Patents
Literature
145 results about "Event-related potential" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
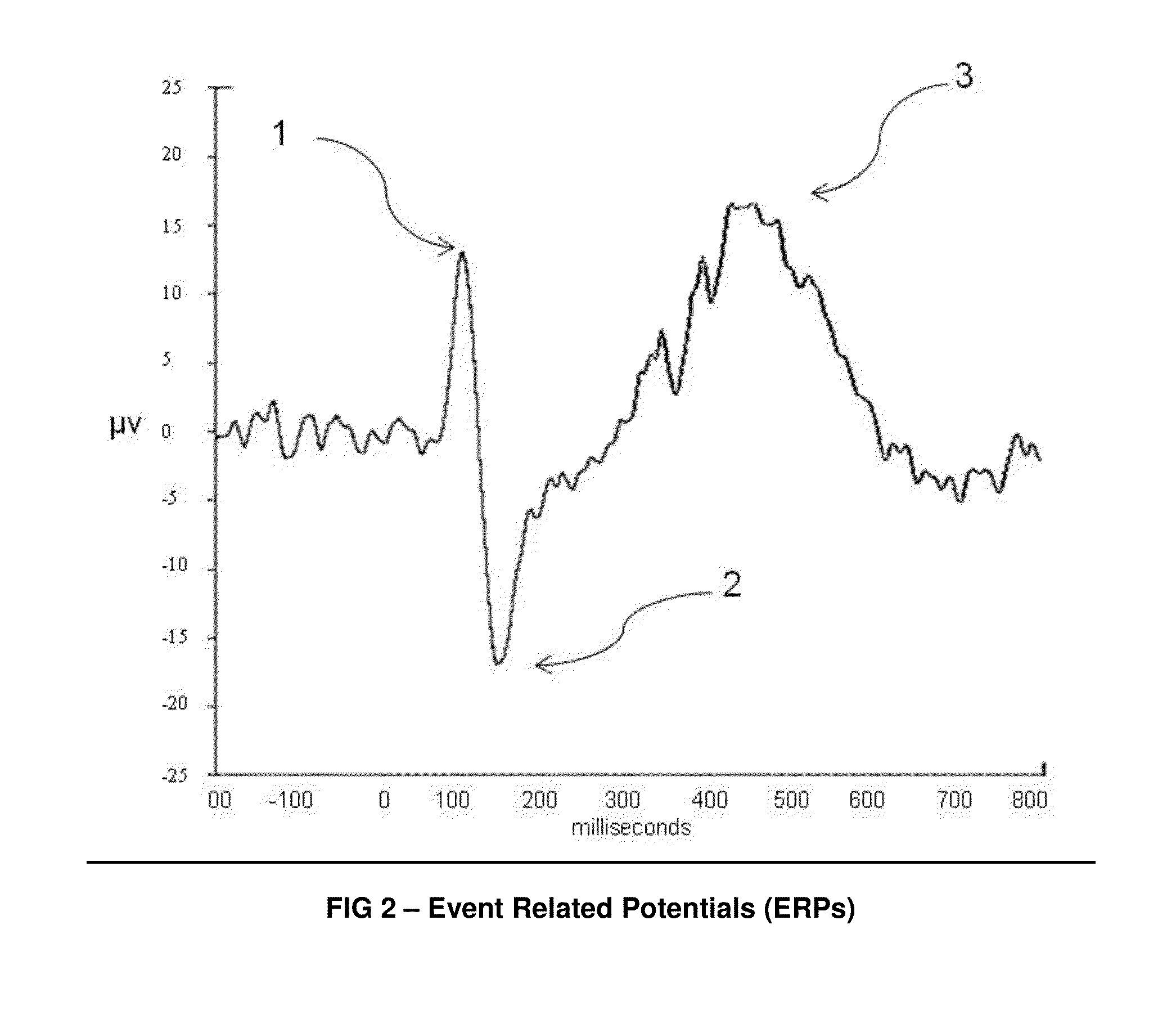
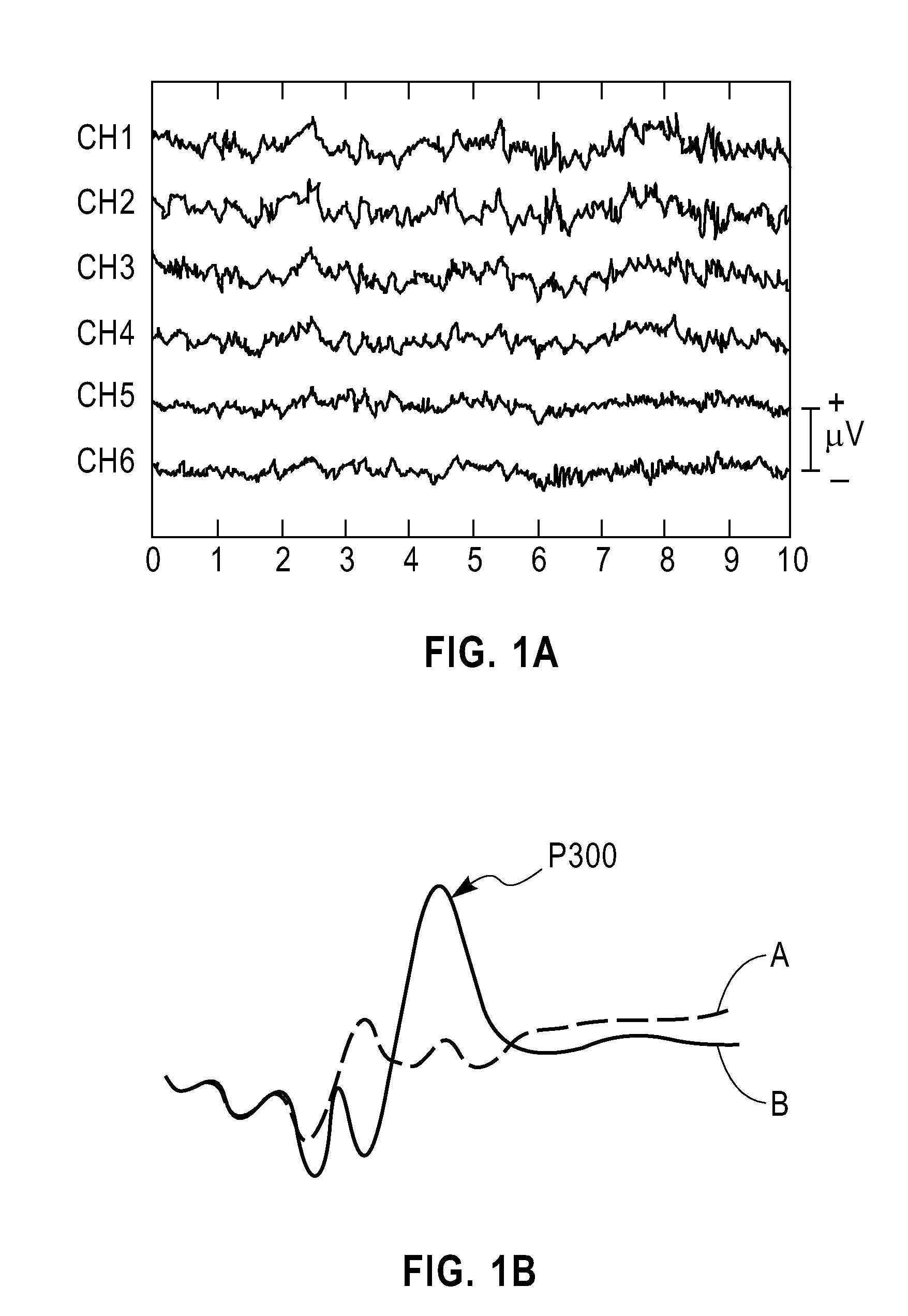
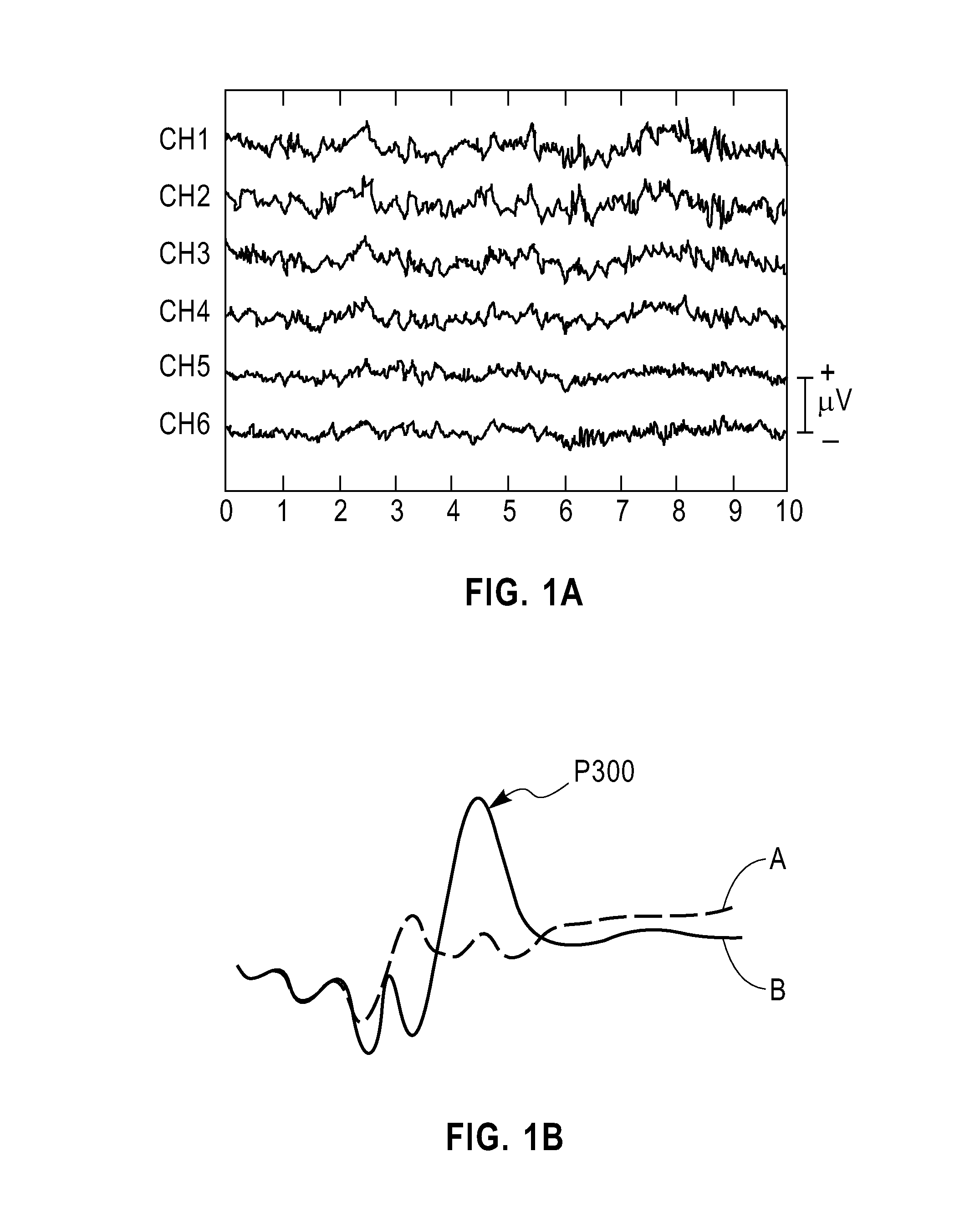
An event-related potential (ERP) is the measured brain response that is the direct result of a specific sensory, cognitive, or motor event. More formally, it is any stereotyped electrophysiological response to a stimulus. The study of the brain in this way provides a noninvasive means of evaluating brain functioning.
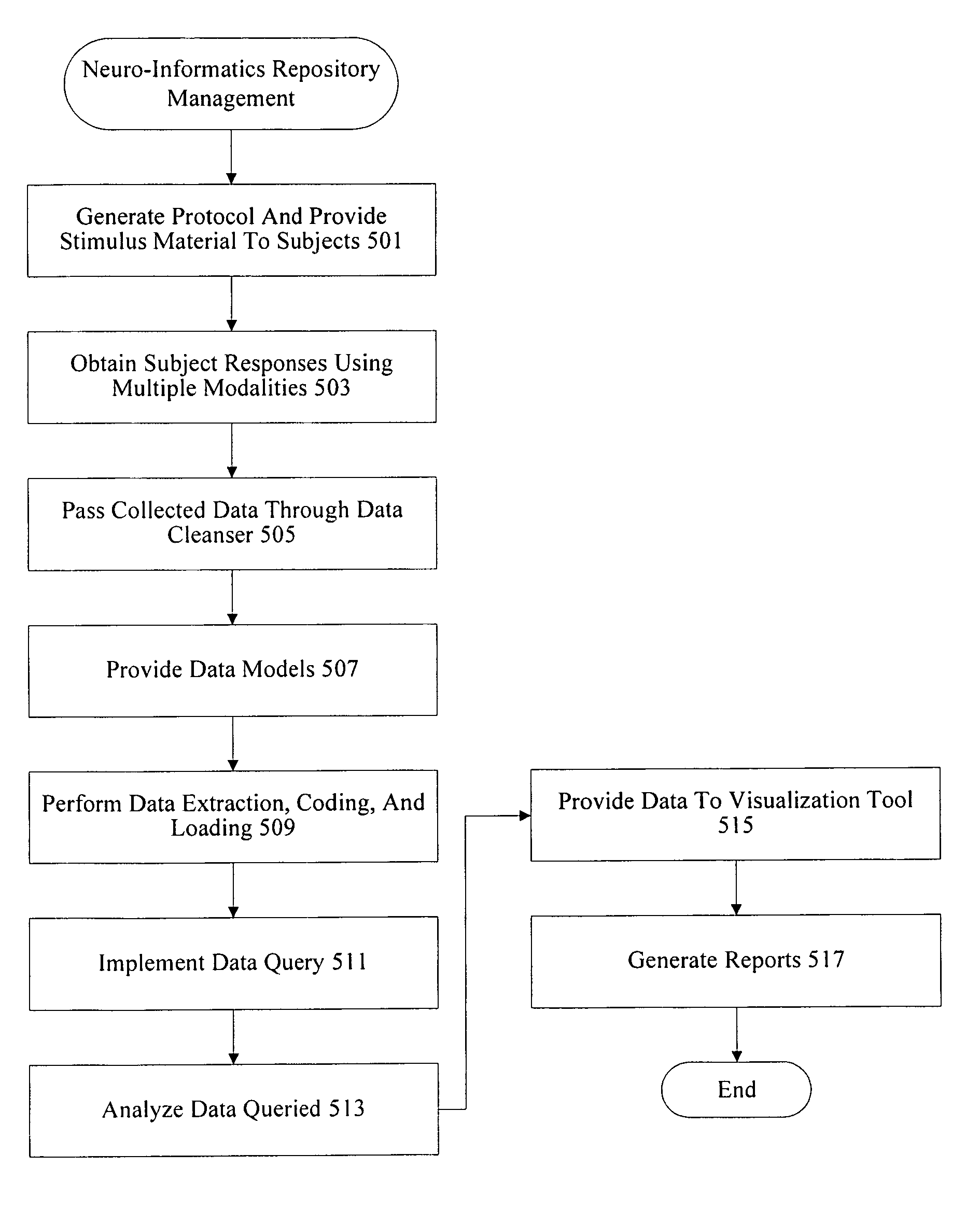
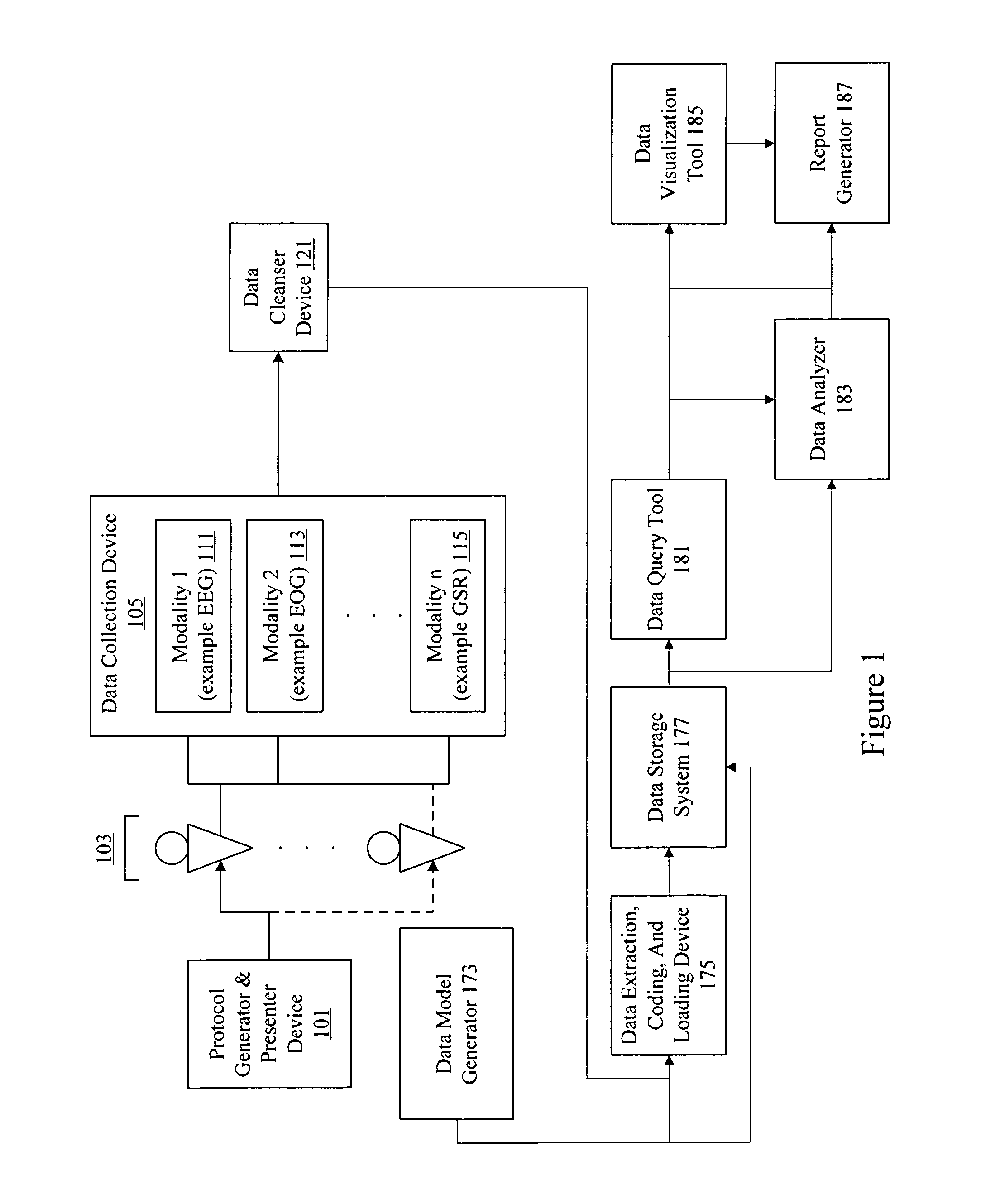
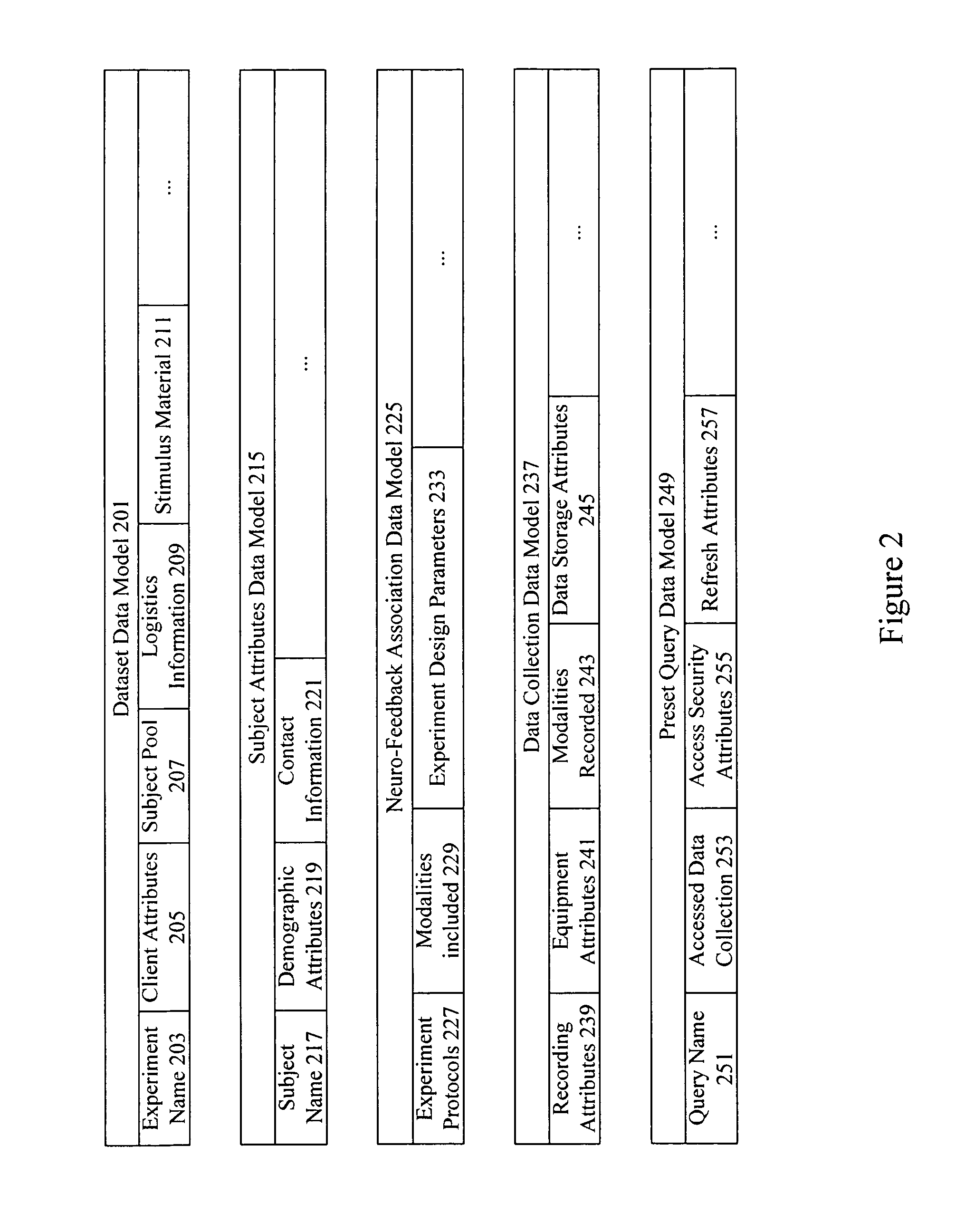
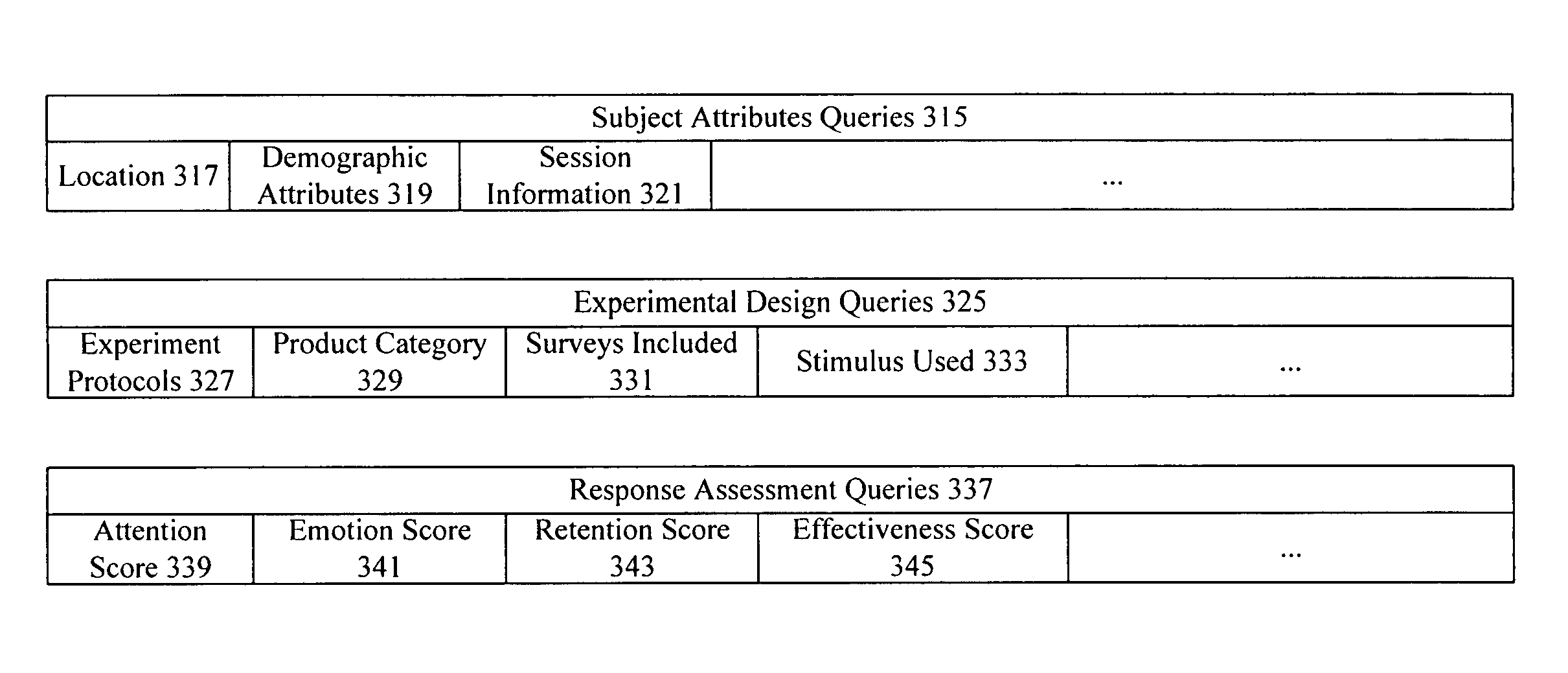
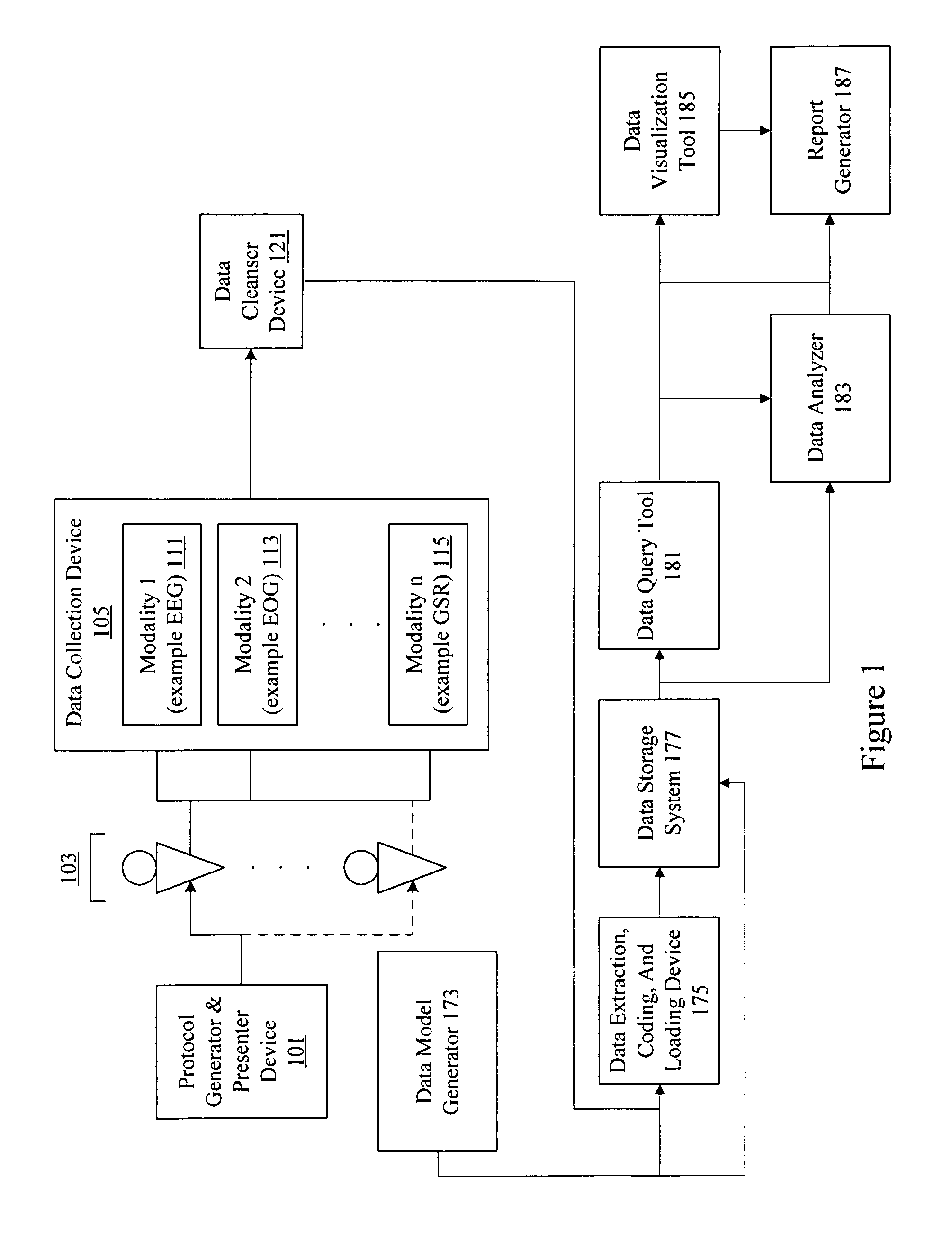
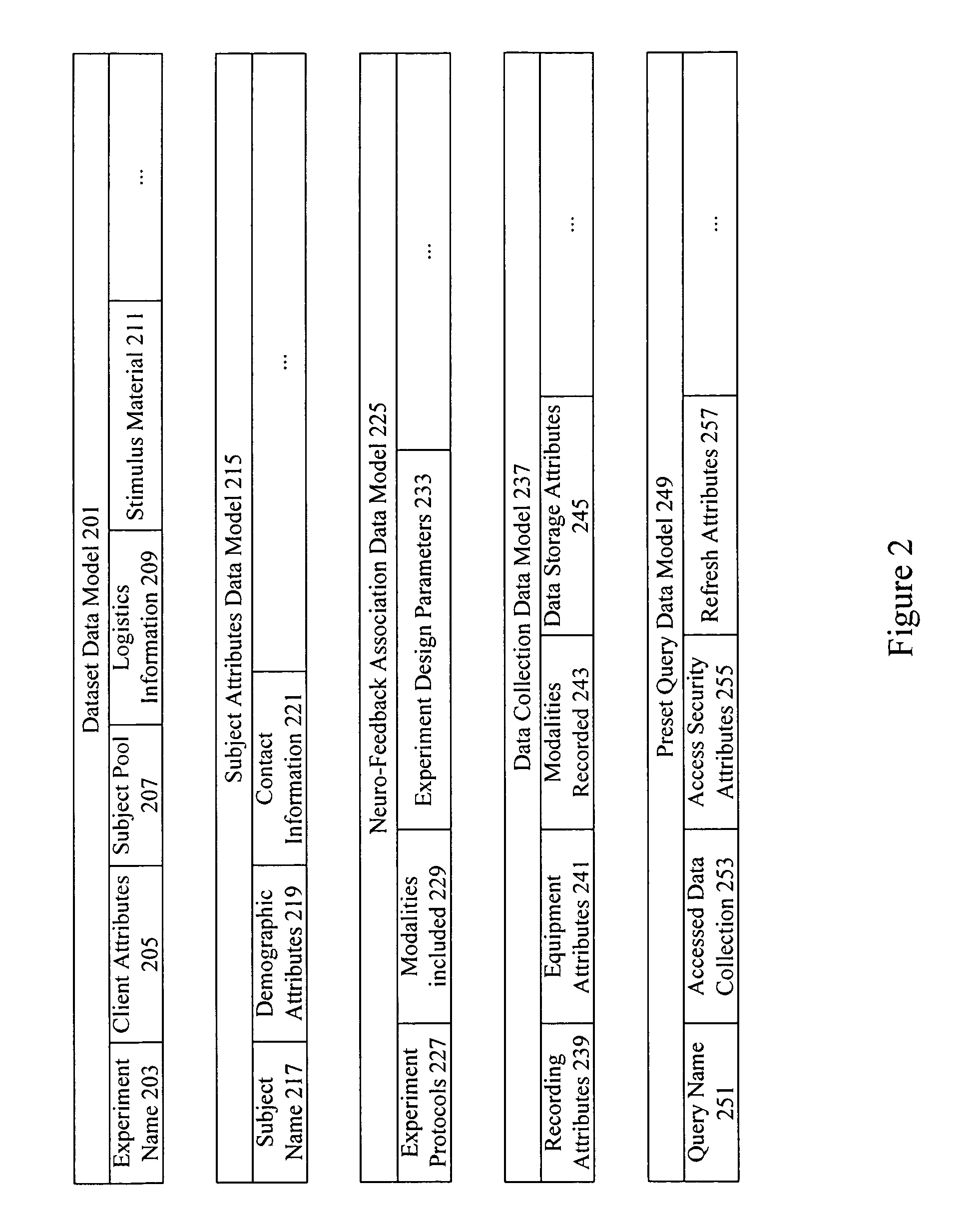
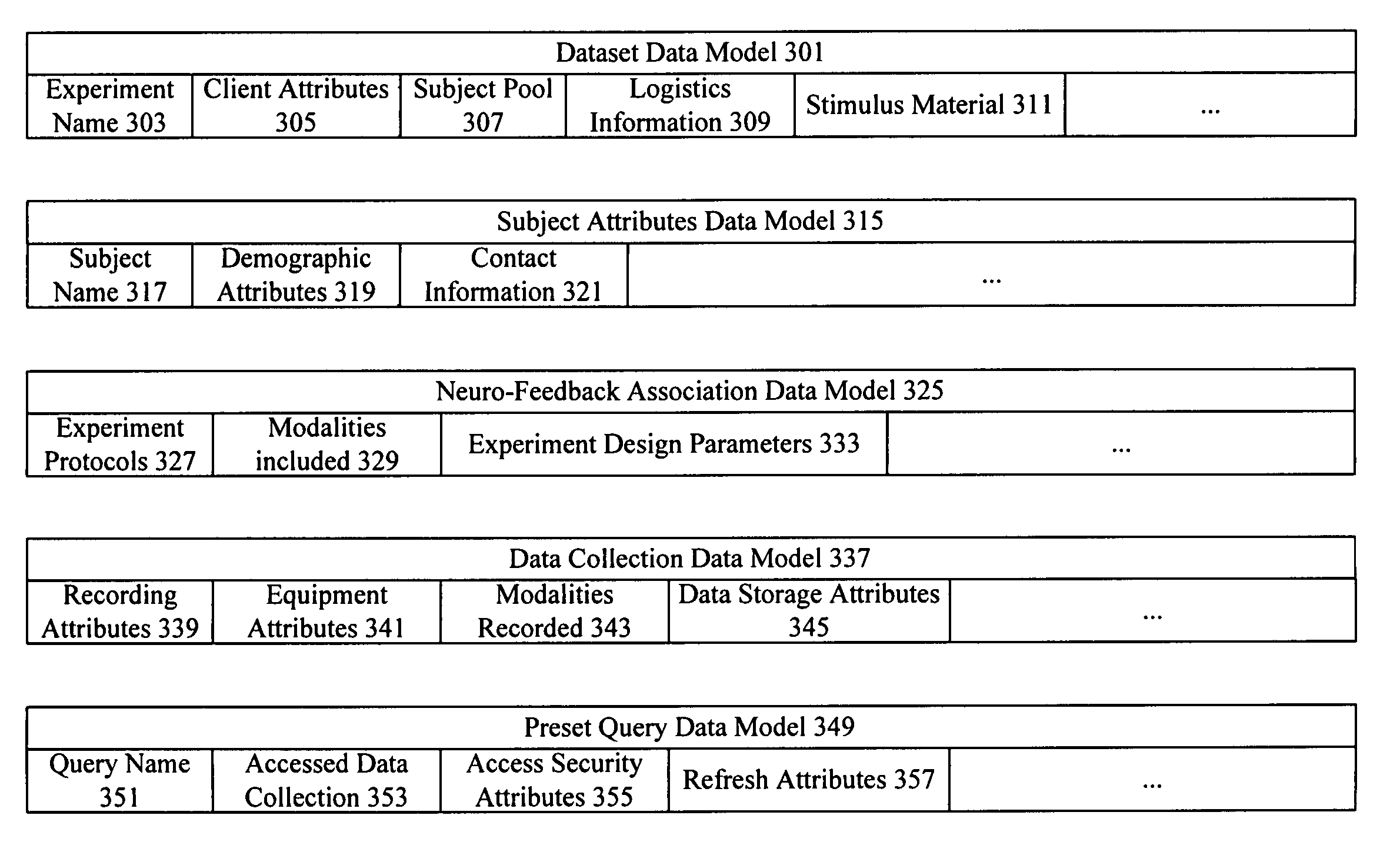
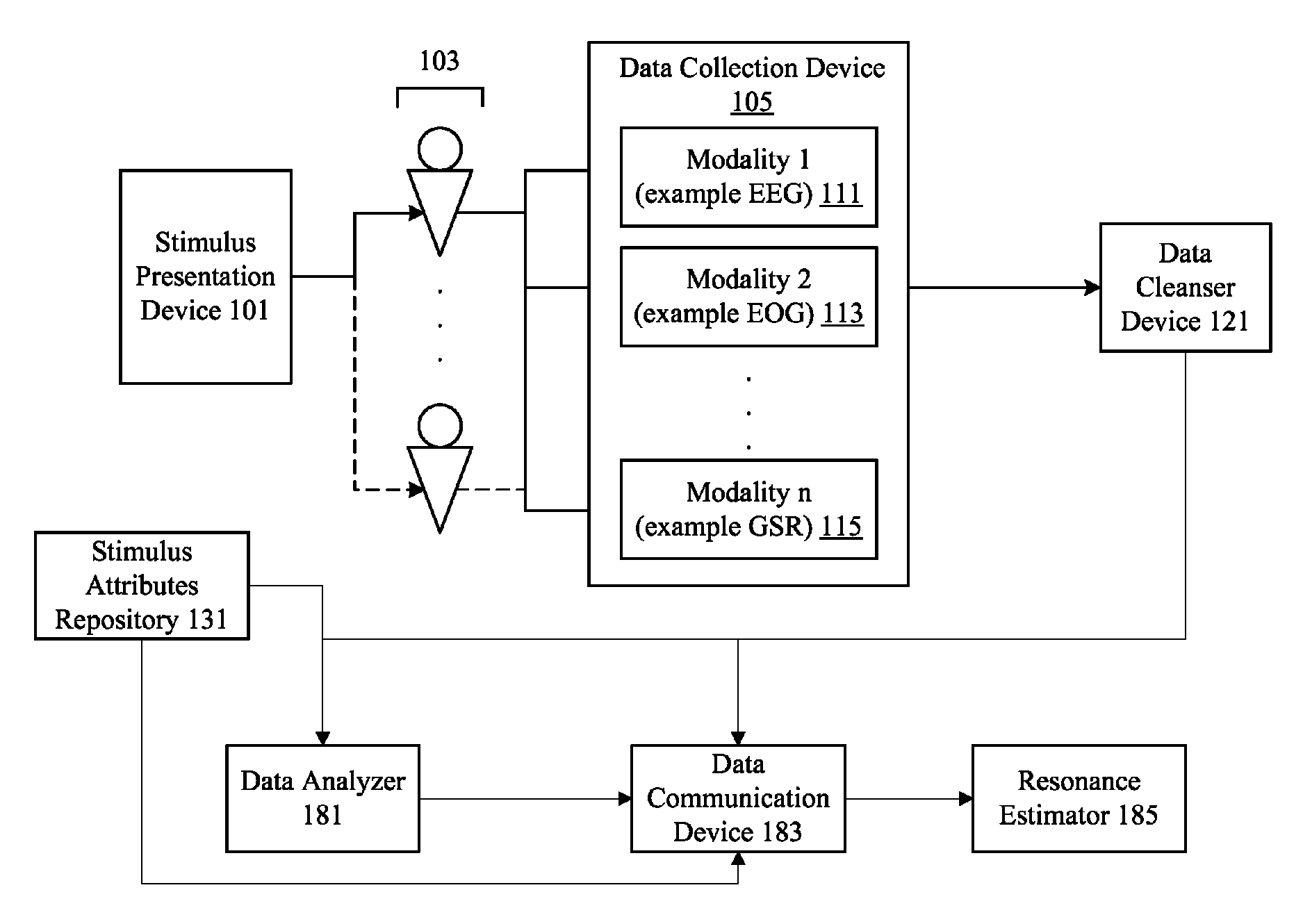
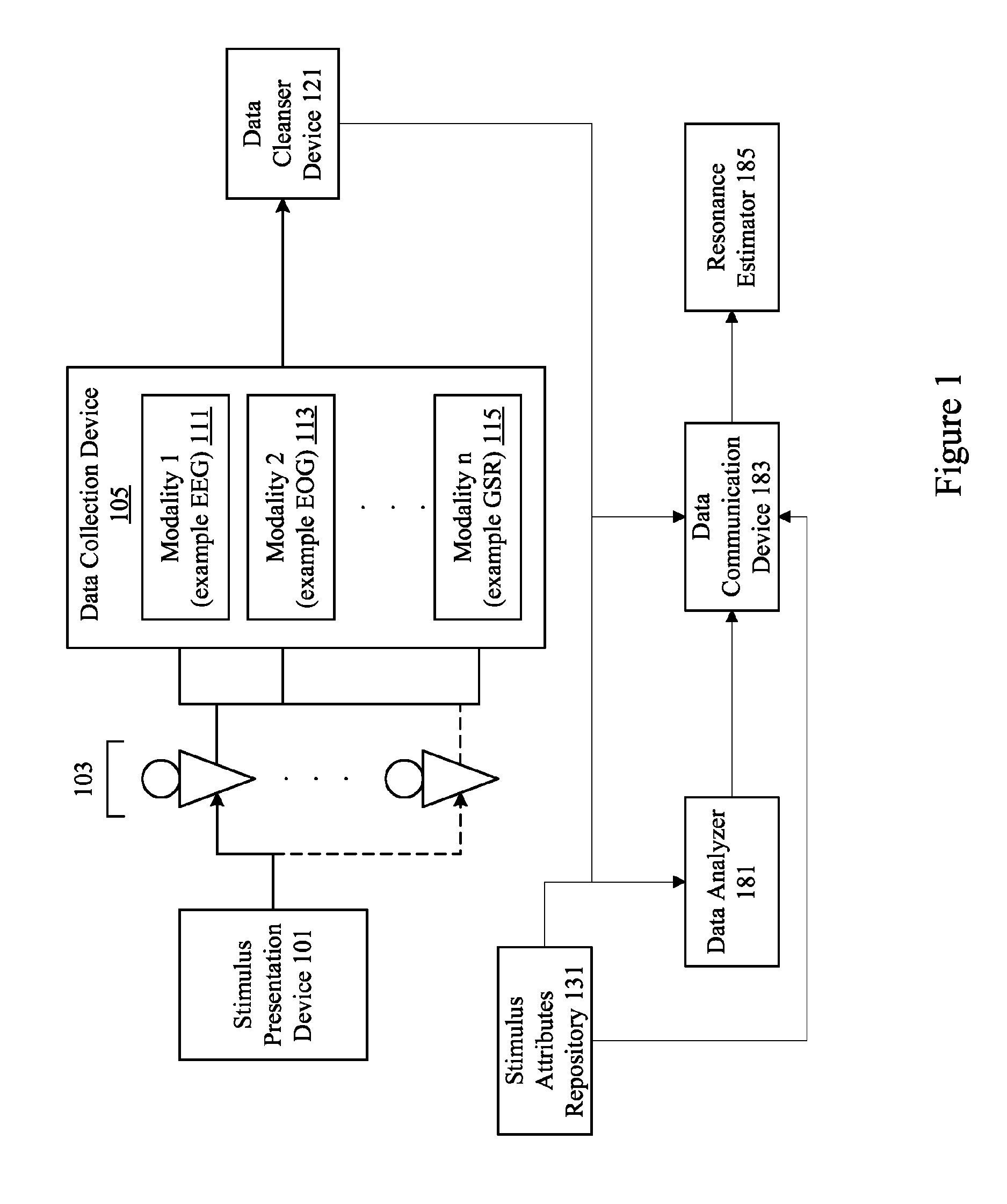
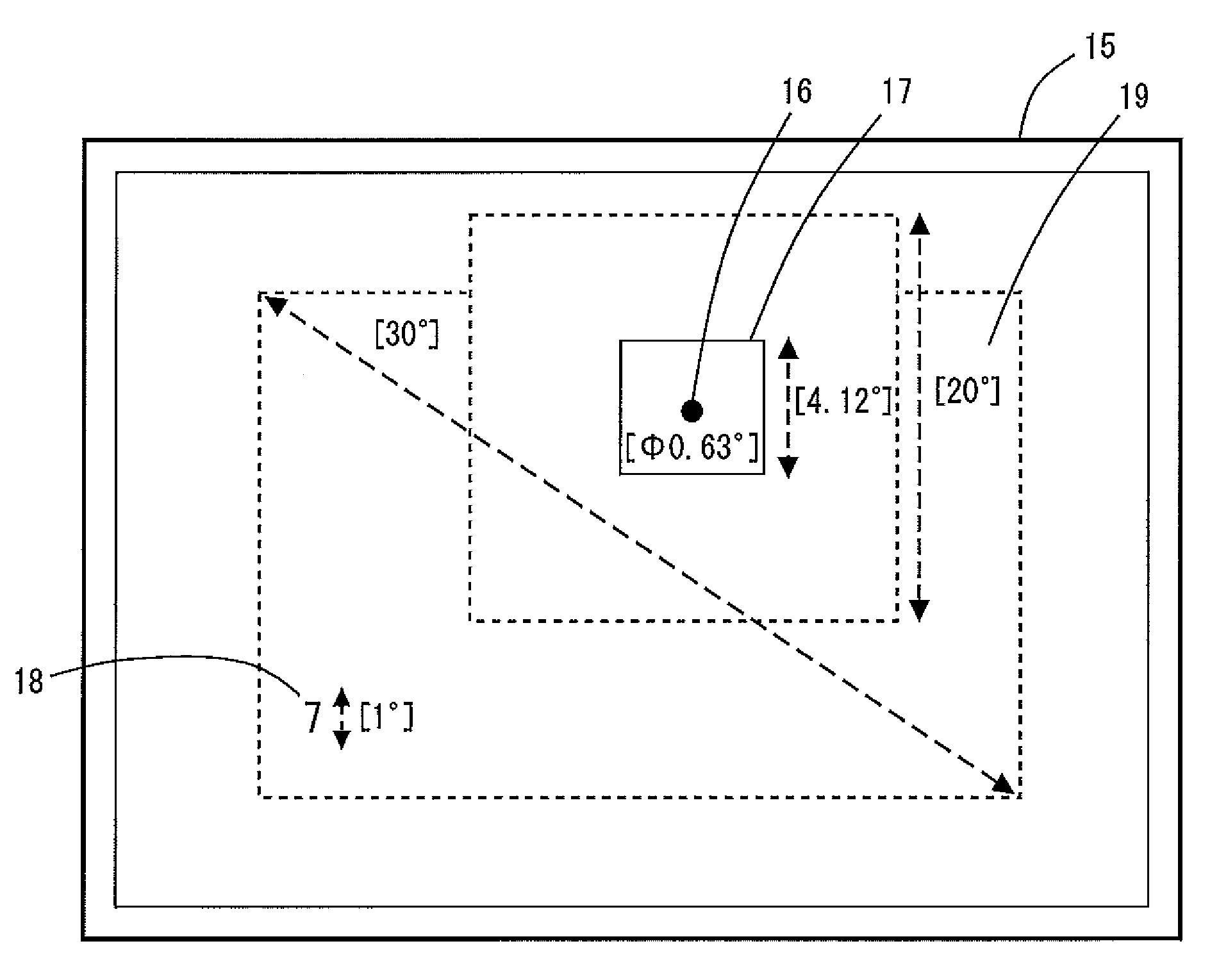
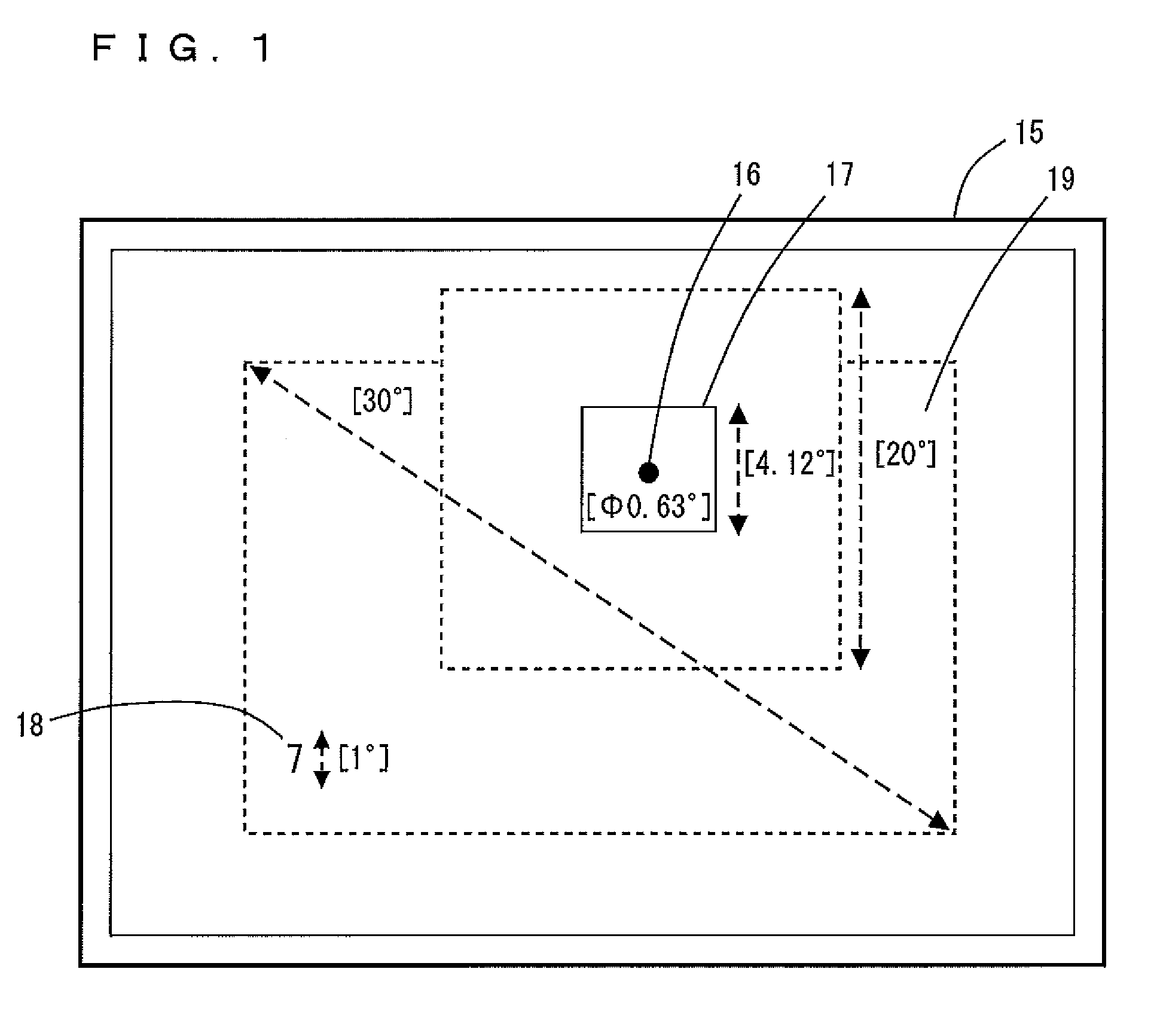
Neuro-informatics repository system
ActiveUS20090030930A1ElectroencephalographyMedical simulationDiagnostic Radiology ModalityInformation repository
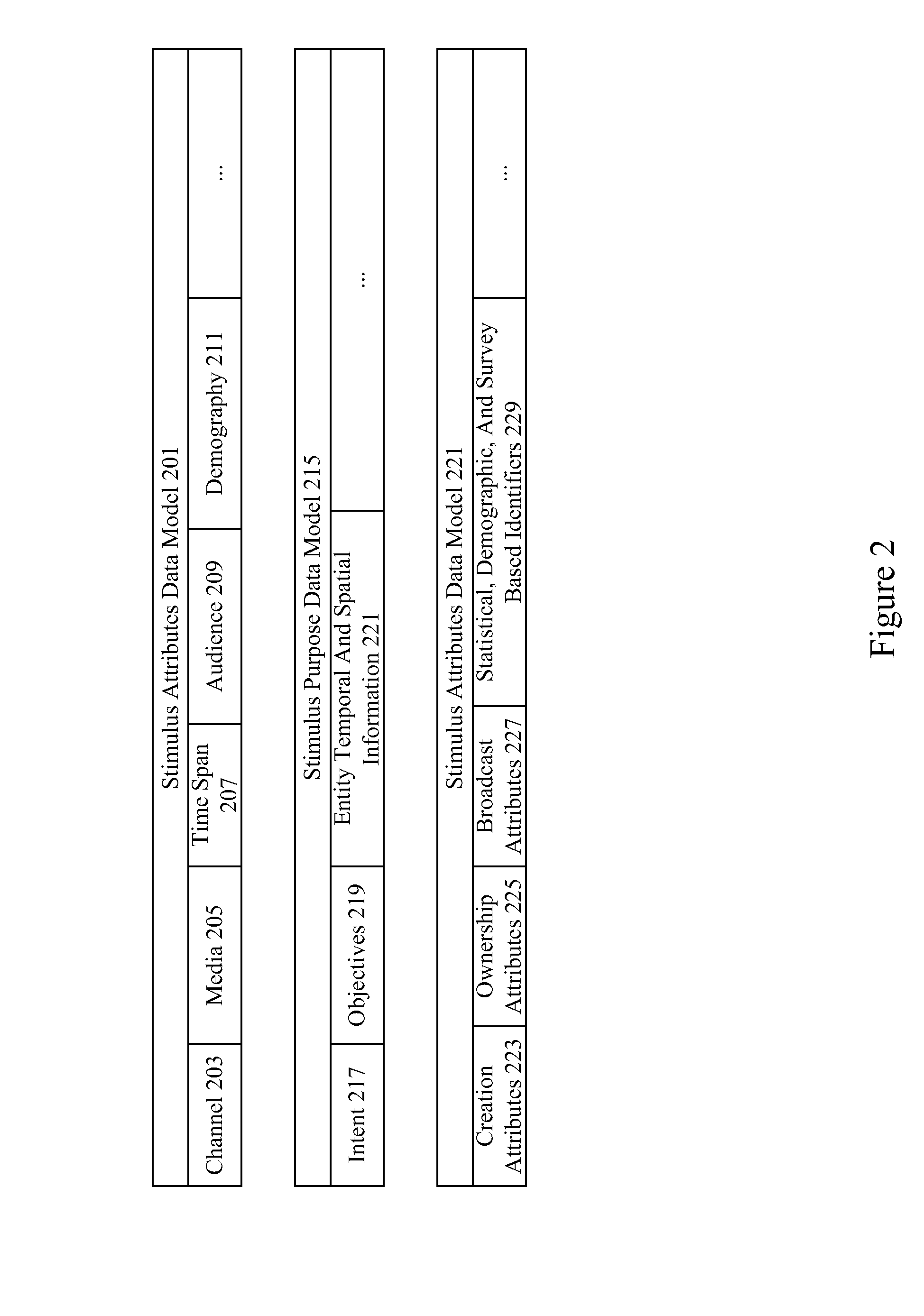
A neuro-informatics repository system is provided to allow efficient generation, management, and access to central nervous system, autonomic nervous system, effector data, and behavioral data obtained from subjects exposed to stimulus material. Data collected using multiple modalities such as Electroencephalography (EEG), Electrooculography (EOG), Galvanic Skin Response (GSR), Event Related Potential (ERP), surveys, etc., is stored using a variety of data models to allow efficient querying, report generation, analysis and / or visualization.
