Patents
Literature
515results about "Synchronisation by photonic/optical means" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
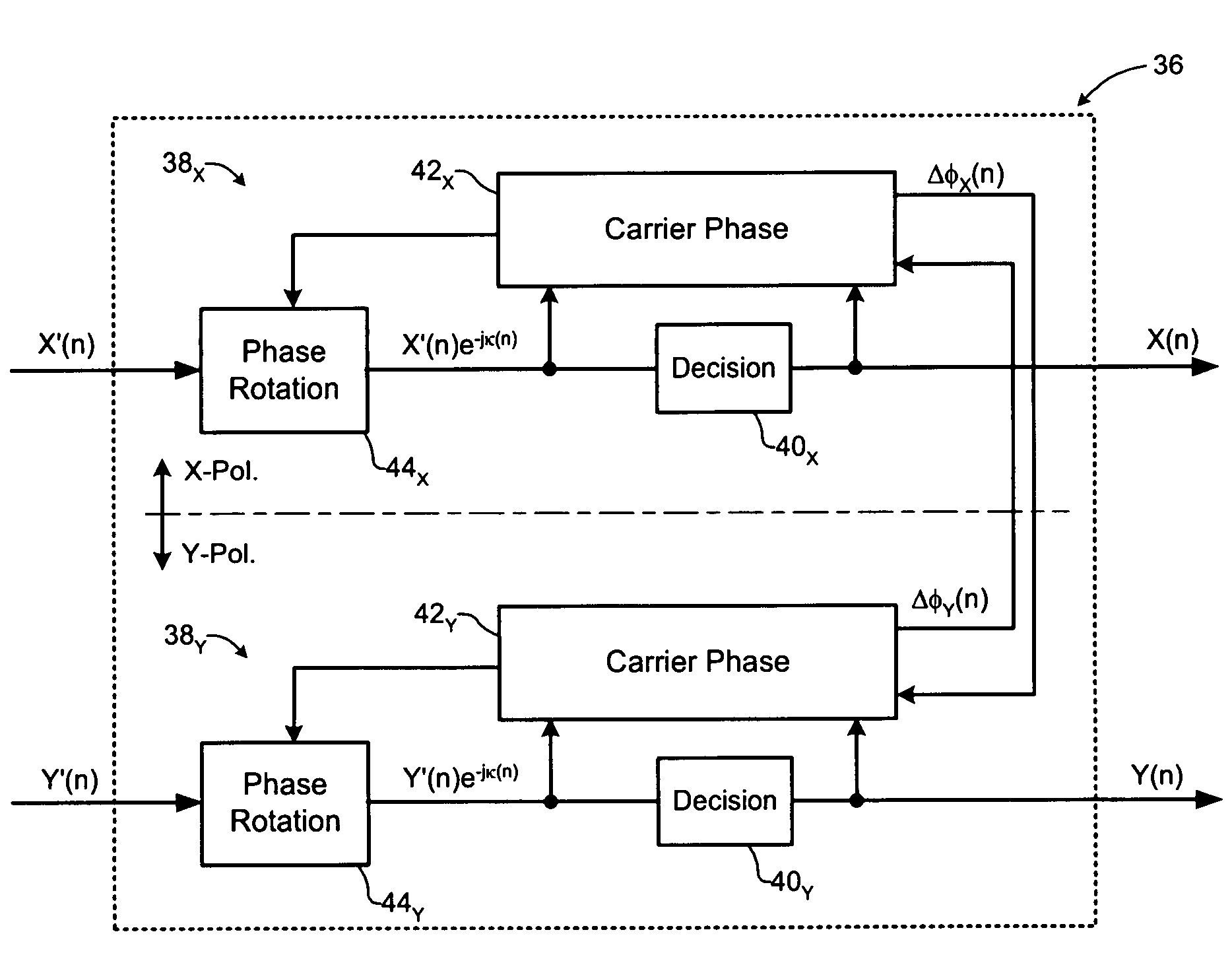
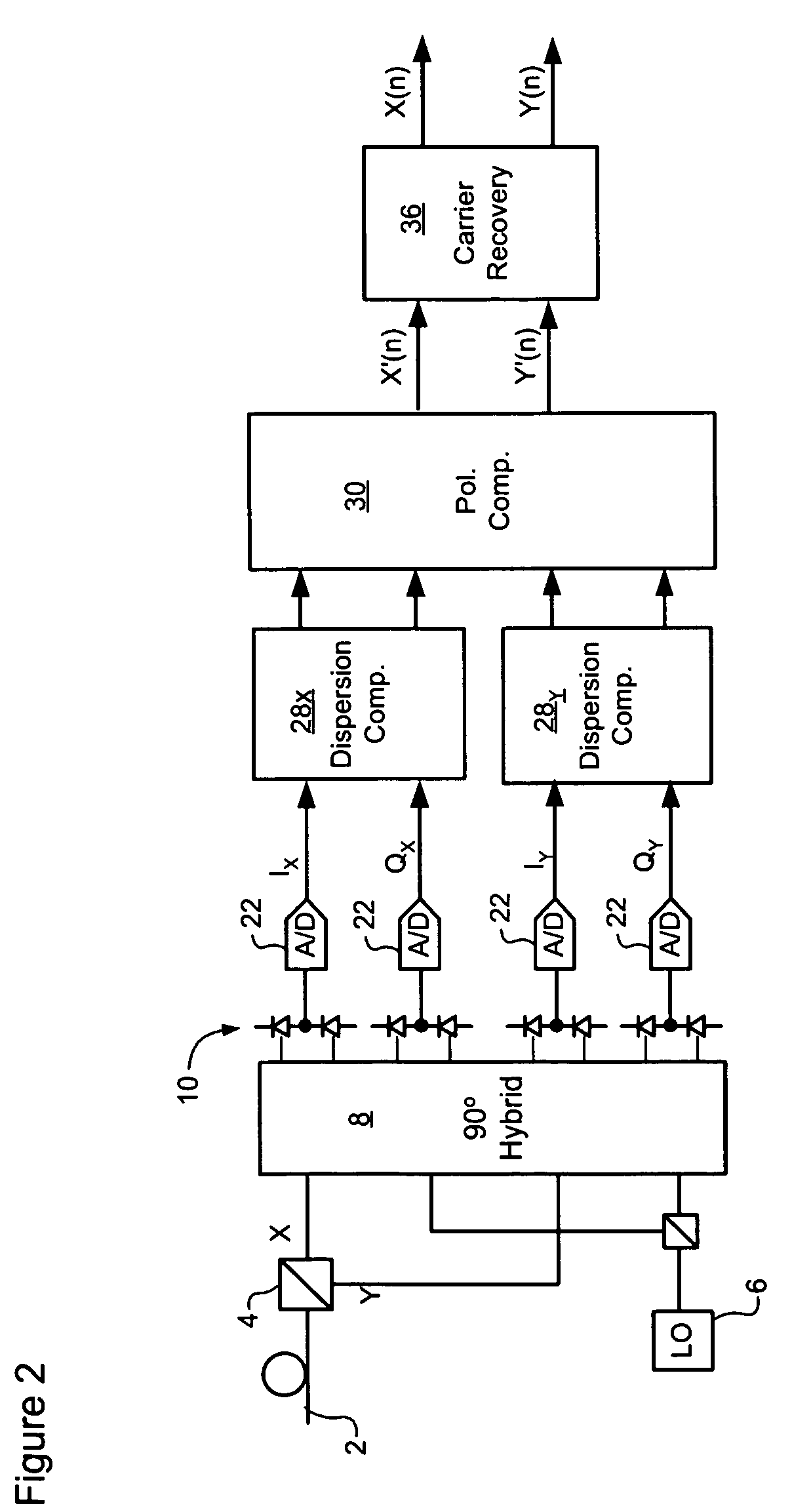
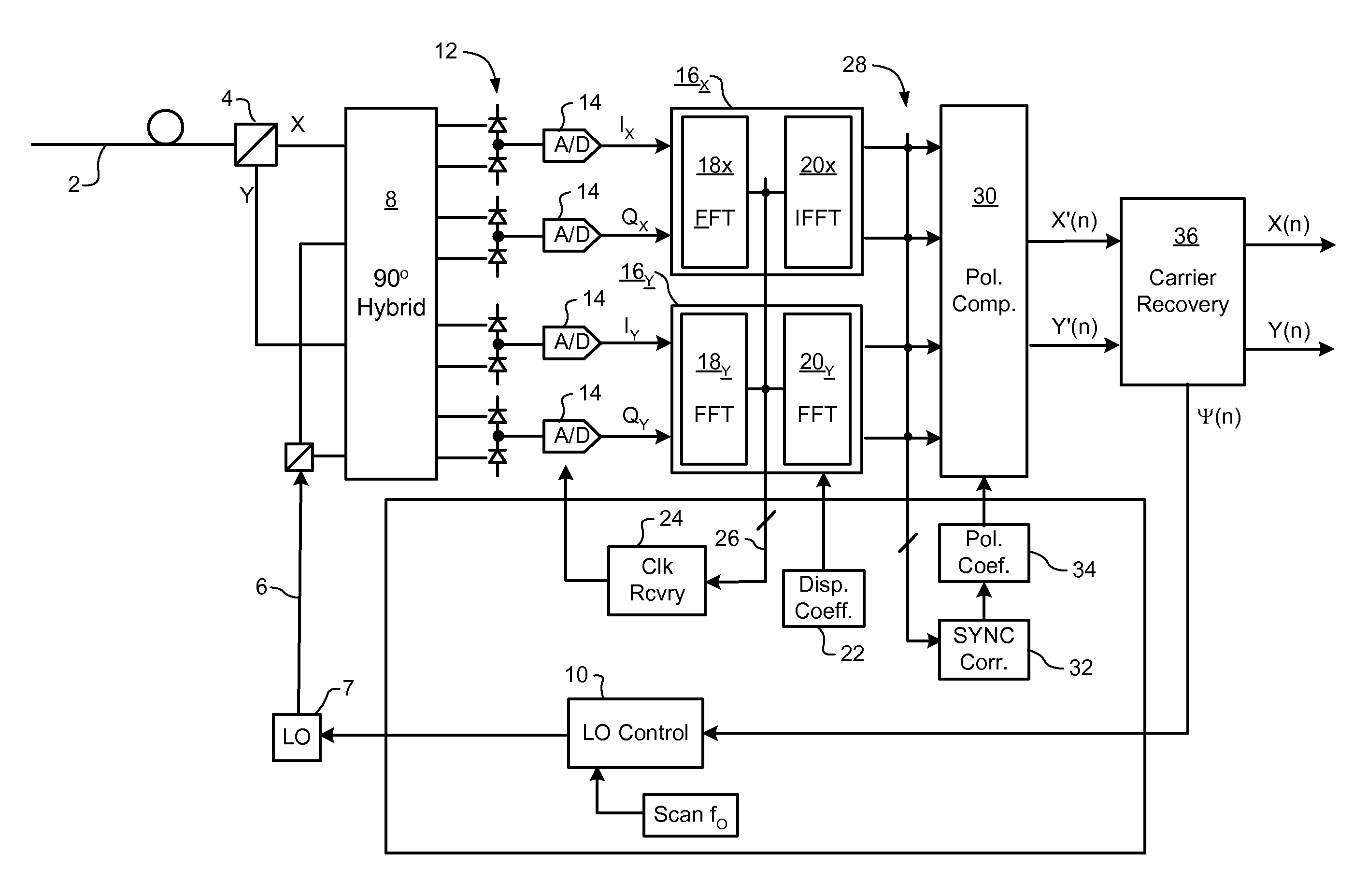
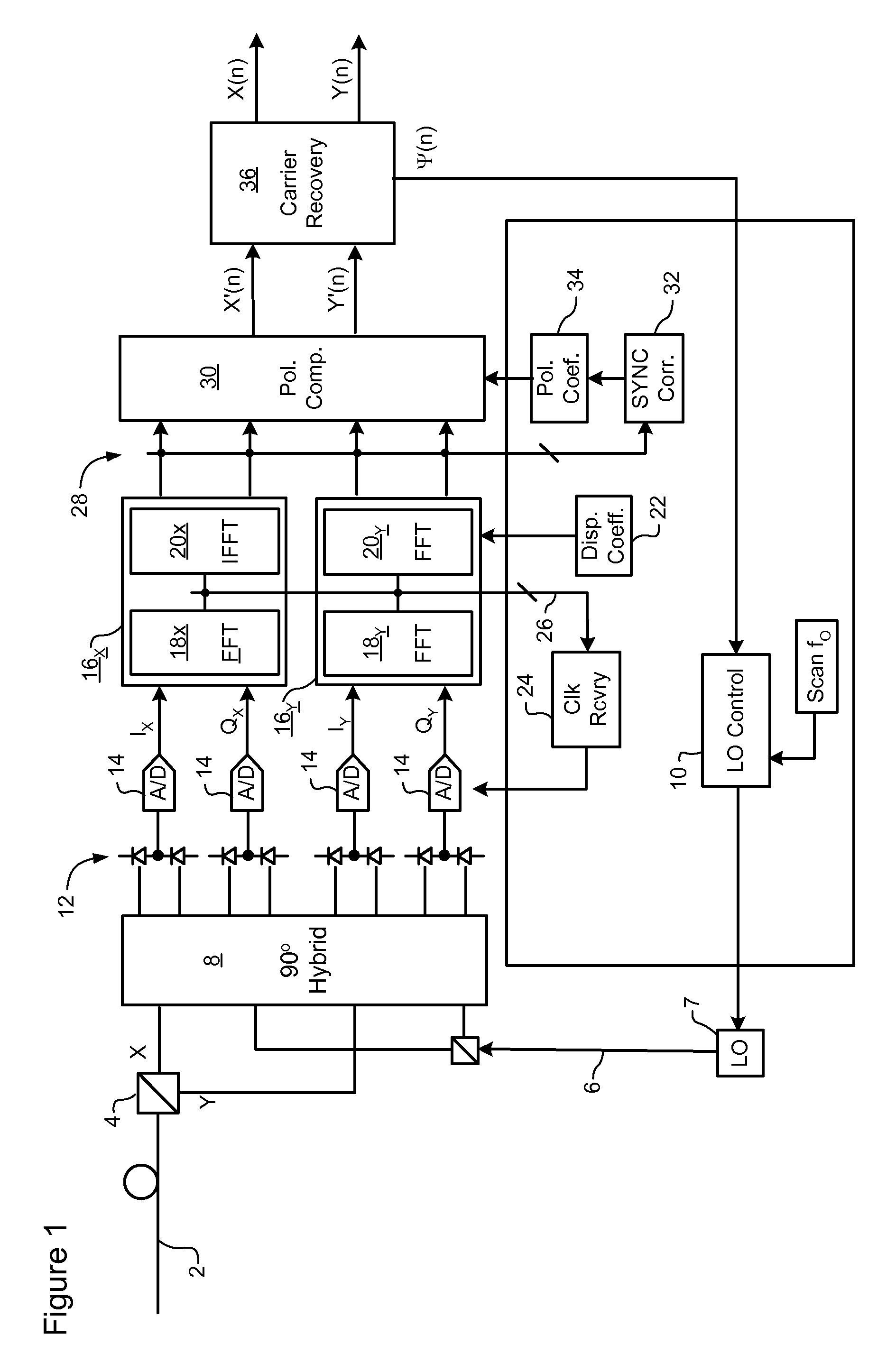
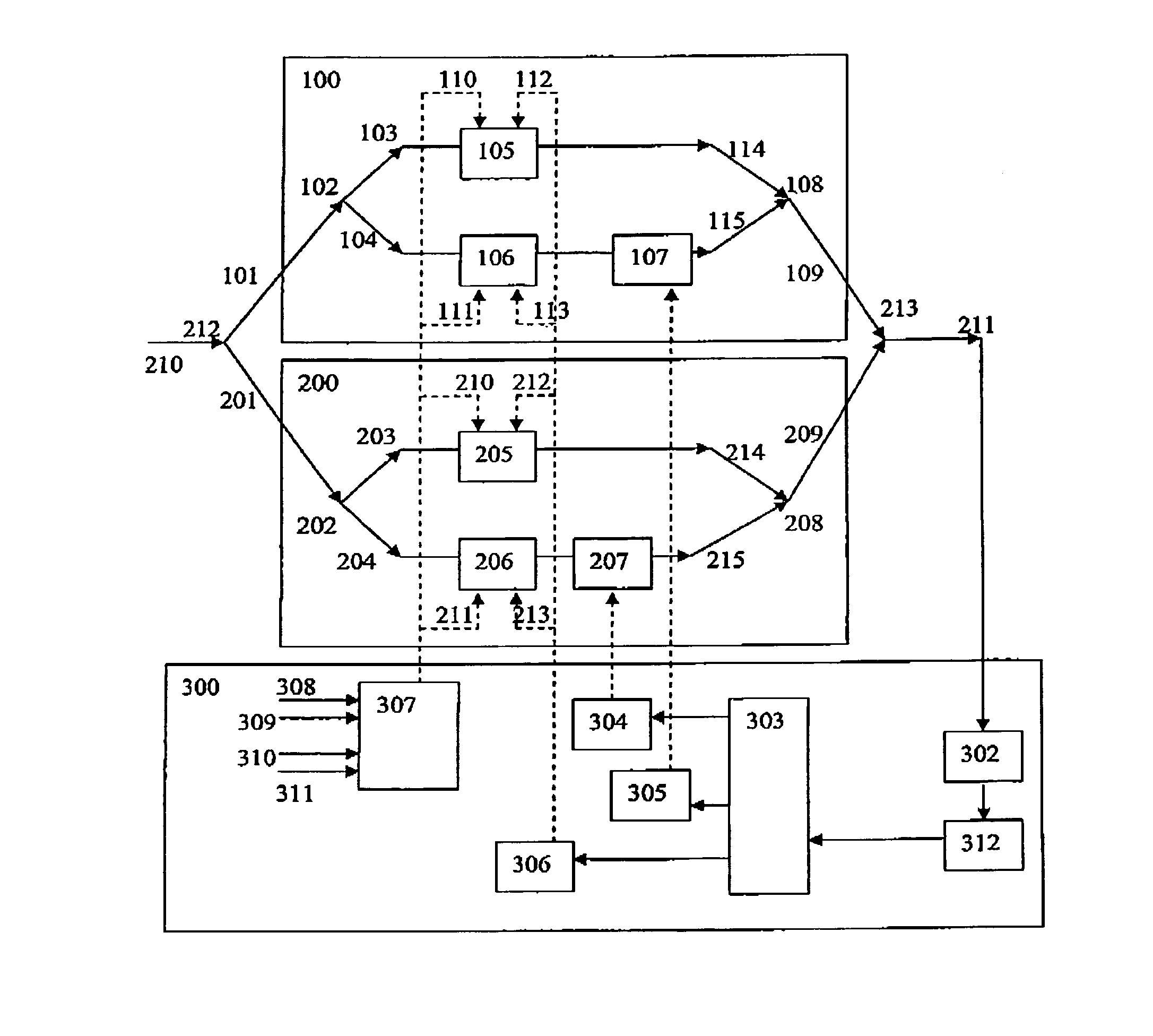
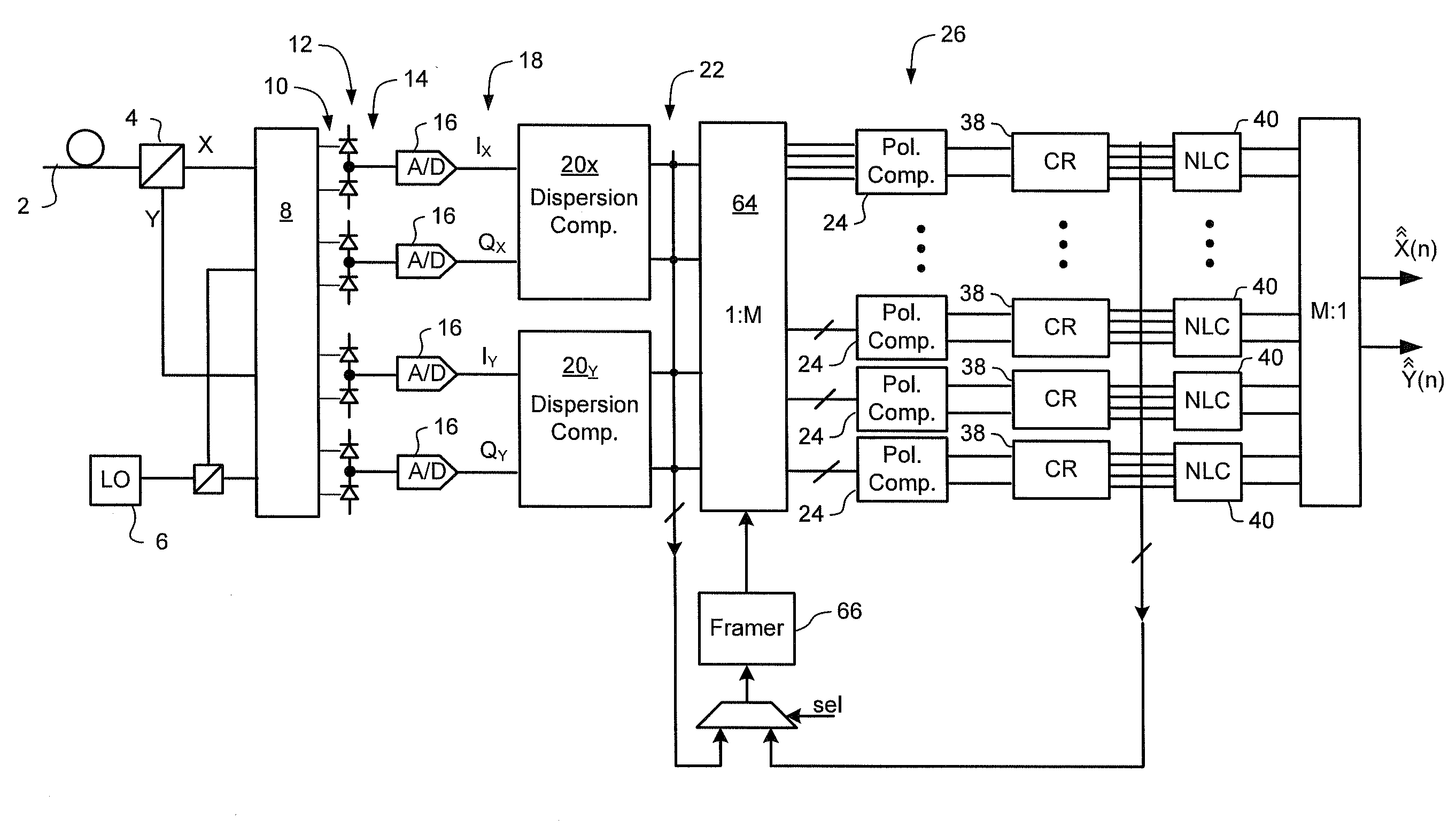
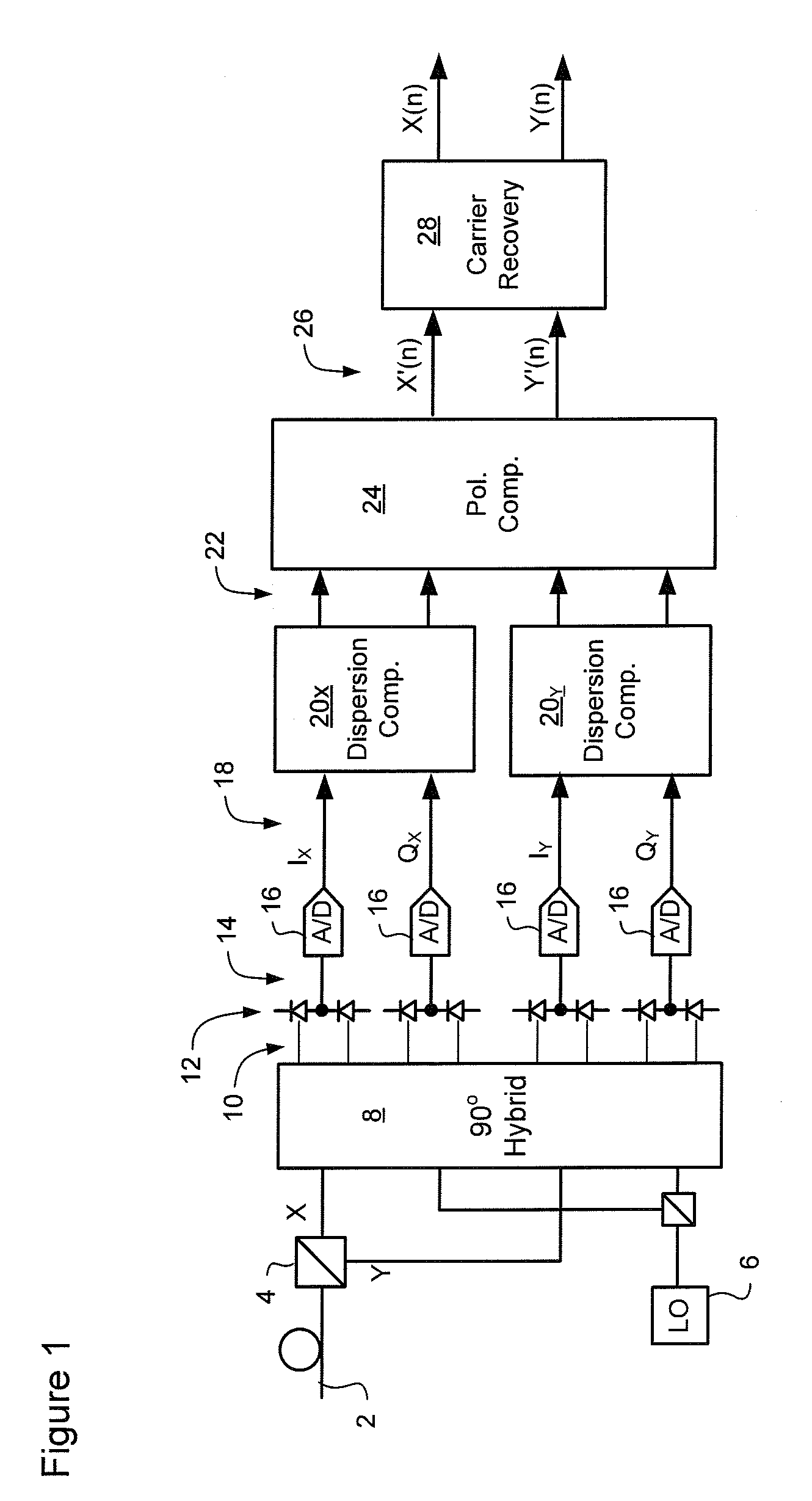
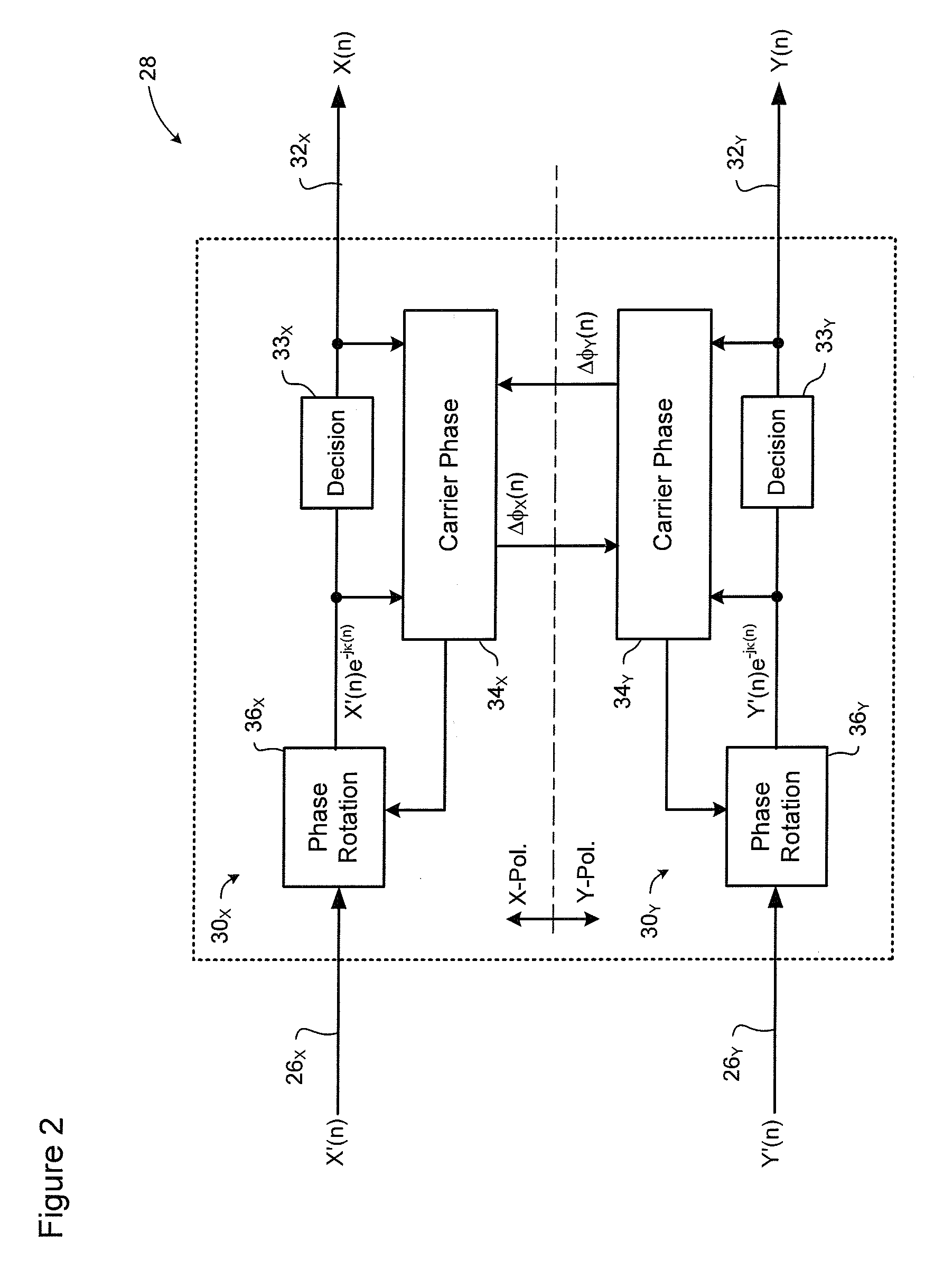
Carrier recovery in a coherent optical receiver
ActiveUS7606498B1Receiver initialisationSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansCarrier recoveryOptical receivers
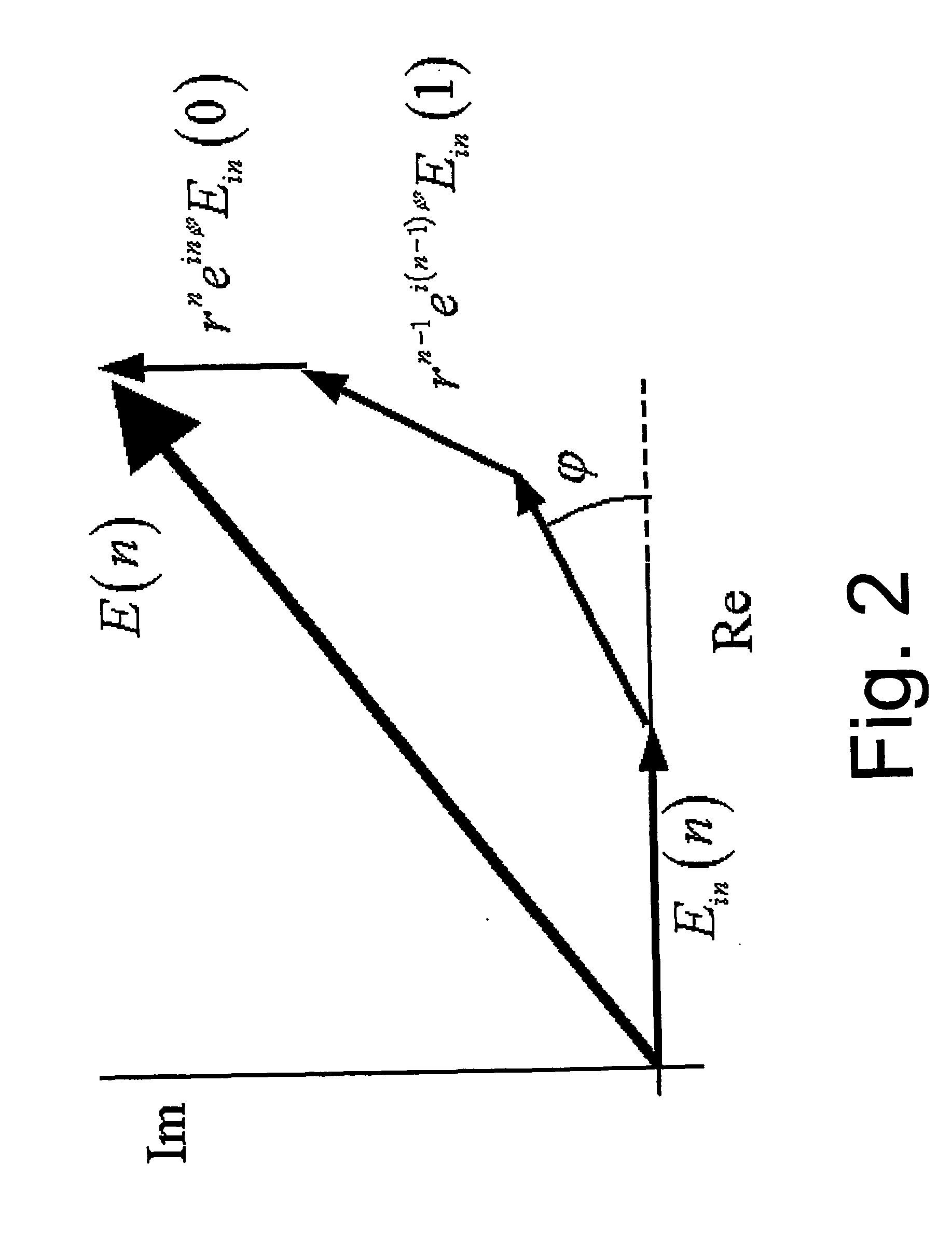
A method of carrier recovery from a high speed optical signal received through an optical communications network. A stream of multi-bit digital samples of the optical signal is processed to generate a multi-bit estimate X′(n) of each one of a plurality of transmitted symbols. A phase of each symbol estimate X′(n) is rotated, and a respective symbol phase error Δφ(n) of the rotated symbol estimate determined.
