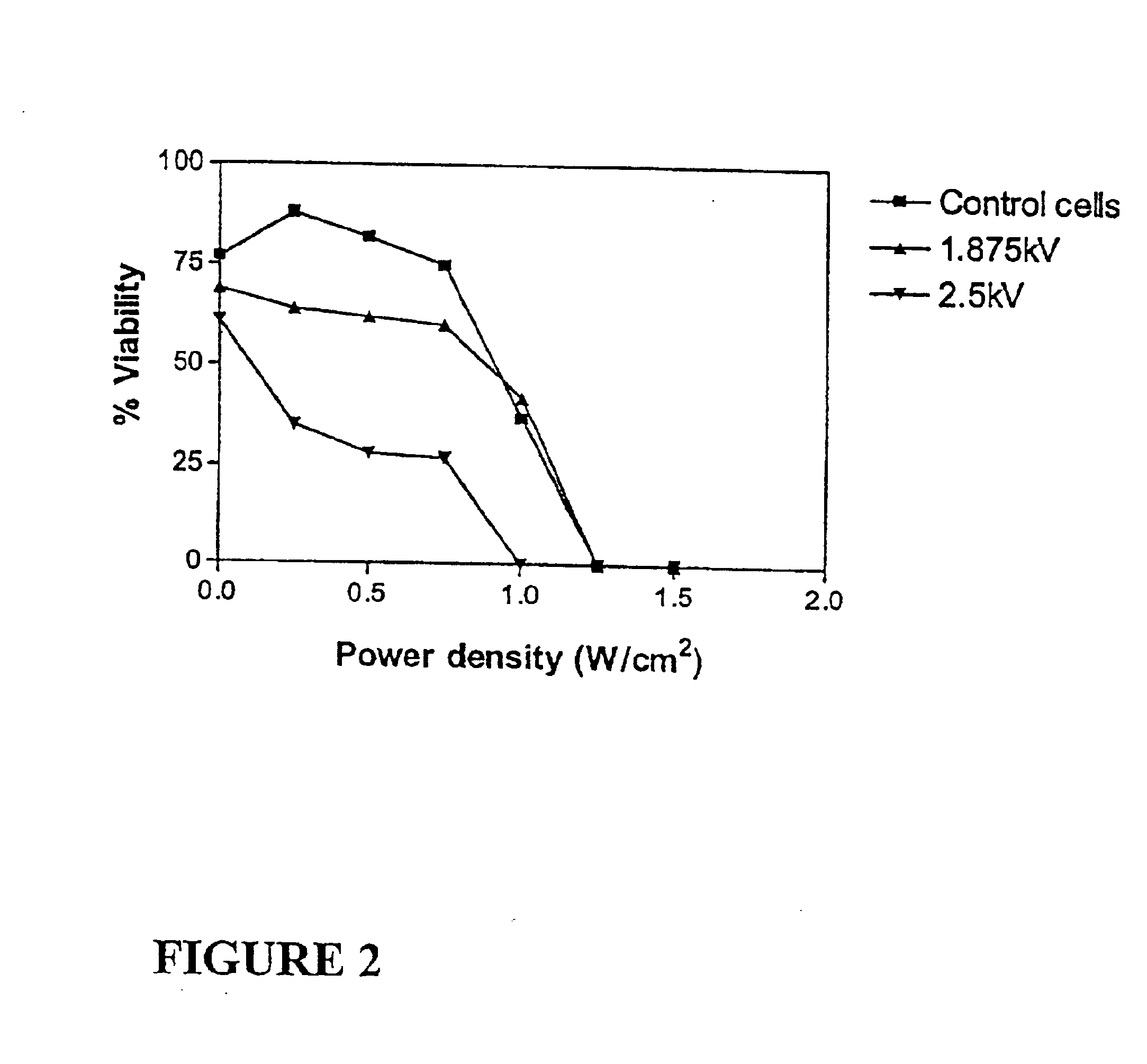
Ultrasound therapy for selective cell ablation
InactiveUS20020193784A1Ultrasound therapyElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentApoptosisGene product
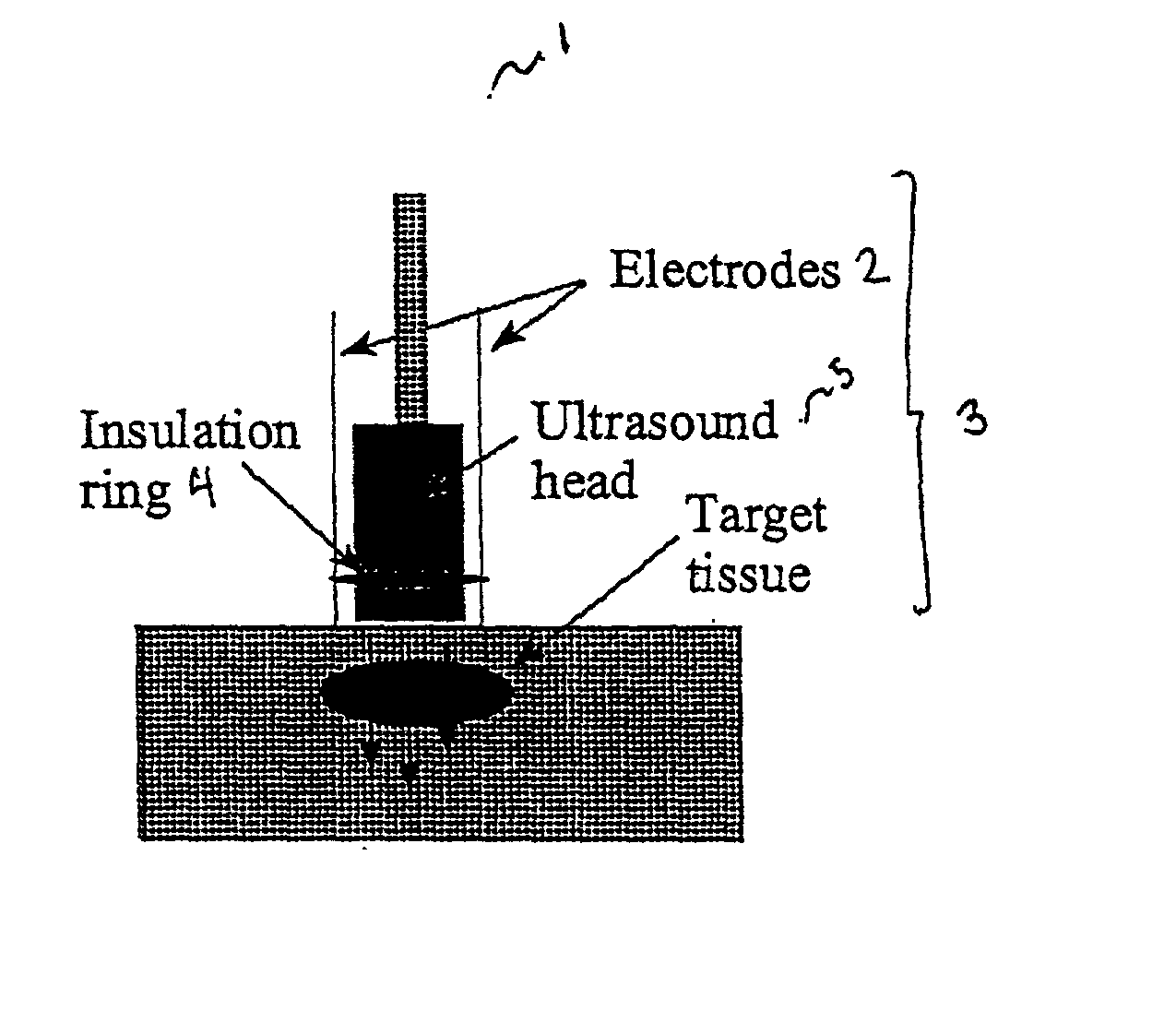
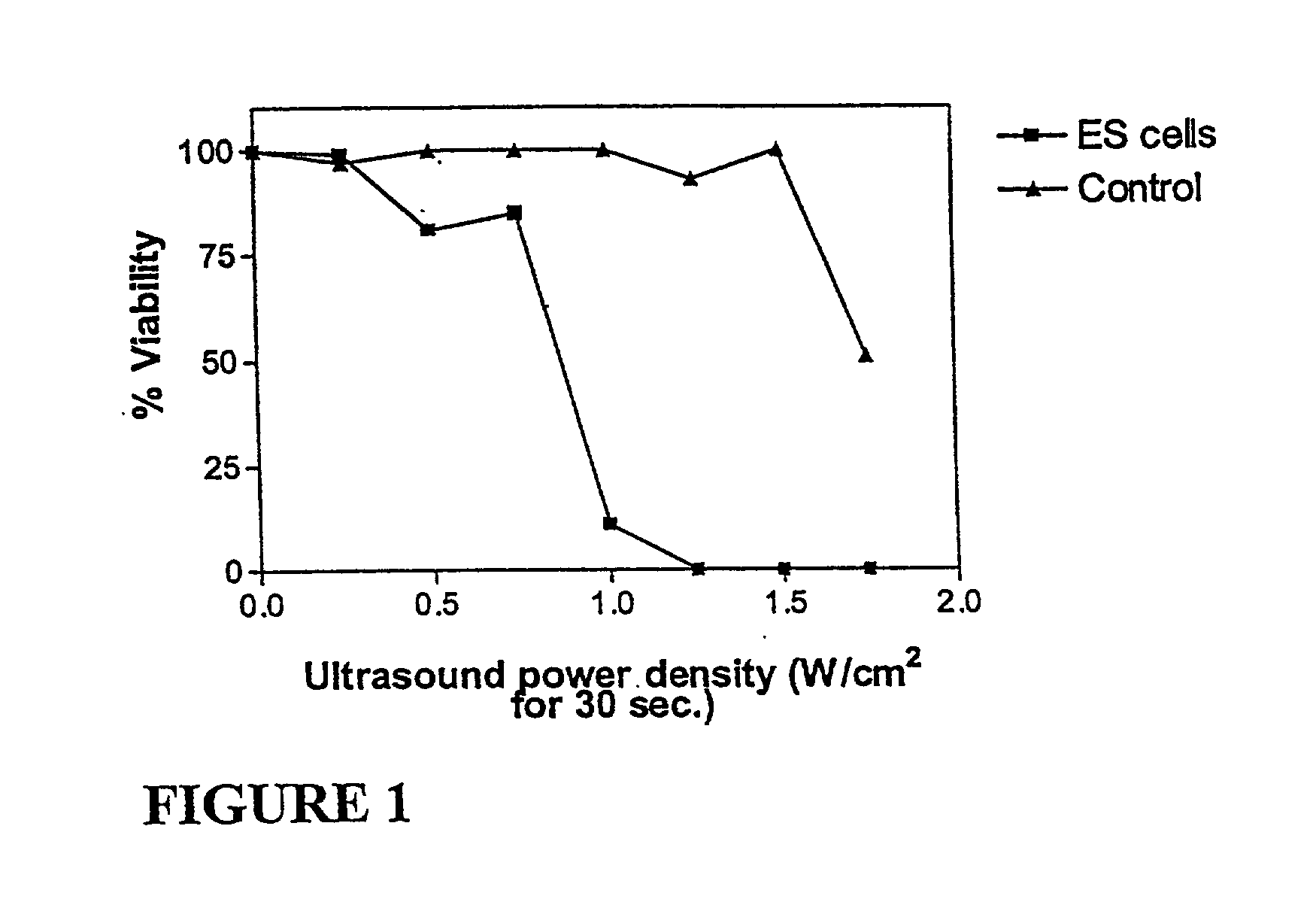
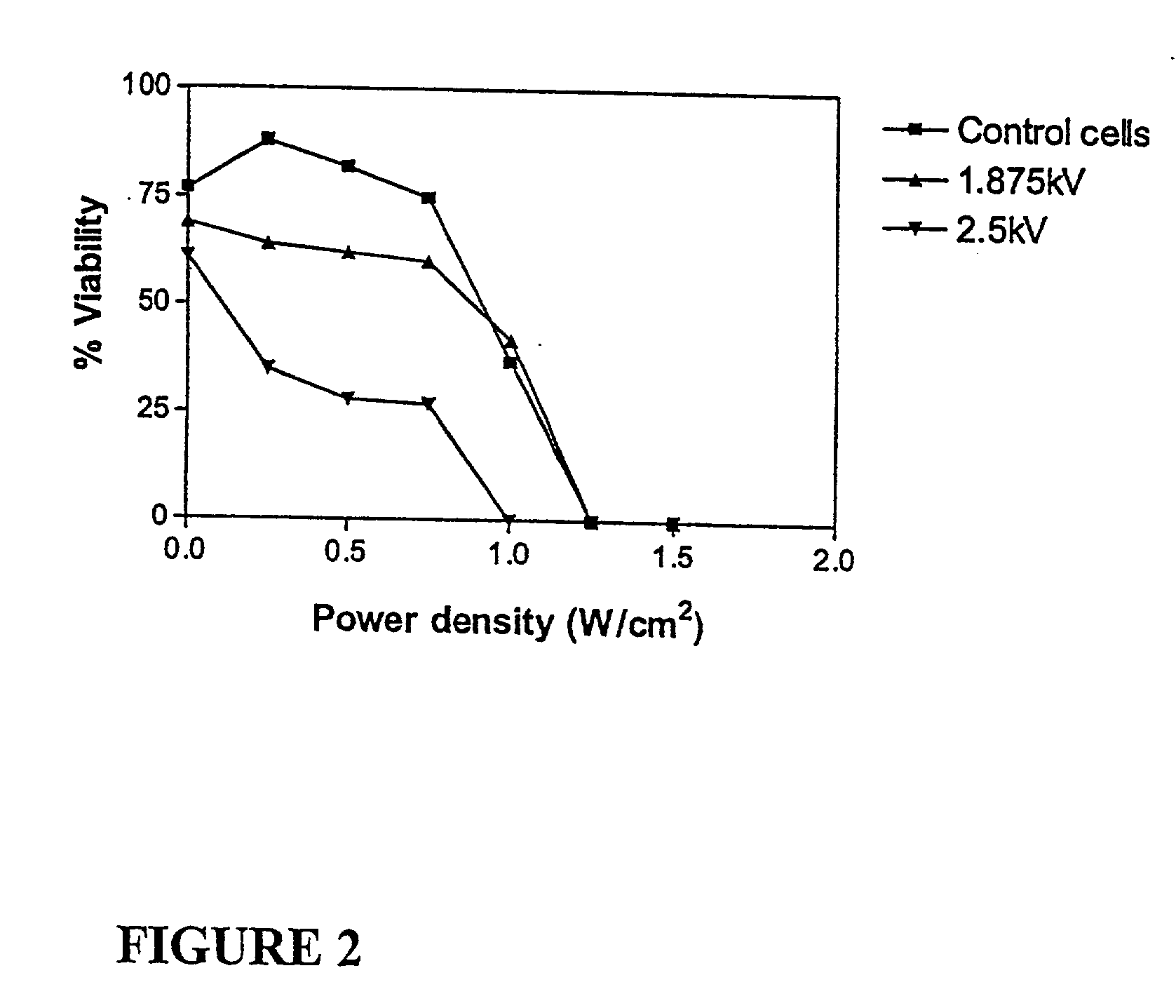
The invention provides a method of sensitising target cells to ultrasound energy using a stimulus such as an electric field. This "electrosensitisation" enables target cells to be disrupted by ultrasound at frequencies and energies of ultrasound which do not cause disruption of non-sensitised (i.e., non-target) cells. As a consequence, the method increases the selectivity of ultrasound therapy, providing a way to ablate undesired cells, such as diseased cells (e.g., tumor cells) while minimising harm to neighboring cells. In another aspect, however, ultrasound can be used to sensitise cells while the electrical field is used to disrupt cells. The invention also provides an apparatus for performing the method and assays for identifying gene products and other molecules involved in apoptosis.