Owner:NIELSEN CONSUMER LLC
Neuro-informatics repository system
ActiveUS8386312B2ElectroencephalographyMedical simulationInformation repositoryDiagnostic Radiology Modality
A neuro-informatics repository system is provided to allow efficient generation, management, and access to central nervous system, autonomic nervous system, effector data, and behavioral data obtained from subjects exposed to stimulus material. Data collected using multiple modalities such as Electroencephalography (EEG), Electrooculography (EOG), Galvanic Skin Response (GSR), Event Related Potential (ERP), surveys, etc., is stored using a variety of data models to allow efficient querying, report generation, analysis and / or visualization.
Owner:NIELSEN CONSUMER LLC
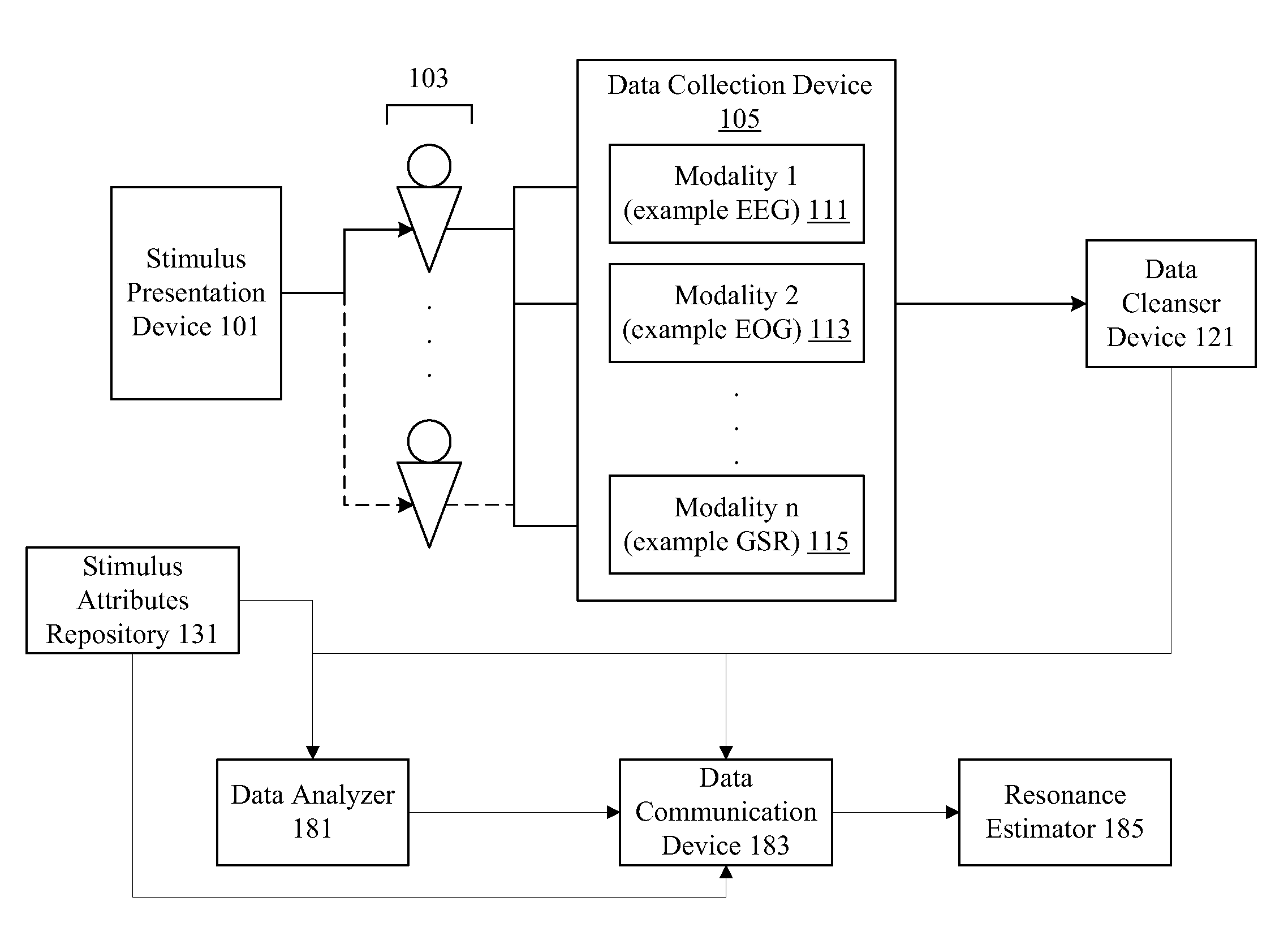
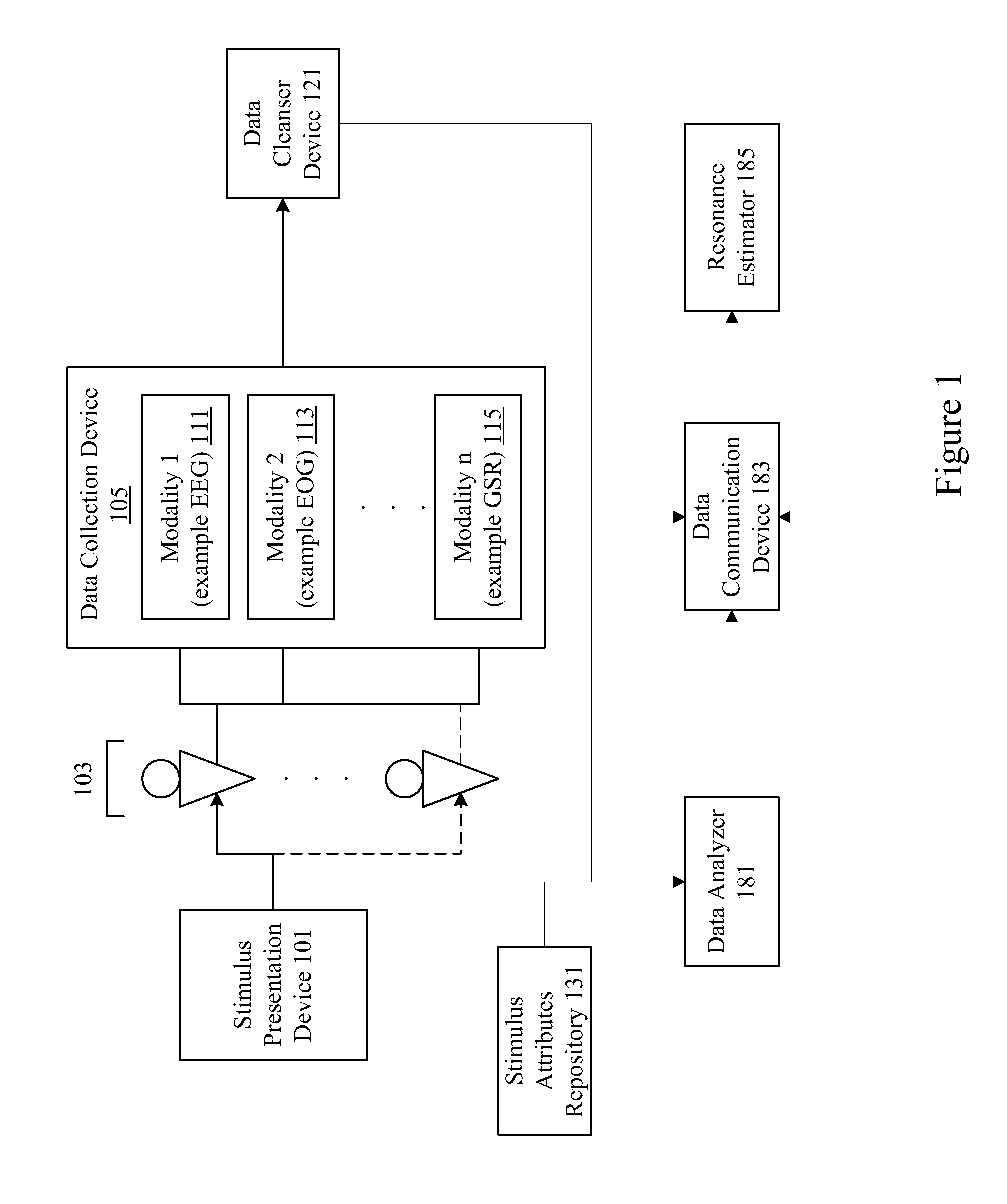
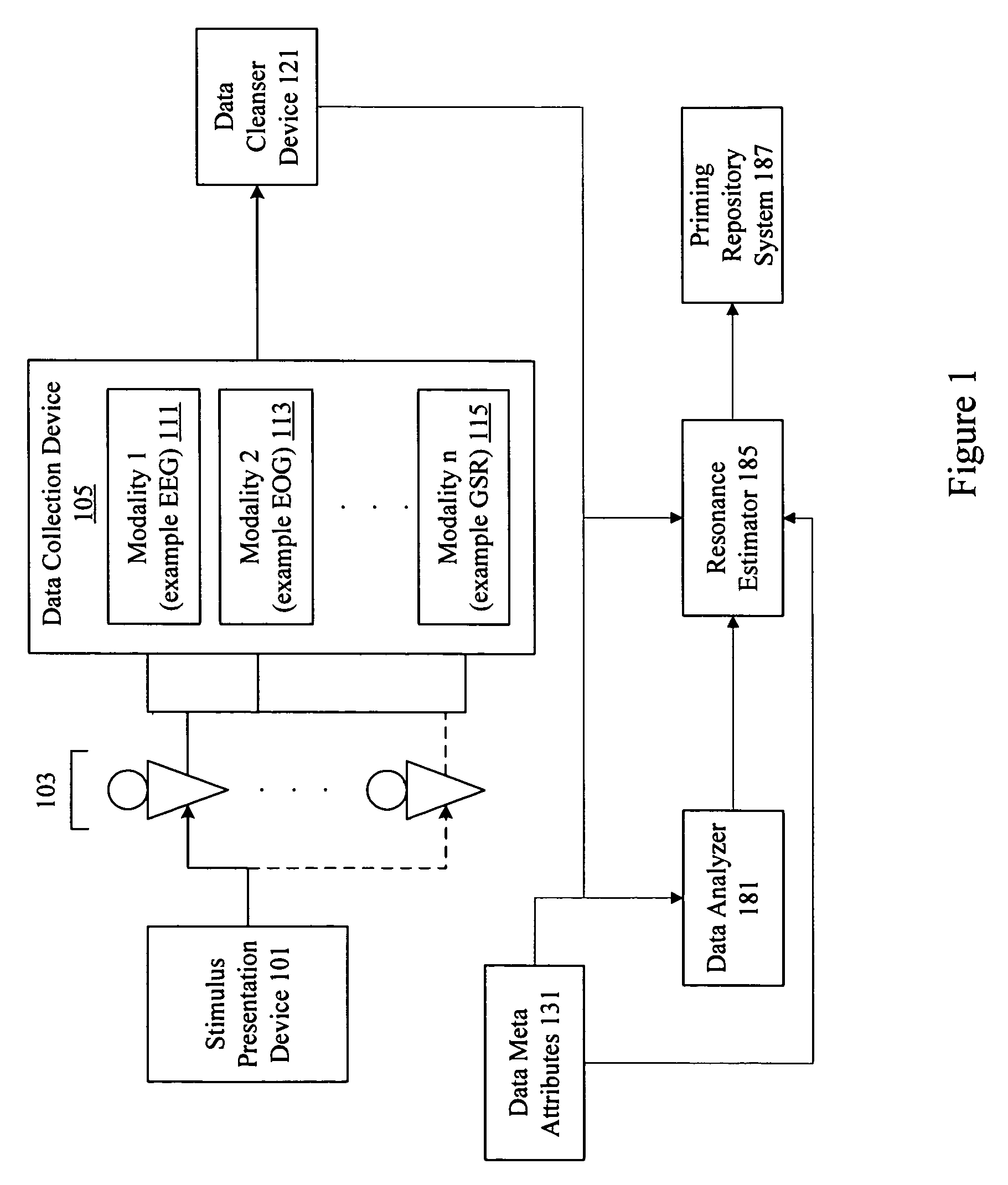
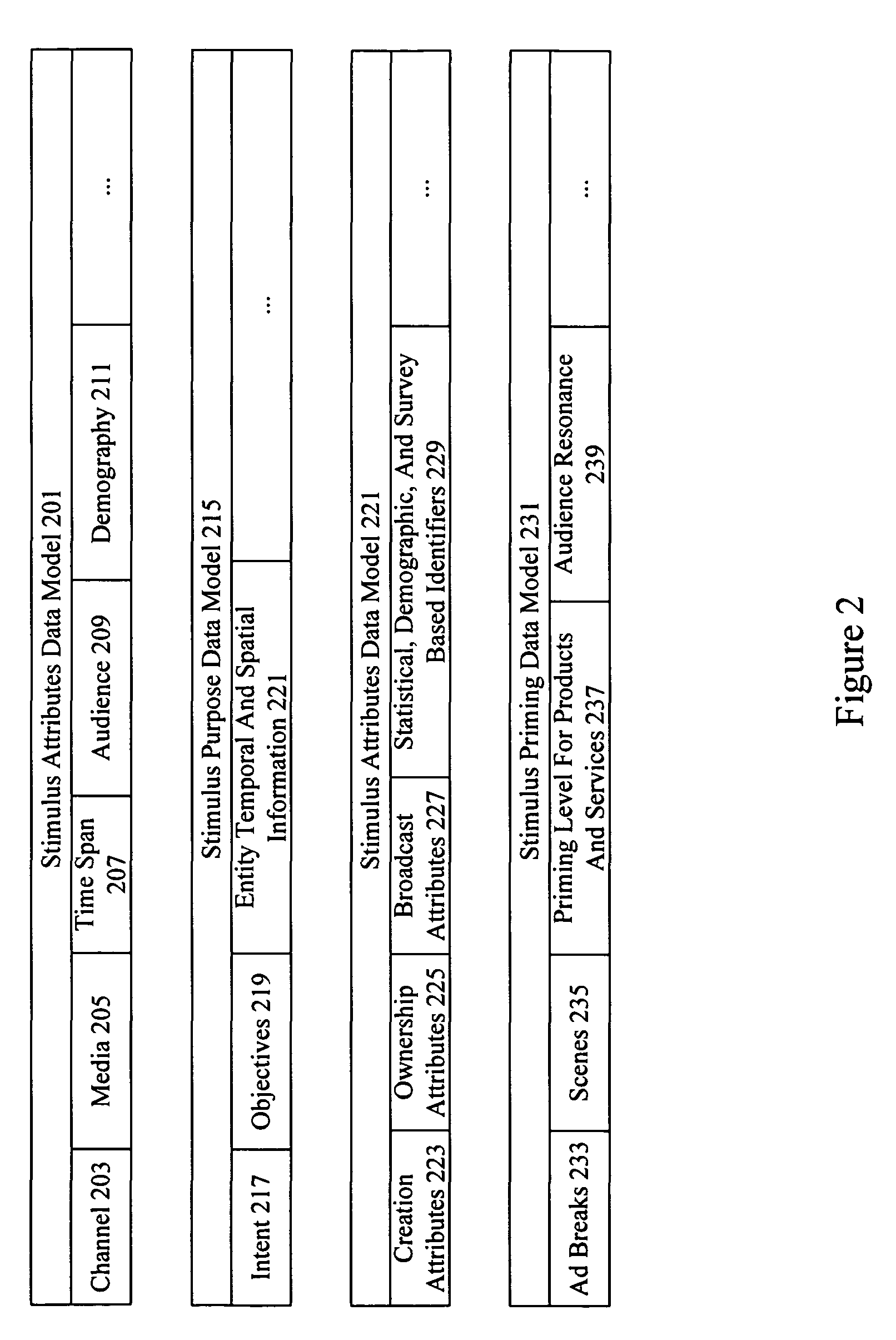
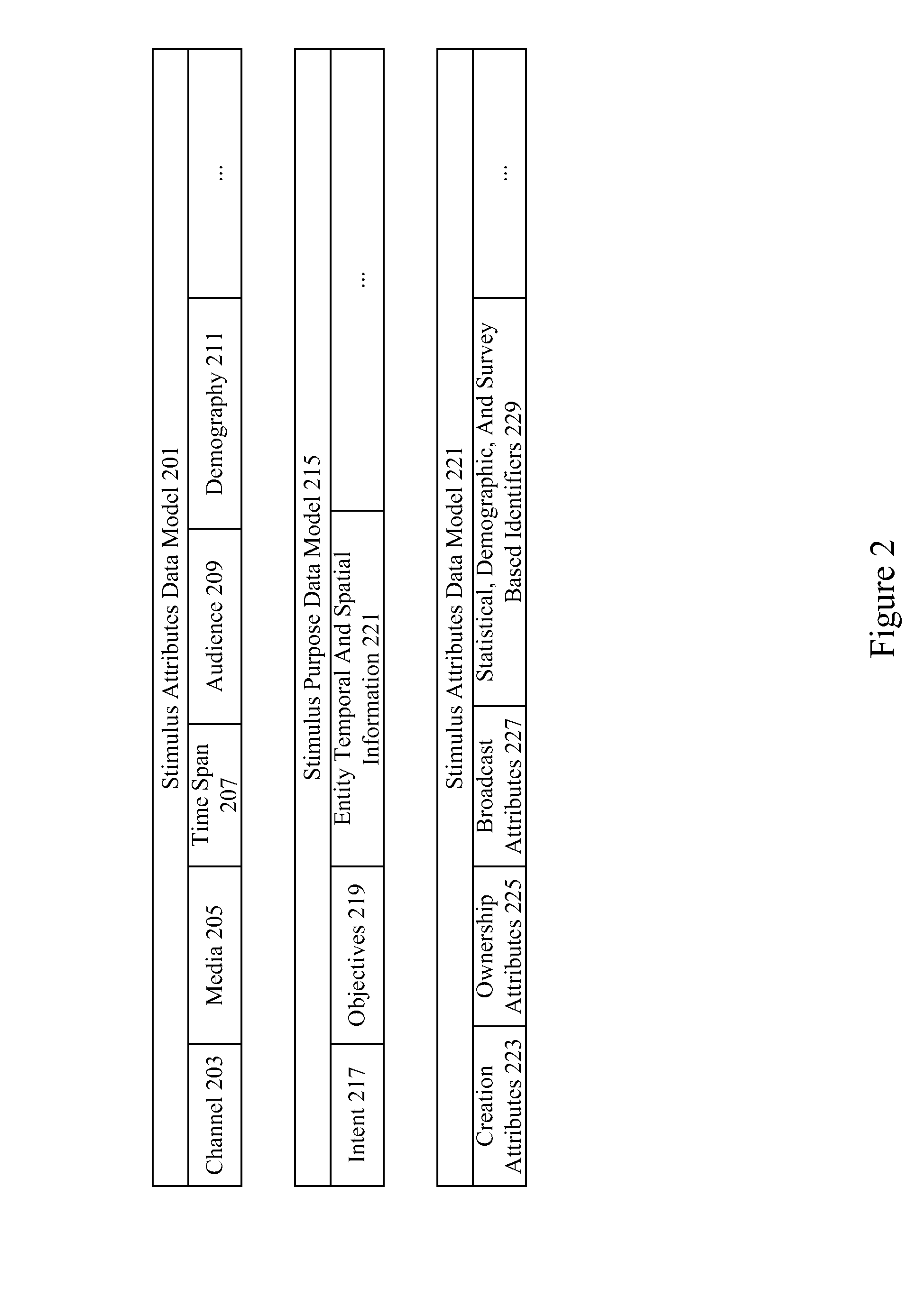
Neuro-response stimulus and stimulus attribute resonance estimator
A system determines neuro-response stimulus and stimulus attribute resonance. Stimulus material and stimulus material attributes such as communication, concept, experience, message, images, audio, pricing, and packaging are evaluated using neuro-response data collected with mechanisms such as Event Related Potential (ERP), Electroencephalography (EEG), Galvanic Skin Response (GSR), Electrocardiograms (EKG), Electrooculography (EOG), eye tracking, and facial emotion encoding. Neuro-response data is analyzed to determine stimulus and stimulus attribute resonance.
