Patents
Literature
3385 results about "Optical receivers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
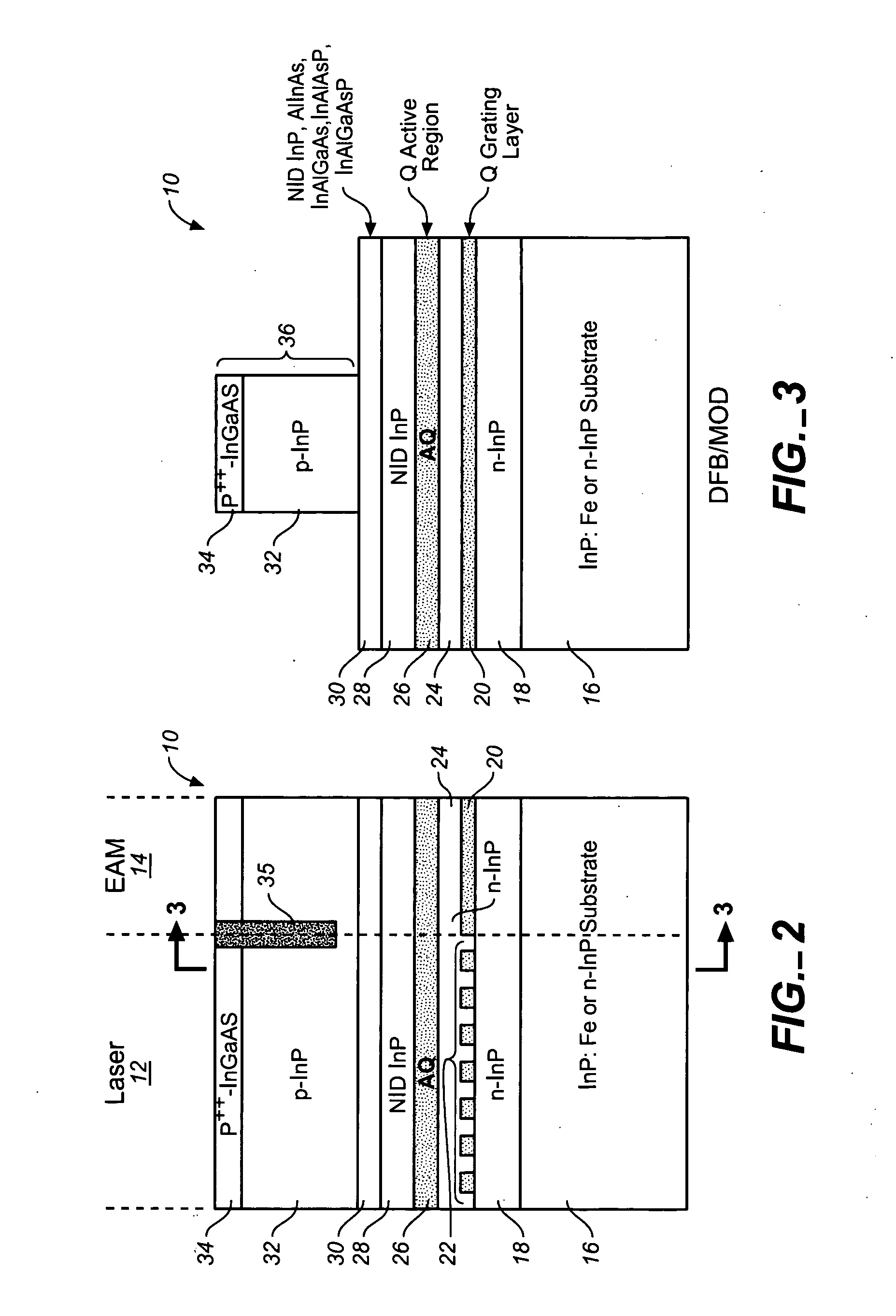
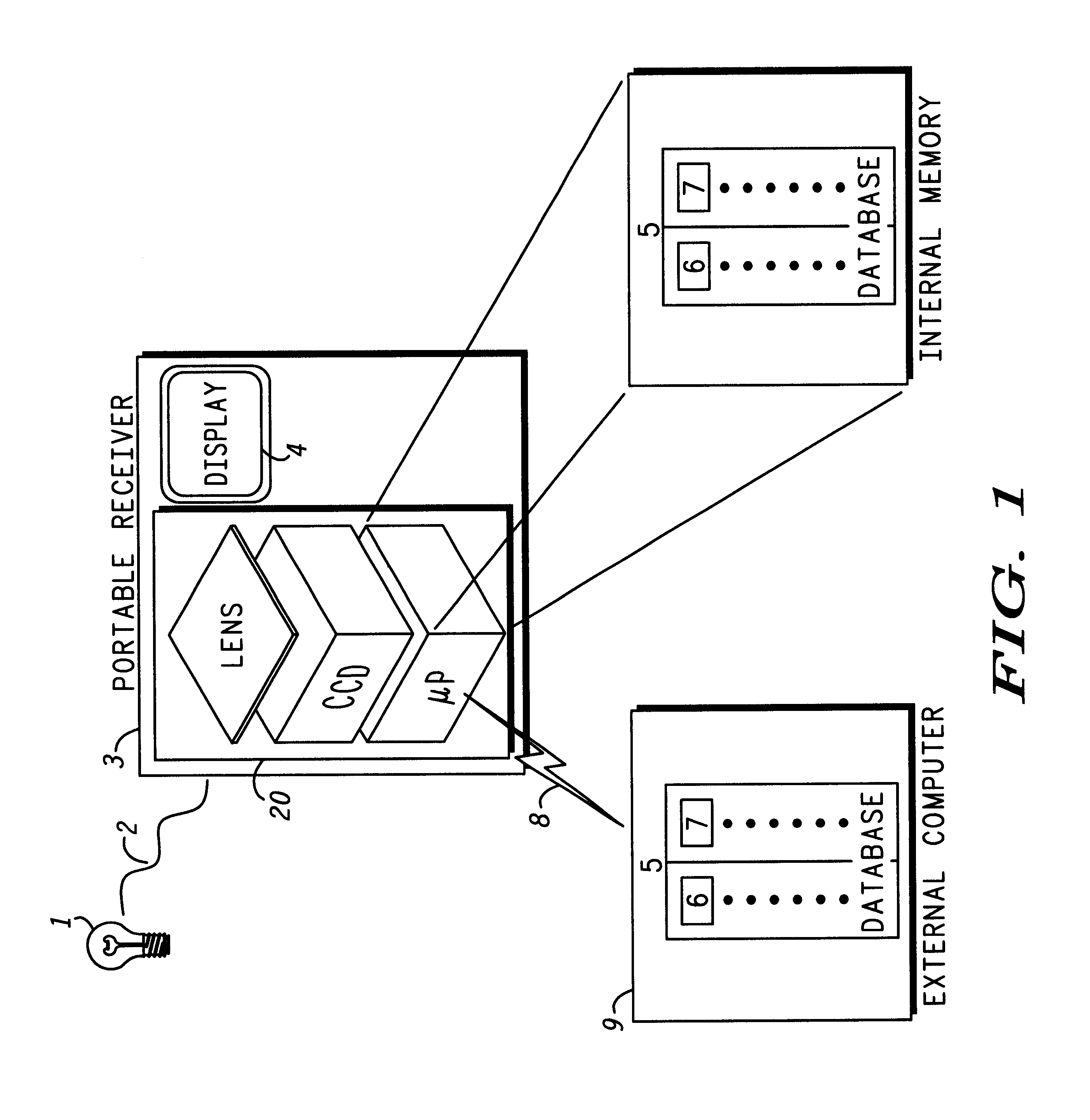
Small-scale optoelectronic package
InactiveUS6910812B2Easy to manufactureSacrifice speedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesFiberElectricity
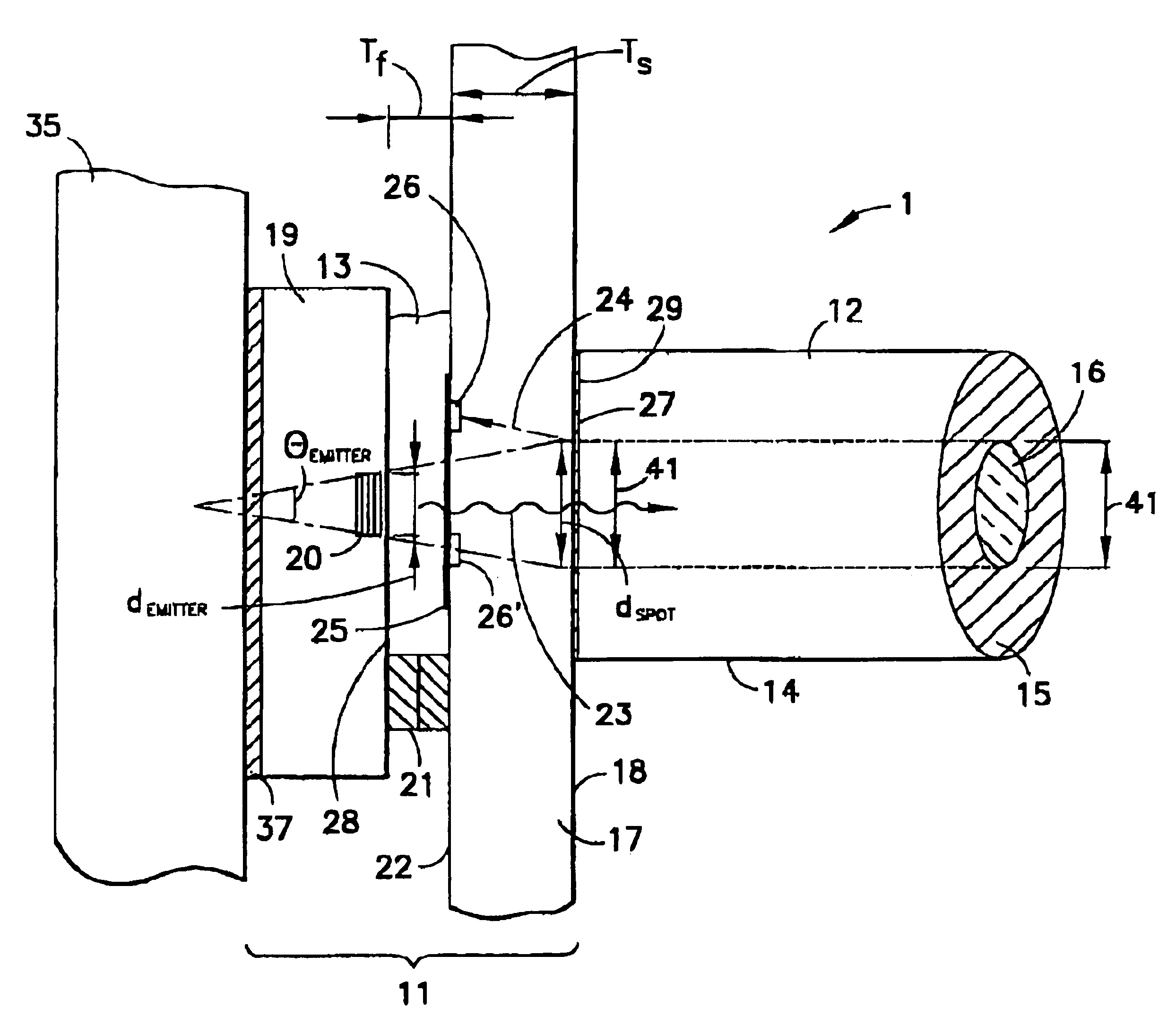
An integrated circuit / optoelectronic packaging system (100) which comprises OE and IC components packaged to provide electrical input / output, thermal management, an optical window, and precise passive or mechanical alignment to external optical receivers or transmitters. A transparent insulating substrate having electrical circuitry in a thin silicon layer formed on its top side is positioned between the optical fiber and the optoelectronic device such that an optical path is described between the optoelectronic device and the optical fiber core through the transparent insulating substrate. The optoelectronic devices are mounted on the transparent insulating substrate in a precise positional relationship to guide holes in the substrate. The optical fibers are fixed in an optical fiber connector and are held in a precise positional relationship to guide holes in the connector. Alignment is accomplished with complementary guide pins that pass through guide holes in the fiber optic connector and in the transparent substrate.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Transverse-mode multiplexing for optical communication systems
ActiveUS20100329671A1Reverses effectOptical mode multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesMultiplexingCommunications system
An optical communication system having an optical transmitter and an optical receiver optically coupled via a multi-path fiber. The optical transmitter launches, into the multi-path fiber, an optical transverse-mode-multiplexed (TMM) signal having a plurality of independently modulated components by coupling each independently modulated component into a respective transverse mode of the multi-path fiber. The TMM signal undergoes inter-mode mixing in the multi-path fiber before being received by the optical receiver. The optical receiver processes the received TMM signal to reverse the effects of inter-mode mixing and recover the data carried by each of the independently modulated components.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
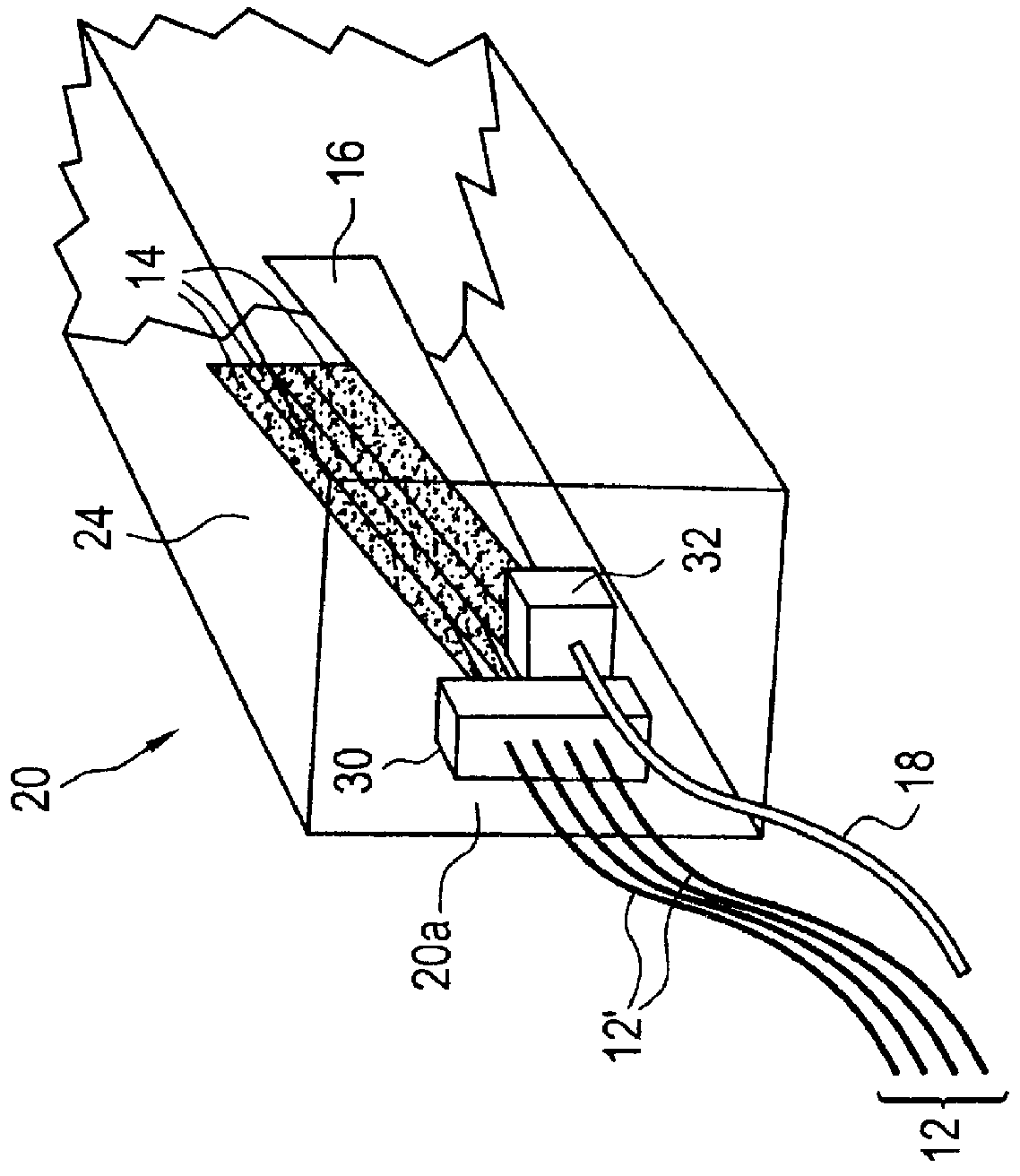
Optical receiver stub fitting
InactiveUSRE36592E1Eliminate pointLayered productsCommunication cablesEngineeringOptical fiber cable
A cable assembly for attachment to an entry port of an optical enclosure. The assembly includes a plug for an end of an optical cable in a sealed housing having a single rigid tube and a single sealed nut. Connectorized optical fibers or an optical ribbon extend from the plug into the equipment enclosure.
Owner:SIECOR A DELAWARE
De-embedment of optical component characteristics and calibration of optical receivers using rayleigh backscatter
InactiveUS6947147B2Accurate analysisIncrease the number ofPhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansRayleigh scatteringFiber
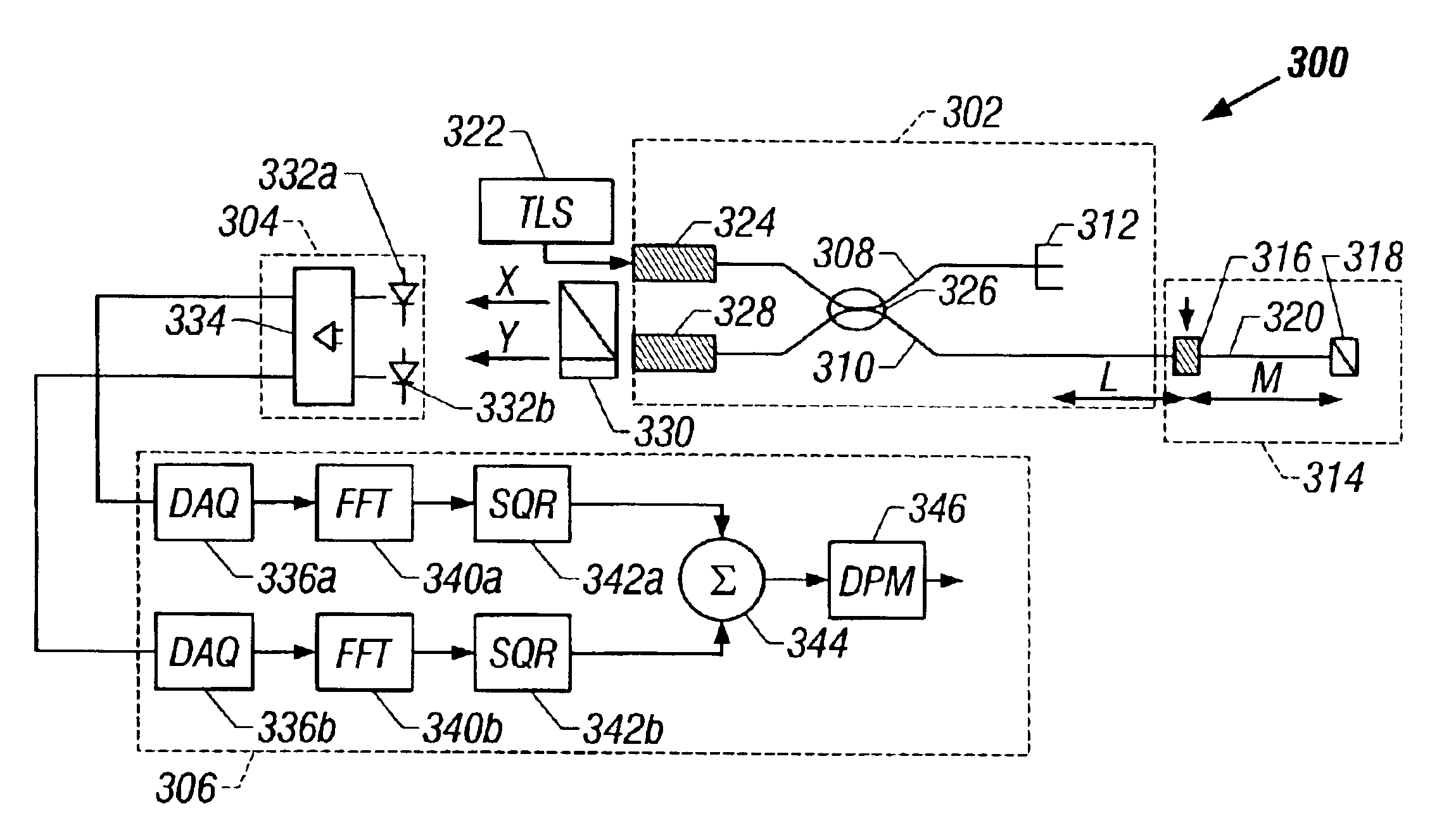
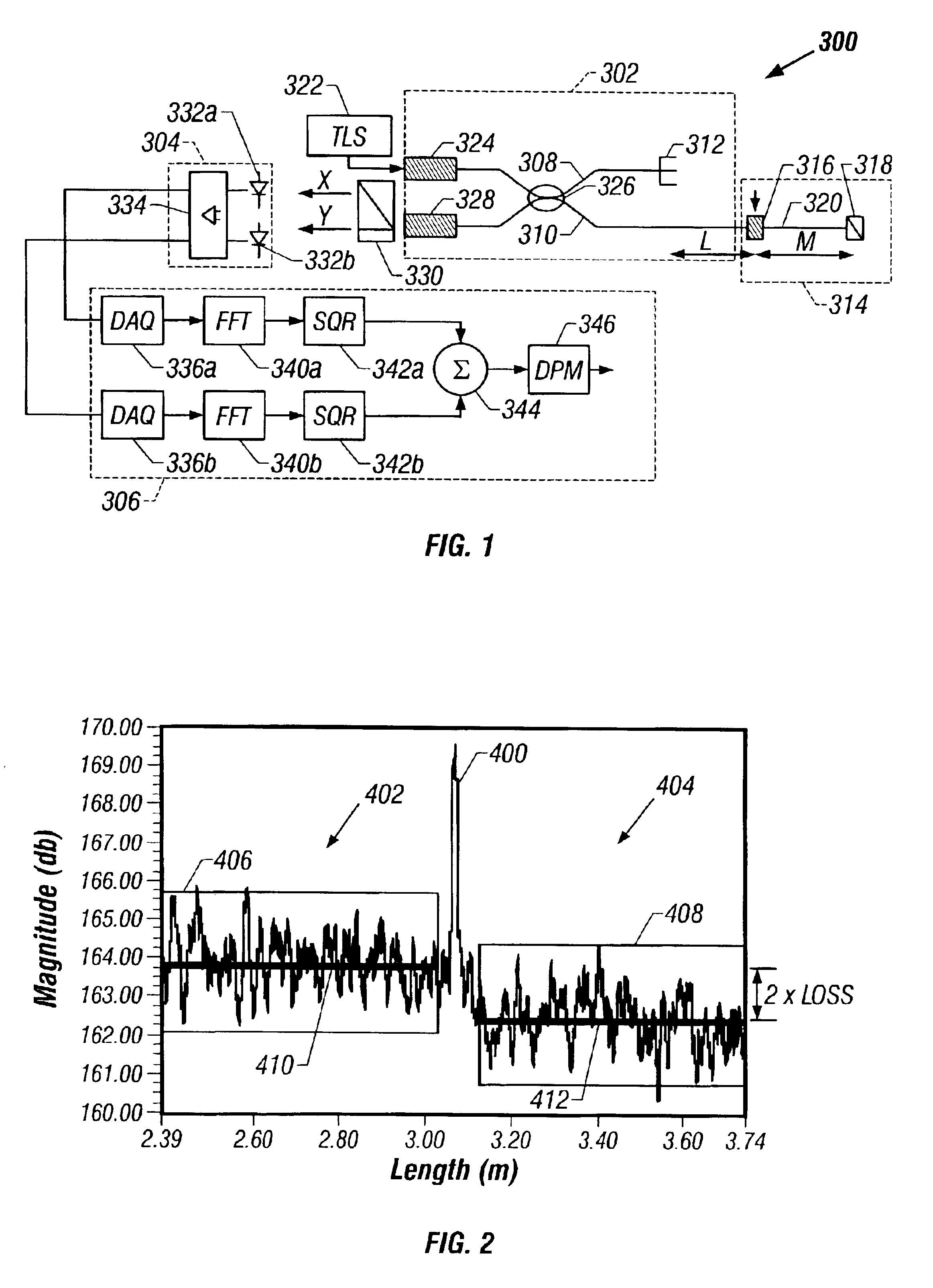
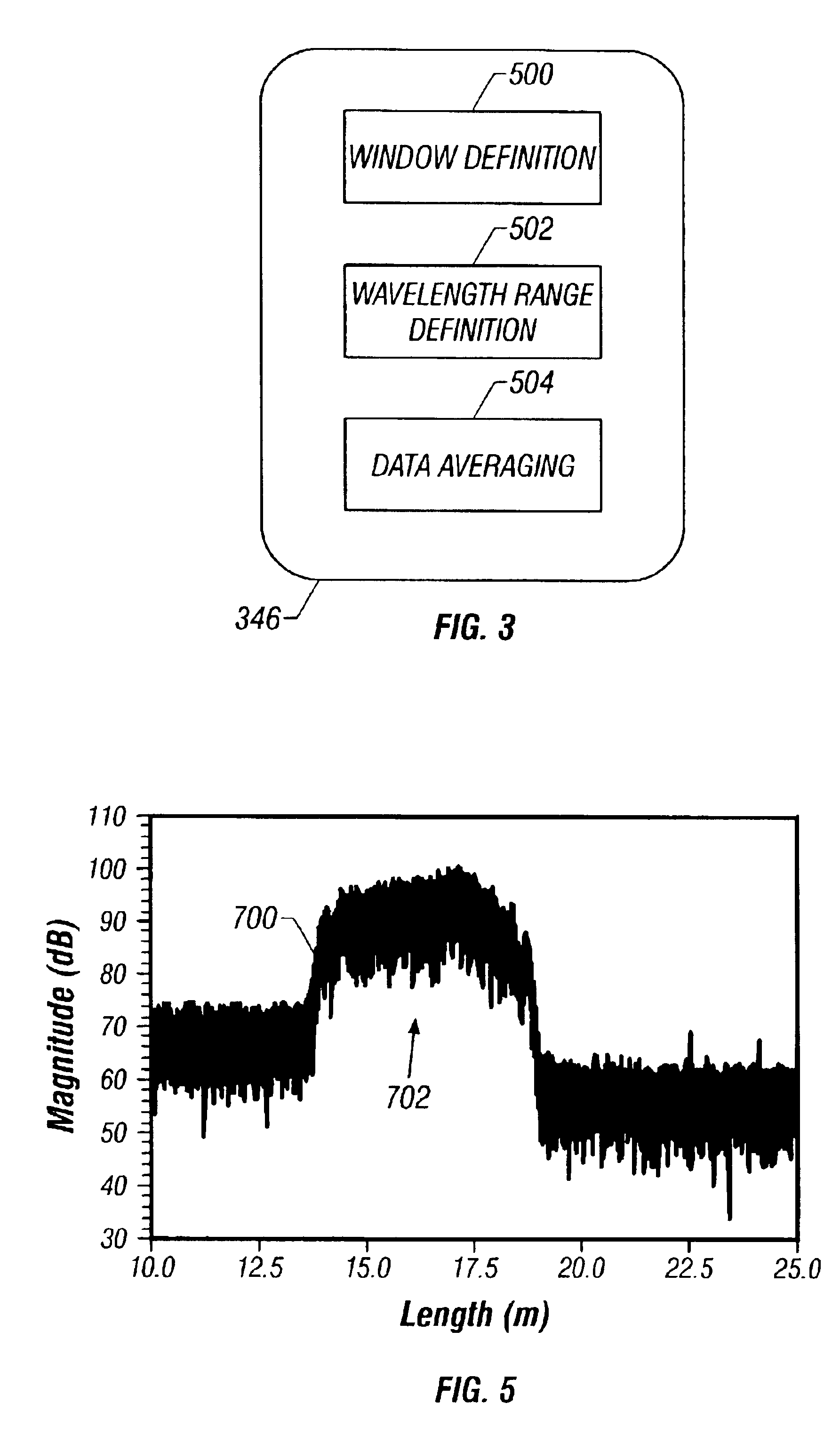
Method and system are disclosed for de-embedding optical component characteristics from optical device measurements. In particular, the invention uses frequency domain averaging of the RBS on both sides of an optical component to determine one or more of its optical characteristics. Where the RBS has a slope (e.g., as in the case of a lossy fiber), a frequency domain least square fit can be used to determine the optical component characteristics. In addition, the invention uses a reference DUT to correct for variations in the frequency response of the photoreceiver. A reference interferometer is used in the invention to correct for sweep non-linearity of the TLS. The optical component characteristics are then de-embedded from optical device measurements to provide a more precise analysis of the optical device.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
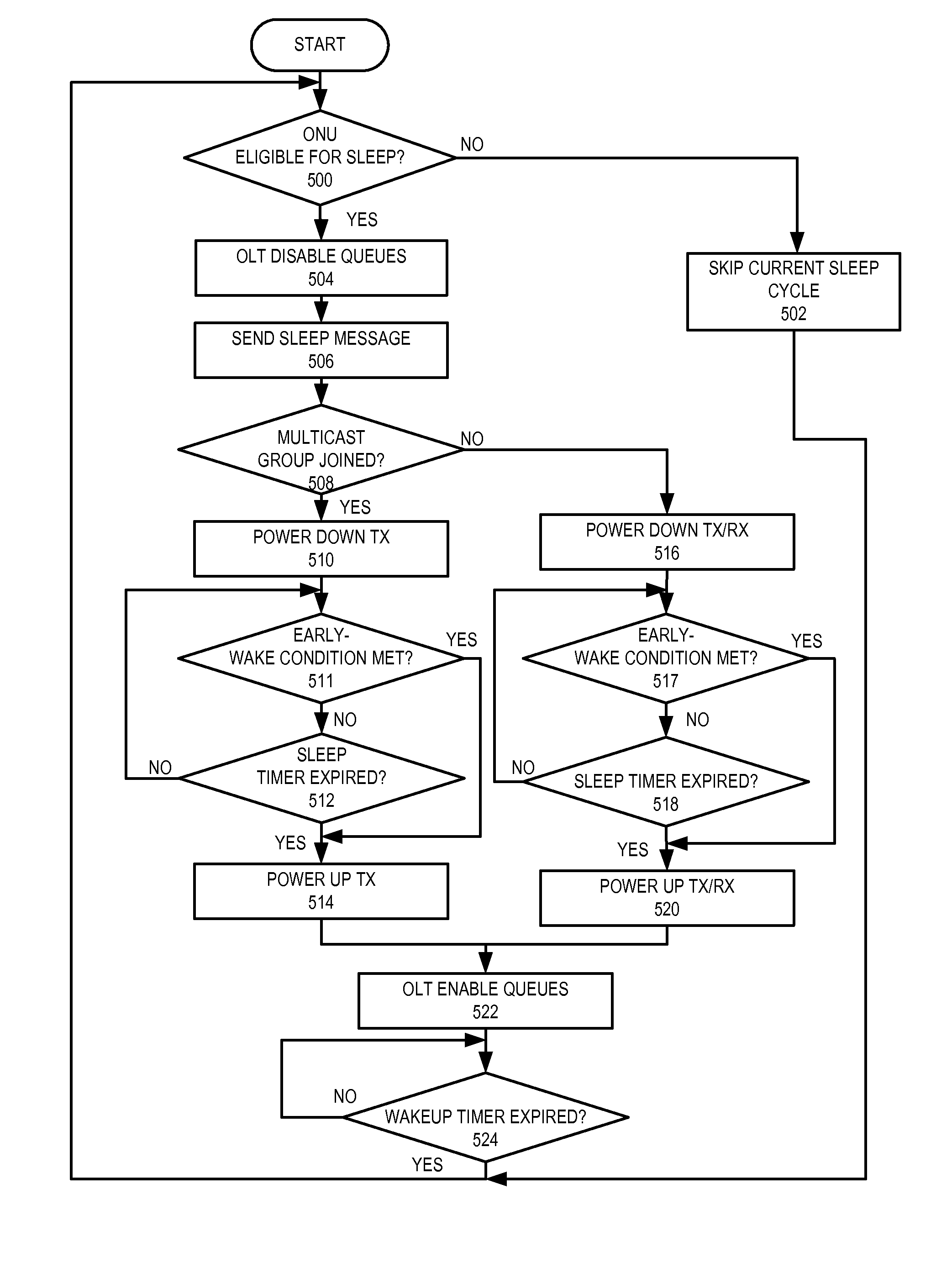
Epon with power-saving features
One embodiment provides a system for power saving in an Ethernet Passive Optic Network (EPON). The system includes an optical line terminal (OLT), an optical network unit (ONU), a traffic-detection module configured to detect status of traffic to and from the ONU, and a power-management module configured to place the ONU in sleep mode based on the detected traffic status. The ONU includes an optical transceiver that includes an optical transmitter configured to transmit optical signals to the OLT and an optical receiver configured to receive optical signals from the OLT.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
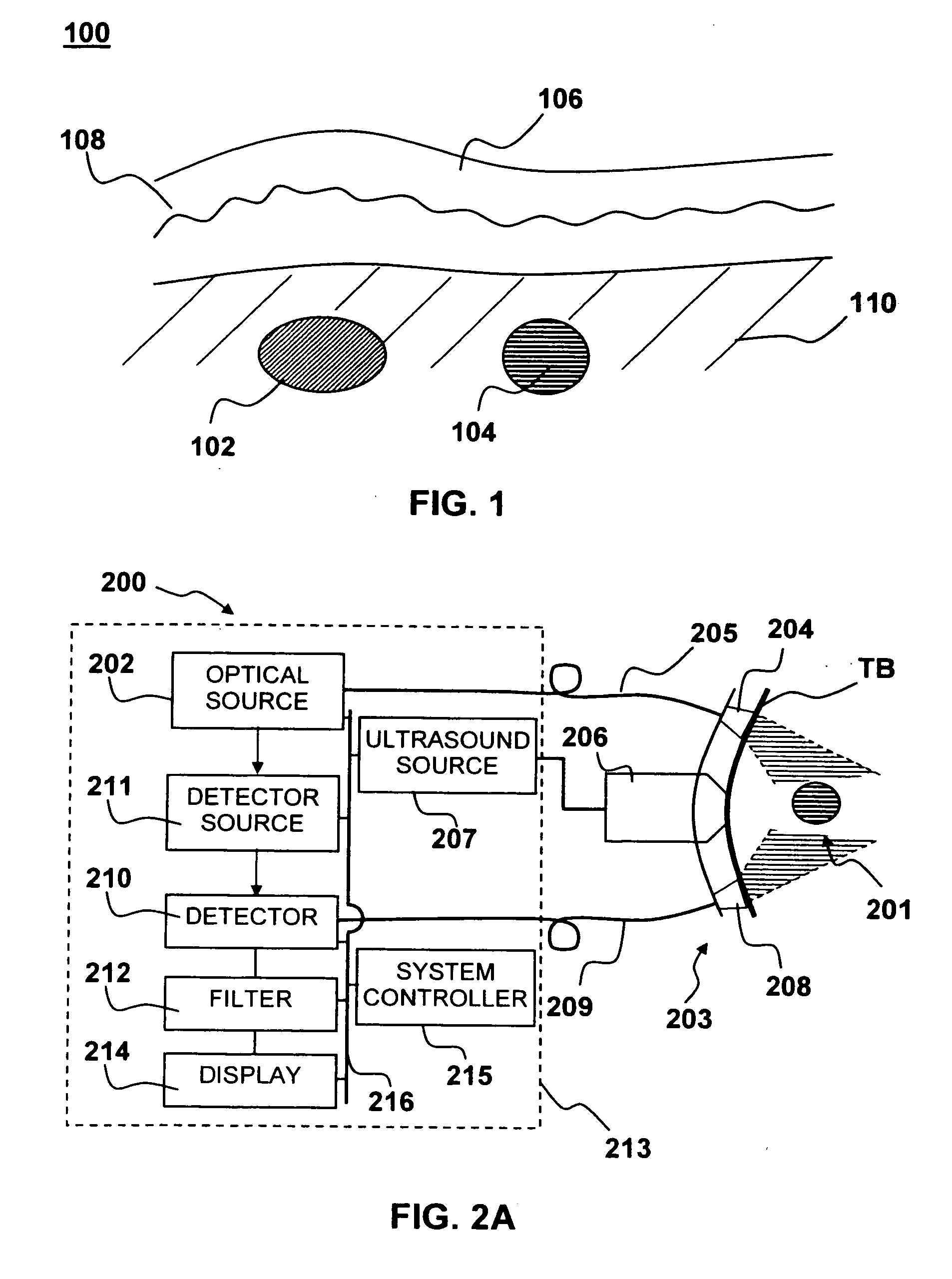
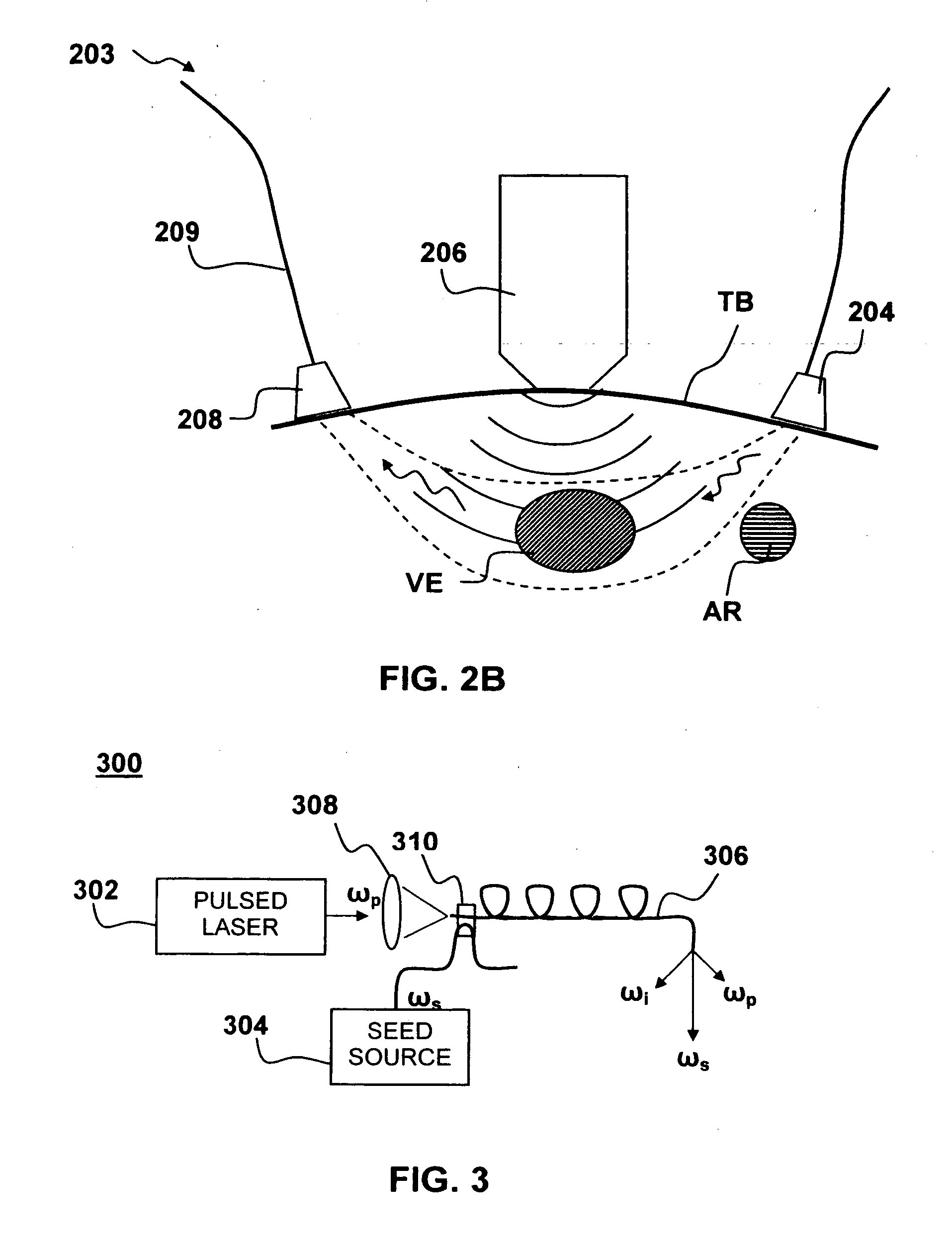
Apparatus and method for non-invasive and minimally-invasive sensing of parameters relating to blood
InactiveUS20060253007A1Reduce disadvantagesImprove accuracyDiagnostics using lightOrgan movement/changes detectionNon invasiveThree vessels
Medical diagnostic system, apparatus and methods are disclosed. Optical transmitters generate radiation-containing photons having a specific interaction with at least one target chromophore in a target structure, preferably a blood vessel such as the interior jugular vein. The optical transmitters transmit the radiation into at least a first area including a substantial portion of the target structure and into a second area not including a substantial portion of the target structure. Optical receivers detect a portion radiation scattered from at least the first area and the second area. A processor estimates oxygenation, pH or cardiac output based on the scattered radiation detected from the first area, and the scattered radiation from the second area.