Owner:GENDEL
Ablation system with blood leakage minimization and tissue protective capabilities
ActiveUS20100168624A1Controlling energy of instrumentChiropractic devicesUltrasonic sensorTransducer
An ablation system is provided that includes an ablating device and a probe. The probe is configured to be positioned in close proximity to a region of non-targeted tissue proximate an ablation site of targeted tissue. The probe includes an elongate shaft having proximal and distal ends, with a handle disposed at the proximal end thereof and a tissue protecting apparatus disposed at the distal end thereof. The ablating device includes an elongate shaft having proximal and distal ends, with a handle mounted at the proximal end thereof and an ablation element mounted at the distal end thereof. The ablation element includes an ultrasound transducer and an inflatable balloon surrounding the ultrasound transducer. The balloon includes a layer of gel disposed on its outer surface.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
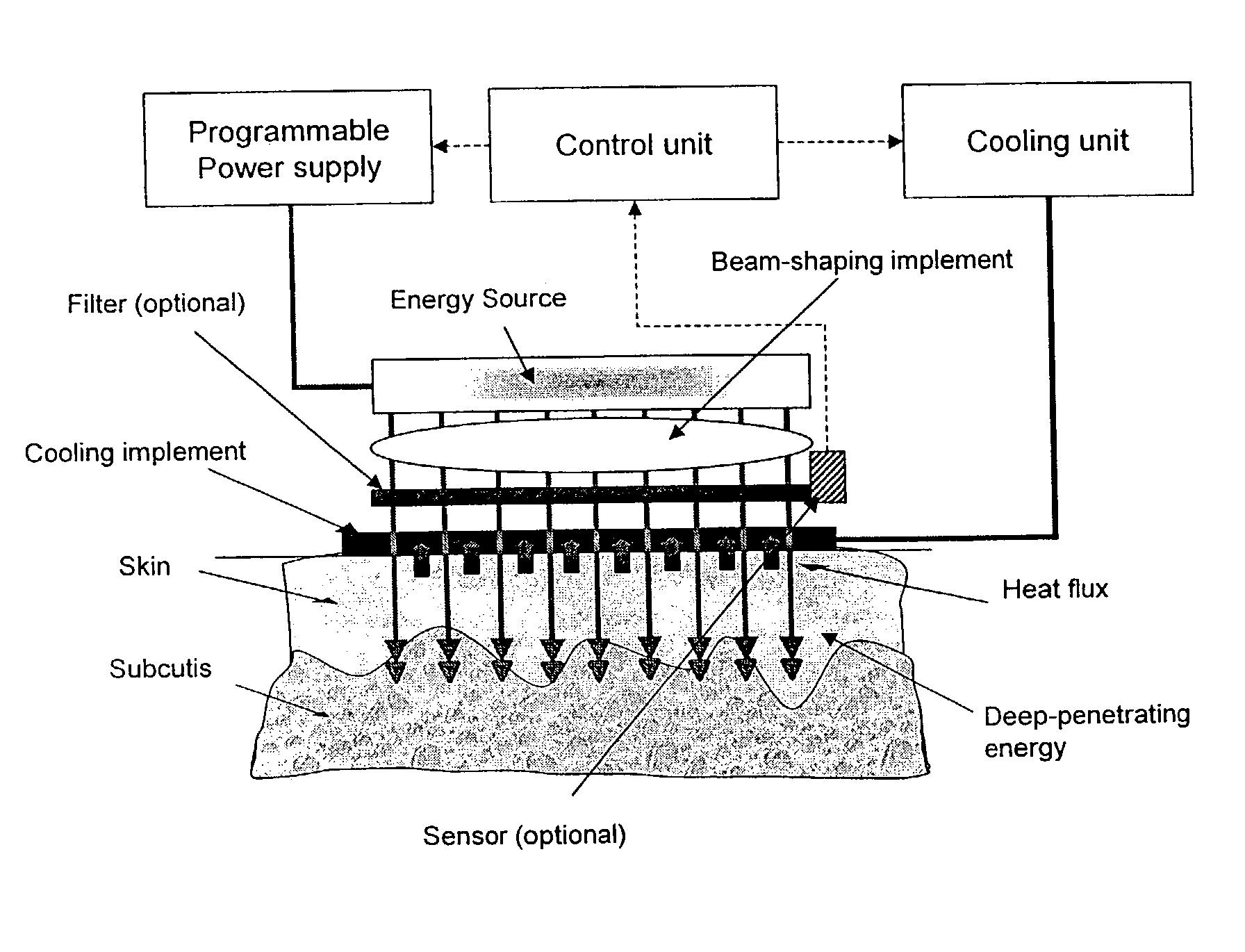
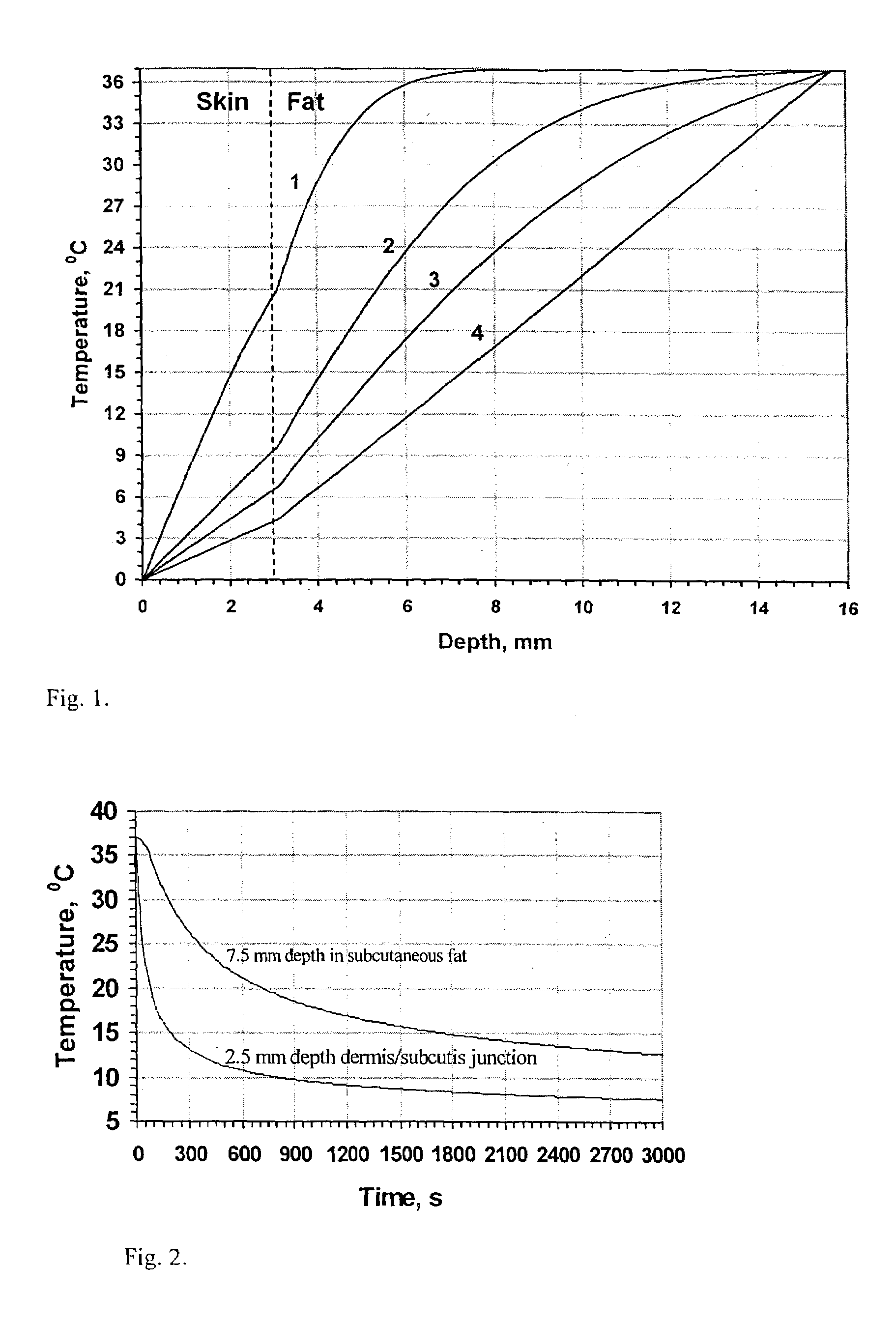
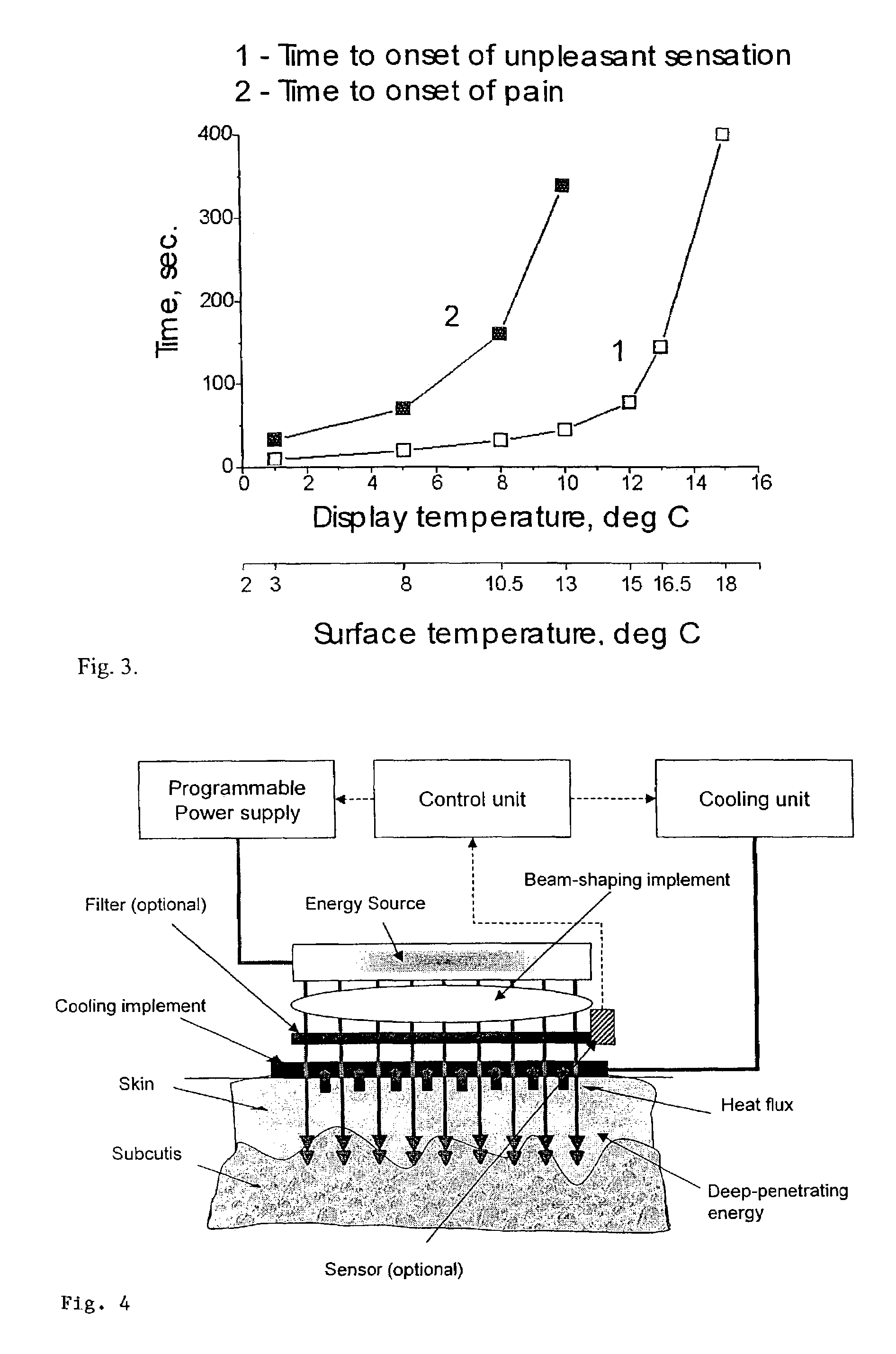
Method and apparatus for treatment of cutaneous and subcutaneous conditions
ActiveUS7276058B2Sufficient durationSufficient powerUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyElectrical stimulationsTarget tissue
The present invention provides method and apparatus for treating tissue in a region at depth while protecting non-targeted tissue by cyclically applying cooling to the patients skin, and preferably to the region, and by applying radiation to the patient's skin above the region to selectively heat tissue during and / or after cooling is applied. At least one of cooling and radiation my be applied by successivly passing a continuous output applicator over the patient's skin. Treatment may also be enhanced by applying mechanical, acoustic or electrical stimulation to the region.
Owner:PALOMAR MEDICAL TECH
Tissue removal probe with sliding burr in cutting window
InactiveUS20050197661A1Endoscopic cutting instrumentsAbrasive surgical cuttersDrive shaftBone tissue
A probe and method for removing tissue is provided. The probe comprises an elongated member, a window laterally formed on the distal end of the member, a drive shaft rotatably disposed within the lumen of the member, and a rotatable and longitudinally slidable tissue removal element disposed on the drive shaft. The probe can be used to remove tissue along the window of the probe. In one method, target tissue along the window, e.g., bone tissue, can be removed without removing non-target tissue, e.g., nerve tissue, by rotating and longitudinally sliding the tissue removal element relative to the window.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
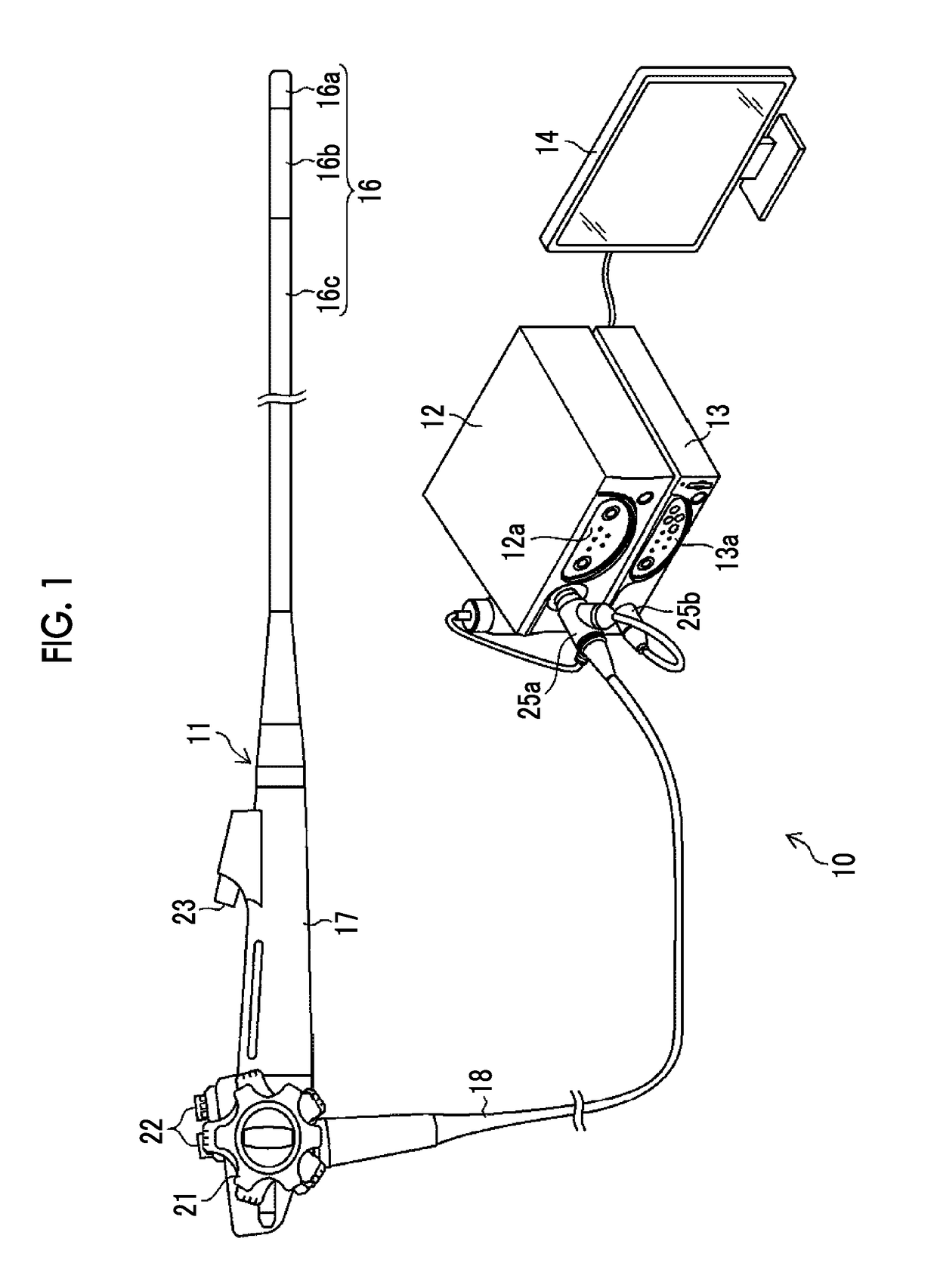
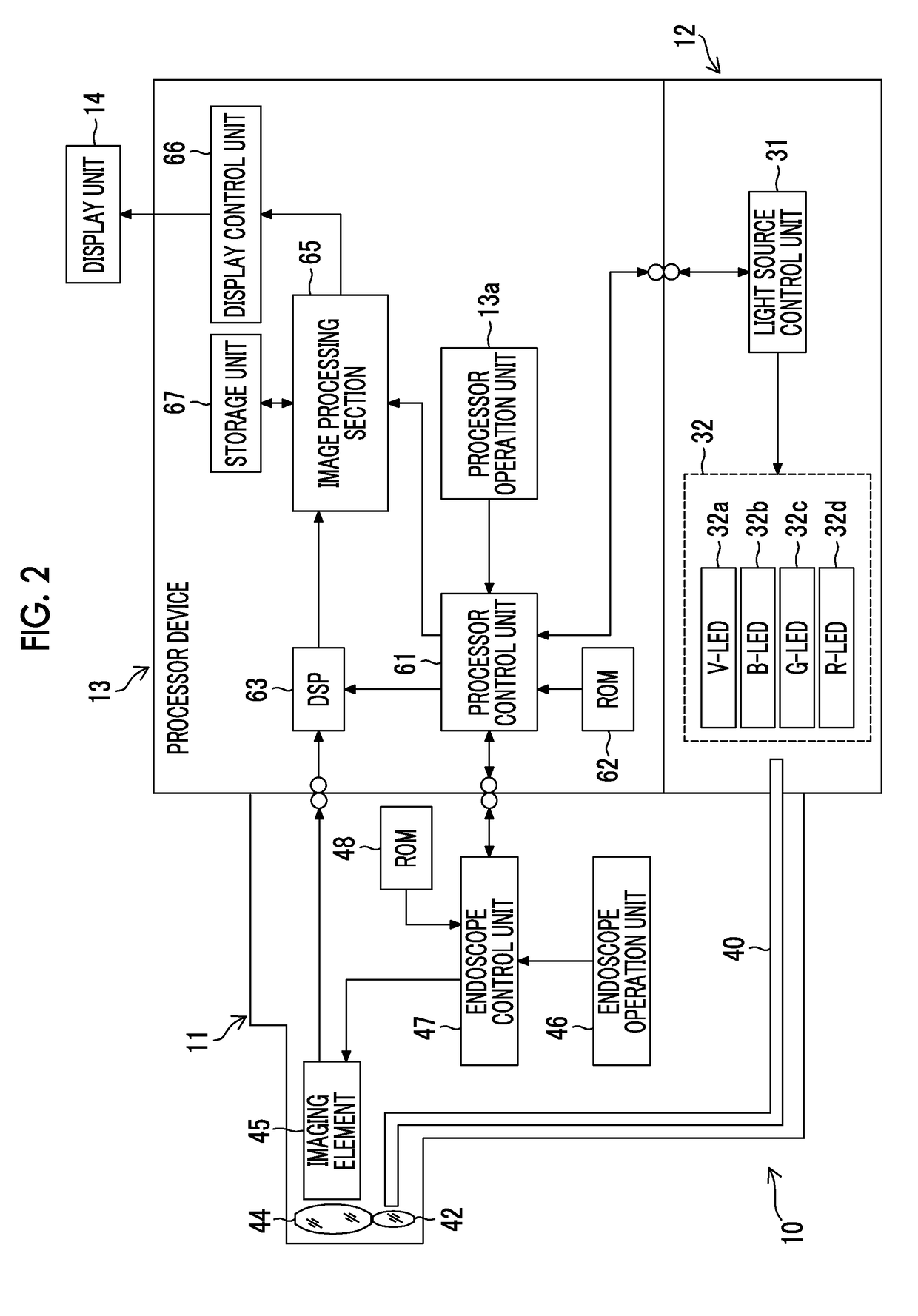
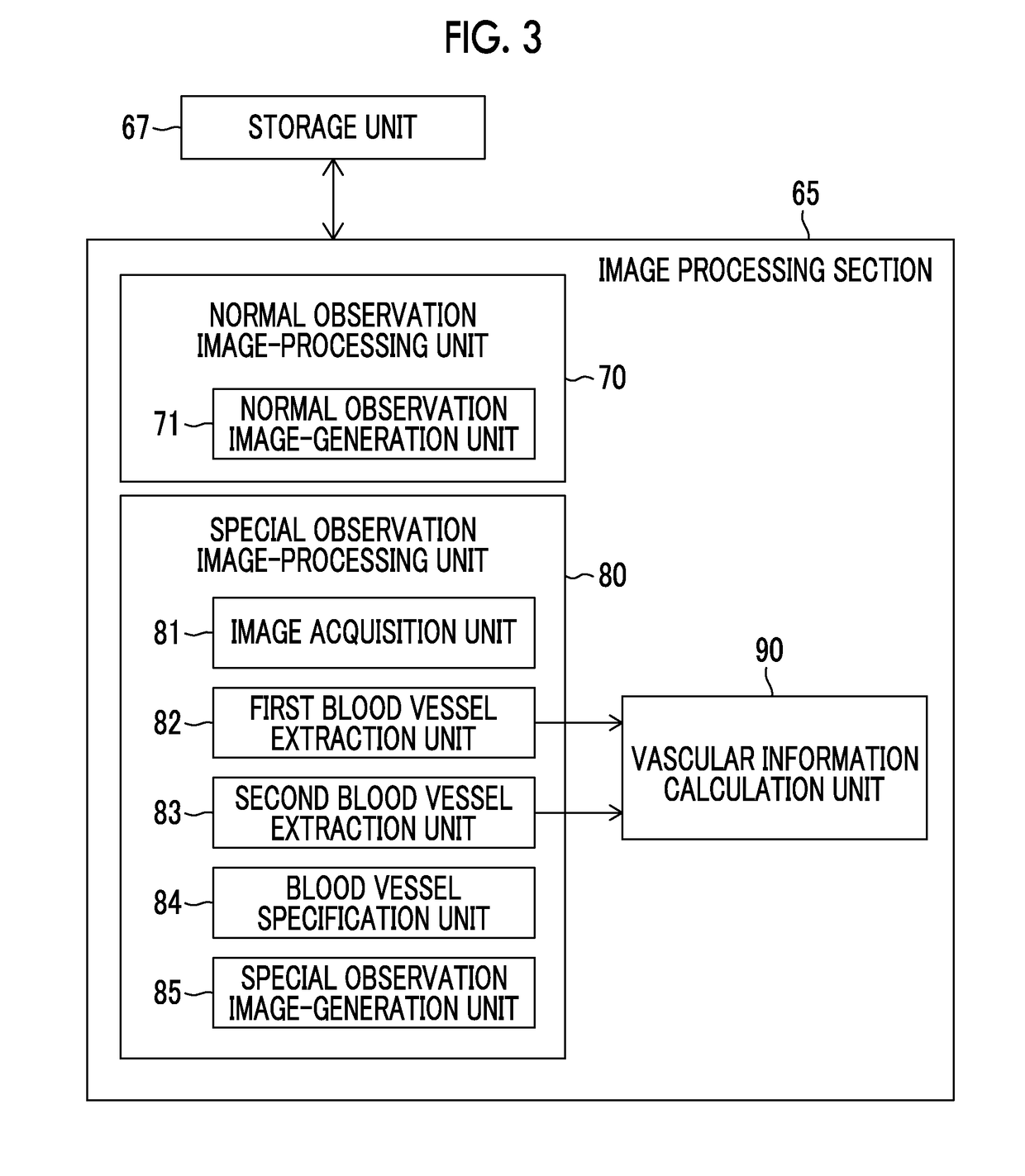
Vascular information acquisition device, endoscope system, and vascular information acquisition method
ActiveUS20190005641A1Accurate collectionAccurate calculationImage enhancementImage analysisNon targetedEndoscope
There are provided a vascular information acquisition device, an endoscope system, and a vascular information acquisition method that can accurately acquire vascular information on a blood vessel of a target layer that is an object to be measured of a subject. A first blood vessel extraction unit (82) analyzes the image of a target layer to be measured and extracts a blood vessel (first blood vessel) from the image of a target layer. A blood vessel specification unit (84) specifies a blood vessel (second blood vessel) extending to a non-target layer from the target layer. In a case in which the second blood vessel is specified, a second blood vessel extraction unit (83) analyzes the image of the non-target layer in which the second blood vessel is present and extracts the specified second blood vessel from the image of the non-target layer.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Non-invasive and minimally invasive denervation methods and systems for performing the same
