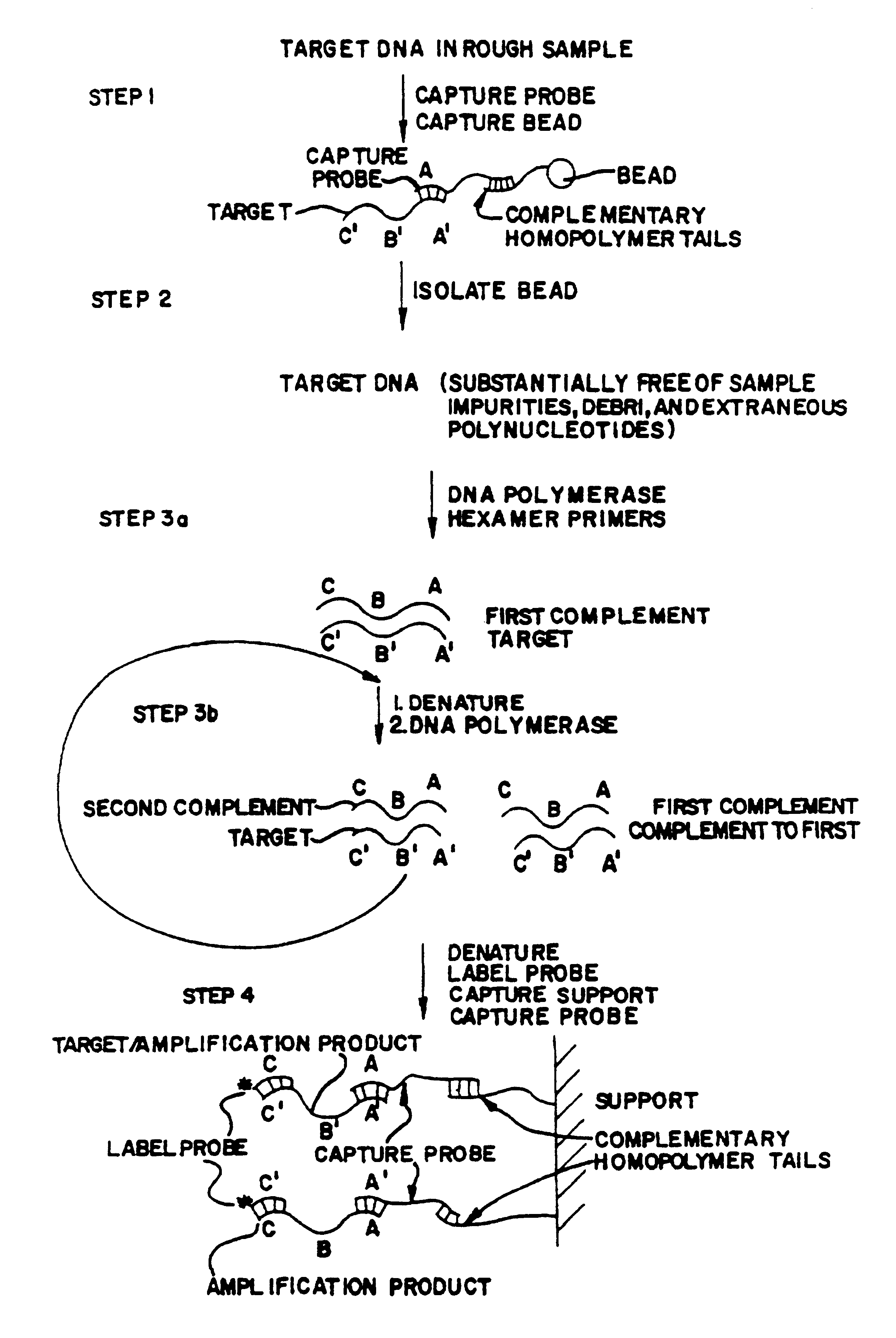
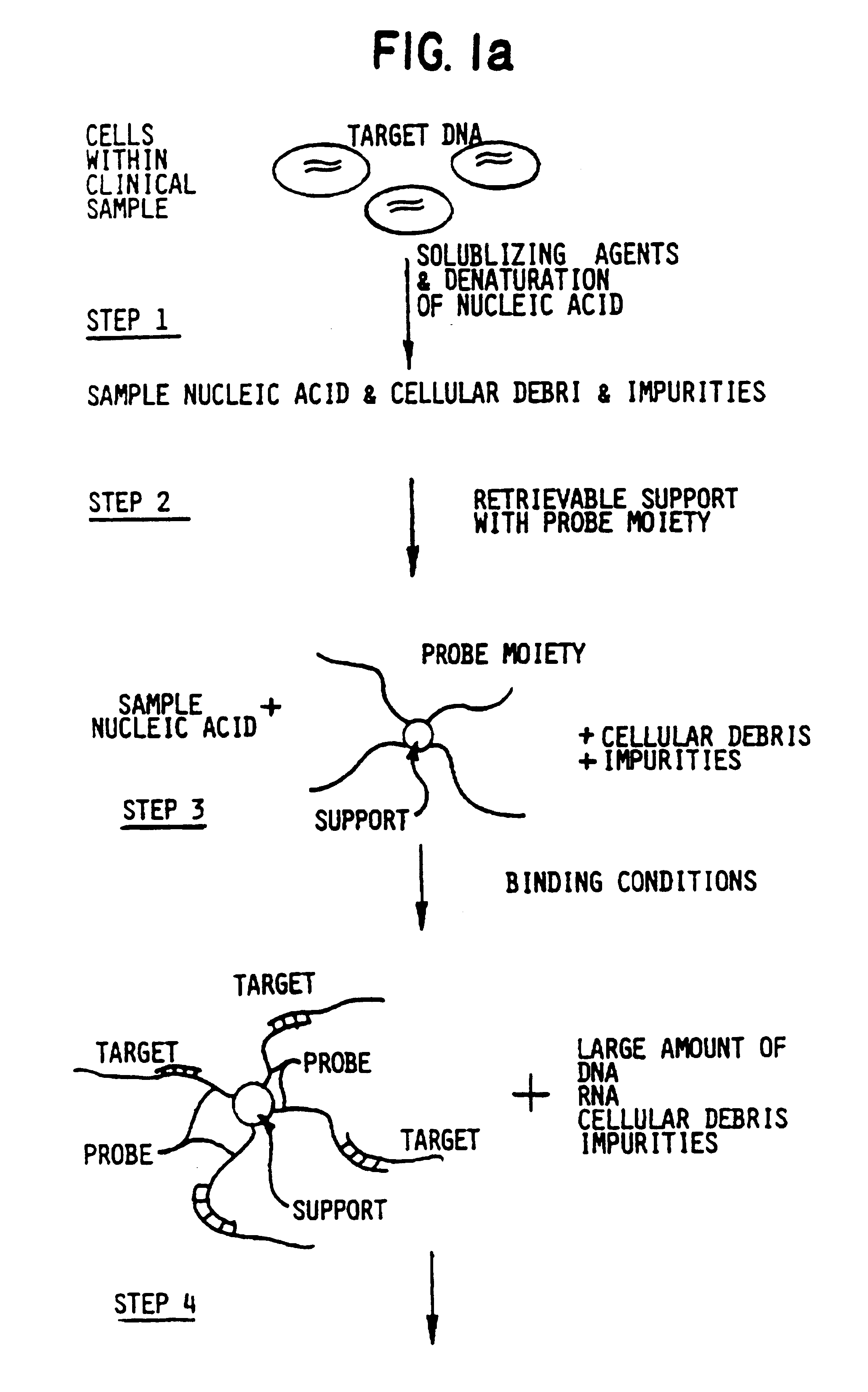
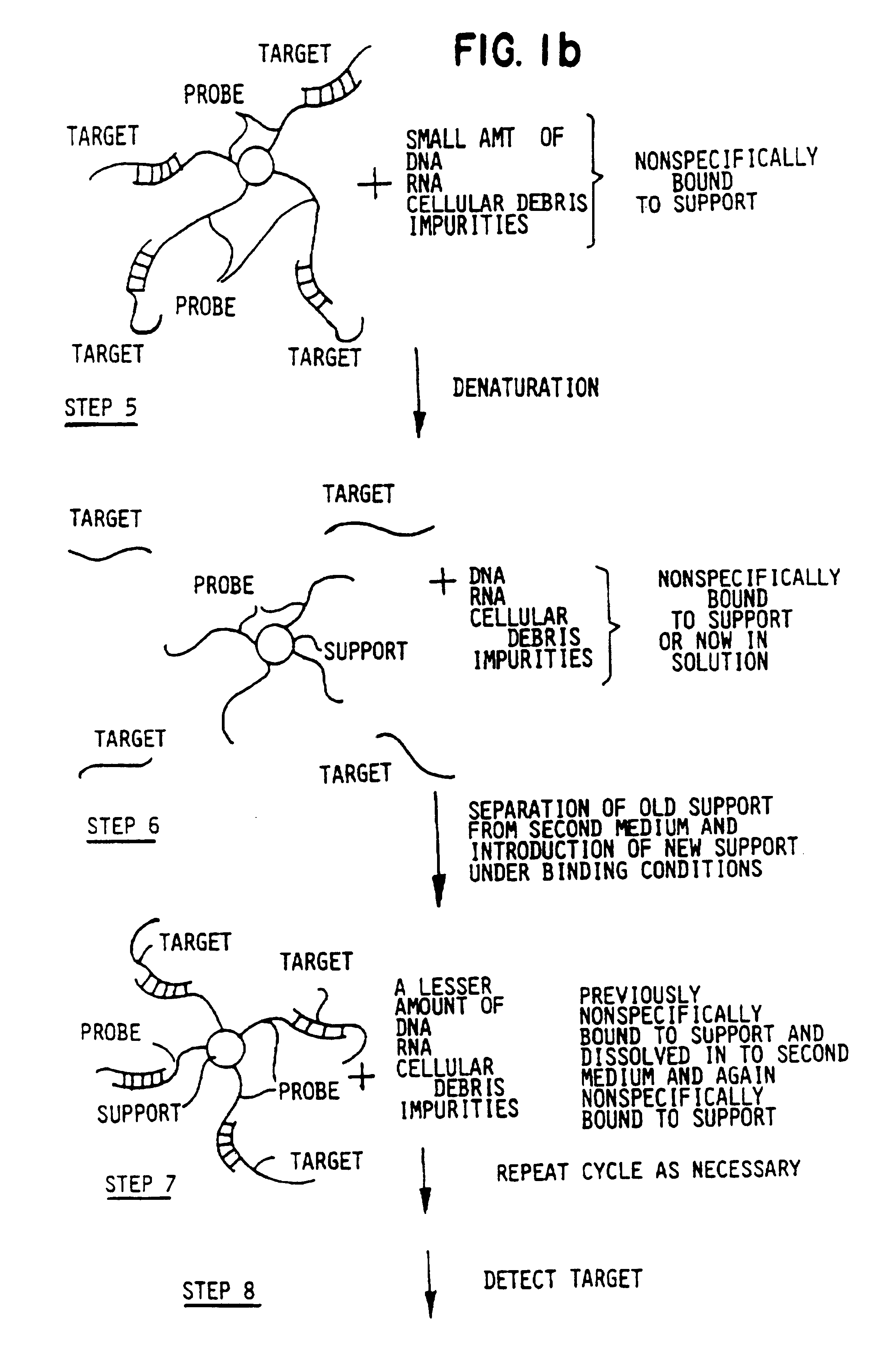
Target and background capture methods with amplification for affinity assays
a background capture and affinity assay technology, applied in the field of affinity assay target and background capture methods with affinity assay, can solve the problems of non-specific binding of labeled probes to supports, background noise that reduces the sensitivity of an assay, and non-specific binding of probes, etc., to achieve the effect of removing background nois
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Target Capture and Assay Using Magnetic Bead
A target capture assay was performed with two probes and a magnetic bead retrievable support. The target included the Xba 1-Hind III fragment of the enterotoxigenic gene elt Al. A first probe included an A532 thirtimer oligonucleotide probe which was tailed with 130 unlabeled dA residues capable fo binding to the dT.sub.10 residues of the magnetic beads support. A second probe included an A483 thirtimer oligonucleotide probe capable of binding to the same target 20 nucleotides downstream from the site of hybridization of the first probe. The second probe was labeled by tailing the thirtimer oligonucleotide with .sup.32 P-dCTP and .sup.32 P-dGTP to a specific radioactivity of 10.sup.10 DPM / microgram.