Owner:SKYLINE BIOMEDICAL
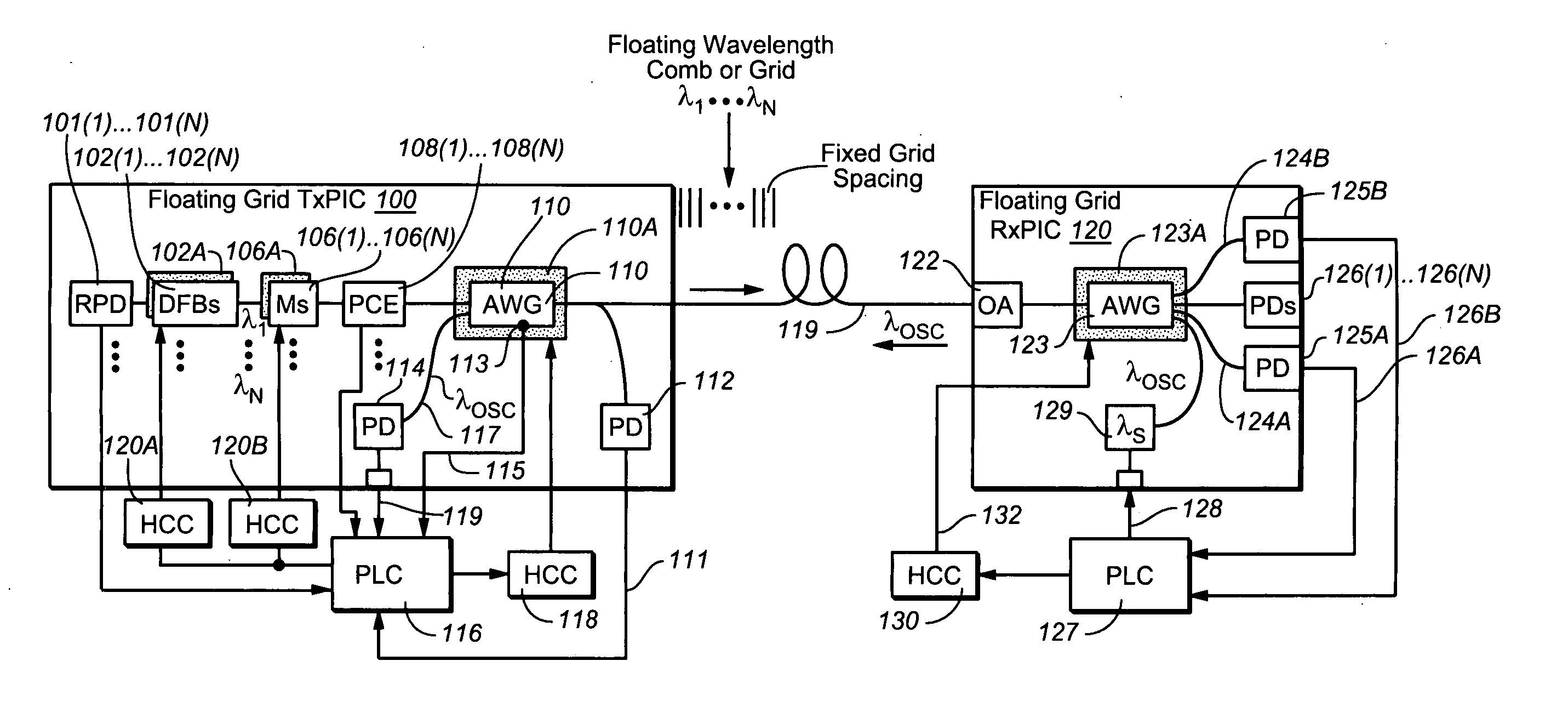
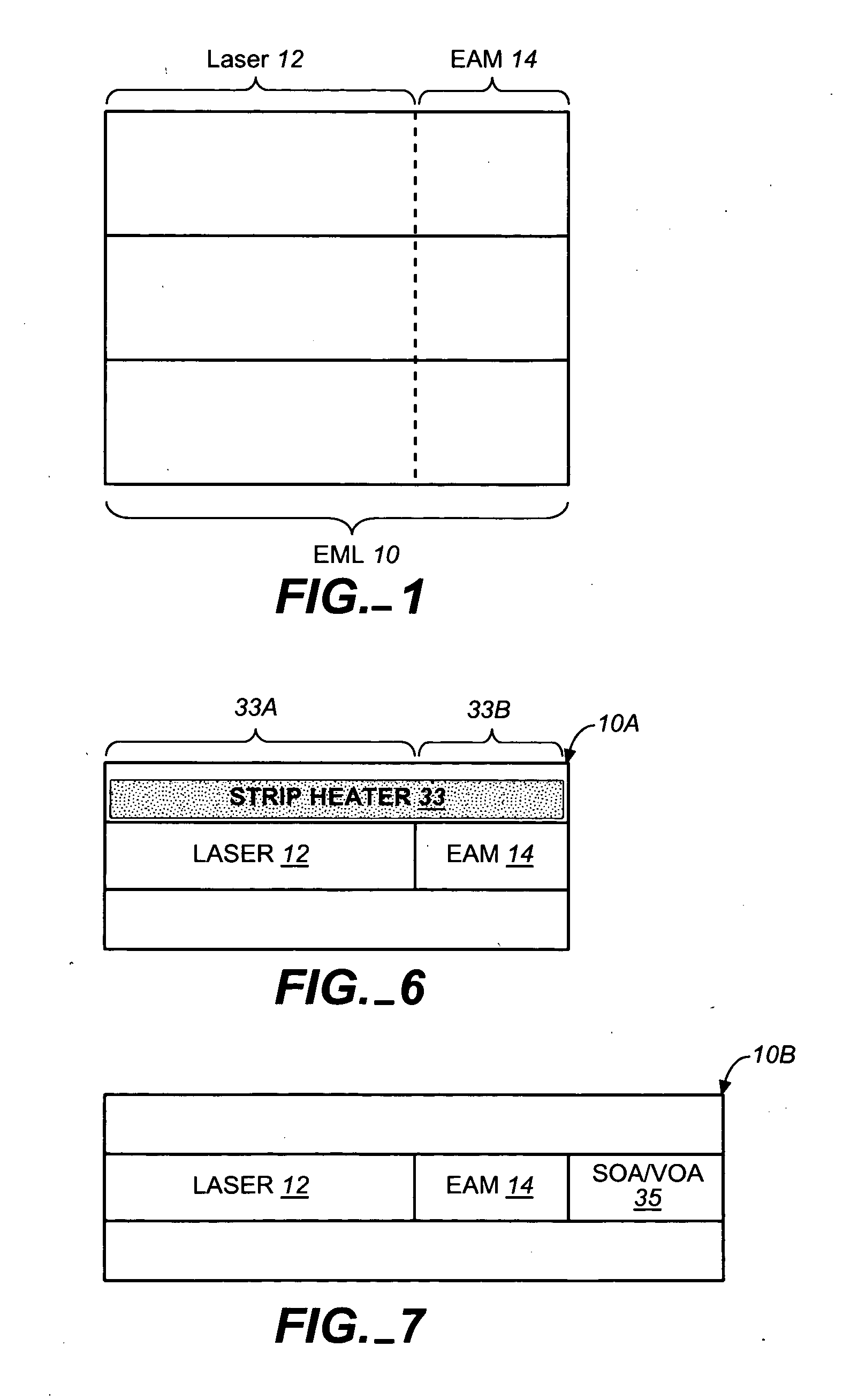
Coolerless photonic integrated circuits (PICs) for WDM transmission networks and PICs operable with a floating signal channel grid changing with temperature but with fixed channel spacing in the floating grid
ActiveUS20050249509A1Requirements for a hermetically sealed package are substantially relievedEasy to controlLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsElectro-absorption modulatorHermetic packaging
A coolerless photonic integrated circuit (PIC), such as a semiconductor electro-absorption modulator / laser (EML) or a coolerless optical transmitter photonic integrated circuit (TxPIC), may be operated over a wide temperature range at temperatures higher then room temperature without the need for ambient cooling or hermetic packaging. Since there is large scale integration of N optical transmission signal WDM channels on a TxPIC chip, a new DWDM system approach with novel sensing schemes and adaptive algorithms provides intelligent control of the PIC to optimize its performance and to allow optical transmitter and receiver modules in DWDM systems to operate uncooled. Moreover, the wavelength grid of the on-chip channel laser sources may thermally float within a WDM wavelength band where the individual emission wavelengths of the laser sources are not fixed to wavelength peaks along a standardized wavelength grid but rather may move about with changes in ambient temperature. However, control is maintained such that the channel spectral spacing between channels across multiple signal channels, whether such spacing is periodic or aperiodic, between adjacent laser sources in the thermally floating wavelength grid are maintained in a fixed relationship. Means are then provided at an optical receiver to discover and lock onto floating wavelength grid of transmitted WDM signals and thereafter demultiplex the transmitted WDM signals for OE conversion.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
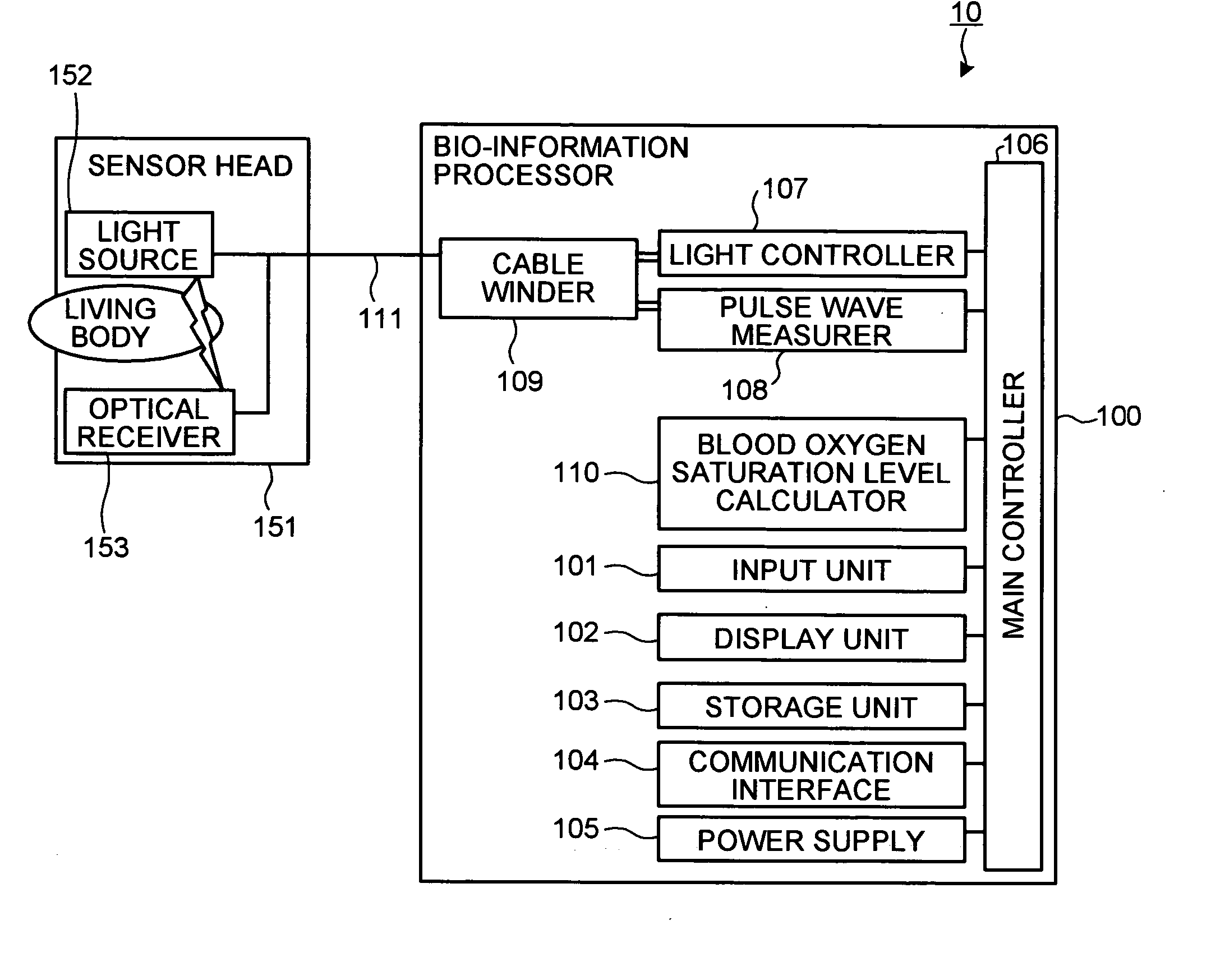
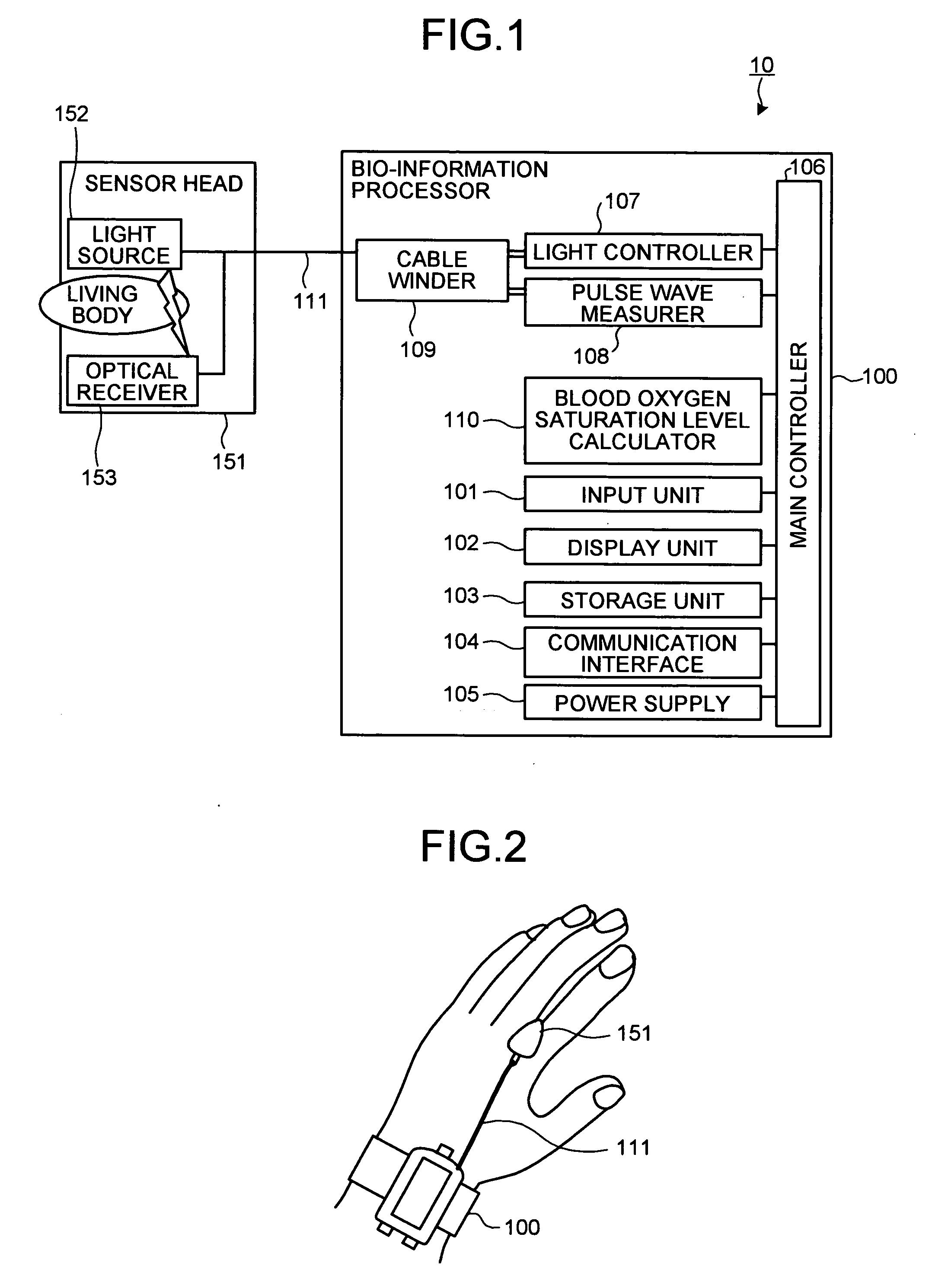
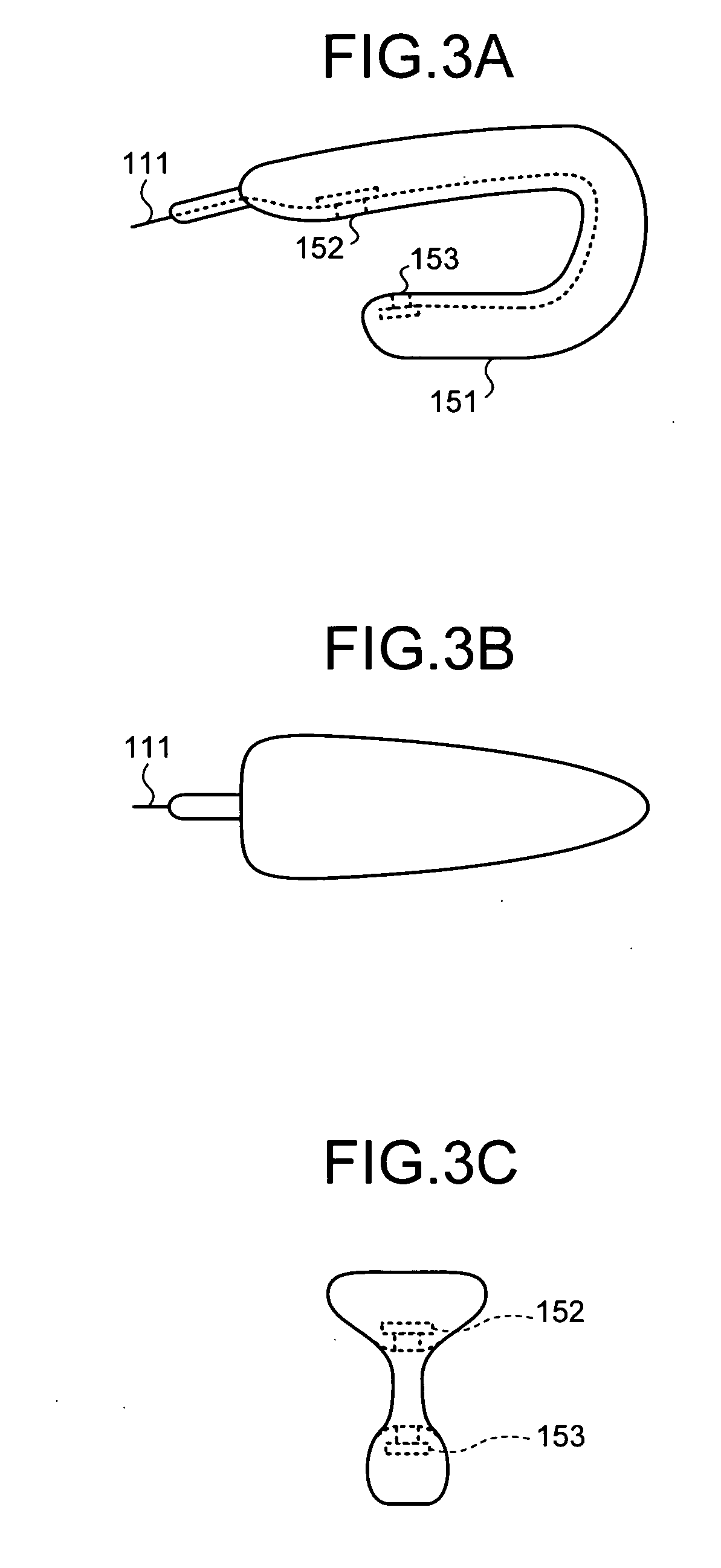
Bio-information measuring apparatus
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
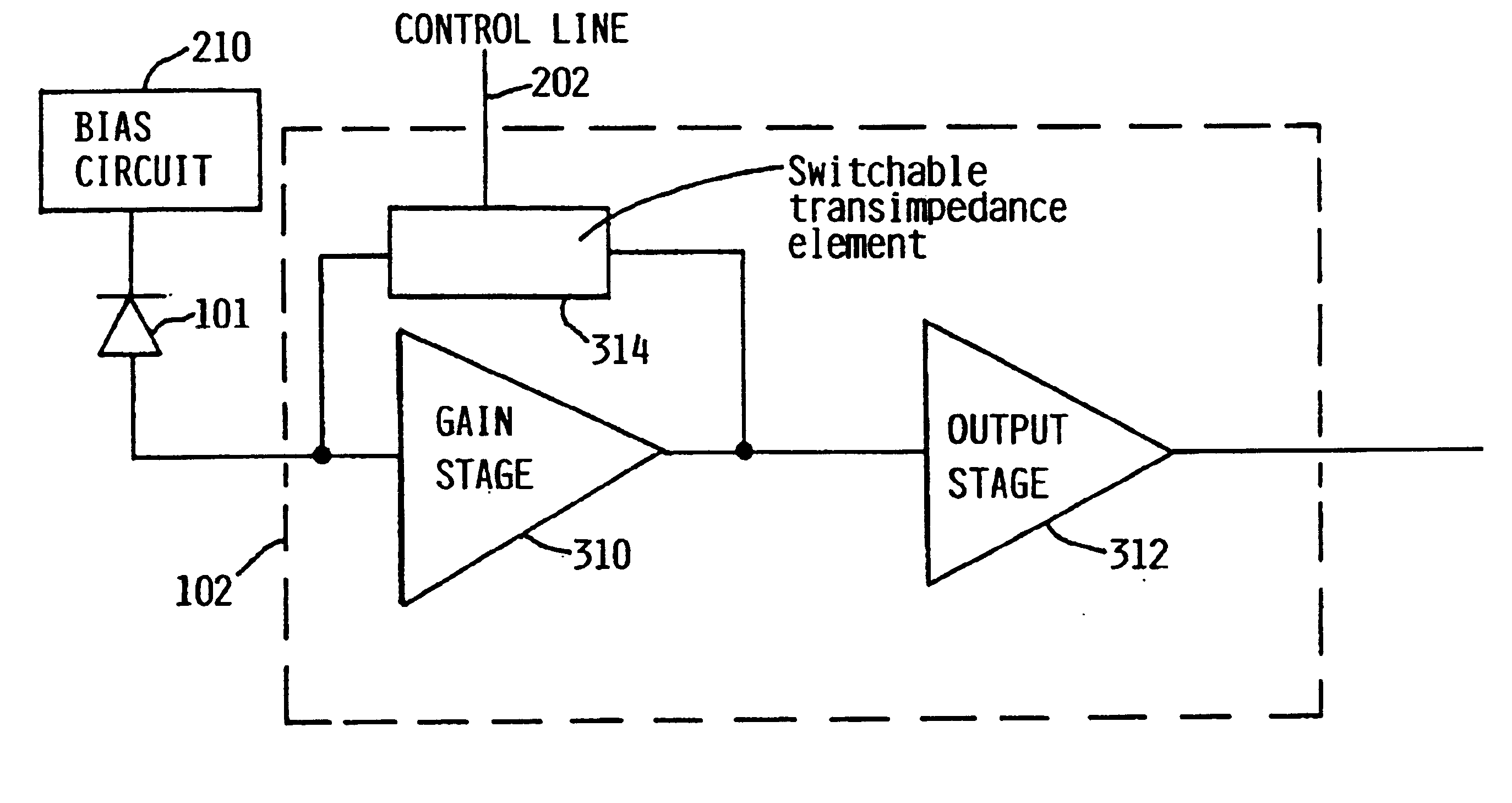
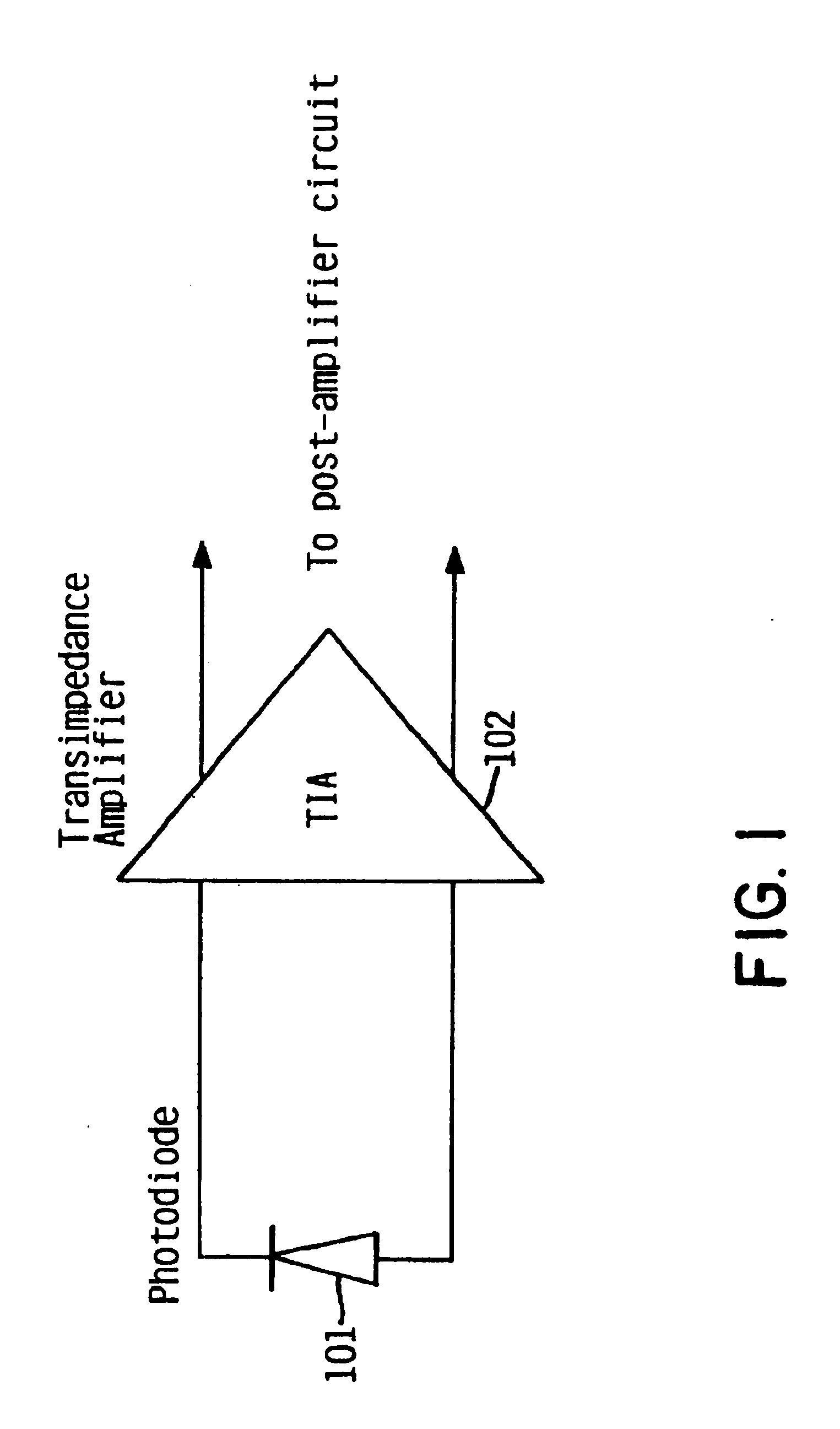
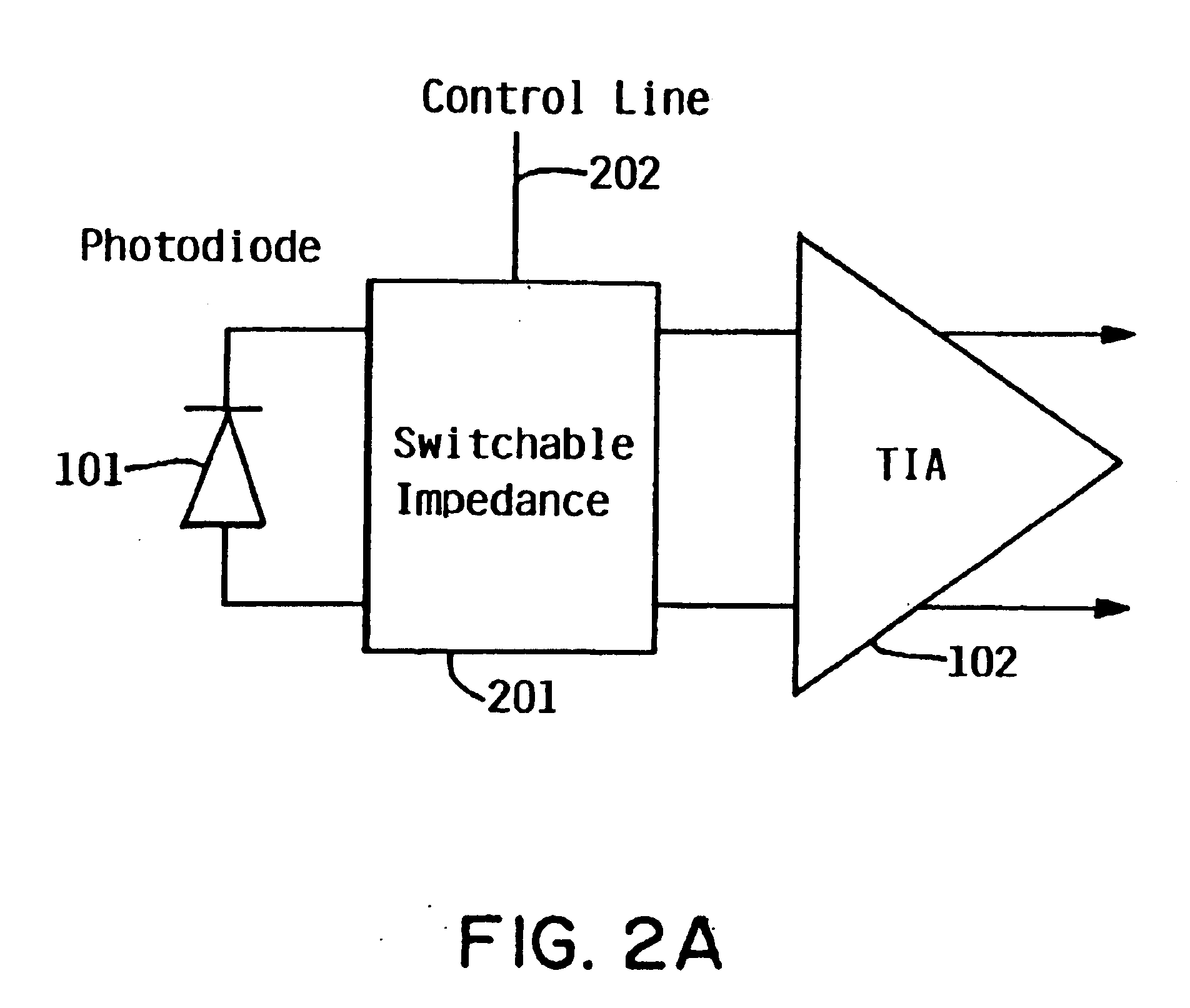
Switchable-bandwidth optical receiver
InactiveUS6862322B1Improve performanceModulated-carrier systemsGain controlAudio power amplifierEngineering
A switchable bandwidth optical receiver is implemented in a front-end of the receiver in at least one of three ways. A switchable impedance may be provided at the input to a preamplifier of the front end, the preamplifier of the front-end may have a switchable impedance therein, and / or a switchable filter may be provided at an output of the preamplifier.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and system for hybrid integration of an opto-electronic integrated circuit