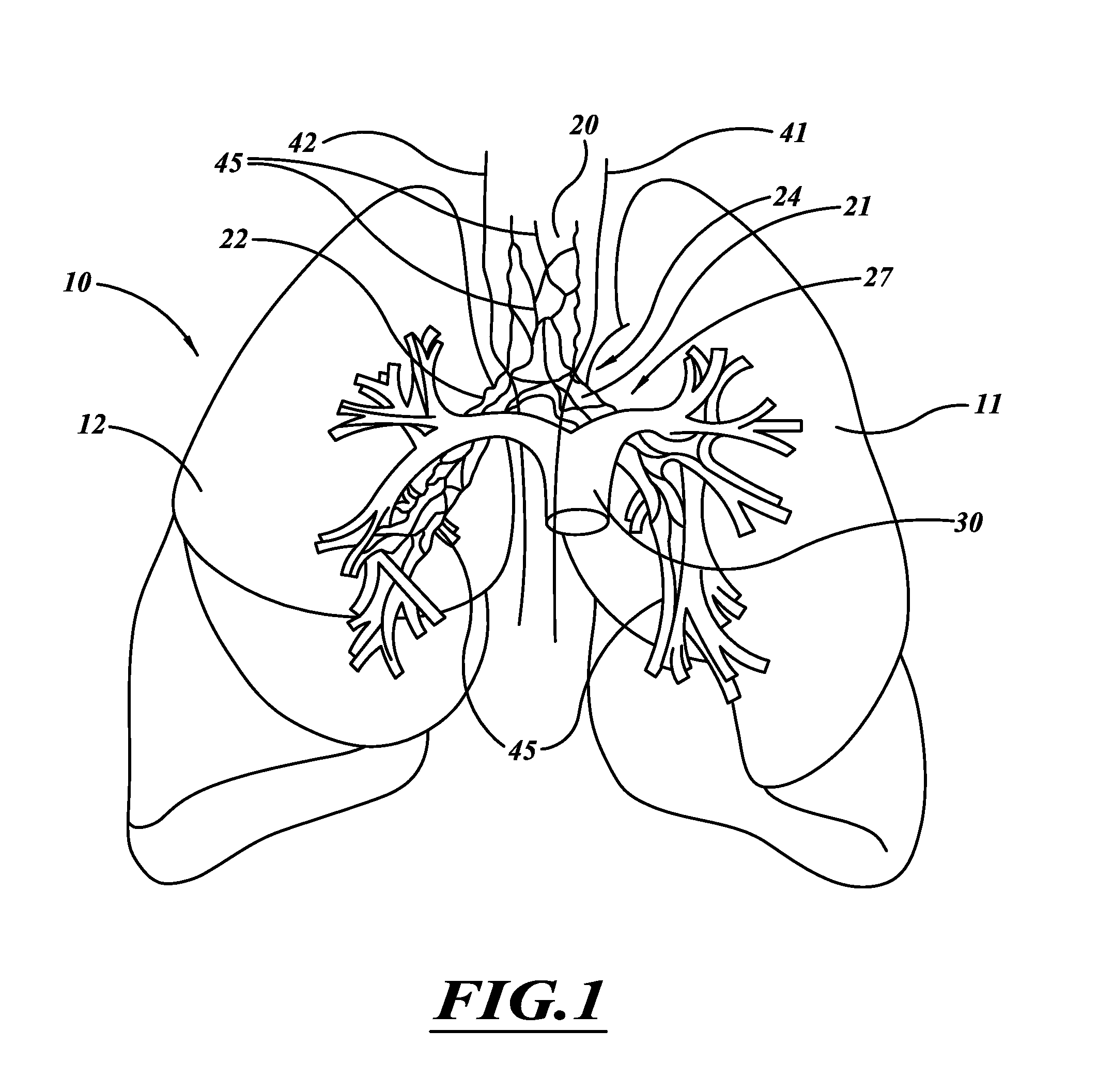
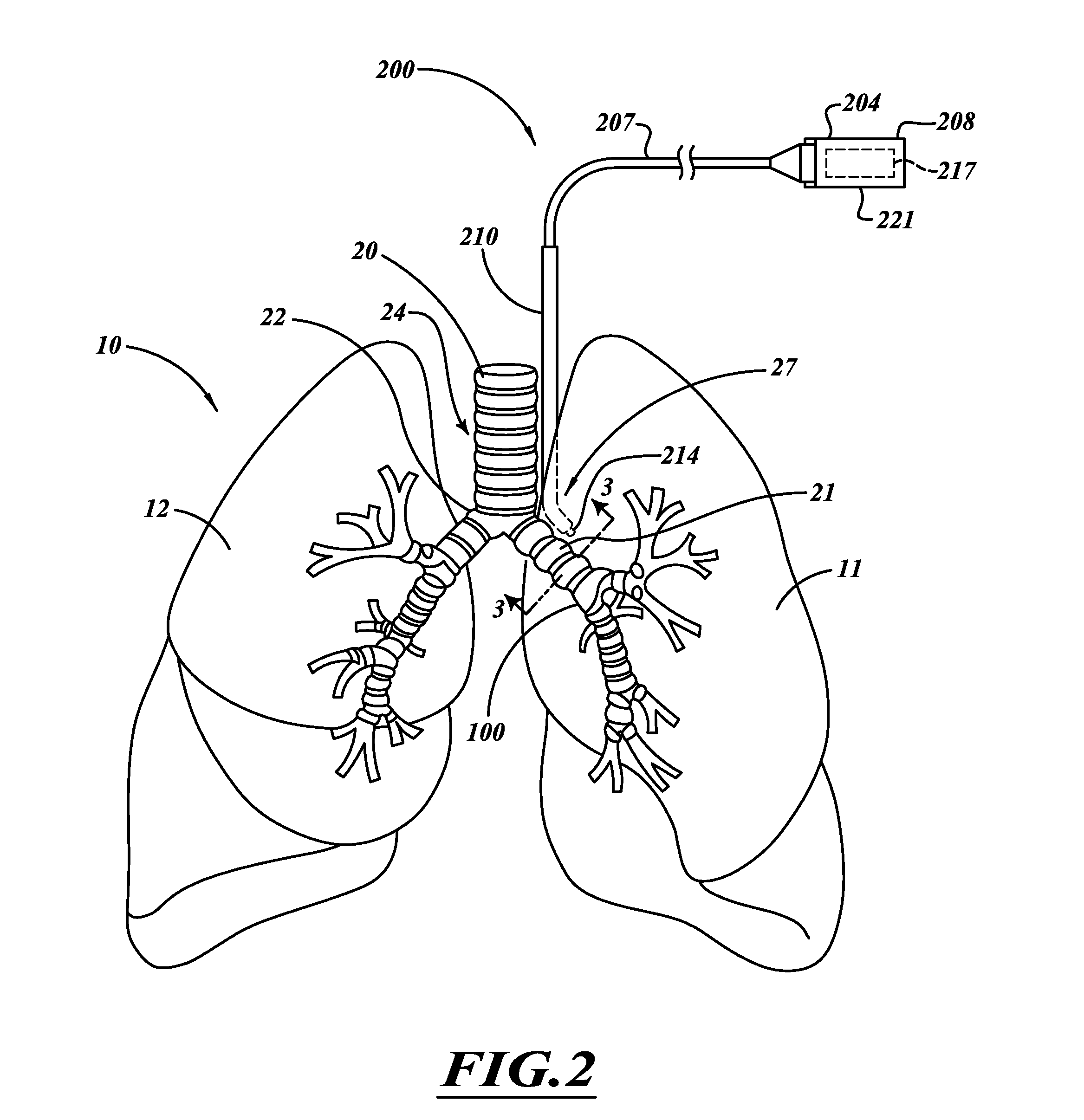
ActiveUS20110118725A1Reduce harmReduce obstructionUltrasound therapySurgical needlesCOPDPartial denervation
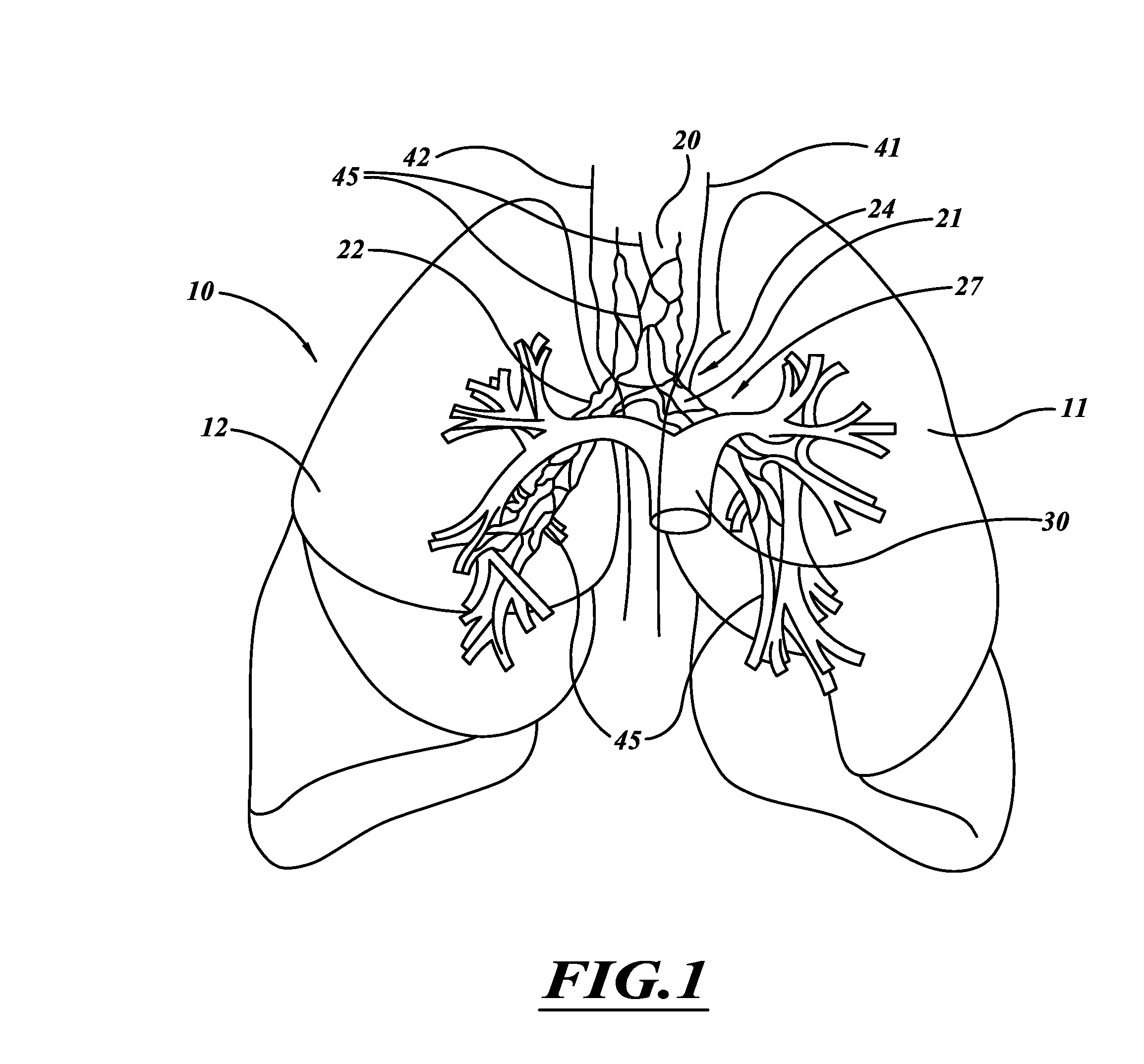
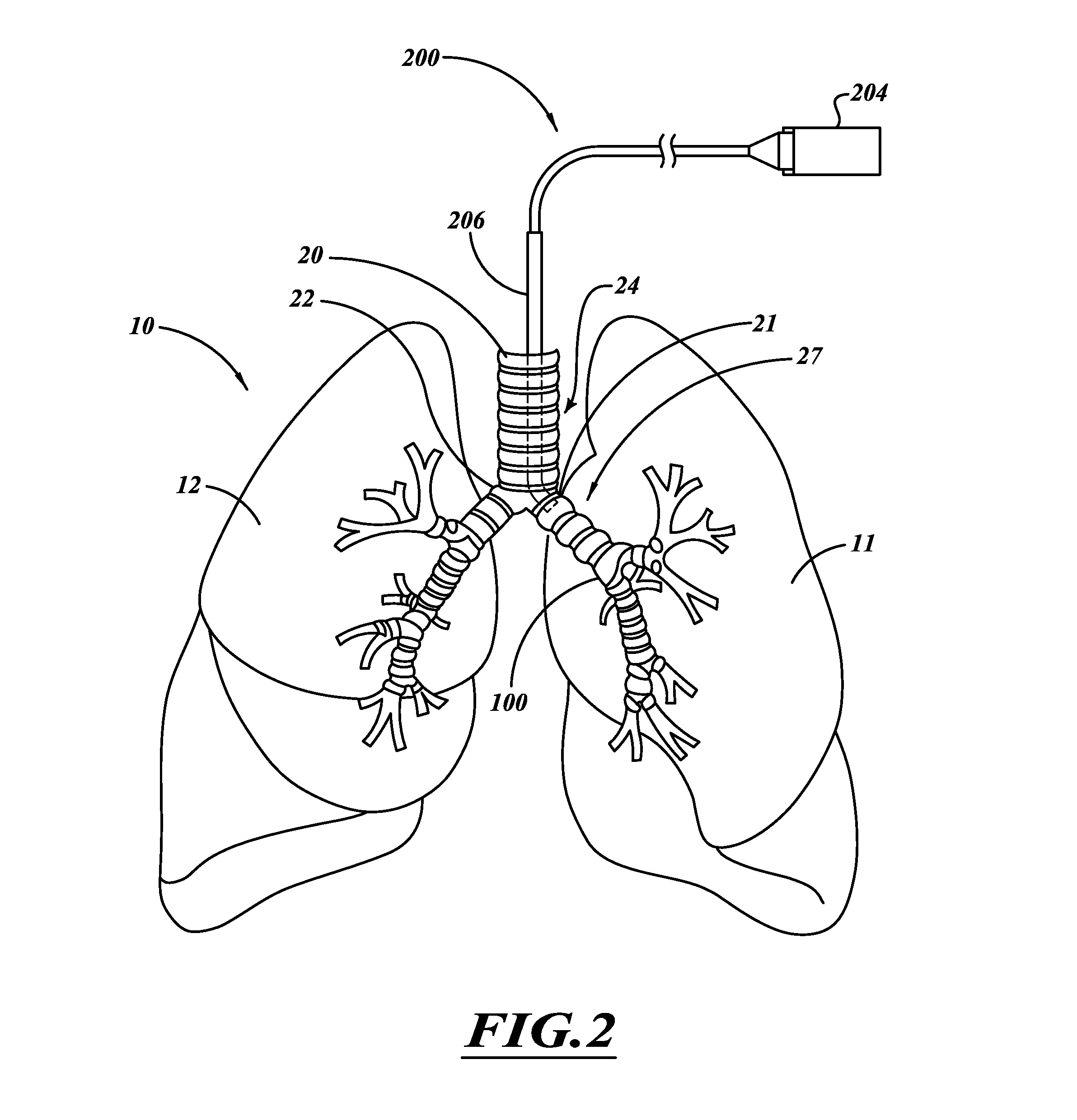
A system and method can be used to denervate at least a portion of a bronchial tree. An energy emitter of an instrument is percutaneously delivered to a treatment site and outputs energy to damage nerve tissue of the bronchial tree. The denervation procedure can be performed without damaging non-targeted tissue. Minimally invasive methods can be used to open airways to improve lung function in subjects with COPD, asthma, or the like. Different sections of the bronchial tree can be denervated while leaving airways intact to reduce recovery times.
Owner:NUVAIRA INC
Use of contrast agents to increase the effectiveness of high intensity focused ultrasound therapy
InactiveUS7686763B2Easy to useGood choiceUltrasound therapyBlood flow measurement devicesCavitationUltrasound contrast media
Ultrasound contrast agents are used to enhance imaging and facilitate HIFU therapy in four different ways. A contrast agent is used: (1) before therapy to locate specific vascular structures for treatment; (2) to determine the focal point of a HIFU therapy transducer while the HIFU therapy transducer is operated at a relatively low power level, so that non-target tissue is not damaged as the HIFU is transducer is properly focused at the target location; (3) to provide a positive feedback mechanism by causing cavitation that generates heat, reducing the level of HIFU energy administered for therapy compared to that required when a contrast agent is not used; and, (4) to shield non-target tissue from damage, by blocking the HIFU energy. Various combinations of these techniques can also be employed in a single therapeutic implementation.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Ultrasound therapy for selective cell ablation
InactiveUS6821274B2Ultrasound therapyElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentSensitized cellApoptosis
The invention provides a method of sensitizing target cells to ultrasound energy using a stimulus such as an electric field. This "electrosensitisation" enables target cells to be disrupted by ultrasound at frequencies and energies of ultrasound which do not cause disruption of non-sensitized (i.e., non-target) cells. As a consequence, the method increases the selectivity of ultrasound therapy, providing a way to ablate undesired cells, such as diseased cells (e.g., tumor cells) while minimizing harm to neighboring cells. In another aspect, however, ultrasound can be used to sensitize cells while the electrical field is used to disrupt cells. The invention also provides an apparatus for performing the method and assays for identifying gene products and other molecules involved in apoptosis.
Owner:GENDEL
Method and apparatus for spatially confined electroporation
InactiveUS20050048651A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrotherapyBiological targetElectroporation
The invention provides hollow-tip-electrodes for spatially localized delivery of substances to one or more biological targets present in a population comprising target and non-target molecules, macromolecules, and / or cells. The invention also provides electrode plates for receiving one or more of such tips, tip-electrode plates comprising electrode plates comprising one or more electrode tips, and systems comprising tip-electrodes and containers for containing one or more biological targets, e.g., such as molecules, macromolecules, and / or cells. The invention further provides methods for using such systems and components thereof. In one preferred aspect, the systems are used for spatially confined electroporation of cells and cell structures. The invention facilitates high throughput screening of agents (e.g., such as drugs) that act on intracellular targets.