Owner:NIELSEN CONSUMER LLC
Access Control System using Stimulus Evoked Cognitive Response
InactiveUS20140020089A1Easily discriminatedIncrease flexibilityDigital data processing detailsPerson identificationBiometric dataCognitive response
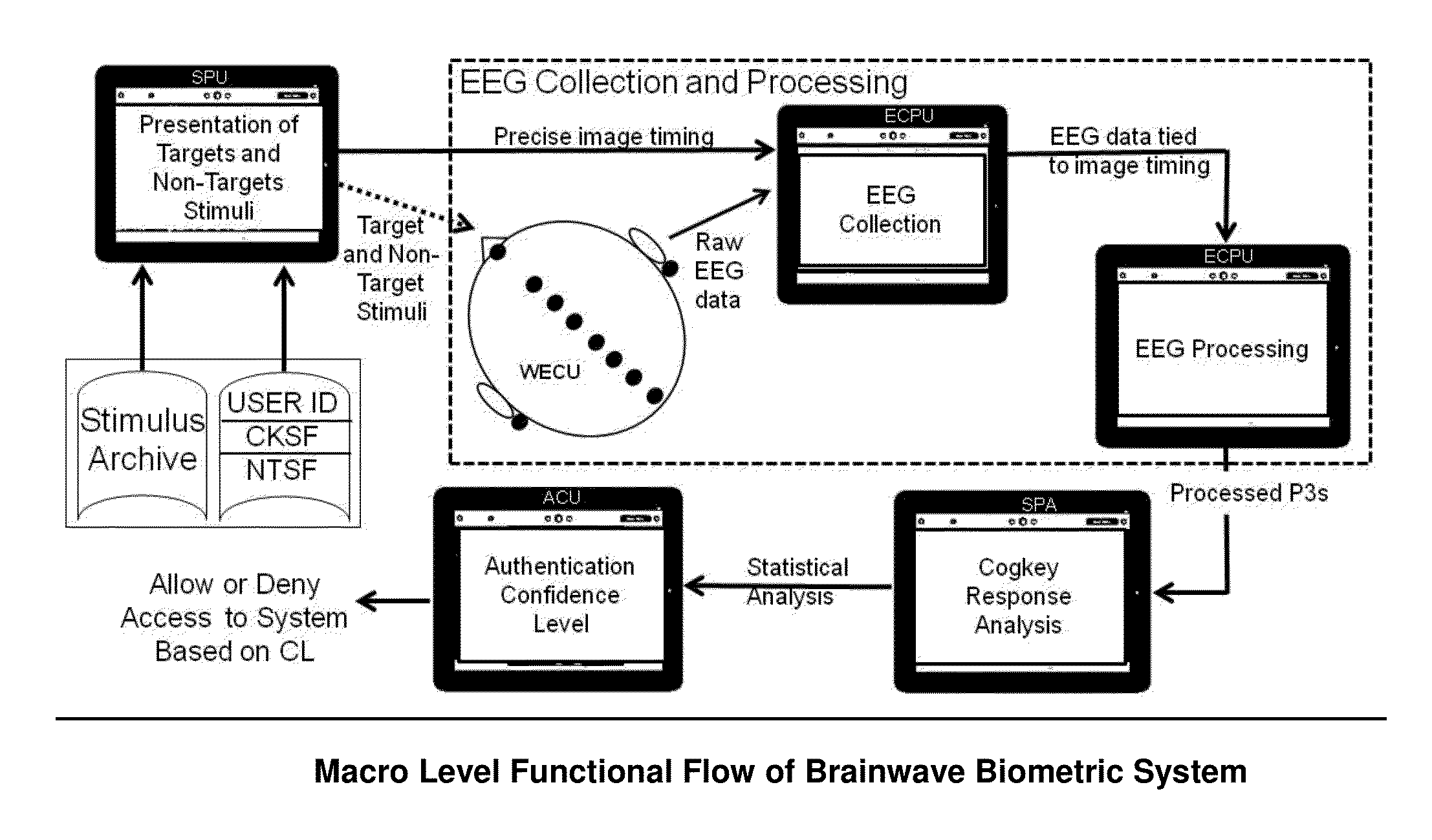
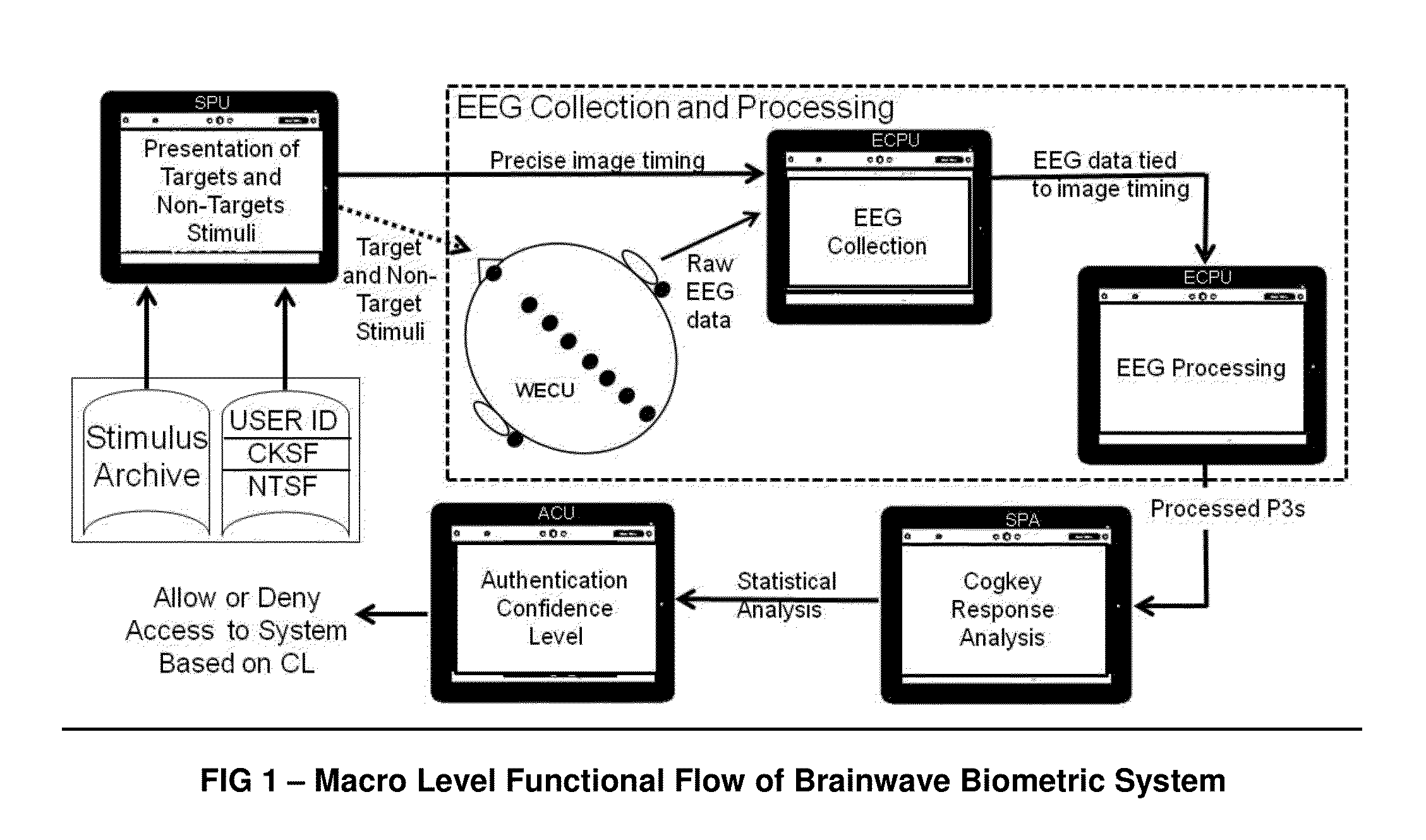
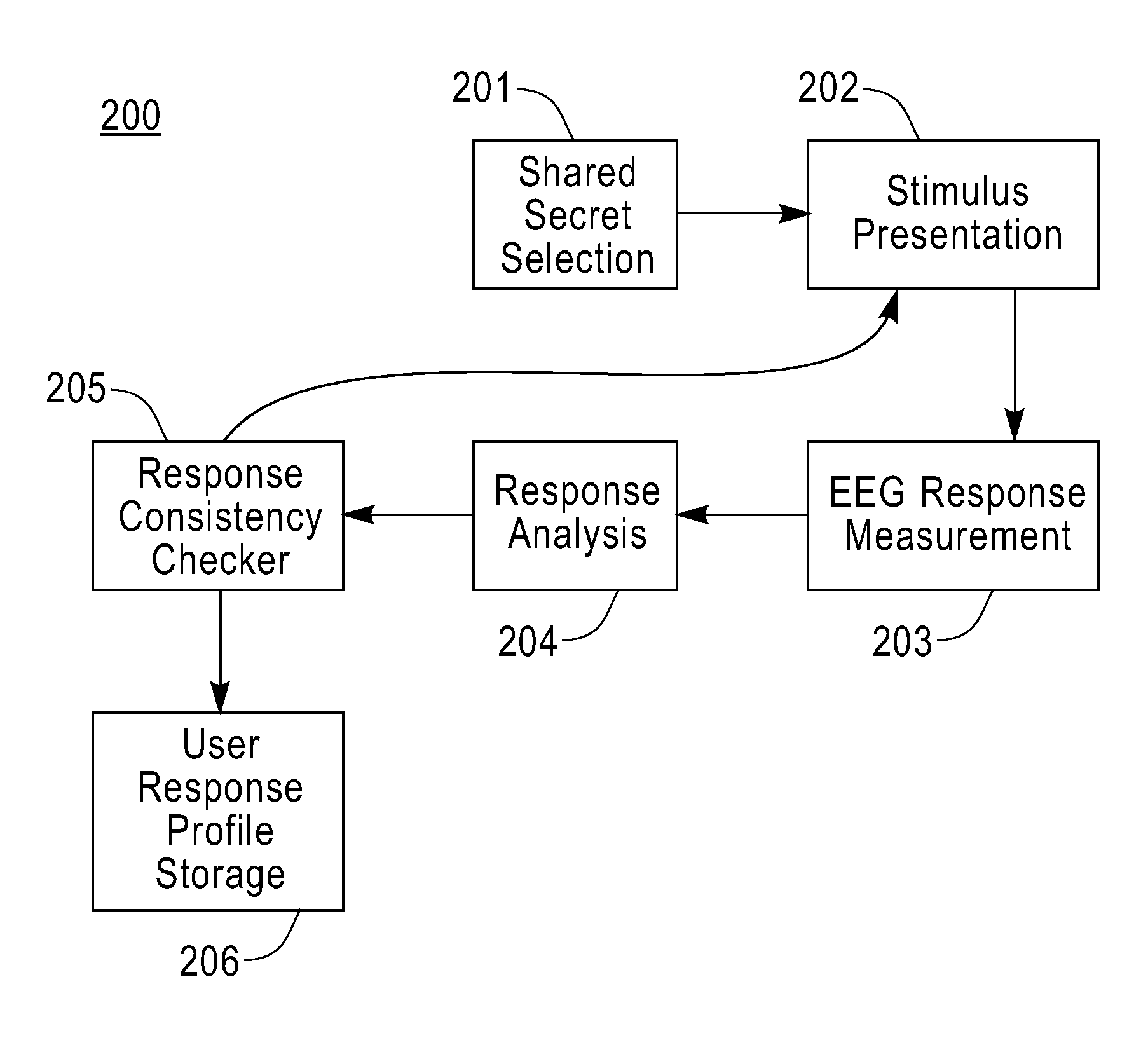
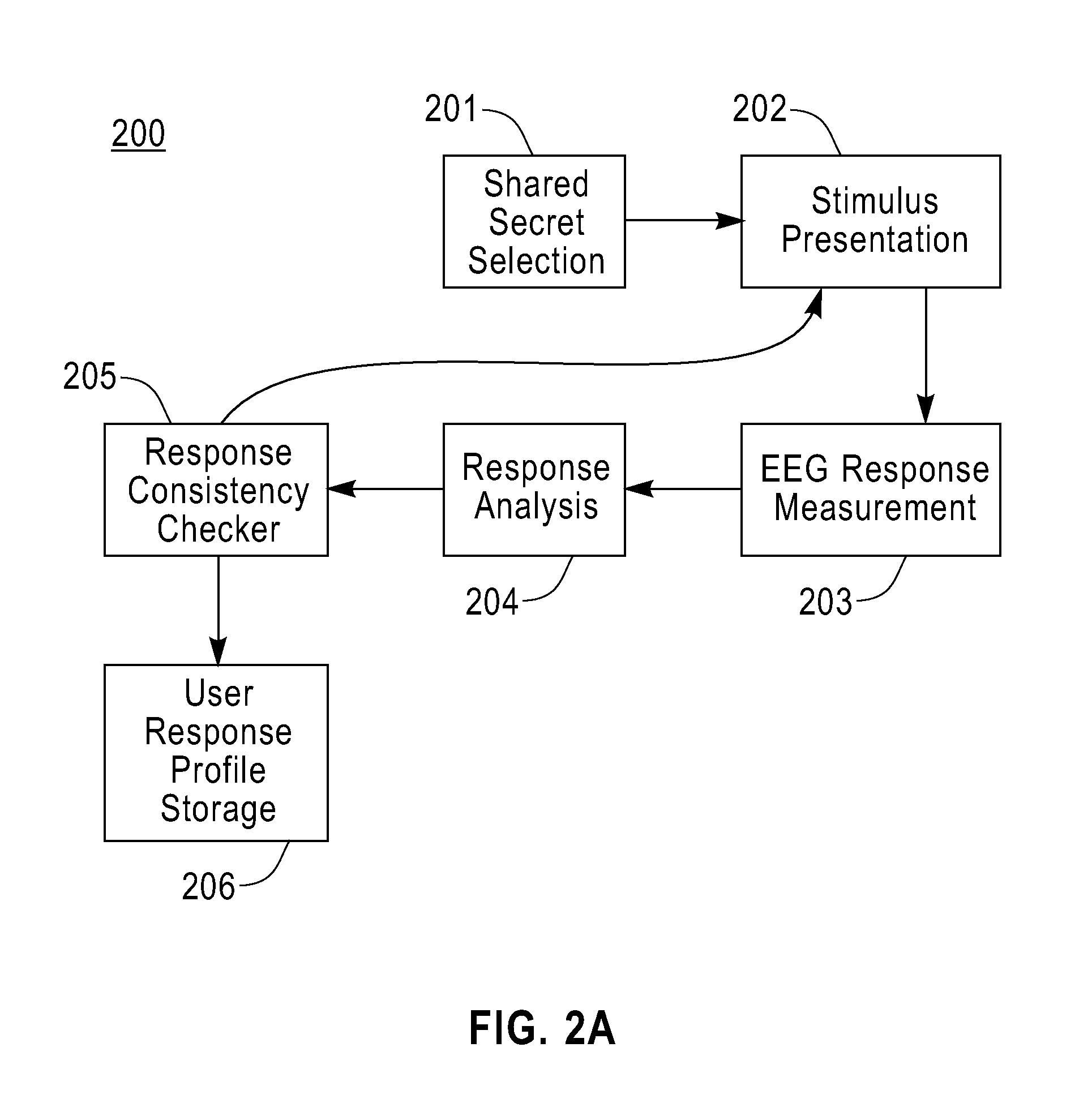
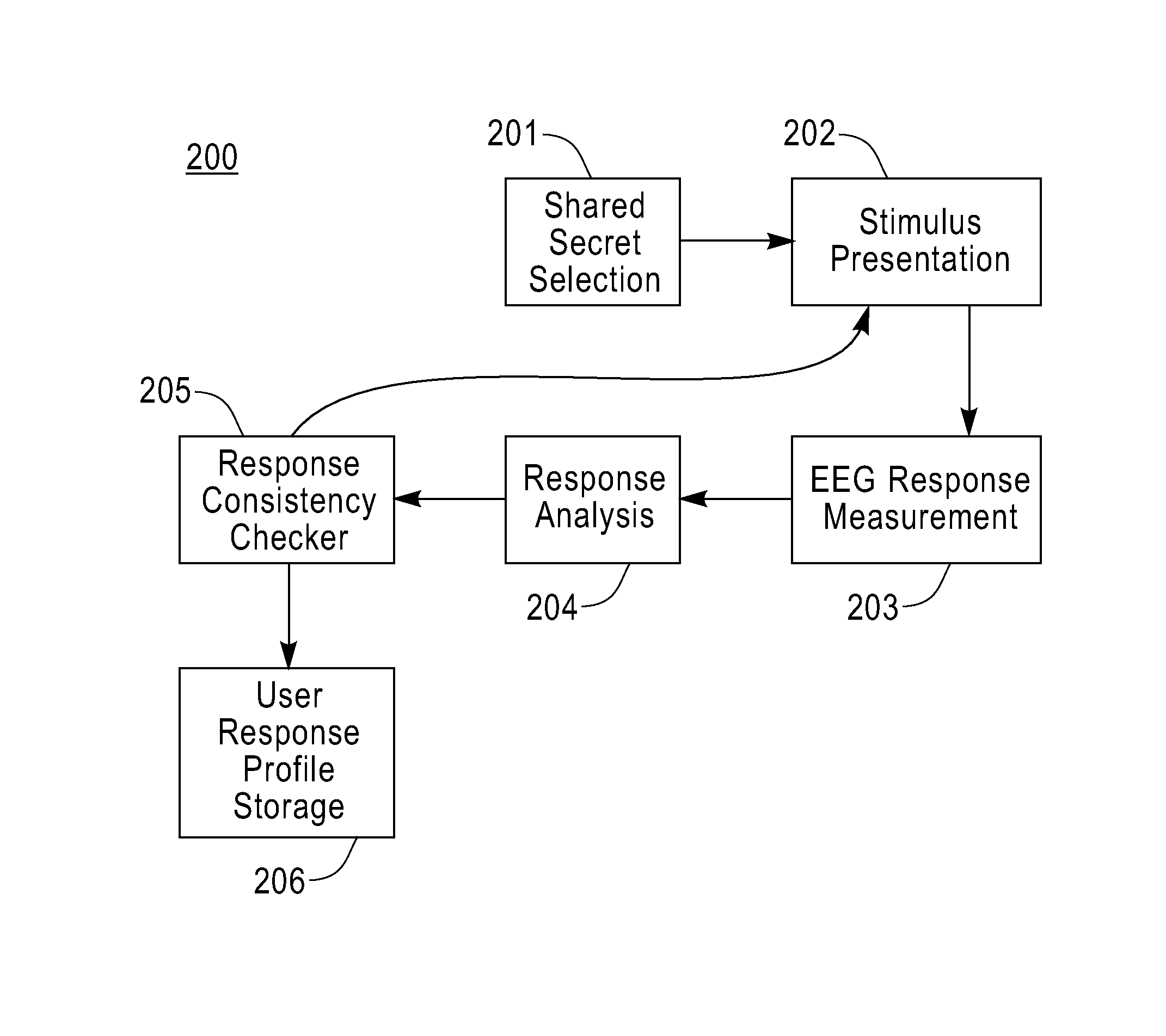
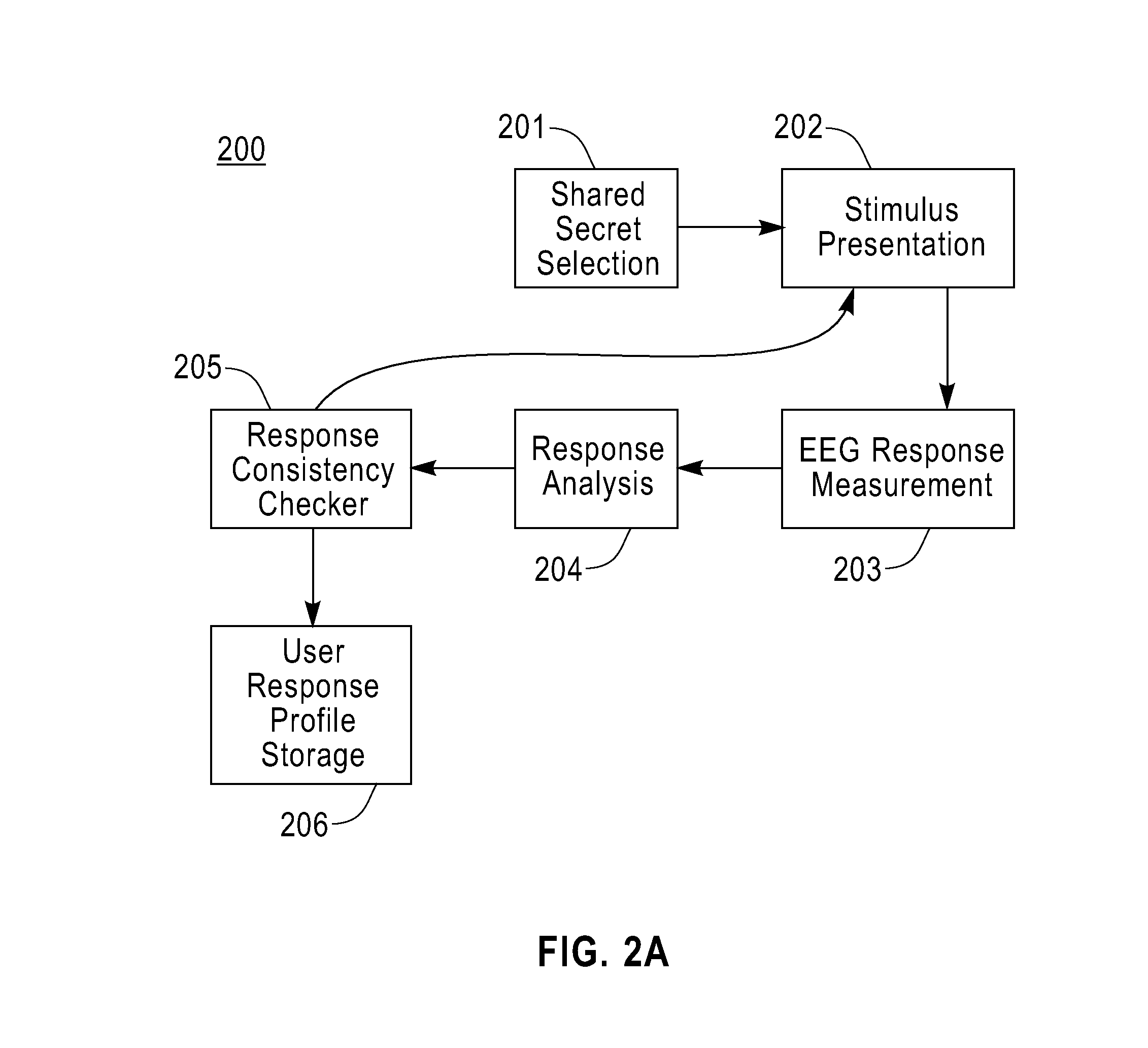
The ACSSECR invention is a biometric access control system and methodology that measures cognitive, psychophysiological responses to stimuli to confirm the identity of an individual. As an alternative to “Logging in” with a user ID and password, this cognitive biometric authentication system is used for “Cogging in” to a system with user ID and user-selected “Cogkey”. ACSSECR is designed for strict access control scenarios where significant authentication confidence is required to gain access to controlled information, facilities, systems, vehicles, or devices. The system takes advantage of a behavioral and physiological characteristic of humans that is an unconscious response to a stimulus. The Event Related Potential (ERP) response (specifically the P3 ERP) involuntarily occurs when an individual perceives and reacts to an unexpected, task-relevant event. The task is for the user to recognize their Cogkey which is presented infrequently amidst more frequent non-target stimuli. There is no requirement for extensive enrollment by users, only the recognition of their Cogkey. The basic system does not store biometric data for comparison, but rather measures the user's Cogkey recognition responses in comparison to non-Cogkey stimulus responses. An individual can have multiple personas with different Cog keys.
Owner:PERINI II REMO PETER
Content based selection and meta tagging of advertisement breaks
A system evaluates stimulus materials such as videos, imagery, web pages, text, etc., in order to determine resonance and priming levels for various products and services at different temporal and spatial locations including advertisement breaks in the stimulus materials. The stimulus materials are tagged with resonance and priming level information to allow intelligent selection of suitable advertisement content for insertion at various locations in the stimulus materials. Response data such as survey data and / or neuro-response data including Event Related Potential (ERP), Electroencephalography (EEG), Galvanic Skin Response (GSR), Electrocardiograms (EKG), Electrooculography (EOG), eye tracking, and facial emotion encoding data may be used to determine resonance and priming levels.
Owner:NIELSEN CONSUMER LLC
Man-machine interfaces system and method, for instance applications in the area of rehabilitation
InactiveUS20050085744A1Input/output for user-computer interactionMedical data miningHuman–machine interfaceBrain computer interfacing
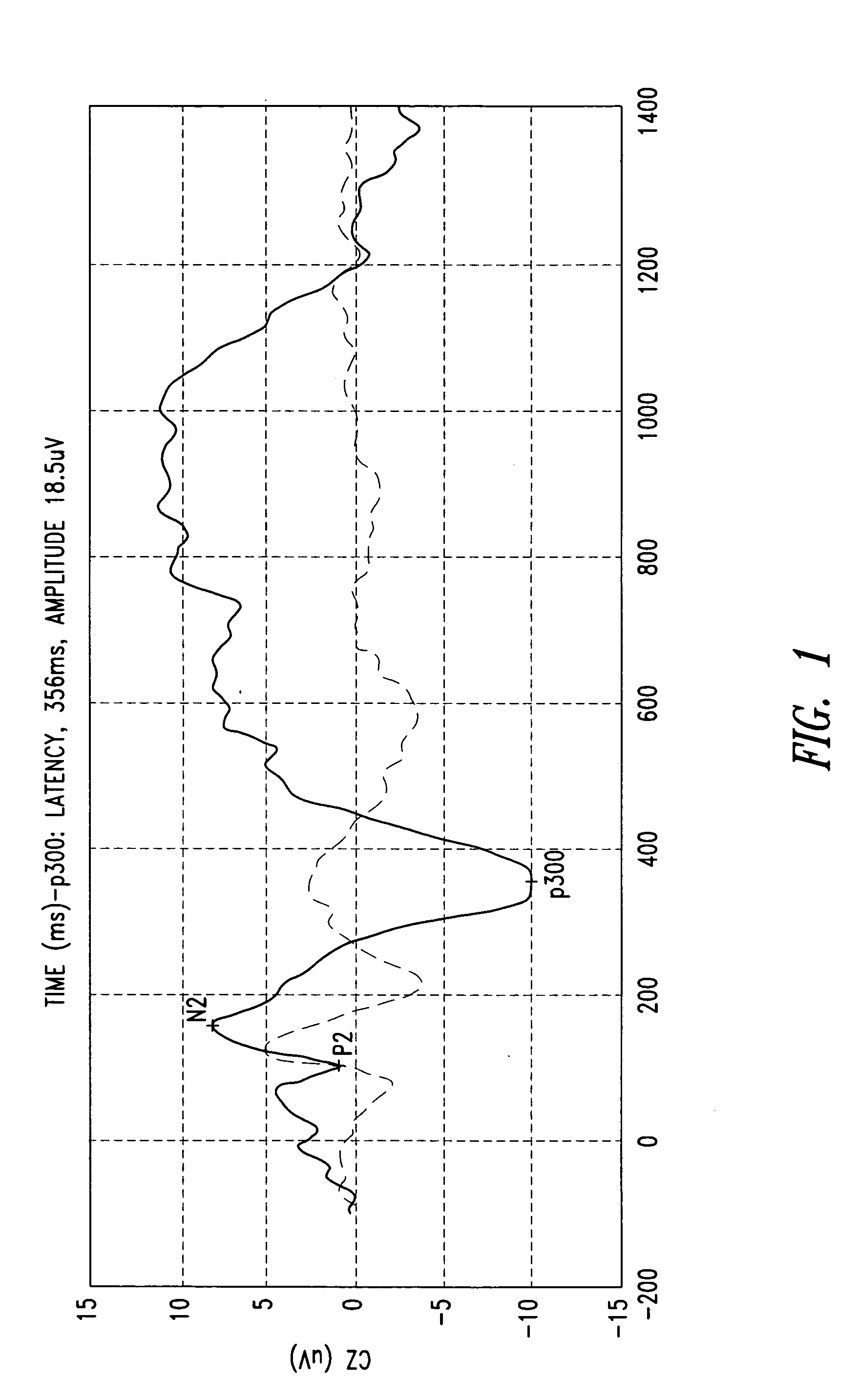
A system for developing a brain-computer interface (BCI), especially for use in rehabilitation, includes an audio-visual interface device for applying to a subject being examined stimuli eliciting event-related potentials and inducing brain reactions in said subject being examined. The system further includes an acquisition device for acquiring brain reaction signals (such as EEG traces) of the subject being examined synchronized with the stimuli and at least one processing device for processing the signals acquired via said acquisition device, The interface device, the acquisition device and the processing device comprise an integrated system. Preferably, the system uses a p300 signal as the event-related potential.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