Owner:CIENA
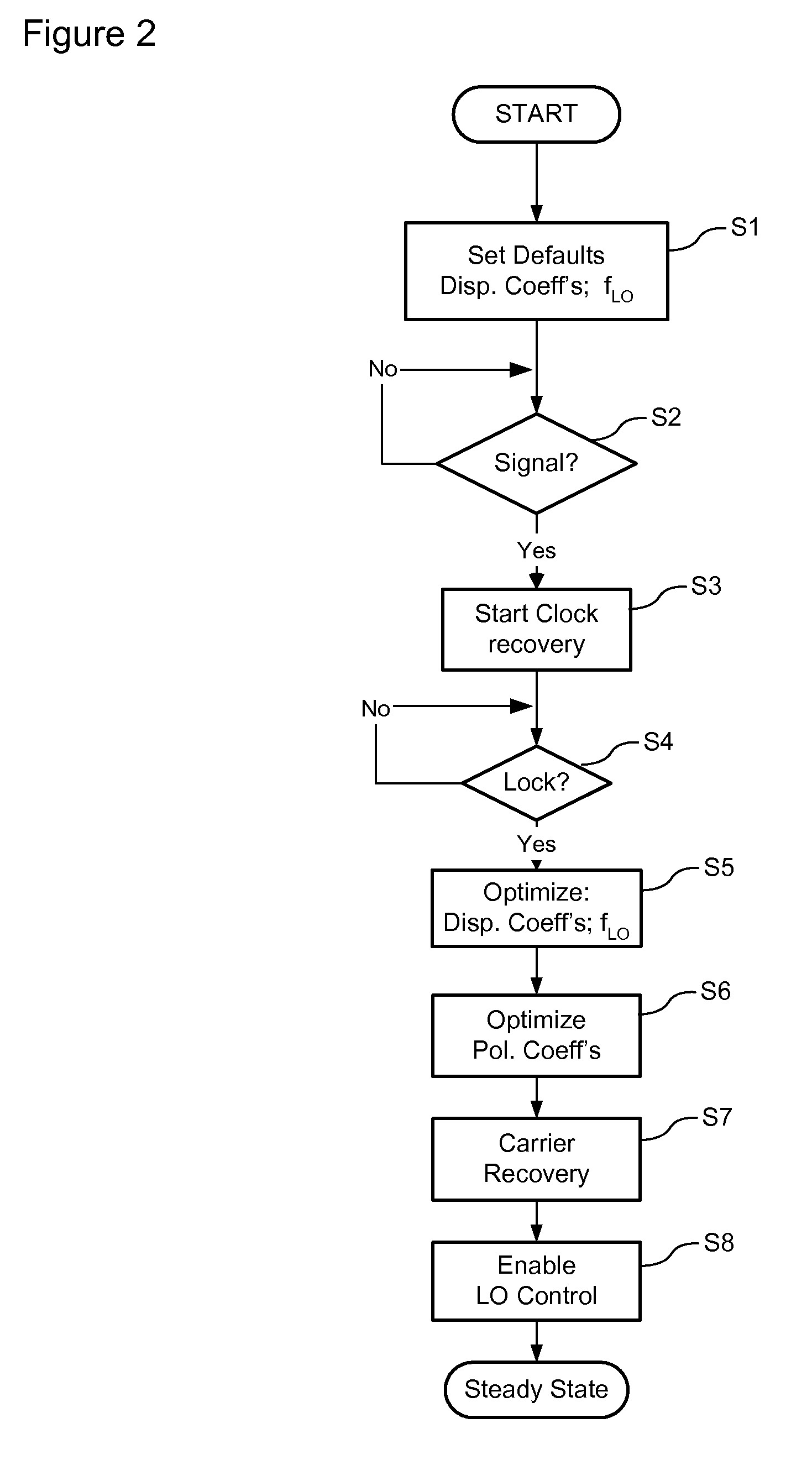
Signal acquisition in a coherent optical receiver
ActiveUS7636525B1Reliably acquire signalSteady-state operationReceiver initialisationSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansClock recoveryEngineering
A method and system for initializing a coherent optical receiver. Upon detection of an optical signal, a multi-bit digital sample stream of the optical signal is digitally processed to initialize each one of a plurality of adaptive control blocks of the coherent optical receiver. The adaptive control blocks include at least a dispersion compensation block and a clock recovery block. The dispersion compensation block is initialized before initializing the clock recovery block.
Owner:CIENA
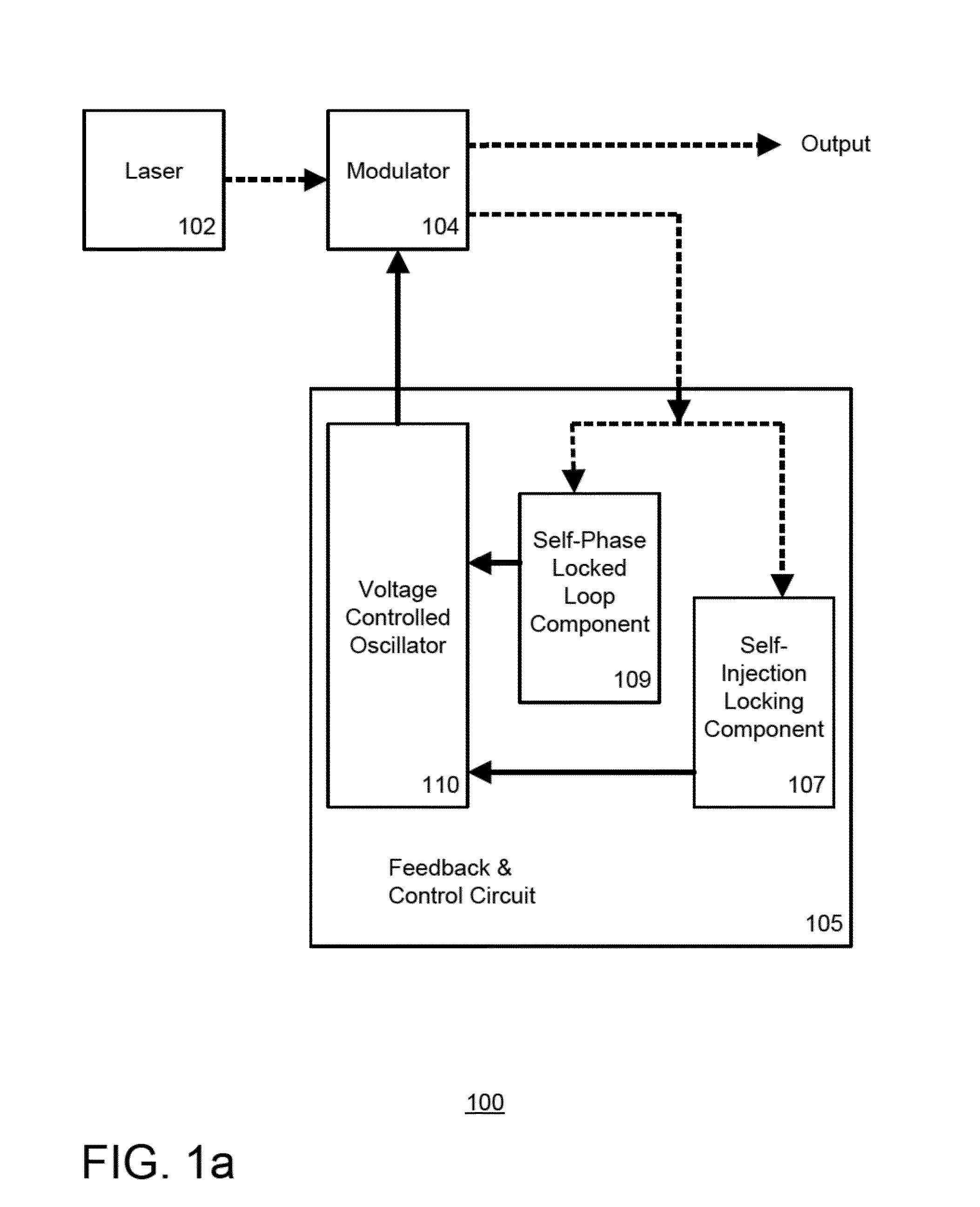
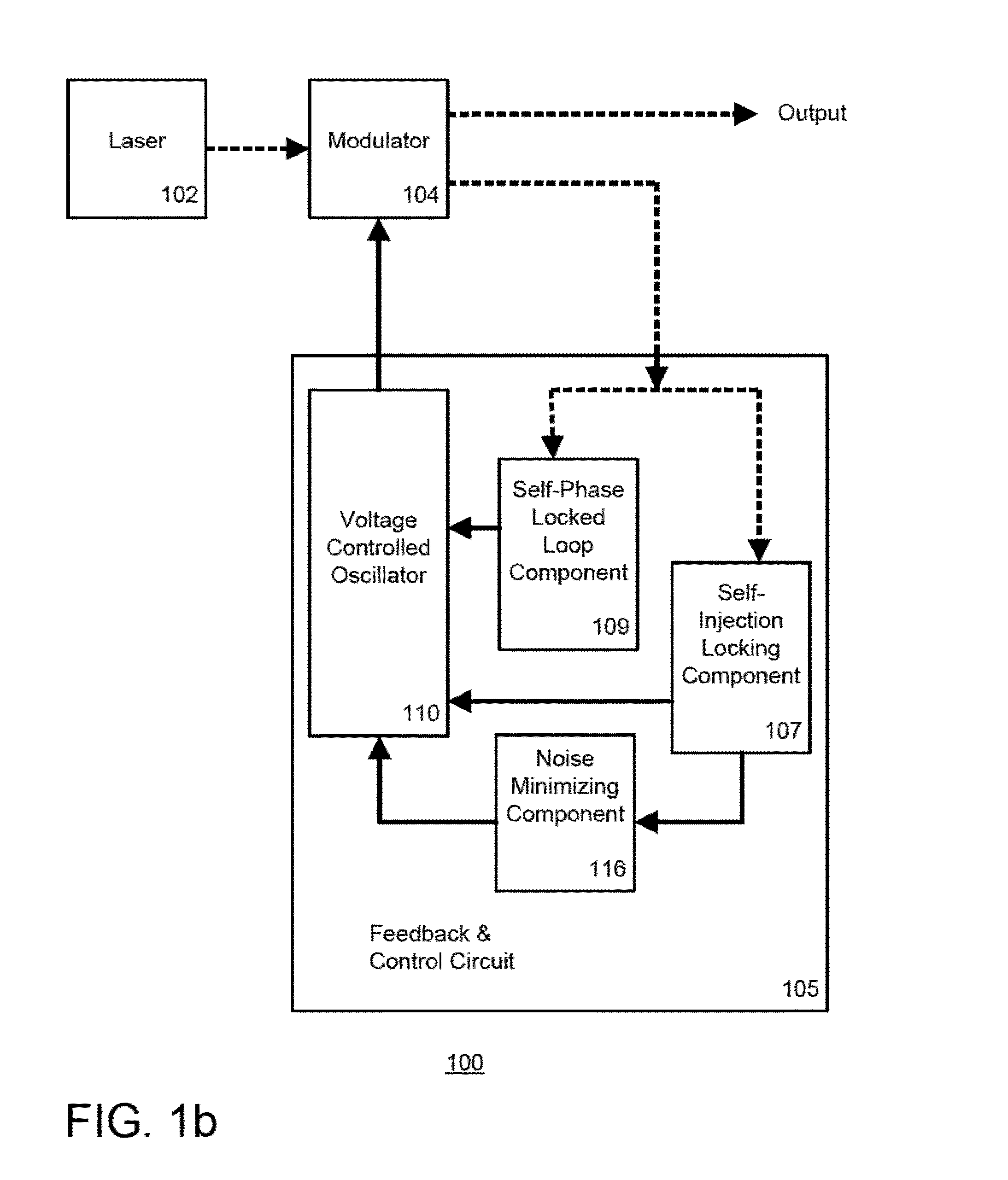
Self injection locked phase locked looped optoelectronic oscillator
Aspects of the disclosure relate generally to a circuit for sustaining an radio frequency (RF) modulated optical signal. The circuit may comprise a self injection locking component having a fiber optic delay line over which a portion of the optical signal propagates. The circuit may also comprise a self phase locked loop component having at least two fiber optic cables having different lengths and over which another portion of the optical signal propagates and a phase detector coupled to the at least two fiber optic cables and configured to determine a phase difference between the signals propagating over one of the respective fiber optic cables. The circuit may further comprise a voltage controlled oscillator configured to generate a stable oscillating signal in response to signals generated by each of the self injection locking and self phase locked loop components, the stable oscillating signal being configured to sustain the optical signal.
Owner:SYNERGY MICROWAVE CORP
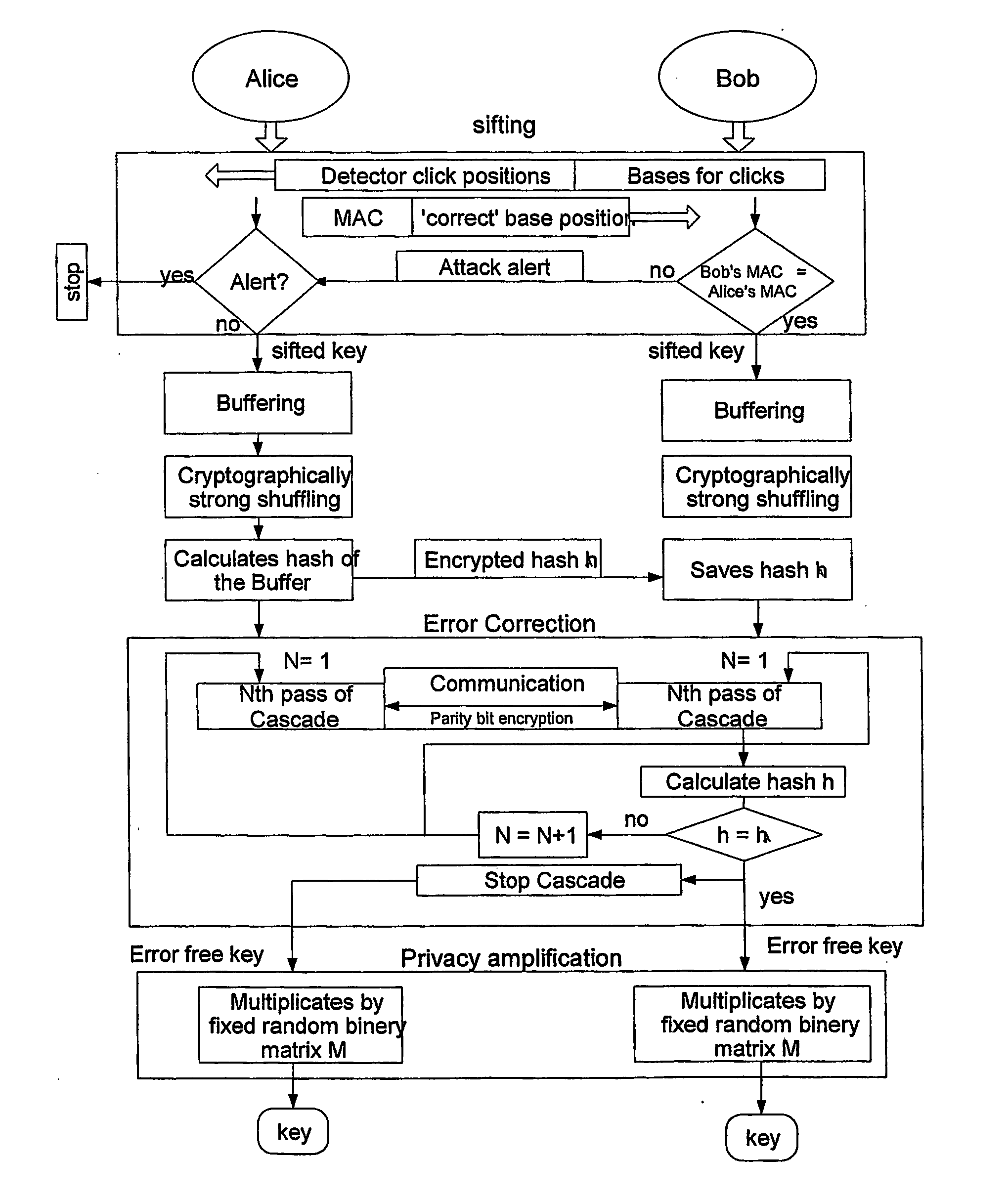
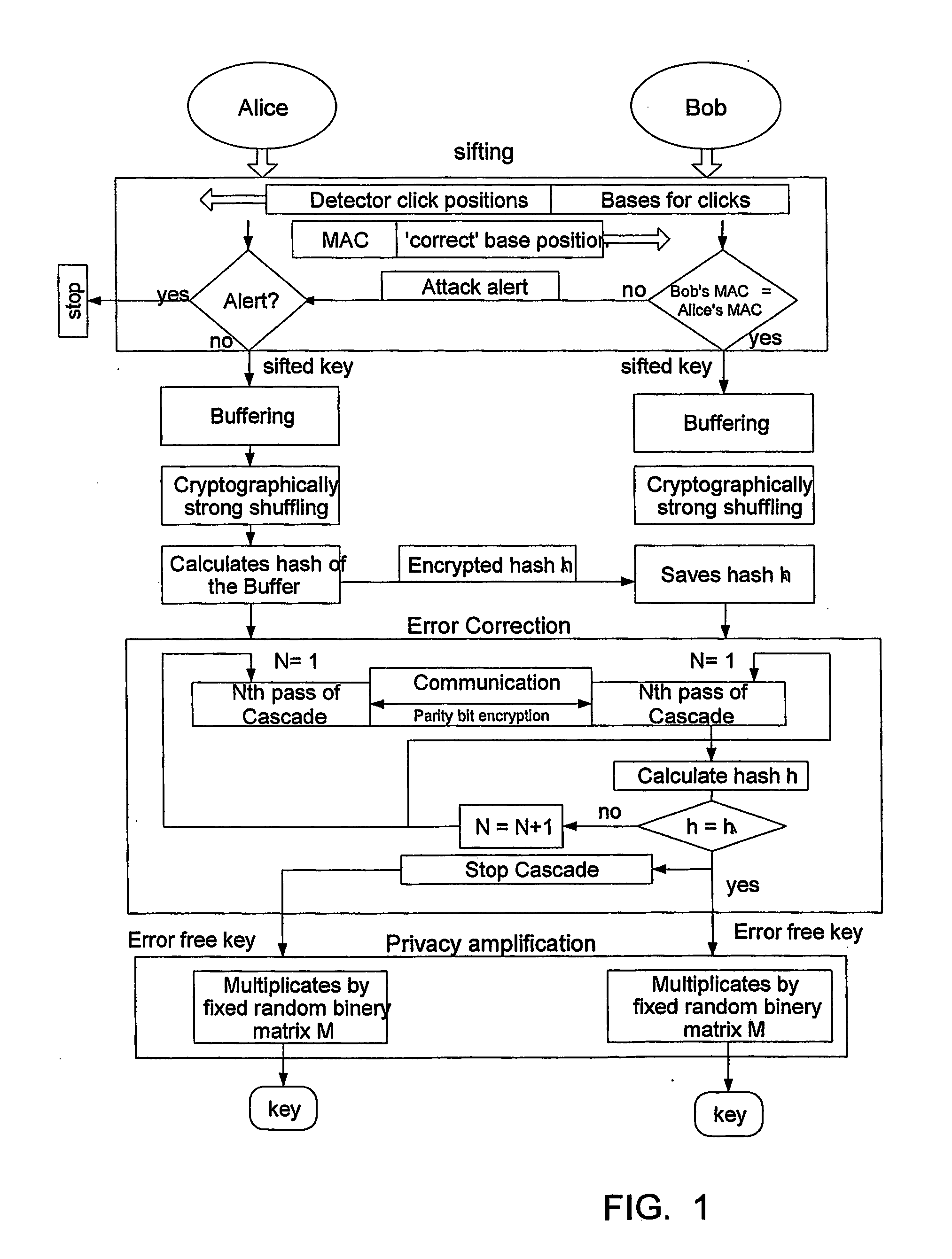
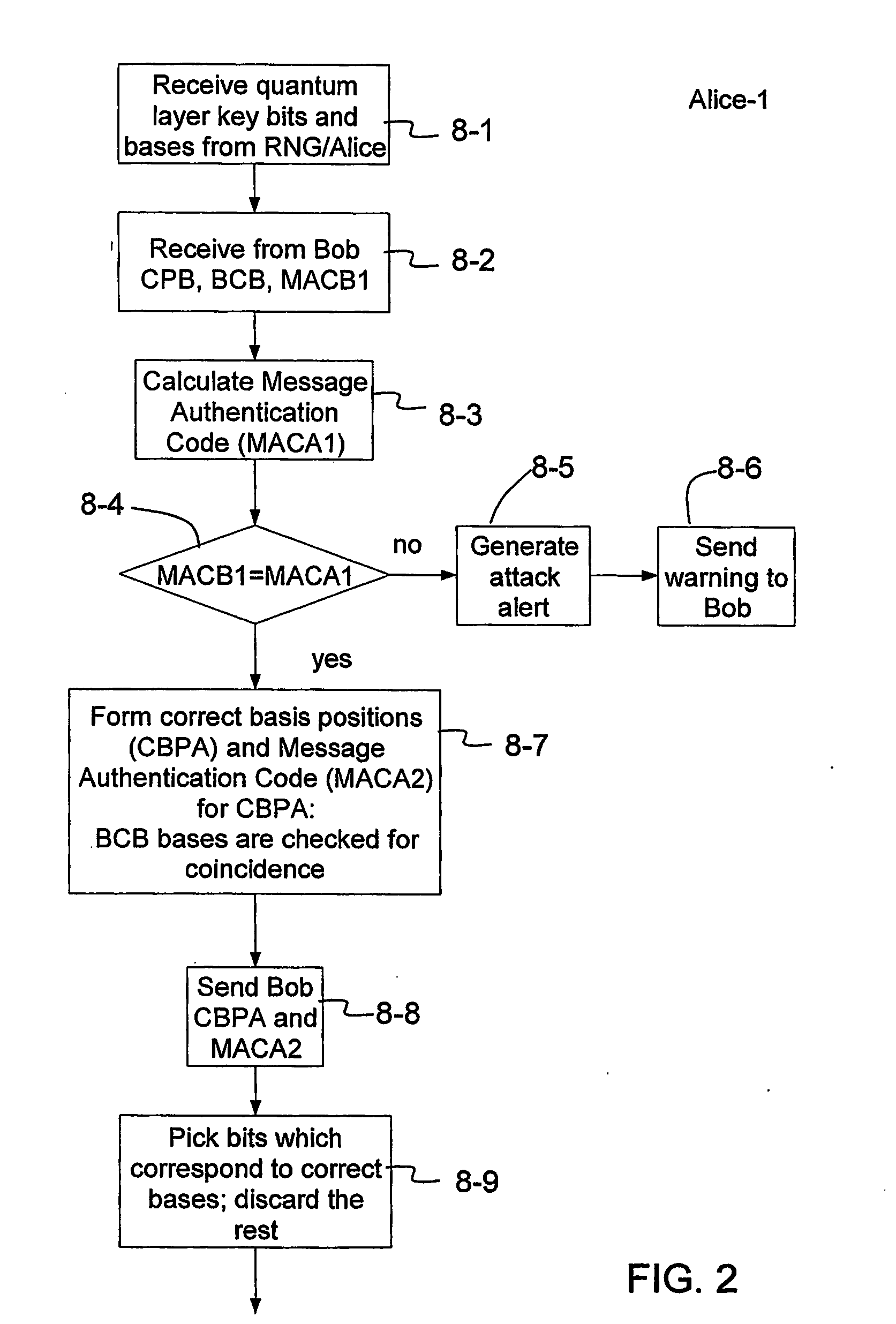
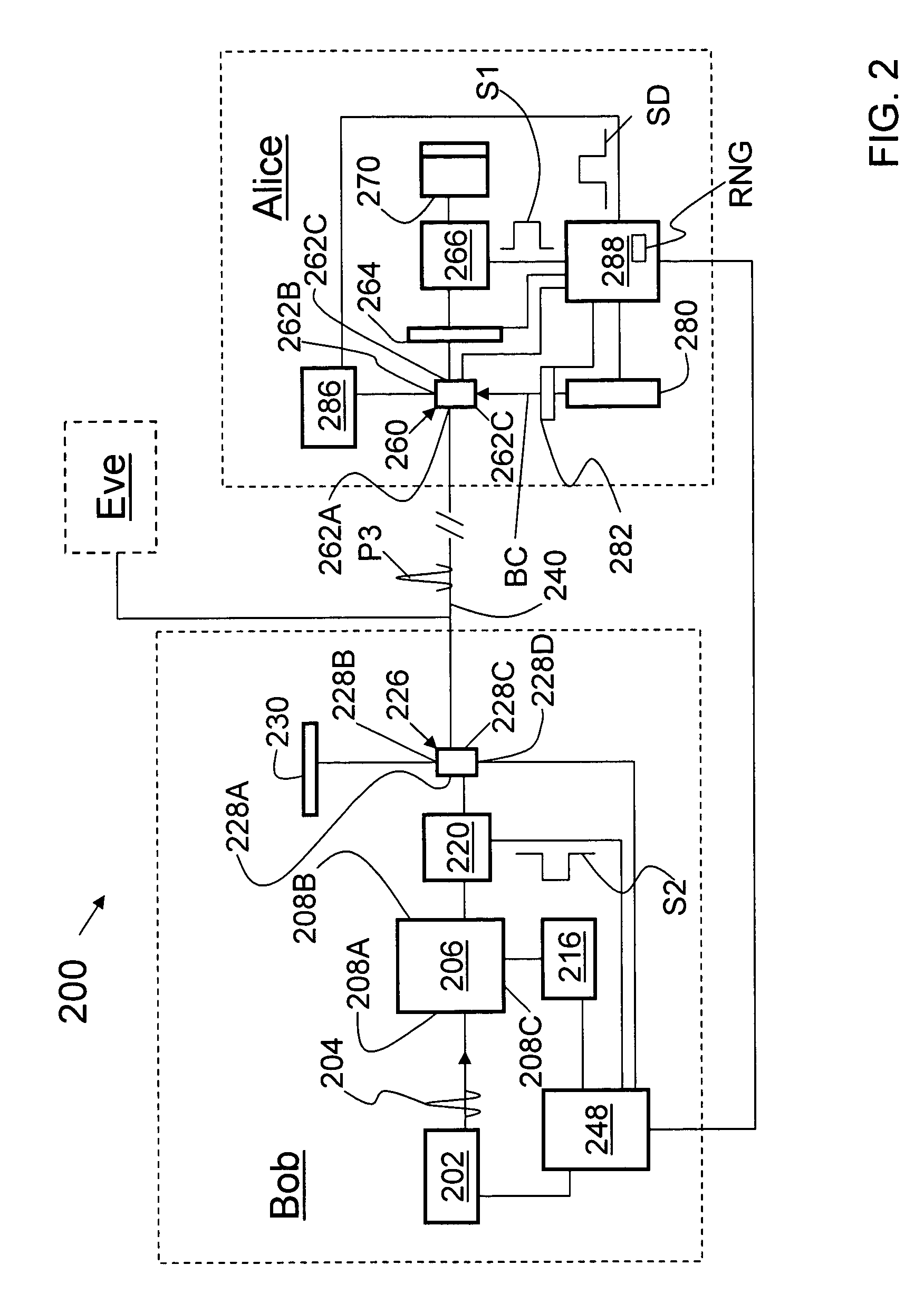
Key expansion for qkd
InactiveUS20060059343A1Key distribution for secure communicationSynchronisation information channelsKey exchangeKey schedule
A method of encrypting information using an encryption pad based on keys exchanged between quantum key distribution (QKD) stations is disclosed. The method includes establishing raw keys between two stations using QKD, processing the keys to establish a plurality of matching privacy amplified keys at each station and buffering the keys in a shared key schedule. The method also includes the option of expanding one or more of the keys in the shared key schedule using a stream cipher to create a supply of expanded keys that serve as pads for one-time-pad encryption.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
Electro-optical integrated transmitter chip for arbitrary quadrature modulation of optical signals
InactiveUS7272271B2Time-division optical multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsQuadrature modulationEngineering
An optical device includes, a first Mach-Zehnder modulator that produces a first output, and a second Mach-Zehnder modulator which produces a second output. A splitter couples the first and second Mach-Zehnder modulators. A combiner combines the first and second outputs. A phase shifter is coupled to the first and second Mach-Zehnder modulators. The first Mach-Zehnder modulator, second Mach-Zehnder modulator, splitter, combiner and the phase shifter are each formed as part of a single chip made of electro-optical material. Such two similar optical device integrated together with polarization combiner provide a two-polarization performance.