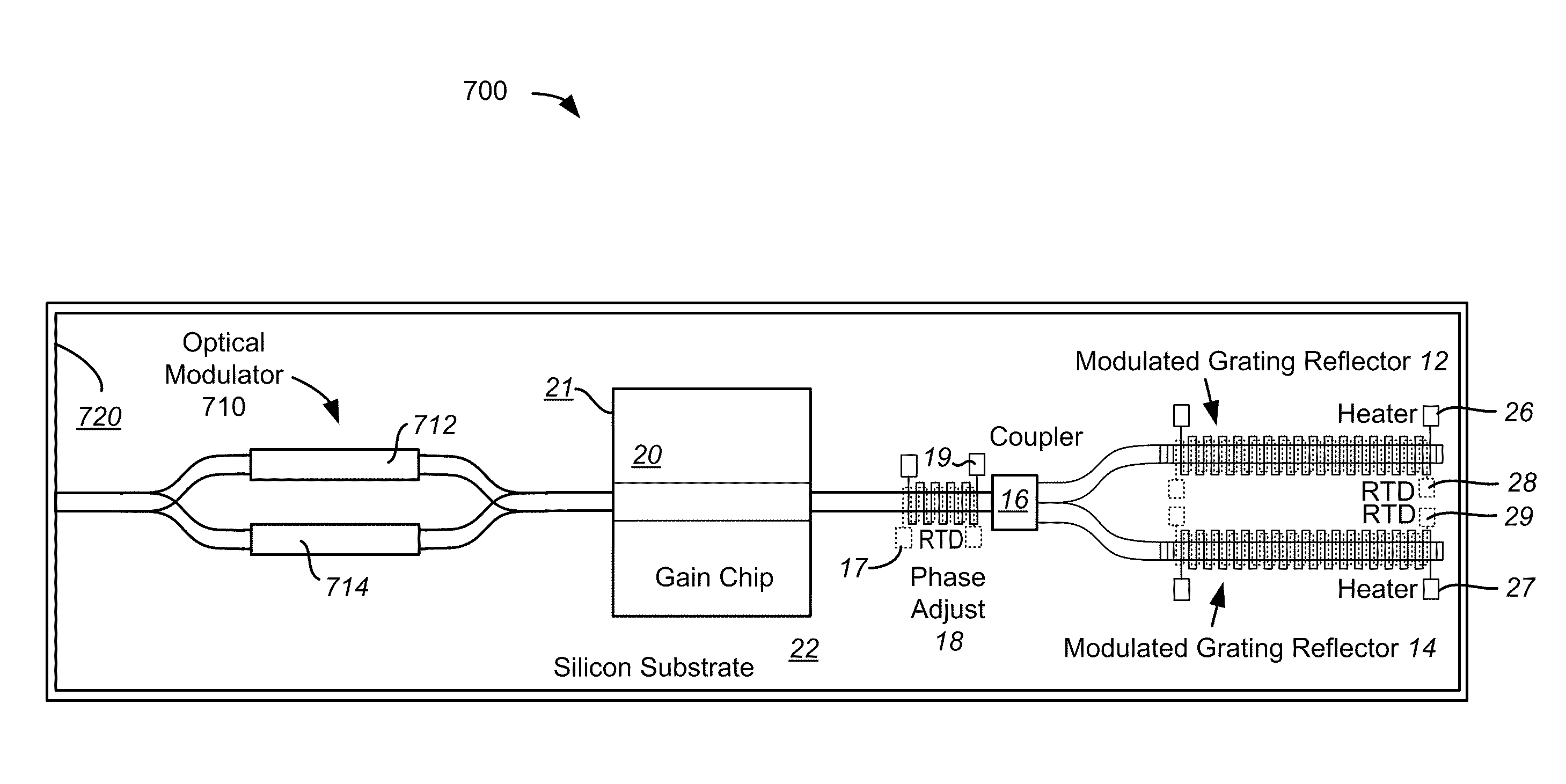
ActiveUS20110267676A1Reduce power consumptionSmall sizeCoupling light guidesSemiconductor lasersEngineeringOpto electronic
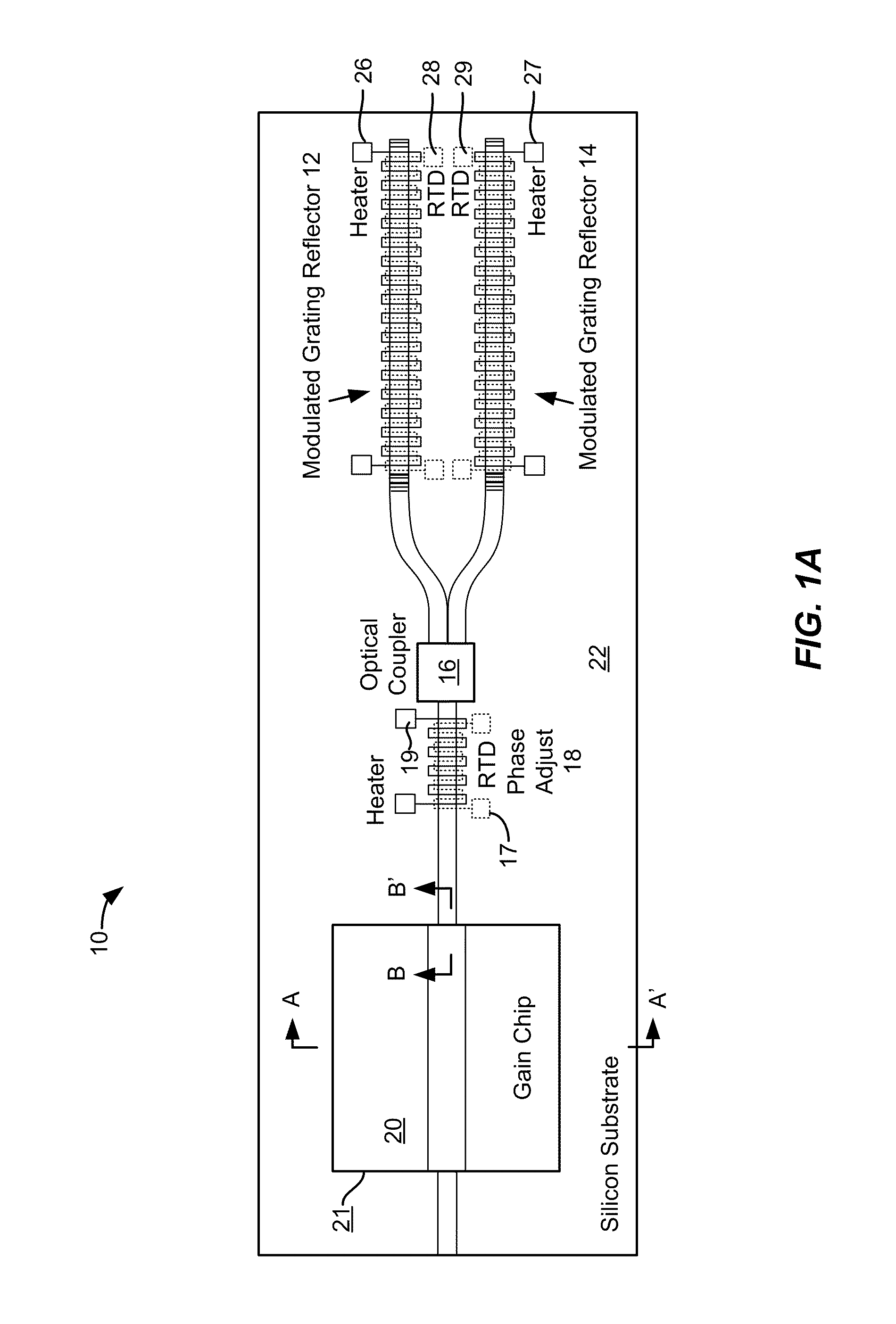
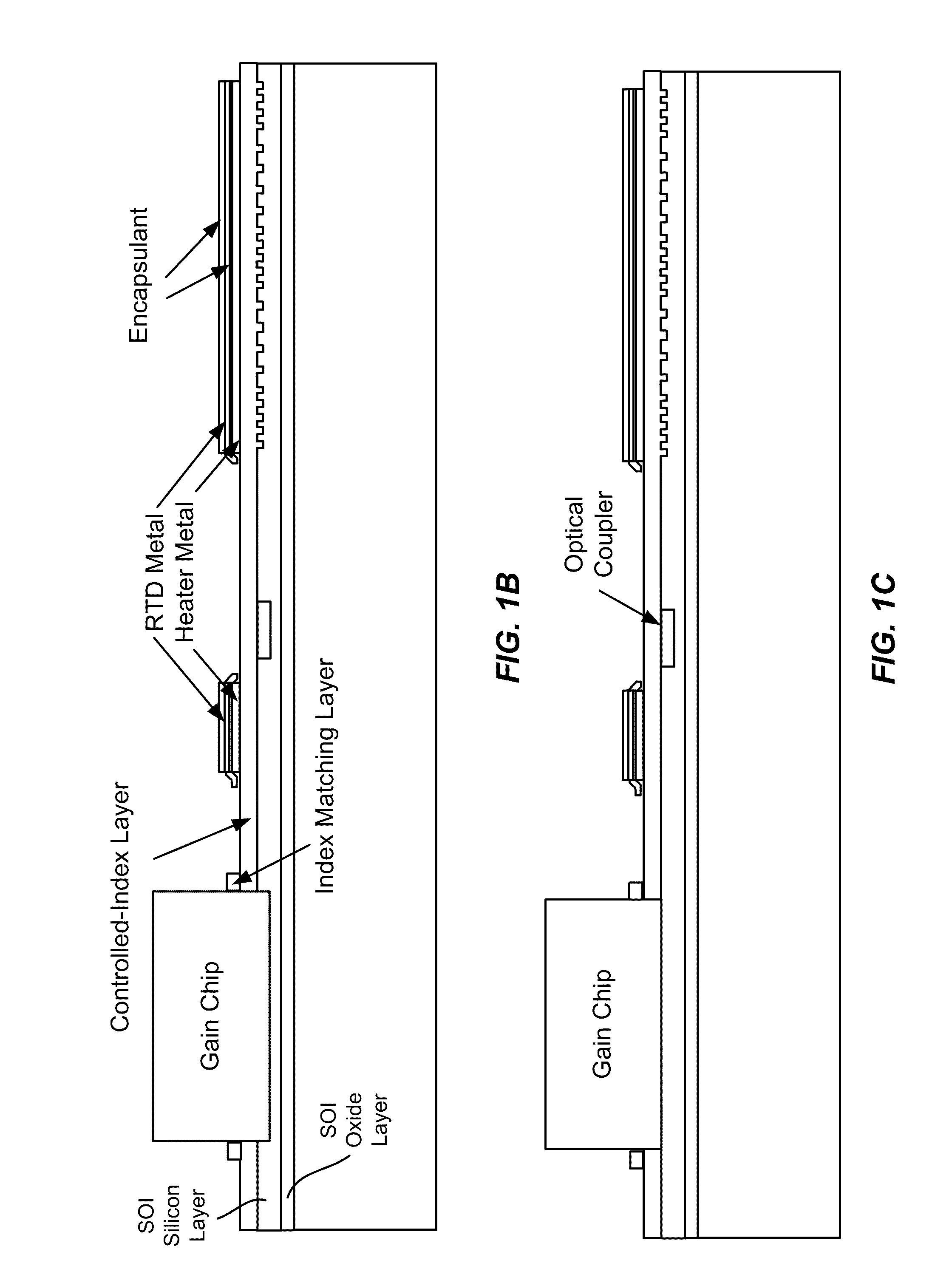
An opto-electronic integrated circuit (OEIC) includes an SOI substrate, a set of composite optical transmitters, a set of composite optical receivers, and control electronics disposed in the substrate and electrically coupled to the set of composite optical transmitters and receivers. Each of the composite optical transmitters includes a gain medium including a compound semiconductor material and an optical modulator. Each of the composite optical receivers includes a waveguide disposed in the SOI substrate, an optical detector bonded to the SOI substrate, and a bonding region disposed between the SOI substrate and the optical detector. The bonding region includes a metal-assisted bond at a first portion of the bonding region and a direct semiconductor-semiconductor bond at a second portion of the bonding region. The OEIC also includes control electronics disposed in the SOI substrate and electrically coupled to the set of composite optical transmitters and the set of composite optical receivers.
Owner:SKORPIOS TECH
Fully integrated amplified loudspeaker
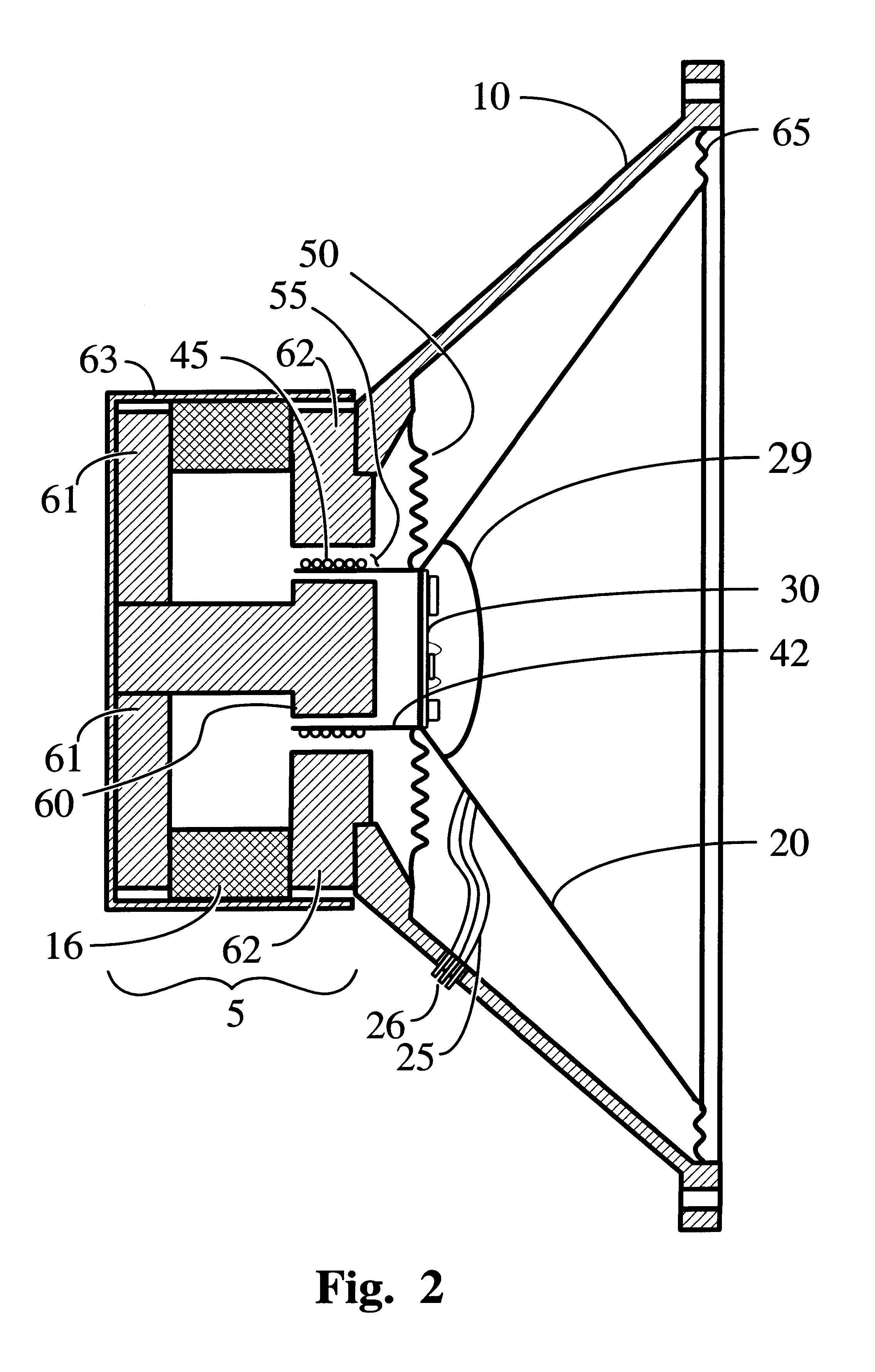
InactiveUS6243472B1Improve matchImprove linearityCircuit lead arrangements/reliefTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsAudio power amplifierLoudspeaker
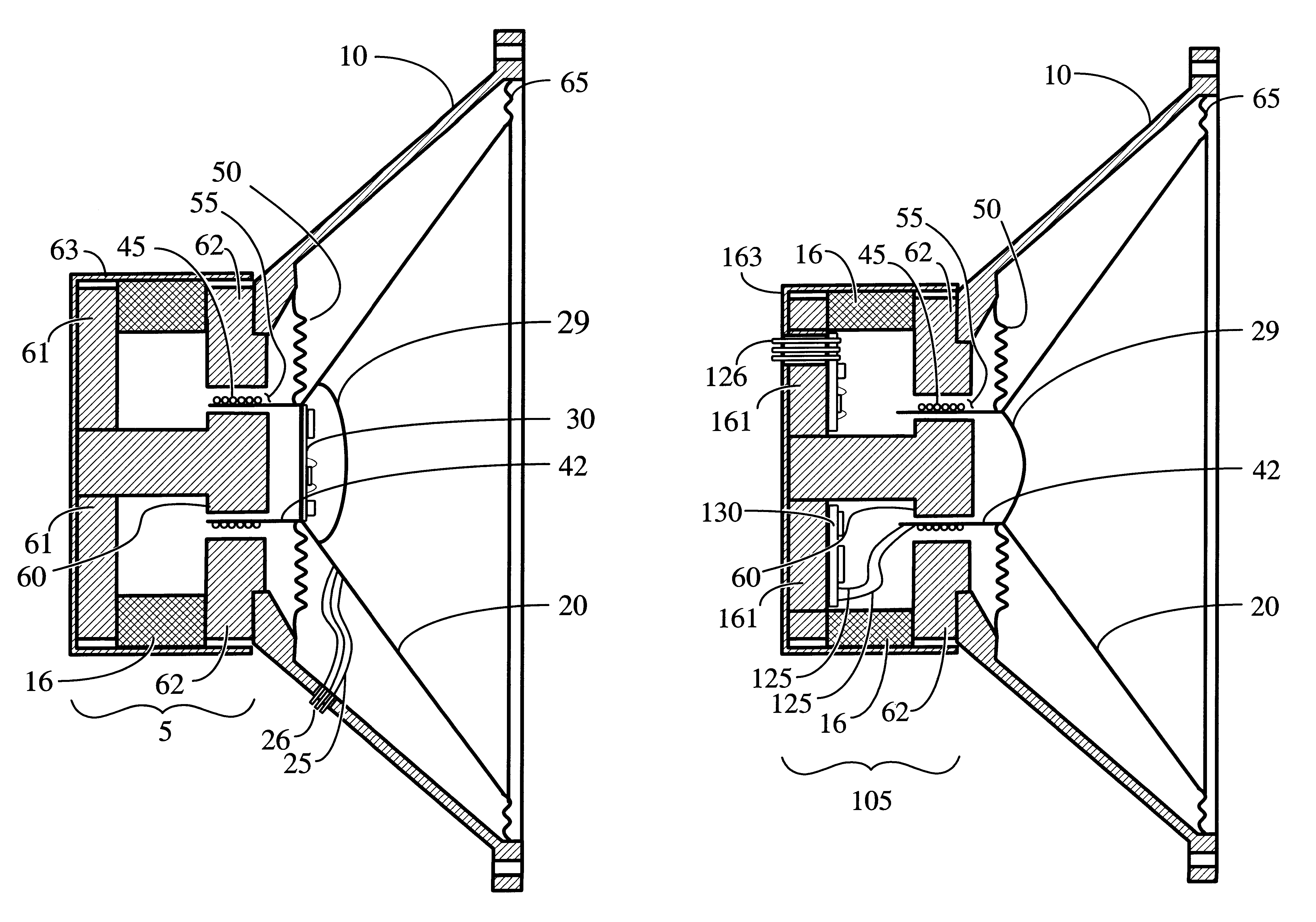
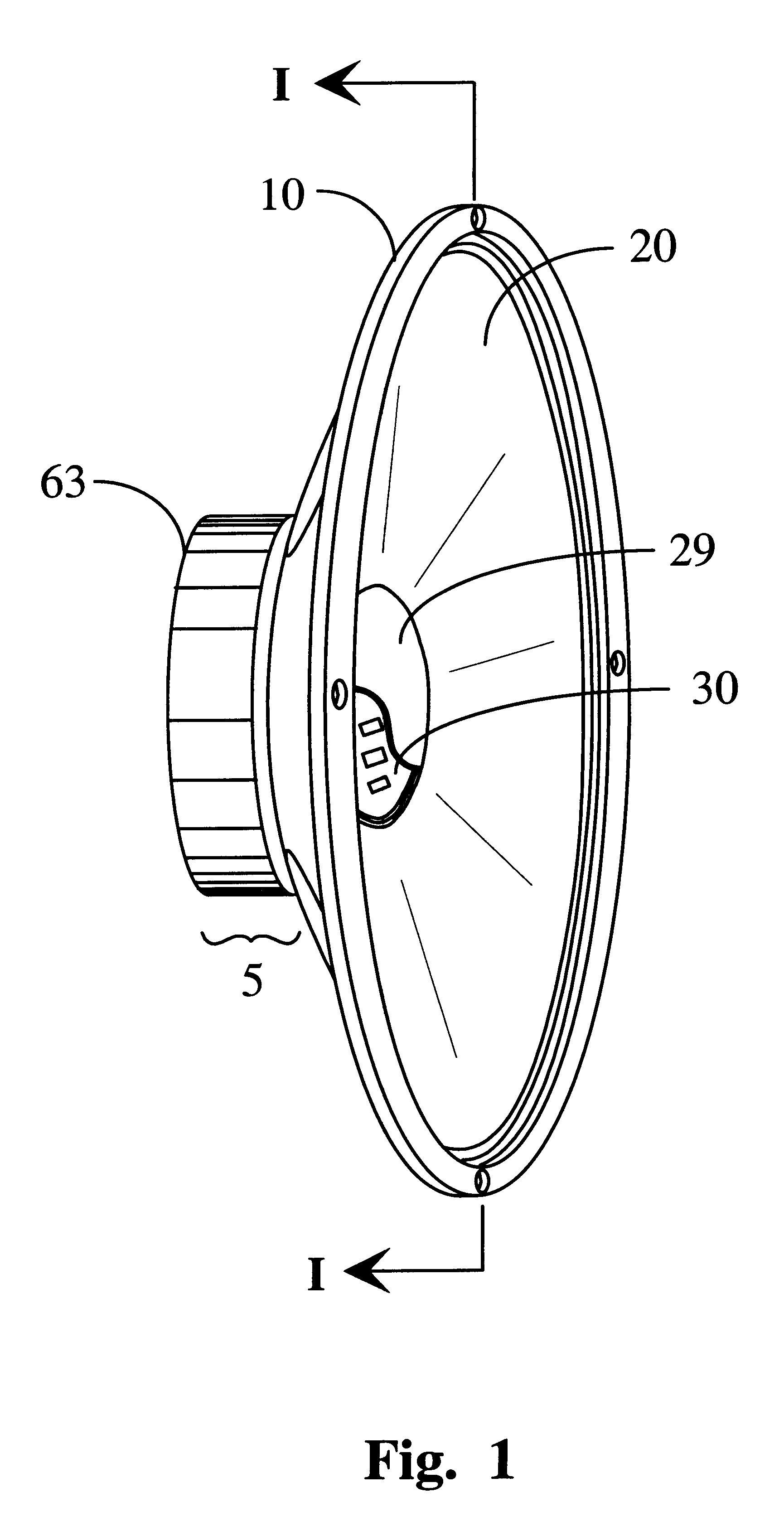
A fully integrated, low cost, amplified electro-acoustic loudspeaker is disclosed in which an amplifier circuit (30, 130, 230, 330, 930, 1030), radio-frequency receiver amplifier circuit (430, 530), optical receiver amplifier circuit (630, 730), or network based amplifier circuit (830) is directly mounted on the loudspeaker's magnetic assembly (105, 505, 705, 805), contained within the loudspeaker's moving assembly (20, 29, 629, 42, 45, 50, 65), or a combination thereof. The amplified loudspeaker's magnetic assembly (5, 105, 405, 505, 705, 805, 905, 1005) is utilized as an electro-magnetic interference shield and / or a heat dissipating element for the attached electronic circuitry. In selected embodiments of the amplified loudspeaker system, the former (42) containing voice coil (45) is additionally utilized for convection cooling of the amplifier circuit (30, 230) or receiver / amplifier circuit combination (430, 630).