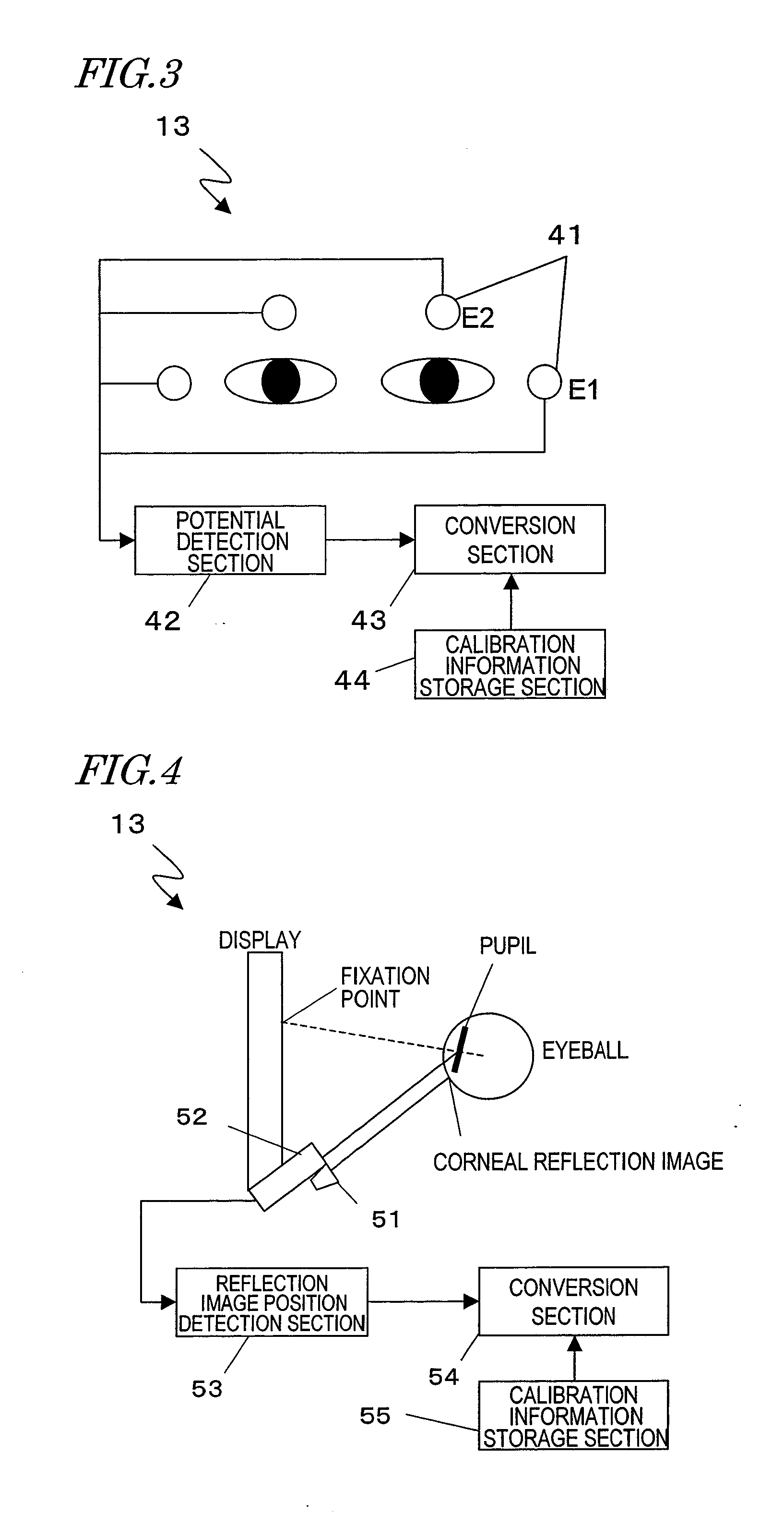
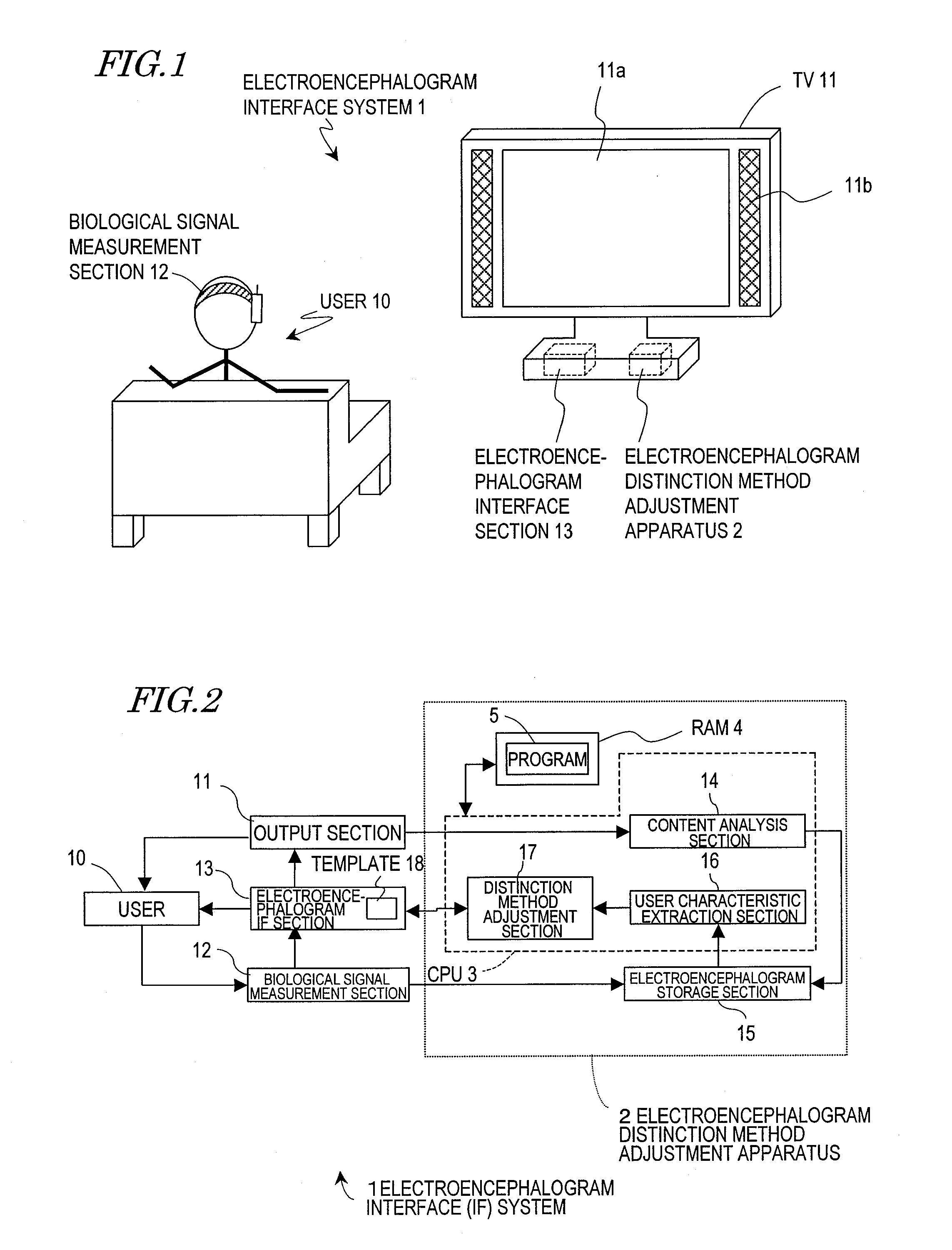
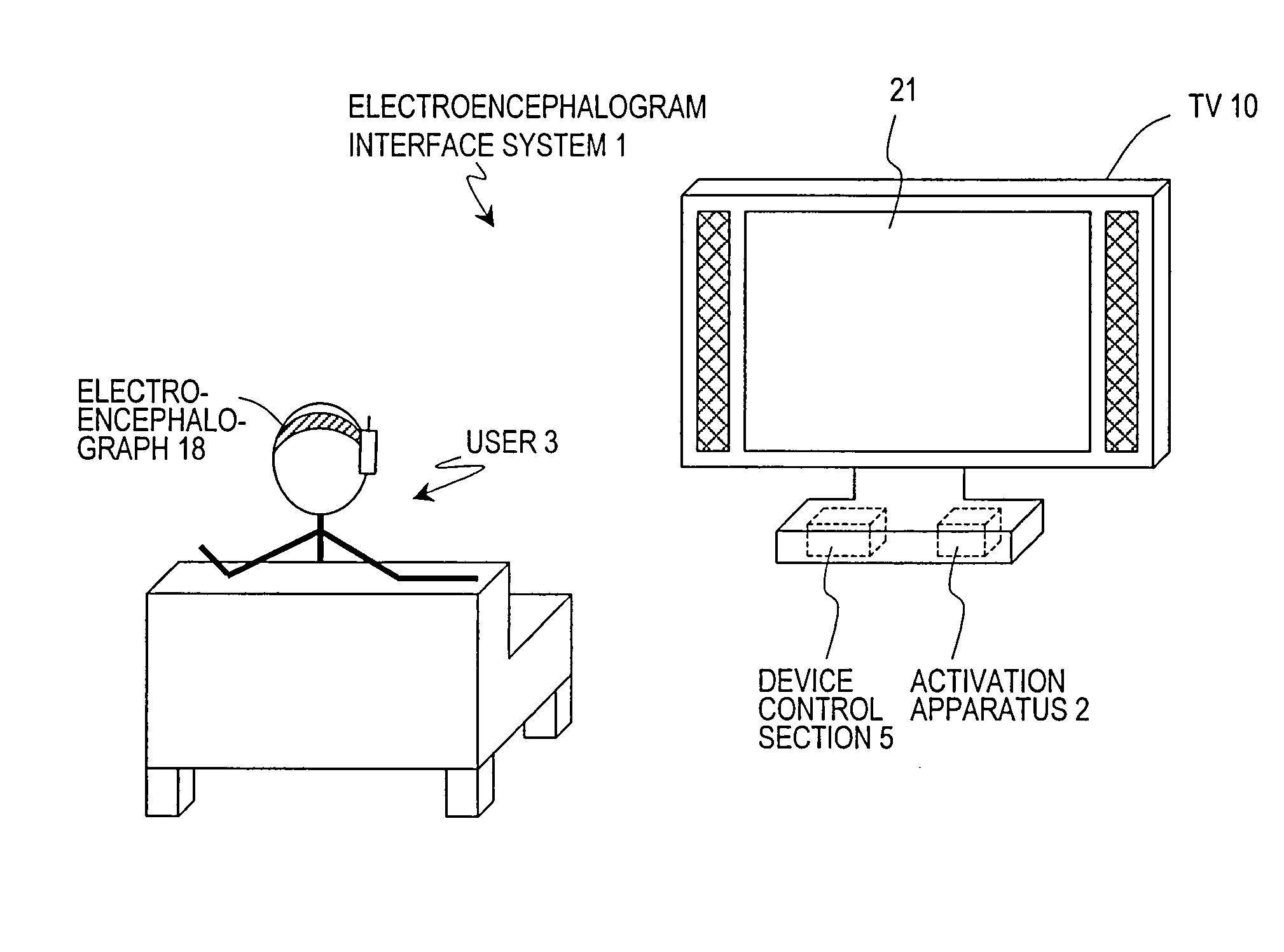
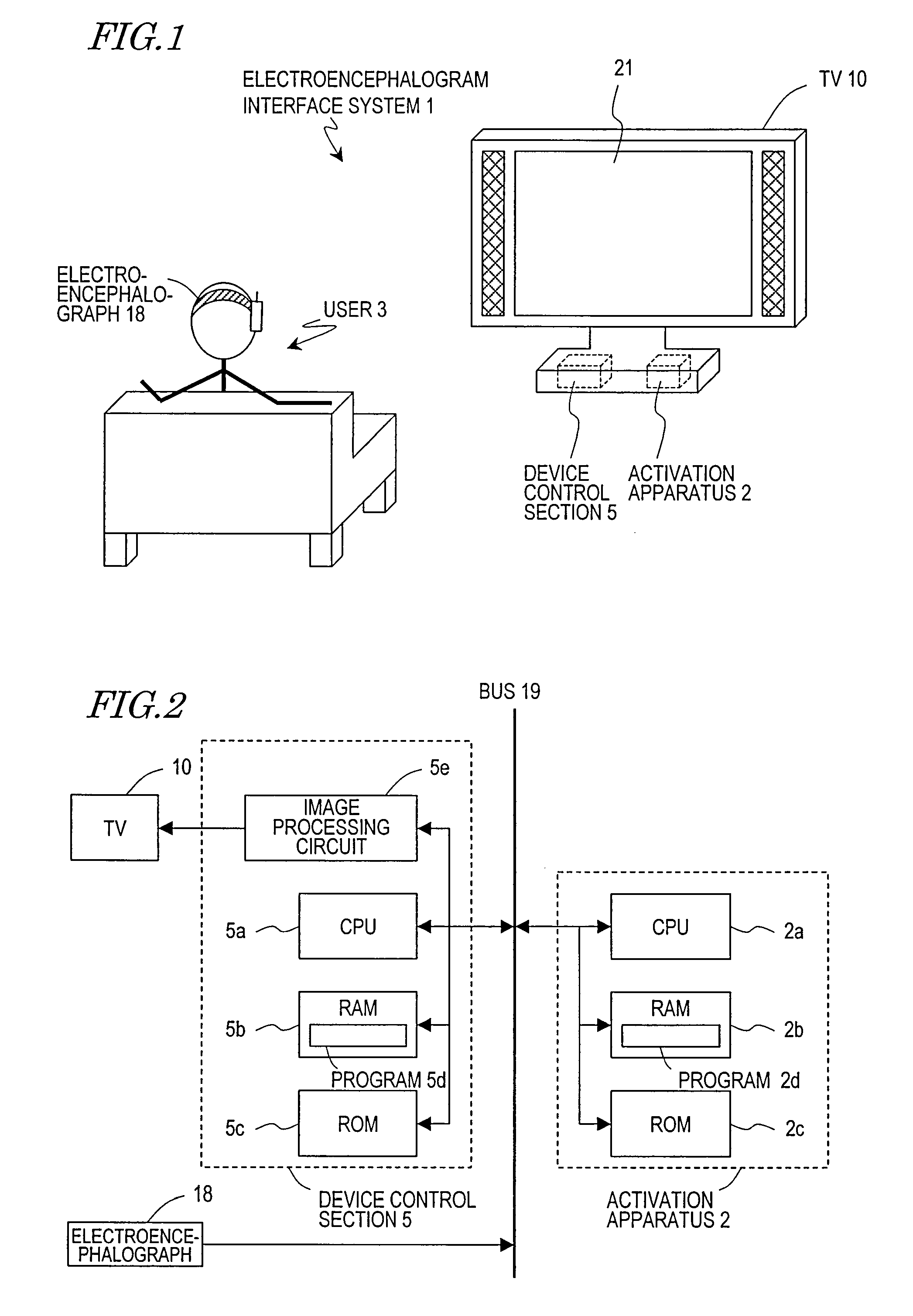
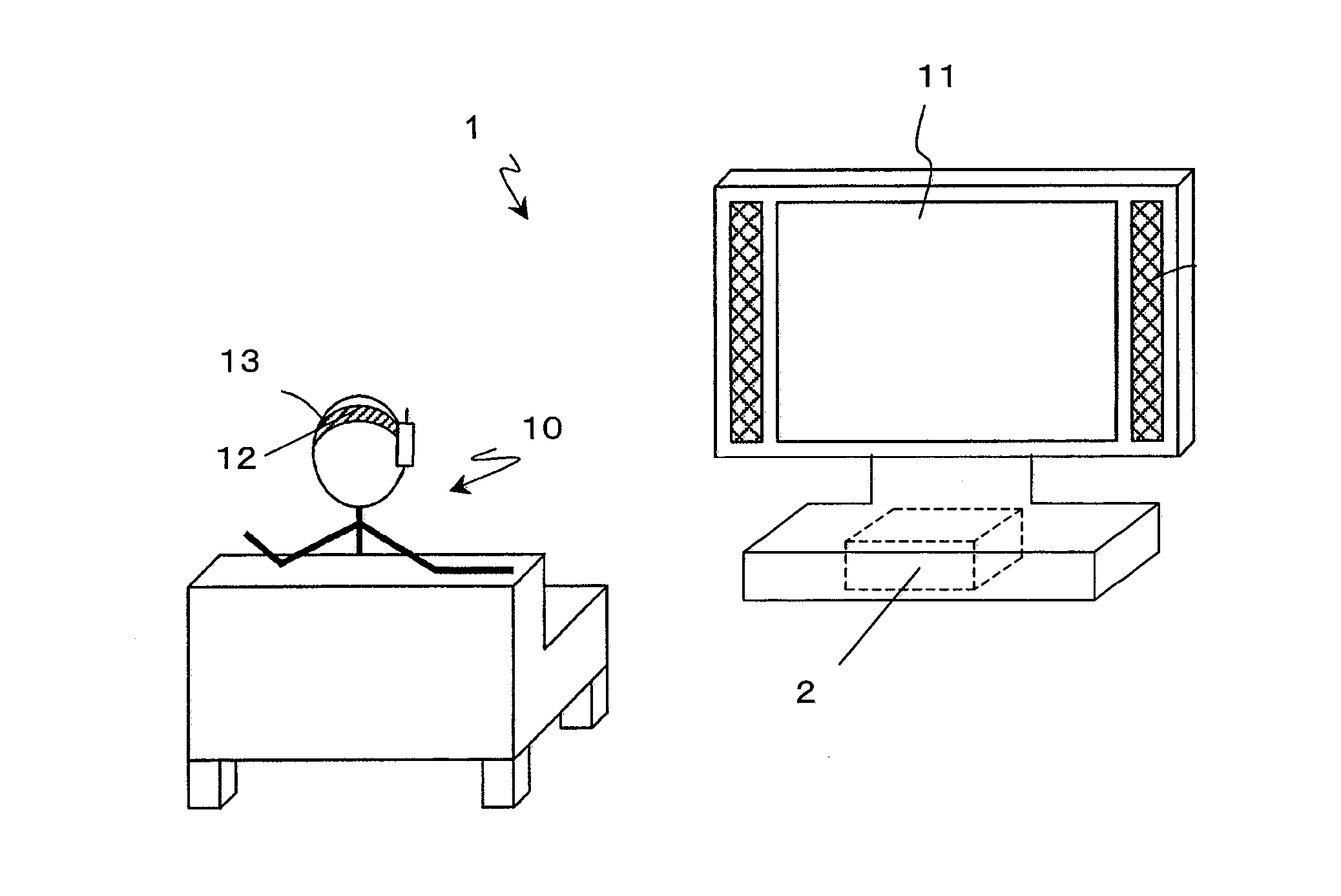
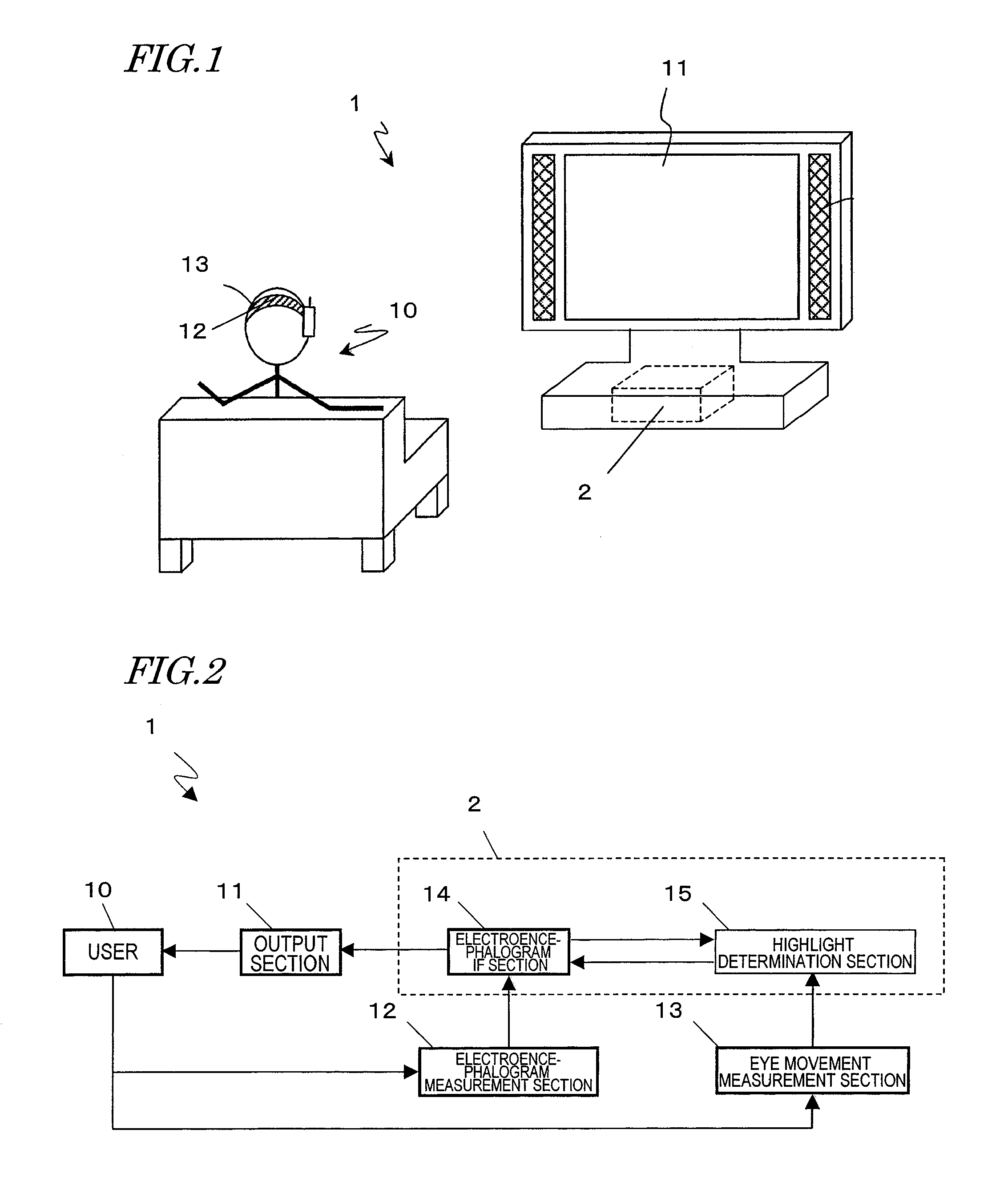
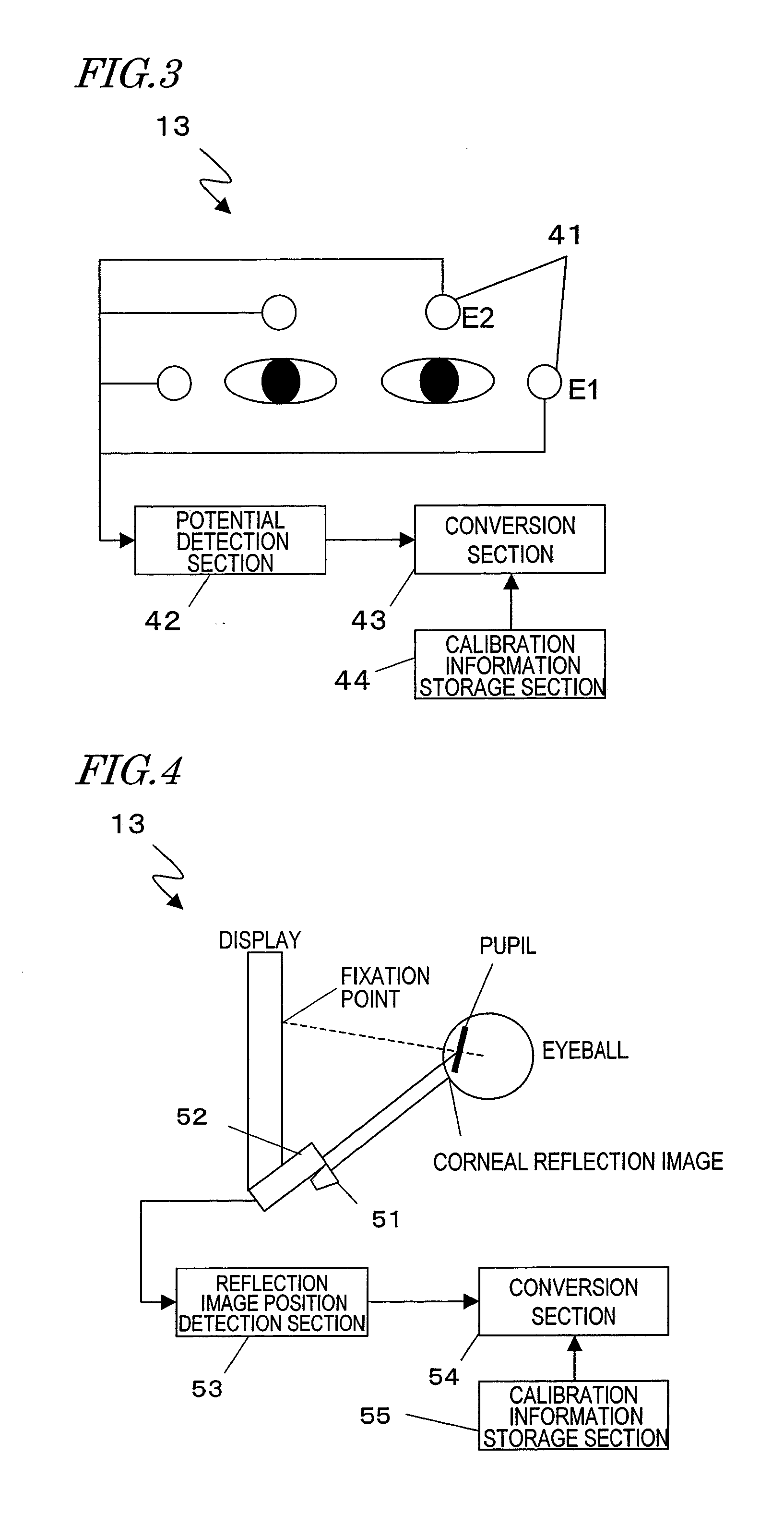
Electroencephalogram interface system, electroencephalogram interface apparatus, method, and computer program
ActiveUS20090289895A1Valid choiceCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingAngular velocityComputer science
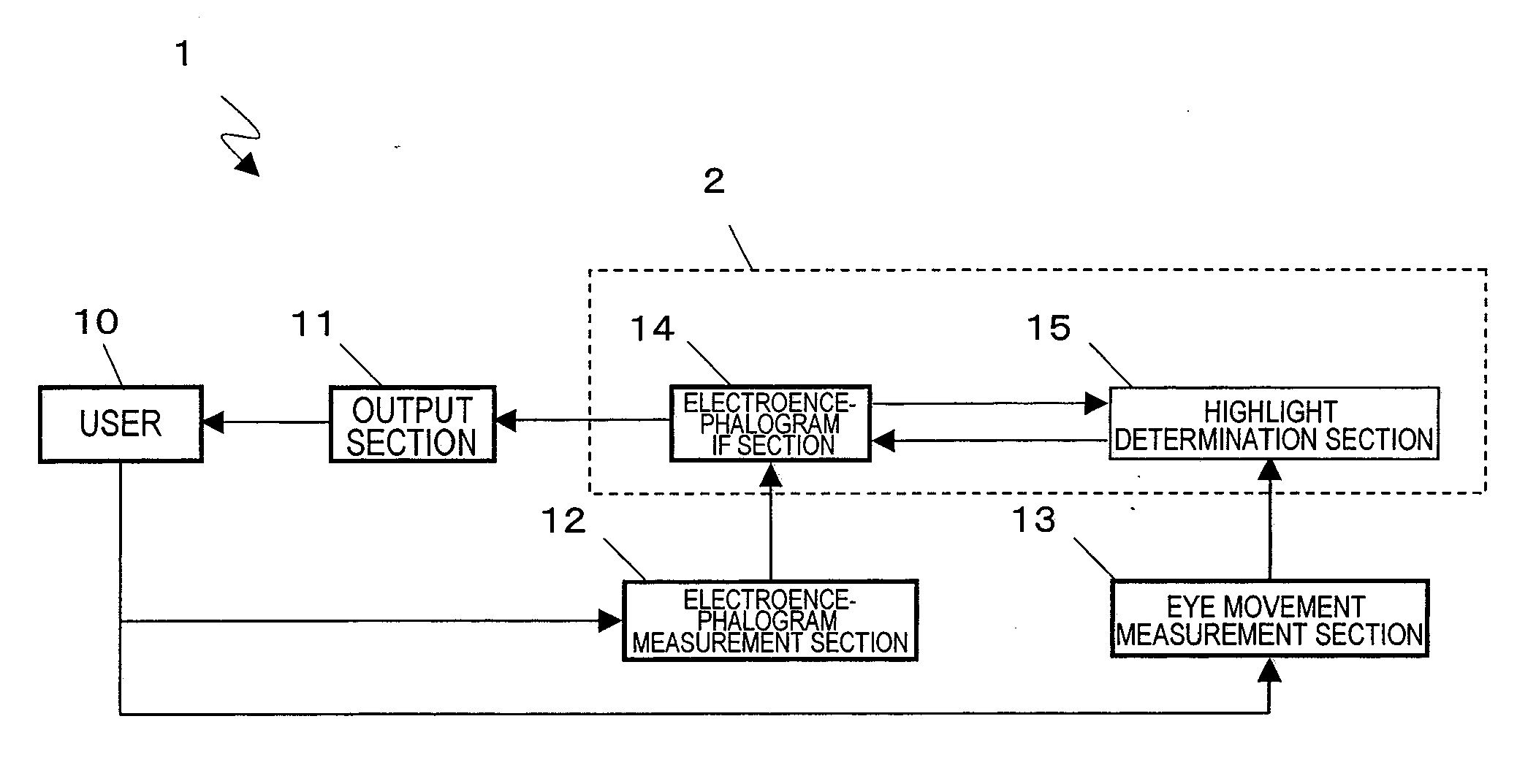
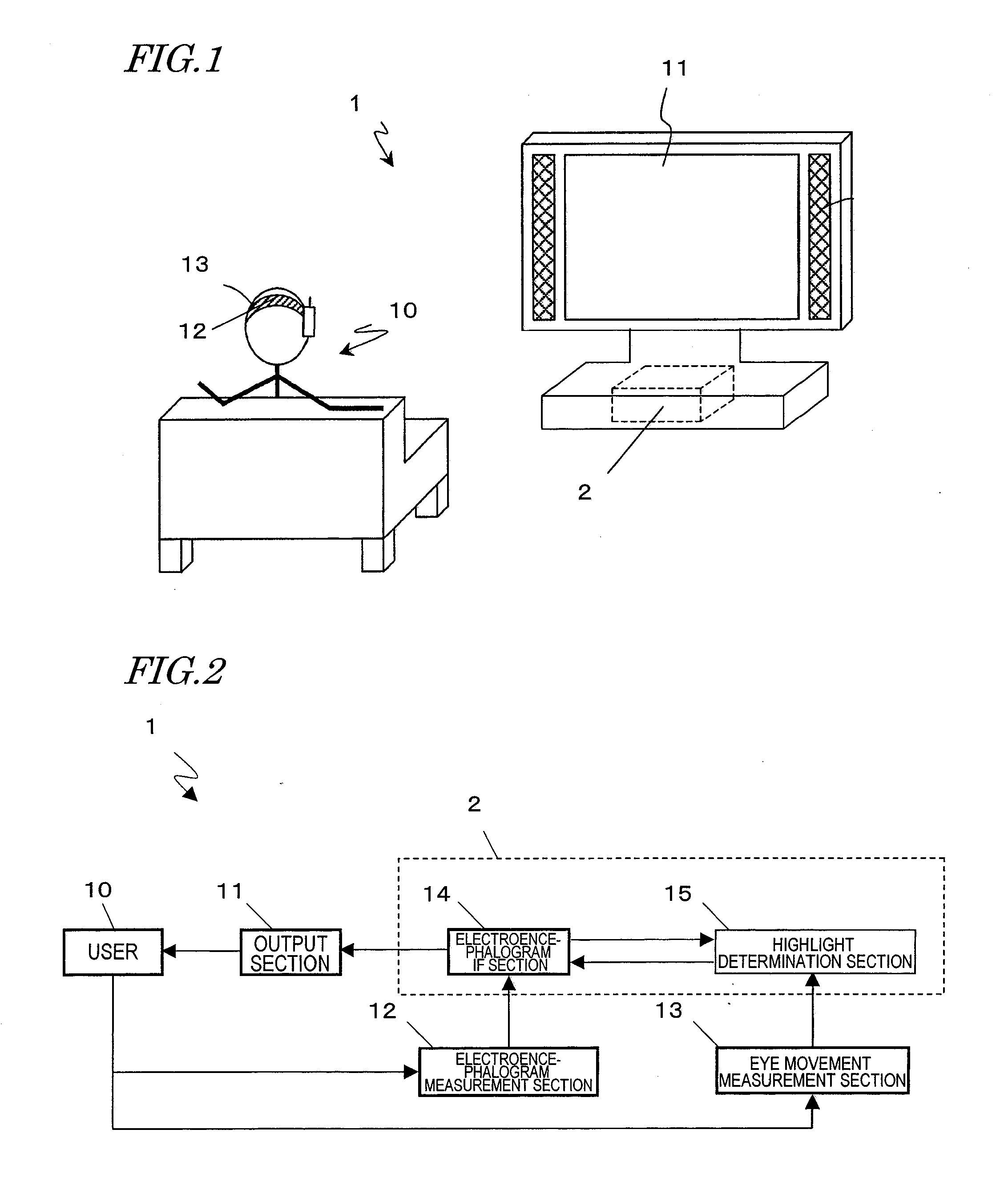
An electroencephalogram interface system includes: sections for measuring an electroencephalogram and an eye movement; an output section for presenting on a screen an option related to a device operation; a highlight determination section for, if a predetermined time has elapsed since a rotational angular velocity of the eye movement becomes equal to or less than a threshold value, identifying a region of the screen in which the user is fixing one's gaze based on the eye movement, and determining an option to be highlighted; an interface section for highlighting the determined option, and determining an operation of the device based on an event-related potential in the signal based on the timing of highlighting the option; and a timing adjustment section for adjusting a timing of beginning highlighting based on the eye movement after a process of displaying the option on the screen is begun and until the option is displayed on the screen.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Neuro-response stimulus and stimulus attribute resonance estimator
Owner:NIELSEN CONSUMER LLC
User authentication via evoked potential in electroencephalographic signals
InactiveUS20090063866A1ElectroencephalographyUser identity/authority verificationPattern recognitionMedicine
Techniques are disclosed for authentication and identification of a user by use of an electroencephalographic (EEG) signal. For example, a method for authenticating a user includes the following steps. At least one electroencephalographic response is obtained from a user in accordance with perceptory stimuli presented to the user. The user is authenticated based on the obtained electroencephalographic response. The authenticating step may be based on detection of an event-related potential in the obtained electroencephalographic response. The event-related potential may be a P300 event-related potential. The method may also include the step of enrolling the user prior to authenticating the user. The enrolling step may include a supervised enrollment procedure or an unsupervised enrollment procedure.
Owner:IBM CORP
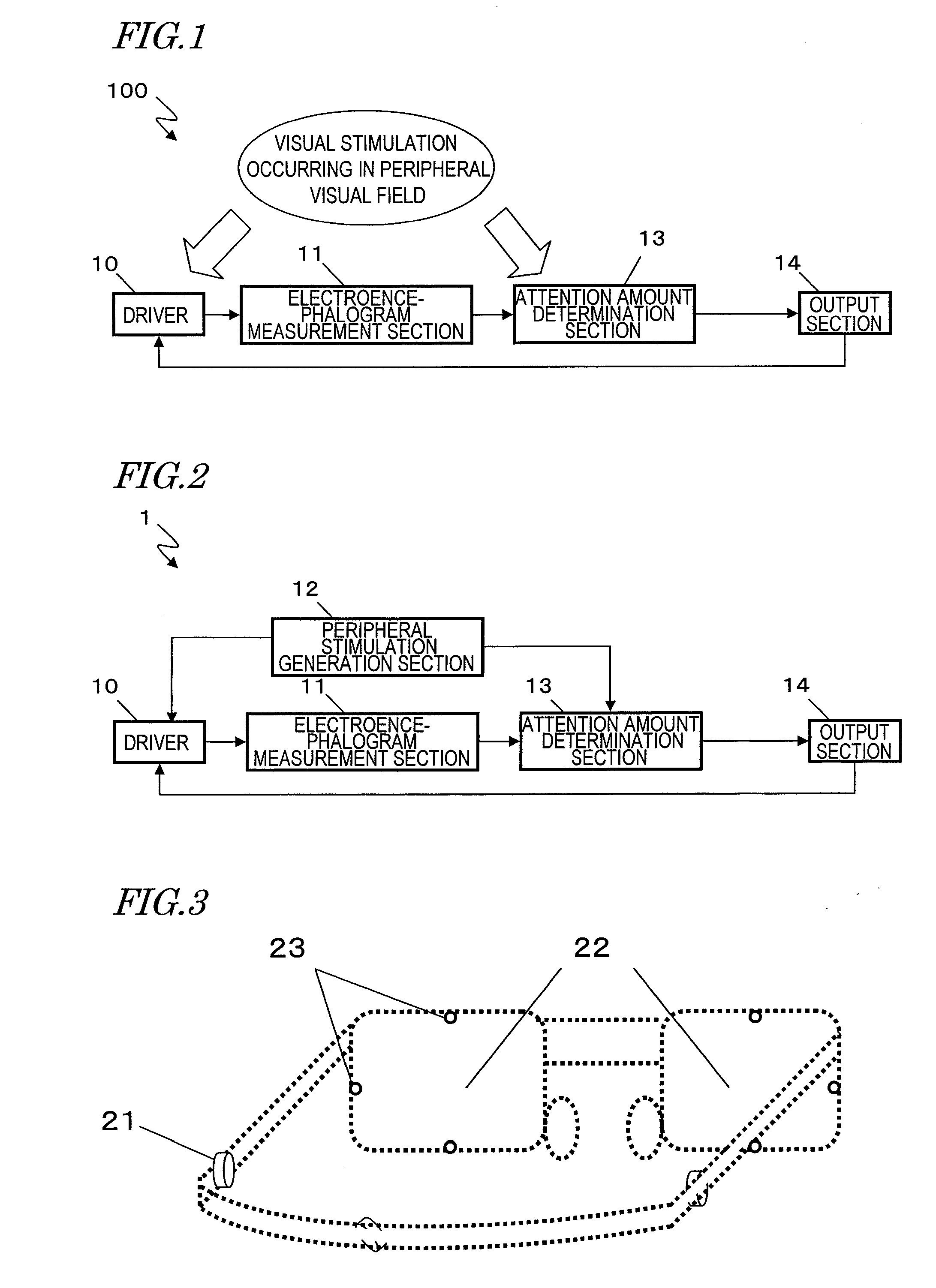
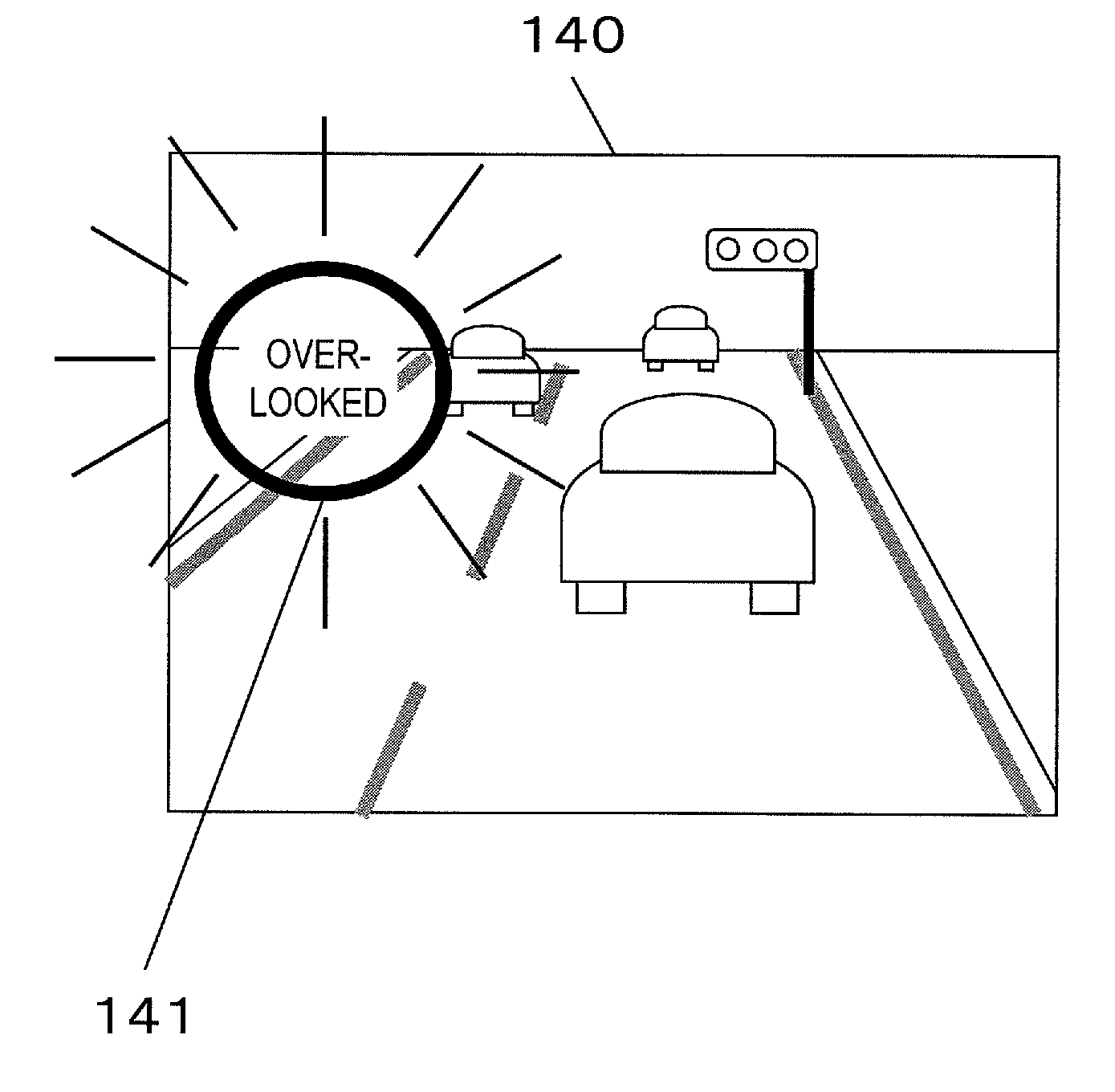
Apparatus, method, and program of driving attention amount determination
InactiveUS20100156617A1Accurately determineElectroencephalographyAnti-collision systemsVisual field lossDriver/operator
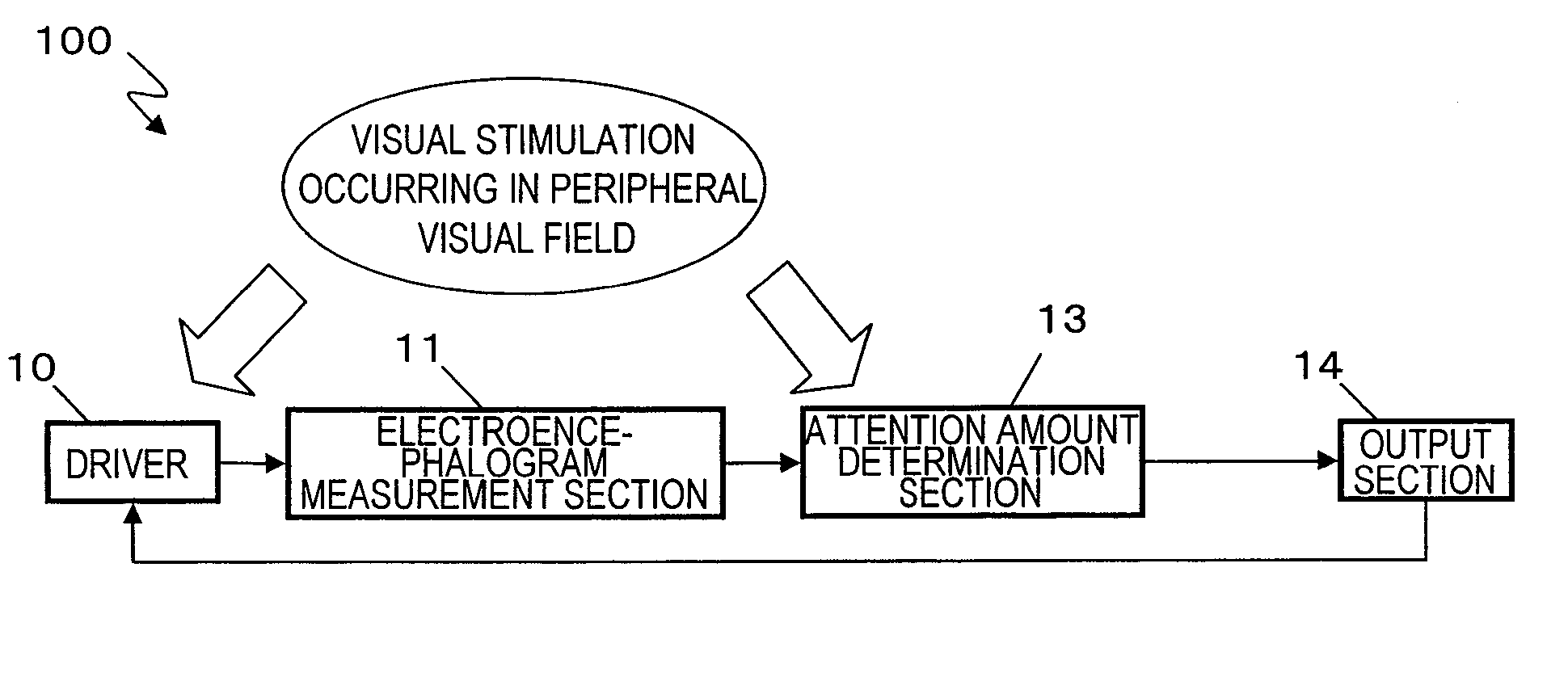
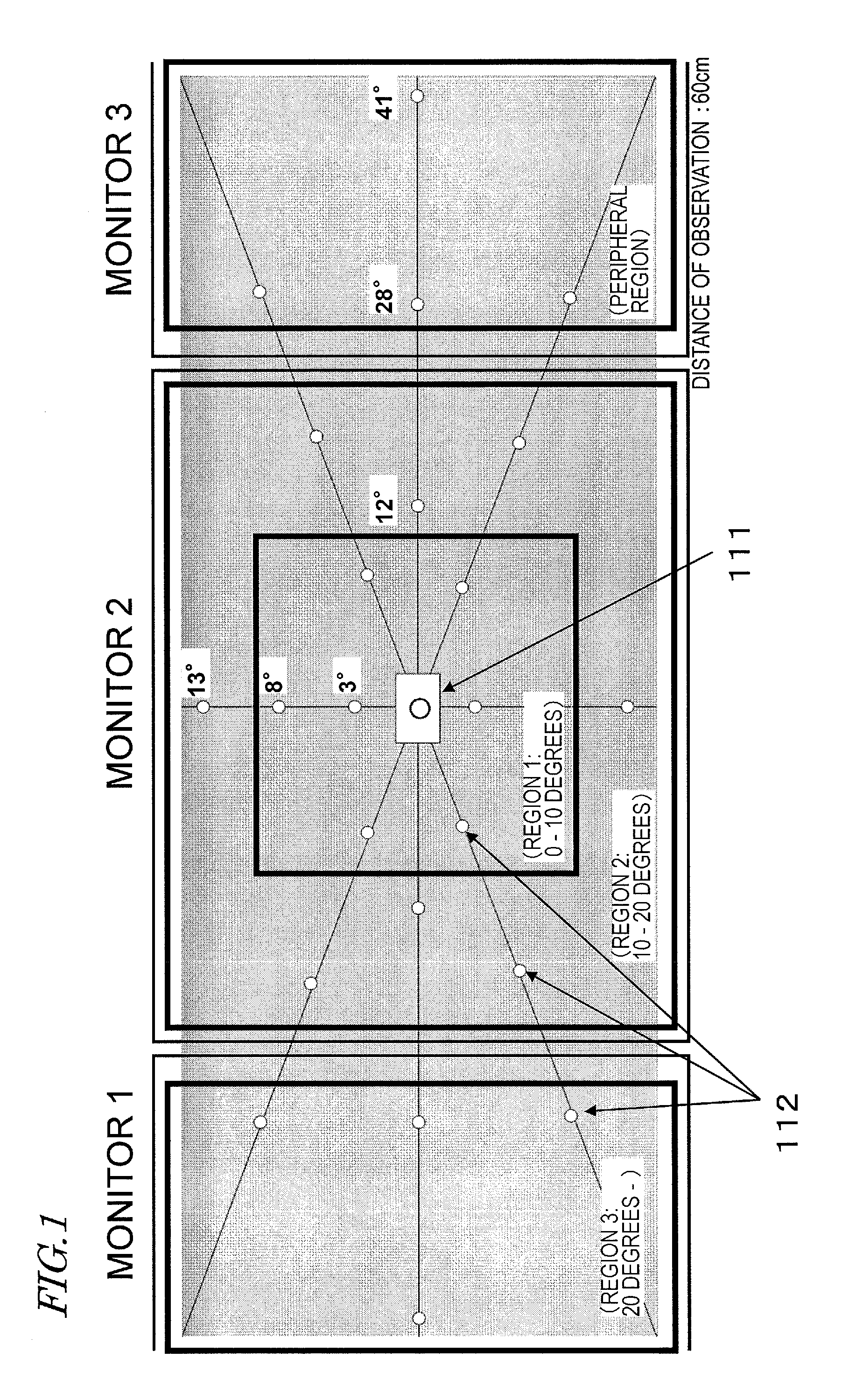
Even when a driver is not directing his or her line of sight to objects in the surroundings, the amount of attention of the driver to the peripheral visual field can be determined, and safe driving assistance in accordance with the result of determination can be provided. A driving attention amount determination apparatus includes: an electroencephalogram measurement section for measuring an electroencephalogram signal of a driver; an attention amount determination section for determining an amount of attention of the driver to a peripheral visual field by utilizing an event-related potential in the electroencephalogram signal, the event-related potential being based on a starting point which is a time point of occurrence of a visual stimulation occurring in the peripheral visual field of the driver; and an output section for calling attention of the driver by outputting a signal based on a result of the determination.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