The tailed first probe and the labeled second probe were incubated at 65.degree. C. for 15 minutes in 1.4M sodium chloride with various quantities of heat denatured 475 mer restriction fragments of the tox gene. As a nonspecific binding backgrou...
example 2
The present example features target capture and background capture. Target and background capture was effected using an unlabeled first target capture probe, A532 as described in target capture, and a second labeled background capture probe A726.
First, 160 ng / ml dA-tailed A532 and 40 ng / ml .sup.32 P-labeled probe A726 were combined to form a probe mix. The probe mix was added to 5 .mu.l of bacterial extract containing various amounts of enterotoxigenic gene. The extract-probe mix was incubated at 22.degree. C. for 15 minutes.
After a fifteen minute hybridization period, the samples were diluted with ten volumes of prehybridization buffer incubated for five minutes with dT-derived magnetic beads in 0.7 ml of 0.75M phosphate buffer (pH 6.8) to effect target capture. The beads were magnetically immobilized and washed extensively. The target-first and second probe complex was eluted from the first support as previously described and the first solid support removed.
Next, the eluate contai...
example 3
The following example features nonradioactive label moieties and multiple rounds of target capture from spiked biological media. The spiked biological media resembles samples which would be obtained clinically in a medical setting.
Cell extracts of enterotoxigenic E. coli and wild type E. coli were prepared as previously described. To measure the sensitivity of the detection of tox genes in an environment analogous to a clinical setting, extract containing toxigenic bacteria was diluted with the extract containing the wild type E. coli as previously described.
The following materials were obtained from anonymous donors: human stool sample, cow's milk, human saliva, human phlegm, human whole blood, human serum, human urine and human semen. Clinical-type samples were solubilized over a time period of ten minutes. The stool sample, due to its solid nature, was solubilized in a solution of 5M GuSCN, 0.3M Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), 0.1M EDTA (pH 7), 1% betamercaptoethanol. Following solubilization...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com