Owner:BILAN FRANK ALBERT +1
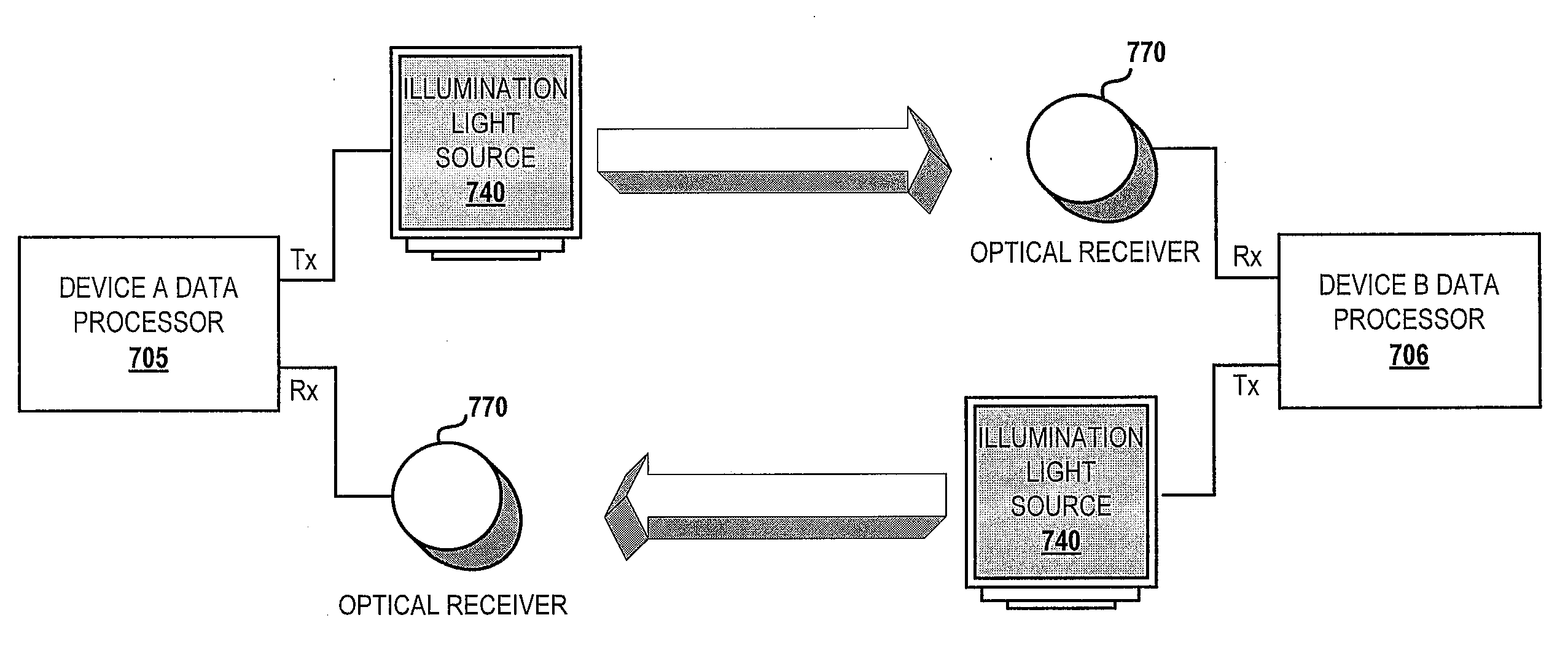
Synchronization and Processing of Secure Information Via Optically Transmitted Data
A method and device enables data communication via optical pulses from a light source of an electronic device. A data transfer interface is provided to support processing of selected data by a processor of the electronic device. The electronic device comprises an illumination light source, which is selectively utilized for illuminating a component in the electronic device and for transmitting data via optical pulses. An optical receiver also receives optically transmitted data. The transmission and receiving of the data is provided on a bidirectional duplex communication link created with a second optical receiver and an optical data transmission mechanism of a second electronic device.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
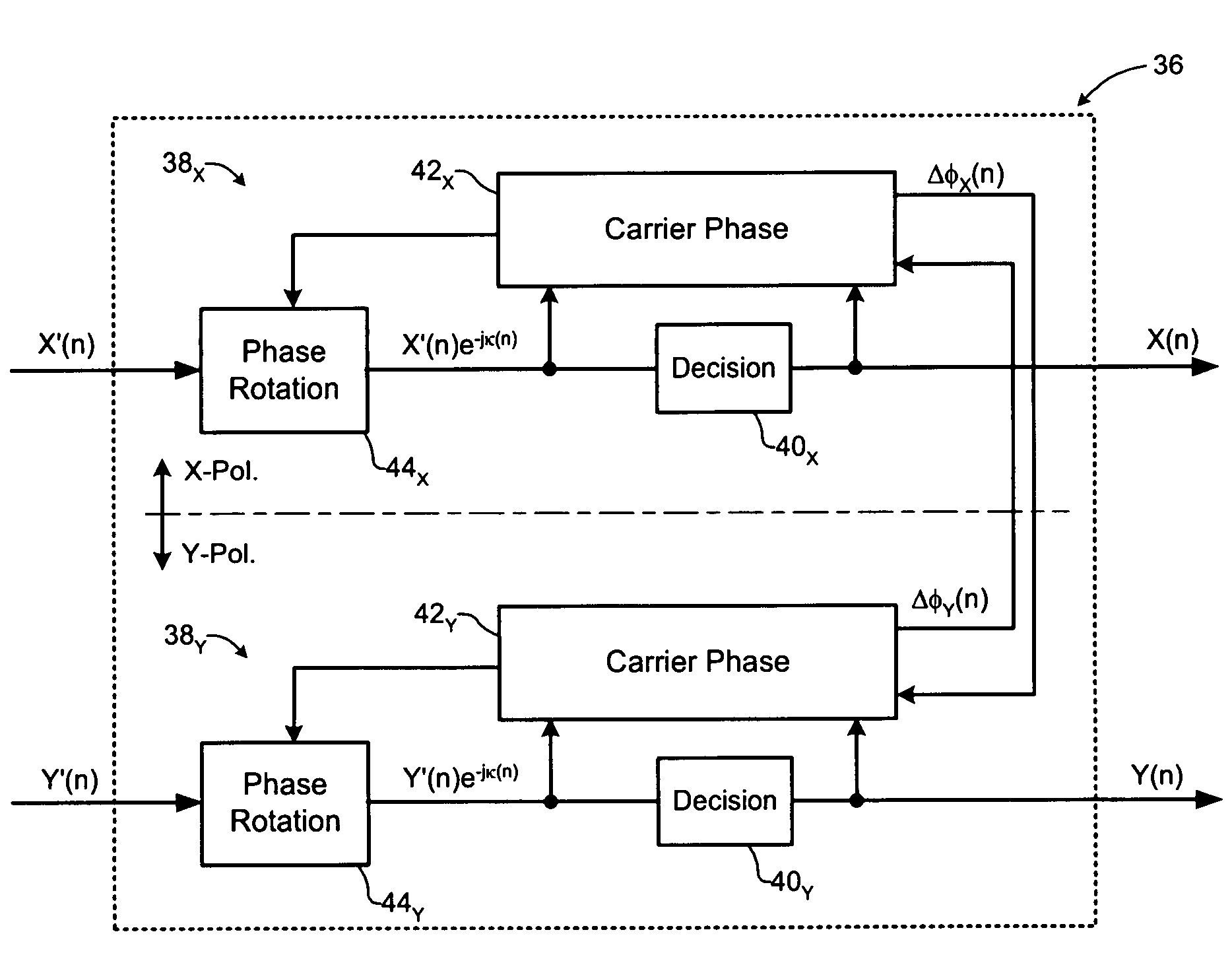
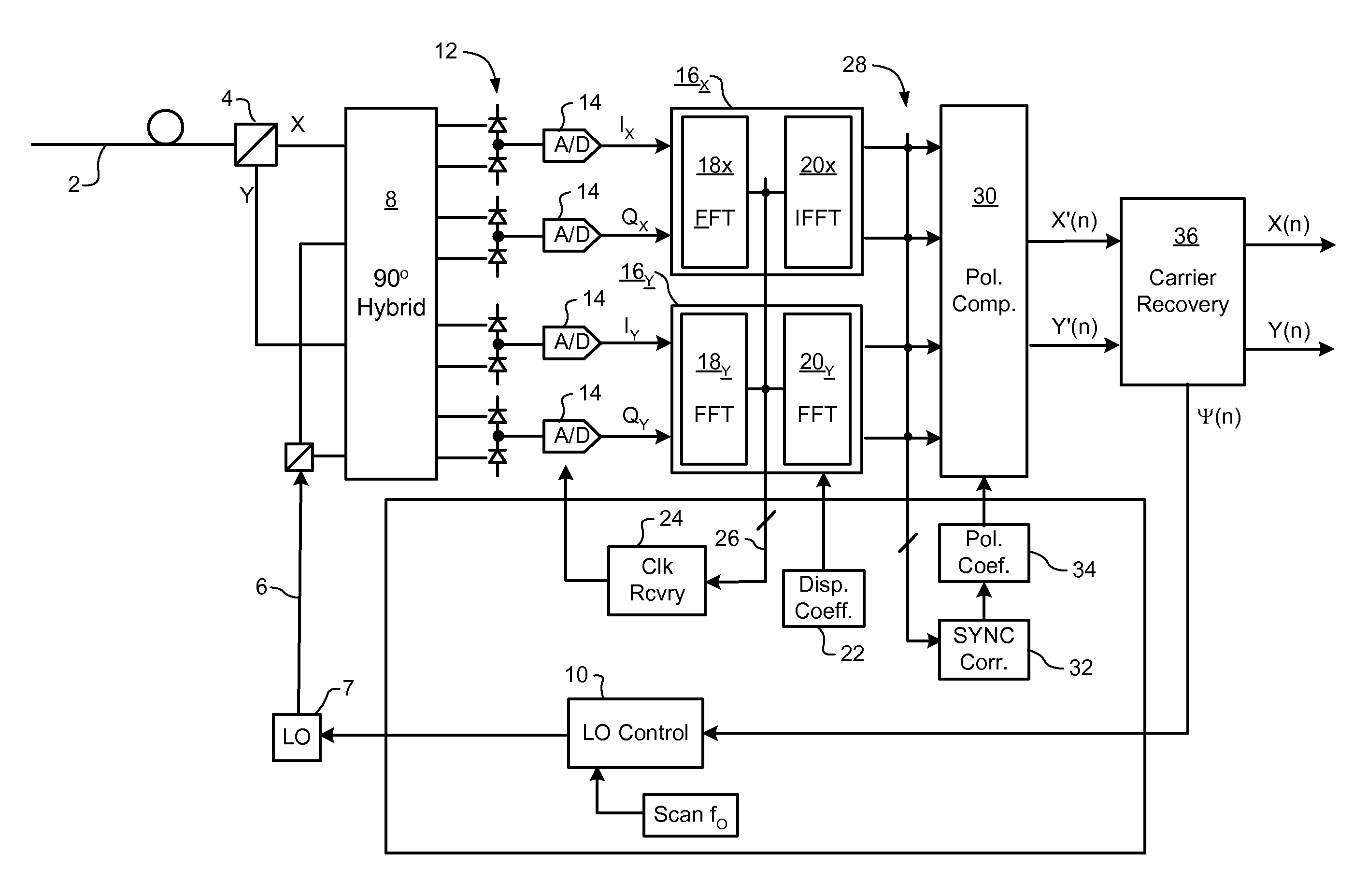
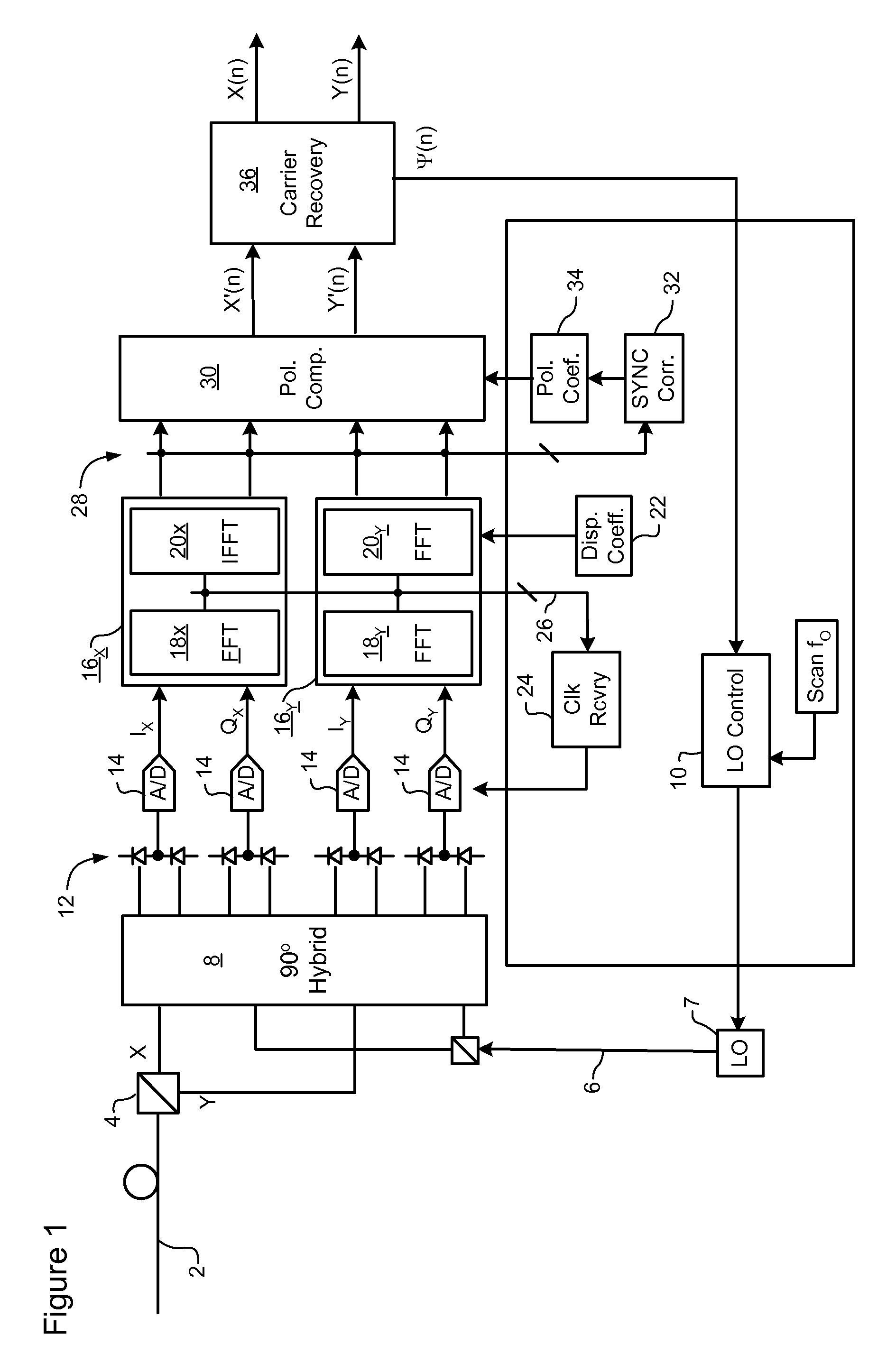
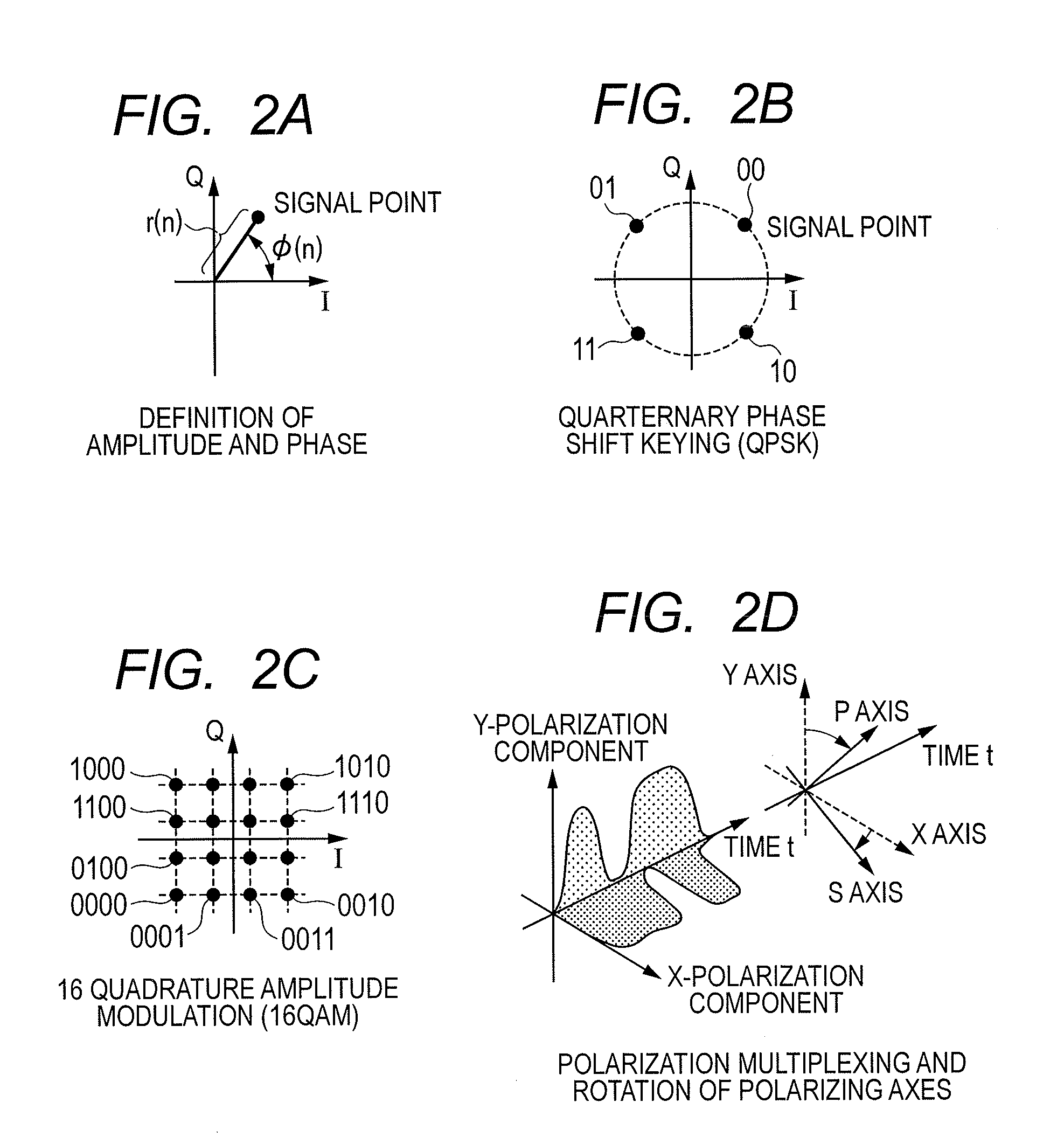
Carrier recovery in a coherent optical receiver
ActiveUS7606498B1Receiver initialisationSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansCarrier recoveryOptical receivers
A method of carrier recovery from a high speed optical signal received through an optical communications network. A stream of multi-bit digital samples of the optical signal is processed to generate a multi-bit estimate X′(n) of each one of a plurality of transmitted symbols. A phase of each symbol estimate X′(n) is rotated, and a respective symbol phase error Δφ(n) of the rotated symbol estimate determined.
Owner:CIENA
Optically-based location system and method for determining a location at a structure
InactiveUS6865347B2Beacon systems using electromagnetic wavesPosition fixationDelayed timePositioning system
An optically based location system and method of determining a location at a structure include a lighting infrastructure having lights at a structure. Each light is configured to illuminate and to transmit a respective relative or absolute terrestrial position through modulation of emitted light. An optical receiver is configured to detect the lights, to demodulate the position of detected lights, and to determine from the detection a position of the receiver. The receiver can have a conventional optical detector for determining a two-dimensional position of the receiver relative to a detected light, or can have a three-dimensional spot collimating lens and charged couple device optical detector for determining a three-dimensional position of the receiver relative to a detected light. The receiver and lights can be synchronized for converting a delay time into a distance measurement to calculate a distance between a light and the receiver.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
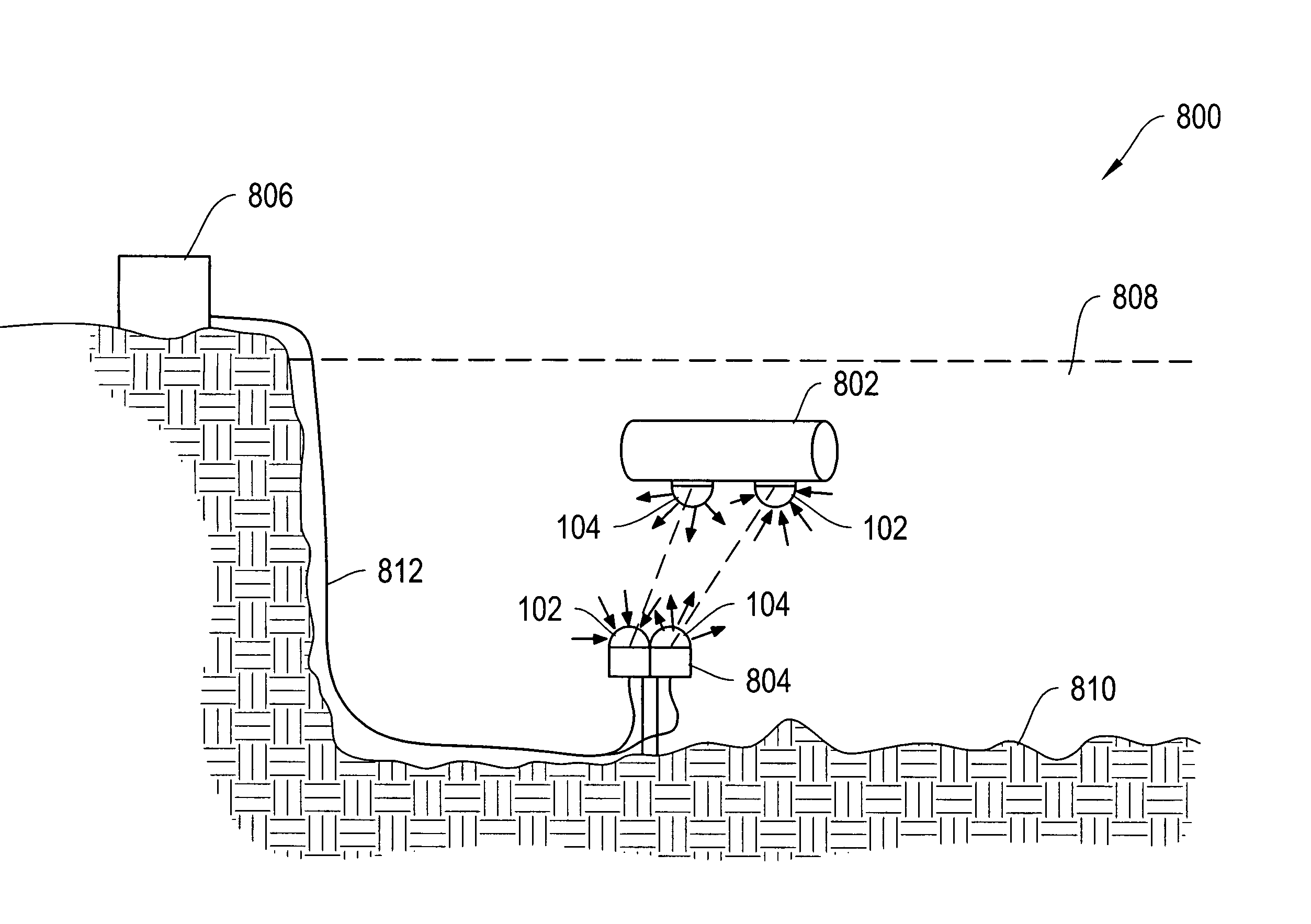
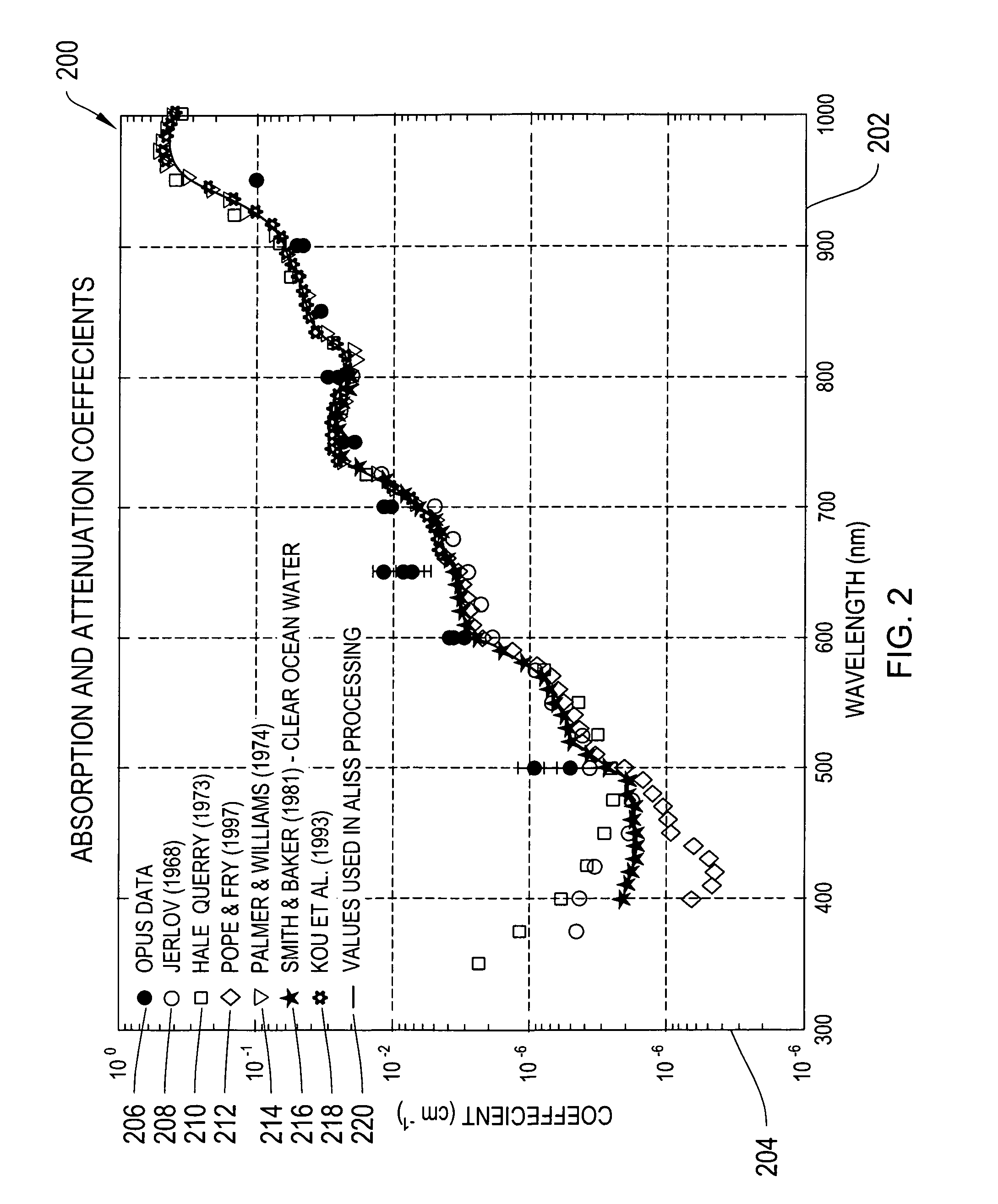
Systems and methods for underwater optical communication
The systems and methods of the invention provide for improved underwater communication systems. In particular, the systems and methods of the invention provide for improved underwater optical modems including optical transmitters and optical receivers that allow omni-directional transmission and reception of optical signals underwater and having a range of about 100 m and allowing data rates greater than 1 Mbit / s. The systems and methods of the invention also provide for underwater communication networks having a plurality of optical modems communicating with each other.