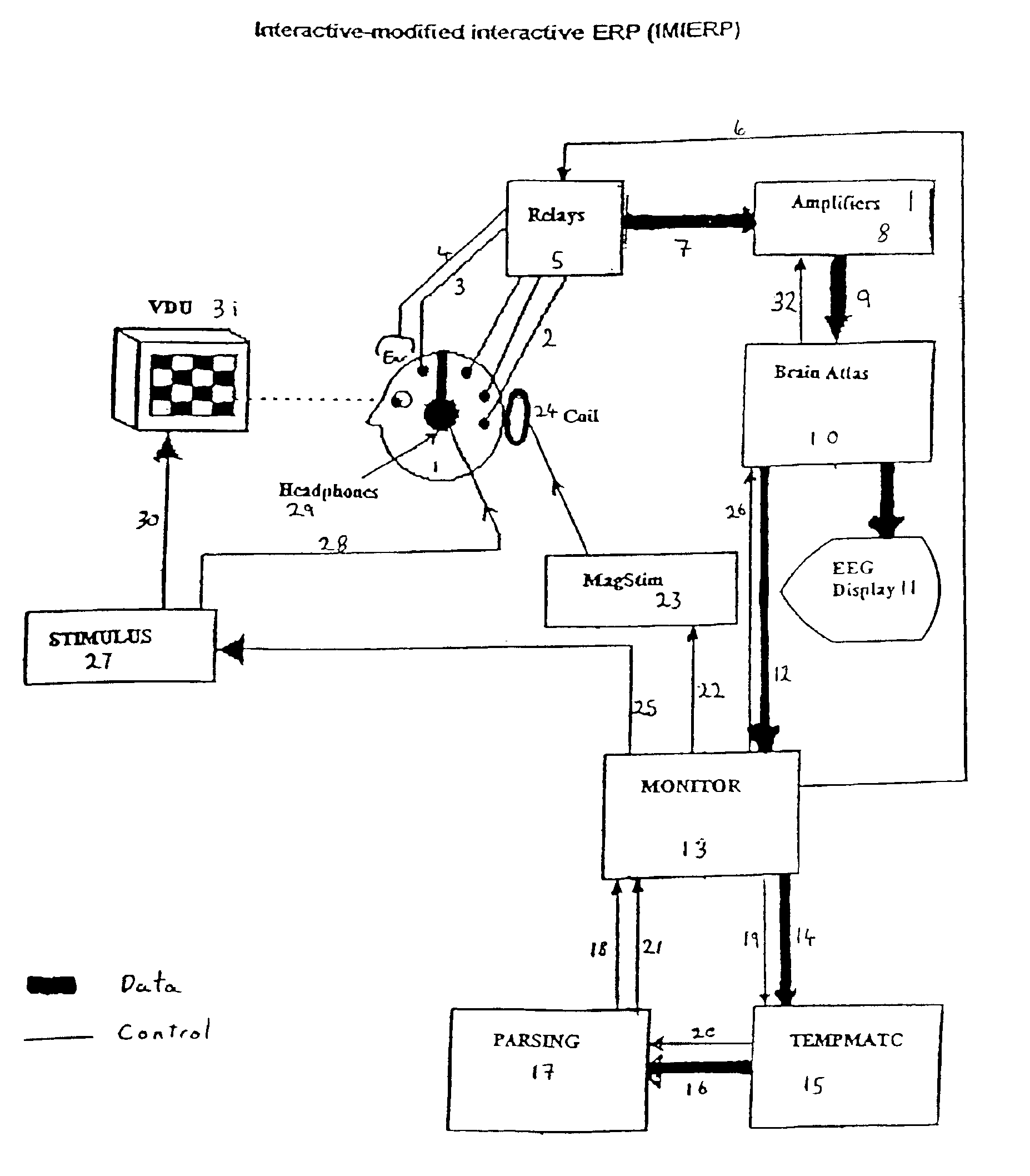
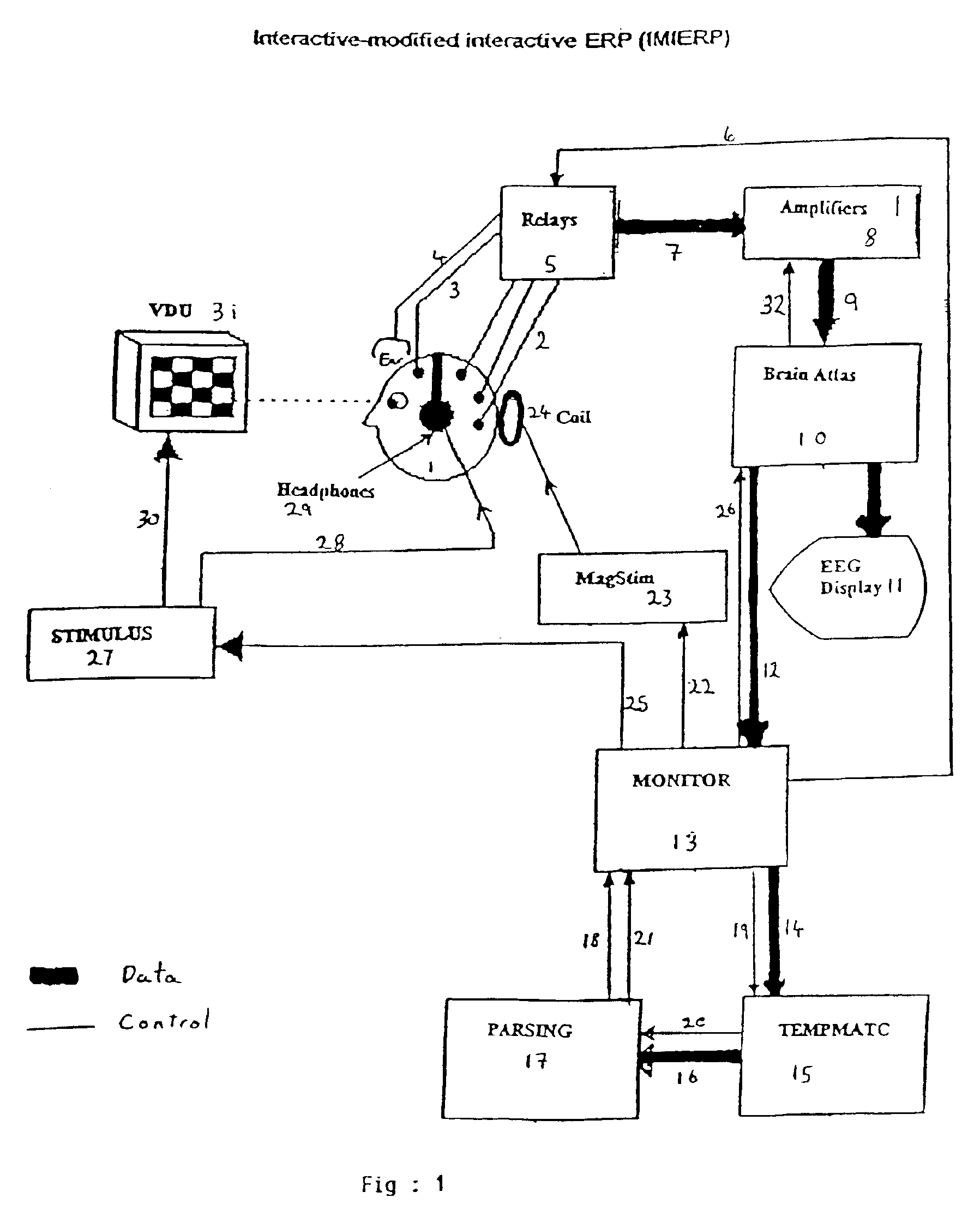
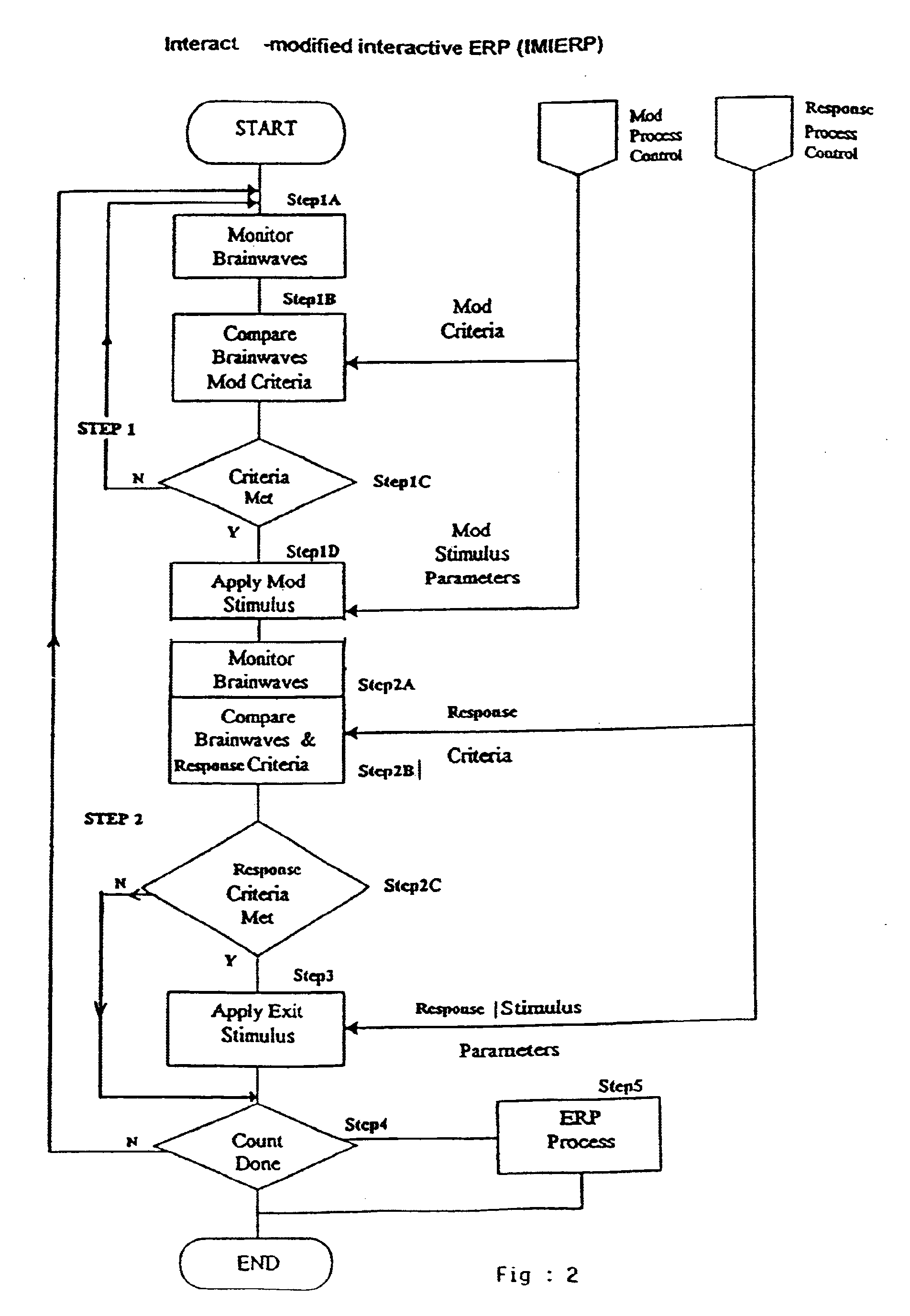
Interactive-modified interactive event related potential (IMIERP)
A method modifying a particular electrophysiological feature generated in response to a stimulus is disclosed. The method involves a repeated process of: sampling the brain wave state in order to apply a modifying pulse; modifying the brain wave state to a state more conducive to a required response; sampling the brain wave state in order to apply a response stimulus; applying a stimulus only when the brain wave state substantially meets the preselected response criteria; recording the brain wave activity of the subject subsequent to the application of the stimulus.
Owner:PRICE GREGORY W DR
Method for controlling device by using brain wave and brain wave interface system
ActiveUS20100191140A1Reduce the burden onUnnecessary wearElectroencephalographySensorsElectroencephalogram featureMedicine
The control method for a device includes steps of: presenting a visual stimulation concerning a manipulation menu for a device; measuring event-related potentials after the visual stimulation is presented, where event-related potentials based on a timing of presenting the visual stimulation as a starting point are measured from a potential difference between each of electrodes and at least one reference electrode respectively worn on a face and in an ear periphery of a user; from each of the measured event-related potentials, extracting electroencephalogram data which is at 5 Hz or less and contains a predetermined time section, and combining the extracted electroencephalogram data into electroencephalogram characteristic data; comparing the electroencephalogram characteristic data against reference data prepared in advance for determining a desire to select an item in the manipulation menu; and, based on a comparison result, executing a manipulation of the device corresponding to the item.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Electroencephalogram interface system
InactiveUS20110071416A1Stable electrode contactContact stabilityElectroencephalographySensorsPotential differenceEvent-related potential
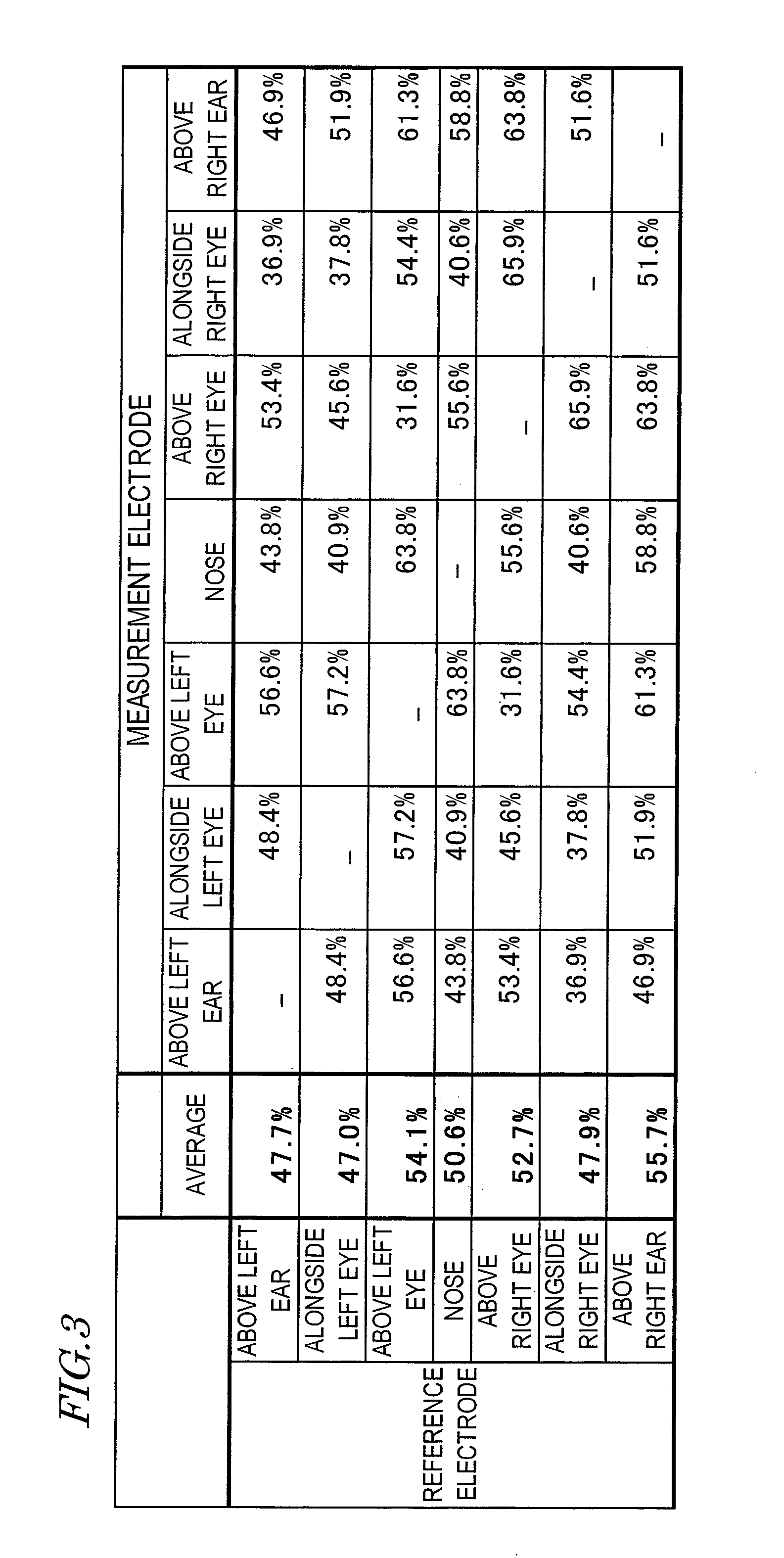
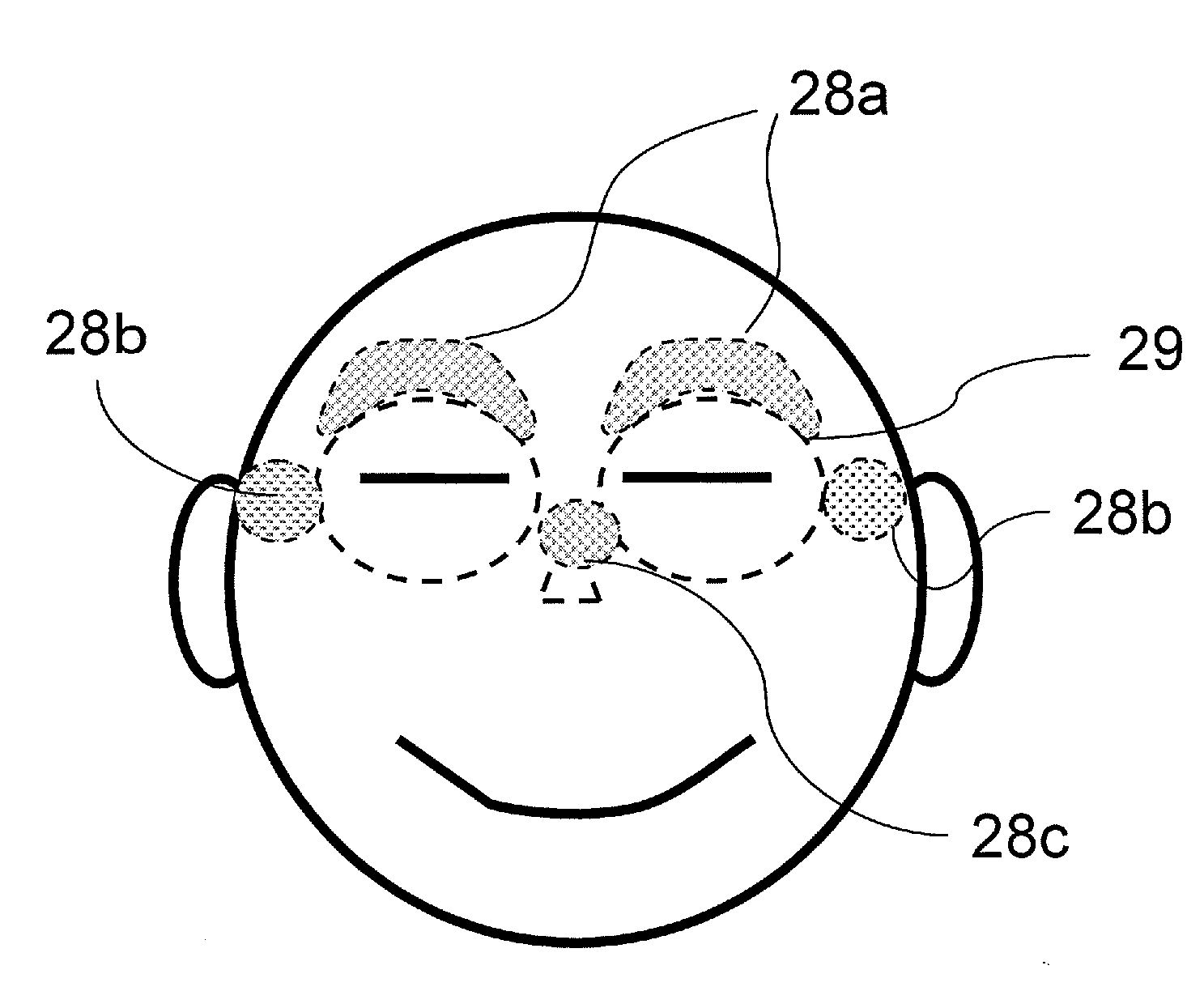
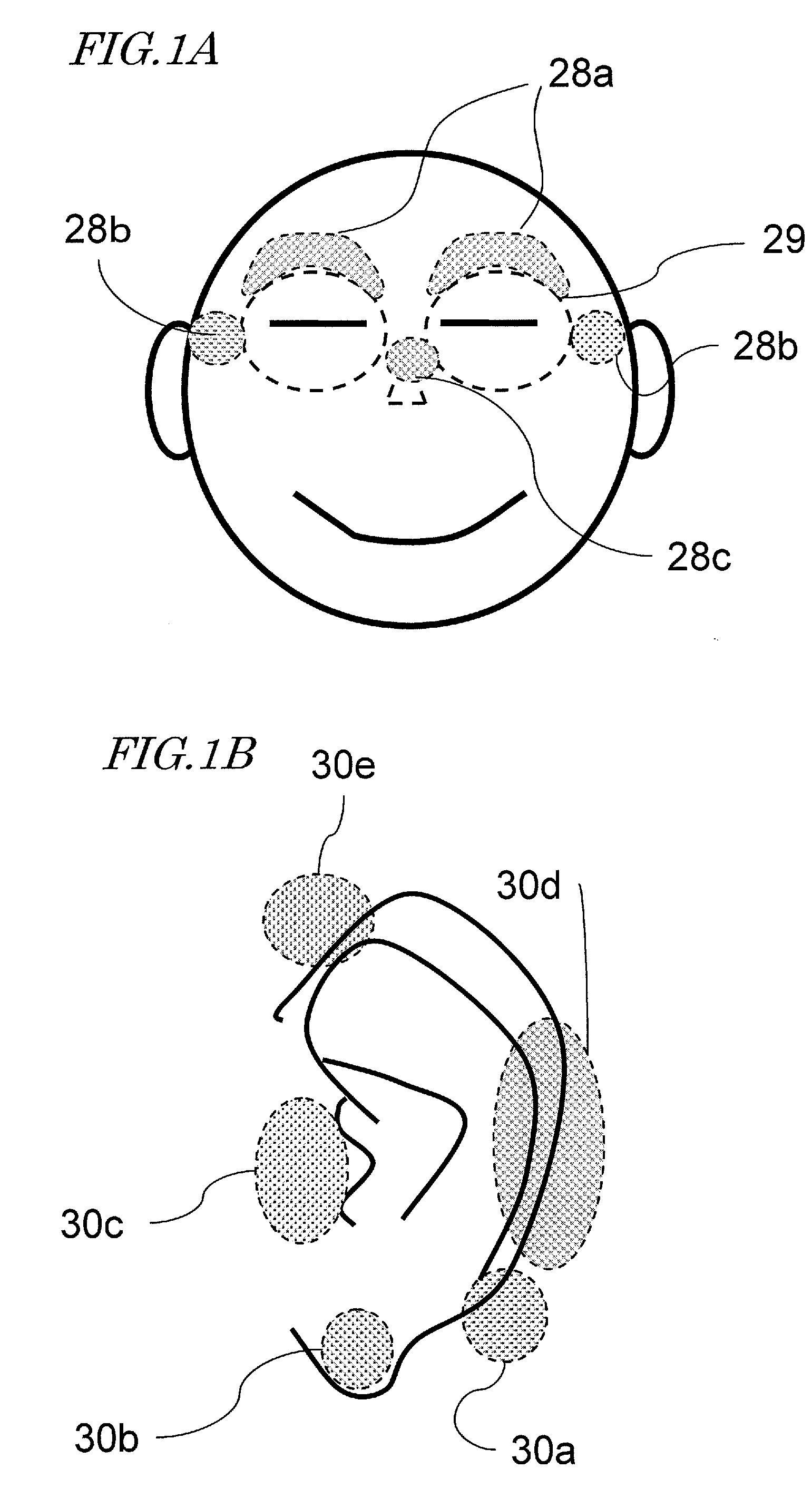
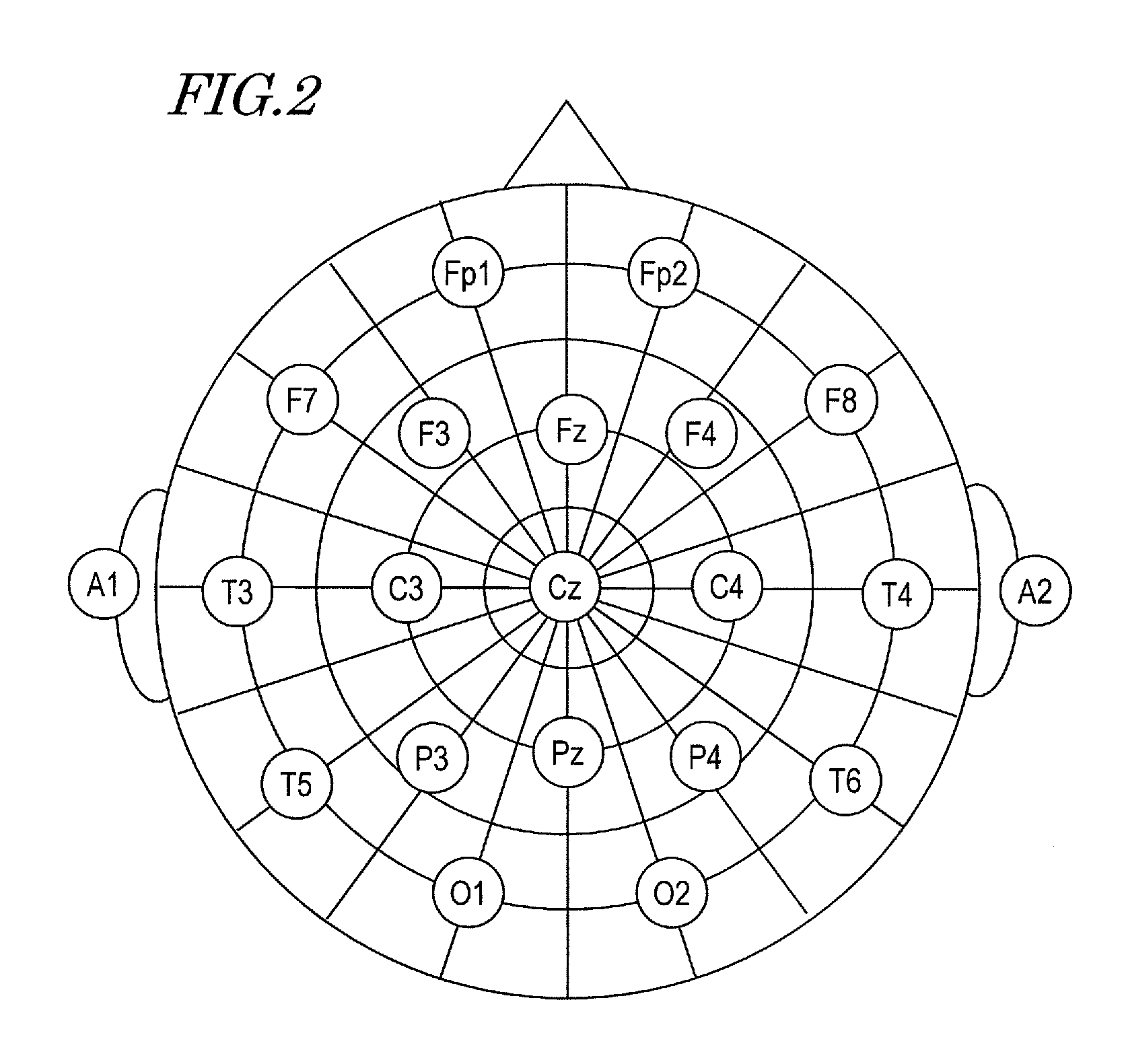
An eyeglass-type electroencephalogram interface system is worn on the head of a user. The system includes: an output section for presenting a visual stimulation to the user; an ear electrode portion disposed at a position coming in contact with an ear of the user when the system is worn; a facial electrode portion disposed at a position coming in contact with the face below a straight line connecting an external canthus and an internal canthus of an eye of the user, such that the mass of the system is supported at the position, when the system is worn; and an electroencephalogram measurement and determination section for measuring an event-related potential on the basis of a potential difference between the ear electrode portion and the facial electrode portion based on the visual stimulation being presented by the output section as a starting point.