Owner:CELIGHT
Non-linear equalizer in a coherent optical receiver
ActiveUS7684712B1Receiver initialisationSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansSignal restorationComputer science
A method of recovering a most likely value of each symbol transmitted through an optical communications network using a high speed optical signal. A stream of multi-bit digital samples of the optical signal is processed to generate a respective multi-bit estimate X′(n) of each transmitted symbol. A first function is applied to each symbol estimate X′(n) to generate a corresponding soft decision value {tilde over (X)}(n). Each soft decision value {tilde over (X)}(n) is processed to generate a corresponding hard decision value. {circumflex over (X)}(n) having an ideal amplitude and phase. A plurality of successive soft decision values and hard decision values are processed to determine a second function, which is applied to each soft decision value {tilde over (X)}(n) to generate a most likely symbol value {circumflex over ({circumflex over (X)}(n).
Owner:CIENA CORP
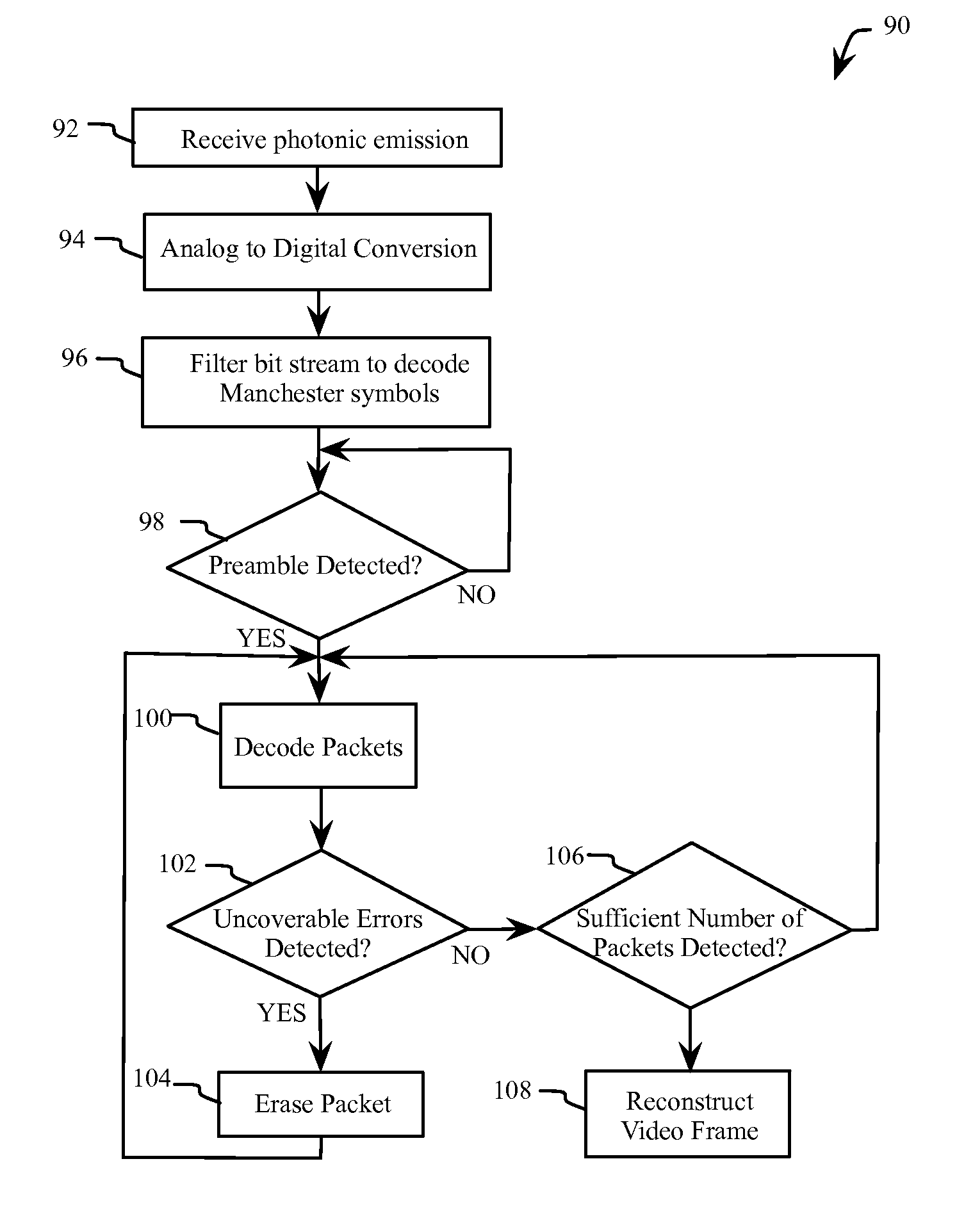
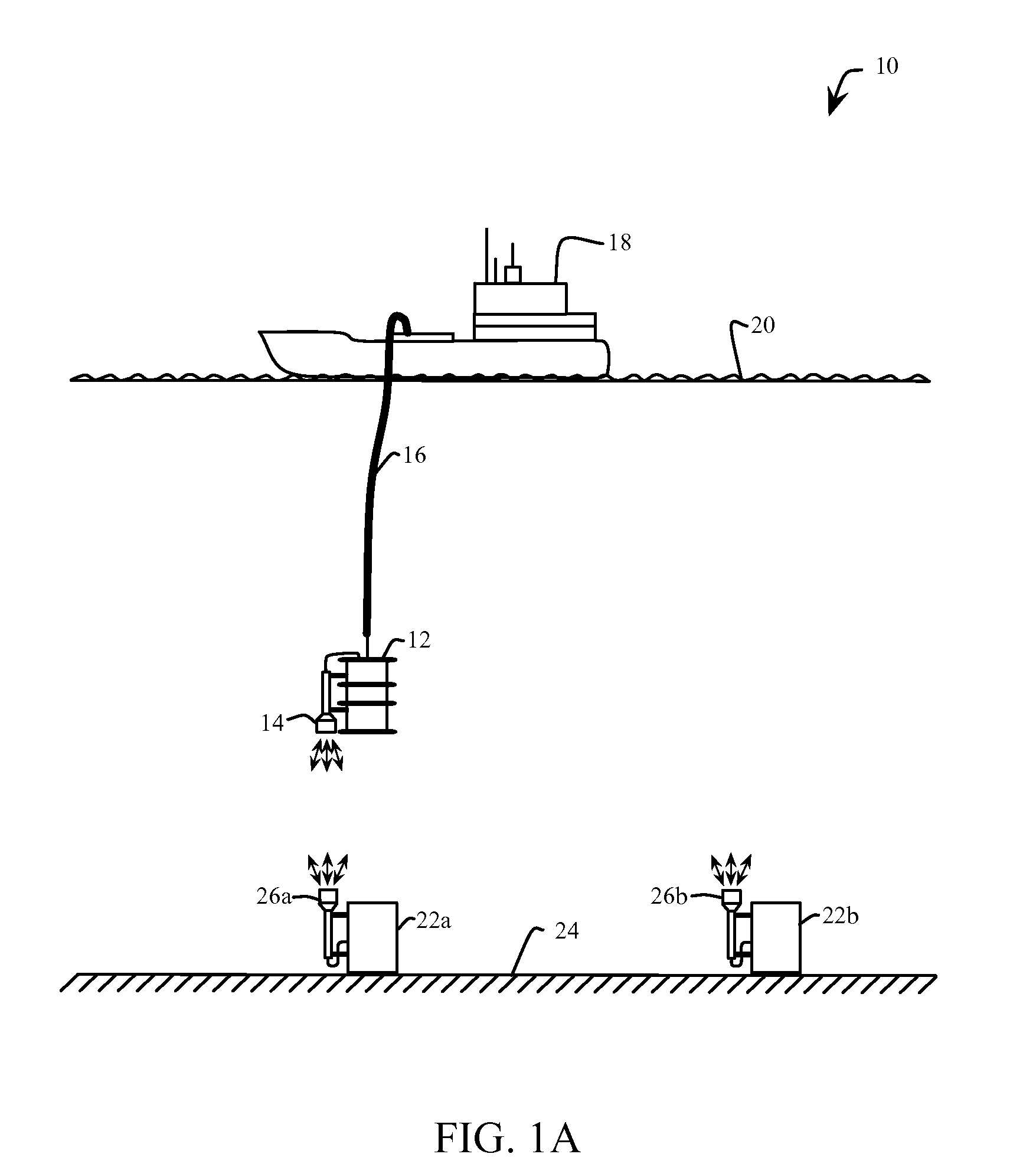
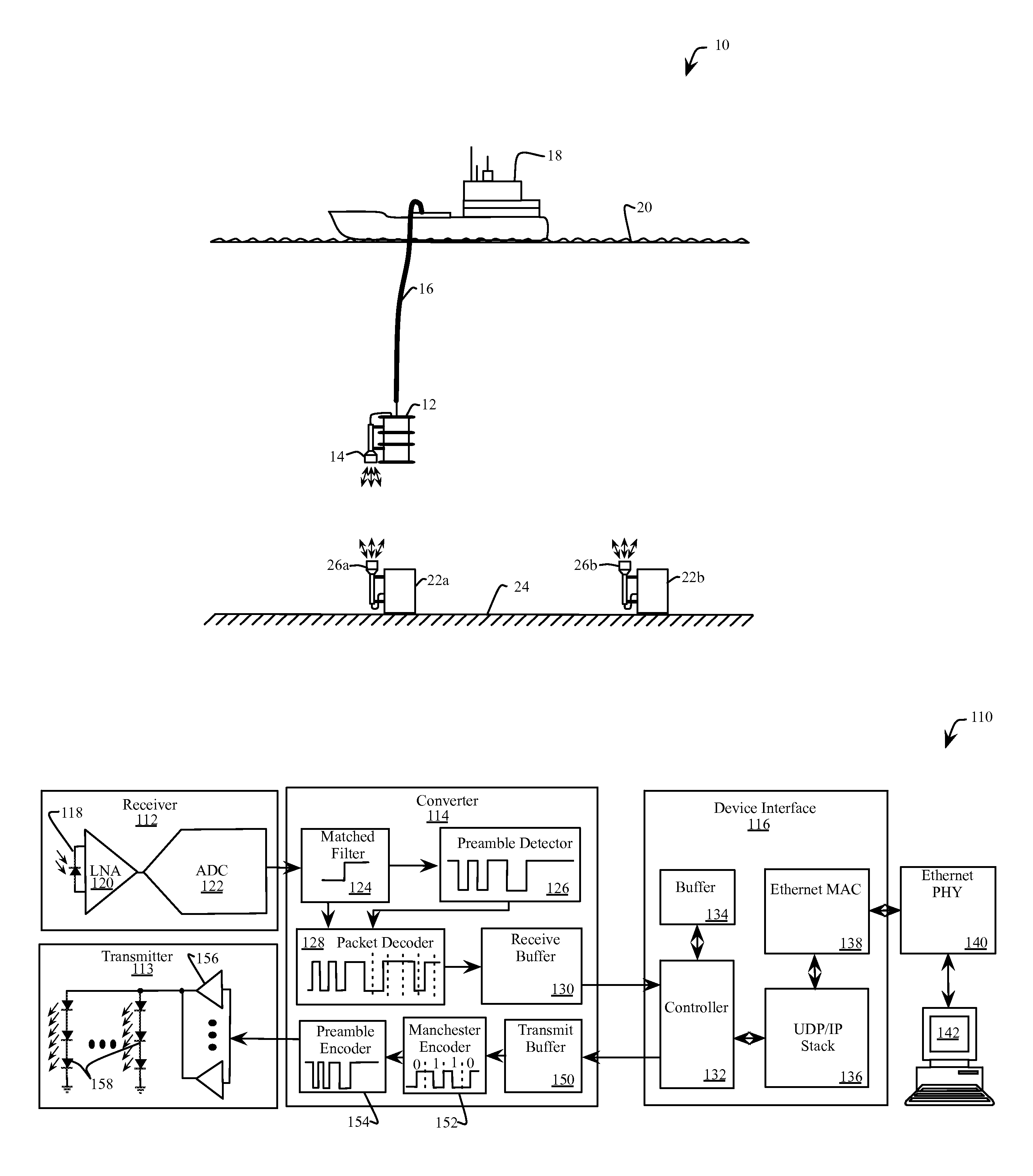
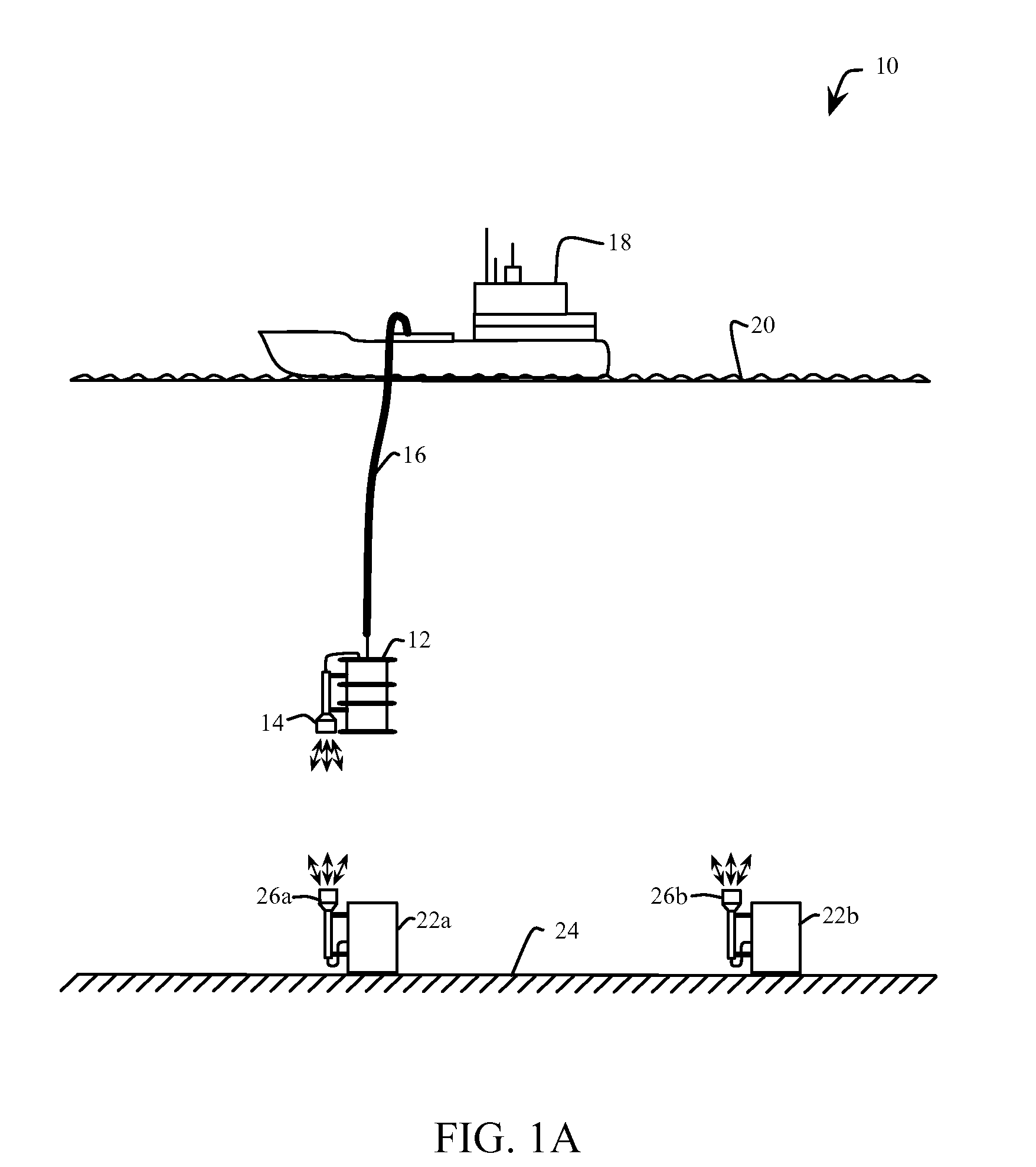
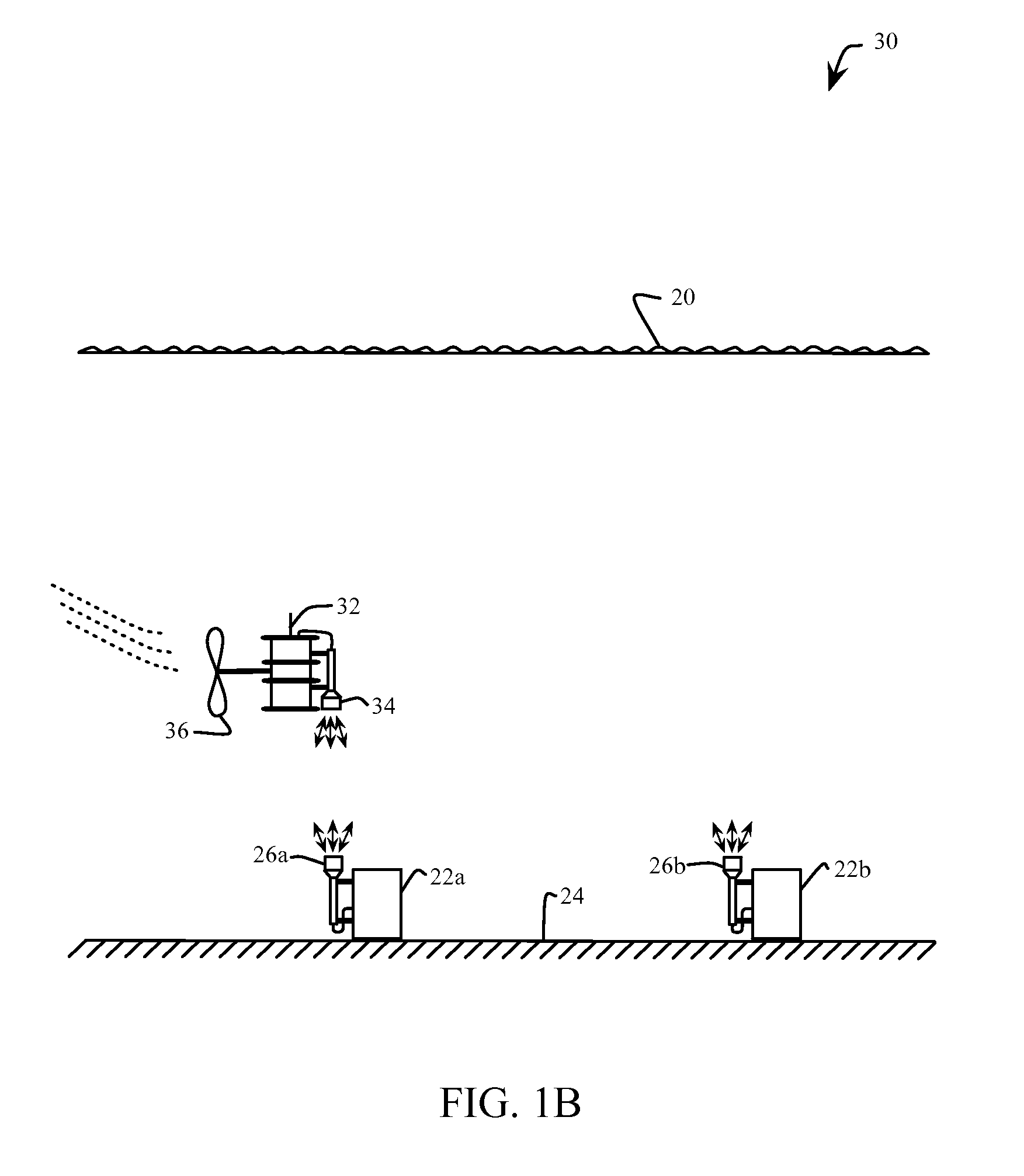
Underwater optical communication system
ActiveUS20140212142A1High bandwidthLower latencySynchronisation by photonic/optical meansElectromagnetic transmission optical aspectsCommunications systemFountain code
A method of optical underwater communications comprises applying a Fountain code to a plurality of data blocks. A sequence of optical data packets is transmitted through an underwater communications channel. Each optical data packet comprises one of the plurality of data blocks preceded by a preamble. The sequence of optical data packets transmitted through the underwater communication channel is received to generate a sequence of received data packets. The sequence of received data packets is sampled with the sampling clock to recover the plurality of data blocks.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
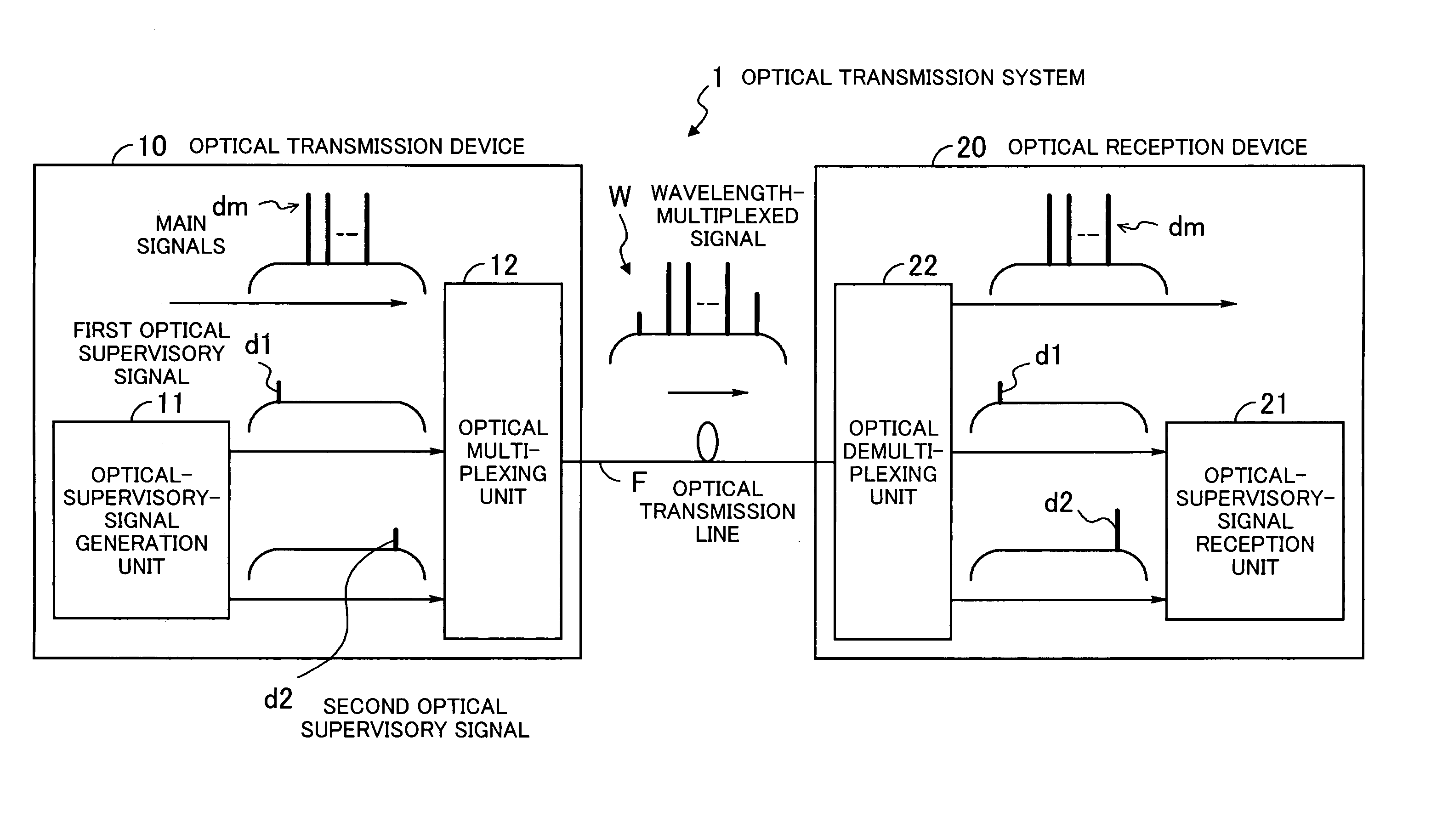
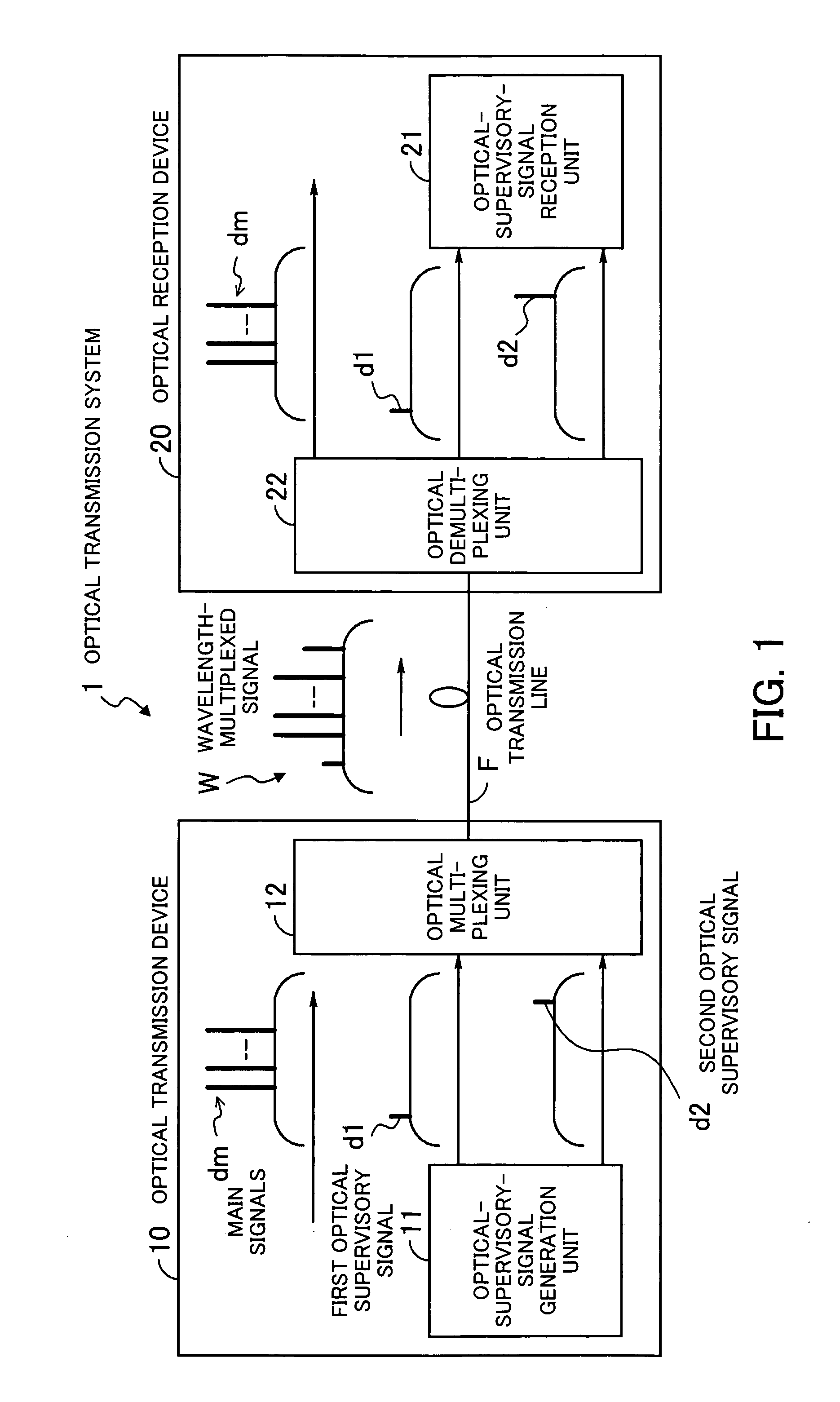
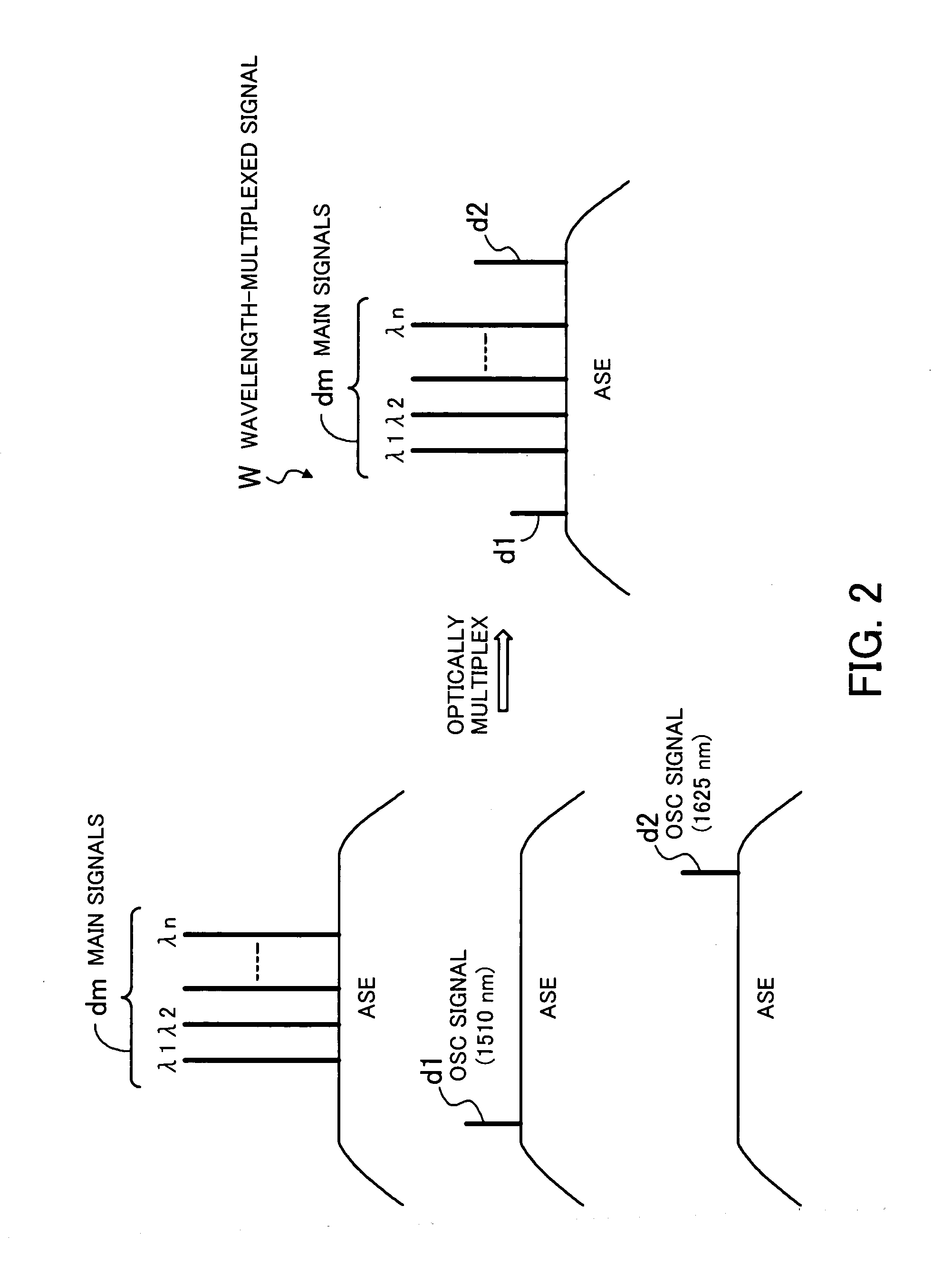
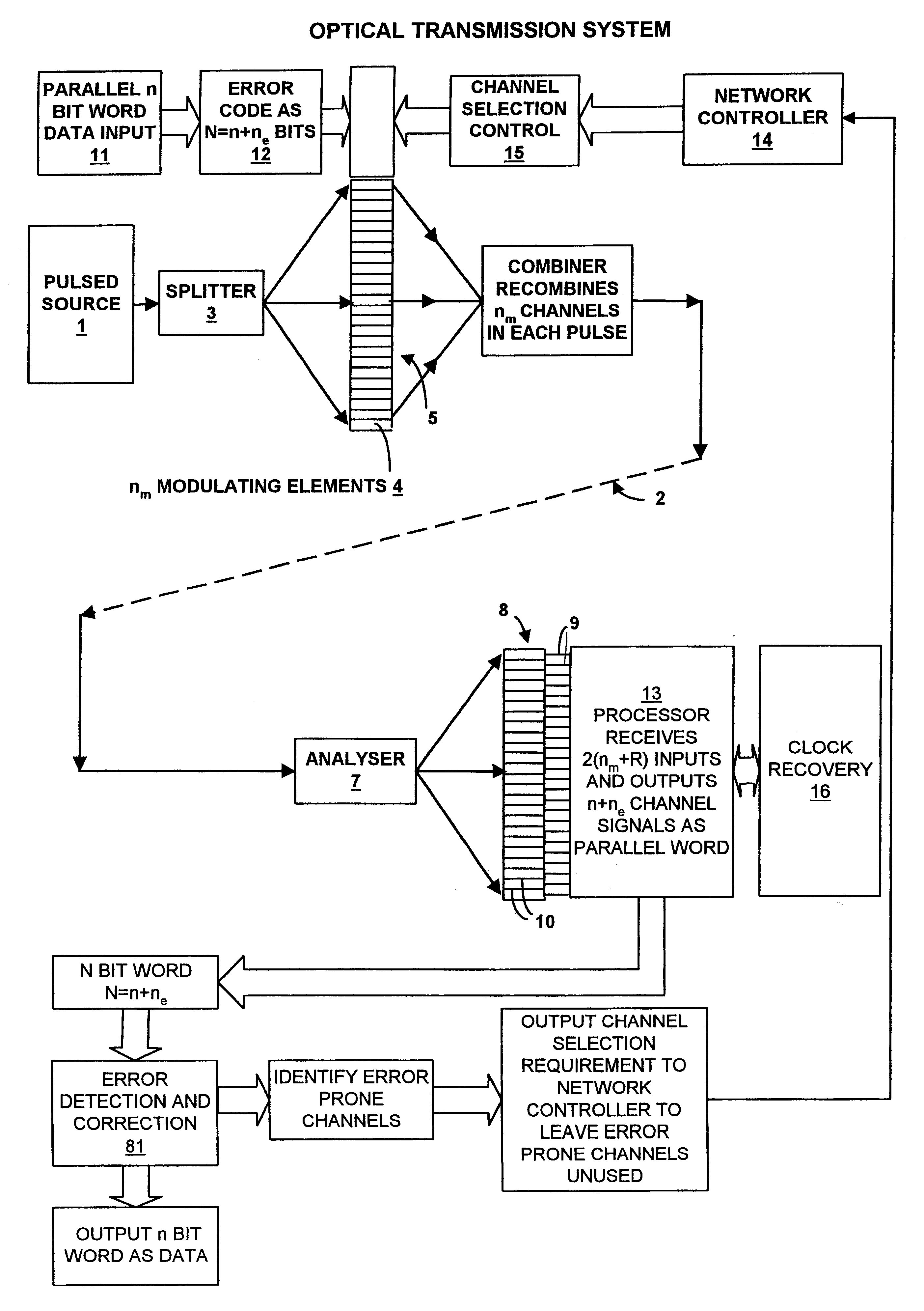
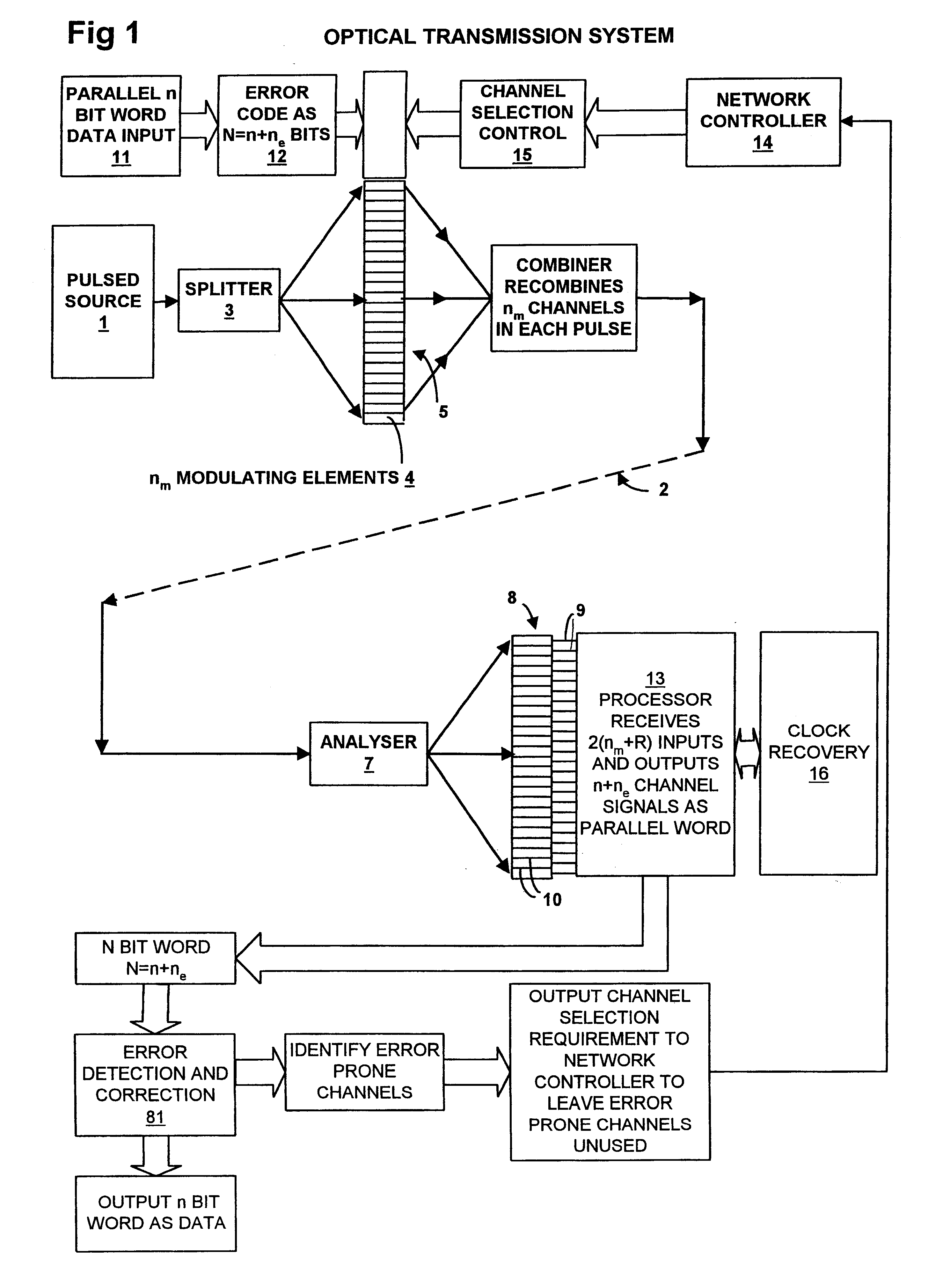
Optical transmission system
InactiveUS20050041968A1High-quality optical transmissionAccurate operationSynchronisation information channelsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansOptical communicationLength wave
In an optical transmission system: a first unit generates a first optical supervisory signal being arranged on the shorter-wavelength side of main signals and containing information for determining continuity of an optical transmission line and a second optical supervisory signal arranged on the longer-wavelength side of the main signals and used for supervisory control of optical communication; a second unit generates a wavelength-multiplexed signal by optically multiplexing the main signals and the first and second optical supervisory signals, and transmits the wavelength-multiplexed signal onto the optical transmission line; a third unit receives the wavelength-multiplexed signal, and optically demultiplexes the wavelength-multiplexed signal into the main signals and the first and second optical supervisory signals; and a fourth unit determines whether or not the optical transmission line is optically continuous, based on the first optical supervisory signal, and performs supervisory control of optical communication based on the second optical supervisory signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method and apparatus for receiving data
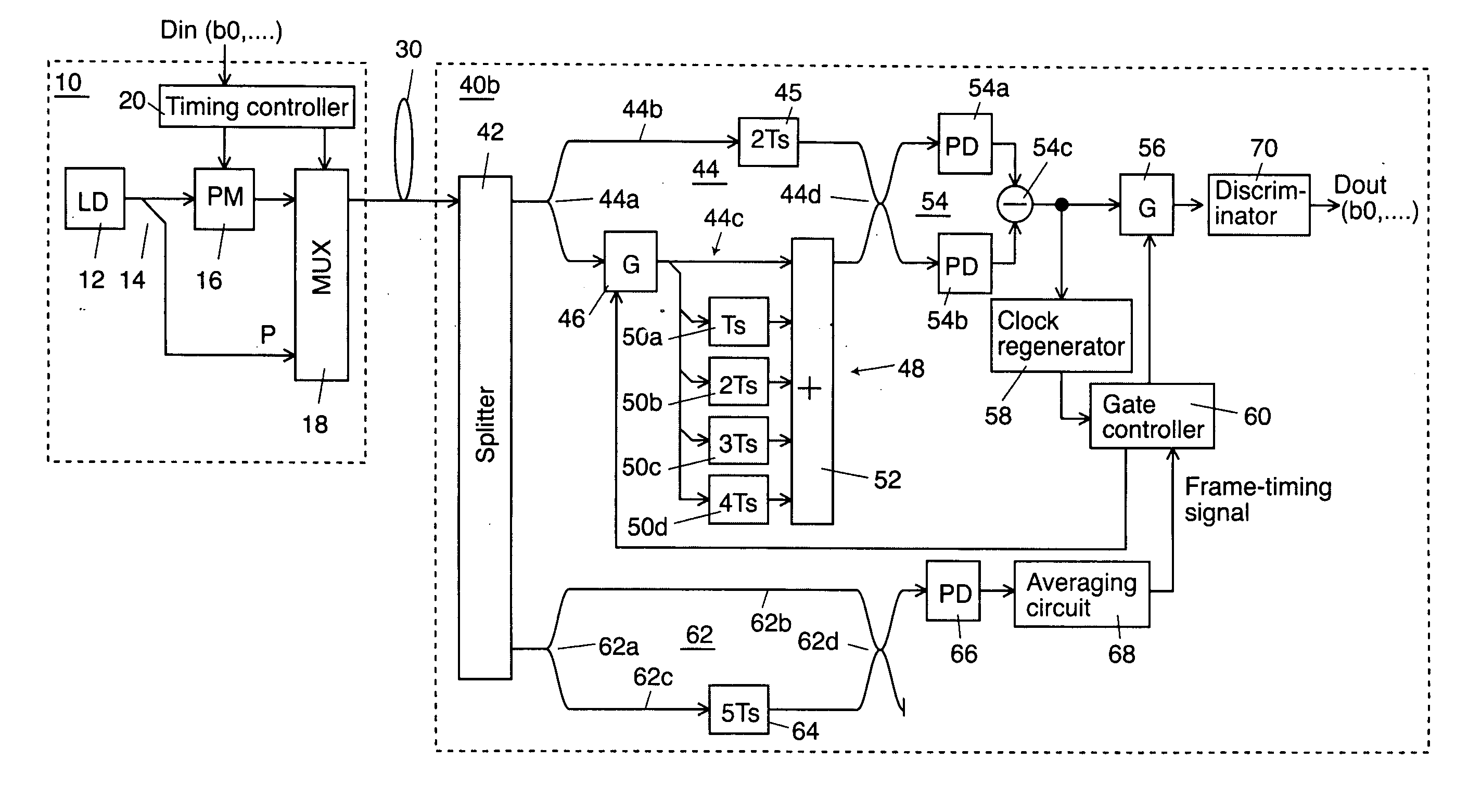
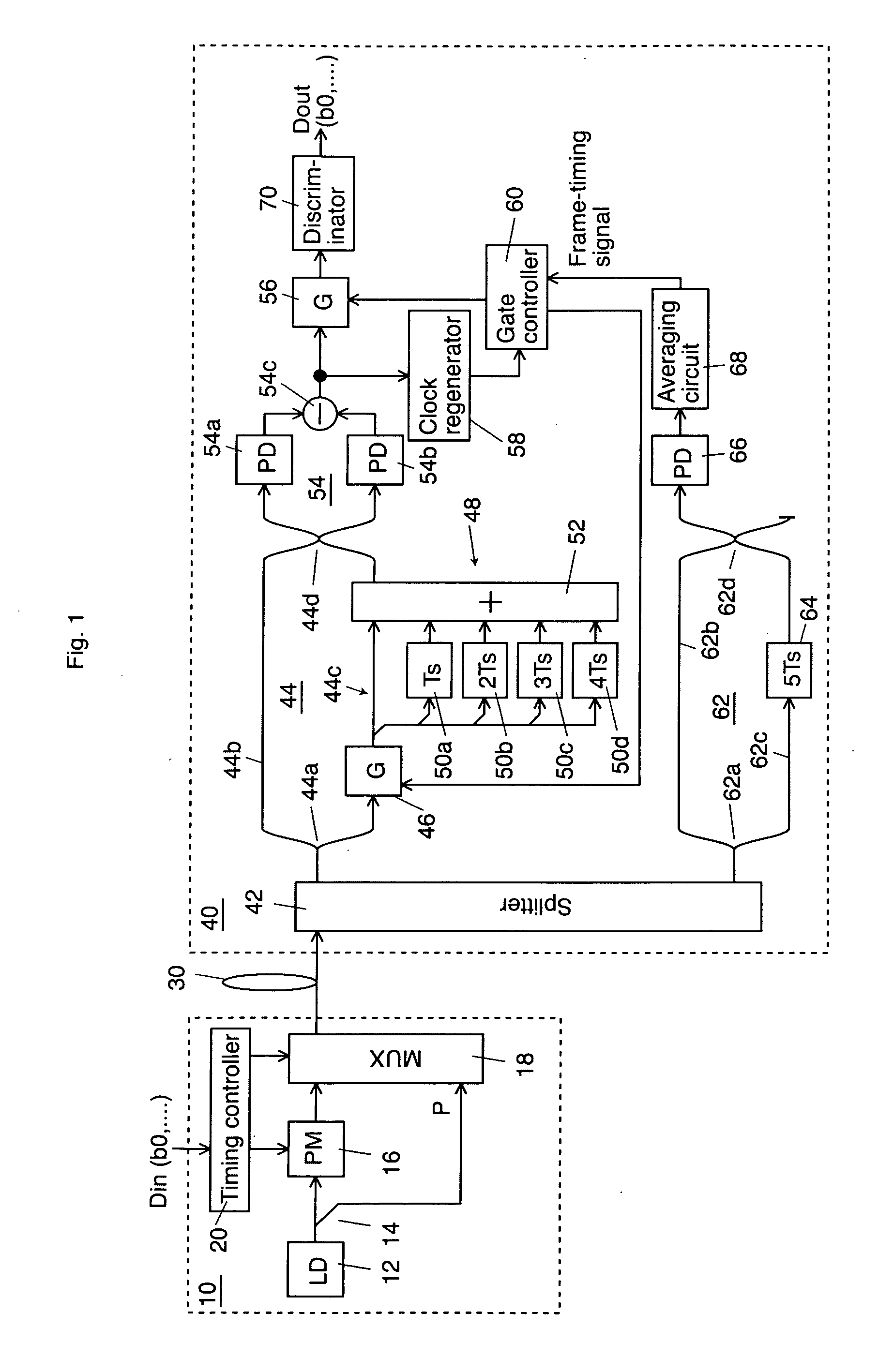
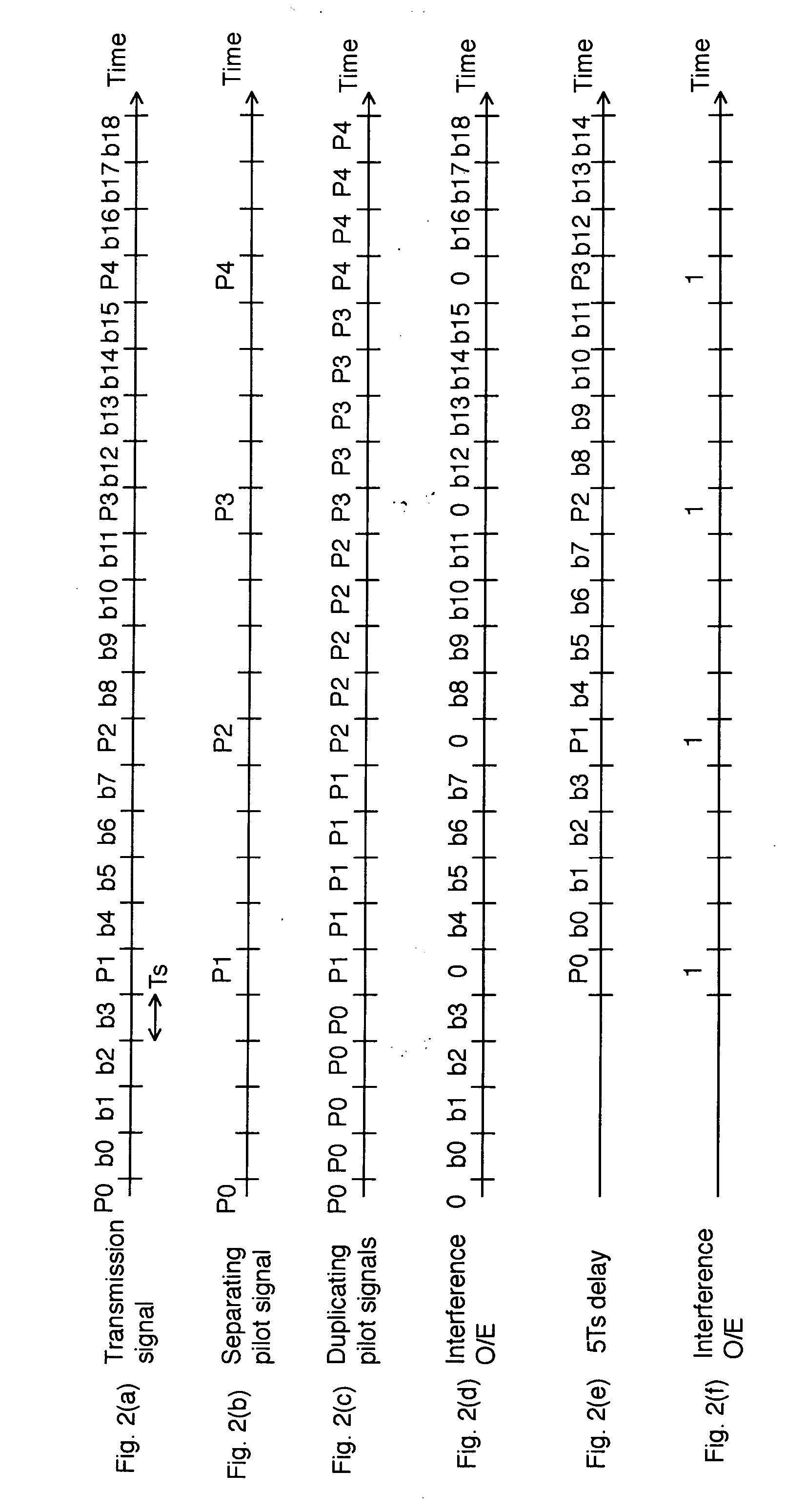
InactiveUS20070025737A1Highly sensitive receiving levelImprove transfer rateSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansElectromagnetic transmittersDiscriminatorMach–Zehnder interferometer
An optical transmitter generates a transmission signal having a frame as a unit, the frame including a single optical pilot signal with a constant optical phase and a plurality of phase-modulated optical data signals, and outputs the transmission signal into a transmission line. In a receiver, a splitter splits the optical signal input from the transmission line. On a second arm of a Mach-Zehnder interferometer, an optical gate transmits the optical pilot signal and a duplicator duplicates the optical pilot signal output from the optical gate at predetermined time intervals. A balanced optical receiver converts the interfered optical signal output from the interferometer into an electrical signal. A gate and a discriminator extract the data from the electrical signal output from the receiver.