Owner:CELLECTRICON
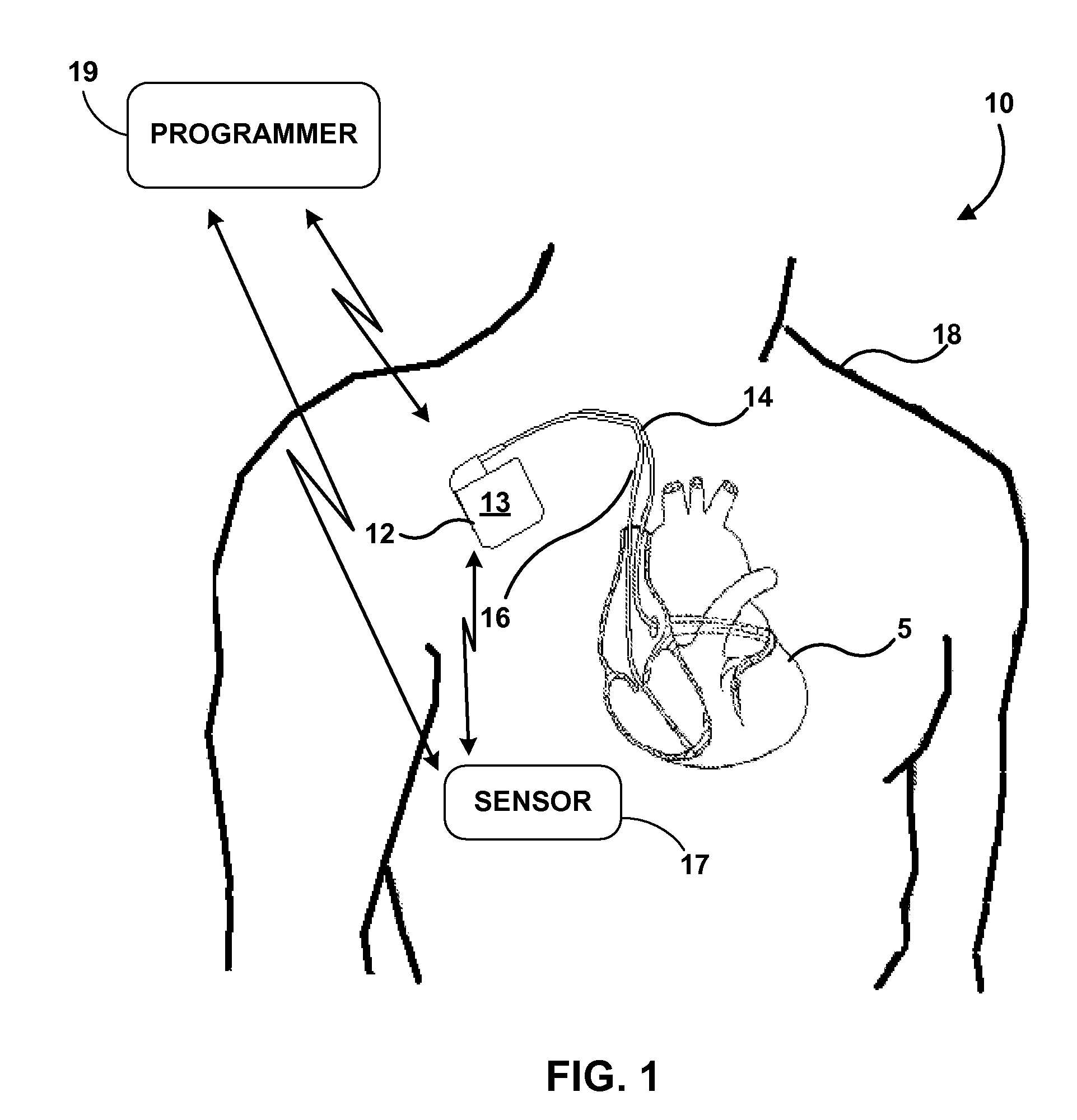
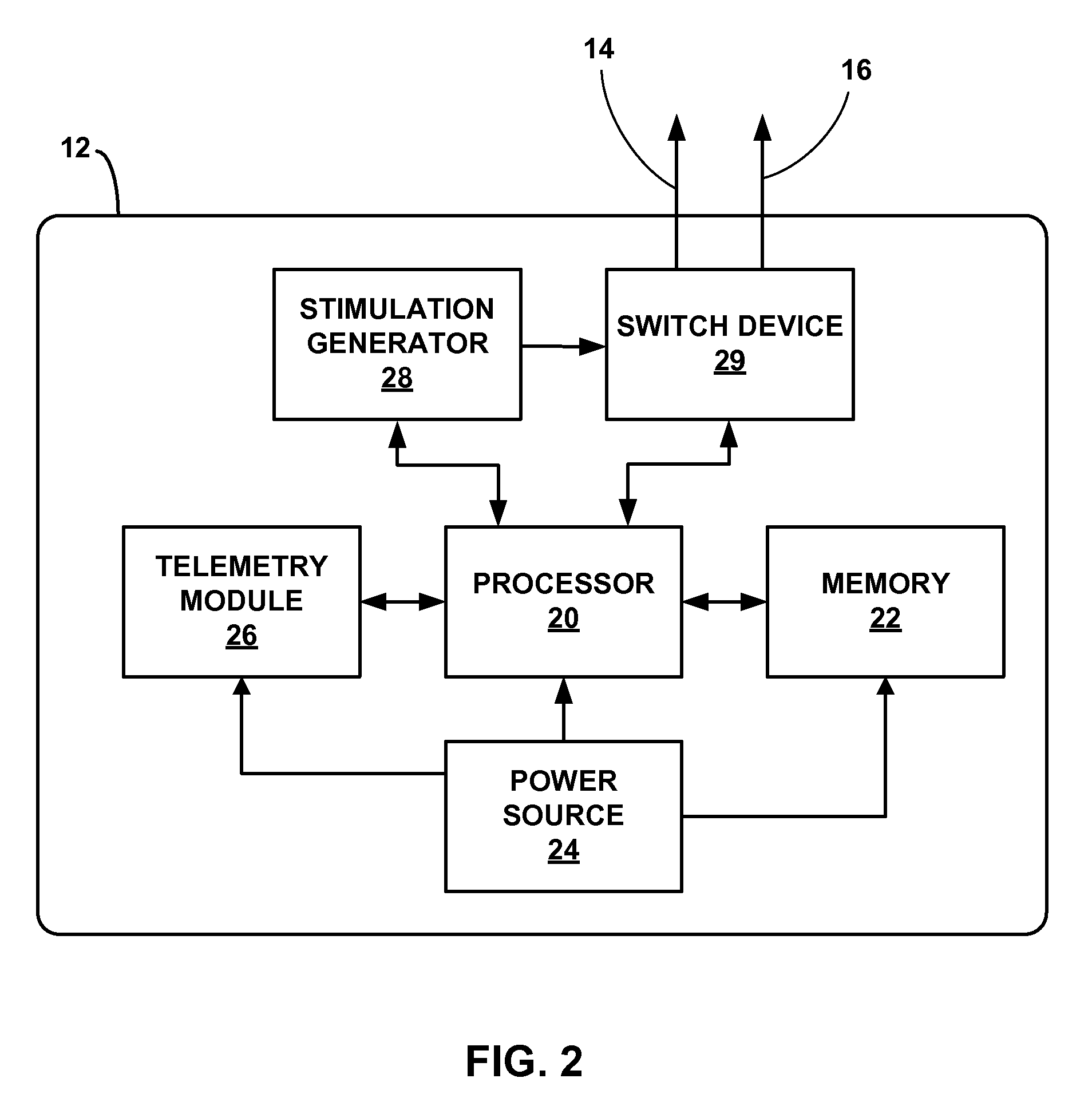
Evaluating therapeutic stimulation electrode configurations based on physiological responses
A medical system comprises a plurality of electrodes; at least one sensor configured to output at least one signal based on at least one physiological parameter of a patient; and a processor. The processor is configured to control delivery of stimulation to the patient using a plurality of electrode configurations. Each of the electrode configurations comprises at least one of the plurality of electrodes. For each of the electrode configurations, the processor is configured to determine a first response of target tissue to the stimulation based on the signals, and a second response of non-target tissue to the stimulation based on the signals. The processor is also configured to select at least one of the electrode configurations for delivery of stimulation to the patient based on the first and second responses for the electrode configurations. As examples, the target tissue may be a left ventricle or vagus nerve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Electrosurgical systems and methods for removing and modifying tissue
InactiveUS7824398B2Thermal damage is minimizedMinimize damageCannulasEnemata/irrigatorsEngineeringNon targeted
The present invention provides systems, apparatus and methods for selectively applying electrical energy to body tissue in order to, ablate, contract, coagulate, or otherwise modify a tissue or organ of a patient. An electrosurgical apparatus includes an electrode support bearing an active electrode in the form of a plasma blade or hook having an active edge and first and second blade sides. The active edge is adapted for severing a target tissue via localized molecular dissociation of tissue components. The first and second blade sides are adapted for engaging against, and coagulating, the severed tissue. s. A method of the present invention comprises positioning an electrosurgical probe adjacent to the target tissue so that a blade- or hook-like active electrode is brought into at least close proximity to the target tissue in the presence of an electrically conductive fluid. A high frequency voltage is applied between the active electrode and a return electrode to effect cool ablation or other modification of the target tissue. During application of the high frequency voltage, the electrosurgical apparatus may be translated, reciprocated, or otherwise manipulated such that the active edge is moved with respect to the tissue. The present invention volumetrically ablates or otherwise modifies the target tissue with minimal or no damage to surrounding, non-target tissue.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
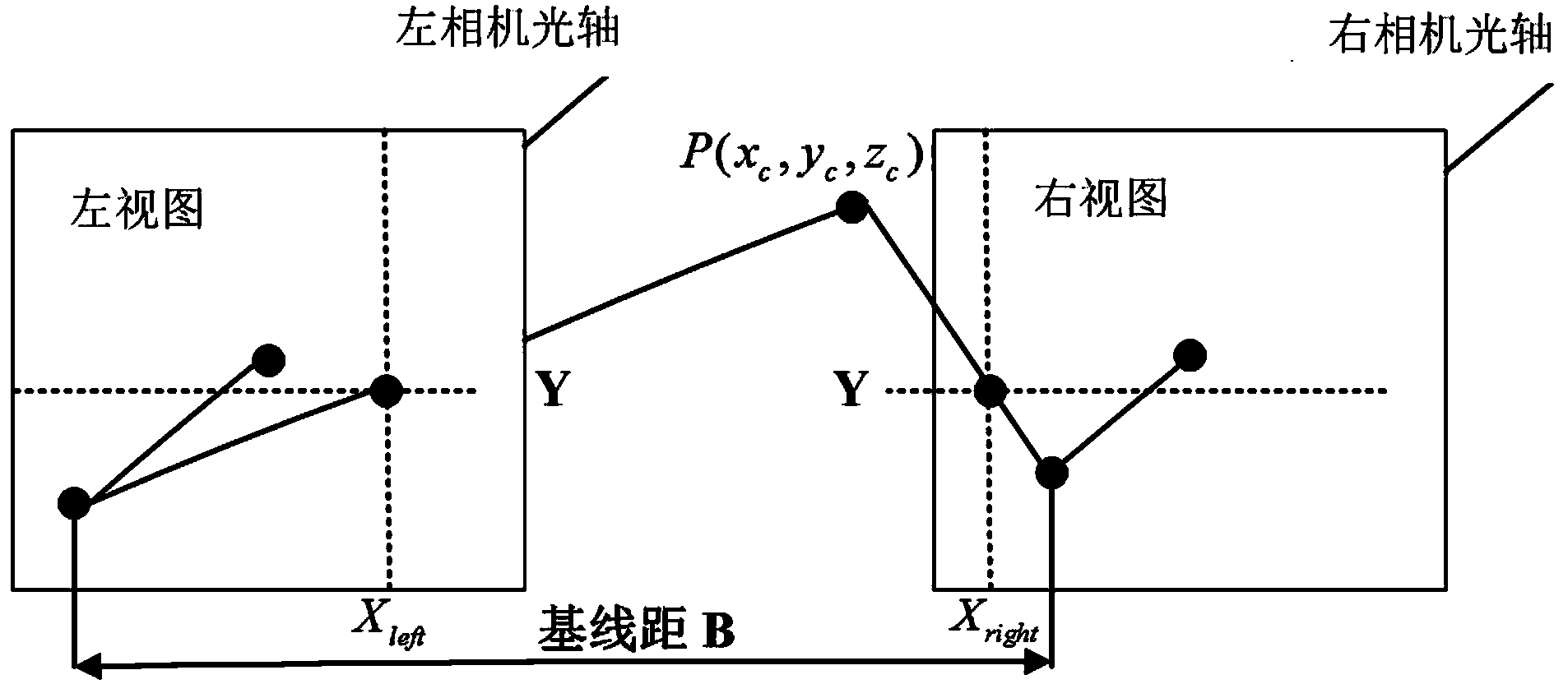
Parallax optimization algorithm-based binocular stereo vision automatic measurement method
InactiveCN103868460AAccurate and automatic acquisitionComplete 3D point cloud informationImage analysisUsing optical meansBinocular stereoNon targeted
The invention discloses a parallax optimization algorithm-based binocular stereo vision automatic measurement method. The method comprises the steps of 1, obtaining a corrected binocular view; 2, matching by using a stereo matching algorithm and taking a left view as a base map to obtain a preliminary disparity map; 3, for the corrected left view, enabling a target object area to be a colorized master map and other non-target areas to be wholly black; 4, acquiring a complete disparity map of the target object area according to the target object area; 5, for the complete disparity map, obtaining a three-dimensional point cloud according to a projection model; 6, performing coordinate reprojection on the three-dimensional point cloud to compound a coordinate related pixel map; 7, using a morphology method to automatically measure the length and width of a target object. By adopting the method, a binocular measuring operation process is simplified, the influence of specular reflection, foreshortening, perspective distortion, low textures and repeated textures on a smooth surface is reduced, automatic and intelligent measuring is realized, the application range of binocular measuring is widened, and technical support is provided for subsequent robot binocular vision.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Laser-based method and system for processing targeted surface material and article produced thereby
InactiveUS20060000814A1Prevent unwanted changesSufficient total fluenceAdditive manufacturing apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTarget surfaceSlag
A laser-based method and system for processing targeted surface material and article produced thereby are provided. The system processes the targeted surface material within a region of a workpiece while avoiding undesirable changes to adjacent non-targeted material. The system includes a primary laser subsystem including a primary laser source for generating a pulsed laser output including at least one pulse having a wavelength and a pulse width less than 1 ns. A delivery subsystem irradiates the targeted surface material of the workpiece with the pulsed laser output including the at least one pulse to texture the targeted surface material. The pulsed laser output has sufficient total fluence to initiate ablation within at least a portion of the targeted surface material and the pulse width is short enough such that the region and the non-targeted material surrounding the material are substantially free of slag.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Tissue liquefaction and aspiration for dental treatment
A method and apparatus are disclosed for liquefying target tissue within a body and aspirating the same while leaving non-target tissue intact. A biocompatible fluid is heated and contacted with target tissue so that the target tissue is melted while non-target tissue remains intact. As the target tissue is being melted it is also aspirated from the body.
Owner:ANDREW MARK S +1
Devices and methods for acoustic shielding
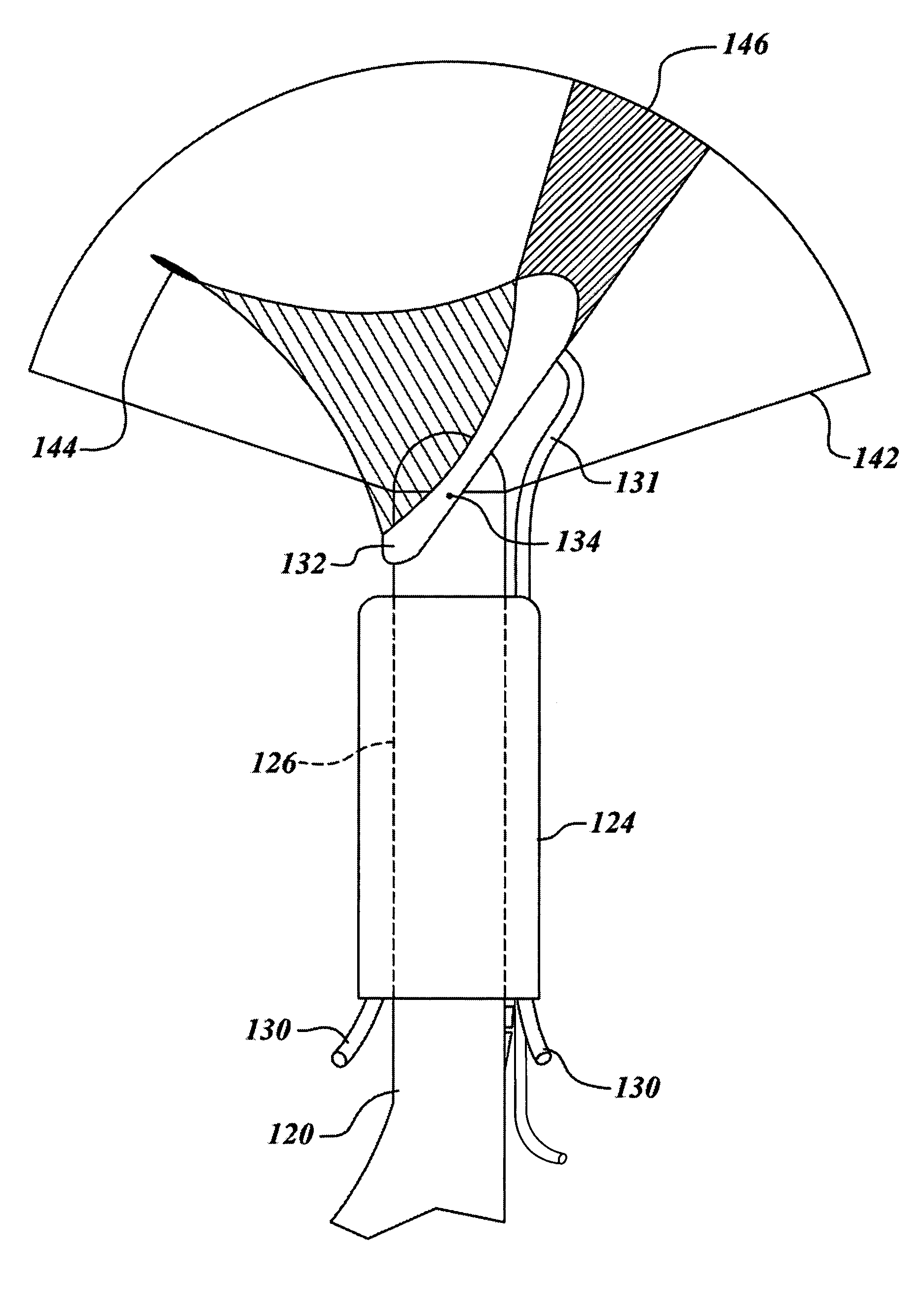
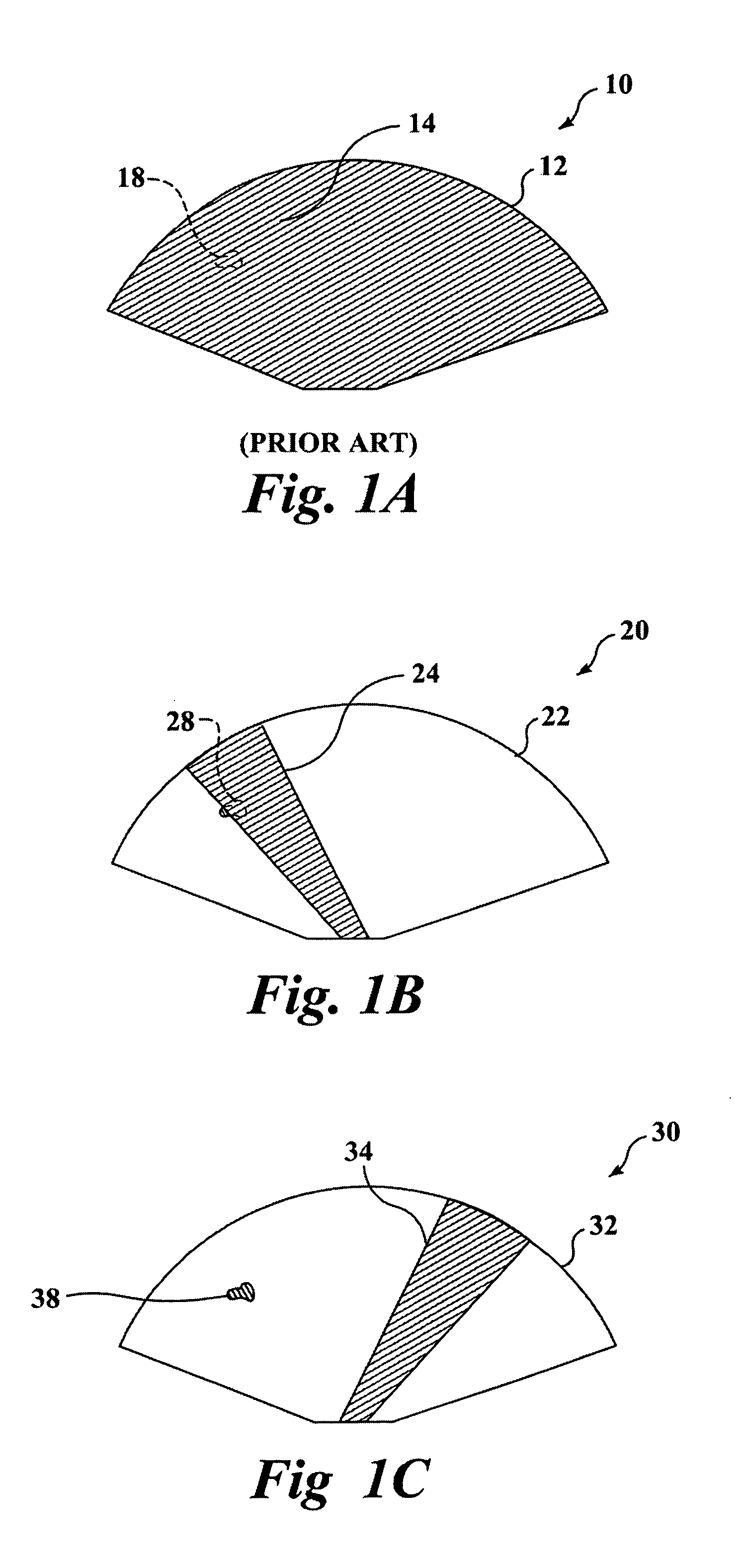
InactiveUS20120111339A1Easy to storeReduce delivery acoustic energyUltrasound therapyRestraining devicesAcoustic energyNose
Acoustic shielding system and method for protecting and shielding non-targeted regions or tissues that are not intended to be treated by ultrasonic procedures from acoustic energy using a shield. In some embodiments, the shield comprises multiple layers made of one or more materials with one or more acoustic impedances. In some embodiments a multilayered shield includes materials with relatively different acoustic impedance levels. In some embodiments, the shield includes active components such as energy diversion devices, heating, cooling, monitoring, and / or sensing. In some embodiments, the shield is configured to protect an eye, mouth, nose or ear while allowing the ultrasound to treat the surrounding tissue. One embodiment of an eye shield is configured to fit under at least one eyelid and over a portion of the eye.