Owner:SOVEREIGN PEAK VENTURES LLC
Apparatus, method, and computer program for adjustment of electroencephalograms distinction method
InactiveUS20090247895A1Accurately determineEasy to operateElectroencephalographySensorsEeg electroencephalographyData mining
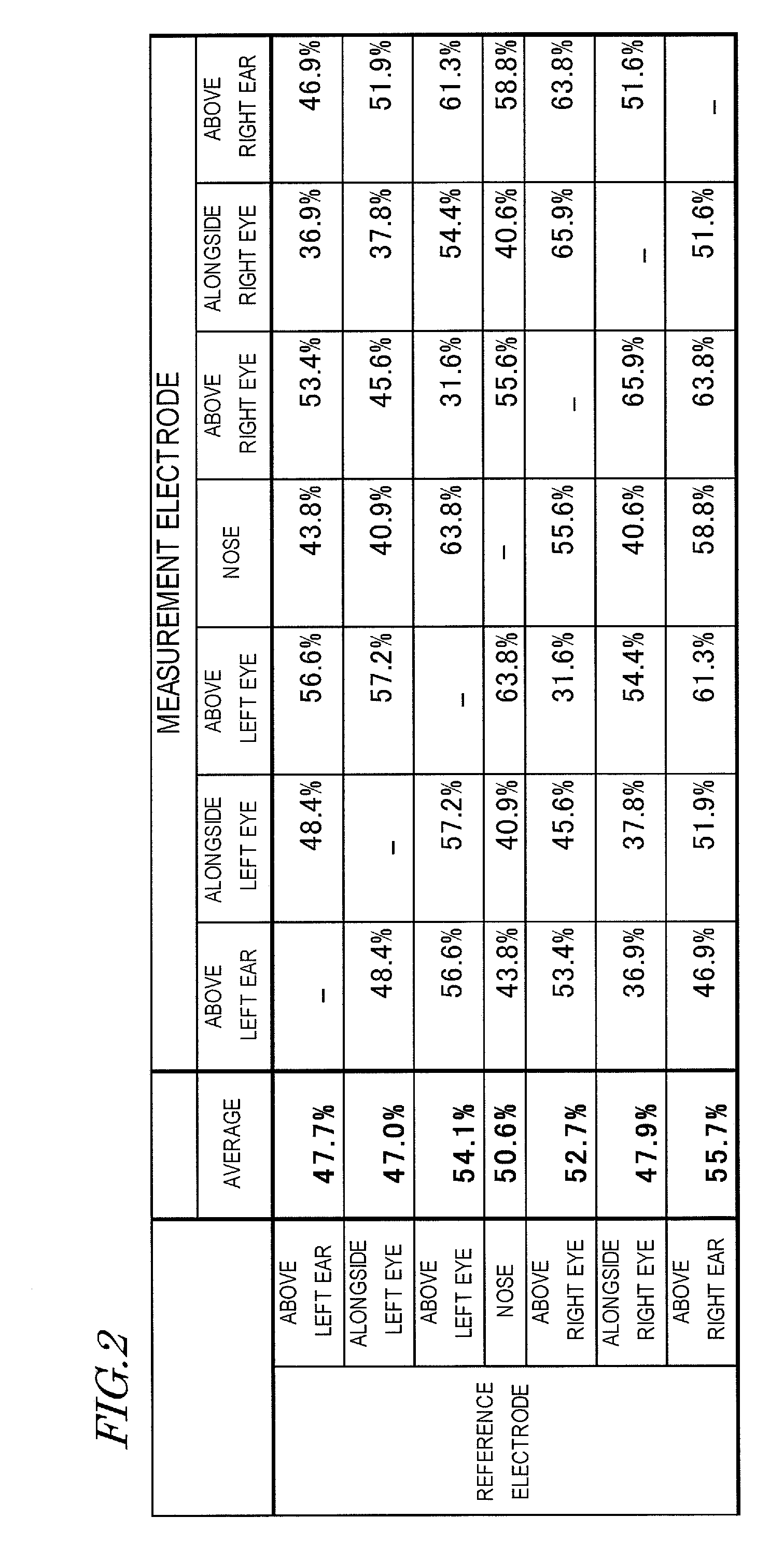
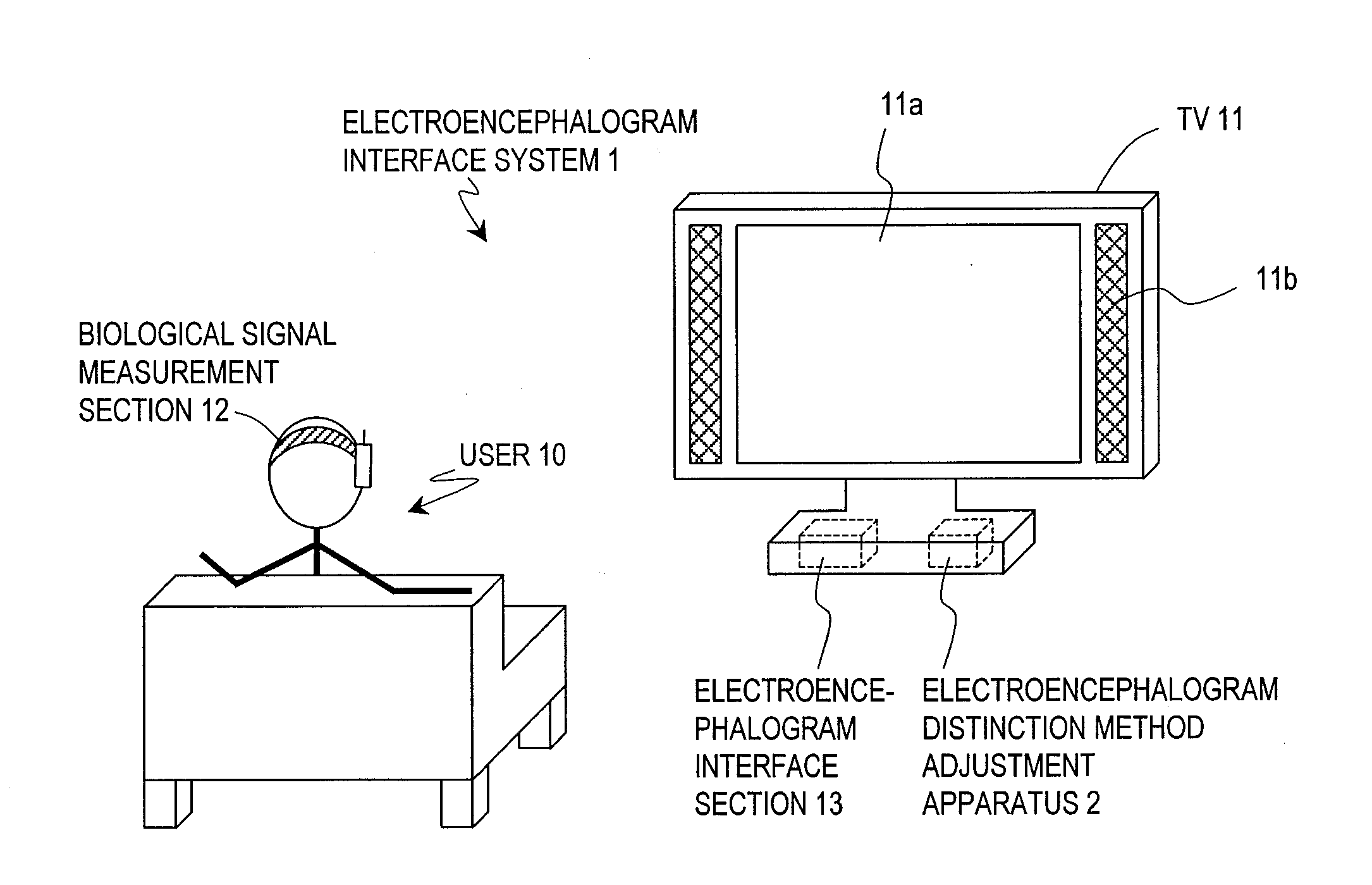
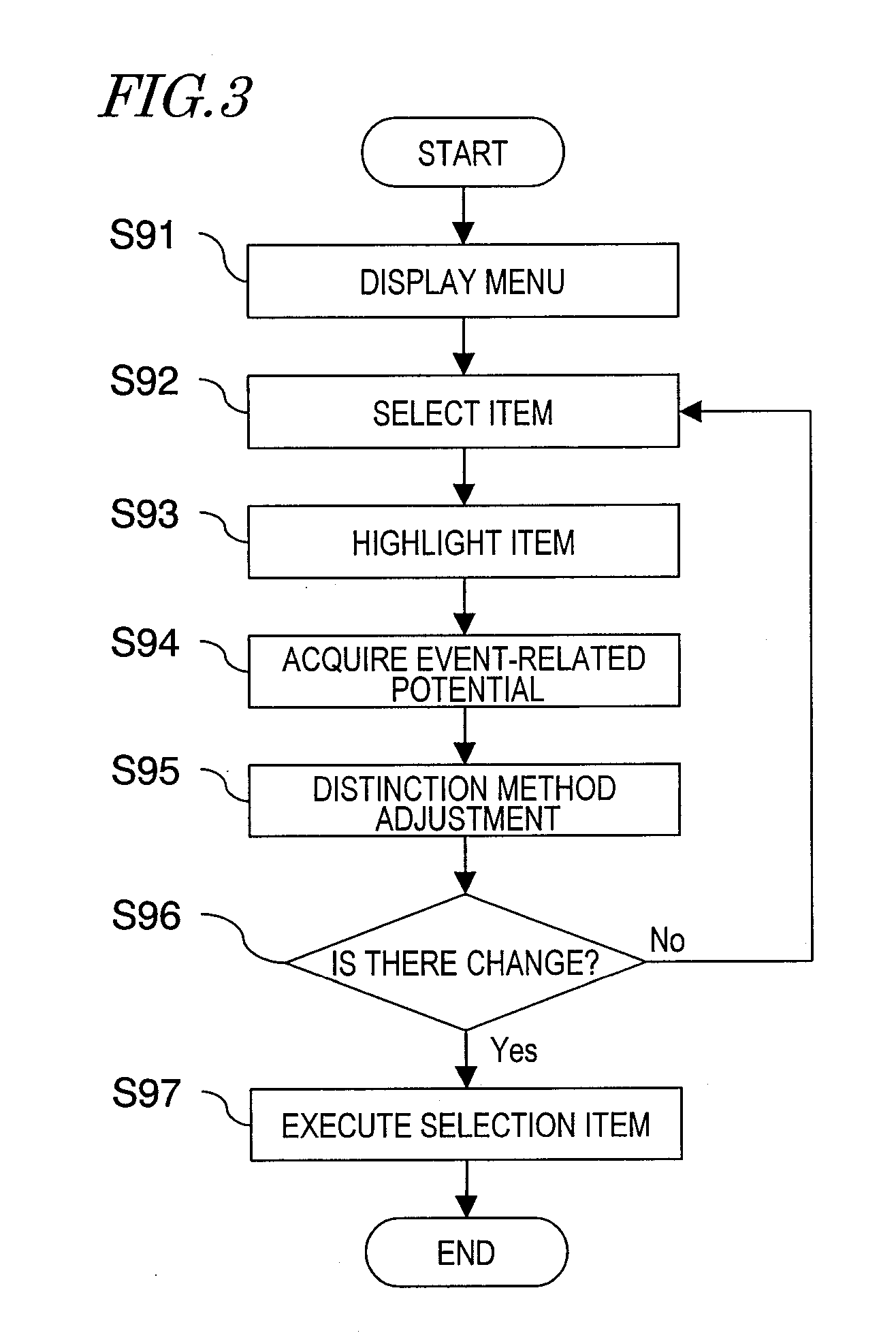
In a system having an interface utilizing electroencephalograms, a user's burden of calibration for accurately measuring electroencephalograms is eliminated, and it becomes possible to maintain a high distinction accuracy of electroencephalograms.An electroencephalogram interface (IF) system 1 includes an electroencephalogram IF section (13) for distinguishing a request of a user based on electroencephalograms, and identifies a function which is in accordance with the request. An electroencephalogram distinction method adjustment apparatus (2, 50) includes: an analysis section (14, 52) for detecting a change in a characteristic quantity of a stimulation given to the user, thus detecting a change in the stimulation; a storage section (15) for storing a waveform of an event-related potential during a period after a point in time when the change in the stimulation is detected; an extraction section (16) for extracting a characteristic quantity of the user based on the stored waveform; and an adjustment section (17) for, based on the extracted characteristic quantity, adjusting in the electroencephalogram IF section (13) a distinction method for a request based on an electroencephalogram signal.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Cognitive Function Assessment in a Patient
ActiveUS20130245422A1Facilitate communicationEasy to manageElectroencephalographySensorsMedicineElectromagnetic field
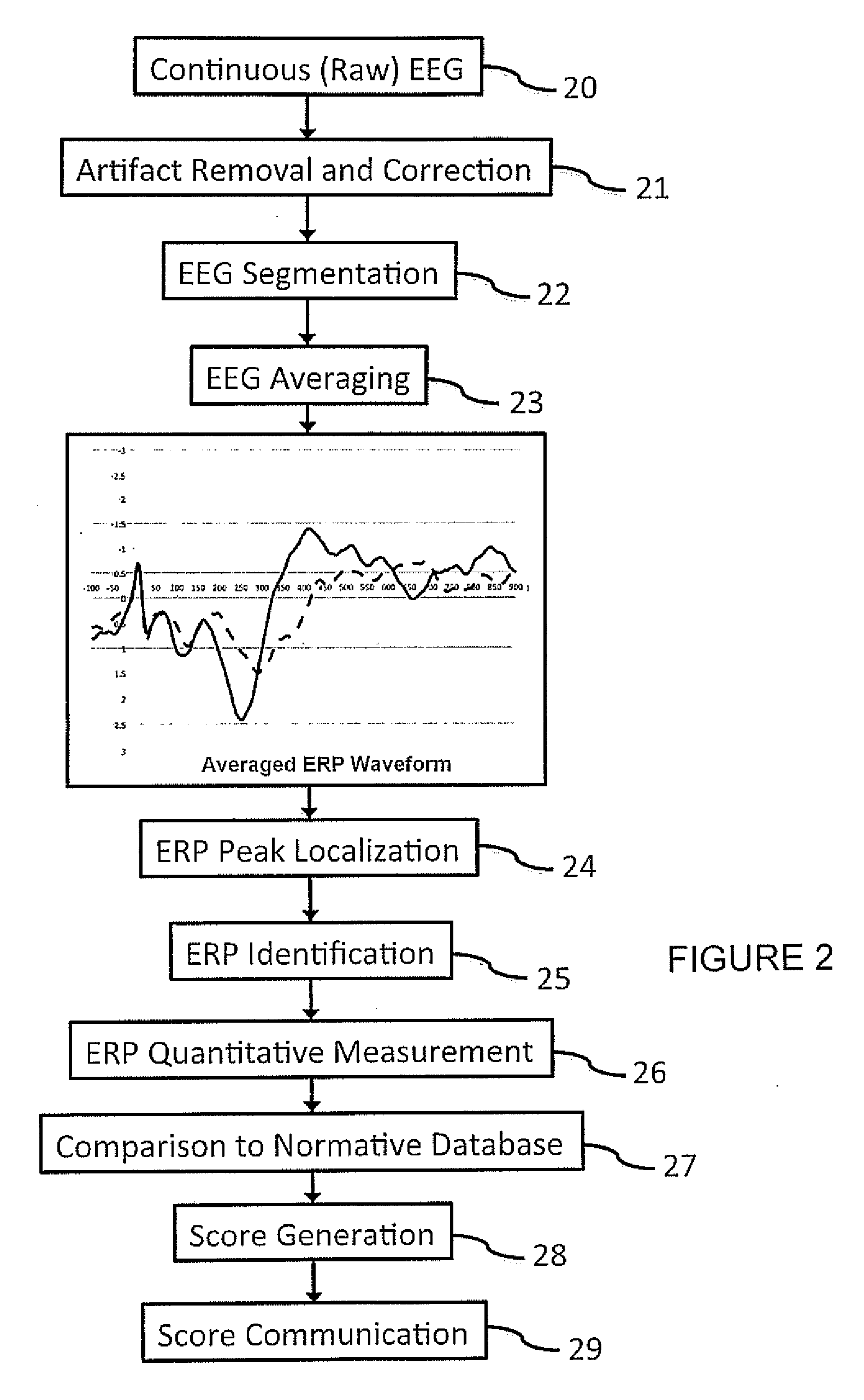
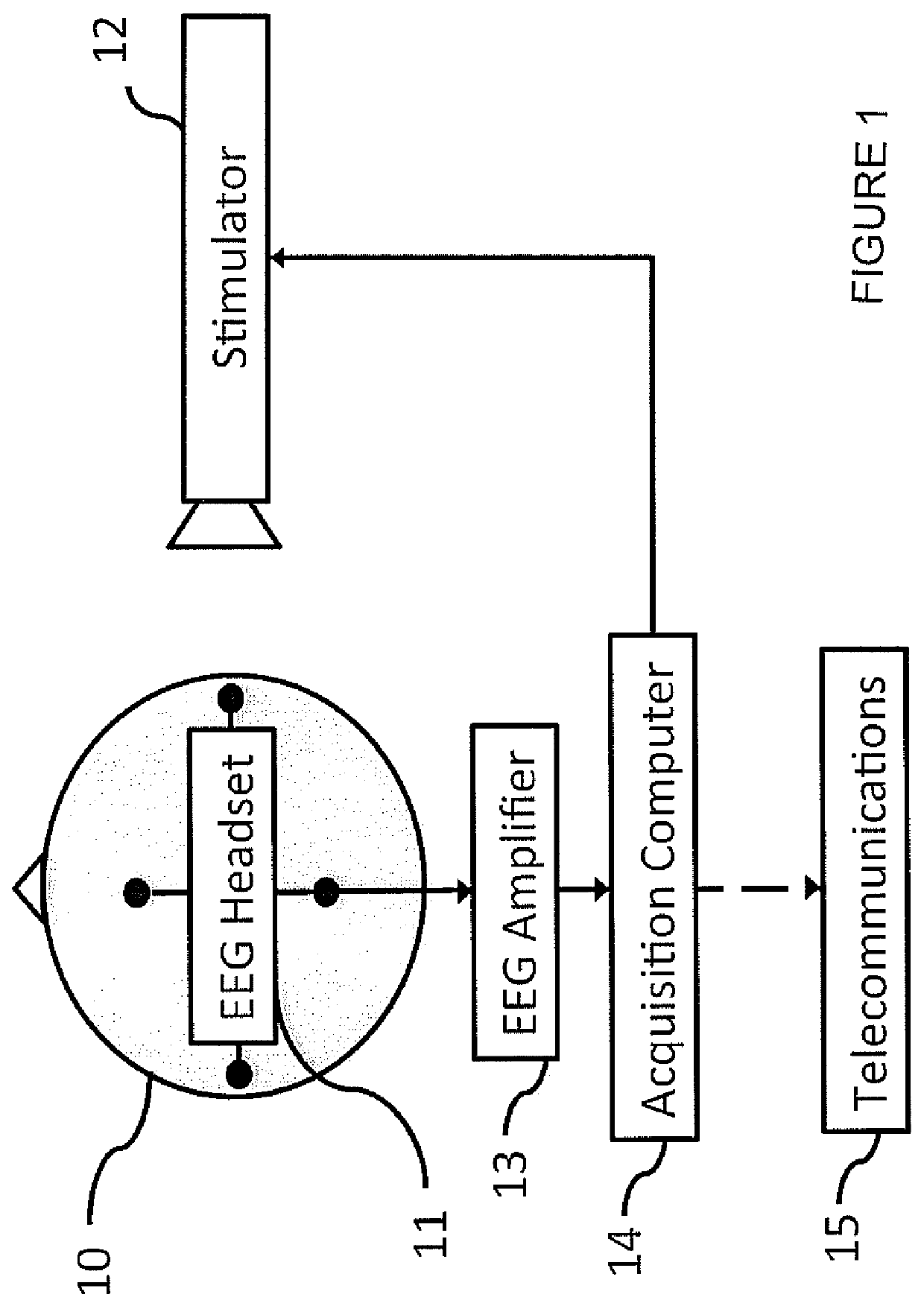
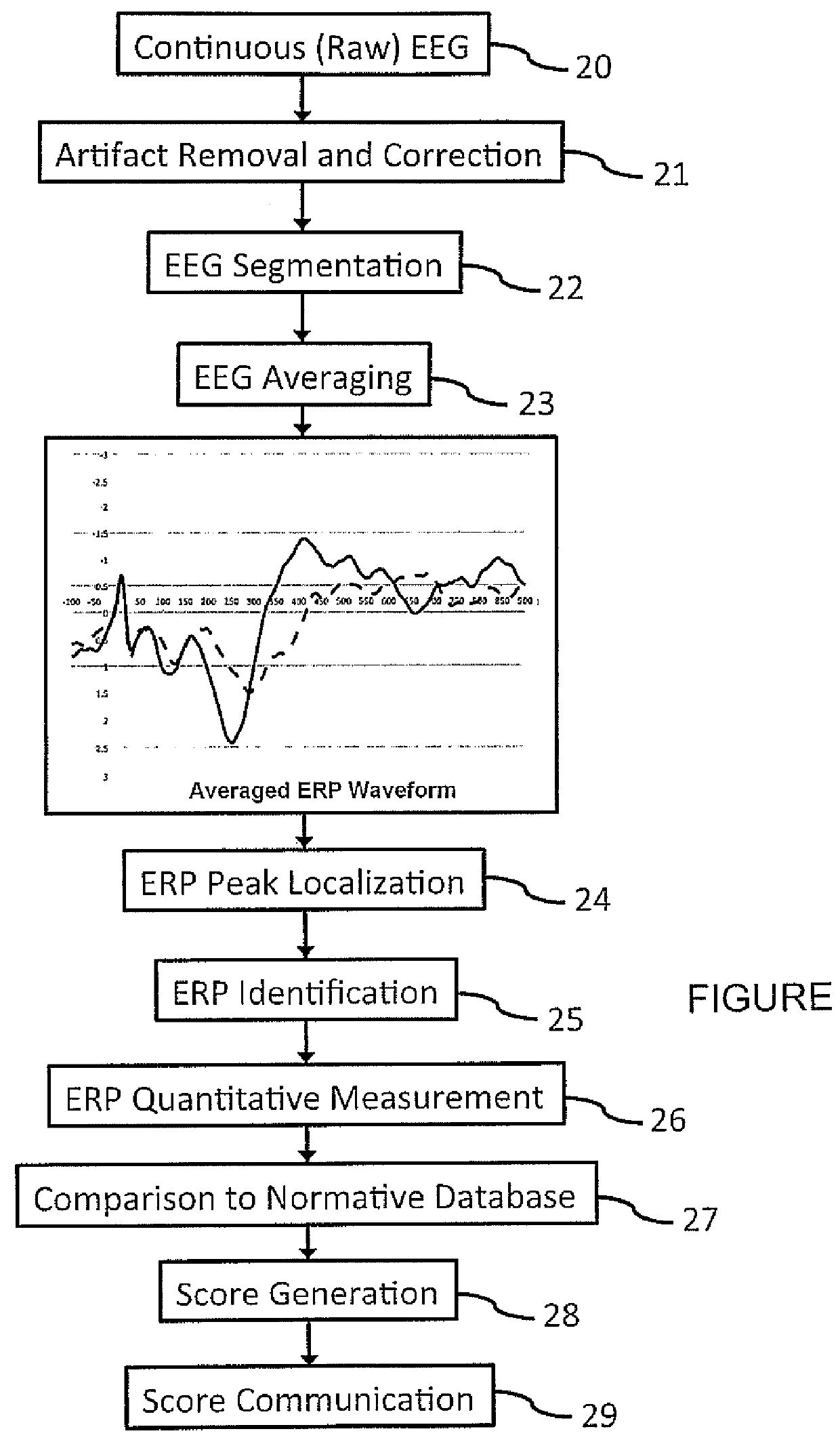
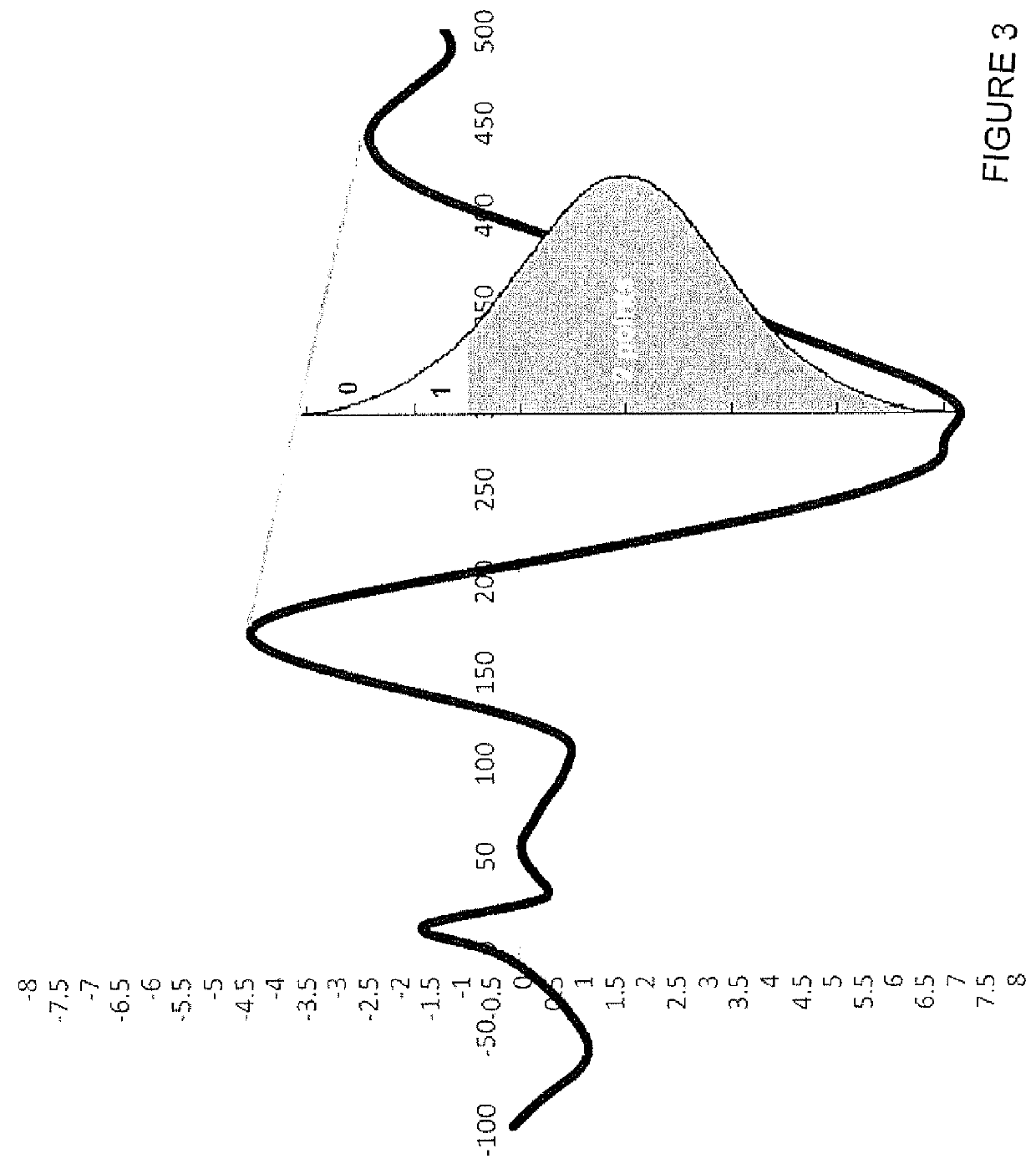
A method for analysis of the extent of conscious awareness and likelihood of recovery of a patient includes the steps of applying to the patient a sensory stimulus sequence which is typically auditory; carrying out an EEG to generate waveform signals to record changes in the electromagnetic fields generated by the patient's neural activity; using software provided in a processor to process the waveform signals in order to locate waveform peaks, identify the event-related potential (ERP) components obtained in the waveform and to obtain quantitative measures of those components; and using the software to generate and communicate scores indicative of the extent of conscious awareness and likelihood of recovery of the patient.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Information processing system, information processing apparatus, and method
ActiveUS7716697B2ElectroencephalographyInput/output for user-computer interactionInformation processingPeak value
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
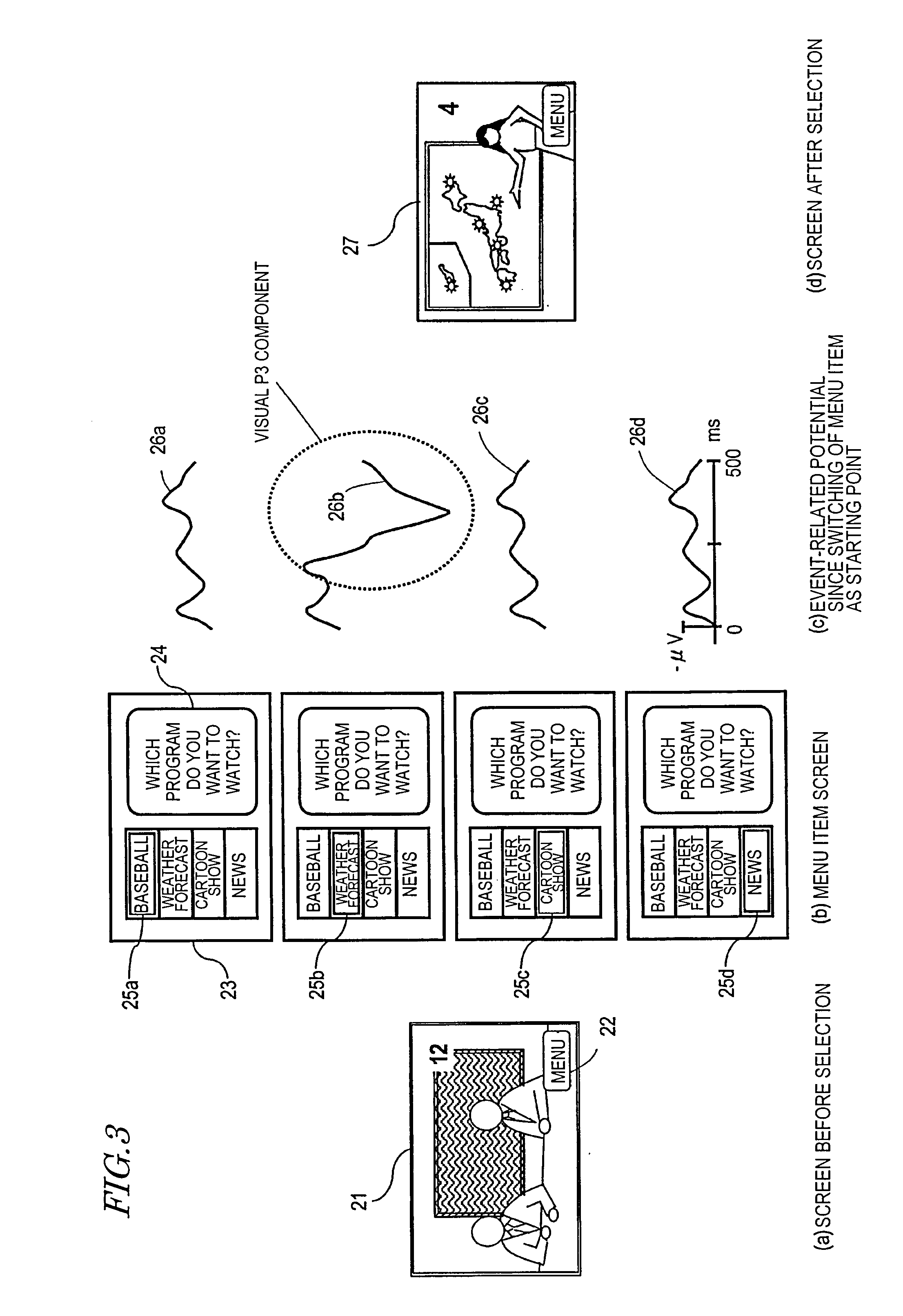
Electroencephalogram interface system and activation apparatus
ActiveUS20090187114A1Input/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system detailsVisual evoked potentialsEngineering
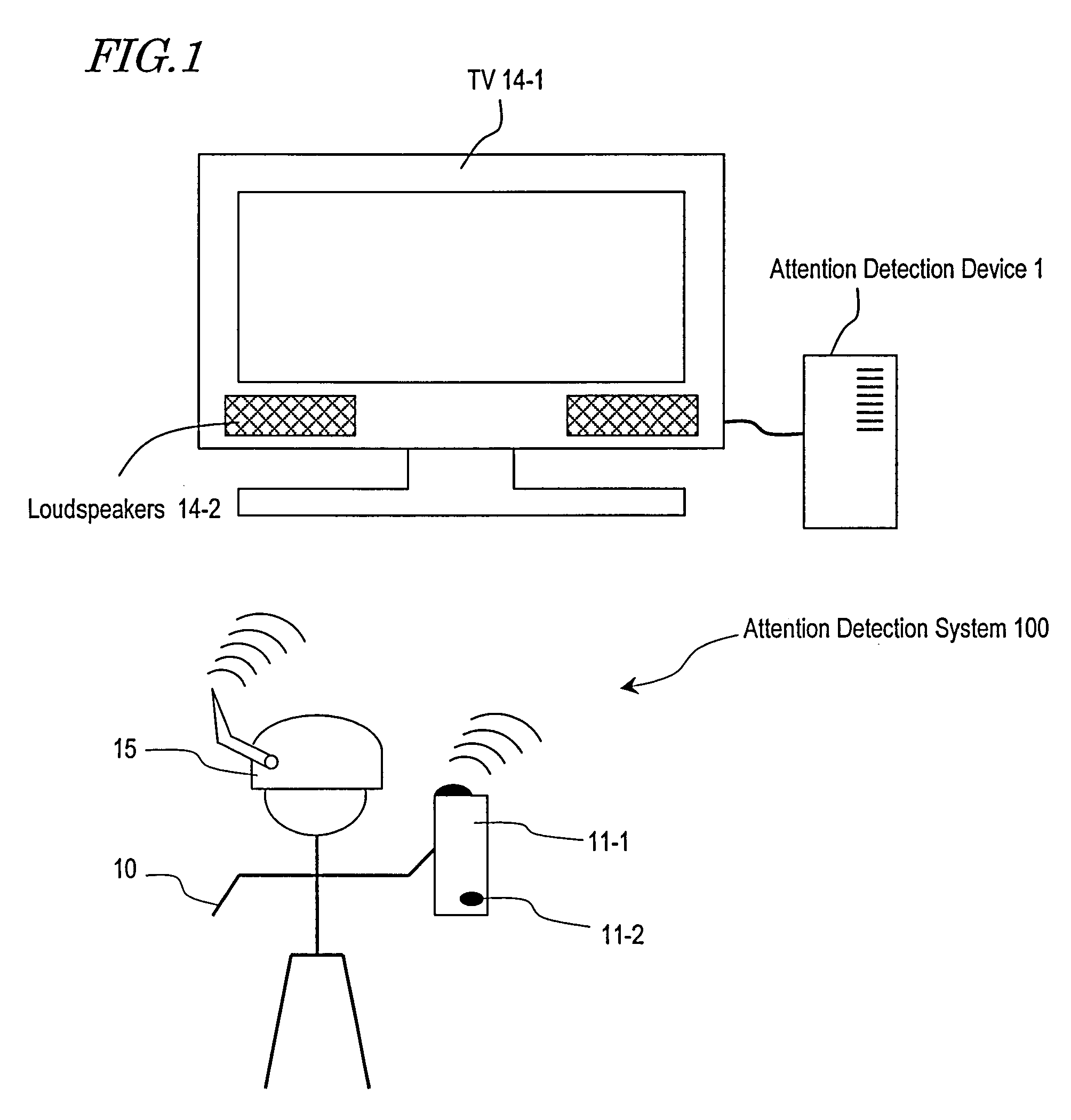
An electroencephalogram interface is activated by utilizing a biological signal, in particular a steady-state visual evoked potential, from a user.An electroencephalogram interface system (1) includes a biological signal detection section (4) for detecting an electroencephalogram signal from a user (3) and a control section (5) for distinguishing a component of an event-related potential which is contained in the electroencephalogram signal and causing a device to operate based on the distinguished event-related potential. The electroencephalogram interface system (1) further includes an activation apparatus (2) for activating the control section (5) and an output section (6) for presenting a visual stimulation which flickers with a predetermined frequency based on a signal from the activation apparatus (2). The activation apparatus (2) includes: a frequency analysis section (7) for analyzing a frequency component of the electroencephalogram signal detected by the biological signal detection section (4), and detecting an intensity corresponding to the predetermined frequency; and a determination section (8) for comparing the detected intensity of the predetermined frequency and a predetermined threshold, and if the intensity of the predetermined frequency is equal to or greater than a predetermined threshold, determining that the user (3) has been paying attention to the visual stimulation and thus activating the control section (5).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
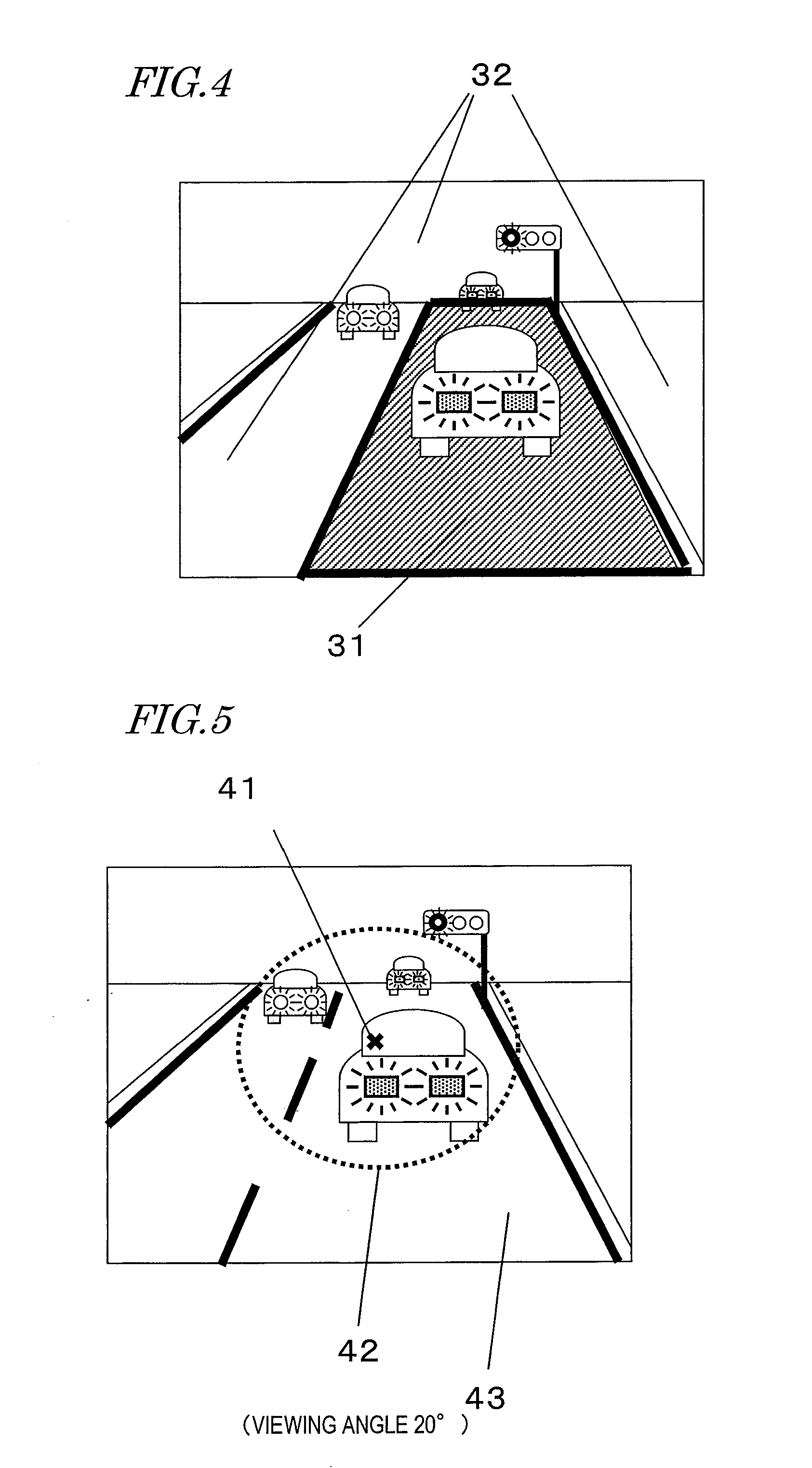
Driving attention amount determination device, method, and computer program
ActiveUS20110279676A1Accurately determineElectroencephalographyEndoscopesVisual field lossDriver/operator
A driving attention amount determination apparatus includes: an electroencephalogram measurement section for measuring an electroencephalogram signal of a driver; a central stimulation presentation section for presenting a visual stimulation in a central visual field of the driver; a peripheral stimulation presentation section for presenting a visual stimulation in a peripheral visual field of the driver; a threshold setting section for setting a determination threshold for attention amount determination from a distribution of amplitude of an event-related potential in the electroencephalogram signal based on a point of presenting the stimulation in the central visual field as a starting point; and an attention amount determination section for determining an attention amount through a comparison between the determination threshold and an amplitude of an event-related potential in the electroencephalogram signal based on a point of presenting the stimulation in the peripheral visual field as a starting point.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Scanning focal point apparatus
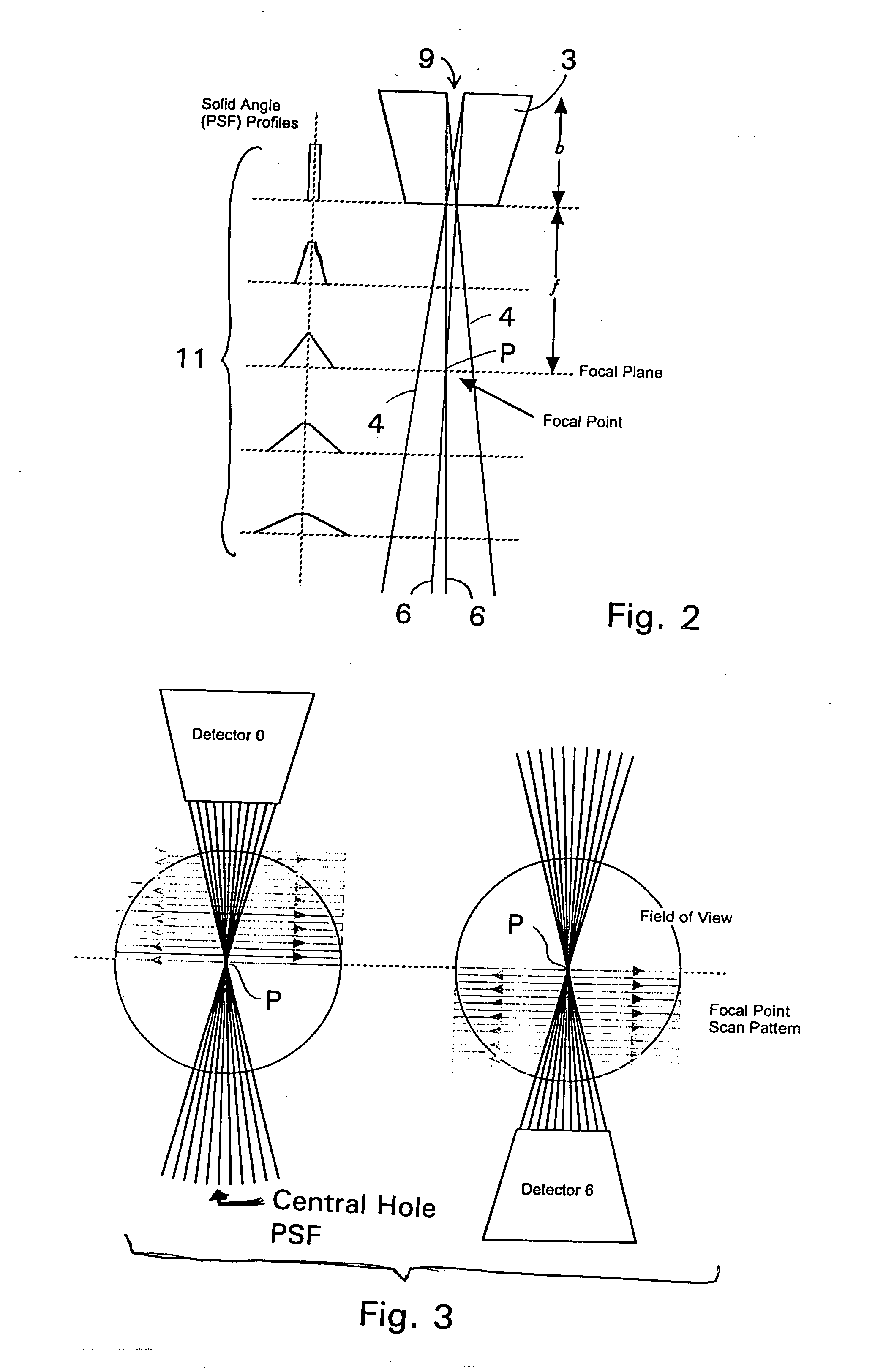
ActiveUS20070029491A1Maximizing spatial resolutionMaximizing sensitivitySolid-state devicesHandling using diaphragms/collimetersDiagnostic Radiology ModalityPhoton emission
A collimator, and in particular a method for making a collimator for use with a small high resolution single-photon emission computed tomographic (SPECT) imaging tool for small animal research. The collimator is sized, both functionally and structurally, particularly smaller than known collimators and appropriately scaled to achieve a highly sensitive collimator which facilitates desired reconstruction resolutions for small animals, as well as compliments other functional imaging modalities such as positron emission tomography (PET), functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), electroencephalography (EEG), and event-related potential (ERP), magneto-encephalography (MEG), and near-infrared optical imaging.
Owner:NEUROLOGICA CORP
Cognitive function assessment in a patient
ActiveUS9339227B2Facilitate communicationEasy to manageElectroencephalographySensorsMedicineElectromagnetic field
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
General system for testing behaviors of nerves
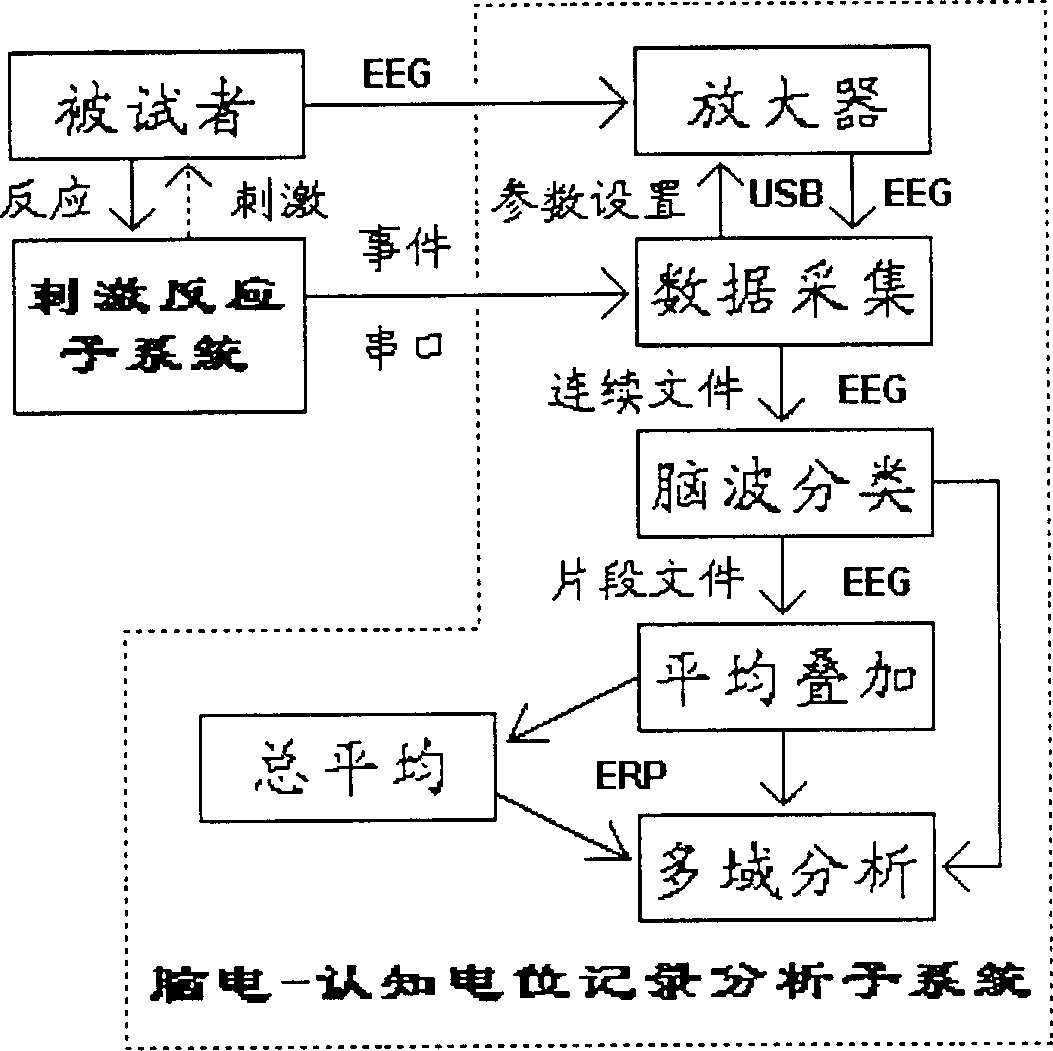
An universal test system based on microcomputer for testing the nervous behaviour is composed of the irritation reaction multimedia subsystem and the cerebral current / cognitive level recording-analyzing subsystem, both of which are connected via serial communication parts. The former can make the video-audio irritation its ns precision, record the reaction of the person to be tested, and send outrelative event. The latter is composed of 5 functional modules (data acquisition, cerebroelectric wave classification, average superimpose, total average and multi-domain analysis) and digitalized cerebroelectric amplifier.