Method of and system for detecting skew between parallel signals
ActiveUS20120020660A1Simple receiver structureSimple codingChannel dividing arrangementsPolarisation multiplex systemsData streamPolarization multiplexed
A method is provided for detecting the skew between parallel light signals generated from a serial data stream. The method can be used with polarization multiplexed signal, as well as with wavelength division multiplexed signals, spatial division multiplexed signals, phase modulated signals, or intensity modulated signals. The method can be used with direct detection schemes as well as with coherent detection schemes. The method is provided with: imprinting dips between a fixed number of transmitted symbols of the parallel signals; detecting an electrical signal related to the dips for each parallel signal; and comparing the electrical signals in delay.
Owner:NEC CORP
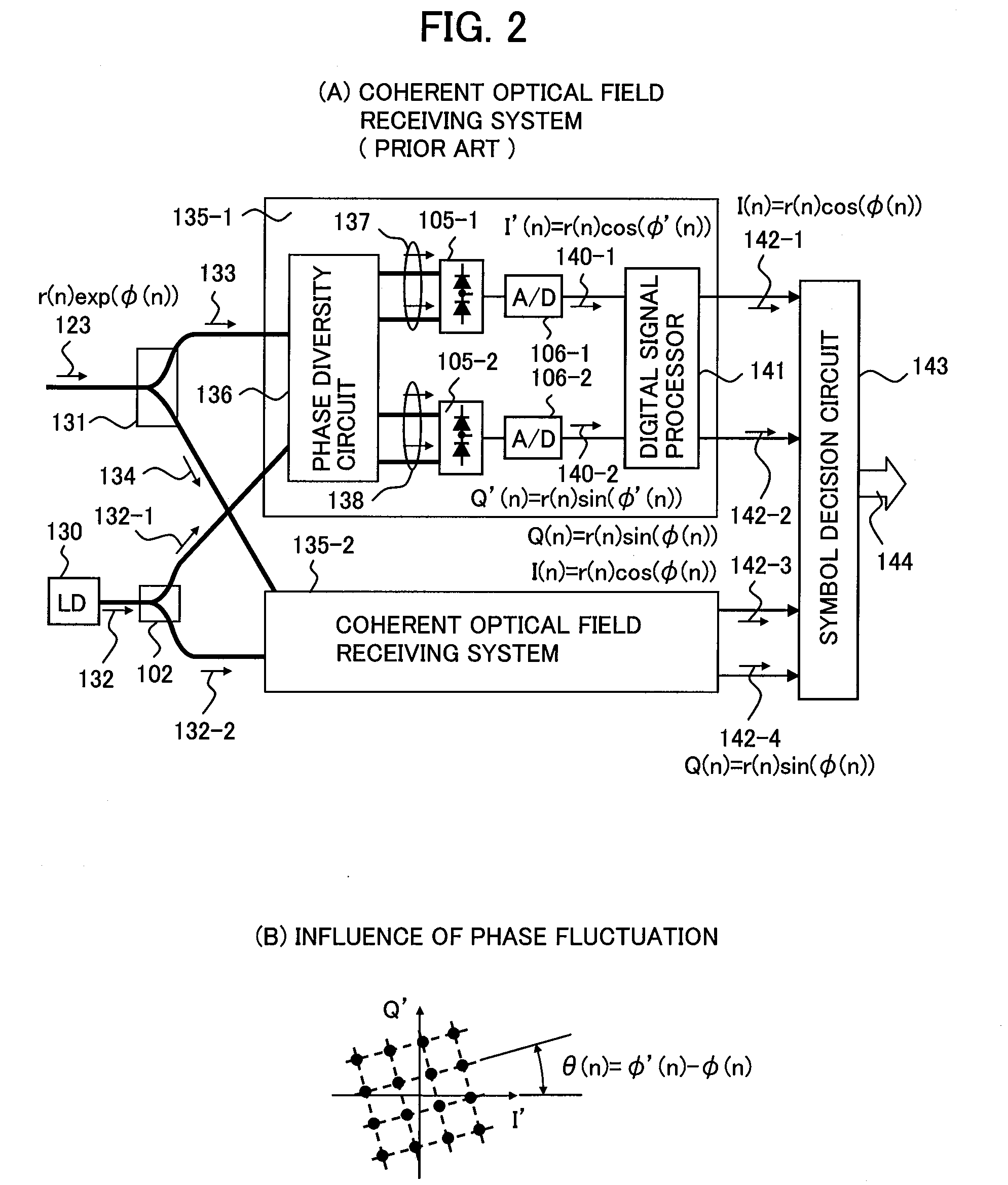
Optical field receiver, optical multilevel signal receiver, and optical transmission system
InactiveUS20090208224A1Simple configurationImprove transmission efficiencySynchronisation information channelsWavelength-division multiplex systemsPhase differenceOptical field
An optical field receiver comprises an optical branching circuit for branching a received optical multilevel signal into first and second optical signals, a first optical delayed demodulator for performing delayed demodulation on the first optical signal at a delay time T (T=symbol time), a second optical delayed demodulator for performing delayed demodulation on the second optical signal at the delay time T with an optical phase difference deviating from the first optical delayed demodulator by 90°, first and second optical receivers for converting each of the delayed demodulation signals representing x and y components of complex signals output from the first and second delayed demodulators into first and second electrical signals, and a field processing unit fort generating a first reconstructed signal representing an inter-symbol phase difference or a phase angle of a received symbol from the first and second electrical signals for each symbol time T.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
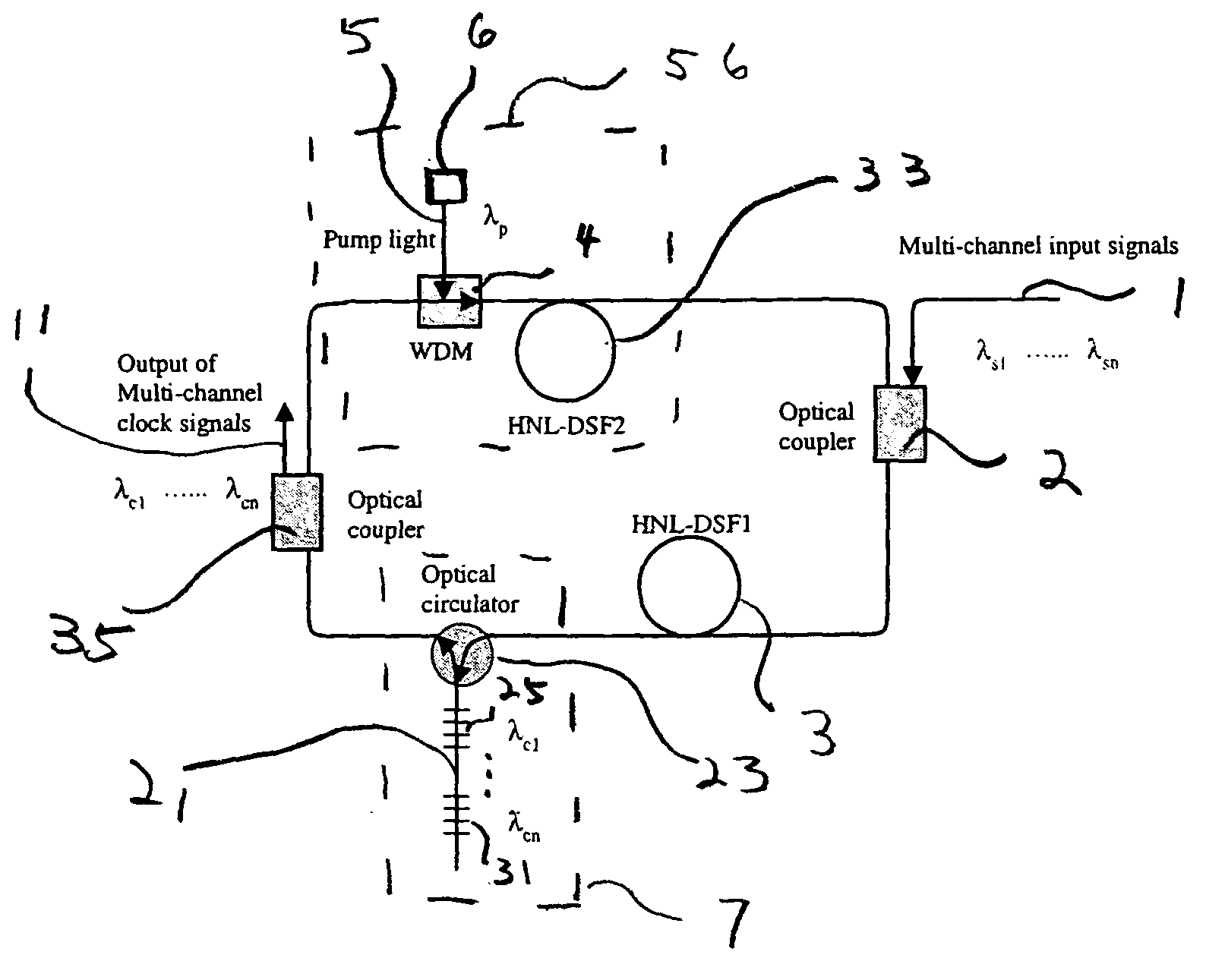
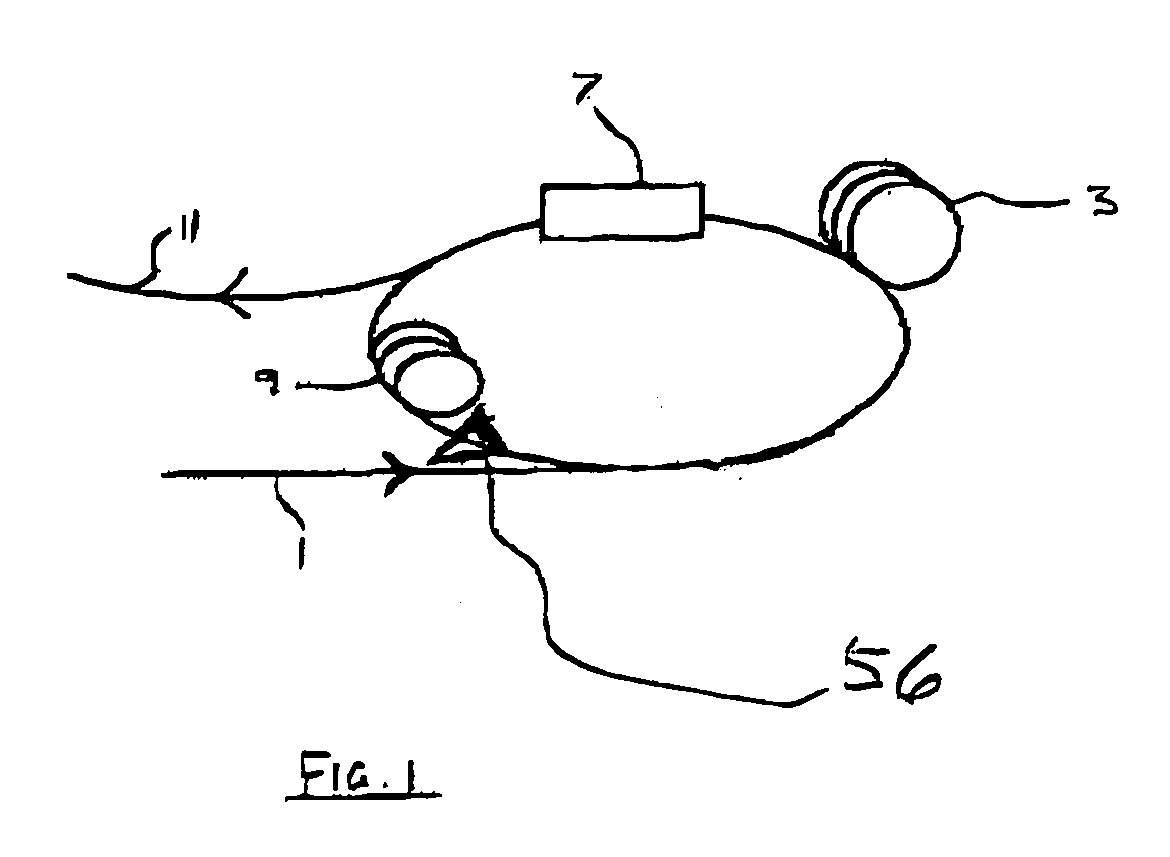
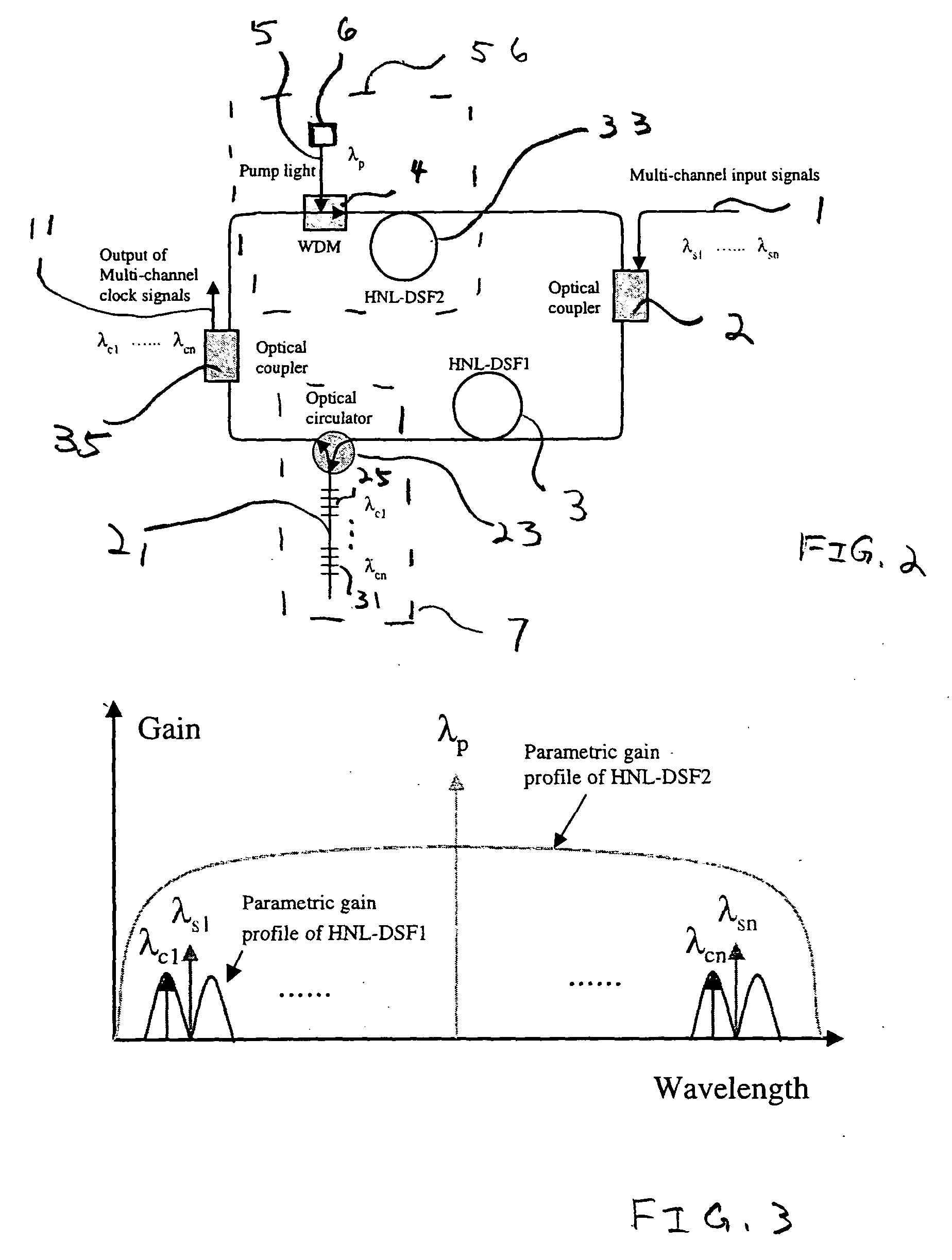
Phase-insensitive recovery of clock pulses of wavelength division multiplexed optical signals
InactiveUS20050063425A1Large dispersionEffective gainLaser using scattering effectsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansMultiplexingMode-locking
An optically-pumped mode-locked fiber ring laser for optical clock recovery of multiple wavelength division multiplexed optical signals actively mode-locks a plurality of outputs of the laser as a plurality of recovered clocks for a plurality of the multiple wavelength division multiplexed optical signals. The laser cavity has a cavity length corresponding to an integer multiple of bit periods of at least one of the multiplexed optical signals for receiving a pre-amplified version of the plurality of wavelength division multiplexed optical signals to provide gain modulation through a phase-insensitive parametric amplification and recirculating a proportion of the output from the laser cavity back through the laser cavity for spatially mode-locking the output of the laser cavity as a recovered clock.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method of and system for detecting skew between parallel signals
ActiveUS8971723B2Simple methodHigh precisionChannel dividing arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsData streamPolarization multiplexed
A method is provided for detecting the skew between parallel light signals generated from a serial data stream. The method can be used with polarization multiplexed signal, as well as with wavelength division multiplexed signals, spatial division multiplexed signals, phase modulated signals, or intensity modulated signals. The method can be used with direct detection schemes as well as with coherent detection schemes. The method is provided with: imprinting dips between a fixed number of transmitted symbols of the parallel signals; detecting an electrical signal related to the dips for each parallel signal; and comparing the electrical signals in delay.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method and system for communicating a clock signal over an optical link
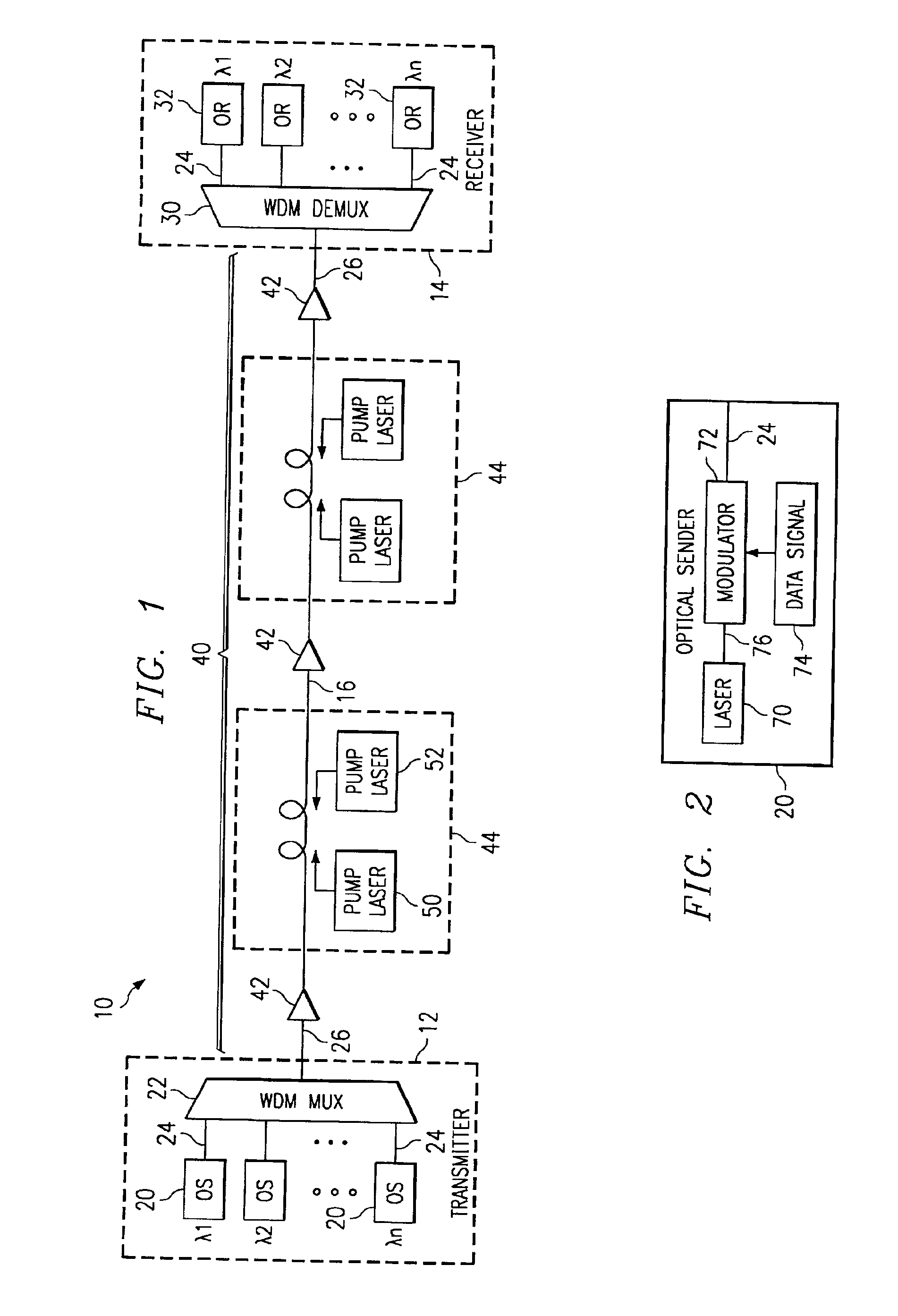
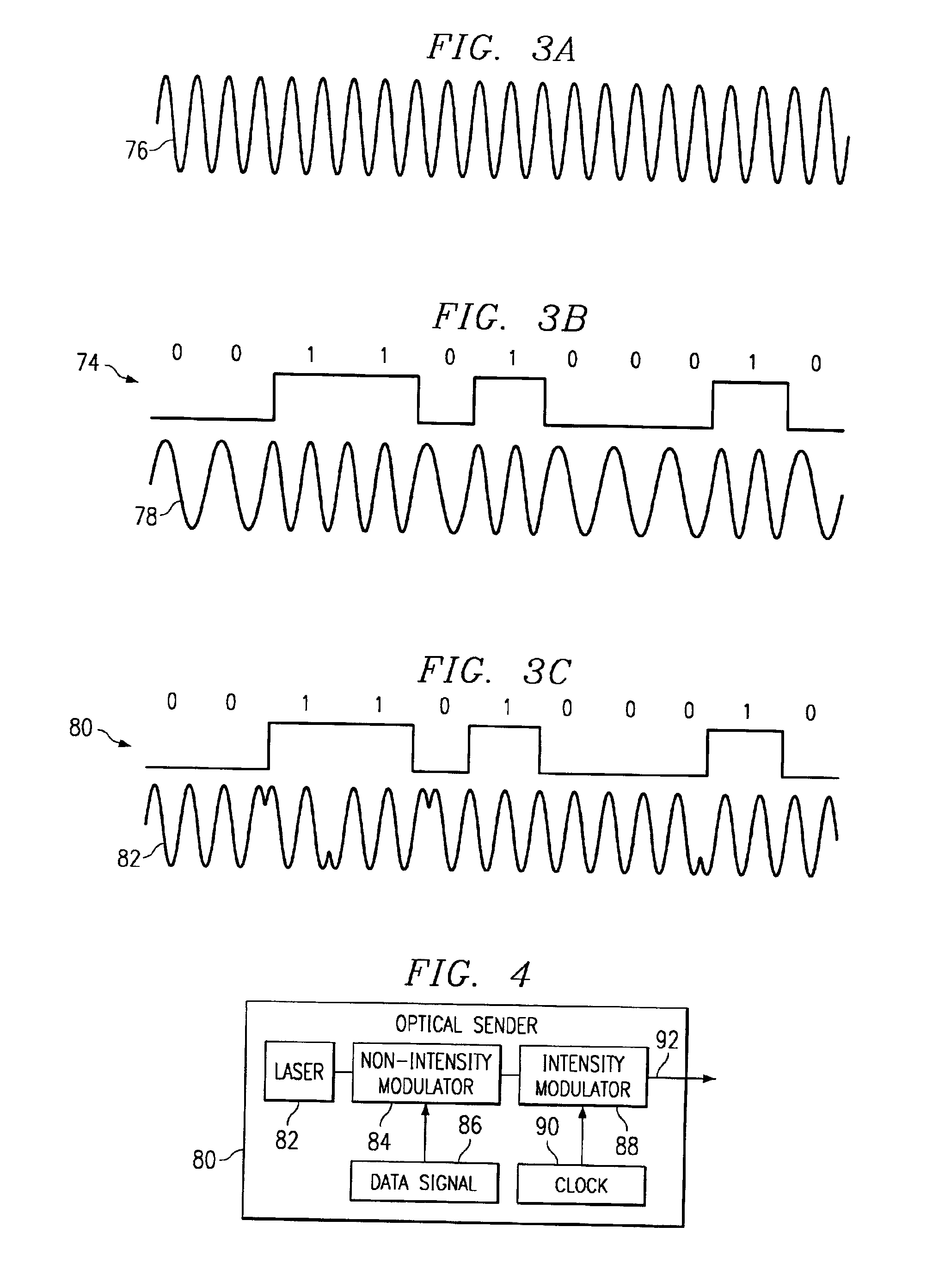
InactiveUS6941078B1Reduces and eliminated problemReduces and eliminated and disadvantageTime-division optical multiplex systemsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansData signalIntensity modulation