Owner:WOODS HOLE OCEANOGRAPHIC INSTITUTION
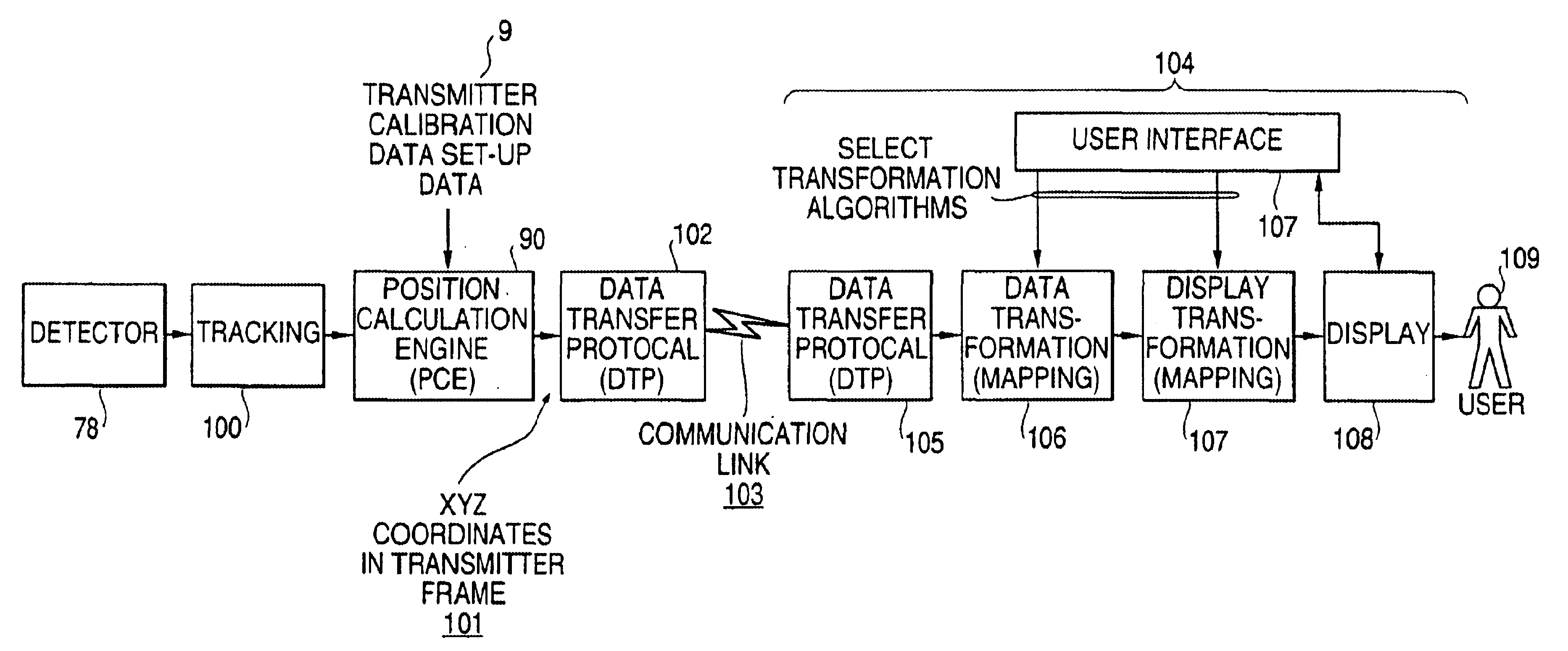
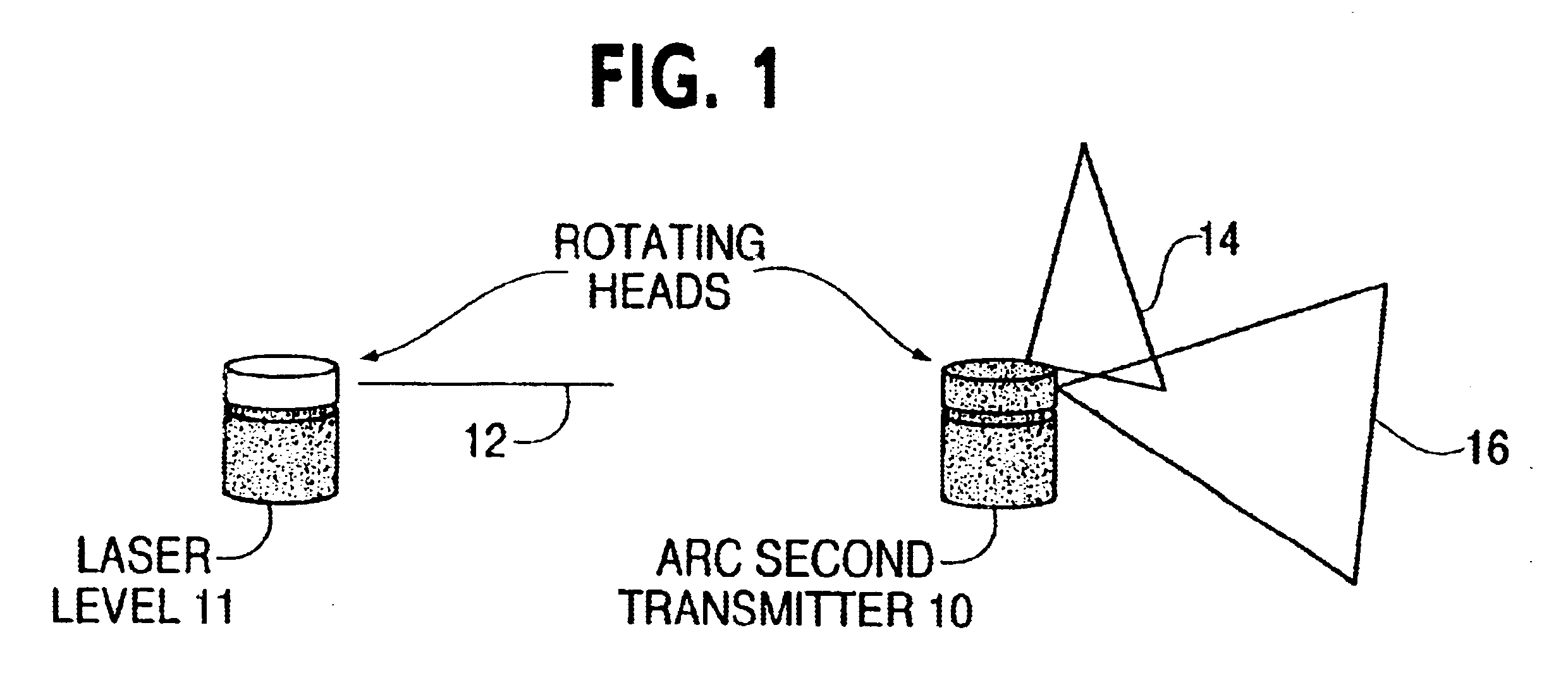
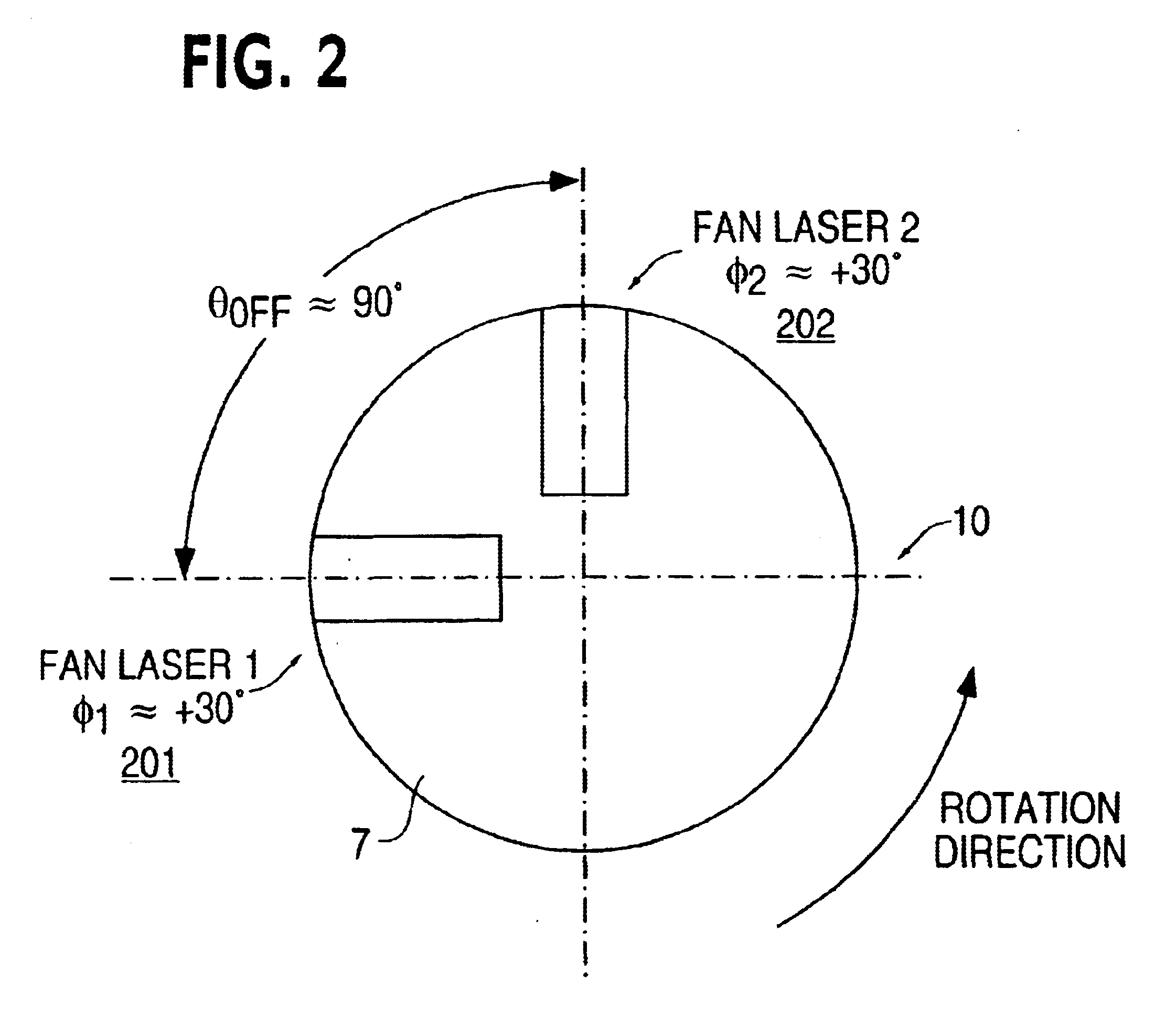
Method and optical receiver with easy setup means for use in position measurement systems
InactiveUS6630993B1Angle measurementBeacon systems using electromagnetic wavesRotational axisThree-dimensional space
Positions can be precisely and accurately fixed instantaneously within a three-dimensional workspace. A system of two or more transmitters each continuously sweep the workspace with two fanned laser beams which are preferably about 90 degrees apart on the rotational axis of the transmitter. A receiving instrument includes, preferably, two light detectors which detect the time at which each fanned laser beam is incident thereon. The light detectors also detect a synchronization pulse from each transmitter that is emitted once per revolution. Beams from different transmitters are differentiated by different rotational speeds and, therefore, different beam incidence cycles. Because three intersecting planes uniquely define a point in three-dimensional space, by detecting at least three of the fan beams from the transmitters, the receiving instrument can calculate its position in the workspace. A Quick Calc setup procedure allows the use to define a desired coordinate system within the workspace.
Owner:ARC SECOND +1
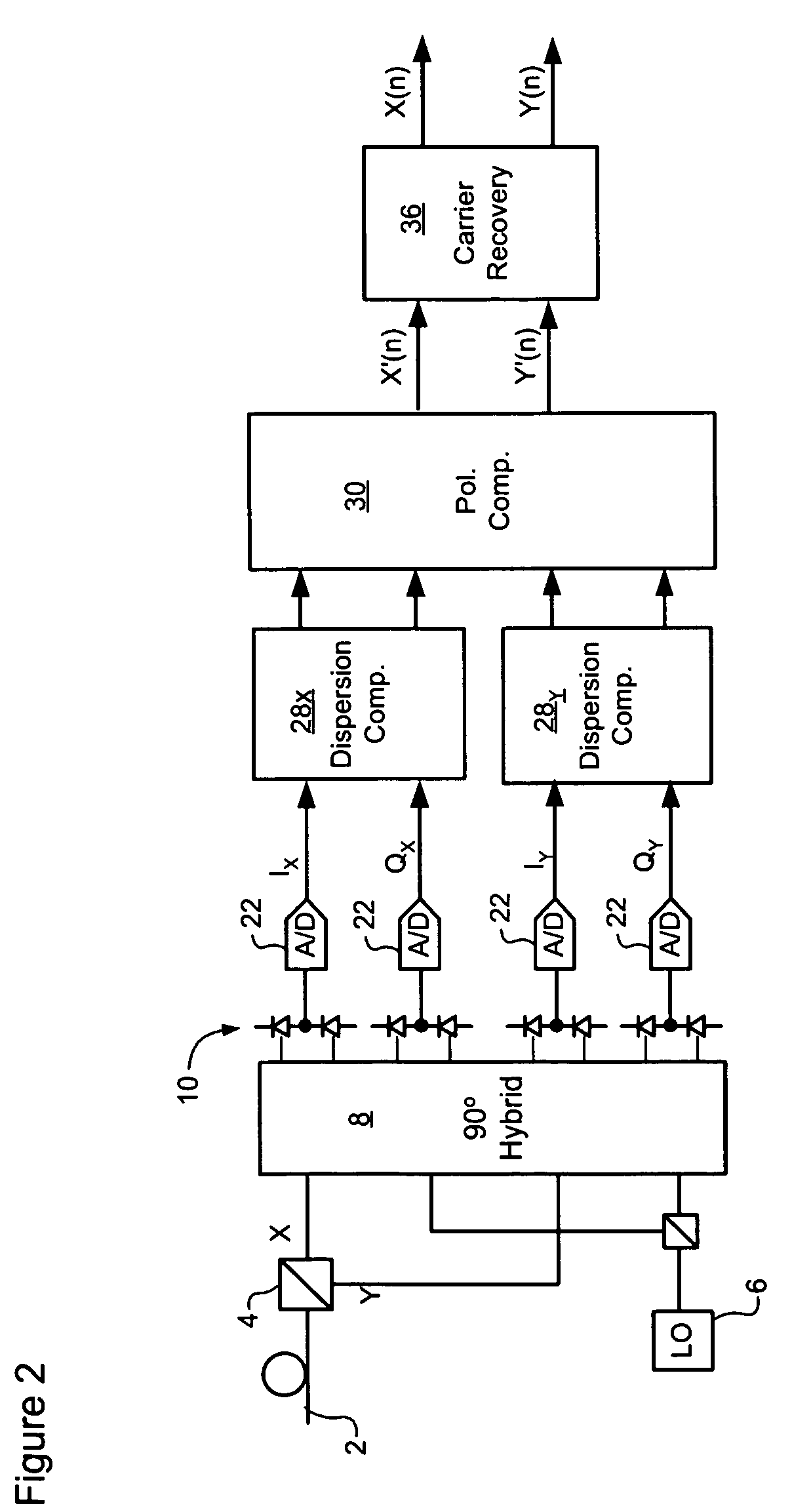
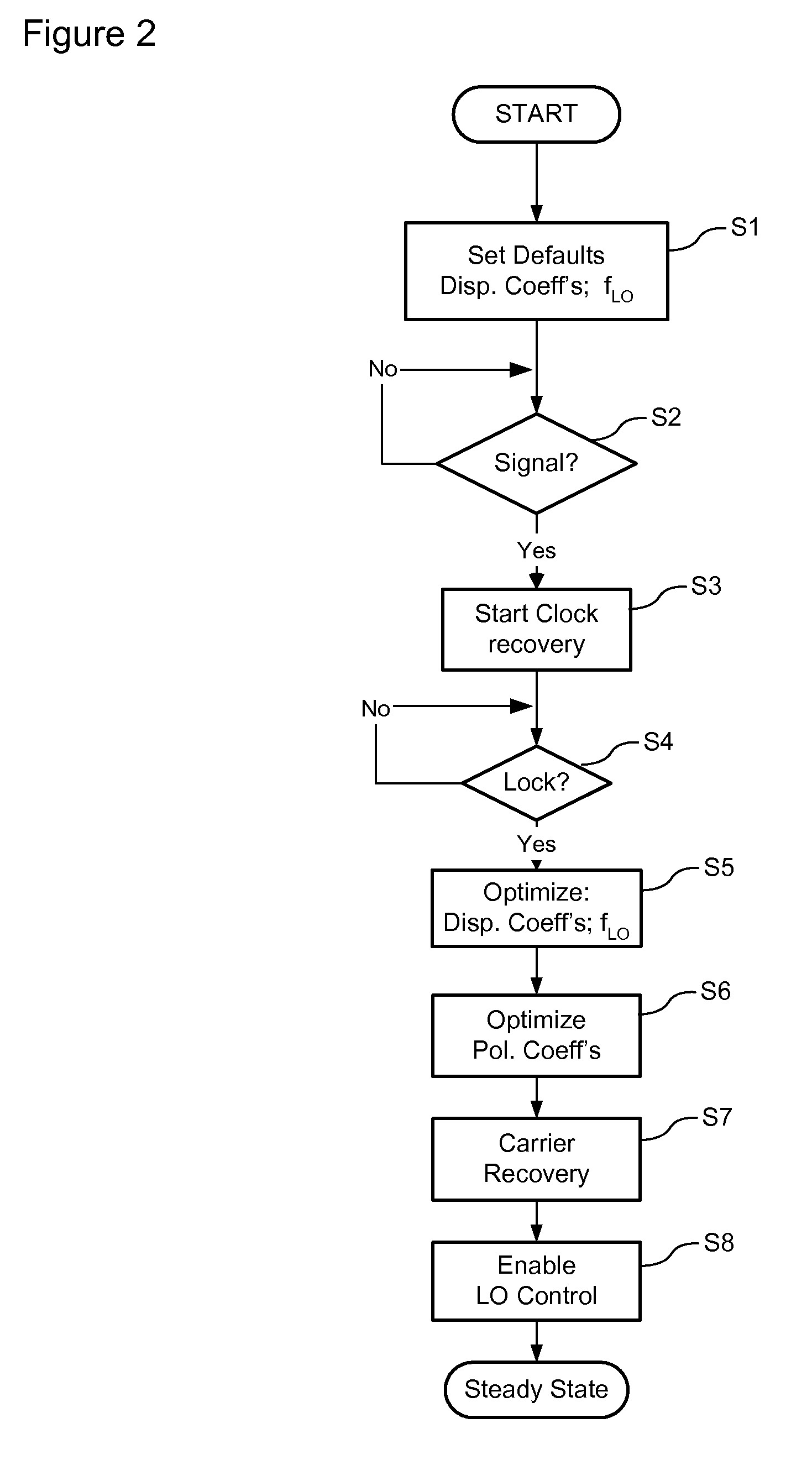
Signal acquisition in a coherent optical receiver
ActiveUS7636525B1Reliably acquire signalSteady-state operationReceiver initialisationSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansClock recoveryEngineering
A method and system for initializing a coherent optical receiver. Upon detection of an optical signal, a multi-bit digital sample stream of the optical signal is digitally processed to initialize each one of a plurality of adaptive control blocks of the coherent optical receiver. The adaptive control blocks include at least a dispersion compensation block and a clock recovery block. The dispersion compensation block is initialized before initializing the clock recovery block.
Owner:CIENA
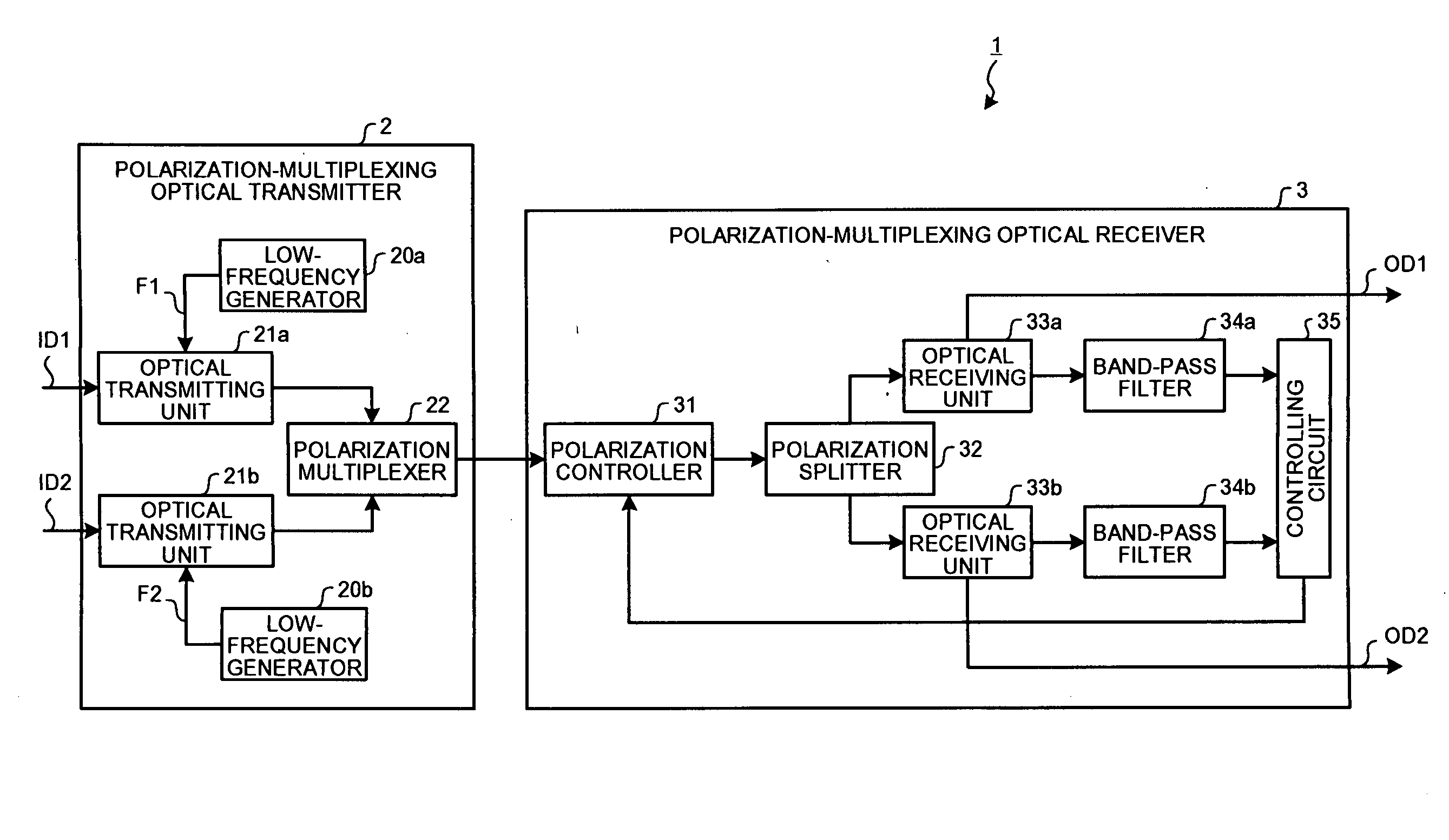
Polarization-multiplexing optical transmitter polarization-multiplexing optical receiver, polarization-multiplexing optical transceiving system, and controlling method thereof
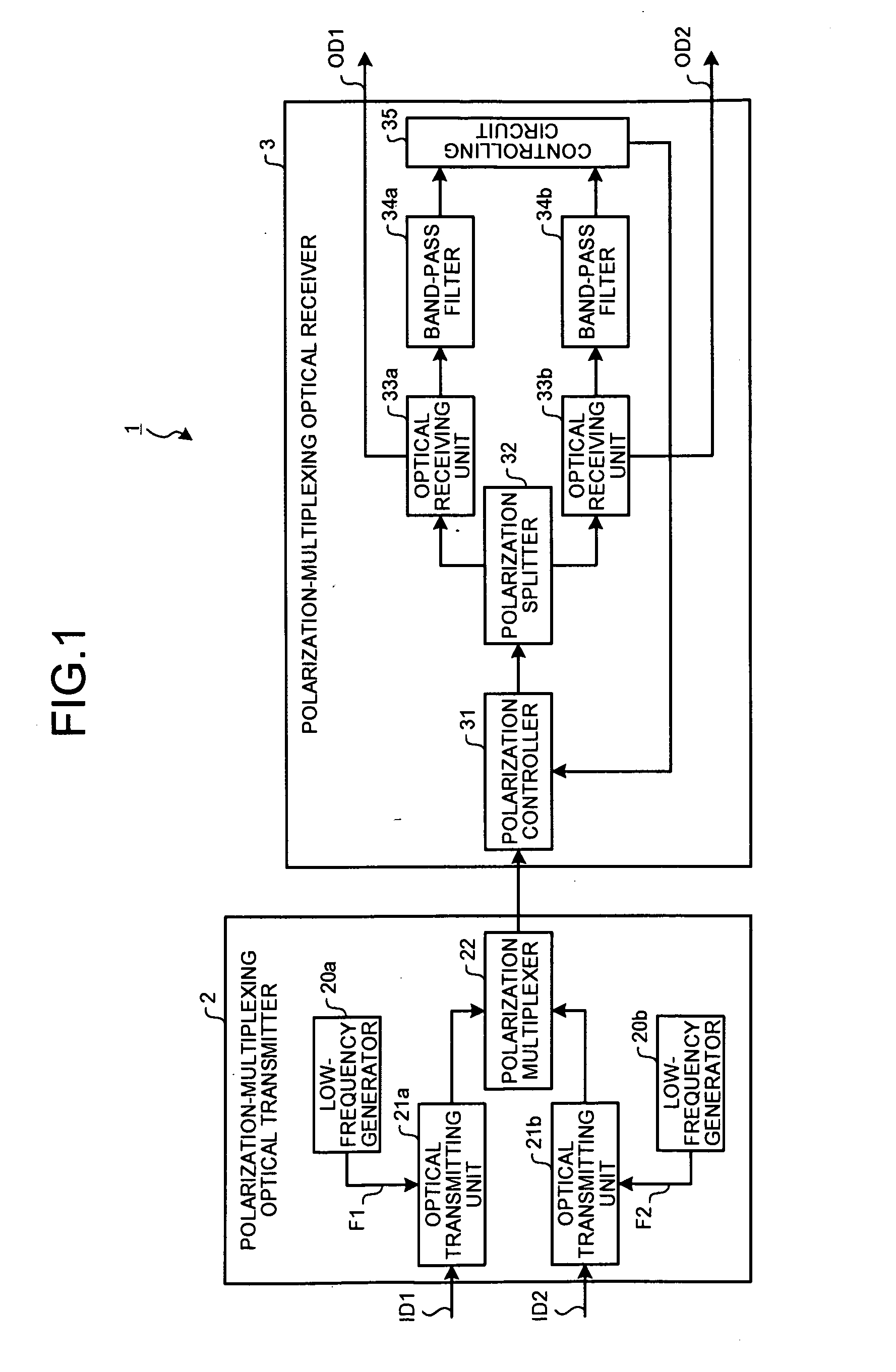
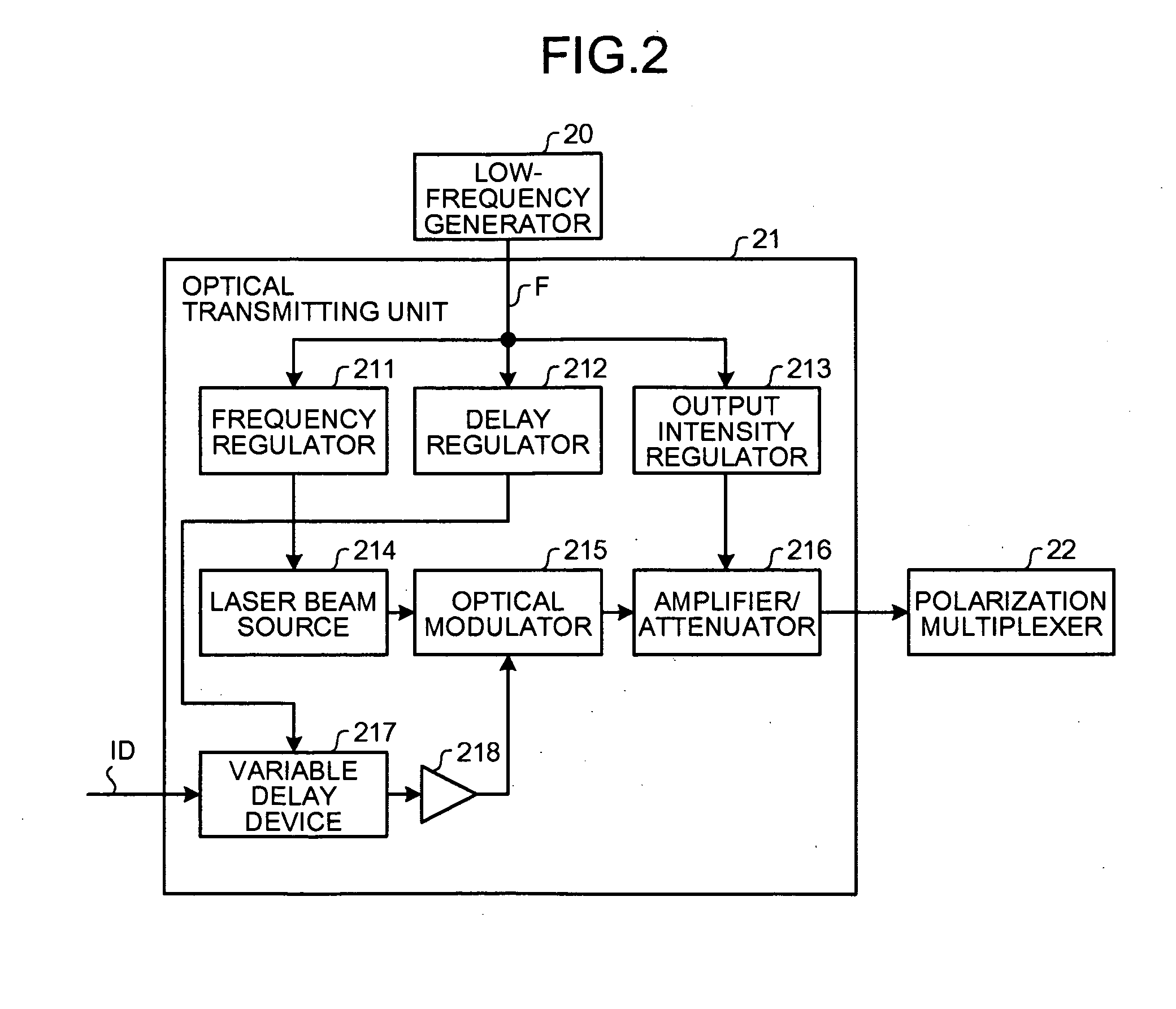
InactiveUS20080232816A1Minimizes valueMaximizing and minimizing outputPolarisation multiplex systemsOptical mode multiplex systemsPolarization multiplexedCarrier signal
By using low-frequency signals, an optical transmitting unit modulates one of a wavelength, a transmission timing, and an intensity of light as a carrier wave. A polarization multiplexer synthesizes the output light signals, modulated by the optical transmitting unit, in polarization states orthogonal to each other and generates polarization-multiplexing signals. A polarization splitter splits by extracting two orthogonal polarization components from the polarization-multiplexing signals. The polarization states of the polarization-multiplexing signals are controlled by a polarization controller in an optical receiving unit. A band-pass filter extracts components transmitting through passbands from output signals of the optical receiving unit and outputs an intensity of the components. Based on the intensity output from the filter, a controlling circuit generates feedback control signals for maximizing a ratio of the components of the low-frequency signals and by using the feedback control signals, the polarization controller controls the polarization states of the optical multiplexing signals.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Integrated bi-directional axial gradient refractive index/diffraction grating wavelength division multiplexer
InactiveUS6011884AIncreased durabilityImprove the environmentLaser detailsCoupling light guidesMultiplexingMultiplexer
A wavelength division multiplexer is provided that integrates an axial gradient refractive index element with a diffraction grating to provide efficient coupling from a plurality of input optical sources (each delivering a single wavelength to the device) which are multiplexed to a single polychromatic beam for output to a single output optical receiver. The device comprises: (a) means for accepting optical input from at least one optical source, the means including a planar surface; (b) a coupler element comprising (1) an axial gradient refractive index collimating lens having a planar entrance surface onto which the optical input is incident and (2) a homogeneous index boot lens affixed to the axial gradient refractive index collimating lens and having a planar but tilted exit surface; (c) a diffraction grating, such as a Littrow diffraction grating, on the tilted surface of the homogeneous index boot lens which combines a plurality of spatially separated wavelengths from the optical light; and (d) means to output at least one multiplexed, polychromatic output beam, the means including a planar surface. The device may be operated in the forward direction as a multiplexer or in the reverse direction as a demultiplexer.