Owner:ULTHERA INC
Apparatus and methods for testing a microprocessor chip using dedicated scan strings
InactiveUS6028983AReduce memory requirementsReduce scan timeElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionTest inputJoint Test Action Group
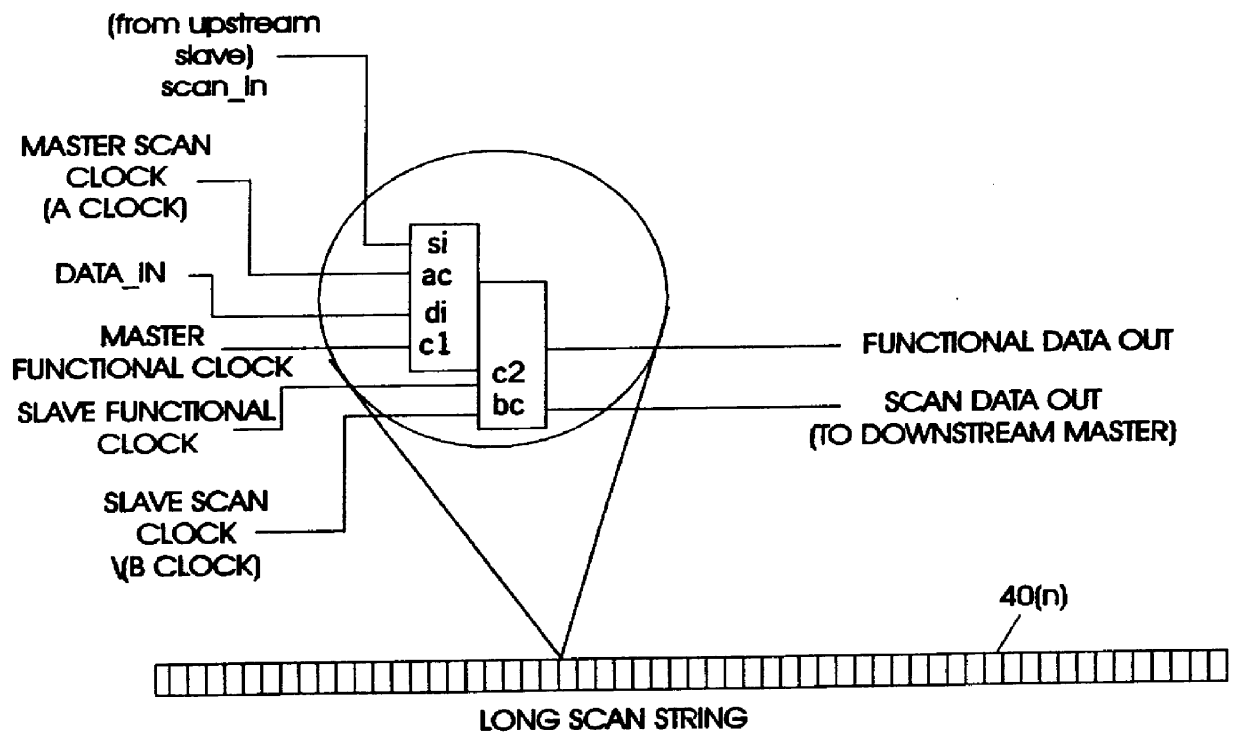
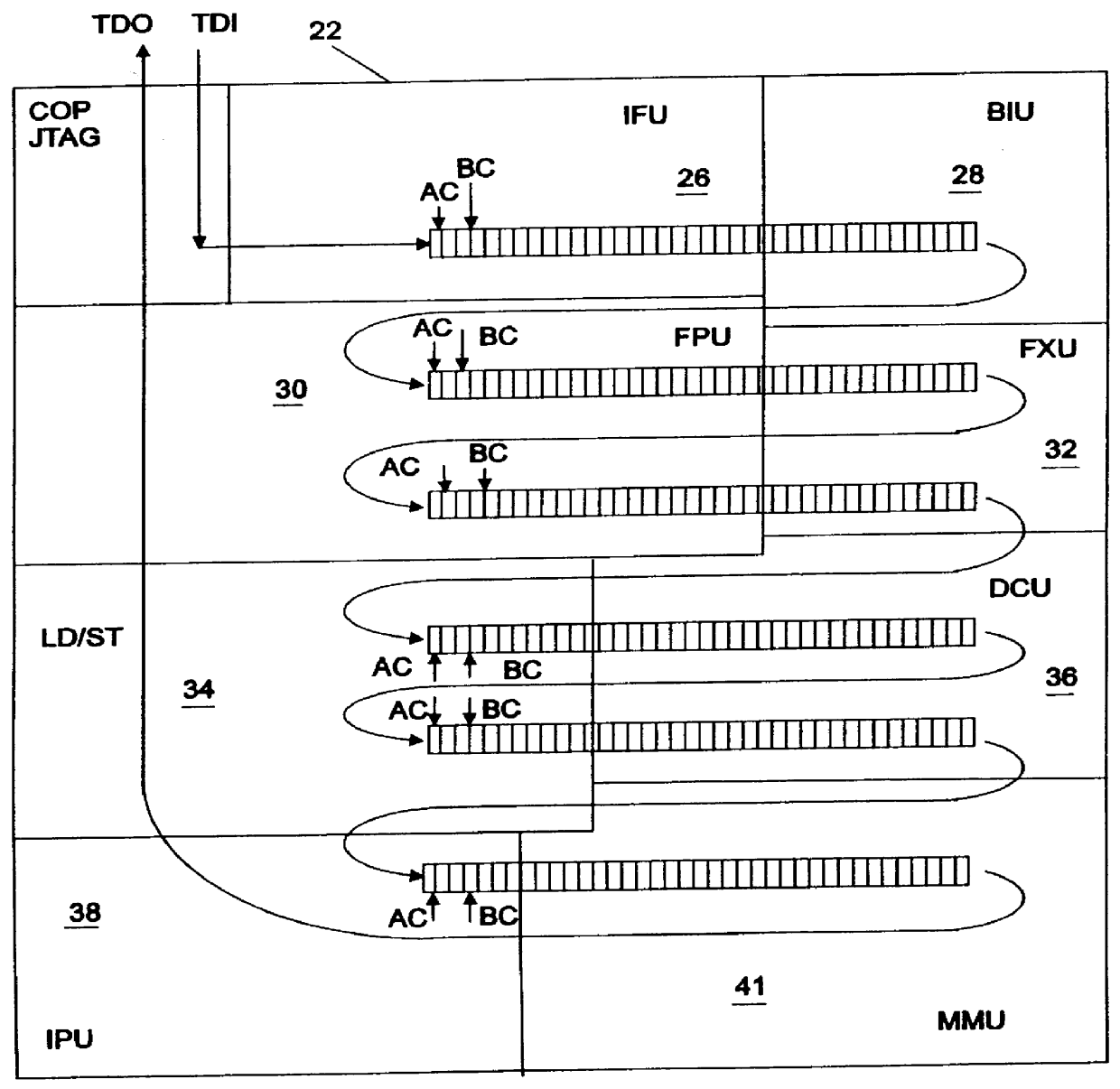
A test apparatus and method for design verification of at least one microprocessor chip includes a compatible Joint Task Action Group (JTAG) terminal for access to a plurality of computer functional units contained in the chip. A test input terminal included in the JTAG terminal receives a scan string, the string being coupled to each computer functional unit through a first multiplexer. The scan input string is separated by the JTAG terminal under program control into a series of dedicated scan strings, each dedicated scan string being supplied to a selected functional unit through the first multiplexer. Each functional unit includes start and stop scan clocks for testing the functional under program control using the dedicated scan train for the functional unit. A test output terminal included in the JTAG terminal is coupled to each functional unit through a second multiplexer. The test results of the dedicated scan string under control of the scan clock are supplied to the output terminal through the second multiplexer. The compatible JTAG terminal includes further elements for controlling the scan clocks to select a targeted functional unit for testing purposes while the scan strings for non-targeted functional units remain in an inactive state.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Target and background capture methods with amplification for affinity assays
InactiveUSRE37891E1Large dispersionFast hybridizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePolynucleotide
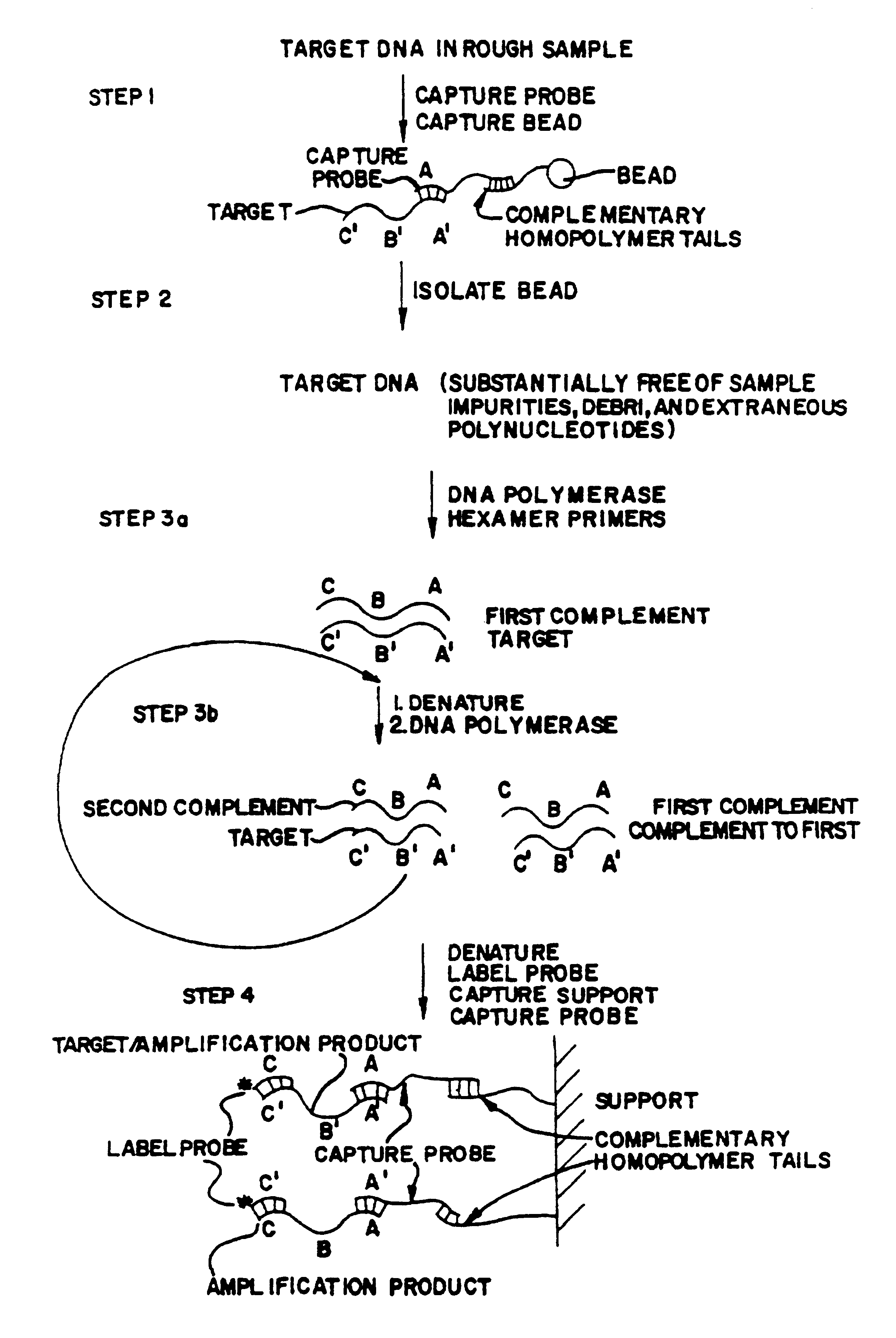
A method of assay for target polynucleotides includes steps of isolating target polynucleotides from extraneous non-target polynucleotides, debris, and impurities and amplifying the target polynucleotide.
Owner:VYSIS INC
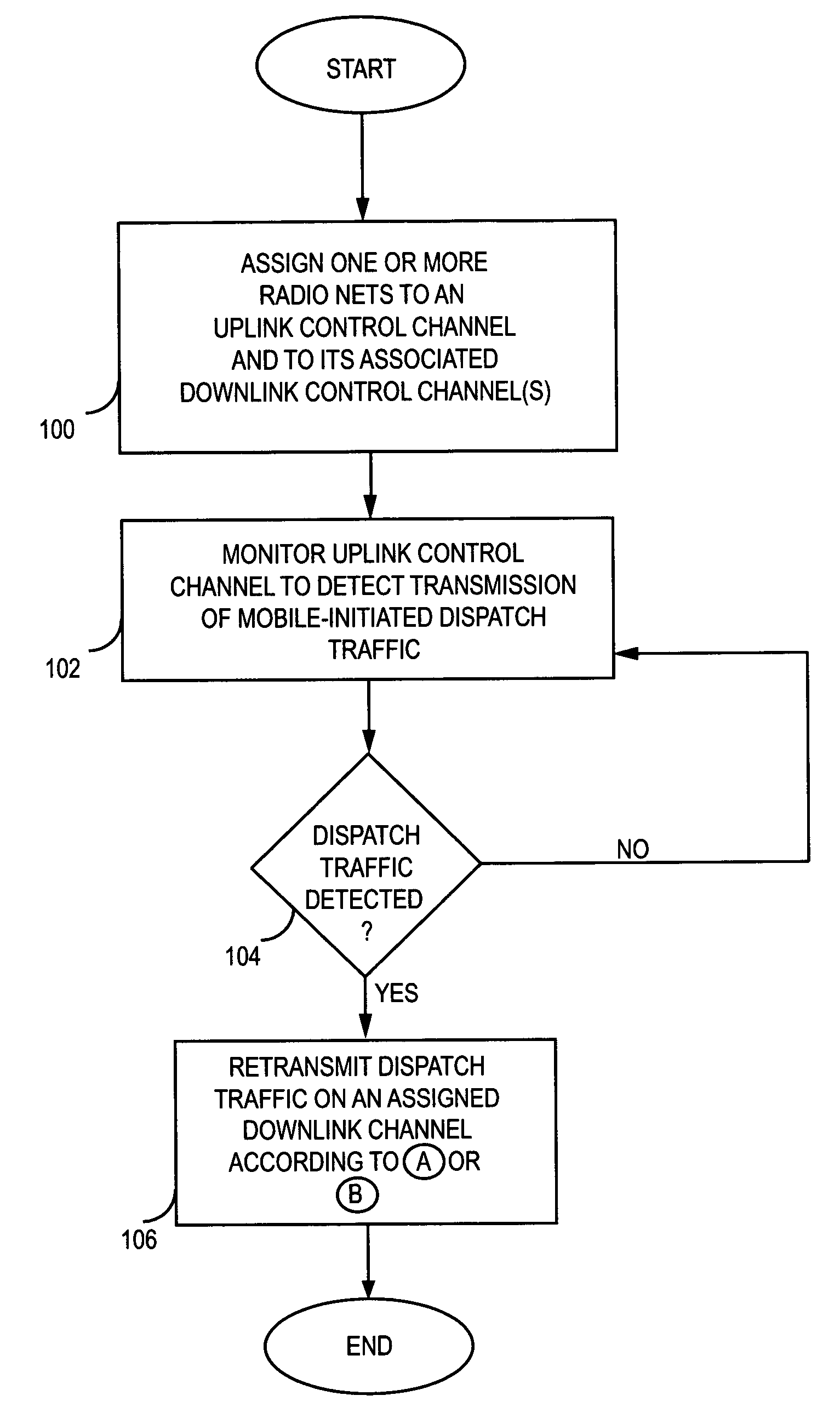
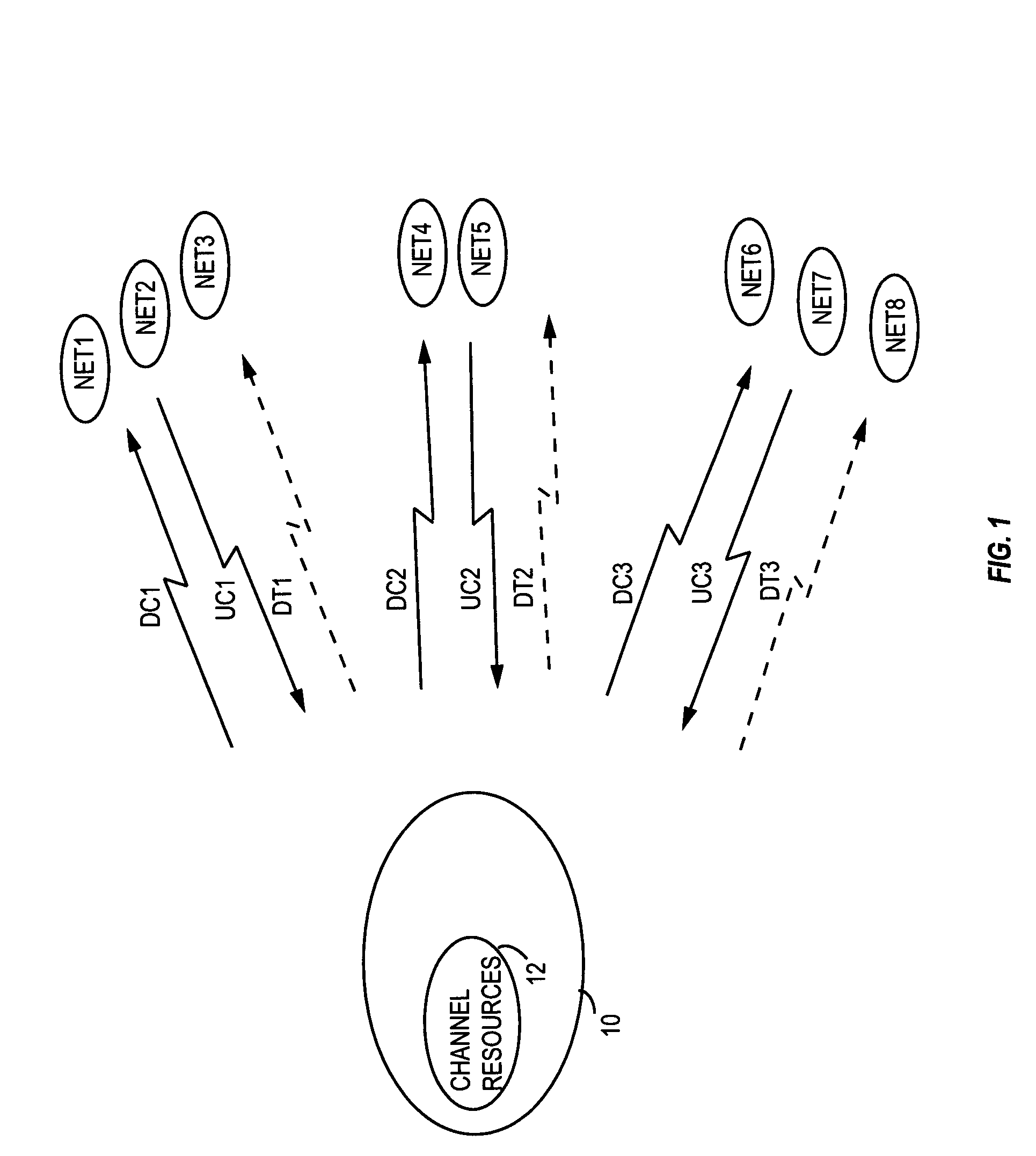
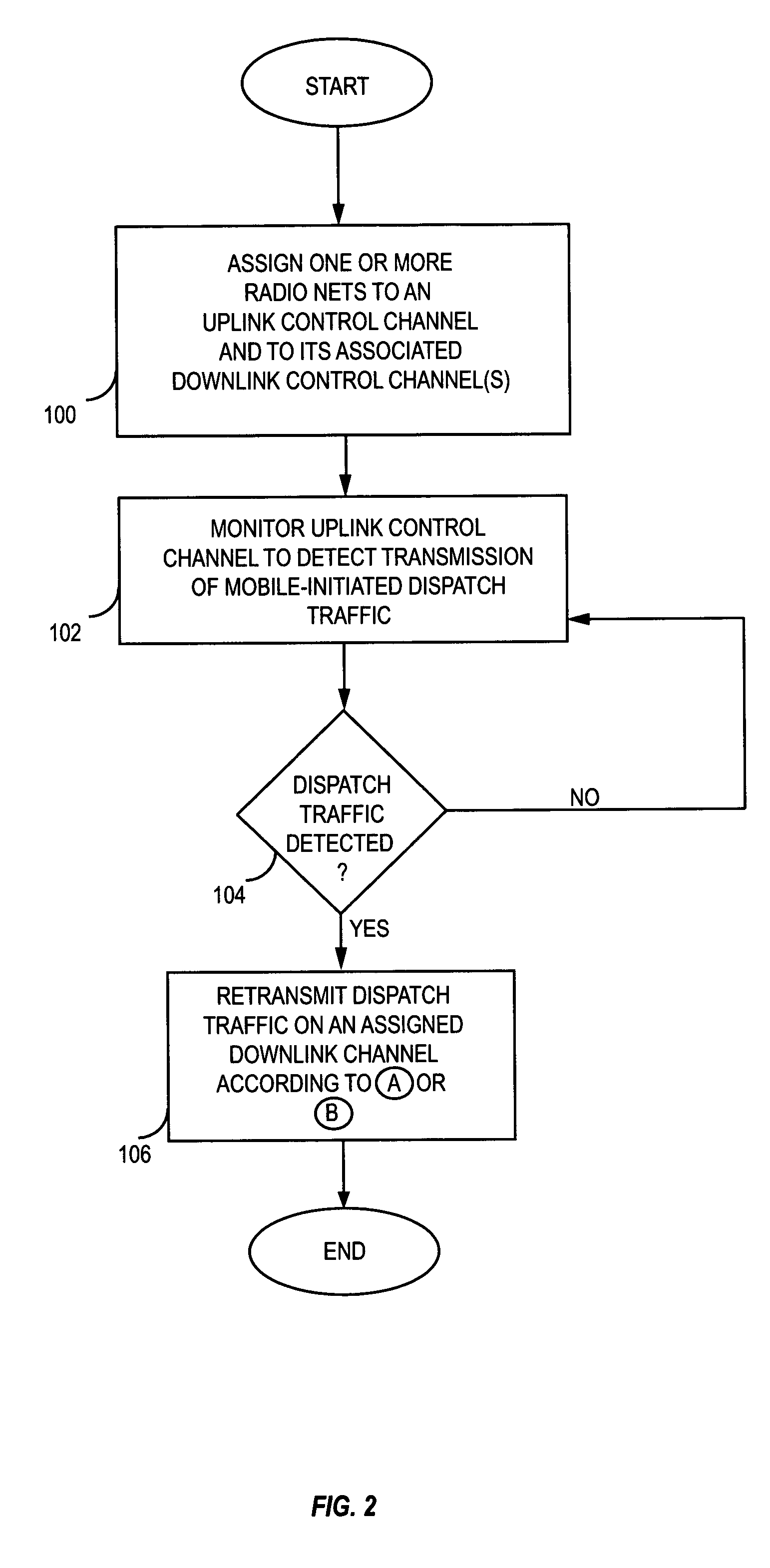
Method and apparatus to reduce dispatch delays in dispatch communication networks
InactiveUS20050070320A1Reduce dispatching delayComponent can be removedNetwork topologiesConnection managementMultiplexingControl channel
A communication network supports push-to-talk communications with reduced dispatching delays by eliminating channel grant / request handshaking on the uplink and the downlink. A pool of communication channels can be associated with a group of nets that include one or more mobile terminals. Any terminal can send dispatch traffic immediately on an assigned uplink channel simply by seizing the channel. The network detects such traffic and retransmits it on a downlink channel monitored by the group of nets. Along with the retransmitted traffic, the network sends a net ID and a new downlink channel assignment. Terminals in the targeted net process the retransmitted traffic and non-targeted terminals switch to the new channel. Alternatively, the control channel can be multiplexed to signal traffic channel assignments as needed for all nets, and traffic can be transmitted on the indicated channels for reception by targeted terminals. The reduced delays particularly benefit networks incorporating satellite relays.