A method and system for communicating a clock signal over an optical link includes receiving a multimodulated optical information signal including non-intensity modulation for a data signal and intensity modulation for a clock signal. The clock signal is recovered based on the intensity modulation of the multimodulated optical information signal. The non-intensity modulation for the data signal is converted to intensity modulation for the data signal. The data signal is recovered from the intensity modulation for the data signal using the clock signal.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method And Apparatus For Locking WDM Transmitter Carriers To A Defined Grid
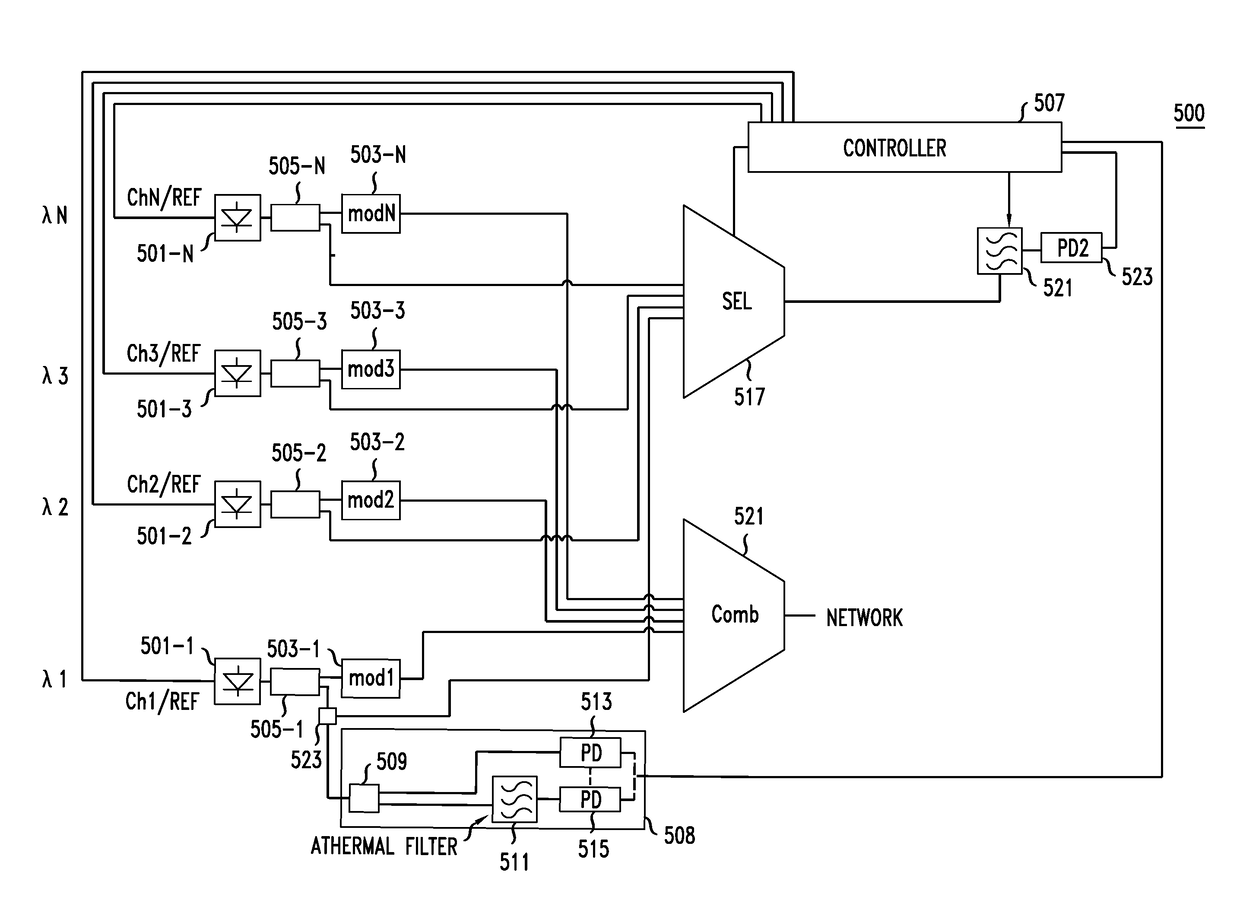
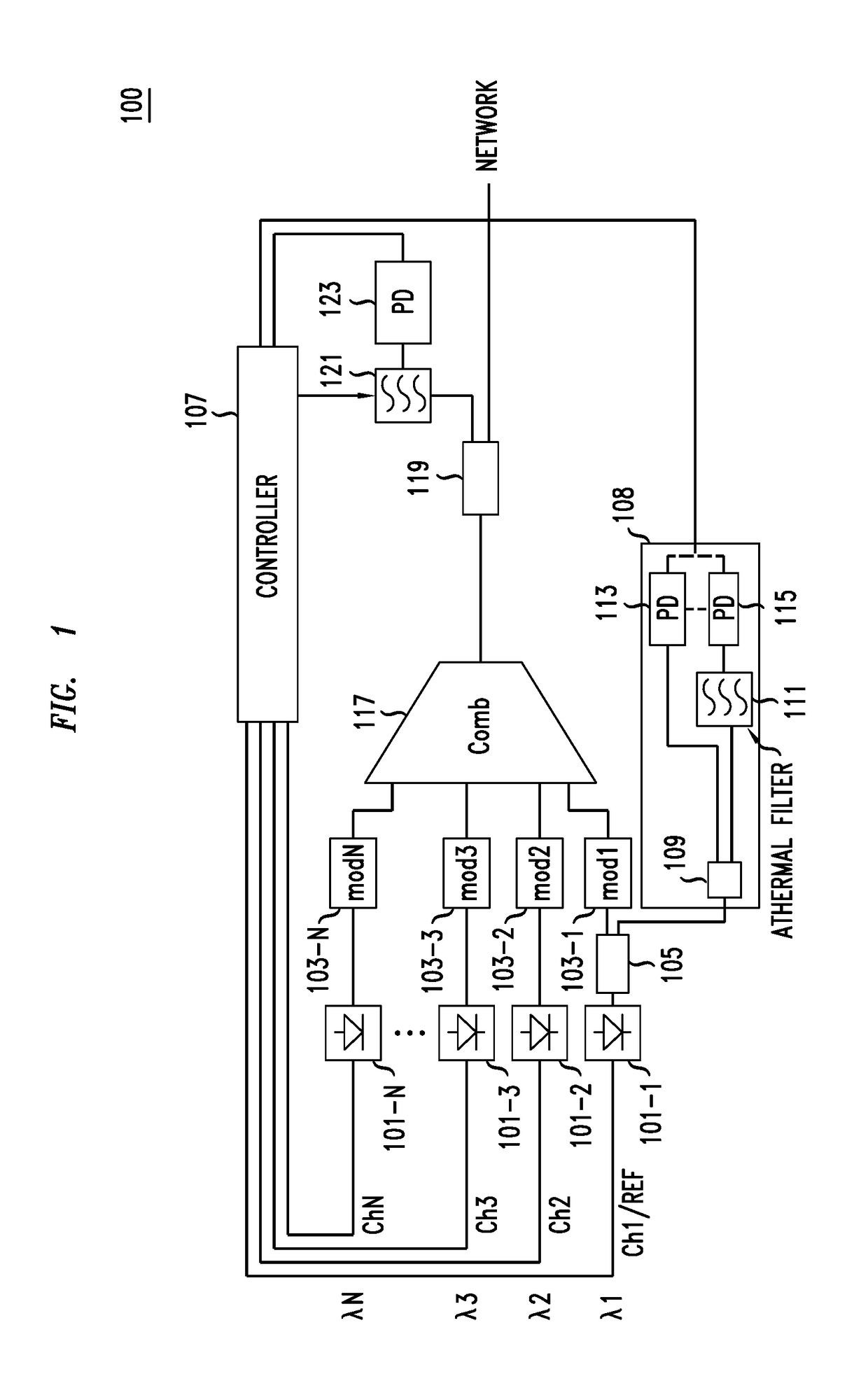
ActiveUS20180115407A1Fabrication errorEliminate needWavelength-division multiplex systemsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansBandpass filteringCarrier signal
The locking of optical carriers to a grid can be achieved by employing an optical filter that exhibits athermal behavior in a frequency range to lock at least the frequency of a first channel to a target frequency. The locked frequency may be used to tune and lock the location of the free spectral range of a bandpass filter having transmission peaks at intervals, e.g., an FSR, corresponding to the target grid. The bandpass filter is used generate feedback signals that are used to lock the remaining frequencies to the grid. The athermal filter may be integrated on a silicon photonic integrated circuit.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
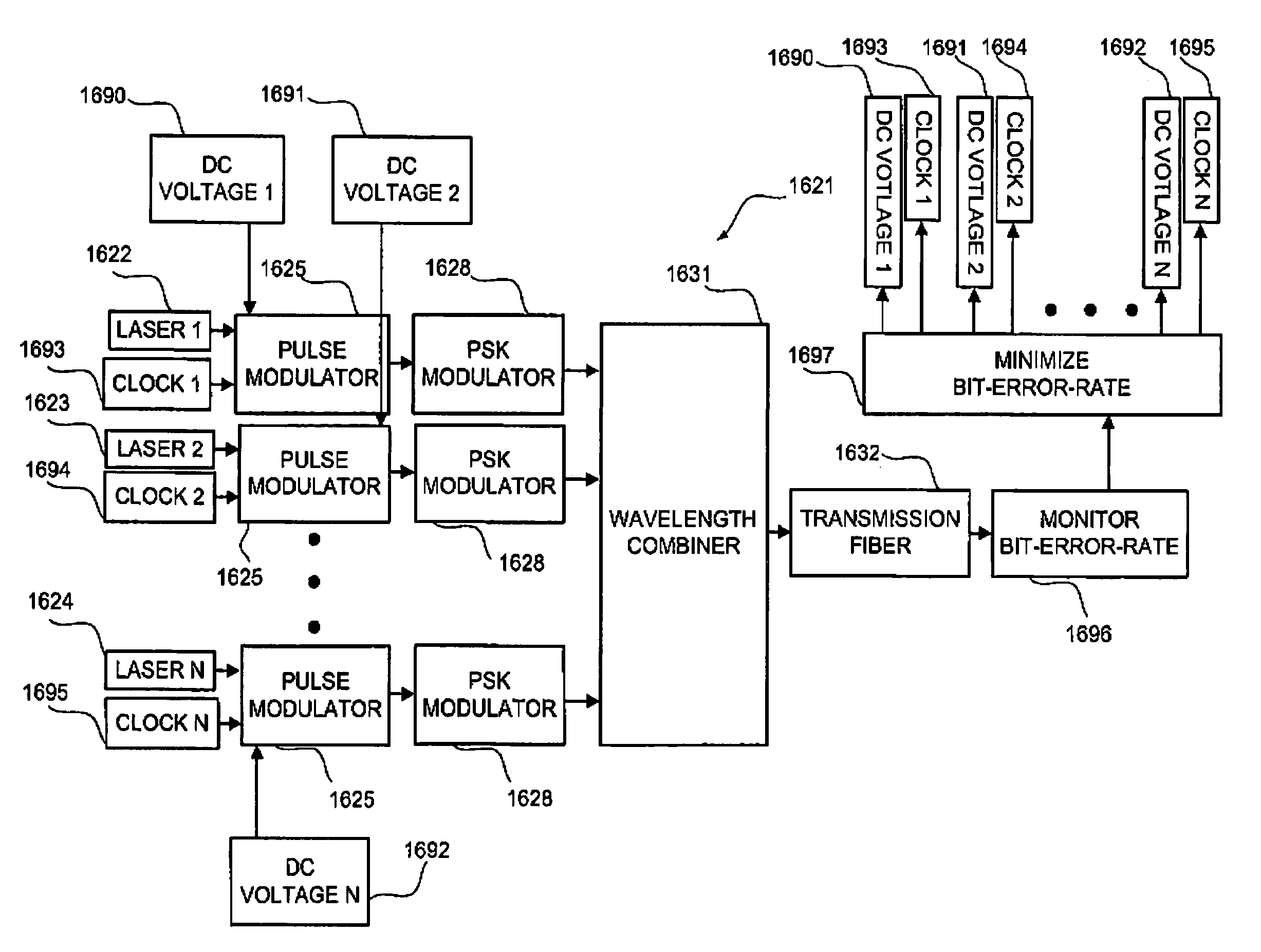
40g/100g/200g/400g pluggable optical transceivers with advanced functionality
ActiveUS20150125158A1Full accessReduce accessTime-division optical multiplex systemsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansTransceiverCarrier grade
Integrated performance monitoring (PM); optical layer operations, administration, maintenance, and provisioning (OAM&P); alarming; amplification, and the like is described in optical transceivers, such as multi-source agreement (MSA)-defined modules. A pluggable optical transceiver defined by an MSA agreement can include advanced integrated functions for carrier-grade operation which preserves the existing MSA specifications allowing the pluggable optical transceiver to operate with any compliant MSA host device with advanced features and functionality, such as Forward Error Correction (FEC), framing, and OAM&P directly on the pluggable optical transceiver. The advanced integrated can be implemented by the pluggable optical transceiver separate and independent from the host device.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
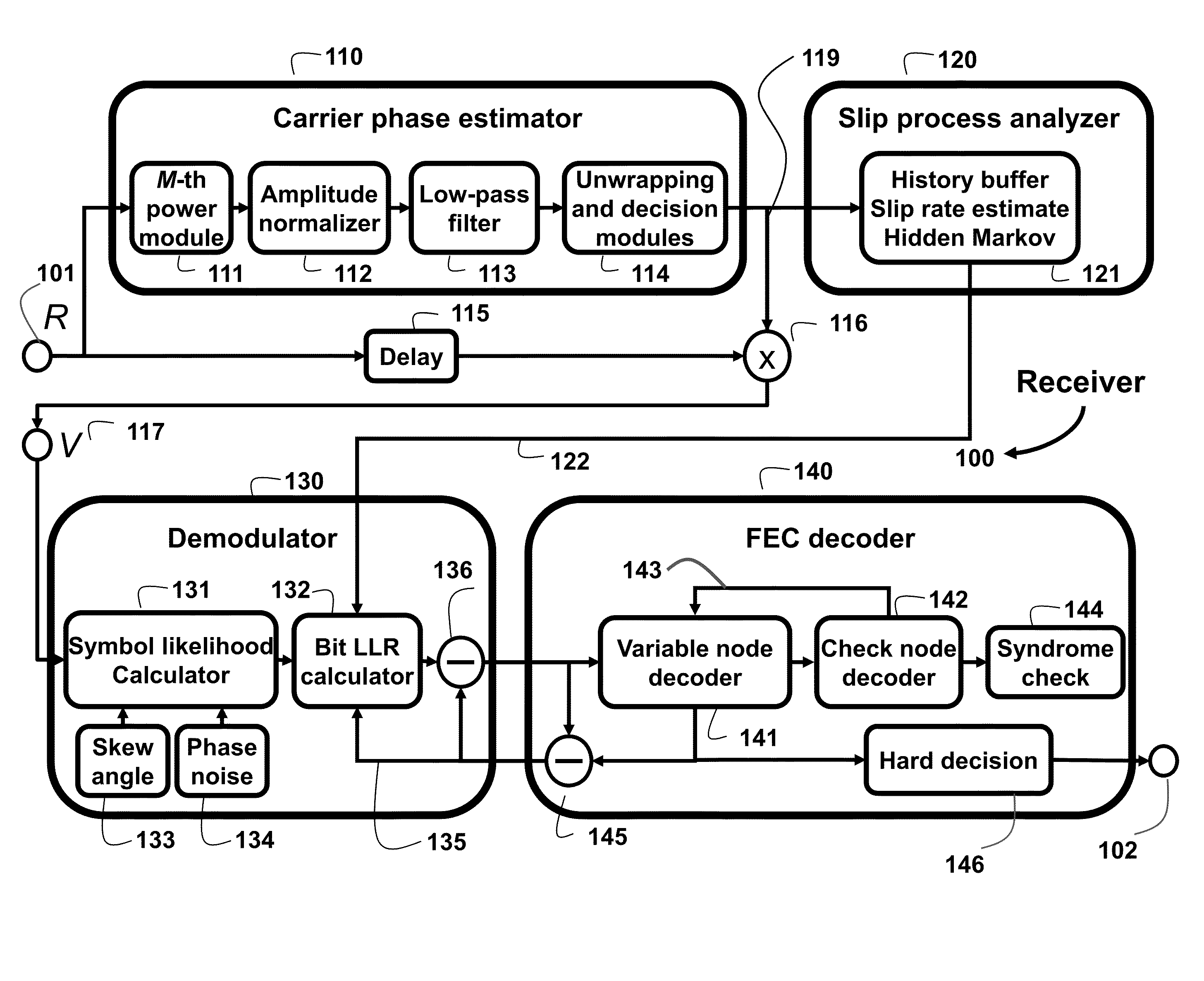
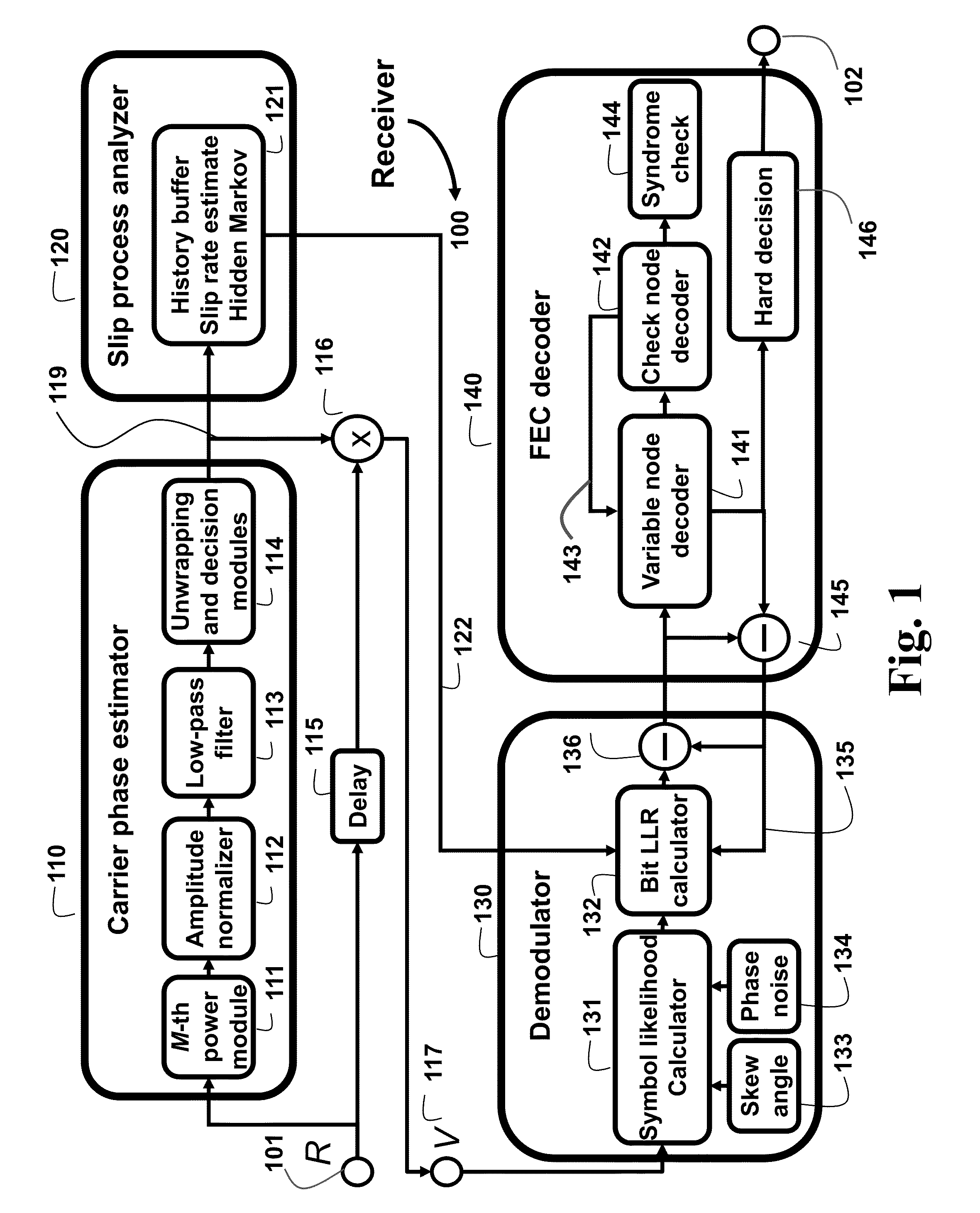
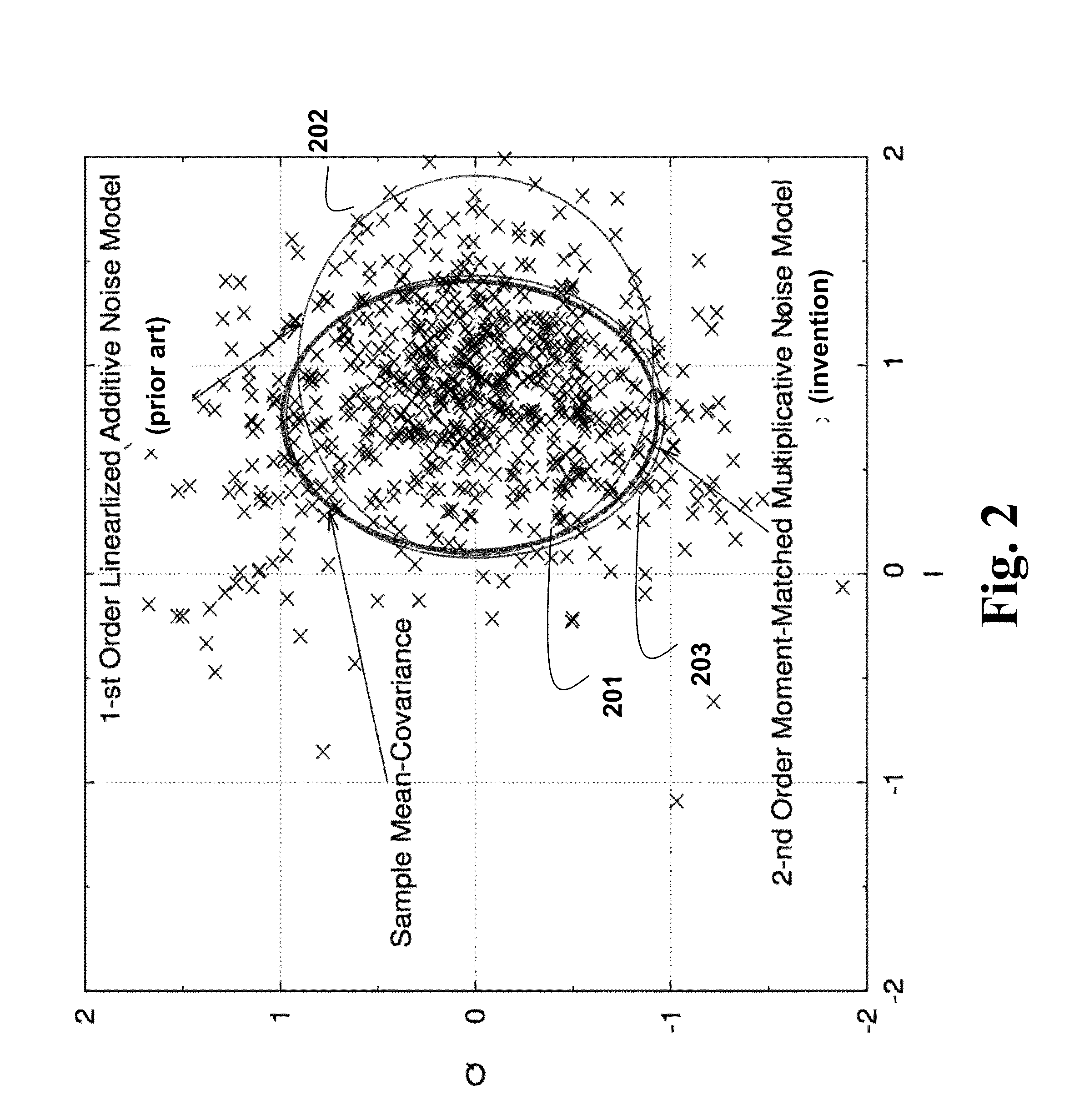
System and Method for Recovering Carrier Phase in Optical Communications
ActiveUS20160065315A1Improve performanceError minimizationError preventionSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansSkew angleHide markov model
The embodiments of the invention provide methods to deal with problems of cycle slips, angular skew, and residual phase noise for high-speed optical communications employing any arbitrary high-order multi-dimensional modulation formats. The embodiments use a slip process analyzer, a skew angle estimator, and a phase noise variance estimator to provide feedforward soft-decision information of a carrier phase recovery (CPE) for more accurate likelihood calculation based on a high-order hidden Markov model (HMM). The log-likelihood calculation can be done jointly in dual polarization with joint Markov state transition. Some embodiments use a kernel filter or a particle filter for log-likelihood calculation.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
All-optical signal processing method and device
InactiveUS20060238866A1Polarisation multiplex systemsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansBandpass filteringOptical clock
A method and an optical device in all-optical signal processing. It provides a novel way of taking into use the potential bandpass filtering capabilities of an optical complex one-pole resonator by, 1) excitating with at least part of the input signal an optical resonator arrangement that comprises two substantially parallel, independent, complex one-pole resonators arranged in a manner that one of the resonators is matched, and the other one is non-matched with the input signal, and 2) based on polarization separating further from the output of the optical resonator arrangement at least one optical output signal so that both the matched and non-matched resonators contribute to the formation of the output signal. The method and device can be utilized, for example, for optical signal analysis, optical clock recovery, or for producing high-frequency outputs from lower frequency input signals, like e.g. optical microwave generation.