Owner:AUXORA
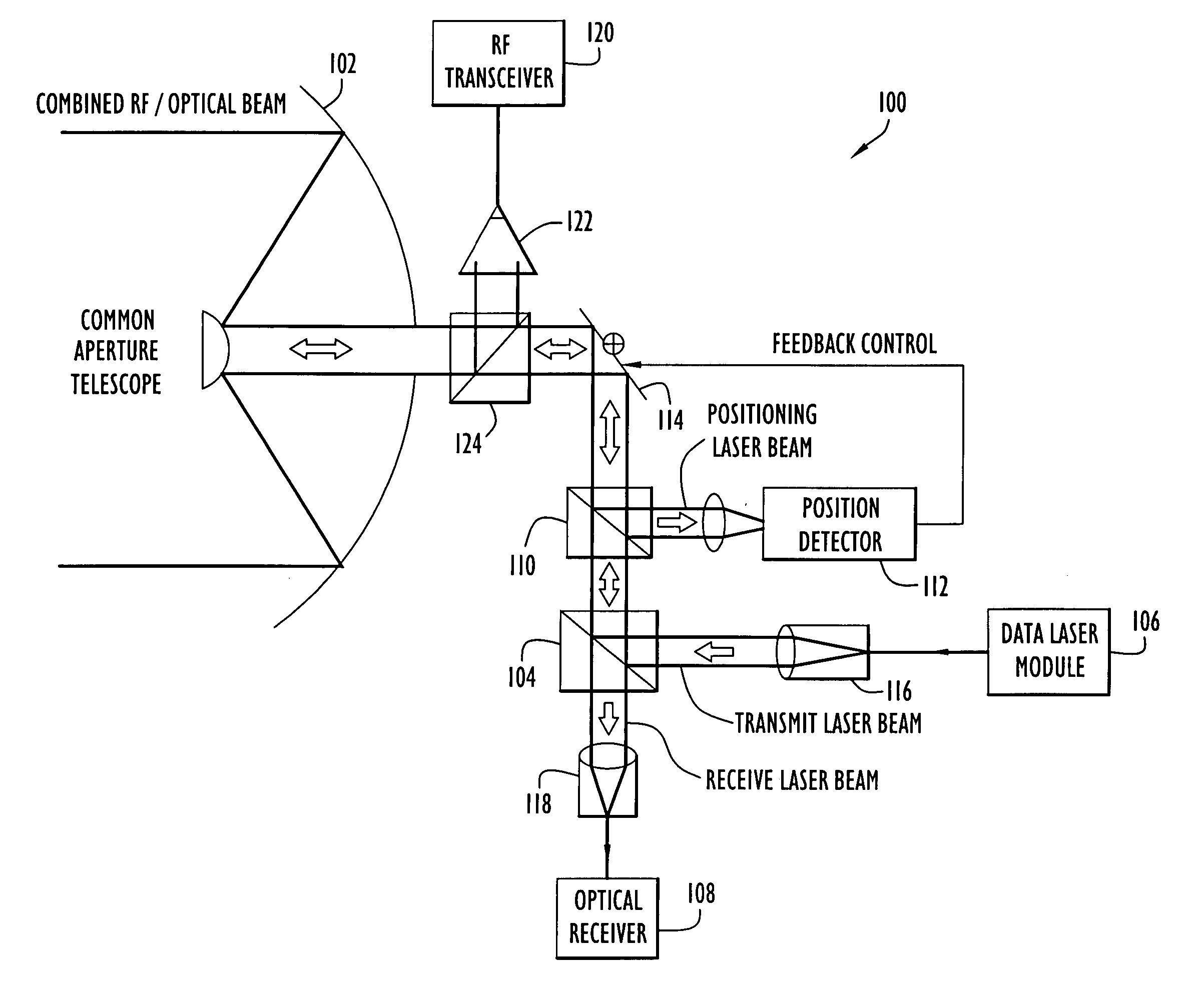
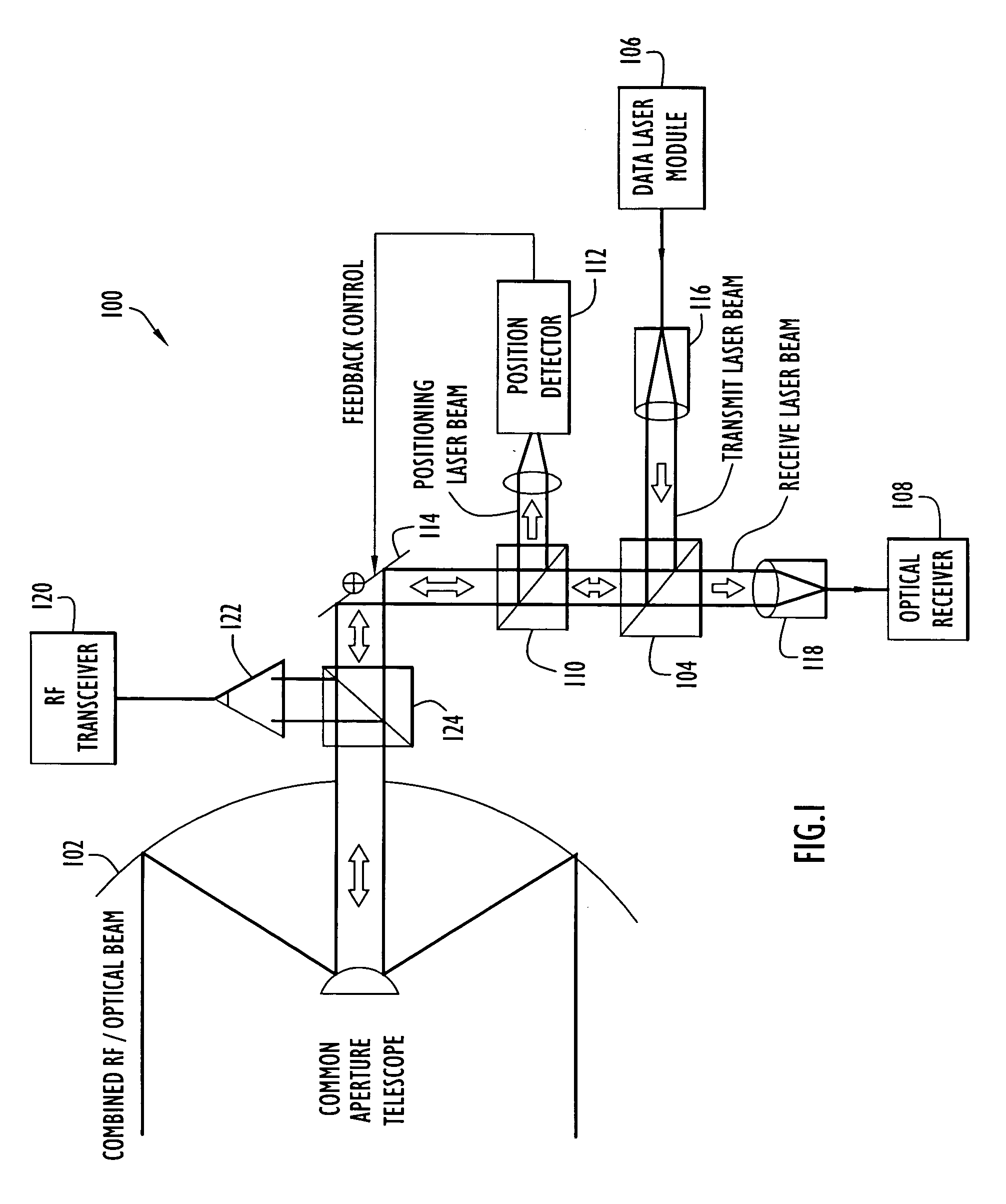
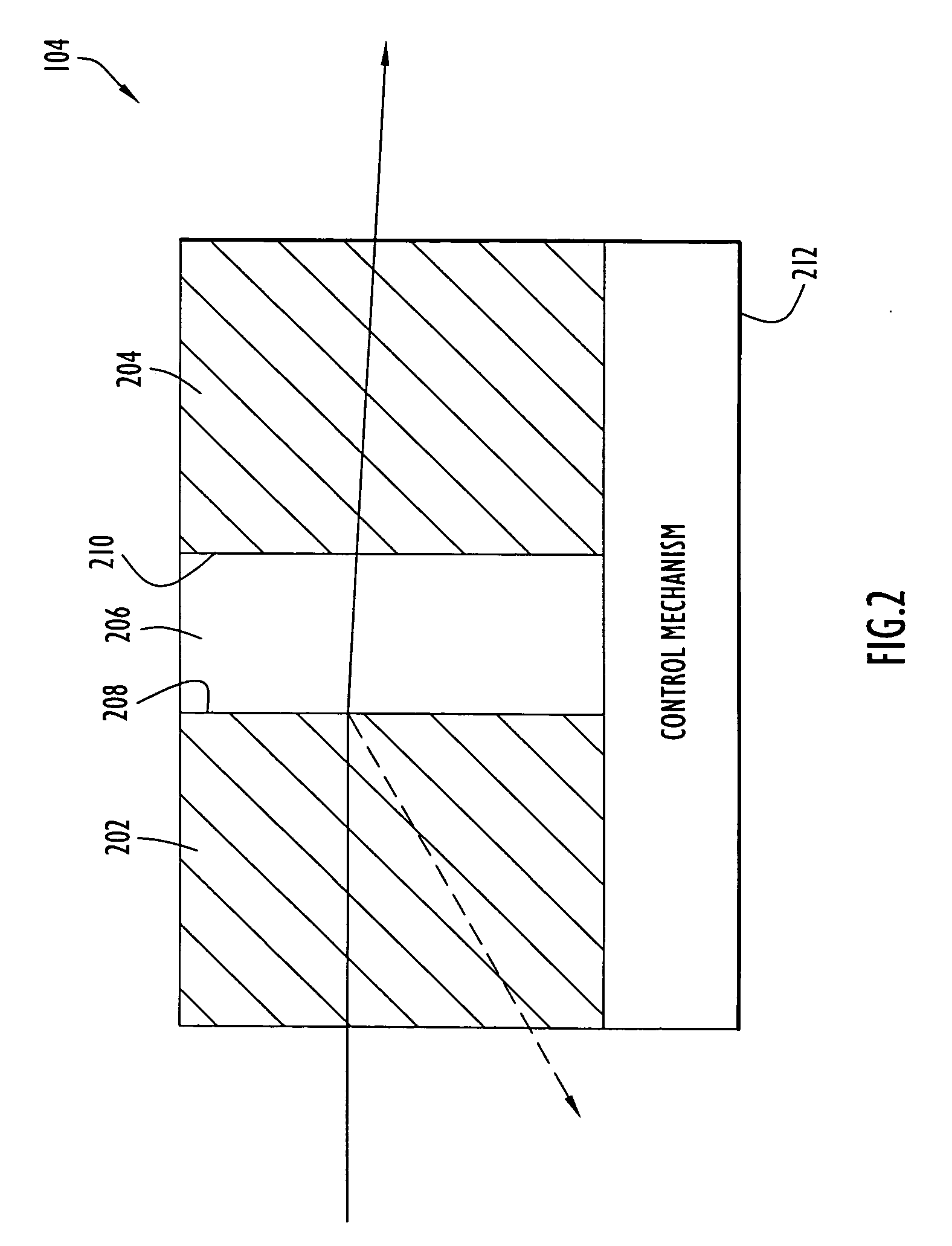
Communication transceiver architecture
ActiveUS20070031150A1Reduce sensitivitySimplifies the transceiver architectureSatellite communication transmissionRadio transmissionLaser transmitterOptical axis
A free-space communication transceiver includes a telescope for transmitting and receiving laser beams, a tunable laser transmitter for generating a transmit laser beam modulated with data, a tunable optical receiver for processing a receive laser beam received from the telescope to recover data, and a tunable beamsplitter that directs the transmit laser beam to the telescope and directs the receive laser beam from the telescope to the optical receiver. Between the telescope and beamsplitter, the transmit and receive laser beams travel along a common optical axis as collinear collimated free-space beams. The transmit and receive laser beams operate at different wavelengths that can be interchanged, thereby support full-duplex operation. The beamsplitter employs a tunable etalon filter whose wavelength-dependent transmission characteristics are adjusted according to the transmit and receive wavelengths. Optionally, RF signals can additionally be couple to the common optical axis and transmitted and received by the telescope.
Owner:PERATON INC
Wavelength dispersion probing system
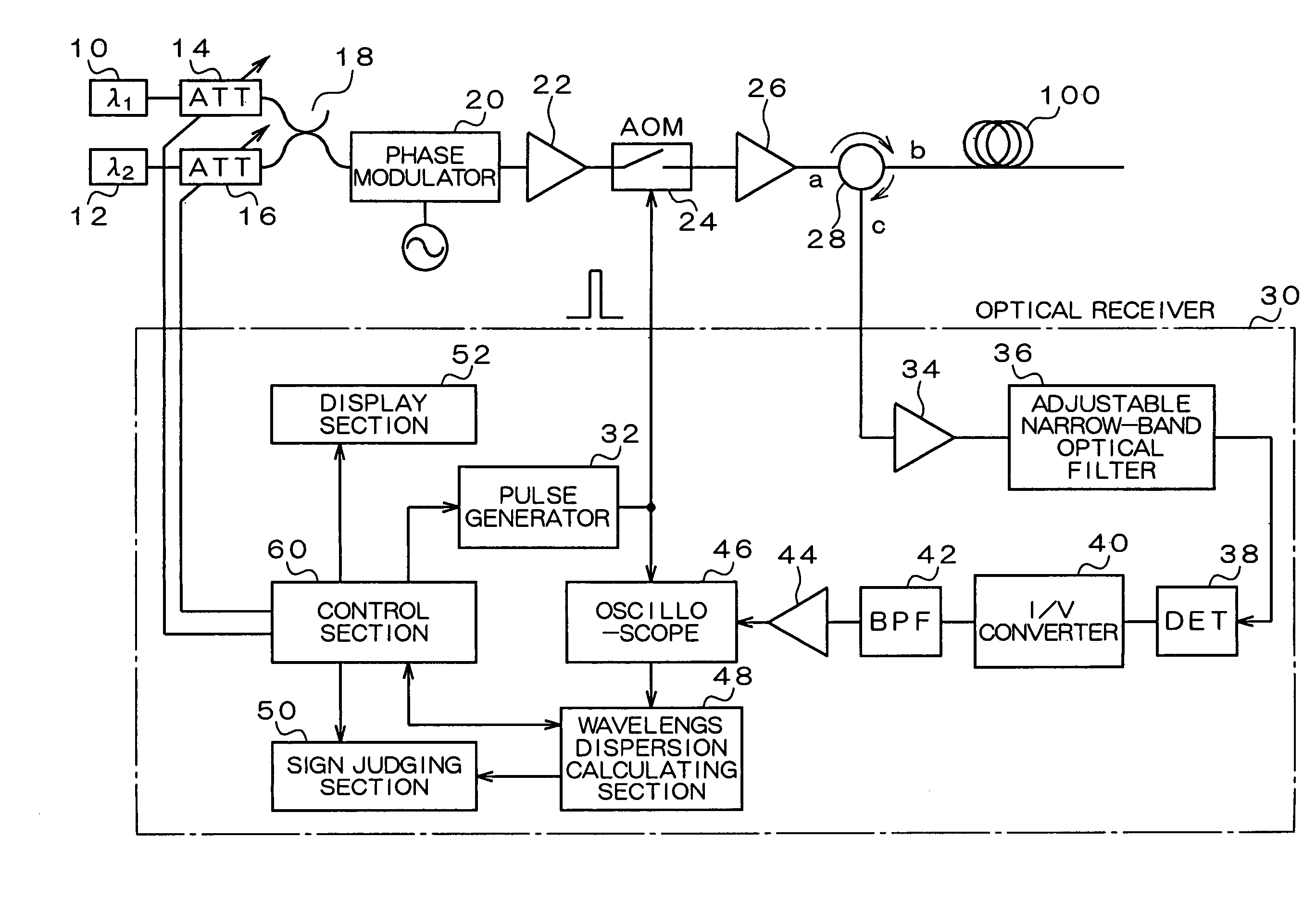
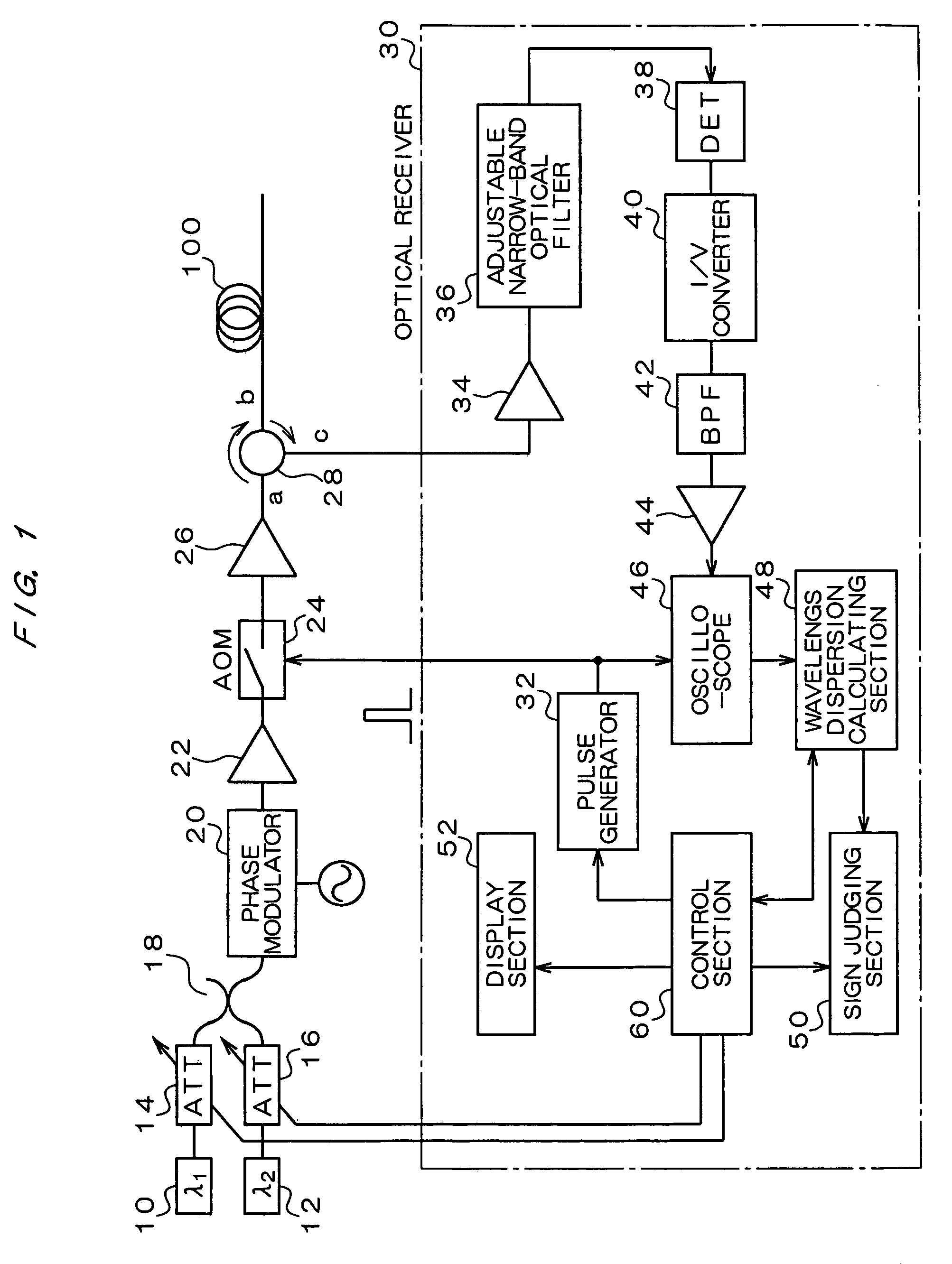
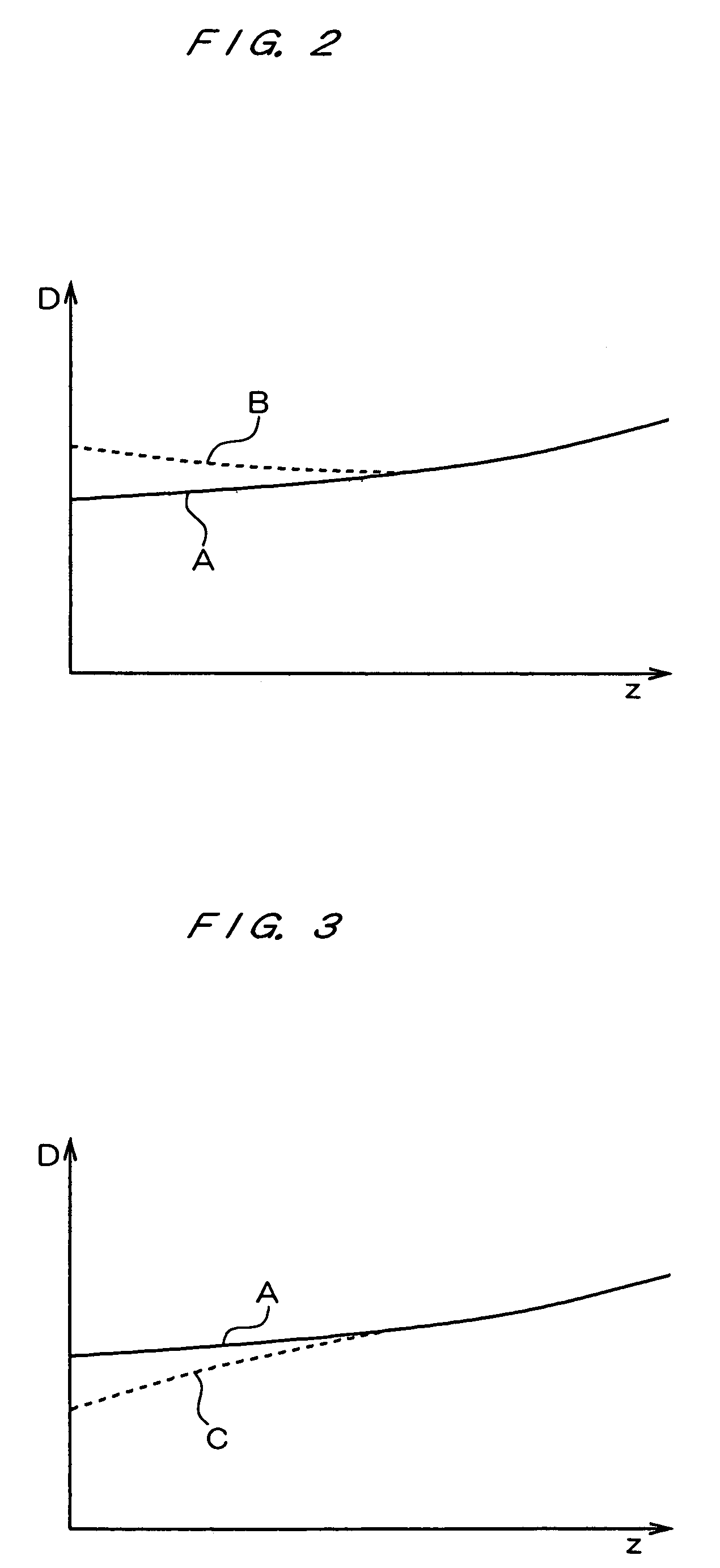
InactiveUS7020360B2Time and troubleMaterial analysis by optical meansCoupling light guidesMultiplexingMultiplexer
A wavelength dispersion probing system for determining a value of wavelength dispersion and its sign and reducing the trouble and time required for this determination. This wavelength dispersion probing system comprises light sources 10, 12, light attenuators 14, 16, optical multiplexer 18, phase modulator 20, optical amplifiers 22, 26, acoustooptical modulator 24, optical receiver 30. The intensity ratio of two wavelengths is set at 1 to 2 to detect Stokes light or anti-Stokes light included in the return light of an optical fiber 100 by the optical receiver 30, so that wavelength dispersion is probed. The wavelength dispersion is probed by changing the intensity ratio of the two wavelengths to observe the state of the change of the wavelength dispersion, so that the sign of wavelength dispersion is determined by the optical receiver 30.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
Optical mapping apparatus
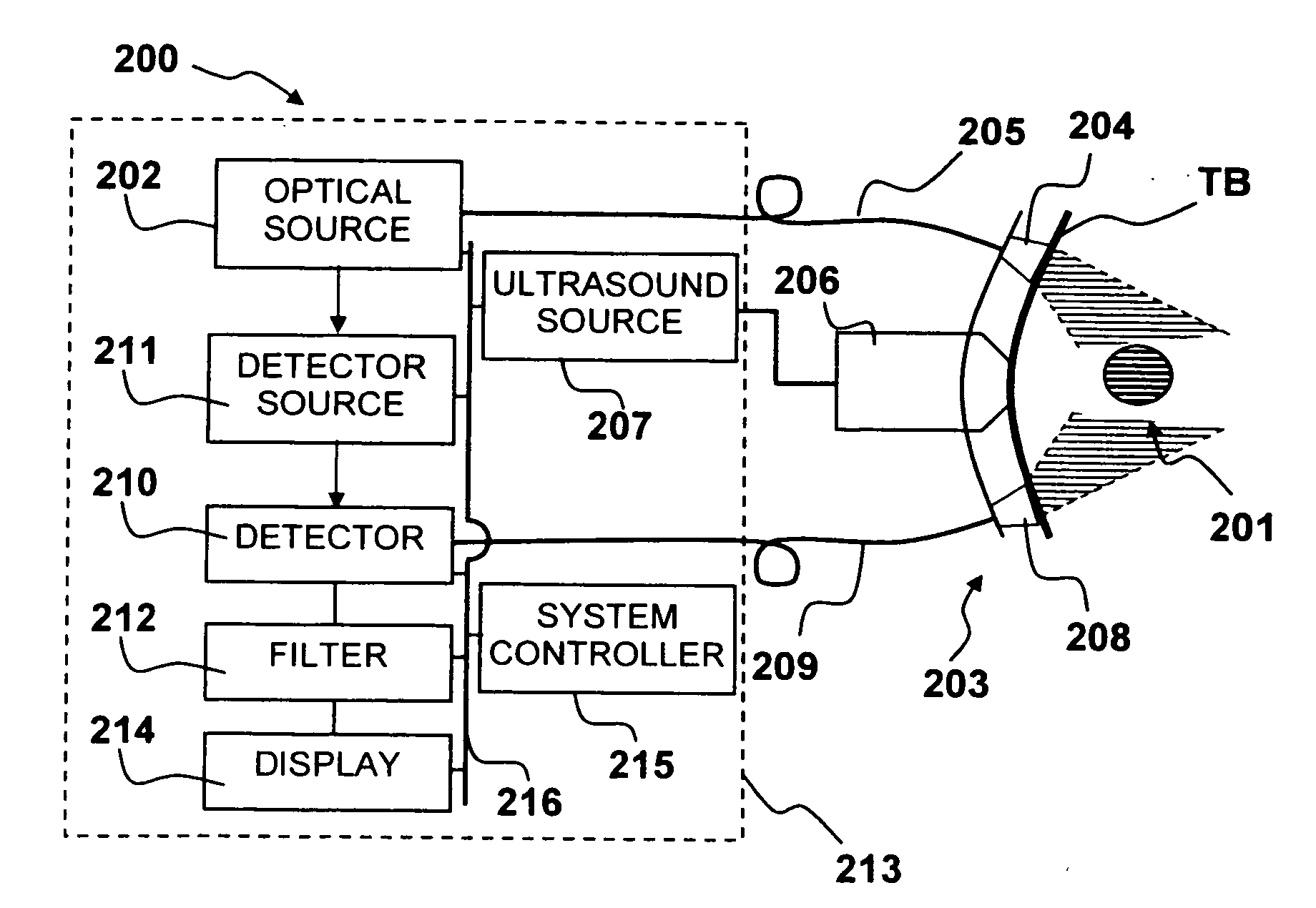
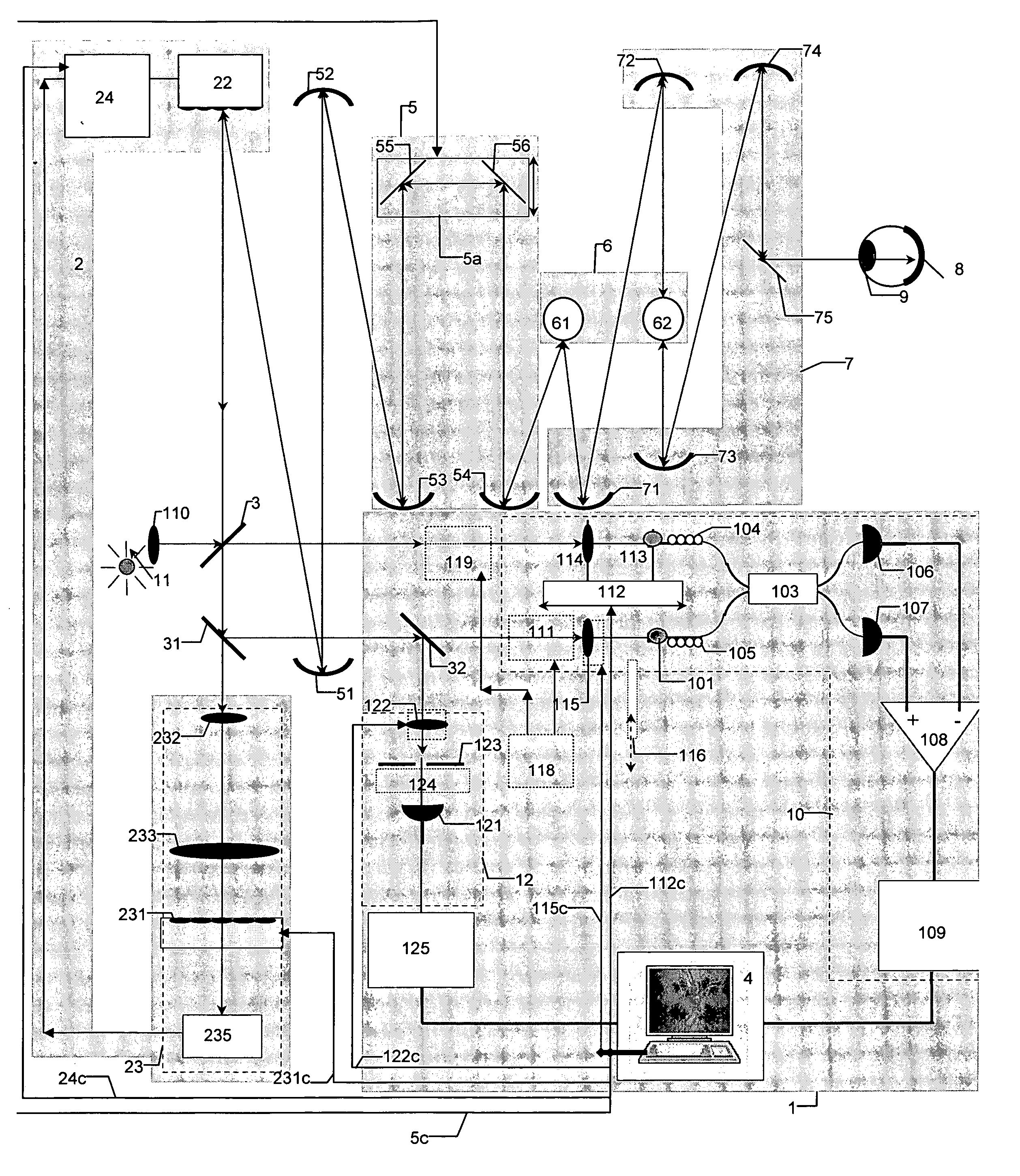
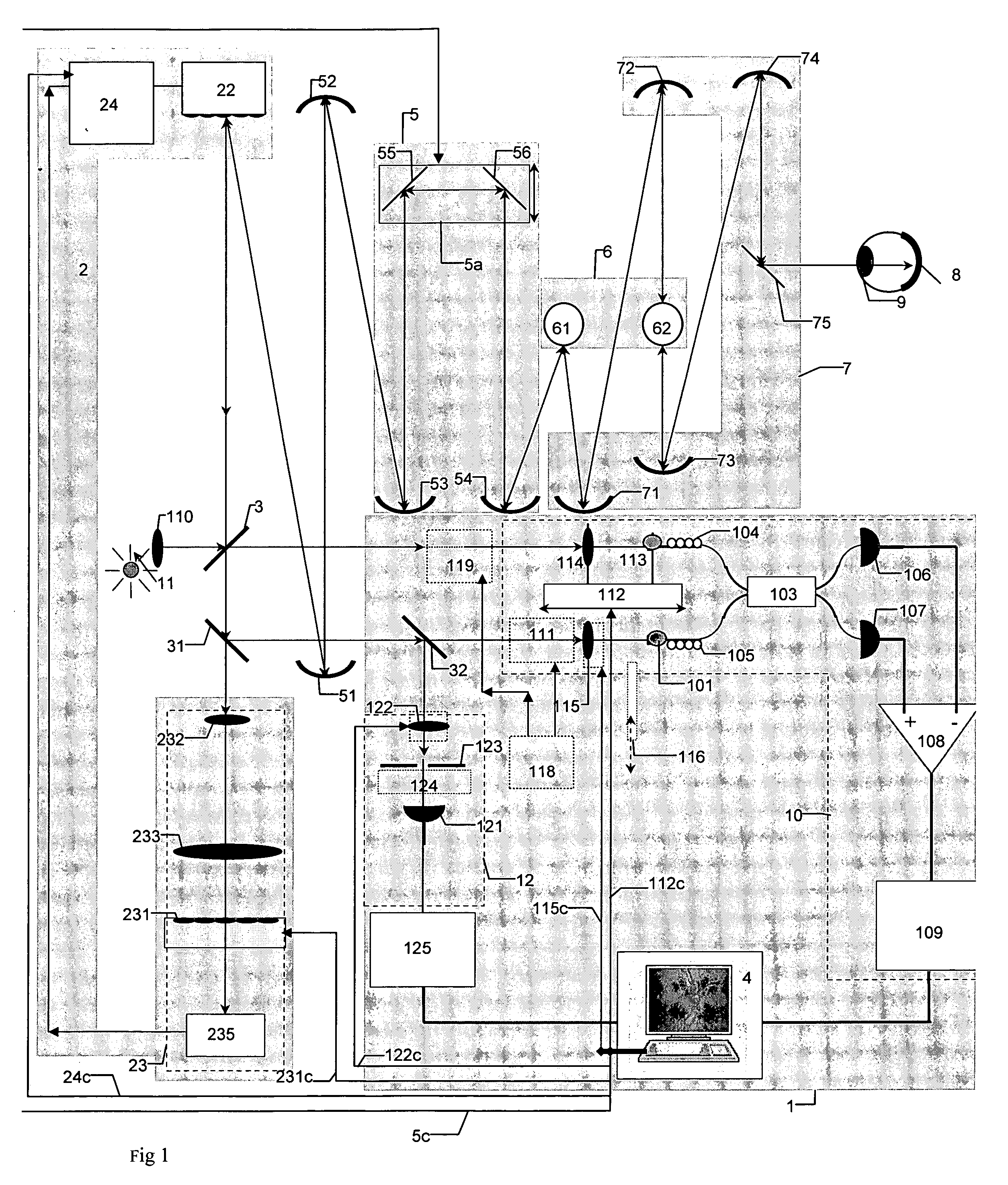
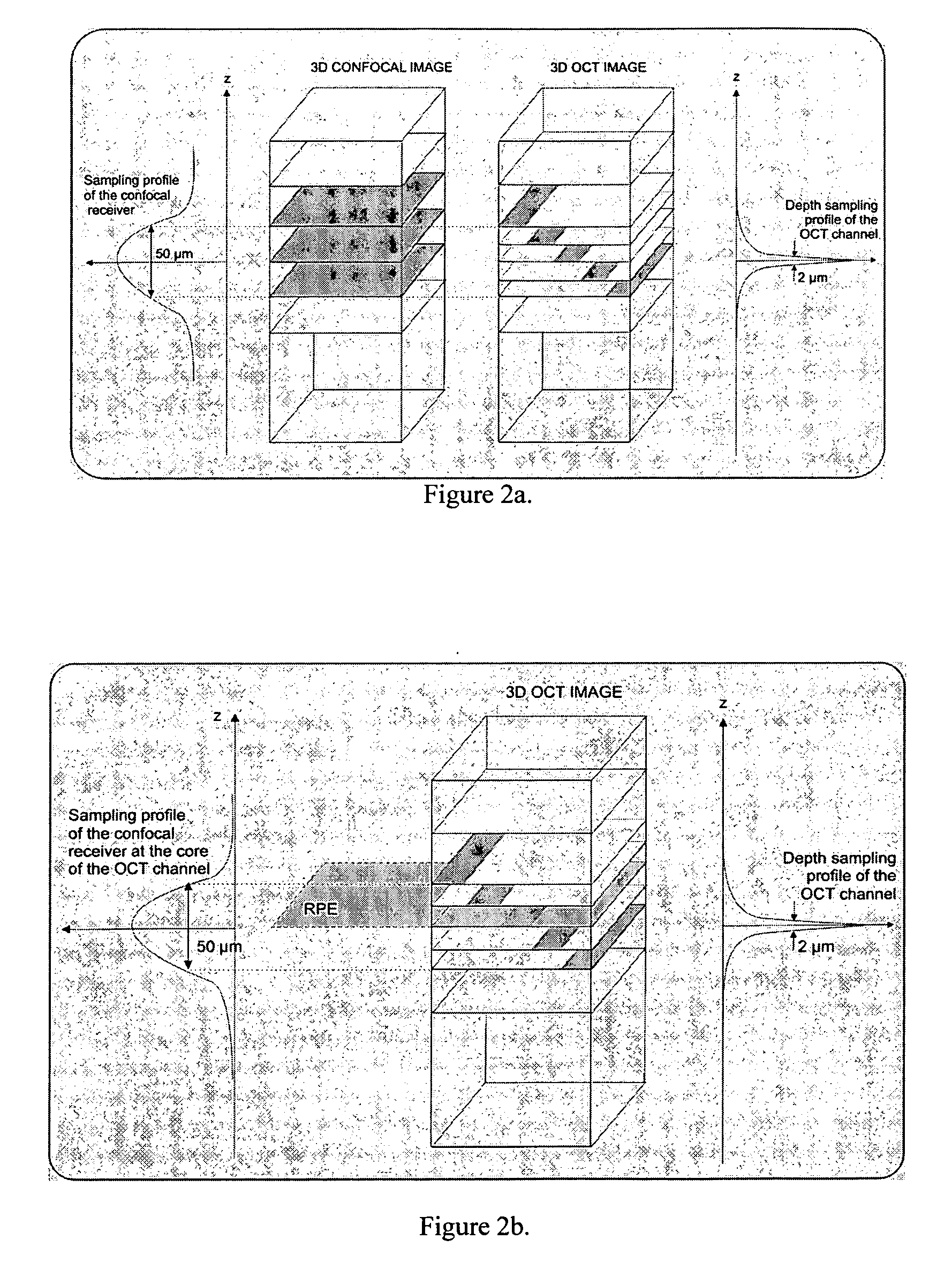
InactiveUS20070046948A1Easy to useHigh depth resolutionUsing optical meansOthalmoscopesOptical mappingTomography
Optical mapping apparatus for imaging an object, comprising an optical coherence tomography (OCT) system including an OCT source, an OCT reference path leading from the OCT source to an OCT receiver, an OCT object path leading from the object to the OCT coupler, an OCT depth scanner adapted to alter at least one of the OCT reference path and the OCT receiver path. A confocal system is provided including a confocal optical receiver a confocal path leading from the object to the confocal optical receiver via a confocal input aperture. An adaptive optics (AO) system is provided to correct optical aberrations in the OCT object path and the confocal path.