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
Systems, apparatuses, and methods for treating tissue and controlling stenosis
ActiveUS20120310233A1Preventing and minimizing and limiting potentialIncrease airflow resistanceUltrasound therapySurgical needlesDamages tissueNervous system
Systems, delivery devices, and methods to treat to ablate, damage, or otherwise affect tissue. The treatment systems are capable of delivering a coolable ablation assembly that ablates targeted tissue without damaging non-targeted tissue. The coolable ablation assembly damages nerve tissue to temporarily or permanently decrease nervous system input. The system, delivery devices, and methods can damage tissue and manage scarring and stenosis.
Owner:NUVAIRA INC
Devices and methods for treating tissue
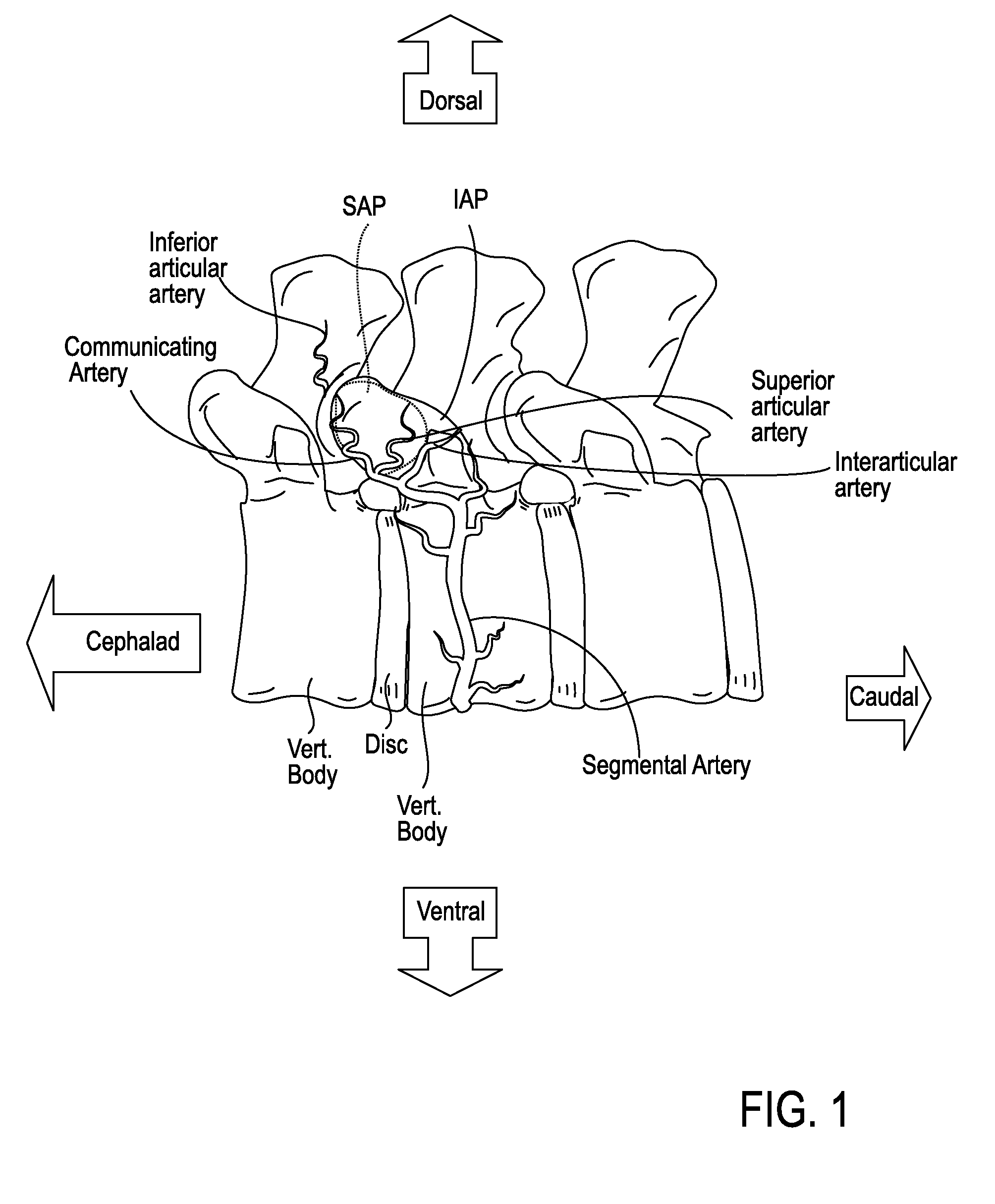
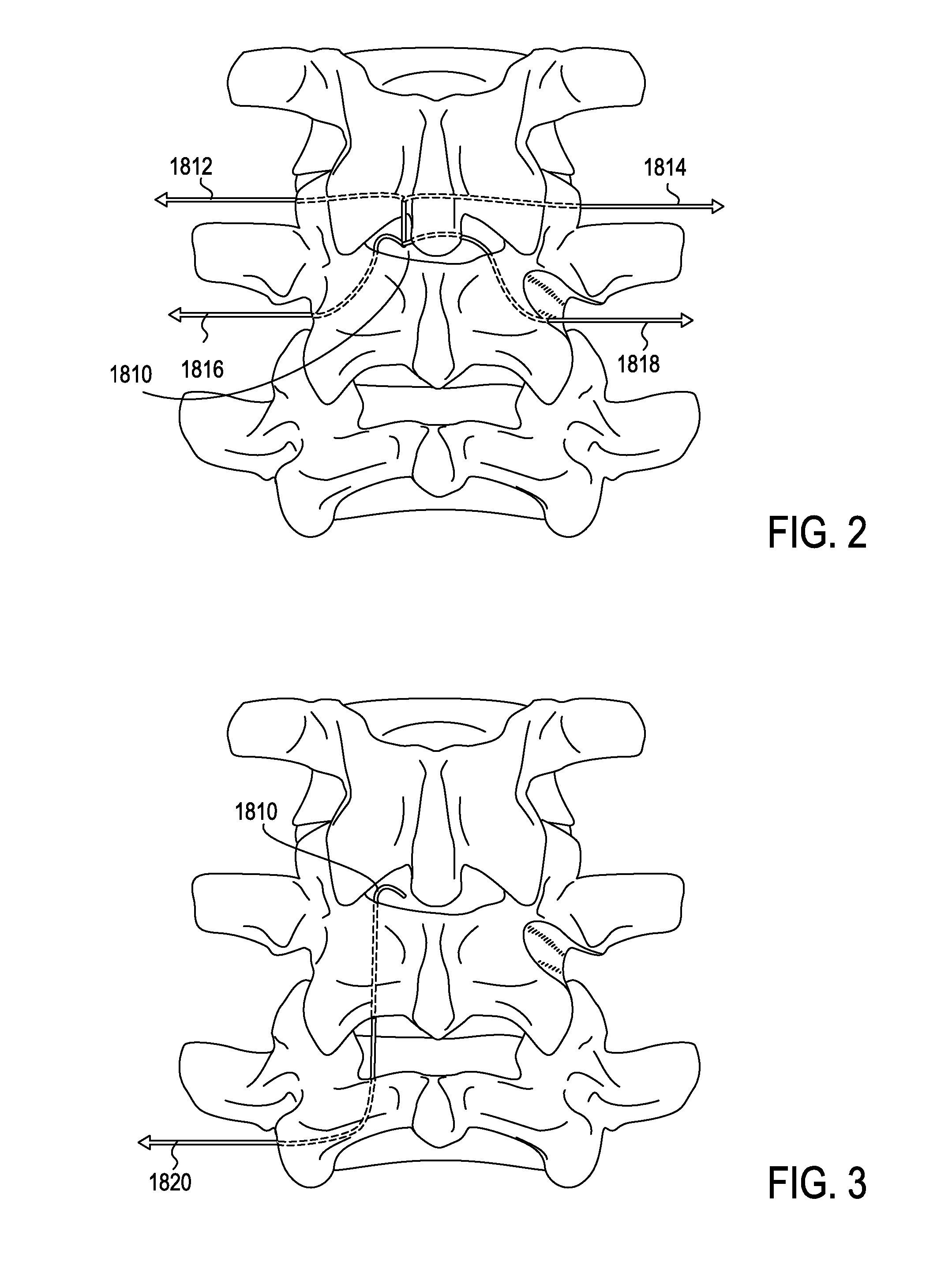
Described herein are devices, systems and methods for treating target tissue in a patient's spine. In general, the methods include the steps of advancing a wire into the patient from a first location, through a neural foramen, and out of the patient from a second location; connecting a tissue modification device to the wire; positioning the tissue modification device through the neural foramen using the wire; modifying target tissue in the spine by moving the tissue modification device against the target tissue; and delivering an agent to modified target tissue, wherein the agent is configured to inhibit blood flow from the modified target tissue. In some embodiments, the step of modifying target tissue comprises removing target tissue located ventral to the superior articular process while avoiding non-target tissue located lateral to the superior articular process.