Owner:LUXDYNE
Method and system for mitigating nonlinear transmission impairments in fiber-optic communications systems
InactiveUS7224906B2Time-division optical multiplex systemsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansFiberReturn-to-zero
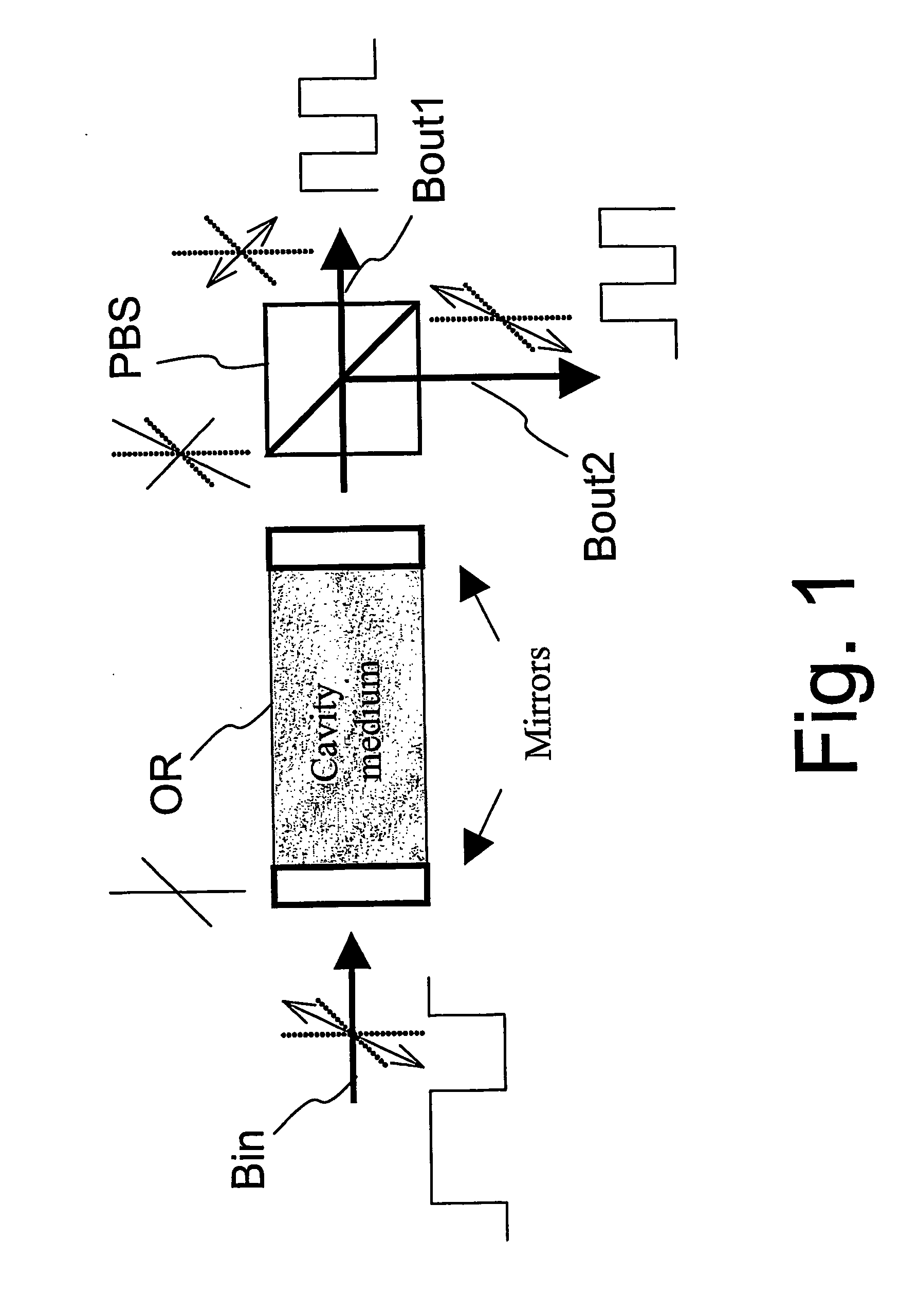
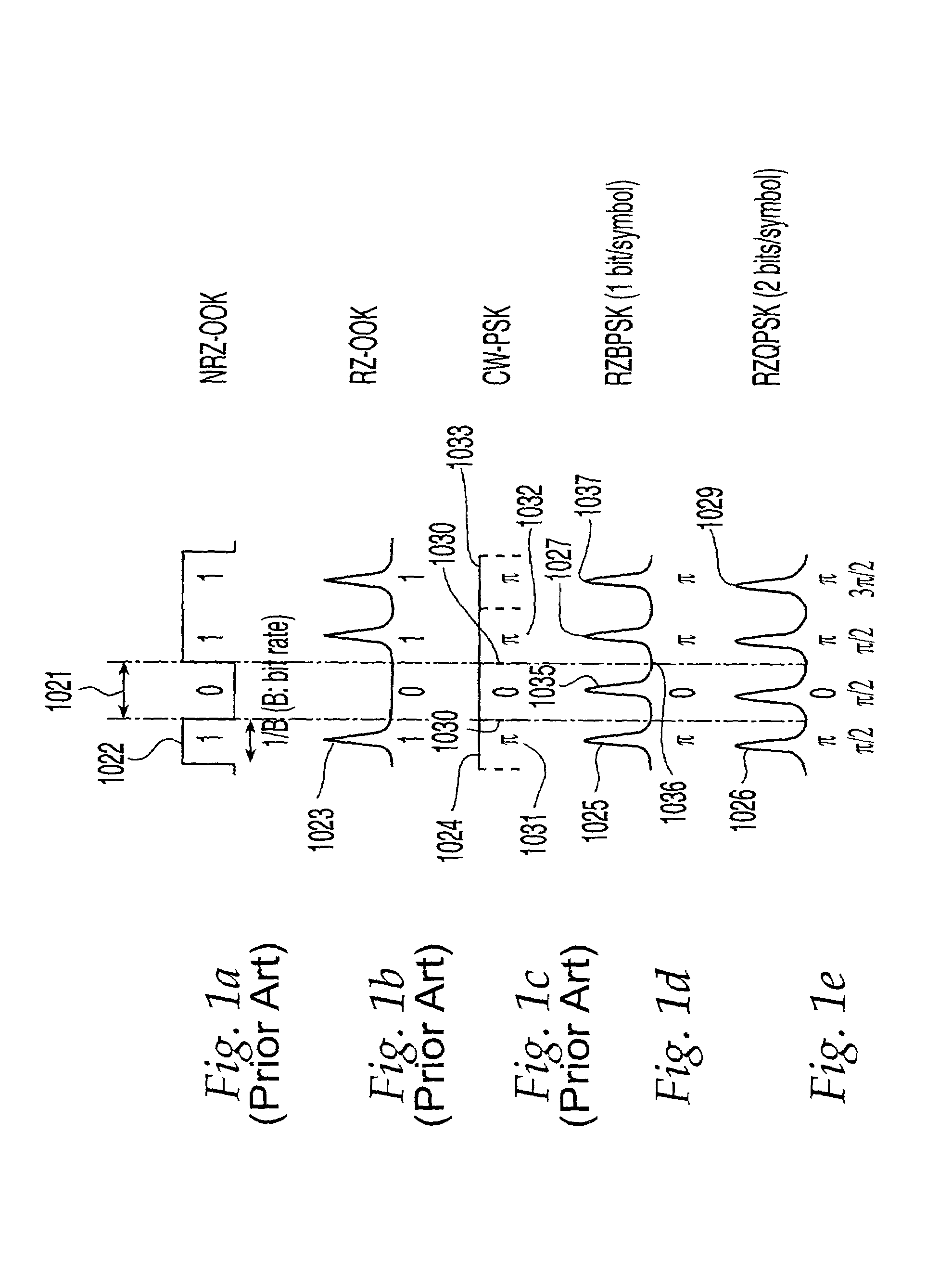
The present invention relates to a method for transmitting data. An optical pulse stream comprising a plurality of return-to-zero optical pulses is prepared by modulating a phase of light output by an optical source to thereby encode data from a data source. The light of the optical pulse stream has a wavelength. The optical pulse stream is transmitted along an optical fiber of an optical network. Optical pulse streams of the invention enhance transmission performance at least in part by reducing noise at the receiver caused by fiber non-linearities.
Owner:CELIGHT
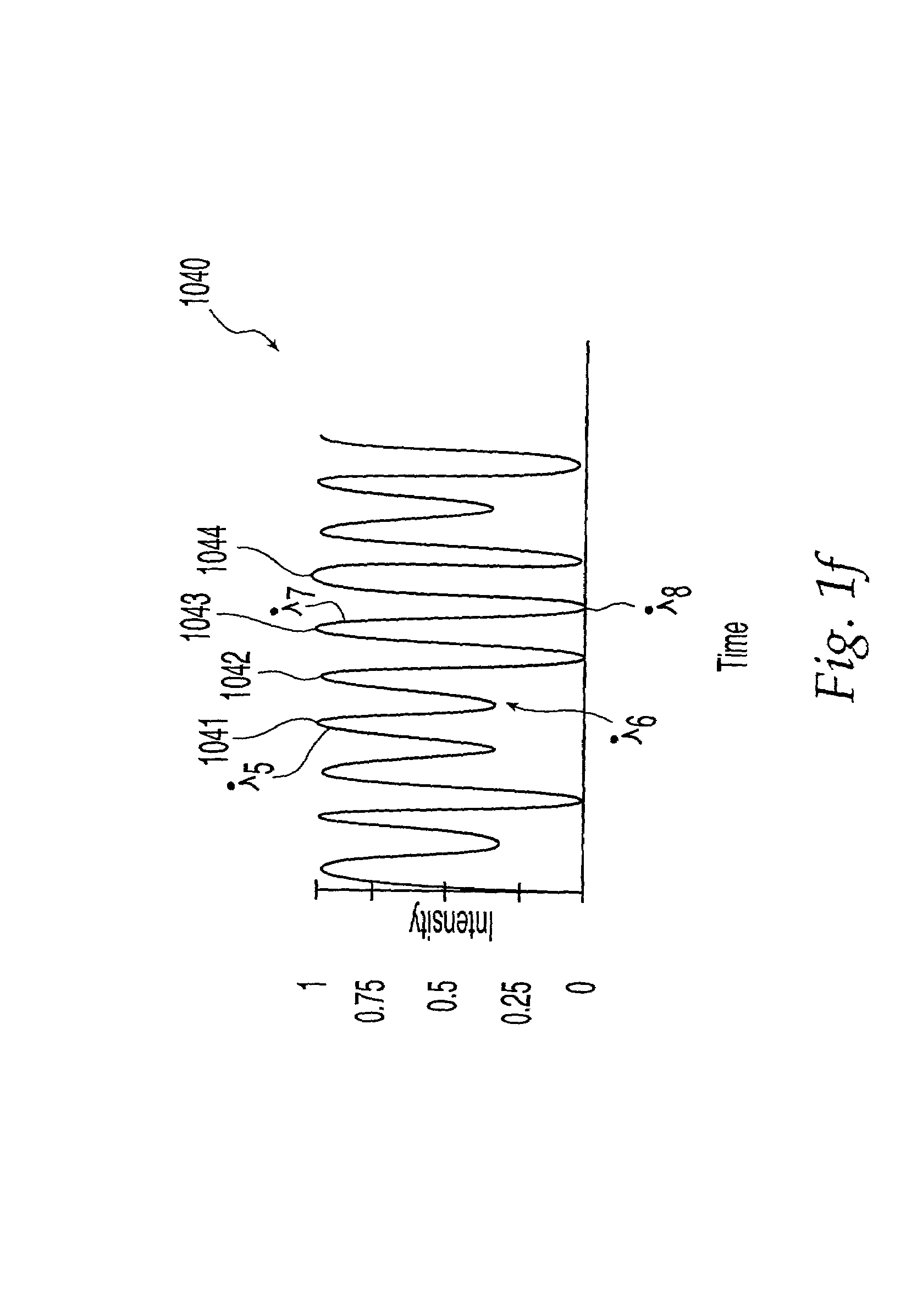
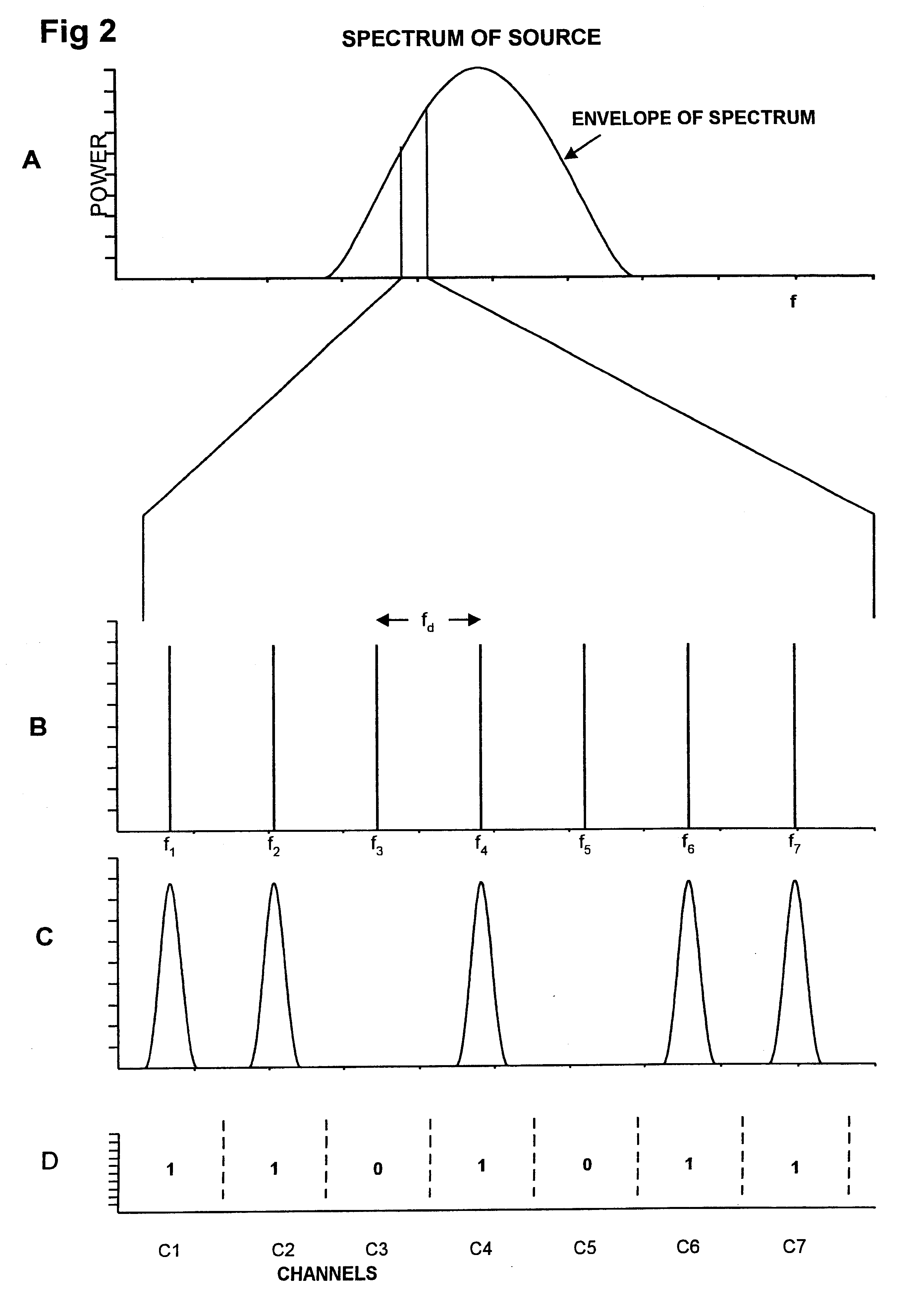
Multiplexed transmission of optical signals
InactiveUS6522436B2Simple methodError prevention/detection by using return channelCorrect operation testingMultiplexingData stream
In an optical communication system, a train of optical pulses is transmitted such that each pulse carries a set of multiplexed channels. In a receiver, the error rate for each channel is monitored and a subset of channels having the most favorable rate is selected to carry a first data stream. The remaining channels carry a second data stream. Error rate performance is determined on the basis of error detecting codes carried by the channels in the first and second data streams.
Owner:CIENA
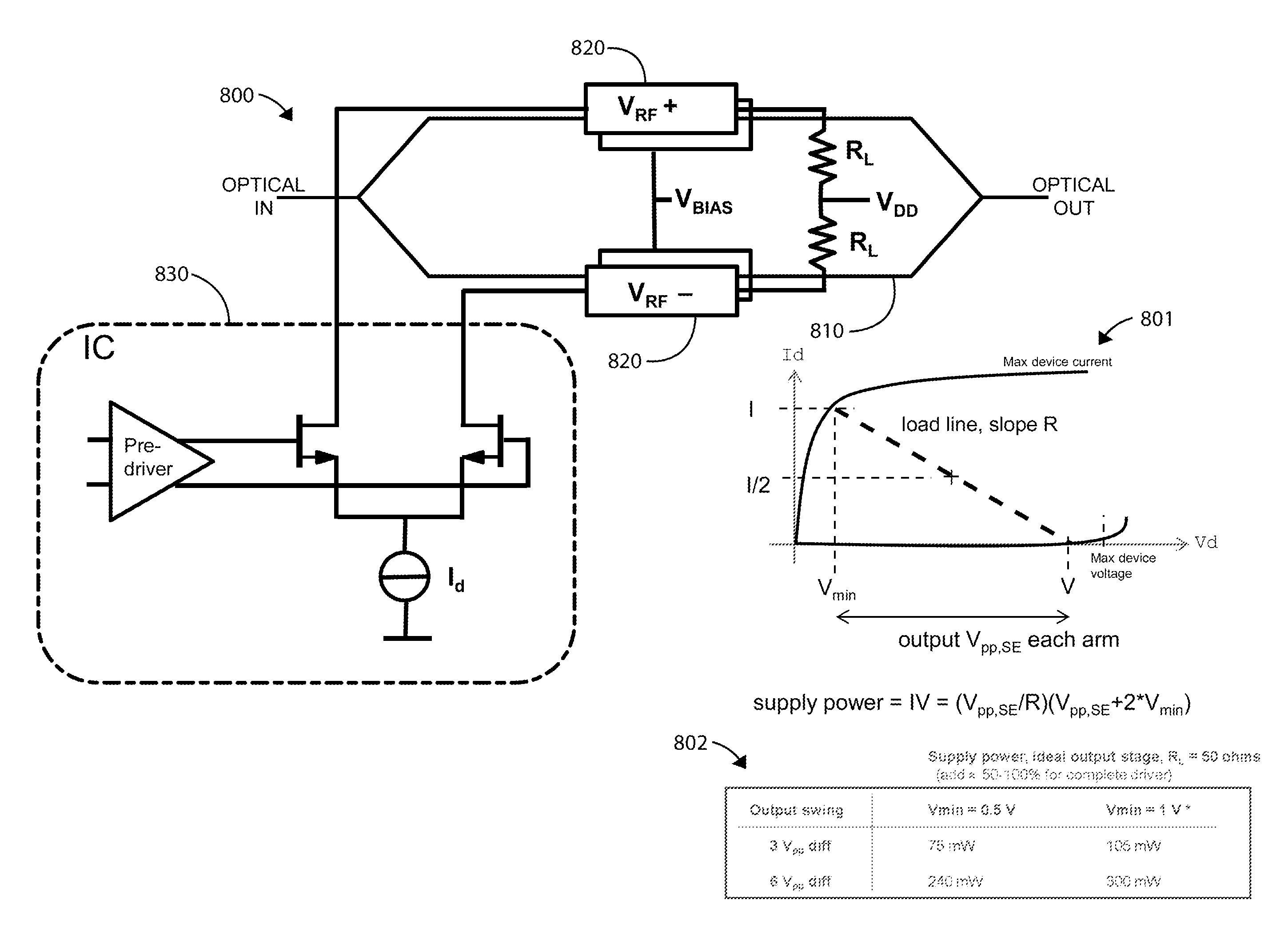
Direct-coupled driver for mach-zehnder optical modulators
ActiveUS8948608B1Versatile drive capabilitySave extra spaceSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansFibre transmissionDriver circuitHemt circuits
An optical modulator device directly-coupled to a driver circuit device. The optical modulator device can include a transmission line electrically coupled to an internal VDD, a first electrode electrically coupled to the transmission line, a second electrode electrically coupled to the first electrode and the transmission line. A wave guide can be operably coupled to the first and second electrodes, and a driver circuit device can be directly coupled to the transmission line and the first and second electrodes. This optical modulator and the driver circuit device can be configured without back termination.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Frequency conversion compensating microwave frequency transmission system and method
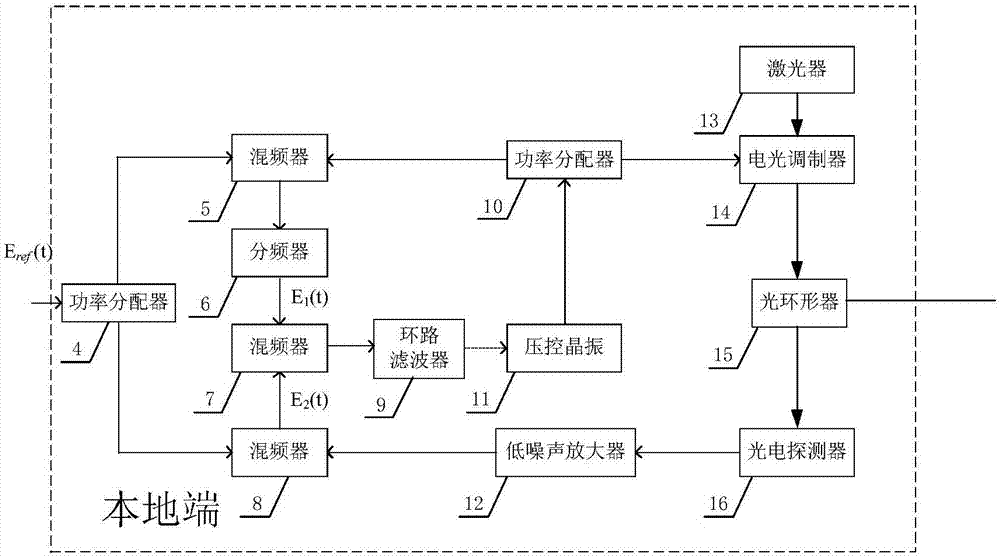
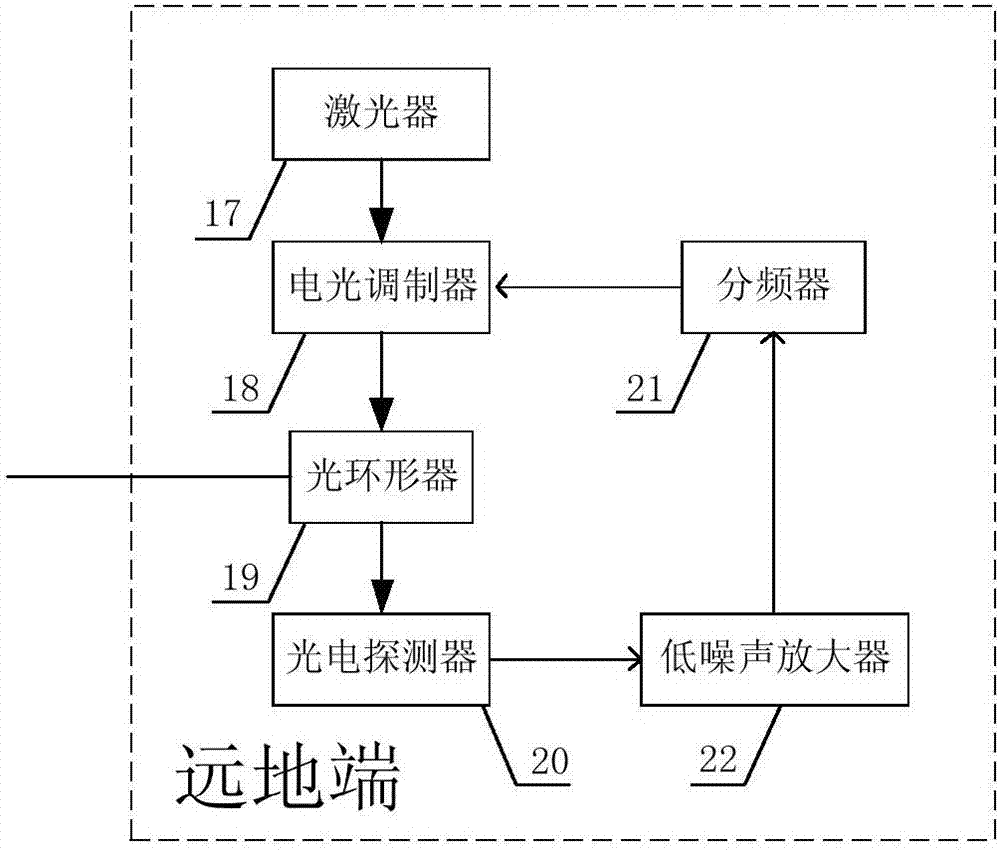
ActiveCN108011667APrevent phase interferenceImprove stabilitySynchronisation by photonic/optical meansDistortion/dispersion eliminationPhase noiseMicrowave emission
The invention discloses a frequency conversion compensating microwave frequency transmission system and method. A phase pre-compensated microwave transmission signal is loaded into a laser signal, thelaser signal is transmitted to a remote end through utilization of an optical fiber, and the remote end restores the laser signal into a frequency signal synchronous with a microwave reference frequency signal of a local end through detection. According to a specific process, after a local signal is transmitted to the remote end, frequency conversion is carried out on a detection signal of the remote end, the detection signal is returned to the local end, a return signal comprises phase noise imported into an optical fiber link; the return signal and the local transmission signal are respectively mixed with the local reference signal, comparison is carried out to acquire pre-compensation quantity and a crystal oscillator generating the transmission signal is controlled according to the compensation quantity, so phase compensation of high precision frequency transmission is finished. Compared with existing frequency transmission, the method mainly has the advantages that frequencies ofthe signals transmitted by the local end and returned by the remote end are different, the phase interference of strong signals of stations at the two ends for detected and received weak signals is avoided, and the frequency transmission stability is further improved.