Owner:KENT UNIVERITY OF +1
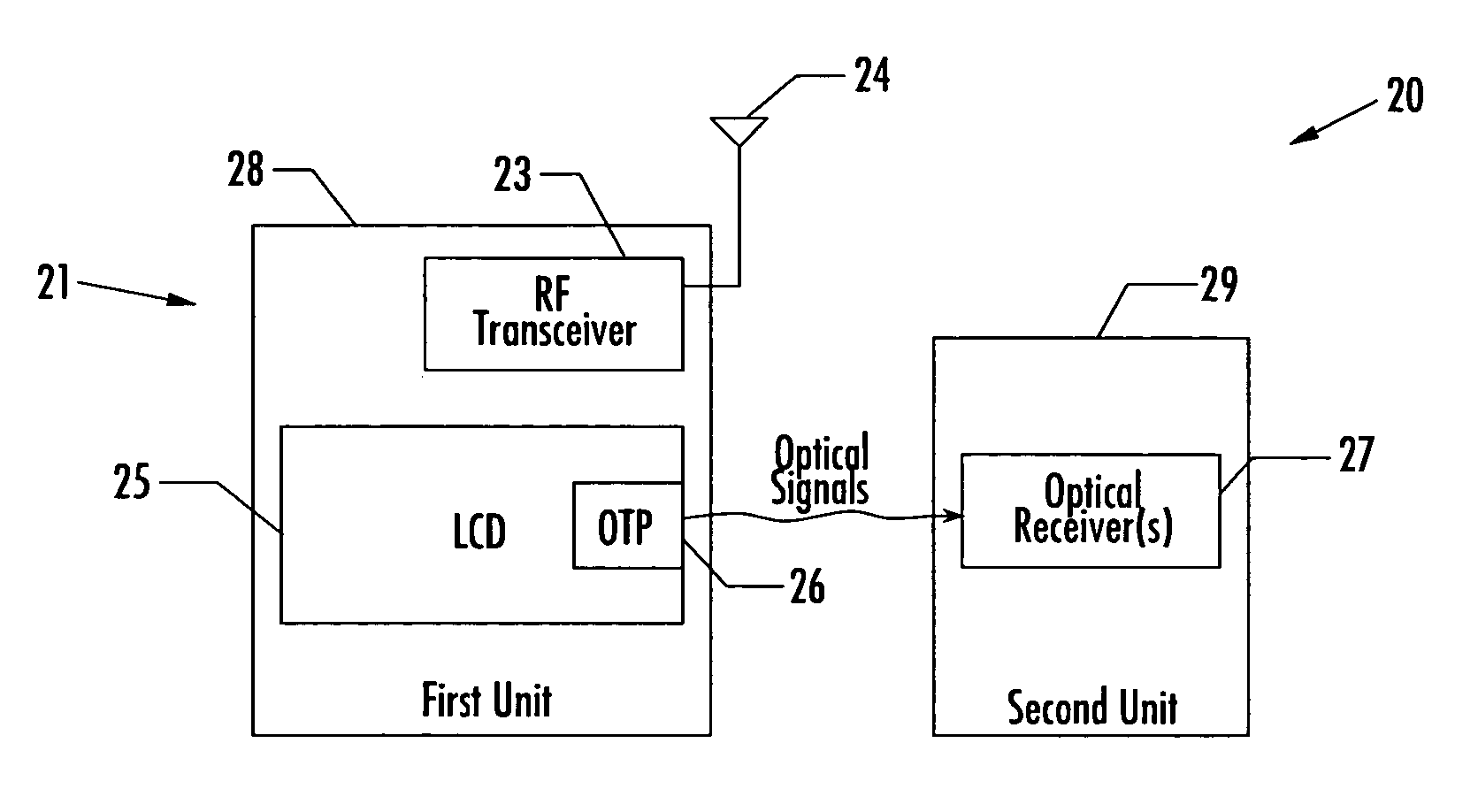
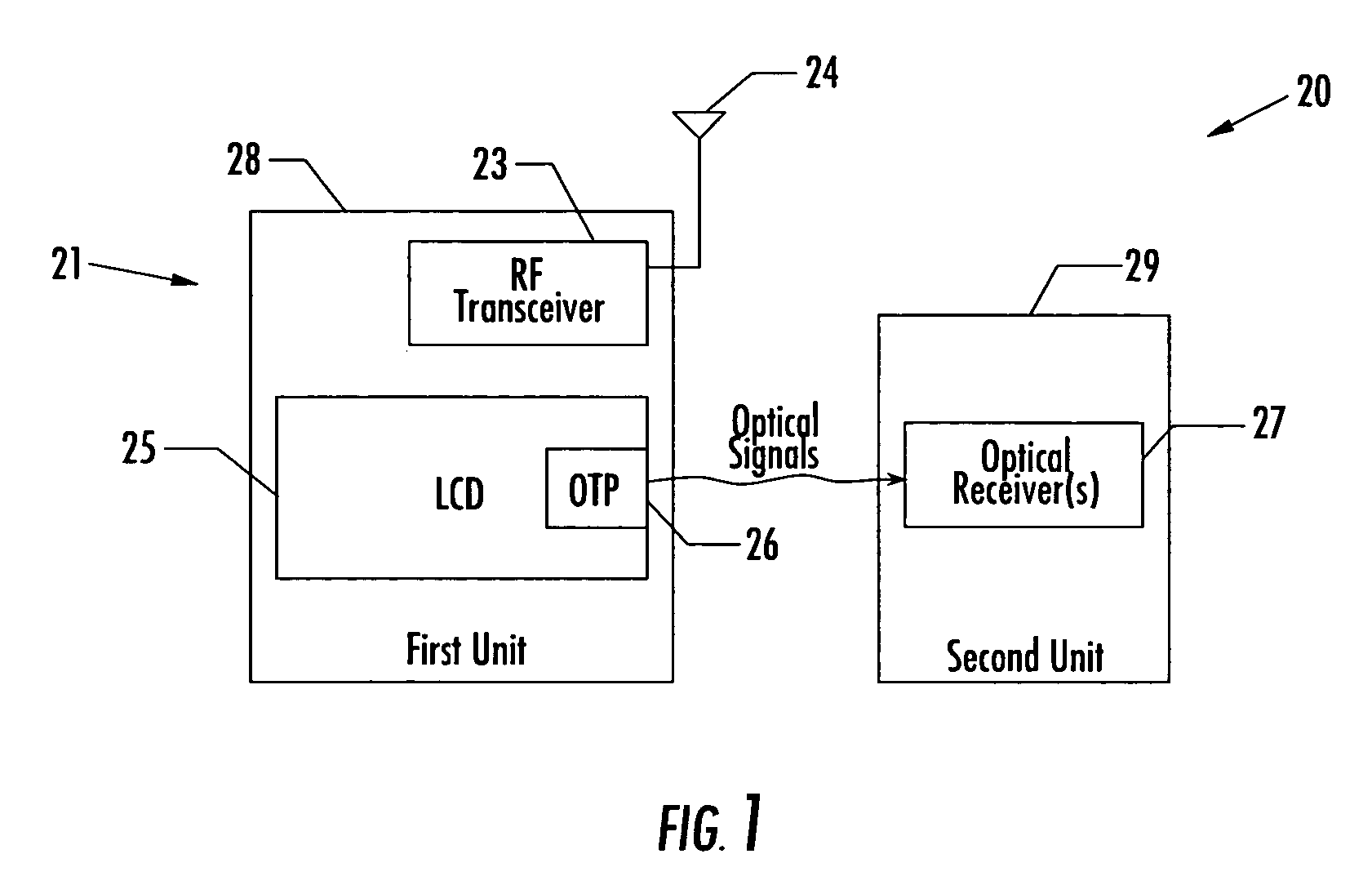
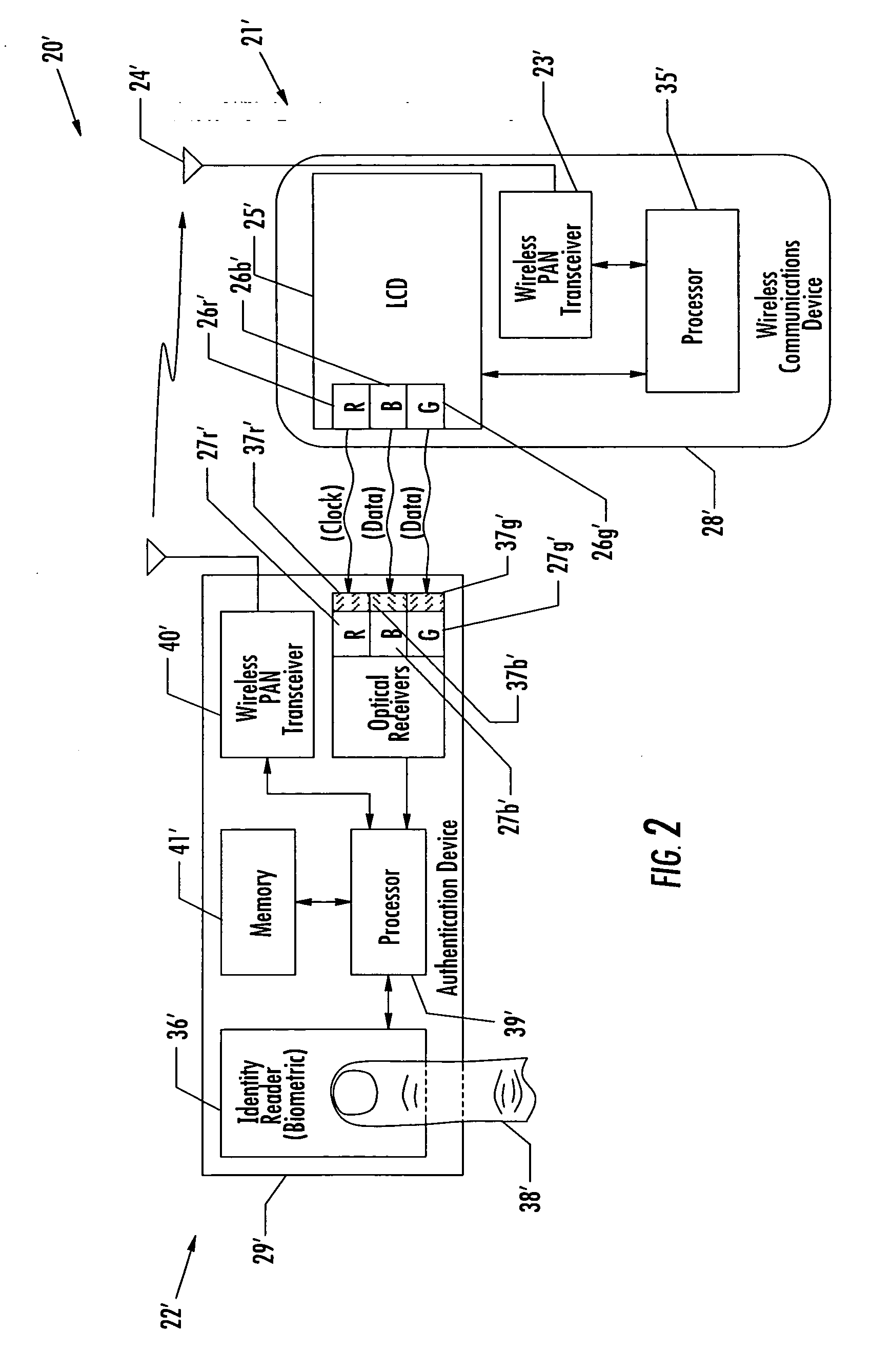
Communications system including units with LCD optical transmitters/receivers and related methods
InactiveUS20060256070A1Static indicating devicesClose-range type systemsLiquid-crystal displayTransceiver
A communications system may include first and second separate units, at least one of which may include a radio frequency (RF) transceiver. The first unit may include a liquid crystal display (LCD) including at least one optical transmitter pixel. Further, the second wireless unit may include at least one optical receiver for receiving optical signals from the at least one optical transmitter pixel of the LCD.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
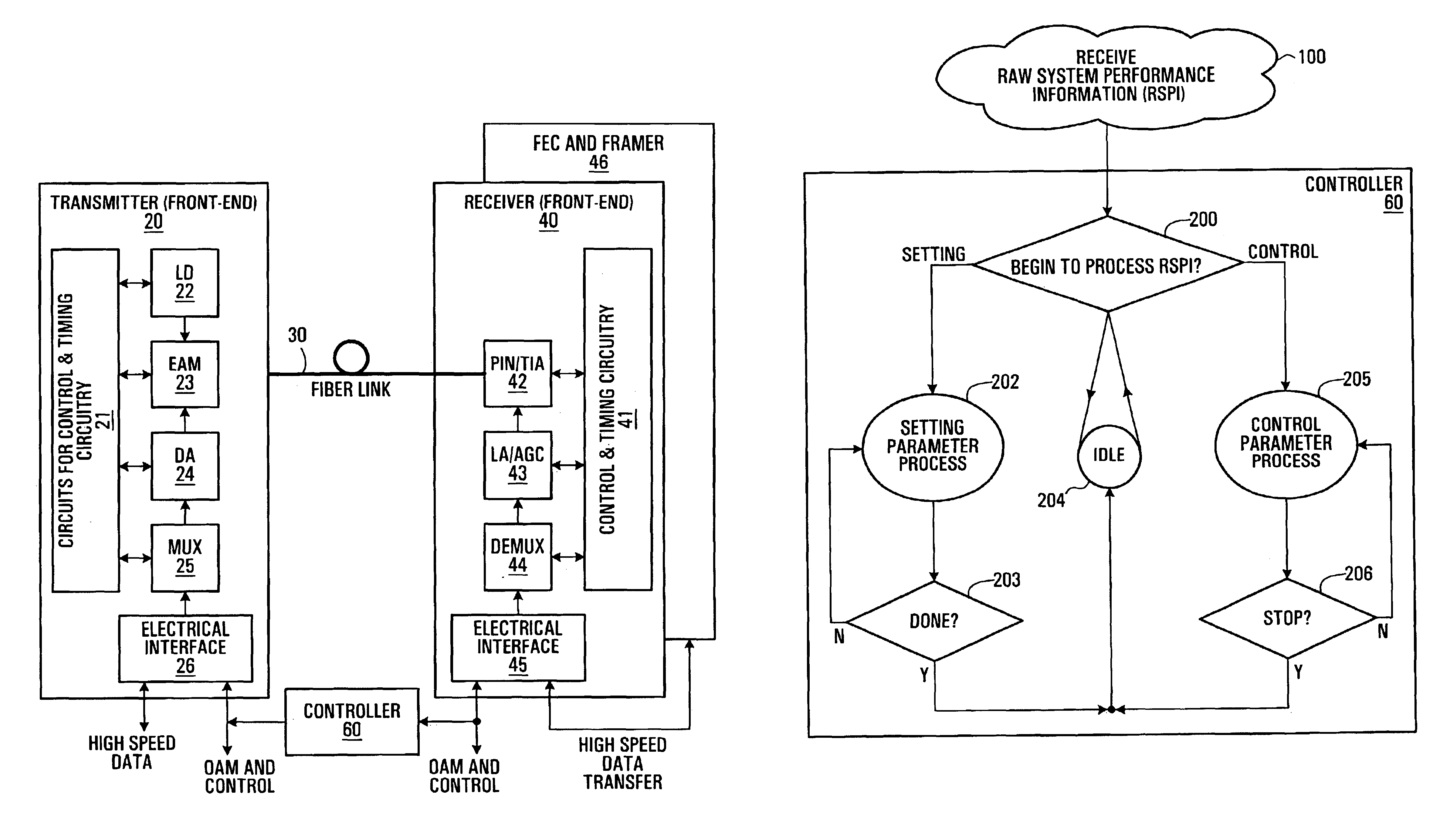
Auto-setting and optimization of EAM with optical line systems
InactiveUS6970652B2Transmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsCommunications systemEngineering
According to the invention there is provided a method of controlling an optical communication system comprising an optical transmitter, an optical receiver and an optical fiber interconnecting the optical transmitter and the optical receiver, the method comprising determining the performance of the optical communication system and controlling at least one setting parameter of the optical transmitter according to the measured performance.
Owner:OPLINK COMM
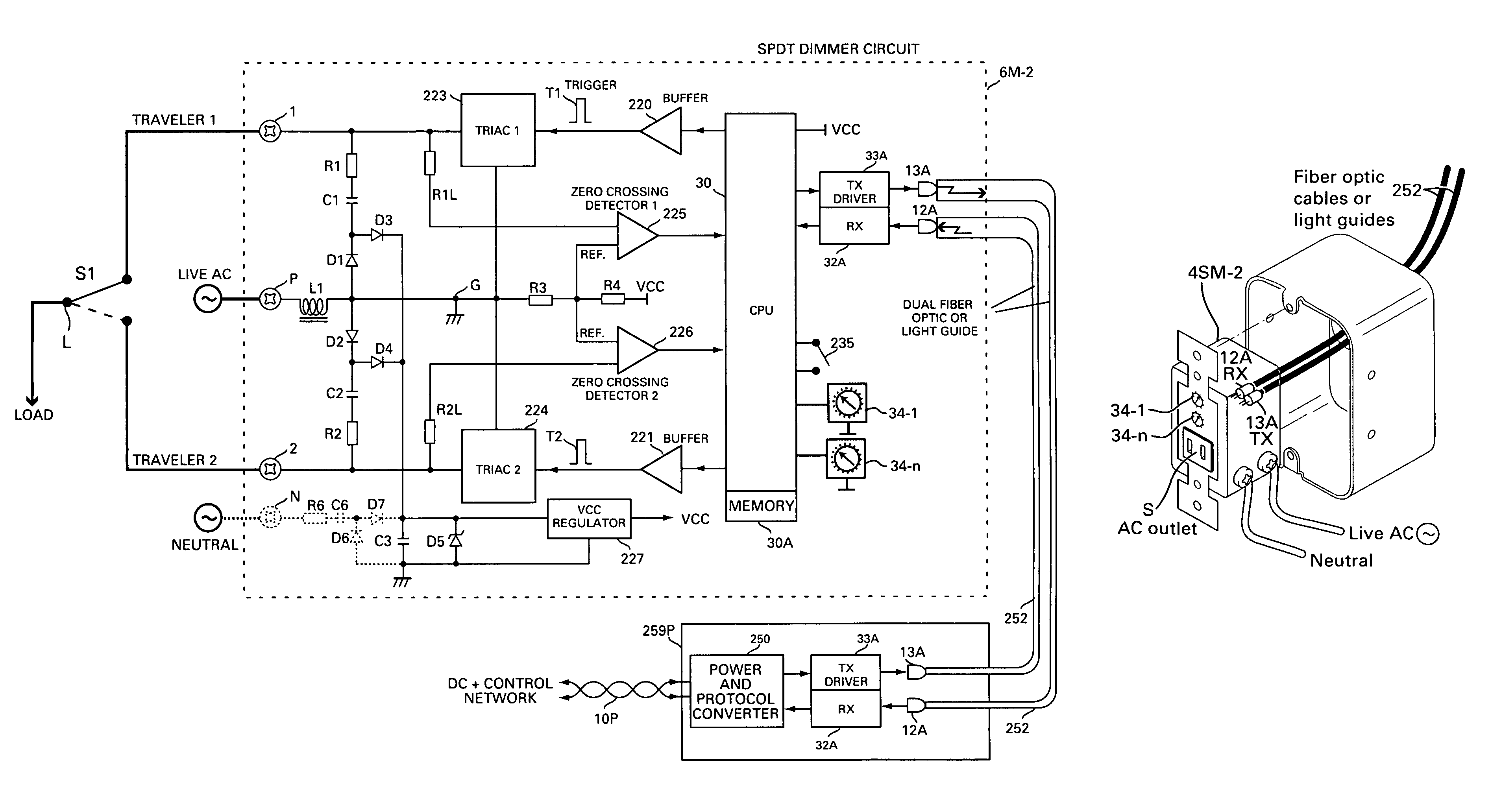
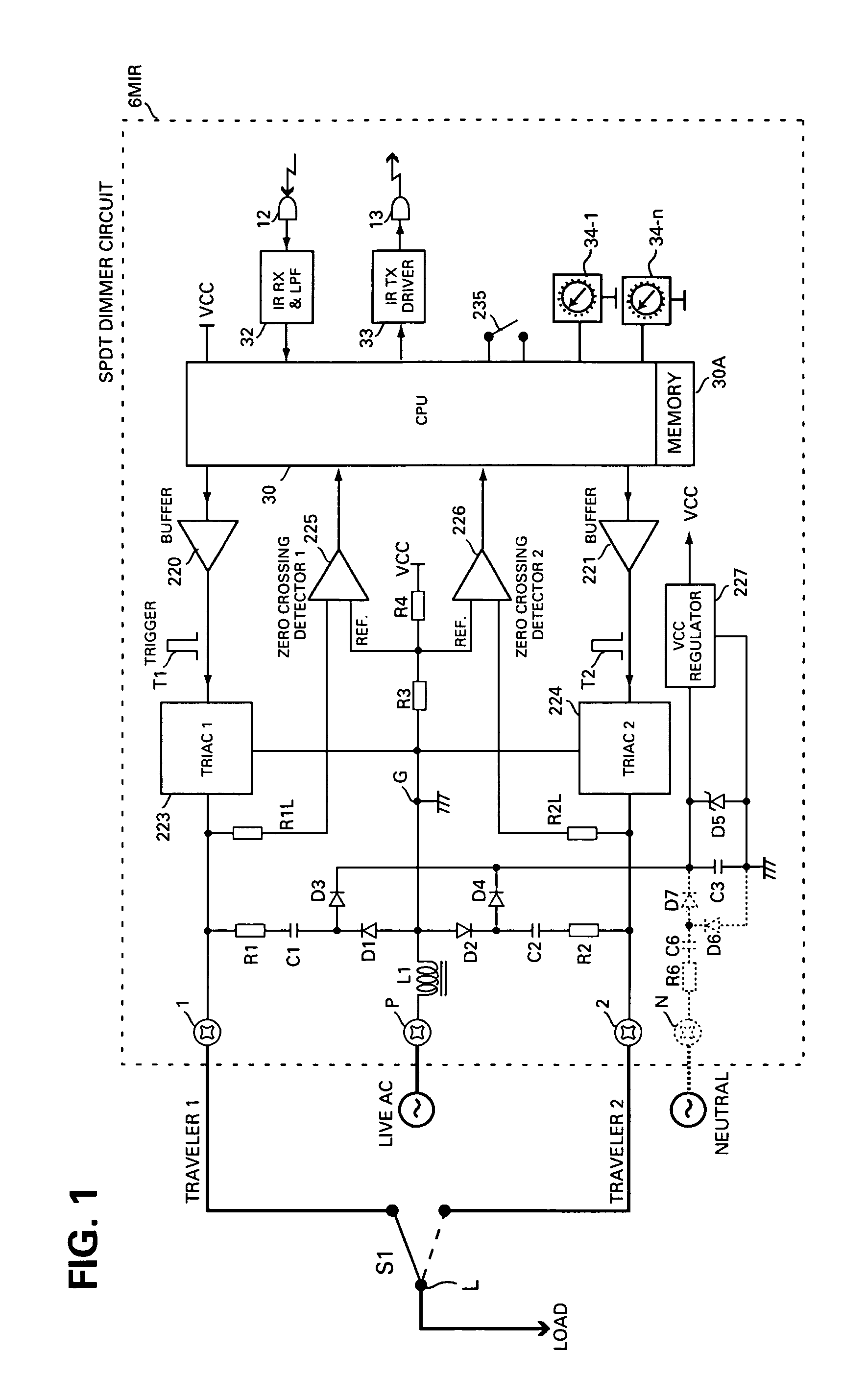
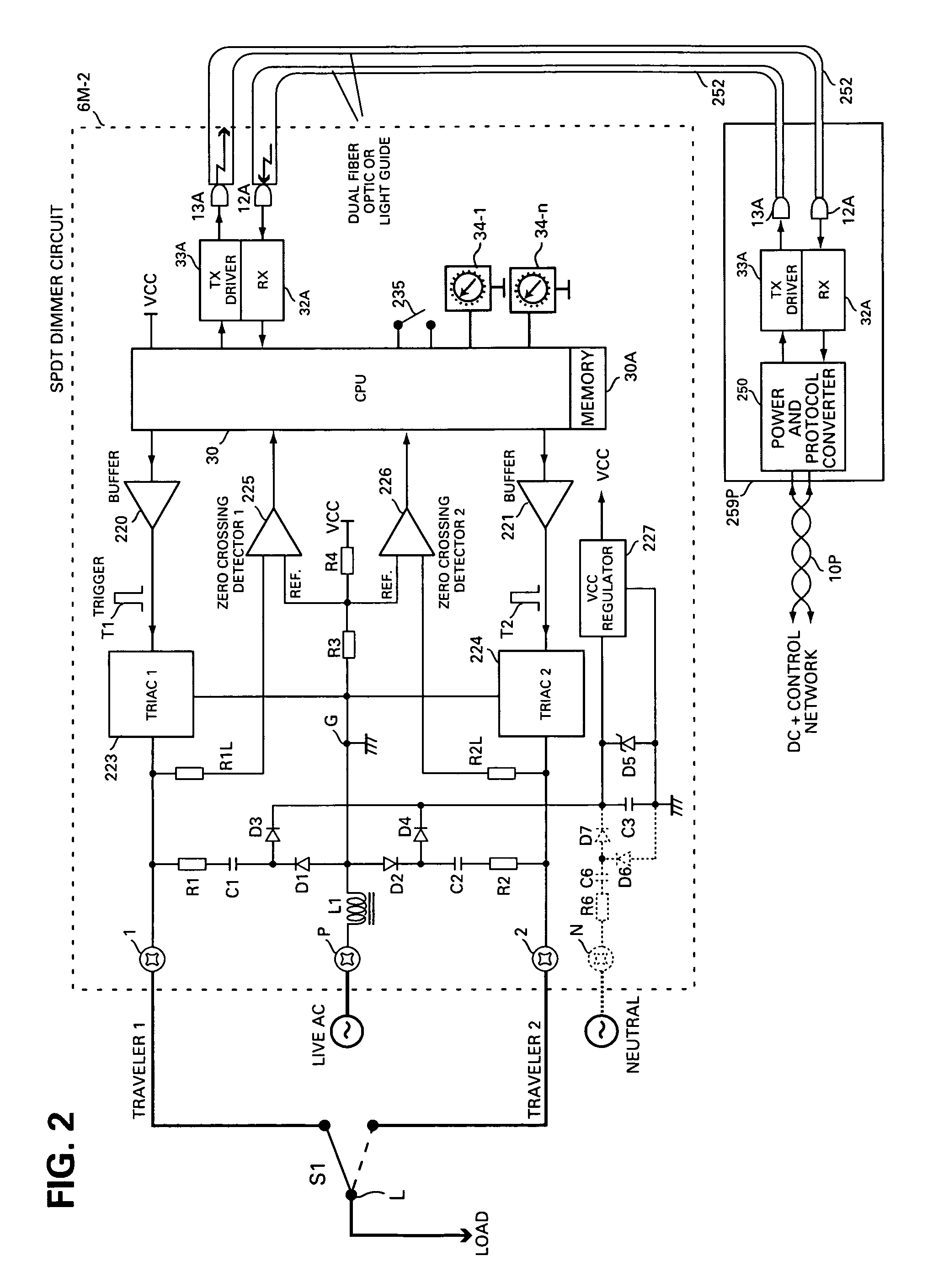
Method and apparatus for connecting AC powered switches, current sensors and control devices via two way IR, fiber optic and light guide cables
ActiveUS8175463B2Low costSimple attachmentNon-electrical signal transmission systemsCurrent supply arrangementsFiberLight guide
A method for connecting an AC powered device, which has an optical receiver, with a control circuit, which has an optical transmitter, using at least on optical medium cable includes the steps of terminating the cable at both of its ends, introducing the processed cable between the receiver and transmitter, attaching and securing one end of the processed cable to the transmitter and the other end of the processed cable to the receiver, and propagating a one way optical signal including control commands from the control circuit to the powered device.