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC
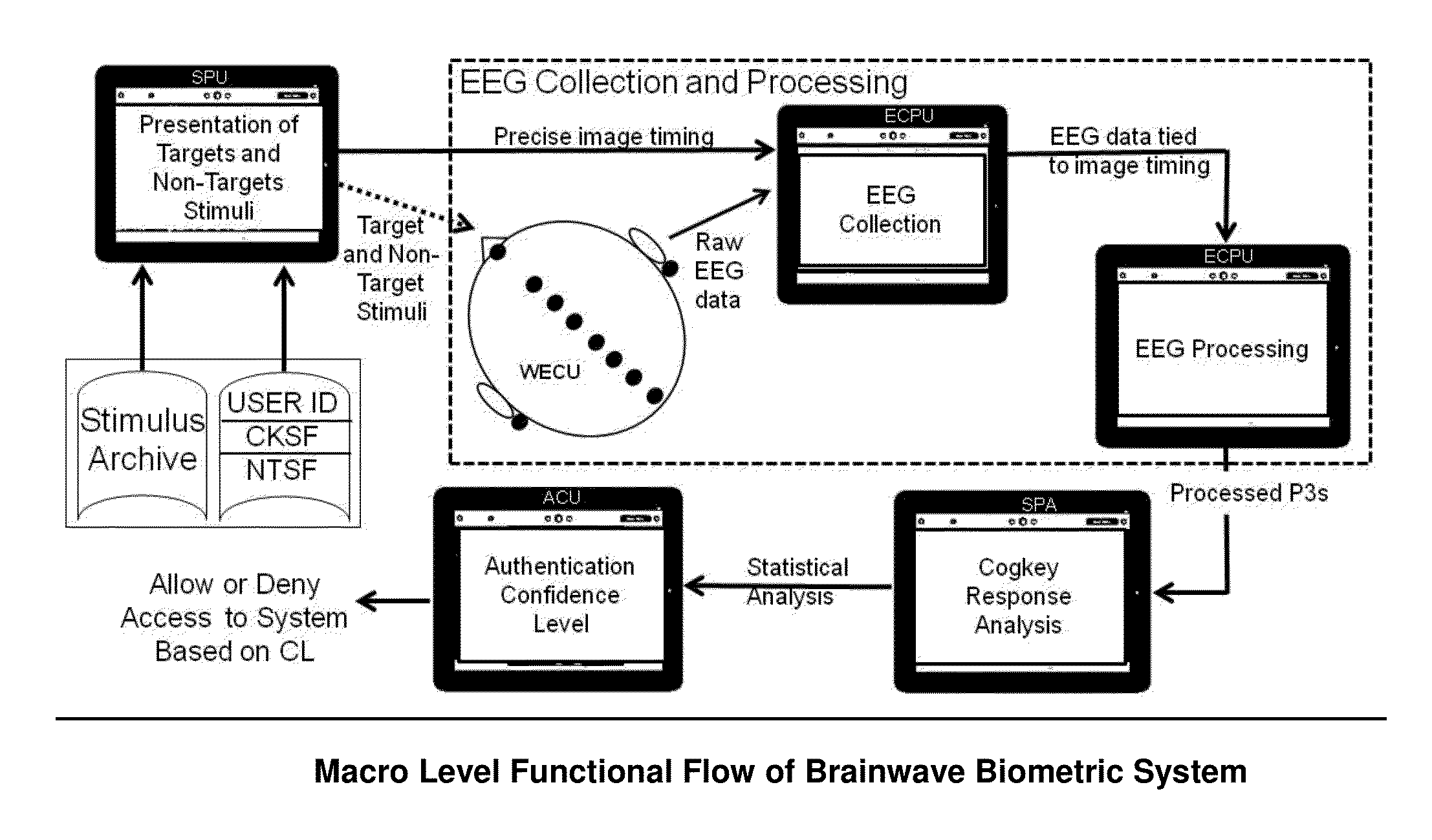
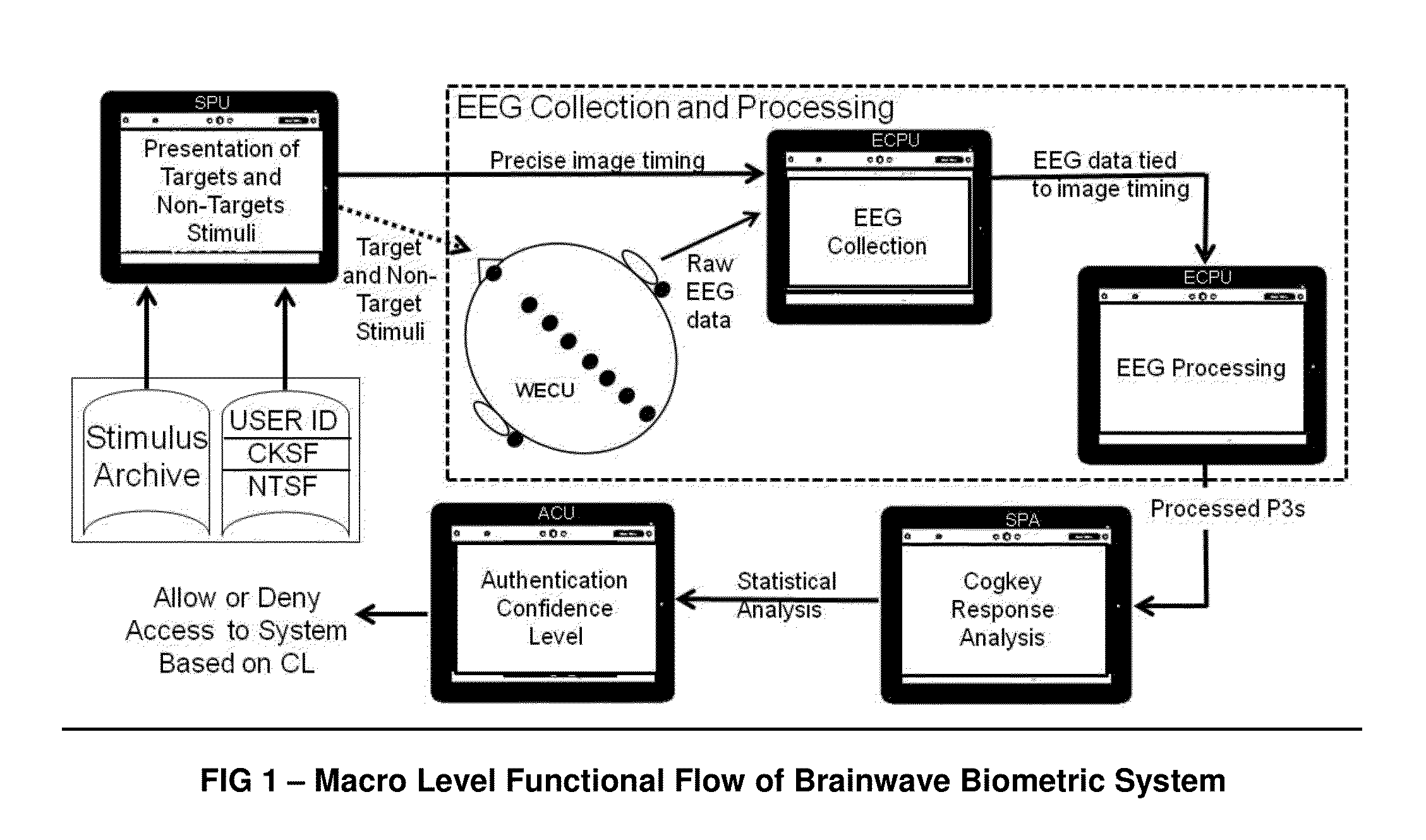
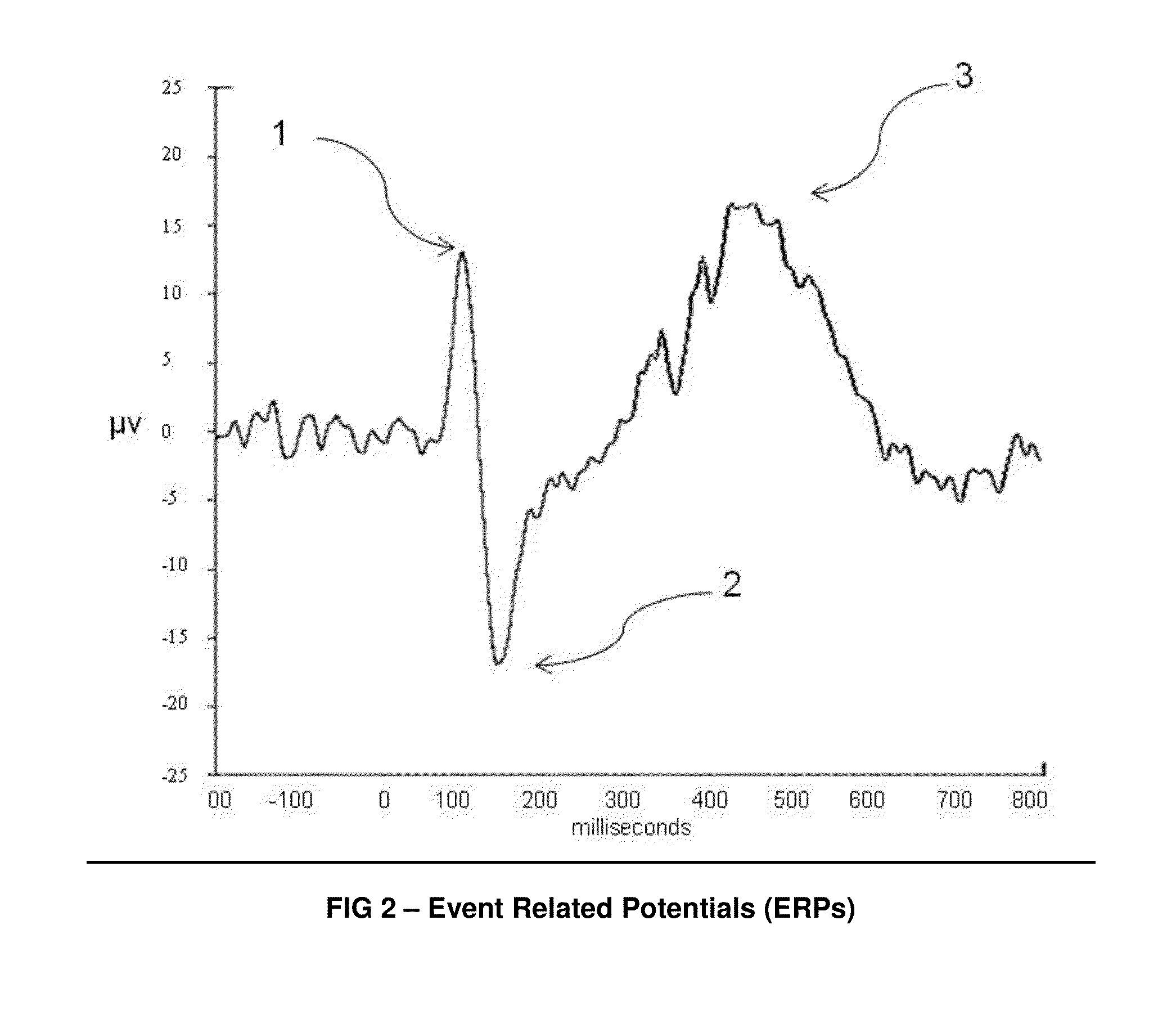
Access Control System using Stimulus Evoked Cognitive Response
InactiveUS20140020089A1Easily discriminatedIncrease flexibilityDigital data processing detailsPerson identificationBiometric dataCognitive response
The ACSSECR invention is a biometric access control system and methodology that measures cognitive, psychophysiological responses to stimuli to confirm the identity of an individual. As an alternative to “Logging in” with a user ID and password, this cognitive biometric authentication system is used for “Cogging in” to a system with user ID and user-selected “Cogkey”. ACSSECR is designed for strict access control scenarios where significant authentication confidence is required to gain access to controlled information, facilities, systems, vehicles, or devices. The system takes advantage of a behavioral and physiological characteristic of humans that is an unconscious response to a stimulus. The Event Related Potential (ERP) response (specifically the P3 ERP) involuntarily occurs when an individual perceives and reacts to an unexpected, task-relevant event. The task is for the user to recognize their Cogkey which is presented infrequently amidst more frequent non-target stimuli. There is no requirement for extensive enrollment by users, only the recognition of their Cogkey. The basic system does not store biometric data for comparison, but rather measures the user's Cogkey recognition responses in comparison to non-Cogkey stimulus responses. An individual can have multiple personas with different Cog keys.
Owner:PERINI II REMO PETER
Radio frequency ablation cooling shield
A medical assembly and method are provided to effectively treat abnormal tissue, such as, a tumor. The target tissue is thermally ablated using a suitable source, such as RF or laser energy. A cooling shield is placed in contact with non-target tissue adjacent the target tissue, and actively cooled to conduct thermal energy away from the non-target tissue. In one method, the cooling shield can be placed between two organs, in which case, one of the two organs can comprise the target tissue, and the other of the two organs can comprise the non-target tissue. In this case, the cooling shield may comprise an actively cooled inflatable balloon, which can be disposed between the two organs when deflated, and then inflated. The inflatable balloon can be actively cooled by pumping a cooling medium through it. In another method, the cooling shield can be embedded within the non-target tissue. In this case, the cooling shield can comprise one or more needles. If a plurality of needles is used, they can be embedded into the non-target tissue in a series, e.g., a rectilinear or curvilinear arrangement. The needle(s) can be actively cooled by pumping a cooling medium through them.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Stabilization of cells and biological specimens for analysis
InactiveUS20050181353A1Improve stabilityMaintain qualityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAbnormal tissue growthIn vivo
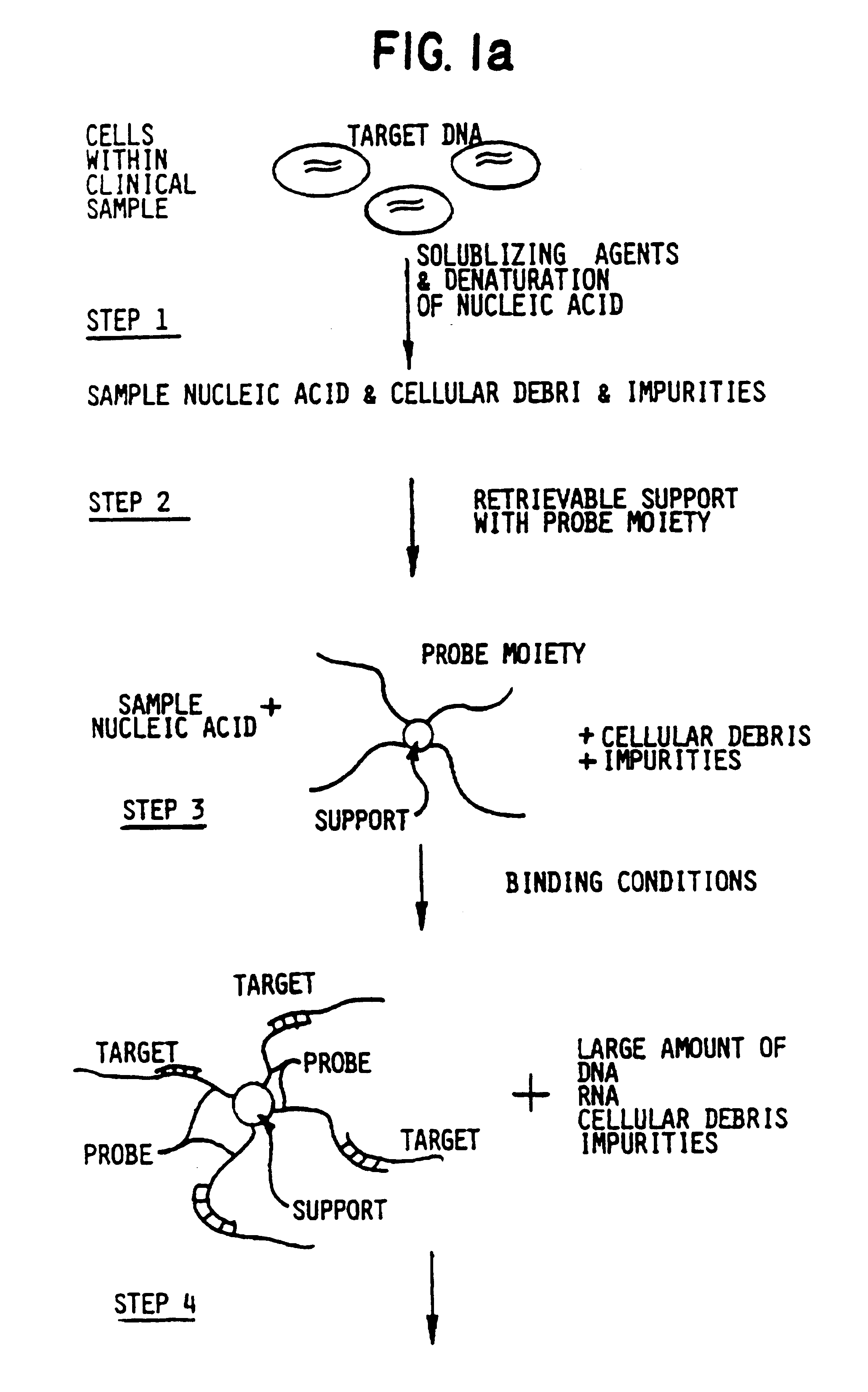
Compositions and methods for stabilizing rare cells in blood specimens, preserving the quality of blood specimens, and also serving as cell fixatives are disclosed which minimize losses of target cells (for example, circulating tumor cells) and formation of debris and aggregates from target cells, non-target cells and plasma components, thereby allowing more accurate analysis and classification of circulating tumor cells (CTC) and, ultimately, of tumor burdens in cancer patients. Stabilization of specimens is particularly desirable in protocols requiring rare cell enrichment from blood specimens drawn from cancer patients. Exposure of such specimens to potentially stressful conditions encountered, for example, in normal processing, mixing, shaking, delays due to transporting the blood, has been observed to not only diminish the number of CTC but also to generate debris and aggregates in the blood specimens that were found to interfere with accurate enumeration of target cells, if present. Stabilizers are necessary to discriminate between in vivo CTC disintegration and in vitro sample degredation.
Owner:VERIDEX LCC
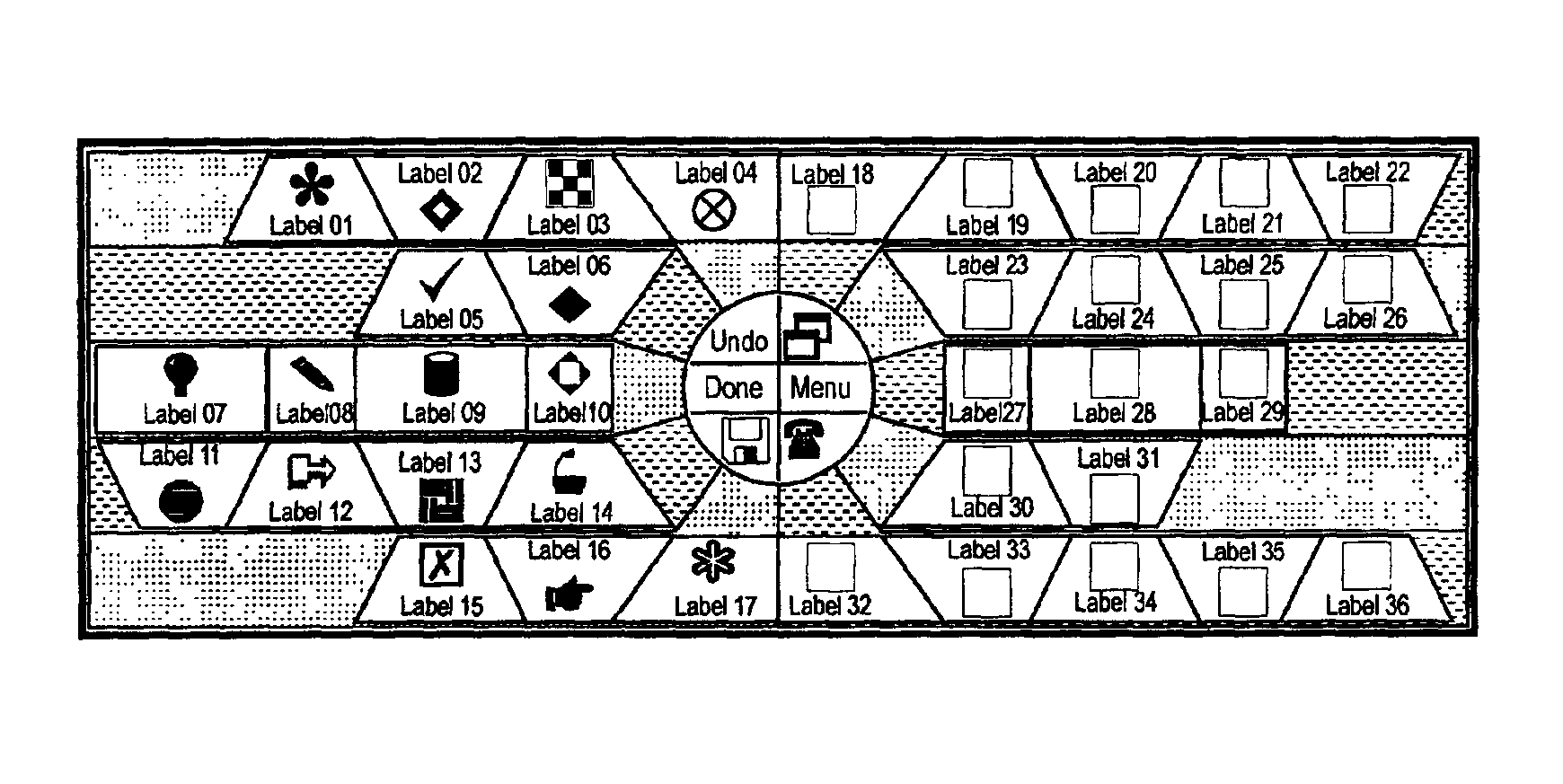
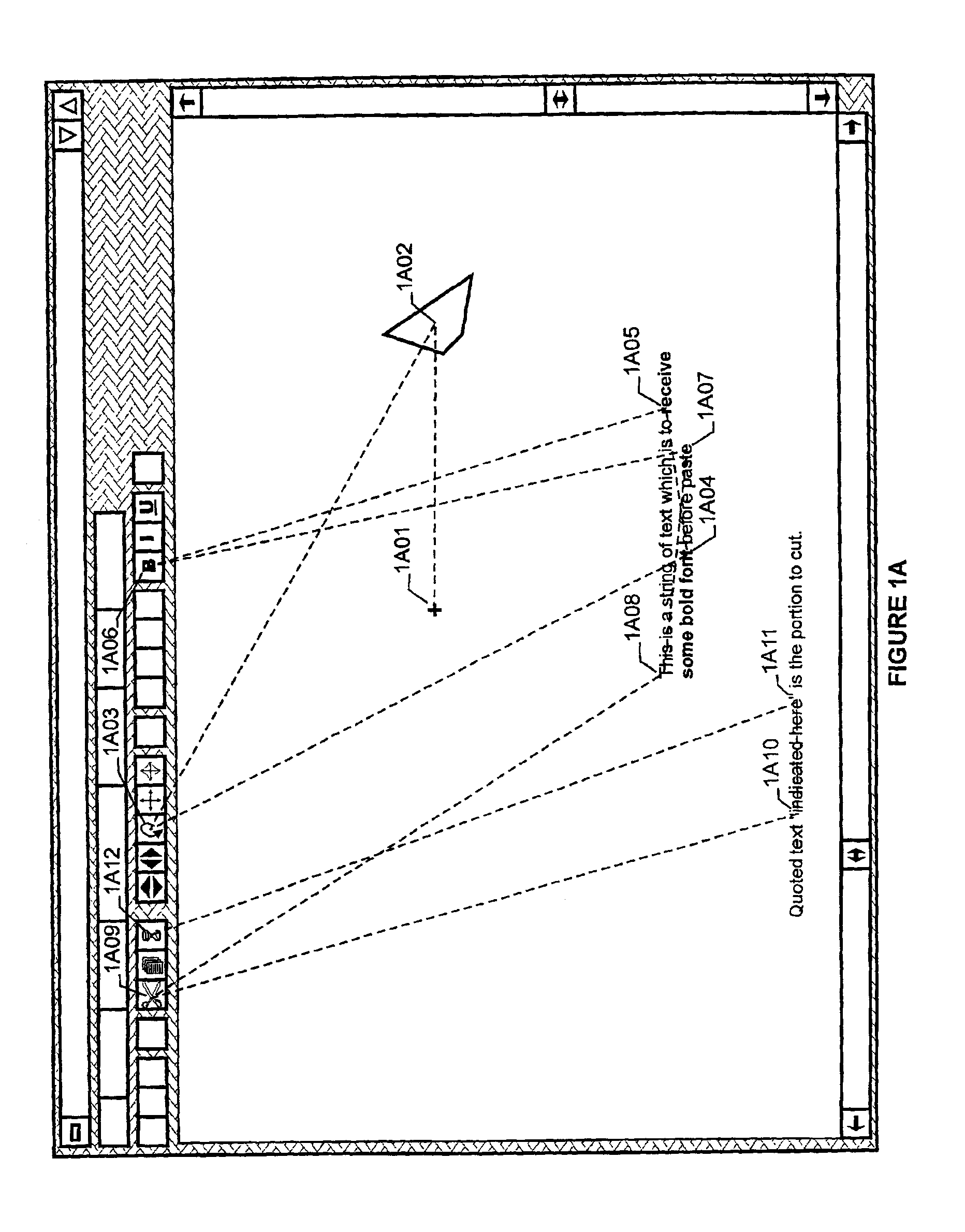
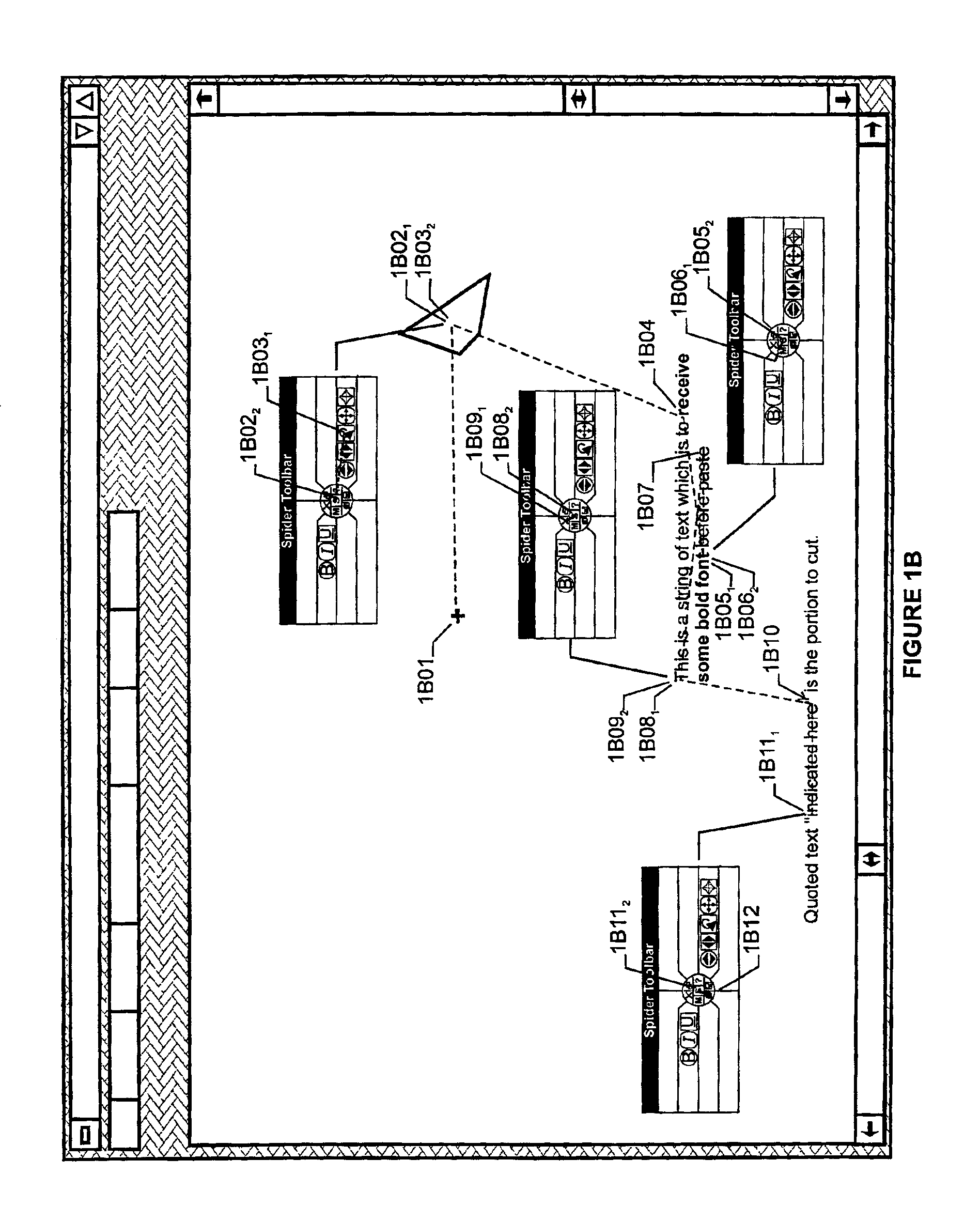
Computer interface toolbar for acquiring most frequently accessed options using short cursor traverses
A pop-up toolbar is disclosed which is demonstrably faster and easier to utilize than the permanently displayed, horizontal toolbar. Two columns provide a variable number of irregularly shaped regions arrayed on either side of a generally circular central-area. Components of regions converge on the central area. Targets, each displaying an icon and an optional, descriptive label, appear within the regions. At pop-up of the toolbar, the cursor moves under system control to the central-area of the toolbar, enabling users to perform short, radial traverses of the cursor into targets, activating related functions by appropriate action. Alternatively, primary and secondary targets for regions may be designated for remote acquisition, whereby alternate user actions in any non-target area of a region activate the primary and secondary targets respectively defined for that region. The central-area is divided into a varying number of shapes permitting users to activate application, system, or toolbar management activities.