Owner:NAT TIME SERVICE CENT CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
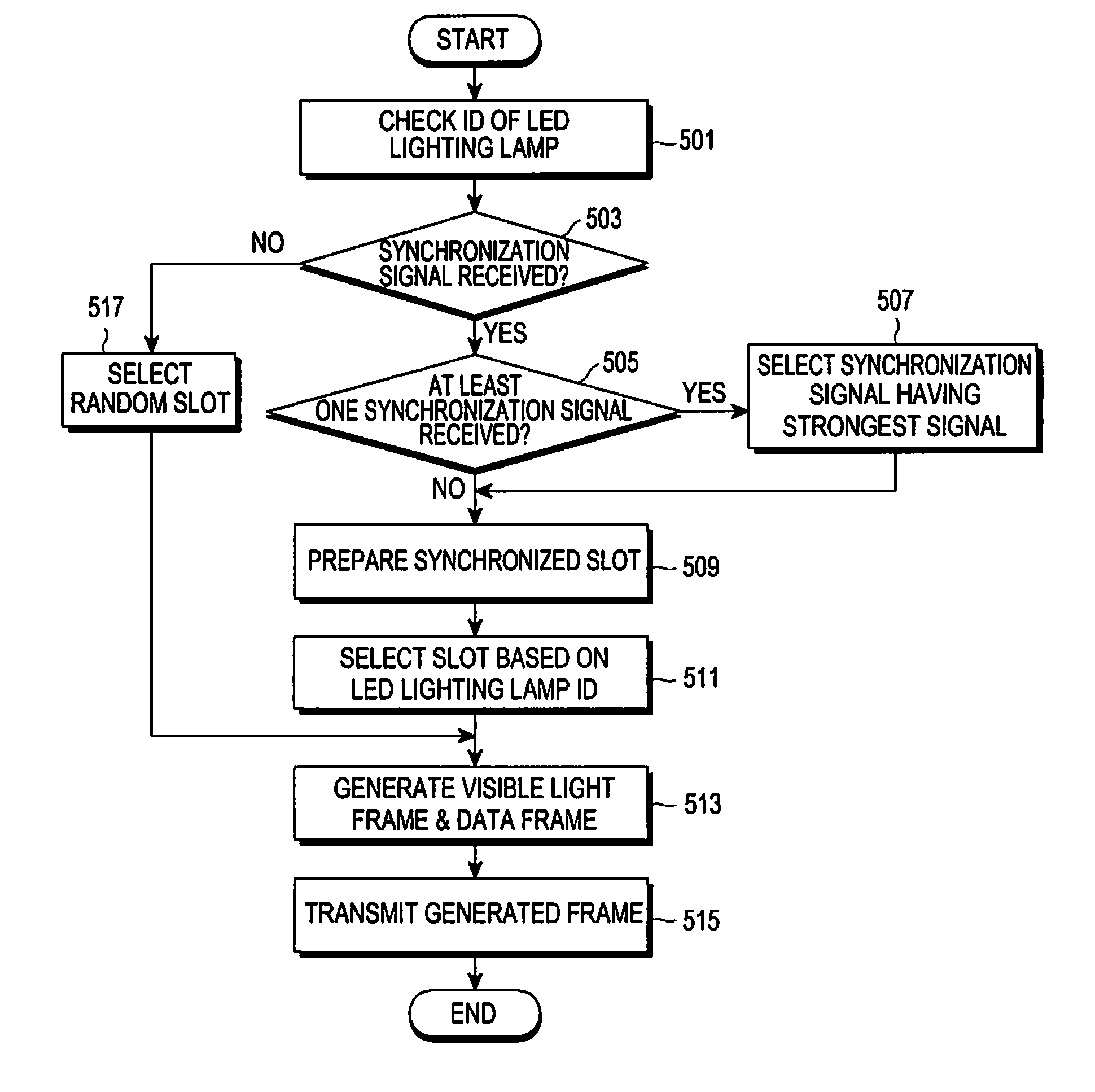
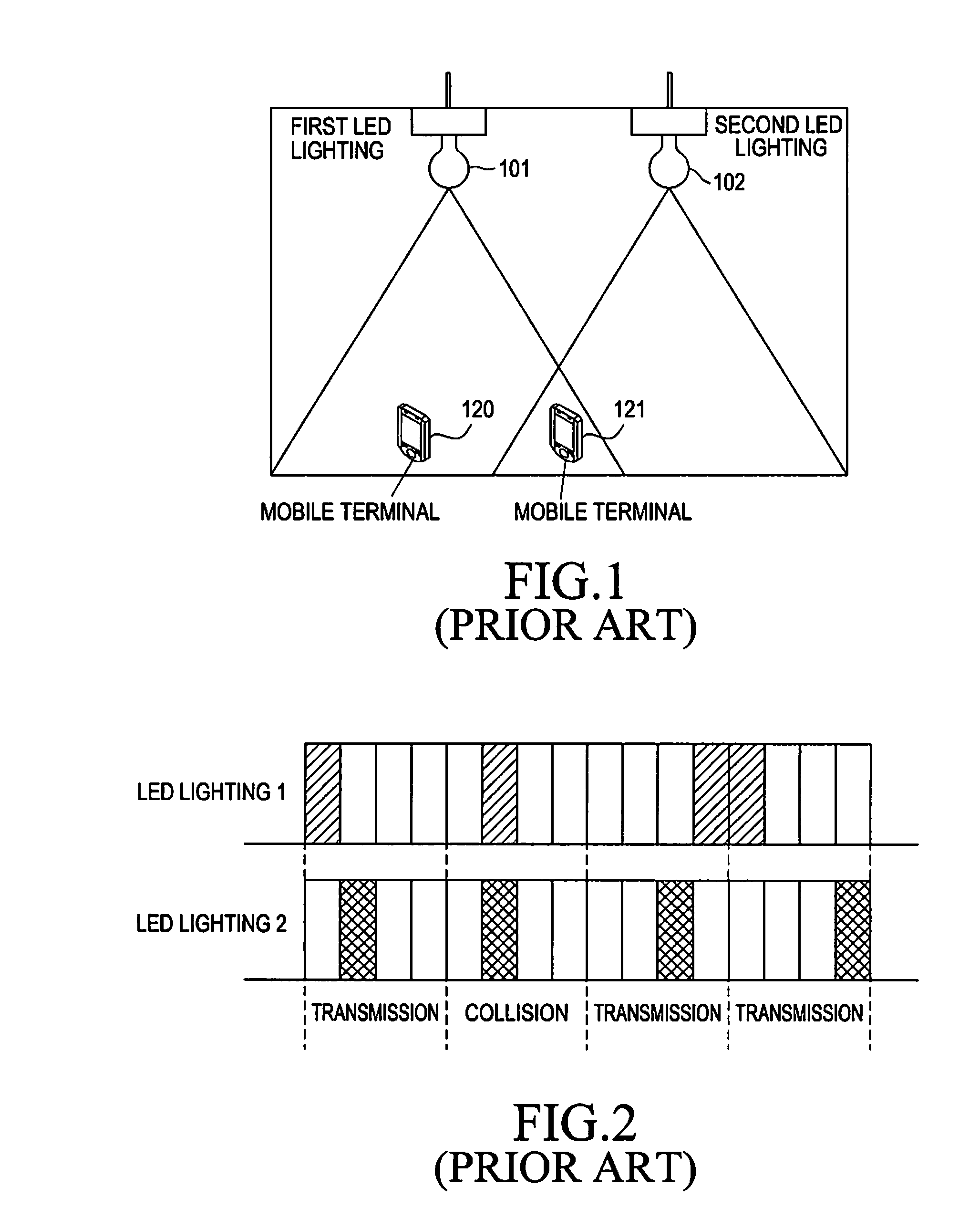
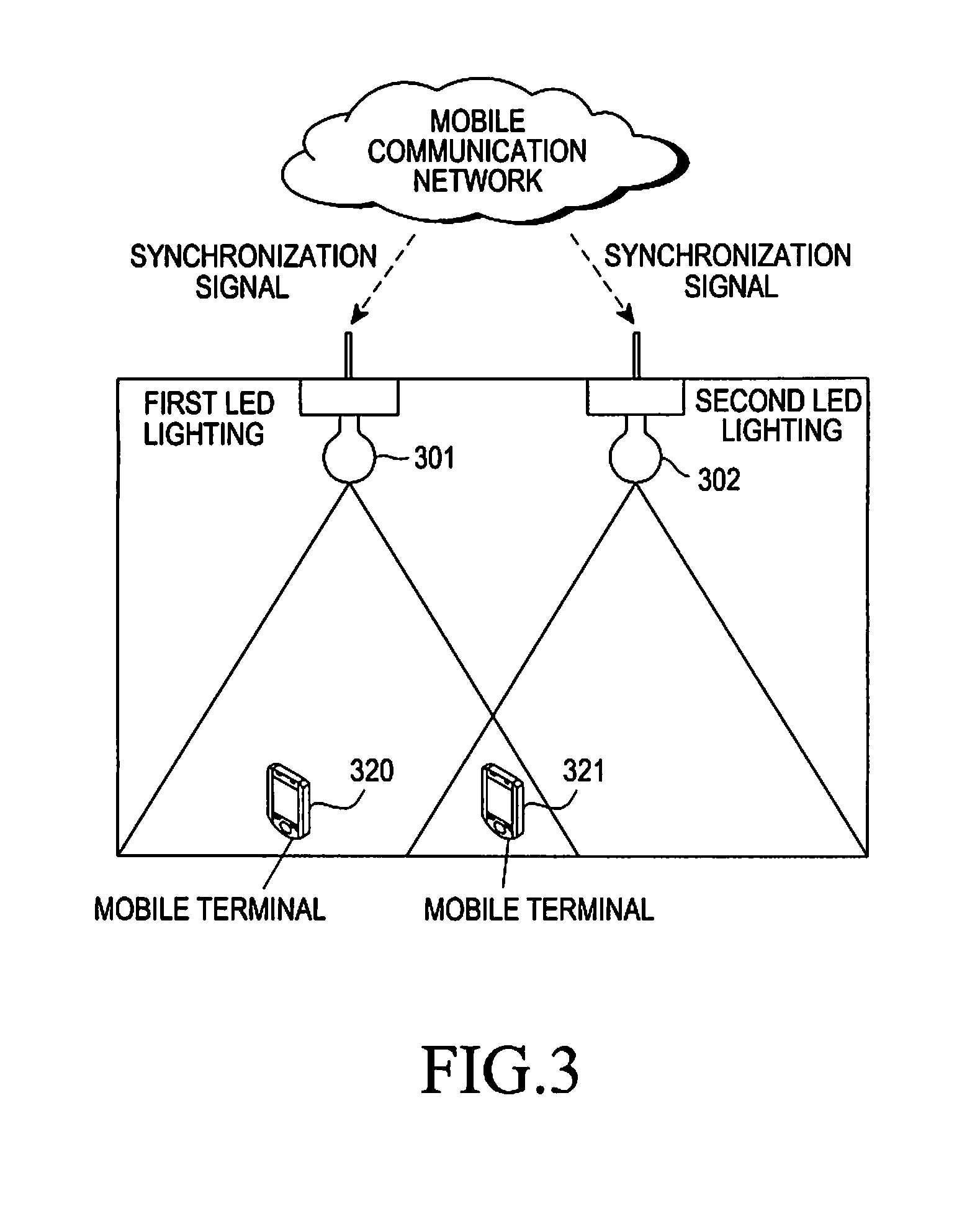
Apparatus and method for providing synchronized data by using visible light communication
ActiveUS20110170872A1Time-division optical multiplex systemsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansComputer terminalSpecific time
An apparatus and a method for providing synchronized data by using visible light communication includes, receiving a synchronization channel from a mobile communication base station using a specific mobile communication network, by a Light Emitting Diode (LED) lighting; analyzing the received synchronization channel, and extracting a synchronization signal for synchronizing the LED lighting with at least one LED lighting adjacent to the LED lighting; selecting a specific time slot of the synchronization signal based on IDentifications (IDs) of the LED lightings; and including a data frame of the LED lighting in the specific time slot, and transmitting the specific time slot, which includes the data frame of the LED lighting, to a mobile terminal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Data in motion storage system and method
ActiveUS20170280211A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsPolarisation multiplex systemsOptical cavityWaveguide
A data storage system is disclosed that includes a recirculating loop storing data in motion. The data may be carried by a signal via the loop including one or more satellites or other vessels that return, for example by reflection or regeneration, the signals through the loop. The loop may also include a waveguide, for example an optical fiber, or an optical cavity. Signal multiplexing may be used to increase the contained data. The signal may be amplified at each roundtrip and sometimes a portion of the signal may be regenerated.
Owner:NKB PROPERTIES MANAGEMENT LLC
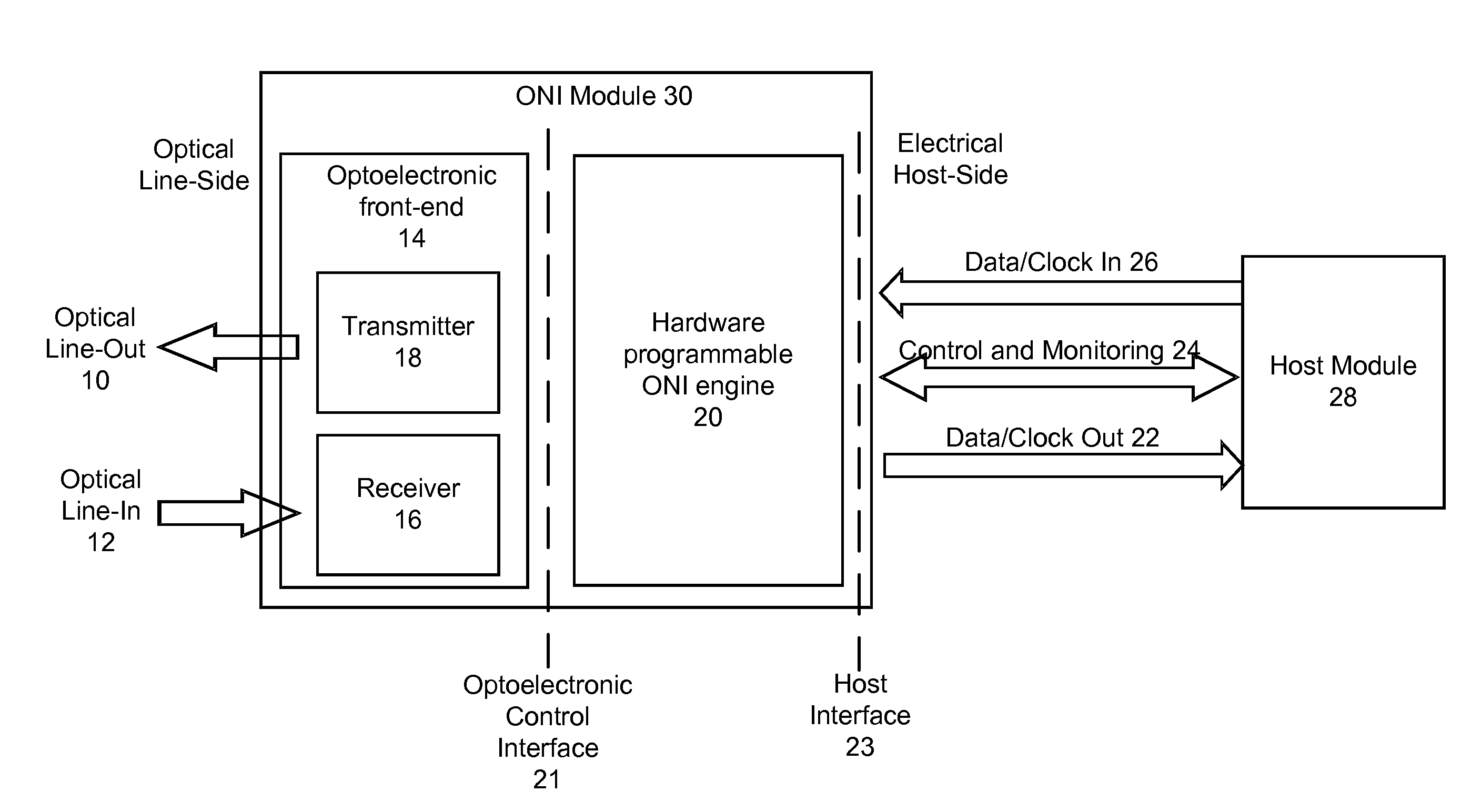
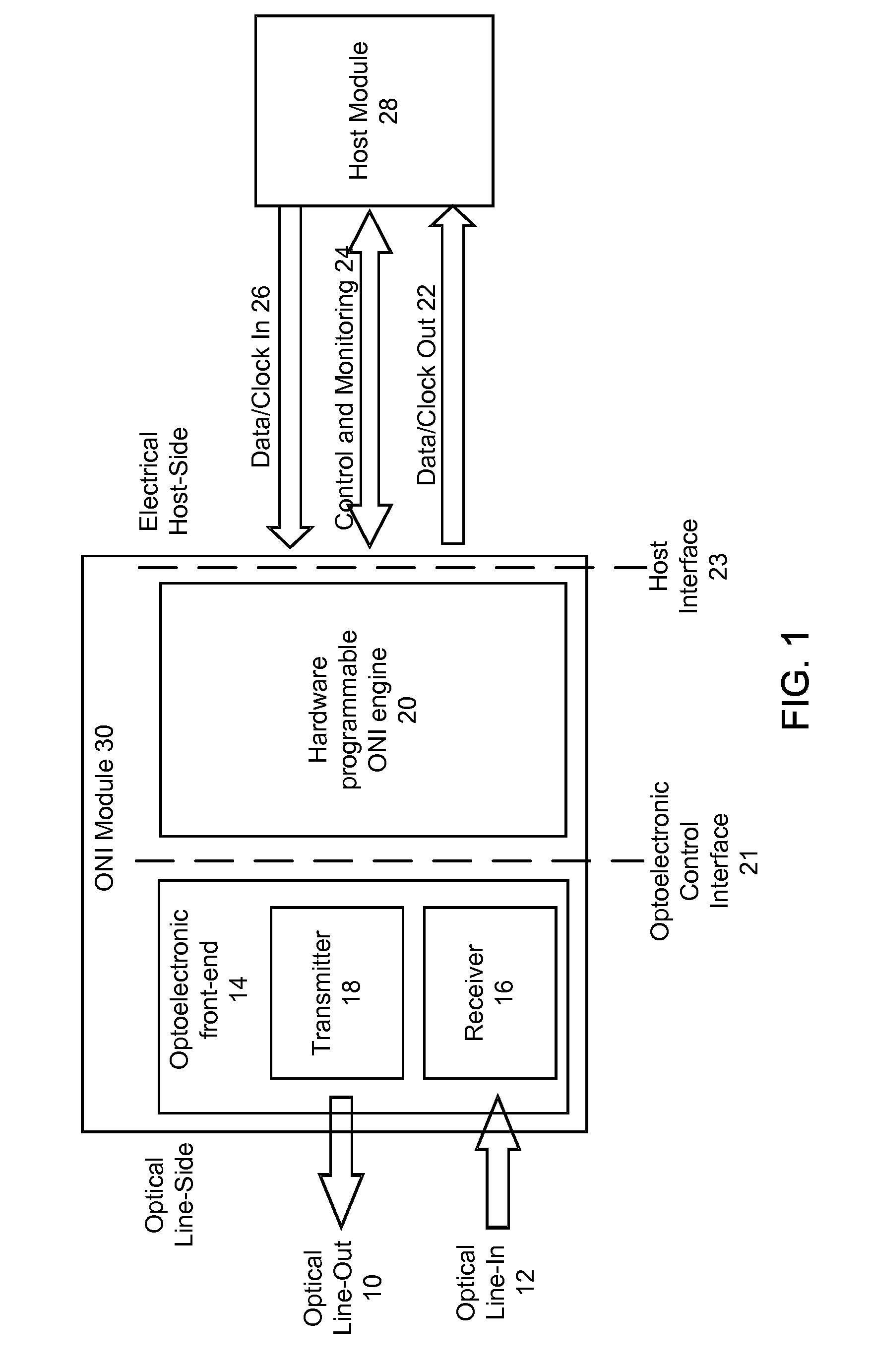
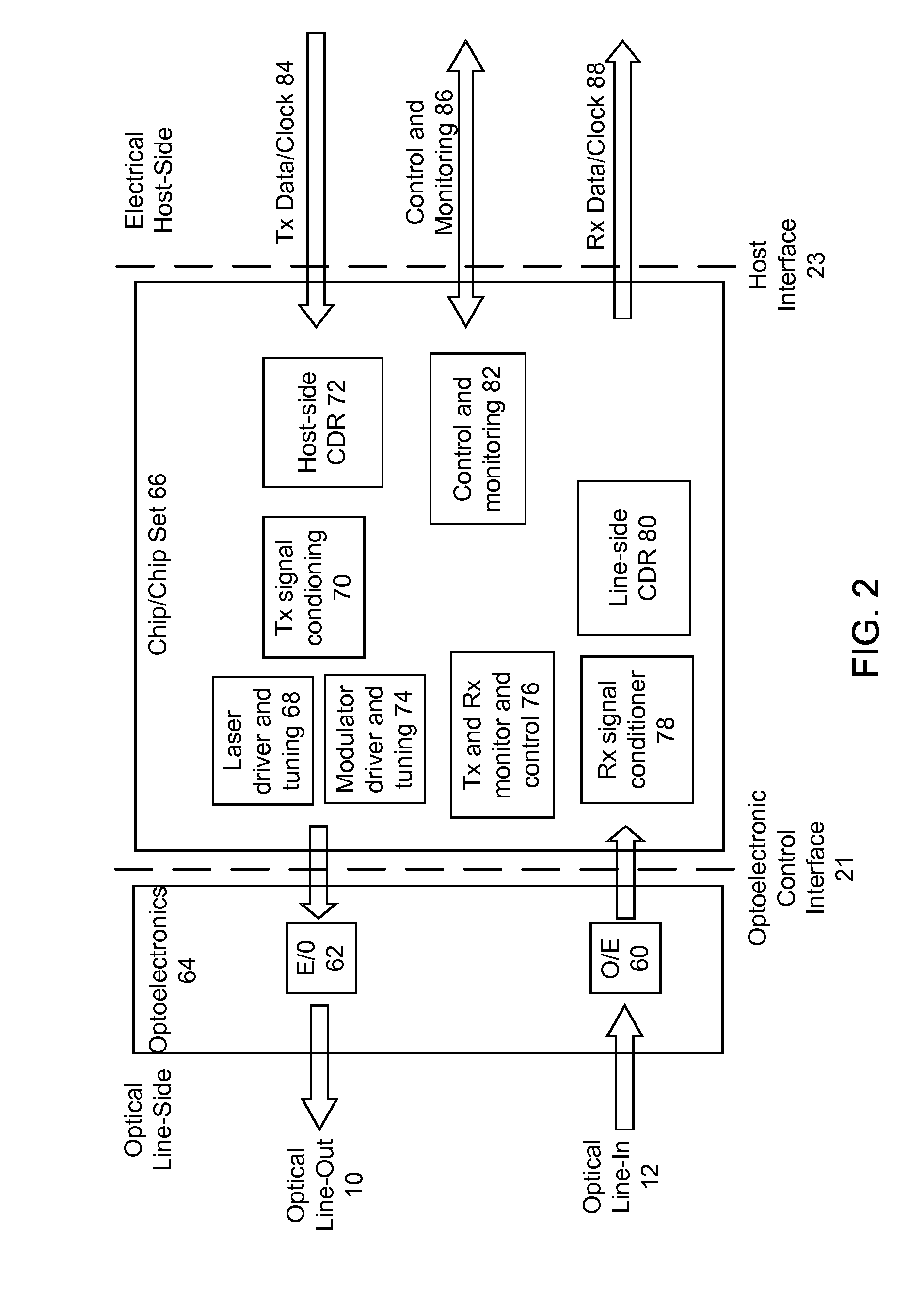
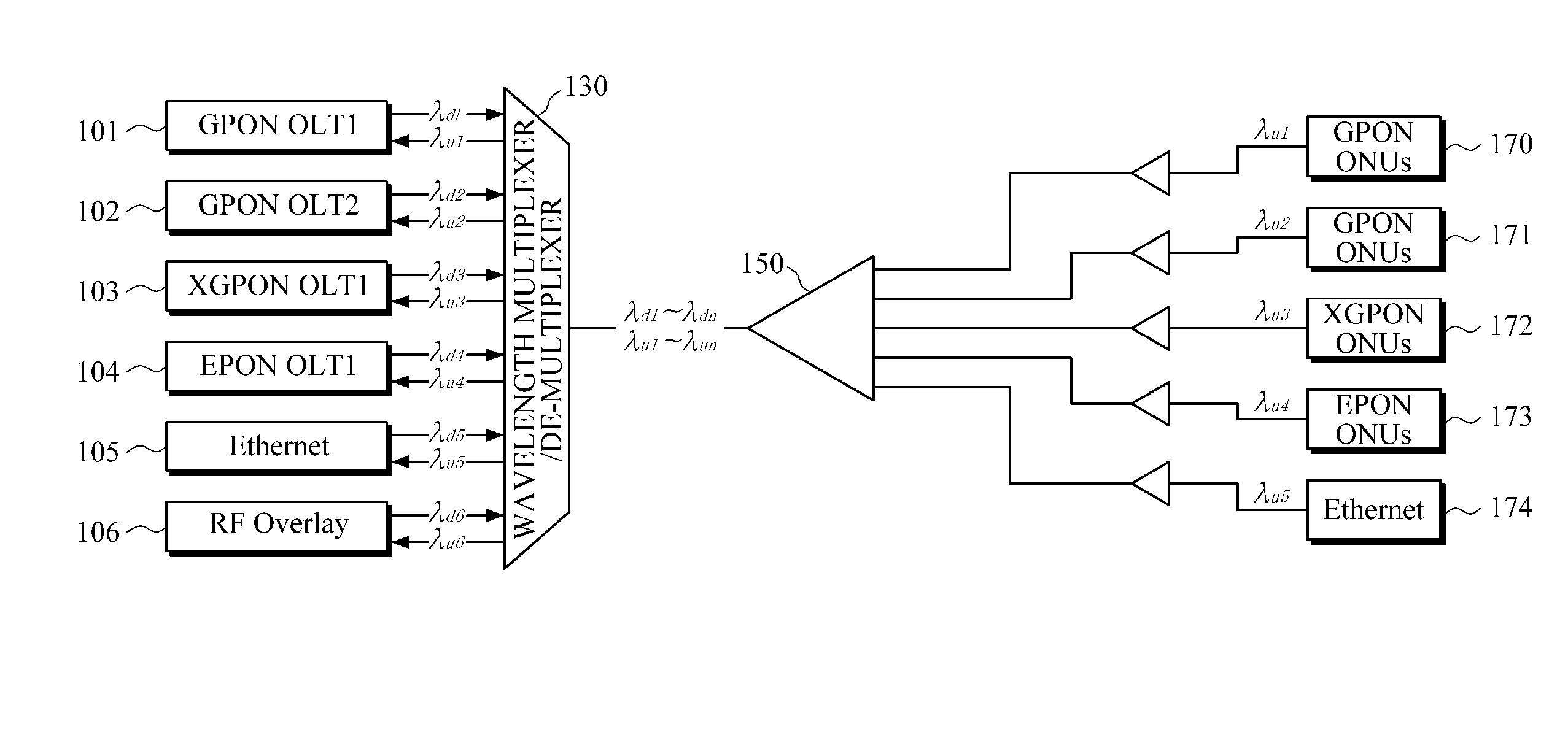
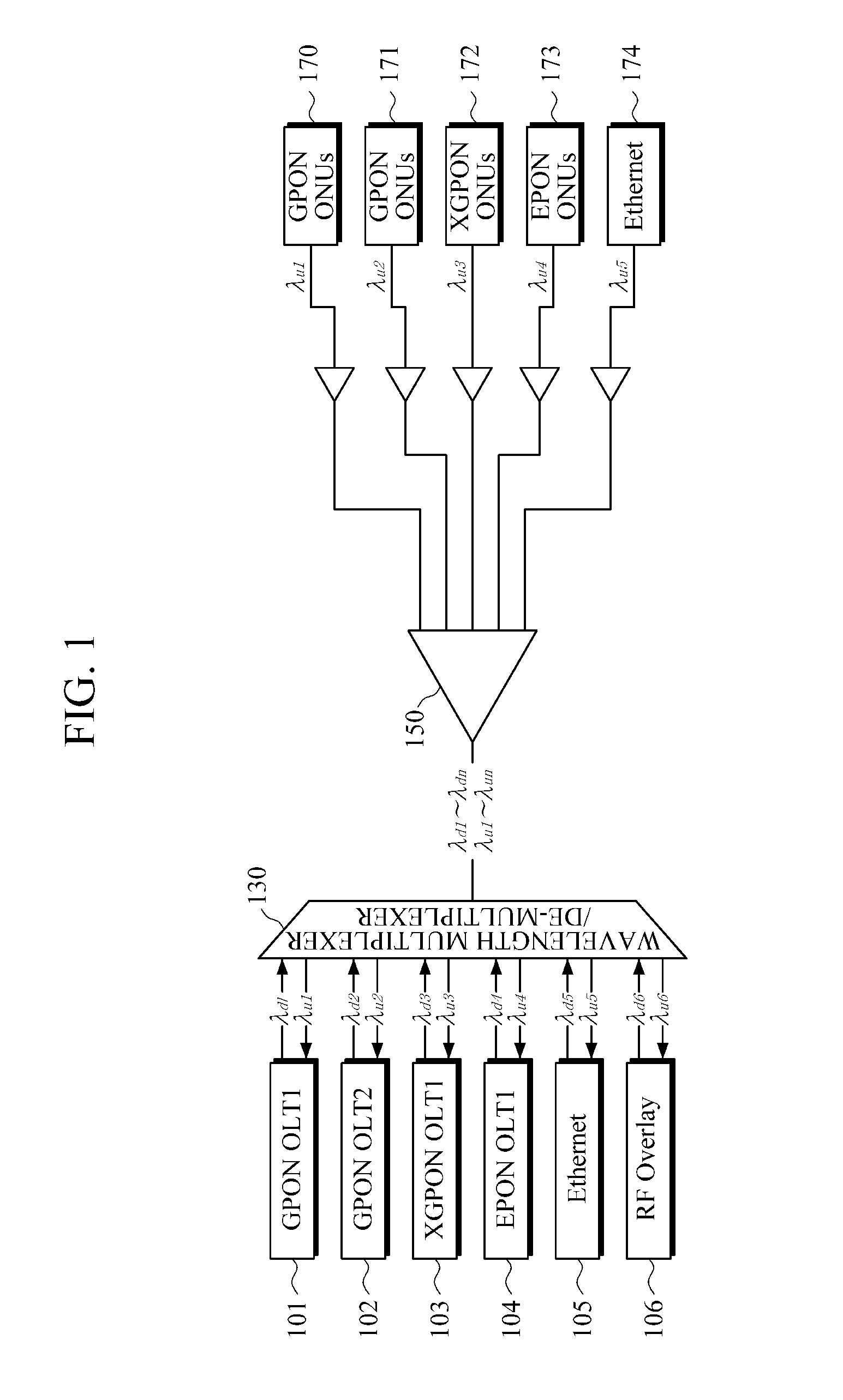
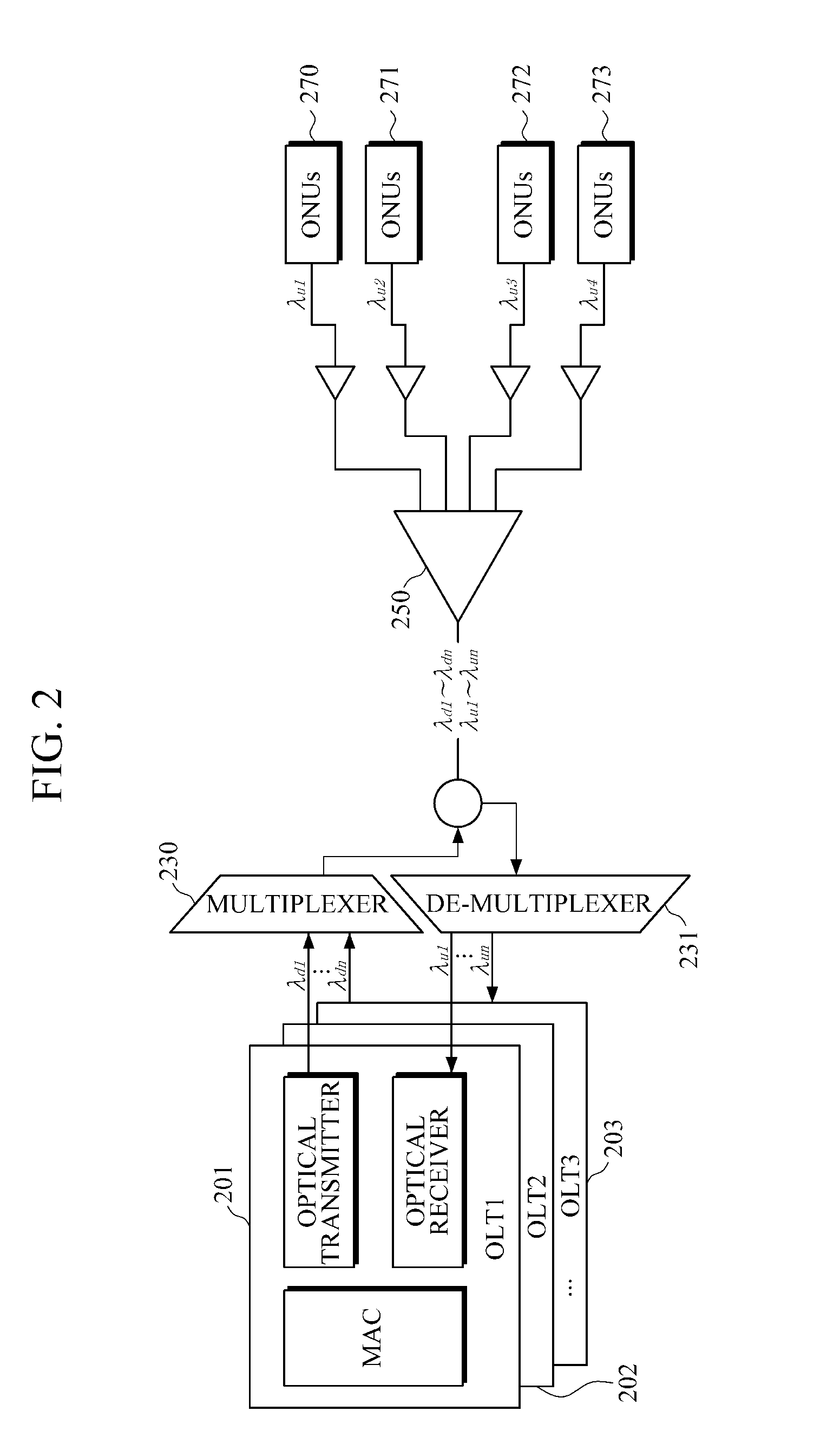
Optical Network Interface Module Using a Hardware Programmable Optical Network Interface Engine
ActiveUS20110116792A1Increase volumeLow costSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansOptical multiplexGeneral purposeComputer module
An optical network interface (ONI) module has two main components: an optoelectronic front-end and a general purpose hardware-programmable optical network interface engine. The ONI engine is hardware programmable, allowing the user to configure the overall ONI module with different optoelectronic front-ends and for use with different host modules. In this way, the ONI module can be configured for different applications and protocols.