Owner:ELBEX VIDEO LTD
Integrated bi-directional gradient refractive index wavelength division multiplexer
A wavelength division multiplexer integrating a dispersive element having a gradient refractive index with optical lenses to provide efficient coupling from a plurality of input optical fibers (each delivering a plurality of discrete wavelengths to the device) which are multiplexed to a single polychromatic beam for output to a single output optical fiber. The device comprises: (a) an input means for accepting a plurality of optical input beams of different wavelengths from a plurality of optical sources, the means including a planar front surface onto which the optical beams are incident; (b) a dispersive element comprising a radial (or axial) gradient refractive index for combining the plurality of optical input beams into a single optical beam and operatively associated with the planar front surface; (c) a coupler subsystem secured to the dispersive element and comprising (1) a first homogeneous index boot lens having a planar front surface onto which the single optical beam from the dispersive element is incident, (2) an axial gradient refractive index collimating lens affixed to the first homogeneous index boot lens, and (3) a planar back surface from which the single optical beam exits, operatively associated with the axial gradient refractive index collimating lens; and (d) an output means for outputting at least one multiplexed, polychromatic output beam to an optical receiver, the means including the planar back surface. The device is fully bi-directional and may be operated in the forward direction as a multiplexer and in the reverse direction as a demultiplexer.
Owner:AUXORA
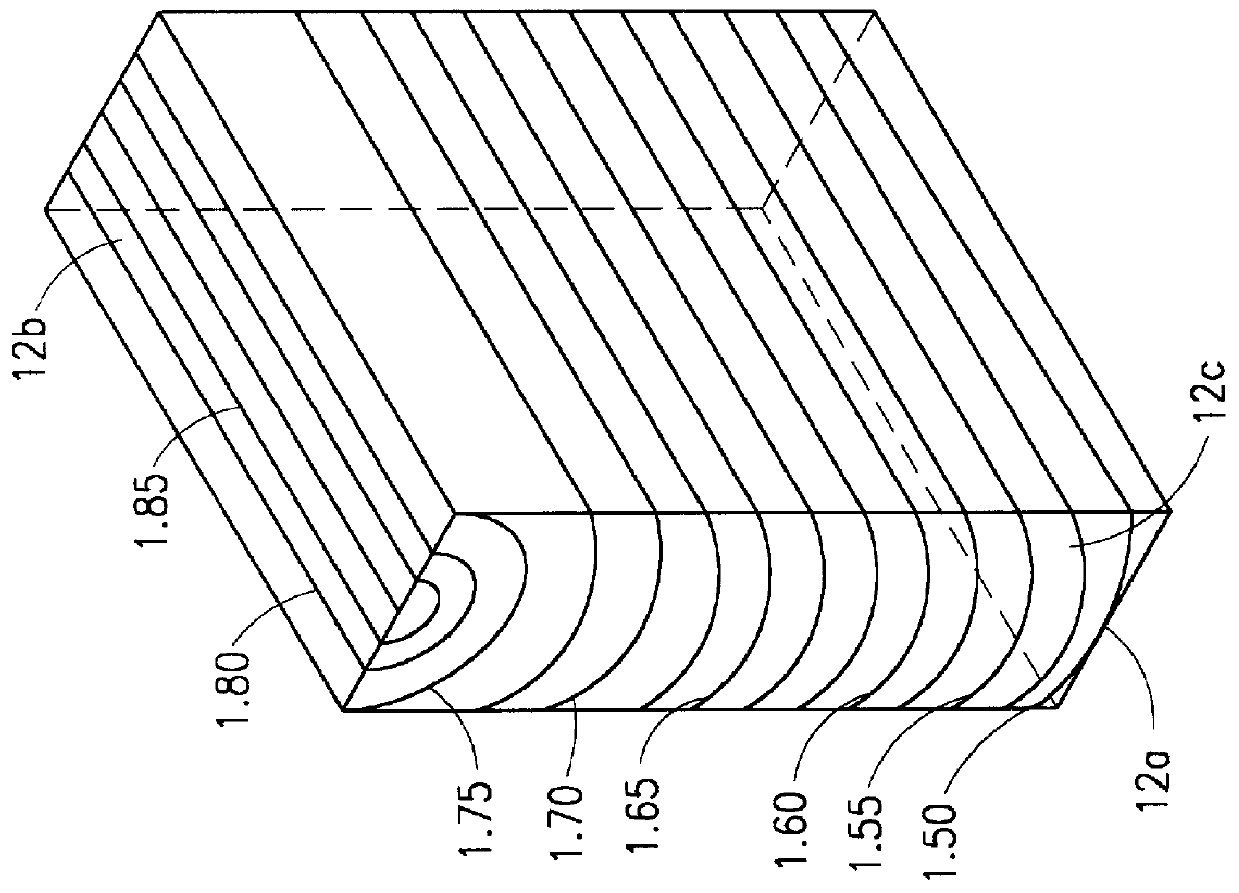
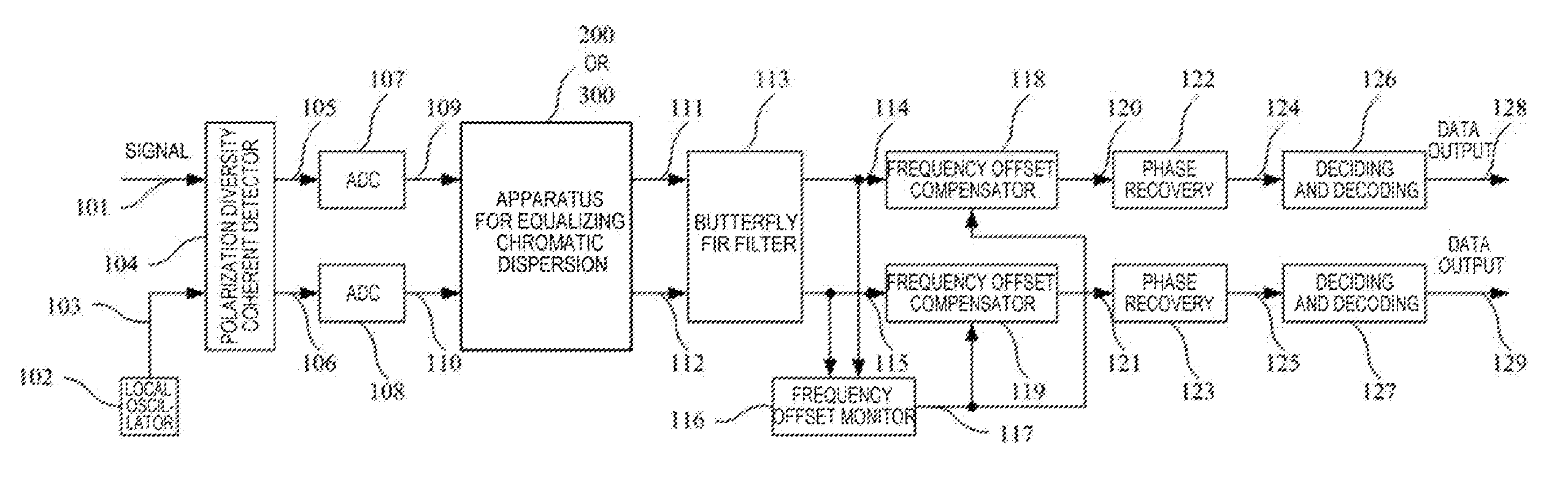
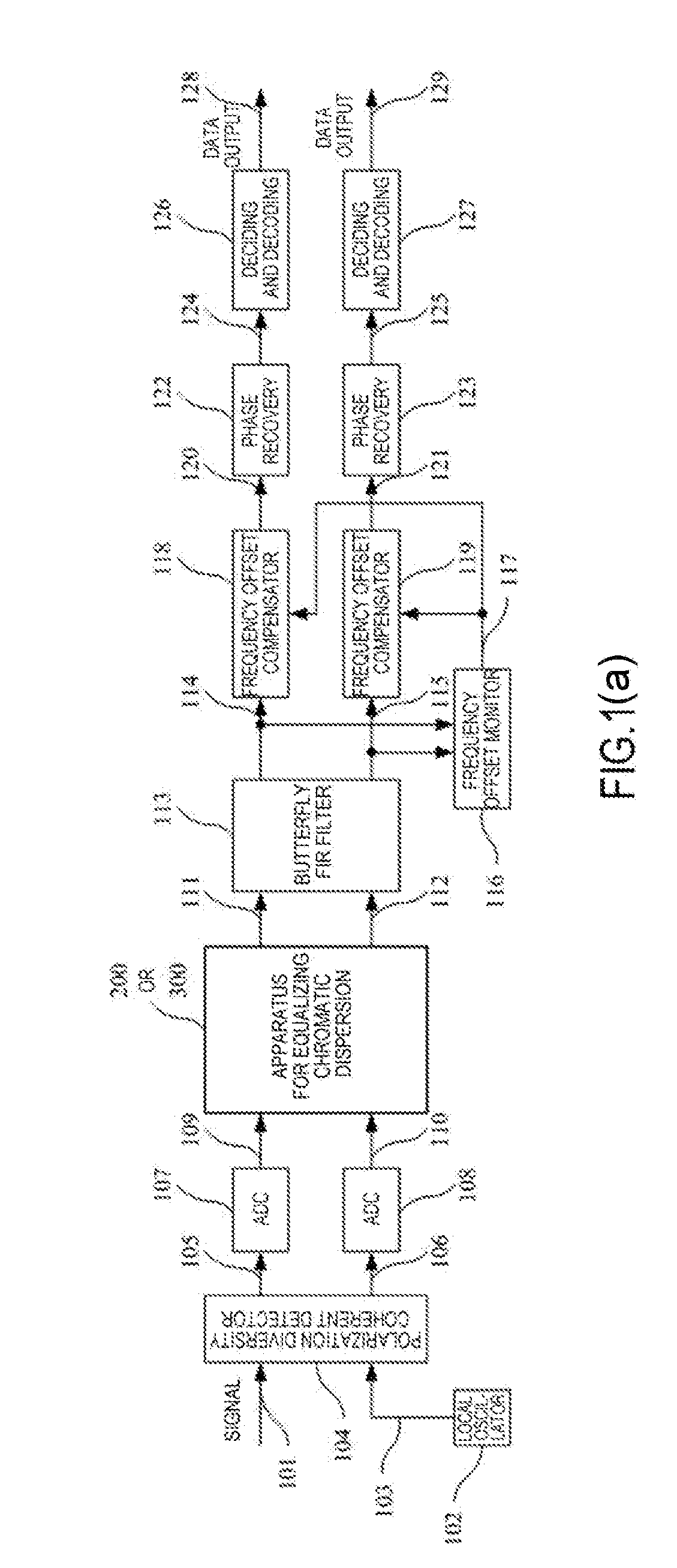
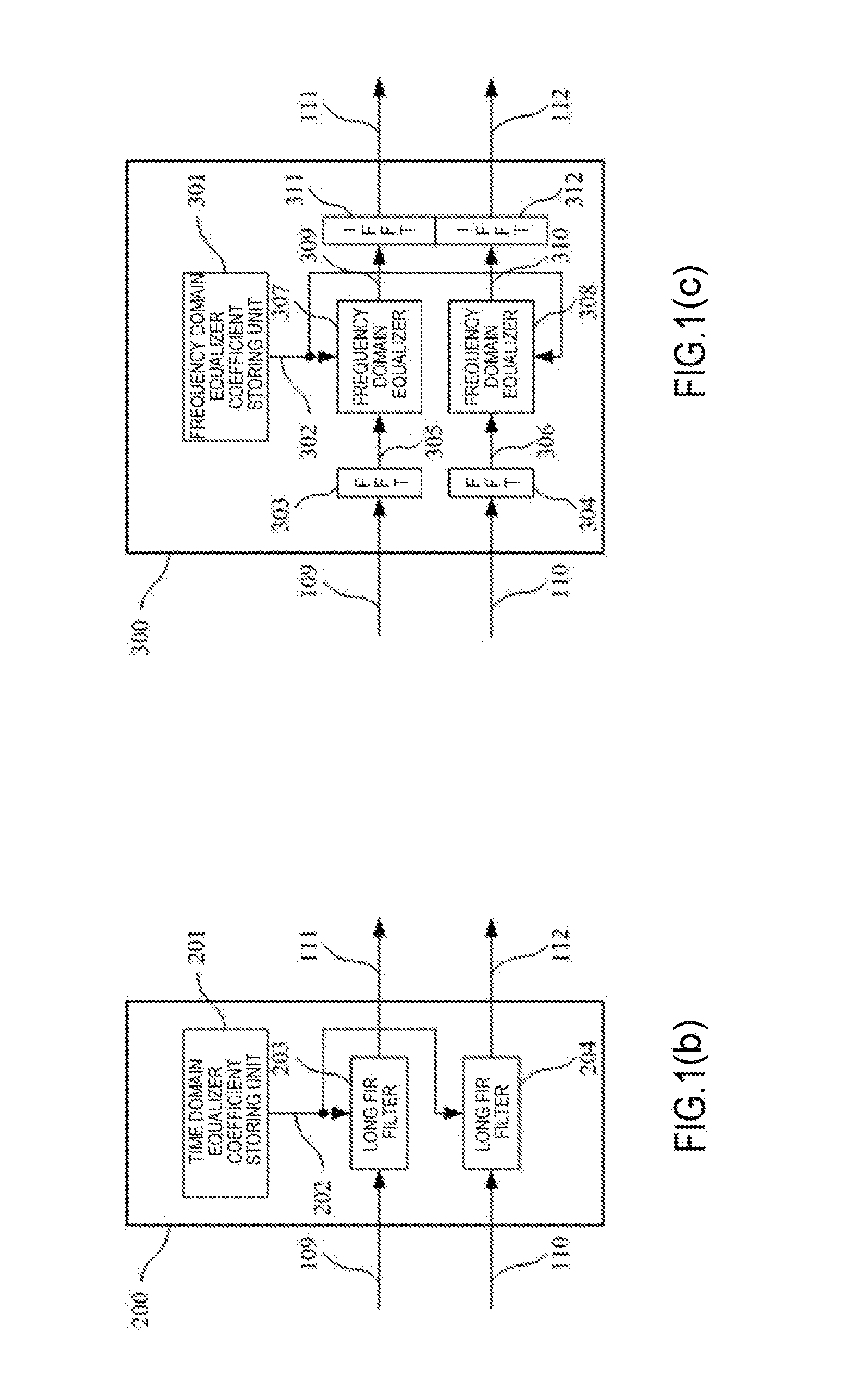
Apparatus and method for equalizing chromatic dispersion and digital coherent optical receiver
This application relates to an apparatus and a method for equalizing chromatic dispersion and a digital coherent optical receiver. The apparatus for equalizing chromatic dispersion comprising: a chromatic dispersion equalizing unit, for compensating chromatic dispersion of an input signal; and an additional time delay removing unit, for removing, in accordance with frequency offset of the input signal, chromatic dispersion equalization time delay generated by the chromatic dispersion equalizing unit.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Surface mount multi-channel optocoupler
An optocoupler package is disclosed. The optocoupler package includes a substrate comprising a leadframe and a molding compound, and a plurality of optocouplers, each optocoupler including (i) an optical emitter, (ii) an optical receiver, (iii) and an optically transmissive medium disposed between the optical emitter and optical receiver, where the optical emitter and the optical receiver are electrically coupled to the leadframe.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
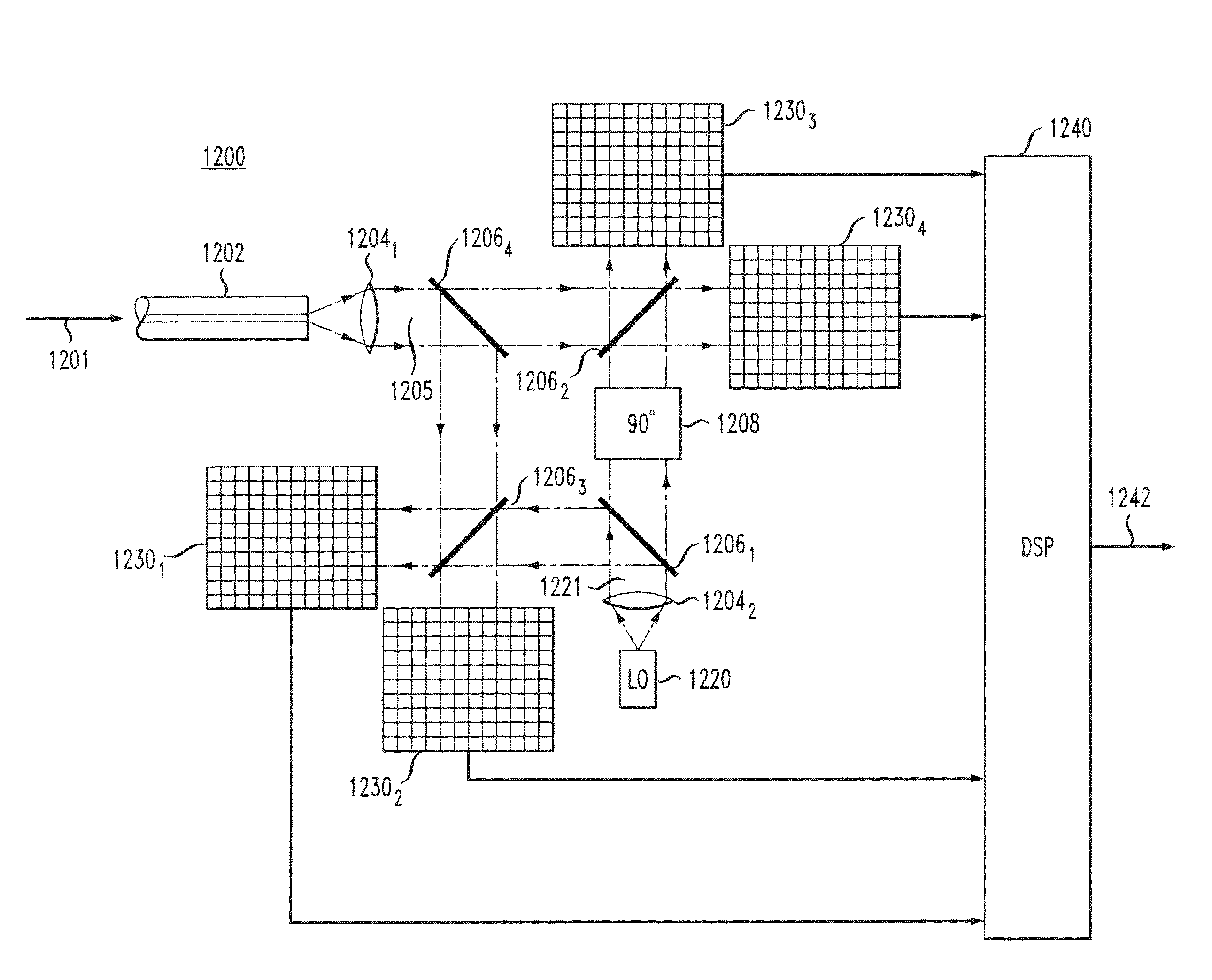
Optical mixer for coherent detection of polarization-multiplexed signals
InactiveUS20100158521A1Data recoveryPolarisation multiplex systemsElectromagnetic receiversLocal oscillator signalBeam splitter
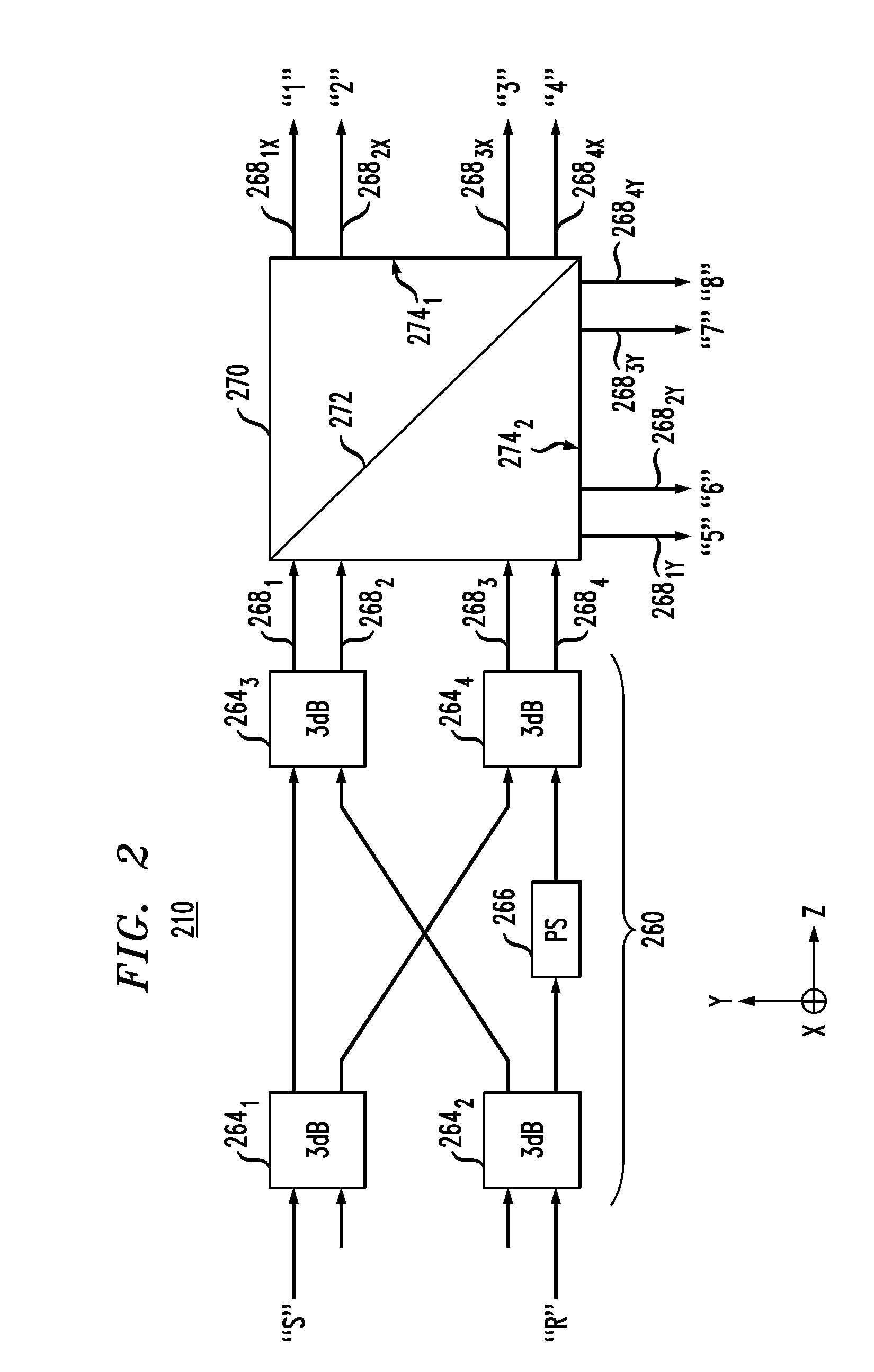
An optical mixer that, in one embodiment, has a single optical hybrid optically coupled to a single polarization beam splitter. The optical hybrid mixes a polarization-multiplexed optical communication signal and a local-oscillator signal to generate four mixed signals, each corresponding to a different relative phase shift between the communication and local-oscillator signals. The polarization beam splitter separates each of the mixed signals into two polarization components, subsequent processing of which enables an optical receiver employing the optical mixer to recover the data carried by the communication signal.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
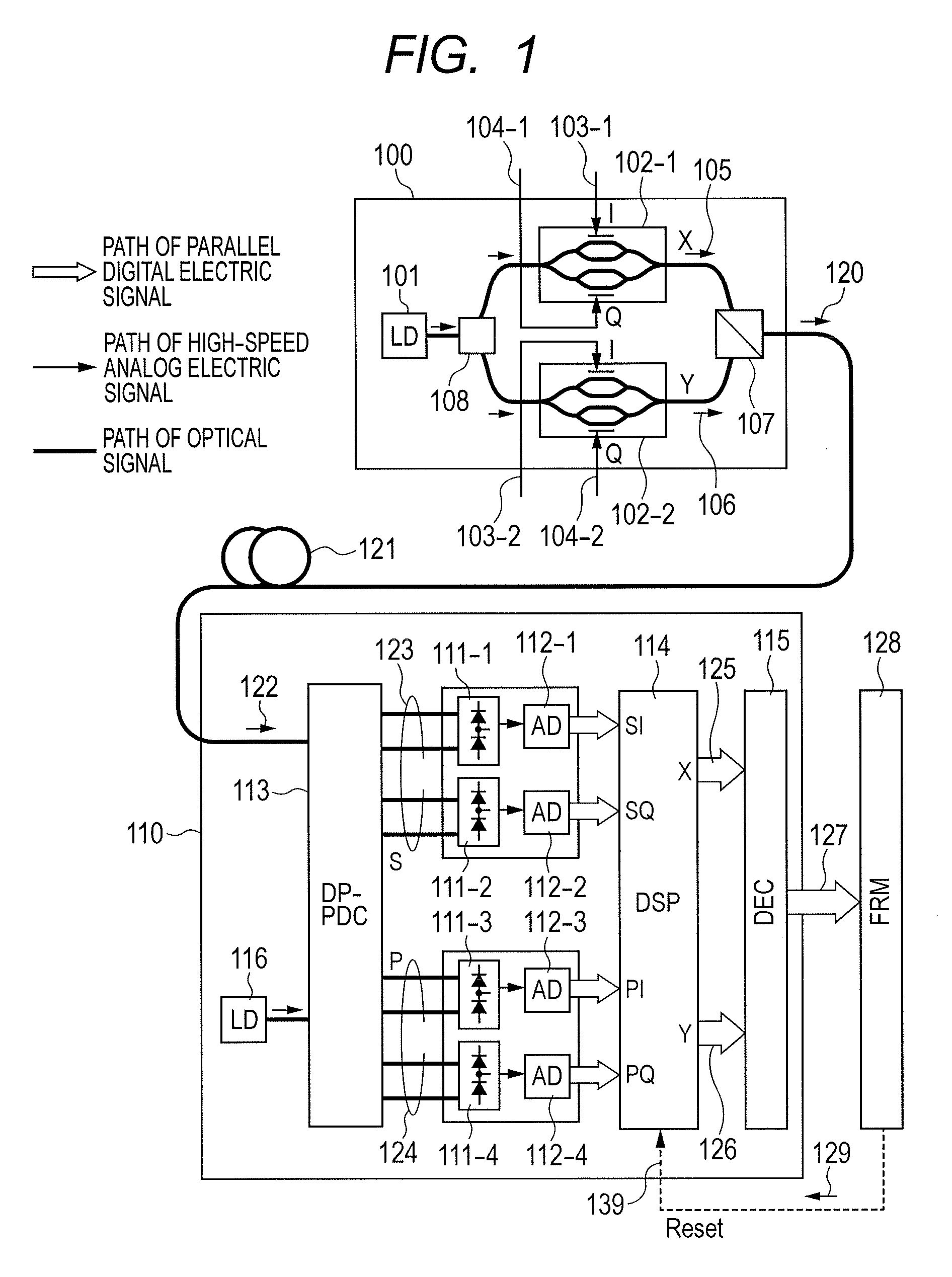
Polarization-Multiplexed Optical Transmission System, Polarization-Multiplexed Optical Transmitter, and Polarization-Multiplexed Optical Receiver
InactiveUS20120134676A1Preventing signal quality degradationReliable polarizationPolarisation multiplex systemsOptical mode multiplex systemsDigital signal processingPolarization diversity
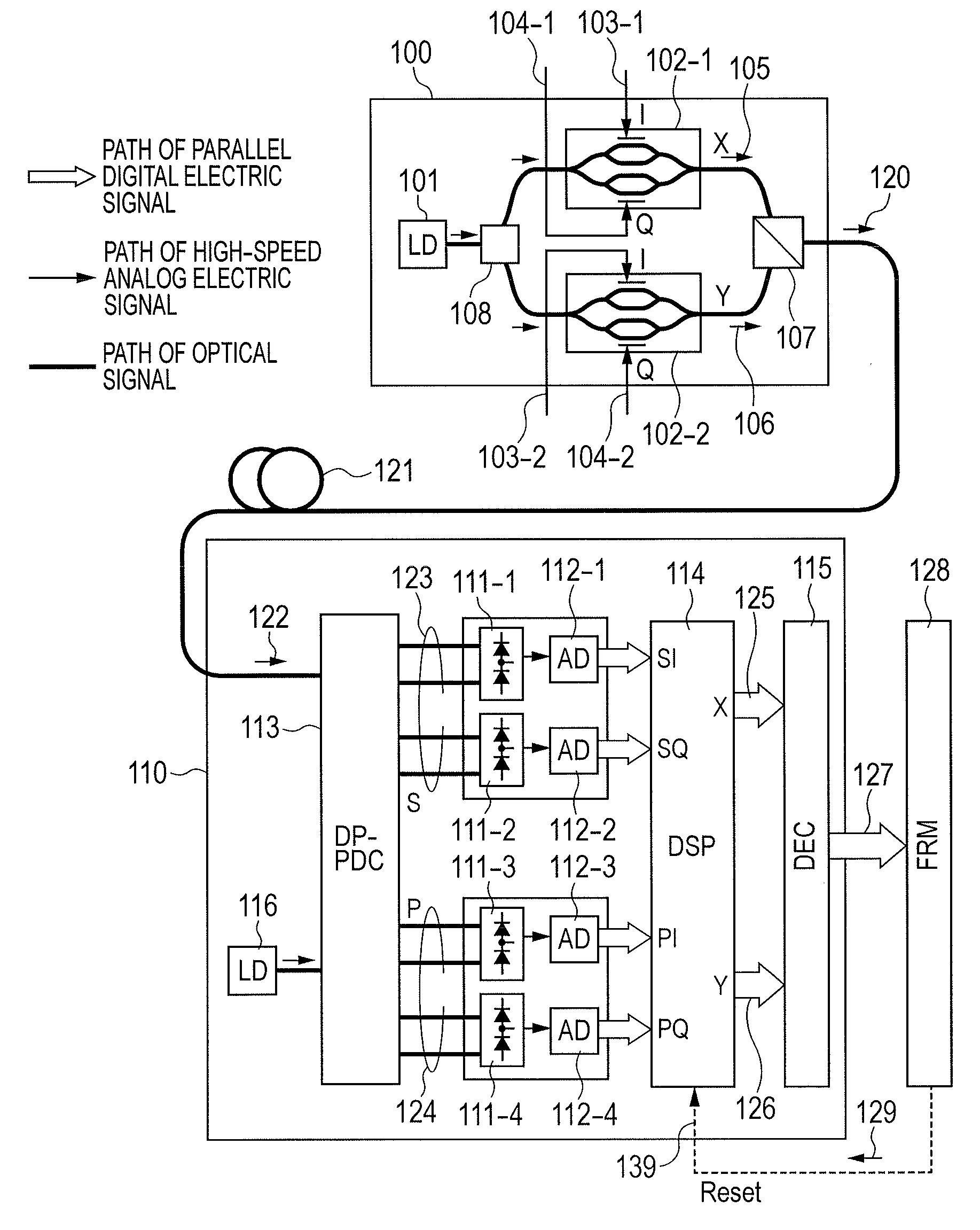
There is a need to prevent two receivers from converging on a state of receiving the same polarization state, fast start receivers, and ensure highly reliable operations. A polarization-multiplexed transmitter previously applies frequency shifts of frequencies +Δf and −Δf to X-polarization and Y-polarization digital information signals to be transmitted. Optical field modulators modulate and polarization-multiplex the signals. As a result, a frequency difference of 2Δf is supplied to X-polarization and Y-polarization components. A polarization diversity coherent optical receiver 215 receives the signal. A frequency estimation portion in a digital signal processing circuit detects a frequency difference signal in both polarization components. This signal is used to a polarization splitting circuit in the digital signal processing circuit.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com