Owner:DRISKELL STANLEY W
Compositions and methods for enhancing discriminatory RNA interference
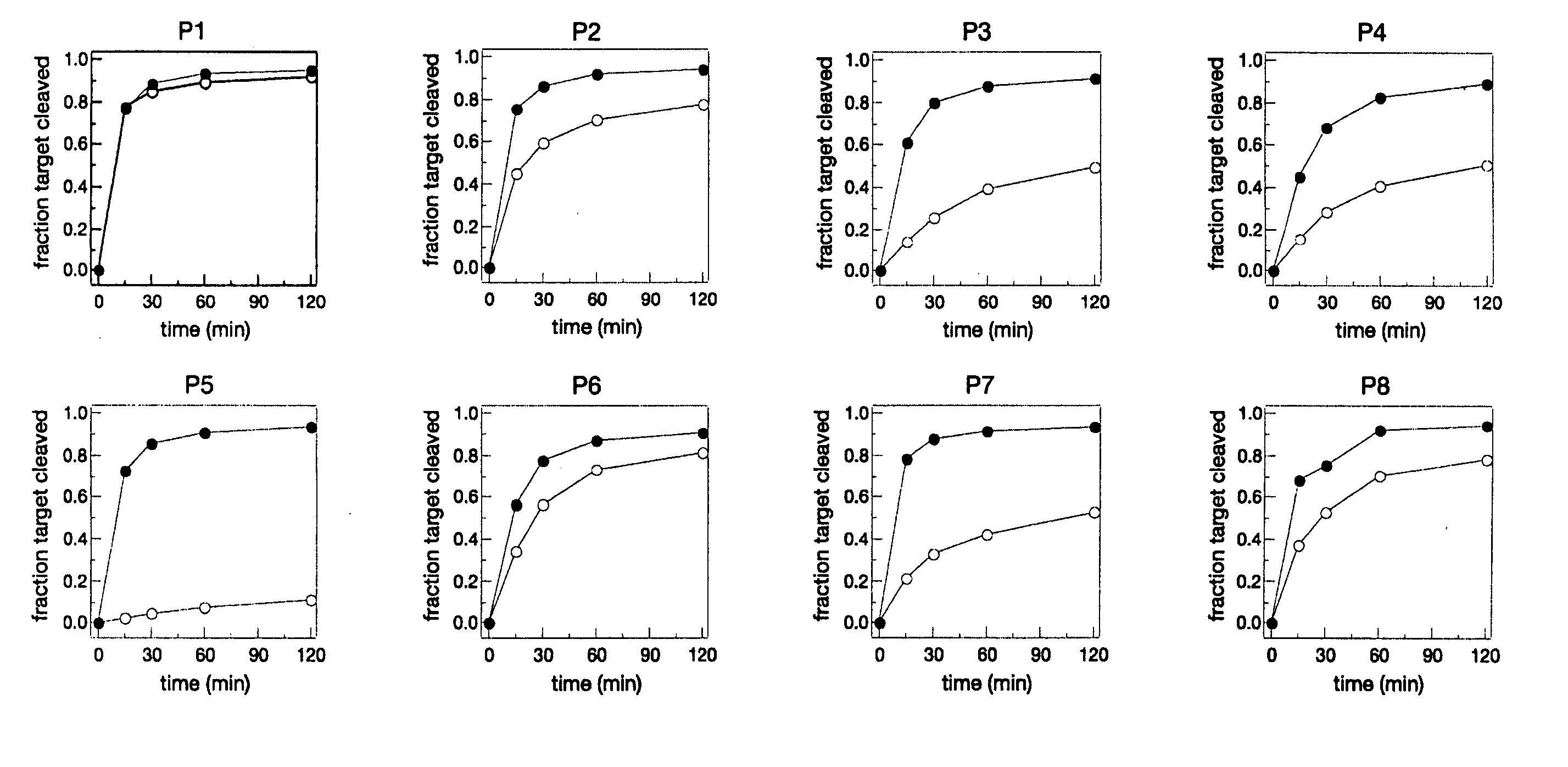
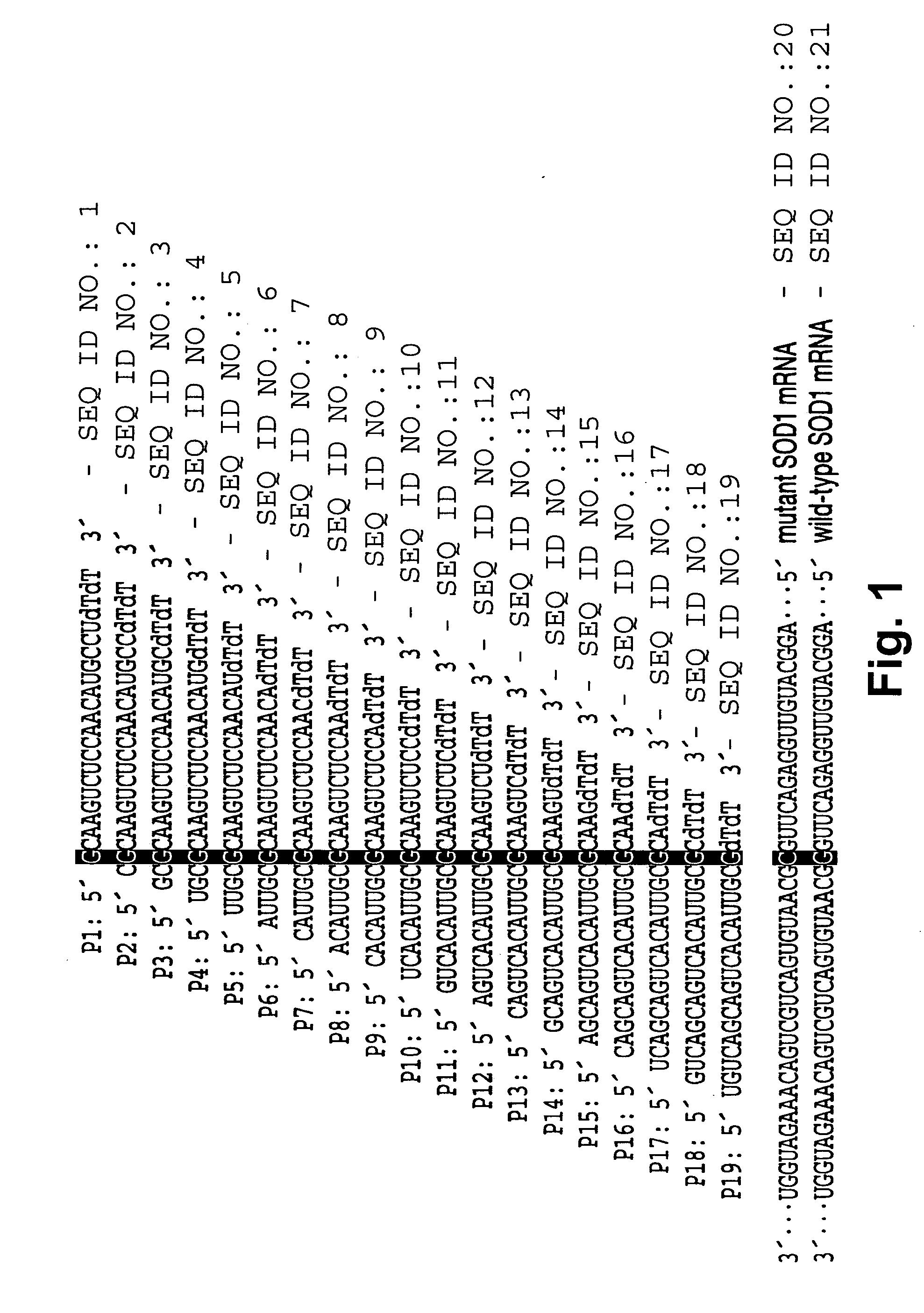
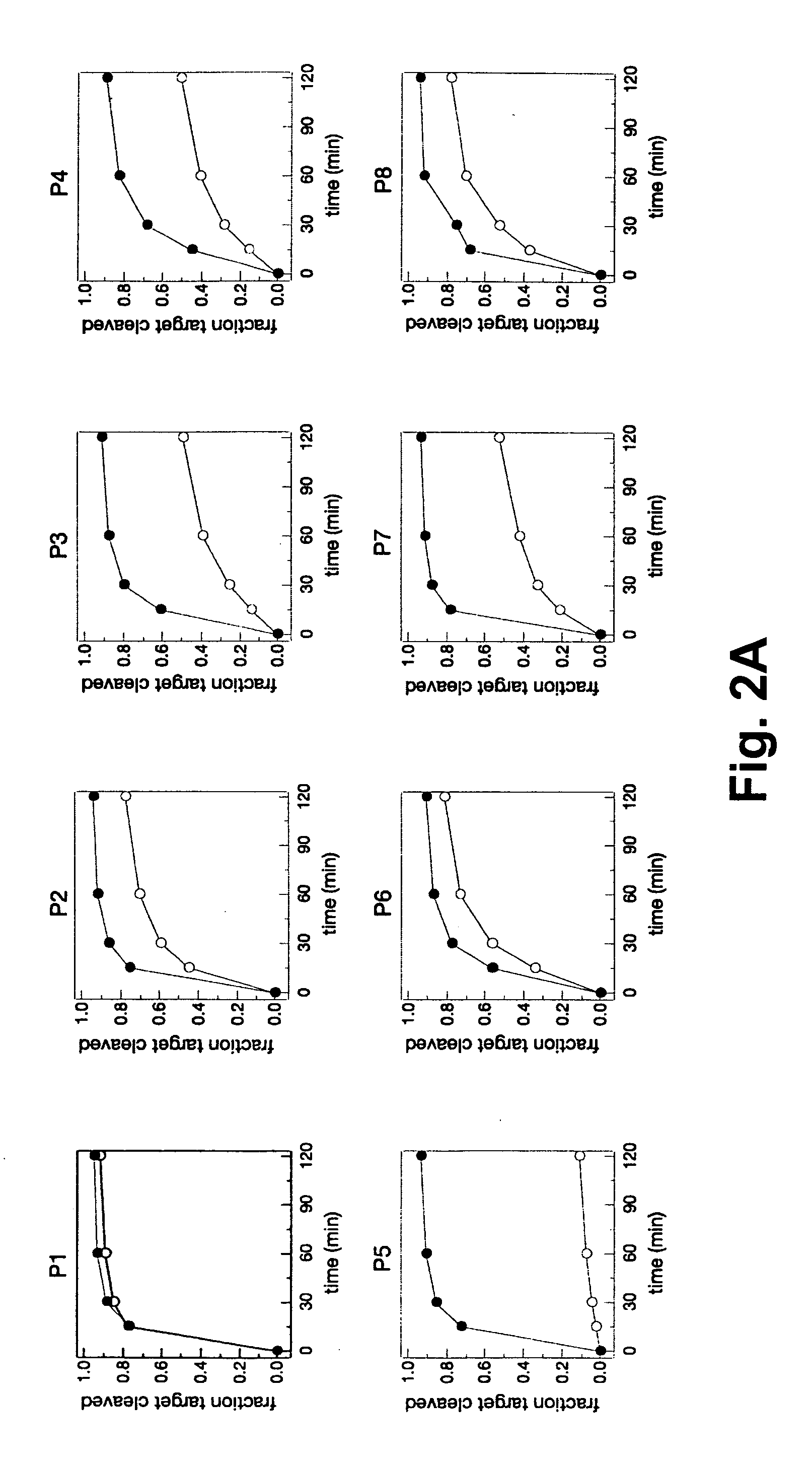
InactiveUS20070259827A1Improved allelic discriminationImprove discriminationOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderNon targetedGenetic disorder
The present invention provides methods for enhancing discriminatory RNA silencing by RNA silencing agents. In particular, the invention provides methods for generating RNA silencing agents which can discriminate between target and non-target mRNAs that differ in sequence by only one nucleotide. Also provided are improved RNA silencing agents with enhanced discriminatory RNA silencing, e.g., single nucleotide discriminatory RNA silencing. The compositions and methods of the invention are useful in therapeutic strategies for treating genetic disorders associated with dominant, gain-of-function gene mutations.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS +1
Delivery devices with coolable energy emitting assemblies
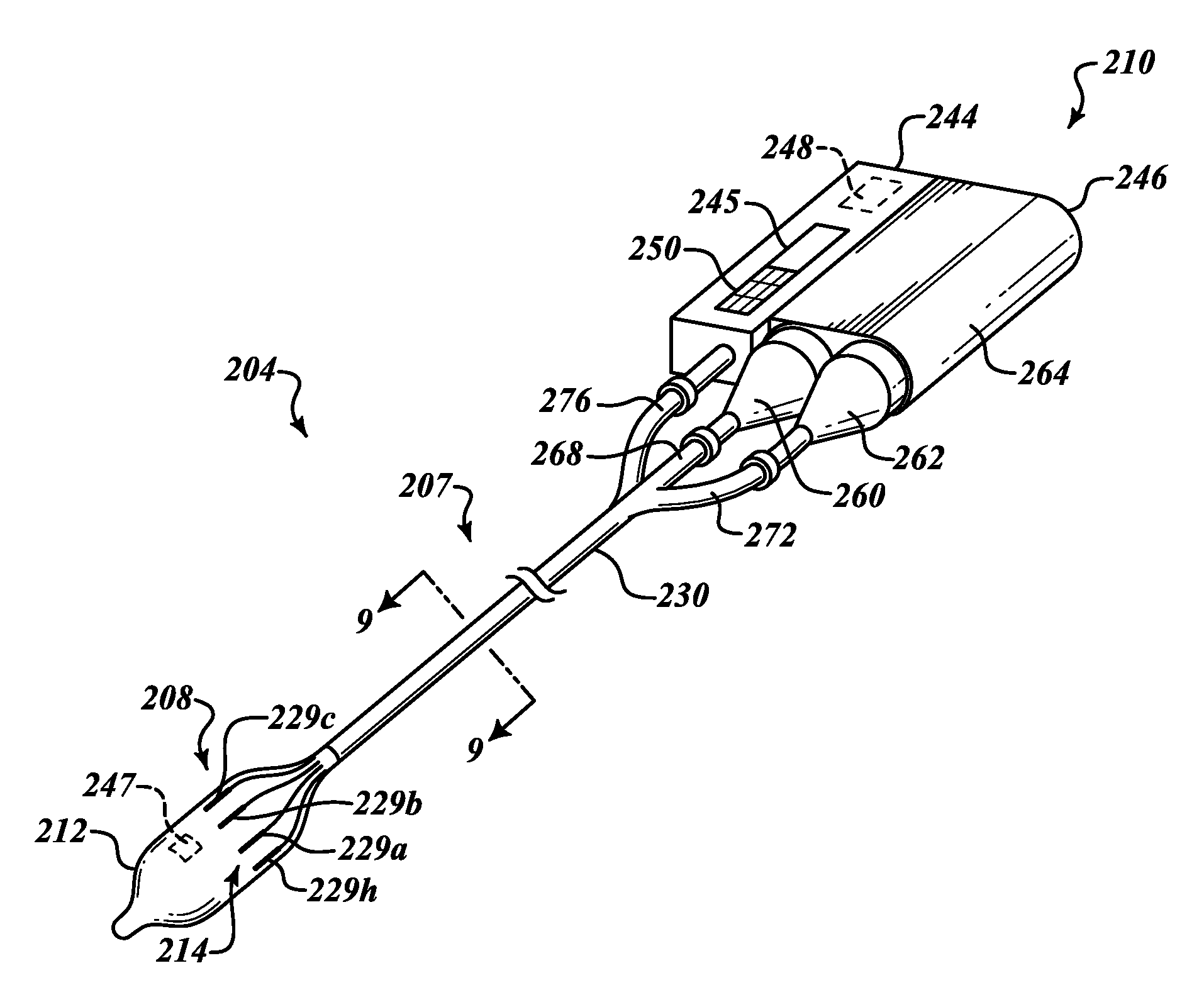
ActiveUS20120016364A1Conveniently passedAvoid and limit destructionUltrasound therapyBronchoscopesNervous systemTarget tissue
Owner:HOLAIRA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com