Owner:周曙 +1
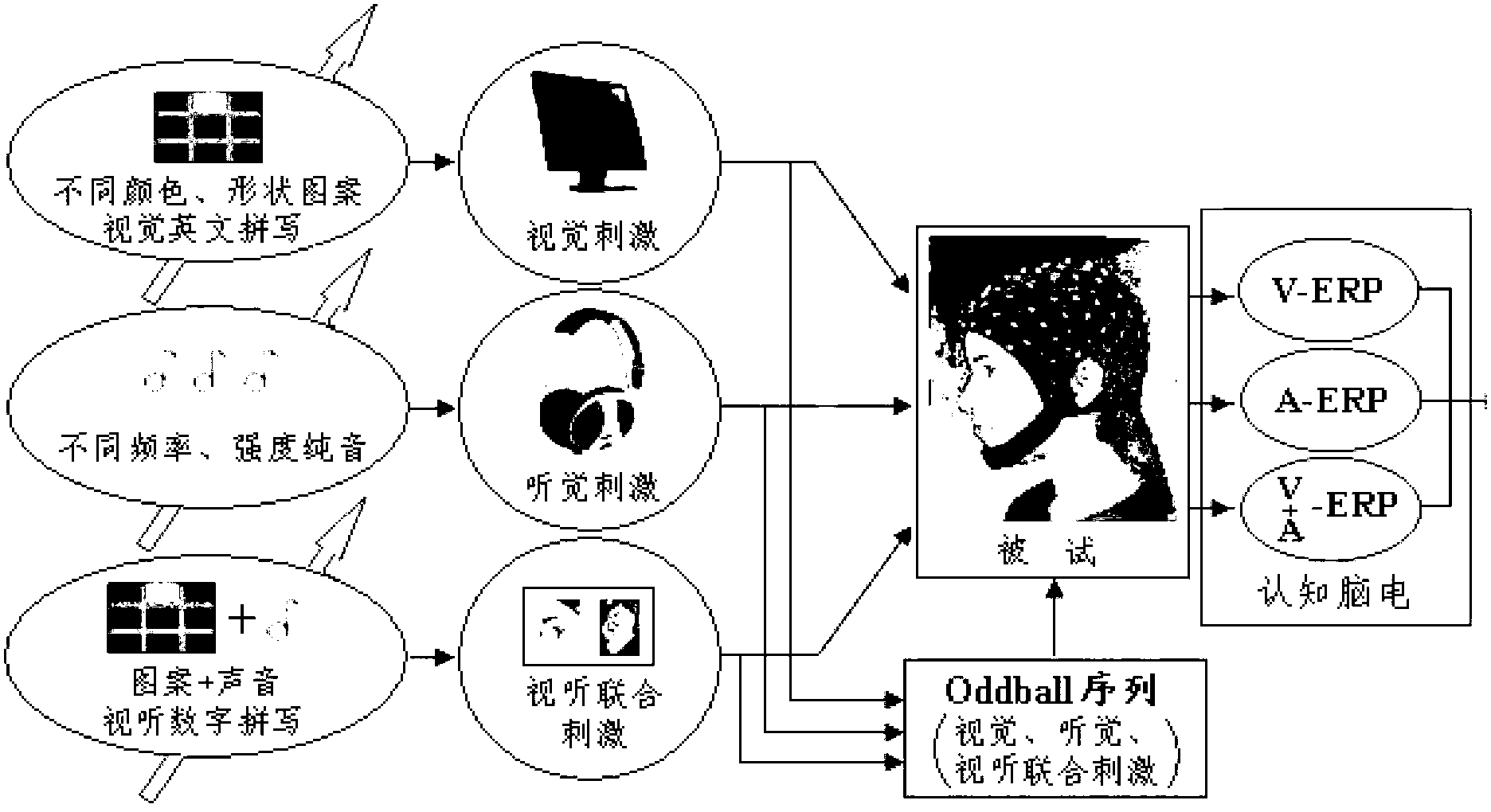
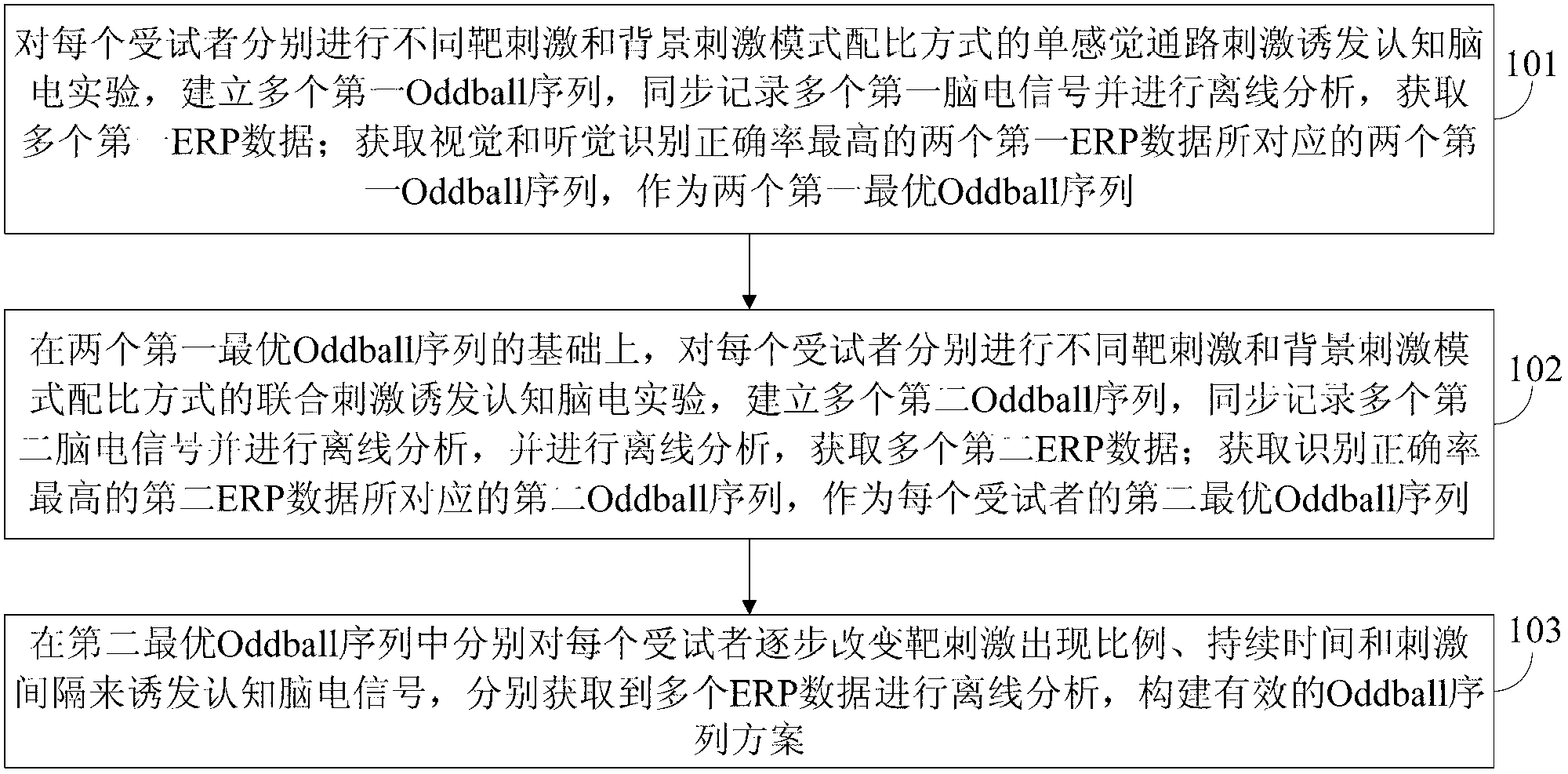
Method for optimizing audio-visual cognitive event-related potential experimental paradigm
ActiveCN102793540AReduce the impact of recognition accuracyImprove execution efficiencyInput/output for user-computer interactionDiagnostic recording/measuringOffline analysisEvent-related potential
The invention discloses a method for optimizing an audio-visual cognitive event-related potential experimental paradigm. The method comprises the following steps of: on the basis of two first optimal Oddball sequences, performing combined stimulation of different matching modes of target stimulation and background stimulation modes on each subject respectively to induce a cognitive electroencephalographic experiment, establishing a plurality of second Oddball sequences, synchronously recording a plurality of second electroencephalographic signals, performing off-line analysis, and acquiring a plurality of second event-related potential data; acquiring the second Oddball sequence which corresponds to the second event-related potential data with the highest identification correct rate, wherein the second Oddball sequence is taken as a second optimal Oddball sequence of each subject; and gradually changing the appearance proportion of target stimulation, the duration and the stimulation interval of each subject in the second optimal Oddball sequence to induce cognitive electroencephalographic signals, acquiring a plurality of event-related potential data respectively, performing off-line analysis, and constructing an effective Oddball sequence scheme. The method is used for the auxiliary identification of the target stimulation, and can accurately position the target stimulation.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
User authentication via evoked potential in electroencephalographic signals
InactiveUS9058473B2Programme controlElectroencephalographyInternet privacyEeg electroencephalography
Techniques are disclosed for authentication and identification of a user by use of an electroencephalographic (EEG) signal. For example, a method for authenticating a user includes the following steps. At least one electroencephalographic response is obtained from a user in accordance with perceptory stimuli presented to the user. The user is authenticated based on the obtained electroencephalographic response. The authenticating step may be based on detection of an event-related potential in the obtained electroencephalographic response. The event-related potential may be a P300 event-related potential. The method may also include the step of enrolling the user prior to authenticating the user. The enrolling step may include a supervised enrollment procedure or an unsupervised enrollment procedure.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
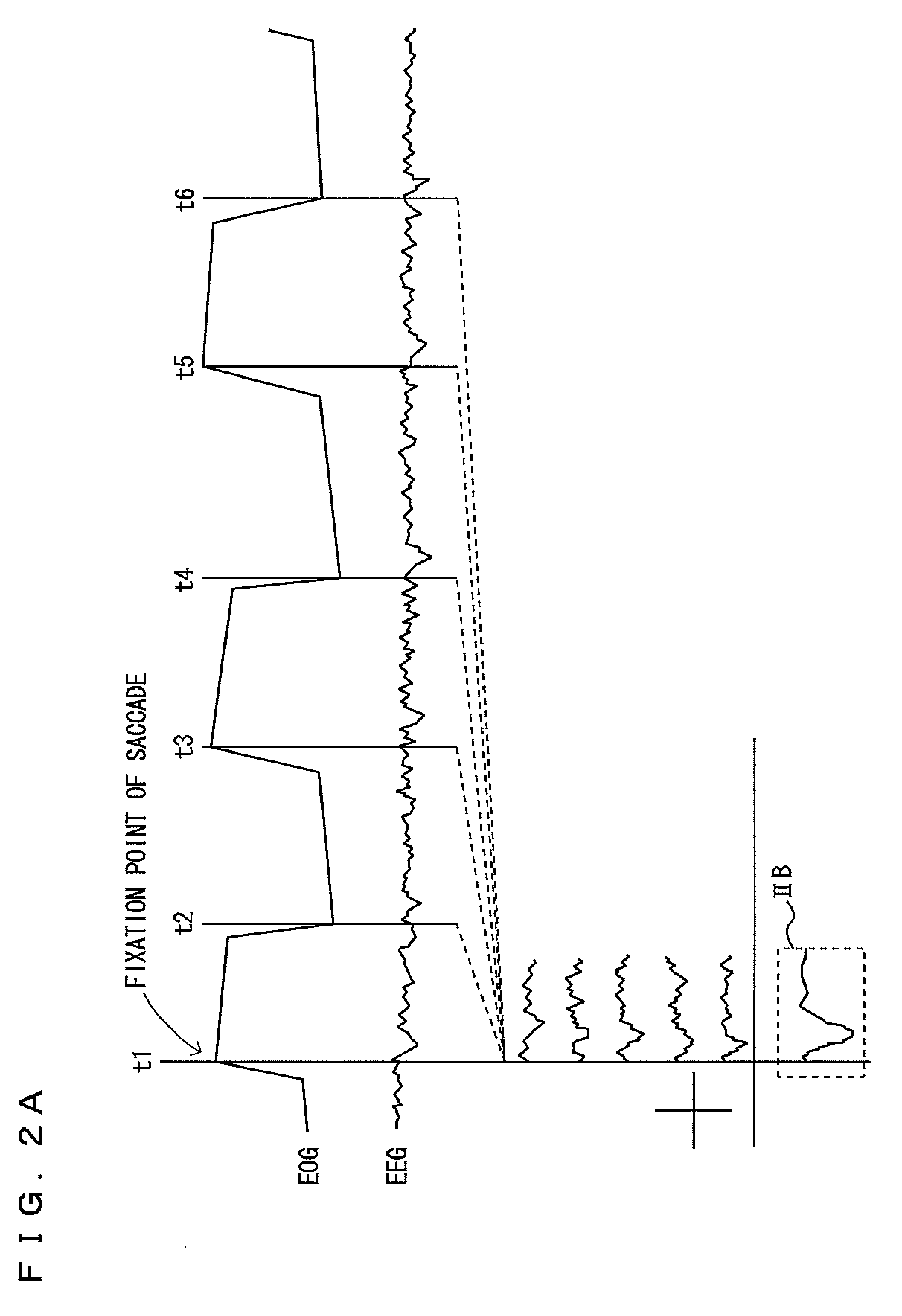
Mental work load detector and motorcycle including the same
InactiveUS20090312665A1ElectroencephalographyElectro-oculographyEeg electroencephalographyEngineering
A mental work load detector arranged to sense the electroencephalogram of a person and estimate a mental work load on the perceptual-motor system and a mental work load on the perceptual-central processing system separately from each other includes a electroencephalogram sensor arranged to sense the electroencephalogram of a rider, an eye fixation-related potential detector arranged to detect an eye fixation-related potential by analyzing the electroencephalogram and to detect a lambda response, an event-related potential measuring device arranged to measure an event-related potential in response to a sound from a speaker and to detect auditory p300, a lambda response comparator arranged to determine whether the lambda response has decreased, an auditory p300 comparator arranged to determine whether the auditory p300 has decreased, and a mental work load determiner arranged to determine that the mental work load on the perceptual-central processing system has increased if the lambda reaction and the auditory p300 has decreased and that the mental work load on the perceptual-central processing system has increased if the auditory p300 has decreased but the lambda response has not decreased.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
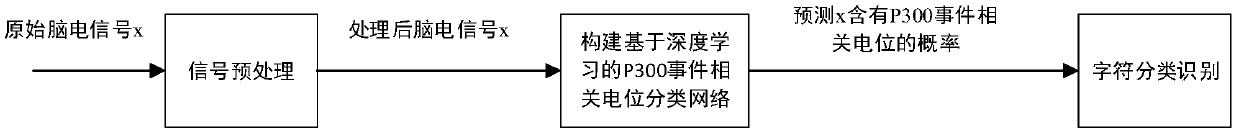
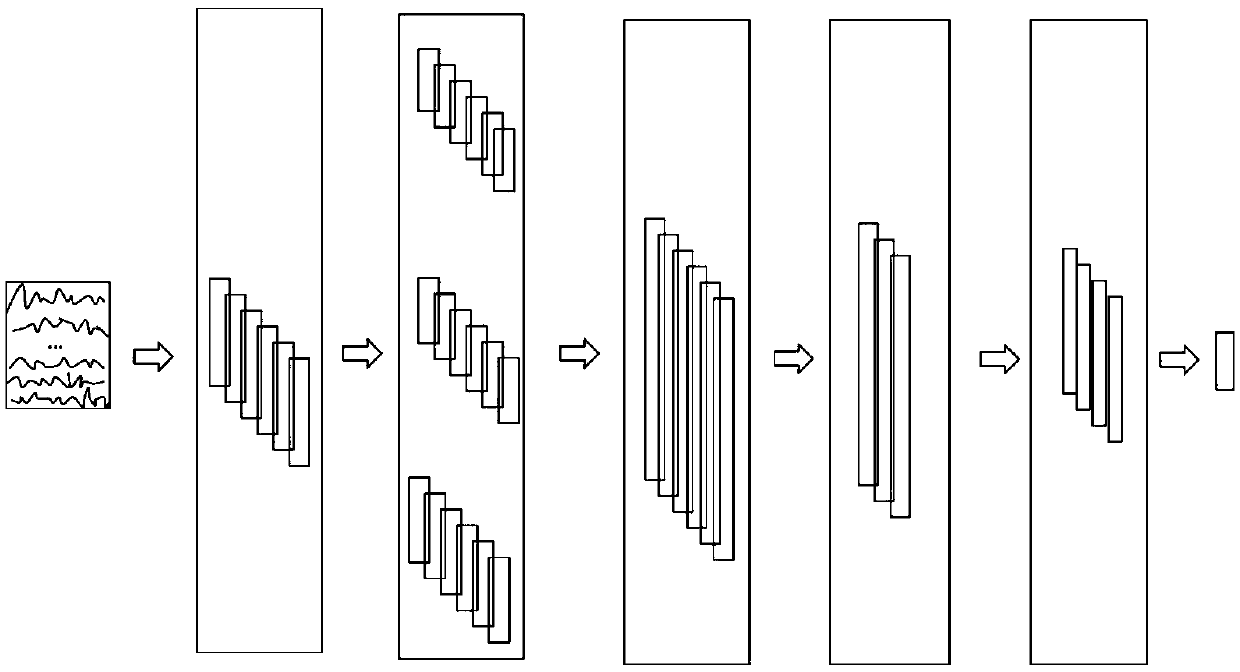
Classification and recognition method for P300 event-related potential based on deep learning
ActiveCN108960182AImprove recognition accuracyReduce the number of experimentsCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesTime domainEeg data
The invention relates to a classification and recognition method for P300 event-related potential based on deep learning, and belongs to the technical field of medical and physiological signal detection and processing analysis. According to the invention, a Butterworth filter is adopted to successively perform high-pass filtering and low-pass filtering on original signals to remove artifacts and power frequency interference; the data is amplified by using a one-time superposition averaging technique, normalization and time domain truncation are performed on EEG signals, and corresponding supervisory signals are formulated according to the signal types; the EEG data is divided into a training set and a verification set after data preprocessing, a deep learning network capable of classifyingand recognizing the P300 event-related potential is constructed, and the feature extraction ability of the network is improved; the probability that an input signal contains the P300 event-related potential is finally predicted through the trained network; and finally, a target character is predicted according to an experimental paradigm and the probability value outputted by the network. The experiment shows that the algorithm is good in performance and can also obtain good character recognition accuracy under the condition of reducing the number of experiments.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Electroencephalogram interface system, electroencephalogram interface apparatus, method, and computer program