Owner:OE SOLUTIONS AMERICA
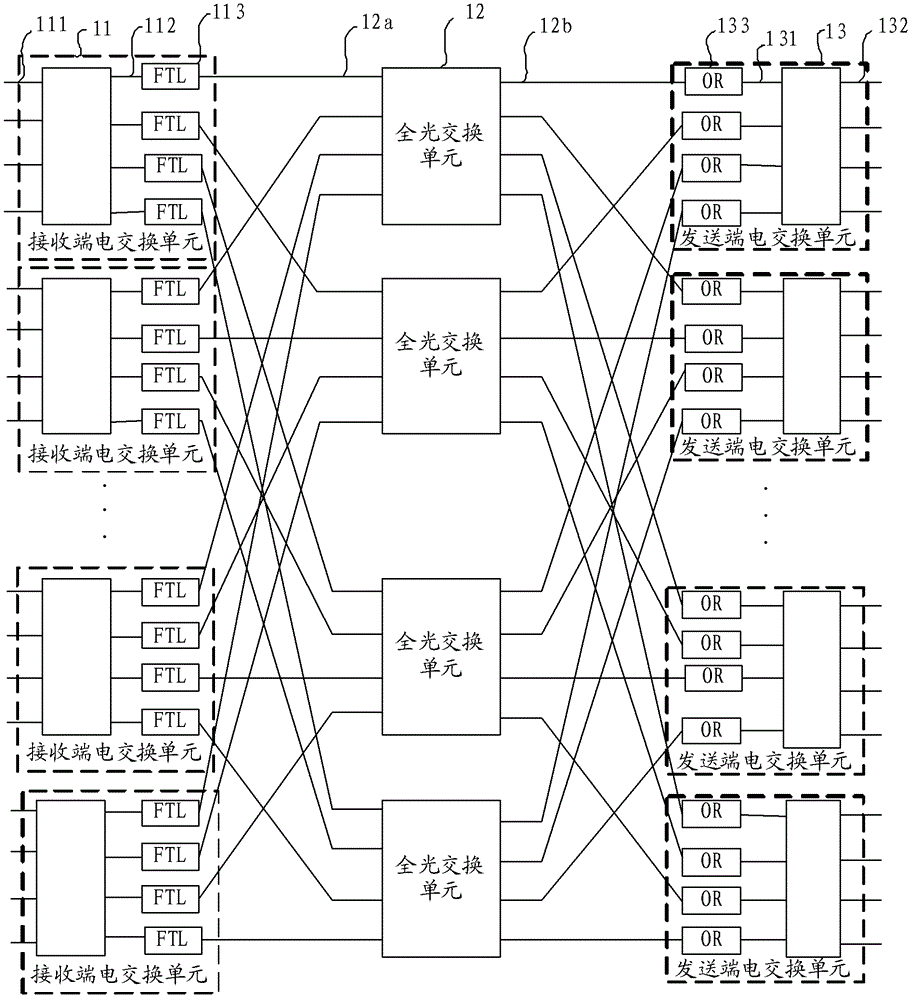
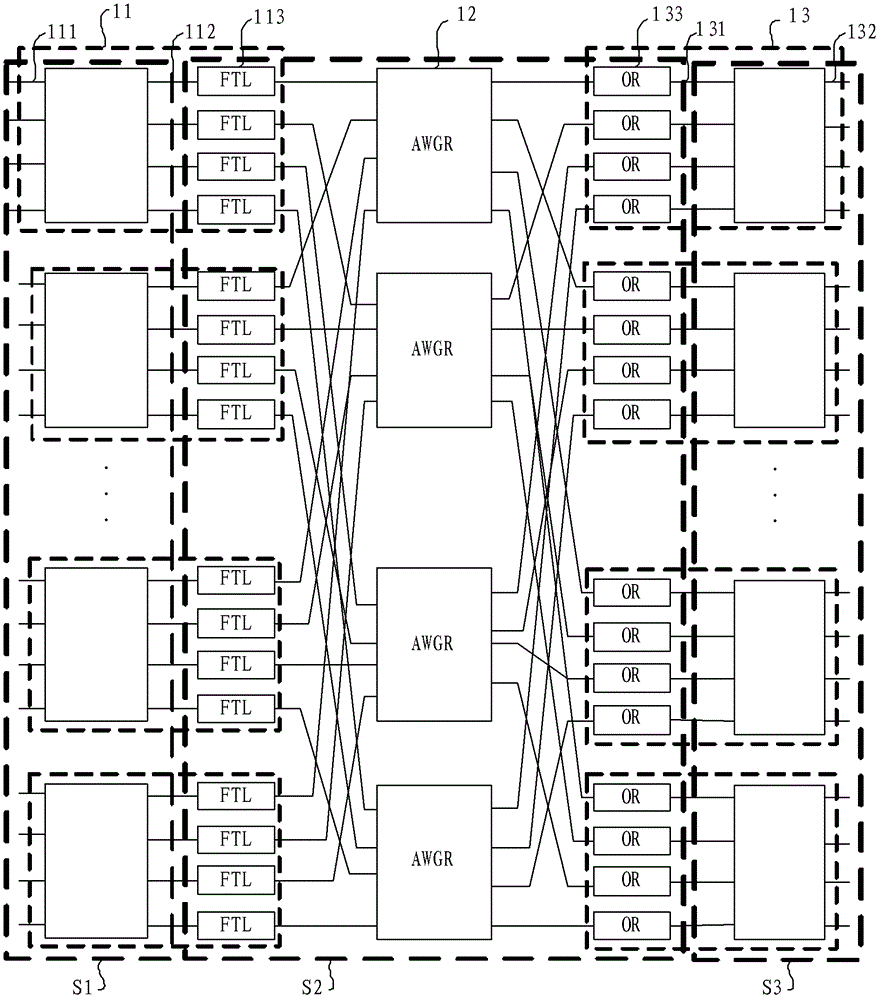
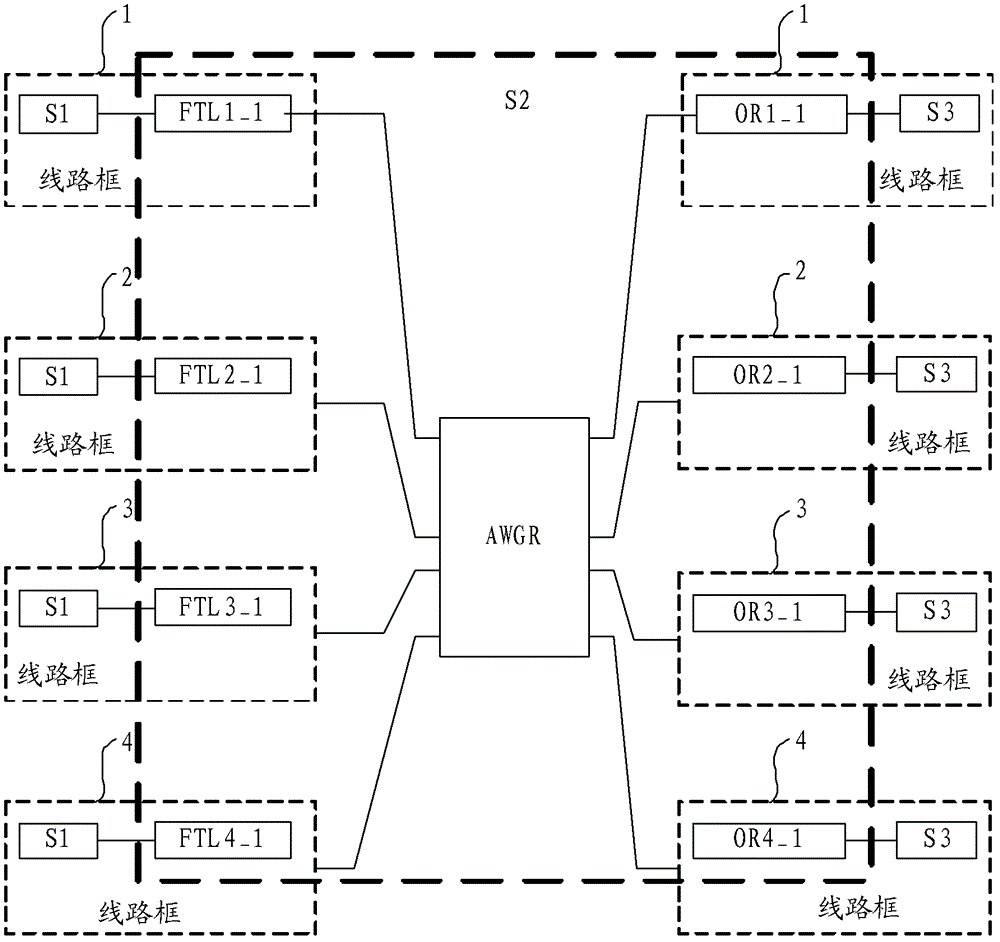
Optical network switching nodes, optical burst synchronization method and circuit frame of multi-frame cluster
ActiveCN102726058ALarge capacityImprove bandwidth utilizationMultiplex system selection arrangementsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansSystem capacityPhase difference
Embodiments of the present invention provide optical network switching nodes, an optical burst synchronization method and circuit frames of a multi-frame cluster. The synchronization method comprises that: a reference frame is selected, wherein output ports in which the FTLs (fast tunable lasers) in the reference frame are positioned transmit optical burst test signals to receiving ports in which the ORs (optical receivers) in other circuit frames are positioned, and the optical burst test signals carry transmission time slot numbers; and the receiving ports in which the ORs in other circuit frames are positioned, according to optical path difference between the receiving ports to the output ports which the FTLs in the reference frame are positioned, the timing that the receiving ports receive the optical burst test signals and the transmission time slot numbers, obtain the time phase difference between the receiving ports and the reference frame, and then local clock phase calibration is conducted on the basis of time difference phase. With the technical schemes, the problem of optical burst synchronization is solved, an OTN-based multi-frame cluster system is realized, system capacity is increased and power consumption is reduced.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Single-photon watch dog detector for folded quantum key distribution system
ActiveUS7227955B2Improve securityKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronisation information channelsQuantum channelKey distribution
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
Method of selecting wavelength of optical network unit in passive optical network
ActiveUS20140219661A1Minimize changesWavelength-division multiplex systemsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansWavelengthOptical network unit
Provided is a method of selecting a wavelength of an optical network unit including selecting a pre-loaded default wavelength as an available wavelength candidate or the wavelength that has been changed when a preset wavelength changing condition is satisfied as the available wavelength candidate, acquiring frame synchronization for a downstream signal having the same wavelength as the selected available wavelength candidate, and transmitting a registration request message to an optical line terminal (OLT) from which the downstream signal has been transmitted when the frame synchronization is acquired, assigning the available wavelength candidate to an available wavelength used for communication with the OLT and registering the terminal in the OLT when a registration allowance message is received from the OLT.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Temperature compensation for transmission between nodes coupled by a unidirectional fiber ring
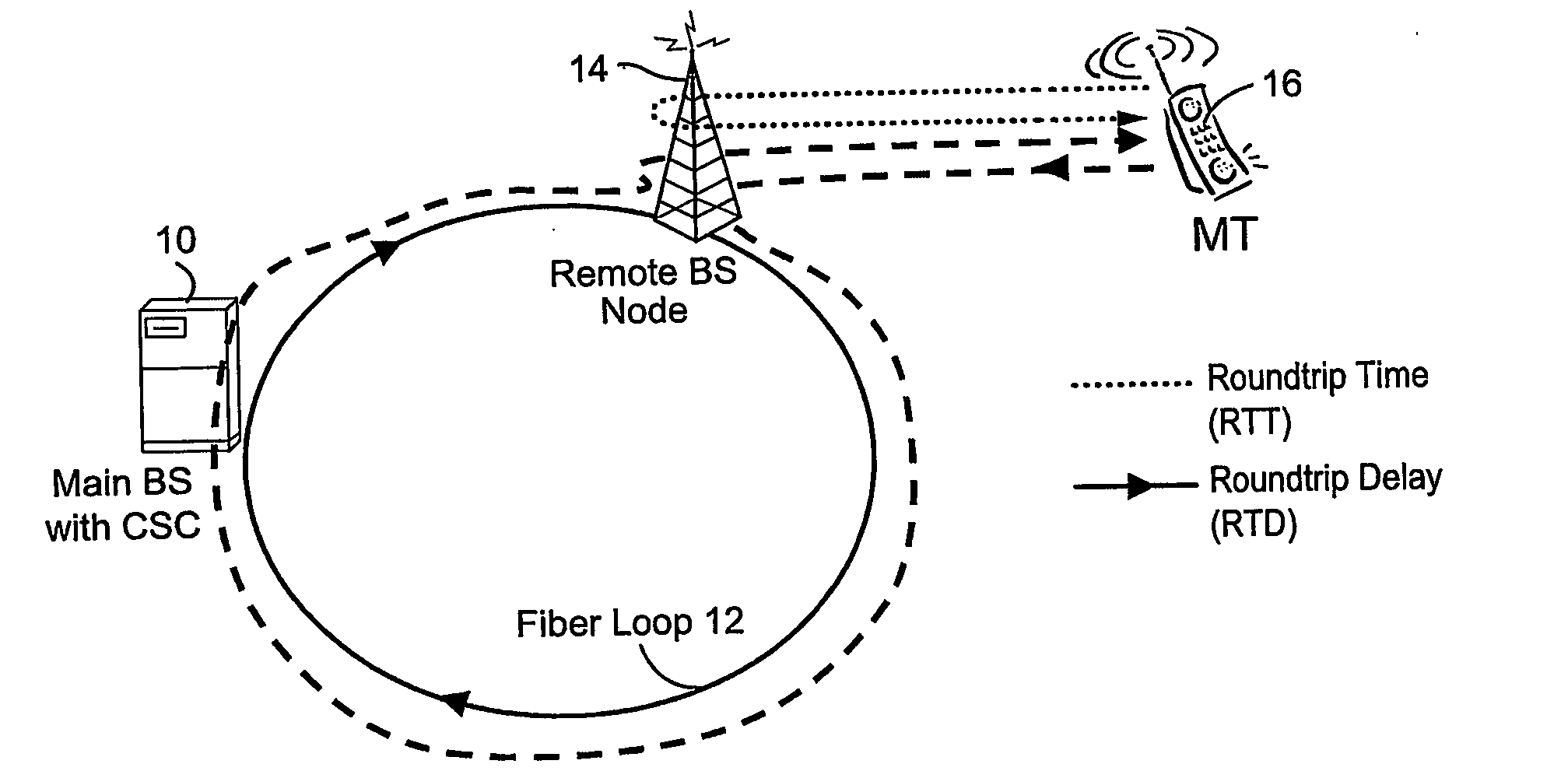
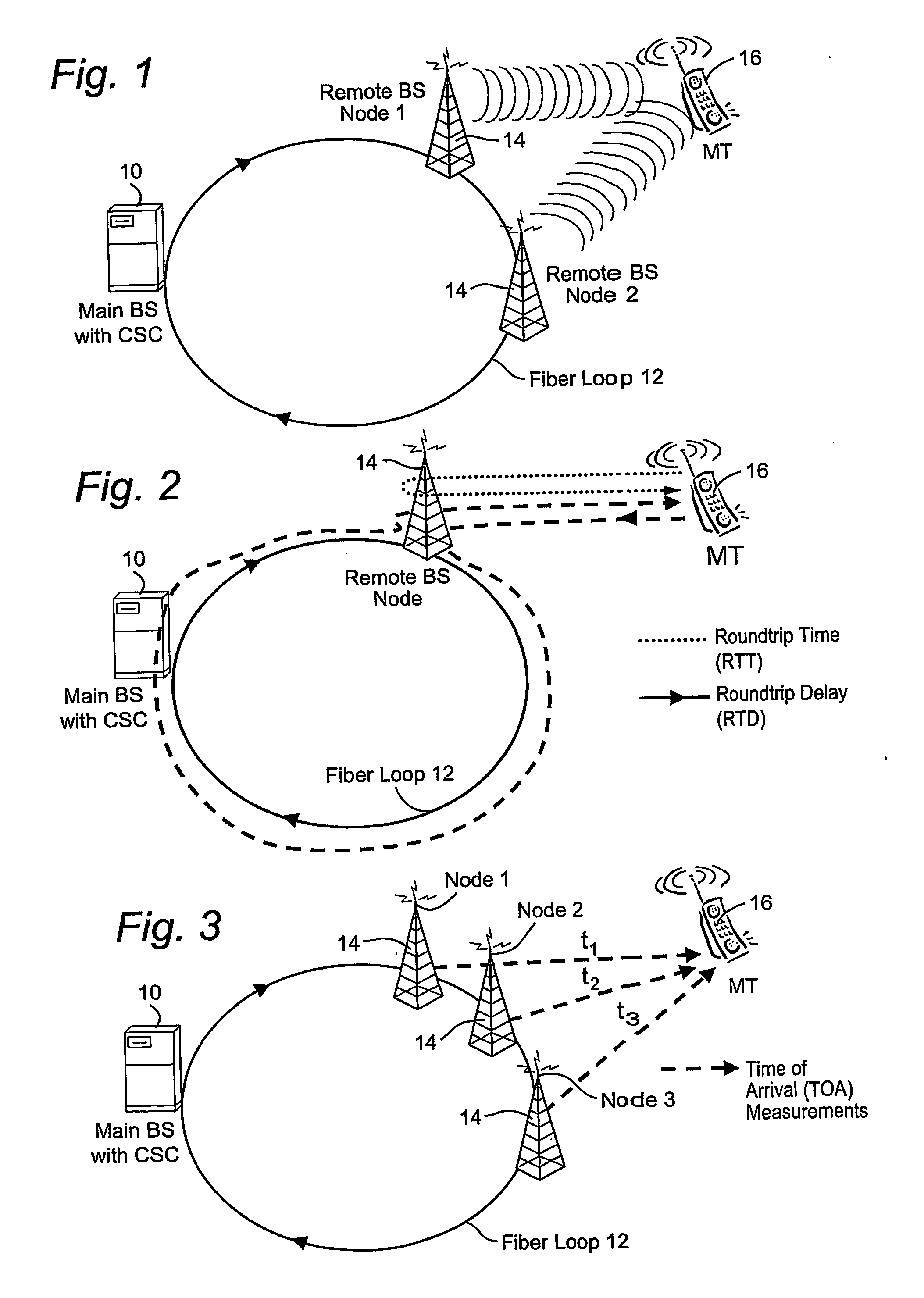
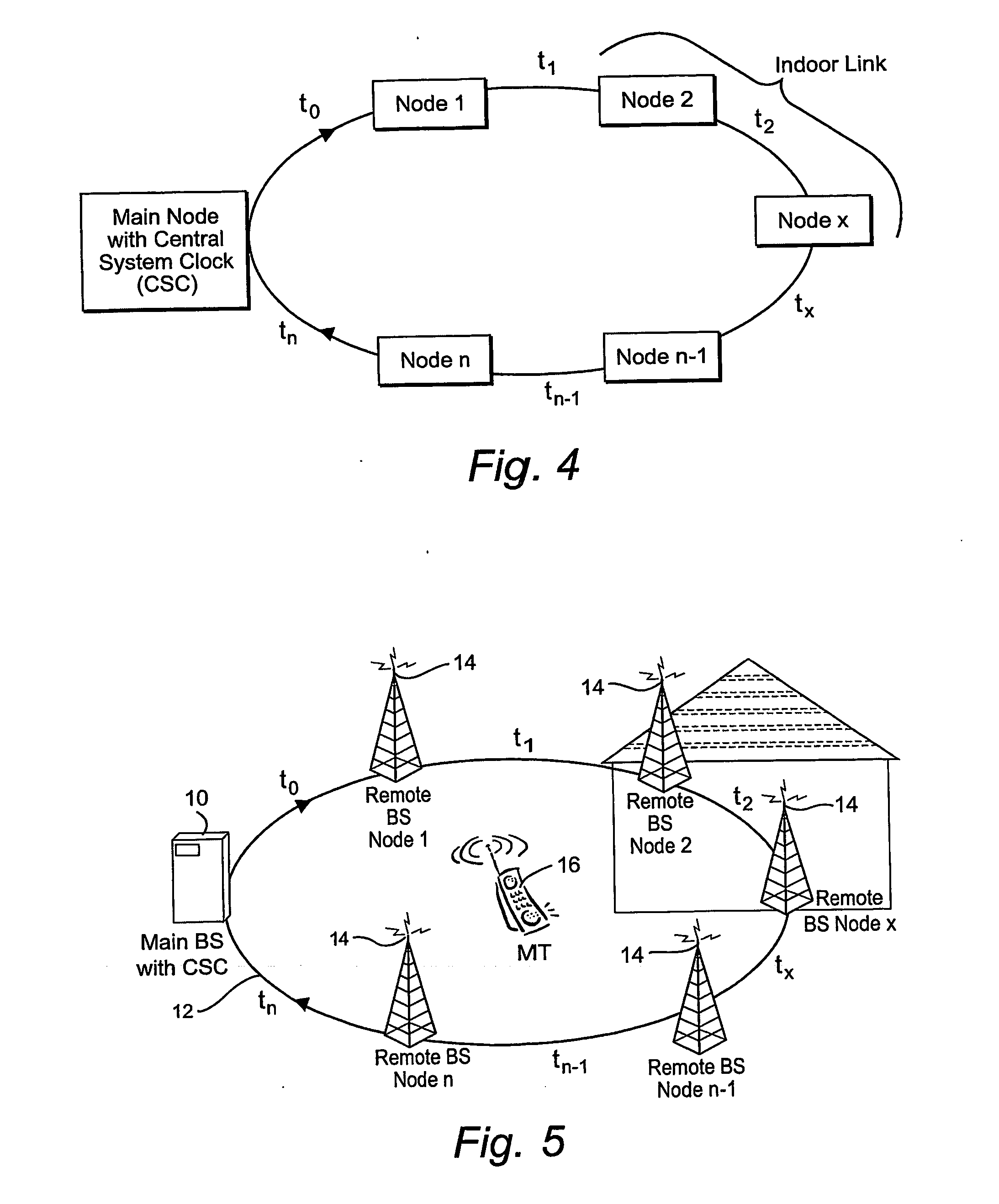
InactiveUS20070127919A1Laser detailsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansDelayed timeRound-trip delay time
Transmissions over a unidirectional optical fiber coupling multiple nodes are compensated for temperature-induced effects. A round-trip delay time is determined for a signal sent from a first node to travel around the unidirectional optical fiber loop and be received back at the first node. That measured round-trip delay time is then used to account for temperature-induced effects on signal transmissions over the unidirectional optical fiber loop. This temperature compensation is particularly beneficial in applications that require a high level of timing accuracy.
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
Underwater optical communication system
ActiveUS9031413B2Synchronisation by photonic/optical meansElectromagnetic transmission optical aspectsCommunications systemFountain code
A method of optical underwater communications comprises applying a Fountain code to a plurality of data blocks. A sequence of optical data packets is transmitted through an underwater communications channel. Each optical data packet comprises one of the plurality of data blocks preceded by a preamble. The sequence of optical data packets transmitted through the underwater communication channel is received to generate a sequence of received data packets. The sequence of received data packets is sampled with the sampling clock to recover the plurality of data blocks.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com