ActiveUS8466875B2Valid choiceCathode-ray tube indicatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringAngular velocityComputer science
An electroencephalogram interface system includes: sections for measuring an electroencephalogram and an eye movement; an output section for presenting on a screen an option related to a device operation; a highlight determination section for, if a predetermined time has elapsed since a rotational angular velocity of the eye movement becomes equal to or less than a threshold value, identifying a region of the screen in which the user is fixing one's gaze based on the eye movement, and determining an option to be highlighted; an interface section for highlighting the determined option, and determining an operation of the device based on an event-related potential in the signal based on the timing of highlighting the option; and a timing adjustment section for adjusting a timing of beginning highlighting based on the eye movement after a process of displaying the option on the screen is begun and until the option is displayed on the screen.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Information processing system, information processing apparatus, and method
ActiveUS20090147148A1Input/output for user-computer interactionElectroencephalographyInformation processingPeak value
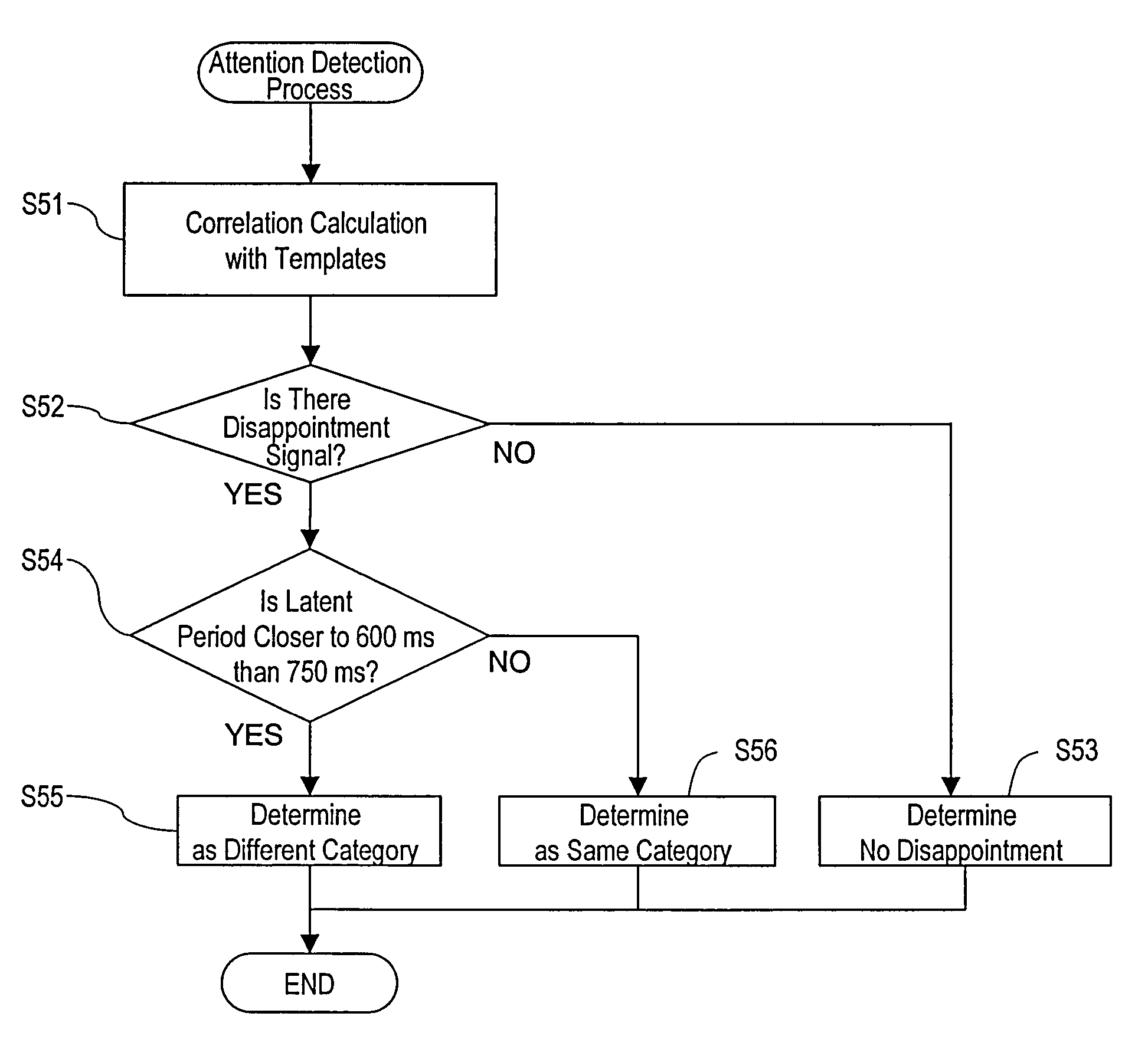
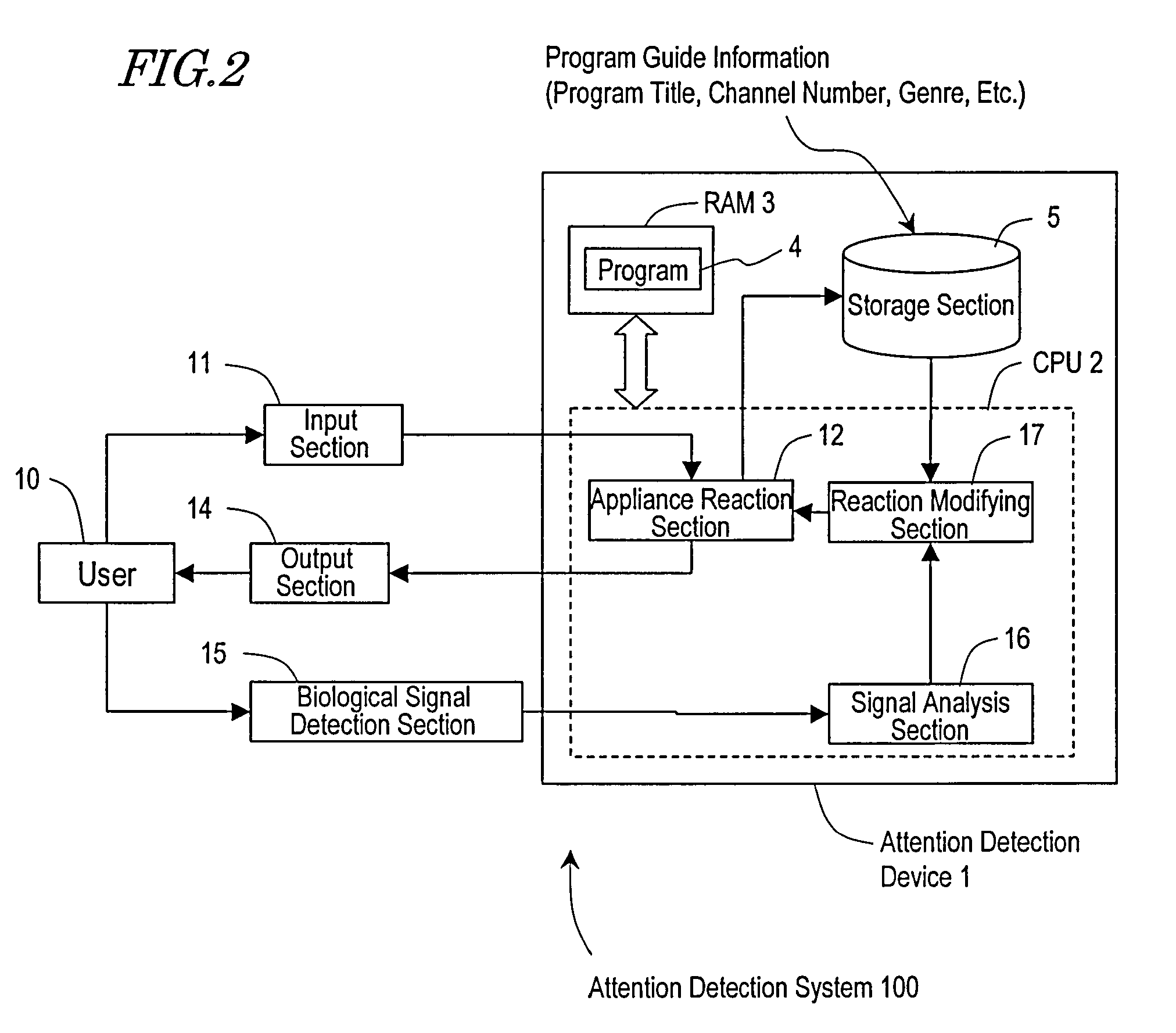
There is provided a technique which, in the case where the operation has not occurred in a manner as expected by the user, determines from which standpoint the operation was not as expected, and makes a response that is closer to the expectation.An information processing system according to the present invention includes: a reaction section for executing a first process based on a request from a user; an output section for outputting a result of a process; a signal detection section for measuring a signal concerning an event-related potential of electroencephalograms of the user; an analysis section for identifying a positive peak in the event-related potential and determining whether an elapsed time since the result is output and until the peak appears is closer to a first reference time or a second reference time; and a reaction modifying section for determining a second process in accordance with the determination result. This determination result indicates a degree of disappointment of the user, and the second process is to be determined in accordance with the degree. By the reaction section executing the second process, an operation is realized which conforms to the user's expectation even if the operation has not occurred in a manner as expected by the user.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
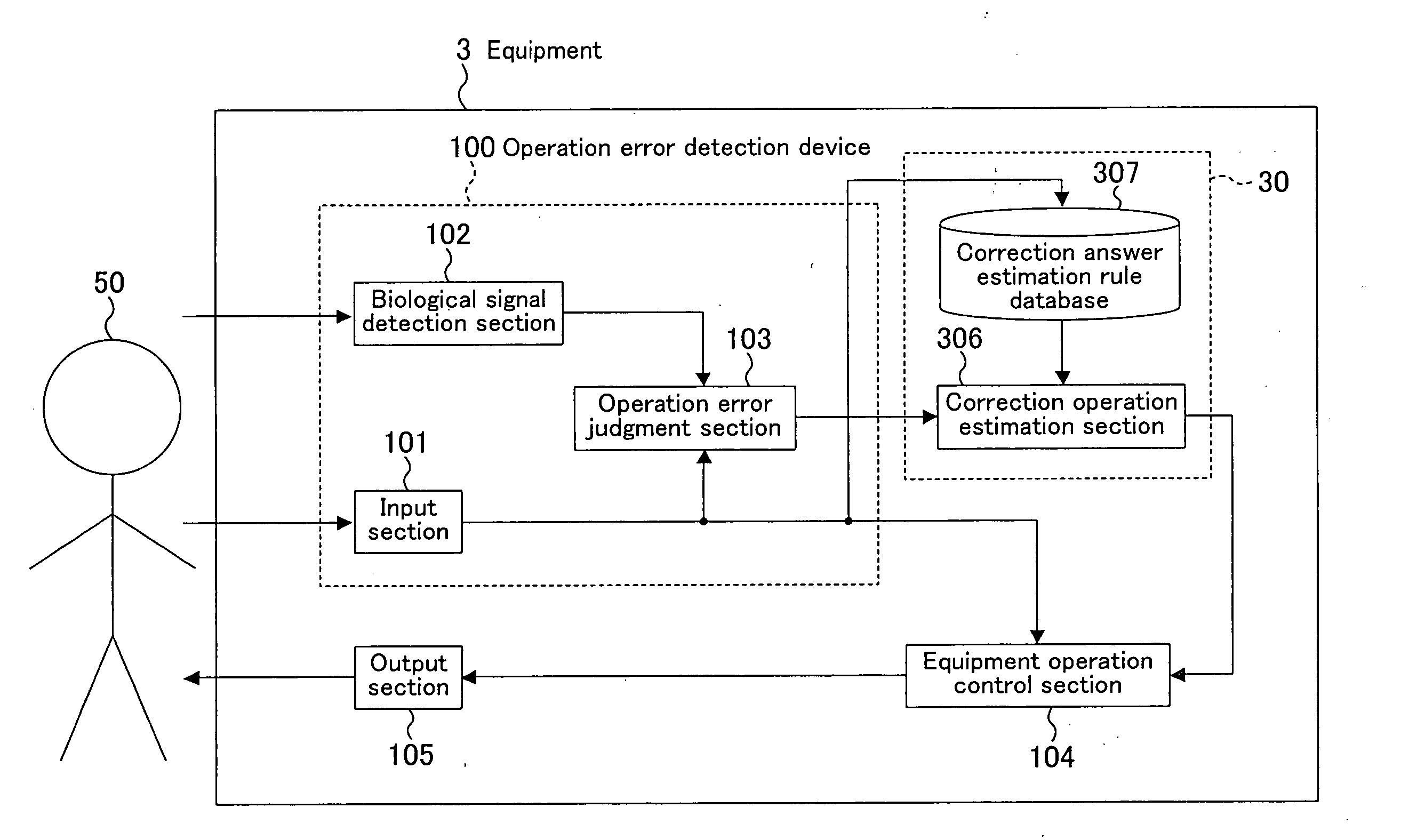
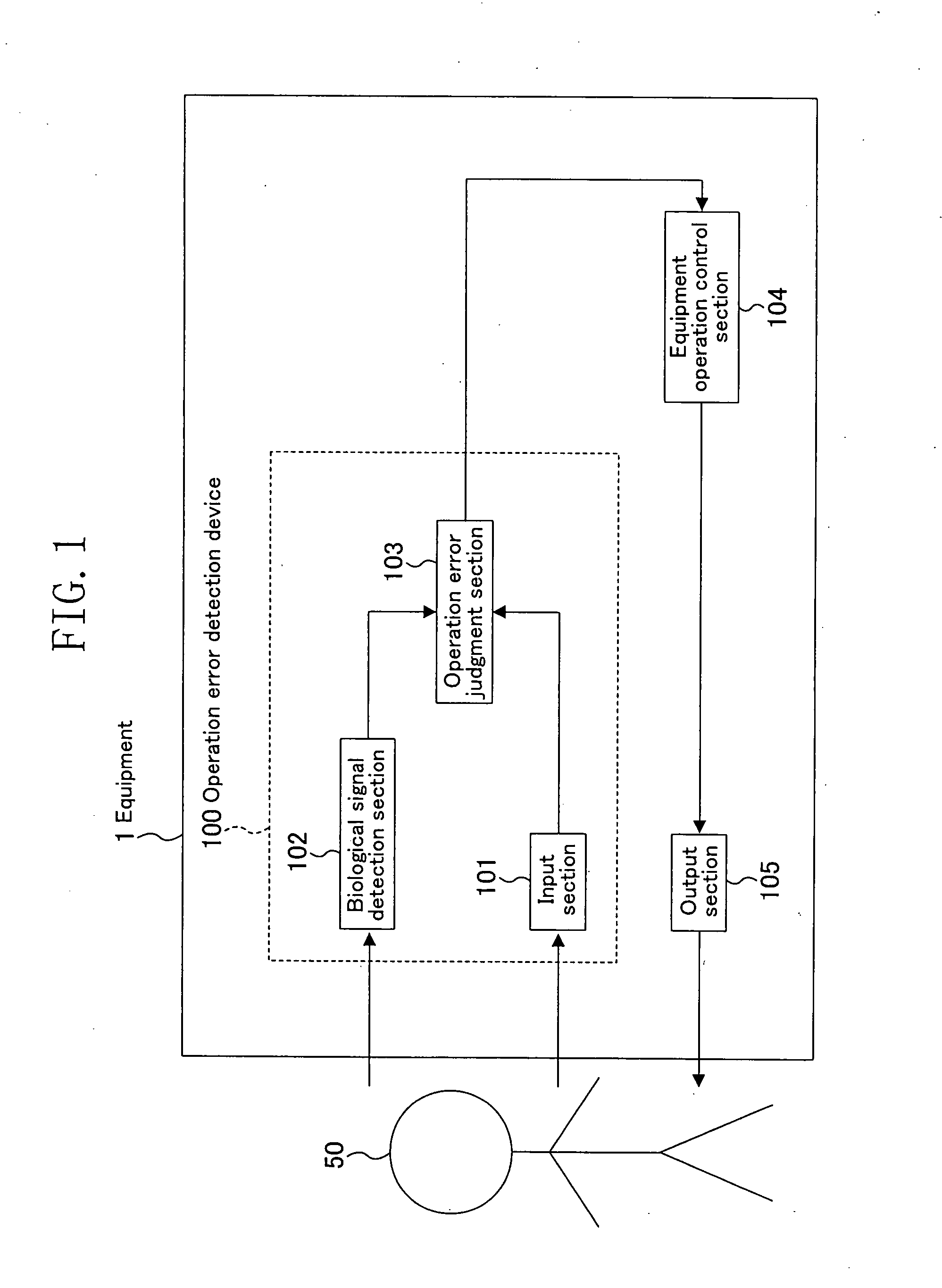
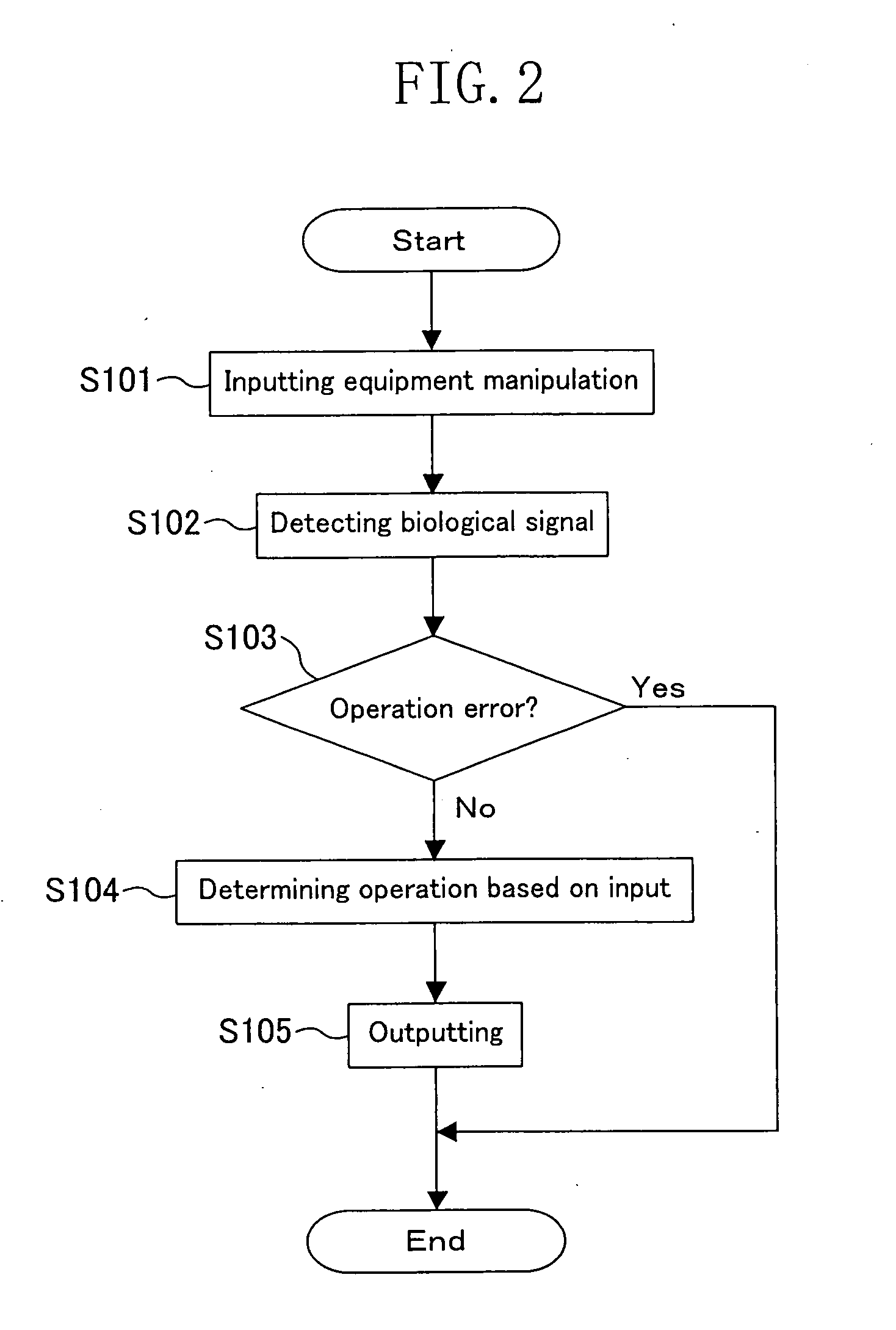
Operation Error Detection Device, Equipment Including the Device, Operation Error Detection Method and Equipment Evaluation Method
ActiveUS20070266273A1Improve usabilityElectroencephalographyError detection/correctionComputer scienceEvent-related potential
An input section (101) receives a manipulation input of a user (50). A biological signal detection section (102) measures an event-related potential of electroencephalogram of the user (50). An operation error judgment section (103) judges using the event-related potential of the electroencephalogram of the user (50) at around 300 ms from a timing when the input section (101) receives the manipulation input as a starting point whether or not the manipulation input is due to an operation error of the user. An equipment operation control section (104) determines an operation of an equipment (1) based on a result of judgment by the operation error judgment section (103).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
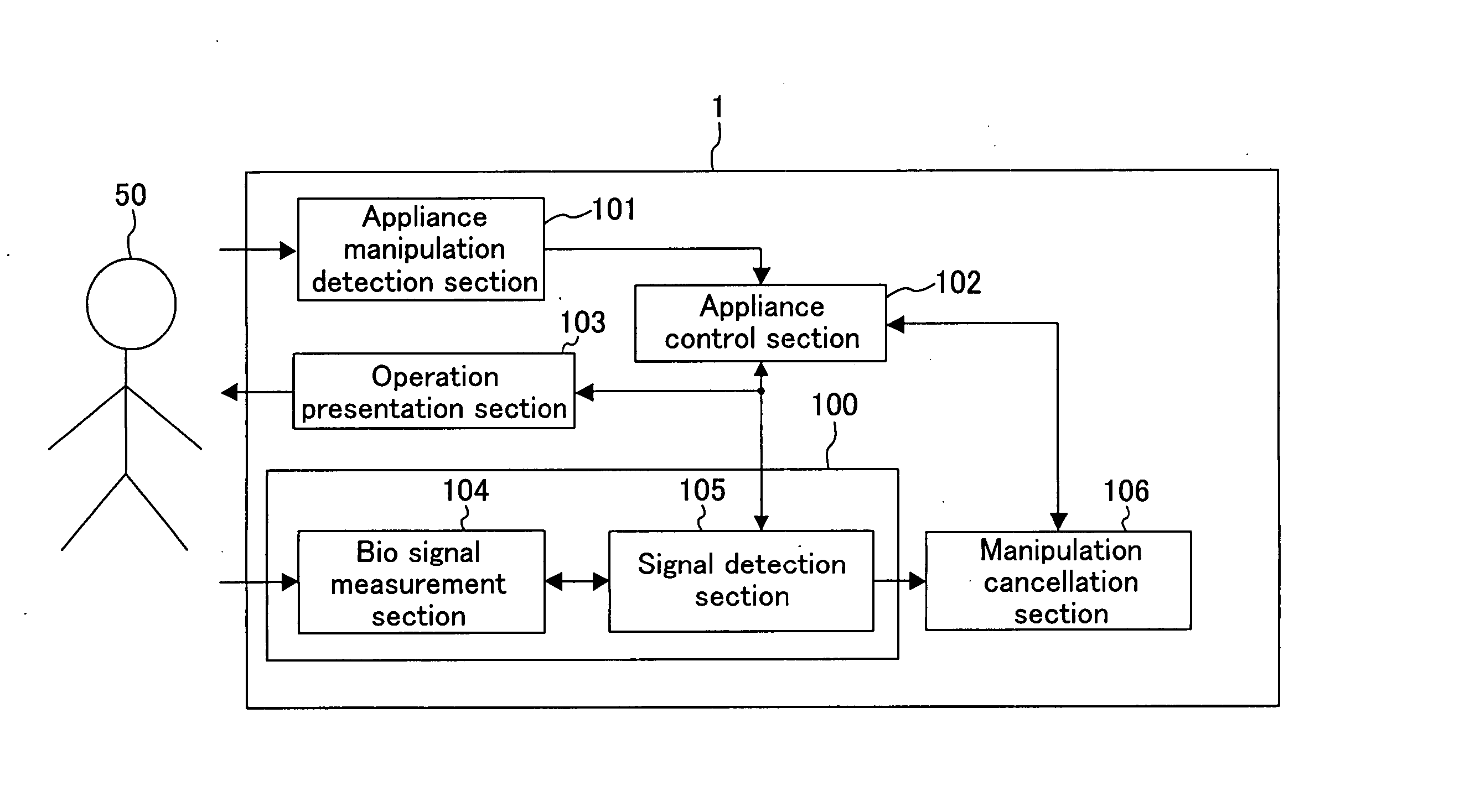
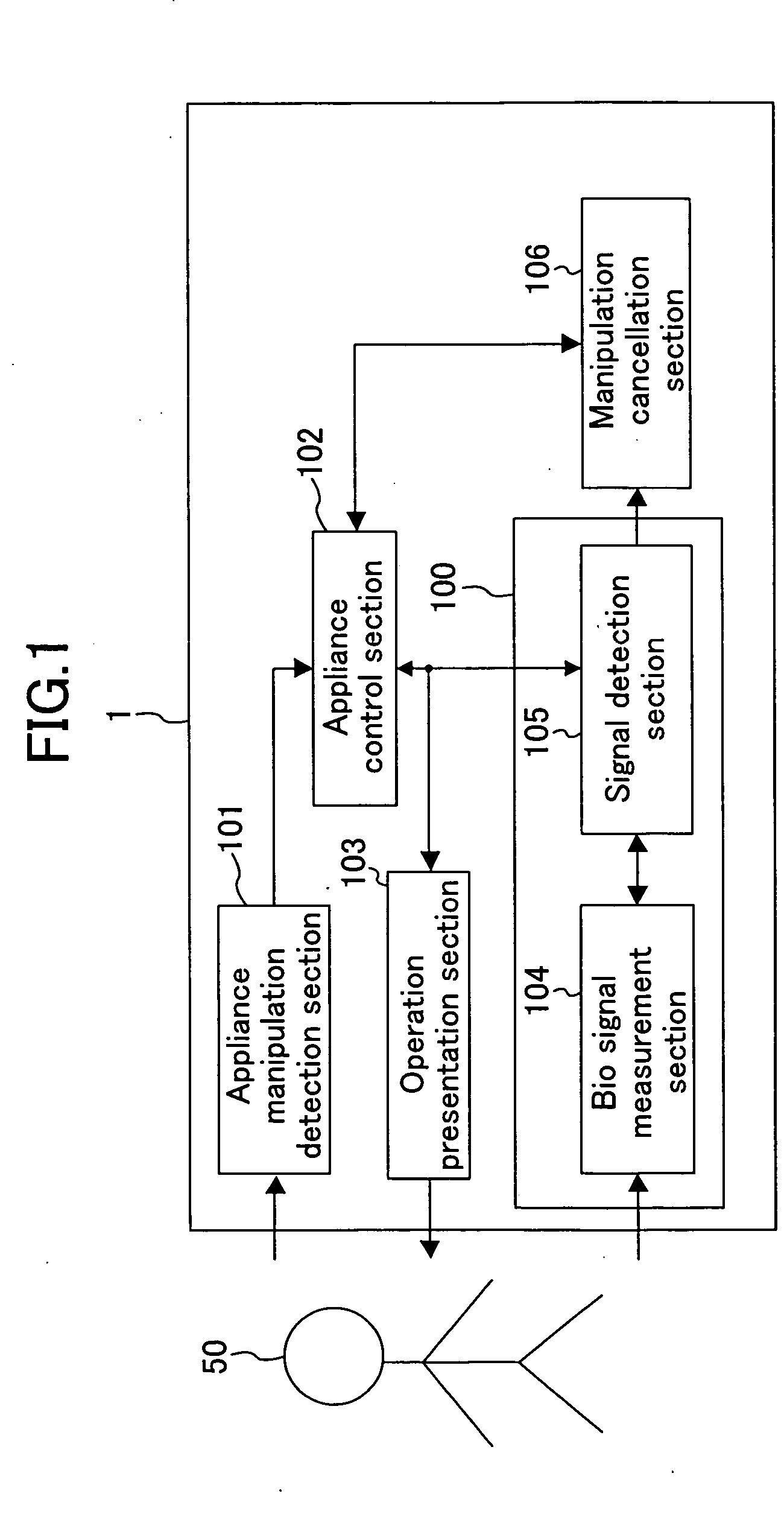
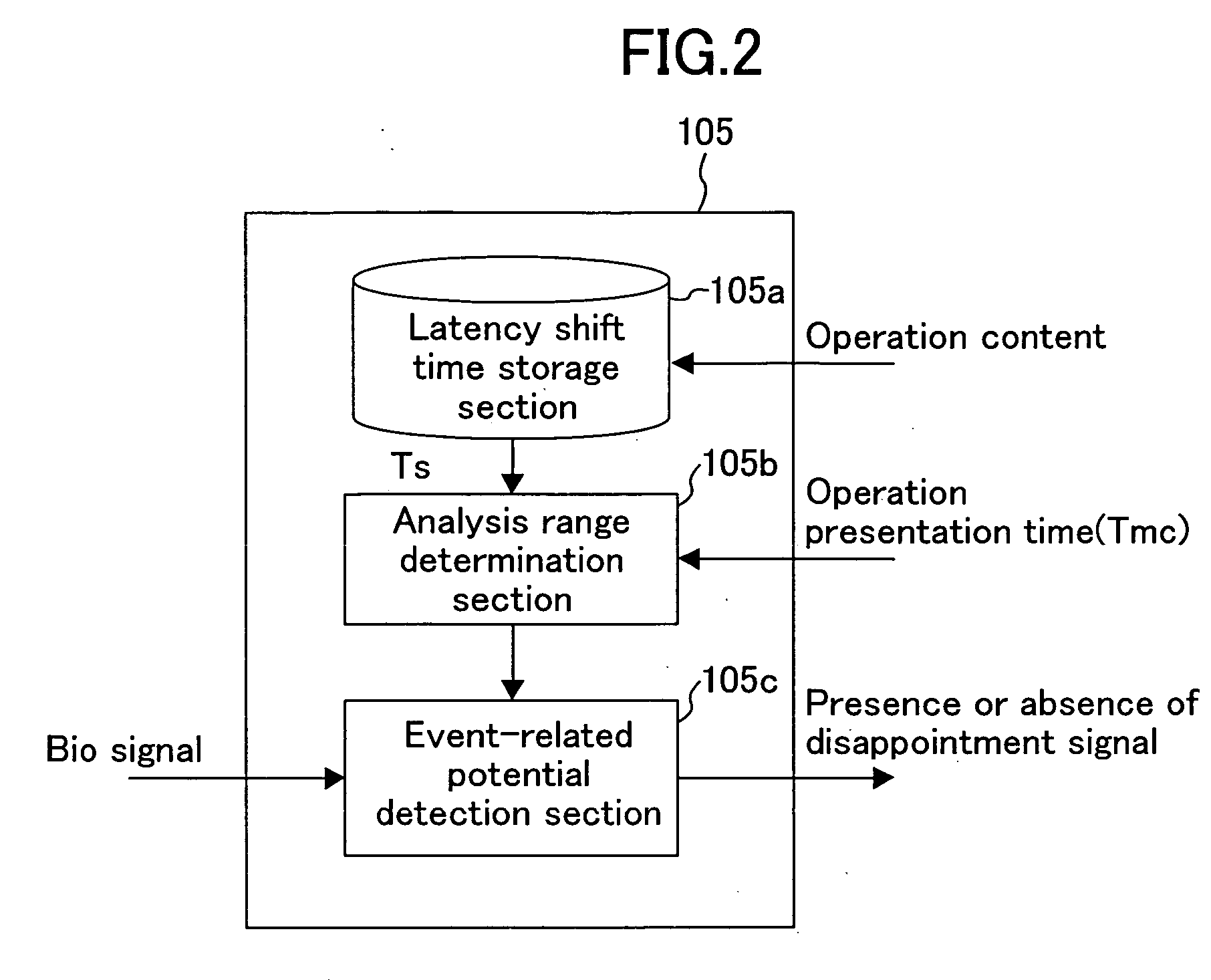
Biological signal utilizing appliance and method for controlling the same
ActiveUS20060114222A1Improve convenienceEliminate needCathode-ray tube indicatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringEngineeringShift time
In a biological signal utilizing appliance, an appliance control section controls the appliance in accordance with user's manipulation. At that time, an operation content is presented to a user through an operation presentation section. A biological signal detection section measures user's biological signal and detects from the biological signal the presence or absence of an event-related potential at the time point when time obtained by adding a predetermined shift time of approximately 150 ms to 600 ms elapses after a timing, as a starting point, when the operation content is presented. Upon detection of the event-related potential, a manipulation cancellation section instructs the appliance control section to cancel the presented operation content.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
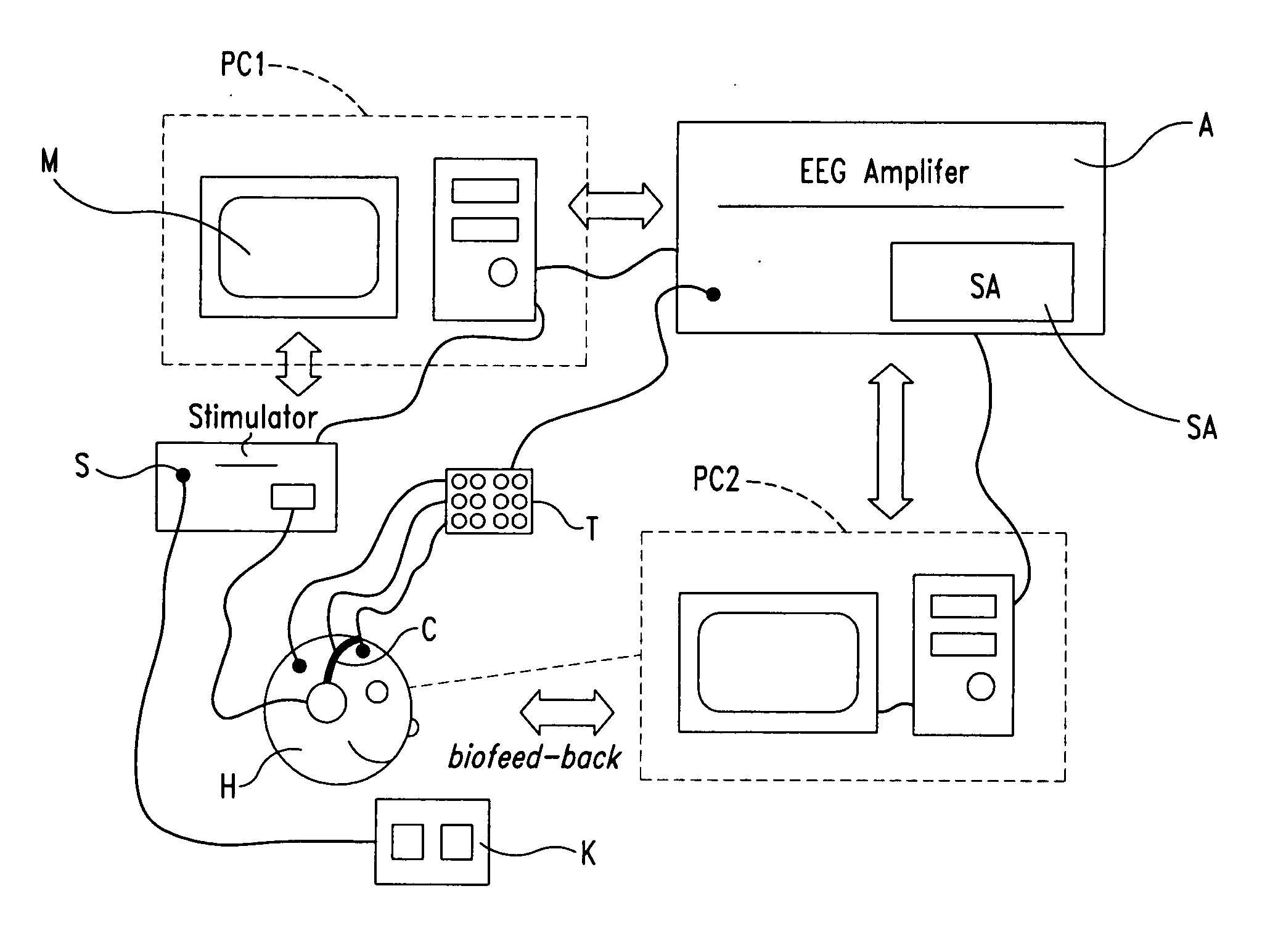
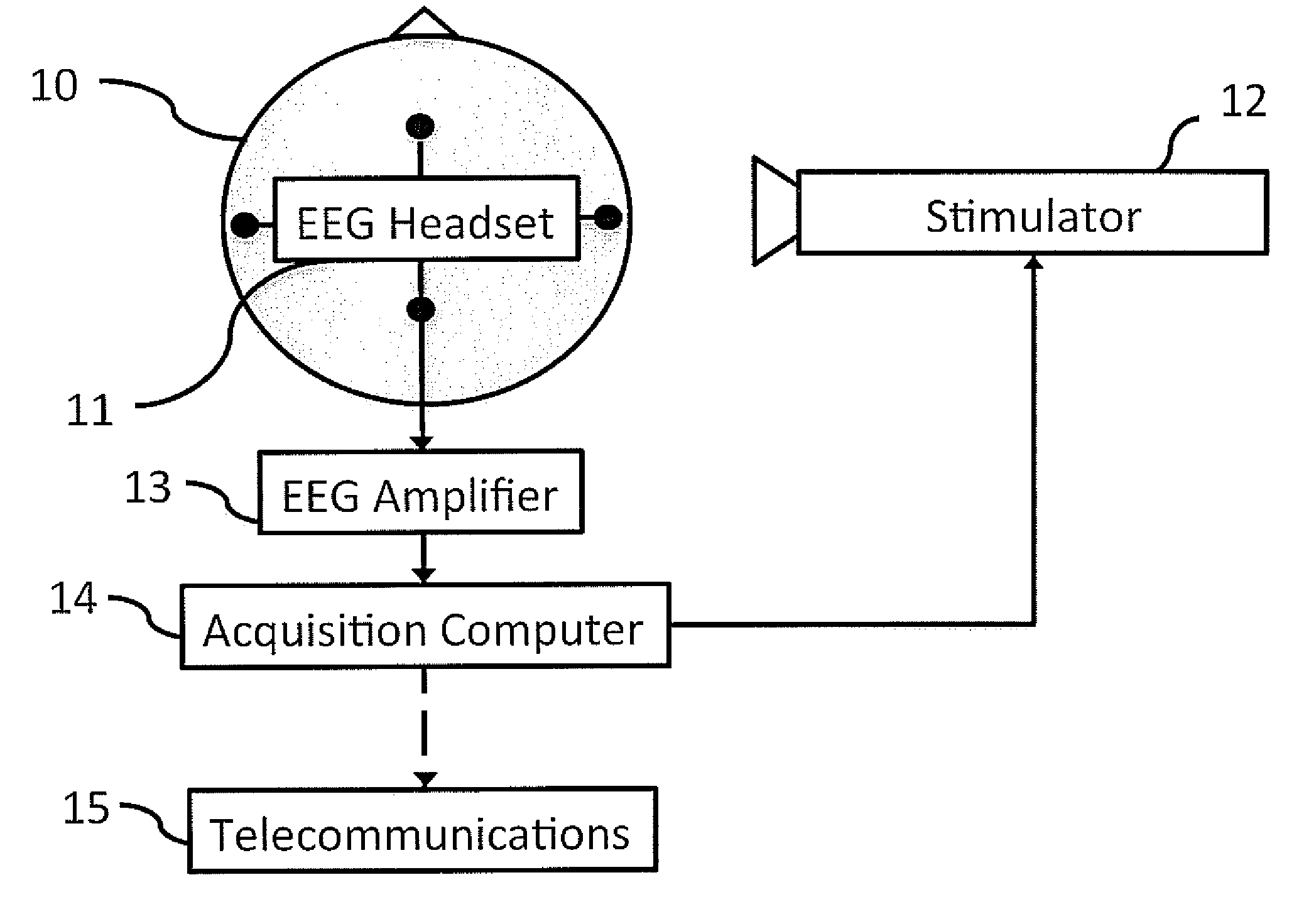
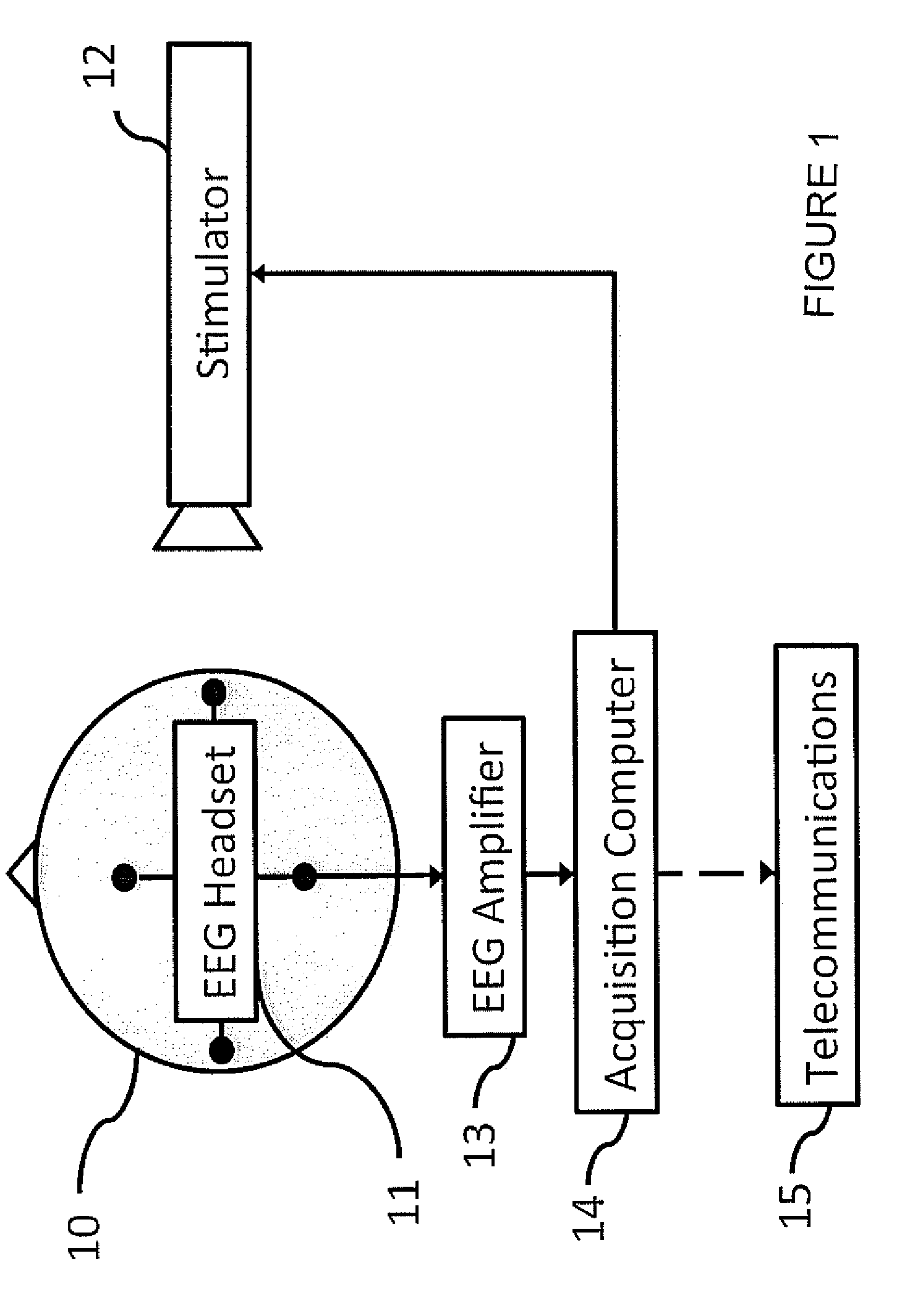
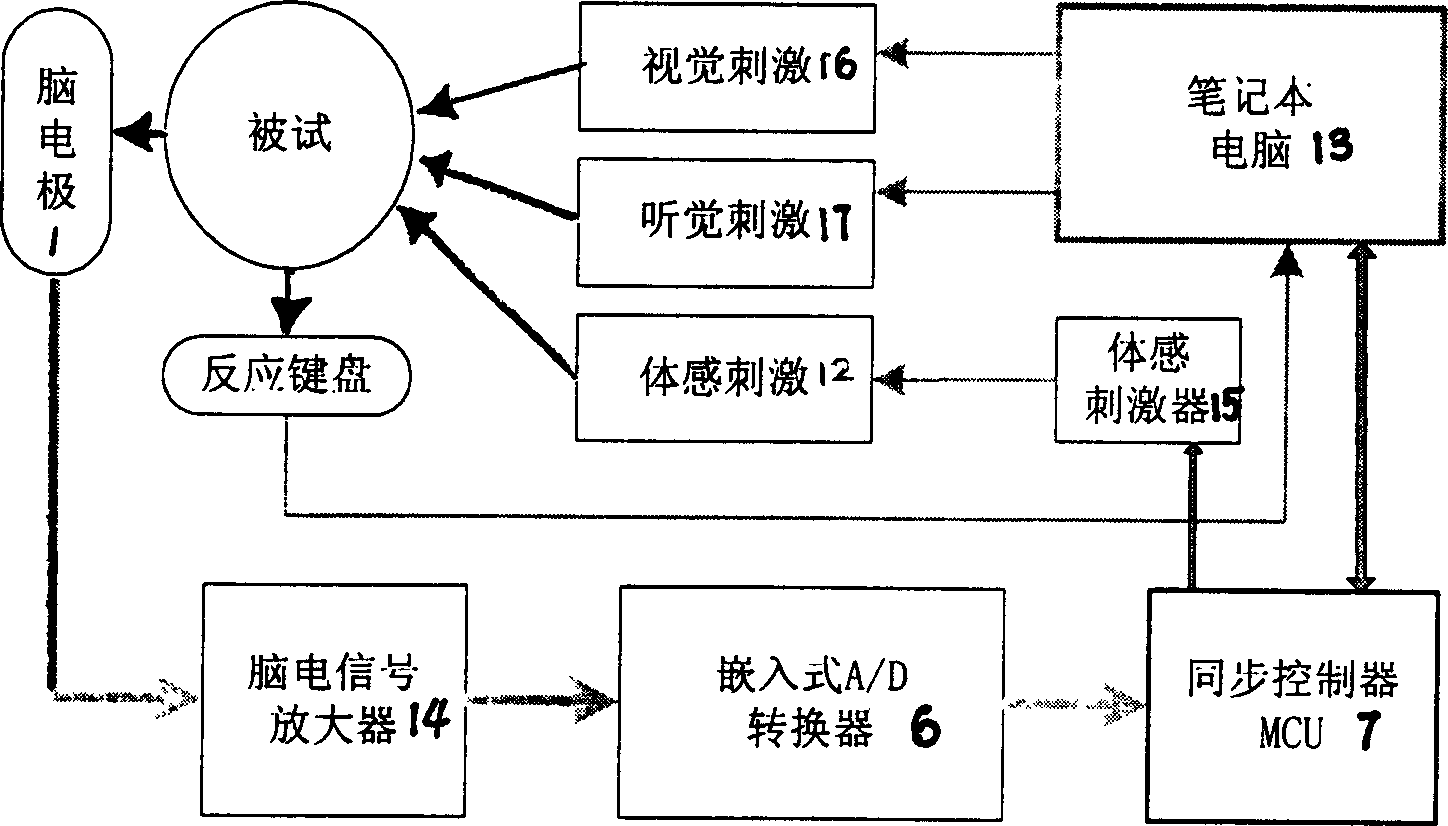
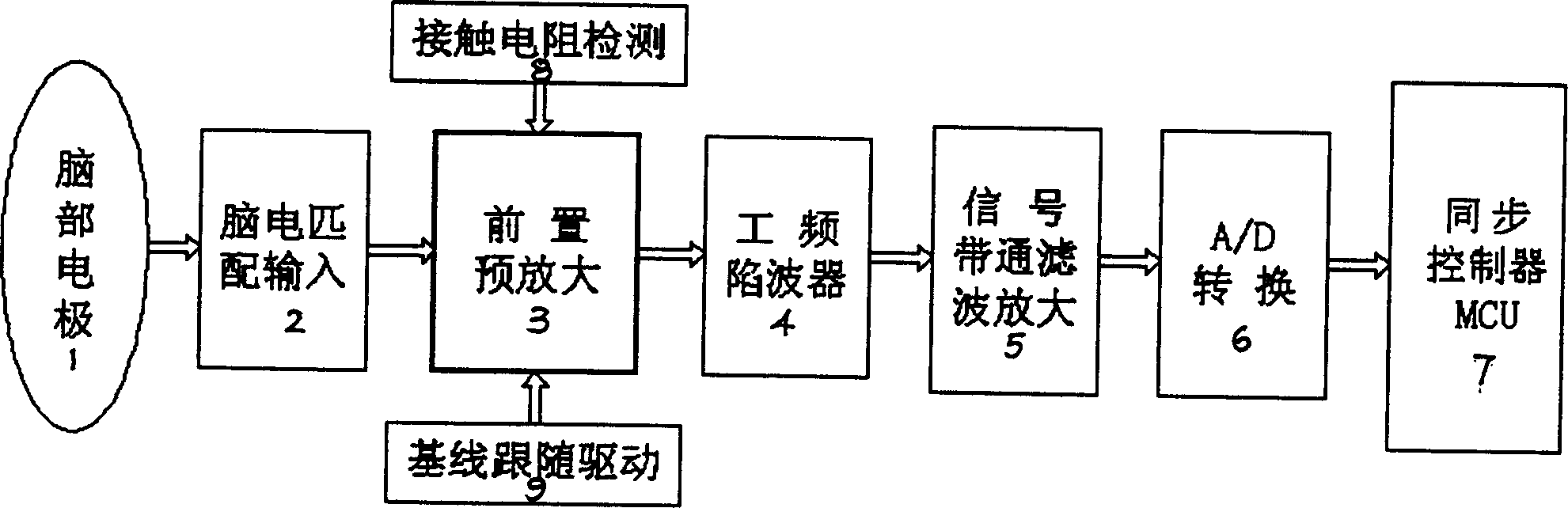
Portable event related potentiometer
InactiveCN1778272AHighly integratedLow power designDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSynchronous controlComputer module
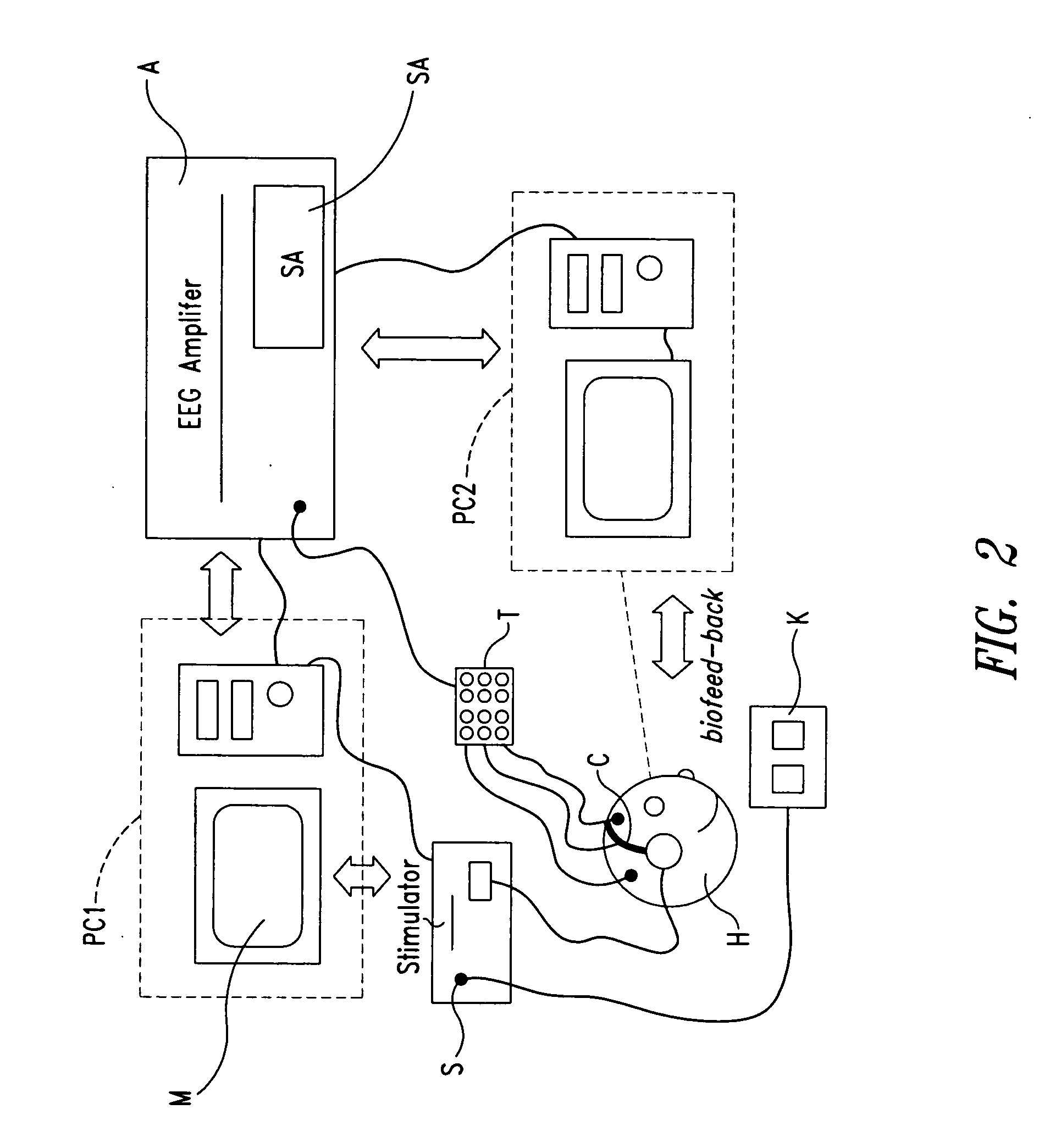
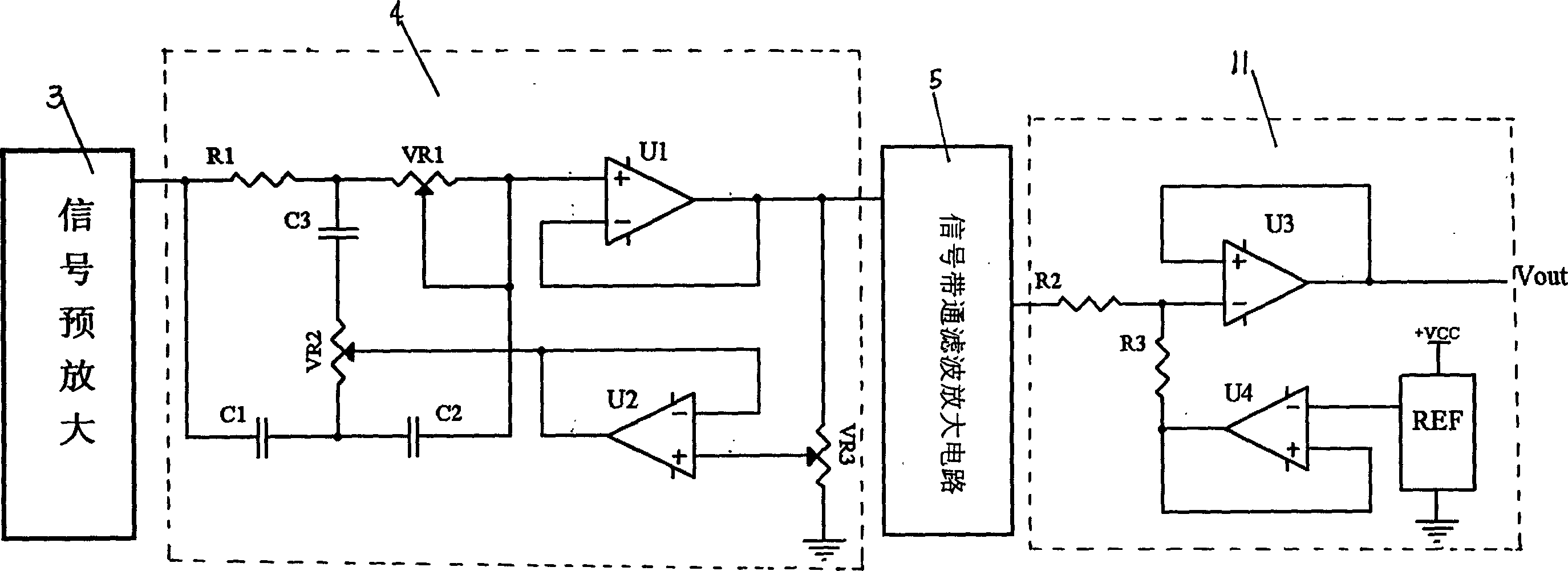
A portable event associated electrocortical potential instrument for taking the event associated encephaloelectric ERP signals and analyzing them to obtain the actual reaction of the event in brain is composed of cerebral electrodes, encephaloelectric signal amplifier, 16 A / D converters, synchronous controller MCU for reading the data of 16í‡8 channels, notebook computer, and body stimulator.
Owner:INST OF PSYCHOLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com